查询SM320C6202BGDP167供应商
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
D Excellent Price/Performance Digital Signal
Processors (DSPs): TMS320C62x
(TMS320C6211 and TMS320C6211B)
− Eight 32-Bit Instructions/Cycle
− C6211, C6211B, C6711, and C6711B are
Pin-Compatible
− 150-, 167-MHz Clock Rates
− 6.7-, 6-ns Instruction Cycle Time
− 1200, 1333 MIPS
− Extended Temperature Device (C6211B)
D VelociTI Advanced Very Long Instruction
Word (VLIW) C62x DSP Core (C6211/11B)
− Eight Highly Independent Functional
Units:
− Six ALUs (32-/40-Bit)
− Two 16-Bit Multipliers (32-Bit Results)
− Load-Store Architecture With 32 32-Bit
General-Purpose Registers
− Instruction Packing Reduces Code Size
− All Instructions Conditional
D Instruction Set Features
− Byte-Addressable (8-, 16-, 32-Bit Data)
− 8-Bit Overflow Protection
− Saturation
− Bit-Field Extract, Set, Clear
− Bit-Counting
− Normalization
D L1/L2 Memory Architecture
− 32K-Bit (4K-Byte) L1P Program Cache
(Direct Mapped)
− 32K-Bit (4K-Byte) L1D Data Cache
(2-Way Set-Associative)
− 512K-Bit (64K-Byte) L2 Unified Mapped
RAM/Cache
(Flexible Data/Program Allocation)
D Device Configuration
− Boot Mode: HPI, 8-, 16-, and 32-Bit ROM
Boot
− Endianness: Little Endian, Big Endian
D 32-Bit External Memory Interface (EMIF)
− Glueless Interface to Asynchronous
Memories: SRAM and EPROM
− Glueless Interface to Synchronous
Memories: SDRAM and SBSRAM
− 512M-Byte Total Addressable External
Memory Space
D Enhanced Direct-Memory-Access (EDMA)
Controller (16 Independent Channels)
D 16-Bit Host-Port Interface (HPI)
− Access to Entire Memory Map
D Two Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports
(McBSPs)
− Direct Interface to T1/E1, MVIP, SCSA
Framers
− ST-Bus-Switching Compatible
− Up to 256 Channels Each
− AC97-Compatible
− Serial-Peripheral-Interface (SPI)
Compatible (Motorola)
D Two 32-Bit General-Purpose Timers
D Flexible Phase-Locked-Loop (PLL) Clock
Generator
D IEEE-1149.1 (JTAG
†
)
Boundary-Scan-Compatible
D 256-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
(GFN Suffix)
D 0.18-µm/5-Level Metal Process
− CMOS Technology
D 3.3-V I/Os, 1.8-V Internal
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
TMS320C62x, VelociTI, and C62x are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Motorola is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
†
IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 Standard-Test-Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
Copyright 2004, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Table of Contents
GFN BGA package (bottom view) 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
description 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
device characteristics 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
device compatibility 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
functional block and CPU (DSP core) diagram 6. . . . . . . . . . .
CPU (DSP core) description 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
memory map summary 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
peripheral register descriptions 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PWRD bits in CPU CSR register description 15. . . . . . . . . . .
EDMA channel synchronization events 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
interrupt sources and interrupt selector 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
signal groups description 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
terminal functions 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
development support 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
documentation support 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
clock PLL 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
power-down logic 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
power-supply sequencing 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IEEE 1149.1 JTAG compatibility statement 38. . . . . . . . . . . . .
EMIF device speed 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
bootmode 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
absolute maximum ratings over operating case
temperature range 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
recommended operating conditions 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of
supply voltage and operating case temperature 40.
parameter measurement information 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
signal transition levels 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
timing parameters and board routing analysis 42. . . . . .
input and output clocks 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
asynchronous memory timing 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
synchronous-burst memory timing 50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
synchronous DRAM timing 52. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HOLD
/HOLDA timing 58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BUSREQ timing 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
reset timing 60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
external interrupt timing 62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
host-port interface timing 63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
multichannel buffered serial port timing 67. . . . . . . . . . . . .
timer timing 78. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
JTAG test-port timing 79. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
mechanical data 80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
revision history 81. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GFN BGA package (bottom view)
GFN 256-PIN BALL GRID ARRAY (BGA) PACKAGE
Y
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
( BOTTOM VIEW)
31
2468 201816141210
75
1915 1713119
2
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443

TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
description
The TMS320C62x DSPs (including the TMS320C6211/C6211B devices) compose one of the fixed-point DSP
families in the TMS320C6000 DSP platform. The TMS320C6211 (C6211) and TMS320C6211B (C6211B)
devices are based on the high-performance, advanced VelociTI very-long-instruction-word (VLIW)
architecture developed by Texas Instruments (TI), making these DSPs an excellent choice for multichannel and
multifunction applications.
With performance of up to 1333 million instructions per second (MIPS) at a clock rate of 167 MHz, the
C6211/C6211B device offers cost-effective solutions to high-performance DSP programming challenges. The
C6211/C6211B DSP possesses the operational flexibility of high-speed controllers and the numerical capability
of array processors. This processor has 32 general-purpose registers of 32-bit word length and eight highly
independent functional units. The eight functional units provide six arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for a high
degree of parallelism and two 16-bit multipliers for a 32-bit result. The C6211/C6211B can produce two
multiply-accumulates (MACs) per cycle for a total of 333 million MACs per second (MMACS). The
C6211/C6211B DSP also has application-specific hardware logic, on-chip memory, and additional on-chip
peripherals.
The C6211/C6211B uses a two-level cache-based architecture and has a powerful and diverse set of
peripherals. The Level 1 program cache (L1P) is a 32-Kbit direct mapped cache and the Level 1 data cache
(L1D) is a 32-Kbit 2-way set-associative cache. The Level 2 memory/cache (L2) consists of a 512-Kbit memory
space that is shared between program and data space. L2 memory can be configured as mapped memory,
cache, or combinations of the two.The peripheral set includes two multichannel buffered serial ports (McBSPs),
two general-purpose timers, a host-port interface (HPI), and a glueless external memory interface (EMIF)
capable of interfacing to SDRAM, SBSRAM and asynchronous peripherals.
The C6211/C6211B has a complete set of development tools which includes: a new C compiler, an assembly
optimizer to simplify programming and scheduling, and a Windows debugger interface for visibility into source
code execution.
TMS320C6000 is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
Windows is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
3
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
Periph
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
device characteristics
Table 1 provides an overview of the C6211/C6211B DSP. The table shows significant features of each device,
including the capacity of on-chip RAM, the peripherals, the execution time, and the package type with pin count.
For more details on the C6000 DSP device part numbers and part numbering, see Table 17 and Figure 4.
Table 1. Characteristics of the C6211/C6211B Processors
HARDWARE FEATURES
EMIF
(Clock source = ECLKIN)
EDMA
(Internal clock source =
CPU clock frequency)
erals
On-Chip
Memory
CPU ID+
CPU Rev ID
Frequency MHz 167, 150 167, 150
Cycle Time ns
Voltage
PLL Options CLKIN frequency multiplier Bypass (x1), x4 Bypass (x1), x4
BGA Package 27 x 27 mm 256-Pin BGA (GFN) 256-Pin BGA (GFN)
Process
Technology
Product Status
Product Preview (PP)
Advance Information (AI)
Production Data (PD)
HPI 1 1
McBSPs
(Internal clock source =
CPU/2 clock frequency)
32-Bit Timers
(Internal clock source =
CPU/4 clock frequency)
Size (Bytes) 72K 72K
4K-Byte (4KB) L1 Program (L1P) Cache
Organization
Control Status Register
(CSR.[31:16])
Core (V) 1.8 1.8
I/O (V) 3.3 3.3
µm 0.18 µm 0.18 µm
4KB L1 Data (L1D) Cache
64KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2)
C6211
(FIXED-POINT DSP)
1 1
1 1
2 2
2 2
4K-Byte (4KB) L1 Program (L1P) Cache
4KB L1 Data (L1D) Cache
64KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2)
0x0002 0x0002
6 ns (C6211-167)
6.7 ns (C6211-150)
PD PD
6.7 ns (C6211BGFNA-150)
C6211B
(FIXED-POINT DSP)
6 ns (C6211B-167)
6.7 ns (C6211B-150)
C6000 is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
4
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443

TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
device compatibility
The TMS320C6211/C6211B and C6711/C6711B devices are pin-compatible and have the same peripheral set;
thus, making new system designs easier and providing faster time to market. The following list summarizes the
device characteristic differences among the C6211, C6211B, C6711, and C6711B devices:
D The C6211 and C6211B devices have a fixed-point C62x CPU, while the C6711 and C6711B devices have
a floating-point C67x CPU.
D The C6211/C6211B device runs at -167 and -150 MHz clock speeds (with a C6211BGFNA extended
temperature device that also runs at -150 MHz), while the C6711/C6711B device runs at -150 and -100 MHz
(with a C6711BGFNA extended temperature device that also runs at -100 MHz).
For a more detailed discussion on the similarities/differences between the C6211 and C6711 devices, see the
How to Begin Development Today with the TMS320C6211 DSP and How to Begin Development with the
TMS320C6711 DSP application reports (literature number SPRA474 and SPRA522, respectively).
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
5
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
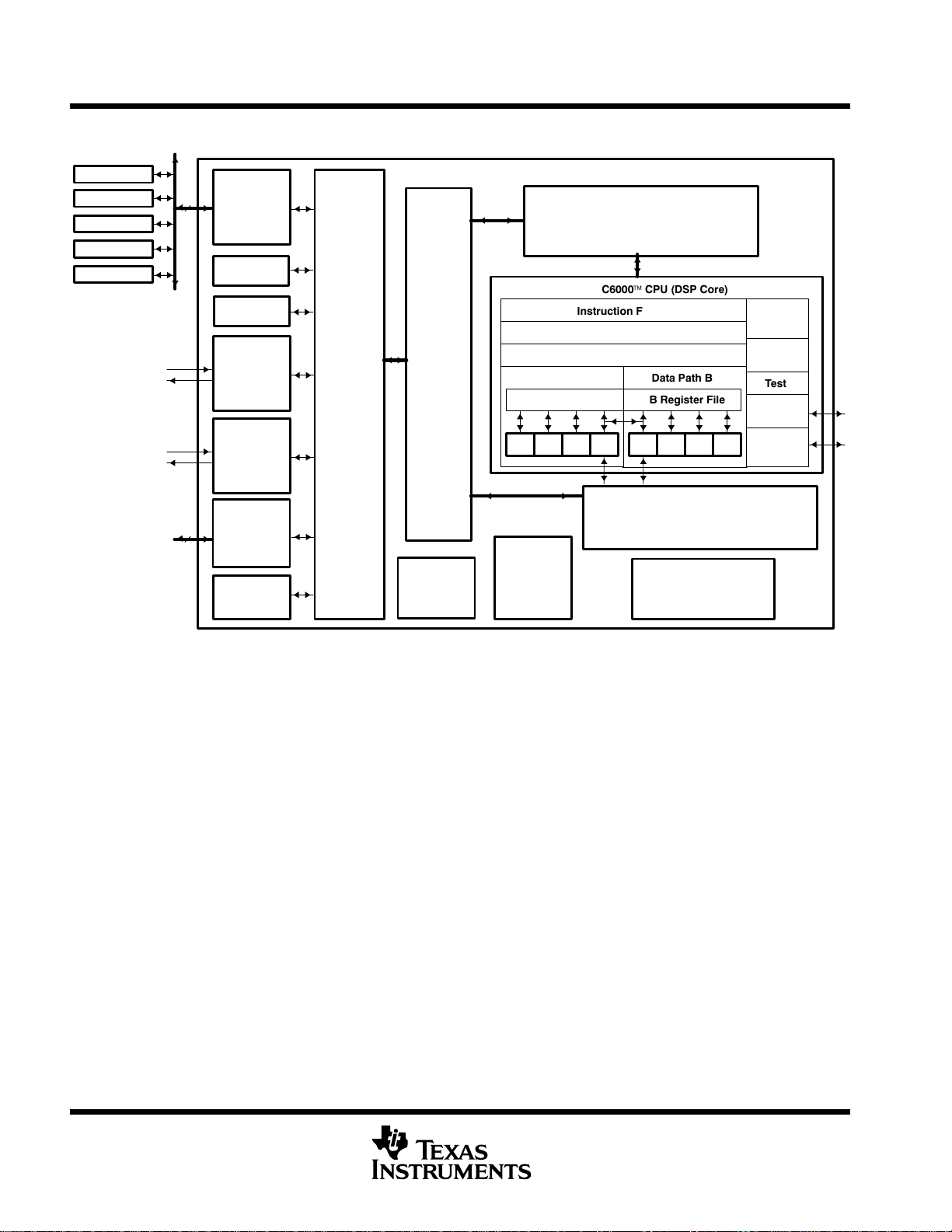
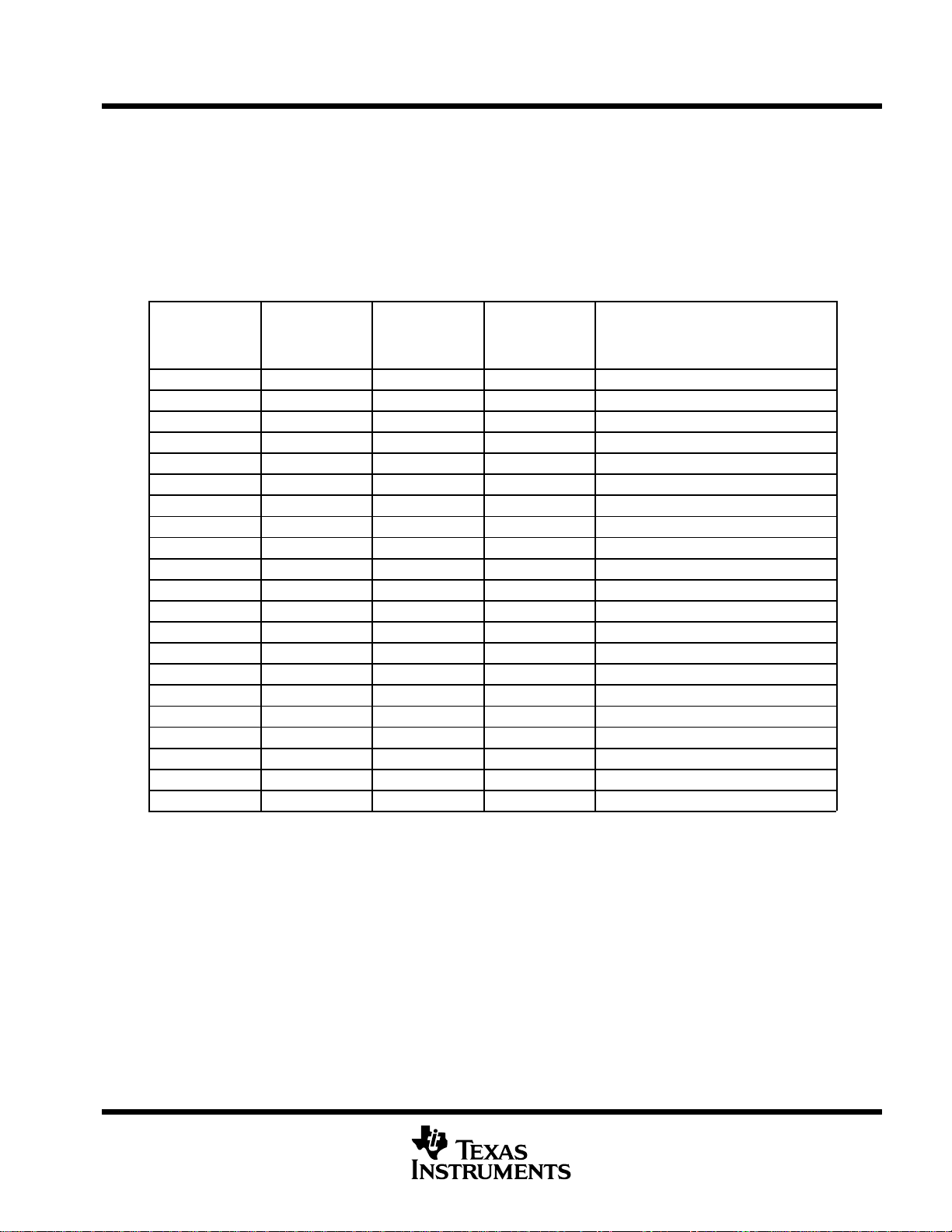
functional block and CPU (DSP core) diagram
SDRAM
SBSRAM
SRAM
ROM/FLASH
I/O Devices
Framing Chips:
H.100, MVIP,
SCSA, T1, E1
AC97 Devices,
SPI Devices,
Codecs
32
16
External
Memory
Interface
(EMIF)
Timer 0
Timer 1
Multichannel
Buffered
Serial Port 1
(McBSP1)
Multichannel
Buffered
Serial Port 0
(McBSP0)
Host Port
Interface
(HPI)
Interrupt
Selector
Enhanced
DMA
Controller
(16 channel)
L2
Memory
4 Banks
64K Bytes
Total
PLL
(x1, x4)
C6211/C6211B Digital Signal Processors
L1P Cache
Direct Mapped
4K Bytes Total
C6000 CPU (DSP Core)
Instruction Fetch
Instruction Dispatch
Instruction Decode
Data Path A
A Register File
.L1 .S1 .M1 .D1 .D2 .M2 .S2 .L2
Power-Down
Logic
Data Path B
B Register File
L1D Cache
2-Way Set
Associative
4K Bytes Total
Boot
Configuration
Control
Registers
Control
Logic
Test
In-Circuit
Emulation
Interrupt
Control
6
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443

TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
CPU (DSP core) description
The CPU fetches VelociTI advanced very-long instruction words (VLIW) (256 bits wide) to supply up to eight
32-bit instructions to the eight functional units during every clock cycle. The VelociTI VLIW architecture
features controls by which all eight units do not have to be supplied with instructions if they are not ready to
execute. The first bit of every 32-bit instruction determines if the next instruction belongs to the same execute
packet as the previous instruction, or whether it should be executed in the following clock as a part of the next
execute packet. Fetch packets are always 256 bits wide; however, the execute packets can vary in size. The
variable-length execute packets are a key memory-saving feature, distinguishing the C62x CPU from other
VLIW architectures.
The CPU features two sets of functional units. Each set contains four units and a register file. One set contains
functional units .L1, .S1, .M1, and .D1; the other set contains units .D2, .M2, .S2, and .L2. The two register files
each contain 16 32-bit registers for a total of 32 general-purpose registers. The two sets of functional units, along
with two register files, compose sides A and B of the CPU (see the functional block and CPU diagram and
Figure 1). The four functional units on each side of the CPU can freely share the 16 registers belonging to that
side. Additionally, each side features a single data bus connected to all the registers on the other side, by which
the two sets of functional units can access data from the register files on the opposite side. While register access
by functional units on the same side of the CPU as the register file can service all the units in a single clock cycle,
register access using the register file across the CPU supports one read and one write per cycle.
Another key feature of the C62x CPU is the load/store architecture, where all instructions operate on registers
(as opposed to data in memory). Two sets of data-addressing units (.D1 and .D2) are responsible for all data
transfers between the register files and the memory. The data address driven by the .D units allows data
addresses generated from one register file to be used to load or store data to or from the other register file. The
C62x CPU supports a variety of indirect addressing modes using either linear- or circular-addressing modes
with 5- or 15-bit offsets. All instructions are conditional, and most can access any one of the 32 registers. Some
registers, however, are singled out to support specific addressing or to hold the condition for conditional
instructions (if the condition is not automatically “true”). The two .M functional units are dedicated for multiplies.
The two .S and .L functional units perform a general set of arithmetic, logical, and branch functions with results
available every clock cycle.
The processing flow begins when a 256-bit-wide instruction fetch packet is fetched from a program memory.
The 32-bit instructions destined for the individual functional units are “linked” together by “1” bits in the least
significant bit (LSB) position of the instructions. The instructions that are “chained” together for simultaneous
execution (up to eight in total) compose an execute packet. A “0” in the LSB of an instruction breaks the chain,
effectively placing the instructions that follow it in the next execute packet. If an execute packet crosses the
fetch-packet boundary (256 bits wide), the assembler places it in the next fetch packet, while the remainder of
the current fetch packet is padded with NOP instructions. The number of execute packets within a fetch packet
can vary from one to eight. Execute packets are dispatched to their respective functional units at the rate of one
per clock cycle and the next 256-bit fetch packet is not fetched until all the execute packets from the current fetch
packet have been dispatched. After decoding, the instructions simultaneously drive all active functional units
for a maximum execution rate of eight instructions every clock cycle. While most results are stored in 32-bit
registers, they can be subsequently moved to memory as bytes or half-words as well. All load and store
instructions are byte-, half-word, or word-addressable.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
7
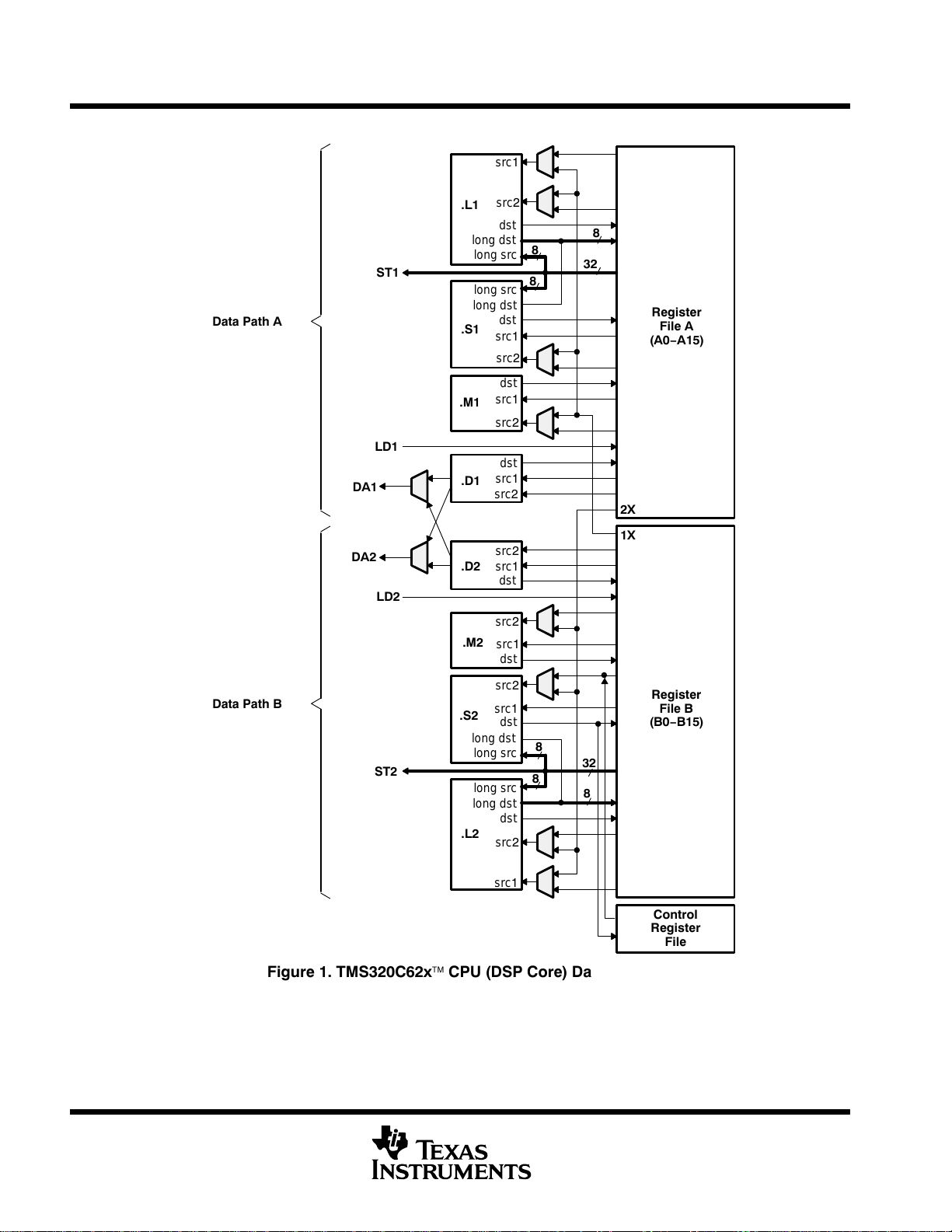
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
CPU (DSP core) description (continued)
ST1
Data Path A
LD1
DA1
DA2
LD2
.L1
long dst
long src
long src
long dst
.S1
.M1
.D1
.D2
.M2
src1
src2
dst
dst
src1
src2
dst
src1
src2
dst
src1
src2
src2
src1
dst
src2
src1
dst
8
8
32
8
Register
File A
(A0−A15)
2X
1X
Data Path B
Figure 1. TMS320C62x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths
ST2
.S2
long dst
long src
long src
long dst
.L2
src2
src1
dst
dst
src2
src1
Register
File B
(B0−B15)
8
32
8
8
Control
Register
File
8
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
memory map summary
Table 2 shows the memory map address ranges of the C6211/C6211B devices. Internal memory is always
located at address 0 and can be used as both program and data memory. The C6211/C6211B configuration
registers for the common peripherals are located at the same hex address ranges. The external memory
address ranges in the C6211/C6211B devices begin at the address location 0x8000 0000.
Table 2. TMS320C6211/C6211B Memory Map Summary
MEMORY BLOCK DESCRIPTION BLOCK SIZE (BYTES) HEX ADDRESS RANGE
Internal RAM (L2) 64K 0000 0000 – 0000 FFFF
Reserved 24M – 64K 0001 0000 – 017F FFFF
External Memory Interface (EMIF) Registers 256K 0180 0000 – 0183 FFFF
L2 Registers 256K 0184 0000 – 0187 FFFF
HPI Registers 256K 0188 0000 – 018B FFFF
McBSP 0 Registers 256K 018C 0000 – 018F FFFF
McBSP 1 Registers 256K 0190 0000 – 0193 FFFF
Timer 0 Registers 256K 0194 0000 – 0197 FFFF
Timer 1 Registers 256K 0198 0000 – 019B FFFF
Interrupt Selector Registers 256K 019C 0000 – 019F FFFF
EDMA RAM and EDMA Registers 256K 01A0 0000 – 01A3 FFFF
Reserved 6M – 256K 01A4 0000 – 01FF FFFF
QDMA Registers 52 0200 0000 – 0200 0033
Reserved 736M – 52 0200 0034 – 2FFF FFFF
McBSP 0/1 Data 256M 3000 0000 – 3FFF FFFF
Reserved 1G 4000 0000 – 7FFF FFFF
EMIF CE0
EMIF CE1
EMIF CE2
EMIF CE3
Reserved 1G C000 0000 – FFFF FFFF
†
The number of EMIF address pins (EA[21:2]) limits the maximum addressable memory (SDRAM) to 128MB per CE space. To get 256MB of
addressable memory, additional general-purpose output pin or external logic is required.
†
†
†
†
256M 8000 0000 – 8FFF FFFF
256M 9000 0000 – 9FFF FFFF
256M A000 0000 – AFFF FFFF
256M B000 0000 – BFFF FFFF
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
9
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
peripheral register descriptions
Table 3 through Table 13 identify the peripheral registers for the C6211/C6211B device by their register names,
acronyms, and hex address or hex address range. For more detailed information on the register contents, bit
names, and their descriptions, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Peripherals Overview Reference Guide (literature
number SPRU190).
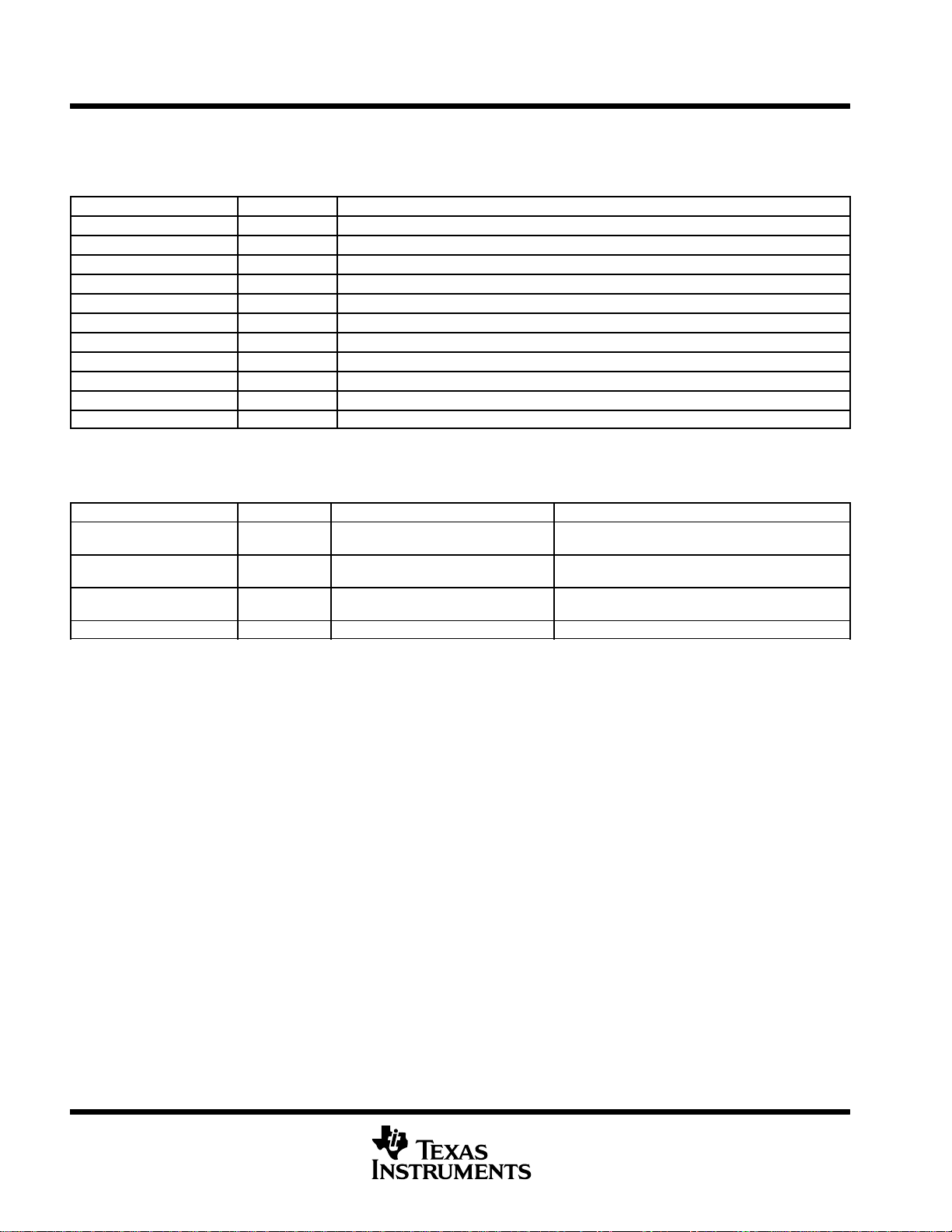
Table 3. EMIF Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
0180 0000 GBLCTL EMIF global control
0180 0004 CECTL1 EMIF CE1 space control
0180 0008 CECTL0 EMIF CE0 space control
0180 000C − Reserved
0180 0010 CECTL2 EMIF CE2 space control
0180 0014 CECTL3 EMIF CE3 space control
0180 0018 SDCTL EMIF SDRAM control
0180 001C SDTIM EMIF SDRAM refresh control
0180 0020 SDEXT EMIF SDRAM extension
0180 0024 − 0183 FFFF − Reserved
Table 4. L2 Cache Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
0184 0000 CCFG Cache configuration register
0184 4000 L2FBAR L2 flush base address register
0184 4004 L2FWC L2 flush word count register
0184 4010 L2CBAR L2 clean base address register
0184 4014 L2CWC L2 clean word count register
0184 4020 L1PFBAR L1P flush base address register
0184 4024 L1PFWC L1P flush word count register
0184 4030 L1DFBAR L1D flush base address register
0184 4034 L1DFWC L1D flush word count register
0184 5000 L2FLUSH L2 flush register
0184 5004 L2CLEAN L2 clean register
0184 8200 MAR0 Controls CE0 range 8000 0000 − 80FF FFFF
0184 8204 MAR1 Controls CE0 range 8100 0000 − 81FF FFFF
0184 8208 MAR2 Controls CE0 range 8200 0000 − 82FF FFFF
0184 820C MAR3 Controls CE0 range 8300 0000 − 83FF FFFF
0184 8240 MAR4 Controls CE1 range 9000 0000 − 90FF FFFF
0184 8244 MAR5 Controls CE1 range 9100 0000 − 91FF FFFF
0184 8248 MAR6 Controls CE1 range 9200 0000 − 92FF FFFF
0184 824C MAR7 Controls CE1 range 9300 0000 − 93FF FFFF
0184 8280 MAR8 Controls CE2 range A000 0000 − A0FF FFFF
0184 8284 MAR9 Controls CE2 range A100 0000 − A1FF FFFF
0184 8288 MAR10 Controls CE2 range A200 0000 − A2FF FFFF
0184 828C MAR11 Controls CE2 range A300 0000 − A3FF FFFF
0184 82C0 MAR12 Controls CE3 range B000 0000 − B0FF FFFF
0184 82C4 MAR13 Controls CE3 range B100 0000 − B1FF FFFF
0184 82C8 MAR14 Controls CE3 range B200 0000 − B2FF FFFF
0184 82CC MAR15 Controls CE3 range B300 0000 − B3FF FFFF
0184 82D0 − 0187 FFFF − Reserved
10
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
peripheral register descriptions (continued)
Table 5. EDMA Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
01A0 FF9C − 01A0 FFDC − Reserved
01A0 FFE0 PQSR Priority queue status register
01A0 FFE4 CIPR Channel interrupt pending register
01A0 FFE8 CIER Channel interrupt enable register
01A0 FFEC CCER Channel chain enable register
01A0 FFF0 ER Event register
01A0 FFF4 EER Event enable register
01A0 FFF8 ECR Event clear register
01A0 FFFC ESR Event set register
01A1 0000 − 01A3 FFFF – Reserved
Table 6. EDMA Parameter RAM
HEX ADDRESS RANGE
01A0 0000 − 01A0 0017 − Parameters for Event 0 (6 words)
01A0 0018 − 01A0 002F − Parameters for Event 1 (6 words)
01A0 0030 − 01A0 0047 − Parameters for Event 2 (6 words)
01A0 0048 − 01A0 005F − Parameters for Event 3 (6 words)
01A0 0060 − 01A0 0077 − Parameters for Event 4 (6 words)
01A0 0078 − 01A0 008F − Parameters for Event 5 (6 words)
01A0 0090 − 01A0 00A7 − Parameters for Event 6 (6 words)
01A0 00A8 − 01A0 00BF − Parameters for Event 7 (6 words)
01A0 00C0 − 01A0 00D7 − Parameters for Event 8 (6 words)
01A0 00D8 − 01A0 00EF − Parameters for Event 9 (6 words)
01A0 00F0 − 01A0 00107 − Parameters for Event 10 (6 words)
01A0 0108 − 01A0 011F − Parameters for Event 11 (6 words)
01A0 0120 − 01A0 0137 − Parameters for Event 12 (6 words)
01A0 0138 − 01A0 014F − Parameters for Event 13 (6 words)
01A0 0150 − 01A0 0167 − Parameters for Event 14 (6 words)
01A0 0168 − 01A0 017F − Parameters for Event 15 (6 words)
01A0 0180 − 01A0 0197 − Reload/link parameters for Event M (6 words)
01A0 0198 − 01A0 01AF − Reload/link parameters for Event N (6 words)
... ...
01A0 07E0 − 01A0 07F7 − Reload/link parameters for Event Z (6 words)
01A0 07F8 − 01A0 07FF − Scratch pad area (2 words)
†
The C6211/C6211B device has sixty-nine parameter sets [six (6) words each] that can be used to reload/link EDMA transfers.
ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
†
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
11
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
peripheral register descriptions (continued)
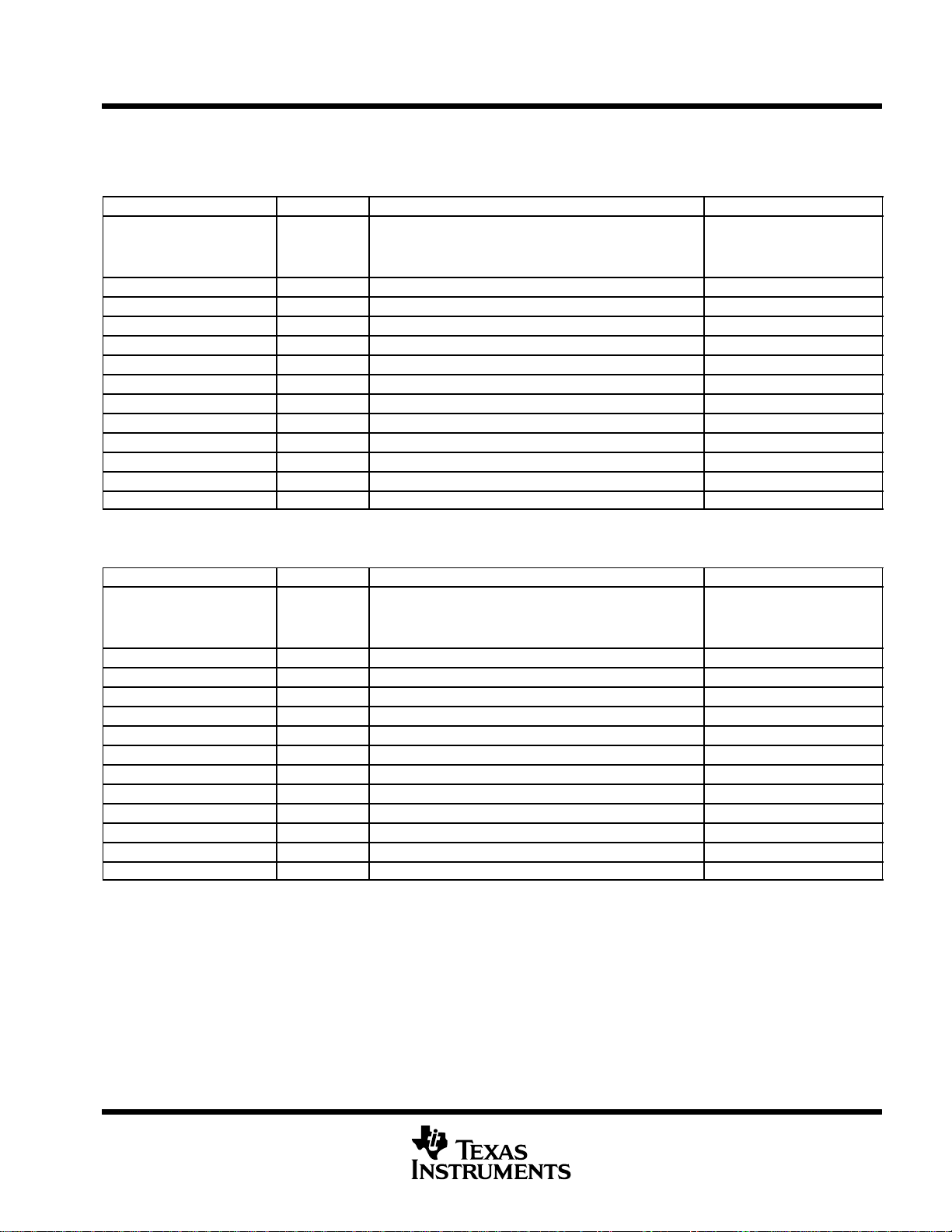
Table 7. Quick DMA (QDMA) and Pseudo Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE
0200 0000 QOPT QDMA options parameter register
0200 0004 QSRC QDMA source address register
0200 0008 QCNT QDMA frame count register
0200 000C QDST QDMA destination address register
0200 0010 QIDX QDMA index register
0200 0014 − 0200 001C − Reserved
0200 0020 QSOPT QDMA pseudo options register
0200 0024 QSSRC QDMA pseudo source address register
0200 0028 QSCNT QDMA pseudo frame count register
0200 002C QSDST QDMA pseudo destination address register
0200 0030 QSIDX QDMA pseudo index register
†
All the QDMA and Pseudo registers are write-accessible only
ACRONYM REGISTER NAME
†
Table 8. Interrupt Selector Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
019C 0000 MUXH Interrupt multiplexer high
019C 0004 MUXL Interrupt multiplexer low
019C 0008 EXTPOL External interrupt polarity
019C 000C − 019F FFFF − Reserved
Selects which interrupts drive CPU interrupts
10−15 (INT10−INT15)
Selects which interrupts drive CPU interrupts 4−9
(INT04−INT09)
Sets the polarity of the external interrupts
(EXT_INT4−EXT_INT7)
12
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
peripheral register descriptions (continued)
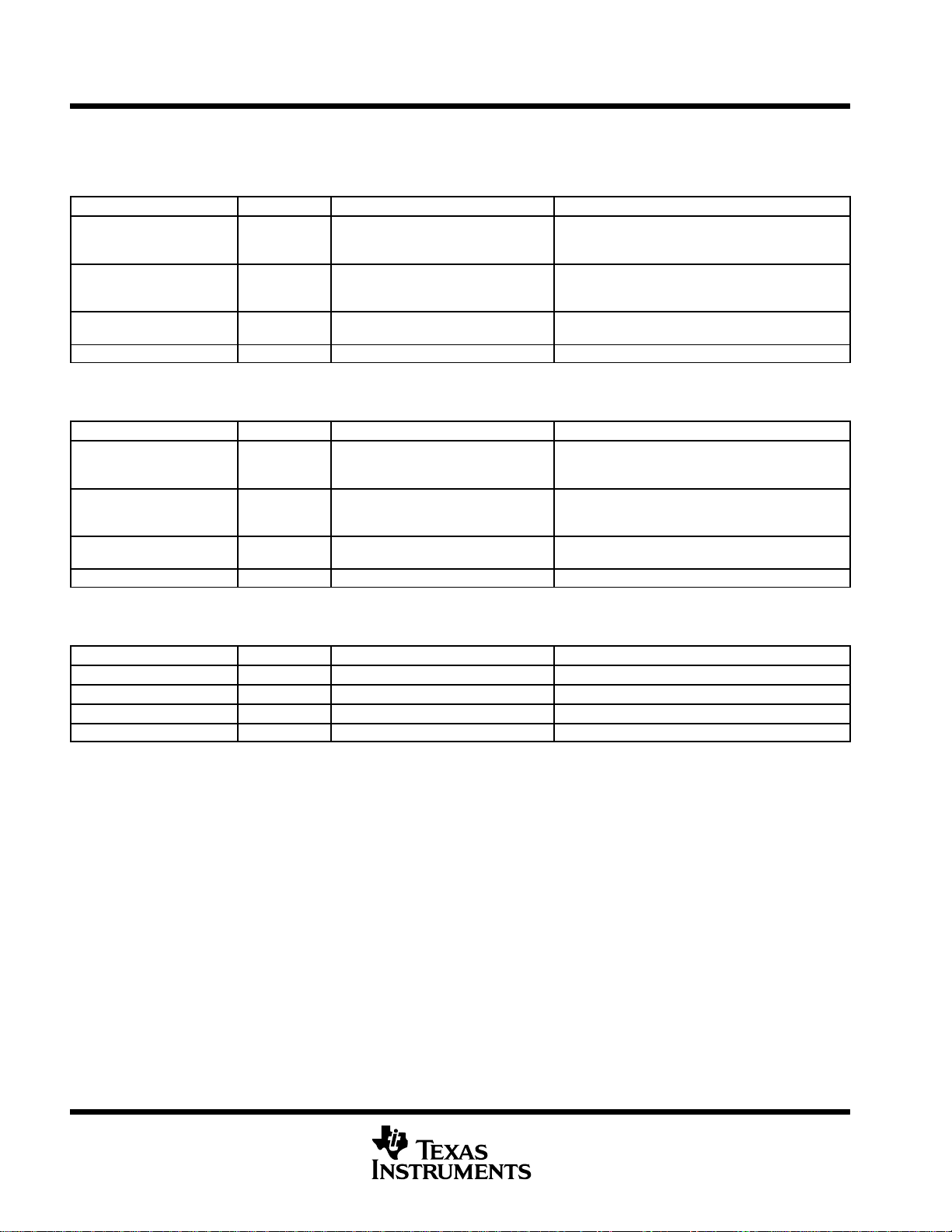
Table 9. McBSP 0 Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
The CPU and DMA/EDMA
018C 0000 DRR0 McBSP0 data receive register via Peripheral Bus
0x3000 0000 − 0x33FF FFFF DRR0 McBSP0 data receive register via EDMA Bus
018C 0004 DXR0 McBSP0 data transmit register via Peripheral Bus
0x3000 0000 − 0x33FF FFFF DXR0 McBSP0 data transmit register via EDMA Bus
018C 0008 SPCR0 McBSP0 serial port control register
018C 000C RCR0 McBSP0 receive control register
018C 0010 XCR0 McBSP0 transmit control register
018C 0014 SRGR0 McBSP0 sample rate generator register
018C 0018 MCR0 McBSP0 multichannel control register
018C 001C RCER0 McBSP0 receive channel enable register
018C 0020 XCER0 McBSP0 transmit channel enable register
018C 0024 PCR0 McBSP0 pin control register
018C 0028 − 018F FFFF − Reserved
controller can only read this
register; they cannot write to
it.
Table 10. McBSP 1 Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
The CPU and DMA/EDMA
0190 0000 DRR1 Data receive register via Peripheral Bus
0x3400 0000 − 0x37FF FFFF DRR1 McBSP1 data receive register via EDMA Bus
0190 0004 DXR1 McBSP1 data transmit register via Peripheral Bus
0x3400 0000 − 0x37FF FFFF DXR1 McBSP1 data transmit register via EDMA Bus
0190 0008 SPCR1 McBSP1 serial port control register
0190 000C RCR1 McBSP1 receive control register
0190 0010 XCR1 McBSP1 transmit control register
0190 0014 SRGR1 McBSP1 sample rate generator register
0190 0018 MCR1 McBSP1 multichannel control register
0190 001C RCER1 McBSP1 receive channel enable register
0190 0020 XCER1 McBSP1 transmit channel enable register
0190 0024 PCR1 McBSP1 pin control register
0190 0028 − 0193 FFFF − Reserved
controller can only read this
register; they cannot write to
it.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
13
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
peripheral register descriptions (continued)
Table 11. Timer 0 Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
Determines the operating mode of the timer,
0194 0000 CTL0 Timer 0 control register
0194 0004 PRD0 Timer 0 period register
0194 0008 CNT0 Timer 0 counter register
0194 000C − 0197 FFFF − Reserved
Table 12. Timer 1 Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
0198 0000 CTL1 Timer 1 control register
0198 0004 PRD1 Timer 1 period register
0198 0008 CNT1 Timer 1 counter register
0198 000C − 019B FFFF − Reserved
monitors the timer status, and controls the function
of the TOUT pin.
Contains the number of timer input clock cycles to
count. This number controls the TSTAT signal
frequency.
Contains the current value of the incrementing
counter.
Determines the operating mode of the timer,
monitors the timer status, and controls the function
of the TOUT pin.
Contains the number of timer input clock cycles to
count. This number controls the TSTAT signal
frequency.
Contains the current value of the incrementing
counter.
Table 13. HPI Registers
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
− HPID HPI data register Host read/write access only
− HPIA HPI address register Host read/write access only
0188 0000 HPIC HPI control register Both Host/CPU read/write access
0188 0001 − 018B FFFF − Reserved
14
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
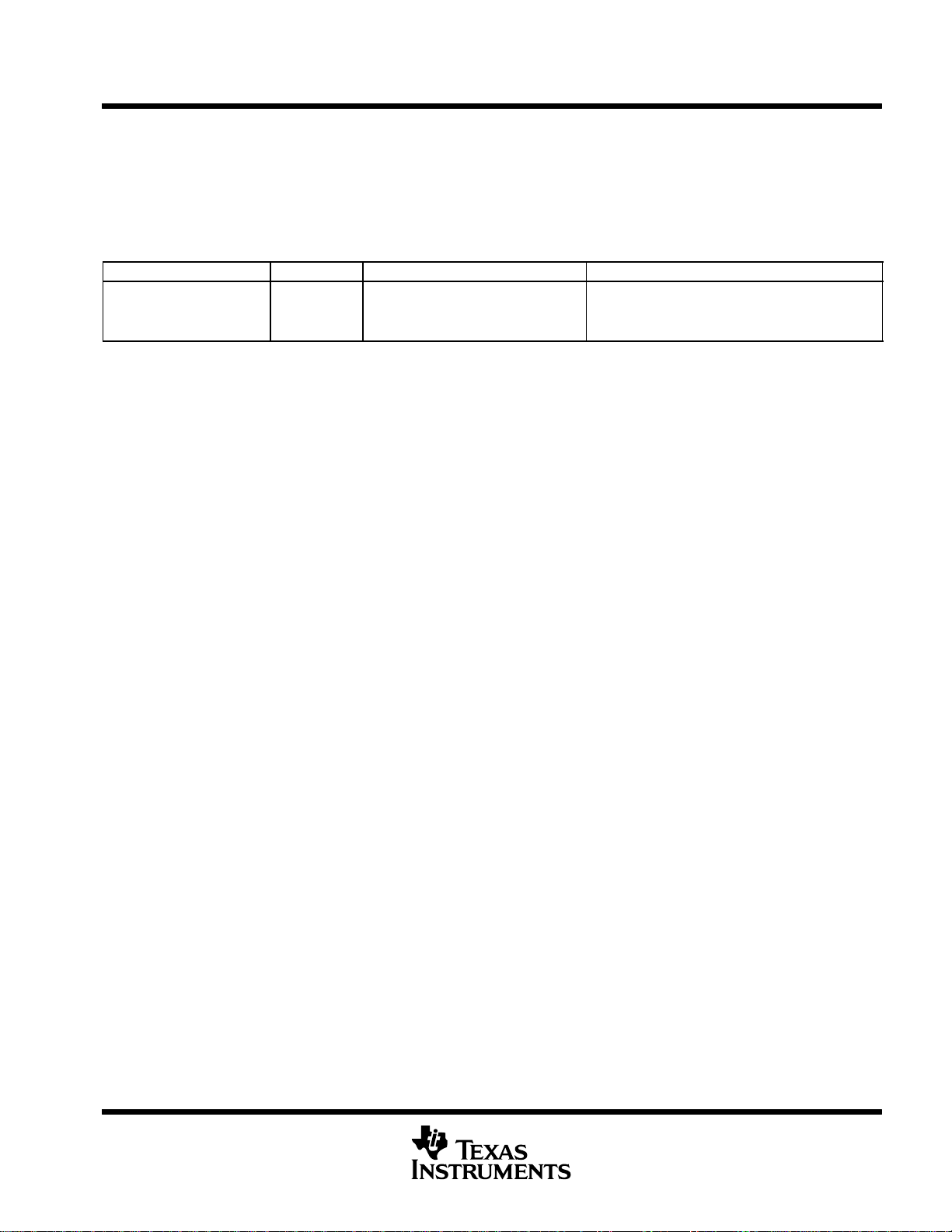
PWRD bits in CPU CSR register description
Table 14 identifies the PWRD field (bits 15−10) in the CPU CSR register. These bits control the device
power-down modes. For more detailed information on the PWRD bit field of the CPU CSR register, see the
TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRU189).
Table 14. PWRD field bits in the CPU CSR Register
HEX ADDRESS RANGE ACRONYM REGISTER NAME COMMENTS
The PWRD field (bits 15−10 in the CPU CSR)
− CSR Control status register
controls the device power-down modes.
Accessible by writing a value to the CSR register.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
15

TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
EDMA channel synchronization events
The C62x EDMA supports up to 16 EDMA channels. Four of the sixteen channels (channels 8−11) are reserved
for EDMA chaining, leaving 12 EDMA channels available to service peripheral devices. Table 15 lists the source
of synchronization events associated with each of the programmable EDMA channels. For the C6211/11B, the
association of an event to a channel is fixed; each of the EDMA channels has one specific event associated
with it. For more detailed information on the EDMA module, associated channels, and event-transfer chaining,
see the TMS320C6000 DSP Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature
number SPRU234).
Table 15. TMS320C6211/C6211B EDMA Channel Synchronization Events
EDMA
CHANNEL
0 DSP_INT Host-port interface (HPI)-to-DSP interrupt
1 TINT0 Timer 0 interrupt
2 TINT1 Timer 1 interrupt
3 SD_INT EMIF SDRAM timer interrupt
4 EXT_INT4 External interrupt pin 4
5 EXT_INT5 External interrupt pin 5
6 EXT_INT6 External interrupt pin 6
7 EXT_INT7 External interrupt pin 7
†
8
†
9
†
10
†
11
12 XEVT0 McBSP0 transmit event
13 REVT0 McBSP0 receive event
14 XEVT1 McBSP1 transmit event
15 REVT1 McBSP1 receive event
†
EDMA channels 8 through 11 are used for transfer chaining only. For more detailed information on event-transfer chaining, see the
TMS320C6000 DSP Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRU234).
EVENT NAME EVENT DESCRIPTION
EDMA_TCC8 EDMA transfer complete code (TCC) 1000b interrupt
EDMA_TCC9 EDMA TCC 1001b interrupt
EDMA_TCC10 EDMA TCC 1010b interrupt
EDMA_TCC11 EDMA TCC 1011b interrupt
16
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
interrupt sources and interrupt selector
The C62x DSP core supports 16 prioritized interrupts, which are listed in Table 16. The highest-priority interrupt
is INT_00 (dedicated to RESET) while the lowest-priority interrupt is INT_15. The first four interrupts
(INT_00−INT_03) are non-maskable and fixed. The remaining interrupts (INT_04−INT_15) are maskable and
default to the interrupt source specified in Table 16. The interrupt source for interrupts 4−15 can be programmed
by modifying the selector value (binary value) in the corresponding fields of the Interrupt Selector Control
registers: MUXH (address 0x019C0000) and MUXL (address 0x019C0004).
Table 16. C6211/C6211B DSP Interrupts
CPU
INTERRUPT
NUMBER
†
INT_00
†
INT_01
†
INT_02
†
INT_03
‡
INT_04
‡
INT_05
‡
INT_06
‡
INT_07
‡
INT_08
‡
INT_09
‡
INT_10
‡
INT_11
‡
INT_12
‡
INT_13
‡
INT_14
‡
INT_15
− − 01100 XINT0 McBSP0 transmit interrupt
− − 01101 RINT0 McBSP0 receive interrupt
− − 01110 XINT1 McBSP1 transmit interrupt
− − 0 1111 RINT1 McBSP1 receive interrupt
− − 10000 − 11111 Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
†
Interrupts INT_00 through INT_03 are non-maskable and fixed.
‡
Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15 are programmable by modifying the binary selector values in the Interrupt Selector Control
registers fields. Table 16 shows the default interrupt sources for Interrupts INT_04 through INT_15. For more detailed
information on interrupt sources and selection, see the TMS320C6000 DSP Interrupt Selector Reference Guide (literature
number SPRU646).
INTERRUPT
SELECTOR
CONTROL
REGISTER
SELECTOR
VALUE
(BINARY)
INTERRUPT
EVENT
INTERRUPT SOURCE
− − RESET
− − NMI
− − Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
− − Reserved Reserved. Do not use.
MUXL[4:0] 00100 EXT_INT4 External interrupt pin 4
MUXL[9:5] 00101 EXT_INT5 External interrupt pin 5
MUXL[14:10] 00110 EXT_INT6 External interrupt pin 6
MUXL[20:16] 00111 EXT_INT7 External interrupt pin 7
MUXL[25:21] 01000 EDMA_INT EDMA channel (0 through 15) interrupt
MUXL[30:26] 01001 Reserved None, but programmable
MUXH[4:0] 00011 SD_INT EMIF SDRAM timer interrupt
MUXH[9:5] 01010 Reserved None, but programmable
MUXH[14:10] 01011 Reserved None, but programmable
MUXH[20:16] 00000 DSP_INT Host-port interface (HPI)-to-DSP interrupt
MUXH[25:21] 00001 TINT0 Timer 0 interrupt
MUXH[30:26] 00010 TINT1 Timer 1 interrupt
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
17
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
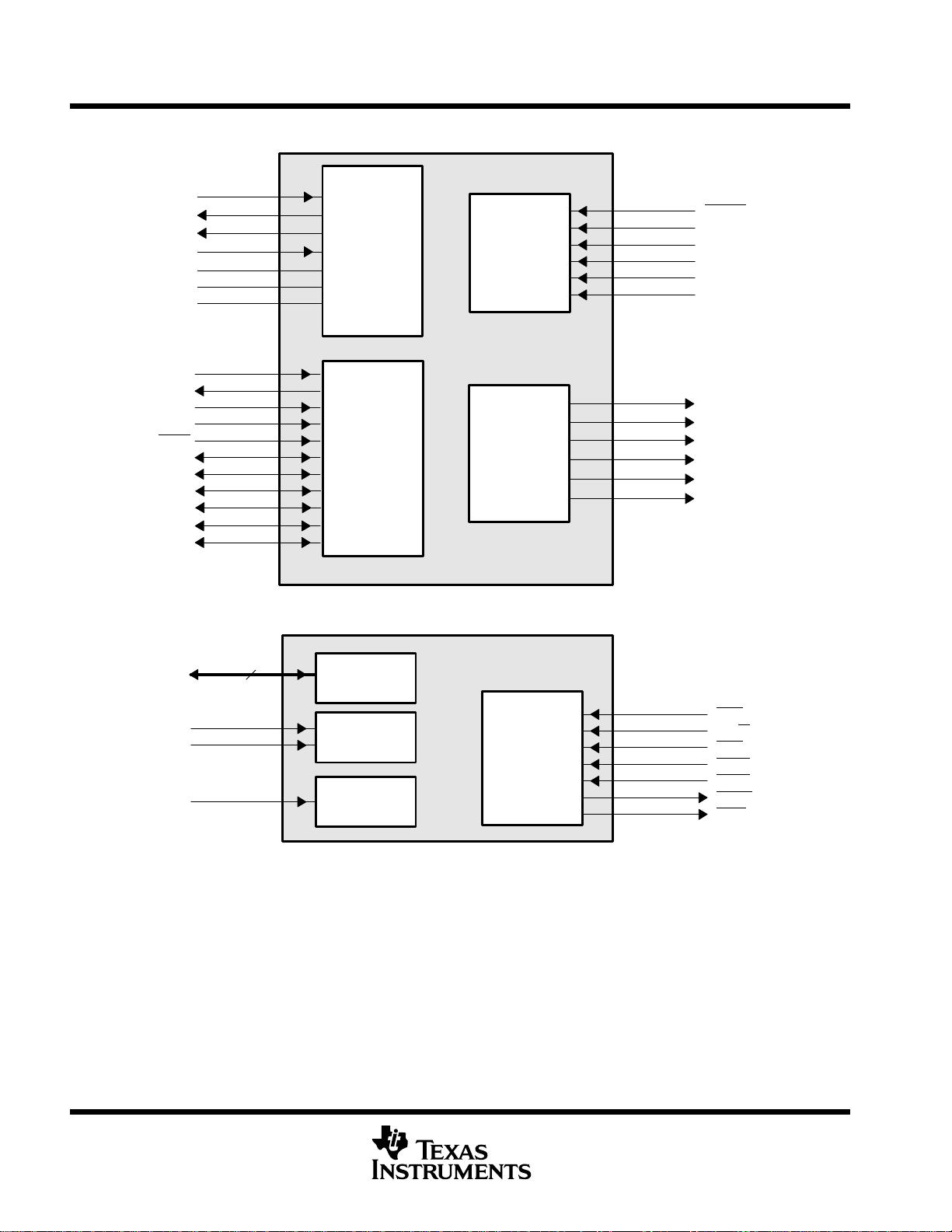
signal groups description
CLKIN
CLKOUT2
CLKOUT1
CLKMODE0
PLLV
PLLG
PLLF
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
TRST
EMU0
EMU1
EMU2
EMU3
EMU4
EMU5
Clock/PLL
IEEE Standard
1149.1
(JTAG)
Emulation
Control/Status
Reset and
Interrupts
Reserved
RESET
NMI
EXT_INT7
EXT_INT6
EXT_INT5
EXT_INT4
RSV5
RSV4
RSV3
RSV2
RSV1
RSV0
HD[15:0]
HCNTL0
HCNTL1
HHWIL
16
Data
Register Select
Half-Word
Select
(Host-Port Interface)
HPI
Control
Figure 2. CPU (DSP Core) and Peripheral Signals
HAS
HR/W
HCS
HDS1
HDS2
HRDY
HINT
18
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
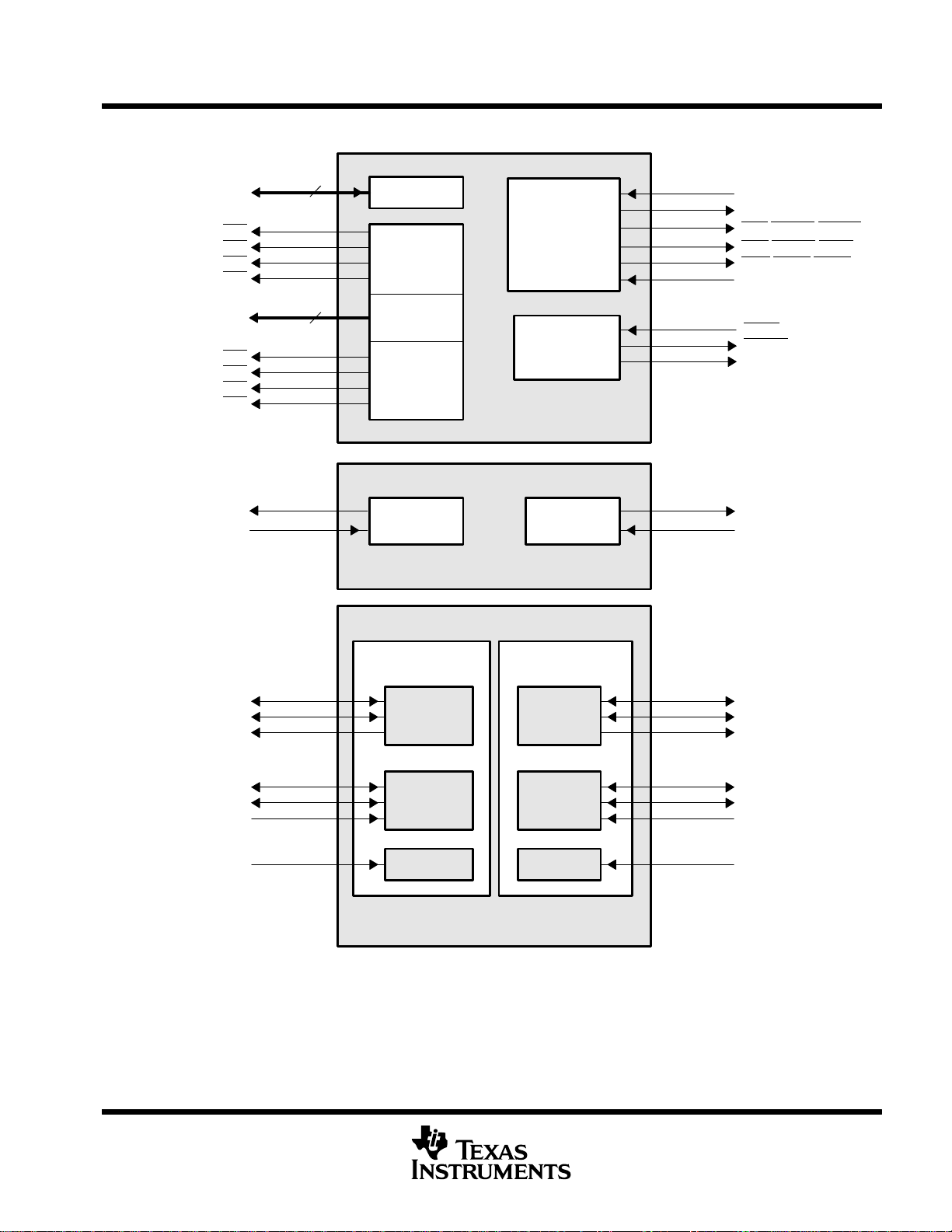
signal groups description (continued)
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
ED[31:0]
CE3
CE2
CE1
CE0
EA[21:2]
BE3
BE2
BE1
BE0
TOUT1
TINP1
32
20
Data
Memory Map
Space Select
Address
Byte Enables
Timer 1
Memory
Control
Bus
Arbitration
EMIF
(External Memory Interface)
Timer 0
Timers
ECLKIN
ECLKOUT
ARE/SDCAS/SSADS
AOE
/SDRAS/SSOE
AWE/SDWE/SSWE
ARDY
HOLD
HOLDA
BUSREQ
TOUT0
TINP0
CLKX1
FSX1
DX1
CLKR1
FSR1
DR1
CLKS1
McBSP1 McBSP0
Transmit Transmit
Receive Receive
Clock Clock
McBSPs
(Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports)
Figure 3. Peripheral Signals
CLKX0
FSX0
DX0
CLKR0
FSR0
DR0
CLKS0
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
19
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
†
IPD/
DESCRIPTION
E
l i
g
• Edge-driven
yp y p yg
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Terminal Functions
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
TYPE
CLKIN A3 I IPD Clock Input
CLKOUT1 D7 O IPD
CLKOUT2 Y12 O IPD
CLKMODE0 C4 I IPU
§
PLLV
PLLG
§
A4 A
C6 A
PLLF B5 A
TMS B7 I IPU JTAG test-port mode select
TDO A8 O/Z IPU JTAG test-port data out
TDI A7 I IPU JTAG test-port data in
TCK A6 I IPU JTAG test-port clock
TRST B6 I IPD JTAG test-port reset
EMU5 B12 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 5. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU4 C11 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 4. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU3 B10 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 3. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU2 D10 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 2. Reserved for future use, leave unconnected.
EMU1 B9 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 1
EMU0 D9 I/O/Z IPU Emulation pin 0
RESET A13 I IPU Device reset
NMI C13 I IPD
EXT_INT7 E3
EXT_INT6 D2
EXT_INT5 C1
EXT_INT4 C2
HINT J20 O IPU Host interrupt (from DSP to host)
HCNTL1 G19 I IPU Host control − selects between control, address, or data registers
HCNTL0 G18 I IPU Host control − selects between control, address, or data registers
HHWIL H20 I IPU Host half-word select − first or second half-word (not necessarily high or low order)
HR/W G20 I IPU Host read or write select
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
IPD/
IPU
¶
¶
¶
I IPU
‡
CLOCK/PLL
Clock output at device speed
The CLK1EN bit in the EMIF GBLCTL register controls the CLKOUT1 pin.
CLK1EN = 0: CLKOUT1 is disabled
CLK1EN = 1: CLKOUT1 enabled to clock [default]
Clock output at half of device speed
When the CLKOUT2 pin is enabled, the CLK2EN bit in the EMIF global control register
(GBLCTL) controls the CLKOUT2 pin.
CLK2EN = 0: CLKOUT2 is disabled
CLK2EN = 1: CLKOUT1 enabled to clock [default]
Clock mode select
• Selects whether the CPU clock frequency = input clock frequency x4 or x1
PLL analog VCC connection for the low-pass filter
PLL analog GND connection for the low-pass filter
PLL low-pass filter connection to external components and a bypass capacitor
JTAG EMULATION
#
#
RESETS AND INTERRUPTS
Nonmaskable interrupt
• Edge-driven (rising edge)
Any noise on the NMI pin may trigger an NMI interrupt; therefore, if the NMI pin is not used, it is
recommended that the NMI pin be grounded versus relying on the IPD.
xterna
• Ed
nterrupts
e-driven
• Polarity independently selected via the External Interrupt Polarity Register bits
(EXTPOL.[3:0])
HOST-PORT INTERFACE (HPI)
20
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
IPD/
Also controls initialization of DSP modes at reset via pullup/pulldown resistors
Device Endian mode
Boot mode
HD[4:3]: 00 HPI boot
11−32-bit ROM boot with default timings
Only one asserted d
access
• Only one asserted during any external data access
B
l
• Decoded from the two lowest bits of the internal address
yypy
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
§
PLLV and PLLG are not part of external voltage supply or ground. See the CLOCK/PLL documentation for information on how to connect these
pins.
¶
A = Analog signal (PLL Filter)
#
The EMU0 and EMU1 pins are internally pulled up with 30-kΩ resistors; therefore, for emulation and normal operation, no external
pullup/pulldown resistors are necessary. However, for boundary scan operation, pull down the EMU1 and EMU0 pins with a dedicated 1-kΩ
resistor.
Terminal Functions (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
TYPE
HD15 B14 IPU
HD14 C14 IPU
HD13 A15 IPU
HD12 C15 IPU
HD11 A16 IPU
HD10 B16 IPU
HD9 C16 IPU
HD8 B17
HD7 A18
I/O/Z
HD6 C17 IPU
HD5 B18 IPU
HD4 C19 IPD
HD3 C20 IPU
HD2 D18 IPU
HD1 D20 IPU
HD0 E20 IPU
HAS E18 I IPU Host address strobe
HCS F20 I IPU Host chip select
HDS1 E19 I IPU Host data strobe 1
HDS2 F18 I IPU Host data strobe 2
HRDY H19 O IPD Host ready (from DSP to host)
CE3 V6 O/Z IPU
CE2 W6 O/Z IPU
CE1 W18 O/Z IPU
CE0 V17 O/Z IPU
BE3 V5 O/Z IPU
BE2 Y4 O/Z IPU
BE1 U19 O/Z IPU
BE0 V20 O/Z IPU
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
IPD/
†
IPU‡
DESCRIPTION
HOST-PORT INTERFACE (HPI) (CONTINUED)
Host-port data
• Used for transfer of data, address, and control
•
− Device Endian mode
IPU
IPU
HD8: 0 – Big Endian
1 − Little Endian
−
−
HD[4:3]: 00 – HPI boot
01 − 8-bit ROM boot with default timings
10 − 16-bit ROM boot with default timings
11 −
2-i R
M
wih fl
imin
EMIF − CONTROL SIGNALS COMMON TO ALL TYPES OF MEMORY
Memory space enables
• Enabled by bits 28 through 31 of the word address
•
uring any external data
yte-enable contro
• Decoded from the two lowest bits of the internal address
• Byte-write enables for most types of memory
• Can be directly connected to SDRAM read and write mask signal (SDQM)
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
21
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
/
IPD/
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Terminal Functions (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
HOLDA J18 O IPU Hold-request-acknowledge to the host
HOLD J17 I IPU Hold request from the host
BUSREQ J19 O IPU Bus request output
EMIF − ASYNCHRONOUS/SYNCHRONOUS DRAM/SYNCHRONOUS BURST SRAM MEMORY CONTROL
ECLKIN Y11 I IPD EMIF input clock
ECLKOUT Y10 O IPD EMIF output clock (based on ECLKIN)
ARE/SDCAS/
SSADS
AOE/SDRAS/
SSOE
AWE/SDWE/
SSWE
ARDY Y5 I IPU Asynchronous memory ready input
EA21 U18
EA20 Y18
EA19 W17
EA18 Y16
EA17 V16
EA16 Y15
EA15 W15
EA14 Y14
EA13 W14
EA12 V14
EA11 W13
EA10 V10
EA9 Y9
EA8 V9
EA7 Y8
EA6 W8
EA5 V8
EA4 W7
EA3 V7
EA2 Y6
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
V11 O/Z IPU Asynchronous memory read enable/SDRAM column-address strobe/SBSRAM address strobe
W10 O/Z IPU Asynchronous memory output enable/SDRAM row-address strobe/SBSRAM output enable
V12 O/Z IPU Asynchronous memory write enable/SDRAM write enable/SBSRAM write enable
TYPE
O/Z IPU EMIF external address
IPD
†
IPU
‡
EMIF − BUS ARBITRATION
EMIF − ADDRESS
DESCRIPTION
22
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
IPD/
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Terminal Functions (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
ED31 N3
ED30 P3
ED29 P2
ED28 P1
ED27 R2
ED26 R3
ED25 T2
ED24 T1
ED23 U3
ED22 U1
ED21 U2
ED20 V1
ED19 V2
ED18 Y3
ED17 W4
ED16 V4
ED15 T19
ED14 T20
ED13 T18
ED12 R20
ED11 R19
ED10 P20
ED9 P18
ED8 N20
ED7 N19
ED6 N18
ED5 M20
ED4 M19
ED3 L19
ED2 L18
ED1 K19
ED0 K18
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
I/O/Z IPU External data
IPD/
†
IPU‡
EMIF − DATA
DESCRIPTION
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
23
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
IPD/
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
Terminal Functions (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
TOUT1 F1 O IPD Timer 1 or general-purpose output
TINP1 F2 I IPD Timer 1 or general-purpose input
TOUT0 G1 O IPD Timer 0 or general-purpose output
TINP0 G2 I IPD Timer 0 or general-purpose input
CLKS1 E1 I IPD External clock source (as opposed to internal)
CLKR1 M1 I/O/Z IPD Receive clock
CLKX1 L3 I/O/Z IPD Transmit clock
DR1 M2 I IPU Receive data
DX1 L2 O/Z IPU Transmit data
FSR1 M3 I/O/Z IPD Receive frame sync
FSX1 L1 I/O/Z IPD Transmit frame sync
CLKS0 K3 I IPD External clock source (as opposed to internal)
CLKR0 H3 I/O/Z IPD Receive clock
CLKX0 G3 I/O/Z IPD Transmit clock
DR0 J1 I IPU Receive data
DX0 H2 O/Z IPU Transmit data
FSR0 J3 I/O/Z IPD Receive frame sync
FSX0 H1 I/O/Z IPD Transmit frame sync
RSV0 C12 O IPU Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV1 D12 O IPU Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV2 A5 O IPU Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV3 D3 O Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV4 N2 O Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
RSV5 Y20 O Reserved (leave unconnected, do not connect to power or ground)
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
‡
IPD = Internal pulldown, IPU = Internal pullup. (These IPD/IPU signal pins feature a 30-kΩ IPD or IPU resistor. To pull up a signal to the opposite
supply rail, a 1-kΩ resistor should be used.)
TYPE
IPD/
†
IPU‡
TIMER 1
TIMER 0
MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT 1 (McBSP1)
MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT 0 (McBSP0)
RESERVED FOR TEST
DESCRIPTION
24
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
FIXED-POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
DV
DD
S
3.3 V supply voltage
Terminal Functions (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME NO.
A17
B3
B8
B13
C5
C10
D1
D16
D19
F3
H18
J2
M18
N1
DV
DD
CV
DD
†
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground
R1
R18
T3
U5
U7
U12
U16
V13
V15
V19
W3
W9
W12
Y7
Y17
A9
A10
A12
B2
B19
C3
C7
C18
D5
D6
D11
D14
†
TYPE
S 3.3-V supply voltage
S 1.8-V supply voltage
SUPPLY VOLTAGE PINS
TMS320C6211, TMS320C6211B
SPRS073K − AUGUST 1998 − REVISED MARCH 2004
DESCRIPTION
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443
25
 Loading...
Loading...