www.ti.com
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
SHUTDOWN
BYPASS
IN+
IN–
VO–
GND
V
DD
VO+
D OR DGN PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
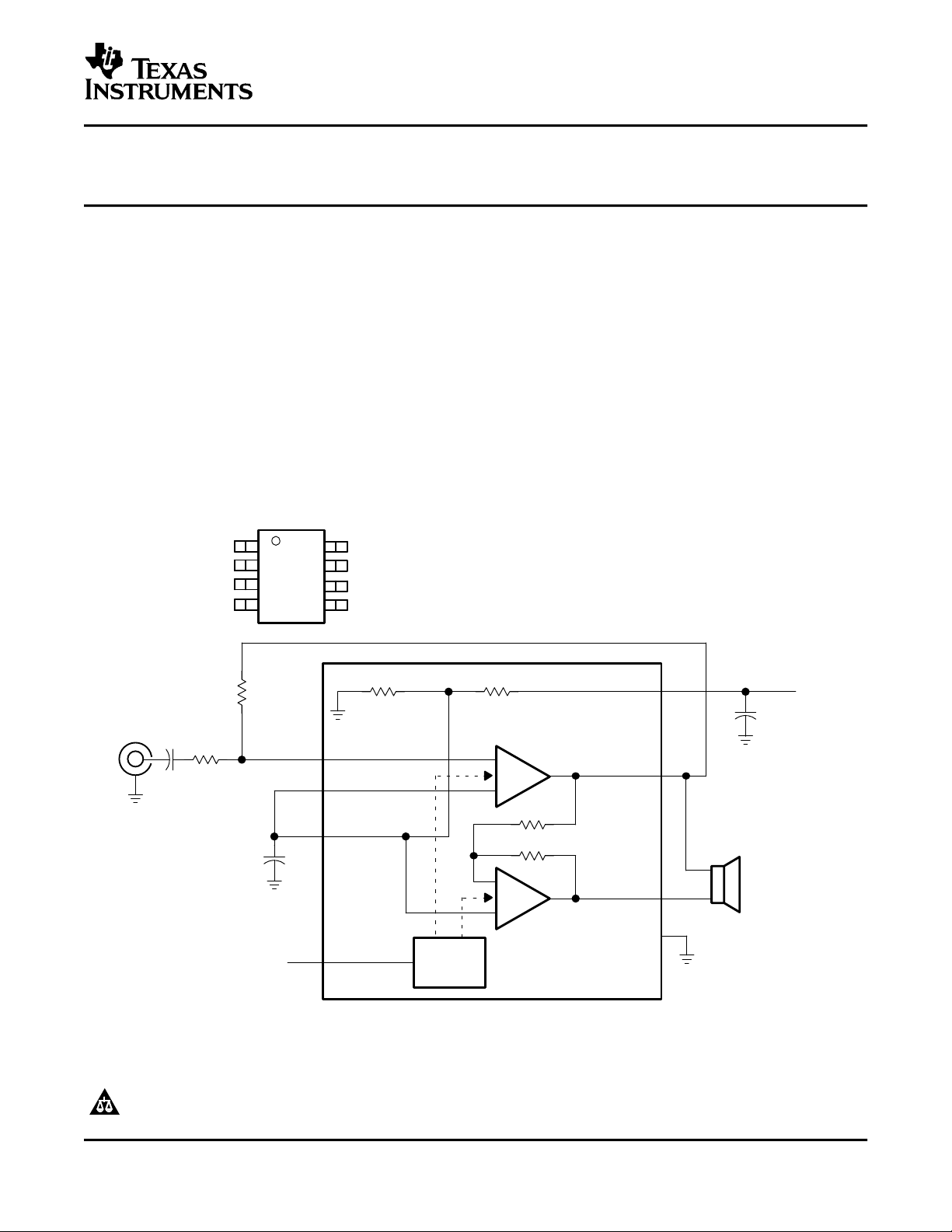
Audio
Input
Bias
Control
V
DD
700 mW
6
5
7
VO+
V
DD
1
24BYPASS
IN–
VDD/2
C
I
R
I
C
S
C
B
R
F
SHUTDOWN
VO– 8
GND
From System Control
3 IN+
–
+
–
+
700-mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER
AMPLIFIER WITH DIFFERENTIAL INPUTS
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
• Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation
• Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V - 5.5 V
• Output Power for R
– 700 mW at V
– 250 mW at V
DD
DD
• Integrated Depop Circuitry
• Thermal and Short-Circuit Protection
• Surface-Mount Packaging
– SOIC
– PowerPAD™ MSOP
= 8 Ω
L
= 5 V
= 3.3 V load at less than 0.6% THD+N throughout voice band
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
The TPA741 is a bridge-tied load (BTL) audio power
amplifier developed especially for low-voltage applications where internal speakers are required.
Operating with a 3.3-V supply, the TPA741 can
deliver 250-mW of continuous power into a BTL 8-Ω
frequencies. Although this device is characterized out
to 20 kHz, its operation is optimized for narrower
band applications such as wireless communications.
The BTL configuration eliminates the need for external coupling capacitors on the output in most applications, which is particularly important for small
battery-powered equipment. This device features a
shutdown mode for power-sensitive applications with
a supply current of 7 µA during shutdown. The
TPA741 is available in an 8-pin SOIC surface-mount
package and the surface-mount PowerPAD™ MSOP,
which reduces board space by 50% and height by
40%.
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright © 2000–2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device
placed in conductive foam during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGED DEVICES
T
A
SMALL OUTLINE
(1)
(D) (DGN)
–40°C to 85°C TPA741D TPA741DGN AJD
(1) In the D package, the maximum output power is thermally limited to 350 mW; 700-mW peaks can be driven, as long as the RMS value
is less than 350 mW.
(2) The D and DGN packages are available taped and reeled. To order a taped and reeled part, add the suffix R to the part number (e.g.,
TPA741DR).
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
BYPASS 2 I
GND 7 GND is the ground connection.
IN- 4 I IN- is the inverting input. IN- is typically used as the audio input terminal.
IN+ 3 I IN+ is the noninverting input. IN+ is typically tied to the BYPASS terminal for SE operations.
SHUTDOWN 1 I SHUTDOWN places the entire device in shutdown mode when held high.
V
DD
V
O+
V
O-
I/O DESCRIPTION
BYPASS is the tap to the voltage divider for internal mid-supply bias. This terminal should be connected
to a 0.1-µF to 2.2-µF capacitor when used as an audio amplifier.
6 V
5 O V
is the supply voltage terminal.
DD
is the positive BTL output.
O+
8 O VO-is the negative BTL output.
(2)
MSOP
MSOP SYMBOLIZATION
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
V
V
T
T
T
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
Supply voltage 6 v
DD
Input voltage –0.3 V to V
I
Continuous total power dissipation Internally limited (see Dissipation Rating Table)
Operating free-air temperature range –40°C to 85°C
A
Operating junction temperature range –40°C to 150°C
J
Storage temperature range –65°C to 150°C
stg
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating
conditions" is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(1)
UNIT
+0.3 V
DD
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE TA≤ 25°C DERATING FACTOR TA= 70°C TA= 85°C
D 725 mW 5.8 mW/°C 464 mW 377 mW
DGN 2.14 W
(1) See the Texas Instruments document, PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package Application Report
(SLMA002), for more information on the PowerPAD package. The thermal data was measured on a
PCB layout based on the information in the section entitled Texas Instruments Recommended Board
for PowerPAD of that document.
(1)
17.1 mW/°C 1.37 W 1.11 W
2

www.ti.com
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
MIN MAX UNIT
V
DD
V
IH
V
IL
T
A
Supply voltage, 2.5 5.5 V
High-level voltage (SHUTDOWN) 0.9V
DD
Low-level voltage (SHUTDOWN) 0.1V
Operating free-air temperature –40 85 °C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
at specified free-air temperature, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
|V
| Output offset voltage (measured differentially) SHUTDOWN = 0 V, RL= 8 Ω, RF = 10 kΩ 20 mV
OS
PSRR Power supply rejection ratio V
I
I
|IIH| SHUTDOWN, V
|IIL| SHUTDOWN, V
Supply current SHUTDOWN = 0 V, RF = 10 kΩ 1.35 2.5 mA
DD
Supply current, shutdown mode
DD(SD)
(see Figure 6 )
= 3.3 V, TA= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
DD
= 3.2 V to 3.4 V 85 dB
DD
SHUTDOWN = VDD, RF = 10 kΩ 7 50 µA
= 3.3 V, Vi= 3.3 V 1 µA
DD
= 3.3 V, Vi= 0 V 1 µA
DD
OPERATING CONDITIONS
V
= 3.3 V, TA= 25°C, RL= 8 Ω
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
P
O
Output power, See
THD + N Total harmonic distortion plus noise PO= 250 mW, f = 200 Hz to 4 kHz, See Figure 7 0.55%
B
OM
B
1
k
SVR
V
n
Maximum output power bandwidth AV= -2 V/V, THD = 2%, See Figure 7 20 kHz
Unity-gain bandwidth Open loop, See Figure 15 1.4 MHz
Supply ripple rejection ratio f = 1 kHz, CB= 1 µF, See Figure 2 79 dB
Noise output voltage AV= -1 V/V, CB= 0.1 µF, See Figure 19 17 µV(rms)
(1) Output power is measured at the output terminals of the device at f = 1 kHz.
(1)
THD = 0.5%, See Figure 9 250 mW
TPA741
V
V
DD
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
at specified free-air temperature, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
|V
| Output offset voltage (measured differentially) SHUTDOWN = 0 V, RL= 8 Ω, RF = 10 kΩ 20 mV
OS
PSRR Power supply rejection ratio V
I
I
|IIH| SHUTDOWN, V
|IIL| SHUTDOWN, V
Supply current SHUTDOWN = 0 V, RF = 10 kΩ 1.45 2.5 mA
DD
Supply current, shutdown mode (see Fig-
DD(SD)
ure 4 )
= 5 V, TA= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
DD
= 4.9 V to 5.1 V 78 dB
DD
SHUTDOWN = VDD, RF = 10 kΩ 50 100 µA
= 5.5 V, Vi= V
DD
= 5.5 V, Vi= 0 V 1 µA
DD
DD
1 µA
3
www.ti.com
Audio
Input
Bias
Control
V
DD
6
5
7
VO+
V
DD
1
24BYPASS
IN–
VDD/2
C
I
R
I
C
S
C
B
R
F
SHUTDOWN
VO– 8
R
L = 8
Ω
GND
3 IN+
–
+
–
+
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 5 V, TA= 25°C, RL= 8Ω
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
P
O
THD + N Total harmonic distortion plus noise 0.5%
B
OM
B
1
k
SVR
V
n
Output power THD = 0.5%, See Figure 13 700
PO= 250 mW, f = 200 Hz to 4 kHz,
See Figure 11
Maximum output power bandwidth AV= -2 V/V, THD = 2%, See Figure 11 20 kHz
Unity-gain bandwidth Open loop, See Figure 16 1.4 MHz
Supply ripple rejection ratio f = 1 kHz, CB= 1 µF, See Figure 2 80 dB
Noise output voltage AV= -1 V/V, CB= 0.1 µF, See Figure 20 17 µV(rms)
(1) The DGN package, properly mounted, can conduct 700-mW RMS power continuously. The D package can only conduct 350-mW RMS
power continuously with peaks to 700 mW.
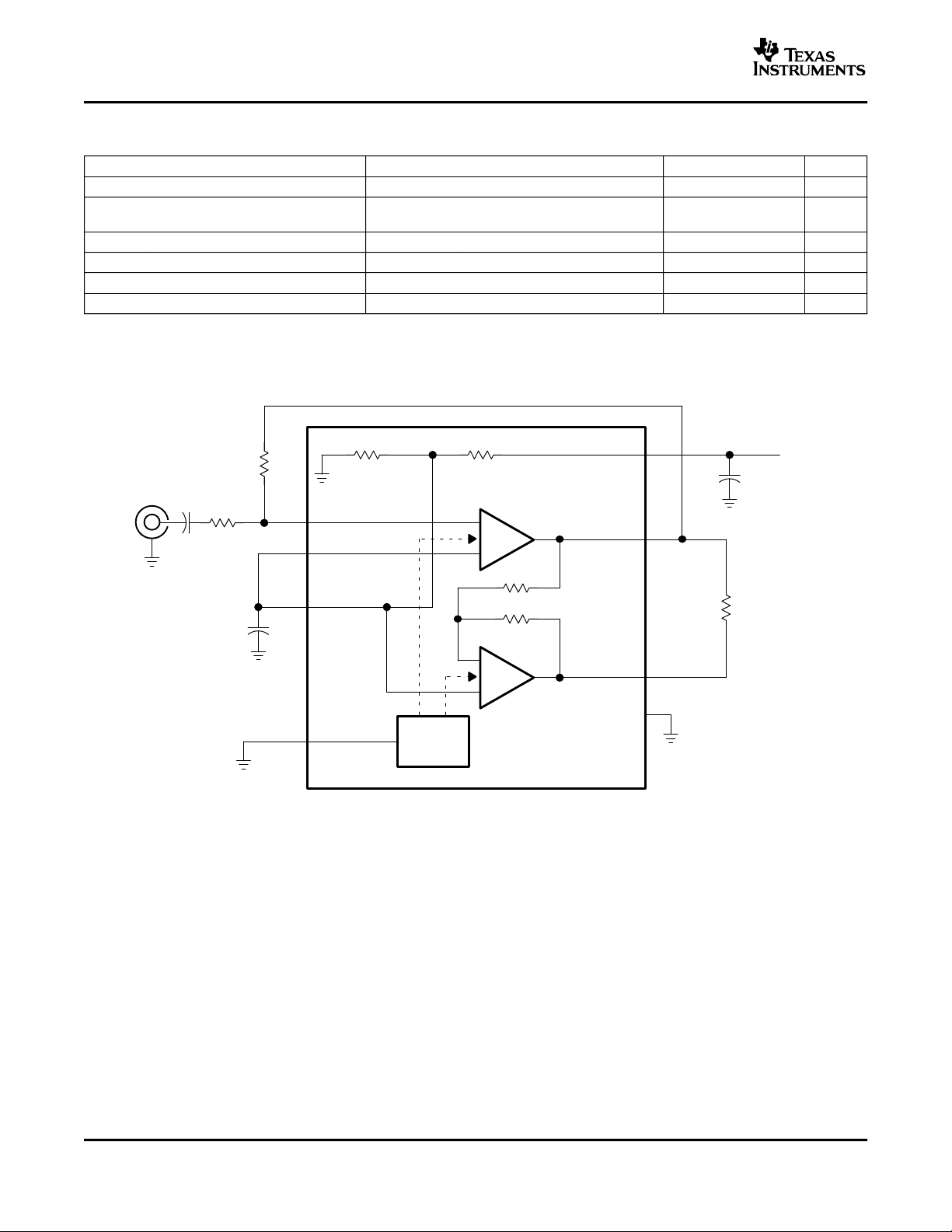
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
(1)
mW
Figure 1. BTL Mode Test Circuit
4
www.ti.com
−50
−60
−80
−100
20 100 1k
−30
−20
f − Frequency − Hz
0
10k 20k
−10
−40
−70
−90
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
CB = 1 µF
k
SVR
− Supply Ripple Rejection Ratio − dB
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
1.8
0.8
0.6
1
3 4
5.5
5
I
DD
− Supply Current − mA
2.5 3.5 4.5
1.6
1.2
1.4
SHUTDOWN = 0 V
RF = 10 kΩ
k
SVR
I
DD
P
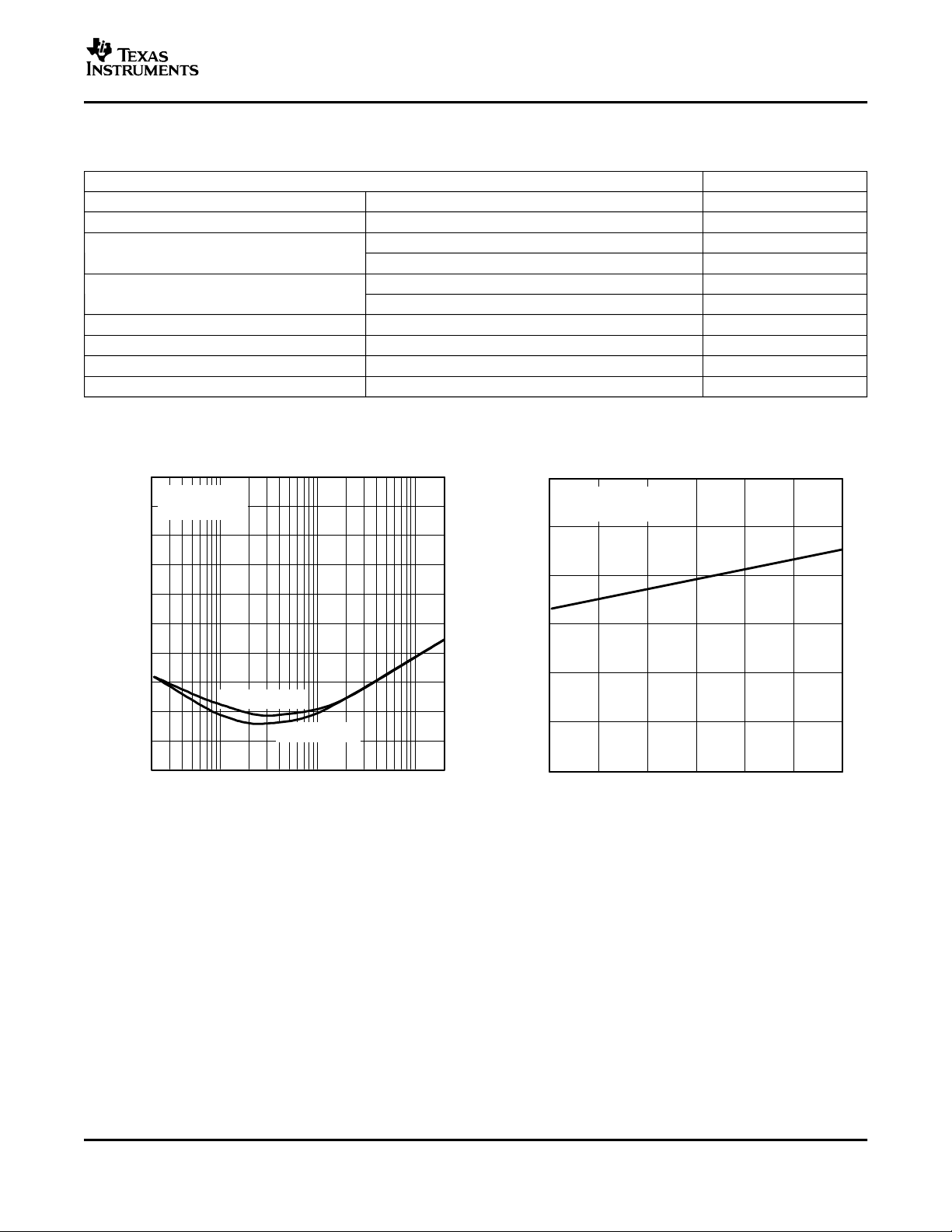
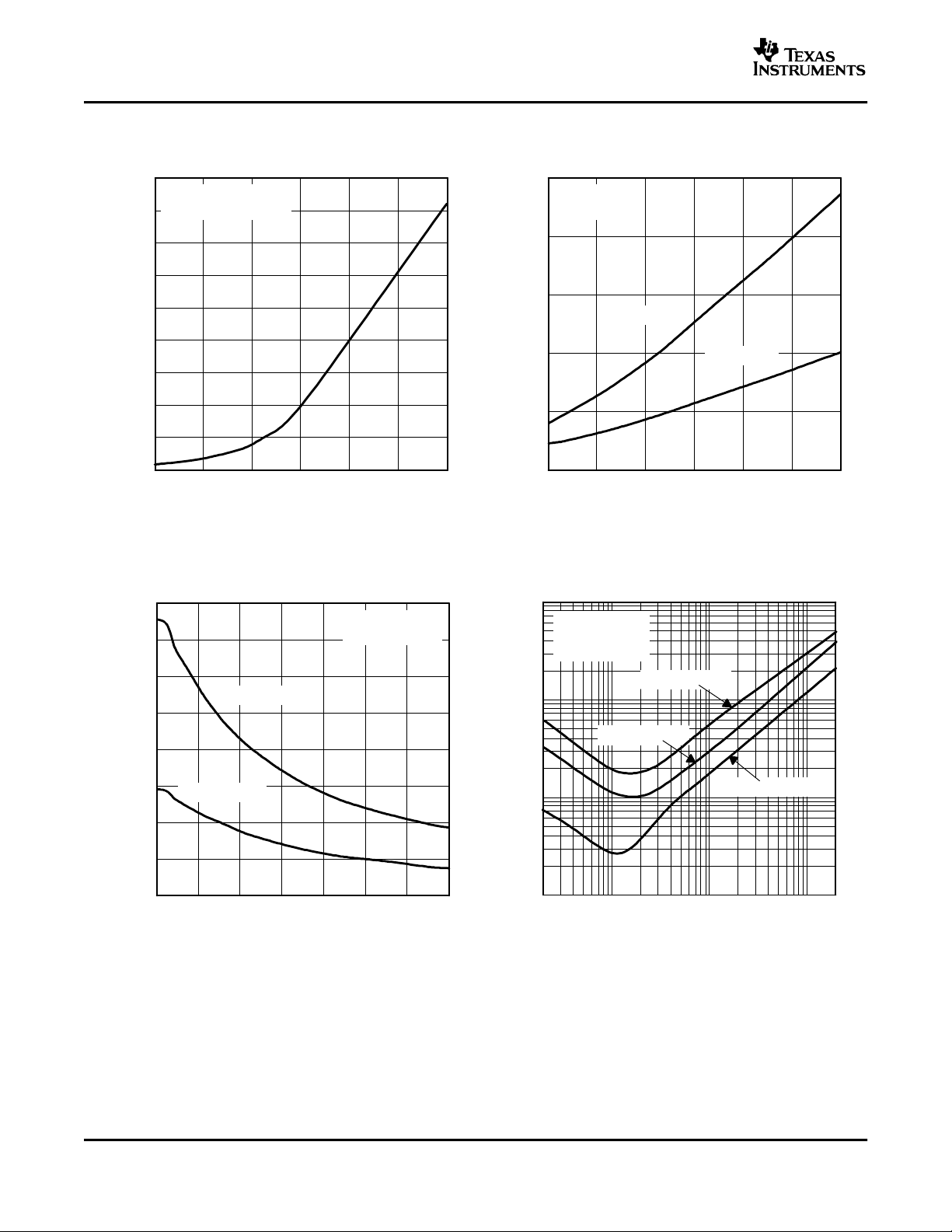
Supply ripple rejection ratio vs Frequency 2
Supply current vs Supply voltage 3, 4
Output power
O
THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise
Open-loop gain and phase vs Frequency 15, 16
Closed-loop gain and phase vs Frequency 17, 18
V
P
Output noise voltage vs Frequency 19, 20
n
Power dissipation vs Output power 21, 22
D
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table of Graphs
FIGURE
vs Supply voltage 5
vs Load resistance 6
vs Frequency 7, 8, 11, 12
vs Output power 9, 10, 13, 14
SUPPLY RIPPLE REJECTION RATIO SUPPLY CURRENT
vs vs
FREQUENCY SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 2. Figure 3.
5
www.ti.com
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
20
10
0
3 43.5 4.5
60
5
30
SHUTDOWN = V
DD
RF = 10 kΩ
40
50
5.52.5
I
DD
− Supply Current − Aµ
70
80
90
VDD − Supply Voltage − V
600
400
200
0
2.5 3.53 4 5.5
1000
P
4.5 5
O
− Output Power − mW
800
THD+N 1%
f = 1 kHz
RL = 32 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
RL − Load Resistance − Ω
300
200
100
0
16 3224 40 64
800
8
P
48 56
O
− Output Power − mW
400
THD+N = 1%
f = 1 kHz
VDD = 5 V
500
600
VDD = 3.3 V
700
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
AV = −2 V/V
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 250 mW
RL = 8 Ω
20 1k 10k
1
0.01
10
0.1
20k100
AV = −20 V/V
AV = −10 V/V
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
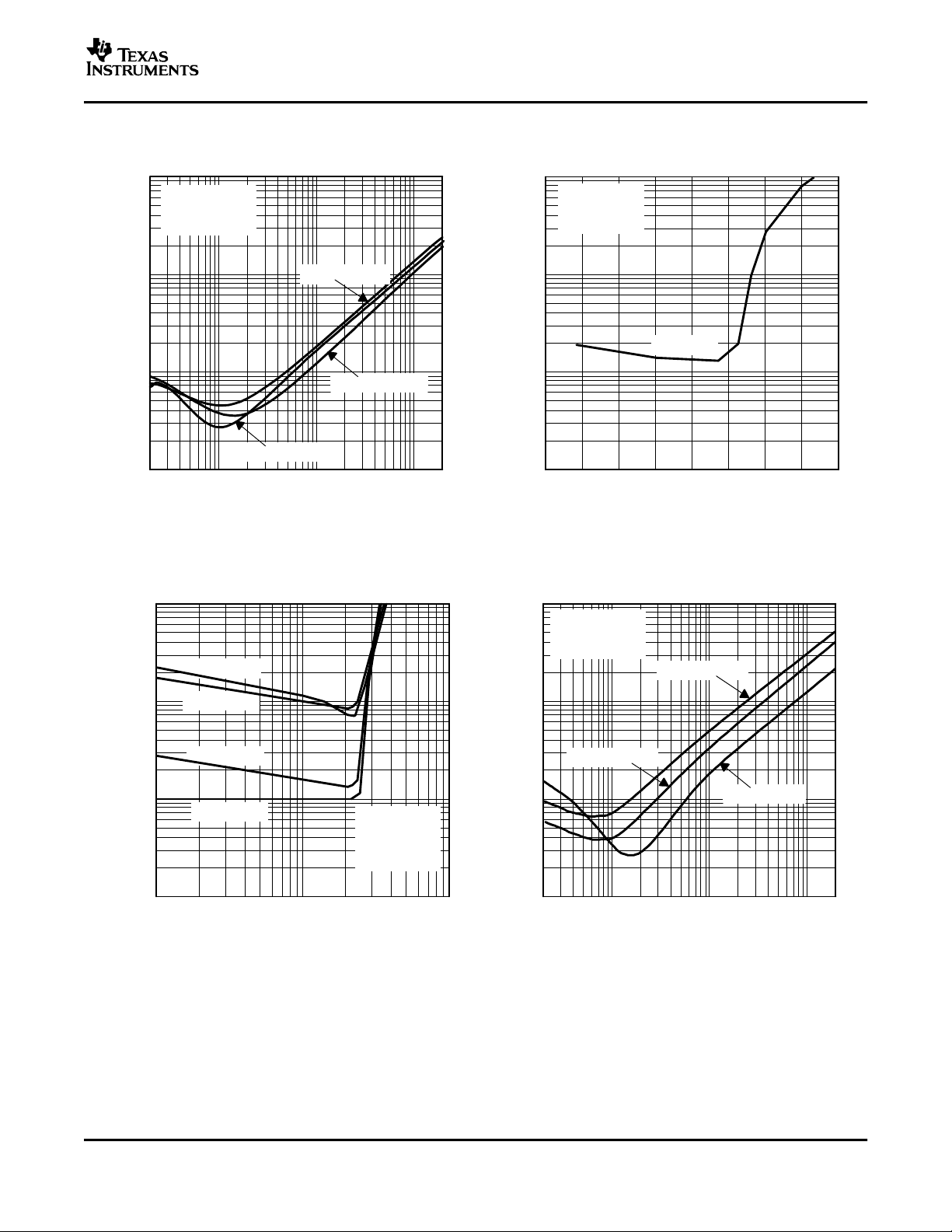
SUPPLY CURRENT OUTPUT POWER
vs vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 4. Figure 5.
OUTPUT POWER TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs vs
LOAD RESISTANCE FREQUENCY
6
Figure 6. Figure 7.
www.ti.com
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
PO = 125 mW
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = −2 V/V
20 1k 10k
1
0.01
10
0.1
20k100
PO = 50 mW
PO = 250 mW
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
0 0.15 0.4
1
0.01
10
0.1
0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35
VDD = 3.3 V
f = 1 kHz
AV = −2 V/V
0.05 0.1
RL = 8 Ω
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
f = 20 kHz
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
CB = 1 µF
AV = −2 V/V
0.01 0.1 1
1
0.01
10
0.1
f = 1 kHz
f = 10 kHz
f = 20 Hz
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
AV =− 2 V/V
VDD = 5 V
PO = 700 mW
RL = 8 Ω
20 1k 10k
1
0.01
10
0.1
20k100
AV = −20 V/V
AV = −10 V/V
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
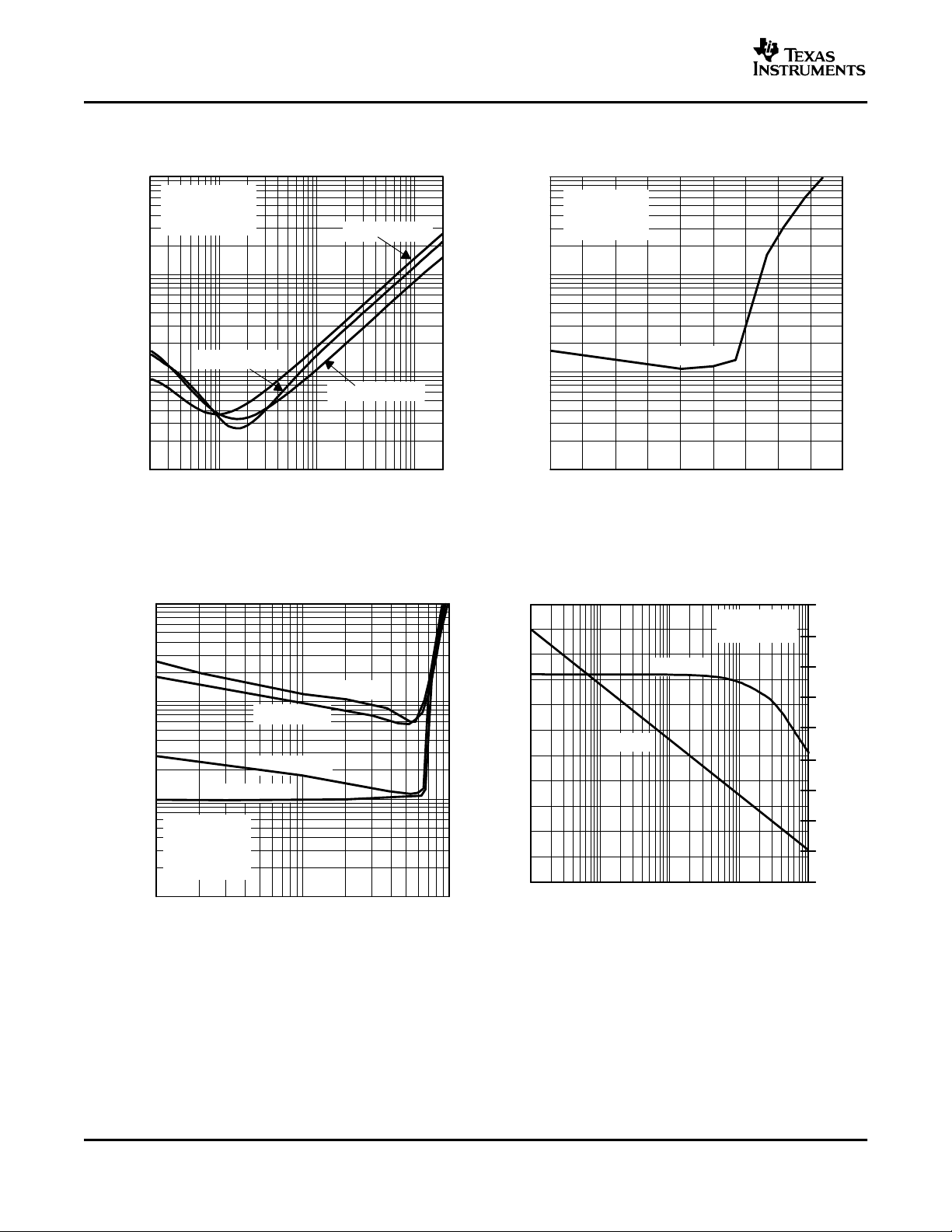
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs vs
FREQUENCY OUTPUT POWER
Figure 8. Figure 9.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs vs
OUTPUT POWER FREQUENCY
Figure 10. Figure 11.
7
www.ti.com
f − Frequency − Hz
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
PO = 700 mW
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = −2 V/V
20 1k 10k
1
0.01
10
0.1
20k100
PO = 50 mW
PO = 350 mW
PO − Output Power − W
0.1 0.2 10.4 0.5 0.7 0.8
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
RL = 8 Ω
VDD = 5 V
f = 1 kHz
AV = −2 V/V
1
0.01
10
0.1
0.3 0.6 0.9
10
0
−20
−30
20
30
f − Frequency − kHz
80
−10
180°
−180°
Phase
60°
−60°
Open-Loop Gain − dB
Phase
1
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
50
40
60
70
140°
100°
20°
−20°
−100°
−140°
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = Open
Gain
PO − Output Power − W
THD+N −Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise − %
f = 20 Hz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
CB = 1 µF
AV = −2 V/V
0.01 0.1 1
1
0.01
10
0.1
f = 1 kHz
f = 10 kHz
f = 20 kHz
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs vs
FREQUENCY OUTPUT POWER
Figure 12. Figure 13.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE OPEN-LOOP GAIN AND PHASE
vs vs
OUTPUT POWER FREQUENCY
8
Figure 14. Figure 15.

www.ti.com
−0.5
−1
−1.5
−2
f − Frequency − Hz
−0.25
−0.75
−1.25
−1.75
0
0.5
Closed-Loop Gain − dB
0.25
0.75
130°
120°
140°
Phase
150°
160°
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
PO = 250 mW
1
170°
180°
Gain
Phase
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
0
−20
−30
1
20
30
f − Frequency − kHz
80
−10
Gain
Phase
Open-Loop Gain − dB
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
50
40
60
70
VDD = 5 V
RL = Open
180°
−180°
60°
−60°
Phase
140°
100°
20°
−20°
−100°
−140°
−0.5
−1
−1.5
−2
f − Frequency − Hz
−0.25
−0.75
−1.25
−1.75
0
0.5
Closed-Loop Gain − dB
0.25
0.75
130°
120°
140°
Phase
150°
160°
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
PO = 700 mW
1
170°
180°
Gain
Phase
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
− Output Noise Voltage − VµV
n
f − Frequency − Hz
20 1k 10k
10
1
100
20k100
VO BTL
VDD = 3.3 V
BW = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
RL = 8 Ω or 32 Ω
AV = −1 V/V
V
o+
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
OPEN-LOOP GAIN AND PHASE CLOSED-LOOP GAIN AND PHASE
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 16. Figure 17.
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN AND PHASE OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE
vs vs
FREQUENCY FREQUENCY
Figure 18. Figure 19.
9

www.ti.com
− Output Noise Voltage − VµV
n
f − Frequency − Hz
20 1k 10k
10
1
100
20k100
VDD = 5 V
BW = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
RL = 8 Ω or 32 Ω
AV = −1 V/V
VO BTL
V
o+
PD − Output Power − mW
6000
150
100
50
0
350
P
D
− Power Dissipation − mW
200
250
300
RL = 8 Ω
200 400
RL = 32 Ω
VDD = 3.3 V
PD − Output Power − mW
400 6000 1000
400
300
100
0
800
P
D
− Power Dissipation − mW
500
700
600
200
RL = 32 Ω
200 800
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE POWER DISSIPATION
vs vs
FREQUENCY OUTPUT POWER
Figure 20. Figure 21.
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
OUTPUT POWER
10
Figure 22.
www.ti.com
Power
V
(rms)
2
R
L
V
(rms)
V
O(PP)
2 2
R
L
2x V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
–V
O(PP)
V
DD
V
DD
f
c
1
2 RLC
C
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
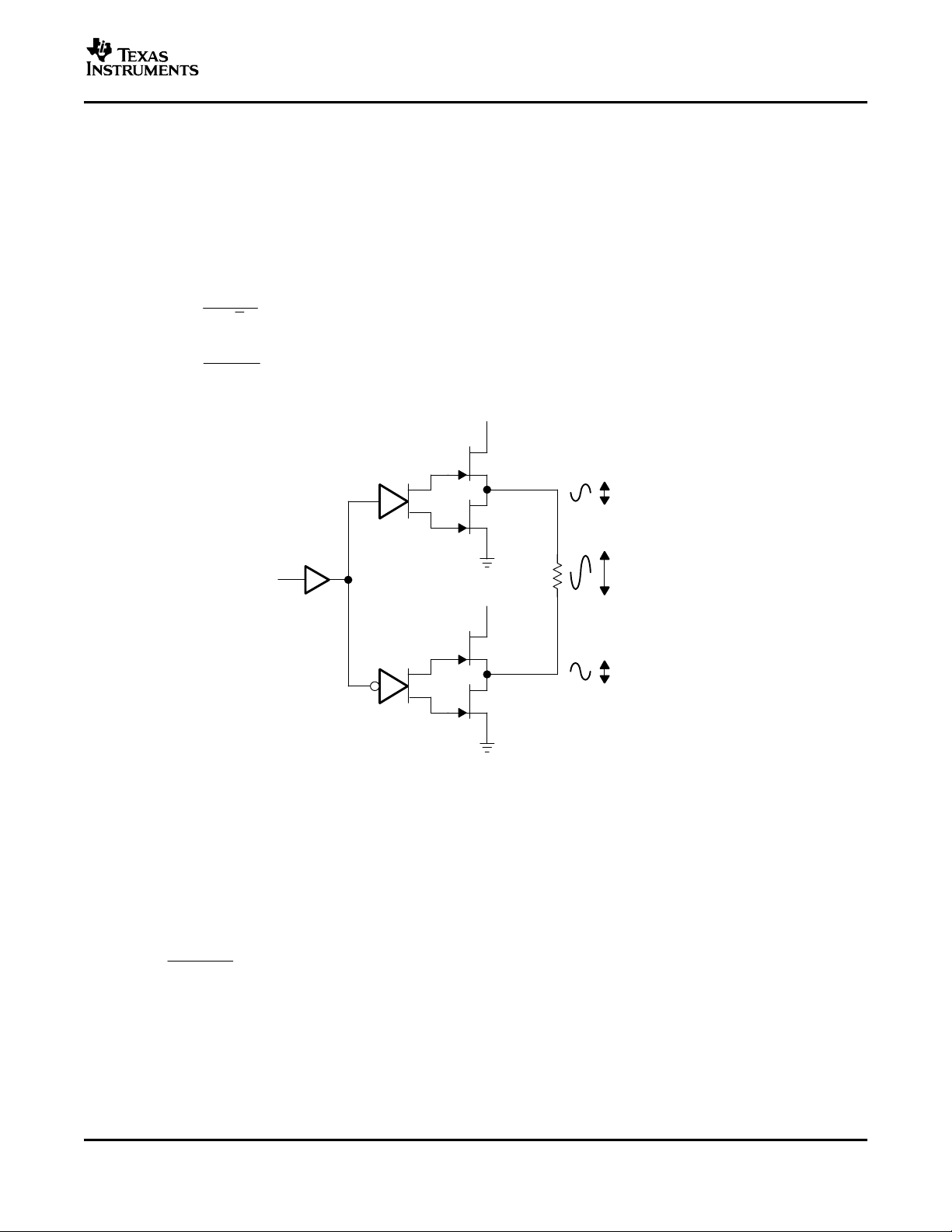
APPLICATION INFORMATION
BRIDGE-TIED LOAD
Figure 23 shows a linear audio power amplifier (APA) in a BTL configuration. The TPA741 BTL amplifier consists
of two linear amplifiers driving both ends of the load. There are several potential benefits to this differential drive
configuration, but initially consider power to the load. The differential drive to the speaker means that as one side
is slewing up, the other side is slewing down, and vice versa. This, in effect, doubles the voltage swing on the
load as compared to a ground referenced load. Plugging 2 × V
squared, yields 4× the output power from the same supply rail and load impedance (see Equation 1 ).
into the power equation, where voltage is
O(PP)
(1)
Figure 23. Bridge-Tied Load Configuration
In a typical portable handheld equipment sound channel operating at 3.3 V, bridging raises the power into an 8-Ω
speaker from a singled-ended (SE, ground reference) limit of 62.5 mW to 250 mW. In sound power that is a 6-dB
improvement, which is loudness that can be heard. In addition to increased power, there are frequency response
concerns. Consider the single-supply, SE configuration shown in Figure 24 . A coupling capacitor is required to
block the dc offset voltage from reaching the load. These capacitors can be quite large (approximately 33 µF to
1000 µF), so they tend to be expensive, heavy, occupy valuable PCB area, and have the additional drawback of
limiting low-frequency performance of the system. This frequency-limiting effect is due to the high-pass filter
network created with the speaker impedance and the coupling capacitance and is calculated with Equation 2 .
For example, a 68-µF capacitor with an 8-Ω speaker would attenuate low frequencies below 293 Hz. The BTL
configuration cancels the dc offsets, which eliminates the need for the blocking capacitors. Low-frequency
performance is then limited only by the input network and speaker response. Cost and PCB space are also
minimized by eliminating the bulky coupling capacitor.
(2)
11

www.ti.com
R
L
C
C
V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
V
DD
–3 dB
f
c
V
L(RMS)
V
O
I
DD
I
DD(RMS)
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
Figure 24. Single-Ended Configuration and Frequency Response
Increasing power to the load does carry a penalty of increased internal power dissipation. The increased
dissipation is understandable considering that the BTL configuration produces 4× the output power of a SE
configuration. Internal dissipation versus output power is discussed further in the thermal considerations section.
BTL AMPLIFIER EFFICIENCY
Linear amplifiers are notoriously inefficient. The primary cause of these inefficiencies is voltage drop across the
output stage transistors. There are two components of the internal voltage drop. One is the headroom or dc
voltage drop that varies inversely to output power. The second component is due to the sine-wave nature of the
output. The total voltage drop can be calculated by subtracting the RMS value of the output voltage from V
The internal voltage drop multiplied by the RMS value of the supply current, IDDrms, determines the internal
power dissipation of the amplifier.
An easy-to-use equation to calculate efficiency starts out being equal to the ratio of power from the power supply
to the power delivered to the load. To accurately calculate the RMS values of power in the load and in the
amplifier, the current and voltage waveform shapes must first be understood (see Figure 25 ).
.
DD
Figure 25. Voltage and Current Waveforms for BTL Amplifiers
Although the voltages and currents for SE and BTL are sinusoidal in the load, currents from the supply are
different between SE and BTL configurations. In an SE application, the current waveform is a half-wave rectified
shape, whereas in BTL it is a full-wave rectified waveform. This means RMS conversion factors are different.
Keep in mind that for most of the waveform both the push and pull transistors are not on at the same time, which
supports the fact that each amplifier in the BTL device only draws current from the supply for half the waveform.
The following equations are the basis for calculating amplifier efficiency.
12

www.ti.com
I
DD(RMS)
2V
P
R
L
P
SUP
VDDI
DD(RMS)
VDD2V
P
R
L
Efficiency
P
L
P
SUP
where
P
L
V
L(RMS)
2
R
L
V
p
2
2R
L
V
L(RMS)
V
P
2
Efficiency of a BTL configuration
V
P
4V
DD
2 PLR
L
12
4V
DD
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
Table 1 employs Equation 4 to calculate efficiencies for three different output power levels. The efficiency of the
amplifier is quite low for lower power levels and rises sharply as power to the load is increased, resulting in a
nearly flat internal power dissipation over the normal operating range. The internal dissipation at full output power
is less than in the half power range. Calculating the efficiency for a specific system is the key to proper power
supply design.
(3)
(4)
OUTPUT POWER EFFICIENCY PEAK VOLTAGE
(1) High-peak voltage values cause the THD to increase.
A final point to remember about linear amplifiers (either SE or BTL) is how to manipulate the terms in the
efficiency equation to utmost advantage when possible. In Equation 4 , V
that as V
goes down, efficiency goes up.
DD
Table 1. Efficiency vs Output Power in 3.3-V, 8-Ω, BTL Systems
(W) (%) (V)
0.125 33.6 1.41 0.26
0.25 47.6 2.00 0.29
0.375 58.3 2.45
(1)
is in the denominator. This indicates
DD
INTERNAL
DISSIPATION
(W)
0.28
13

www.ti.com
Audio
Input
Bias
Control
V
DD
700 mW
6
5
7
VO+
V
DD
1
24BYPASS
IN–
VDD/2
C
I
C
S
1
µ
F
C
B
2.2
µ
F
SHUTDOWN
VO– 8
GND
From System Control
3 IN+
R
I
10 kΩ
R
F
50 kΩ
–
+
–
+
Audio
Input–
Bias
Control
V
DD
700 mW
6
5
7
VO+
V
DD
1
24BYPASS
IN–
VDD/2
C
I
C
S
1
µ
F
C
B
2.2
µ
F
SHUTDOWN
VO– 8
GND
From System Control
3 IN+
R
I
10 kΩ
R
F
50 kΩ
–
+
–
+
R
I
10 kΩ
Audio
Input+
C
I
R
F
50 kΩ
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
APPLICATION SCHEMATICS
Figure 26 is a schematic diagram of a typical handheld audio application circuit, configured for a gain of –10 V/V.
Figure 26. TPA741 Application Circuit
Figure 27 is a schematic diagram of a typical handheld audio application circuit, configured for a gain of –10 V/V
with a differential input.
It is important to note that using the additional R
to shift slightly, which could influence the THD+N performance of the amplifier. Although an additional external
operational amplifier could be used to buffer BYPASS from RF, tests in the laboratory have shown that the
THD+N performance is only minimally affected by operating in the fully differential mode as shown in Figure 27 .
The following sections discuss the selection of the components used in Figure 26 and Figure 27 .
Figure 27. TPA741 Application Circuit With Differential Input
14
resistor connected between IN+ and BYPASS will cause V
F
DD
/2
www.ti.com
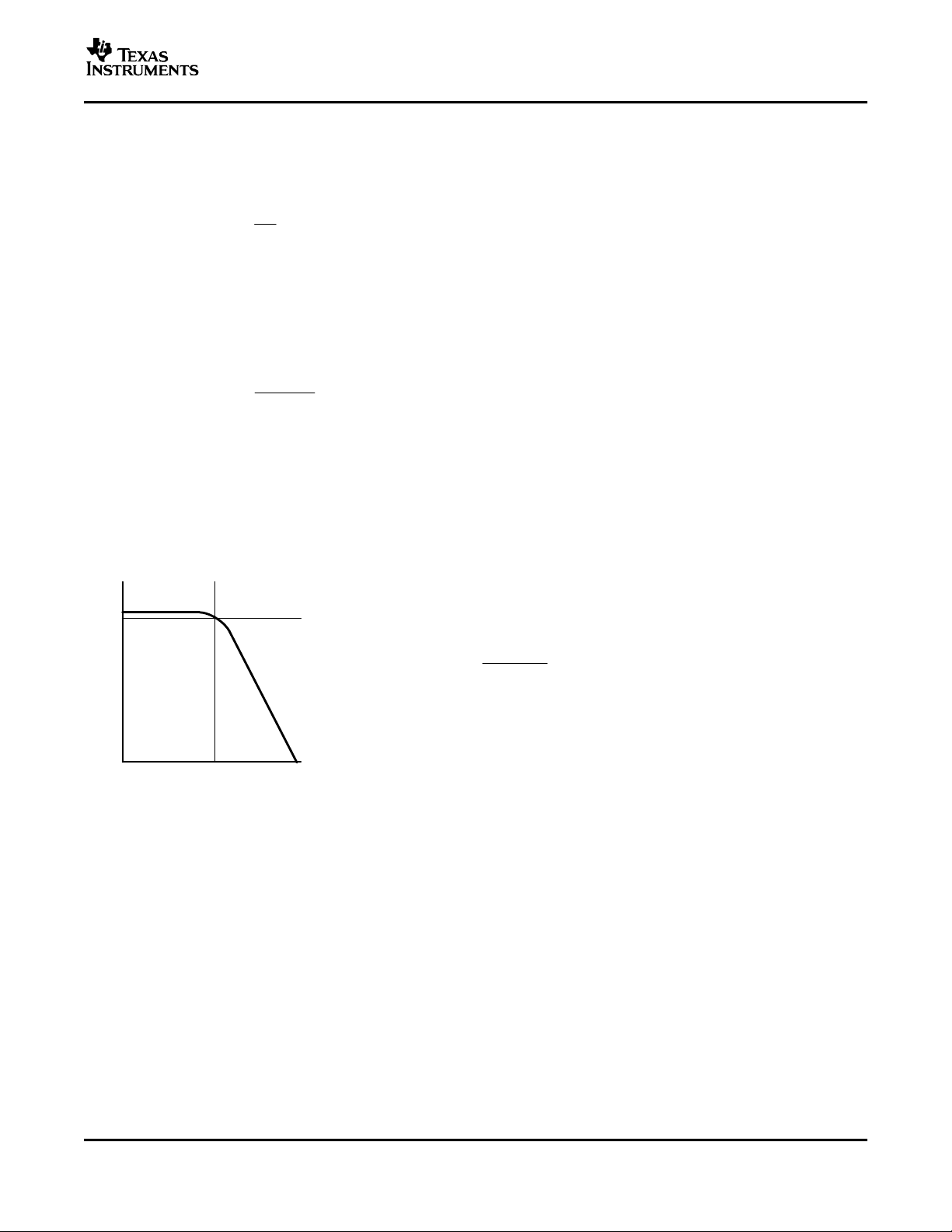
COMPONENT SELECTION
BTL gain 2
R
F
R
I
Effective impedance
RFR
I
RF R
I
(7)
f
c
1
2 RFC
F
−3 dB
f
c
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
Gain-Setting Resistors, R
The gain for each audio input of the TPA741 is set by resistors R
and R
F
I
and RIaccording to Equation 5 for BTL mode.
F
BTL mode operation brings about the factor 2 in the gain equation due to the inverting amplifier mirroring the
voltage swing across the load. Given that the TPA741 is an MOS amplifier, the input impedance is high;
consequently, input leakage currents are not generally a concern, although noise in the circuit increases as the
value of R
increases. In addition, a certain range of R
F
values is required for proper start-up operation of the
F
amplifier. Taken together, it is recommended that the effective impedance seen by the inverting node of the
amplifier be set between 5 kΩ and 20 kΩ. The effective impedance is calculated in Equation 6 .
As an example, consider an input resistance of 10 kΩ and a feedback resistor of 50 kΩ. The BTL gain of the
amplifier would be -10 V/V and the effective impedance at the inverting terminal would be 8.3 kΩ, which is well
within the recommended range.
For high-performance applications, metal film resistors are recommended because they tend to have lower noise
levels than carbon resistors. For values of R
formed from R
and the inherent input capacitance of the MOS input structure. For this reason, a small
F
compensation capacitor of approximately 5 pF should be placed in parallel with R
above 50 kΩ, the amplifier tends to become unstable due to a pole
F
F
when R
is greater than 50
F
kΩ. This, in effect, creates a low-pass filter network with the cutoff frequency defined in Equation 7 .
(5)
(6)
For example, if R
Input Capacitor, C
In the typical application an input capacitor, CI, is required to allow the amplifier to bias the input signal to the
proper dc level for optimum operation. In this case, C
determined in Equation 8 .
is 100 kΩ and C
F
I
is 5 pF, then fcis 318 kHz, which is well outside of the audio range.
F
and R
I
form a high-pass filter with the corner frequency
I
(7)
15

www.ti.com
f
c
1
2 RIC
I
−3 dB
f
c
C
I
1
2 RIf
c
10
CB 250 k
Ω
1
RF R
I
C
I
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
The value of CIis important to consider as it directly affects the bass (low-frequency) performance of the circuit.
Consider the example where R
Equation 8 is reconfigured as Equation 9 .
In this example, C
is 0.4 µF, so one would likely choose a value in the range of 0.47 µF to 1 µF. A further
I
consideration for this capacitor is the leakage path from the input source through the input network (R
the feedback resistor (R
) to the load. This leakage current creates a dc offset voltage at the input to the amplifier
F
that reduces useful headroom, especially in high-gain applications. For this reason, a low-leakage tantalum or
ceramic capacitor is the best choice. When polarized capacitors are used, the positive side of the capacitor
should face the amplifier input in most applications as the dc level there is held at V
than the source dc level. It is important to confirm the capacitor polarity in the application.
is 10 kΩ and the specification calls for a flat bass response down to 40 Hz.
I
/2, which is likely higher
DD
, CI) and
I
(8)
(9)
Power Supply Decoupling, C
S
The TPA741 is a high-performance CMOS audio amplifier that requires adequate power supply decoupling to
ensure the output total harmonic distortion (THD) is as low as possible. Power supply decoupling also prevents
oscillations for long lead lengths between the amplifier and the speaker. The optimum decoupling is achieved by
using two capacitors of different types that target different types of noise on the power supply leads. For higher
frequency transients, spikes, or digital hash on the line, a good low equivalent-series-resistance (ESR) ceramic
capacitor, typically 0.1 µF, placed as close as possible to the device V
lead, works best. For filtering lower
DD
frequency noise signals, a larger aluminum electrolytic capacitor of 10 µF or greater, placed near the audio
power amplifier is recommended.
Midrail Bypass Capacitor, C
B
The midrail bypass capacitor, CB, is the most critical capacitor and serves several important functions. During
start-up or recovery from shutdown mode, C
determines the rate at which the amplifier starts up. The second
B
function is to reduce noise produced by the power supply caused by coupling into the output drive signal. This
noise is from the midrail generation circuit internal to the amplifier, which appears as degraded PSRR and THD +
N. The capacitor is fed from a 250-kΩ source inside the amplifier. To keep the start-up pop as low as possible,
the relationship shown in Equation 10 should be maintained. This ensures that the input capacitor is fully charged
before the bypass capacitor is fully charged and the amplifier starts up.
As an example, consider a circuit where C
is 2.2 µF, CIis 0.47 µF, R
B
is 50 kΩ, and RIis 10 kΩ. Inserting these
F
values into the Equation 10 we get:
18.2 ≤ 35.5
which satisfies the rule. Bypass capacitor, CB, values of 0.1-µF to 2.2-µF ceramic or tantalum low-ESRcapacitors
are recommended for the best THD and noise performance.
(10)
16

www.ti.com
PdB 10Log
P
W
P
ref
10Log
700 mW
1 W
–1.5 dB
W
10
PdB10
x P
ref
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
USING LOW-ESR CAPACITORS
Low-ESR capacitors are recommended throughout this applications section. A real (as opposed to ideal)
capacitor can be modeled simply as a resistor in series with an ideal capacitor. The voltage drop across this
resistor minimizes the beneficial effects of the capacitor in the circuit. The lower the equivalent value of this
resistance, the more the real capacitor behaves like an ideal capacitor.
5-V Versus 3.3-V OPERATION
The TPA741 operates over a supply range of 2.5 V to 5.5 V. This data sheet provides full specifications for 5-V
and 3.3-V operation, as these are considered to be the two most common standard voltages. There are no
special considerations for 3.3-V versus 5-V operation with respect to supply bypassing, gain setting, or stability.
The most important consideration is that of output power. Each amplifier in TPA741 can produce a maximum
voltage swing of V
opposed to V
O(PP)
power into an 8-Ω load before distortion becomes significant.
Operation from 3.3-V supplies, as can be shown from the efficiency formula in Equation 4 , consumes
approximately two-thirds the supply power of operation from 5-V supplies for a given output-power level.
HEADROOM AND THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
Linear power amplifiers dissipate a significant amount of heat in the package under normal operating conditions.
A typical music CD requires 12 dB to 15 dB of dynamic headroom to pass the loudest portions without distortion
as compared with the average power output. From the TPA741 data sheet, one can see that when the TPA741
is operating from a 5-V supply into a 8-Ω speaker that 700-mW peaks are available. Converting watts to dB:
- 1 V. This means, for 3.3-V operation, clipping starts to occur when V
DD
O(PP)
= 4 V for 5-V operation. The reduced voltage swing subsequently reduces maximum output
= 2.3 V, as
Subtracting the headroom restriction to obtain the average listening level without distortion yields:
1.5 dB – 15 dB = –16.5 (15-dB headroom)
1.5 dB – 12 dB = –13.5 (12-dB headroom)
1.5 dB – 9 dB = –10.5 (9-dB headroom)
1.5 dB – 6 dB = –7.5 (6-dB headroom)
1.5 dB – 3 dB = –4.5 (3-dB headroom)
Converting dB back into watts:
= 22 mW (15-dB headroom)
= 44 mW (12-dB headroom)
= 88 mW (9-dB headroom)
= 175 mW (6-dB headroom)
= 350 mW (3- dB headroom)
This is valuable information to consider when attempting to estimate the heat dissipation requirements for the
amplifier system. Comparing the absolute worst case, which is 700 mW of continuous power output with 0 dB of
headroom, against 12-dB and 15-dB applications drastically affects maximum ambient temperature ratings for
the system. Using the power dissipation curves for a 5-V, 8-Ω system, the internal dissipation in the TPA741 and
maximum ambient temperatures is shown in Table 2 .
17

www.ti.com
TPA741
SLOS316C – JUNE 2000 – REVISED JUNE 2004
Table 2. TPA741 Power Rating, 5-V, 8-Ω, BTL
D PACKAGE DGN PACKAGE
PEAK OUTPUT POWER
POWER DISSIPATION
(mW) (mW)
700 700 mW 675 34°C 110°C
700 350 mW (3 dB) 595 47°C 115°C
700 176 mW (6 dB) 475 68°C 122°C
700 88 mW (9 dB) 350 89°C 125°C
700 44 mW (12 dB) 225 111°C 125°C
AVERAGE
OUTPUT POWER
Table 2 shows that the TPA741 can be used to its full 700-mW rating without any heat sinking in still air up to
110°C and 34°C for the DGN package (MSOP) and D package (SOIC), respectively.
(SOIC) (MSOP)
MAXIMUM AMBIENT MAXIMUM AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE TEMPERATURE
(0° CFM) (0° CFM)
18

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
7-May-2007
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
TPA741D ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA741DG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA741DGN ACTIVE MSOP-
Power
DGN 8 80 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
PAD
TPA741DGNG4 ACTIVE MSOP-
Power
DGN 8 80 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
PAD
TPA741DGNR ACTIVE MSOP-
Power
DGN 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
PAD
TPA741DGNRG4 ACTIVE MSOP-
Power
DGN 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
PAD
TPA741DR ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
TPA741DRG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
(3)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
TPA741DGNR MSOP-
Power
TPA741DR SOIC D 8 2500 330.0 12.4 6.4 5.2 2.1 8.0 12.0 Q1
Type
PAD
Package
Drawing
DGN 8 2500 330.0 12.4 5.3 3.4 1.4 8.0 12.0 Q1
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
TPA741DGNR MSOP-PowerPAD DGN 8 2500 358.0 335.0 35.0
TPA741DR SOIC D 8 2500 346.0 346.0 29.0
Pack Materials-Page 2





IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...