TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
D
Single Positive Power Supply (No Negative
Voltage Required)
D
Advanced Silicon RFMOS Technology
D
4.8-V Operation for GSM Applications
D
35-dBm Typical Output Power
D
30-dB Typical Power Gain
D
40% Typical PAE with 5-dBm Input Power
D
45% Typical PAE with 8-dBm Input Power
D
Output Power Control
D
Few External Components Required for
Operation
D
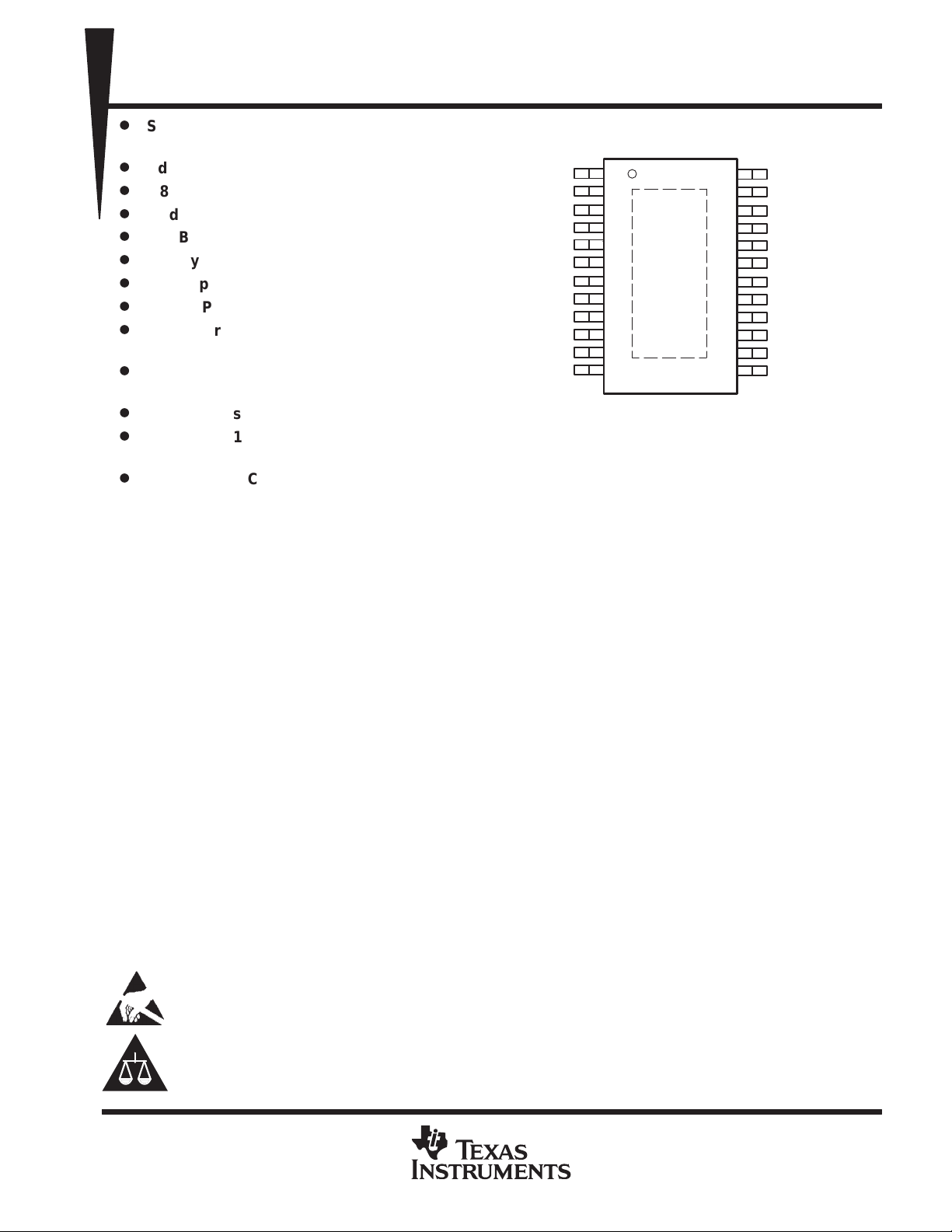
Thermally Enhanced Surface-Mount
VG2
VG3
VPC
VG1
NC
RFIN
RFIN
NC
VG1
VPC
VG3
VG2
PWP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
VD1/VD2
GND
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
GND
VD1/VD2
Package for Small Circuit Footprint
D
Rugged, Sustains 20:1 Load Mismatch
D
800-MHz to 1000-MHz Wide Operational
NC – No internal connection
Frequency Range
D
Low Standby Current (<10 µA)
description
The TRF7610 is a silicon MOSFET power amplifier IC for 900-MHz applications, tailored specifically for global
systems for mobile communications (GSM). It uses Texas Instruments RFMOS process and consists of a
three-stage amplifier with output power control. Few external components are required for operation.
The TRF7610 amplifies the RF signal from a preceding modulator and the upconverter stages in an RF section
of a transmitter to a level that is sufficient for connection to the antenna. The RF input port, RFIN, and the RF
output port, RFOUT, require simple external matching networks.
A control signal applied to the VPC input can ramp the RF output power up or down to meet ramp and spurious
emission specifications for time-division multiple-access (TDMA) systems. The power control signal causes a
change in output power as the voltage applied to VPC varies between 0 V and 3 V. With the RF input power
applied to RFIN at 5 dBm, adjusting VPC from 0 V to 3 V increases the output power from a typical value of
–43 dBm at VPC = 0 V to a typical value of 35 dBm at VPC = 3 V. Forward isolation with the RF input power
applied to RFIN at 5 dBm, VPC = 0 V, is typically 48 dB.
The TRF7610 is available in a thermally enhanced, surface-mount, 24-pin PowerPAD (PWP) thin-shrink
small-outline package (TSSOP). It is characterized for operation from –40°C to 85°C operating free-air
temperature. In order to maintain acceptable thermal operating conditions, the device should be operated in
pulse applications such as the GSM standard 1/8 duty cycle. The package has a solderable pad that improves
the package thermal performance by bonding the pad to an external thermal plane. The pad also acts as a
low-inductance electrical path to ground and must be electrically connected to the printed circuit-board (PCB)
ground plane as a continuation of the regular package terminals that are designated GND.
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam
during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
RFMOS and PowerPAD are trademarks of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
TRF7610
I/O
DESCRIPTION
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
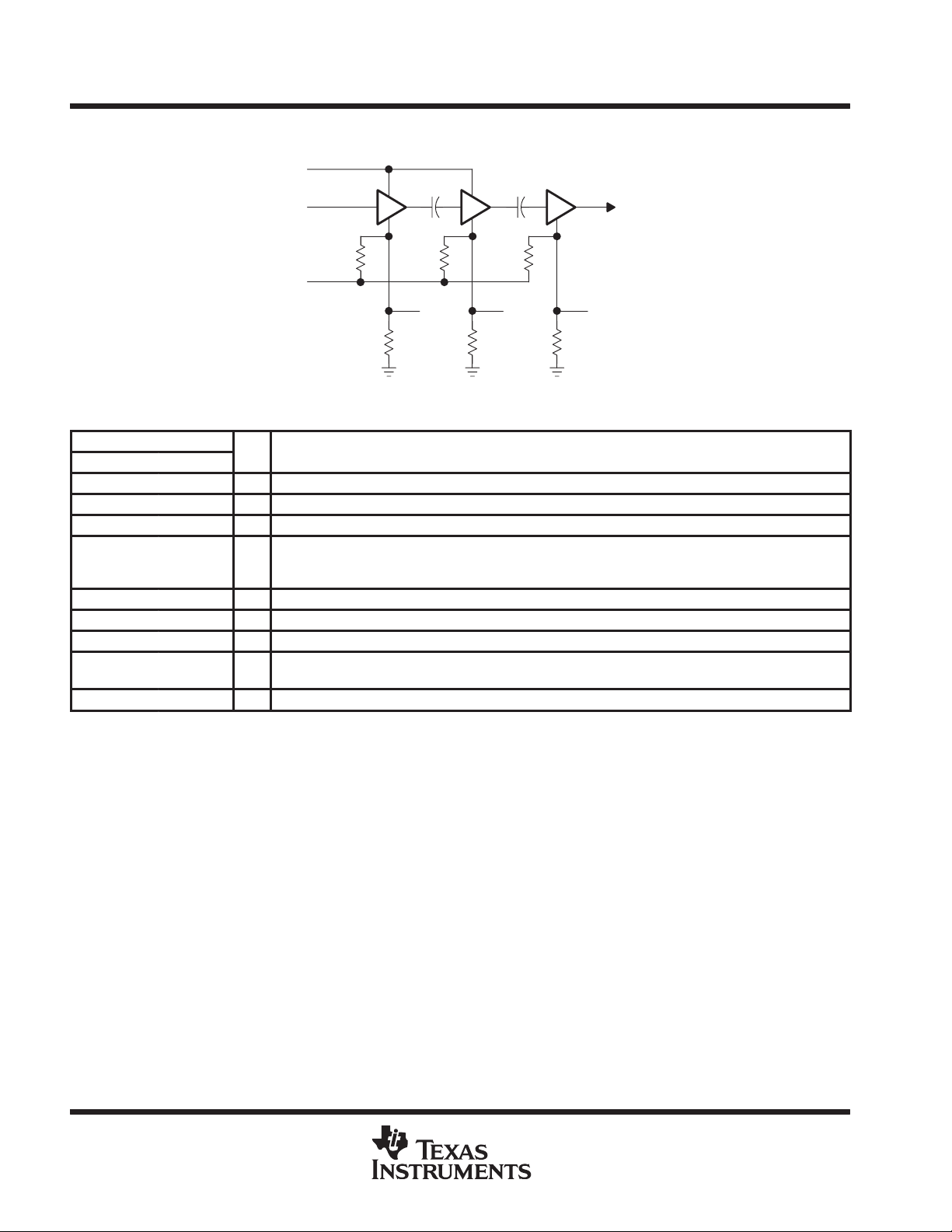
schematic
RFIN
VPC
13, 24
6, 7
3 or 10
4 or 9
VG1
1, 12
VG2
15 – 22
2 or 11
RFOUT/VD3
VG3
VD1/VD2
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
GND 14, 23 Analog ground for all internal circuits. All signals are referenced to the ground terminals.
NC 5, 8 No internal connection. It is recommended that all NC terminals be connected to ground.
RFIN 6, 7 I RF input. RFIN accepts signals between 800 MHz and 1000 MHz.
RFOUT/VD3 15, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20,
21, 22
VG1 4, 9 I First-stage gate bias set by resistor. Either terminal may be used or both may be connected externally.
VG2 1, 12 I Second-stage gate bias set by resistor. These terminals must be connected externally.
VG3 2, 11 I Third-stage gate bias set by resistor. Either terminal may be used or both may be connected externally.
VPC 3, 10 I Voltage power control. VPC is a signal between 0 V and 3 V that adjusts the output power from a typical
VD1/VD2 13, 24 I First- and second-stage drain bias. These terminals must be connected externally.
I/O RF output and third-stage drain bias. RFOUT requires an external matching network.
value of –43 dBm to 35 dBm. Either terminal may be used, or both may be connected externally.
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, V
Input voltage range, VPC –0.6 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input power at RFIN 13 dBm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thermal resistance, junction to case, R
Junction temperature, T
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. Voltage values are with respect to GND.
2
2. No air flow and with infinite heatsink
(see Note 1) –0.6 V to 8 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DD
(see Note 2) 3.5°C/W. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
max 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J
θJC
A
stg
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
–40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
I
pply current
Output power
dBm
Power added efficiency (PAE)
Harmonics
dBc
Noise power in 30-kHz bandwidth
dBm
TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
recommended operating conditions
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage VDD (see Note 1 and Note 3) 3.5 4.8 6 V
Operating free-air temperature, T
Operating frequency range (see Note 4) 800 1000 MHz
NOTES: 1. Voltage values are with respect to GND.
3 .Performance varies with drain voltage, see Figure 8.
4. External matching network dependent.
A
electrical characteristics over full range of recommended operating conditions
supply current, VDD = 4.8 V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
pp
Su
DD
†
Typical values are at TA = 25°C
Operating at maximum output power VPC = 3 V 2 A
Operating with no RF input power VPC = 0 V <10 µA
–40 85 °C
GSM operation, VDD = 4.8 V, VPC = 3 V, PI = 5 dBm, T
PARAMETER
Operating frequency range 870 925 MHz
p
p
Input return loss (externally matched, small signal) PI = –20 dBm 10 dB
2f
0
3f
0
p
Ruggedness test
‡
Specific applications circuit
§
No degradation in output power after test.
20 MHz above f
10 MHz above f
0
0
= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
A
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
VPC = 3 V 34 35 36
VPC = 0 V –43
PI = 8 dBm 45%
With external matching –28
With external matching –40
Frequency = 900 MHz,
Load VSWR = 20:1,
All phase angles
‡
40%
–88
–88
§
stability, GSM operation
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
No parasitic
oscillations (all
spurious < –70 dBc)
Stability
¶
VSWR = voltage standing wave ratio
Output VSWR¶ < 6:1 all phases, VDD < 6 V, PI = 5 dBm,
PO ≤ 35 dBm, Output frequency band: 200 MHz – 1200 MHz
switching characteristics
GSM operation
t
Switching time, RF output OFF to ON VPC stepped from 0 V to 3 V 2 µs
on
t
Switching time, RF output ON to OFF VPC stepped from 3 V to 0 V 2 µs
off
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
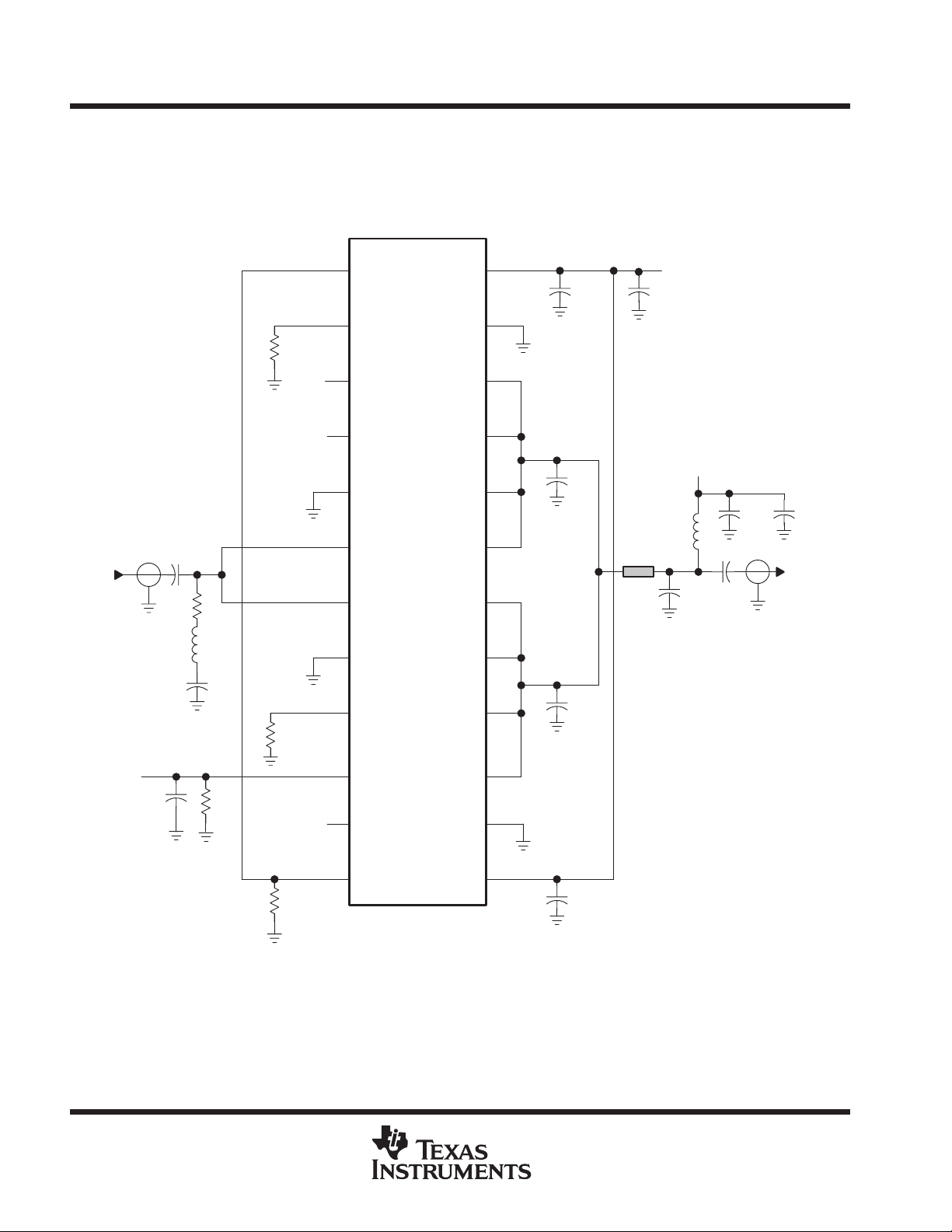
APPLICATION INFORMATION
In all cases, a capacitor must be connected from the positive power supply to ground as close to the terminals as
possible for power-supply bypassing. The dc-blocking capacitors are required on the RF input and RF output. A list
of components and their functions is shown in Table 1.
TRF7610
RFIN
C2
C1
L1
R4
R1
R2
GND
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
C4
C5
C6
+
50 Ω
245 mil
C8
VD1/VD2
C11
L2
VD3
C9
C10
+
C3
RFOUT
1
VG2
2
VG3
3
VPC
4
VG1
5
NC
6
RFIN
7
RFIN
8
NC
9
VG1
VD1/VD2
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
RFOUT/VD3
GND
15
14
13
C7
VPC
C12
R5
R3
10
11
12
VPC
VG3
VG2
RFOUT/VD3
VD1/VD2
Figure 1. Typical GSM Cellular Telephone Application
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
Table 1. External Component Selection
design philosophy
COMPONENT
DESIGNATION
C1 100 pF DC blocking capacitor
C2 100 pF Matching capacitor
C3 330 µF Drain-bias decoupling capacitor
C4 0.033 µF Drain-bias decoupling capacitor
C5, C6 22 pF High-Q matching capacitor
C7 0.033 µF Drain-bias decoupling capacitor
C8 11 pF High-Q matching capacitor
C9 100 pF DC blocking capacitor
C10 100 pF Drain-bias decoupling capacitor
C11 100 µF Drain-bias decoupling capacitor
C12 100 pF Decoupling capacitor
R1 2200 Ω Gate-bias setting resistor
R2, R3 5100 Ω Gate-bias setting resistor
R4 3.9 Ω Matching resistor
R5 51 Ω Vpc termination resistor
L1 2.7 nH Matching inductor
L2 18.5 nH high-current inductor
†
On a FR4 substrate with
TYPICAL VALUE FUNCTION
Drain bias inductor
or λ/4 microstrip line
∈
of 4.3, a λ/4 50 Ω line is 40 mm.
r
†
The TRF7610 is a three-stage integrated power amplifier for use in cellular phone handsets. The device and
applications board are optimized to operate under 900-MHz, 4.8-V GSM conditions. External matching
networks provide design flexibility in centering the frequency response from 800 to 1000 MHz. Typical
performance at 900 MHz, driven by a 5-dBm GSM signal, is 30 dB of power gain, 35 dBm output power, and
40 percent PAE.
Discrete component selection was made to optimize output power, gain, pulse flatness in the GSM pulse
window, and PAE. Where possible, size and cost goals were considered: the smallest, least expensive
components available were included in the applications board design. Some of the components, however, were
chosen for their ability to increase performance. The following sections explain the design options and
compromises to consider when substituting parts of differents types and values.
output matching network
The output matching network provides the majority of the design flexibility . First, the shunt capacitors, C5, C6,
and C8 are American T echnical Ceramics high-Q capacitors, which increase performance. The A TC capacitors
achieve a 0.4-dB increase in output power and a 3-percent increase in PAE compared to the performance
achieved using 0402-sized capacitors. However, if size and cost are more important, 0402-sized capacitors can
be used, while sacrificing the performance gains achieved using the high-Q capacitors.
Second, the dc bias network on the amplifier output stage, designed using a Coilcraft 18.5 nH high-current
inductor (L2), minimizes the board layout area. An alternative to this high-current inductor is a quarter-wave stub
with a bias decoupling capacitor to ground (C10, C3). On the FR4 board with ∈
900 MHz is 40 mm in length. One advantage that the quarter-wave stub offers over the inductor is improved
second harmonic suppression. The inductor offers a much smaller footprint; however, it does sacrifice 10 dB
= 4.3, a quarter-wave stub at
r
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
of second harmonic suppression. The PAE is only slightly affected: it is reduced by approximately 1 percent
compared to the quarter-wave stub. The system designer must decide if size or performance is of greatest
concern.
The 330 µF bias decoupling capacitors, C3 and C11, provide pulse flatness in the GSM application. These
surface mount capacitors provide a gain slope of –0.4 dB over the duration of the GSM duty cycle. If that is not
acceptable, the performance can be improved by adding a larger value capacitor in parallel with the two existing
capacitors. Measured results, using a standard 4700 µF electrolytic taken from a cellular phone, is –0.1 dB of
gain slope for the duration of the GSM duty cycle. Capacitor size considerations must be decided by the system
designer.
dc bias network
The dc bias network consists of resistors R1, R2, R3, and R5, which set the gate bias voltage of the device. R1,
R2, and R3 are used as voltage divider resistors which set the gate voltages at approximately 1.7 V. Resistor
R5 is a 51 Ω termination resistor that is needed only for a 50 Ω pulse generator. When a high-impedance pulse
generator is used, the 51 Ω resistor can be omitted as it is not necessary for device function.
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
POWER ADDED EFFICIENCY
50
Frequency = 900 MHz
45
VDD = 4.8 V
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
PAE – Power Added Efficiency – %
5
0
–20
–15
vs
INPUT POWER
TA = –40°C
TA = 25°C
–10 –5
PI – Input Power – dBm
Figure 2
TA = 85°C
0510
POWER ADDED EFFICIENCY
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
PAE – Power Added Efficiency – %
10
5
TA = –40°C
850 860 870 880 890 900 910
f – Frequency – MHz
Figure 3
vs
FREQUENCY
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
PI = 5 dBm
VDD = 4.8 V
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
920 930 940 950
POWER ADDED EFFICIENCY
60
50
40
30
20
PAE – Power Added Efficiency – %
10
TA = –40°C
5
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5
VDD – Drain Voltage – V
vs
DRAIN VOLTAGE
TA = 25°C
Frequency = 900 MHz
PI = 5 dBm
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
Figure 4
TA = 85°C
5 5.5 6
POWER ADDED EFFICIENCY
POWER CONTROL VOLTAGE
50
Frequency = 900 MHz
45
VDD = 4.8 V
40
PI = 5 dBm
35
30
25
20
15
10
PAE – Power Added Efficiency – %
5
0
–5
0 0.5
VPC – Power Control Voltage – V
vs
1.5 2
1
Figure 5
TA = 85°C
TA = 25°C
TA = –40°C
2.5 3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
OUTPUT POWER
40
Frequency = 900 MHz
VDD = 4.8 V
35
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
30
25
20
15
10
PO – Output Power – dBm
5
0
–20 –15 –10 –5
TA = –40°C
PI – Input Power – dBm
OUTPUT POWER
DRAIN VOLTAGE
40
35
30
25
20
15
PO – Output Power – dBm
10
Frequency = 900 MHz
5
PI = 5 dBm
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
0
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5
VDD – Drain Voltage – V
vs
INPUT POWER
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
Figure 6
vs
TA = –40°C
TA = 25°C
Figure 8
0510
TA = 85°C
5 5.5 6
OUTPUT POWER
38
37
TA = –40°C
36
35
34
33
PO – Output Power – dBm
32
31
30
850 860 870 880 890 900 910
f – Frequency – MHz
OUTPUT POWER
POWER CONTROL VOLTAGE
40
Frequency = 900 MHz
VDD = 4.8 V
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
30
20
10
0
TA = 85°C
–10
PO – Output Power – dBm
–20
–30
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
VPC – Power Control Voltage – V
vs
FREQUENCY
PI = 5 dBm
VDD = 4.8 V
VPC = 3 V Pulsed
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
920 930 940 950
Figure 7
vs
TA = –40°C
TA = 25°C
2.5 3
Figure 9
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
INPUT RETURN LOSS
vs
FREQUENCY
0
VDD = 4.8 V
VPC = 3 V
PI = 5 dBm
–2
TA = 25°C
Matched Application Board
–4
–6
–8
S11 – Input Return Loss – dB
–10
–12
700 800 900
f – Frequency – MHz
Figure 10
SMALL SIGNAL GAIN
FREQUENCY
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
S21 – Small Signal Gain – dB
VDD = 4.8 V
10
VPC = 3 V
5
Matched Application Board
0
850 860 870 880 890 900 910
TA = –40°C
TA = 85°C
f – Frequency – MHz
1000 1100
vs
TA = 25°C
920 930 940 950
Figure 11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9

TRF7610
SILICON MOSFET POWER AMPLIFIER IC FOR GSM
SLWS059B – MAY 1997 – REVISED AUGUST 1998
MECHANICAL DATA
PWP (R-PDSO-G**) PowerPAD PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
0,65
20
1
1,20 MAX
0,30
0,19
11
4,50
4,30
10
A
Seating Plane
0,15
0,05
M
0,10
Thermal Pad (3,18 2,41 NOM)
(see Note C)
6,60
6,20
0,10
0,15 NOM
Gage Plane
0,25
0°–8°
0,75
0,50
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. The package thermal performance may be enhanced by bonding the thermal pad to an external thermal plane. This solderable pad
is electrically and thermally connected to the backside of the die.
14
5,10
16
5,10
4,904,90
20
6,60
6,40
24
7,90
28
9,80
9,607,70
4073225/E 03/97
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOL VE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...