Page 1

l
! "
Data M anua
August 2007 MSDS Bus Solutions
SLLS442E
Page 2

TUSB2136
r
Data Manual
Universal Serial Bus Compound Hub
with General-Purpose 8052 MCU
Literature Number: SLLS442E
August 2007
Printed on Recycled Pape
Page 3

Contents
Section Title Page
1 Introduction 1−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Features 1−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Functional Block Diagram 1−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Terminal Assignments 1−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Ordering Information 1−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Terminal Functions 1−4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.6 Revision History 1−5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Functional Description 2−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 MCU Memory Map 2−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Miscellaneous Registers 2−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.1 TUSB2136 Boot Operation 2−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.2 MCNFG: MCU Configuration Register 2−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.3 PUR_n: GPIO Pullup Register for Port n (n = 0 to 3) 2−2. . . . .
2.2.4 INTCFG: Interrupt Configuration 2−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.5 WDCSR: Watchdog Timer, Control, and Status Register 2−3.
2.2.6 PCON: Power Control Register (at SFR 87h) 2−4. . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Buffers + I/O RAM Map 2−4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4 Endpoint Descriptor Block (EDB-1 to EDB-3) 2−5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.1 OEPCNF_n: Output Endpoint Configuration 2−7. . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.2 OEPBBAX_n: Output Endpoint X-Buffer Base-Address 2−7. .
2.4.3 OEPBCTX_n: Output Endpoint X Byte Count 2−8. . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.4 OEPBBAY_n: Output Endpoint Y-Buffer Base-Address 2−8. .
2.4.5 OEPBCTY_n: Output Endpoint Y Byte Count 2−8. . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.6 OEPSIZXY_n: Output Endpoint X/Y Byte Count 2−9. . . . . . . .
2.4.7 IEPCNF_n: Input Endpoint Configuration 2−9. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.8 IEPBBAX_n: Input Endpoint X-Buffer Base-Address 2−9. . . .
2.4.9 IEPBCTX_n: Input Endpoint X-Byte Base-Address 2−10. . . . . .
2.4.10 IEPBBAY_n: Input Endpoint Y-Buffer Base-Address 2−10. . . . .
2.4.11 IEPBCTY_n: Input Endpoint Y Byte Count 2−10. . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4.12 IEPSIZXY_n: Input Endpoint X/Y-Buffer Size 2−11. . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 Endpoint-0 Descriptor Registers 2−11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5.1 IEPCNFG_0: Input Endpoint-0 Configuration Register 2−11. . .
2.5.2 IEPBCNT_0: Input Endpoint-0 Byte Count Register 2−12. . . . .
2.5.3 OEPCNFG_0: Output Endpoint-0 Configuration
Register 2−12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5.4 OEPBCNT_0: Output Endpoint-0 Byte Count Register 2−13. . .
2.6 USB Registers 2−13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iii
Page 4

2.6.1 FUNADR: Function Address Register 2−13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.2 USBSTA: USB Status Register 2−14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.3 USBMSK: USB Interrupt Mask Register 2−15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.4 USBCTL: USB Control Register 2−16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.5 HUBCNFG: HUB-Configuration Register 2−17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.6 HUBPOTG: HUB Power-On to Power-Good
Descriptor Register 2−17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.7 HUBCURT: HUB Current Descriptor Register 2−17. . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.8 HUBPIDL: HUB-PID Register (Low-Byte) 2−18. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.9 HUBPIDH: HUB-PID Register (High-Byte) 2−18. . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.10 HUBVIDL: HUB-VID Register (Low-Byte) 2−18. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.11 HUBVIDH: HUB-VID Register (High-Byte) 2−18. . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6.12 VIDSTA: VID/PID Status Register 2−18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7 Function Reset and Power-Up Reset Interconnect 2−19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8 Pullup Resistor Connect/Disconnect 2−19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.9 8052 Interrupt and Status Registers 2−20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.9.1 8052 Standard Interrupt Enable Register 2−21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.9.2 Additional Interrupt Sources 2−21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.9.3 VECINT: Vector Interrupt Register 2−22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
) 2−23. . . . . . . . . . .
2.10 I
2.9.4 Logical Interrupt Connection Diagram (INT0
2.9.5 P2[7:0] Interrupt (INT1
2
C Registers 2−24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.10.1 I2CSTA: I
2.10.2 I2CADR: I
2.10.3 I2CDAI: I
2.10.4 I2CDAO: I
2
C Status and Control Register 2−24. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
C Address Register 2−25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
C Data-Input Register 2−25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
C Data-Output Register 2−25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
) 2−23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11 Read/Write Operations 2−25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11.1 Read Operation (Serial EEPROM) 2−25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11.2 Current Address Read Operation 2−26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11.3 Sequential Read Operation 2−26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11.4 Write Operation (Serial EEPROM) 2−27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.11.5 Page Write Operation 2−28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Electrical Specifications 3−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Free-Air
Temperature Range 3−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Commercial Operating Condition 3−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Electrical Characteristics, T
= 25°C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V,
A
GND = 0 V 3−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Application 4−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Keyboard Section 4−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Reset Timing 4−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Mechanical Data 5−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv
Page 5

List of Illustrations
Figure Title Page
1−1 TUSB2136 Block Diagram 1−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−1 MCU Memory Map (TUSB2136B) 2−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−2 Reset Diagram 2−19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−3 Pullup Resistor Connect/Disconnect Circuit 2−20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−4 Internal Vector Interrupt (INT0
2−5 P2[7:0] Input Port Interrupt Generation 2−23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−1 Keyboard LED Connection 4−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−2 Keyboard Matrix Scan Connection 4−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−3 Partial Connection Bus Power Mode 4−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−4 Upstream Connection (a) Non-Switching Power Mode (b) Switching
Power Mode 4−2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−5 Downstream Connection − Only One Port Shown 4−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−6 Reset Timing 4−3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
) 2−23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of Tables
Table Title Page
2−1 XDATA Space 2−4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−2 Memory Mapped Registers Summary (XDATA Range = FF80 → FFFF) 2−5. .
2−3 EDB and Buffer Allocations in XDATA 2−6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−4 EDB Entries in RAM (n = 1 to 3) 2−7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−5 Input/Output EDB-0 Registers 2−11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−6 External Pins Mapping to S[3:0] in VIDSTA Register 2−19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−7 8052 Interrupt Location Map 2−20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2−8 Vector Interrupt Values 2−22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4−1 GPIO Assignment for Matrix Scan and LED Drive 4−1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
v
Page 6

vi
Page 7

1 Introduction
The TUSB2136 is an integrated universal serial bus (USB) hub with a general-purpose 8052 microcontroller that can
be used for various USB controller applications. The TUSB2136 has 8K × 8 RAM space for application development.
Using a 12-MHz crystal, the onboard oscillator generates the internal system clocks. No additional programming is
required for any part of the hub functions. The device is programmed via an inter-IC (I
on from an EEPROM, or optionally, the application firmware can be downloaded from a host PC via USB. The
8052-based microprocessor allows several third-party standard tools to be used for application development. In
addition, the application code available in the general market can also be used (this may or may not require some
code modification due to hardware variations).
1.1 Features
• Multiproduct support with one code and one chip (up to 16 products with one chip)
• Fully compliant with the USB specification as a compound full-speed device: TID #30270119
• Supports 1.5- and 12-Mbits/s USB data rates
• Supports USB suspend/resume and remote wake-up operation
• Integrated two-port hub with individual power management per port
• Integrated 8052 microcontroller with:
− 256 × 8 RAM for internal data
− 8K × 8 RAM code space available for downloadable firmware from host or I
− 512 × 8 shared RAM used for data buffers and endpoint descriptor blocks (EDB) [1]
− Four 8052 GPIO ports (ports 0,1, 2 and 3)
− Master I
− Watchdog timer
2
C controller for external slave device access
2
C) serial interface at power
2
C port.
• Operates from a 12-MHz crystal
• On-chip PLL generates 48 MHz
• Supports a total of three input and three output (interrupt, bulk) endpoints
• Power-down mode
• 64-pin TQFP package
[1] This is the buffer space for USB packet transactions.
1−1
Page 8
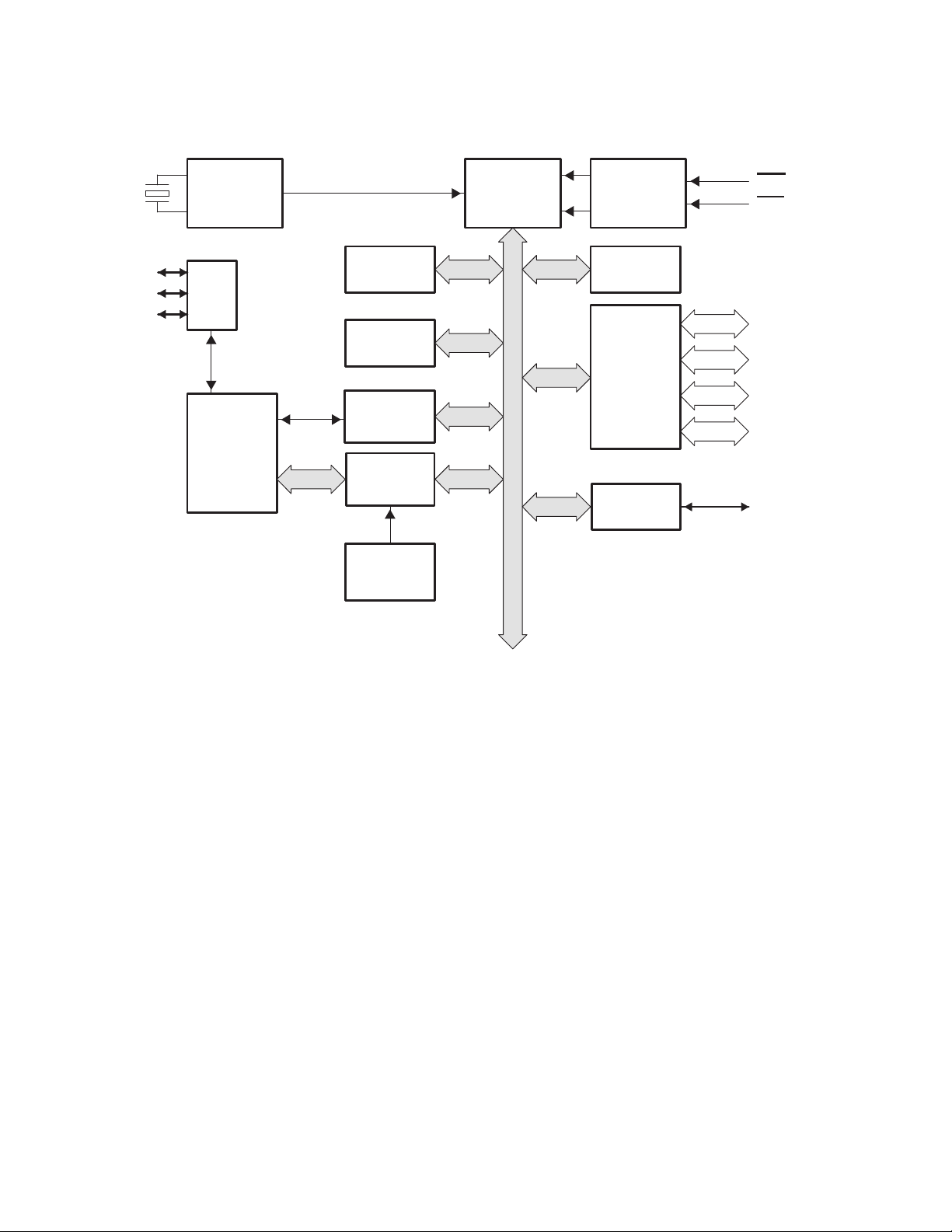
1.2 Functional Block Diagram
12 MHz
USB0
USB1
USB2
Clock,
PLL
and
Dividers
USB
HUB
USB
SIE
6K y 8
ROM
8K y 8
SRAM
CPU − I/F
Susp/Res
UBM
USB Buffer
Manager
TDM
Control
Logic
8052
Core
8
8
8
88
8
8
8
Reset and
Interrupt
Logic
2 y 16-Bit
Timers
Port-1
Port-2
Port-3
Port-4
I2C
Controller
8 P0[7:0]
8 P1[7:0]
8 P2[7:0]
8 P3[7:0]
RSTI
INT1
I2C Bus
Figure 1−1. TUSB2136 Block Diagram
1−2
Page 9
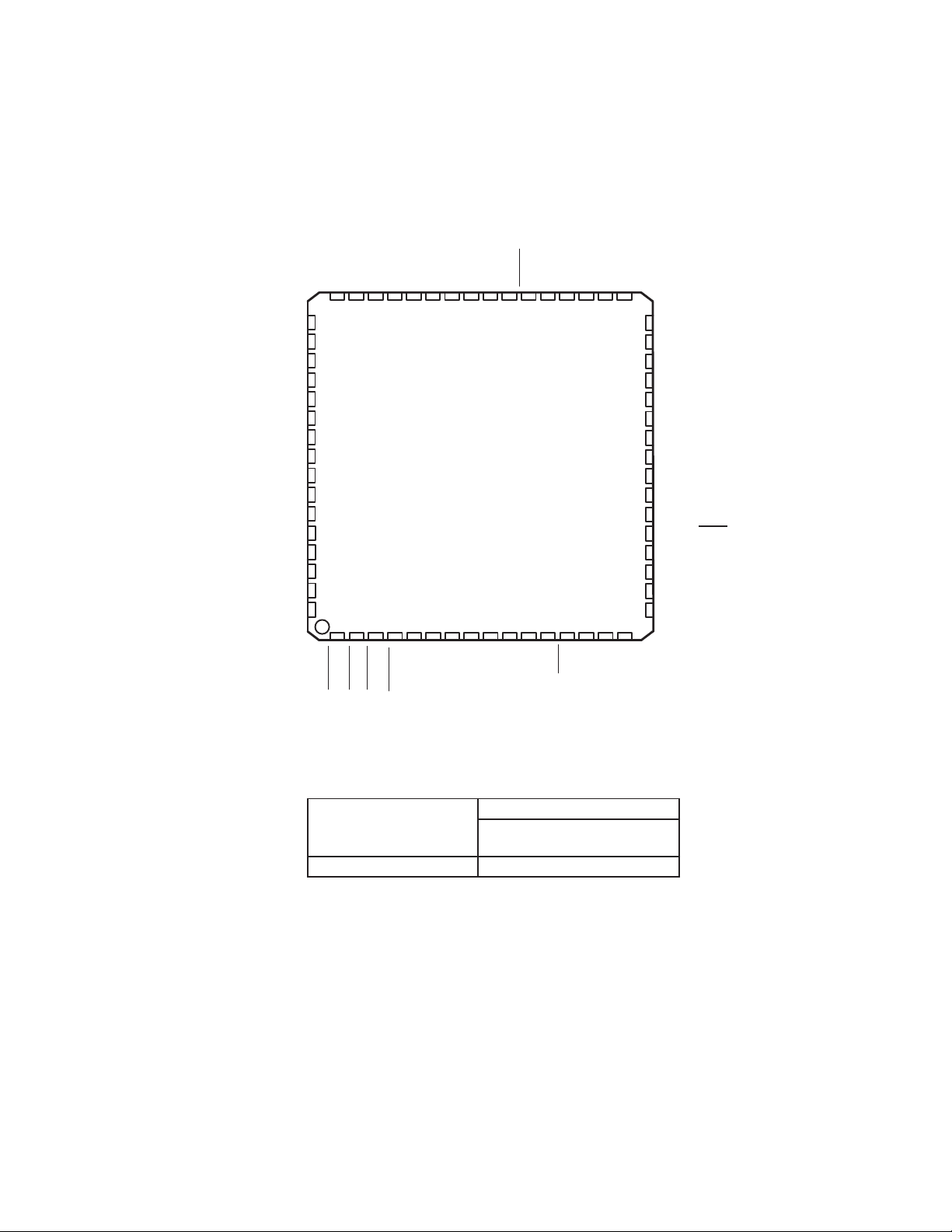
1.3 Terminal Assignments
P0.5
P0.4
P0.3
P0.2
P0.1
PM PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
P0.0
GND
P1.7
P1.6
V
CC
VDD18
VREN
P1.5
P1.4
P1.3
P1.2
P0.6
P0.7
P3.7
P3.6
P3.5
P3.4
P3.3
P3.2
P3.1/S1/TXD
P3.0/S0/RXD
GND
X2
X1
V
CC
DM2
DP2
1.4 Ordering Information
47 46 45 44 4348 42
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
12 3
PWR01
OVCR2
PWR02
5678
4
GND
OVCR1
DM1
40 39 3841
910111213
S2
S3
DP1
V
CC
37 36
SDA
SCL
35 34 33
14 15 16
RST
TEST0
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
SUSP
TEST1
P1.1
P1.0
P2.7
P2.6
P2.5
P2.4
P2.3
P2.2
GND
P2.1
P2.0
SELF/BUS
GND
DM0
DP0
PUR
PACKAGE
T
A
0°C to 70°C TUSB2136PM
PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
(PM)
1−3
Page 10
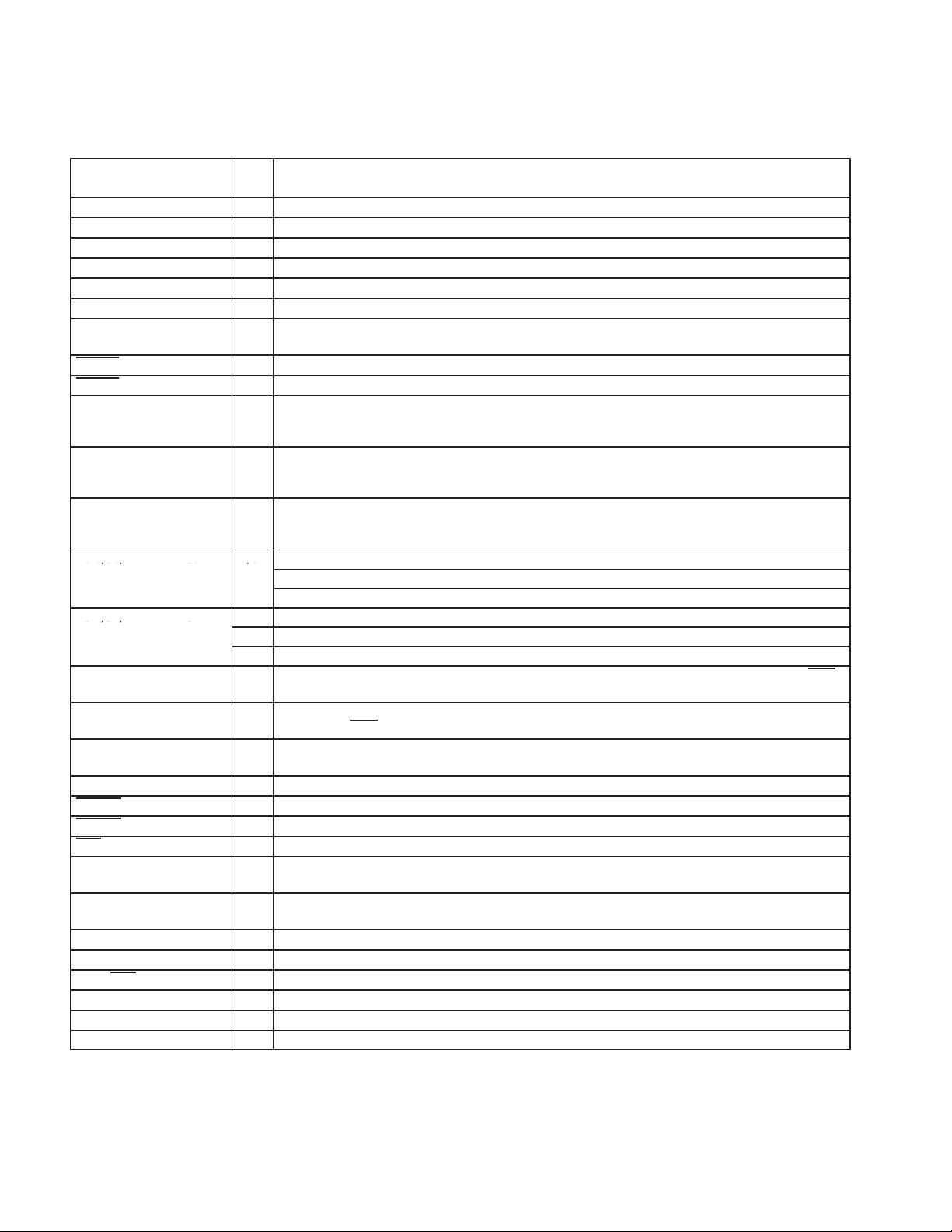
1.5 Terminal Functions
I/O
DESCRIPTION
P3.0/S0/RXD
58
I/O
P3.1/S1/TXD
57
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
DM0 19 I/O Differential data-minus USB port 0: upstream
DM1 6 I/O Differential data-minus port 1: downstream
DM2 63 I/O Differential data-minus port 2: downstream
DP0 18 I/O Differential data-plus USB port 0: upstream
DP1 7 I/O Differential data-plus port 1: downstream
DP2 64 I/O Differential data-plus port 2: downstream
GND 5, 20, 24,
42, 59
OVCR1 4 I Port 1: Overcorrect indicator; Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup
OVCR2 1 I Port 2: Overcorrect indicator; Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup
P0.[0:7] 43, 44, 45,
46, 47, 48,
49, 50
P1.[0:7] 31, 32, 33,
34, 35, 36,
40, 41
P2.[0:7] 22, 23, 25,
26, 27, 28,
29, 30
P3.0/S0/RXD 58 I/O
P3.1/S1/TXD 57
P3.2 56 I/O General-purpose I/O port 3 bit 2, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output†; INT0
P3.3 55 I/O General-purpose I/O port 3 bit 3, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
P3.[4:7] 54, 53, 52,51I/O General-purpose I/O port 3 bit 4, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
— Power supply ground
I/O General-purpose I/O port 0 bits 0−7, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
I/O General-purpose I/O port 1 bits 0−7, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
I/O General-purpose I/O port 2 bits 0−7, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
P3.0: General-purpose I/O port 3 bit 0, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
S0: See Section 2.6.12
RXD: Can be used as a UART interface
I/O P3.1: General-purpose I/O port 3 bit 1, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup, open-drain output
I/O S1: See Section 2.6.12
I/O TXD: Can be used as a UART interface
only used internally (see Section 2.9.4)
†;
may support INT1
input, depending on configuration (see Figure 2−5)
†
†
†
†
†
†
1−4
PUR 17 O Pullup resistor connection pin (3-state); push-pull CMOS output (±8 mA)
PWRO1 3 O Port 1: power on/off control signal; push-pull CMOS output (±8 mA)
PWRO2 2 O Port 2: power on/off control signal; push-pull CMOS output (±8 mA)
RST 13 I Controller master reset signal, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup
S2 8 I General-purpose input; can be used for VID/PID selection under firmware control. This input has no
S3 9 I General-purpose input. This input has no internal pullup, so it must be driven/pulled either low or high
SCL 12 O Serial clock I2C; push-pull output
SDA 11 I/O Serial data I2C; open-drain output
SELF/BUS 21 I USB power MODE select: self powered (HIGH), bus powered (LOW)
SUSP 16 O Suspend status signal: suspended (HIGH); unsuspended (LOW)
‡
TEST0
‡
TEST1
†
All open-drain output pins can sink up to 8 mA.
‡
The functions controlled by TEST0 and TEST1 are shown in the following table. Because these two pins have internal pullups, they can be left
unconnected for the default mode.
14 I Test input 0, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup
15 I Test input 1, Schmitt-trigger input, 100-µA active pullup
internal pullup, so it must be driven/pulled either low or high and connot be left unconnected.
and connot be left unconnected.
†
Page 11
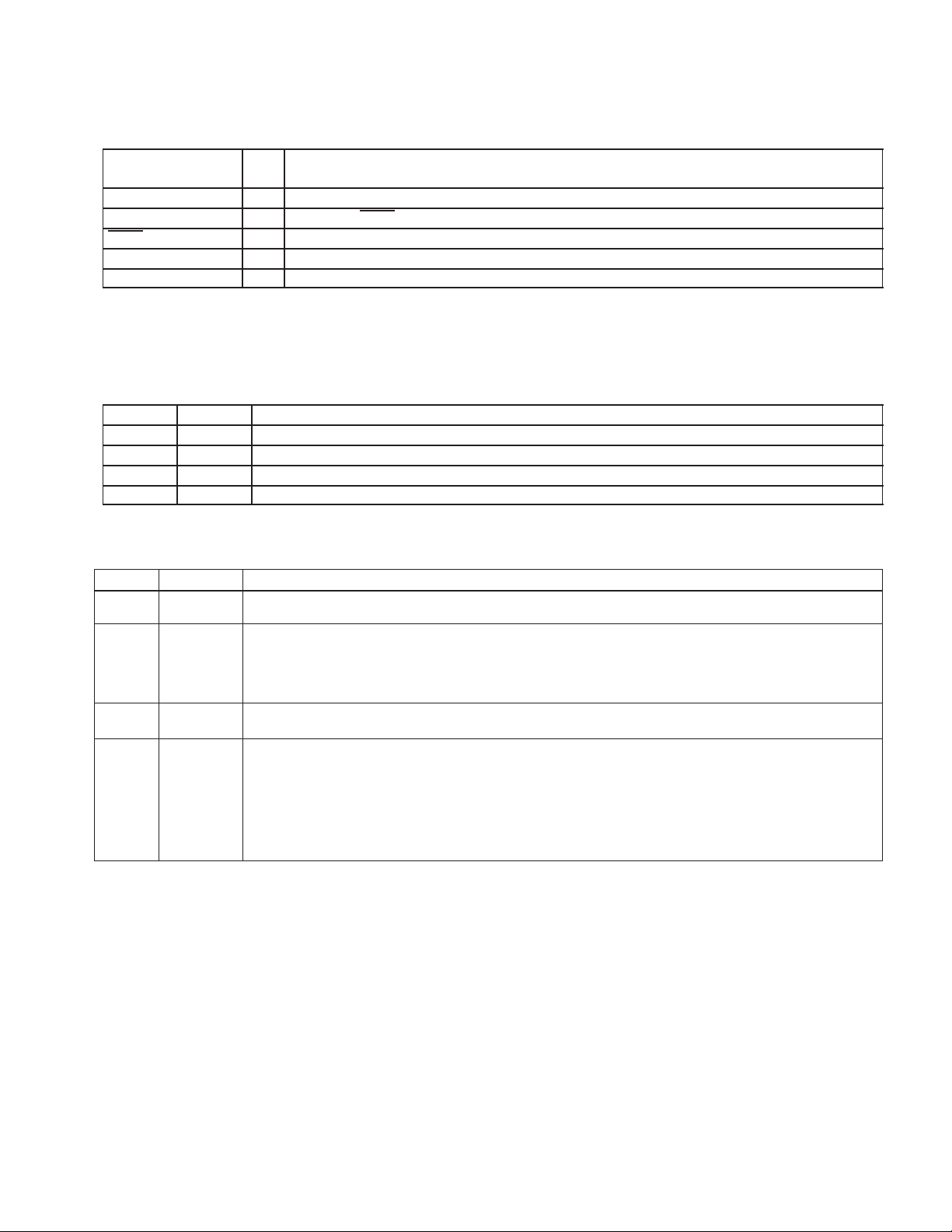
1.5 Terminal Functions (Continued)
I/O
DESCRIPTION
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
V
CC
VDD18
VREN 38 I Voltage regulator enable: enable active LOW; disable active HIGH
X2 60 O 12-MHz crystal output
X1 61 I 12-MHz crystal input
†
During normal o p e r a t i o n , t h e i n t e r n a l 3 . 3 - t o 1 . 8 - V v o ltage regulator of the TUSB2136 is enabled and provides power to the core. To save power
during the suspend mode, the internal regulator is disabled. In this case, the pin becomes an input, and a simple external power source is required
to provide power to the core. This source needs to supply a very limited amount of power (10 µA maximum) within the voltage range of 1 V to
1.95 V.
NOTE 1: The MCU treats the outputs as open-drain types in that the output can be driven low continuously, but a high output is driven for two
10,39,62 — Power supply input, 3.3 V typical
†
37 1.8 V. When VREN is low, 1.8 V must be applied to provide current for the core during suspend.
clock cycles and then the output is placed in a high-impedance state.
TEST0
0 0 Selects 48-MHz clock input (from an oscillator or other onboard clock source)
0 1 Reserved for testing purposes
1 0 Reserved for testing purposes
1 1 Selects 12-MHz crystal as clock source (default)
TEST1 FUNCTION
1.6 Revision History
Version Date Changes
Dec−2000 Initial Release
A Feb−2001 1. Clarified pin descriptions for P3.2 (56), P3.3 (55), and VDDOUT (37).
B Jun−2002 1. Changed name of pin 37 from VDDOUT to VDD18 and enhanced pin description.
C Apr−2003 1. Simplified Terminal Function Table for GPIO Ports
2. Add red/write capability for each of the register bits.
3. Corrected Quiescent and Suspend current figures in Table 3.3.
4. Added Section 4.2 Reset Timing
5. Added NOTE to cover page.
2. Removed NOTE from cover page.
2. Clarified GPIO Port 3 pin descriptions in Terminal Function Table
3. Clarified functional description for Pins S2 and S3 (8 & 9)
4. Clarified TEST0 & TEST1 (14 & 15) pin functions in Terminal Functions Table
5. Added note on open-drain output pins for Terminal Functions Table
6. Added additional note for operation of VDD18 (pin 37) to Terminal Functions Table.
7. Removed most references to ROM version including Fig 2.2.
8. Added USB Logo to Cover page
1−5
Page 12

1−6
Page 13
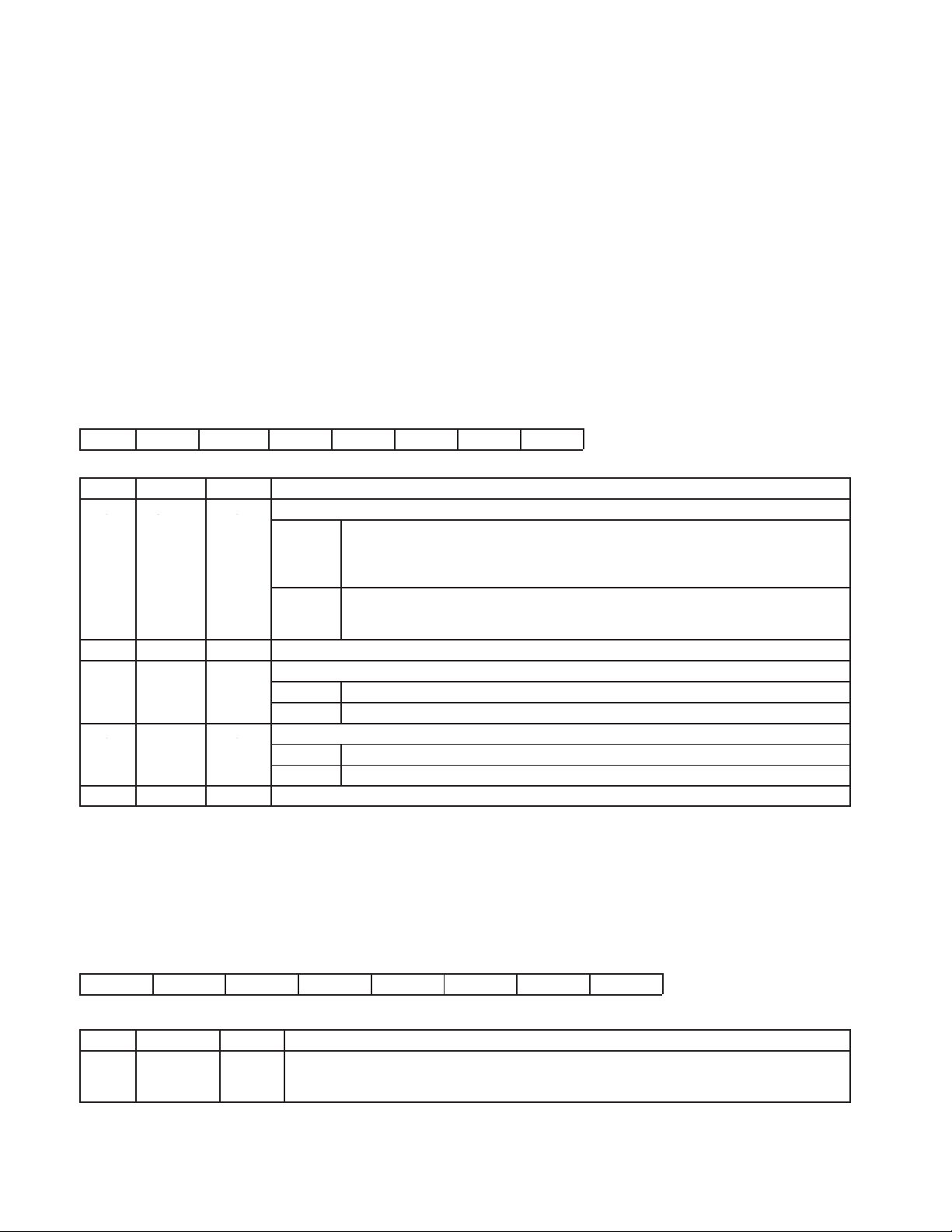
2 Functional Description
2.1 MCU Memory Map
Figure 2−1 illustrates the MCU memory map under boot and normal operation. It must be noted that the internal 256
bytes of IDATA are not shown since it is assumed to be in the standard 8052 location (0000 to 00FF). The shaded
areas represent the internal ROM/RAM. For more information regarding the integrated 8052, see the TUSBxxxx
Microcontroller Reference Guide (SLLU044).
When the SDW bit = 0 (boot mode): The 6K ROM is mapped to address (0000−17FF) and is duplicated in location
(8000−97FF) in code space. The internal 8K RAM is mapped to address range (0000−1FFF) in data space. Buffers,
memory-mapped registers (MMRs), and I/O are mapped to address range (FD80−FFFF) in data space.
When the SDW bit = 1 (normal mode): The 6K ROM is mapped to (8000−97FF) in code space. The internal 8K RAM
is mapped to address range (0000−1FFF) code space. Buffers, MMR, and I/O are mapped to address range
(FD80−FFFF) in data space.
0000
17FF
1FFF
8000
97FF
FD80
Boot Mode (SDW = 0)
CODE
6K Boot ROM
6K Boot ROM
XDATA
8K
RAM
Read/Write
512 Bytes
RAM
Normal Mode (SDW = 1)
CODE
8K
Code RAM
Read Only
6K Boot ROM
XDATA
512 Bytes
RAM
FF80
FFFF
MMR
MMR
Figure 2−1. MCU Memory Map (TUSB2136B)
2.2 Miscellaneous Registers
2.2.1 TUSB2136 Boot Operation
Because the code space is in RAM (with the exception of the boot ROM), the TUSB2136 firmware must be loaded
from an external source. Two options for booting are available: an external serial EEPROM source connected to the
2−1
Page 14
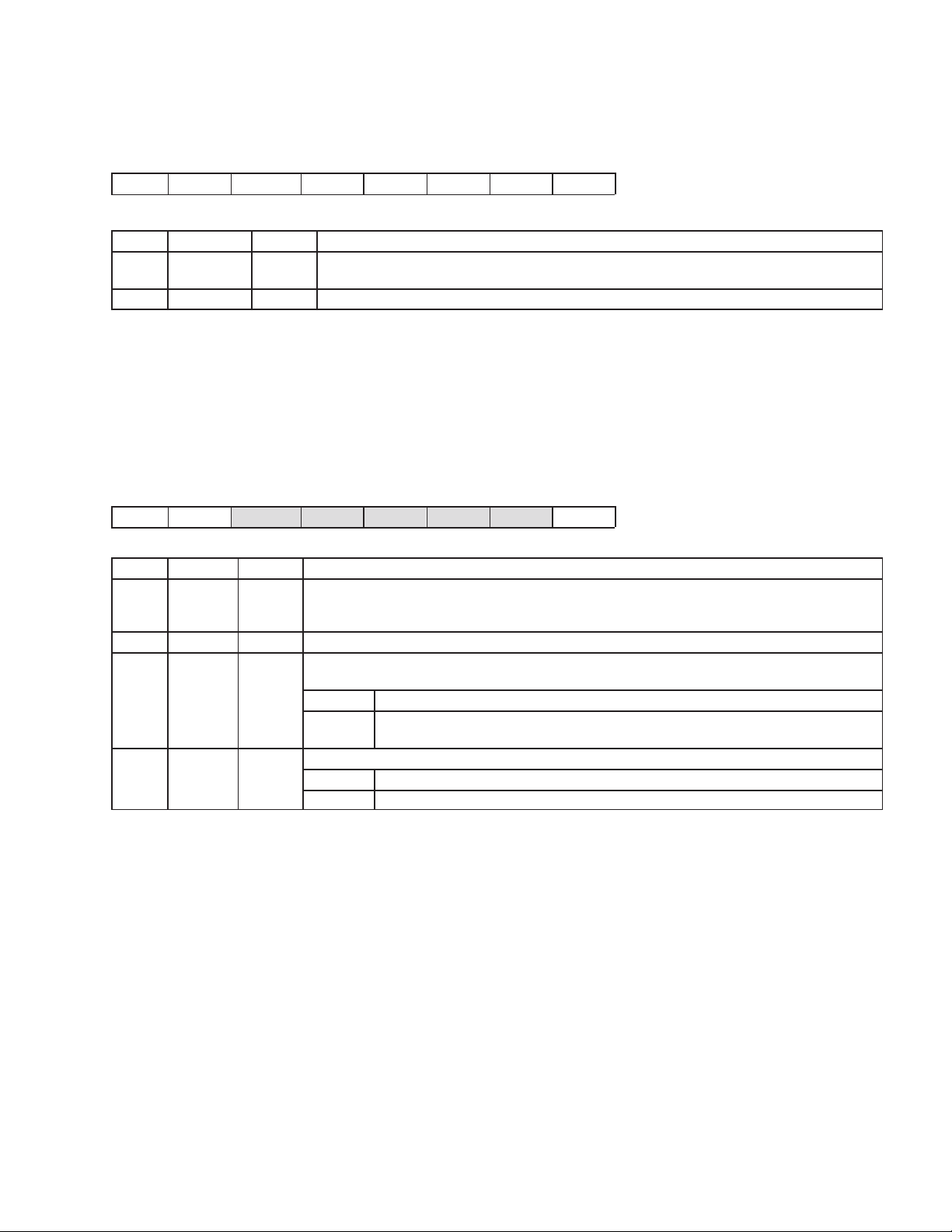
I2C bus, or the host can be used via the USB. On device reset, the SDW bit (in the ROM register) and the CONT bit
0
SDW
0
5
OVCE
0
6
XINT
0
in the USB control register (USBCTL) are cleared. This configures the memory space to boot mode (see memory
map, Table 2−2) and keeps the device disconnected from the host.
The first instruction is fetched from location 0000 (which is in the 6K ROM). The 8K RAM is mapped to XDATA space
(location 0000h). The MCU executes a read from an external EEPROM and tests to see if it contains the code (test
for boot signature). If it contains the code, the MCU reads from EEPROM and writes to the 8K RAM in XDATA space.
If not, the MCU proceeds to boot from USB.
Once the code is loaded, the MCU sets SDW to 1. This switches the memory map to normal mode, i.e. the 8K RAM
is mapped to code space, and the MCU starts executing from location 0000h. Once the switch is done, the MCU sets
CONT to 1 (in the USBCTL register) This connects the device to the USB, resulting in the normal USB device
enumeration.
2.2.2 MCNFG: MCU Configuration Register
This register is used to control the MCU clock rate.
76 5 43210
RSV XINT OVCE R3 R2 R1 R0 SDW
R/W R/W R/W R/O R/O R/O R/O R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 SDW 0
4−1 R[3:0] No effect These bits reflect the device revision number.
5 OVCE 0
6 XINT 0
7 RSV 0 Reserved
This bit enables/disables boot ROM.
SDW = 0 When clear, the MCU executes from the 6K boot ROM space. The boot ROM appears in two
locations: 0000 and 8000h. The 8K RAM is mapped to XDATA space; therefore, read/write
operation is possible. This bit is set by the MCU after the RAM load is completed. The MCU
cannot clear this bit. It is cleared on power-up reset or function reset.
SDW = 1 When set by MCU, the 6K boot ROM maps to location 8000h, and the 8K RAM is mapped to
code space, starting at location 0000h. At this point, the MCU executes from RAM, and write
operation is disabled (no write operation is possible in code space).
Hub overcorrect detection enable/disable bit.
OVCE = 0 Hub overcorrect detection is disabled.
OVCE = 1 Hub overcorrect detection is enabled.
INT1 source control bit
XINT = 0 INT1 is connected to the P3.3 pin and operates as a standard INT1 interrupt.
XINT = 1 INT1 is connected to the OR of port-2 inputs.
2.2.3 PUR_n: GPIO Pullup Register for Port n (n = 0 to 3)
PUR_0: GPIO pullup register for port 0
PUR_1: GPIO pullup register for port 1
PUR_2: GPIO pullup register for port 2
PUR_3: GPIO pullup register for port 3
76543210
PORT_n.7 PORT_n.6 PORT_n.5 PORT_n.4 PORT_n.3 PORT_n.2 PORT_n.1 PORT_n.0
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0−7 PORT_n.N
(N = 0 to 7)
2−2
0 The MCU can write to this register. If the MCU sets this bit to 1, the pullup resistor is disconnected from
the pin. If the MCU clears this bit to 0, the pullup resistor is connected to the pin. The pullup resistor is
connected to the VCC power supply.
Page 15
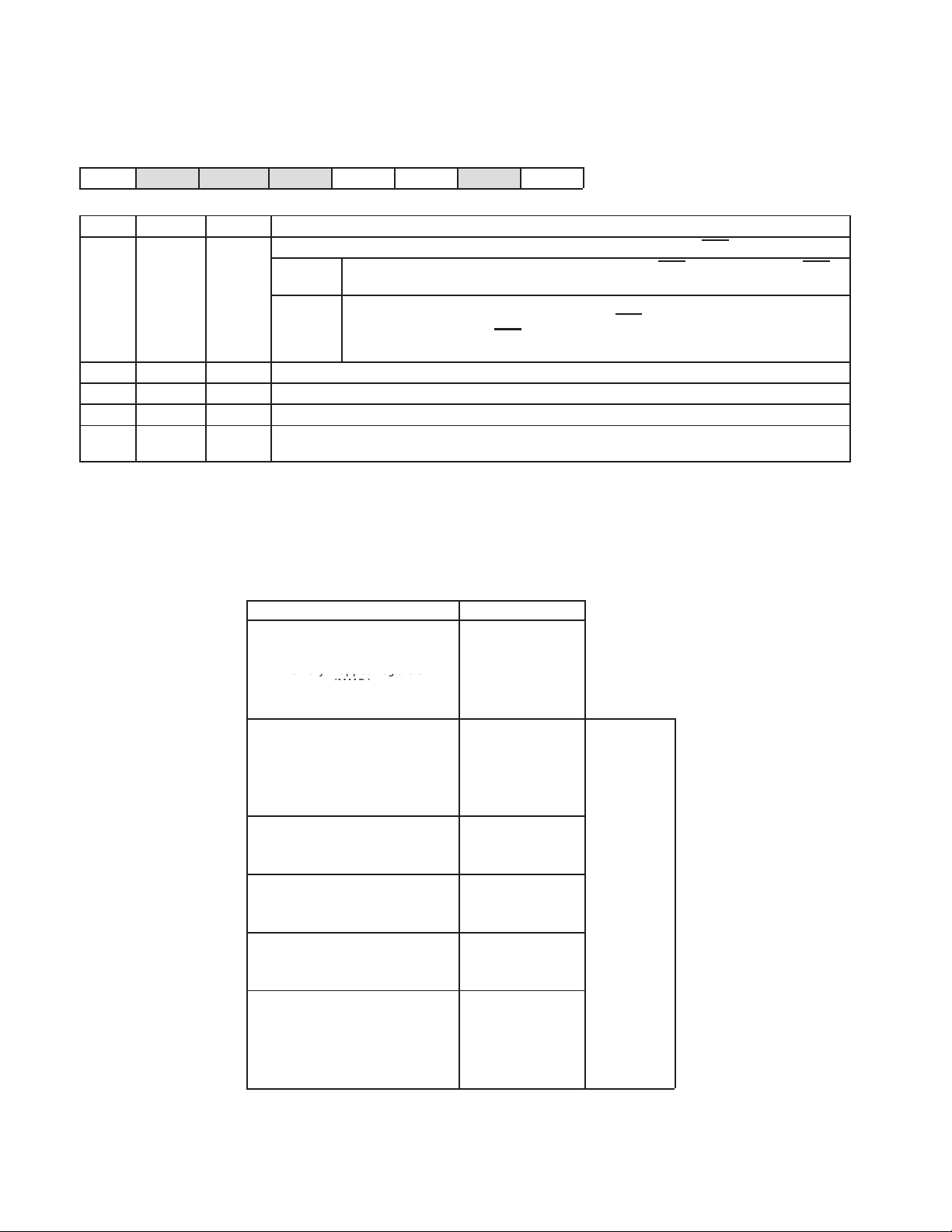
2.2.4 INTCFG: Interrupt Configuration
7
WDE
0
76 5 43210
RSV RSV RSV RSV I3 I2 I1 I0
R/O R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0−3 I[3:0] 0010 The MCU can write to this register to set the interrupt delay time for port 2 on the MCU. The value of the
4−7 RSV 0 Reserved
lower nibble represents the delay in ms. Default after reset is 2 ms.
2.2.5 WDCSR: Watchdog Timer, Control, and Status Register
A watchdog timer (WDT) with 1-ms clock is provided. The watchdog timer only works when a USB start-of-frame has
been detected by the TUSB3210. If this register is not accessed for a period of 32 ms, the WDT counter resets the
MCU (see Figure 2−2, Reset Diagram). When the IDL bit in PCON is set, the WDT is suspended until an interrupt
is detected. At this point, the IDL bit is cleared and the WDT resumes operation. The WDE bit of this register is cleared
only on power-up or USB reset (if enabled). When the MCU writes a 1 to the WDE bit of this register the WDT starts
running.
76 5 43210
WDE WDR RSV RSV RSV RSV RSV WDT
R/W R/W R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O W/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 WDT 0 The MCU must write a 1 to this bit to prevent the WDT from resetting the MCU. If MCU does not write a 1 in a
5−1 RSV 0 Reserved
6 WDR 0
7 WDE 0
period of 31 ms, the WDT resets the device. Writing a 0 has no effect on the WDT. (The WDT is a 5-bit
counter using a 1-ms CLK). This bit is read as 0.
Watchdog reset indication bit. This bit indicates if the reset occurred due to power-on reset or watchdog
timer reset.
WDR = 0 A power-up or USB reset occurred.
WDR = 1 A watchdog time-out reset occurred. To clear this bit, the MCU must write a 1. Writing a 0 has
no effect.
Watchdog timer enable
WDE = 0 Disabled
WDE = 1 Enabled
2−3
Page 16
2.2.6 PCON: Power Control Register (at SFR 87h)
0
IDL
0
Internal
memory mapped registers
↑
memory mapped registers
(EDB)
Setup packet buffer
Input endpoint-0 buffer
RAM
Output endpoint-0 buffer
Data buffers
Data buffers
↑
(368 bytes)
76 5 43210
SMOD RSV RSV RSV GF1 GF0 RSV IDL
R/W R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/O R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 IDL 0
1 RSV 0 Reserved
3−2 GF[1:0] 00 General-purpose bits. The MCU can write and read them.
6−4 RSV 0 Reserved
7 SMOD 0 Double baud-rate control bit. For more information see the UART serial interface in the M8052 core
MCU idle mode bit. This bit can be set by the MCU and is cleared only by the INT1 interrupt.
IDL = 0 The MCU is not in idle mode. This bit is cleared by the INT1 interrupt logic when INT1 is
IDL = 1 The MCU is in idle mode and RAM is in low-power mode. The oscillator/APLL is off and the
specification.
asserted for at least 400 µs.
WDT is suspended. When in suspend mode, only INT1
and generate an interrupt. INT1
recognized.
must be asserted for at least 400 µs for the interrupt to be
can be used to exit from the idle state
2.3 Buffers + I/O RAM Map
The address range from FD80 to FFFF is reserved for data buffers, setup packet, endpoint descriptor blocks (EDB),
and all I/O. RAM space of 512 bytes [FD80−FF7F] is used for EDB and buffers. The FF80−FFFF range is used for
memory-mapped registers (MMR). Table 2−1 represents the internal XDATA space allocation.
Table 2−1. XDATA Space
DESCRIPTION ADDRESS RANGE
(MMR)
Endpoint descriptor blocks
Setup packet buffer
Input endpoint-0 buffer
Output endpoint-0 buffer
FFFF
FF80
FF7F
↑
FF08
FF07
↑
FF00
FEFF
↑
FEF8
FEF7
↑
FEF0
FEEF
512 -Byte
2−4
FD80
Page 17

Table 2−2. Memory-Mapped Registers Summary (XDATA Range = FF80 → FFFF)
ADDRESS REGISTER DESCRIPTION
FFFF FUNADR FUNADR: Function address register
FFFE USBSTA USBSTA: USB status register
FFFD USBMSK USBMSK: USB interrupt mask register
FFFC USBCTL USBCTL: USB control register
FFFB HUBVIDH HUBVIDH: HUB-VID register (high-byte)
FFFA HUBVIDL HUBVIDL: HUB-VID register (low-byte)
FFF9 HUBPIDH HUBPIDH: HUB-PID register (high-byte)
FFF8 HUBPIDL HUBPIDL: HUB-PID register (low-byte)
FFF7 HUBCNFG HUBCNFG: HUB-configuration register
FFF6 VIDSTA VIDSTA: VID/PID status register
FFF5 HUBPOTG HUBPOTG: HUB power-on to power-good descriptor register
FFF4 HUBCURT HUBCURT: HUB current descriptor register
FFF3 I2CADR I2CADR: I2C address register
FFF2 I2CDAI I2CDAI: I2C data-input register
FFF1 I2CDAO I2CDAO: I2C data-output register
FFF0 I2CSTA I2CSTA: I2C status and control register
↑ RESERVED
FF97 PUR3 Port 3 pullup resistor register
FF96 PUR2 Port 2 pullup resistor register
FF95 PUR1 Port 1 pullup resistor register
FF94 PUR0 Port 0 pullup resistor register
FF93 WDCSR WDCSR: Watchdog timer, control and status register
FF92 VECINT VECINT: Vector interrupt register
FF91 RESERVED
FF90 MCNFG MCNFG: MCU configuration register
↑ RESERVED
FF84 INTCFG INTCFG: Interrupt delay configuration register
FF83 OEPBCNT_0 OEPBCNT_0: Output endpoint-0 byte count register
FF82 OEPCNFG_0 OEPCNFG_0: Output endpoint-0 configuration register
FF81 IEPBCNT_0 IEPBCNT_0: Input endpoint-0 byte count register
FF80 IEPCNFG_0 IEPCNFG_0: Input endpoint-0 configuration register
2.4 Endpoint Descriptor Block (EDB-1 to EDB-3)
Data transfers between USB, MCU and external devices are defined by an endpoint descriptor block (EDB). Four
input and four output EDBs are provided. With the exception of EDB-0 (I/O endpoint 0), all EDBs are located in SRAM
as shown in Table 2−3. Each EDB contains information describing the X and Y buffers. In addition, it provides general
status information.
2−5
Page 18

Table 2−3. EDB and Buffer Allocations in XDATA
32 bytes
RESERVED
8 bytes
Input endpoint 3: configuration
8 bytes
Input endpoint 2: configuration
8 bytes
Input endpoint 1: configuration
8 bytes
Output endpoint 3: configuration
8 bytes
Output endpoint 2: configuration
8 bytes
Output endpoint 1: configuration
8 bytes
Setup packet block
8 bytes
Input endpoint 0: buffer
8 bytes
Output endpoint 0: buffer
ADDRESS SIZE DESCRIPTION
FF7F
↑
FF60
FF5F
↑
FF58
FF57
↑
FF50
FF4F
↑
FF48
FF47
↑ 40 bytes RESERVED
FF20
FF1F
↑
FF18
FF17
↑
FF10
FF0F
↑
FF08
FF07
↑
FF00
FEFF
↑
FEF8
FEF7
↑
FEF0
FEEF Top of buffer space
↑
368 bytes Buffers space
FD80 Start of buffer space
32 bytes RESERVED
8 bytes Input endpoint 3: configuration
8 bytes Input endpoint 2: configuration
8 bytes Input endpoint 1: configuration
8 bytes Output endpoint 3: configuration
8 bytes Output endpoint 2: configuration
8 bytes Output endpoint 1: configuration
8 bytes Setup packet block
8 bytes Input endpoint 0: buffer
8 bytes Output endpoint 0: buffer
2−6
Page 19

Table 2−4 illustrates the EDB entries for EDB-1 to EDB-3. EDB-0 registers are described separately.
2
USBIE
x
3
STALL
0
4
DBUF
x
7
UBME
x
Table 2−4. EDB Entries in RAM (n = 1 to 3)
Offset ENTRY NAME DESCRIPTION
07 EPSIZXY_n I/O endpoint_n: X/Y buffer size
06 EPBCTY_n I/O endpoint_n: Y byte count
05 EPBBAY_n I/O endpoint_n: Y buffer base address
04 SPARE Not used
03 SPARE Not used
02 EPBCTX_n I/O endpoint_n: X byte count
01 EPBBAX_n I/O endpoint_n: X buffer base address
00 EPCNF_n I/O endpoint_n: configuration
2.4.1 OEPCNF_n: Output Endpoint Configuration (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
UBME ISO TOGLE DBUF STALL USBIE RSV RSV
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
1−0 RSV x Reserved = 0
2 USBIE x
3 STALL 0
4 DBUF x
5 TOGLE x USB toggle bit. This bit reflects the toggle sequence bit of DATA0, DATA1
6 ISO x ISO = 0 Non-isochronous transfer. This bit must be cleared by the MCU because only
7 UBME x
USB interrupt enable on transaction completion. Set/clear by MCU.
USBIE = 0 No interrupt
USBIE = 1 Interrupt on transaction completion
USB stall condition indication. Set/clear by MCU.
STALL = 0 No stall
STALL = 1 USB stall condition. If set by the MCU, a STALL handshake is initiated and the bit is cleared by
the MCU.
Double buffer enable. Set/clear by MCU.
DBUF = 0 Primary buffer only (X-buffer only)
DBUF = 1 Toggle bit selects buffer
non-isochronous transfer is supported.
USB buffer manager (UBM) enable/disable bit. Set/clear by MCU.
UBME = 0 UBM cannot use this endpoint.
UBME = 1 UBM can use this endpoint.
2.4.2 OEPBBAX_n: Output Endpoint X-Buffer Base-Address (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
A
10
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 A[10:3] x A[10:3] of X-buffer base address (padded with 3 LSB of zeros for a total of 11-bits). This value is set by the
A
9
A
8
A
7
MCU. UBM or DMA uses this value as the start address of a given transaction. Furthermore, UBM or DMA
does not change this value at the end of a transaction.
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
2−7
Page 20

2.4.3 OEPBCTX_n: Output Endpoint X-Byte Count (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
NAK C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 C[6:0] x X-buffer byte count:
7 NAK x NAK= 0 No valid data in buffer. Ready for host out
6
C
5
C
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
NAK= 1 Buffer contains a valid packet from host (host-out request is NAK)
C
3
C
2
C
1
C
0
2.4.4 OEPBBAY_n: Output Endpoint Y-Buffer Base-Address (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
A
10
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 A[10:3] x A[10:3] of Y-buffer base address (padded with 3 LSB of zeros for a total of 11 bits). This value is set by the
A
9
A
8
A
7
MCU. UBM or DMA uses this value as the start address of a given transaction. Furthermore, UBM or DMA
does not change this value at the end of a transaction.
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
2.4.5 OEPBCTY_n: Output Endpoint Y-Byte Count (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
NAK C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 C[6:0] x Y -buffer byte count:
7 NAK x NAK= 0 No valid data in buffer. Ready for host out
6
C
5
C
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
NAK= 1 Buffer contains a valid packet from host (host-out request is NAK)
C
3
C
2
C
1
C
0
2−8
Page 21

2.4.6 OEPSIZXY_n: Output Endpoint X-/Y-Byte Count (n = 1 to 3)
2
USBIE
x
3
STALL
0
4
DBUF
x
7
UBME
x
76 5 43210
RSV S
R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 S[6:0] x X- and Y-buffer size:
7 RSV x Reserved = 0
6
S
5
S
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
S
3
S
2
S
1
S
0
2.4.7 IEPCNF_n: Input Endpoint Configuration (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
UBME
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
1−0 RSV x Reserved = 0
2 USBIE x
3 STALL 0
4 DBUF x
5 TOGLE x USB toggle bit. This bit reflects the toggle sequence bit of DATA0, DATA1
6 ISO x ISO = 0 Non-isochronous transfer. This bit must be cleared by the MCU because only
7 UBME x
ISO TOGLE DBUF STALL USBIE RSV RSV
USB interrupt enable on transaction completion
USBIE = 0 No interrupt
USBIE = 1 Interrupt on transaction completion
USB stall condition indication. Set by UBM, but can be set/cleared by the MCU.
STALL = 0 No stall
STALL = 1 USB stall condition. If set by the MCU, a ST ALL handshake is initiated and the bit is cleared
automatically.
Double buffer enable
DBUF = 0 Primary buffer only (X-buffer only)
DBUF = 1 Toggle bit selects buffer
non-isochronous transfer is supported.
UBM enable/disable bit. Set/clear by MCU.
UBME = 0 UBM cannot use this endpoint.
UBME = 1 UBM can use this endpoint.
2.4.8 IEPBBAX_n: Input Endpoint X-Buffer Base-Address (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
A
10
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 A[10:3] x A[10:3] of X-buffer base address (padded with 3 LSB of zeros for a total of 11 bits). This value is set by the
A
9
A
8
A
7
MCU. UBM or DMA uses this value as the start-address of a given transaction. Furthermore, UBM or DMA
does not change this value at the end of a transaction.
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
2−9
Page 22

2.4.9 IEPBCTX_n: Input Endpoint X-Byte Count (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
NAK C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 C[6:0] x X-buffer byte count:
7 NAK x NAK = 0 Buffer contains a valid packet for host-in transaction
6
C
5
C
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
NAK = 1 Buffer is empty (host-in request is NAK)
C
3
C
2
C
1
C
0
2.4.10 IEPBBAY_n: Input Endpoint Y-Buffer Base-Address (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
A
10
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 A[10:3] x A[10:3] of Y-buffer base address (padded with 3 LSB of zeros for a total of 11 bits). This value is set by the
A
9
A
8
A
7
MCU. UBM or DMA uses this value as the start-address of a given transaction. Furthermore, UBM or DMA
does not change this value at the end of a transaction.
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
2.4.11 IEPBCTY_n: Input Endpoint Y-Byte Count (n = 1 to 3)
76 5 43210
NAK C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 C[6:0] x Y -buffer byte count:
7 NAK x NAK = 0 Buffer contains a valid packet for host-in transaction
6
C
5
C
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
NAK = 1 Buffer is empty (host-in request is NAK)
C
3
C
2
C
1
C
0
2−10
Page 23

2.4.12 IEPSIZXY_n: Input Endpoint X-/Y-Buffer Size (n = 1 to 3)
2
USBIE
0
3
STALL
0
7
UBME
0
76 5 43210
RSV S
R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 S[6:0] x X- and Y-buffer size:
7 RSV x Reserved = 0
6
S
5
S
4
000 0000b ³ Count = 0
000 0001b ³ Count = 1 byte
L
011 1111b ³ Count = 63 bytes
100 0000b ³ Count = 64 bytes
Any value ≥ 100 0001b produces unpredictable results.
S
3
S
2
S
1
S
0
2.5 Endpoint-0 Descriptor Registers
Unlike EDB-1 to EDB-3, which are defined as memory entries in SRAM, endpoint-0 is described by a set of 4 registers
(two for output and two for input). Table 2−5 defines the registers and their respective addresses used for EDB-0
description. EDB-0 has no Base-Address Register, because these addresses are hardwired to FEF8 and FEF0. Note
that the bit positions have been preserved to provide consistency with EDB-n (n = 1 to 3).
Table 2−5. Input/Output EDB-0 Registers
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME DESCRIPTION BASE ADDRESS
FF83 OEPBCNT_0 Output endpoint-0: byte-count register
FF82 OEPCNFG_0 Output endpoint-0: configuration register FEF0
FF81 IEPBCNT_0 Input endpoint-0: byte-count register
FF80 IEPCNFG_0 Input endpoint-0: configuration register FEF8
2.5.1 IEPCNFG_0: Input Endpoint-0 Configuration Register
76 5 43210
UBME
R/W R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
1−0 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
2 USBIE 0
3 STALL 0
4 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
5 TOGLE 0 USB toggle bit. This bit reflects the toggle sequence bit of DATA0, DATA1.
6 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
7 UBME 0
RSV TOGLE RSV STALL USBIE RSV RSV
USB interrupt enable on transaction completion. Set/clear by MCU.
USBIE = 0 No interrupt
USBIE = 1 Interrupt on transaction completion
USB stall condition indication. Set/clear by MCU.
STALL = 0 No stall
STALL = 1 USB stall condition. If set by the MCU, a ST ALL handshake is initiated and the bit is cleared
automatically by the next setup transaction.
UBM enable/disable bit. Set/clear by MCU.
UBME = 0 UBM cannot use this endpoint.
UBME = 1 UBM can use this endpoint.
2−11
Page 24

2.5.2 IEPBCNT_0: Input Endpoint-0 Byte Count Register
2
USBIE
0
3
STALL
0
7
UBME
0
76 5 43210
NAK RSV RSV RSV C
R/W R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
3−0 C[3:0] 0000 Byte count:
0000b ³ Count = 0
L
0111b ³ Count = 7
1000b ³ Count = 8
1001b to 1111b are reserved. (If used, defaults to 8)
6−4 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
7 NAK 1 NAK= 0 Buffer contains a valid packet for host-in transaction.
NAK= 1 Buffer is empty (host-in request is NAK).
3
C
2
C
1
C
0
2.5.3 OEPCNFG_0: Output Endpoint-0 Configuration Register
76 5 43210
UBME
R/W R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
1−0 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
2 USBIE 0
3 STALL 0
4 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
5 TOGLE 0 USB toggle bit. This bit reflects the toggle sequence bit of DATA0, DATA1.
6 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
7 UBME 0
RSV TOGLE RSV STALL USBIE RSV RSV
USB interrupt enable on transaction completion. Set/clear by MCU.
USBIE = 0 No interrupt
USBIE = 1 Interrupt on transaction completion
USB stall condition indication. Set/clear by MCU.
STALL = 0 No stall
STALL = 1 USB stall condition. If set by the MCU, a ST ALL handshake is initiated and the bit is cleared
automatically.
UBM enable/disable bit. Set/clear by MCU.
UBME = 0 UBM cannot use this endpoint.
UBME = 1 UBM can use this endpoint.
2−12
Page 25

2.5.4 OEPBCNT_0: Output Endpoint-0 Byte Count Register
76 5 43210
NAK RSV RSV RSV C
R/W R/O R/O R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
3−0 C[3:0] 0000 Byte count:
0000b ³ Count = 0
L
0111b ³ Count = 7
1000b ³ Count = 8
1001b to 1111b are reserved. (If used, defaults to 8)
6−4 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
7 NAK 1 NAK= 0 No valid data in buffer. Ready for host out
NAK= 1 Buffer contains a valid packet from the host (NAK the host).
3
C
2
C
1
C
2.6 USB Registers
2.6.1 FUNADR: Function Address Register
This register contains the device function address.
76 5 43210
RSV FA6 FA5 FA4 FA3 FA2 FA1 FA0
R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
0
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
6−0 FA[6:0] 0000000 These bits define the current device address assigned to the function. The MCU writes a value to this
7 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
register as a result of the SET-ADDRESS host command.
2−13
Page 26

2.6.2 USBSTA: USB Status Register
5
RESR
0
6
SUSR
0
All bits in this register are set by the hardware and are cleared by the MCU when writing a 1 to the proper bit location
(writing a 0 has no effect). In addition, each bit can generate an interrupt if its corresponding mask bit is set (R/C
notation indicates read and clear only by the MCU).
76 5 43210
RSTR SUSR RESR PWOFF PWON SETUP RSV STPOW
R/C R/C R/C R/C R/C R/C R/O R/C
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 STPOW 0
1 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
2 SETUP 0
3 PWON 0
4 PWOFF 0
5 RESR 0
6 SUSR 0
7 RSTR 0
SETUP overwrite bit. Set by hardware when a setup packet is received while there is already a packet in the
setup buffer.
STPOW = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
STPOW = 1 SETUP overwrite
SETUP transaction received bit.
As long as SETUP is 1, IN and OUT on endpoint-0 are NAK regardless of the value of their real NAK bits.
SETUP = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
SETUP = 1 SETUP transaction received.
Power on request for port 3.
This bit indicates if power-on to port 3 has been received. This bit generates a PWON interrupt (if enabled).
PWON = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
PWON = 1 Power on to port 3 has been received.
Power off request for port 3. This bit indicates whether power-off to port 3 has been received. This bit
generates a PWOFF interrupt (if enabled).
PWOFF = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
PWOFF = 1 Power off to port 3 has been received.
Function resume request bit
RESR = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
RESR = 1 Function resume is detected.
Function suspended request bit. This bit is set in response to a global or selective suspend condition.
SUSR = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
SUSR = 1 Function suspend is detected.
Function reset request bit. This bit is set in response to the host initiating a port reset. This bit is not af fected
by a USB function reset.
RSTR = 0 The MCU can clear this bit by writing a 1. (Writing a 0 has no effect.)
RSTR = 1 Function reset is detected.
2−14
Page 27

2.6.3 USBMSK: USB Interrupt Mask Register
0
STPOW
0
2
SETUP
0
3
PWON
0
4
PWOFF
0
5
RESR
0
6
SUSR
0
7
RSTR
0
76 5 43210
RSTR SUSR RESR PWOFF PWON SETUP RSV STPOW
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/O R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 STPOW 0
1 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
2 SETUP 0
3 PWON 0
4 PWOFF 0
5 RESR 0
6 SUSR 0
7 RSTR 0
SETUP overwrite interrupt enable bit
STPOW = 0 STPOW interrupt disabled
STPOW = 1 STPOW interrupt enabled
SETUP interrupt enable bit
SETUP = 0 SETUP interrupt disabled
SETUP = 1 SETUP interrupt enabled
Power-on interrupt enable bit
PWON = 0 PWON interrupt disabled
PWON = 1 PWON interrupt enabled
Power-off interrupt enable bit
PWOFF = 0 PWOFF interrupt disabled
PWON = 1 PWOFF interrupt enabled
Function resume interrupt enable
RESR = 0 Function resume interrupt disabled
RESR = 1 Function resume interrupt enabled
Function suspend interrupt enable
SUSR = 0 Function suspend interrupt disabled
SUSR = 1 Function suspend interrupt enabled
Function reset interrupt enable
RSTR = 0 Function reset interrupt disabled
RSTR = 1 Function reset interrupt enabled
2−15
Page 28
2.6.4 USBCTL: USB Control Register
2
B/S
0
3
RWE
0
4
FRSTE
1
5
RWUP
0
6
U1/2
0
7
CONT
0
Unlike the other registers, this register is cleared by the power-up-reset signal only . The USB reset cannot reset this
register (see the reset diagram in Figure 2−2).
76 5 43210
CONT
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 DIR 0
1 SIR 0
2 B/S 0
3 RWE 0
4 FRSTE 1
5 RWUP 0
6 U1/2 0
7 CONT 0
U1/2 RWUP FRSTE RWE B/S SIR DIR
As a response to a setup packet, the MCU decodes the request and sets or clears this bit to reflect the data
transfer direction.
DIR = 0 USB data OUT transaction (from host to TUSB2136)
DIR = 1 USB data IN transaction (from TUSB2136 to host)
SETUP interrupt status bit. This bit is controlled by the MCU to indicate to the hardware when SETUP
interrupt is being served.
SIR = 0 SETUP interrupt is not served. The MCU clears this bit before exiting the SETUP interrupt
routine.
SIR = 1 SETUP interrupt is in progress. The MCU sets this bit when servicing the SETUP interrupt.
Bus/self power control bit
B/S = 0 The device is bus powered.
B/S = 1 The device is self powered.
Remote wake-up enable bit
RWE = 0 The MCU clears this bit when the host sends a command to clear the feature.
RWE = 1 The MCU writes 1 to this bit when the host sends set device feature command to enable the
remote wake-up feature.
Function reset connection bit. This bit connects/disconnects the USB function reset from the MCU reset.
FRSTE = 0 Function reset is not connected to MCU reset.
FRSTE = 1 Function reset is connected to MCU reset.
Device remote wake-up request. This bit is set by the MCU and is cleared automatically.
RWUP = 0 Writing a 0 to this bit has no effect.
RWUP = 1 When the MCU writes a 1, a remote wake-up pulse is generated.
USB hub version
U1/2 = 0 This is a USB1.x hub.
U1/2 = 1 This is a USB2.x hub.
Connect/disconnect bit
CONT = 0 Upstream port is disconnected. Pullup disabled.
CONT = 1 Upstream port is connected. Pullup enabled.
2−16
Page 29

2.6.5 HUBCNFG: Hub Configuration Register
0
P1E
0
1
P1A
0
2
P2E
0
3
P2A
0
6
I/G
0
7
OCP
0
76 5 43210
OCP I/G P3.1 P3.0 P2A P2E P1A P1E
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 P1E 0
1 P1A 0
2 P2E 0
3 P2A 0
5−4 P3[1:0] 00 Hub port-3 embedded-function control field
6 I/G 0
7 OCP 0
Hub port-1 enable/disable control bit
P1E = 0 Port 1 is disabled.
P1E = 1 Port 1 is enabled.
Hub port−1; permanent attachment control bit.
P1A = 0 Port 1 is connected to a removable function.
P1A = 1 Port 1 is connected to a permanent attachment function.
Hub port-2 enable/disable control bit
P2E = 0 Port 2 is disabled.
P2E = 1 Port-2 is enabled.
Hub port-2 permanent-attachment control bit
P2A = 0 Port 2 is connected to a removable function.
P2A = 1 Port 2 is connected to a permanent-attachment function.
00b = Port 3 is disabled (doesn’t exist).
01b = Port 3 is permanently attached.
10b = Port 3 is connected to a removable function, but is not attached.
11b = Port 3 is connected to a removable function, and is attached.
Individual/gang power control bit
I/G = 0 Overcurrent and power control are controlled individually.
I/G = 1 Overcurrent and power control are gang controlled.
Overcurrent protection control bit
OCP = 0 Overcurrent protection is disabled.
OCP = 1 Overcurrent protection is enabled.
2.6.6 HUBPOTG: Hub Power-On to Power-Good Descriptor Register
76 5 43210
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 00h Offset-5 in hub descriptor table
2.6.7 HUBCURT: Hub Current Descriptor Register
76 5 43210
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 00h Offset-6 in hub descriptor table
2−17
Page 30

2.6.8 HUBPIDL: Hub PID Register (Low-Byte)
76 5 43210
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 00h Hub PID low-byte value
2.6.9 HUBPIDH: Hub PID Register (High-Byte)
76 5 43210
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[15:8] 00h Hub PID high-byte value
2.6.10 HUBVIDL: Hub VID Register (Low-Byte)
76 5 43210
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 00h Hub VID low-byte value
2.6.11 HUBVIDH: Hub VID Register (High-Byte)
76 5 43210
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[15:8] 00h Hub VID high-byte value
2.6.12 VIDSTA: VID/PID Status Register
This register is used to read the value on four external pins. The firmware can use this value to select one of the vendor
identification/product identifications (VID/PID) stored in memory. The TUSB2136 supports up to 16 unique VID/PIDs
with application code to support different products. This provides a unique opportunity for original equipment
manufacturers (OEMs) to have one device to support up to 16 dif ferent product lines by using S0−S3 to select VID/PID
and behavioral application code for the selected product.
76 5 43210
RSV RSV RSV RSV S3 S2 S1 S0
R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
3−0 S[3:0] x VID/PID selection bits. These bits reflect the status of the external pins as defined by Table 2−6. Note that a
7−4 RSV 0 Reserved = 0
pin tied low is reflected as a 0 and a pin tied high is reflected as a 1.
2−18
Page 31

Table 2−6. External Pins Mapping to S[3:0] in VIDSTA Register
COMMENTS
VIDSTA REGISTER PIN
S[3:0] NO. NAME
S0 58 P3.0 Dual function, P3.0 I/O or S0 input
S1 57 P3.1 Dual function, P3.1 I/O or S1 input
S2 8 S2 S2-pin is input
S3 9 S3 S3-pin is input
2.7 Function Reset and Power-Up Reset Interconnect
Figure 2−2 represents the logical connection of USB-function reset (USBR) and power-up reset (RST) pins. The
internal RESET
can be enabled or disabled by the FRSTE bit in the USBCTL register (on power up FRSTE = 0). The internal RESET
is used to reset all registers and logic, with the exception of the USBCTL and MISCTL registers. The USBCTL and
MCU configuration registers (MCNFG) are cleared by the PURS
signal is generated from the RST pin (PURS signal) or from the USB reset (USBR signal). The USBR
signal only.
USBCTL Register
MCNFG Register
All Internal MMR
RST
WDT Reset
WDE
PURS
USBR
RESET
USB Function Reset
FRSTE
MCU
Figure 2−2. Reset Diagram
2.8 Pullup Resistor Connect/Disconnect
After reading firmware into RAM, the TUSB2136 can reenumerate using the new firmware (no need to physically
disconnect and re-connect the cable). Figure 2−3 shows an equivalent circuit implementation for Connect and
Disconnect from a USB upstream port (also see Figure 4−4b). When the CONT bit in the USBCTL register is 1, the
CMOS driver sources V
(high speed). When the CONT bit is 0, the PUR pin is driven low . In this state, the 1.5-kΩ resistor is connected to GND,
resulting in device disconnection state. The PUR driver is a CMOS driver that can provide V
8-mA source current.
DD to the pullup resistor (PUR pin), presenting a normal connect condition to the USB hub
DD − 0.1 V minimum at
2−19
Page 32

CMOS
CONT-BitPUR
TUSB2046B
HUB
D+
D−
15 kΩ15 kΩ
1.5 kΩ
DP0
DM0
TUSB2136
Figure 2−3. Pullup Resistor Connect/Disconnect Circuit
2.9 8052 Interrupt and Status Registers
All seven 8052-standard interrupt sources are preserved. SIE is the standard interrupt enable register, which controls
the seven interrupt sources. All the additional interrupt sources are connected together as an OR to generate INT0
The INT0
signal is provided to interrupt the MCU (see interrupt connection diagram, Figure 2−4).
Table 2−7. 8052 Interrupt Location Map
INTERRUPT
SOURCE
ET2 Timer-2 interrupt 002BH
ES UART interrupt 0023H
DESCRIPTION START
ADDRESS
COMMENTS
.
ET1 Timer-1 interrupt 001BH
EX1 Internal INT1 or INT1 0013H Used for P2[7:0] interrupt
ET0 Timer-0 interrupt 000BH
EX0 Internal INT0 0003H Used for all internal peripherals
Reset 0000H
2−20
Page 33

2.9.1 8052 Standard Interrupt Enable Register
0
INT0
0
1
ET0
0
2
EX1
0
3
ET1
0
4ES0
5
ET2
0
7EA0
76 5 43210
EA RSV ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 INT0
R/W R/O R/O R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 INT0 0
1 ET0 0
2 EX1 0
3 ET1 0
4 ES 0
5 ET2 0
6 RSV 0 Reserved
7 EA 0
Enable or disable external interrupt-0
EX0 = 0 External interrupt-0 is disabled.
EX0 = 1 External interrupt-0 is enabled.
Enable or disable timer-0 interrupt
ET0 = 0 Timer-0 interrupt is disabled.
ET0 = 1 Timer-0 interrupt is enabled.
Enable or disable external interrupt-1
EX1 = 0 External interrupt-1 is disabled.
EX1 = 1 External interrupt-1 is enabled.
Enable or disable timer-1 interrupt
ET1 = 0 Timer-1 interrupt is disabled.
ET1 = 1 Timer-1 interrupt is enabled.
Enable or disable serial port interrupts
ES = 0 Serial port interrupt is disabled.
ES = 1 Serial port interrupt is enabled.
Enable or disable timer-2 interrupt
ET2 = 0 Timer-2 interrupt is disabled.
ET2 = 1 Timer-2 interrupt is enabled.
Enable or disable all interrupts (global disable)
EA = 0 Disable all interrupts.
EA = 1 Each interrupt source is individually controlled.
2.9.2 Additional Interrupt Sources
All nonstandard 8052 interrupts (USB, I2C, etc.) are connected as an OR to generate an internal INT0. It must be
noted that the external INT0
interrupt (not edge-triggered). A vector interrupt register is provided to identify all interrupt sources (see vector
interrupt register definition, Section 2.9.3). Up to 64 interrupt vectors are provided. It is the responsibility of the MCU
to read the vector and dispatch the proper interrupt routine.
and INT1 are not used. Furthermore, INT0 must be programmed as an active-low level
2−21
Page 34

2.9.3 VECINT: Vector Interrupt Register
This register contains a vector value identifying the internal interrupt source that trapped to location 0003h. Writing
any value to this register removes the vector and updates the next vector value (if another interrupt is pending). Note
that the vector value is offset. Therefore, its value is in increments of two (bit 0 is set to 0). When no interrupt is pending,
the vector is set to 00h. Table 2−8 is a table of the vector interrupt values. As shown, the interrupt vector is divided
into two fields, I[2:0] and G[3:0]. The I-field defines the interrupt source within a group (on a first-come, first-served
basis) and the G-field defines the group number. Group G0 is the lowest and G15 is the highest priority.
76 5 43210
G3
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
3−1 I[2:0] 000 This field defines the interrupt source in a given group. See Table 2−8, Vector Interrupt Values.
7−4 G[3:0] 0000 This field defines the interrupt group. I[2:0] and G[3:0] combine to produce the actual interrupt vector.
G2 G1 G0 I2 I1 I0 0
Bit 0 is always 0; therefore, vector values are offset by two.
Table 2−8. Vector Interrupt Values
G[3:0]
(Hex)
0 0 00 No interrupt
1 0 10 RESERVED
1 1 12 Output endpoint 1
1 2 14 Output endpoint 2
1 3 16 Output endpoint 3
1 4−7 18−1E RESERVED
2 0 20 RESERVED
2 1 22 Input endpoint 1
2 2 24 Input endpoint 2
2 3 26 Input endpoint 3
2 4−7 28−2E RESERVED
3 0 30 STPOW packet received
3 1 32 SETUP packet received
3 2 34 PWON interrupt
3 3 36 PWOFF interrupt
3 4 38 RESR interrupt
3 5 3A SUSR interrupt
3 6 3C RSTR interrupt
3 7 3E RESERVED
4 0 40 I2C TXE interrupt
4 1 42 I2C RXF interrupt
4 2 44 Input endpoint 0
4 3 46 Output endpoint 0
4 4−7 48 → 4E RESERVED
5−15 X 90 → FE RESERVED
I[2:0]
(Hex)
VECTOR
(Hex)
INTERRUPT SOURCE
2−22
Page 35

2.9.4 Logical Interrupt Connection Diagram (INT0)
Figure 2−4 represents the logical connection of the interrupt sources and the relation of the logical connection with
INT0
. The priority encoder generates an 8-bit vector, corresponding to 64 interrupt sources (not all are used). The
interrupt priorities are hard wired. V ector 46h is the highest and 12h is the lowest. Table 2−8 lists the interrupt source
for each valid interrupt vector.
Interrupts
Priority
Encoder
46h
Interrupt Sources
L
12h
Vector
INT0
Figure 2−4. Internal Vector Interrupt (INT0)
2.9.5 P2[7:0] Interrupt (INT1)
Figure 2−5 illustrates the conceptual port-2 interrupt. All port-2 input signals are connected in a logical OR to generate
the INT1
addition, INT1
the MCU configuration register (MCNFG) is used to select the EX1 interrupt source. When XINT = 0, P3.3 is the
source, and when XINT = 1, P2[7:0] is the source.
interrupt. Note that the inputs are active low and INT1 is programmed as a level-triggered interrupt. In
is connected to the suspend/resume logic for remote wake-up support. As illustrated, the XINT bit in
P2[7:0]
INT1
P3.3
Suspend/
Resume
Logic
XINT Bit
Figure 2−5. P2[7:0] Input Port Interrupt Generation
2−23
Page 36

2.10 I2C Registers
2
TIE
0
4
1/4
0
6
RIE
0
The TUSB2136 only supports a master-slave relationship; therefore, it does not support bus arbitration.
2.10.1 I2CSTA: I2C Status and Control Register
This register is used to control the stop condition for read and write operations. In addition, it provides transmitter and
receiver handshake signals with their respective interrupt enable bits.
76 5 43210
RXF
R/C R/W R/C R/W R/C R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 SWR 0
1 SRD 0
2 TIE 0
3 TXE 1
4 1/4 0
5 ERR 0
6 RIE 0
7 RXF 0
RIE ERR 1/4 TXE TIE SRD SWR
Stop write condition. This bit defines whether the I2C controller generates a stop condition when data from
the I2CDAO register is transmitted to an external device.
SWR = 0 Stop condition is not generated when data from I2CDAO register is shifted out to an external
device.
SWR = 1 Stop condition is generated when data from I2CDAO register is shifted out to an external device.
Stop read condition. This bit defines whether the I2C controller generates a stop condition when data is
received and loaded into I2CDAI register.
SRD = 0 Stop condition is not generated when data from SDA line is shifted into the I2CDAI register.
SRD = 1 Stop condition is generated when data from SDA line is shifted into the I2CDAI register.
I2C transmitter empty interrupt enable
TIE = 0 Interrupt disabled
TIE = 1 Interrupt enabled
I2C transmitter empty. This bit indicates that data can be written to the transmitter. It can be used for polling or
it can generate an interrupt.
TXE = 0 Transmitter is full. This bit is cleared when the MCU writes a byte to I2CDAO register.
TXE = 1 Transmitter is empty. The I2C controller sets this bit when the content of the I2CDAO register is
copied to the SDA shift register.
Bus speed selection
1/4 = 0 100-kHz bus speed
1/4 = 1 400-kHz bus speed
Bus error condition. This bit is set by the hardware when the device does not respond. It is cleared by the
MCU.
ERR = 0 No bus error
ERR = 1 Bus error condition has been detected. Clears when MCU writes a 1. Writing a 0 has no effect.
I2C receiver ready interrupt enable
RIE = 0 Interrupt disabled
RIE = 1 Interrupt enabled
I2C receiver full. This bit indicates that the receiver contains new data. It can be used for polling or it can
generate an interrupt.
RXF = 0 Receiver is empty. This bit is cleared when MCU reads the I2CDAI register.
RXF = 1 Receiver contains n e w d a t a . T h i s bit is set by the I2C controller when the received serial data has
been loaded into I2CDAI register.
2−24
Page 37

2.10.2 I2CADR: I2C Address Register
0
R/W
0
This register holds the device address and the read/write command bit.
76 5 43210
A
6
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
0 R/W 0
7−1 A[6:0] 0000000 Seven address bits for device addressing
A
5
A
4
A
3
Read/write command bit.
R/W = 0 Write operation
R/W = 1 Read operation
A
2
A
1
A
0
R/W
2.10.3 I2CDAI: I2C Data-Input Register
This register holds the received data from an external device.
76 5 43210
D
7
R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O R/O
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 0 8-bit input data from an I2C device
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
2.10.4 I2CDAO: I2C Data-Output Register
0
This register holds the data to be transmitted to an external device. Writing to this register starts the transfer on the
SDA line.
76 5 43210
D7
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
BIT NAME RESET FUNCTION
7−0 D[7:0] 0 8-bit output data to an I2C device
D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
2.11 Read/Write Operations
2.11.1 Read Operation (Serial EEPROM)
A serial read requires a dummy byte write sequence to load in the 16-bit data word address. Once the device address
word and data word are clocked out and acknowledged by the device, the MCU starts a current address sequence.
The following describes the sequence of events to accomplish this transaction:
Device Address + EEPROM [high byte]
• The MCU sets I2CSTA[SRD] = 0. This prevents the I
content of the I2CDAI register is received.
• The MCU sets I2CSTA[SWR] = 0. This prevents the I
the content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
• The MCU writes the device address (R/W bit = 0) to the I2CADR register (write operation).
2
C controller from generating a stop condition after the
2
C controller from generating a stop condition after
• The MCU writes the high byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register, starting the transfer on
the SDA line.
2−25
Page 38

• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CADR register is transmitted to the EEPROM (preceded by start condition on SDA).
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the EEPROM (EEPROM address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been
transmitted.
• No stop condition is generated.
EEPROM [low byte]
• The MCU writes the low byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been
transmitted.
• This completes the dummy write operation. At this point, the EEPROM address is set and the MCU can
perform a single or a sequential read operation.
2.11.2 Current Address Read Operation
Once the EEPROM address is set, the MCU can read a single byte by executing the following steps:
1. The MCU sets I2CSTA[SRD] = 1, forcing the I
register is received.
2
C controller to generate a stop condition after the I2CDAI
2. The MCU writes the device address (R/W bit = 1) to the I2CADR register (read operation).
3. The MCU writes a dummy byte to the I2CDAO register, starting the transfer on the SDA line.
4. The RXF bit in I2CSTA is cleared.
5. The content of the I2CADR register is transmitted to the device, preceded by a start condition on SDA.
6. Data from the EEPROM is latched into the I2CDAI register (stop condition is transmitted).
7. The RXF bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the data is available.
8. The MCU reads the I2CDAI register. This clears the RXF bit (I2CSTA[RXF] = 0).
2.11.3 Sequential Read Operation
Once the EEPROM address is set, the MCU can execute a sequential read operation by executing the following steps
(Note: this example illustrates a 32-byte sequential read):
1. Device Address
• The MCU sets I2CSTA[SRD] = 0. This prevents the I
the I2CDAI register is received.
• The MCU writes the device address (R/W bit = 1) to the I2CADR register (read operation).
• The MCU writes a dummy byte to the I2CDAO register, starting the transfer on the SDA line.
• The RXF bit in I2CSTA is cleared.
• The content of the I2CADR register is transmitted to the device (preceded by a start condition on SDA).
2
C controller from generating a stop condition after
2−26
2. N-Byte Read (31 bytes)
• Data from the device is latched into the I2CDAI register (stop condition is not transmitted).
Page 39

• The RXF bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that data is available.
• The MCU reads the I2CDAI register, clearing the RXF bit (I2CSTA[RXF] = 0).
• This operation repeats 31 times.
3. Last-Byte Read (byte 32)
2
• The MCU sets I2CST A[SRD] = 1. This forces the I
C controller to generate a stop condition after the
I2CDAI register is received.
• Data from the device is latched into the I2CDAI register (stop condition is transmitted).
• The RXF bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that data is available.
• The MCU reads the I2CDAI register, clearing the RXF bit (I2CSTA[RXF] = 0).
2.11.4 Write Operation (Serial EEPROM)
The byte write operation involves three phases: 1) device address + EEPROM [high byte] phase, 2) EEPROM [low
byte] phase, and 3) EEPROM [DATA]. The following describes the sequence of events to accomplish the byte write
transaction:
Device Address + EEPROM [high byte]
2
• The MCU sets I2CSTA[SWR] = 0. This prevents the I
the content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
• The MCU writes the device address (R/W bit = 0) to the I2CADR register (write operation).
C controller from generating a stop condition after
• The MCU writes the high byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register, starting the transfer on
the SDA line.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CADR register is transmitted to the device (preceded by a start condition on SDA).
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM high-address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been
transmitted.
EEPROM [low byte]
• The MCU writes the low byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been
transmitted.
2−27
Page 40

EEPROM [DATA]
2
• The MCU sets I2CST A[SWR] = 1. This forces the I
C controller to generate a stop condition after the content
of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
• The MCU writes the DATA to be written to the EEPROM into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM data).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been
transmitted.
2
• The I
C controller generates a stop condition after the content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
2.11.5 Page Write Operation
The page write operation is initiated the same way as byte write, with the exception that a stop condition is not
generated after the first EEPROM [DATA] is transmitted. The following describes the sequence of writing 32 bytes
in page mode:
Device Address + EEPROM [high byte]
2
• The MCU sets I2CSTA[SWR] = 0. This prevents the I
the content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
• The MCU writes the device address (R/W bit = 0) to the I2CADR register (write operation).
• The MCU writes the high byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register.
C controller from generating a stop condition after
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CADR register is transmitted to the device (preceded by a start condition on SDA).
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been sent.
EEPROM [low byte]
• The MCU writes the low byte of the EEPROM address into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM address).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been sent.
31 Bytes EEPROM [DATA]
• The MCU writes the DATA to be written to the EEPROM into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the device (EEPROM data).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been sent.
• This operation repeats 31 times.
2−28
Page 41

Last Byte EEPROM [DATA]
2
• The MCU sets I2CST A[SWR] = 1. This forces the I
C controller to generate a stop condition after the content
of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
• The MCU writes the last DATA byte to be written to the EEPROM into the I2CDAO register.
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is cleared, indicating busy.
• The content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted to the EEPROM (EEPROM data).
• The TXE bit in I2CSTA is set, and interrupts the MCU, indicating that the I2CDAO register has been sent.
2
• The I
C controller generates a stop condition after the content of the I2CDAO register is transmitted.
2−29
Page 42

2−30
Page 43

3 Electrical Specifications
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Free-Air Temperature Range
(unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage, V
Input voltage, V
Output voltage, V
Input clamp current, I
Output clamp current, I
Storage temperature −65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only , a nd
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
CC
I
O
IK
OK
†
−0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
−0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
−0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Commercial Operating Conditions
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
V
V
V
T
Supply voltage 3 3.3 3.6 V
CC
Input voltage 0 V
I
High-level input voltage 2 V
IH
Low-level input voltage 0 0.8 V
IL
Operating temperature 0 70 °C
A
CC
CC
V
V
3.3 Electrical Characteristics, TA = 25°C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, GND = 0 V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
OH
V
OL
V
IT+
V
IT−
V
hys
I
IH
I
IL
I
OZ
C
I
C
O
I
CC
I
CCx
I
CCx
High-level output voltage I
Low-level output voltage I
Positive input threshold voltage VI = V
Negative input threshold voltage VI = V
Hysteresis (V
High-level input current VI = V
Low-level input current VI = V
Output leakage current (Hi-Z) VI = VCC or V
Input capacitance 5 pF
Output capacitance 7 pF
Quiescent 25 45 mA
Suspend 45 µA
1.8 Suspend 1.8 VDD 1 µA
IT+
− V
) VI = V
IT−
= –4 mA V
OH
= 4 mA 0.5 V
OL
IH
IL
IH
IH
IL
SS
–0.5 V
CC
0.8 V
1 V
±1 µA
±1 µA
10 µA
2 V
3−1
Page 44

3−2
Page 45

4 Application
V
4.1 Keyboard Section
Table 4−1 outlines the GPIO assignment for the switch-matrix scanning and for keyboard LED drive. Figure 4−1
illustrates the port-3 pins that are assigned to drive the four keyboard LEDs. As shown, P3[5:2] can sink up to 12 mA
(open-drain output) on each pin. Figure 4−2 illustrates the 18 outputs (open-drain) and the 8 inputs (internal pullups)
that are used for the switch-matrix scanning. Figure 4−3 illustrates the partial connection bus power mode. Figure
4−4 shows the USB upstream connection, and Figure 4−5 illustrates the downstream connection (only one port
shown).
Table 4−1. GPIO Assignment for Matrix Scan and LED Drive
GPIO I/O
P0[7:0] O 8-bit matrix-scan outputs
P1[7:0] O 8-bit matrix-scan outputs
P3.6 O 1-bit matrix-scan output
P3.7 O 1-bit matrix-scan output
P2[7:0] I 8-bit matrix-scan inputs
P3.2 O Keyboard LED-1
P3.3 O Keyboard LED-2
P3.4 O Keyboard LED-3
P3.5 O Keyboard LED-4
P3.0 I/O GPIO (Not used for keyboard)
P3.1 I/O GPIO (Not used for keyboard)
TUSB2136
P3.2
P3.3
P3.4
P3.5
Figure 4−1. Keyboard LED Connection
CC
4−1
Page 46
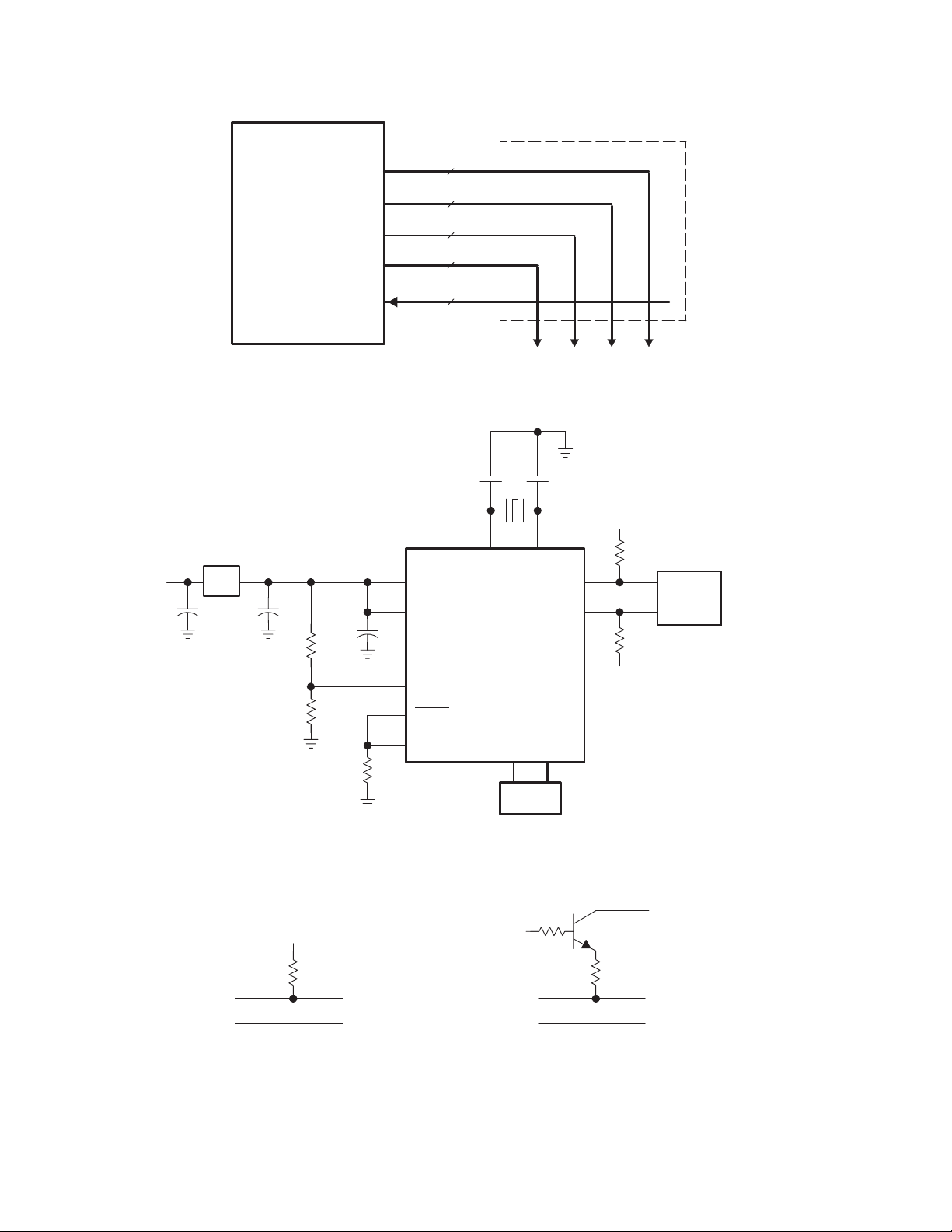
TUSB2136
PUR
8
P0[7:0]
8
P1[7:0]
1
P3.6
1
P3.7
8
P2[7:0]
18 × 8 Matrix
Figure 4−2. Keyboard Matrix Scan Connection
5 V
C1
TPS76333
VR
C2
PS
C5
SCL
SDA
V
CC
V
CC
R1
R2
C3
R3
V
CC
V
CC
V
reg
VREN
SUSP
C4
X1 X2
TUSB2136
PWR OVCR
TPS2042
Figure 4−3. Partial Connection Bus Power Mode
3.3 V
Bus PWR
(5 V)
R4
I2C
EEPROM
R5
4−2
1.5 kΩ
DP0
DM0
D+
D−
1.5 kΩ
DP0
DM0
(a) (b)
D+
D−
Figure 4−4. Upstream Connection (a) Non-Switching Power Mode (b) Switching Power Mode
Page 47

D+
5 V
To Power Switch
D−
R1
R2
DP1
DM1
15 kΩ
GND
15 kΩ
Figure 4−5. Downstream Connection − Only One Port Shown
4.2 Reset Timing
There are two requirements for the reset signal timing. First, the reset window should be between 100 ms and 10 ms.
At power up, this time is measured from the time the power ramps up to 90% of the nominal V
goes high (above 1.2 V). The second requirement is that the clock has to be valid during the last 60 ms of the reset
window. These two requirements are depicted in Figure 4−6. Notice that when using a 12-MHz crystal or the 48-MHz
oscillator, the clock signal may take several milliseconds to ramp up and become valid after power up. Therefore, the
reset window may need to be elongated up to 10 ms to ensure that there is a 60-ms overlap with a valid clock.
V
3.3 V
90%
1.2 V
CC
CLK
RESET
until the reset signal
CC
0 V
>60 µs
100 µs < RESET TIME < 10 ms
Figure 4−6. Reset Timing
t
4−3
Page 48

4−4
Page 49

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
20-Mar-2008
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
TUSB2136PM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TUSB2136PMG4 ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 50

MECHANICAL DATA
MTQF008A – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED DECEMBER 1996
PM (S-PQFP-G64) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
49
64
0,50
48
0,27
0,17
33
1
7,50 TYP
10,20
SQ
9,80
12,20
SQ
11,80
16
0,08
32
17
M
0,05 MIN
0,13 NOM
Gage Plane
0,25
0°–7°
1,45
1,35
1,60 MAX
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-026
D. May also be thermally enhanced plastic with leads connected to the die pads.
0,75
0,45
Seating Plane
0,08
4040152/C 11/96
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
1
Page 51

Page 52

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
DSP dsp.ti.com Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Medical www.ti.com/medical
Interface interface.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Logic logic.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Transportation and www.ti.com/automotive
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Wireless www.ti.com/wireless-apps
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf
TI E2E Community Home Page e2e.ti.com
Automotive
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...