
查询SN65MLVD200供应商
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
D Low-Voltage Differential 30-Ω Line Drivers
and Receivers for Signaling Rates
100 Mbps
†
up to
D Power Dissipation at 100 Mbps
– Driver: 50 mW Typical
– Receiver: 30 mW Typical
D Meets or Exceeds Current Revision of
M-L VDS Standard TIA/EIA–899 for
Multipoint Data Interchange
D Controlled Driver Output Voltage Transition
Times for Improved Signal Quality
D –1-V to 3.4-V Common-Mode Voltage Range
Allows Data Transfer With up to 2 V of
Ground Noise
D Type-1 Receivers Incorporate 25 mV of
Hysteresis
SN65MLVD200D (Marked as MF200)
SN65MLVD204D (Marked as MF204)
RE
DE
R
D
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V
CC
B
A
GND
D Type-2 Receivers Provide an Offset
(100 mV) Threshold to Detect Open-Circuit
and Idle-Bus Conditions
D Operates From a Single 3.3-V Supply
D Propagation Delay Times Typically 2.3 ns
for Drivers and 5 ns for Receivers
D Power-Up/Down Glitch-Free Driver
D Driver Handles Operation Into a
Continuous Short Circuit Without Damage
D Bus Pins High Impedance When Disabled
or V
≤ 1.5 V
CC
D 200-Mbps Devices Available
(SN65MLVD201, 203, 206, and 207)
SN65MLVD202D (Marked as MLVD202)
SN65MLVD205D (Marked as MLVD205)
NC
RE
DE
GND
GND
R
D
(TOP VIEW)
1
14
2
13
3
12
4
11
5
10
6
7
9
8
V
V
A
B
Z
Y
NC
CC
CC
NC – No internal connection
logic diagram (positive logic)
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD204
3
DE
4
D
2
RE
1
R
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
†
The signaling rate of a line is the number of voltage transitions that are made per second expressed in bps (bits per second) units.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
6
A
7
B
SN65MLVD202, SN65MLVD205
9
5
D
4
DE
3
RE
2
R
Copyright 2001–2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
10
12
11
Y
Z
A
B
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
1

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
description
This series of SN65ML VD20x devices are low-voltage differential line drivers and receivers complying with the
proposed multipoint low-voltage differential signaling (M-LVDS) standard (TIA/EIA–899). These circuits are
similar to their TIA/EIA-644 standard compliant L VDS counterparts, with added features to address multipoint
applications. Driver output current has been increased to support doubly-terminated, 50-Ω load multipoint
applications. Driver output slew rates are optimized for signaling rates up to 100 Mbps.
Types 1 and 2 receivers are available. Both types of receivers operate over a common-mode voltage range of
–1 V to 3.4 V to provide increased noise immunity in harsh electrical environments. Type-1 receivers have their
differential input voltage thresholds near zero volts (±50 mV), and include 25 mV of hysteresis to prevent output
oscillations in the presence of noise. Type-2 receivers include an of fset threshold to detect open-circuit, idle-bus,
and other fault conditions, and provide a known output state under these conditions.
The intended application of these devices is in half-duplex or multipoint baseband data transmission over
controlled impedance media of approximately 100-Ω characteristic impedance. The transmission media may
be printed circuit board traces, backplanes, or cables. (Note: The ultimate rate and distance of data transfer is
dependent upon the attenuation characteristics of the media, the noise coupling to the environment, and other
application-specific characteristics).
These devices are characterized for operation from –40°C to 85°C.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
NOMINAL
SIGNALING RATE,
Mbps
100 SN75176 Type 1 SN65MLVD200D
100 SN75ALS180 Type 1 SN65MLVD202D
100 SN75176 Type 2 SN65MLVD204D
100 SN75ALS180 Type 2 SN65MLVD205D
†
The D package is available taped and reeled. Add the R suffix to the device type (e.g., SN65ML VD200DR)
FOOTPRINT RECEIVER TYPE
PART NUMBER
†
Function Tables
TYPE-1 RECEIVER (200, 202)
INPUTS OUTPUT
VID = VA – V
VID ≥ 50 mV
–50 mV < VID < 50 mV
VID ≤ –50 mV
Open Circuit
H = high level, L = low level, Z = high impedance, X = Don’t care, ? = indeterminate
B
X
X
RE
L
L
L
H
Open
L
OPEN
R
H
?
L
Z
Z
?
DRIVER
INPUT OUTPUTS
ENABLE
D DE A OR Y
L
H
X
X
H
H
H
OPEN
L
L
H
L
Z
Z
TYPE-2 RECEIVER (204, 205)
INPUTS OUTPUT
VID = VA – V
VID ≥ 150 mV
50 mV < VID < 150 mV
VID ≤ 50 mV L
Open Circuit
B OR Z
B
X
X
H
L
H
Z
Z
RE
L
L
H
Open
L
R
H
?
L
Z
Z
L
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
equivalent input and output schematic diagrams
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
DRIVER INPUT AND DRIVER ENABLE
400 Ω
D or DE
7 V
360 kΩ
DRIVER OUTPUT
V
CC
RECEIVER ENABLE
V
V
CC
360 kΩ
400 Ω
RE
7 V
A/Y or B/Z
CC
RECEIVER INPUT
100 kΩ
250 kΩ
200 kΩ
RECEIVER OUTPUT
V
CC
200 kΩ
10 Ω
10 Ω
V
CC
100 kΩ
250 kΩ
R
7 V
BA
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, V
Input voltage range: D, DE, RE
(see Note 1) –0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CC
–0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
A, B (200, 204) –1.8 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A, B (202, 205) –4 V to 6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage range: R –0.3 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Y, Z, A, or B –1.8 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic discharge: Human body model (see Note 2) A, B, Y, or Z ±3 kV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
All pins ±2 kV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charged-device model (see Note 3) All pins ±500 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous power dissipation (see Dissipation Rating table). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range –65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied.
Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. All voltage values, except differential I/O bus voltages, are with respect to network ground terminal.
2. Tested in accordance with JEDEC Standard 22, Test Method A114-A.
3. Tested in accordance with JEDEC Standard 22, Test Method C101.
DISSIPATION RATING
PACKAGE
D(8) 725 mW 5.8 mW/°C 377 mW
D(14) 950 mW 7.6 mW/°C 494 mW
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
OPERATING FACTOR
ABOVE TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
POWER RATING
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
High-level input voltage, V
Low-level input voltage, V
Magnitude of differential input voltage, VID 0.05 V
Voltage at any bus terminal, VA, VY, VZ, or V
Common-mode input voltage VCM, (VA + VB)/2 –1 3.4 V
Receiver load capacitance, C
Operating free-air temperature, T
CC
IH
IL
B
L
A
3 3.3 3.6 V
2 V
0 0.8 V
–1.4 3.8 V
5 15 pF
–40 85 °C
CC
CC
V
V
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
device electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN†TYP‡MAX UNIT
Receiver disabled and driver enabled
Driver and receiver disabled
I
Supply current
CC
†
The algebraic convention, in which the least positive (most negative) limit is designated as minimum, is used in this data sheet.
‡
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
Receiver enabled and driver enabled
Receiver enabled and driver disabled
driver electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN†TYP
VABor
VYZ
∆VABor
∆VYZ
V
OS(SS)
∆V
OS(SS)
V
OS(PP)
V
A(OC)
V
Y(OC)
V
B(OC)
V
Z(OC)
V
P(H)
V
P(L)
I
IH
I
IL
I
OS
I
OZ
I
O(OFF)
†
The algebraic convention, in which the least positive (most negative) limit is designated as minimum, is used in this data sheet.
‡
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
Differential output voltage magnitude See Figure 2 480 650 mV
Change in differential output voltage magnitude
between logic states
Steady-state common-mode output voltage 0.8 1.2 V
Change in steady-state common-mode output
voltage between logic states
Peak-to-peak common-mode output voltage 150 mV
or
Maximum steady-state open-circuit output voltage
or
Maximum steady-state open-circuit output voltage
Voltage overshoot, low-to-high level output
Voltage overshoot, high-to-low level output
High-level input current VIH = 2 V 0 10 µA
Low-level input current VIL = 0.8 V 0 10 µA
Differential short-circuit output current See Figure 4 24 mA
High-impedance state output current (driver only)
Power-off output current (driver only)
RE and DE at VCC,
RL = 50 Ω, All others open
RE at VCC, DE at 0 V,
RL = No load, All others open
RE at 0 V, DE at VCC,
RL = 50 Ω, All others open,
No receiver load
RE at 0 V, DE at 0 V ,
All others open, No receiver load
See Figure 2 –50 50 mV
See Figure 3
See Figure 7
See Figure 5
–1.4 V ≤ (VY or VZ) ≤ 3.8 V,
Other output at 1.2 V
–1.4 V ≤ (VY or VZ) ≤ 3.8 V,
VCC ≤ 1.5 V,
Other output at 1.2 V
–50 50 mV
0 2.4 V
0 2.4 V
–0.2V
SS
–15 10 µA
–10 10 µA
13 22
1 7
16 26
4 11
‡
MAX UNIT
1.2V
SS
mA
V
V
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
See Figure 8
I
A
t
µA
I
B
t
µA
(
)
I
A(OFF)
t
µA
(
)
I
B(OFF)
t
µA
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
receiver electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
IT+
V
IT–
V
ID(HYS)
V
OH
V
OL
I
IH
I
IL
I
OZ
†
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
Positive-going differential input voltage threshold
Negative-going differential input voltage threshold
Differential input voltage hysteresis, V
High-level output voltage IOH = –8 mA 2.4 V
Low-level output voltage IOL = 8 mA 0.4 V
High-level input current VIH = 2 V –10 0 µA
Low-level input current VIL = 0.8 V –10 0 µA
High-impedance output current VO = 0 V or 3.6 V –10 15 µA
IT+
– V
bus input and output electrical characteritics over recommended operating conditions (unless
otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
I
A
I
B
I
AB
I
A
OFF
I
B
OFF
I
AB(OFF)
C
A
C
B
†
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
curren
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
curren
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
differential current (IA – IB)
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
p
-
power-off curren
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
power-off curren
p
-
Receiver input or transceiver input/output
power-off differential current (IA – IB)
Receiver input, driver high-impedance
p
output, or transceiver input/output
capacitance
p
p
Type 1 50
Type 2
Type 1
Type 2
Type 1 25
IT–
Type 2
VA = 3.8 V, VB = 1.2 V 0 32
VA = 0 V or 2.4 V, VB = 1.2 V –20 20
VA = –1.4 V, VB = 1.2 V –32 0
VB = 3.8 V, VA = 1.2 V 0 32
VB = 0 V or 2.4 V, VA = 1.2 V –20 20
VB = –1.4 V, VA = 1.2 V –32 0
VA = VB, –1.4 ≤ VA ≤ 3.8 V –4 4 µA
VA = 3.8 V, VB = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V 0 32
VA = 0 V or 2.4 V, VB = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V –20 20
VA = –1.4 V, VB = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V –32 0
VB = 3.8 V, VA = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V 0 32
VB = 0 V or 2.4 V, VA = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V –20 20
VB = –1.4 V, VA = 1.2 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V –32 0
VA = VB, –1.4 ≤ VA ≤ 3.8 V, VCC ≤ 1.5 V –4 4 µA
VA = 0.4 sin(2E8πt) +0.5, VB = 1.2 V 3 pF
VB = 0.4 sin(2E8πt) +0.5, VA = 1.2 V 3 pF
See Figure 8,
Table 1 and Table 2
,
–50
50
0
150
mV
mV
mV
µA
µA
µA
µA
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
driver switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
r
t
f
t
sk(p)
t
sk(pp)
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
t
jit(per)
t
jit(cc)
t
jit(pp)
†
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
NOTES: 4. t
Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output 1.6 2.3 4.1 ns
Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output 1.6 2.3 4.1 ns
Differential output signal rise time
Differential output signal fall time
Pulse skew (|t
Part-to-part skew (see Note 4) 900 ps
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-high-level output 1.5 3.7 6.5 ns
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-low-level output
Propagation delay time, high-level-to-high-impedance output
Propagation delay time, low-level-to-high-impedance output 1.8 3.5 6.1 ns
Period jitter, rms (1 standard deviation) (see Notes 5 and 6)
Cycle-to-cycle jitter, peak (see Notes 5 and 6)
Peak-to-peak jitter, (see Notes 5, 7, and 8)
is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any specified terminals of two devices when both
sk(pp)
devices operate with the same supply voltages, at the same temperature, and have identical packages and test circuits.
5. Jitter parameters are based on design and characterization. Stimulus system jitter of 11 ps t
been subtracted from the values.
6. Input voltage = 0 V to VCC, tr = tf ≤ 1 ns (20% to 80%), measured over 30k samples.
7. Input voltage = 0 V to VCC, tr = tf ≤ 1 ns (20% to 80%), measured over 100k samples.
8. Peak-to-peak jitter includes jitter due to pulse skew (t
PHL
–- t
|) 30 ps
PLH
).
sk(p)
See Figure 5
See Figure 6
50-MHz clock input
(see Figure 8)
50-MHz clock input
(see Figure 8)
100 Mbps 215–1 PRBS
input (see Figure 8)
1.5 2 3 ns
1.5 2 3 ns
1.5 3.7 6.5 ns
1.3 3.5 6.8 ns
23 ps
180 ps
210 ps
, 43 ps t
jit(per)
jit(cc)
, or 54 ps t
jit(pp)
have
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
Period jitter, rms (1 standard deviation)
50 MHz clock in ut
50 MHz clock in ut
100 Mb s 2 1 PRBS
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
receiver switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
sk(p)
t
sk(pp)
t
r
t
f
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
sk(p)
t
sk(pp)
t
r
t
f
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
jit(per)
t
jit(cc)
t
jit(pp)
†
All typical values are at 25°C and with a 3.3-V supply voltage.
NOTES: 9. t
Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output 3 5 6.7 ns
Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output 3 4.6 6.7 ns
Pulse skew (|t
Part-to-part skew (see Note 9)
Output signal rise time 0.8 1.4 2 ns
Output signal fall time 0.8 1.5 2 ns
Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output 3.4 5.8 9 ns
Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output 3.4 5.4 9 ns
Pulse skew (|t
Part-to-part skew (see Note 9)
Output signal rise time 1 2 2.6 ns
Output signal fall time 1 1.4 2.6 ns
Propagation delay time, high-level-to-high-impedance
output
Propagation delay time, low-level-to-high-impedance
output
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-high-level
output
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-low-level
output
Period jitter, rms (1 standard deviation) 50-MHz clock input
(see Notes 10 and 11)
Cycle-to-cycle jitter, peak (see Notes 10 and 11)
Peak-to-peak jitter, (see Notes 10, 12, and 13)
is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any specified terminals of two devices when both
sk(pp)
devices operate with the same supply voltages, at the same temperature, and have identical packages and test circuits.
10. Jitter parameters are based on design and characterization. Stimulus system jitter of 11 ps t
been subtracted from the values.
11. Differential input voltage = 250 mV
samples.
12. Differential input voltage = 250 mV
samples.
13. Peak-to-peak jitter includes jitter due to pulse skew (t
PHL
PHL
–- t
–- t
PLH
PLH
|)
|)
(Type 1) or 500 mV
p–p
(Type 1) or 500 mV
p–p
CL = 5 pF, See Figure 10
CL = 15 pF, See Figure 10
See Figure 11
Type 1 10
(see Figure 12)
50-MHz clock input
(see Figure 12)
100 Mbps 215–1 PRBS
input (see Figure 12)
(Type 2), VCM = 1 V , tr = tf ≤ 1 ns (20% to 80%), measured over 30k
p–p
(Type 2), VCM = 1 V , tr = tf ≤ 1 ns (20% to 80%), measured over 100k
p–p
).
sk(p)
Type 2 10
Type 1 93
Type 2 86
Type 1 850
Type 2 790
, 43 ps t
jit(per)
400 ps
1.5 ns
400 ps
2.5 ns
4.5 6 15 ns
2 3.4 5 ns
3.5 9.8 15 ns
4 8.7 15 ns
, or 54 ps t
jit(cc)
jit(pp)
ps
ps
ps
have
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
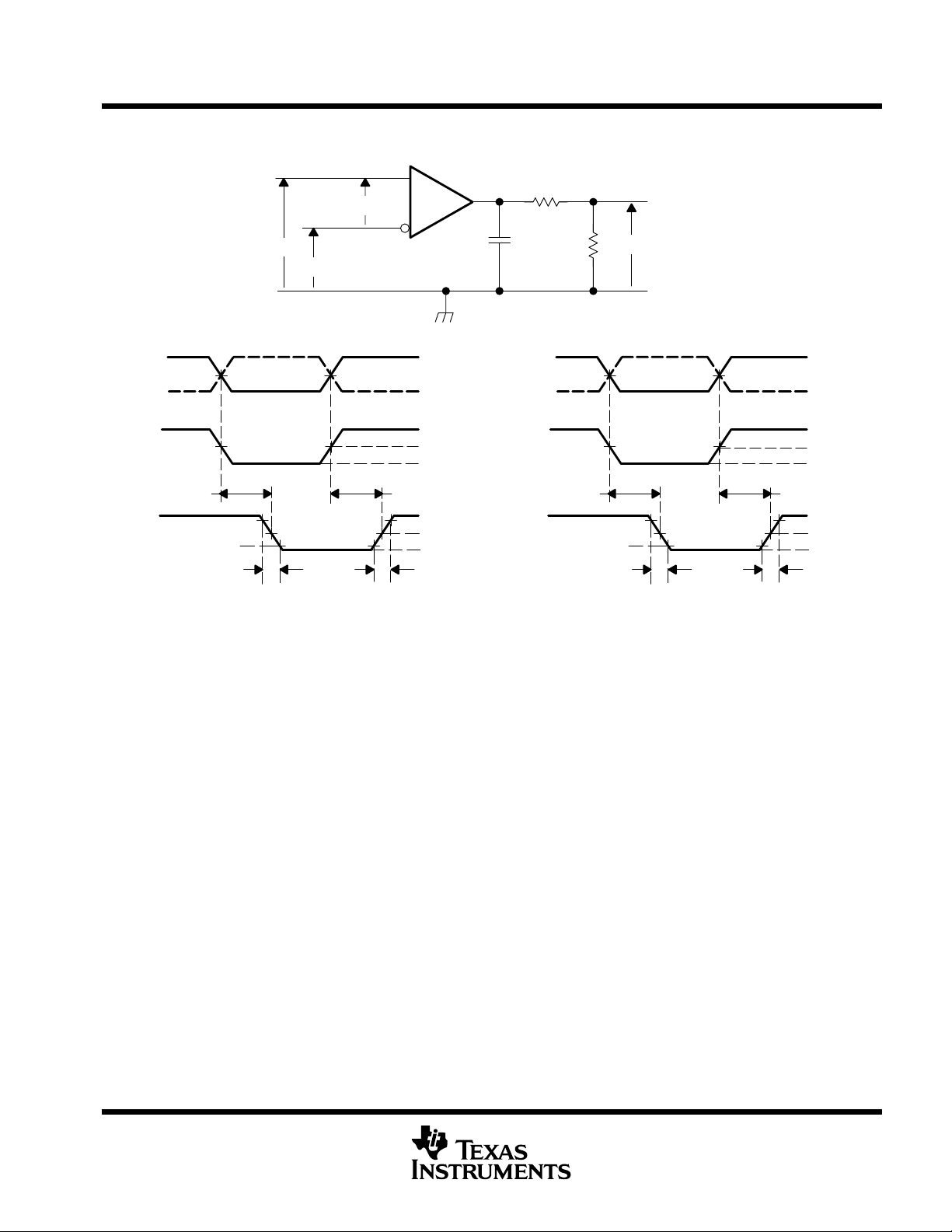
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
V
CC
IA or I
IB or I
Y
Z
VAB or V
VB or V
YZ
Z
VA or V
Y
V
OS
VA + V
2
B
VY + V
or
Z
2
I
I
V
I
A/Y
D
B/Z
Figure 1. Driver Voltage and Current Definitions
3.32 kΩ
49.9 Ω
3.32 kΩ
+
_
–1 V ≤ V
test
≤ 3.4 V
D
NOTE: All resistors are 1% tolerance.
A/Y
VAB or V
B/Z
YZ
Figure 2. Differential Output Voltage Test Circuit
A/Y
24.9 Ω ±1%
A/Y
D
B/Z
24.9 Ω ±1%
NOTE: All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 0.25 Mpps,
pulse width = 500 ±10 ns. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0,06 m of the D.U.T . The measurement of V
is made on test equipment with a –3-dB bandwidth of at least 1 GHz.
C
L
2 pF
V
OS
B/Z
V
OS(PP)
V
OS
V
OS(SS)
≈ 1.3 V
≈ 0.7 V
OS(PP)
Figure 3. Test Circuit and Definitions for the Driver Common-Mode Output Voltage
I
OS
+
V
Test
–1 V or 3.4 V
0 V or V
A/Y
CC
B/Z
–
Figure 4. Driver Short-Circuit Test Circuit
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
A/Y
C
0.5 pF
D
B/Z
Input
t
PLH
V
Output
V
P(L)
NOTE: All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 1 Mpps,
pulse width = 0.5 ±0.05 µs. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0,06 m of the D.U.T.
P(H)
0 V
L
t
f
Output
t
PHL
49.9 Ω ±1%
(Metal Film Surface Mount)
V
CC
VCC/2
0 V
V
SS
0.9V
0.1V
0 V
0 V
SS
t
r
SS
SS
Figure 5. Driver Test Circuit, Timing, and Voltage Definitions for the Differential Output Signal
24.9 Ω ±1%
Output
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
(2 Places)
V
CC
VCC/2
0 V
∼ 0.6 V
0.1 V
0 V
0 V
–0.1 V
∼ –0.6 V
+
1 V
A/Y
C
L
0 V or V
Output With
NOTE: All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 0.25 Mpps,
pulse width = 500 ±10 ns. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0,06 m of the D.U.T.
CC
DE
DE
Output With
D at V
CC
D at 0 V
t
PZH
t
PZL
B/Z
0.5 pF
10
Figure 6. Driver Enable and DIsable Time Circuit and Definitions
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
A/Y
0 V or V
CC
B/Z
C
Figure 7. Maximum Steady-State Output Voltage Test Circuit
VA, VB, VY or V
1.62 kΩ
Z
V
CLOCK
INPUT
1/f0
Period Jitter
IDEAL
OUTPUT
VA –VB or VY –V
ACTUAL
OUTPUT
VA –VB or VY –V
NOTES: A. All input pulses are supplied by an Agilent 8304A Stimulus System.
0 V
jit(per)
1/f0
t
c(n)
= t
c(n)
–1/f0
Z
0 V
Z
t
B. The measurement is made on a TEK TDS6604 running TDSJIT3 application software
C. Period jitter is measured using a 100 MHz 50 ±1% duty cycle clock input.
D. Peak-to-peak jitter is measured using a 200Mbps 215–1 PRBS input.
CC
VCC/2
0 V
VA –VB or VY –V
OUTPUT
0 V DIFF
PRBS INPUT
VA – VB or VY – V
OUTPUT
Figure 8. Driver Jitter Measurement Waveforms
I
A
V
I
ID
B
Z
0 V Diff
A
B
t
c(n)
t
= | t
jit(cc)
Z
R
c(n)
Peak to Peak Jitter
t
jit(pp)
I
O
– t
t
c(n+1)
c(n+1)
|
V
CC
VCC/2
0 V
V
V
CM
(VA + VB)/2
A
V
B
Figure 9. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
V
O
11

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Table 1. Type-1 Receiver Input Threshold Test Voltages
APPLIED VOLTAGES
V
A
3.425 V 3.375 V 50 mV 3.4 V H
3.375 V 3.425 V –50 mV 3.4 V L
–0.975 V –1.025 V 50 mV –1.0 V H
–1.025 V –0.975 V –50 mV –1.0 V L
3.800 V 3.000 V 800 mV 3.4 V H
3.000 V 3.800 V –800 mV 3.4 V L
–0.600 V –1.400 V 800 mV –1.0 V H
–1.400 V –0.600 V –800 mV –1.0 V L
NOTE: H= high level, L = low level. Output state assumes receiver is enabled (RE is Low).
V
B
RESULTING DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT VOLTAGE
V
ID
RESULTING COMMON-
MODE INPUT VOLTAGE
V
CM
RECEIVER OUTPUT
Table 2. Type-2 Receiver Input Threshold Test Voltages
APPLIED VOLTAGES
V
A
3.475 V 3.325 V 150 mV 3.4 V H
3.425 V 3.375 V 50 mV 3.4 V L
–0.925 V –1.075 V 150 mV –1.0 V H
–0.975 V –1.025 V 50 mV –1.0 V L
3.800 V 3.000 V 800 mV 3.4 V H
3.000 V 3.800 V –800 mV 3.4 V L
–0.600 V –1.400 V 800 mV –1.0 V H
–1.400 V –0.600 V –800 mV –1.0 V L
NOTE: H= high level, L = low level. Output state assumes receiver is enabled (RE is Low).
V
B
RESULTING DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT VOLTAGE
V
ID
RESULTING COMMON–
MODE INPUT VOLTAGE
V
CM
RECEIVER OUTPUT
V
O
V
O
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
R1
453 Ω
V
ID
V
V
V
ID
V
49.9 Ω
A
B
O
R2
t
PHL
90%
10%
V
O
1.2 V
0.8 V
0.4 V
0.1 V
–0.4 V
t
PLH
0.1 V
OH
0.1 VCC/2
0.1 V
OL
t
f
Type 2
t
r
C
1.1 V
0.9 V
0.2 V
0 V
0.1 V
OH
0.1 VCC/2
0.1 V
OL
L
V
A
V
B
V
A
V
B
V
ID
–0.2 V
t
pHL
V
O
NOTES: A. All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 1 Mpps,
B. Resistors are 1% tolerance, metal film, and surface mount.
C. CL is 20% tolerance, low-loss ceramic, and surface mount.
D. R1 and CL are located within 2 cm of the D.U.T.
E. R2 is located within 15 cm of the D.U.T.
90%
10%
t
f
Type 1
pulse width = 0.5 ±0.05 µs.
t
r
t
pLH
Figure 10. Receiver Timing Test Circuit and Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
RE
t
t
B
A
PZL
PZH
R
C
L
5 pF
1.2 V
Inputs
V
TEST
A
Inputs
RE
V
TEST
R
A
RE
R
Output
Inputs
Output
NOTE: All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 0.25 Mpps,
pulse width = 500 ±10 ns. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0,06 m of the D.U.T.
500 Ω ±1%
Output
t
PLZ
t
PHZ
+
V
_
V
1 V
V
VCC/2
0 V
V
VCC/2
VOL +0.5 V
V
0 V
1.4 V
V
VCC/2
0 V
V
VOH –0.5 V
VCC/2
0 V
test
CC
CC
CC
OL
CC
OH
14
Figure 11. Receiver Enable/Disable Time T est Circuit and Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
CLOCK INPUT
VA – V
B
V
IDEAL
OUTPUT
ACTUAL
OUTPUT
NOTES: A. All input pulses are supplied by an Agilent 8304A Stimulus System.
OH
VCC/2
V
OL
V
OH
VCC/2
V
OL
t
B. The measurement is made on a TEK TDS6604 running TDSJIT3 application software
C. Period jitter is measured using a 100 MHz 50 ±1% duty cycle clock input.
D. Peak-to-peak jitter is measured using a 200Mbps 215–1 PRBS input.
Period Jitter
= t
jit(per)
1/f0
1/f0
t
c(n)
c(n)
–1/f0
INPUTS
VA – V
B
0.25 V – Type 1
0.5 V – Type 2
V
1 V
IC
OUTPUT
V
OH
VCC/2
V
OL
PRBS INPUT
OUTPUT
VCC/2
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
t
c(n)
t
= | t
jit(cc)
V
A
V
B
V
OH
V
OL
c(n)
Peak to Peak Jitter
t
jit(pp)
– t
t
c(n+1)
c(n+1)
|
Figure 12. Receiver Jitter Measurement Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
15

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DRIVER LOW-TO-HIGH PROPAGATION DELAY
vs
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
2.5
See Figure 5
VCC = 3 V
2.4
2.3
2.2
– Driver Low-to-High Propagation Delay – ns
PLH
2.1
t
–50 0 50 100
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
VCC = 3.3 V
VCC = 3.6 V
Figure 13
RECEIVER LOW-TO-HIGH PROPAGATION DELAY
vs
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
5.5
CL = 5 pF
See Figure 9
VCC = 3 V
DRIVER HIGH-TO-LOW PROPAGATION DELAY
vs
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
2.5
See Figure 5
VCC = 3 V
2.4
VCC = 3.3 V
2.3
VCC = 3.6 V
2.2
– Driver High-to-Low Propagation Delay – ns
PHL
t
2.1
–50 0 50 100
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
Figure 14
RECEIVER HIGH-TO-LOW PROPAGATION DELAY
vs
FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE
5.5
CL = 5 pF
See Figure 9
VCC = 3.3 V
5
VCC = 3.6 V
4.5
– Receiver Low-to-High Propagation Delay – ns
PLH
4
t
–50 0 50 100
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
Figure 15
16
5
VCC = 3.3 V
4.5
– Receiver High-to-Low Propagation Delay – ns
PHL
t
4
–50 0 50 100
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
VCC = 3 V
VCC = 3.6 V
TA – Free-Air Temperature – °C
Figure 16

MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
DRIVER LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs
LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
15
TA = 25 °C
VCC = 3.3 V
10
5
0
– Driver Low-Level Output Current – mA
OL
I
–5
–10 1 2 3
VOL – Low-Level Output Voltage – V
Figure 17
RECEIVER LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs
LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
120
TA = 25 °C
VCC = 3.3 V
100
DRIVER HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs
HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
5
TA = 25 °C
VCC = 3.3 V
0
–5
–10
– Driver High-Level Output Current – mA
OH
I
–15
4
–10123
VOH – High-Level Output Voltage – V
4
Figure 18
RECEIVER HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs
HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
20
TA = 25 °C
VCC = 3.3 V
0
80
60
40
20
– Receiver Low-Level Output Current – mA
OL
I
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
VOL – Low-Level Output Voltage – V
Figure 19
–20
–40
–60
– Receiver High-Level Output Current – mA
OH
I
3.5 4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
–80
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
VOH – High-Level Output Voltage – V
3 3.5 4
Figure 20
17

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs
OUTPUT CURRENT
2
1.6
1.2
0.8
Differential Output Voltage – V
0.4
VCC = 3.3 V
TA = 25°C
0
046 12
28
IO – Output Current – mA
10
Figure 21
AVERAGE RECEIVER SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
20
50% Duty Cycle
RL = 500 Ω
CL = 5 pF
TA = 25°C
15
See Figure 9
FREQUENCY
VCC = 3.6 V
AVERAGE DRIVER SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
FREQUENCY
17
50% Duty Cycle
RL = 50 Ω
TA = 25°C
See Figure 5
16
VCC = 3.3 V
15
14
13
– Average Driver Supply Current – mA
CC
I
Note: 100 MHz = 200 Mbps
12
0 25 50 75 100
f – Frequency – MHz
VCC = 3.6 V
VCC = 3 V
Figure 22
ADDED DRIVER PERIOD JITTER (1 SIGMA)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
50
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = Clock
40
18
VCC = 3.3 V
10
VCC = 3 V
5
– Average Receiver Supply Current – mA
CC
I
Note: 100 MHz = 200 Mbps
0
0 25 50 75 100
f – Frequency – MHz
Figure 23
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
30
20
– Driver Period Jitter (1 Sigma) – ps
10
jit(per)
t
0
10 20 30 40 50
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
Figure 24

MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
ADDED TYPE 1 RECEIVER PERIOD JITTER (1 SIGMA)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
25
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = Clock,
20
VID = 250 mV
VIC = 3 V
15
10
– Receiver Period Jitter (1 Sigma) – ps
5
jit(per)
t
0
10 20 30 40 50
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
VIC = –0.5 V
VIC = 1 V
Figure 25
ADDED DRIVER CYCLE-TO-CYCLE JITTER (PEAK)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
250
ADDED TYPE 2 RECEIVER PERIOD JITTER (1 SIGMA)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
25
VCC = 3.3 V,
20
15
10
– Receiver Period Jitter (1 Sigma) – ps
jit(per)
t
TA = 25°C,
Input = Clock,
VID = 500 mV
VIC = 1 V
5
0
10 20 30 40 50
VIC = 3 V
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
VIC = –0.5 V
Figure 26
ADDED TYPE 1 RECEIVER CYCLE-TO-CYCLE
JITTER (PEAK)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
250
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = Clock
0
10 20 30 40 50
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
– Driver Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter (Peak) – ps
jit(cc)
t
200
150
100
50
Figure 27
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = Clock,
VID = 250 mV
VIC = –0.5 V
VIC = 3 V
VIC = 1 V
0
10 20 30 40 50
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
– Receiver Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter (Peak) – ps
jit(cc)
t
200
150
100
50
Figure 28
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
19

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ADDED TYPE 2 RECEIVER CYCLE-TO-CYCLE
JITTER (PEAK)
vs
CLOCK FREQUENCY
250
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
200
Input = Clock,
VID = 500 mV
150
VIC = –0.5 V
100
50
– Receiver Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter (Peak) – ps
jit(cc)
t
0
10 20 30 40 50
VIC = 3 V
f – Clock Frequency – MHz
VIC = 1 V
Figure 29
ADDED DRIVER PEAK-TO-PEAK JITTER
vs
DATA RATE
250
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = PRBS(215 – 1)
50
0
20 40 60 80 100
Data Rate – Mbps
– Driver Peak-to-Peak Jitter – ps
jit(pp)
t
200
150
100
Figure 30
ADDED TYPE 1 RECEIVER PEAK-TO-PEAK JITTER
vs
DATA RATE
2000
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
1600
1200
– Receiver Peak-to-Peak Jitter – ps
jit(pp)
t
Input = PRBS(215 – 1),
VID = 250 mV
800
400
0
20 40 60 80 100
Data Rate – Mbps
Figure 31
ADDED TYPE 2 RECEIVER PEAK-TO-PEAK JITTER
vs
DATA RATE
– Receiver Peak-to-Peak Jitter – ps
jit(pp)
t
2000
1600
1200
800
400
VCC = 3.3 V,
TA = 25°C,
Input = PRBS(215 – 1),
VID = 500 mV
0
20 40 60 80 100
Data Rate – Mbps
Figure 32
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Type-1 and Type-2 receivers
The M-L VDS standard defines Type-1 and T ype-2 receivers. T ype-1 receivers include no provisions for failsafe
and have their differential input voltage thresholds near zero volts. T ype-2 receivers have their differential input
voltage thresholds offset from zero volts to detect the absence of a voltage difference. Type-1 receivers
maximize the differential noise margin and are intended for maximum signaling rates. Type-2 receivers are
intended for control signals and slower signaling rates. The impact on receiver output by the offset input can
be seen in Table 3 and Figure 33.
Table 3. M-LVDS Receiver Input Voltage Threshold Requirements
Receiver T ype Output Low Output High
1 –2.4 V ≤ VID ≤ –0.05 V 0.05 V ≤ VID ≤ 2.4 V
2 –2.4 V ≤ VID ≤ 0.05 V 0.15 V ≤ VID ≤ 2.4 V
200
Type 1
Type 2
High
150
High
100
50
0
– Differential Input Voltage – mV
ID
V
–50
Low
Low
–100
Transition Regions
Figure 33. Receiver Differential Input Voltage Showing Transition Region
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
21

SN65MLVD200, SN65MLVD202
SN65MLVD204, SN65MLVD205
MULTIPOINT–LVDS LINE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
SLLS463E – SEPTEMBER 2001 – REVISED JUNE 2003
APPLICATION INFORMATION
comparison of M-LVDS with RS-485
RS-485 applications are similar to M-L VDS. The two standards define balanced multipoint systems with some
basic architecture changes due to the different applications. Table 4 gives a high-level comparison of the two
different technologies.
Table 4. Comparison Between M-L VDS and RS-485 Standards
Number of Loads
RS-485 32 1.5 V to 5 V –7 V to 12 V 50 Mbps ±200 mV
M-LVDS 32 480 mV to 650 mV –1 V to 3.4 V 500 Mbps ±50 mV
Differential Voltage
Range
Common-Mode
Voltage Range
Maximum Signaling
Rate (Mbps)
Receiver Minimum
Threshold
It can be seen that with the greater differential output voltage and common-mode voltage range of the
RS-485-type device, it can handle longer signaling distances where M-L VDS offers ten times the signaling rate
of RS-485.
SN65MLVD200SN65MLVD200
R
T
Up to 32
Transceivers
NOTE A: The line should be terminated at both ends in its characteristic impedance (RT = ZO). Stub lengths off the main line should be kept
as short as possible.
R
T
Figure 34. Typical Application Circuit
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty . Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. T o minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third–party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party , or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products & application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated

Copyright © Each Manufacturing Company.
All Datasheets cannot be modified without permission.
This datasheet has been download from :
www.AllDataSheet.com
100% Free DataSheet Search Site.
Free Download.
No Register.
Fast Search System.
www.AllDataSheet.com
 Loading...
Loading...