Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
TP A0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
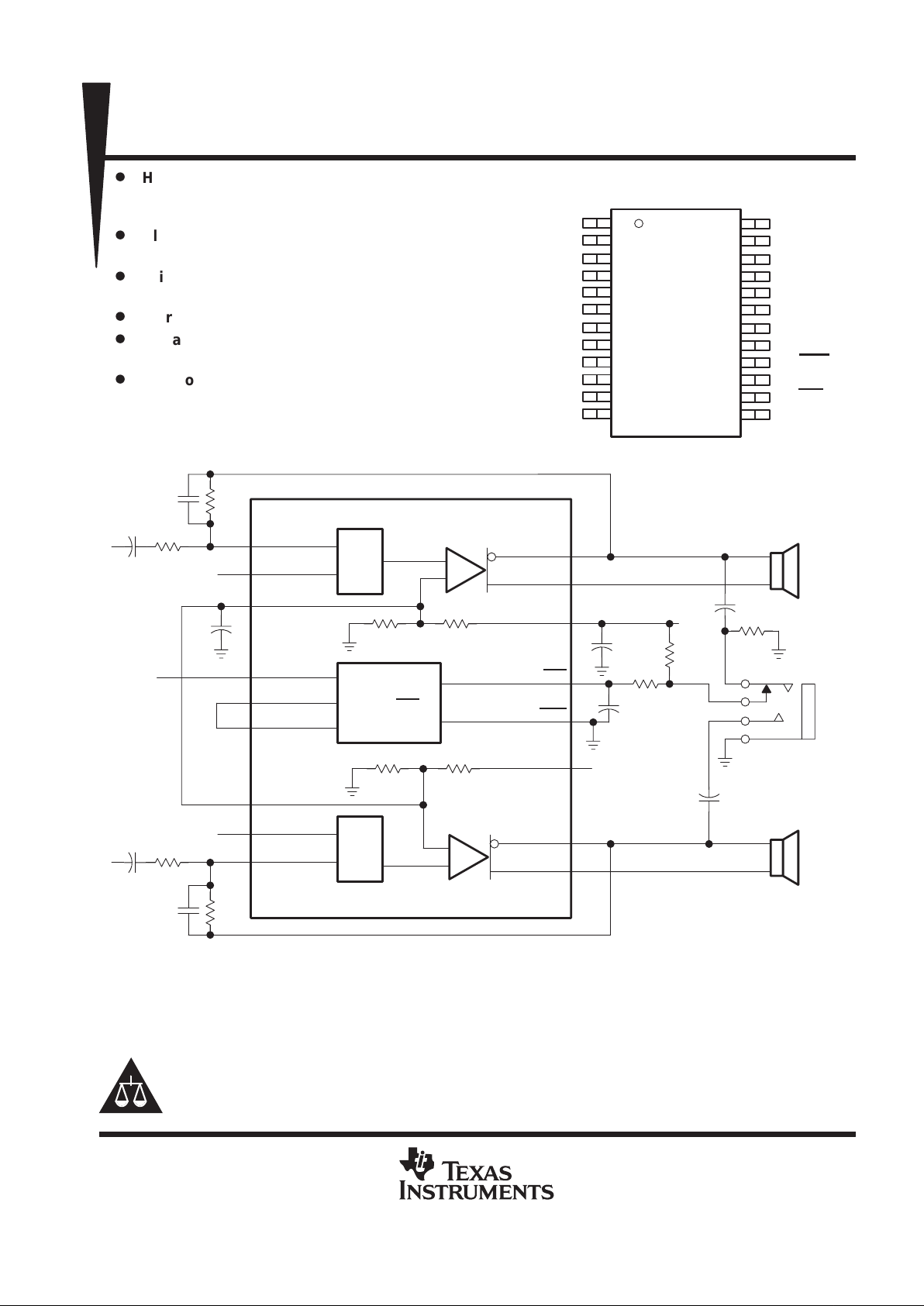
D
High Power with PC Power Supply
– 1.5 W/Ch at 5 V
– 600 mW/Ch at 3 V
D
Ultra-Low Distortion
< 0.05% THD+N at 1.5 W and 4-Ω Load
D
Bridge-Tied Load (BTL) or Single Ended
(SE) Modes
D
Stereo Input MUX
D
Surface-Mount Power Package
24-Pin TSSOP PowerP AD
D
Shutdown Control ...IDD < 10 µA
C
B
C
S
Right
MUX
RLINEIN
RHPIN
Left
MUX
LHPIN
LLINEIN
Bias, Mute,
Shutdown,
and SE/BTL
MUX Control
+
–
+
–
RBYPASS
MUTE IN
MUTE OUT
SHUTDOWN
LBYPASS
ROUT+
ROUT–
RV
DD
LV
DD
LOUT+
LOUT–
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
C
IR
R
IR
R
FR
C
FR
System
Control
C
IL
R
IL
NC
NC
4
5
6
8
9
11
19
20
21
R
FL
C
FL
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
V
DD
V
DD
C
OUTR
C
OUTL
10
3
16
7
14
18
15
22
1 kΩ
0.1 µF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
GND/HS
NC
LOUT+
LLINEIN
LHPIN
LBYPASS
LV
DD
SHUTDOWN
MUTE OUT
LOUT–
MUTE IN
GND/HS
GND/HS
NC
ROUT+
RLINEIN
RHPIN
RBYPASS
RV
DD
NC
HP/LINE
ROUT–
SE/BTL
GND/HS
PWP PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
description
The TPA0102 is a stereo audio power amplifier in a 24-pin TSSOP thermal package capable of delivering
greater than 1.5 W of continuous RMS power per channel into 4-Ω loads. This device functionality provides a
very efficient upgrade path from the TP A4860 and TP A4861 mono amplifiers where three separate devices are
required for stereo applications: two for speaker drive, plus a third for headphone drive. The TP A0102 simplifies
design and frees up board space for other features. Full power distortion levels of less than 0.1% THD+N from
a 5-V supply are typical. This provides significant improvement in fidelity for speech and music over the popular
TPA4860/61 series. Low-voltage applications are also well served by the TPA0102 providing 600-mW per
channel into 4-Ω loads with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
Amplifier gain is externally configured by means of two resistors per input channel and does not require external
compensation for settings of 2 to 20 in BTL mode (1 to 10 in SE mode). An internal input MUX allows two sets
of stereo inputs to the amplifier. In notebook applications, where internal speakers are driven as BTL and the
line (often headphone drive) outputs are required to be SE, the TP A0102 automatically switches into SE mode
when the SE/BTL
input is activated. Using the TP A0102 to drive line outputs up to 500 mW/channel into external
4 Ω loads is ideal for small non-powered external speakers in portable multimedia systems. The TPA0102 also
features a shutdown function for power sensitive applications, holding the supply current below 5 µA. In
speakerphone or other monaural applications, the TP A0102 is configured through the power supply terminals
to activate only half of the amplifier which reduces supply current by approximately one-half over stereo
applications.
The PowerPAD package (PWP) delivers a level of thermal performance that was previously achievable only
in TO-220-type packages. Thermal impedances of approximately 35°C/W are readily realized in multilayer PCB
applications. This allows the TP A0102 to operate at full power into 4- Ω loads at ambient temperature of up to
55°C. Into 8-Ω loads, the operating ambient temperature increases to 100°C.
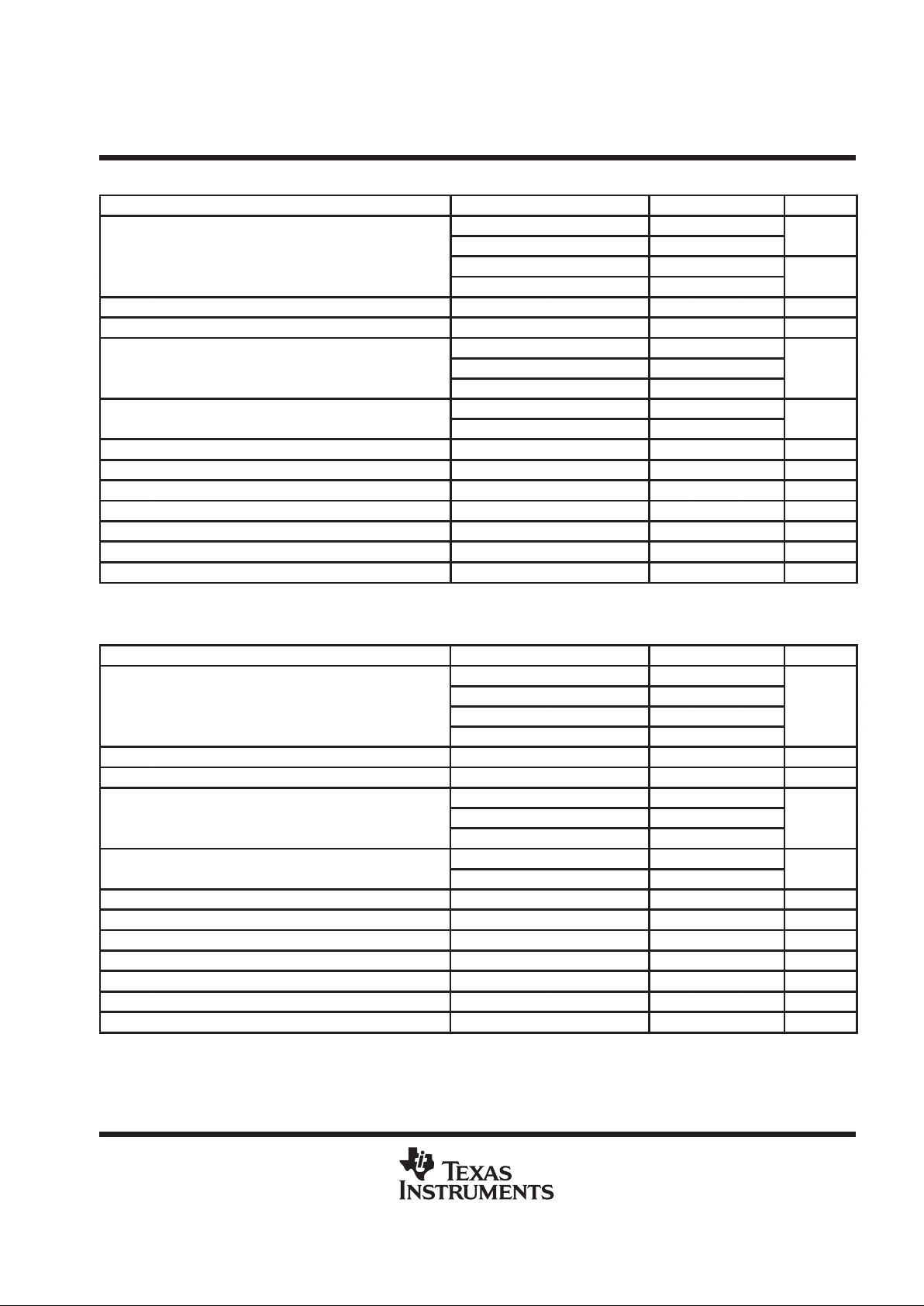
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
TSSOP
(PWP)
40°C to 85°C TPA0102PWP
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
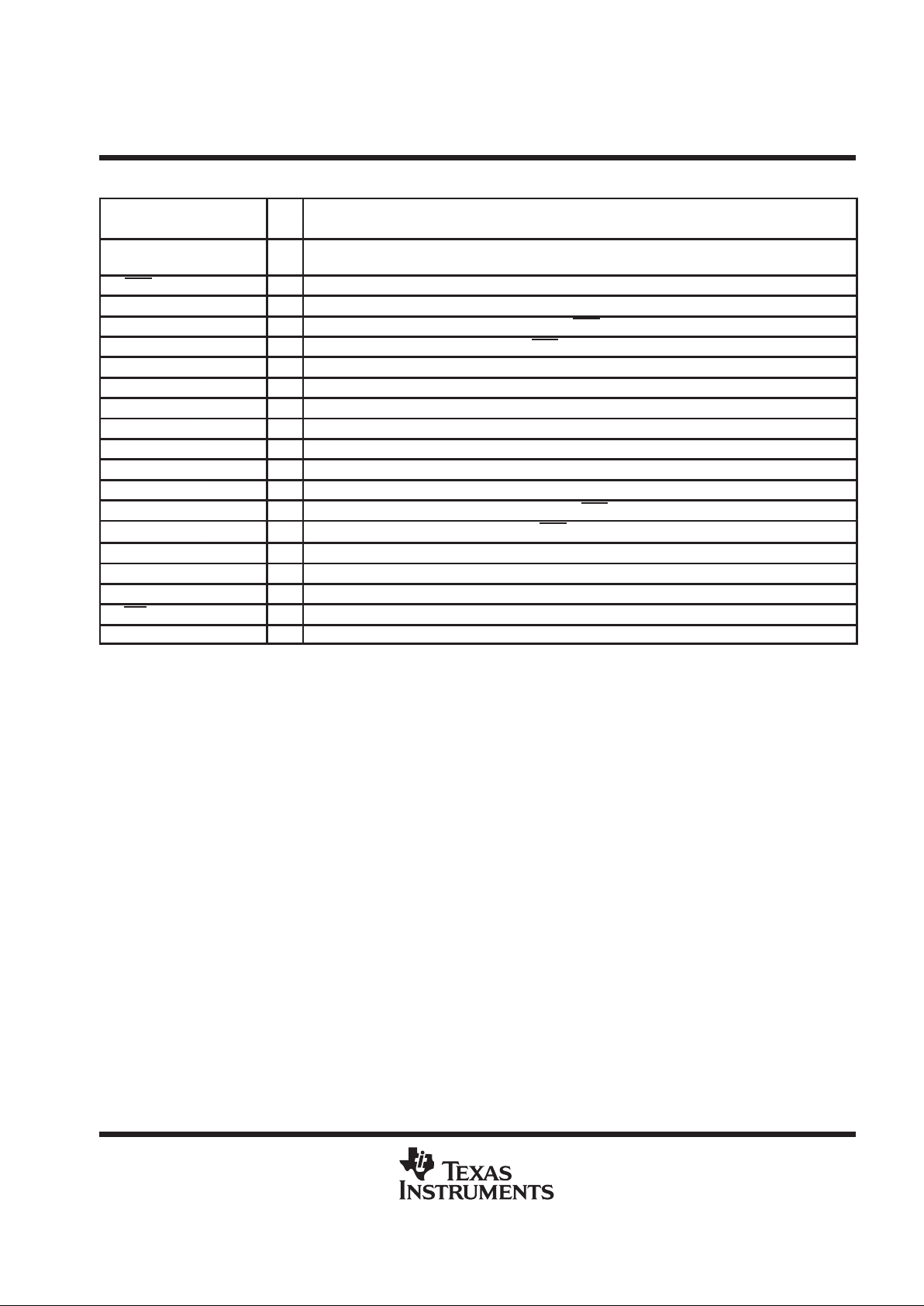
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
GND/HS 1, 12,
13, 24
Ground connection for circuitry, directly connected to thermal pad
HP/LINE 16 I Input MUX control input, hold high to select L/RHPIN (5, 20), hold low to select L/RLINEIN (4, 21)
LBYPASS 6 Tap to voltage divider for left channel internal mid-supply bias
LHP IN 5 I Left channel headphone input, selected when HP/LINE terminal (16) is held high
LLINE IN 4 I Left channel line input, selected when HP/LINE terminal (16) is held low
LOUT+ 3 O Left channel + output in BTL mode, + output in SE mode
LOUT– 10 O Left channel – output in BTL mode, high-impedance state in SE mode
LV
DD
7 I Supply voltage input for left channel and for primary bias circuits
MUTE IN 11 I Mute all amplifiers, hold low for normal operation, hold high to mute
MUTE OUT 9 O Follows MUTE IN terminal (11), provides buffered output
NC 2, 17, 23 No internal connection
RBYPASS 19 Tap to voltage divider for right channel internal mid–supply bias
RHP IN 20 I Right channel headphone input, selected when HP/LINE terminal (16) is held high
RLINE IN 21 I Right channel line input, selected when HP/LINE terminal (16) is held low
ROUT+ 22 O Right channel + output in BTL mode, + output in SE mode
ROUT– 15 O Right channel – output in BTL mode, high impedance state in SE mode
RV
DD
18 I Supply voltage input for right channel
SE/BTL 14 I Hold low for BTL mode, hold high for SE mode
SHUTDOWN 8 I Places entire IC in shutdown mode when held high, I
DD
< I µA
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
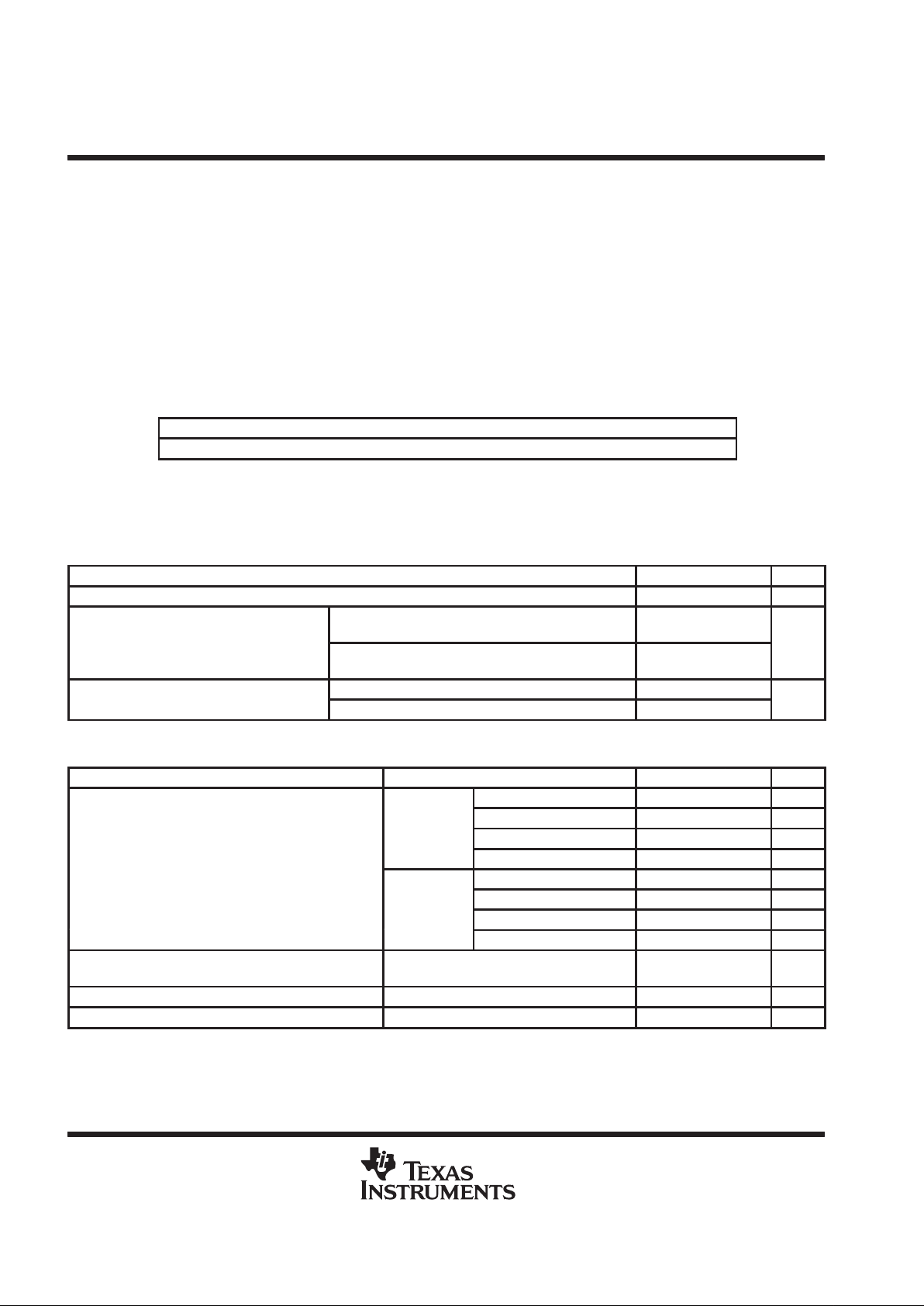
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage, VDD 6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage, VI –0.3 V to VDD +0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total power dissipation internally limited (see Dissipation Rating Table). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
A
–40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating junction temperature range, TJ –40°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
TA ≤ 25°C DERATING FACTOR TA = 70°C TA = 85°C
PWP 2.7 W
‡
21.8 mW/°C 1.7 W 1.4 W
‡
Please see the Texas Instruments document,
PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package Application Report
(literature number SLMA002), for more information on the PowerPAD package. The thermal data was
measured on a PCB layout based on the information in the section entitled
T exas Instruments Recommended
Board for PowerPAD
on page 33 of the before mentioned document.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
DD
3 5 5.5 V
p
p
VDD = 5 V, 4-Ω stereo BTL drive,
250 mW/ch average power, With proper PCB design
–40 85
°
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
VDD = 5 V, 4-Ω stereo BTL drive,
1.5 W/ch average power, With proper PCB design
–40 55
°C
p
VDD = 5 V 1.25 4.5
Common mode input voltage, V
ICM
VDD = 3.3 V 1.25 2.7
V
dc electrical characteristics, TA = 25°C
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TYP†MAX UNIT
Stereo BTL 19 25 mA
Stereo SE 9 15 mA
V
DD
= 5
V
Mono BTL 9 15 mA
pp
Mono SE 3 10 mA
IDDSupply current
Stereo BTL 13 20 mA
Stereo SE 3 10 mA
V
DD
=
3.3 V
Mono BTL 3 10 mA
Mono SE 3 10 mA
V
OO
Output offset voltage
(measured differentially)
VDD = 5 V Gain = 2, See Note 1 5 25 mV
I
DD(MUTE)
Supply current in mute mode VDD = 5 V 800 µA
I
DD(SD)
IDD in shutdown VDD = 5 V 5 15 µA
NOTE 1: At 3 V < VDD < 5 V the dc output voltage is approximately VDD/2.
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
ac operating characteristics, V
DD
= 5 V, T
A
= 25°C, R
L
= 4 Ω
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
THD = 0.2%, BTL 1.25
p
p
THD = 1%, BTL 1.5
W
POOutput power (each channel) see Note 2
THD = 0.2%, SE 500
THD = 1%, SE 600
mW
THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise Po = 1 W, f = 20 to 20 kHz 200 m%
B
OM
Maximum output power bandwidth G = 10, THD < 5 % >20 kHz
BTL 72°
Phase margin
Open Load
71°
SE 52°
pp
pp
f = 1 kHz 75
Power supply ripple rejection
f = 20 – 20 kHz, 60
dB
Mute attenuation 85 dB
Channel-to-channel output separation f = 1 kHz 65 dB
Line/HP input separation 100 dB
BTL attenuation in SE mode 100 dB
Z
I
Input impedance 2 MΩ
Signal-to-noise ratio Po = 500 mW, BTL 95 dB
V
n
Output noise voltage 25 µV(rms)
NOTE 2: Output power is measured at the output terminals of the IC at 1 kHz.
ac operating characteristics, V
DD
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, RL = 4 Ω
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
THD = 0.2% BTL 600
p
p
THD = 1% BTL 750
POOutput power (each channel) see Note 2
THD = 0.2%, SE 200
mW
THD = 1%, SE 250
THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise Po = 600 mW, f = 20 to 20 kHz 250 m%
B
OM
Maximum output power bandwidth G = 10, THD < 5 % >20 kHz
BTL 92°
Phase margin
Open Load
70°
SE 57°
pp
pp
f = 1 kHz 70
Power supply ripple rejection
f = 20 – 20 kHz 55
dB
Mute attenuation 85 dB
Channel-to-channel output separation f = 1 kHz 65 dB
Line/HP input separation 100 dB
BTL attenuation in SE mode 100 dB
Z
I
Input impedance 2 MΩ
Signal-to-noise ratio Po = 500 mW, BTL 95 dB
V
n
Output noise voltage 25 µV(rms)
NOTE 2 Output power is measured at the output terminals of the IC at 1 kHz.
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
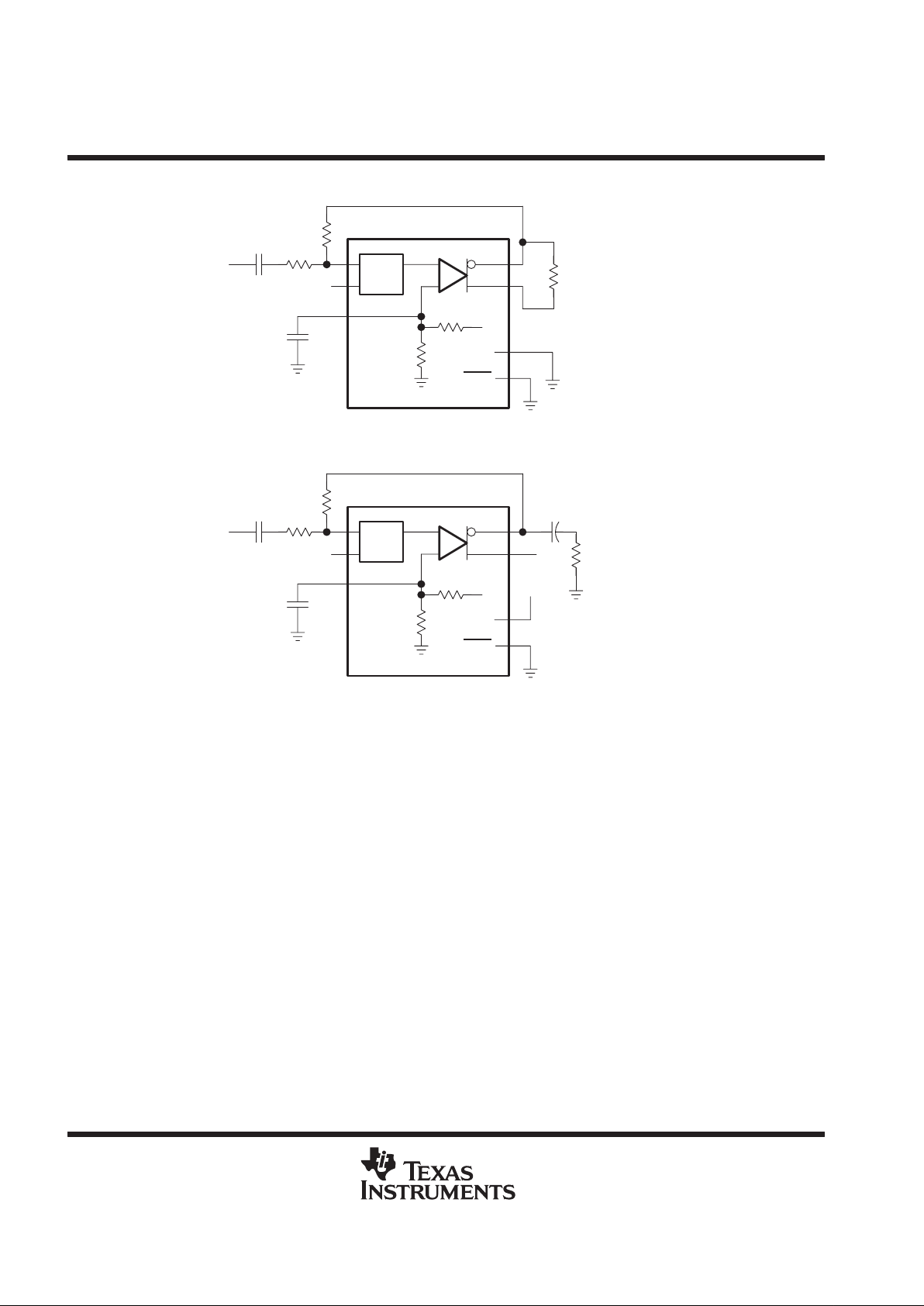
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
MUX
R
I
C
I
R
F
4.7 µF
C
B
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
RL = 4 Ω or 8 Ω
Figure 1. BTL Test Circuit
MUX
R
I
C
I
R
F
C
B
C
O
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω, or 32 Ω
4.7 µF
V
DD
Figure 2. SE Test Circuit
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table of Graphs
FIGURE
p
vs Frequency
4, 5, 7, 8, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17, 18, 20,
21, 23, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 32, 33
THD
+
N
Total harmonic distortion plus noise
vs Output power
3, 6, 9, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28,
31, 34
V
n
Output noise voltage vs Frequency 35, 36
Supply ripple rejection ratio vs Frequency 37, 38
Crosstalk vs Frequency 39–40
Open loop response vs Frequency 43, 44
Closed loop response vs Frequency 45 – 48
I
DD
Supply current vs Supply voltage 49
P
O
Output power
vs Supply voltage
vs Load resistance
50,51
52,53
P
D
Power dissipation vs Output power 54 – 57
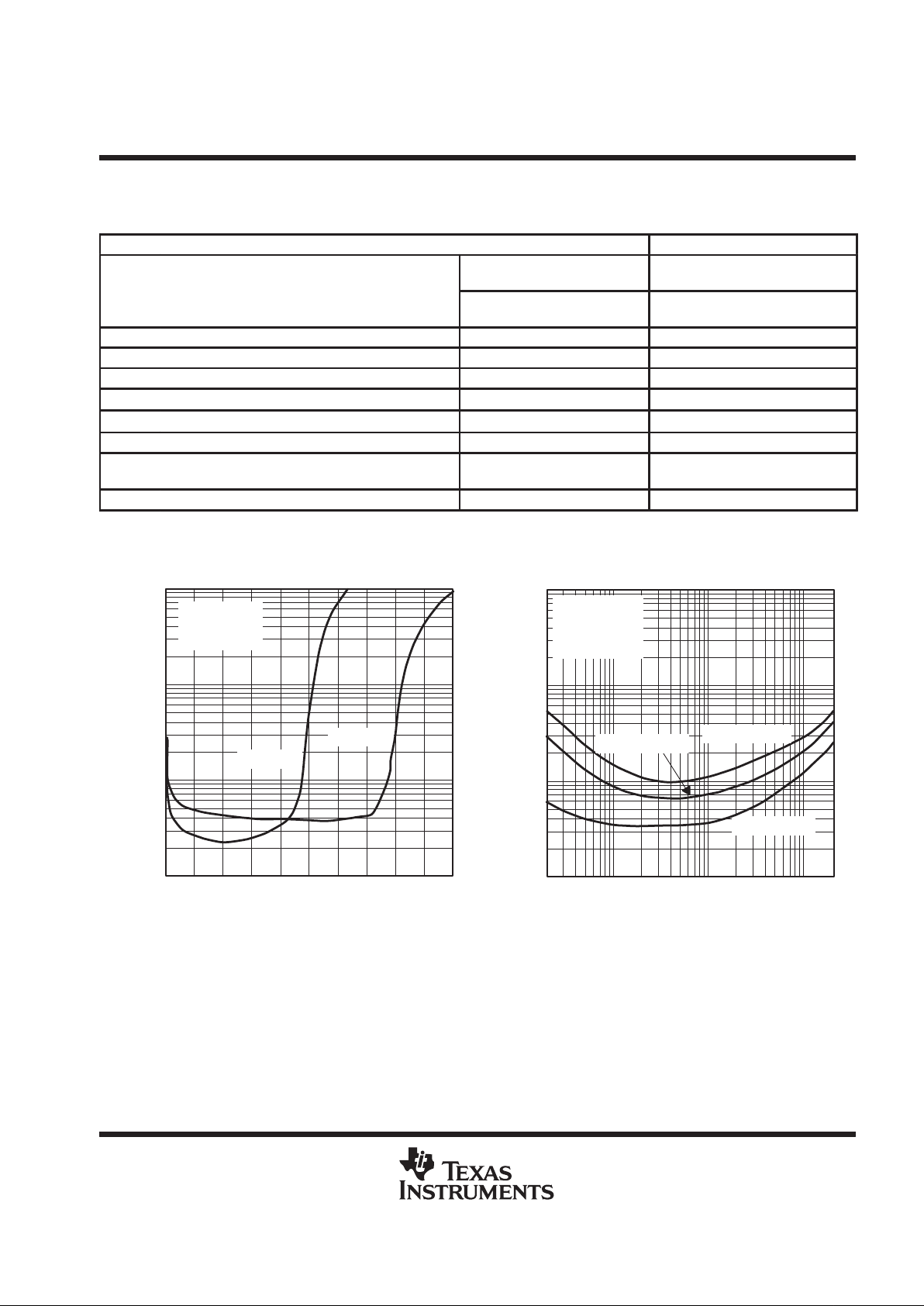
Figure 3
0.1
0.01
0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 1.25 1.5
1
10
1.75 2 2.25 2.5
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 5 V
f = 1 kHz
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
Figure 4
0.01
10
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
1
VDD = 5 V
PO = 1.5 W
RL = 4 Ω
BTL
AV = –2 V/V
AV = –20 V/V
AV = –10 V/V
0.1

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
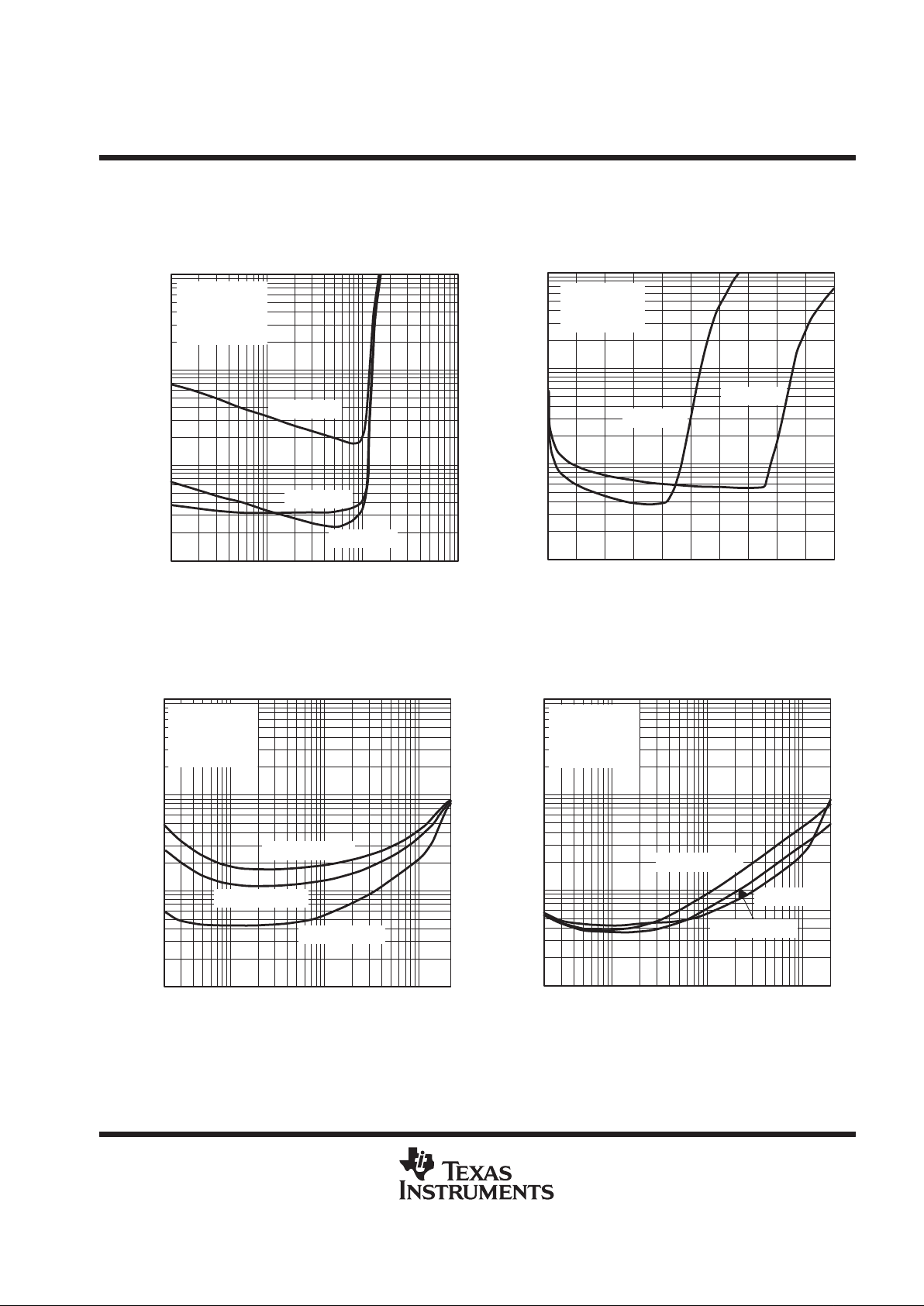
Figure 5
PO = 1.5 W
PO = 0.25 W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
PO = 0.75 W
Figure 6
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
0.1
0.01
0.01 0.1
1
10
110
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 7
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
PO = 1 W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 0.5 W
Figure 8
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
PO = 1 W
RL = 8 Ω
BTL
AV = –2 V/V
AV = –20 V/V
AV = –10 V/V
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 9
0.1
0.01
0.01 0.1
1
10
110
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 10
0.1
0.01
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
1
10
0.7 0.8 0.9 1
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 3.3 V
f = 1 kHz
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
Figure 11
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 0.75 W
RL = 4 Ω
BTL
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –20 V/V
AV = –2 V/V
Figure 12
PO = 0.35 W
PO = 0.1 W
PO = 0.75 W
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
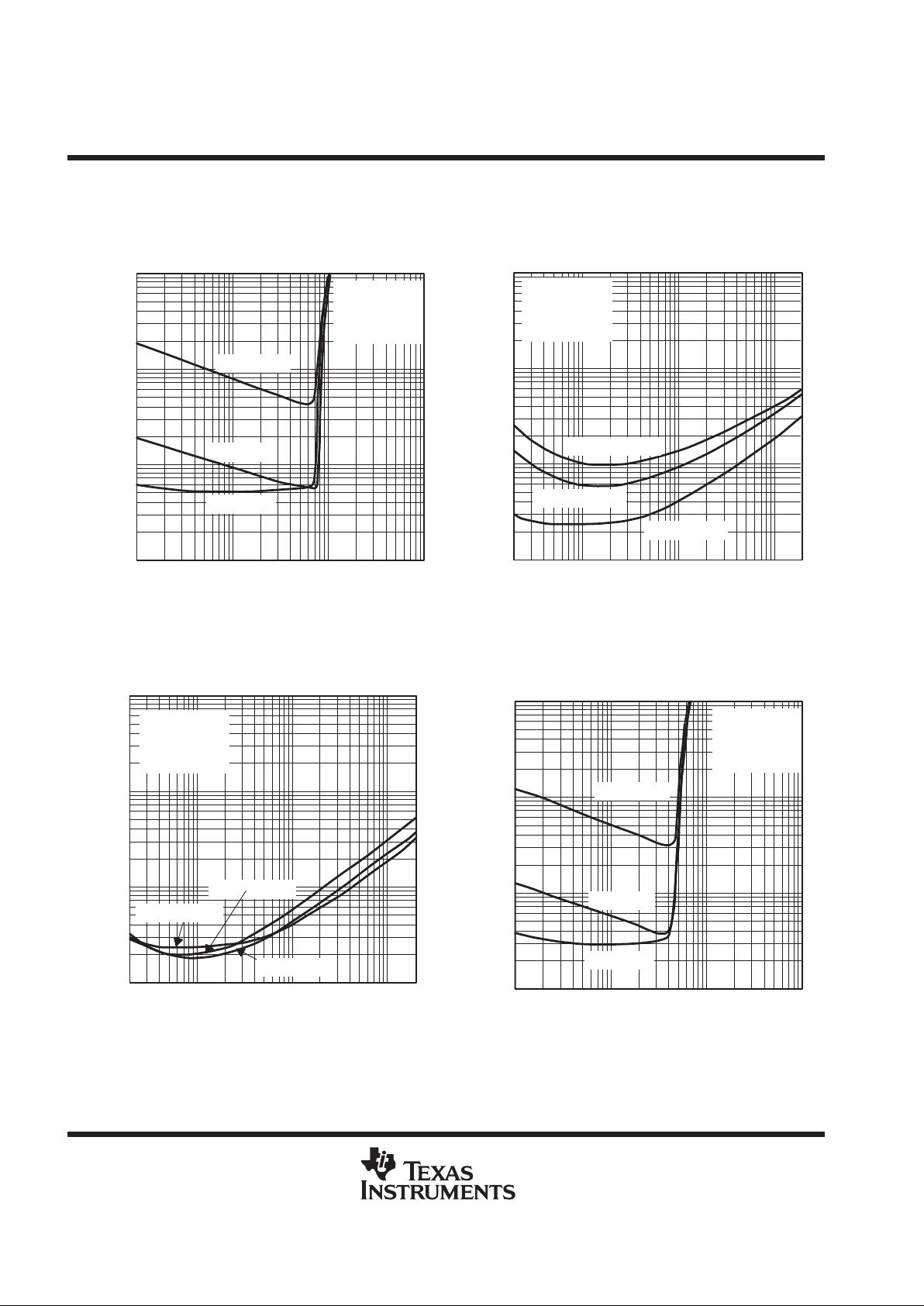
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 13
0.1
0.01
0.01
1
10
1100.1
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 14
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
AV = –20 V/V
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –2 V/V
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 0.4 W
RL = 8 Ω
BTL
Figure 15
PO = 0.4 W
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 0.1 W
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
Figure 16
0.1
0.01
0.01 0.1
1
10
110
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
BTL
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
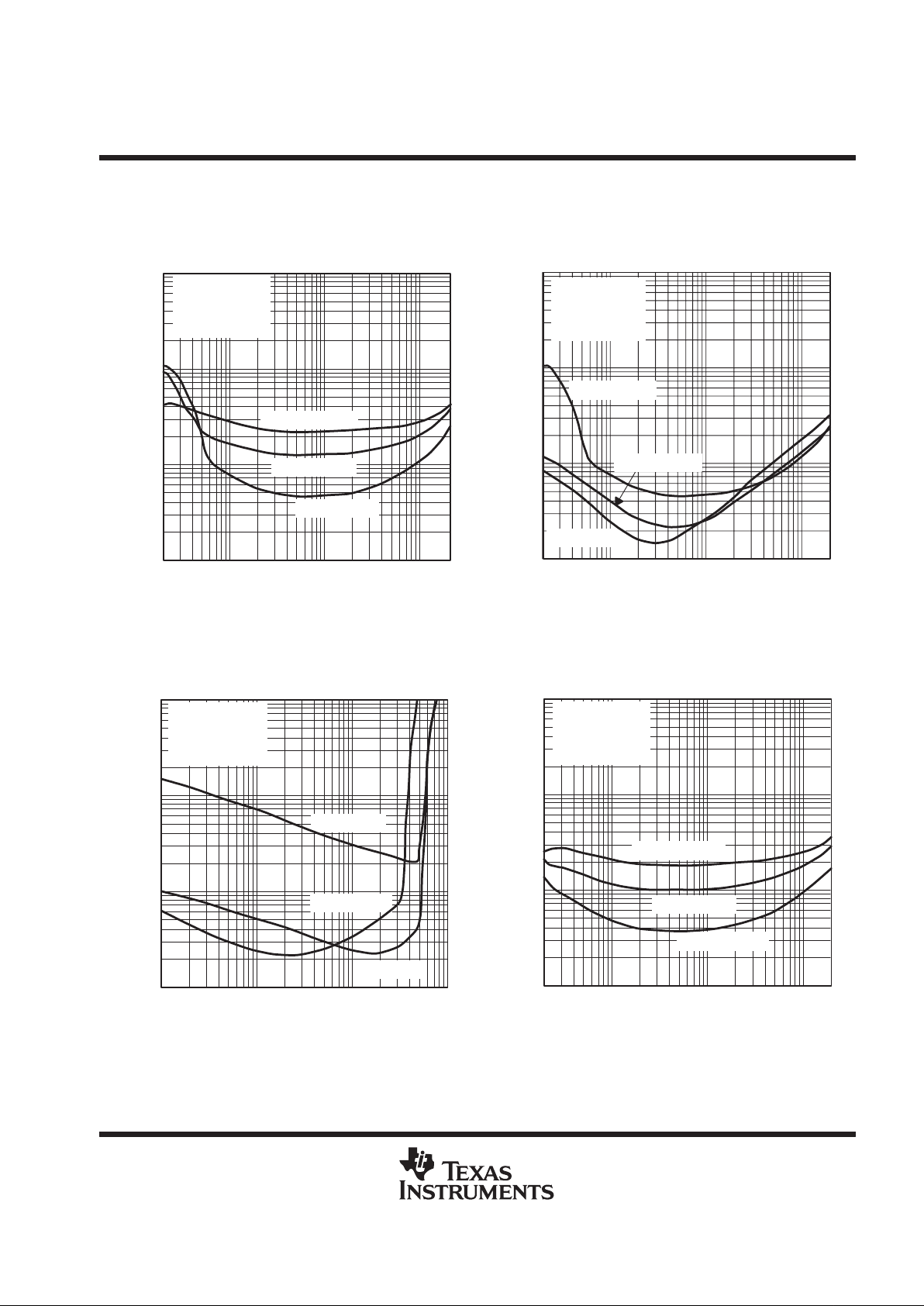
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 17
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
PO = 0.5 W
RL = 4 Ω
SE
Figure 18
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 0.1 W
PO = 0.5 W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
SE
Figure 19
f = 20 kHz
f =100 Hz
f = 1 kHz
VDD = 5 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
SE
0.1
0.01
0.001 0.01
1
10
0.1 1
PO – Output Power – W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 20
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
PO = 0.25 W
RL = 8 Ω
SE
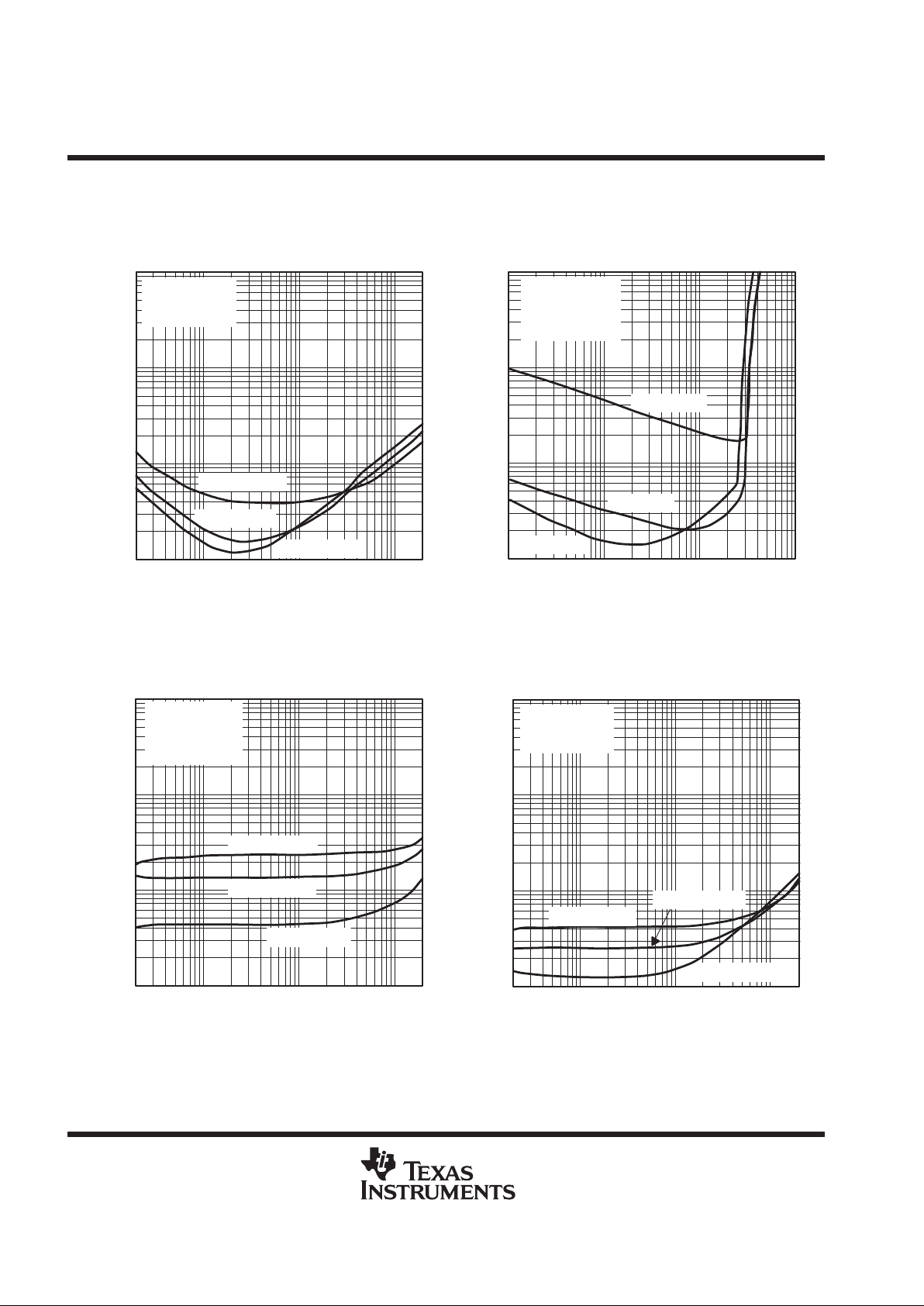
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 21
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 0.25 W
PO = 0.05 W
PO = 0.1 W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
SE
Figure 22
0.1
0.01
0.001 0.1
1
10
1
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 8 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
SE
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
0.01
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 100 Hz
Figure 23
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
PO = 0.075 W
RL = 32 Ω
SE
Figure 24
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 75 mW
PO = 25 mW
PO = 50 mW
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 5 V
RL = 32 Ω
SE

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 25
0.1
0.01
0.001 0.01
1
10
0.1 1
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 Hz
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 5 V
RL = 32 Ω
SE
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 26
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 0.2 W
RL = 4 Ω
SE
Figure 27
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 0.05 W
PO = 0.1 W
PO = 0.2 W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
SE
Figure 28
f = 100 Hz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 kHz
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
AV = –2 V/V
SE
0.1
0.01
0.001 0.01
1
10
10.1
PO – Output Power – W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
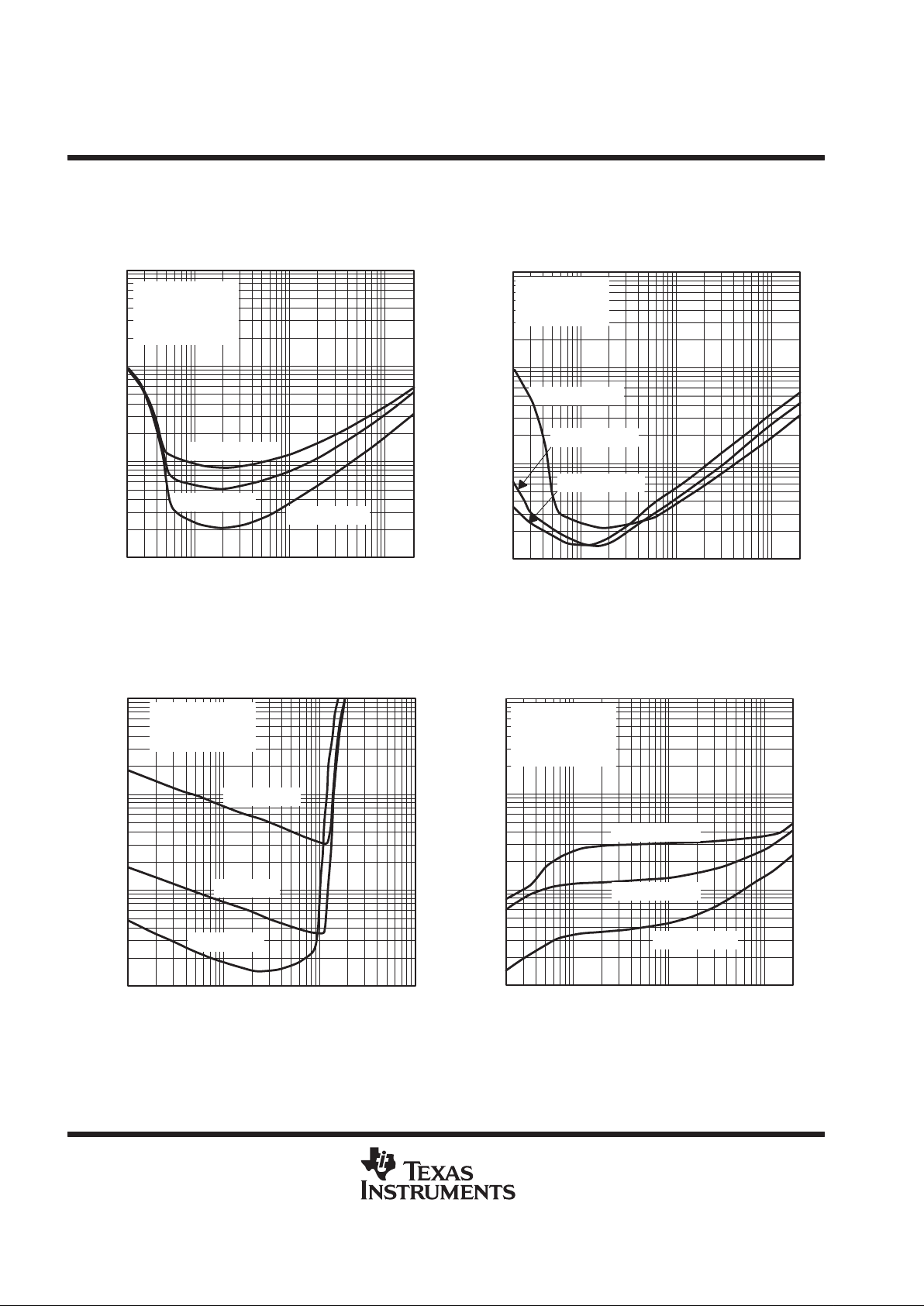
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 29
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 100 mW
RL = 8 Ω
SE
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
Figure 30
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 25 mW
PO = 50 mW
PO = 100 mW
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
SE
Figure 31
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 8 Ω
SE
0.1
0.01
0.001 0.1
1
10
1
PO – Output Power – W
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
f = 20 kHz
f = 1 kHz
f = 100 Hz
0.01
Figure 32
0.1
0.01
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
AV = –10 V/V
AV = –5 V/V
AV = –1 V/V
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 30 mW
RL = 32 Ω
SE

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 33
0.1
0.01
0.001
20 100 1 k
1
10
10 k 20 k
PO = 10 mW
PO = 20 mW
PO = 30 mW
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
f – Frequency – Hz
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
FREQUENCY
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 32 Ω
SE
Figure 34
0.1
0.01
0.001
0.001 0.01
1
10
0.1 1
f = 20 Hz
f = 1 kHz
f = 20 kHz
PO – Output Power – W
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 32 Ω
SE
THD+N –Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise – %
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs
OUTPUT POWER
Figure 35
10
1
20 100 1 k
f – Frequency – Hz
OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE
vs
FREQUENCY
100
10 k 20 k
VDD = 5 V
BW = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
RL = 4Ω
VO BTL
V
O+
V
O–
– Output Noise Voltage –
V
n
Vµ
(rms)
Figure 36
10
1
20 100 1 k
f – Frequency – Hz
OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE
vs
FREQUENCY
100
10 k 20 k
VDD = 3.3 V
BW = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
RL = 4Ω
VO BTL
V
O+
V
O–
– Output Noise Voltage –
V
n
Vµ
(rms)

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 37
–50
–60
–80
–100
20 100 1 k
Supply Ripple Rejection Ratio – dB
–30
–20
f – Frequency – Hz
SUPPLY RIPPLE REJECTION RATIO
vs
FREQUENCY
0
10 k 20 k
–10
–40
–70
–90
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
CB = 4.7 µF
BTL
Figure 38
–50
–60
–80
–100
20 100 1 k
–30
–20
f – Frequency – Hz
SUPPLY RIPPLE REJECTION RATIO
vs
FREQUENCY
0
10 k 20 k
–10
–40
–70
–90
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3.3 V
RL = 4 Ω
CB = 4.7 µF
SE
Supply Ripple Rejection Ratio – dB
Figure 39
Left to Right
Right to Left
–80
–90
–110
–120
–60
–50
–40
–70
–100
20 100 1 k
Crosstalk – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
CROSSTALK
vs
FREQUENCY
10 k 20 k
VDD = 5 V
PO = 1.5 W
RL = 4 Ω
BTL
Figure 40
–80
–90
–110
–120
–60
–50
–40
–70
–100
20 100 1 k
Crosstalk – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
CROSSTALK
vs
FREQUENCY
10 k 20 k
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 0.75 W
RL = 4 Ω
BTL
Left to Right
Right to Left

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 41
–80
–90
–110
–120
–60
–50
–40
–70
–100
20 100 1 k
Crosstalk – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
CROSSTALK
vs
FREQUENCY
10 k 20 k
VDD = 5 V
PO = 75 mW
RL = 32 Ω
SE
Left to Right
Right to Left
Figure 42
–80
–90
–110
–120
–60
–50
–40
–70
–100
20 100 1 k
Crosstalk – dB
f – Frequency – Hz
CROSSTALK
vs
FREQUENCY
10 k 20 k
VDD = 3.3 V
PO = 35 mW
RL = 32 Ω
SE
Left to Right
Right to Left
40
20
–20
–40
0.01
Gain – dB
60
80
f – Frequency – kHz
OPEN LOOP RESPONSE
100
0
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
180°
90°
0°
–90°
–180°
VDD = 5 V
BTL
Gain
Phase
Figure 43
Phase

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
20
0
–20
–40
40
60
80
180°
90°
0°
–90°
–180°
0.01
Gain – dB
f – Frequency – kHz
OPEN LOOP RESPONSE
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
VDD = 3.3 V
BTL
Gain
Figure 44
Phase
Phase
5
3
2
0
20 100 1 k 10 k
Gain – dB
7
9
f – Frequency – Hz
CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE
10
100 k 200 k
8
6
4
1
–45°
0°
–90°
–135°
–180°
–225°
–270°
Phase
Phase
Gain
VDD = 5 V
AV = –2 V/V
PO = 1.5 W
BTL
Figure 45

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
19
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
5
3
2
0
20 100 1 k 10 k
Gain – dB
7
9
f – Frequency – Hz
CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE
10
100 k 200 k
8
6
4
1
–45°
0°
–90°
–135°
–180°
–225°
–270°
Phase
Phase
Gain
VDD = 3.3 V
AV = –2 V/V
PO = 0.75 W
BTL
Figure 46
Figure 47
–5
–7
–8
–10
20 100 1 k 10 k
Gain – dB
–3
–1
f – Frequency – Hz
CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE
0
100 k 200 k
–2
–4
–6
–9
–45°
0°
–90°
–135°
–180°
–225°
–270°
Phase
VDD = 5 V
AV = –1 V/V
PO = 0.5 W
SE
Phase
Gain

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
–5
–7
–8
–10
20 100 1 k 10 k
Gain – dB
–3
–1
f – Frequency – Hz
CLOSED LOOP RESPONSE
0
100 k 200 k
–2
–4
–6
–9
–45°
0°
–90°
–135°
–180°
–225°
–270°
Phase
VDD = 3.3V
AV = –1 V/V
PO = 0.25 W
SE
Phase
Gain
Figure 48
Figure 49
Stereo BTL
15
10
5
0
3
20
25
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
30
465
VDD – Supply Voltage – V
Stereo SE
– Supply Current – mA
I
DD
Figure 50
1.5
1
0.5
0
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
2
2.5
3
5.5 6
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
– Output Power – WP
O
OUTPUT POWER
vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
VDD – Supply Voltage – V
THD+N = 1%
BTL
Each Channel

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 51
0.4
0.2
0
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
0.6
0.8
1
5.5 6
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
RL = 32 Ω
THD+N = 1%
SE
Each Channel
– Output Power – WP
O
OUTPUT POWER
vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
VDD – Supply Voltage – V
Figure 52
RL – Load Resistance – Ω
1.5
1
0.5
0
04 8121620
2
2.5
3
24 28 32
THD+N = 1%
BTL
Each Channel
– Output Power – WP
O
OUTPUT POWER
vs
LOAD RESISTANCE
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3.3 V
Figure 53
0.4
0.2
0
04 8121620
0.6
0.8
1
24 28 32
RL – Load Resistance – Ω
THD+N = 1%
SE
Each Channel
– Output Power – WP
O
OUTPUT POWER
vs
LOAD RESISTANCE
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3.3 V
Figure 54
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0 0.5 1
– Power Dissipation – W
1
1.2
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
OUTPUT POWER
1.4
1.5 2
0.8
PO – Output Power – W
P
D
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
VDD = 5 V
BTL
Each Channel

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 55
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.25 0.5
– Power Dissipation – W
0.4
0.5
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
OUTPUT POWER
0.6
0.75 1
PO – Output Power – W
P
D
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
VDD = 3.3 V
BTL
Each Channel
Figure 56
0.4
0.2
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3
0.6
0.8
0.4 0.5 0.6
– Power Dissipation – W
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
OUTPUT POWER
PO – Output Power – W
P
D
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
VDD = 5 V
SE
Each Channel
RL = 32Ω
Figure 57
0.2
0
0 0.05 0.1 0.15
0.4
0.6
0.2 0.25
– Power Dissipation – W
POWER DISSIPATION
vs
OUTPUT POWER
PO – Output Power – W
P
D
RL = 4 Ω
RL = 8 Ω
VDD = 3.3V
SE
Each Channel
RL = 32Ω

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
23
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
THERMAL INFORMATION
The thermally enhanced PWP package is based on the 24-pin TSSOP, but includes a thermal pad (see Figure 58)
to provide an effective thermal contact between the IC and the PWB.
Traditionally, surface mount and power have been mutually exclusive terms. A variety of scaled-down TO-220-type
packages have leads formed as gull wings to make them applicable for surface-mount applications. These packages,
however, have only two shortcomings: they do not address the very low profile requirements (<2 mm) of many of
today’s advanced systems, and they do not offer a terminal-count high enough to accommodate increasing
integration. On the other hand, traditional low-power surface-mount packages require power-dissipation derating that
severely limits the usable range of many high-performance analog circuits.
The PowerP AD package (thermally enhanced TSSOP) combines fine-pitch surface-mount technology with thermal
performance comparable to much larger power packages.
The PowerPAD package is designed to optimize the heat transfer to the PWB. Because of the very small size and
limited mass of a TSSOP package, thermal enhancement is achieved by improving the thermal conduction paths that
remove heat from the component. The thermal pad is formed using a patented lead-frame design and manufacturing
technique to provide a direct connection to the heat-generating IC. When this pad is soldered or otherwise thermally
coupled to an external heat dissipator, high power dissipation in the ultra-thin, fine-pitch, surface-mount package can
be reliably achieved.
DIE
Side View (a)
End View (b)
Bottom View (c)
DIE
Thermal
Pad
Figure 58. Views of Thermally Enhanced PWP Package

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
24
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
bridged-tied load versus single-ended mode
Figure 59 shows a linear audio power amplifier (APA) in a BTL configuration. The TPA0102 BTL amplifier
consists of two linear amplifiers driving both ends of the load. There are several potential benefits to this
differential drive configuration but initially consider power to the load. The differential drive to the speaker means
that as one side is slewing up, the other side is slewing down, and vice versa. This in effect doubles the voltage
swing on the load as compared to a ground referenced load. Plugging 2 × V
O(PP)
into the power equation, where
voltage is squared, yields 4× the output power from the same supply rail and load impedance (see equation 1).
Power
+
V
(rms)
2
R
L
(1)
V
(rms)
+
V
O(PP)
22
Ǹ
R
L
2x V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
–V
O(PP)
V
DD
V
DD
Figure 59. Bridge-Tied Load Configuration
In a typical computer sound channel operating at 5 V, bridging raises the power into an 8-Ω speaker from a
singled-ended (SE, ground reference) limit of 250 mW to 1 W. In sound power that is a 6-dB improvement —
which is loudness that can be heard. In addition to increased power there are frequency response concerns.
Consider the single-supply SE configuration shown in Figure 60. A coupling capacitor is required to block the
dc offset voltage from reaching the load. These capacitors can be quite large (approximately 33 µF to 1000 µF)
so they tend to be expensive, heavy , occupy valuable PCB area, and have the additional drawback of limiting
low-frequency performance of the system. This frequency limiting effect is due to the high pass filter network
created with the speaker impedance and the coupling capacitance and is calculated with equation 2.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
25
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
fc+
1
2pR
L
C
C
(2)
For example, a 68-µF capacitor with an 8-Ω speaker would attenuate low frequencies below 293 Hz. The BTL
configuration cancels the dc offsets, which eliminates the need for the blocking capacitors. Low-frequency
performance is then limited only by the input network and speaker response. Cost and PCB space are also
minimized by eliminating the bulky coupling capacitor.
R
L
C
C
V
O(PP)
V
O(PP)
V
DD
–3 dB
f
c
Figure 60. Single-Ended Configuration and Frequency Response
Increasing power to the load does carry a penalty of increased internal power dissipation. The increased
dissipation is understandable considering that the BTL configuration produces 4× the output power of the SE
configuration. Internal dissipation versus output power is discussed further in the
thermal considerations
section.
BTL amplifier efficiency
Linear amplifiers are notoriously inefficient. The primary cause of these inefficiencies is voltage drop across the
output stage transistors. There are two components of the internal voltage drop. One is the headroom or dc
voltage drop that varies inversely to output power. The second component is due to the sinewave nature of the
output. The total voltage drop can be calculated by subtracting the RMS value of the output voltage from VDD.
The internal voltage drop multiplied by the RMS value of the supply current, I
DD
rms, determines the internal
power dissipation of the amplifier.
An easy-to-use equation to calculate efficiency starts out as being equal to the ratio of power from the power
supply to the power delivered to the load. To accurately calculate the RMS values of power in the load and in
the amplifier, the current and voltage waveform shapes must first be understood (see Figure 61).
V
(LRMS)
V
O
I
DD
I
DD(RMS)
Figure 61. Voltage and Current Waveforms for BTL Amplifiers

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
26
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Although the voltages and currents for SE and BTL are sinusoidal in the load, currents from the supply are very
different between SE and BTL configurations. In an SE application the current waveform is a half-wave rectified
shape whereas in BTL it is a full-wave rectified waveform. This means RMS conversion factors are different.
Keep in mind that for most of the waveform both the push and pull transistors are not on at the same time, which
supports the fact that each amplifier in the BTL device only draws current from the supply for half the waveform.
The following equations are the basis for calculating amplifier efficiency.
I
DD
rms
+
2V
P
p
R
L
P
SUP
+
VDDIDDrms
+
VDD2V
P
p
R
L
Efficiency
+
P
L
P
SUP
Efficiency of a BTL Configuration
+
p
V
P
2V
+
p
ǒ
PLR
L
2
Ǔ
1ń2
2V
(3)
Where:
(4)
PL+
VLrms
2
R
L
+
V
p
2
2R
L
VLrms
+
V
P
2
Ǹ
T able 1 employs equation 4 to calculate efficiencies for four different output power levels. Note that the efficiency
of the amplifier is quite low for lower power levels and rises sharply as power to the load is increased resulting
in a nearly flat internal power dissipation over the normal operating range. Note that the internal dissipation at
full output power is less than in the half power range. Calculating the efficiency for a specific system is the key
to proper power supply design. For a stereo 1-W audio system with 8-Ω loads and a 5-V supply , the maximum
draw on the power supply is almost 3.25 W.
Table 1. Efficiency Vs Output Power in 5-V 8-Ω BTL Systems
OUTPUT POWER
(W)
EFFICIENCY
(%)
PEAK-TO-PEAK
VOLTAGE
(V)
INTERNAL
DISSIPATION
(W)
0.25 31.4 2.00 0.55
0.50 44.4 2.83 0.62
1.00 62.8 4.00 0.59
1.25 70.2 4.47
†
0.53
†
High peak voltages cause the THD to increase.
A final point to remember about linear amplifiers (either SE or BTL) is how to manipulate the terms in the
efficiency equation to utmost advantage when possible. Note that in equation 4, VDD is in the denominator. This
indicates that as VDD goes down, efficiency goes up.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
27
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
For example, if the 5-V supply is replaced with a 3.3-V supply (TP A0102 has a maximum recommended V
DD
of 5.5 V) in the calculations of T able 1, then ef ficiency at 0.5 W would rise from 44% to 67% and internal power
dissipation would fall from 0.62 W to 0.25 W at 5 V. Then for a stereo 0.5-W system from a 3.3-V supply, the
maximum draw would only be 1.5 W as compared to 2.24 W from 5 V . In other words, use the efficiency analysis
to chose the correct supply voltage and speaker impedance for the application.
selection of components
Figure 62 and Figure 63 are a schematic diagrams of a typical notebook computer application circuits.
C
B
C
S
Right
MUX
RLINEIN
RHPIN
Left
MUX
LHPIN
LLINEIN
Bias, Mute,
Shutdown,
and SE/BTL
MUX Control
+
–
+
–
RBYPASS
MUTE IN
MUTE OUT
SHUTDOWN
LBYPASS
ROUT+
ROUT–
RV
DD
LV
DD
LOUT+
LOUT–
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
C
IR
R
IR
R
FR
C
FR
System
Control
C
IL
R
IL
NC
NC
4
5
6
8
9
11
19
20
21
R
FL
C
FL
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
V
DD
V
DD
C
OUTR
C
OUTL
10
3
16
7
14
18
15
22
1 kΩ
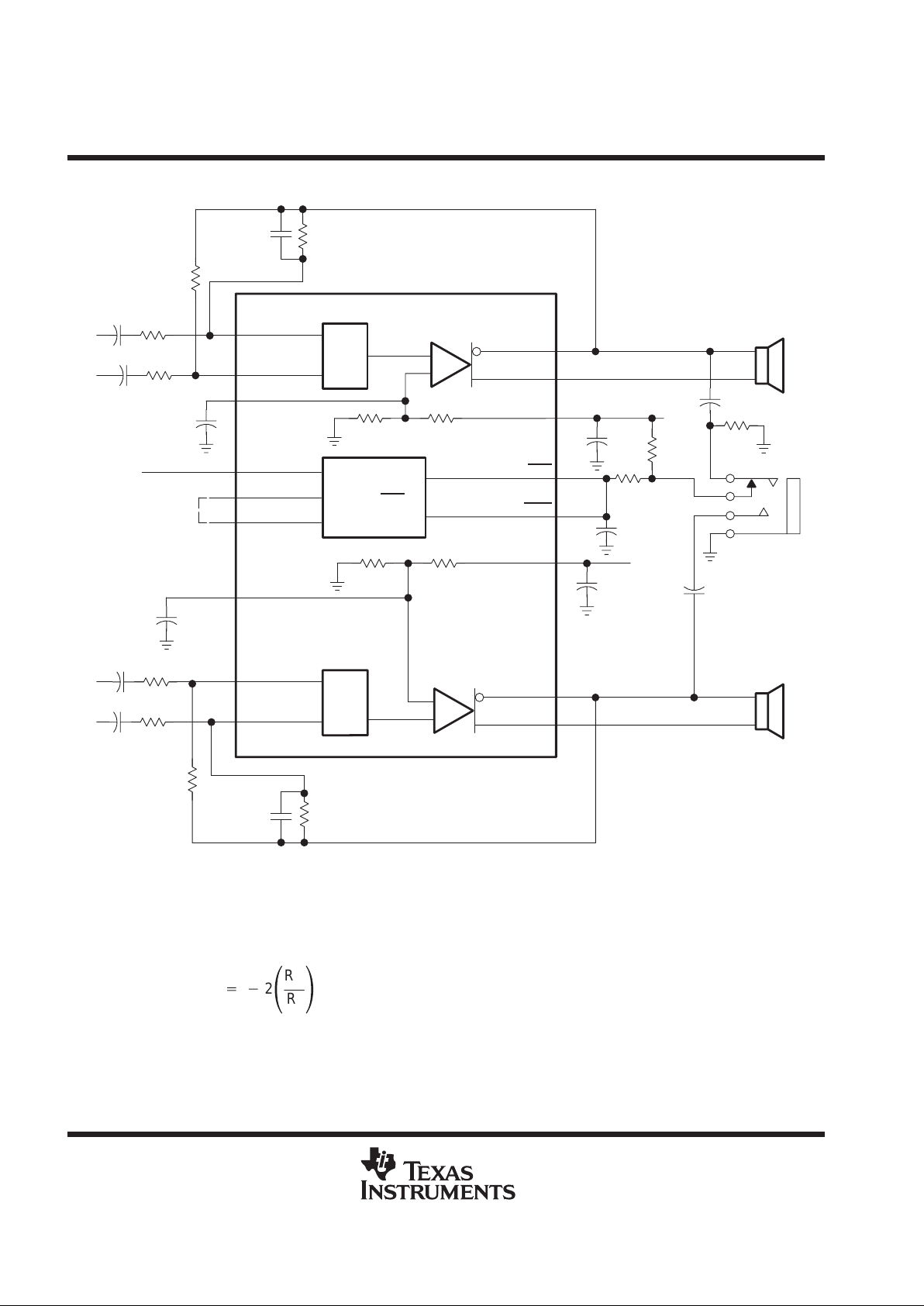
0.1 µF
Figure 62. TPA0102 Minimum Configuration Application Circuit
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
28
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
C
BR
C
SR
Right
MUX
RLINEIN
RHPIN
Left
MUX
LHPIN
LLINEIN
Bias, Mute,
Shutdown,
and SE/BTL
MUX Control
+
–
+
–
RBYPASS
MUTE IN
MUTE OUT
SHUTDOWN
LBYPASS
ROUT+
ROUT–
RV
DD
LV
DD
LOUT+
LOUT–
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
C
IRLINE
R
IRLINE
R
FRLINE
C
FRLINE
System
Control
C
ILLINE
R
ILLINE
4
5
6
8
9
11
19
20
21
R
FLLINE
C
FLLINE
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
V
DD
C
OUTR
C
OUTL
10
3
16
7
14
18
15
22
1 kΩ
C
IRHP
R
IRHP
R
FRHP
See Note A
C
BL
C
ILHP
R
ILHP
R
FLHP
C
SR
V
DD
0.1 µF
NOTE A: This connection is for ultralow current in shutdown mode.
Figure 63. TPA0102 Full Configuration Application Circuit
gain setting resistors, RF and R
I
The gain for each audio input of the TP A0102 is set by resistors RF and RI according to equation 5 for BTL mode.
(5)
BTL Gain+*
2
ǒ
R
F
R
I
Ǔ
TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
29
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
gain setting resistors, RF and RI (continued)
BTL mode operation brings about the factor 2 in the gain equation due to the inverting amplifier mirroring the
voltage swing across the load. Given that the TPA0102 is a MOS amplifier, the input impedance is very high,
consequently input leakage currents are not generally a concern although noise in the circuit increases as the
value of RF increases. In addition, a certain range of RF values are required for proper startup operation of the
amplifier. Taken together it is recommended that the effective impedance seen by the inverting node of the
amplifier be set between 5 kΩ and 20 kΩ. The effective impedance is calculated in equation 6.
(6)
Effective Impedance
+
R
FRI
RF)
R
I
As an example consider an input resistance of 10 kΩ and a feedback resistor of 50 kΩ. The BTL gain of the
amplifier would be –10 and the effective impedance at the inverting terminal would be 8.3 kΩ, which is well within
the recommended range.
For high performance applications metal film resistors are recommended because they tend to have lower noise
levels than carbon resistors. For values of RF above 50 kΩ the amplifier tends to become unstable due to a pole
formed from RF and the inherent input capacitance of the MOS input structure. For this reason, a small
compensation capacitor of approximately 5 pF should be placed in parallel with R
F
when RF is greater than
50 kΩ. This, in effect, creates a low pass filter network with the cutoff frequency defined in equation 7.
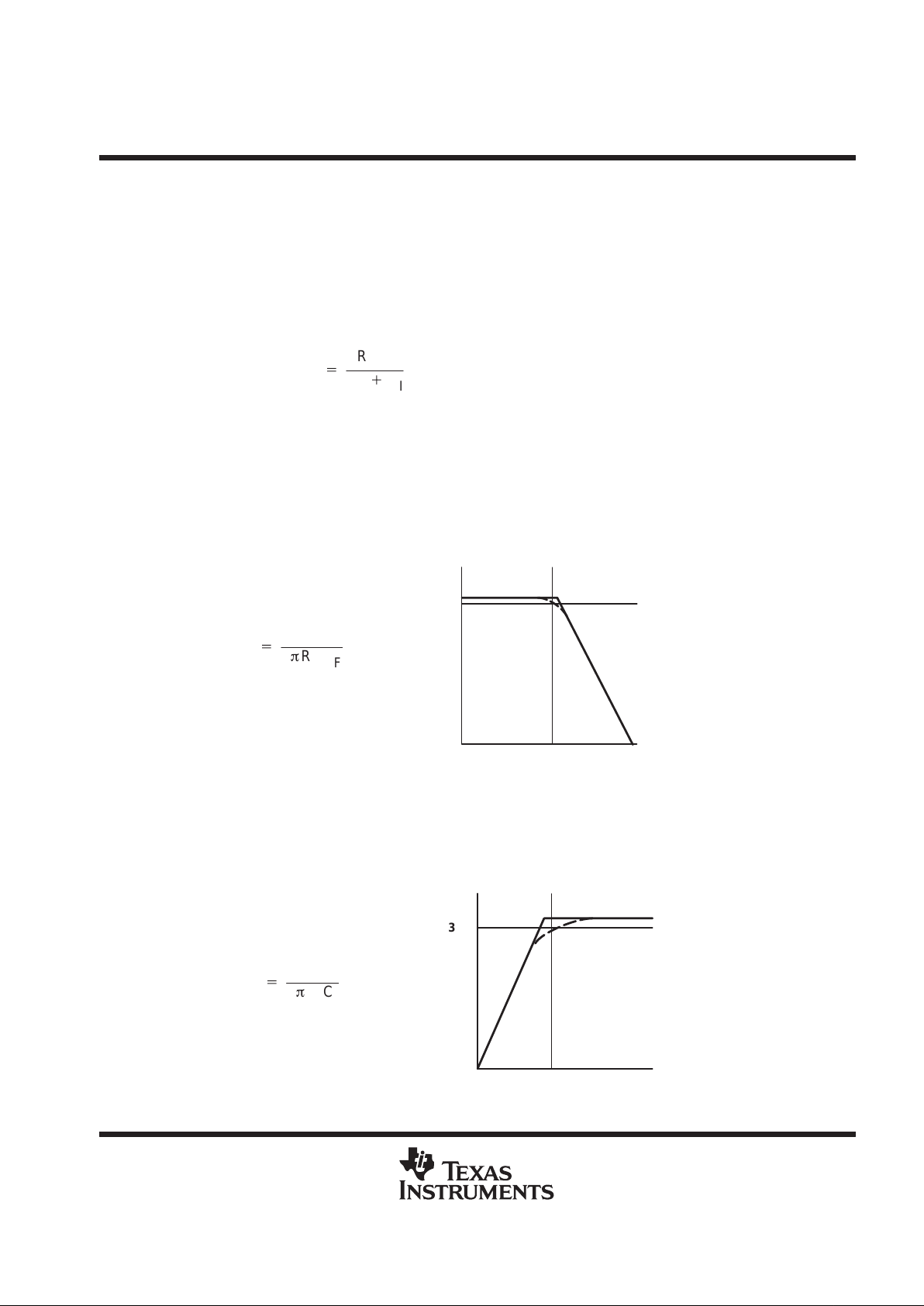
(7)
f
c(lowpass)
+
1
2pRFC
F
–3 dB
f
c
For example, if RF is 100 kΩ and Cf is 5 pF then fc is 318 kHz, which is well outside of the audio range.
input capacitor, C
I
In the typical application an input capacitor, CI, is required to allow the amplifier to bias the input signal to the
proper dc level for optimum operation. In this case, CI and RI form a high-pass filter with the corner frequency
determined in equation 8.
(8)
f
c(highpass)
+
1
2pRIC
I
–3 dB
f
c

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
30
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
input capacitor, CI (continued)
The value of CI is important to consider as it directly affects the bass (low frequency) performance of the circuit.
Consider the example where RI is 10 kΩ and the specification calls for a flat bass response down to 40 Hz.
Equation 8 is reconfigured as equation 9.
(9)
C
I
+
1
2pRIf
c
In this example, CI is 0.40 µF so one would likely choose a value in the range of 0.47 µF to 1 µF. A further
consideration for this capacitor is the leakage path from the input source through the input network (RI, CI) and
the feedback resistor (RF) to the load. This leakage current creates a dc offset voltage at the input to the amplifier
that reduces useful headroom, especially in high gain applications. For this reason a low-leakage tantalum or
ceramic capacitor is the best choice. When polarized capacitors are used, the positive side of the capacitor
should face the amplifier input in most applications as the dc level there is held at V
DD
/2, which is likely higher
than the source dc level. Please note that it is important to confirm the capacitor polarity in the application.
power supply decoupling, C
S
The TPA0102 is a high-performance CMOS audio amplifier that requires adequate power supply decoupling
to ensure the output total harmonic distortion (THD) is as low as possible. Power supply decoupling also
prevents oscillations for long lead lengths between the amplifier and the speaker. The optimum decoupling is
achieved by using two capacitors of different types that target different types of noise on the power supply leads.
For higher frequency transients, spikes, or digital hash on the line, a good low equivalent-series-resistance
(ESR) ceramic capacitor, typically 0.1 µF placed as close as possible to the device V
DD
lead works best. For
filtering lower-frequency noise signals, a larger aluminum electrolytic capacitor of 10 µF or greater placed near
the audio power amplifier is recommended.
midrail bypass capacitor, C
B
The midrail bypass capacitor, CB, serves several important functions. During startup or recovery from shutdown
mode, CB determines the rate at which the amplifier starts up. The second function is to reduce noise produced
by the power supply caused by coupling into the output drive signal. This noise is from the midrail generation
circuit internal to the amplifier. The capacitor is fed from a 25-kΩ source inside the amplifier . T o keep the start-up
pop as low as possible, the relationship shown in equation 10 should be maintained.
(10)
1
ǒ
CB
25 kΩ
Ǔ
v
1
ǒ
CIR
I
Ǔ
As an example, consider a circuit where CB is 0.1 µF, CI is 0.22 µF and RI is 10 kΩ. Inserting these values into
the equation 10 we get 400 ≤ 454 which satisfies the rule. Bypass capacitor, CB, values of 0.1 µF to 1 µF ceramic
or tantalum low-ESR capacitors are recommended for the best THD and noise performance.
In Figure 63, the full feature configuration, two bypass capacitors are used. This provides the maximum
separation between right and left drive circuits. When absolute minimum cost and/or component space is
required, one bypass capacitor can be used as shown in Figure 62. It is critical that terminals 6 and 19 be tied
together in this configuration.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
31
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
single-ended operation
In SE mode (see Figure 59 and Figure 60), the load is driven from the primary amplifier output for each channel
(OUT+, terminals 22 and 3).
In SE mode the gain is set by the RF and RI resistors and is shown in equation 1 1. Since the inverting amplifier
is not used to mirror the voltage swing on the load, the factor of 2, from equation 5, is not included.
(11)
SE Gain
+
*
ǒ
R
F
R
I
Ǔ
The output coupling capacitor required in single-supply SE mode also places additional constraints on the
selection of other components in the amplifier circuit. The rules described earlier still hold with the addition of
the following relationship:
(12)
1
ǒ
CB
25 kΩ
Ǔ
v
1
ǒ
CIR
I
Ǔ
Ơ
1
RLC
C
output coupling capacitor, C
C
In the typical single-supply SE configuration, an output coupling capacitor (C
C
) is required to block the dc bias
at the output of the amplifier thus preventing dc currents in the load. As with the input coupling capacitor, the
output coupling capacitor and impedance of the load form a high-pass filter governed by equation 13.
(13)
f
c(high)
+
1
2pRLC
C
–3 dB
f
c
The main disadvantage, from a performance standpoint, is the load impedances are typically small, which drives
the low-frequency corner higher degrading the bass response. Large values of C
C
are required to pass low
frequencies into the load. Consider the example where a CC of 330 µF is chosen and loads vary from 4 Ω, 8
Ω, 32 Ω, to 47 kΩ. Table 2 summarizes the frequency response characteristics of each configuration.
Table 2. Common Load Impedances Vs Low Frequency Output Characteristics in SE Mode
R
L
C
C
LOWEST FREQUENCY
4 Ω 330 µF 120 Hz
8 Ω 330 µF 60 Hz
32 Ω 330 µF
15 Hz
47,000 Ω 330 µF 0.01 Hz
As Table 2 indicates, most of the bass response is attenuated into a 4-Ω load, an 8-Ω load is adequate,
headphone response is good, and drive into line level inputs (a home stereo for example) is exceptional.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
32
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SE/BTL
operation
The ability of the TP A0102 to easily switch between BTL and SE modes is one of its most important cost saving
features. This feature eliminates the requirement for an additional headphone amplifier in applications where
internal stereo speakers are driven in BTL mode but external headphone or speakers must be accommodated.
Internal to the TPA0102, two separate amplifiers drive OUT+ and OUT–. The SE/BTL input (terminal 14)
controls the operation of the follower amplifier that drives LOUT– and ROUT– (terminals 10 and 15). When
SE/BTL
is held low, the amplifier is on and the TP A0102 is in the BTL mode. When SE/BTL is held high, the OUT–
amplifiers are in a high output impedance state, which configures the TPA0102 as an SE driver from LOUT+
and ROUT+ (terminals 3 and 22). IDD is reduced by approximately one-half in SE mode. Control of the SE/BTL
input can be from a logic-level CMOS source or, more typically, from a resistor divider network as shown in
Figure 64.
MUX
RLINE IN
RHP IN
+
–
Bypass
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
R
m2
100 kΩ
R
m1
100 kΩ
V
DD
C
OUTR
16
14
R
m3
1 kΩ
+
–
ROUT–
15
ROUT+ 22
Left
Channel
20
21
0.1 µF
Figure 64. TPA0102 Resistor Divider Network Circuit
Using a readily available 1/8-in. (3.5 mm) stereo headphone jack, the control switch is closed when no plug is
inserted. When closed the 100-kΩ/1-kΩ divider pulls the SE/BTL
input low. When a plug is inserted, the 1-kΩ
resistor is disconnected and the SE/BTL input is pulled high. When the input goes high, the OUT– amplifier is
shutdown causing the speaker to mute (virtually open-circuits the speaker). The OUT+ amplifier then drives
through the output capacitor (CO) into the headphone jack.
As shown in the full feature application (Figure 63), the input MUX control can be tied to the SE/BTL input. The
benefits of doing this are described in the following input MUX operation section.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
33
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Input MUX operation
Working in concert with the SE/BTL feature, the HP/LINE MUX feature gives the audio designer the flexibility
of a multichip design in a single IC (see Figure 65). The primary function of the MUX is to allow different gain
settings for BTL versus SE mode. Speakers typically require approximately a factor of 10 more gain for similar
volume listening levels as compared to headphones. To achieve headphone and speaker listening parity, the
resistor values would need to be set as follows:
(14)
SE Gain
(HP)
+
*
ǒ
R
F(HP)
R
I(HP)
Ǔ
If, for example R
I(HP)
= 20 kΩ and R
F(HP)
= 20 kΩ then SE Gain
(HP)
= –1
(15)
BTL Gain
(LINE)
+*
2
ǒ
R
F(LINE)
R
I(LINE)
Ǔ
If, for example R
I(LINE)
= 20 kΩ and R
F(LINE)
= 100 kΩ then BTL Gain
(LINE)
= –10
ROUT+
ROUT–
C
IRLINE
R
IRLINE
15
22
C
IRHP
R
IRHP
R
FRHP
MUX
RLINE IN
RHP IN
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
V
DD
16
14
+
–
Left Channel
20
21
Right Channel
MID
R
FRLINE
0.1 µF
Figure 65. TPA0102 Example Input MUX Circuit
Another advantage of using the MUX feature is setting the gain of the headphone channel to –1. This provides
the optimum distortion performance into the headphones where clear sound is more important. Refer to the
SE/BTL operation section for a description of the headphone jack control circuit.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
34
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
mute and shutdown modes
The TP A0102 employs both a mute and a shutdown mode of operation designed to reduce supply current, IDD,
to the absolute minimum level during periods of nonuse for battery-power conservation. The SHUTDOWN input
terminal should be held low during normal operation when the amplifier is in use. Pulling SHUTDOWN high
causes the outputs to mute and the amplifier to enter a low-current state, IDD < 1 µA. SHUTDOWN or MUTE
IN should never be left unconnected because amplifier operation would be unpredictable. Mute mode alone
reduces I
DD
< 1 mA.
Table 3. Shutdown and Mute Mode Functions
INPUTS
†
OUTPUT
AMPLIFIER STATE
SE/BTL
HP/LINE
MUTE IN SHUTDOWN MUTE OUT
INPUT OUTPUT
Low Low Low Low Low L/R Line BTL
X X — High — X Mute
X X High — High X Mute
Low High Low Low Low L/R HP BTL
High Low Low Low Low L/R Line SE
High High Low Low Low L/R HP SE
†
Inputs should never be left unconnected.
X = do not care
using low-ESR capacitors
Low-ESR capacitors are recommended throughout this applications section. A real (as opposed to ideal)
capacitor can be modeled simply as a resistor in series with an ideal capacitor. The voltage drop across this
resistor minimizes the beneficial effects of the capacitor in the circuit. The lower the equivalent value of this
resistance the more the real capacitor behaves like an ideal capacitor.
5-V versus 3.3-V operation
The TP A0102 operates over a supply range of 3 V to 5.5 V. This data sheet provides full specifications for 5-V
and 3.3-V operation, as these are considered to be the two most common standard voltages. There are no
special considerations for 3.3-V versus 5-V operation as far as supply bypassing, gain setting, or stability goes.
For 3.3-V operation, supply current is reduced from 19 mA (typical) to 13 mA (typical). The most important
consideration is that of output power. Each amplifier in TPA0102 can produce a maximum voltage swing of
V
DD
– 1 V. This means, for 3.3-V operation, clipping starts to occur when V
O(PP)
= 2.3 V as opposed to
V
O(PP)
= 4 V at 5 V . The reduced voltage swing subsequently reduces maximum output power into an 8-Ω load
before distortion becomes significant.
Operation from 3.3-V supplies, as can be shown from the efficiency formula in equation 4, consumes
approximately two-thirds the supply power for a given output-power level than operation from 5-V supplies.
When the application demands less than 500 mW, 3.3-V operation should be strongly considered, especially
in battery-powered applications.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
35
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
headroom and thermal considerations
Linear power amplifiers dissipate a significant amount of heat in the package under normal operating conditions.
A typical music CD requires 12 dB to 15 dB of dynamic headroom to pass the loudest portions without distortion
as compared with the average power output. From the TPA0102 data sheet, one can see that when the
TPA0102 is operating from a 5-V supply into a 4-Ω speaker that 1.5 W peaks are available. Converting watts
to dB:
PdB+
10Log
ǒ
P
W
P
ref
Ǔ
+
10Log
ǒ
1.5
1
Ǔ
+
1.76 dB
Subtracting the headroom restriction to obtain the average listening level without distortion yields:
1.76 dB*15 dB
+*
13.24 dB(15 dB headroom
)
1.76 dB*12 dB
+*
10.24 dB(12 dB headroom
)
1.76 dB*9dB
+*
7.24 dB(9 dB headroom
)
1.76 dB*6dB
+*
4.24 dB(6 dB headroom
)
1.76 dB*3dB
+*
1.24 dB(3 dB headroom
)
Converting dB back into watts:
P
W
+
10
PdBń10
P
ref
+
47 mW (15 dB headroom)
+
94 mW (12 dB headroom)
+
188 mW (9 dB headroom)
+
376 mW (6 dB headroom)
+
752 mW (3 dB headroom)
This is valuable information to consider when attempting to estimate the heat dissipation requirements for the
amplifier system. Comparing the absolute worst case, which is 1.5 W of continuous power output with 0 dB of
headroom, against 12 dB and 15 dB applications drastically affects maximum ambient temperature ratings for
the system. Using the power dissipation curves for a 5-V, 4-Ω system, the internal dissipation in the TPA0102
and maximum ambient temperatures is shown in Table 4.
Table 4. TPA0102 Power Rating, 5-V, 4-Ω, Stereo
PEAK OUTPUT POWER
(W)
AVERAGE OUTPUT POWER
POWER DISSIPATION
(W/Channel)
MAXIMUM AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
1.5 1.5 W 1.35 28°C
1.5 752 mW (3 dB) 1.3 33°C
1.5 376 mW (6 dB) 0.9 69°C
1.5 188 mW (9 dB) 0.7 87°C
1.5 94 mW (12 dB) 0.55 100°C
1.5 47 mW (15 dB) 0.4 114°C

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
36
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
headroom and thermal considerations (continued)
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
TA ≤ 25°C
DERATING FACTOR TA = 70°C TA = 85°C
PWP
†
2.7 W
21.8 mW/°C
1.7 W
1.4 W
PWP
‡
2.8 W
22.1 mW/°C 1.8 W 1.4 W
†
This parameter is measured with the recommended copper heat sink pattern on a 1-layer PCB, 4 in2 5-in × 5-in PCB,
1 oz. copper, 2-in × 2-in coverage.
‡
This parameter is measured with the recommended copper heat sink pattern on an 8-layer PCB, 6.9 in2 1.5-in × 2-in PCB,
1 oz. copper with layers 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, and 8 at 5% coverage (0.9 in2) and layers 3 and 6 at 100% coverage (6 in2).
The maximum ambient temperature depends on the heatsinking ability of the PCB system. Using the 0 CFM
and 300 CFM data from the dissipation rating table, the derating factor for the PWP package with 6.9 in
2
of
copper area on a multilayer PCB is 22 mW/°C and 54 mW/°C respectively. Converting this to ΘJA:
Θ
JA
+
1
Derating
+
1
0.022
+
45°CńW
To calculate maximum ambient temperatures, first consider that the numbers from the dissipation graphs are
per channel so the dissipated heat needs to be doubled for two channel operation. Given Θ
JA
, the maximum
allowable junction temperature, and the total internal dissipation, the maximum ambient temperature can be
calculated with the following equation. The maximum recommended junction temperature for the TP A0102 is
150 °C. The internal dissipation figures are taken from the Power Dissipation vs Output Power graphs.
TAMax+TJMax
*
Θ
JA
P
D
+
150*45(0.4 2)+
114°C(15 dB headroom, 0 CFM
)
NOTE:
Internal dissipation of 0.4 W is estimated for a 1.5-W system with 15 dB headroom per channel.
Table 4 shows that for most applications no airflow is required to keep junction temperatures in the specified
range. The TP A0102 is designed with thermal protection that turns the device off when the junction temperature
surpasses 150°C to prevent damage to the IC. Table 4 was calculated for maximum listening volume without
distortion. When the output level is reduced the numbers in the table change significantly. Also, using 8-Ω
speakers dramatically increases the thermal performance by increasing amplifier efficiency.

TPA0102
1.5-W STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
SLOS166E – MARCH 1997 – REVISED MARCH 2000
37
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PWP (R-PDSO-G**) PowerPAD PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE
2820
6,40
6,60
1614
5,10
4,904,90
5,10
4073225/F 10/98
0,50
0,75
0,25
0,15 NOM
Thermal Pad
(See Note D)
Gage Plane
24
7,70
7,90
9,60
9,80
6,60
6,20
11
0,19
4,50
4,30
10
0,15
20
A
1
0,30
1,20 MAX
PINS **
DIM
A MIN
A MAX
0,05
Seating Plane
0,65
0,10
M
0,10
0°–8°
20 PINS SHOWN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusions.
D. The package thermal performance may be enhanced by bonding the thermal pad to an external thermal plane.
This pad is electrically and thermally connected to the backside of the die and possibly selected leads.
E. Falls within JEDEC MO-153
For the latest package information, go to http://www.ti.com/sc/docs/package/pkg_info.htm
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...