Page 1

PRELIMINARY
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DATA SHEET
Copyright © 2007 Luminary Micro, Inc.DS-LM3S2533-1972
Page 2

Legal Disclaimers and Trademark Information
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH LUMINARY MICRO PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT
AS PROVIDED IN LUMINARY MICRO'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, LUMINARY MICRO ASSUMES NO
LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,AND LUMINARYMICRO DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY,RELATING TO SALE AND/OR
USE OF LUMINARY MICRO'S PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
LUMINARY MICRO'S PRODUCTS ARE NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN MEDICAL, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE-SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS.
Luminary Micro may make changes to specications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Contact your local Luminary Micro sales ofce
or your distributor to obtain the latest specications before placing your product order.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undened." Luminary Micro reserves these
for future denition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Copyright © 2007 Luminary Micro, Inc. All rights reserved. Stellaris, Luminary Micro, and the Luminary Micro logo are registered trademarks of
Luminary Micro, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. ARM and Thumb are registered trademarks and Cortex is a trademark
of ARM Limited. Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Luminary Micro, Inc.
108 Wild Basin, Suite 350
Austin, TX 78746
Main: +1-512-279-8800
Fax: +1-512-279-8879
http://www.luminarymicro.com
Preliminary
November 30, 20072
Page 3

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Table of Contents
About This Document .................................................................................................................... 20
Audience .............................................................................................................................................. 20
About This Manual ................................................................................................................................ 20
Related Documents ............................................................................................................................... 20
Documentation Conventions .................................................................................................................. 20
1 Architectural Overview ...................................................................................................... 22
1.1 Product Features ...................................................................................................................... 22
1.2 Target Applications .................................................................................................................... 28
1.3 High-Level Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 28
1.4 Functional Overview .................................................................................................................. 29
1.4.1 ARM Cortex™-M3 ..................................................................................................................... 30
1.4.2 Motor Control Peripherals .......................................................................................................... 30
1.4.3 Analog Peripherals .................................................................................................................... 31
1.4.4 Serial Communications Peripherals ............................................................................................ 32
1.4.5 System Peripherals ................................................................................................................... 33
1.4.6 Memory Peripherals .................................................................................................................. 34
1.4.7 Additional Features ................................................................................................................... 34
1.4.8 Hardware Details ...................................................................................................................... 35
2 ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core ...................................................................................... 36
2.1 Block Diagram .......................................................................................................................... 37
2.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................... 37
2.2.1 Serial Wire and JTAG Debug ..................................................................................................... 37
2.2.2 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) ............................................................................................. 38
2.2.3 Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU) ................................................................................................. 38
2.2.4 ROM Table ............................................................................................................................... 38
2.2.5 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) ................................................................................................... 38
2.2.6 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) ................................................................................ 38
3 Memory Map ....................................................................................................................... 42
4 Interrupts ............................................................................................................................ 44
5 JTAG Interface .................................................................................................................... 47
5.1 Block Diagram .......................................................................................................................... 48
5.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................... 48
5.2.1 JTAG Interface Pins .................................................................................................................. 49
5.2.2 JTAG TAP Controller ................................................................................................................. 50
5.2.3 Shift Registers .......................................................................................................................... 51
5.2.4 Operational Considerations ........................................................................................................ 51
5.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................... 54
5.4 Register Descriptions ................................................................................................................ 54
5.4.1 Instruction Register (IR) ............................................................................................................. 54
5.4.2 Data Registers .......................................................................................................................... 56
6 System Control ................................................................................................................... 58
6.1 Functional Description ............................................................................................................... 58
6.1.1 Device Identification .................................................................................................................. 58
6.1.2 Reset Control ............................................................................................................................ 58
Preliminary
3November 30, 2007
Page 4

Table of Contents
6.1.3 Power Control ........................................................................................................................... 61
6.1.4 Clock Control ............................................................................................................................ 61
6.1.5 System Control ......................................................................................................................... 63
6.2 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................... 64
6.3 Register Map ............................................................................................................................ 64
6.4 Register Descriptions ................................................................................................................ 65
7 Hibernation Module .......................................................................................................... 118
7.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 119
7.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 119
7.2.1 Register Access Timing ........................................................................................................... 119
7.2.2 Clock Source .......................................................................................................................... 120
7.2.3 Battery Management ............................................................................................................... 120
7.2.4 Real-Time Clock ...................................................................................................................... 120
7.2.5 Non-Volatile Memory ............................................................................................................... 121
7.2.6 Power Control ......................................................................................................................... 121
7.2.7 Interrupts and Status ............................................................................................................... 121
7.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 122
7.3.1 Initialization ............................................................................................................................. 122
7.3.2 RTC Match Functionality (No Hibernation) ................................................................................ 122
7.3.3 RTC Match/Wake-Up from Hibernation ..................................................................................... 122
7.3.4 External Wake-Up from Hibernation .......................................................................................... 123
7.3.5 RTC/External Wake-Up from Hibernation .................................................................................. 123
7.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 123
7.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 124
8 Internal Memory ............................................................................................................... 137
8.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 137
8.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 137
8.2.1 SRAM Memory ........................................................................................................................ 137
8.2.2 Flash Memory ......................................................................................................................... 138
8.3 Flash Memory Initialization and Configuration ........................................................................... 139
8.3.1 Flash Programming ................................................................................................................. 139
8.3.2 Nonvolatile Register Programming ........................................................................................... 140
8.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 140
8.5 Flash Register Descriptions (Flash Control Offset) ..................................................................... 141
8.6 Flash Register Descriptions (System Control Offset) .................................................................. 148
9 General-Purpose Input/Outputs (GPIOs) ....................................................................... 161
9.1 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 161
9.1.1 Data Control ........................................................................................................................... 162
9.1.2 Interrupt Control ...................................................................................................................... 163
9.1.3 Mode Control .......................................................................................................................... 164
9.1.4 Commit Control ....................................................................................................................... 164
9.1.5 Pad Control ............................................................................................................................. 164
9.1.6 Identification ........................................................................................................................... 164
9.2 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 164
9.3 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 166
9.4 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 167
Preliminary
November 30, 20074
Page 5

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
10 General-Purpose Timers ................................................................................................. 202
10.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 202
10.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 203
10.2.1 GPTM Reset Conditions .......................................................................................................... 204
10.2.2 32-Bit Timer Operating Modes .................................................................................................. 204
10.2.3 16-Bit Timer Operating Modes .................................................................................................. 205
10.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 209
10.3.1 32-Bit One-Shot/Periodic Timer Mode ....................................................................................... 209
10.3.2 32-Bit Real-Time Clock (RTC) Mode ......................................................................................... 210
10.3.3 16-Bit One-Shot/Periodic Timer Mode ....................................................................................... 210
10.3.4 16-Bit Input Edge Count Mode ................................................................................................. 211
10.3.5 16-Bit Input Edge Timing Mode ................................................................................................ 211
10.3.6 16-Bit PWM Mode ................................................................................................................... 212
10.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 212
10.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 213
11 Watchdog Timer ............................................................................................................... 238
11.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 238
11.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 238
11.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 239
11.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 239
11.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 240
12 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) ................................................................................. 261
12.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 262
12.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 262
12.2.1 Sample Sequencers ................................................................................................................ 262
12.2.2 Module Control ........................................................................................................................ 263
12.2.3 Hardware Sample Averaging Circuit ......................................................................................... 264
12.2.4 Analog-to-Digital Converter ...................................................................................................... 264
12.2.5 Test Modes ............................................................................................................................. 264
12.2.6 Internal Temperature Sensor .................................................................................................... 264
12.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 265
12.3.1 Module Initialization ................................................................................................................. 265
12.3.2 Sample Sequencer Configuration ............................................................................................. 265
12.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 266
12.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 267
13 Universal Asynchronous Receivers/Transmitters (UARTs) ......................................... 294
13.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 295
13.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 295
13.2.1 Transmit/Receive Logic ........................................................................................................... 295
13.2.2 Baud-Rate Generation ............................................................................................................. 296
13.2.3 Data Transmission .................................................................................................................. 297
13.2.4 Serial IR (SIR) ......................................................................................................................... 297
13.2.5 FIFO Operation ....................................................................................................................... 298
13.2.6 Interrupts ................................................................................................................................ 298
13.2.7 Loopback Operation ................................................................................................................ 299
13.2.8 IrDA SIR block ........................................................................................................................ 299
13.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 299
13.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 300
Preliminary
5November 30, 2007
Page 6

Table of Contents
13.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 301
14 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) ................................................................................ 335
14.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 335
14.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 335
14.2.1 Bit Rate Generation ................................................................................................................. 336
14.2.2 FIFO Operation ....................................................................................................................... 336
14.2.3 Interrupts ................................................................................................................................ 336
14.2.4 Frame Formats ....................................................................................................................... 337
14.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 344
14.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 345
14.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 346
15 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface ............................................................................ 372
15.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 372
15.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 372
15.2.1 I2C Bus Functional Overview .................................................................................................... 373
15.2.2 Available Speed Modes ........................................................................................................... 375
15.2.3 Interrupts ................................................................................................................................ 376
15.2.4 Loopback Operation ................................................................................................................ 376
15.2.5 Command Sequence Flow Charts ............................................................................................ 377
15.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 383
15.4 I2C Register Map ..................................................................................................................... 384
15.5 Register Descriptions (I2C Master) ........................................................................................... 385
15.6 Register Descriptions (I2C Slave) ............................................................................................. 398
16 Controller Area Network (CAN) Module ......................................................................... 407
16.1 Controller Area Network Overview ............................................................................................ 407
16.2 Controller Area Network Features ............................................................................................ 407
16.3 Controller Area Network Block Diagram .................................................................................... 408
16.4 Controller Area Network Functional Description ......................................................................... 409
16.4.1 Initialization ............................................................................................................................. 409
16.4.2 Operation ............................................................................................................................... 410
16.4.3 Transmitting Message Objects ................................................................................................. 410
16.4.4 Configuring a Transmit Message Object .................................................................................... 410
16.4.5 Updating a Transmit Message Object ....................................................................................... 411
16.4.6 Accepting Received Message Objects ...................................................................................... 411
16.4.7 Receiving a Data Frame .......................................................................................................... 412
16.4.8 Receiving a Remote Frame ...................................................................................................... 412
16.4.9 Receive/Transmit Priority ......................................................................................................... 412
16.4.10 Configuring a Receive Message Object .................................................................................... 412
16.4.11 Handling of Received Message Objects .................................................................................... 413
16.4.12 Handling of Interrupts .............................................................................................................. 413
16.4.13 Bit Timing Configuration Error Considerations ........................................................................... 414
16.4.14 Bit Time and Bit Rate ............................................................................................................... 414
16.4.15 Calculating the Bit Timing Parameters ...................................................................................... 416
16.5 Controller Area Network Register Map ...................................................................................... 418
16.6 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 420
17 Analog Comparators ....................................................................................................... 448
17.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 449
Preliminary
November 30, 20076
Page 7

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
17.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 449
17.2.1 Internal Reference Programming .............................................................................................. 451
17.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 452
17.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 452
17.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 453
18 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) ........................................................................................ 461
18.1 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................ 461
18.2 Functional Description ............................................................................................................. 461
18.2.1 PWM Timer ............................................................................................................................. 461
18.2.2 PWM Comparators .................................................................................................................. 462
18.2.3 PWM Signal Generator ............................................................................................................ 463
18.2.4 Dead-Band Generator ............................................................................................................. 464
18.2.5 Interrupt/ADC-Trigger Selector ................................................................................................. 464
18.2.6 Synchronization Methods ......................................................................................................... 464
18.2.7 Fault Conditions ...................................................................................................................... 465
18.2.8 Output Control Block ............................................................................................................... 465
18.3 Initialization and Configuration ................................................................................................. 465
18.4 Register Map .......................................................................................................................... 466
18.5 Register Descriptions .............................................................................................................. 468
19 Pin Diagram ...................................................................................................................... 497
20 Signal Tables .................................................................................................................... 498
21 Operating Characteristics ............................................................................................... 512
22 Electrical Characteristics ................................................................................................ 513
22.1 DC Characteristics .................................................................................................................. 513
22.1.1 Maximum Ratings ................................................................................................................... 513
22.1.2 Recommended DC Operating Conditions .................................................................................. 513
22.1.3 On-Chip Low Drop-Out (LDO) Regulator Characteristics ............................................................ 514
22.1.4 Power Specifications ............................................................................................................... 514
22.1.5 Flash Memory Characteristics .................................................................................................. 516
22.2 AC Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 516
22.2.1 Load Conditions ...................................................................................................................... 516
22.2.2 Clocks .................................................................................................................................... 516
22.2.3 Analog-to-Digital Converter ...................................................................................................... 517
22.2.4 Analog Comparator ................................................................................................................. 518
22.2.5 I2C ......................................................................................................................................... 518
22.2.6 Hibernation Module ................................................................................................................. 519
22.2.7 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) ........................................................................................... 519
22.2.8 JTAG and Boundary Scan ........................................................................................................ 521
22.2.9 General-Purpose I/O ............................................................................................................... 522
22.2.10 Reset ..................................................................................................................................... 523
23 Package Information ........................................................................................................ 525
A Serial Flash Loader .......................................................................................................... 527
A.1 Serial Flash Loader ................................................................................................................. 527
A.2 Interfaces ............................................................................................................................... 527
A.2.1 UART ..................................................................................................................................... 527
A.2.2 SSI ......................................................................................................................................... 527
Preliminary
7November 30, 2007
Page 8

Table of Contents
A.3 Packet Handling ...................................................................................................................... 528
A.3.1 Packet Format ........................................................................................................................ 528
A.3.2 Sending Packets ..................................................................................................................... 528
A.3.3 Receiving Packets ................................................................................................................... 528
A.4 Commands ............................................................................................................................. 529
A.4.1 COMMAND_PING (0X20) ........................................................................................................ 529
A.4.2 COMMAND_GET_STATUS (0x23) ........................................................................................... 529
A.4.3 COMMAND_DOWNLOAD (0x21) ............................................................................................. 529
A.4.4 COMMAND_SEND_DATA (0x24) ............................................................................................. 530
A.4.5 COMMAND_RUN (0x22) ......................................................................................................... 530
A.4.6 COMMAND_RESET (0x25) ..................................................................................................... 530
B Register Quick Reference ............................................................................................... 532
C Ordering and Contact Information ................................................................................. 552
C.1 Ordering Information ................................................................................................................ 552
C.2 Kits ......................................................................................................................................... 552
C.3 Company Information .............................................................................................................. 552
C.4 Support Information ................................................................................................................. 553
Preliminary
November 30, 20078
Page 9

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Stellaris®2000 Series High-Level Block Diagram ............................................................... 29
Figure 2-1. CPU Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 37
Figure 2-2. TPIU Block Diagram ........................................................................................................ 38
Figure 5-1. JTAG Module Block Diagram ............................................................................................ 48
Figure 5-2. Test Access Port State Machine ....................................................................................... 51
Figure 5-3. IDCODE Register Format ................................................................................................. 56
Figure 5-4. BYPASS Register Format ................................................................................................ 57
Figure 5-5. Boundary Scan Register Format ....................................................................................... 57
Figure 6-1. External Circuitry to Extend Reset .................................................................................... 59
Figure 7-1. Hibernation Module Block Diagram ................................................................................. 119
Figure 8-1. Flash Block Diagram ...................................................................................................... 137
Figure 9-1. GPIO Port Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 162
Figure 9-2. GPIODATA Write Example ............................................................................................. 163
Figure 9-3. GPIODATA Read Example ............................................................................................. 163
Figure 10-1. GPTM Module Block Diagram ........................................................................................ 203
Figure 10-2. 16-Bit Input Edge Count Mode Example .......................................................................... 207
Figure 10-3. 16-Bit Input Edge Time Mode Example ........................................................................... 208
Figure 10-4. 16-Bit PWM Mode Example ............................................................................................ 209
Figure 11-1. WDT Module Block Diagram .......................................................................................... 238
Figure 12-1. ADC Module Block Diagram ........................................................................................... 262
Figure 12-2. Internal Temperature Sensor Characteristic ..................................................................... 265
Figure 13-1. UART Module Block Diagram ......................................................................................... 295
Figure 13-2. UART Character Frame ................................................................................................. 296
Figure 13-3. IrDA Data Modulation ..................................................................................................... 298
Figure 14-1. SSI Module Block Diagram ............................................................................................. 335
Figure 14-2. TI Synchronous Serial Frame Format (Single Transfer) .................................................... 337
Figure 14-3. TI Synchronous Serial Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) ............................................ 338
Figure 14-4. Freescale SPI Format (Single Transfer) with SPO=0 and SPH=0 ...................................... 339
Figure 14-5. Freescale SPI Format (Continuous Transfer) with SPO=0 and SPH=0 .............................. 339
Figure 14-6. Freescale SPI Frame Format with SPO=0 and SPH=1 ..................................................... 340
Figure 14-7. Freescale SPI Frame Format (Single Transfer) with SPO=1 and SPH=0 ........................... 341
Figure 14-8. Freescale SPI Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) with SPO=1 and SPH=0 .................... 341
Figure 14-9. Freescale SPI Frame Format with SPO=1 and SPH=1 ..................................................... 342
Figure 14-10. MICROWIRE Frame Format (Single Frame) .................................................................... 343
Figure 14-11. MICROWIRE Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) ......................................................... 344
Figure 14-12. MICROWIRE Frame Format, SSIFss Input Setup and Hold Requirements ........................ 344
Figure 15-1. I2C Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 372
Figure 15-2. I2C Bus Configuration .................................................................................................... 373
Figure 15-3. START and STOP Conditions ......................................................................................... 373
Figure 15-4. Complete Data Transfer with a 7-Bit Address ................................................................... 374
Figure 15-5. R/S Bit in First Byte ........................................................................................................ 374
Figure 15-6. Data Validity During Bit Transfer on the I2C Bus ............................................................... 374
Figure 15-7. Master Single SEND ...................................................................................................... 377
Figure 15-8. Master Single RECEIVE ................................................................................................. 378
Figure 15-9. Master Burst SEND ....................................................................................................... 379
Preliminary
9November 30, 2007
Page 10

Table of Contents
Figure 15-10. Master Burst RECEIVE .................................................................................................. 380
Figure 15-11. Master Burst RECEIVE after Burst SEND ........................................................................ 381
Figure 15-12. Master Burst SEND after Burst RECEIVE ........................................................................ 382
Figure 15-13. Slave Command Sequence ............................................................................................ 383
Figure 16-1. CAN Module Block Diagram ........................................................................................... 408
Figure 16-2. CAN Bit Time ................................................................................................................ 415
Figure 17-1. Analog Comparator Module Block Diagram ..................................................................... 449
Figure 17-2. Structure of Comparator Unit .......................................................................................... 450
Figure 17-3. Comparator Internal Reference Structure ........................................................................ 451
Figure 18-1. PWM Module Block Diagram .......................................................................................... 461
Figure 18-2. PWM Count-Down Mode ................................................................................................ 462
Figure 18-3. PWM Count-Up/Down Mode .......................................................................................... 463
Figure 18-4. PWM Generation Example In Count-Up/Down Mode ....................................................... 463
Figure 18-5. PWM Dead-Band Generator ........................................................................................... 464
Figure 19-1. Pin Connection Diagram ................................................................................................ 497
Figure 22-1. Load Conditions ............................................................................................................ 516
Figure 22-2. I2C Timing ..................................................................................................................... 519
Figure 22-3. Hibernation Module Timing ............................................................................................. 519
Figure 22-4. SSI Timing for TI Frame Format (FRF=01), Single Transfer Timing Measurement .............. 520
Figure 22-5. SSI Timing for MICROWIRE Frame Format (FRF=10), Single Transfer ............................. 520
Figure 22-6. SSI Timing for SPI Frame Format (FRF=00), with SPH=1 ................................................. 521
Figure 22-7. JTAG Test Clock Input Timing ......................................................................................... 522
Figure 22-8. JTAG Test Access Port (TAP) Timing .............................................................................. 522
Figure 22-9. JTAG TRST Timing ........................................................................................................ 522
Figure 22-10. External Reset Timing (RST) .......................................................................................... 523
Figure 22-11. Power-On Reset Timing ................................................................................................. 524
Figure 22-12. Brown-Out Reset Timing ................................................................................................ 524
Figure 22-13. Software Reset Timing ................................................................................................... 524
Figure 22-14. Watchdog Reset Timing ................................................................................................. 524
Figure 23-1. 100-Pin LQFP Package .................................................................................................. 525
Preliminary
November 30, 200710
Page 11

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
List of Tables
Table 1. Documentation Conventions ............................................................................................ 20
Table 3-1. Memory Map ................................................................................................................... 42
Table 4-1. Exception Types .............................................................................................................. 44
Table 4-2. Interrupts ........................................................................................................................ 45
Table 5-1. JTAG Port Pins Reset State ............................................................................................. 49
Table 5-2. JTAG Instruction Register Commands ............................................................................... 54
Table 6-1. System Control Register Map ........................................................................................... 64
Table 7-1. Hibernation Module Register Map ................................................................................... 123
Table 8-1. Flash Protection Policy Combinations ............................................................................. 139
Table 8-2. Flash Resident Registers ............................................................................................... 140
Table 8-3. Flash Register Map ........................................................................................................ 140
Table 9-1. GPIO Pad Configuration Examples ................................................................................. 165
Table 9-2. GPIO Interrupt Configuration Example ............................................................................ 165
Table 9-3. GPIO Register Map ....................................................................................................... 166
Table 10-1. Available CCP Pins ........................................................................................................ 203
Table 10-2. 16-Bit Timer With Prescaler Configurations ..................................................................... 206
Table 10-3. Timers Register Map ...................................................................................................... 212
Table 11-1. Watchdog Timer Register Map ........................................................................................ 239
Table 12-1. Samples and FIFO Depth of Sequencers ........................................................................ 262
Table 12-2. ADC Register Map ......................................................................................................... 266
Table 13-1. UART Register Map ....................................................................................................... 300
Table 14-1. SSI Register Map .......................................................................................................... 345
Table 15-1. Examples of I2C Master Timer Period versus Speed Mode ............................................... 375
Table 15-2. Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface Register Map ......................................................... 384
Table 15-3. Write Field Decoding for I2CMCS[3:0] Field (Sheet 1 of 3) ................................................ 389
Table 16-1. Transmit Message Object Bit Settings ............................................................................. 411
Table 16-2. Receive Message Object Bit Settings .............................................................................. 413
Table 16-3. CAN Protocol Ranges .................................................................................................... 415
Table 16-4. CAN Register Map ......................................................................................................... 418
Table 17-1. Comparator 0 Operating Modes ...................................................................................... 450
Table 17-2. Comparator 1 Operating Modes ..................................................................................... 450
Table 17-3. Comparator 2 Operating Modes ...................................................................................... 451
Table 17-4. Internal Reference Voltage and ACREFCTL Field Values ................................................. 451
Table 17-5. Analog Comparators Register Map ................................................................................. 453
Table 18-1. PWM Register Map ........................................................................................................ 466
Table 20-1. Signals by Pin Number ................................................................................................... 498
Table 20-2. Signals by Signal Name ................................................................................................. 502
Table 20-3. Signals by Function, Except for GPIO ............................................................................. 506
Table 20-4. GPIO Pins and Alternate Functions ................................................................................. 509
Table 21-1. Temperature Characteristics ........................................................................................... 512
Table 21-2. Thermal Characteristics ................................................................................................. 512
Table 22-1. Maximum Ratings .......................................................................................................... 513
Table 22-2. Recommended DC Operating Conditions ........................................................................ 513
Table 22-3. LDO Regulator Characteristics ....................................................................................... 514
Table 22-4. Detailed Power Specifications ........................................................................................ 515
Table 22-5. Flash Memory Characteristics ........................................................................................ 516
Preliminary
11November 30, 2007
Page 12

Table of Contents
Table 22-6. Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Characteristics ....................................................................... 516
Table 22-7. Clock Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 516
Table 22-8. Crystal Characteristics ................................................................................................... 517
Table 22-9. ADC Characteristics ....................................................................................................... 517
Table 22-10. Analog Comparator Characteristics ................................................................................. 518
Table 22-11. Analog Comparator Voltage Reference Characteristics .................................................... 518
Table 22-12. I2C Characteristics ......................................................................................................... 518
Table 22-13. Hibernation Module Characteristics ................................................................................. 519
Table 22-14. SSI Characteristics ........................................................................................................ 519
Table 22-15. JTAG Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 521
Table 22-16. GPIO Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 523
Table 22-17. Reset Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 523
Table C-1. Part Ordering Information ............................................................................................... 552
Preliminary
November 30, 200712
Page 13

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
List of Registers
System Control .............................................................................................................................. 58
Register 1: Device Identification 0 (DID0), offset 0x000 ....................................................................... 66
Register 2: Brown-Out Reset Control (PBORCTL), offset 0x030 .......................................................... 68
Register 3: LDO Power Control (LDOPCTL), offset 0x034 ................................................................... 69
Register 4: Raw Interrupt Status (RIS), offset 0x050 ........................................................................... 70
Register 5: Interrupt Mask Control (IMC), offset 0x054 ........................................................................ 71
Register 6: Masked Interrupt Status and Clear (MISC), offset 0x058 .................................................... 72
Register 7: Reset Cause (RESC), offset 0x05C .................................................................................. 73
Register 8: Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC), offset 0x060 .......................................................... 74
Register 9: XTAL to PLL Translation (PLLCFG), offset 0x064 .............................................................. 78
Register 10: Run-Mode Clock Configuration 2 (RCC2), offset 0x070 ...................................................... 79
Register 11: Deep Sleep Clock Configuration (DSLPCLKCFG), offset 0x144 .......................................... 81
Register 12: Device Identification 1 (DID1), offset 0x004 ....................................................................... 82
Register 13: Device Capabilities 0 (DC0), offset 0x008 ......................................................................... 84
Register 14: Device Capabilities 1 (DC1), offset 0x010 ......................................................................... 85
Register 15: Device Capabilities 2 (DC2), offset 0x014 ......................................................................... 87
Register 16: Device Capabilities 3 (DC3), offset 0x018 ......................................................................... 89
Register 17: Device Capabilities 4 (DC4), offset 0x01C ......................................................................... 92
Register 18: Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (RCGC0), offset 0x100 .................................... 93
Register 19: Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (SCGC0), offset 0x110 .................................. 95
Register 20: Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (DCGC0), offset 0x120 ......................... 97
Register 21: Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 1 (RCGC1), offset 0x104 .................................... 99
Register 22: Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 1 (SCGC1), offset 0x114 ................................. 102
Register 23: Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 1 (DCGC1), offset 0x124 ....................... 105
Register 24: Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 2 (RCGC2), offset 0x108 ................................... 108
Register 25: Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 2 (SCGC2), offset 0x118 ................................. 110
Register 26: Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 2 (DCGC2), offset 0x128 ....................... 112
Register 27: Software Reset Control 0 (SRCR0), offset 0x040 ............................................................. 114
Register 28: Software Reset Control 1 (SRCR1), offset 0x044 ............................................................. 115
Register 29: Software Reset Control 2 (SRCR2), offset 0x048 ............................................................. 117
Hibernation Module ..................................................................................................................... 118
Register 1: Hibernation RTC Counter (HIBRTCC), offset 0x000 ......................................................... 125
Register 2: Hibernation RTC Match 0 (HIBRTCM0), offset 0x004 ....................................................... 126
Register 3: Hibernation RTC Match 1 (HIBRTCM1), offset 0x008 ....................................................... 127
Register 4: Hibernation RTC Load (HIBRTCLD), offset 0x00C ........................................................... 128
Register 5: Hibernation Control (HIBCTL), offset 0x010 ..................................................................... 129
Register 6: Hibernation Interrupt Mask (HIBIM), offset 0x014 ............................................................. 131
Register 7: Hibernation Raw Interrupt Status (HIBRIS), offset 0x018 .................................................. 132
Register 8: Hibernation Masked Interrupt Status (HIBMIS), offset 0x01C ............................................ 133
Register 9: Hibernation Interrupt Clear (HIBIC), offset 0x020 ............................................................. 134
Register 10: Hibernation RTC Trim (HIBRTCT), offset 0x024 ............................................................... 135
Register 11: Hibernation Data (HIBDATA), offset 0x030-0x12C ............................................................ 136
Internal Memory ........................................................................................................................... 137
Register 1: Flash Memory Address (FMA), offset 0x000 .................................................................... 142
Register 2: Flash Memory Data (FMD), offset 0x004 ......................................................................... 143
Preliminary
13November 30, 2007
Page 14

Table of Contents
Register 3: Flash Memory Control (FMC), offset 0x008 ..................................................................... 144
Register 4: Flash Controller Raw Interrupt Status (FCRIS), offset 0x00C ............................................ 146
Register 5: Flash Controller Interrupt Mask (FCIM), offset 0x010 ........................................................ 147
Register 6: Flash Controller Masked Interrupt Status and Clear (FCMISC), offset 0x014 ..................... 148
Register 7: USec Reload (USECRL), offset 0x140 ............................................................................ 149
Register 8: Flash Memory Protection Read Enable 0 (FMPRE0), offset 0x130 and 0x200 ................... 150
Register 9: Flash Memory Protection Program Enable 0 (FMPPE0), offset 0x134 and 0x400 ............... 151
Register 10: User Debug (USER_DBG), offset 0x1D0 ......................................................................... 152
Register 11: User Register 0 (USER_REG0), offset 0x1E0 .................................................................. 153
Register 12: User Register 1 (USER_REG1), offset 0x1E4 .................................................................. 154
Register 13: Flash Memory Protection Read Enable 1 (FMPRE1), offset 0x204 .................................... 155
Register 14: Flash Memory Protection Read Enable 2 (FMPRE2), offset 0x208 .................................... 156
Register 15: Flash Memory Protection Read Enable 3 (FMPRE3), offset 0x20C ................................... 157
Register 16: Flash Memory Protection Program Enable 1 (FMPPE1), offset 0x404 ............................... 158
Register 17: Flash Memory Protection Program Enable 2 (FMPPE2), offset 0x408 ............................... 159
Register 18: Flash Memory Protection Program Enable 3 (FMPPE3), offset 0x40C ............................... 160
General-Purpose Input/Outputs (GPIOs) ................................................................................... 161
Register 1: GPIO Data (GPIODATA), offset 0x000 ............................................................................ 168
Register 2: GPIO Direction (GPIODIR), offset 0x400 ......................................................................... 169
Register 3: GPIO Interrupt Sense (GPIOIS), offset 0x404 .................................................................. 170
Register 4: GPIO Interrupt Both Edges (GPIOIBE), offset 0x408 ........................................................ 171
Register 5: GPIO Interrupt Event (GPIOIEV), offset 0x40C ................................................................ 172
Register 6: GPIO Interrupt Mask (GPIOIM), offset 0x410 ................................................................... 173
Register 7: GPIO Raw Interrupt Status (GPIORIS), offset 0x414 ........................................................ 174
Register 8: GPIO Masked Interrupt Status (GPIOMIS), offset 0x418 ................................................... 175
Register 9: GPIO Interrupt Clear (GPIOICR), offset 0x41C ................................................................ 176
Register 10: GPIO Alternate Function Select (GPIOAFSEL), offset 0x420 ............................................ 177
Register 11: GPIO 2-mA Drive Select (GPIODR2R), offset 0x500 ........................................................ 179
Register 12: GPIO 4-mA Drive Select (GPIODR4R), offset 0x504 ........................................................ 180
Register 13: GPIO 8-mA Drive Select (GPIODR8R), offset 0x508 ........................................................ 181
Register 14: GPIO Open Drain Select (GPIOODR), offset 0x50C ......................................................... 182
Register 15: GPIO Pull-Up Select (GPIOPUR), offset 0x510 ................................................................ 183
Register 16: GPIO Pull-Down Select (GPIOPDR), offset 0x514 ........................................................... 184
Register 17: GPIO Slew Rate Control Select (GPIOSLR), offset 0x518 ................................................ 185
Register 18: GPIO Digital Enable (GPIODEN), offset 0x51C ................................................................ 186
Register 19: GPIO Lock (GPIOLOCK), offset 0x520 ............................................................................ 187
Register 20: GPIO Commit (GPIOCR), offset 0x524 ............................................................................ 188
Register 21: GPIO Peripheral Identification 4 (GPIOPeriphID4), offset 0xFD0 ....................................... 190
Register 22: GPIO Peripheral Identification 5 (GPIOPeriphID5), offset 0xFD4 ....................................... 191
Register 23: GPIO Peripheral Identification 6 (GPIOPeriphID6), offset 0xFD8 ....................................... 192
Register 24: GPIO Peripheral Identification 7 (GPIOPeriphID7), offset 0xFDC ...................................... 193
Register 25: GPIO Peripheral Identification 0 (GPIOPeriphID0), offset 0xFE0 ....................................... 194
Register 26: GPIO Peripheral Identification 1 (GPIOPeriphID1), offset 0xFE4 ....................................... 195
Register 27: GPIO Peripheral Identification 2 (GPIOPeriphID2), offset 0xFE8 ....................................... 196
Register 28: GPIO Peripheral Identification 3 (GPIOPeriphID3), offset 0xFEC ...................................... 197
Register 29: GPIO PrimeCell Identification 0 (GPIOPCellID0), offset 0xFF0 .......................................... 198
Register 30: GPIO PrimeCell Identification 1 (GPIOPCellID1), offset 0xFF4 .......................................... 199
Register 31: GPIO PrimeCell Identification 2 (GPIOPCellID2), offset 0xFF8 .......................................... 200
Preliminary
November 30, 200714
Page 15

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Register 32: GPIO PrimeCell Identification 3 (GPIOPCellID3), offset 0xFFC ......................................... 201
General-Purpose Timers ............................................................................................................. 202
Register 1: GPTM Configuration (GPTMCFG), offset 0x000 .............................................................. 214
Register 2: GPTM TimerA Mode (GPTMTAMR), offset 0x004 ............................................................ 215
Register 3: GPTM TimerB Mode (GPTMTBMR), offset 0x008 ............................................................ 217
Register 4: GPTM Control (GPTMCTL), offset 0x00C ........................................................................ 219
Register 5: GPTM Interrupt Mask (GPTMIMR), offset 0x018 .............................................................. 222
Register 6: GPTM Raw Interrupt Status (GPTMRIS), offset 0x01C ..................................................... 224
Register 7: GPTM Masked Interrupt Status (GPTMMIS), offset 0x020 ................................................ 225
Register 8: GPTM Interrupt Clear (GPTMICR), offset 0x024 .............................................................. 226
Register 9: GPTM TimerA Interval Load (GPTMTAILR), offset 0x028 ................................................. 228
Register 10: GPTM TimerB Interval Load (GPTMTBILR), offset 0x02C ................................................ 229
Register 11: GPTM TimerA Match (GPTMTAMATCHR), offset 0x030 ................................................... 230
Register 12: GPTM TimerB Match (GPTMTBMATCHR), offset 0x034 .................................................. 231
Register 13: GPTM TimerA Prescale (GPTMTAPR), offset 0x038 ........................................................ 232
Register 14: GPTM TimerB Prescale (GPTMTBPR), offset 0x03C ....................................................... 233
Register 15: GPTM TimerA Prescale Match (GPTMTAPMR), offset 0x040 ........................................... 234
Register 16: GPTM TimerB Prescale Match (GPTMTBPMR), offset 0x044 ........................................... 235
Register 17: GPTM TimerA (GPTMTAR), offset 0x048 ........................................................................ 236
Register 18: GPTM TimerB (GPTMTBR), offset 0x04C ....................................................................... 237
Watchdog Timer ........................................................................................................................... 238
Register 1: Watchdog Load (WDTLOAD), offset 0x000 ...................................................................... 241
Register 2: Watchdog Value (WDTVALUE), offset 0x004 ................................................................... 242
Register 3: Watchdog Control (WDTCTL), offset 0x008 ..................................................................... 243
Register 4: Watchdog Interrupt Clear (WDTICR), offset 0x00C .......................................................... 244
Register 5: Watchdog Raw Interrupt Status (WDTRIS), offset 0x010 .................................................. 245
Register 6: Watchdog Masked Interrupt Status (WDTMIS), offset 0x014 ............................................. 246
Register 7: Watchdog Test (WDTTEST), offset 0x418 ....................................................................... 247
Register 8: Watchdog Lock (WDTLOCK), offset 0xC00 ..................................................................... 248
Register 9: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 4 (WDTPeriphID4), offset 0xFD0 ................................. 249
Register 10: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 5 (WDTPeriphID5), offset 0xFD4 ................................. 250
Register 11: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 6 (WDTPeriphID6), offset 0xFD8 ................................. 251
Register 12: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 7 (WDTPeriphID7), offset 0xFDC ................................ 252
Register 13: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 0 (WDTPeriphID0), offset 0xFE0 ................................. 253
Register 14: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 1 (WDTPeriphID1), offset 0xFE4 ................................. 254
Register 15: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 2 (WDTPeriphID2), offset 0xFE8 ................................. 255
Register 16: Watchdog Peripheral Identification 3 (WDTPeriphID3), offset 0xFEC ................................. 256
Register 17: Watchdog PrimeCell Identification 0 (WDTPCellID0), offset 0xFF0 .................................... 257
Register 18: Watchdog PrimeCell Identification 1 (WDTPCellID1), offset 0xFF4 .................................... 258
Register 19: Watchdog PrimeCell Identification 2 (WDTPCellID2), offset 0xFF8 .................................... 259
Register 20: Watchdog PrimeCell Identification 3 (WDTPCellID3 ), offset 0xFFC .................................. 260
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) ............................................................................................. 261
Register 1: ADC Active Sample Sequencer (ADCACTSS), offset 0x000 ............................................. 268
Register 2: ADC Raw Interrupt Status (ADCRIS), offset 0x004 ........................................................... 269
Register 3: ADC Interrupt Mask (ADCIM), offset 0x008 ..................................................................... 270
Register 4: ADC Interrupt Status and Clear (ADCISC), offset 0x00C .................................................. 271
Register 5: ADC Overflow Status (ADCOSTAT), offset 0x010 ............................................................ 272
Register 6: ADC Event Multiplexer Select (ADCEMUX), offset 0x014 ................................................. 273
Preliminary
15November 30, 2007
Page 16

Table of Contents
Register 7: ADC Underflow Status (ADCUSTAT), offset 0x018 ........................................................... 276
Register 8: ADC Sample Sequencer Priority (ADCSSPRI), offset 0x020 ............................................. 277
Register 9: ADC Processor Sample Sequence Initiate (ADCPSSI), offset 0x028 ................................. 278
Register 10: ADC Sample Averaging Control (ADCSAC), offset 0x030 ................................................. 279
Register 11: ADC Sample Sequence Input Multiplexer Select 0 (ADCSSMUX0), offset 0x040 ............... 280
Register 12: ADC Sample Sequence Control 0 (ADCSSCTL0), offset 0x044 ........................................ 282
Register 13: ADC Sample Sequence Result FIFO 0 (ADCSSFIFO0), offset 0x048 ................................ 285
Register 14: ADC Sample Sequence Result FIFO 1 (ADCSSFIFO1), offset 0x068 ................................ 285
Register 15: ADC Sample Sequence Result FIFO 2 (ADCSSFIFO2), offset 0x088 ................................ 285
Register 16: ADC Sample Sequence Result FIFO 3 (ADCSSFIFO3), offset 0x0A8 ............................... 285
Register 17: ADC Sample Sequence FIFO 0 Status (ADCSSFSTAT0), offset 0x04C ............................. 286
Register 18: ADC Sample Sequence FIFO 1 Status (ADCSSFSTAT1), offset 0x06C ............................. 286
Register 19: ADC Sample Sequence FIFO 2 Status (ADCSSFSTAT2), offset 0x08C ............................ 286
Register 20: ADC Sample Sequence FIFO 3 Status (ADCSSFSTAT3), offset 0x0AC ............................ 286
Register 21: ADC Sample Sequence Input Multiplexer Select 1 (ADCSSMUX1), offset 0x060 ............... 287
Register 22: ADC Sample Sequence Input Multiplexer Select 2 (ADCSSMUX2), offset 0x080 ............... 287
Register 23: ADC Sample Sequence Control 1 (ADCSSCTL1), offset 0x064 ........................................ 288
Register 24: ADC Sample Sequence Control 2 (ADCSSCTL2), offset 0x084 ........................................ 288
Register 25: ADC Sample Sequence Input Multiplexer Select 3 (ADCSSMUX3), offset 0x0A0 ............... 290
Register 26: ADC Sample Sequence Control 3 (ADCSSCTL3), offset 0x0A4 ........................................ 291
Register 27: ADC Test Mode Loopback (ADCTMLB), offset 0x100 ....................................................... 292
Universal Asynchronous Receivers/Transmitters (UARTs) ..................................................... 294
Register 1: UART Data (UARTDR), offset 0x000 ............................................................................... 302
Register 2: UART Receive Status/Error Clear (UARTRSR/UARTECR), offset 0x004 ........................... 304
Register 3: UART Flag (UARTFR), offset 0x018 ................................................................................ 306
Register 4: UART IrDA Low-Power Register (UARTILPR), offset 0x020 ............................................. 308
Register 5: UART Integer Baud-Rate Divisor (UARTIBRD), offset 0x024 ............................................ 309
Register 6: UART Fractional Baud-Rate Divisor (UARTFBRD), offset 0x028 ....................................... 310
Register 7: UART Line Control (UARTLCRH), offset 0x02C ............................................................... 311
Register 8: UART Control (UARTCTL), offset 0x030 ......................................................................... 313
Register 9: UART Interrupt FIFO Level Select (UARTIFLS), offset 0x034 ........................................... 315
Register 10: UART Interrupt Mask (UARTIM), offset 0x038 ................................................................. 317
Register 11: UART Raw Interrupt Status (UARTRIS), offset 0x03C ...................................................... 319
Register 12: UART Masked Interrupt Status (UARTMIS), offset 0x040 ................................................. 320
Register 13: UART Interrupt Clear (UARTICR), offset 0x044 ............................................................... 321
Register 14: UART Peripheral Identification 4 (UARTPeriphID4), offset 0xFD0 ..................................... 323
Register 15: UART Peripheral Identification 5 (UARTPeriphID5), offset 0xFD4 ..................................... 324
Register 16: UART Peripheral Identification 6 (UARTPeriphID6), offset 0xFD8 ..................................... 325
Register 17: UART Peripheral Identification 7 (UARTPeriphID7), offset 0xFDC ..................................... 326
Register 18: UART Peripheral Identification 0 (UARTPeriphID0), offset 0xFE0 ...................................... 327
Register 19: UART Peripheral Identification 1 (UARTPeriphID1), offset 0xFE4 ...................................... 328
Register 20: UART Peripheral Identification 2 (UARTPeriphID2), offset 0xFE8 ...................................... 329
Register 21: UART Peripheral Identification 3 (UARTPeriphID3), offset 0xFEC ..................................... 330
Register 22: UART PrimeCell Identification 0 (UARTPCellID0), offset 0xFF0 ........................................ 331
Register 23: UART PrimeCell Identification 1 (UARTPCellID1), offset 0xFF4 ........................................ 332
Register 24: UART PrimeCell Identification 2 (UARTPCellID2), offset 0xFF8 ........................................ 333
Register 25: UART PrimeCell Identification 3 (UARTPCellID3), offset 0xFFC ........................................ 334
Preliminary
November 30, 200716
Page 17

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) ............................................................................................ 335
Register 1: SSI Control 0 (SSICR0), offset 0x000 .............................................................................. 347
Register 2: SSI Control 1 (SSICR1), offset 0x004 .............................................................................. 349
Register 3: SSI Data (SSIDR), offset 0x008 ...................................................................................... 351
Register 4: SSI Status (SSISR), offset 0x00C ................................................................................... 352
Register 5: SSI Clock Prescale (SSICPSR), offset 0x010 .................................................................. 354
Register 6: SSI Interrupt Mask (SSIIM), offset 0x014 ......................................................................... 355
Register 7: SSI Raw Interrupt Status (SSIRIS), offset 0x018 .............................................................. 357
Register 8: SSI Masked Interrupt Status (SSIMIS), offset 0x01C ........................................................ 358
Register 9: SSI Interrupt Clear (SSIICR), offset 0x020 ....................................................................... 359
Register 10: SSI Peripheral Identification 4 (SSIPeriphID4), offset 0xFD0 ............................................. 360
Register 11: SSI Peripheral Identification 5 (SSIPeriphID5), offset 0xFD4 ............................................. 361
Register 12: SSI Peripheral Identification 6 (SSIPeriphID6), offset 0xFD8 ............................................. 362
Register 13: SSI Peripheral Identification 7 (SSIPeriphID7), offset 0xFDC ............................................ 363
Register 14: SSI Peripheral Identification 0 (SSIPeriphID0), offset 0xFE0 ............................................. 364
Register 15: SSI Peripheral Identification 1 (SSIPeriphID1), offset 0xFE4 ............................................. 365
Register 16: SSI Peripheral Identification 2 (SSIPeriphID2), offset 0xFE8 ............................................. 366
Register 17: SSI Peripheral Identification 3 (SSIPeriphID3), offset 0xFEC ............................................ 367
Register 18: SSI PrimeCell Identification 0 (SSIPCellID0), offset 0xFF0 ............................................... 368
Register 19: SSI PrimeCell Identification 1 (SSIPCellID1), offset 0xFF4 ............................................... 369
Register 20: SSI PrimeCell Identification 2 (SSIPCellID2), offset 0xFF8 ............................................... 370
Register 21: SSI PrimeCell Identification 3 (SSIPCellID3), offset 0xFFC ............................................... 371
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface ........................................................................................ 372
Register 1: I2C Master Slave Address (I2CMSA), offset 0x000 ........................................................... 386
Register 2: I2C Master Control/Status (I2CMCS), offset 0x004 ........................................................... 387
Register 3: I2C Master Data (I2CMDR), offset 0x008 ......................................................................... 391
Register 4: I2C Master Timer Period (I2CMTPR), offset 0x00C ........................................................... 392
Register 5: I2C Master Interrupt Mask (I2CMIMR), offset 0x010 ......................................................... 393
Register 6: I2C Master Raw Interrupt Status (I2CMRIS), offset 0x014 ................................................. 394
Register 7: I2C Master Masked Interrupt Status (I2CMMIS), offset 0x018 ........................................... 395
Register 8: I2C Master Interrupt Clear (I2CMICR), offset 0x01C ......................................................... 396
Register 9: I2C Master Configuration (I2CMCR), offset 0x020 ............................................................ 397
Register 10: I2C Slave Own Address (I2CSOAR), offset 0x000 ............................................................ 399
Register 11: I2C Slave Control/Status (I2CSCSR), offset 0x004 ........................................................... 400
Register 12: I2C Slave Data (I2CSDR), offset 0x008 ........................................................................... 402
Register 13: I2C Slave Interrupt Mask (I2CSIMR), offset 0x00C ........................................................... 403
Register 14: I2C Slave Raw Interrupt Status (I2CSRIS), offset 0x010 ................................................... 404
Register 15: I2C Slave Masked Interrupt Status (I2CSMIS), offset 0x014 .............................................. 405
Register 16: I2C Slave Interrupt Clear (I2CSICR), offset 0x018 ............................................................ 406
Controller Area Network (CAN) Module ..................................................................................... 407
Register 1: CAN Control (CANCTL), offset 0x000 ............................................................................. 421
Register 2: CAN Status (CANSTS), offset 0x004 ............................................................................... 423
Register 3: CAN Error Counter (CANERR), offset 0x008 ................................................................... 426
Register 4: CAN Bit Timing (CANBIT), offset 0x00C .......................................................................... 427
Register 5: CAN Interrupt (CANINT), offset 0x010 ............................................................................. 429
Register 6: CAN Test (CANTST), offset 0x014 .................................................................................. 430
Register 7: CAN Baud Rate Prescalar Extension (CANBRPE), offset 0x018 ....................................... 432
17November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 18

Table of Contents
Register 8: CAN IF1 Command Request (CANIF1CRQ), offset 0x020 ................................................ 433
Register 9: CAN IF2 Command Request (CANIF2CRQ), offset 0x080 ................................................ 433
Register 10: CAN IF1 Command Mask (CANIF1CMSK), offset 0x024 .................................................. 434
Register 11: CAN IF2 Command Mask (CANIF2CMSK), offset 0x084 .................................................. 434
Register 12: CAN IF1 Mask 1 (CANIF1MSK1), offset 0x028 ................................................................ 437
Register 13: CAN IF2 Mask 1 (CANIF2MSK1), offset 0x088 ................................................................ 437
Register 14: CAN IF1 Mask 2 (CANIF1MSK2), offset 0x02C ................................................................ 438
Register 15: CAN IF2 Mask 2 (CANIF2MSK2), offset 0x08C ................................................................ 438
Register 16: CAN IF1 Arbitration 1 (CANIF1ARB1), offset 0x030 ......................................................... 439
Register 17: CAN IF2 Arbitration 1 (CANIF2ARB1), offset 0x090 ......................................................... 439
Register 18: CAN IF1 Arbitration 2 (CANIF1ARB2), offset 0x034 ......................................................... 440
Register 19: CAN IF2 Arbitration 2 (CANIF2ARB2), offset 0x094 ......................................................... 440
Register 20: CAN IF1 Message Control (CANIF1MCTL), offset 0x038 .................................................. 441
Register 21: CAN IF2 Message Control (CANIF2MCTL), offset 0x098 .................................................. 441
Register 22: CAN IF1 Data A1 (CANIF1DA1), offset 0x03C ................................................................. 443
Register 23: CAN IF1 Data A2 (CANIF1DA2), offset 0x040 ................................................................. 443
Register 24: CAN IF1 Data B1 (CANIF1DB1), offset 0x044 ................................................................. 443
Register 25: CAN IF1 Data B2 (CANIF1DB2), offset 0x048 ................................................................. 443
Register 26: CAN IF2 Data A1 (CANIF2DA1), offset 0x09C ................................................................. 443
Register 27: CAN IF2 Data A2 (CANIF2DA2), offset 0x0A0 ................................................................. 443
Register 28: CAN IF2 Data B1 (CANIF2DB1), offset 0x0A4 ................................................................. 443
Register 29: CAN IF2 Data B2 (CANIF2DB2), offset 0x0A8 ................................................................. 443
Register 30: CAN Transmission Request 1 (CANTXRQ1), offset 0x100 ................................................ 444
Register 31: CAN Transmission Request 2 (CANTXRQ2), offset 0x104 ................................................ 444
Register 32: CAN New Data 1 (CANNWDA1), offset 0x120 ................................................................. 445
Register 33: CAN New Data 2 (CANNWDA2), offset 0x124 ................................................................. 445
Register 34: CAN Message 1 Interrupt Pending (CANMSG1INT), offset 0x140 ..................................... 446
Register 35: CAN Message 2 Interrupt Pending (CANMSG2INT), offset 0x144 ..................................... 446
Register 36: CAN Message 1 Valid (CANMSG1VAL), offset 0x160 ....................................................... 447
Register 37: CAN Message 2 Valid (CANMSG2VAL), offset 0x164 ....................................................... 447
Analog Comparators ................................................................................................................... 448
Register 1: Analog Comparator Masked Interrupt Status (ACMIS), offset 0x00 .................................... 454
Register 2: Analog Comparator Raw Interrupt Status (ACRIS), offset 0x04 ......................................... 455
Register 3: Analog Comparator Interrupt Enable (ACINTEN), offset 0x08 ........................................... 456
Register 4: Analog Comparator Reference Voltage Control (ACREFCTL), offset 0x10 ......................... 457
Register 5: Analog Comparator Status 0 (ACSTAT0), offset 0x20 ....................................................... 458
Register 6: Analog Comparator Status 1 (ACSTAT1), offset 0x40 ....................................................... 458
Register 7: Analog Comparator Status 2 (ACSTAT2), offset 0x60 ....................................................... 458
Register 8: Analog Comparator Control 0 (ACCTL0), offset 0x24 ....................................................... 459
Register 9: Analog Comparator Control 1 (ACCTL1), offset 0x44 ....................................................... 459
Register 10: Analog Comparator Control 2 (ACCTL2), offset 0x64 ...................................................... 459
Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) .................................................................................................... 461
Register 1: PWM Master Control (PWMCTL), offset 0x000 ................................................................ 469
Register 2: PWM Time Base Sync (PWMSYNC), offset 0x004 ........................................................... 470
Register 3: PWM Output Enable (PWMENABLE), offset 0x008 .......................................................... 471
Register 4: PWM Output Inversion (PWMINVERT), offset 0x00C ....................................................... 472
Register 5: PWM Output Fault (PWMFAULT), offset 0x010 ................................................................ 473
Register 6: PWM Interrupt Enable (PWMINTEN), offset 0x014 ........................................................... 474
Preliminary
November 30, 200718
Page 19

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Register 7: PWM Raw Interrupt Status (PWMRIS), offset 0x018 ........................................................ 475
Register 8: PWM Interrupt Status and Clear (PWMISC), offset 0x01C ................................................ 476
Register 9: PWM Status (PWMSTATUS), offset 0x020 ...................................................................... 477
Register 10: PWM0 Control (PWM0CTL), offset 0x040 ....................................................................... 478
Register 11: PWM1 Control (PWM1CTL), offset 0x080 ....................................................................... 478
Register 12: PWM2 Control (PWM2CTL), offset 0x0C0 ...................................................................... 478
Register 13: PWM0 Interrupt and Trigger Enable (PWM0INTEN), offset 0x044 .................................... 480
Register 14: PWM1 Interrupt and Trigger Enable (PWM1INTEN), offset 0x084 .................................... 480
Register 15: PWM2 Interrupt and Trigger Enable (PWM2INTEN), offset 0x0C4 .................................... 480
Register 16: PWM0 Raw Interrupt Status (PWM0RIS), offset 0x048 .................................................... 482
Register 17: PWM1 Raw Interrupt Status (PWM1RIS), offset 0x088 .................................................... 482
Register 18: PWM2 Raw Interrupt Status (PWM2RIS), offset 0x0C8 ................................................... 482
Register 19: PWM0 Interrupt Status and Clear (PWM0ISC), offset 0x04C ........................................... 483
Register 20: PWM1 Interrupt Status and Clear (PWM1ISC), offset 0x08C ........................................... 483
Register 21: PWM2 Interrupt Status and Clear (PWM2ISC), offset 0x0CC ........................................... 483
Register 22: PWM0 Load (PWM0LOAD), offset 0x050 ....................................................................... 484
Register 23: PWM1 Load (PWM1LOAD), offset 0x090 ....................................................................... 484
Register 24: PWM2 Load (PWM2LOAD), offset 0x0D0 ....................................................................... 484
Register 25: PWM0 Counter (PWM0COUNT), offset 0x054 ................................................................ 485
Register 26: PWM1 Counter (PWM1COUNT), offset 0x094 ................................................................ 485
Register 27: PWM2 Counter (PWM2COUNT), offset 0x0D4 ............................................................... 485
Register 28: PWM0 Compare A (PWM0CMPA), offset 0x058 ............................................................. 486
Register 29: PWM1 Compare A (PWM1CMPA), offset 0x098 ............................................................. 486
Register 30: PWM2 Compare A (PWM2CMPA), offset 0x0D8 ............................................................. 486
Register 31: PWM0 Compare B (PWM0CMPB), offset 0x05C ............................................................. 487
Register 32: PWM1 Compare B (PWM1CMPB), offset 0x09C ............................................................. 487
Register 33: PWM2 Compare B (PWM2CMPB), offset 0x0DC ............................................................ 487
Register 34: PWM0 Generator A Control (PWM0GENA), offset 0x060 ................................................ 488
Register 35: PWM1 Generator A Control (PWM1GENA), offset 0x0A0 ................................................ 488
Register 36: PWM2 Generator A Control (PWM2GENA), offset 0x0E0 ................................................ 488
Register 37: PWM0 Generator B Control (PWM0GENB), offset 0x064 ................................................ 491
Register 38: PWM1 Generator B Control (PWM1GENB), offset 0x0A4 ................................................ 491
Register 39: PWM2 Generator B Control (PWM2GENB), offset 0x0E4 ................................................ 491
Register 40: PWM0 Dead-Band Control (PWM0DBCTL), offset 0x068 ................................................ 494
Register 41: PWM1 Dead-Band Control (PWM1DBCTL), offset 0x0A8 ................................................. 494
Register 42: PWM2 Dead-Band Control (PWM2DBCTL), offset 0x0E8 ................................................ 494
Register 43: PWM0 Dead-Band Rising-Edge Delay (PWM0DBRISE), offset 0x06C ............................. 495
Register 44: PWM1 Dead-Band Rising-Edge Delay (PWM1DBRISE), offset 0x0AC ............................. 495
Register 45: PWM2 Dead-Band Rising-Edge Delay (PWM2DBRISE), offset 0x0EC ............................. 495
Register 46: PWM0 Dead-Band Falling-Edge-Delay (PWM0DBFALL), offset 0x070 ............................. 496
Register 47: PWM1 Dead-Band Falling-Edge-Delay (PWM1DBFALL), offset 0x0B0 ............................. 496
Register 48: PWM2 Dead-Band Falling-Edge-Delay (PWM2DBFALL), offset 0x0F0 ............................. 496
Preliminary
19November 30, 2007
Page 20

About This Document
About This Document
This data sheet provides reference information for the LM3S2533 microcontroller, describing the
functional blocks of the system-on-chip (SoC) device designed around the ARM® Cortex™-M3
core.
Audience
This manual is intended for system software developers, hardware designers, and application
developers.
About This Manual
This document is organized into sections that correspond to each major feature.
Related Documents
The following documents are referenced by the data sheet, and available on the documentation CD
or from the Luminary Micro web site at www.luminarymicro.com:
■
ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual
■
ARM® CoreSight Technical Reference Manual
■
ARM® v7-M Architecture Application Level Reference Manual
The following related documents are also referenced:
■
IEEE Standard 1149.1-Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture
This documentation list was current as of publication date. Please check the Luminary Micro web
site for additional documentation, including application notes and white papers.
Documentation Conventions
This document uses the conventions shown in Table 1 on page 20.
Table 1. Documentation Conventions
MeaningNotation
General Register Notation
REGISTER
offset 0xnnn
Register N
APB registers are indicated in uppercase bold. For example, PBORCTL is the Power-On and
Brown-Out Reset Control register. If a register name contains a lowercase n, it represents more
than one register. For example, SRCRn represents any (or all) of the three Software Reset Control
registers: SRCR0, SRCR1 , and SRCR2.
A single bit in a register.bit
Two or more consecutive and related bits.bit field
A hexadecimal increment to a register's address, relative to that module's base address as specified
in “Memory Map” on page 42.
Registers are numbered consecutively throughout the document to aid in referencing them. The
register number has no meaning to software.
Preliminary
November 30, 200720
Page 21

reserved
yy:xx
Register Bit/Field
Types
R/W1C
W1C
Reset Value
Pin/Signal Notation
assert a signal
SIGNAL
SIGNAL
Numbers
X
0x
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
MeaningNotation
Register bits marked reserved are reserved for future use. In most cases, reserved bits are set to
0; however, user software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide software
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be preserved across a
read-modify-write operation.
The range of register bits inclusive from xx to yy. For example, 31:15 means bits 15 through 31 in
that register.
This value in the register bit diagram indicates whether software running on the controller can
change the value of the bit field.
Software can read this field. The bit or field is cleared by hardware after reading the bit/field.RC
Software can read this field. Always write the chip reset value.RO
Software can read or write this field.R/W
Software can read or write this field. A write of a 0 to a W1C bit does not affect the bit value in the
register. A write of a 1 clears the value of the bit in the register; the remaining bits remain unchanged.
This register type is primarily used for clearing interrupt status bits where the read operation
provides the interrupt status and the write of the read value clears only the interrupts being reported
at the time the register was read.
Software can write this field. A write of a 0 to a W1C bit does not affect the bit value in the register.
A write of a 1 clears the value of the bit in the register; the remaining bits remain unchanged. A
read of the register returns no meaningful data.
This register is typically used to clear the corresponding bit in an interrupt register.
Only a write by software is valid; a read of the register returns no meaningful data.WO
This value in the register bit diagram shows the bit/field value after any reset, unless noted.Register Bit/Field
Bit cleared to 0 on chip reset.0
Bit set to 1 on chip reset.1
Nondeterministic.-
Pin alternate function; a pin defaults to the signal without the brackets.[ ]
Refers to the physical connection on the package.pin
Refers to the electrical signal encoding of a pin.signal
Change the value of the signal from the logically False state to the logically True state. For active
High signals, the asserted signal value is 1 (High); for active Low signals, the asserted signal value
is 0 (Low). The active polarity (High or Low) is defined by the signal name (see SIGNAL and SIGNAL
below).
Change the value of the signal from the logically True state to the logically False state.deassert a signal
Signal names are in uppercase and in the Courier font. An overbar on a signal name indicates that
it is active Low. To assert SIGNAL is to drive it Low; to deassert SIGNAL is to drive it High.
Signal names are in uppercase and in the Courier font. An active High signal has no overbar. To
assert SIGNAL is to drive it High; to deassert SIGNAL is to drive it Low.
An uppercase X indicates any of several values is allowed, where X can be any legal pattern. For
example, a binary value of 0X00 can be either 0100 or 0000, a hex value of 0xX is 0x0 or 0x1, and
so on.
Hexadecimal numbers have a prefix of 0x. For example, 0x00FF is the hexadecimal number FF.
All other numbers within register tables are assumed to be binary. Within conceptual information,
binary numbers are indicated with a b suffix, for example, 1011b, and decimal numbers are written
without a prefix or suffix.
Preliminary
21November 30, 2007
Page 22

Architectural Overview
1 Architectural Overview
The Luminary Micro Stellaris®family of microcontrollers—the first ARM® Cortex™-M3 based
controllers—brings high-performance 32-bit computing to cost-sensitive embedded microcontroller
applications. These pioneering parts deliver customers 32-bit performance at a cost equivalent to
legacy 8- and 16-bit devices, all in a package with a small footprint.
The Stellaris®family offers efficient performance and extensive integration, favorably positioning
the device into cost-conscious applications requiring significant control-processing and connectivity
capabilities. The Stellaris®LM3S1000 series extends the Stellaris®family with larger on-chip
memories, enhanced power management, and expanded I/O and control capabilities. The Stellaris
LM3S2000 series, designed for Controller Area Network (CAN) applications, extends the Stellaris
family with Bosch CAN networking technology, the golden standard in short-haul industrial networks.
The Stellaris®LM3S2000 series also marks the first integration of CAN capabilities with the
revolutionary Cortex-M3 core. The Stellaris®LM3S6000 series combines both a 10/100 Ethernet
Media Access Control (MAC) and Physical (PHY) layer, marking the first time that integrated
connectivity is available with an ARM Cortex-M3 MCU and the only integrated 10/100 Ethernet MAC
and PHY available in an ARM architecture MCU. The Stellaris®LM3S8000 series combines Bosch
Controller Area Network technology with both a 10/100 Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) and
Physical (PHY) layer.
®
The LM3S2533 microcontroller is targeted for industrial applications, including remote monitoring,
electronic point-of-sale machines, test and measurement equipment, network appliances and
switches, factory automation, HVAC and building control, gaming equipment, motion control, medical
instrumentation, and fire and security.
For applications requiring extreme conservation of power, the LM3S2533 microcontroller features
a Battery-backed Hibernation module to efficiently power down the LM3S2533 to a low-power state
during extended periods of inactivity. With a power-up/power-down sequencer, a continuous time
counter (RTC), a pair of match registers, an APB interface to the system bus, and dedicated
non-volatile memory, the Hibernation module positions the LM3S2533 microcontroller perfectly for
battery applications.
In addition, the LM3S2533 microcontroller offers the advantages of ARM's widely available
development tools, System-on-Chip (SoC) infrastructure IP applications, and a large user community.
Additionally, the microcontroller uses ARM's Thumb®-compatible Thumb-2 instruction set to reduce
memory requirements and, thereby, cost. Finally, the LM3S2533 microcontroller is code-compatible
to all members of the extensive Stellaris®family; providing flexibility to fit our customers' precise
needs.
Luminary Micro offers a complete solution to get to market quickly, with evaluation and development
boards, white papers and application notes, an easy-to-use peripheral driver library, and a strong
support, sales, and distributor network.
1.1 Product Features
The LM3S2533 microcontroller includes the following product features:
■ 32-Bit RISC Performance
– 32-bit ARM® Cortex™-M3 v7M architecture optimized for small-footprint embedded
applications
November 30, 200722
Preliminary
Page 23

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
– System timer (SysTick), providing a simple, 24-bit clear-on-write, decrementing, wrap-on-zero
counter with a flexible control mechanism
– Thumb®-compatible Thumb-2-only instruction set processor core for high code density
– 50-MHz operation
– Hardware-division and single-cycle-multiplication
– Integrated Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) providing deterministic interrupt
handling
– 36 interrupts with eight priority levels
– Memory protection unit (MPU), providing a privileged mode for protected operating system
functionality
– Unaligned data access, enabling data to be efficiently packed into memory
– Atomic bit manipulation (bit-banding), delivering maximum memory utilization and streamlined
peripheral control
■ Internal Memory
– 96 KB single-cycle flash
• User-managed flash block protection on a 2-KB block basis
• User-managed flash data programming
• User-defined and managed flash-protection block
– 64 KB single-cycle SRAM
■ General-Purpose Timers
– Four General-Purpose Timer Modules (GPTM), each of which provides two 16-bit timers.
Each GPTM can be configured to operate independently:
• As a single 32-bit timer
• As one 32-bit Real-Time Clock (RTC) to event capture
• For Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
• To trigger analog-to-digital conversions
– 32-bit Timer modes
• Programmable one-shot timer
• Programmable periodic timer
• Real-Time Clock when using an external 32.768-KHz clock as the input
Preliminary
23November 30, 2007
Page 24

Architectural Overview
• User-enabled stalling in periodic and one-shot mode when the controller asserts the CPU
• ADC event trigger
– 16-bit Timer modes
• General-purpose timer function with an 8-bit prescaler
• Programmable one-shot timer
• Programmable periodic timer
• User-enabled stalling when the controller asserts CPU Halt flag during debug
• ADC event trigger
– 16-bit Input Capture modes
• Input edge count capture
• Input edge time capture
Halt flag during debug
– 16-bit PWM mode
• Simple PWM mode with software-programmable output inversion of the PWM signal
■ ARM FiRM-compliant Watchdog Timer
– 32-bit down counter with a programmable load register
– Separate watchdog clock with an enable
– Programmable interrupt generation logic with interrupt masking
– Lock register protection from runaway software
– Reset generation logic with an enable/disable
– User-enabled stalling when the controller asserts the CPU Halt flag during debug
■ Controller Area Network (CAN)
– Supports CAN protocol version 2.0 part A/B
– Bit rates up to 1Mb/s
– 32 message objects, each with its own identifier mask
– Maskable interrupt
– Disable automatic retransmission mode for TTCAN
– Programmable loop-back mode for self-test operation
■ Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
Preliminary
November 30, 200724
Page 25

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
– Master or slave operation
– Programmable clock bit rate and prescale
– Separate transmit and receive FIFOs, 16 bits wide, 8 locations deep
– Programmable interface operation for Freescale SPI, MICROWIRE, or Texas Instruments
synchronous serial interfaces
– Programmable data frame size from 4 to 16 bits
– Internal loopback test mode for diagnostic/debug testing
■ UART
– Two fully programmable 16C550-type UARTs with IrDA support
– Separate 16x8 transmit (TX) and 16x12 receive (RX) FIFOs to reduce CPU interrupt service
loading
– Programmable baud-rate generator with fractional divider
– Programmable FIFO length, including 1-byte deep operation providing conventional
double-buffered interface
– FIFO trigger levels of 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8
– Standard asynchronous communication bits for start, stop, and parity
– False-start-bit detection
– Line-break generation and detection
■ ADC
– Single- and differential-input configurations
– Three 10-bit channels (inputs) when used as single-ended inputs
– Sample rate of 250 thousand samples/second
– Flexible, configurable analog-to-digital conversion
– Four programmable sample conversion sequences from one to eight entries long, with
corresponding conversion result FIFOs
– Each sequence triggered by software or internal event (timers, analog comparators, PWM
or GPIO)
– On-chip temperature sensor
■ Analog Comparators
– Three independent integrated analog comparators
Preliminary
25November 30, 2007
Page 26

Architectural Overview
– Configurable for output to: drive an output pin, generate an interrupt, or initiate an ADC sample
sequence
– Compare external pin input to external pin input or to internal programmable voltage reference
■ I2C
– Master and slave receive and transmit operation with transmission speed up to 100 Kbps in
Standard mode and 400 Kbps in Fast mode
– Interrupt generation
– Master with arbitration and clock synchronization, multimaster support, and 7-bit addressing
mode
■ PWM
– Three PWM generator blocks, each with one 16-bit counter, two comparators, a PWM
generator, and a dead-band generator
– One 16-bit counter
• Runs in Down or Up/Down mode
• Output frequency controlled by a 16-bit load value
• Load value updates can be synchronized
• Produces output signals at zero and load value
– Two PWM comparators
• Comparator value updates can be synchronized
• Produces output signals on match
– PWM generator
• Output PWM signal is constructed based on actions taken as a result of the counter and
PWM comparator output signals
• Produces two independent PWM signals
– Dead-band generator
• Produces two PWM signals with programmable dead-band delays suitable for driving a
half-H bridge
• Can be bypassed, leaving input PWM signals unmodified
– Flexible output control block with PWM output enable of each PWM signal
• PWM output enable of each PWM signal
• Optional output inversion of each PWM signal (polarity control)
Preliminary
November 30, 200726
Page 27

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
• Optional fault handling for each PWM signal
• Synchronization of timers in the PWM generator blocks
• Synchronization of timer/comparator updates across the PWM generator blocks
• Interrupt status summary of the PWM generator blocks
– Can initiate an ADC sample sequence
■ GPIOs
– 11-48 GPIOs, depending on configuration
– 5-V-tolerant input/outputs
– Programmable interrupt generation as either edge-triggered or level-sensitive
– Bit masking in both read and write operations through address lines
– Can initiate an ADC sample sequence
– Programmable control for GPIO pad configuration:
• Weak pull-up or pull-down resistors
• 2-mA, 4-mA, and 8-mA pad drive
• Slew rate control for the 8-mA drive
• Open drain enables
• Digital input enables
■ Power
– On-chip Low Drop-Out (LDO) voltage regulator, with programmable output user-adjustable
from 2.25 V to 2.75 V
– Hibernation module handles the power-up/down 3.3 V sequencing and control for the core
digital logic and analog circuits
– Low-power options on controller: Sleep and Deep-sleep modes
– Low-power options for peripherals: software controls shutdown of individual peripherals
– User-enabled LDO unregulated voltage detection and automatic reset
– 3.3-V supply brown-out detection and reporting via interrupt or reset
■ Flexible Reset Sources
– Power-on reset (POR)
– Reset pin assertion
– Brown-out (BOR) detector alerts to system power drops
Preliminary
27November 30, 2007
Page 28

Architectural Overview
– Software reset
– Watchdog timer reset
– Internal low drop-out (LDO) regulator output goes unregulated
■ Additional Features
– Six reset sources
– Programmable clock source control
– Clock gating to individual peripherals for power savings
– IEEE 1149.1-1990 compliant Test Access Port (TAP) controller
– Debug access via JTAG and Serial Wire interfaces
– Full JTAG boundary scan
■ Industrial-range 100-pin RoHS-compliant LQFP package
1.2 Target Applications
■ Remote monitoring
■ Electronic point-of-sale (POS) machines
■ Test and measurement equipment
■ Network appliances and switches
■ Factory automation
■ HVAC and building control
■ Gaming equipment
■ Motion control
■ Medical instrumentation
■ Fire and security
■ Power and energy
■ Transportation
1.3 High-Level Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 on page 29 represents the full set of features in the Stellaris®2000 series of devices;
not all features may be available on the LM3S2533 microcontroller.
Preliminary
November 30, 200728
Page 29
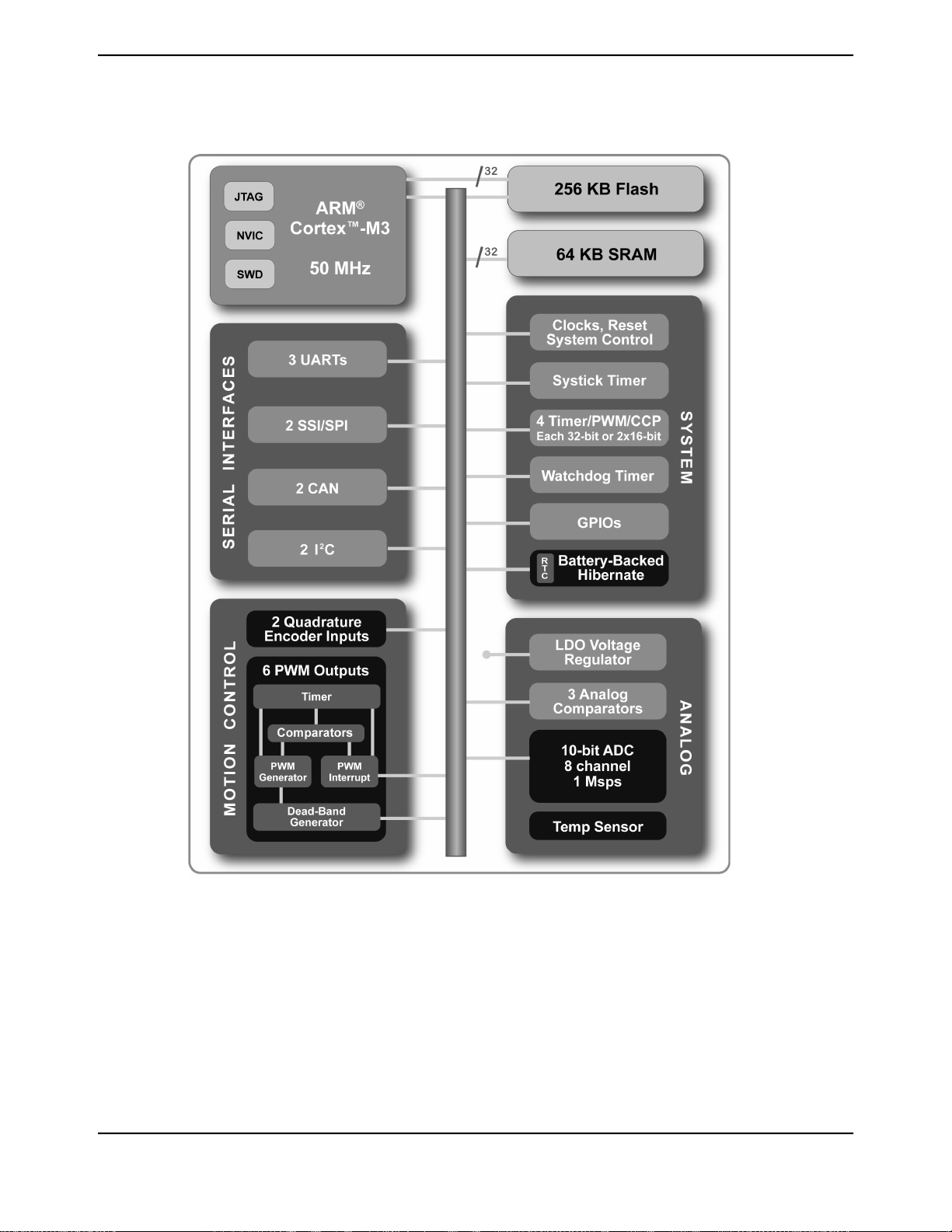
Figure 1-1. Stellaris®2000 Series High-Level Block Diagram
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
1.4 Functional Overview
The following sections provide an overview of the features of the LM3S2533 microcontroller. The
page number in parenthesis indicates where that feature is discussed in detail. Ordering and support
information can be found in “Ordering and Contact Information” on page 552.
29November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 30

Architectural Overview
1.4.1 ARM Cortex™-M3
1.4.1.1 Processor Core (see page 36)
All members of the Stellaris®product family, including the LM3S2533 microcontroller, are designed
around an ARM Cortex™-M3 processor core. The ARM Cortex-M3 processor provides the core for
a high-performance, low-cost platform that meets the needs of minimal memory implementation,
reduced pin count, and low-power consumption, while delivering outstanding computational
performance and exceptional system response to interrupts.
“ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core” on page 36 provides an overview of the ARM core; the core is
detailed in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
1.4.1.2 System Timer (SysTick)
Cortex-M3 includes an integrated system timer, SysTick. SysTick provides a simple, 24-bit
clear-on-write, decrementing, wrap-on-zero counter with a flexible control mechanism. The counter
can be used in several different ways, for example:
■ An RTOS tick timer which fires at a programmable rate (for example, 100 Hz) and invokes a
SysTick routine.
■ A high-speed alarm timer using the system clock.
■ A variable rate alarm or signal timer—the duration is range-dependent on the reference clock
used and the dynamic range of the counter.
■ A simple counter. Software can use this to measure time to completion and time used.
■ An internal clock source control based on missing/meeting durations. The COUNTFLAG bit-field
in the control and status register can be used to determine if an action completed within a set
duration, as part of a dynamic clock management control loop.
1.4.1.3 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)
The LM3S2533 controller includes the ARM Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) on the
ARM Cortex-M3 core. The NVIC and Cortex-M3 prioritize and handle all exceptions. All exceptions
are handled in Handler Mode. The processor state is automatically stored to the stack on an
exception, and automatically restored from the stack at the end of the Interrupt Service Routine
(ISR). The vector is fetched in parallel to the state saving, which enables efficient interrupt entry.
The processor supports tail-chaining, which enables back-to-back interrupts to be performed without
the overhead of state saving and restoration. Software can set eight priority levels on 7 exceptions
(system handlers) and 36 interrupts.
“Interrupts” on page 44 provides an overview of the NVIC controller and the interrupt map. Exceptions
and interrupts are detailed in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
1.4.2 Motor Control Peripherals
To enhance motor control, the LM3S2533 controller features Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) outputs.
1.4.2.1 PWM
Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a powerful technique for digitally encoding analog signal levels.
High-resolution counters are used to generate a square wave, and the duty cycle of the square
wave is modulated to encode an analog signal. Typical applications include switching power supplies
and motor control.
November 30, 200730
Preliminary
Page 31

On the LM3S2533, PWM motion control functionality can be achieved through:
■ Dedicated, flexible motion control hardware using the PWM pins
■ The motion control features of the general-purpose timers using the CCP pins
PWM Pins (see page 461)
The LM3S2533 PWM module consists of three PWM generator blocks and a control block. Each
PWM generator block contains one timer (16-bit down or up/down counter), two comparators, a
PWM signal generator, a dead-band generator, and an interrupt/ADC-trigger selector. The control
block determines the polarity of the PWM signals, and which signals are passed through to the pins.
Each PWM generator block produces two PWM signals that can either be independent signals or
a single pair of complementary signals with dead-band delays inserted. The output of the PWM
generation blocks are managed by the output control block before being passed to the device pins.
CCP Pins (see page 208)
The General-Purpose Timer Module's CCP (Capture Compare PWM) pins are software programmable
to support a simple PWM mode with a software-programmable output inversion of the PWM signal.
1.4.3 Analog Peripherals
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
To handle analog signals, the LM3S2533 microcontroller offers an Analog-to-Digital Converter
(ADC).
For support of analog signals, the LM3S2533 microcontroller offers three analog comparators.
1.4.3.1 ADC (see page 261)
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is a peripheral that converts a continuous analog voltage to a
discrete digital number.
The LM3S2533 ADC module features 10-bit conversion resolution and supports three input channels,
plus an internal temperature sensor. Four buffered sample sequences allow rapid sampling of up
to eight analog input sources without controller intervention. Each sample sequence provides flexible
programming with fully configurable input source, trigger events, interrupt generation, and sequence
priority.
1.4.3.2 Analog Comparators (see page 448)
An analog comparator is a peripheral that compares two analog voltages, and provides a logical
output that signals the comparison result.
The LM3S2533 microcontroller provides three independent integrated analog comparators that can
be configured to drive an output or generate an interrupt or ADC event.
A comparator can compare a test voltage against any one of these voltages:
■ An individual external reference voltage
■ A shared single external reference voltage
■ A shared internal reference voltage
The comparator can provide its output to a device pin, acting as a replacement for an analog
comparator on the board, or it can be used to signal the application via interrupts or triggers to the
ADC to cause it to start capturing a sample sequence. The interrupt generation and ADC triggering
31November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 32

Architectural Overview
logic is separate. This means, for example, that an interrupt can be generated on a rising edge and
the ADC triggered on a falling edge.
1.4.4 Serial Communications Peripherals
The LM3S2533 controller supports both asynchronous and synchronous serial communications
with:
■ Two fully programmable 16C550-type UARTs
■ One SSI module
■ One I2C module
■ One CAN unit
1.4.4.1 UART (see page 294)
A Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is an integrated circuit used for RS-232C
serial communications, containing a transmitter (parallel-to-serial converter) and a receiver
(serial-to-parallel converter), each clocked separately.
The LM3S2533 controller includes two fully programmable 16C550-type UARTs that support data
transfer speeds up to 460.8 Kbps. (Although similar in functionality to a 16C550 UART, it is not
register-compatible.) In addition, each UART is capable of supporting IrDA.
Separate 16x8 transmit (TX) and 16x12 receive (RX) FIFOs reduce CPU interrupt service loading.
The UART can generate individually masked interrupts from the RX, TX, modem status, and error
conditions. The module provides a single combined interrupt when any of the interrupts are asserted
and are unmasked.
1.4.4.2 SSI (see page 335)
Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) is a four-wire bi-directional communications interface.
The LM3S2533 controller includes one SSI module that provides the functionality for synchronous
serial communications with peripheral devices, and can be configured to use the Freescale SPI,
MICROWIRE, or TI synchronous serial interface frame formats. The size of the data frame is also
configurable, and can be set between 4 and 16 bits, inclusive.
The SSI module performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data received from a peripheral device,
and parallel-to-serial conversion on data transmitted to a peripheral device. The TX and RX paths
are buffered with internal FIFOs, allowing up to eight 16-bit values to be stored independently.
The SSI module can be configured as either a master or slave device. As a slave device, the SSI
module can also be configured to disable its output, which allows a master device to be coupled
with multiple slave devices.
The SSI module also includes a programmable bit rate clock divider and prescaler to generate the
output serial clock derived from the SSI module's input clock. Bit rates are generated based on the
input clock and the maximum bit rate is determined by the connected peripheral.
1.4.4.3 I2C (see page 372)
The Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) bus provides bi-directional data transfer through a two-wire design
(a serial data line SDA and a serial clock line SCL).
November 30, 200732
Preliminary
Page 33

The I2C bus interfaces to external I2C devices such as serial memory (RAMs and ROMs), networking
devices, LCDs, tone generators, and so on. The I2C bus may also be used for system testing and
diagnostic purposes in product development and manufacture.
The LM3S2533 controller includes one I2C module that provides the ability to communicate to other
IC devices over an I2C bus. The I2C bus supports devices that can both transmit and receive (write
and read) data.
Devices on the I2C bus can be designated as either a master or a slave. The I2C module supports
both sending and receiving data as either a master or a slave, and also supports the simultaneous
operation as both a master and a slave. The four I2C modes are: Master Transmit, Master Receive,
Slave Transmit, and Slave Receive.
A Stellaris®I2C module can operate at two speeds: Standard (100 Kbps) and Fast (400 Kbps).
Both the I2C master and slave can generate interrupts. The I2C master generates interrupts when
a transmit or receive operation completes (or aborts due to an error). The I2C slave generates
interrupts when data has been sent or requested by a master.
1.4.4.4 Controller Area Network (see page 407)
Controller Area Network (CAN) is a multicast shared serial-bus standard for connecting electronic
control units (ECUs). CAN was specifically designed to be robust in electromagnetically noisy
environments and can utilize a differential balanced line like RS-485 or a more robust twisted-pair
wire. Originally created for automotive purposes, now it is used in many embedded control
applications (for example, industrial or medical). Bit rates up to 1Mb/s are possible at network lengths
below 40 meters. Decreased bit rates allow longer network distances (for example, 125 Kb/s at
500m).
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
A transmitter sends a message to all CAN nodes (broadcasting). Each node decides on the basis
of the identifier received whether it should process the message. The identifier also determines the
priority that the message enjoys in competition for bus access. Each CAN message can transmit
from 0 to 8 bytes of user information. The LM3S2533 includes one CAN units.
1.4.5 System Peripherals
1.4.5.1 Programmable GPIOs (see page 161)
General-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins offer flexibility for a variety of connections.
The Stellaris®GPIO module is composed of eight physical GPIO blocks, each corresponding to an
individual GPIO port. The GPIO module is FiRM-compliant (compliant to the ARM Foundation IP
for Real-Time Microcontrollers specification) and supports 11-48 programmable input/output pins.
The number of GPIOs available depends on the peripherals being used (see “Signal Tables” on page
498 for the signals available to each GPIO pin).
The GPIO module features programmable interrupt generation as either edge-triggered or
level-sensitive on all pins, programmable control for GPIO pad configuration, and bit masking in
both read and write operations through address lines.
1.4.5.2 Four Programmable Timers (see page 202)
Programmable timers can be used to count or time external events that drive the Timer input pins.
The Stellaris®General-Purpose Timer Module (GPTM) contains four GPTM blocks. Each GPTM
block provides two 16-bit timers/counters that can be configured to operate independently as timers
or event counters, or configured to operate as one 32-bit timer or one 32-bit Real-Time Clock (RTC).
Timers can also be used to trigger analog-to-digital (ADC) conversions.
Preliminary
33November 30, 2007
Page 34

Architectural Overview
When configured in 32-bit mode, a timer can run as a Real-Time Clock (RTC), one-shot timer or
periodic timer. When in 16-bit mode, a timer can run as a one-shot timer or periodic timer, and can
extend its precision by using an 8-bit prescaler. A 16-bit timer can also be configured for event
capture or Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) generation.
1.4.5.3 Watchdog Timer (see page 238)
A watchdog timer can generate nonmaskable interrupts (NMIs) or a reset when a time-out value is
reached. The watchdog timer is used to regain control when a system has failed due to a software
error or to the failure of an external device to respond in the expected way.
The Stellaris®Watchdog Timer module consists of a 32-bit down counter, a programmable load
register, interrupt generation logic, and a locking register.
The Watchdog Timer can be configured to generate an interrupt to the controller on its first time-out,
and to generate a reset signal on its second time-out. Once the Watchdog Timer has been configured,
the lock register can be written to prevent the timer configuration from being inadvertently altered.
1.4.6 Memory Peripherals
The LM3S2533 controller offers both single-cycle SRAM and single-cycle Flash memory.
1.4.6.1 SRAM (see page 137)
The LM3S2533 static random access memory (SRAM) controller supports 64 KB SRAM. The internal
SRAM of the Stellaris®devices is located at offset 0x0000.0000 of the device memory map. To
reduce the number of time-consuming read-modify-write (RMW) operations, ARM has introduced
bit-banding technology in the new Cortex-M3 processor. With a bit-band-enabled processor, certain
regions in the memory map (SRAM and peripheral space) can use address aliases to access
individual bits in a single, atomic operation.
1.4.6.2 Flash (see page 138)
The LM3S2533 Flash controller supports 96 KB of flash memory. The flash is organized as a set
of 1-KB blocks that can be individually erased. Erasing a block causes the entire contents of the
block to be reset to all 1s. These blocks are paired into a set of 2-KB blocks that can be individually
protected. The blocks can be marked as read-only or execute-only, providing different levels of code
protection. Read-only blocks cannot be erased or programmed, protecting the contents of those
blocks from being modified. Execute-only blocks cannot be erased or programmed, and can only
be read by the controller instruction fetch mechanism, protecting the contents of those blocks from
being read by either the controller or by a debugger.
1.4.7 Additional Features
1.4.7.1 Memory Map (see page 42)
A memory map lists the location of instructions and data in memory. The memory map for the
LM3S2533 controller can be found in “Memory Map” on page 42. Register addresses are given as
a hexadecimal increment, relative to the module's base address as shown in the memory map.
The ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual provides further information on the memory
map.
1.4.7.2 JTAG TAP Controller (see page 47)
The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) port provides a standardized serial interface for controlling the
Test Access Port (TAP) and associated test logic. The TAP, JTAG instruction register, and JTAG
data registers can be used to test the interconnects of assembled printed circuit boards, obtain
Preliminary
November 30, 200734
Page 35

manufacturing information on the components, and observe and/or control the inputs and outputs
of the controller during normal operation. The JTAG port provides a high degree of testability and
chip-level access at a low cost.
The JTAG port is comprised of the standard five pins: TRST, TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO. Data is
transmitted serially into the controller on TDI and out of the controller on TDO. The interpretation of
this data is dependent on the current state of the TAP controller. For detailed information on the
operation of the JTAG port and TAP controller, please refer to the IEEE Standard 1149.1-Test
Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture.
The Luminary Micro JTAG controller works with the ARM JTAG controller built into the Cortex-M3
core. This is implemented by multiplexing the TDO outputs from both JTAG controllers. ARM JTAG
instructions select the ARM TDO output while Luminary Micro JTAG instructions select the Luminary
Micro TDO outputs. The multiplexer is controlled by the Luminary Micro JTAG controller, which has
comprehensive programming for the ARM, Luminary Micro, and unimplemented JTAG instructions.
1.4.7.3 System Control and Clocks (see page 58)
System control determines the overall operation of the device. It provides information about the
device, controls the clocking of the device and individual peripherals, and handles reset detection
and reporting.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
1.4.7.4 Hibernation Module (see page 118)
The Hibernation module provides logic to switch power off to the main processor and peripherals,
and to wake on external or time-based events. The Hibernation module includes power-sequencing
logic, a real-time clock with a pair of match registers, low-battery detection circuitry, and interrupt
signalling to the processor. It also includes 64 32-bit words of non-volatile memory that can be used
for saving state during hibernation.
1.4.8 Hardware Details
Details on the pins and package can be found in the following sections:
■ “Pin Diagram” on page 497
■ “Signal Tables” on page 498
■ “Operating Characteristics” on page 512
■ “Electrical Characteristics” on page 513
■ “Package Information” on page 525
Preliminary
35November 30, 2007
Page 36

ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core
2 ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core
The ARM Cortex-M3 processor provides the core for a high-performance, low-cost platform that
meets the needs of minimal memory implementation, reduced pin count, and low power consumption,
while delivering outstanding computational performance and exceptional system response to
interrupts. Features include:
■ Compact core.
■ Thumb-2 instruction set, delivering the high-performance expected of an ARM core in the memory
size usually associated with 8- and 16-bit devices; typically in the range of a few kilobytes of
memory for microcontroller class applications.
■ Rapid application execution through Harvard architecture characterized by separate buses for
instruction and data.
■ Exceptional interrupt handling, by implementing the register manipulations required for handling
an interrupt in hardware.
■ Memory protection unit (MPU) to provide a privileged mode of operation for complex applications.
■ Migration from the ARM7™ processor family for better performance and power efficiency.
■ Full-featured debug solution with a:
– Serial Wire JTAG Debug Port (SWJ-DP)
– Flash Patch and Breakpoint (FPB) unit for implementing breakpoints
– Data Watchpoint and Trigger (DWT) unit for implementing watchpoints, trigger resources,
and system profiling
– Instrumentation Trace Macrocell (ITM) for support of printf style debugging
– Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU) for bridging to a Trace Port Analyzer
The Stellaris®family of microcontrollers builds on this core to bring high-performance 32-bit computing
to cost-sensitive embedded microcontroller applications, such as factory automation and control,
industrial control power devices, building and home automation, and stepper motors.
For more information on the ARM Cortex-M3 processor core, see the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical
Reference Manual. For information on SWJ-DP, see the ARM® CoreSight Technical Reference
Manual.
Preliminary
November 30, 200736
Page 37

2.1 Block Diagram
Private Peripheral
Bus
(internal)
Data
Watchpoint
and Trace
Interrupts
Debug
Sleep
Instrumentation
Trace Macrocell
Trace
Port
Interface
Unit
CM3 Core
Instructions Data
Flash
Patch and
Breakpoint
Memory
Protection
Unit
Adv. High-
Perf. Bus
Access Port
Nested
Vectored
Interrupt
Controller
Serial Wire JTAG
Debug Port
Bus
Matrix
Adv. Peripheral
Bus
I-code bus
D-code bus
System bus
ROM
Table
Private
Peripheral
Bus
(external)
Serial
Wire
Output
Trace
Port
(SWO)
ARM
Cortex-M3
Figure 2-1. CPU Block Diagram
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
2.2 Functional Description
2.2.1 Serial Wire and JTAG Debug
Important:
Luminary Micro has implemented the ARM Cortex-M3 core as shown in Figure 2-1 on page 37. As
noted in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual, several Cortex-M3 components are
flexible in their implementation: SW/JTAG-DP, ETM, TPIU, the ROM table, the MPU, and the Nested
Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC). Each of these is addressed in the sections that follow.
Luminary Micro has replaced the ARM SW-DP and JTAG-DP with the ARM CoreSight™-compliant
Serial Wire JTAG Debug Port (SWJ-DP) interface. This means Chapter 12, “Debug Port,” of the
ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual does not apply to Stellaris®devices.
The SWJ-DP interface combines the SWD and JTAG debug ports into one module. See the
CoreSight™ Design Kit Technical Reference Manual for details on SWJ-DP.
The ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual describes all the features of an
ARM Cortex-M3 in detail. However, these features differ based on the implementation.
This section describes the Stellaris®implementation.
Preliminary
37November 30, 2007
Page 38
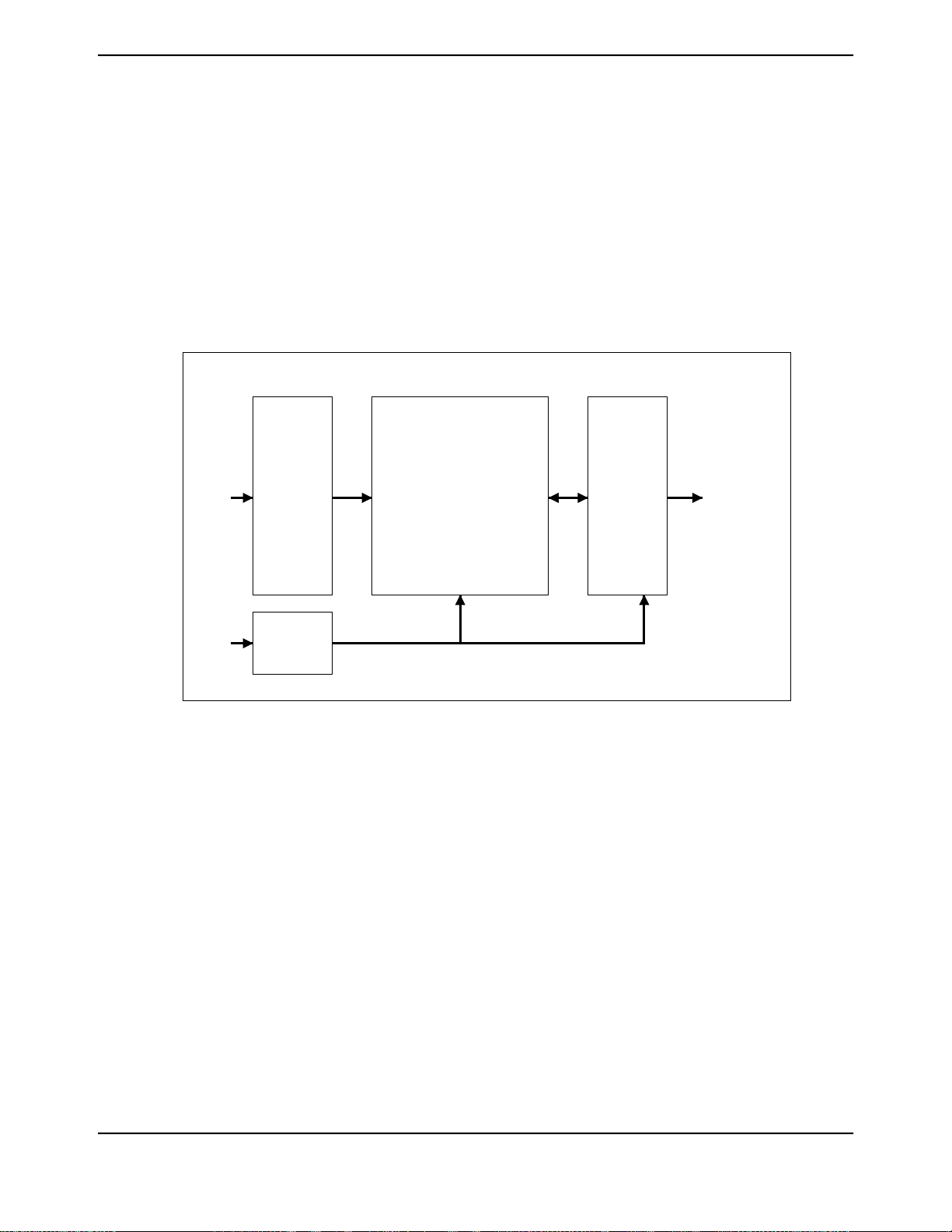
ATB
Interface
Asynchronous FIFO
APB
Interface
Trace Out
(serializer)
Debug
ATB
Slave
Port
APB
Slave
Port
Serial Wire
Trace Port
(SWO)
ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core
2.2.2 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM)
ETM was not implemented in the Stellaris®devices. This means Chapters 15 and 16 of the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual can be ignored.
2.2.3 Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU)
The TPIU acts as a bridge between the Cortex-M3 trace data from the ITM, and an off-chip Trace
Port Analyzer. The Stellaris®devices have implemented TPIU as shown in Figure 2-2 on page 38.
This is similar to the non-ETM version described in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference
Manual, however, SWJ-DP only provides SWV output for the TPIU.
Figure 2-2. TPIU Block Diagram
2.2.4 ROM Table
The default ROM table was implemented as described in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical
Reference Manual.
2.2.5 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) is included on the LM3S2533 controller and supports the standard
ARMv7 Protected Memory System Architecture (PMSA) model. The MPU provides full support for
protection regions, overlapping protection regions, access permissions, and exporting memory
attributes to the system.
2.2.6 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)
The Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC):
■ Facilitates low-latency exception and interrupt handling
■ Controls power management
■ Implements system control registers
Preliminary
November 30, 200738
Page 39

The NVIC supports up to 240 dynamically reprioritizable interrupts each with up to 256 levels of
priority. The NVIC and the processor core interface are closely coupled, which enables low latency
interrupt processing and efficient processing of late arriving interrupts. The NVIC maintains knowledge
of the stacked (nested) interrupts to enable tail-chaining of interrupts.
You can only fully access the NVIC from privileged mode, but you can pend interrupts in user-mode
if you enable the Configuration Control Register (see the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference
Manual). Any other user-mode access causes a bus fault.
All NVIC registers are accessible using byte, halfword, and word unless otherwise stated.
All NVIC registers and system debug registers are little endian regardless of the endianness state
of the processor.
2.2.6.1 Interrupts
The ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual describes the maximum number of interrupts
and interrupt priorities. The LM3S2533 microcontroller supports 36 interrupts with eight priority
levels.
2.2.6.2 System Timer (SysTick)
Cortex-M3 includes an integrated system timer, SysTick. SysTick provides a simple, 24-bit
clear-on-write, decrementing, wrap-on-zero counter with a flexible control mechanism. The counter
can be used in several different ways, for example:
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
■ An RTOS tick timer which fires at a programmable rate (for example, 100 Hz) and invokes a
SysTick routine.
■ A high-speed alarm timer using the system clock.
■ A variable rate alarm or signal timer—the duration is range-dependent on the reference clock
used and the dynamic range of the counter.
■ A simple counter. Software can use this to measure time to completion and time used.
■ An internal clock source control based on missing/meeting durations. The COUNTFLAG bit-field
in the control and status register can be used to determine if an action completed within a set
duration, as part of a dynamic clock management control loop.
Functional Description
The timer consists of three registers:
■ A control and status counter to configure its clock, enable the counter, enable the SysTick
interrupt, and determine counter status.
■ The reload value for the counter, used to provide the counter's wrap value.
■ The current value of the counter.
A fourth register, the SysTick Calibration Value Register, is not implemented in the Stellaris®devices.
When enabled, the timer counts down from the reload value to zero, reloads (wraps) to the value
in the SysTick Reload Value register on the next clock edge, then decrements on subsequent clocks.
Writing a value of zero to the Reload Value register disables the counter on the next wrap. When
the counter reaches zero, the COUNTFLAG status bit is set. The COUNTFLAG bit clears on reads.
39November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 40

ARM Cortex-M3 Processor Core
Writing to the Current Value register clears the register and the COUNTFLAG status bit. The write
does not trigger the SysTick exception logic. On a read, the current value is the value of the register
at the time the register is accessed.
If the core is in debug state (halted), the counter will not decrement. The timer is clocked with respect
to a reference clock. The reference clock can be the core clock or an external clock source.
SysTick Control and Status Register
Use the SysTick Control and Status Register to enable the SysTick features. The reset is
0x0000.0000.
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide compatibility with
0ROreserved31:17
future products, the value of a reserved bit should be preserved across a
read-modify-write operation.
Returns 1 if timer counted to 0 since last time this was read. Clears on read by
0R/WCOUNTFLAG16
application. If read by the debugger using the DAP, this bit is cleared on read-only
if the MasterType bit in the AHB-AP Control Register is set to 0. Otherwise, the
COUNTFLAG bit is not changed by the debugger read.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide compatibility with
0ROreserved15:3
future products, the value of a reserved bit should be preserved across a
read-modify-write operation.
0 = external reference clock. (Not implemented for Stellaris microcontrollers.)
0R/WCLKSOURCE2
1 = core clock.
If no reference clock is provided, it is held at 1 and so gives the same time as the
core clock. The core clock must be at least 2.5 times faster than the reference clock.
If it is not, the count values are unpredictable.
1 = counting down to 0 pends the SysTick handler.
0R/WTICKINT1
0 = counting down to 0 does not pend the SysTick handler. Software can use the
COUNTFLAG to determine if ever counted to 0.
1 = counter operates in a multi-shot way. That is, counter loads with the Reload
0R/WENABLE0
value and then begins counting down. On reaching 0, it sets the COUNTFLAG to
1 and optionally pends the SysTick handler, based on TICKINT. It then loads the
Reload value again, and begins counting.
0 = counter disabled.
SysTick Reload Value Register
Use the SysTick Reload Value Register to specify the start value to load into the current value
register when the counter reaches 0. It can be any value between 1 and 0x00FF.FFFF. A start value
of 0 is possible, but has no effect because the SysTick interrupt and COUNTFLAG are activated
when counting from 1 to 0.
Therefore, as a multi-shot timer, repeated over and over, it fires every N+1 clock pulse, where N is
any value from 1 to 0x00FF.FFFF. So, if the tick interrupt is required every 100 clock pulses, 99
must be written into the RELOAD. If a new value is written on each tick interrupt, so treated as single
shot, then the actual count down must be written. For example, if a tick is next required after 400
clock pulses, 400 must be written into the RELOAD.
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide compatibility with
0ROreserved31:24
future products, the value of a reserved bit should be preserved across a read-modify-write
operation.
November 30, 200740
Preliminary
Page 41

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
Value to load into the SysTick Current Value Register when the counter reaches 0.-W1CRELOAD23:0
SysTick Current Value Register
Use the SysTick Current Value Register to find the current value in the register.
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide compatibility with
0ROreserved31:24
future products, the value of a reserved bit should be preserved across a
read-modify-write operation.
Current value at the time the register is accessed. No read-modify-write protection is
-W1CCURRENT23:0
provided, so change with care.
This register is write-clear. Writing to it with any value clears the register to 0. Clearing
this register also clears the COUNTFLAG bit of the SysTick Control and Status Register.
SysTick Calibration Value Register
The SysTick Calibration Value register is not implemented.
Preliminary
41November 30, 2007
Page 42

Memory Map
3 Memory Map
The memory map for the LM3S2533 controller is provided in Table 3-1 on page 42.
In this manual, register addresses are given as a hexadecimal increment, relative to the module’s
base address as shown in the memory map. See also Chapter 4, “Memory Map” in the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
Important: In Table 3-1 on page 42, addresses not listed are reserved.
Table 3-1. Memory Map
Memory
FiRM Peripherals
Peripherals
a
DescriptionEndStart
0x0001.7FFF0x0000.0000
0x2000.FFFF0x2000.0000
b
c
For details on
registers, see
page ...
141On-chip flash
141Bit-banded on-chip SRAM
-Reserved non-bit-banded SRAM space0x21FF.FFFF0x2010.0000
137Bit-band alias of 0x2000.0000 through 0x200F.FFFF0x23FF.FFFF0x2200.0000
-Reserved non-bit-banded SRAM space0x3FFF.FFFF0x2400.0000
240Watchdog timer0x4000.0FFF0x4000.0000
167GPIO Port A0x4000.4FFF0x4000.4000
167GPIO Port B0x4000.5FFF0x4000.5000
167GPIO Port C0x4000.6FFF0x4000.6000
167GPIO Port D0x4000.7FFF0x4000.7000
346SSI00x4000.8FFF0x4000.8000
301UART00x4000.CFFF0x4000.C000
301UART10x4000.DFFF0x4000.D000
385I2C Master 00x4002.07FF0x4002.0000
398I2C Slave 00x4002.0FFF0x4002.0800
167GPIO Port E0x4002.4FFF0x4002.4000
167GPIO Port F0x4002.5FFF0x4002.5000
167GPIO Port G0x4002.6FFF0x4002.6000
167GPIO Port H0x4002.7FFF0x4002.7000
468PWM0x4002.8FFF0x4002.8000
213Timer00x4003.0FFF0x4003.0000
213Timer10x4003.1FFF0x4003.1000
213Timer20x4003.2FFF0x4003.2000
213Timer30x4003.3FFF0x4003.3000
267ADC0x4003.8FFF0x4003.8000
448Analog Comparators0x4003.CFFF0x4003.C000
420CAN0 Controller0x4004.0FFF0x4004.0000
124Hibernation Module0x400F.CFFF0x400F.C000
Preliminary
November 30, 200742
Page 43

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Private Peripheral Bus
a. All reserved space returns a bus fault when read or written.
b. The unavailable flash will bus fault throughout this range.
c. The unavailable SRAM will bus fault throughout this range.
DescriptionEndStart
Instrumentation Trace Macrocell (ITM)0xE000.0FFF0xE000.0000
Data Watchpoint and Trace (DWT)0xE000.1FFF0xE000.1000
Flash Patch and Breakpoint (FPB)0xE000.2FFF0xE000.2000
Reserved0xE000.DFFF0xE000.3000
Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)0xE000.EFFF0xE000.E000
Reserved0xE003.FFFF0xE000.F000
Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU)0xE004.0FFF0xE004.0000
For details on
registers, see
page ...
141Flash control0x400F.DFFF0x400F.D000
65System control0x400F.EFFF0x400F.E000
-Bit-banded alias of 0x4000.0000 through 0x400F.FFFF0x43FF.FFFF0x4200.0000
ARM®
Cortex™-M3
Technical
Reference
Manual
-Reserved0xE004.1FFF0xE004.1000
-Reserved0xE00F.FFFF0xE004.2000
-Reserved for vendor peripherals0xFFFF.FFFF0xE010.0000
Preliminary
43November 30, 2007
Page 44

Interrupts
4 Interrupts
The ARM Cortex-M3 processor and the Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) prioritize and
handle all exceptions. All exceptions are handled in Handler Mode. The processor state is
automatically stored to the stack on an exception, and automatically restored from the stack at the
end of the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR). The vector is fetched in parallel to the state saving, which
enables efficient interrupt entry. The processor supports tail-chaining, which enables back-to-back
interrupts to be performed without the overhead of state saving and restoration.
Table 4-1 on page 44 lists all the exceptions. Software can set eight priority levels on seven of these
exceptions (system handlers) as well as on 36 interrupts (listed in Table 4-2 on page 45).
Priorities on the system handlers are set with the NVIC System Handler Priority registers. Interrupts
are enabled through the NVIC Interrupt Set Enable register and prioritized with the NVIC Interrupt
Priority registers. You can also group priorities by splitting priority levels into pre-emption priorities
and subpriorities. All the interrupt registers are described in Chapter 8, “Nested Vectored Interrupt
Controller” in the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
Internally, the highest user-settable priority (0) is treated as fourth priority, after a Reset, NMI, and
a Hard Fault. Note that 0 is the default priority for all the settable priorities.
If you assign the same priority level to two or more interrupts, their hardware priority (the lower the
position number) determines the order in which the processor activates them. For example, if both
GPIO Port A and GPIO Port B are priority level 1, then GPIO Port A has higher priority.
See Chapter 5, “Exceptions” and Chapter 8, “Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller” in the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual for more information on exceptions and interrupts.
Note: In Table 4-2 on page 45 interrupts not listed are reserved.
Table 4-1. Exception Types
a
PositionException Type
-3 (highest)1Reset
Interrupt (NMI)
settable4Memory Management
settable5Bus Fault
settable6Usage Fault
DescriptionPriority
Stack top is loaded from first entry of vector table on reset.-0-
Invoked on power up and warm reset. On first instruction, drops to lowest
priority (and then is called the base level of activation). This is
asynchronous.
Cannot be stopped or preempted by any exception but reset. This is
-22Non-Maskable
asynchronous.
An NMI is only producible by software, using the NVIC Interrupt Control
State register.
All classes of Fault, when the fault cannot activate due to priority or the
-13Hard Fault
configurable fault handler has been disabled. This is synchronous.
MPU mismatch, including access violation and no match. This is
synchronous.
The priority of this exception can be changed.
Pre-fetch fault, memory access fault, and other address/memory related
faults. This is synchronous when precise and asynchronous when
imprecise.
You can enable or disable this fault.
Usage fault, such as undefined instruction executed or illegal state
transition attempt. This is synchronous.
Reserved.-7-10-
System service call with SVC instruction. This is synchronous.settable11SVCall
Preliminary
November 30, 200744
Page 45

a
PositionException Type
settable12Debug Monitor
settable14PendSV
Interrupts
above
a. 0 is the default priority for all the settable priorities.
settable16 and
DescriptionPriority
Debug monitor (when not halting). This is synchronous, but only active
when enabled. It does not activate if lower priority than the current
activation.
Reserved.-13-
Pendable request for system service. This is asynchronous and only
pended by software.
System tick timer has fired. This is asynchronous.settable15SysTick
Asserted from outside the ARM Cortex-M3 core and fed through the NVIC
(prioritized). These are all asynchronous. Table 4-2 on page 45 lists the
interrupts on the LM3S2533 controller.
Table 4-2. Interrupts
DescriptionInterrupt (Bit in Interrupt Registers)
GPIO Port A0
GPIO Port B1
GPIO Port C2
GPIO Port D3
GPIO Port E4
UART05
UART16
SSI07
I2C08
PWM Fault9
PWM Generator 010
PWM Generator 111
PWM Generator 212
ADC Sequence 014
ADC Sequence 115
ADC Sequence 216
ADC Sequence 317
Watchdog timer18
Timer0 A19
Timer0 B20
Timer1 A21
Timer1 B22
Timer2 A23
Timer2 B24
Analog Comparator 025
Analog Comparator 126
Analog Comparator 227
System Control28
Flash Control29
GPIO Port F30
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Preliminary
45November 30, 2007
Page 46

Interrupts
DescriptionInterrupt (Bit in Interrupt Registers)
GPIO Port G31
GPIO Port H32
Timer3 A35
Timer3 B36
CAN039
Hibernation Module43
Preliminary
November 30, 200746
Page 47

5 JTAG Interface
The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) port is an IEEE standard that defines a Test Access Port and
Boundary Scan Architecture for digital integrated circuits and provides a standardized serial interface
for controlling the associated test logic. The TAP, Instruction Register (IR), and Data Registers (DR)
can be used to test the interconnections of assembled printed circuit boards and obtain manufacturing
information on the components. The JTAG Port also provides a means of accessing and controlling
design-for-test features such as I/O pin observation and control, scan testing, and debugging.
The JTAG port is comprised of the standard five pins: TRST, TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO. Data is
transmitted serially into the controller on TDI and out of the controller on TDO. The interpretation of
this data is dependent on the current state of the TAP controller. For detailed information on the
operation of the JTAG port and TAP controller, please refer to the IEEE Standard 1149.1-Test
Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture.
The Luminary Micro JTAG controller works with the ARM JTAG controller built into the Cortex-M3
core. This is implemented by multiplexing the TDO outputs from both JTAG controllers. ARM JTAG
instructions select the ARM TDO output while Luminary Micro JTAG instructions select the Luminary
Micro TDO outputs. The multiplexer is controlled by the Luminary Micro JTAG controller, which has
comprehensive programming for the ARM, Luminary Micro, and unimplemented JTAG instructions.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
The JTAG module has the following features:
■ IEEE 1149.1-1990 compatible Test Access Port (TAP) controller
■ Four-bit Instruction Register (IR) chain for storing JTAG instructions
■ IEEE standard instructions:
– BYPASS instruction
– IDCODE instruction
– SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction
– EXTEST instruction
– INTEST instruction
■ ARM additional instructions:
– APACC instruction
– DPACC instruction
– ABORT instruction
■ Integrated ARM Serial Wire Debug (SWD)
See the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual for more information on the ARM JTAG
controller.
47November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 48

Instruction Register(IR)
TAP Controller
BYPASS Data Register
Boundary Scan Data Register
IDCODE Data Register
ABORT Data Register
DPACC Data Register
APACC Data Register
TRST
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
Cortex-M3
Debug
Port
JTAG Interface
5.1 Block Diagram
Figure 5-1. JTAG Module Block Diagram
5.2 Functional Description
A high-level conceptual drawing of the JTAG module is shown in Figure 5-1 on page 48. The JTAG
module is composed of the Test Access Port (TAP) controller and serial shift chains with parallel
update registers. The TAP controller is a simple state machine controlled by the TRST, TCK and
TMS inputs. The current state of the TAP controller depends on the current value of TRST and the
sequence of values captured on TMS at the rising edge of TCK. The TAP controller determines when
the serial shift chains capture new data, shift data from TDI towards TDO, and update the parallel
load registers. The current state of the TAP controller also determines whether the Instruction
Register (IR) chain or one of the Data Register (DR) chains is being accessed.
The serial shift chains with parallel load registers are comprised of a single Instruction Register (IR)
chain and multiple Data Register (DR) chains. The current instruction loaded in the parallel load
register determines which DR chain is captured, shifted, or updated during the sequencing of the
TAP controller.
Some instructions, like EXTEST and INTEST, operate on data currently in a DR chain and do not
capture, shift, or update any of the chains. Instructions that are not implemented decode to the
BYPASS instruction to ensure that the serial path between TDI and TDO is always connected (see
Table 5-2 on page 54 for a list of implemented instructions).
See “JTAG and Boundary Scan” on page 521 for JTAG timing diagrams.
Preliminary
November 30, 200748
Page 49

5.2.1 JTAG Interface Pins
The JTAG interface consists of five standard pins: TRST, TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO. These pins and
their associated reset state are given in Table 5-1 on page 49. Detailed information on each pin
follows.
Table 5-1. JTAG Port Pins Reset State
5.2.1.1 Test Reset Input (TRST)
The TRST pin is an asynchronous active Low input signal for initializing and resetting the JTAG TAP
controller and associated JTAG circuitry. When TRST is asserted, the TAP controller resets to the
Test-Logic-Reset state and remains there while TRST is asserted. When the TAP controller enters
the Test-Logic-Reset state, the JTAG Instruction Register (IR) resets to the default instruction,
IDCODE.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Drive ValueDrive StrengthInternal Pull-DownInternal Pull-UpData DirectionPin Name
N/AN/ADisabledEnabledInputTRST
N/AN/ADisabledEnabledInputTCK
N/AN/ADisabledEnabledInputTMS
N/AN/ADisabledEnabledInputTDI
High-Z2-mA driverDisabledEnabledOutputTDO
By default, the internal pull-up resistor on the TRST pin is enabled after reset. Changes to the pull-up
resistor settings on GPIO Port B should ensure that the internal pull-up resistor remains enabled
on PB7/TRST; otherwise JTAG communication could be lost.
5.2.1.2 Test Clock Input (TCK)
The TCK pin is the clock for the JTAG module. This clock is provided so the test logic can operate
independently of any other system clocks. In addition, it ensures that multiple JTAG TAP controllers
that are daisy-chained together can synchronously communicate serial test data between
components. During normal operation, TCK is driven by a free-running clock with a nominal 50%
duty cycle. When necessary, TCK can be stopped at 0 or 1 for extended periods of time. While TCK
is stopped at 0 or 1, the state of the TAP controller does not change and data in the JTAG Instruction
and Data Registers is not lost.
By default, the internal pull-up resistor on the TCK pin is enabled after reset. This assures that no
clocking occurs if the pin is not driven from an external source. The internal pull-up and pull-down
resistors can be turned off to save internal power as long as the TCK pin is constantly being driven
by an external source.
5.2.1.3 Test Mode Select (TMS)
The TMS pin selects the next state of the JTAG TAP controller. TMS is sampled on the rising edge
of TCK. Depending on the current TAP state and the sampled value of TMS, the next state is entered.
Because the TMS pin is sampled on the rising edge of TCK, the IEEE Standard 1149.1 expects the
value on TMS to change on the falling edge of TCK.
Holding TMS high for five consecutive TCK cycles drives the TAP controller state machine to the
Test-Logic-Reset state. When the TAP controller enters the Test-Logic-Reset state, the JTAG
Instruction Register (IR) resets to the default instruction, IDCODE. Therefore, this sequence can
be used as a reset mechanism, similar to asserting TRST. The JTAG Test Access Port state machine
can be seen in its entirety in Figure 5-2 on page 51.
Preliminary
49November 30, 2007
Page 50

JTAG Interface
By default, the internal pull-up resistor on the TMS pin is enabled after reset. Changes to the pull-up
resistor settings on GPIO Port C should ensure that the internal pull-up resistor remains enabled
on PC1/TMS; otherwise JTAG communication could be lost.
5.2.1.4 Test Data Input (TDI)
The TDI pin provides a stream of serial information to the IR chain and the DR chains. TDI is
sampled on the rising edge of TCK and, depending on the current TAP state and the current
instruction, presents this data to the proper shift register chain. Because the TDI pin is sampled on
the rising edge of TCK, the IEEE Standard 1149.1 expects the value on TDI to change on the falling
edge of TCK.
By default, the internal pull-up resistor on the TDI pin is enabled after reset. Changes to the pull-up
resistor settings on GPIO Port C should ensure that the internal pull-up resistor remains enabled
on PC2/TDI; otherwise JTAG communication could be lost.
5.2.1.5 Test Data Output (TDO)
The TDO pin provides an output stream of serial information from the IR chain or the DR chains.
The value of TDO depends on the current TAP state, the current instruction, and the data in the
chain being accessed. In order to save power when the JTAG port is not being used, the TDO pin
is placed in an inactive drive state when not actively shifting out data. Because TDO can be connected
to the TDI of another controller in a daisy-chain configuration, the IEEE Standard 1149.1 expects
the value on TDO to change on the falling edge of TCK.
By default, the internal pull-up resistor on the TDO pin is enabled after reset. This assures that the
pin remains at a constant logic level when the JTAG port is not being used. The internal pull-up and
pull-down resistors can be turned off to save internal power if a High-Z output value is acceptable
during certain TAP controller states.
5.2.2 JTAG TAP Controller
The JTAG TAP controller state machine is shown in Figure 5-2 on page 51. The TAP controller
state machine is reset to the Test-Logic-Reset state on the assertion of a Power-On-Reset (POR)
or the assertion of TRST. Asserting the correct sequence on the TMS pin allows the JTAG module
to shift in new instructions, shift in data, or idle during extended testing sequences. For detailed
information on the function of the TAP controller and the operations that occur in each state, please
refer to IEEE Standard 1149.1.
Preliminary
November 30, 200750
Page 51

Figure 5-2. Test Access Port State Machine
Test Logic Reset
Run Test Idle Select DR Scan Select IR Scan
Capture DR Capture IR
Shift DR Shift IR
Exit 1 DR Exit 1 IR
Exit 2 DR Exit 2 IR
Pause DR Pause IR
Update DR Update IR
1 11
1 1
1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 10 0
00
00
0 0
0 0
0 0
00
0
0
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
5.2.3 Shift Registers
The Shift Registers consist of a serial shift register chain and a parallel load register. The serial shift
register chain samples specific information during the TAP controller’s CAPTURE states and allows
this information to be shifted out of TDO during the TAP controller’s SHIFT states. While the sampled
data is being shifted out of the chain on TDO, new data is being shifted into the serial shift register
on TDI. This new data is stored in the parallel load register during the TAP controller’s UPDATE
states. Each of the shift registers is discussed in detail in “Register Descriptions” on page 54.
5.2.4 Operational Considerations
There are certain operational considerations when using the JTAG module. Because the JTAG pins
can be programmed to be GPIOs, board configuration and reset conditions on these pins must be
considered. In addition, because the JTAG module has integrated ARM Serial Wire Debug, the
method for switching between these two operational modes is described below.
Preliminary
51November 30, 2007
Page 52

JTAG Interface
5.2.4.1 GPIO Functionality
When the controller is reset with either a POR or RST, the JTAG/SWD port pins default to their
JTAG/SWD configurations. The default configuration includes enabling digital functionality (setting
GPIODEN to 1), enabling the pull-up resistors (setting GPIOPUR to 1), and enabling the alternate
hardware function (setting GPIOAFSEL to 1) for the PB7 and PC[3:0] JTAG/SWD pins.
It is possible for software to configure these pins as GPIOs after reset by writing 0s to PB7 and
PC[3:0] in the GPIOAFSEL register. If the user does not require the JTAG/SWD port for debugging
or board-level testing, this provides five more GPIOs for use in the design.
Caution – If the JTAG pins are used as GPIOs in a design, PB7 and PC2 cannot have external pull-down
resistors connected to both of them at the same time. If both pins are pulled Low during reset, the
controller has unpredictable behavior. If this happens, remove one or both of the pull-down resistors,
and apply RST or power-cycle the part.
In addition, it is possible to create a software sequence that prevents the debugger from connecting to
the Stellaris®microcontroller. If the program code loaded into ash immediately changes the JTAG
pins to their GPIO functionality, the debugger may not have enough time to connect and halt the
controller before the JTAG pin functionality switches. This may lock the debugger out of the part. This
can be avoided with a software routine that restores JTAG functionality based on an external or software
trigger.
The commit control registers provide a layer of protection against accidental programming of critical
hardware peripherals. Writes to protected bits of the GPIO Alternate Function Select (GPIOAFSEL)
register (see page 177) are not committed to storage unless the GPIO Lock (GPIOLOCK) register
(see page 187) has been unlocked and the appropriate bits of the GPIO Commit (GPIOCR) register
(see page 188) have been set to 1.
Recovering a "Locked" Device
If software configures any of the JTAG/SWD pins as GPIO and loses the ability to communicate
with the debugger, there is a debug sequence that can be used to recover the device. Performing
a total of ten JTAG-to-SWD and SWD-to-JTAG switch sequences while holding the device in reset
mass erases the flash memory. The sequence to recover the device is:
1. Assert and hold the RST signal.
2. Perform the JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence.
3. Perform the SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence.
4. Perform the JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence.
5. Perform the SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence.
6. Perform the JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence.
7. Perform the SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence.
8. Perform the JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence.
9. Perform the SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence.
10. Perform the JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence.
11. Perform the SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence.
Preliminary
November 30, 200752
Page 53

12. Release the RST signal.
The JTAG-to-SWD and SWD-to-JTAG switch sequences are described in “ARM Serial Wire Debug
(SWD)” on page 53. When performing switch sequences for the purpose of recovering the debug
capabilities of the device, only steps 1 and 2 of the switch sequence need to be performed.
5.2.4.2 ARM Serial Wire Debug (SWD)
In order to seamlessly integrate the ARM Serial Wire Debug (SWD) functionality, a serial-wire
debugger must be able to connect to the Cortex-M3 core without having to perform, or have any
knowledge of, JTAG cycles. This is accomplished with a SWD preamble that is issued before the
SWD session begins.
The preamble used to enable the SWD interface of the SWJ-DP module starts with the TAP controller
in the Test-Logic-Reset state. From here, the preamble sequences the TAP controller through the
following states: Run Test Idle, Select DR, Select IR, Test Logic Reset, Test Logic Reset, Run Test
Idle, Run Test Idle, Select DR, Select IR, Test Logic Reset, Test Logic Reset, Run Test Idle, Run
Test Idle, Select DR, Select IR, and Test Logic Reset states.
Stepping through this sequences of the TAP state machine enables the SWD interface and disables
the JTAG interface. For more information on this operation and the SWD interface, see the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual and the ARM® CoreSight Technical Reference Manual.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Because this sequence is a valid series of JTAG operations that could be issued, the ARM JTAG
TAP controller is not fully compliant to the IEEE Standard 1149.1. This is the only instance where
the ARM JTAG TAP controller does not meet full compliance with the specification. Due to the low
probability of this sequence occurring during normal operation of the TAP controller, it should not
affect normal performance of the JTAG interface.
JTAG-to-SWD Switching
To switch the operating mode of the Debug Access Port (DAP) from JTAG to SWD mode, the
external debug hardware must send a switch sequence to the device. The 16-bit switch sequence
for switching to SWD mode is defined as b1110011110011110, transmitted LSB first. This can also
be represented as 16'hE79E when transmitted LSB first. The complete switch sequence should
consist of the following transactions on the TCK/SWCLK and TMS/SWDIO signals:
1. Send at least 50 TCK/SWCLK cycles with TMS/SWDIO set to 1. This ensures that both JTAG and
SWD are in their reset/idle states.
2. Send the 16-bit JTAG-to-SWD switch sequence, 16'hE79E.
3. Send at least 50 TCK/SWCLK cycles with TMS/SWDIO set to 1. This ensures that if SWJ-DP was
already in SWD mode, before sending the switch sequence, the SWD goes into the line reset
state.
SWD-to-JTAG Switching
To switch the operating mode of the Debug Access Port (DAP) from SWD to JTAG mode, the
external debug hardware must send a switch sequence to the device. The 16-bit switch sequence
for switching to JTAG mode is defined as b1110011110011110, transmitted LSB first. This can also
be represented as 16'hE73C when transmitted LSB first. The complete switch sequence should
consist of the following transactions on the TCK/SWCLK and TMS/SWDIO signals:
1. Send at least 50 TCK/SWCLK cycles with TMS/SWDIO set to 1. This ensures that both JTAG and
SWD are in their reset/idle states.
53November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 54

JTAG Interface
2. Send the 16-bit SWD-to-JTAG switch sequence, 16'hE73C.
3. Send at least 5 TCK/SWCLK cycles with TMS/SWDIO set to 1. This ensures that if SWJ-DP was
already in JTAG mode, before sending the switch sequence, the JTAG goes into the Test Logic
Reset state.
5.3 Initialization and Configuration
After a Power-On-Reset or an external reset (RST), the JTAG pins are automatically configured for
JTAG communication. No user-defined initialization or configuration is needed. However, if the user
application changes these pins to their GPIO function, they must be configured back to their JTAG
functionality before JTAG communication can be restored. This is done by enabling the five JTAG
pins (PB7 and PC[3:0]) for their alternate function using the GPIOAFSEL register.
5.4 Register Descriptions
There are no APB-accessible registers in the JTAG TAP Controller or Shift Register chains. The
registers within the JTAG controller are all accessed serially through the TAP Controller. The registers
can be broken down into two main categories: Instruction Registers and Data Registers.
5.4.1 Instruction Register (IR)
The JTAG TAP Instruction Register (IR) is a four-bit serial scan chain with a parallel load register
connected between the JTAG TDI and TDO pins. When the TAP Controller is placed in the correct
states, bits can be shifted into the Instruction Register. Once these bits have been shifted into the
chain and updated, they are interpreted as the current instruction. The decode of the Instruction
Register bits is shown in Table 5-2 on page 54. A detailed explanation of each instruction, along
with its associated Data Register, follows.
Table 5-2. JTAG Instruction Register Commands
DescriptionInstructionIR[3:0]
EXTEST0000
INTEST0001
SAMPLE / PRELOAD0010
IDCODE1110
Drives the values preloaded into the Boundary Scan Chain by the SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction onto the pads.
Drives the values preloaded into the Boundary Scan Chain by the SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction into the controller.
Captures the current I/O values and shifts the sampled values out of the Boundary Scan
Chain while new preload data is shifted in.
Shifts data into the ARM Debug Port Abort Register.ABORT1000
Shifts data into and out of the ARM DP Access Register.DPACC1010
Shifts data into and out of the ARM AC Access Register.APACC1011
Loads manufacturing information defined by the IEEE Standard 1149.1 into the IDCODE
chain and shifts it out.
Connects TDI to TDO through a single Shift Register chain.BYPASS1111
Defaults to the BYPASS instruction to ensure that TDI is always connected to TDO.ReservedAll Others
5.4.1.1 EXTEST Instruction
The EXTEST instruction does not have an associated Data Register chain. The EXTEST instruction
uses the data that has been preloaded into the Boundary Scan Data Register using the
SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction. When the EXTEST instruction is present in the Instruction Register,
the preloaded data in the Boundary Scan Data Register associated with the outputs and output
enables are used to drive the GPIO pads rather than the signals coming from the core. This allows
November 30, 200754
Preliminary
Page 55

tests to be developed that drive known values out of the controller, which can be used to verify
connectivity.
5.4.1.2 INTEST Instruction
The INTEST instruction does not have an associated Data Register chain. The INTEST instruction
uses the data that has been preloaded into the Boundary Scan Data Register using the
SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction. When the INTEST instruction is present in the Instruction Register,
the preloaded data in the Boundary Scan Data Register associated with the inputs are used to drive
the signals going into the core rather than the signals coming from the GPIO pads. This allows tests
to be developed that drive known values into the controller, which can be used for testing. It is
important to note that although the RST input pin is on the Boundary Scan Data Register chain, it
is only observable.
5.4.1.3 SAMPLE/PRELOAD Instruction
The SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction connects the Boundary Scan Data Register chain between
TDI and TDO. This instruction samples the current state of the pad pins for observation and preloads
new test data. Each GPIO pad has an associated input, output, and output enable signal. When the
TAP controller enters the Capture DR state during this instruction, the input, output, and output-enable
signals to each of the GPIO pads are captured. These samples are serially shifted out of TDO while
the TAP controller is in the Shift DR state and can be used for observation or comparison in various
tests.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
While these samples of the inputs, outputs, and output enables are being shifted out of the Boundary
Scan Data Register, new data is being shifted into the Boundary Scan Data Register from TDI.
Once the new data has been shifted into the Boundary Scan Data Register, the data is saved in the
parallel load registers when the TAP controller enters the Update DR state. This update of the
parallel load register preloads data into the Boundary Scan Data Register that is associated with
each input, output, and output enable. This preloaded data can be used with the EXTEST and
INTEST instructions to drive data into or out of the controller. Please see “Boundary Scan Data
Register” on page 57 for more information.
5.4.1.4 ABORT Instruction
The ABORT instruction connects the associated ABORT Data Register chain between TDI and
TDO. This instruction provides read and write access to the ABORT Register of the ARM Debug
Access Port (DAP). Shifting the proper data into this Data Register clears various error bits or initiates
a DAP abort of a previous request. Please see the “ABORT Data Register” on page 57 for more
information.
5.4.1.5 DPACC Instruction
The DPACC instruction connects the associated DPACC Data Register chain between TDI and
TDO. This instruction provides read and write access to the DPACC Register of the ARM Debug
Access Port (DAP). Shifting the proper data into this register and reading the data output from this
register allows read and write access to the ARM debug and status registers. Please see “DPACC
Data Register” on page 57 for more information.
5.4.1.6 APACC Instruction
The APACC instruction connects the associated APACC Data Register chain between TDI and
TDO. This instruction provides read and write access to the APACC Register of the ARM Debug
Access Port (DAP). Shifting the proper data into this register and reading the data output from this
register allows read and write access to internal components and buses through the Debug Port.
Please see “APACC Data Register” on page 57 for more information.
55November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 56

JTAG Interface
5.4.1.7 IDCODE Instruction
The IDCODE instruction connects the associated IDCODE Data Register chain between TDI and
TDO. This instruction provides information on the manufacturer, part number, and version of the
ARM core. This information can be used by testing equipment and debuggers to automatically
configure their input and output data streams. IDCODE is the default instruction that is loaded into
the JTAG Instruction Register when a power-on-reset (POR) is asserted, TRST is asserted, or the
Test-Logic-Reset state is entered. Please see “IDCODE Data Register” on page 56 for more
information.
5.4.1.8 BYPASS Instruction
The BYPASS instruction connects the associated BYPASS Data Register chain between TDI and
TDO. This instruction is used to create a minimum length serial path between the TDI and TDO ports.
The BYPASS Data Register is a single-bit shift register. This instruction improves test efficiency by
allowing components that are not needed for a specific test to be bypassed in the JTAG scan chain
by loading them with the BYPASS instruction. Please see “BYPASS Data Register” on page 56 for
more information.
5.4.2 Data Registers
The JTAG module contains six Data Registers. These include: IDCODE, BYPASS, Boundary Scan,
APACC, DPACC, and ABORT serial Data Register chains. Each of these Data Registers is discussed
in the following sections.
5.4.2.1 IDCODE Data Register
The format for the 32-bit IDCODE Data Register defined by the IEEE Standard 1149.1 is shown in
Figure 5-3 on page 56. The standard requires that every JTAG-compliant device implement either
the IDCODE instruction or the BYPASS instruction as the default instruction. The LSB of the IDCODE
Data Register is defined to be a 1 to distinguish it from the BYPASS instruction, which has an LSB
of 0. This allows auto configuration test tools to determine which instruction is the default instruction.
The major uses of the JTAG port are for manufacturer testing of component assembly, and program
development and debug. To facilitate the use of auto-configuration debug tools, the IDCODE
instruction outputs a value of 0x3BA00477. This value indicates an ARM Cortex-M3, Version 1
processor. This allows the debuggers to automatically configure themselves to work correctly with
the Cortex-M3 during debug.
Figure 5-3. IDCODE Register Format
5.4.2.2 BYPASS Data Register
The format for the 1-bit BYPASS Data Register defined by the IEEE Standard 1149.1 is shown in
Figure 5-4 on page 57. The standard requires that every JTAG-compliant device implement either
the BYPASS instruction or the IDCODE instruction as the default instruction. The LSB of the BYPASS
Data Register is defined to be a 0 to distinguish it from the IDCODE instruction, which has an LSB
of 1. This allows auto configuration test tools to determine which instruction is the default instruction.
Preliminary
November 30, 200756
Page 57

Figure 5-4. BYPASS Register Format
O
TDOTDI
O
I
N E
U
T
O
O
I
N E
U
T
O
O
I
N E
U
T
O
O
I
N E
U
T
I
N
...
...
RSTGPIO PB6 GPIOm GPIO m+1 GPIO n
5.4.2.3 Boundary Scan Data Register
The format of the Boundary Scan Data Register is shown in Figure 5-5 on page 57. Each GPIO
pin, in a counter-clockwise direction from the JTAG port pins, is included in the Boundary Scan Data
Register. Each GPIO pin has three associated digital signals that are included in the chain. These
signals are input, output, and output enable, and are arranged in that order as can be seen in the
figure. In addition to the GPIO pins, the controller reset pin, RST, is included in the chain. Because
the reset pin is always an input, only the input signal is included in the Data Register chain.
When the Boundary Scan Data Register is accessed with the SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction, the
input, output, and output enable from each digital pad are sampled and then shifted out of the chain
to be verified. The sampling of these values occurs on the rising edge of TCK in the Capture DR
state of the TAP controller. While the sampled data is being shifted out of the Boundary Scan chain
in the Shift DR state of the TAP controller, new data can be preloaded into the chain for use with
the EXTEST and INTEST instructions. These instructions either force data out of the controller, with
the EXTEST instruction, or into the controller, with the INTEST instruction.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Figure 5-5. Boundary Scan Register Format
For detailed information on the order of the input, output, and output enable bits for each of the
GPIO ports, please refer to the Stellaris®Family Boundary Scan Description Language (BSDL) files,
downloadable from www.luminarymicro.com.
5.4.2.4 APACC Data Register
The format for the 35-bit APACC Data Register defined by ARM is described in the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
5.4.2.5 DPACC Data Register
The format for the 35-bit DPACC Data Register defined by ARM is described in the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
5.4.2.6 ABORT Data Register
The format for the 35-bit ABORT Data Register defined by ARM is described in the ARM®
Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual.
57November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 58

System Control
6 System Control
System control determines the overall operation of the device. It provides information about the
device, controls the clocking to the core and individual peripherals, and handles reset detection and
reporting.
6.1 Functional Description
The System Control module provides the following capabilities:
■ Device identification, see “Device Identification” on page 58
■ Local control, such as reset (see “Reset Control” on page 58), power (see “Power
Control” on page 61) and clock control (see “Clock Control” on page 61)
■ System control (Run, Sleep, and Deep-Sleep modes), see “System Control” on page 63
6.1.1 Device Identification
Seven read-only registers provide software with information on the microcontroller, such as version,
part number, SRAM size, flash size, and other features. See the DID0, DID1, and DC0-DC4 registers.
6.1.2 Reset Control
This section discusses aspects of hardware functions during reset as well as system software
requirements following the reset sequence.
6.1.2.1 CMOD0 and CMOD1 Test-Mode Control Pins
Two pins, CMOD0 and CMOD1, are defined for use by Luminary Micro for testing the devices during
manufacture. They have no end-user function and should not be used. The CMOD pins should be
connected to ground.
6.1.2.2 Reset Sources
The controller has five sources of reset:
1. External reset input pin (RST) assertion, see “RST Pin Assertion” on page 58.
2. Power-on reset (POR), see “Power-On Reset (POR)” on page 59.
3. Internal brown-out (BOR) detector, see “Brown-Out Reset (BOR)” on page 59.
4. Software-initiated reset (with the software reset registers), see “Software Reset” on page 60.
5. A watchdog timer reset condition violation, see “Watchdog Timer Reset” on page 60.
After a reset, the Reset Cause (RESC) register is set with the reset cause. The bits in this register
are sticky and maintain their state across multiple reset sequences, except when an internal POR
is the cause, and then all the other bits in the RESC register are cleared except for the POR indicator.
6.1.2.3 RST Pin Assertion
The external reset pin (RST) resets the controller. This resets the core and all the peripherals except
the JTAG TAP controller (see “JTAG Interface” on page 47). The external reset sequence is as
follows:
November 30, 200758
Preliminary
Page 59

1. The external reset pin (RST) is asserted and then de-asserted.
R
1
C
1
R
2
RST
Stellaris
D
1
2. The internal reset is released and the core loads from memory the initial stack pointer, the initial
program counter, the first instruction designated by the program counter, and begins execution.
A few clocks cycles from RST de-assertion to the start of the reset sequence is necessary for
synchronization.
The external reset timing is shown in Figure 22-10 on page 523.
6.1.2.4 Power-On Reset (POR)
The Power-On Reset (POR) circuit monitors the power supply voltage (VDD). The POR circuit
generates a reset signal to the internal logic when the power supply ramp reaches a threshold value
(VTH). If the application only uses the POR circuit, the RSTinput needs to be connected to the power
supply (VDD) through a pull-up resistor (1K to 10K Ω).
The device must be operating within the specified operating parameters at the point when the on-chip
power-on reset pulse is complete. The 3.3-V power supply to the device must reach 3.0 V within
10 msec of it crossing 2.0 V to guarantee proper operation. For applications that require the use of
an external reset to hold the device in reset longer than the internal POR, the RST input may be
used with the circuit as shown in Figure 6-1 on page 59.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
Figure 6-1. External Circuitry to Extend Reset
The R1and C1components define the power-on delay. The R2resistor mitigates any leakage from
the RST input. The diode (D1) discharges C1rapidly when the power supply is turned off.
The Power-On Reset sequence is as follows:
1. The controller waits for the later of external reset (RST) or internal POR to go inactive.
2. The internal reset is released and the core loads from memory the initial stack pointer, the initial
program counter, the first instruction designated by the program counter, and begins execution.
The internal POR is only active on the initial power-up of the controller. The Power-On Reset timing
is shown in Figure 22-11 on page 524.
Note: The power-on reset also resets the JTAG controller. An external reset does not.
6.1.2.5 Brown-Out Reset (BOR)
A drop in the input voltage resulting in the assertion of the internal brown-out detector can be used
to reset the controller. This is initially disabled and may be enabled by software.
The system provides a brown-out detection circuit that triggers if the power supply (VDD) drops
below a brown-out threshold voltage (V
). If a brown-out condition is detected, the system may
BTH
generate a controller interrupt or a system reset.
Preliminary
59November 30, 2007
Page 60

System Control
Brown-out resets are controlled with the Power-On and Brown-Out Reset Control (PBORCTL)
register. The BORIOR bit in the PBORCTL register must be set for a brown-out condition to trigger
a reset.
The brown-out reset is equivelent to an assertion of the external RST input and the reset is held
active until the proper VDDlevel is restored. The RESC register can be examined in the reset interrupt
handler to determine if a Brown-Out condition was the cause of the reset, thus allowing software to
determine what actions are required to recover.
The internal Brown-Out Reset timing is shown in Figure 22-12 on page 524.
6.1.2.6 Software Reset
Software can reset a specific peripheral or generate a reset to the entire system .
Peripherals can be individually reset by software via three registers that control reset signals to each
peripheral (see the SRCRn registers). If the bit position corresponding to a peripheral is set and
subsequently cleared, the peripheral is reset. The encoding of the reset registers is consistent with
the encoding of the clock gating control for peripherals and on-chip functions (see “System
Control” on page 63). Note that all reset signals for all clocks of the specified unit are asserted as
a result of a software-initiated reset.
The entire system can be reset by software by setting the SYSRESETREQ bit in the Cortex-M3
Application Interrupt and Reset Control register resets the entire system including the core. The
software-initiated system reset sequence is as follows:
1. A software system reset is initiated by writing the SYSRESETREQ bit in the ARM Cortex-M3
Application Interrupt and Reset Control register.
2. An internal reset is asserted.
3. The internal reset is deasserted and the controller loads from memory the initial stack pointer,
the initial program counter, and the first instruction designated by the program counter, and
then begins execution.
The software-initiated system reset timing is shown in Figure 22-13 on page 524.
6.1.2.7 Watchdog Timer Reset
The watchdog timer module's function is to prevent system hangs. The watchdog timer can be
configured to generate an interrupt to the controller on its first time-out, and to generate a reset
signal on its second time-out.
After the first time-out event, the 32-bit counter is reloaded with the value of the Watchdog Timer
Load (WDTLOAD) register, and the timer resumes counting down from that value. If the timer counts
down to its zero state again before the first time-out interrupt is cleared, and the reset signal has
been enabled, the watchdog timer asserts its reset signal to the system. The watchdog timer reset
sequence is as follows:
1. The watchdog timer times out for the second time without being serviced.
2. An internal reset is asserted.
3. The internal reset is released and the controller loads from memory the initial stack pointer, the
initial program counter, the first instruction designated by the program counter, and begins
execution.
November 30, 200760
Preliminary
Page 61

The watchdog reset timing is shown in Figure 22-14 on page 524.
6.1.3 Power Control
The Stellaris®microcontroller provides an integrated LDO regulator that may be used to provide
power to the majority of the controller's internal logic. The LDO regulator provides software a
mechanism to adjust the regulated value, in small increments (VSTEP), over the range of 2.25 V
to 2.75 V (inclusive)—or 2.5 V ± 10%. The adjustment is made by changing the value of the VADJ
field in the LDO Power Control (LDOPCTL) register.
Note: The use of the LDO is optional. The internal logic may be supplied by the on-chip LDO or
by an external regulator. If the LDO is used, the LDO output pin is connected to the VDD25
pins on the printed circuit board. The LDO requires decoupling capacitors on the printed
circuit board. If an external regulator is used, it is strongly recommended that the external
regulator supply the controller only and not be shared with other devices on the printed
circuit board.
6.1.4 Clock Control
System control determines the control of clocks in this part.
6.1.4.1 Fundamental Clock Sources
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
There are four clock sources for use in the device:
■ Internal Oscillator (IOSC): The internal oscillator is an on-chip clock source. It does not require
the use of any external components. The frequency of the internal oscillator is 12 MHz ± 30%.
Applications that do not depend on accurate clock sources may use this clock source to reduce
system cost. The internal oscillator is the clock source the device uses during and following POR.
If the main oscillator is required, software must enable the main oscillator following reset and
allow the main oscillator to stabilize before changing the clock reference.
■ Main Oscillator: The main oscillator provides a frequency-accurate clock source by one of two
means: an external single-ended clock source is connected to the OSC0 input pin, or an external
crystal is connected across the OSC0 input and OSC1 output pins. The crystal value allowed
depends on whether the main oscillator is used as the clock reference source to the PLL. If so,
the crystal must be one of the supported frequencies between 3.579545 MHz through 8.192
MHz (inclusive). If the PLL is not being used, the crystal may be any one of the supported
frequencies between 1 MHz and 8.192 MHz. The single-ended clock source range is from DC
through the specified speed of the device. The supported crystals are listed in the XTAL bit in
the RCC register (see page 74).
■ Internal 30-kHz Oscillator: The internal 30-kHz oscillator is similar to the internal oscillator,
except that it provides an operational frequency of 30 kHz ± 30%. It is intended for use during
Deep-Sleep power-saving modes. This power-savings mode benefits from reduced internal
switching and also allows the main oscillator to be powered down.
■ External Real-Time Oscillator: The external real-time oscillator provides a low-frequency,
accurate clock reference. It is intended to provide the system with a real-time clock source. The
real-time oscillator is part of the Hibernation Module (“Hibernation Module” on page 118) and may
also provide an accurate source of Deep-Sleep or Hibernate mode power savings.
The internal system clock (sysclk), is derived from any of the four sources plus two others: the output
of the internal PLL, and the internal oscillator divided by four (3 MHz ± 30%). The frequency of the
PLL clock reference must be in the range of 3.579545 MHz to 8.192 MHz (inclusive).
61November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 62

System Control
The Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) and Run-Mode Clock Configuration 2 (RCC2)
registers provide control for the system clock. The RCC2 register is provided to extend fields that
offer additional encodings over the RCC register. When used, the RCC2 register field values are
used by the logic over the corresponding field in the RCC register. In particular, RCC2 provides for
a larger assortment of clock configuration options.
6.1.4.2 Crystal Configuration for the Main Oscillator (MOSC)
The main oscillator supports the use of a select number of crystals. If the main oscillator is used by
the PLL as a reference clock, the supported range of crystals is 3.579545 to 8.192 MHz, otherwise,
the range of supported crystals is 1 to 8.192 MHz.
The XTAL bit in the RCC register (see page 74) describes the available crystal choices and default
programming values.
Software configures the RCC register XTAL field with the crystal number. If the PLL is used in the
design, the XTAL field value is internally translated to the PLL settings.
6.1.4.3 PLL Frequency Configuration
The PLL is disabled by default during power-on reset and is enabled later by software if required.
Software configures the PLL input reference clock source, specifies the output divisor to set the
system clock frequency, and enables the PLL to drive the output.
If the main oscillator provides the clock reference to the PLL, the translation provided by hardware
and used to program the PLL is available for software in the XTAL to PLL Translation (PLLCFG)
register (see page 78). The internal translation provides a translation within ± 1% of the targeted
PLL VCO frequency.
The Crystal Value field (XTAL) on page 74 describes the available crystal choices and default
programming of the PLLCFG register. The crystal number is written into the XTAL field of the
Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register. Any time the XTAL field changes, the new settings
are translated and the internal PLL settings are updated.
6.1.4.4 PLL Modes
The PLL has two modes of operation: Normal and Power-Down
■ Normal: The PLL multiplies the input clock reference and drives the output.
■ Power-Down: Most of the PLL internal circuitry is disabled and the PLL does not drive the output.
The modes are programmed using the RCC/RCC2 register fields (see page 74 and page 79).
6.1.4.5 PLL Operation
If the PLL configuration is changed, the PLL output frequency is unstable until it reconverges (relocks)
to the new setting. The time between the configuration change and relock is T
22-6 on page 516). During this time, the PLL is not usable as a clock reference.
The PLL is changed by one of the following:
READY
(see Table
■ Change to the XTAL value in the RCC register—writes of the same value do not cause a relock.
■ Change in the PLL from Power-Down to Normal mode.
A counter is defined to measure the T
oscillator. The range of the main oscillator has been taken into account and the down counter is set
Preliminary
requirement. The counter is clocked by the main
READY
November 30, 200762
Page 63

to 0x1200 (that is, ~600 μs at an 8.192 MHz external oscillator clock). . Hardware is provided to
keep the PLL from being used as a system clock until the T
two changes above. It is the user's responsibility to have a stable clock source (like the main oscillator)
before the RCC/RCC2 register is switched to use the PLL.
6.1.5 System Control
For power-savings purposes, the RCGCn , SCGCn , and DCGCn registers control the clock gating
logic for each peripheral or block in the system while the controller is in Run, Sleep, and Deep-Sleep
mode, respectively.
In Run mode, the processor executes code. In Sleep mode, the clock frequency of the active
peripherals is unchanged, but the processor is not clocked and therefore no longer executes code.
In Deep-Sleep mode, the clock frequency of the active peripherals may change (depending on the
Run mode clock configuration) in addition to the processor clock being stopped. An interrupt returns
the device to Run mode from one of the sleep modes; the sleep modes are entered on request from
the code. Each mode is described in more detail below.
There are four levels of operation for the device defined as:
■ Run Mode. Run mode provides normal operation of the processor and all of the peripherals that
are currently enabled by the RCGCn registers. The system clock can be any of the available
clock sources including the PLL.
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
condition is met after one of the
READY
■ Sleep Mode. Sleep mode is entered by the Cortex-M3 core executing a WFI (Wait for
Interrupt) instruction. Any properly configured interrupt event in the system will bring the
processor back into Run mode. See the system control NVIC section of the ARM® Cortex™-M3
Technical Reference Manual for more details.
In Sleep mode, the Cortex-M3 processor core and the memory subsystem are not clocked.
Peripherals are clocked that are enabled in the SCGCn register when auto-clock gating is enabled
(see the RCC register) or the RCGCn register when the auto-clock gating is disabled. The system
clock has the same source and frequency as that during Run mode.
■ Deep-Sleep Mode. Deep-Sleep mode is entered by first writing the Deep Sleep Enable bit in
the ARM Cortex-M3 NVIC system control register and then executing a WFI instruction. Any
properly configured interrupt event in the system will bring the processor back into Run mode.
See the system control NVIC section of the ARM® Cortex™-M3 Technical Reference Manual
for more details.
The Cortex-M3 processor core and the memory subsystem are not clocked. Peripherals are
clocked that are enabled in the DCGCn register when auto-clock gating is enabled (see the RCC
register) or the RCGCn register when auto-clock gating is disabled. The system clock source is
the main oscillator by default or the internal oscillator specified in the DSLPCLKCFG register if
one is enabled. When the DSLPCLKCFG register is used, the internal oscillator is powered up,
if necessary, and the main oscillator is powered down. If the PLL is running at the time of the
WFI instruction, hardware will power the PLL down and override the SYSDIV field of the active
RCC/RCC2 register to be /16 or /64, respectively. When the Deep-Sleep exit event occurs,
hardware brings the system clock back to the source and frequency it had at the onset of
Deep-Sleep mode before enabling the clocks that had been stopped during the Deep-Sleep
duration.
■ Hibernate Mode. In this mode, the power supplies are turned off to the main part of the device
and only the Hibernation module's circuitry is active. An external wake event or RTC event is
required to bring the device back to Run mode. The Cortex-M3 processor and peripherals outside
63November 30, 2007
Preliminary
Page 64

System Control
of the Hibernation module see a normal "power on" sequence and the processor starts running
code. It can determine that it has been restarted from Hibernate mode by inspecting the
Hibernation module registers.
6.2 Initialization and Configuration
The PLL is configured using direct register writes to the RCC/RCC2 register. If the RCC2 register
is being used, the USERCC2 bit must be set and the appropriate RCC2 bit/field is used. The steps
required to successfully change the PLL-based system clock are:
1. Bypass the PLL and system clock divider by setting the BYPASS bit and clearing the USESYS
bit in the RCC register. This configures the system to run off a “raw” clock source (using the
main oscillator or internal oscillator) and allows for the new PLL configuration to be validated
before switching the system clock to the PLL.
2. Select the crystal value (XTAL) and oscillator source (OSCSRC), and clear the PWRDN bit in
RCC/RCC2. Setting the XTAL field automatically pulls valid PLL configuration data for the
appropriate crystal, and clearing the PWRDN bit powers and enables the PLL and its output.
3. Select the desired system divider (SYSDIV) in RCC/RCC2 and set the USESYS bit in RCC. The
SYSDIV field determines the system frequency for the microcontroller.
4. Wait for the PLL to lock by polling the PLLLRIS bit in the Raw Interrupt Status (RIS) register.
5. Enable use of the PLL by clearing the BYPASS bit in RCC/RCC2.
6.3 Register Map
Table 6-1 on page 64 lists the System Control registers, grouped by function. The offset listed is a
hexadecimal increment to the register’s address, relative to the System Control base address of
0x400F.E000.
Note: Spaces in the System Control register space that are not used are reserved for future or
internal use by Luminary Micro, Inc. Software should not modify any reserved memory
address.
Table 6-1. System Control Register Map
DescriptionResetTypeNameOffset
See
page
66Device Identification 0-RODID00x000
82Device Identification 1-RODID10x004
84Device Capabilities 00x00FF.002FRODC00x008
85Device Capabilities 10x0111.31FFRODC10x010
87Device Capabilities 20x070F.1013RODC20x014
Preliminary
89Device Capabilities 30x3F07.B7FFRODC30x018
92Device Capabilities 40x0000.00FFRODC40x01C
68Brown-Out Reset Control0x0000.7FFDR/WPBORCTL0x030
69LDO Power Control0x0000.0000R/WLDOPCTL0x034
November 30, 200764
Page 65

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameOffset
See
page
114Software Reset Control 00x00000000R/WSRCR00x040
115Software Reset Control 10x00000000R/WSRCR10x044
117Software Reset Control 20x00000000R/WSRCR20x048
70Raw Interrupt Status0x0000.0000RORIS0x050
71Interrupt Mask Control0x0000.0000R/WIMC0x054
72Masked Interrupt Status and Clear0x0000.0000R/W1CMISC0x058
73Reset Cause-R/WRESC0x05C
74Run-Mode Clock Configuration0x07AE.3AD1R/WRCC0x060
78XTAL to PLL Translation-ROPLLCFG0x064
79Run-Mode Clock Configuration 20x0780.2800R/WRCC20x070
93Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 00x00000040R/WRCGC00x100
99Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 10x00000000R/WRCGC10x104
108Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 20x00000000R/WRCGC20x108
95Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 00x00000040R/WSCGC00x110
102Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 10x00000000R/WSCGC10x114
6.4 Register Descriptions
All addresses given are relative to the System Control base address of 0x400F.E000.
110Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 20x00000000R/WSCGC20x118
97Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 00x00000040R/WDCGC00x120
105Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 10x00000000R/WDCGC10x124
112Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 20x00000000R/WDCGC20x128
81Deep Sleep Clock Configuration0x0780.0000R/WDSLPCLKCFG0x144
Preliminary
65November 30, 2007
Page 66

System Control
Register 1: Device Identification 0 (DID0), offset 0x000
This register identifies the version of the device.
Device Identification 0 (DID0)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x000
Type RO, reset -
16171819202122232425262728293031
CLASSreservedVERreserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1000000000001000Reset
0123456789101112131415
MINORMAJOR
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
----------------Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0x1ROVER30:28
DID0 Version
This field defines the DID0 register format version. The version number
is numeric. The value of the VER field is encoded as follows:
DescriptionValue
First revision of the DID0 register format, for Stellaris®
0x1
Fury-class devices .
0x0ROreserved27:24
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0x1ROCLASS23:16
Device Class
The CLASS field value identifies the internal design from which all mask
sets are generated for all devices in a particular product line. The CLASS
field value is changed for new product lines, for changes in fab process
(for example, a remap or shrink), or any case where the MAJOR or MINOR
fields require differentiation from prior devices. The value of the CLASS
field is encoded as follows (all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
Stellaris® Sandstorm-class devices.0x0
Stellaris® Fury-class devices.0x1
Preliminary
November 30, 200766
Page 67

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
-ROMAJOR15:8
-ROMINOR7:0
Major Revision
This field specifies the major revision number of the device. The major
revision reflects changes to base layers of the design. The major revision
number is indicated in the part number as a letter (A for first revision, B
for second, and so on). This field is encoded as follows:
DescriptionValue
Revision A (initial device)0x0
Revision B (first base layer revision)0x1
Revision C (second base layer revision)0x2
and so on.
Minor Revision
This field specifies the minor revision number of the device. The minor
revision reflects changes to the metal layers of the design. The MINOR
field value is reset when the MAJOR field is changed. This field is numeric
and is encoded as follows:
DescriptionValue
Initial device, or a major revision update.0x0
First metal layer change.0x1
Second metal layer change.0x2
and so on.
Preliminary
67November 30, 2007
Page 68

System Control
Register 2: Brown-Out Reset Control (PBORCTL), offset 0x030
This register is responsible for controlling reset conditions after initial power-on reset.
Brown-Out Reset Control (PBORCTL)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x030
Type R/W, reset 0x0000.7FFD
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedBORIORreserved
ROR/WROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0x0ROreserved31:2
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WBORIOR1
BOR Interrupt or Reset
This bit controls how a BOR event is signaled to the controller. If set, a
reset is signaled. Otherwise, an interrupt is signaled.
0ROreserved0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200768
Page 69

Register 3: LDO Power Control (LDOPCTL), offset 0x034
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
The VADJ field in this register adjusts the on-chip output voltage (V
LDO Power Control (LDOPCTL)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x034
Type R/W, reset 0x0000.0000
).
OUT
16171819202122232425262728293031
reserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
VADJreserved
R/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:6
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0x0R/WVADJ5:0
LDO Output Voltage
This field sets the on-chip output voltage. The programming values for
the VADJ field are provided below.
V
(V)Value
OUT
2.500x00
2.450x01
2.400x02
2.350x03
2.300x04
2.250x05
Reserved0x06-0x3F
2.750x1B
2.700x1C
2.650x1D
2.600x1E
2.550x1F
Preliminary
69November 30, 2007
Page 70

System Control
Register 4: Raw Interrupt Status (RIS), offset 0x050
Central location for system control raw interrupts. These are set and cleared by hardware.
Raw Interrupt Status (RIS)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x050
Type RO, reset 0x0000.0000
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedBORRISreservedPLLLRISreserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0ROreserved31:7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0ROPLLLRIS6
0ROreserved5:2
PLL Lock Raw Interrupt Status
This bit is set when the PLL T
READY
Timer asserts.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0ROBORRIS1
Brown-Out Reset Raw Interrupt Status
This bit is the raw interrupt status for any brown-out conditions. If set,
a brown-out condition is currently active. This is an unregistered signal
from the brown-out detection circuit. An interrupt is reported if the BORIM
bit in the IMC register is set and the BORIOR bit in the PBORCTL register
is cleared.
0ROreserved0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200770
Page 71

Register 5: Interrupt Mask Control (IMC), offset 0x054
Central location for system control interrupt masks.
Interrupt Mask Control (IMC)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x054
Type R/W, reset 0x0000.0000
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedBORIMreservedPLLLIMreserved
ROR/WROROROROR/WROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0ROreserved31:7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WPLLLIM6
PLL Lock Interrupt Mask
This bit specifies whether a current limit detection is promoted to a
controller interrupt. If set, an interrupt is generated if PLLLRIS in RIS
is set; otherwise, an interrupt is not generated.
0ROreserved5:2
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WBORIM1
Brown-Out Reset Interrupt Mask
This bit specifies whether a brown-out condition is promoted to a
controller interrupt. If set, an interrupt is generated if BORRIS is set;
otherwise, an interrupt is not generated.
0ROreserved0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
71November 30, 2007
Page 72

System Control
Register 6: Masked Interrupt Status and Clear (MISC), offset 0x058
Central location for system control result of RIS AND IMC to generate an interrupt to the controller.
All of the bits are R/W1C and this action also clears the corresponding raw interrupt bit in the RIS
register (see page 70).
Masked Interrupt Status and Clear (MISC)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x058
Type R/W1C, reset 0x0000.0000
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedBORMISreservedPLLLMISreserved
ROR/W1CROROROROR/W1CROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0ROreserved31:7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/W1CPLLLMIS6
PLL Lock Masked Interrupt Status
This bit is set when the PLL T
READY
timer asserts. The interrupt is cleared
by writing a 1 to this bit.
0ROreserved5:2
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/W1CBORMIS1
BOR Masked Interrupt Status
The BORMIS is simply the BORRIS ANDed with the mask value, BORIM.
0ROreserved0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200772
Page 73

Register 7: Reset Cause (RESC), offset 0x05C
This register is set with the reset cause after reset. The bits in this register are sticky and maintain
their state across multiple reset sequences, except when an external reset is the cause, and then
all the other bits in the RESC register are cleared.
Reset Cause (RESC)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x05C
Type R/W, reset -
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
EXTPORBORWDTSWLDOreserved
R/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROROROROROROROType
------0000000000Reset
0ROreserved31:6
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
-R/WLDO5
LDO Reset
When set, indicates the LDO circuit has lost regulation and has
generated a reset event.
-R/WSW4
Software Reset
When set, indicates a software reset is the cause of the reset event.
-R/WWDT3
Watchdog Timer Reset
When set, indicates a watchdog reset is the cause of the reset event.
-R/WBOR2
Brown-Out Reset
When set, indicates a brown-out reset is the cause of the reset event.
-R/WPOR1
Power-On Reset
When set, indicates a power-on reset is the cause of the reset event.
-R/WEXT0
External Reset
When set, indicates an external reset (RST assertion) is the cause of
the reset event.
Preliminary
73November 30, 2007
Page 74

System Control
Register 8: Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC), offset 0x060
This register is defined to provide source control and frequency speed.
Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x060
Type R/W, reset 0x07AE.3AD1
16171819202122232425262728293031
SYSDIVACGreserved
USESYSDIV
reserved
USEPWMDIV
reservedPWMDIV
ROR/WR/WR/WR/WROR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROType
0111000111100000Reset
0123456789101112131415
MOSCDISIOSCDISreservedOSCSRCXTALreservedBYPASSreservedPWRDNreserved
R/WR/WROROR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROR/WROR/WROROType
1000101101011100Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x0ROreserved31:28
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WACG27
Auto Clock Gating
This bit specifies whether the system uses the Sleep-Mode Clock
Gating Control (SCGCn) registers and Deep-Sleep-Mode Clock
Gating Control (DCGCn) registers if the controller enters a Sleep or
Deep-Sleep mode (respectively). If set, the SCGCn or DCGCn registers
are used to control the clocks distributed to the peripherals when the
controller is in a sleep mode. Otherwise, the Run-Mode Clock Gating
Control (RCGCn) registers are used when the controller enters a sleep
mode.
The RCGCn registers are always used to control the clocks in Run
mode.
This allows peripherals to consume less power when the controller is
in a sleep mode and the peripheral is unused.
Preliminary
November 30, 200774
Page 75

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0xFR/WSYSDIV26:23
System Clock Divisor
Specifies which divisor is used to generate the system clock from the
PLL output.
The PLL VCO frequency is 400 MHz.
Frequency (BYPASS=0)Divisor (BYPASS=1)Value
reservedreserved0x0
reserved/20x1
reserved/30x2
50 MHz/40x3
40 MHz/50x4
33.33 MHz/60x5
28.57 MHz/70x6
25 MHz/80x7
22.22 MHz/90x8
20 MHz/100x9
18.18 MHz/110xA
16.67 MHz/120xB
15.38 MHz/130xC
14.29 MHz/140xD
13.33 MHz/150xE
12.5 MHz (default)/160xF
When reading the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register (see
page 74), the SYSDIV value is MINSYSDIV if a lower divider was
requested and the PLL is being used. This lower value is allowed to
divide a non-PLL source.
0R/WUSESYSDIV22
0ROreserved21
0R/WUSEPWMDIV20
Enable System Clock Divider
Use the system clock divider as the source for the system clock. The
system clock divider is forced to be used when the PLL is selected as
the source.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Enable PWM Clock Divisor
Use the PWM clock divider as the source for the PWM clock.
Preliminary
75November 30, 2007
Page 76

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x7R/WPWMDIV19:17
0ROreserved16:14
1R/WPWRDN13
PWM Unit Clock Divisor
This field specifies the binary divisor used to predivide the system clock
down for use as the timing reference for the PWM module. This clock
is only power 2 divide and rising edge is synchronous without phase
shift from the system clock.
DivisorValue
/20x0
/40x1
/80x2
/160x3
/320x4
/640x5
/640x6
/64 (default)0x7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PLL Power Down
This bit connects to the PLL PWRDN input. The reset value of 1 powers
down the PLL.
1ROreserved12
1R/WBYPASS11
0ROreserved10
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PLL Bypass
Chooses whether the system clock is derived from the PLL output or
the OSC source. If set, the clock that drives the system is the OSC
source. Otherwise, the clock that drives the system is the PLL output
clock divided by the system divider.
Note: The ADC must be clocked from the PLL or directly from a
14-MHz to 18-MHz clock source to operate properly. While
the ADC works in a 14-18 MHz range, to maintain a 1 M
sample/second rate, the ADC must be provided a 16-MHz
clock source.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200776
Page 77

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0xBR/WXTAL9:6
Crystal Value
This field specifies the crystal value attached to the main oscillator. The
encoding for this field is provided below.
Value
Crystal Frequency (MHz)
Not Using the PLL
6 MHz (reset value)0xB
Crystal Frequency (MHz)
Using the PLL
reserved1.0000x0
reserved1.84320x1
reserved2.0000x2
reserved2.45760x3
3.579545 MHz0x4
3.6864 MHz0x5
4 MHz0x6
4.096 MHz0x7
4.9152 MHz0x8
5 MHz0x9
5.12 MHz0xA
6.144 MHz0xC
7.3728 MHz0xD
8 MHz0xE
8.192 MHz0xF
0x1R/WOSCSRC5:4
0x0ROreserved3:2
0R/WIOSCDIS1
1R/WMOSCDIS0
Oscillator Source
Picks among the four input sources for the OSC. The values are:
Input SourceValue
Main oscillator (default)0x0
Internal oscillator (default)0x1
Internal oscillator / 4 (this is necessary if used as input to PLL)0x2
reserved0x3
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Internal Oscillator Disable
0: Internal oscillator (IOSC) is enabled.
1: Internal oscillator is disabled.
Main Oscillator Disable
0: Main oscillator is enabled.
1: Main oscillator is disabled (default).
Preliminary
77November 30, 2007
Page 78
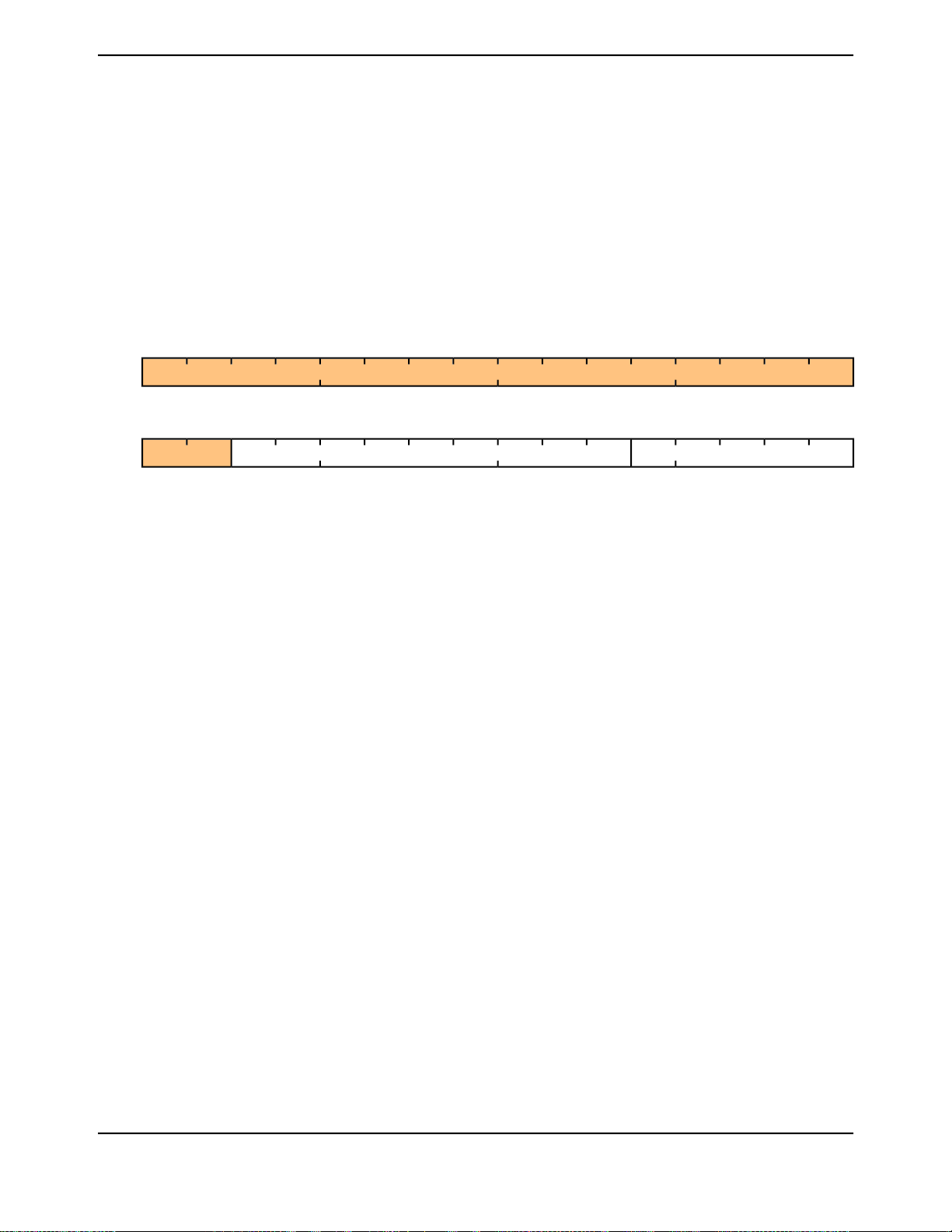
System Control
Register 9: XTAL to PLL Translation (PLLCFG), offset 0x064
This register provides a means of translating external crystal frequencies into the appropriate PLL
settings. This register is initialized during the reset sequence and updated anytime that the XTAL
field changes in the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register (see page 74).
The PLL frequency is calculated using the PLLCFG field values, as follows:
PLLFreq = OSCFreq * F / (R + 1)
XTAL to PLL Translation (PLLCFG)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x064
Type RO, reset -
reserved
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
RFreserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
--------------00Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x0ROreserved31:14
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
-ROF13:5
PLL F Value
This field specifies the value supplied to the PLL’s F input.
-ROR4:0
PLL R Value
This field specifies the value supplied to the PLL’s R input.
Preliminary
November 30, 200778
Page 79
Register 10: Run-Mode Clock Configuration 2 (RCC2), offset 0x070
This register overrides the RCC equivalent register fields when the USERCC2 bit is set. This allows
RCC2 to be used to extend the capabilities, while also providing a means to be backward-compatible
to previous parts. The fields within the RCC2 register occupy the same bit positions as they do
within the RCC register as LSB-justified.
The SYSDIV2 field is wider so that additional larger divisors are possible. This allows a lower system
clock frequency for improved Deep Sleep power consumption.
Run-Mode Clock Configuration 2 (RCC2)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x070
Type R/W, reset 0x0780.2800
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
reservedSYSDIV2reservedUSERCC2
ROROROROROROROR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROROR/WType
0000000111100000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedOSCSRC2reservedBYPASS2reservedPWRDN2reserved
ROROROROR/WR/WR/WROROROROR/WROR/WROROType
0000000000010100Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0R/WUSERCC231
0x0ROreserved30:29
0x0FR/WSYSDIV228:23
0x0ROreserved22:14
1R/WPWRDN213
Use RCC2
When set, overrides the RCC register fields.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
System Clock Divisor
Specifies which divisor is used to generate the system clock from the
PLL output.
The PLL VCO frequency is 400 MHz.
This field is wider than the RCC register SYSDIV field in order to provide
additional divisor values. This permits the system clock to be run at
much lower frequencies during Deep Sleep mode. For example, where
the RCC register SYSDIV encoding of 1111 provides /16, the RCC2
register SYSDIV2 encoding of 111111 provides /64.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Power-Down PLL
When set, powers down the PLL.
0ROreserved12
1R/WBYPASS211
Preliminary
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Bypass PLL
When set, bypasses the PLL for the clock source.
79November 30, 2007
Page 80

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x0ROreserved10:7
0x0R/WOSCSRC26:4
0ROreserved3:0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
System Clock Source
DescriptionValue
Main oscillator (MOSC)0x0
Internal oscillator (IOSC)0x1
Internal oscillator / 40x2
30 kHz internal oscillator0x3
32 kHz external oscillator0x7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200780
Page 81

Register 11: Deep Sleep Clock Configuration (DSLPCLKCFG), offset 0x144
This register provides configuration information for the hardware control of Deep Sleep Mode.
Deep Sleep Clock Configuration (DSLPCLKCFG)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x144
Type R/W, reset 0x0780.0000
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
reservedDSDIVORIDEreserved
ROROROROROROROR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROType
0000000111100000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedDSOSCSRCreserved
ROROROROR/WR/WR/WROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x0ROreserved31:29
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0x0FR/WDSDIVORIDE28:23
Divider Field Override
6-bit system divider field to override when Deep-Sleep occurs with PLL
running.
0x0ROreserved22:7
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0x0R/WDSOSCSRC6:4
Clock Source
When set, forces IOSC to be clock source during Deep Sleep mode.
DescriptionNameValue
No override to the oscillator clock source is doneNOORIDE0x0
Use internal 12 MHz oscillator as sourceIOSC0x1
Use 30 kHz internal oscillator30kHz0x3
Use 32 kHz external oscillator32kHz0x7
0x0ROreserved3:0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
81November 30, 2007
Page 82

System Control
Register 12: Device Identification 1 (DID1), offset 0x004
This register identifies the device family, part number, temperature range, pin count, and package
type.
Device Identification 1 (DID1)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x004
Type RO, reset -
16171819202122232425262728293031
PARTNOFAMVER
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0101101000001000Reset
0123456789101112131415
QUALROHSPKGTEMPreservedPINCOUNT
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
--11010000000010Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x1ROVER31:28
DID1 Version
This field defines the DID1 register format version. The version number
is numeric. The value of the VER field is encoded as follows (all other
encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
First revision of the DID1 register format, indicating a Stellaris
0x1
Fury-class device.
0x0ROFAM27:24
Family
This field provides the family identification of the device within the
Luminary Micro product portfolio. The value is encoded as follows (all
other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
Stellaris family of microcontollers, that is, all devices with
0x0
external part numbers starting with LM3S.
0x5AROPARTNO23:16
Part Number
This field provides the part number of the device within the family. The
value is encoded as follows (all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
LM3S25330x5A
0x2ROPINCOUNT15:13
Preliminary
Package Pin Count
This field specifies the number of pins on the device package. The value
is encoded as follows (all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
100-pin package0x2
November 30, 200782
Page 83

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved12:8
0x1ROTEMP7:5
0x1ROPKG4:3
1ROROHS2
-ROQUAL1:0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Temperature Range
This field specifies the temperature rating of the device. The value is
encoded as follows (all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
Industrial temperature range (-40°C to 85°C)0x1
Package Type
This field specifies the package type. The value is encoded as follows
(all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
LQFP package0x1
RoHS-Compliance
This bit specifies whether the device is RoHS-compliant. A 1 indicates
the part is RoHS-compliant.
Qualification Status
This field specifies the qualification status of the device. The value is
encoded as follows (all other encodings are reserved):
DescriptionValue
Engineering Sample (unqualified)0x0
Pilot Production (unqualified)0x1
Fully Qualified0x2
Preliminary
83November 30, 2007
Page 84

System Control
Register 13: Device Capabilities 0 (DC0), offset 0x008
This register is predefined by the part and can be used to verify features.
Device Capabilities 0 (DC0)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x008
Type RO, reset 0x00FF.002F
SRAMSZ
FLASHSZ
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111111100000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111010000000000Reset
0x00FFROSRAMSZ31:16
SRAM Size
Indicates the size of the on-chip SRAM memory.
DescriptionValue
64 KB of SRAM0x00FF
0x002FROFLASHSZ15:0
Flash Size
Indicates the size of the on-chip flash memory.
DescriptionValue
96 KB of Flash0x002F
Preliminary
November 30, 200784
Page 85

Register 14: Device Capabilities 1 (DC1), offset 0x010
This register provides a list of features available in the system. The Stellaris family uses this register
format to indicate the availability of the following family features in the specific device: CANs, PWM,
ADC, Watchdog timer, Hibernation module, and debug capabilities. This register also indicates the
maximum clock frequency and maximum ADC sample rate. The format of this register is consistent
with the RCGC0, SCGC0, and DCGC0 clock control registers and the SRCR0 software reset control
register.
Device Capabilities 1 (DC1)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x010
Type RO, reset 0x0111.31FF
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ADCreservedPWMreservedCAN0reserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1000100010000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
JTAGSWDSWOWDTPLLTEMPSNSHIBMPUMAXADCSPDMINSYSDIV
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111111110001100Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:25
1ROCAN024
0ROreserved23:21
1ROPWM20
0ROreserved19:17
1ROADC16
0x3ROMINSYSDIV15:12
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
CAN Module 0 Present
When set, indicates that CAN unit 0 is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PWM Module Present
When set, indicates that the PWM module is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC Module Present
When set, indicates that the ADC module is present.
System Clock Divider
Minimum 4-bit divider value for system clock. The reset value is
hardware-dependent. See the RCC register for how to change the
system clock divisor using the SYSDIV bit.
Preliminary
DescriptionValue
Specifies a 50-MHz CPU clock with a PLL divider of 4.0x3
85November 30, 2007
Page 86

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0x1ROMAXADCSPD11:8
1ROMPU7
1ROHIB6
1ROTEMPSNS5
1ROPLL4
1ROWDT3
1ROSWO2
Max ADC Speed
Indicates the maximum rate at which the ADC samples data.
DescriptionValue
250K samples/second0x1
MPU Present
When set, indicates that the Cortex-M3 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
module is present. See the ARM Cortex-M3 Technical Reference Manual
for details on the MPU.
Hibernation Module Present
When set, indicates that the Hibernation module is present.
Temp Sensor Present
When set, indicates that the on-chip temperature sensor is present.
PLL Present
When set, indicates that the on-chip Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is
present.
Watchdog Timer Present
When set, indicates that a watchdog timer is present.
SWO Trace Port Present
When set, indicates that the Serial Wire Output (SWO) trace port is
present.
1ROSWD1
1ROJTAG0
SWD Present
When set, indicates that the Serial Wire Debugger (SWD) is present.
JTAG Present
When set, indicates that the JTAG debugger interface is present.
Preliminary
November 30, 200786
Page 87
Register 15: Device Capabilities 2 (DC2), offset 0x014
This register provides a list of features available in the system. The Stellaris family uses this register
format to indicate the availability of the following family features in the specific device: Analog
Comparators, General-Purpose Timers, I2Cs, QEIs, SSIs, and UARTs. The format of this register
is consistent with the RCGC1, SCGC1, and DCGC1 clock control registers and the SRCR1 software
reset control register.
Device Capabilities 2 (DC2)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x014
Type RO, reset 0x070F.1013
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
TIMER0TIMER1TIMER2TIMER3reservedCOMP0COMP1COMP2reserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111000011100000Reset
0123456789101112131415
UART0UART1reservedSSI0reservedI2C0reserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1100100000001000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:27
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
1ROCOMP226
Analog Comparator 2 Present
When set, indicates that analog comparator 2 is present.
1ROCOMP125
Analog Comparator 1 Present
When set, indicates that analog comparator 1 is present.
1ROCOMP024
Analog Comparator 0 Present
When set, indicates that analog comparator 0 is present.
0ROreserved23:20
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
1ROTIMER319
Timer 3 Present
When set, indicates that General-Purpose Timer module 3 is present.
1ROTIMER218
Timer 2 Present
When set, indicates that General-Purpose Timer module 2 is present.
1ROTIMER117
Timer 1 Present
When set, indicates that General-Purpose Timer module 1 is present.
1ROTIMER016
0ROreserved15:13
Preliminary
Timer 0 Present
When set, indicates that General-Purpose Timer module 0 is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
87November 30, 2007
Page 88

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
1ROI2C012
0ROreserved11:5
1ROSSI04
0ROreserved3:2
1ROUART11
1ROUART00
I2C Module 0 Present
When set, indicates that I2C module 0 is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
SSI0 Present
When set, indicates that SSI module 0 is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
UART1 Present
When set, indicates that UART module 1 is present.
UART0 Present
When set, indicates that UART module 0 is present.
Preliminary
November 30, 200788
Page 89

Register 16: Device Capabilities 3 (DC3), offset 0x018
This register provides a list of features available in the system. The Stellaris family uses this register
format to indicate the availability of the following family features in the specific device: Analog
Comparator I/Os, CCP I/Os, ADC I/Os, and PWM I/Os.
Device Capabilities 3 (DC3)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x018
Type RO, reset 0x3F07.B7FF
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ADC0ADC1ADC2reservedCCP0CCP1CCP2CCP3CCP4CCP5reserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1110000011111100Reset
0123456789101112131415
PWM0PWM1PWM2PWM3PWM4PWM5C0MINUSC0PLUSC0OC1MINUSC1PLUSreservedC2MINUSC2PLUSreservedPWMFAULT
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111111111101101Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:30
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
1ROCCP529
CCP5 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 5 is present.
1ROCCP428
CCP4 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 4 is present.
1ROCCP327
CCP3 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 3 is present.
1ROCCP226
CCP2 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 2 is present.
1ROCCP125
CCP1 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 1 is present.
1ROCCP024
CCP0 Pin Present
When set, indicates that Capture/Compare/PWM pin 0 is present.
0ROreserved23:19
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
1ROADC218
1ROADC117
Preliminary
ADC2 Pin Present
When set, indicates that ADC pin 2 is present.
ADC1 Pin Present
When set, indicates that ADC pin 1 is present.
89November 30, 2007
Page 90

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
1ROADC016
1ROPWMFAULT15
0ROreserved14
1ROC2PLUS13
1ROC2MINUS12
0ROreserved11
1ROC1PLUS10
1ROC1MINUS9
ADC0 Pin Present
When set, indicates that ADC pin 0 is present.
PWM Fault Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM Fault pin is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
C2+ Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 2 (+) input pin is present.
C2- Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 2 (-) input pin is present.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
C1+ Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 1 (+) input pin is present.
C1- Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 1 (-) input pin is present.
1ROC0O8
1ROC0PLUS7
1ROC0MINUS6
1ROPWM55
1ROPWM44
1ROPWM33
1ROPWM22
1ROPWM11
C0o Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 0 output pin is present.
C0+ Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 0 (+) input pin is present.
C0- Pin Present
When set, indicates that the analog comparator 0 (-) input pin is present.
PWM5 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 5 is present.
PWM4 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 4 is present.
PWM3 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 3 is present.
PWM2 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 2 is present.
PWM1 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 1 is present.
Preliminary
November 30, 200790
Page 91

LM3S2533 Microcontroller
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
1ROPWM00
PWM0 Pin Present
When set, indicates that the PWM pin 0 is present.
Preliminary
91November 30, 2007
Page 92

System Control
Register 17: Device Capabilities 4 (DC4), offset 0x01C
This register provides a list of features available in the system. The Stellaris family uses this register
format to indicate the availability of the following family features in the specific device: Ethernet MAC
and PHY, GPIOs, and CCP I/Os. The format of this register is consistent with the RCGC2, SCGC2,
and DCGC2 clock control registers and the SRCR2 software reset control register.
Device Capabilities 4 (DC4)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x01C
Type RO, reset 0x0000.00FF
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
reserved
16171819202122232425262728293031
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
GPIOAGPIOBGPIOCGPIODGPIOEGPIOFGPIOGGPIOHreserved
ROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROROType
1111111100000000Reset
0ROreserved31:8
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
1ROGPIOH7
GPIO Port H Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port H is present.
1ROGPIOG6
GPIO Port G Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port G is present.
1ROGPIOF5
GPIO Port F Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port F is present.
1ROGPIOE4
GPIO Port E Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port E is present.
1ROGPIOD3
GPIO Port D Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port D is present.
1ROGPIOC2
GPIO Port C Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port C is present.
1ROGPIOB1
GPIO Port B Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port B is present.
1ROGPIOA0
Preliminary
GPIO Port A Present
When set, indicates that GPIO Port A is present.
November 30, 200792
Page 93
Register 18: Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (RCGC0), offset 0x100
This register controls the clock gating logic. Each bit controls a clock enable for a given interface,
function, or unit. If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled (saving power). If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
The reset state of these bits is 0 (unclocked) unless otherwise noted, so that all functional units are
disabled. It is the responsibility of software to enable the ports necessary for the application. Note
that these registers may contain more bits than there are interfaces, functions, or units to control.
This is to assure reasonable code compatibility with other family and future parts. RCGC0 is the
clock configuration register for running operation, SCGC0 for Sleep operation, and DCGC0 for
Deep-Sleep operation. Setting the ACG bit in the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register
specifies that the system uses sleep modes.
Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (RCGC0)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x100
Type R/W, reset 0x00000040
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ADCreservedPWMreservedCAN0reserved
R/WROROROR/WROROROR/WROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedWDTreservedHIBreservedMAXADCSPDreserved
ROROROR/WROROR/WROR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:25
0R/WCAN024
0ROreserved23:21
0R/WPWM20
0ROreserved19:17
0R/WADC16
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
CAN0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for CAN unit 0. If set, the unit receives
a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PWM Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the PWM module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for SAR ADC module 0. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Preliminary
93November 30, 2007
Page 94

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved15:12
0R/WMAXADCSPD11:8
0ROreserved7
0R/WHIB6
0ROreserved5:4
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC Sample Speed
This field sets the rate at which the ADC samples data. You cannot set
the rate higher than the maximum rate. You can set the sample rate by
setting the MAXADCSPD bit as follows:
DescriptionValue
250K samples/second0x1
125K samples/second0x0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
HIB Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the Hibernation module. If set, the
unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WWDT3
0ROreserved2:0
WDT Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the WDT module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200794
Page 95

Register 19: Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (SCGC0), offset 0x110
This register controls the clock gating logic. Each bit controls a clock enable for a given interface,
function, or unit. If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled (saving power). If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
The reset state of these bits is 0 (unclocked) unless otherwise noted, so that all functional units are
disabled. It is the responsibility of software to enable the ports necessary for the application. Note
that these registers may contain more bits than there are interfaces, functions, or units to control.
This is to assure reasonable code compatibility with other family and future parts. RCGC0 is the
clock configuration register for running operation, SCGC0 for Sleep operation, and DCGC0 for
Deep-Sleep operation. Setting the ACG bit in the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register
specifies that the system uses sleep modes.
Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (SCGC0)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x110
Type R/W, reset 0x00000040
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ADCreservedPWMreservedCAN0reserved
R/WROROROR/WROROROR/WROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedWDTreservedHIBreservedMAXADCSPDreserved
ROROROR/WROROR/WROR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:25
0R/WCAN024
0ROreserved23:21
0R/WPWM20
0ROreserved19:17
0R/WADC16
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
CAN0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for CAN unit 0. If set, the unit receives
a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PWM Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the PWM module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for SAR ADC module 0. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Preliminary
95November 30, 2007
Page 96

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved15:12
0R/WMAXADCSPD11:8
0ROreserved7
0R/WHIB6
0ROreserved5:4
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC Sample Speed
This field sets the rate at which the ADC samples data. You cannot set
the rate higher than the maximum rate. You can set the sample rate by
setting the MAXADCSPD bit as follows:
DescriptionValue
250K samples/second0x1
125K samples/second0x0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
HIB Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the Hibernation module. If set, the
unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WWDT3
0ROreserved2:0
WDT Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the WDT module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200796
Page 97

Register 20: Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (DCGC0), offset 0x120
This register controls the clock gating logic. Each bit controls a clock enable for a given interface,
function, or unit. If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled (saving power). If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
The reset state of these bits is 0 (unclocked) unless otherwise noted, so that all functional units are
disabled. It is the responsibility of software to enable the ports necessary for the application. Note
that these registers may contain more bits than there are interfaces, functions, or units to control.
This is to assure reasonable code compatibility with other family and future parts. RCGC0 is the
clock configuration register for running operation, SCGC0 for Sleep operation, and DCGC0 for
Deep-Sleep operation. Setting the ACG bit in the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register
specifies that the system uses sleep modes.
Deep Sleep Mode Clock Gating Control Register 0 (DCGC0)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x120
Type R/W, reset 0x00000040
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
ADCreservedPWMreservedCAN0reserved
R/WROROROR/WROROROR/WROROROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
reservedWDTreservedHIBreservedMAXADCSPDreserved
ROROROR/WROROR/WROR/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:25
0R/WCAN024
0ROreserved23:21
0R/WPWM20
0ROreserved19:17
0R/WADC16
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
CAN0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for CAN unit 0. If set, the unit receives
a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
PWM Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the PWM module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for SAR ADC module 0. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Preliminary
97November 30, 2007
Page 98

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved15:12
0R/WMAXADCSPD11:8
0ROreserved7
0R/WHIB6
0ROreserved5:4
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
ADC Sample Speed
This field sets the rate at which the ADC samples data. You cannot set
the rate higher than the maximum rate. You can set the sample rate by
setting the MAXADCSPD bit as follows:
DescriptionValue
250K samples/second0x1
125K samples/second0x0
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
HIB Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the Hibernation module. If set, the
unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WWDT3
0ROreserved2:0
WDT Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for the WDT module. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, a read or write to the unit generates
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
November 30, 200798
Page 99
Register 21: Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 1 (RCGC1), offset 0x104
This register controls the clock gating logic. Each bit controls a clock enable for a given interface,
function, or unit. If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled (saving power). If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
The reset state of these bits is 0 (unclocked) unless otherwise noted, so that all functional units are
disabled. It is the responsibility of software to enable the ports necessary for the application. Note
that these registers may contain more bits than there are interfaces, functions, or units to control.
This is to assure reasonable code compatibility with other family and future parts. RCGC1 is the
clock configuration register for running operation, SCGC1 for Sleep operation, and DCGC1 for
Deep-Sleep operation. Setting the ACG bit in the Run-Mode Clock Configuration (RCC) register
specifies that the system uses sleep modes.
Run Mode Clock Gating Control Register 1 (RCGC1)
Base 0x400F.E000
Offset 0x104
Type R/W, reset 0x00000000
LM3S2533 Microcontroller
16171819202122232425262728293031
TIMER0TIMER1TIMER2TIMER3reservedCOMP0COMP1COMP2reserved
R/WR/WR/WR/WROROROROR/WR/WR/WROROROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
0123456789101112131415
UART0UART1reservedSSI0reservedI2C0reserved
R/WR/WROROR/WROROROROROROROR/WROROROType
0000000000000000Reset
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0ROreserved31:27
0R/WCOMP226
0R/WCOMP125
0R/WCOMP024
0ROreserved23:20
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Analog Comparator 2 Clock Gating
This bit controls the clock gating for analog comparator 2. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate
a bus fault.
Analog Comparator 1 Clock Gating
This bit controls the clock gating for analog comparator 1. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate
a bus fault.
Analog Comparator 0 Clock Gating
This bit controls the clock gating for analog comparator 0. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate
a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
Preliminary
99November 30, 2007
Page 100

System Control
DescriptionResetTypeNameBit/Field
0R/WTIMER319
0R/WTIMER218
0R/WTIMER117
0R/WTIMER016
0ROreserved15:13
Timer 3 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for General-Purpose Timer module 3.
If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is
unclocked and disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the
unit will generate a bus fault.
Timer 2 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for General-Purpose Timer module 2.
If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is
unclocked and disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the
unit will generate a bus fault.
Timer 1 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for General-Purpose Timer module 1.
If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is
unclocked and disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the
unit will generate a bus fault.
Timer 0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for General-Purpose Timer module 0.
If set, the unit receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is
unclocked and disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the
unit will generate a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
0R/WI2C012
0ROreserved11:5
0R/WSSI04
0ROreserved3:2
0R/WUART11
I2C0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for I2C module 0. If set, the unit receives
a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and disabled. If
the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
SSI0 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for SSI module 0. If set, the unit receives
a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and disabled. If
the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate a bus fault.
Software should not rely on the value of a reserved bit. To provide
compatibility with future products, the value of a reserved bit should be
preserved across a read-modify-write operation.
UART1 Clock Gating Control
This bit controls the clock gating for UART module 1. If set, the unit
receives a clock and functions. Otherwise, the unit is unclocked and
disabled. If the unit is unclocked, reads or writes to the unit will generate
a bus fault.
Preliminary
November 30, 2007100
 Loading...
Loading...