Texas Instruments bq76PL455A-Q1 Datasheet
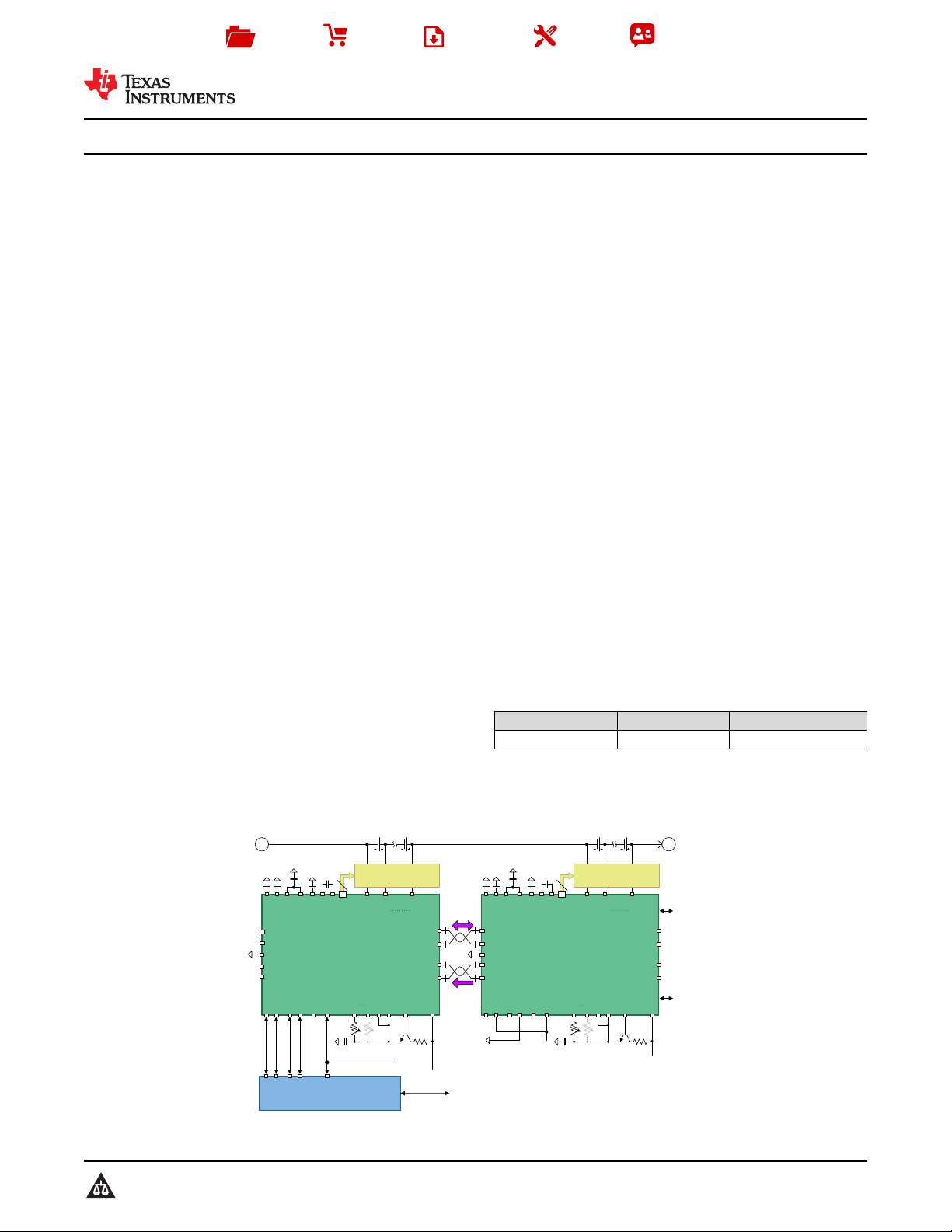
To Additional
Battery Monitors
Differential
Signaling
Daisy-Chain
Ce ll B al an ci ng C ir cu it s
Lo w Pa ss F il te rs -
Pr ot ec ti on
AUX0
AUX7
VP
NPNB
TOP
EQx
16
Cell Temperature
Measurement
COMMH±
COMMH+
FAULTH+
FAULTH±
VSENSE1
VSENSE16
VDIG
All GND connections
are local to this IC. See
text for layout details.
R
T
Highest Cell
(VSENSE16)
Ce ll B al an ci ng C ir cu it s
Lo w Pa ss F il te rs -
Pr ot ec ti on
AUX0
AUX7
VP
NPNB
TOP
EQx
16
Cell Temperature
Measurement
COMMH±
COMMH+
FAULTH+
FAULTH±
VSENSE1
VSENSE16
VDIG
R
T
Highest Cell
(VSENSE16)
High
Current
Bus
²
GPIO0..5
RX
TX
FAULT_N
WAKEUP
VIO
VP
CHP
VREF
V5VAO
OUT2
CHM
VM
OUT1
CHP
VREF
V5VAO
OUT2
CHM
VM
OUT1
GPIO0..5
RX
TX
FAULT_N
WAKEUP
VIO
CAN Bus, etc.
GPIO (Out)
GPIO (In)TXRX
+
Texas Instruments
µC
C2000Œ
TMS570Œ
I/O Power
Supply
FAULTL±
FAULTL+
GND
COMML±
COMML+
COMML+
COMML±
GND
FAULTL±
FAULTL+
All GND connections
are local to this IC. See
text for layout details.
VSENSE0
VSENSE0
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product
Folder
Sample &
Buy
Technical
Documents
Tools &
Software
Support &
Community
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
bq76PL455A-Q1 16-Cell EV/HEV Integrated Battery Monitor and Protector
1 Features
1
• Monitors and Balances 6-to-16 Cells per Device
• Highly Accurate Monitoring
– High Performance 14-bit Analog-to-Digital
Converter (ADC) With Internal Reference
– All Cells Converted in 2.4 ms (Nominal)
– Eight AUX Inputs for Temperature and Other
Sensors with Input Voltage of 0 V to 5 V
– Internal Precision Reference
• Integrated Protector With Separate Vref for
Overvoltage (OV) and Undervoltage (UV)
Comparators and Programmable V
• Engineered for High System Robustness
– Up to 1-Mb/s Stackable Isolated Differential-
UART
– Up to 16 ICs in Daisy-Chain With Twisted Pair
– Passes Bulk Current Injection (BCI) Test
– Designed for Robust Hot-Plug Performance
• Passive Balancing with External n-FETs and
Active Balancing with EMB1428Q/EMB1499Q
• Can Help Customers Meet Functional Safety
Standard Requirements (For Example, ISO26262)
– Built-in Self-Tests to Validate Defined Internal
Functions
– Support for Open Wire Detection
• AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
– Device Temperature Grade 2: –40°C to 105°C
Ambient Operating Temperature Range
– Device HBM ESD Classification Level 2
– Device CDM ESD Classification Level C3
CELL
Set Points
2 Applications
• Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (EV, HEV,
PHEV, Mild Hybrid)
• 48-V Systems (Single-Chip Solution)
• Energy Storage (ESS) and UPS
• E-Bikes, E-Scooters
3 Description
The bq76PL455A-Q1 device is an integrated 16-cell
battery monitoring and protection device, designed for
high-reliability automotive applications. The integrated
high-speed, differential, capacitor-isolated
communications interface allows up to sixteen
bq76PL455A-Q1 devices to communicate with a host
via a single high-speed Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter (UART) interface.
The bq76PL455A-Q1 monitors and detects several
different fault conditions, including: overvoltage,
undervoltage, overtemperature, and communication
faults. Six GPIO ports as well as eight analog AUX
ADC inputs are included for additional monitoring and
programmable functionality. A secondary thermal
shutdown is included for further protection.
The bq76PL455A-Q1 has features that customers
may find useful to help them meet functional safety
standard requirements. See Safety Manual for
bq76PL455A-Q1 (SLUUB67).
Device Information
PART NUMBER PACKAGE BODY SIZE (NOM)
bq76PL455A-Q1 TQFP (80) 12.00 mm × 12.00 mm
(1) For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at
the end of the data sheet.
(1)
Simplified Schematic
An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this data sheet addresses availability, warranty, changes, use in safety-critical applications,
intellectual property matters and other important disclaimers. PRODUCTION DATA.
1

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
Table of Contents
1 Features.................................................................. 1
2 Applications ........................................................... 1
3 Description ............................................................. 1
4 Revision History..................................................... 2
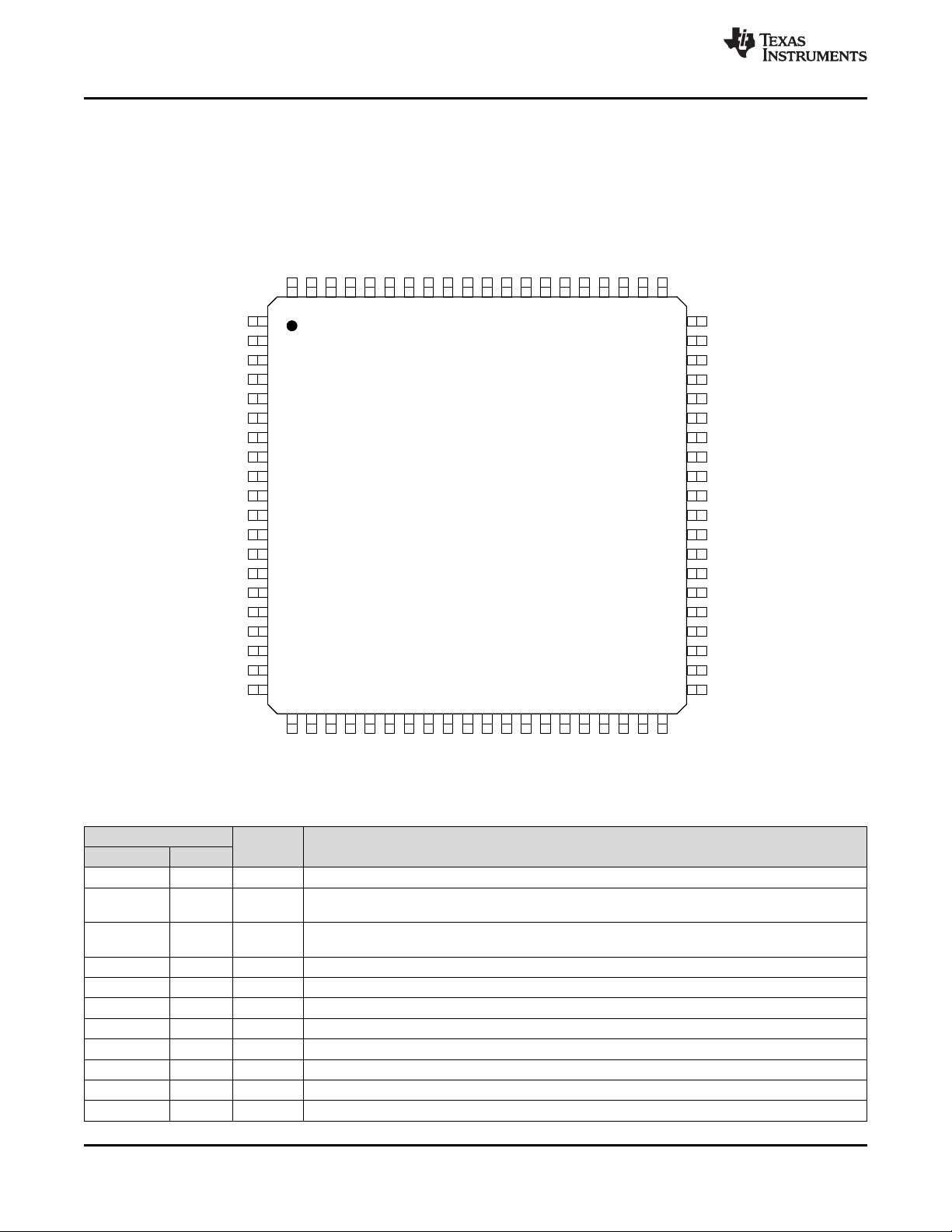
5 Pin Configuration and Functions......................... 4
6 Specifications......................................................... 8
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings...................................... 8
6.2 ESD Ratings ............................................................ 8
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions....................... 9
6.4 Thermal Information.................................................. 9
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Supply Current................. 9
6.6 VP 5.3-V Supply Regulation Voltage...................... 10
6.7 VDD18 1.8-V Internal Digital Supply....................... 10
6.8 V5VAO Analog Supply............................................ 10
6.9 VM –5-V Integrated Charge Pump ........................ 10
6.10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): Analog Front
End........................................................................... 10
6.11 ADC: VSENSEn Cell Measurement Inputs........... 11
6.12 ADC: V
6.13 ADC: Post Board Assembly
Measurement Inputs ................................................ 12
6.14 ADC: AUXn General Purpose Inputs.................... 12
6.15 ADC: Internal Temperature Measurement and
Thermal Shutdown (TSD)........................................ 13
6.16 Passive Balancing Control Outputs...................... 13
6.17 Digital Input/Output: VIO-Based Single-Ended
I/O ............................................................................ 13
6.18 Digital Input/Output: Daisy Chain Vertical Bus ..... 14
6.19 Digital Input/Output: Wakeup................................ 14
6.20 EEPROM............................................................... 14
6.21 Secondary Protector – Window Comparators ..... 14
6.22 Power-On-Reset (POR) and FAULT Flag
Input.............................................. 11
MODULE
(6)
: VSENSEn Cell
Thresholds ............................................................... 15
6.23 Miscellaneous ....................................................... 15
6.24 Typical Characteristics.......................................... 16
7 Detailed Description............................................ 18
7.1 Overview................................................................. 18
7.2 Functional Block Diagram....................................... 19
7.3 Feature Description................................................. 19
7.4 Device Functional Modes........................................ 46
7.5 Command and Response Protocol......................... 50
7.6 Register Maps......................................................... 65
8 Application and Implementation ........................ 99
8.1 Application Information............................................ 99
8.2 Typical Application................................................ 111
8.3 Initialization Set Up .............................................. 116
9 Power Supply Recommendations.................... 118
9.1 NPN LDO Supply.................................................. 118
10 Layout................................................................. 120
10.1 Layout Guidelines............................................... 120
10.2 Layout Example.................................................. 120
10.3 Board Construction and Accuracy...................... 121
11 Device and Documentation Support ............... 123
11.1 Device Support .................................................. 123
11.2 Documentation Support ..................................... 124
11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation
Updates.................................................................. 124
11.4 Community Resources........................................ 124
11.5 Trademarks......................................................... 124
11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution.......................... 124
11.7 Glossary.............................................................. 124
12 Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable
Information......................................................... 124
4 Revision History
NOTE: Page numbers for previous revisions may differ from page numbers in the current version.
Changes from Revision B (December 2015) to Revision C Page
• Changed VSENSEn resister values From: 1 kΩ To: 100 Ω in Figure 24 ............................................................................ 45
• Deleted Z1, Changed C2 to 0.1 µF, RINto 100 Ω, and R2 to 100 Ω in Figure 25 .............................................................. 99
• Changed 1 kΩ to 100 Ω in Figure 26 ................................................................................................................................. 100
• Changed RIN From: 1 kΩ To: 100 Ω in Figure 27 ............................................................................................................ 101
• Changed R24, R69, and R76 From: 1 kΩ To 100 Ω in Figure 28 ..................................................................................... 101
• Changed multiple resistors From: 1 kΩ To: 100 Ω in Figure 35......................................................................................... 111
• Deleted diode on TOP pin; Changed values of C19, C21, C22, C24, and C25 in Figure 36 ........................................... 112
• Deleted Z29; Changed values of C21, C33, C38, C40, and C41 in Figure 37 ................................................................. 113
• Changed R24, R69, and R76 From: 1 kΩ To: 100 Ω in Figure 38..................................................................................... 115
• Changed Equation 17......................................................................................................................................................... 118
2
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1

bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
Changes from Revision A (September 2015) to Revision B Page
• Updated the Features list ....................................................................................................................................................... 1
• Change paragraph 3 of the Description ................................................................................................................................ 1
• Added ADC: Post Board Assembly: VSENSEn Cell Measurement Inputs ......................................................................... 12
Changes from Original (April 2015) to Revision A Page
• Updated VCHERR25NB and VCHERR values, deleted Note 3 in the ADC: VSENSEn Cell Measurement Inputs
table ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
• Changed the Test Conditions for V
COMP_REF_45
in the Secondary Protector – Window Comparators table, From:
Measured by ADC To: Measured by ADC as HREF - HREF_GND ................................................................................... 15
• Changed VDD18, First Sample From: "CMD_OVS_GPER" To: "Approximately 30 µs" in Table 2 ................................... 26
• Deleted TSD (DIG) row and Note 4 from Table 3 ............................................................................................................... 26
• Changed text From: "Allowing for the lowest possible module voltage (V
lowest possible module voltage (V
min) of 12 V" in the NPN LDO Supply section....................................................... 119
BAT
• Added section Board Construction and Accuracy ............................................................................................................. 121
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
min) of 16 V" To: "Allowing for the
BAT
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
VSENSE15
VSENSE16
TOP
NC2
AGND1
OUT1
AGND2
NPNB
VP
AGND3
OUT2
VREF
AUX0
AUX1
AUX2
AUX3
AUX4
AUX5
VM
CHP
CHM
VDIG
NC1
TX
RX
VSENSE14
1 60
AUX6
EQ14
2 59
AUX7
VSENSE13
3 58
V5VAO
EQ13
4 57
FAULTH+
VSENSE12
5 56
FAULTH-
EQ12
6 55
COMMH+
VSENSE11
7 54
COMMH-
EQ11
8 53
COMML-
VSENSE10
9 52
COMML+
EQ10
10
VSENSE9
11
EQ9
12
VSENSE8
13
EQ8
14
VSENSE7
15
EQ7
16
VSENSE6
17
EQ6
18
VSENSE5
19
EQ5
20
51
FAULTL-
50
FAULTL+
49
WAKEUP
48
CGND
47
GPIO0
46
GPIO1
45
GPIO2
44
GPIO3
43
GPIO4
42
GPIO5
41
VIO
EQ4
EQ3
EQ2
EQ1
DGND1
DG ND2
DG ND3
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
www.ti.com
PFC Package
80-Pin TQFP
Top View
NAME
PIN NO.
AGND1 74 P Analog Ground
AGND2 72 P
AGND3 69 P
AUX0 66 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX1 65 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX2 64 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX3 63 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX4 62 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX5 61 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX6 60 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
AUX7 59 AI Ground referenced general-purpose analog measurement input.
4
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
TYPE DESCRIPTION
Analog Ground
the printed-circuit board (PCB) layout. Connect to ground plane.
Analog Ground
the PCB layout. Connect to ground plane.
Pin Functions
(2)
. Connect to ground plane.
(2)
for VREF. Internally shorted to AGND3, also make this connection externally in
(2)
for VREF. Internally shorted to AGND2, also make this connection externally in
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
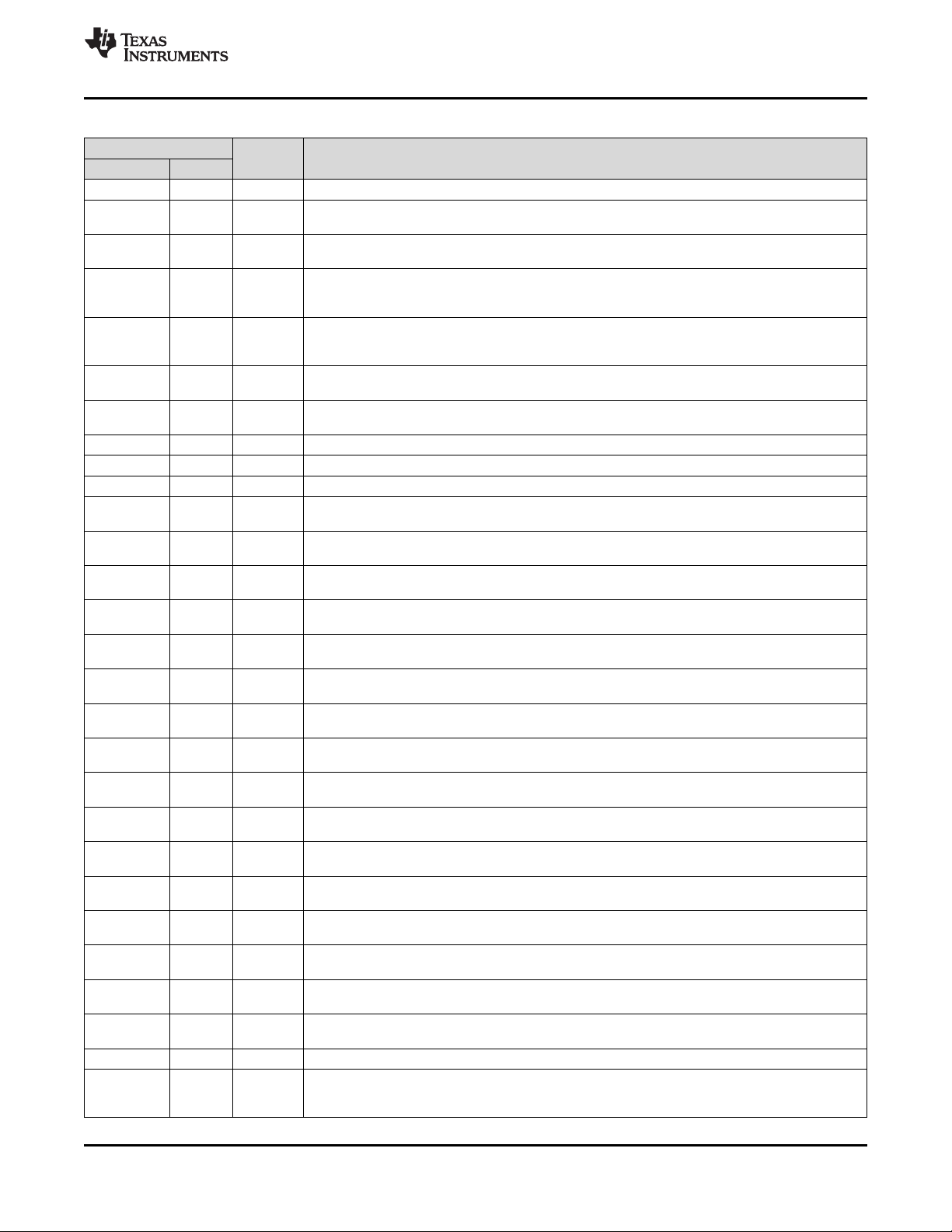
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Pin Functions (continued)
NAME
PIN NO.
CGND 48 P Communication ground
CHM 33 P
CHP 32 P
COMMH– 54 DIO
COMMH+ 55 DIO
COMML– 53 DIO
COMML+ 52 DIO
DGND1 30 P Digital Ground
DGND2 35 P Digital Ground
DGND3 37 P Digital Ground
EQ1 28 DO
EQ2 26 DO
EQ3 24 DO
EQ4 22 DO
EQ5 20 DO
EQ6 18 DO
EQ7 16 DO
EQ8 14 DO
EQ9 12 DO
EQ10 10 DO
EQ11 8 DO
EQ12 6 DO
EQ13 4 DO
EQ14 2 DO
EQ15 80 DO
EQ16 78 DO
FAULT_N 40 DO Single-ended active-low fault output. Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
FAULTH– 56 DI
TYPE DESCRIPTION
(2)
. Connect to ground plane.
Charge pump flying capacitor connection. Connect a 22-nF ceramic capacitor
and CHP.
Charge pump flying capacitor connection. Connect a 22-nF ceramic capacitor
and CHM.
Inverting, high-side differential connection to the COMML– pin of the higher adjacent module in a
daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
Non-inverting, high-side differential connection to the COMML+ pin of the higher adjacent module in
a daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
Inverting, low-side differential connection to the COMMH– pin of the lower adjacent module in a
daisy chain. Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
Non-inverting, low-side differential connection to the COMMH+ pin of the lower adjacent module in a
daisy chain. Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
(2)
. Connect to ground plane.
(2)
. Connect to ground plane.
(2)
. Connect to ground plane.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 1. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 2. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 3. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 4. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 5. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 6. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 7. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 8. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 9. May leave this pin
unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 10. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 11. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 12. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 13. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 14. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 15. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Cell Equalization control output used to drive an external N-FET balancing cell 16. May leave this
pin unconnected if not used.
Inverting, high-side differential connection to the FAULTL– pin of the higher adjacent module in a
daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
bq76PL455A-Q1
(3)
between this pin
(3)
between this pin
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
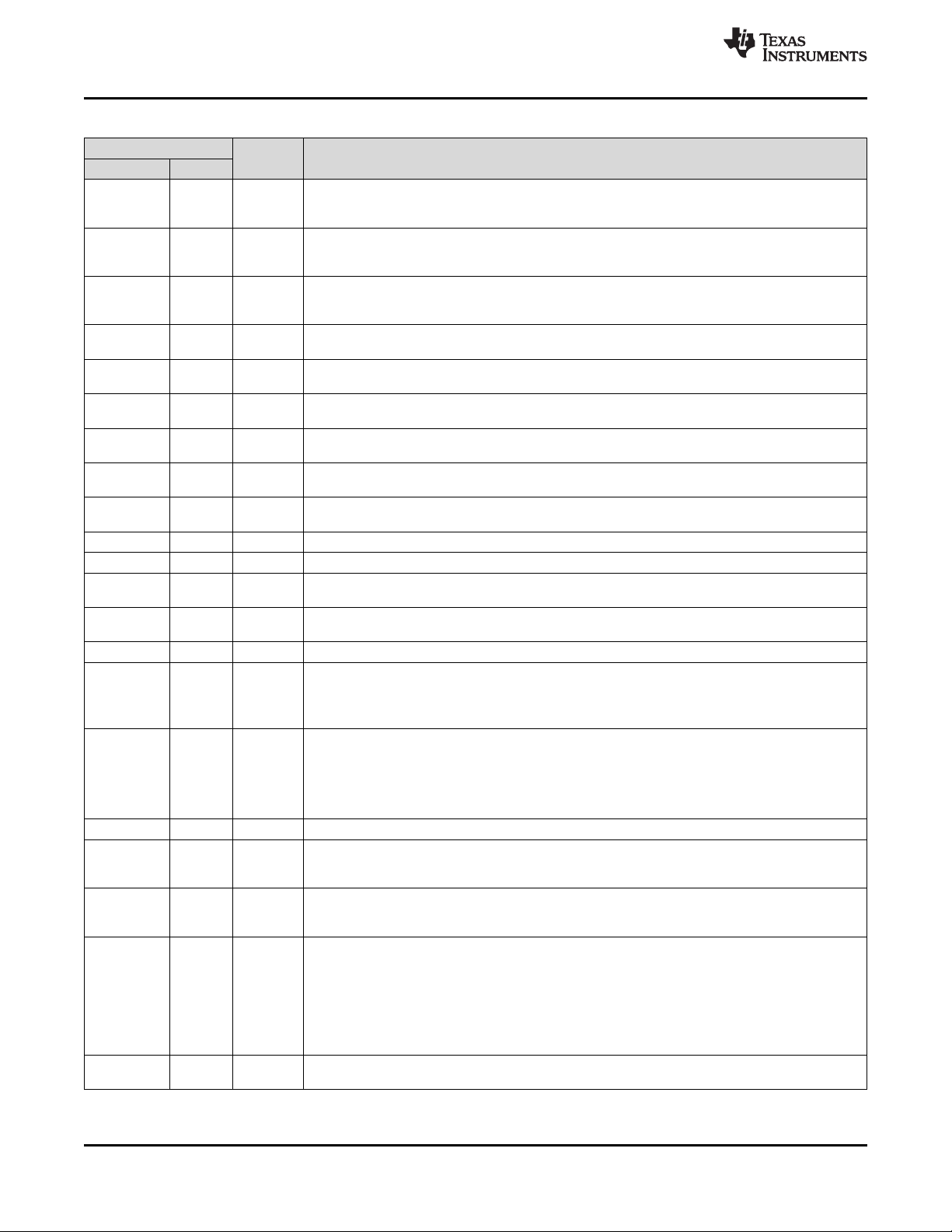
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Pin Functions (continued)
NAME
PIN NO.
FAULTH+ 57 DI
FAULTL– 51 DO
FAULTL+ 50 DO
GPIO0 47 DIO
GPIO1 46 DIO
GPIO2 45 DIO
GPIO3 44 DIO
GPIO4 43 DIO
GPIO5 42 DIO
NC1 36 NC Do not connect to this pin. This pin must remain floating for correct operation.
NC2 75 NC Do not connect to this pin. This pin must remain floating for correct operation.
NPNB 71 AO
OUT1 73 AO
OUT2 68 AI ADC input pin. Connect externally to pin OUT1. Internally tied to pin OUT1.
RX 39 DI
TOP 76 P
TX 38 DO Single-ended UART transmit output. Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
V5VAO 58 P
VDIG 34 P
VIO 41 P
VM 31 P
TYPE DESCRIPTION
Non-inverting, high-side differential connection to the FAULTL+ pin of the higher adjacent module in
a daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
Inverting, low-side differential connection to the FAULTH– pin of the lower adjacent module in a
daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
Non-inverting, low-side differential connection to the FAULTH+ pin of the lower adjacent module in a
daisy chain.
Leave this pin unconnected if not used.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input or address assignment.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input or address assignment.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input or address assignment.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input or address assignment.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input or address assignment.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
General Purpose I/O. Optionally use this pin as an external FAULT input.
Do not allow GPIO pins to float when configured as inputs.
Internal voltage regulator controller output pin. Connect to the base of the external NPN transistor.
Leave unconnected if not used.
Analog multiplexer output. Connect a 390-pF filter capacitor type C0G or NP0 between this pin and
AGND. Connect externally to pin OUT2. Internally tied to pin OUT2.
Single-ended UART receive input. This pin must be either:
• Driven from a UART signal OR
• Pulled up to VIO
Do not allow this pin to float at any time.
Power supply input and module voltage-measurement pin. Connect to the top cell of the module
through a series resistor. Requires a decoupling capacitor
TOP Pin Connection for details. Locate decoupling capacitor as close to pin as possible. The low-
pass filter created by the RC should have a tau similar to the low-pass filter used in the VSENSE
circuits. See VP Regulated Output or Application and Implementation for component selection
details.
Connection to internal 5-V always-on supply. Decouple with a 4.7-µF capacitor
ground plane. Locate decoupling capacitor as close to pin as possible. This pin should not be used
to supply external circuitry.
5.3-V Digital Supply input. Always connect VDIG to VP with 1-Ω resistor. Decouple with 4.7-µF and
0.1-µF capacitors
(3)
in parallel to the ground plane. Locate decoupling capacitors as close to the
VDIG pin as possible.
3-V to 5-V power input for IO supply. Connect this pin to the same power supply used to drive the
source/receiver for the GPIO, FAULT_N, RX, and TX pins. Typically, connect this pin to VP/VDIG
for all devices except the base device in the stack. In the base (or single) device, this pin is typically
driven from the same supply as the microcontroller I/O pins.
If VP/VDIG is connected as the power source, this pin should be decoupled with a 0.1-µF
capacitor
(3)
to the digital ground plane. Place a 1-Ω resistor in series from VP to VIO. Locate the
decoupling capacitor as close to the VIO pin as possible.
If another supply is used, decouple with parallel 10-µF and 0.1-µF capacitors
Internal –5-V charge pump output. Decouple with 4.7-µF and 0.1-µF capacitors
ground plane. Locate decoupling capacitor as close to pin as possible.
(3)
from TOP to the ground plane. See
(3)
connected to the
(3)
.
(3)
in parallel to the
www.ti.com
6
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Pin Functions (continued)
NAME
PIN NO.
VP 70 P
VREF 67 P
VSENSE0 29 AI Connect to the negative pin of the 1stcell.
VSENSE1 27 AI Channel 1. Connect to the positive pin of the 1stcell.
VSENSE2 25 AI Channel 2. Connect to the positive pin of the 2ndcell.
VSENSE3 23 AI Channel 3. Connect to the positive pin of the 3rdcell.
VSENSE4 21 AI Channel 4. Connect to the positive pin of the 4thcell.
VSENSE5 19 AI Channel 5. Connect to the positive pin of the 5thcell.
VSENSE6 17 AI Channel 6. Connect to the positive pin of the 6thcell.
VSENSE7 15 AI Channel 7. Connect to the positive pin of the 7thcell.
VSENSE8 13 AI Channel 8. Connect to the positive pin of the 8thcell.
VSENSE9 11 AI Channel 9. Connect to the positive pin of the 9thcell.
VSENSE10 9 AI Channel 10. Connect to the positive pin of the 10thcell.
VSENSE11 7 AI Channel 11. Connect to the positive pin of the 11thcell.
VSENSE12 5 AI Channel 12.Connect to the positive pin of the 12thcell.
VSENSE13 3 AI Channel 13. Connect to the positive pin of the 13thcell.
VSENSE14 1 AI Channel 14. Connect to the positive pin of the 14thcell.
VSENSE15 79 AI Channel 15. Connect to the positive pin of the 15thcell.
VSENSE16 77 AI Channel 16. Connect to the positive pin of the 16thcell.
WAKEUP 49 DI Wakeup input. Pull this pin low or tie to ground if not used. Do not allow this pin to float at any time.
(1) Key: AI = analog input; AO = analog output; DI = digital input; DO = digital output; DIO = digital I/O; P = Power; NC = no connect.
(2) Externally connected pins as common ground or GND in the design. See Grounding for details.
(3) All capacitors are type X7R or better, unless otherwise noted.
TYPE DESCRIPTION
5.3-V regulated analog power supply input/sense pin.
Connect to external NPN transistor's emitter and decouple with a 0.1-µF capacitor
4.7-µF capacitor
(3)
in series with a 0.390-Ω resistor to GND. Locate decoupling capacitors as close
to the VP pin as possible.
Always connect VDIG to VP with 1-Ω resistor.
VREF output filter pin. Decouple with parallel 0.1-µF and 1.8-µF (25 V+) capacitors
plane. Locate decoupling capacitors as close to the pin as possible. To maintain measurement
fidelity, do not place external loads on this pin.
(3)
to AGND and a
(3)
to the ground
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over specified Ambient Temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
VP –0.3 6 V
VDIG –0.3 6 V
VIO –0.3 6 V
AUX0–7 Lesser of two MAX values –0.3 6 or (VP + 0.3) V
Lesser of two MAX values –0.3 6 or (V5VAO + 0.3) V
COMMH+, COMMH–, COMML+, COMMH–,
FAULTH+, FAULTH–, FAULTL+, FAULTL–
GPIO0–5 Lesser of two MAX values –0.3 6 or (VIO + 0.3) V
RX Lesser of two MAX values –0.3 6 or (VIO + 0.3) V
(4)
TOP
TOP to VSENSE16 delta
VSENSE0 –0.3 0.3 V
VSENSEn – VSENSEn–1
WAKEUP –0.3 6 V
Ambient free-air temperature, T
Junction temperature, T
Storage temperature, T
(4)(5)
A
J
stg
AC pulse specification
pins only:
Vpkmaximum ≤ 6.5 V for 100 ns or less,
100 kHz ≤ f ≤ 400 MHz
(VSENSE16 + 5.5 V) ≥ TOP ≥
(VSENSE16 – 1 V)
n = 1 to 16 –0.3 5.5
n = 1 to 16, 0.1% duty cycle –0.3 6.5
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating
Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Unless otherwise noted, voltages are given with respect to device commons (AGND1–3, DGND1–3, CGND) tied together (device VSS
or GND).
(3) Specified by design, not tested in production.
(4) Must meet all stated conditions for the TOP pin at all times.
(5) Must short the highest-connected cell to the unused VSENSEn inputs above it in configurations that use < 16 cells. For example, a 14-
cell configuration must short pins VSENSE14, VSENSE15, VSENSE16.
(3)
for these eight
(1)(2)
MIN MAX UNIT
–0.3 6.5 V
–0.3 88 V
(VSENSE16 – 1 V) (VSENSE16 + 5.5 V) V
–40 105 ⁰C
–40 125 ⁰C
–65 150 °C
pk
V
6.2 ESD Ratings
(1)
All pins ±2000
All pins except 1, 20, 21, 40, 41, 60, 61,
76, and 80
Pin 76 ±450
Corner pins (1, 20, 21, 40, 41, 60, 61,
and 80)
V
Electrostatic discharge
(ESD)
Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002
Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates that HBM stressing shall be in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
8
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
VALUE UNIT
±500
±750
V
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
TA= 25°C and TOP = 57.6 V; Min/Max values stated where TA= –40°C to 105⁰C and TOP = 12 V to 79.2 V (unless
otherwise noted)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
TOP
V
IO
V
TOP_DELTA
I
I/O
I
I/O_T
(1) V
SENSE
Ratings table.
(2) Must short the highest-connected cell to the unused VSENSEn inputs above it in configurations that use < 16 cells. For example, a 14-
cell configuration must short pins VSENSE14, VSENSE15, and VSENSE16.
Supply voltage TOP – GND (VSENSE16 = TOP) 12 79.2 V
Digital interface voltage 2.7 5.5 V
Max delta, TOP to highest cell
Output current, any one pin
Output current, sum of
input measurement accuracy is degraded when V
(1)(2)
VSENSE16 – TOP 0 300 mV
GPIO0, GPIO1, GPIO2, GPIO3, GPIO4, GPIO5, TX,
FAULT_N
GPIO0 + GPIO1 + GPIO2 + GPIO3 + GPIO4 + GPIO5
+ TX + FAULT_N
TOP_DELTA
is exceeded. Delta cannot exceed the limit in the Absolute Maximum
5 mA
20 mA
6.4 Thermal Information
(1)
R
θJA, High K
R
θJC(top)
R
θJB
ψ
JT
ψ
JB
R
θJC(bottom)
THERMAL METRIC
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance 44.3 °C/W
Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance 6.4 °C/W
Junction-to-board thermal resistance 21.5 °C/W
Junction-to-top characterization parameter 0.2 °C/W
Junction-to-board characterization parameter 21 °C/W
Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance — °C/W
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application
report.
bq76PL455A-Q1
UNITTQFP (PFC)
80 PINS
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Supply Current
(1)
The following applies to all Electrical Characteristics in the following tables, unless otherwise noted: TYP values are stated in
each table where VP = VDIG = 5.3 V, VIO = 5 V, TA= 25°C and V
TOP = 57.6 V. MIN/MAX values are stated where VP = VDIG = 5.3 V, VIO = 5 V, –40°C ≤ TA≤ 85⁰C, 1 V < V
CELL
= 3.6 V (V
= VSENSEn – VSENSEn–1; n=1 to 16),
CELL
CELL
< 4.95 V,
12 V ≤ TOP < 79.2 V and GND = 0 V.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
IDLE
I
TOP_IDLE
I
SLEEP
I
ACTIVE
I
VIO_IDLE
I
SLP_DELTA
(4)
(4)
Total input current from the monitored
Power state: IDLE
cells.
Input current into TOP pin, IDLE mode Power state: IDLE
Total input current from the monitored
cells into TOP pin
Total input current from the monitored
cells while communicating.
Power state: SHUTDOWN
VP = VDIG = VIO = 0 V, TOP = 57.6
Power state: IDLE plus comms
differential comm capacitance 70 pF, no
load on GPIO.
VIO input current Power state: IDLE
Delta I
stack
SHUTDOWN
between devices in a
TA= 25°C ± 5°C for all devices 4 10 µA
(1) All internal pull-up and pull-down resistors are disabled and their current is not included in parameters listed in this table.
(2) IDLE mode defined as: device awake, ready for communications, and not communicating.
(3) SHUTDOWN mode defined as: test conditions, no communications, no wakeup tone activity, and no FAULT heartbeat.
(4) Specified from characterization data.
(5) ACTIVE mode defined as: UART, differential communications link, and FAULT heartbeat active.
(2)
(2)
(3)
(5)
,
4 5 7 mA
250 350 450 µA
22 50
µA
8 mA
(2)
40 µA
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
6.6 VP 5.3-V Supply Regulation Voltage
Characteristics stated using NPN transistor in circuit rated at BV
I
COLLECTOR
VP
I
NPNB
VP
(1) Time measured from VP falling below threshold until the part enters SHUTDOWN, or from the part attempting to exit SHUTDOWN
VR
SD_DLY
> 100 mA, R
Regulated Voltage 5.1 5.3 5.5 V
External NPN base drive current 0.5 mA
VP/VDIG delay before SHUTDOWN
COLLECTOR
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 400 Ω.
(wakeup) until re-entering SHUTDOWN.
(1)
> 100V, β ≥ 100 at 5 mA, Base-Collector C ≤ 35 pF,
CEO
30 75 160 ms
6.7 VDD18 1.8-V Internal Digital Supply
VDD18
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
VO
VDD18 Output voltage
(1)
(1)
As measured by internal ADC 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
(1) Internal node only, no external access. This parameter is for internal measurement and verification purposes only.
6.8 V5VAO Analog Supply
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V5VAO
V5VAO
SD
IDLE
Output Voltage Power state: SHUTDOWN,
Output Voltage Power state: IDLE
VP = VDIG = VIO = 0 V
(1)
, unloaded VDIG – 0.5 VDIG V
4 4.7 5.3 V
(1) VDIG internally connected to V5VAO in IDLE mode.
6.9 VM –5-V Integrated Charge Pump
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
VM
f
CP
VM
VM
VM_ON
TRIP
VO
VM Output Voltage –5.5 –5 –4.5 V
Charge pump switching frequency 375 kHz
VM low-voltage monitor trip point –3.8 V
Measured value read back from ADC VM
monitor
–5.56 –5 –4.54 V
6.10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): Analog Front End
All ADC specifications stated are for the sampling intervals and register settings shown in Table 3. A 390-pF capacitor is on
pin OUT1.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
OUT1
R
OUT_PIN
RANGE
Pin OUT1 Analog Front End / Level
Shifter output voltage range
OUT1 pin internal series resistance 1 1.2 1.35 kΩ
0 VP V
10
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
6.11 ADC: VSENSEn Cell Measurement Inputs
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
= VSENSEn – VSENSEn–1, n= 1
V
CELL_VR
VCHERR25NB Total Channel Measurement Accuracy at 25°C VSENSE = 3.6 V ±0.75 mV
VCHERR
VCHERR
(3)(4)
I
SENSE_SEL
I
SENSE_NSEL
I
SENSE_SD
(4)
R
SENSE_SEL
OWD
SR
LT_Drift
VCHAN
V
ADC_REF_25
ERR
ADC_REF_25
Input voltage range
Total Channel Measurment Accuracy,
temperature range of 0°C to 65°C
Total Channel Measurment Accuracy,
temperature range of –40°C to 105°C
VSENSEn input current n = 1 to 16 VSENSEn–1 pin; on selected channel 2 7.6 µA
VSENSE input resistance
Open-wire detection shunt resistance
Long-term drift (total channel path)
ADC reference 2.5 V
ADC reference error
(1)(2)
(1)(2)
(1) Error measured with averaging enabled.
(2) User adjustable Gain and Offset registers are provided for further error trim at VSGAIN and VSOFFSET, respectively.
(3) When the bq76PL455A is in IDLE power mode, but not converting any ADC input channel, the part idles the multiplexer on the highest
channel enabled for conversions in the CHAN register.
(4) The current into VSENSEn = ISENSE_SEL + VCELL/RSENSE_SEL.
(5) Computed from the first 500-hour operating life test at a stress temperature of 65°C.
(6) Computed from the first 500-hour operating life test at a stress temperature of 105°C.
CELL
to 16
VSENSE = 1.5 V –2.00 2.00
VSENSE = 2.0 V –2.50 2.50
VSENSE = 3.3 V –3.75 3.75
VSENSE = 3.6 V –4.25 4.25
VSENSE = 4.2 V –4.75 4.75
VSENSE = 4.5 V –5.00 5.00
VSENSE = 1.5 V –3.50 3.50
VSENSE = 2.0 V –4.00 4.00
VSENSE = 3.3 V –5.75 5.75
VSENSE = 3.6 V –6.25 6.25
VSENSE = 4.2 V –7.00 7.00
VSENSE = 4.5 V –7.25 7.25
Channel not selected < ±100 nA
VSENSEn input current in
SHUTDOWN Mode
Channel selected for conversion,
measured differentially
[VSENSEn–VSENSE(n–1)]
Open-wire test mode, TSTCONFIG[4]
= 1
all odd (CBENBL = 0xAA); or all even
(CBENBL=0x55) cell squeeze resistors
on (alternate resistors only)
VSENSE = 4.5 V, TA= 65°C
VSENSE = 4.5 V, TA= 105°C
0°C ≤ TA≤ 65°C –3.5 3.5 mV
–40°C ≤ TA≤ 105°C –4.5 4.5 mV
(5)
(6)
1 4.95 V
mV
mV
< ±100 nA
1 MΩ
4 kΩ
18.47
50.24
ppm/ 1000
hours
6.12 ADC: V
V
MODULE_VR
V
MODULE_ERR105
MODULE
Input
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input voltage range Measured from TOP to GND (AGND1) V
MIN V
TOP
MAX V
TOP
Total error from all internal sources TA= –40°C to 105°C –650 ±100 650 mV
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
11
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
6.13 ADC: Post Board Assembly
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
CELL_VR
V
CHERR65NB
V
CHERR105NB
LT_Drift
VCHAN
Input voltage range
Total Channel Measurement Accuracy
in temperature range of 0°C to 65°C
Total Channel Measurement Accuracy,
temperature range of –40°C to 105°C
Long-term drift (total channel path)
(6)
: VSENSEn Cell Measurement Inputs
V
= VSENSEn – VSENSEn–1, n= 1
CELL
to 16
VSENSE = 1.5 V –3 3
(1)(2)(3)
(1)(2)(3)
VSENSE = 2.5 V –3.5 3.5
VSENSE = 3.6 V –5 5
VSENSE = 4.5 V –7.6 7.6
VSENSE = 1.5 V –4.5 4.5
VSENSE = 2.5 V –6.3 6.3
VSENSE = 3.6 V –8.4 8.4
VSENSE = 4.5 V –11. 11.1
VSENSE = 4.5 V, TA= 65°C
VSENSE = 4.5 V, TA= 105°C
(4)
(5)
1 4.95 V
18.47
50.24
ppm/ 1000
hours
mV
(1) Error measured with averaging enabled.
(2) User adjustable Gain and Offset registers are provided for further error trim at VSGAIN and VSOFFSET, respectively.
(3) Calculated and statistically projected worst case from characterization data. Includes inaccuracies due to IR reflow and thermal
hysteresis over 3 cycles (25°C -> –40°C -> 25°C -> 105°C -> 25°C)
(4) Computed from the first 500-hour operating life test at a stress temperature of 65°C.
(5) Computed from the first 500-hour operating life test at a stress temperature of 105°C.
(6) See Board Construction and Accuracy for board stack build information
6.14 ADC: AUXn General Purpose Inputs
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
AUX_VR
V
AUXERR65
V
AUXERR105
Input voltage range
Total AUX Channel Measurement
(2)
Accuracy
Total AUX Channel Measurement
(2)
Accuracy
(1) Specified by design, not tested in production.
(2) Calculated and statistically projected worst case from characterization data. Not tested in production.
(1)
VP/VDIG = 5.3 V 0 5 V
VAUX = 0.05 V, 0°C ≤ TA≤ 65°C –3 0.1 3 mV
VAUX = 4.95 V, 0°C ≤ TA≤ 65°C –10 0.1 10 mV
VAUX = 0.05 V, –40°C ≤ TA≤ 105°C –4.5 0.1 4.5 mV
VAUX = 4.95 V, –40°C ≤ TA≤ 105°C –12.5 0.1 12.5 mV
12
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
ADC: AUXn General Purpose Inputs (continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
DCL_AUX
R
IN_AUX
C
AUX
R
AUX_PU
DC Leakage Current
(1)
(1)
Equivalent input resistance Channel selected In Acquisition Mode > 3 MΩ
Input capacitance Channel selected 30 pF
Internal switched pull-up resistor per
AUXn input, supplied from VP pin
Channel not selected for conversion,
TESTAUXPU = 0
< ±0.1 µA
TESTAUXPU[n] = 1; n = 0 to 7 18 26 46 kΩ
6.15 ADC: Internal Temperature Measurement and Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
T
INT_AD
T
INT_DD
TSD
(1)
(1)
(2)
T
Internal temperature accuracy of analog
die
Internal temperature accuracy of digital
die
Thermal shutdown, junction temperature
both analog and digital dies
–7 3 13 °C
–34 8 54 °C
Increasing temperature 115 140 °C
(1) Specified from characterization data, not tested in production.
(2) Specified by design, not tested in production.
6.16 Passive Balancing Control Outputs
PARAMETER
EQ
EQ
EQ
VS1
SR_OFF
SR_ON
VMIN
MIN
(2)
Output resistance, internally in series
with driver
Cell voltage required for balancing 1.8 V
VSENSE1 minimum voltage for
balancing
(1) For more functional information, see Passive Balancing .
(2) In the event of an open wire condition, if TSTCONFIG[EQ_SQUEEZE_EN] = 1 and this causes EQVMIN to be violated, it may be
necessary to power down the device to disable the squeeze resistor.
(3) VSENSE1 minimum voltage required for correct operation of any or all EQn outputs. If VSENSE1 falls below this value, any or all other
EQ outputs may fail to assert when requested. The opposite is not true. Outputs will not assert unintentionally when set to the OFF
state.
(1)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
EQn = 0 (OFF) 1.2 1.5 1.8 kΩ
EQn = 1 (ON) 1.9 2.3 2.9 kΩ
(3)
1.8 V
6.17 Digital Input/Output: VIO-Based Single-Ended I/O
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
V
IL
C
DIG_IN
R
PU
R
PD
I
LKG
RXTX
BAUD
ERR
BAUD_RX
ERR
BAUD_TX
t
COMM_BREAK
t
COMM_RESET
(1) Specified by design, not tested in production.
(2) Defaults: RX = TX = 250 kBd at communications RESET or (factory set) EEPROM setting at POR.
(3) Discrete rates only, not continuously variable.
Logic-level output-voltage high
FAULT_N, TX, GPIO
Logic-level output-voltage low FAULT_N,
TX, GPIO
I
= 5 mA VIO – 0.7 VIO V
LOAD
I
= 5 mA DGND 0.7 V
LOAD
Logic-level input-voltage high RX, GPIO VIO – 0.7 V
Logic-level input-voltage low RX, GPIO 0.7 V
Input Capacitance
(1)
RX, GPIO 5 pF
GPIO0..5 pull-up resistor 13 17 25 kΩ
GPIO0..5 pull-down resistor 16 22 31 kΩ
Input leakage source/sink current RX,
GPIOx
RX/TX signaling rate
Input Baud rate error
Output Baud rate error
Communications Clear (Break)
Communications Reset
(2)(3)
(1)
125 1000 Kbaud
–3% 3%
(1)
(1)
(1)
–1.5% 1.5%
10 15 bit periods
200 µs
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
< ±1 µA
13
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
6.18 Digital Input/Output: Daisy Chain Vertical Bus
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
OH_DCC_TX
V
OL_DCC_TX
T
PD
T
DCC_BIT_TIME
f
WAKE_TONE
t
WAKE TONE
Logic level output voltage high Single driver loaded, I
Logic level output voltage low Single driver loaded, I
Internal propagation delay, COMML to
(1)
COMMH
Diff. Comms. Bit Time
WAKE TONE frequency
(1)
(1)
50% duty-cycle WAKE TONE
transmitted on differential pins
COMMH+/COMMH–
WAKE TONE duration
(1)
WAKE TONE transmitted on differential
pins COMMH+/COMMH–
= 5 mA VDIG−1 VDIG V
LOAD
= 5 mA GND 1 V
LOAD
(1) Specified by design, not tested in production.
6.19 Digital Input/Output: Wakeup
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
IH_WAKEUP
V
IL_WAKEUP
t
WAKEUP_HOLD
t
WAKEUP_DLY
t
WAKE TONE DELAY_DC
t
WAKEUP_TO_DCOMM
t
WAKEUP_TO_UART
(1) Pulses shorter than 100 µs may wake the device, but must maintain 100 µs to assure start up.
(2) Environmental noise may affect tone detection.
(3) Specified by design, not tested in production.
WAKEUP high-input voltage 2.3 V
WAKEUP low-input voltage 0.7 V
(1)
WAKEUP hold time (high-pulse width) Pulse driven 0-1-0 100 µs
Delay between WAKEUP pin assertion and
WAKETONE transmission
(2)
Delay
between start of WAKETONE received
and WAKETONE transmission
Required delay from WAKETONE transmission
to ready for differential communications
Required delay from WAKETONE transmission
to ready for UART communications
(3)
Typical application circuit with typical
components as outlined in the Application and
Implementation section.
After POR exit condition [VDD18VO> 1.7 V] is
met.
(3)
www.ti.com
<60 ns
250 ns
100 kHz
1 ms
1.2 ms
1.2 ms
1.1 ms
200 µs
6.20 EEPROM
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
EE
EE
EE
PGM
CYCLES
RETN
(1)
EEPROM total program time
Erase / Program cycles
Data retention
(2)(3)
(2)
(2)
(1) Program EEPROM temperature (TA) between 0°C and 30°C.
(2) Specified by design, not tested in production.
(3) Erase / Program cycles not to exceed EE
No writes to the device are allowed
during the programming cycle
.
CYCLES
6.21 Secondary Protector – Window Comparators
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
OV
RANGE
UV
RANGE
OVUV
ERR
CMP_UV
ERR
CMP_UV_EXT
ERR
COMP_OV
ERR
COMP_OV_EXT
V
COMP_HYST
STEP
Over-voltage comparator register set-point
(1)
limits
Under-voltage comparator register set-point
(1)
limits
Threshold step resolution 25 mV
Total UV threshold error (includes
ERR
VCOMP_REF_45
UV threshold error when range-extend bit is set COMP_UV[CMP_TST_SHF_UV] = 1 –100 100 mV
Total OV threshold error (includes
ERRVCOMP_REF_45)
OV threshold error when range-extend bit is set COMP_UV[CMP_TST_SHF_OV] = 1 –60 60 mV
Threshold hysteresis
)
Vin = 0.7 to 3.875 V –50 50 mV
Vin = 2 to 5.175 V –50 50 mV
Hysteresis enabled;
DEVCONFIG[COMP_HYST_EN] = 1
210 500 ms
5 cycles
10 years
2 5.175 V
0.7 3.875 V
50 85 130 mV
(1) Normal range specification. Ranges can be extended by using the COMP_UV[CMP_TST_SHF_UV] and
COMP_OV[CMP_TST_SHF_OV] bits. See register bit description in Table 7 for additional details.
14
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
Secondary Protector – Window Comparators (continued)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
T
COMP_UV
T
COMP_OV
V
COMP_REF_45
ERR
VCOMP_REF_45
UVP Response time Overdrive = 100 mV 20 µs
OVP Response time Overdrive = 100 mV 20 µs
Comparator reference Measured by ADC as HREF - HREF_GND 4.5 V
Comparator reference error
0°C ≤ TA≤ 65°C, measured by ADC –22 –7 9.5 mV
–40°C ≤ TA≤ 85°C, measured by ADC –27 –7 15 mV
6.22 Power-On-Reset (POR) and FAULT Flag Thresholds
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
VP
FLT_TRIP
VM
FLT_TRIP
DDIE
V5VAO
VIO
POR
VIO
SD_DLY
POR
VP_FAULT voltage threshold, analog die
VM_FAULT voltage threshold, analog die
VP/VDIG POR voltage threshold, digital
die
SD
V5VAO SHUTDOWN voltage threshold,
digital die
VIO POR voltage threshold, digital die
VIO delay before SHUTDOWN VIO ≤ VIO
Falling VP 4.3 4.5 4.7
Rising VP 4.3 4.5 4.7
Falling VM (more negative) –4.2 –4 –3.8
Rising VM (more positive) –3.9 –3.8 –3.7
Falling voltage, VP connected to VDIG 3.9 4.15 4.4
Rising voltage, VP connected to VDIG 4.1 4.5 4.7
Falling V5VAO 1.8 2.3 2.8 V
Rising V5VAO 2.5 V
Falling VIO 2.1 2.3 2.5
Rising VIO 2.3 2.5 2.7
POR
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
V
V
V
V
35 57 100 ms
6.23 Miscellaneous
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
OSC
f
HBEAT
HB
PULSE
t
CKSUM_USER
t
CKSUM_TI
t
CKSUM_PER
t
ADCFullTest
t
ADCTest
V
HREF_GND_FAUL
T
V
HREF_FAULT_OV
V
HREF_FAULT_UV
(1) Specified by design, not tested in production.
Main oscillator frequency (±1.5%) 47.28 48 48.72 MHz
Fault tone (heartbeat) frequency at pins
FAULTL±
Fault heartbeat pulse width at pins
FAULTL±
Time to complete User-space checksum
(1)
test
Time to complete TI-space checksum
(1)
test
Period for automatic checksum
(1)
updates
Time to complete full ADC test
Time to complete abbreviated ADC
(1)
test
Voltage threshold for 4.5-V reference
ground fault
Overvoltage threshold for 4.5-V
reference fault
Undervoltage threshold for 4.5-V
reference fault
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
No fault condition present, heartbeat
enabled
No fault condition present, heartbeat
enabled
10 kHz
125 ns
5 ms
5 ms
2 µs
450 ms
15 ms
0.96 V
4.75 V
4.25 V
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
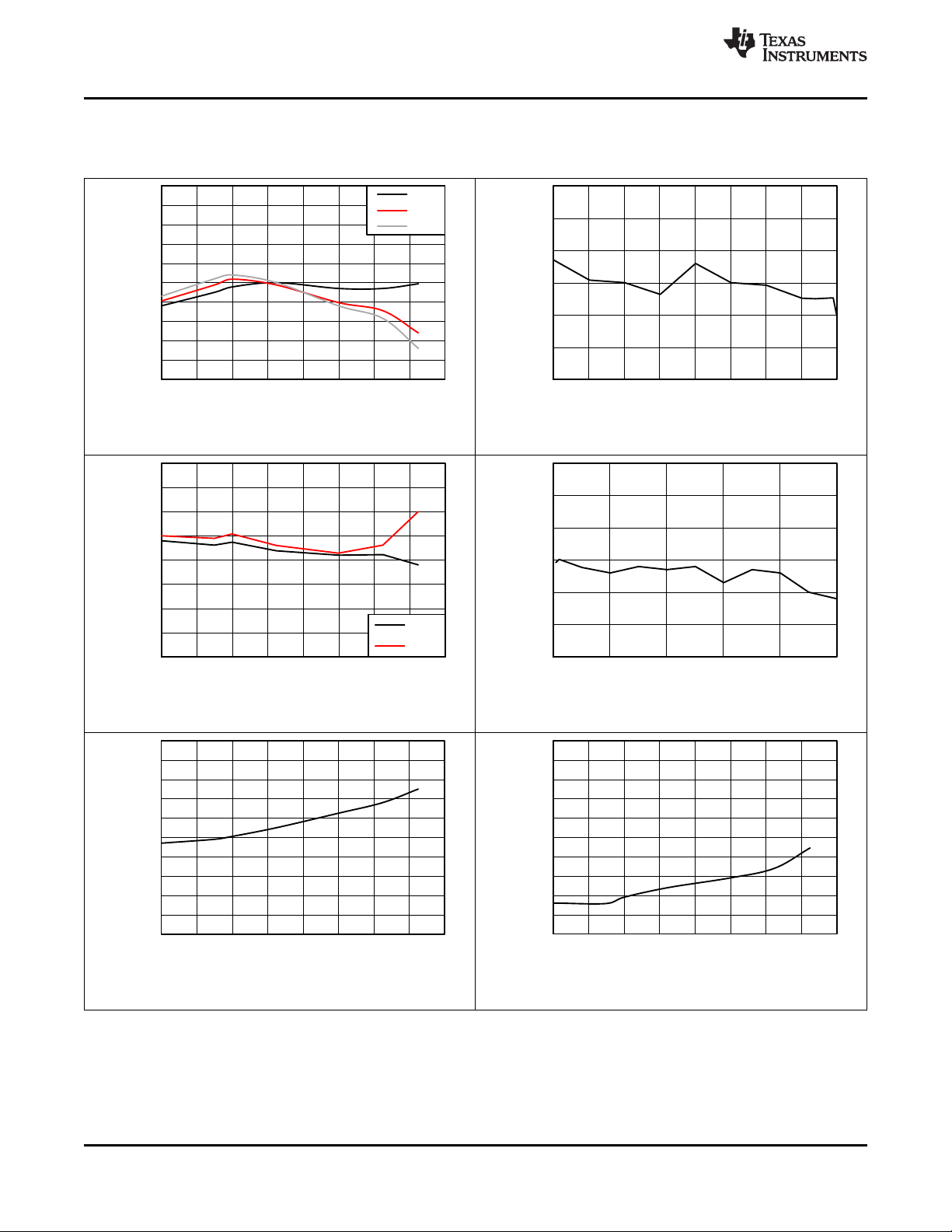
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
C005
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
C006
±2.0
±1.5
±1.0
±0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
0.5 V
4.95 V
C003
±3
±2
±1
0
1
2
3
0 1 2 3 4 5
Error (mV)
AUX Voltage (V)
C004
±5
±4
±3
±2
±1
0
1
2
3
4
5
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
1.5 V
3.6 V
4.5 V
C001
±3
±2
±1
0
1
2
3
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
Error (mV)
Cell Voltage (V)
C002
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
6.24 Typical Characteristics
The following conditions apply: Typical Operating Circuit, VTOP = 60 V, 16 cells, TA= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
www.ti.com
Figure 1. Cell Voltage Measurement Error
Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 3. AUX Measurement Error
Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 2. Cell Voltage Measurement Error
Versus Cell Voltage
Figure 4. AUX Measurement Error Versus AUX Voltage
Figure 5. Overvoltage Comparator Error
16
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 6. Undervoltage Comparator Error
Versus Ambient Temperature
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
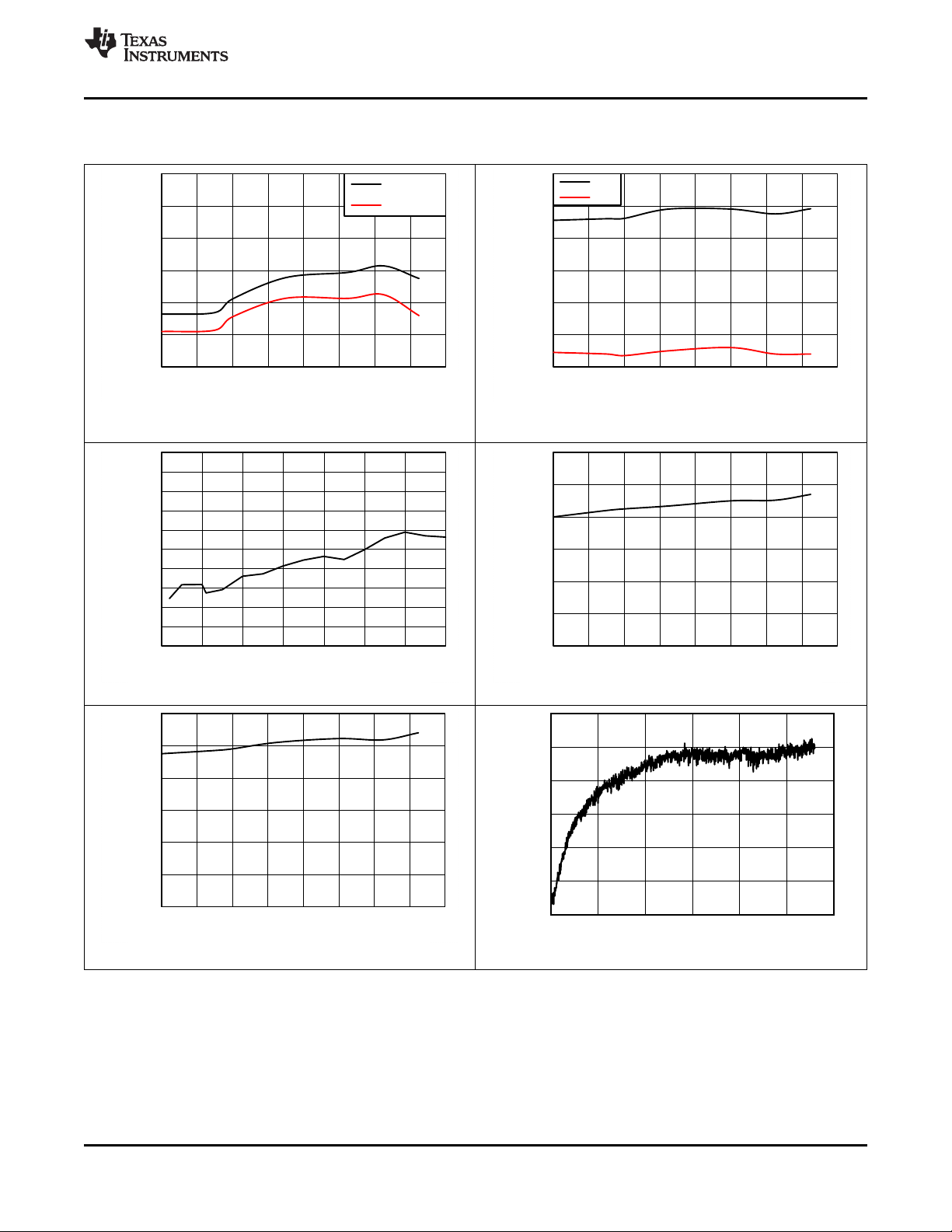
Time (hrs)
T
A
= 105°C
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
2.5007
2.5008
2.5009
2.501
2.5011
2.5012
2.5013
D001
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
I
ACTIVE
(mA)
TA (ƒC)
C011
±50
±40
±30
±20
±10
0
10
20
30
40
50
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Error (mV)
VSTACK (V)
C009
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
I
SLEEP
(A)
TA (ƒC)
C010
±30
±20
±10
0
10
20
30
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
Analog Die
Digital Die
C007
±90
±70
±50
±30
±10
10
30
±40 ±20
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Error (mV)
TA (ƒC)
16 V
80 V
C008
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Typical Characteristics (continued)
The following conditions apply: Typical Operating Circuit, VTOP = 60 V, 16 cells, TA= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
Figure 7. DIE Temperature Measurement Error
Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 8. Stack Measurement Error
Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 9. Stack Measurement Error Versus Stack Voltage Figure 10. SLEEP Current Versus Ambient Temperature
Figure 11. ACTIVE Current Versus Ambient Temperature
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Figure 12. ADC VREF Long Term Drift at 105°C
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
7 Detailed Description
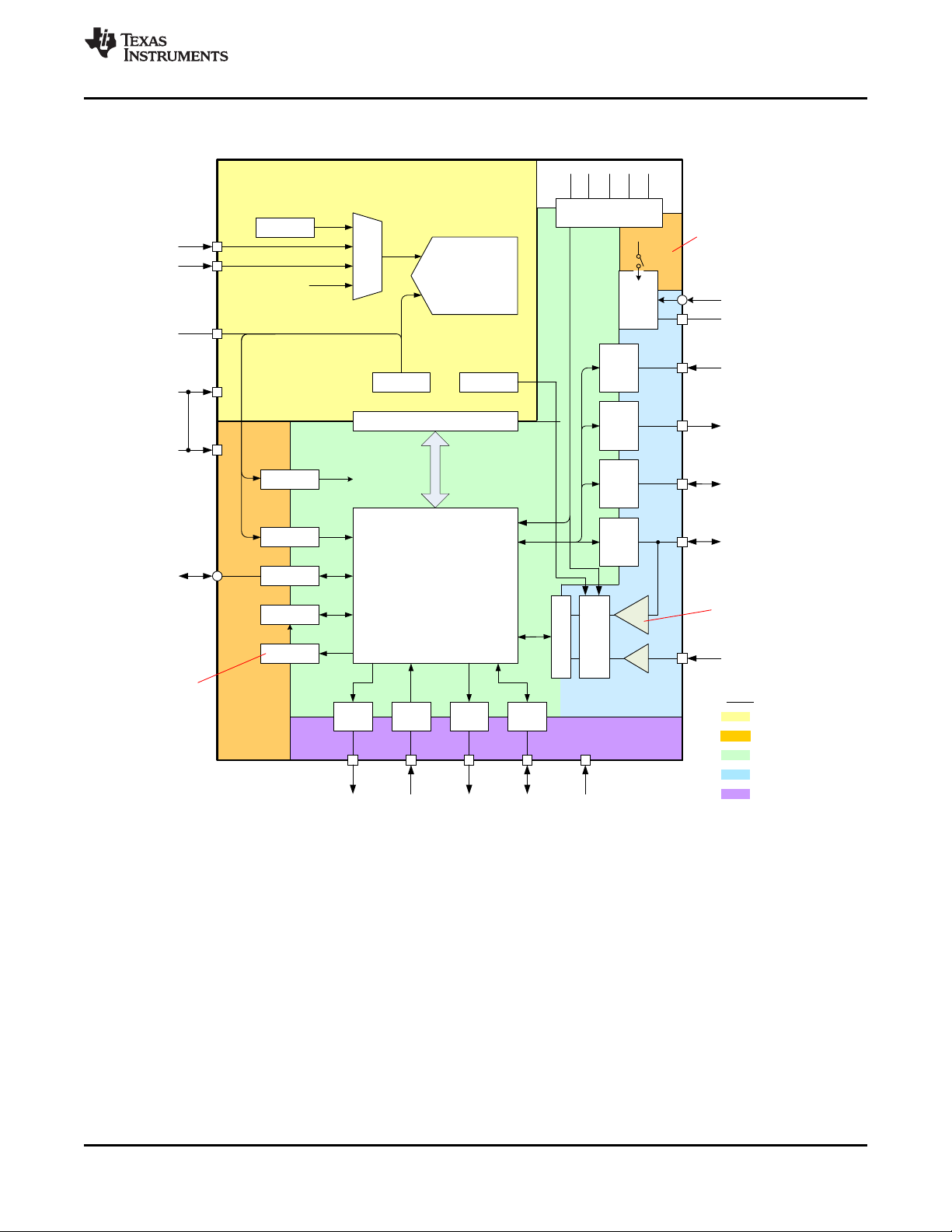
7.1 Overview
The bq76PL455A-Q1 is an integrated 16-cell monitor, protector, and cell balancer designed for high-reliability
automotive applications with many built-in self-diagnostic features.
Up to 16 bq76PL455A-Q1 devices can be connected in series using the high-speed differential communications
interface, which has been evaluated for compliance with Bulk Current Injection (BCI) standards. This capacitorisolated communications link provides effective common-mode noise rejection. The bq76PL455A-Q1
communicates with the host through a high-speed UART interface. The bq76PL455A-Q1 provides up to six
general-purpose, programmable, digital I/O ports, as well as eight AUX ADC inputs, typically used to monitor
externally supplied temperature sensors. Configuration of the digital I/O ports can be set to generate faults based
on conditions set in register GP_FLT_IN. Further configuration of these faults can be for an indication of a fault
on the FAULT_N output pin.
Designed for high-reliability automotive applications, the bq76PL455A-Q1 includes many functional blocks and
self-diagnostic test features covering defined single-fault conditions in analog and digital blocks. The host
microcontroller receives fault notifications through a separate communications path. The device contains userselectable self-test features to diagnose functional blocks within the device, such as automatic shutdown in the
event of overtemperature, calibration integrity, and so forth. The Safety Manual for bq76PL455A-Q1 (SLUUB67)
is available upon request for reference to aid the user in the evaluation of the built-in test features of the
bq76PL455A-Q1.
A provided built-in secondary protection block, with two dedicated programmable comparators per cell input,
separately senses and reports overvoltage and undervoltage conditions. The comparators utilize a second
separate testable internal band gap reference.
The bq76PL455A-Q1 provides pins for direct drive of external N-FETs for passive cell balancing with power
resistors. The balancing function configuration responds to on or off commands or specified to run for a specific
time.
The device is powered from the stack of cells to which it is connected and all required voltages are generated
internally.
18
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
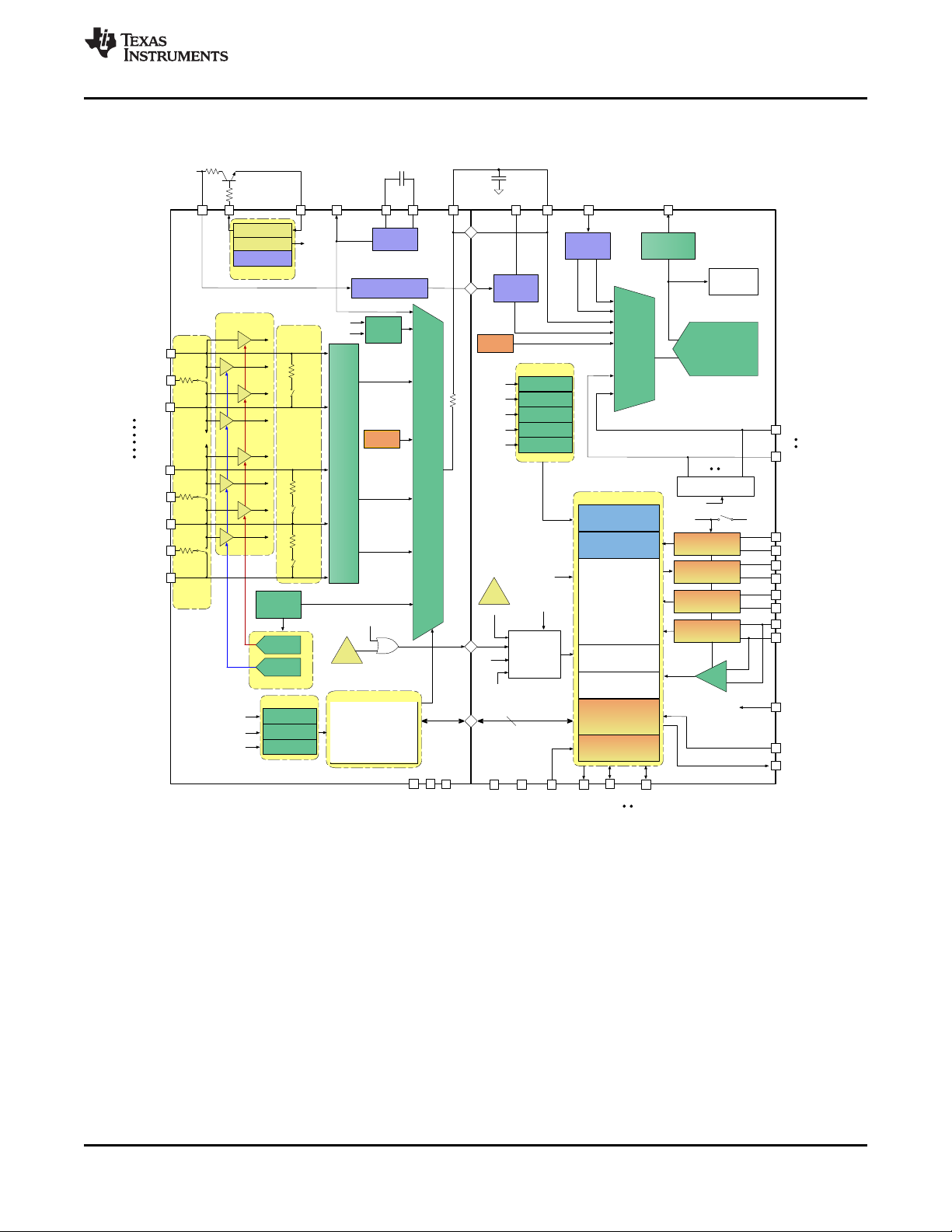
Registers
Control
Squeeze
Resistors
Threshold Set
NPN Regulator
EQ
Control
WinComp
VP
NPNB
TOP
V5VAO
VDIG
VM
CHM
CHP
OSC
MUX
OV DAC
UV DAC
10 V ALWAYS ON
4.5V
VREF
5.3 V REF
NPN PROTECT
VP CLAMP
1k
2.5V
VREF
OUT2
OUT1
LPF
RX
ADC
MUX
ADC
VREF
Registers
I/O
TSD
OV
UV
OV
UV
OV
UV
OV
UV
VDIG
VP
VIO
VDD18
V5VAO
ANALOG DIE DIGITAL DIE
VDD18
TX
TX / RX
TX / RX
V5VAO VDIG
Charge
Pump
VDIG
VP
VM
HIGHEST
CELL
EEPROM
VREG1.8
5 V
ALWAYS
ON
Comms
Interface
AUX0
AUX7
FAULTH-
FAULTH+
FAULTL-
FAULTL+
COMMH-
COMMH+
COMML-
COMML+
WAKEUP
RX
TX
POR
VP POR
V5VAO POR
1.8V POR
VIO POR
VDIG POR
POR
VP POR
VDIG POR
VM POR
GPIO5
GPIO0
FAULT_N
VIO
CGND
DGND
AGND2
AGND1
Temp
Sensor
AFE
VSENSE0
EQ1
VSENSE1
VSENSE2
EQ2
VSENSE15
EQ16
VSENSE16
Temp
Sensor
Checksum
Engine
EEC Decoder
AUX Pullup
AUXPUEN
Digital
Comparators
Stack
Monitor
AGND3
VTOP
AGND
NPN PROTECT
!
TSD
!
WAKE
WAKEUP
V5VAO
Wakeup
Control
Registers
Control
WAKEUP
WAKE
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Block Descriptions
7.3.1.1 Power
The bq76PL455A-Q1 operates from internally generated regulated voltages. The group of cells monitoring the
device is the source for the internal regulators. Power comes from the most-positive and most-negative pins of
the series-connected cells to minimize the likelihood of cell unbalancing. In most applications, the bq76PL455AQ1 operates using its internal supplies.
19
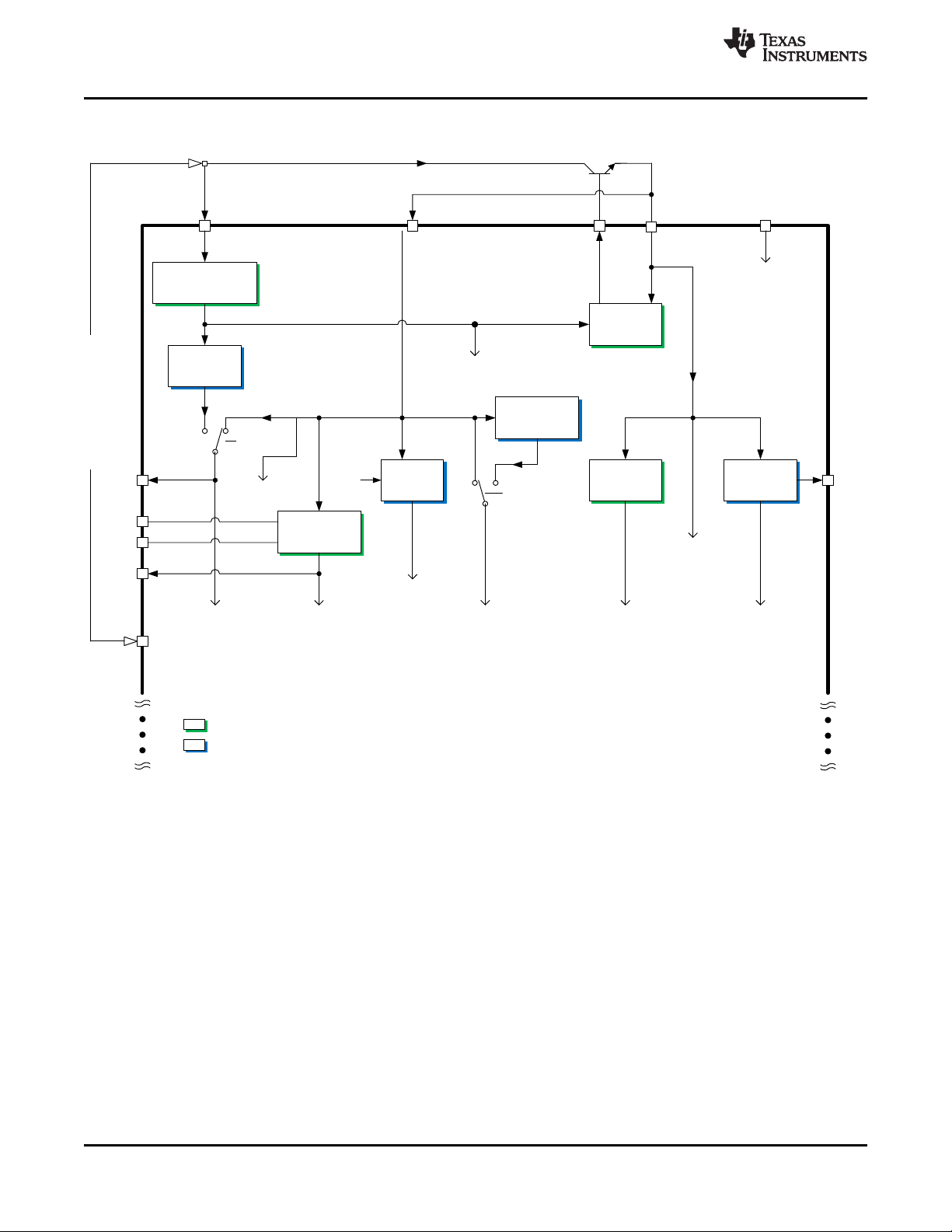
TOP
V10VAO
PRE-REGULATOR
V5VAO
LDO
4.5 V
REF2
VM
CHARGE PUMP
VP
REGULATOR
VP
NPNB
VDIG
2.5 V
VREF
1.8 V
LDO
OSC
ADC
1.8 V LDO
DIGITAL CORE
LOGIC
VIO
RX / TX
GPIO
FAULT_N
VDIG_OK
:,1'2:&203¶6
AFE
:,1'2:&203¶6
5.3 V VDIG RAIL
5.3 V VP RAIL
AFE
ADC
:,1'2:&203¶6
ANALOG DIE TSD
GND
PROGRAM
16 V EEPROM
CHARGE PUMP
EEPROM
(-) 8-16 CELL MODULE (+)
12 to 79.2 V
Partial diagram, some components omitted for clarity.
Inter-die connections not shown for clarity.
Refer to complete schematics (available from TI) for details.
WAKEUP CIRCUITS
VBUS DRIVERS
VBUS RECEIVERS
DIGITAL DIE TSD
OSC
CHP
CHM
VM
- ANALOG DIE
- DIGITAL DIE
DIGITAL DIE TSD
OSC
V5VAO VREFVREF
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Feature Description (continued)
www.ti.com
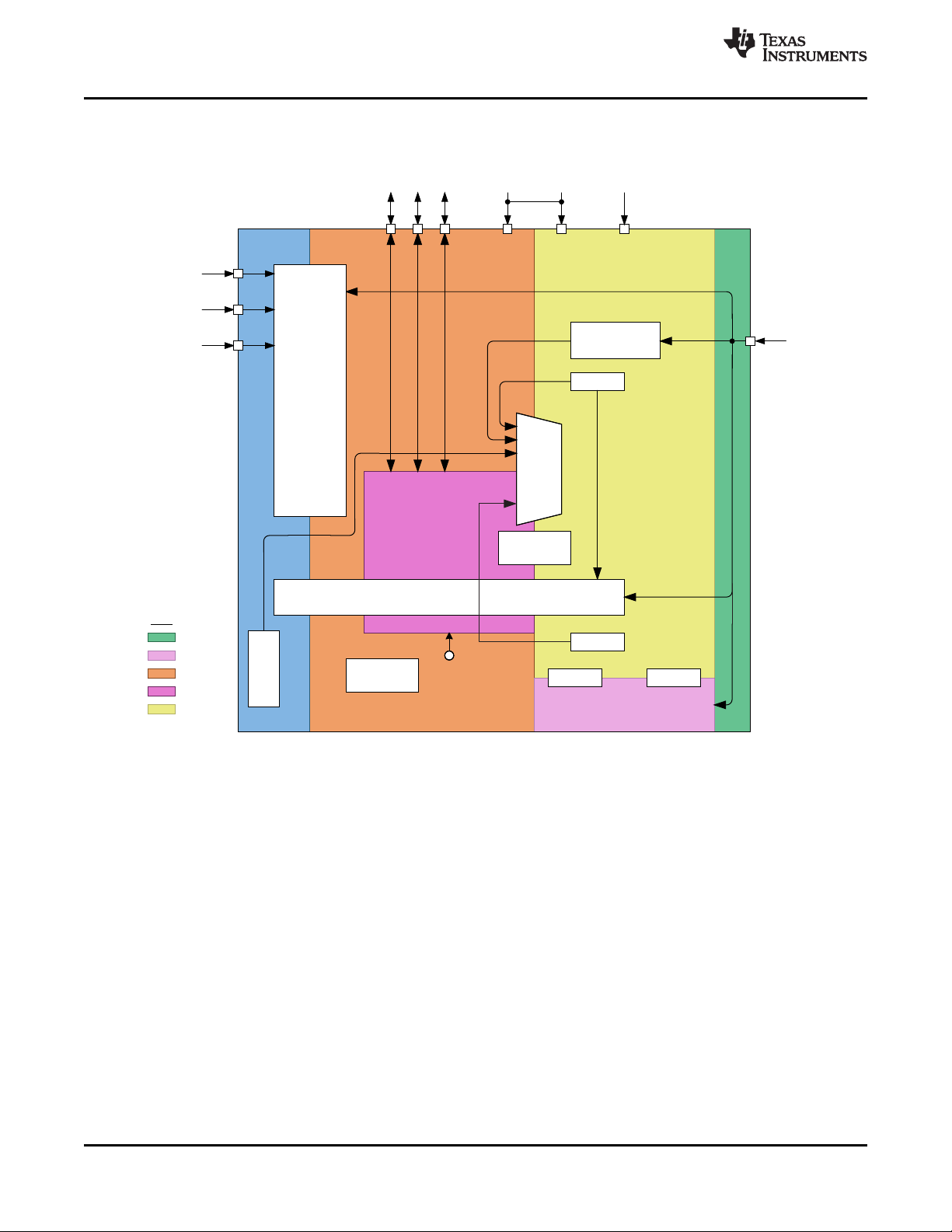
Figure 13. Power Flow Diagram
20
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
VP Power Domain
VDD18
Power Domain
VDIG
Power
Domain
V5VAO
Power Domain
VIO Power Domain
FAULTH
COMMH
FAULTL
COMML
WAKEUP
TX/
RX
TX/
RX
TX/
RX
TX/
RX
LPR
Level Shifters
GPIOI/OI/OI/O
GPIO[0..5]
FAULT_N
RX
TX
VIO
+10 V (from ANALOG die)
V5VAO (bypass cap)
VDIG
POR
VP
VDIG
V5VAO
VIO
VDD18
V5VAO
LDO
Digital Control Logic
1.8 V LDO
OSC
I/O
HVGEN
EEPROM
ANALOG die I/O
VDD18
VDIG
VP
Level Shifters
VREF TSD
TSENSE
MUX
ADC
AUX[0..7]
OUT2
VDD18
VREF
(bypass cap)
VP
VDIG
VDD18
V5VAO
VIO
KEY:
EEPROM
Programming
Voltage
Low-Power
Receiver
Power-Up
Control
V5VAO
POR OK
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
Feature Description (continued)
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Figure 14. Digital Die Power Domains
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
21
TOP
VP
VDIG
V10VAO
KEY:
VP Power Domain
VDIG Power Domain
VM
Power Domain
VM Monitor
REF2
TOP
V10VAO
Power Domain
VM
VSENSEn
VSENSEn-1
VP
VDIG
CELLS 1-16
CHM
CHP
VM
Window Comparators
VDIG
NPNB
VSENSE ...
TOP
TSDLDO
TSENSE
Balancing
Control
Circuits
Control
Registers
Cell
AFE/
Mux
V
Measurement
MODULE
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Feature Description (continued)
www.ti.com
Figure 15. Analog Die Power Domains
7.3.1.1.1 TOP Pin Connection
The bq76PL455A-Q1 has a connection from the top of the cell-module battery stack to the TOP pin, typically
through an external-series resistor and capacitor to GND forming a low-pass filter. The low-pass filter design
typically has a similar time constant to the VSENSE input pins. The minimum recommended values are 100 Ω
and 0.1 µF. See the Application and Implementation section for details.
7.3.1.1.2 V10VAO
V10VAO is an internal-only, always on, pre-regulator supplied from the TOP pin. It supplies the power to the
V5VAO block, Analog Die TSD block, and VP control and regulator circuits. It is not externally accessible.
7.3.1.1.3 V5VAO
V5VAO is the always-on power supply that ensures power is supplied to the differential communications circuits
(COMML+/–) and the WAKEUP input at all times. This ensures that the IC always detects the WAKEUP signal
and the differential communications receive the WAKE tone. The V5VAO is supplied by a combination of an
internal regulator and the VDIG supply. If VDIG falls below the normal operating voltage (during startup), the
internal regulator supplies V5VAO. Once VDIG reaches regulation, V5VAO is supplied directly from VDIG.
22
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1

bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
Feature Description (continued)
NOTE
V5VAO can only supply enough power to meet internal IC requirements; it should not
connect to external circuitry.
7.3.1.1.4 VP Regulated Output
The bq76PL455A-Q1 power comes directly from the cells to which it is connected. Current draw is from the top
and bottom of the n-cell battery assembly, so that current through each cell is the same. An integrated linear
regulator utilizes an external NPN transistor (Zetex ZXTN4004K or similar) to generate a nominal 5.3-V rail on
pin VP. VP is both a power input and the sense node for this supply. The NPNB pin controls the external NPN
transistor of the regulator. A capacitor or resistor-capacitor combination must connect externally from VP to GND,
see Pin Configuration and Functions for details. VP must connect externally to VDIG and can optionally connect
to VIO. Both of these connections are through series 1-Ω resistors and separately decoupled. This regulator is
OFF in SHUTDOWN mode.
Table 1. Recommended NPN Transistor Characteristics
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION TEST CONDITION TYPICAL VALUE UNIT
BV
CEO
Beta β Gain at 5 mA > 100
C
CB
P
IC Collector current rating > 100 mA
(1) Choose this value with respect to the locally supplied maximum-cell voltage and derate appropriately for operating conditions and
temperature.
(2) Derate this value appropriately for operating conditions and temperature.
Collector-Emitter voltage
Collector-Base capacitance ≤ 35 pF
Power handling
Add a collector resistor between the NPN collector and the TOP pin to reduce power dissipation in the NPN
under normal and system fault conditions. The value of this resistor is chosen based on the minimum batterystack voltage, the bq76PL455A-Q1 VP/VDIG total load current, and the load current of any external I/O circuitry
powered directly or indirectly by VP/VDIG. Also, the recommendation is to add a 1-µF decoupling capacitor
directly from the collector to AGND.
(1)
(2)
See the following text for
collector resistor details.
100 V
500 mW
7.3.1.1.5 VDIG Power Input
VDIG is the digital voltage supply input. Always connect it to the VP pin, which normally receives power from the
NPN. Optionally, an external supply may drive VDIG, but still must be connected to VP. This applies in all
operating modes. The VDIG source is from VP through a 1-Ω resistor. Decouple VDIG with a separate capacitor
at the pin.
7.3.1.1.6 VDD18 Regulator
A provided internal regulator generates a 1.8-V digital supply for internal device use only. The 1.8-V supply does
not require an external capacitor, and there is no pin or external connection. Faults on VDD18 that cause the
voltage to drop below its regulation may cause UART communication errors. If the fault is caused by LDO_TEST,
reset or shutdown/wakeup the device to regain functionality.
7.3.1.1.7 VIO Power Input
VIO is the voltage supply input used to power the digital I/O pins TX, RX, FAULT_N, and GPIOn. VIO may
connect to an externally regulated-supply rail, which is common to an I/O device such as a microcontroller.
Alternately, the source for VIO may be from VP through a 1-Ω resistor. Decouple VIO with a separate capacitor
at the pin.
If VIO does not have power, the part holds in reset and enters shutdown after a short delay. This gives a very
good reset mechanism for non-stacked systems. Upon power up from a SHUTDOWN, the
SHDN_STS[GTSD_PD_STAT] bit will be set. This flag bit is the logical <OR> of this condition or triggering the
thermal shutdown of the digital die in a die overtemperature situation.
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
23

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
7.3.1.1.8 VM Charge Pump
www.ti.com
The included internal-charge pump is for biasing the Analog Front End (AFE) and other analog circuits. It
requires an external flying capacitor connected between the CHP and CHM pins plus a storage capacitor on pin
VM to generate a rail of –5 V for internal use. The charge pump (VM) is always on in IDLE and off in
SHUTDOWN. VM requires the oscillator to be running and stable and does not start until the other supplies are
above their POR thresholds. The VM charge pump will start ramping at the start of the WAKEUP tone on COMH.
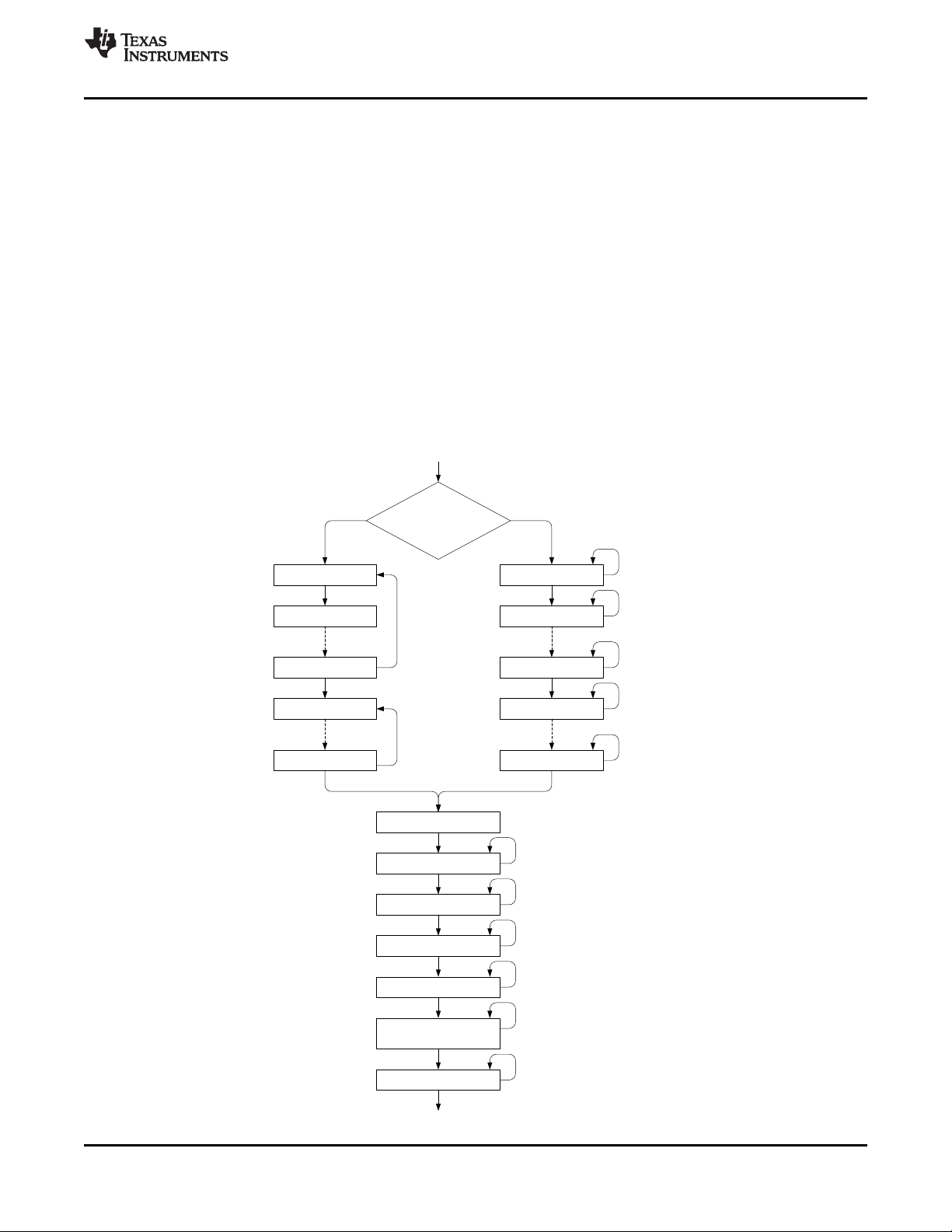
7.3.2 Analog Front End (AFE)/Level Shifter
The bq76PL455A-Q1 AFE allows monitoring of up to 16 cells. Provided for this purpose are seventeen VSENSE
inputs, labeled VSENSE0 through VSENSE16. The programming for bq76PL455A-Q1 can be set to sample all,
or a subset, of the connected cells. Sampling always begins at the highest-selected cell and finishes with the
lowest-selected cell. During measurement, the AFE selects the cell addressed by the logic block and level-shift
the sensed cell voltage with a gain of 1 down to the ground-referred OUT1 pin. The output of the AFE (OUT1)
has a See section '' for component selection.
The analog output of the AFE connects to OUT1 through an internal 1.2-kΩ series resistor. Connect OUT1
externally to OUT2. At this external connection between the AFE and the ADC, the requirement is to place an
external filter capacitor to form an RC filter to reduce noise bandwidth. A filter capacitor will increase the settling
time of the signal presented to the ADC input. A trade-off can be made between ADC sample time, filtering, and
accuracy. The AFE output must settle to within < 1/4 of the ADC LSB for best measurement accuracy.
7.3.3 ADC
The ADC in the bq76PL455A-Q1 is a 14-bit Successive Approximation Register (SAR) ADC. It has a fixed
conversion (hold) time of 3.44 µs, with a user-selectable sample interval or period between conversions. The
user-selectable sample interval determines the acquisition (tracking) settling time between conversions, used
mostly to allow the input capacitor on OUT1 to settle between conversions, and to allow for internal settling.
The ADC input mux on the digital die allows it to connect to the following:
• The AFE (analog die) mux output on OUT1 which measures:
– Up to 16 cell voltage channels
– The V
MODULE
voltage
– The internal temperature of the analog die
– The REF2 analog die reference
– The VM (–5V) charge pump generated voltage supply on the analog die
• Measurement channels on the digital die:
– The 8 AUX input channels
– The VDD18 1.8-V voltage supply on the digital die
– The internal temperature of the digital die
The ADC can be set up to take single samples or multiple samples in one of two averaging modes. This
selection is made using OVERSMPL[CMD_OVS_CYCLE].
7.3.3.1 Channel Selection Registers
Program channels for measurement by setting bits in the CHANNELS and NCHAN registers. Each channel can
be set up for measurement individually. User programmable correction factors are available for cell and AUX
channels. Conversion times are individually user programmable for different types of inputs (that is, cells, AUX,
and internal measurements).
The NCHAN register sets the number of VSENSE channels (cell inputs) for use by the device. Unused channels
are dropped consecutively starting from channel 16. Set this register for the number of cells used, that is, for 14
cells, program 0x0E. This register also sets mask cell overvoltage and undervoltage faults for unused channels,
and turns off the UV and OV comparators associated with the channel. The idle channel (the channel the mux
rests on between sample intervals) is set to the value in this register. This allows the OUT1 pin to hold the filter
capacitor at the voltage, which will be sampled first on the next cycle.
24
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
CMD_OVS_CYCLE = ?
VSENSE16
VSENSE15
VSENSE1
AUX7
AUX0
1 0
Averaging?
Averaging?
Digital Die Temperature
Analog Die Temperature
Digital Die VDD18
Analog Die REF2 GND
Analog Die V
MODULE
(2 samples averaged per iteration)
Analog Die VM
VSENSE16
VSENSE15
VSENSE1
AUX7
AUX0
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging?
Averaging is not available
for this node
Analog Die REF2
Averaging?
bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
7.3.3.2 Averaging
The oversampling for the ADC average measurements is programmable to 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 times. Individual
samples are arithmetically averaged by the bq76PL455A-Q1, which then outputs a single 16-bit (14 bits + 2
additional bits created by the averaging process) average measurement. The individual samples used to create
the average value are not available.
As shown in Figure 16, the ADC averages any selected cell voltages first, then any selected AUX input channels,
and then any remaining channels selected in the CHANNELS register in the order listed. Depending on the state
of the CMD_OVS_CYCLE bit in the OVERSMPL register, oversampling of the Voltage and AUX channels follows
one of the following procedures:
• Sampling each channel once and cycling through all channels before oversampling again in the case of
CMD_OVS_CYCLE = 1 (cycled averaging) OR
• Sampling multiple times on a single channel before changing channel in the case of CMD_OVS_CYCLE = 0
(non-cycled averaging).
Figure 16 shows these on the left and right, respectively.
When oversampling, Table 2 shows the oversample periods for each channel after the first sample. The first
sample can have a different period programmed (see Table 2), followed by all subsequent samples at different
period shown in Table 3. The first sample and subsequent sample periods are separate of each other.
Figure 16. Sampling/Oversampling (Averaging) Sequence
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
25
bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
Table 2. Channel Sample Period Settings
CHANNEL FIRST SAMPLE
VSENSEn (n=1..16) ADC_PERIOD_VOL CMD_OVS_HPER ADC_PERIOD_VOL
AUXn (n=0..7) ADC_PERIOD_AUXn CMD_OVS_GPER ADC_PERIOD_AUXn
DIGITAL DIE TEMP
ANALOG DIE TEMP ADC_PERIOD_TEMP CMD_OVS_HPER CMD_OVS_HPER
VDD18 Approximately 30 µs CMD_OVS_GPER CMD_OVS_GPER
ANALOG DIE VREF ADC_PERIOD_REF CMD_OVS_HPER CMD_OVS_HPER
MODULE MONITOR
VM ADC_PERIOD_VM CMD_OVS_HPER CMD_OVS_HPER
(1) Oversampling (averaging) is not available for this measurement.
(2) TSTCONFIG[MODULE_MON_EN] determines whether 2 conversions or 1 conversion takes place.
(1)
(2)
Approximately 50 µs n/a n/a
ADC_PERIOD_MON CMD_OVS_HPER CMD_OVS_HPER
CMD_OVS_CYCLE=0 CMD_OVS_CYCLE=1
OTHER SAMPLES (AVERAGING)
The ADC_PERIOD_VOL bits set the period between ADC samples for the indicated channels whether
oversampling or not. When CMD_OVS_CYCLE = 1, the oversampling period of the Cell and AUX channels
remains fixed at the single sample period of CELL_SPER[ADC_PERIOD_VOL] and
AUX_SPER[ADC_PERIOD_AUX], respectively. Otherwise, if CMD_OVS_CYCLE = 0, then the oversample
period for the Cell channels is set by bits CMD_OVS_HPER and for the AUX channels is CMD_OVS_GPER.
CMD_OVS_HPER must be programmed to 12.6 µs and CMD_OVS_GPER can be programmed between 4.13
µs and 12.6 µs in the OVERSMPL register.
After the initial sample period performed per a single sample, oversampling on all other channels are at the
CMD_OVS_GPER and CMD_OVS_HPER period settings as indicated in Table 2.
Writing to the CMD register is used to start the voltage sampling process. This is usually done with a
BROADCAST Write_With_Response_Command sent to the CMD register. Using the BROADCAST version of
the synchronously sample channels command will result in all devices in the stack sampling at the same time.
That is, all devices begin sampling their respective cells, then AUX, and so on, simultaneously.
7.3.3.3 Recommended Sample Periods
Refer to Table 3 for initial recommended settings. Other settings are possible; see the Application and
Implementation section for additional information.
Table 3. ADC Recommended Sample Periods and Setup
MEASURED
PARAMETER
VCELL 60 µs 12.6 µs CELL_SPER 0xBC
VAUX 12.6 µs 12.6 µs AUX_SPER 0x44444444
VMODULE 1000 µs 12.6 µs TEST_SPER 0xF999
Die Temp (ANL) 100 µs 12.6 µs CELL_SPER 0xBC
Die Temp (DIG) 50 µs
VM 30 µs 12.6 µs TEST_SPER 0xF999
VDD18 30 µs 12.6 µs N/A N/A
REF2 30 µs 12.6 µs TEST_SPER 0xF999
(1) Sampling periods and averaging mode will affect device accuracy. Device accuracy and register settings (including the sampling period)
used to achieve stated device accuracy are specified under "Electrical Characteristics, ADC" in Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC):
Analog Front End. Other settings are possible. Device accuracy is not assured at settings other than those specified in the Electrical
Characteristics tables.
(2) Other register settings used: OVERSMPL = 0x7B; PWRCONFIG = 0x80
(3) This is not a programmable parameter. No averaging is performed, but there is an inherent delay in the design for the ADC
measurement of the die temperature.
1stSAMPLE SAMPLES 2–8 NAME AS SHIPPED
PERIOD
(3)
(1)
N/A N/A N/A
PERIOD REGISTER
(2)
26
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1

bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
7.3.3.4 VSENSE Input Channels
The VSENSE input channels measure the voltages of individual cells in the range of 1 V-to-4.95 V. Each input
should connect to an external low-pass filter (LPF) to reduce noise at the input, and a Zener diode to provide
protection to the device during random hot-plug cell connection. Typical values for the LPF range from 100 Ω to
1 kΩ, and 0.1 µF to 1 µF. Values outside this range may degrade accuracy due to system-level noise or from
excessive IR loss in the series resistor.
Tie up unused inputs to the highest-connected cell. For example, in a 14-cell system, tied to VSENSE14 are
unused inputs VSENSE15 and VSENSE16. Channels are used from lowest to highest, with VSENSE0
connected to the (–) terminal of the bottom cell.
The values returned from an ADC conversion for these channels convert to volts by:
V
= [(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE (1)
CELL
A number of factors affect total channel measurement accuracy, including, but not limited to, variations due to IR
reflow, board-level stresses, any current leakage in external components, and the method of sampling. It is highly
recommended that the end user perform GAIN and OFFSET calibration as described in the Application and
Implementation section.
7.3.3.5 AUXn Input Channels
The AUXn input channels are used to measure external analog voltages from approximately 0 V to 5 V. A typical
use for these channels is to measure temperature using thermistors. These channels require a simple external
low-pass filter to reduce high frequency noise for best operation. The RC values correspond to the user's
application requirements.
The values returned from an ADC conversion for these channels convert to volts by:
V
= [(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE (2)
AUX
7.3.3.6 V
V
MODULE
MODULE
is the voltage measured from the TOP pin to GND. The value scales by 25 with an internal resistor
Measurement Result Conversion to Voltage
voltage divider. Setting TSTCONFIG[MODULE_MON_EN] enables measuring of VMODULE voltage. Enable or
disable the measurement to aid with self-testing. When set to 0, the channel should measure close to 0 V.
The values returned from an ADC conversion for this channel converts to volts by:
V
= ([(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE) × 25 (3)
MODULE
7.3.3.7 Digital Die Temperature Measurement
The temperature of the digital die may be measured as a part of the normal ADC measurement sequence by
setting bit CHANNELS[CMD_TSEL]. The reported result is the voltage from the temperature sensor, not the
actual temperature.
No averaging is ever performed on this channel, but the timing will appear as if the requested oversampling was
performed.
FAULT_SYS[INT_TEMP_FAULT] is continuously updated based on the currently stored measurement result and
threshold. To allow clearing of the fault, sample the temperature within a normal operating range.
Conversion formula:
Internal Digital Die Temperature °C = (V
7.3.3.7.1 Automatic Temperature Sampling
– 2.287) × 131.944 (4)
ADC
After initialization is complete, an internal timer will cause the digital-die temperature sensor sampling to be
scheduled once per second. No oversampling is performed. If a command or an auto-monitor cycle occurs that
samples the digital die temperature sensor, the timer resets. A command will interrupt an automatic temperature
sample, but if the command does not sample the digital die temperature, the automatic temperature sample will
occur as soon as the command completes. This can cause sample values to appear to change without a sample
request.
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
27

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
7.3.3.8 Analog Die Temperature Measurement
The temperature measurement of the analog die is programmable as part of the normal ADC measurement
sequence by setting bit CHANNELS[CMD_HTSEL]. The reported result is the voltage from the temperature
sensor, not the actual temperature.
There is no internal threshold checking for this value. For self-testing purposes, the expectation is that the
microcontroller compares this value with the converted temperature from the digital die and decides if they are
reporting the same temperature. The analog die temperature measurement is more accurate than the digital-die
temperature measurement. Therefore, the digital die temperature measurement should be considered only a
rough estimation of the temperature measured by the analog die temperature monitor. The host firmware must
account for any offset between the two measurements.
Conversion formula:
Internal Analog Die Temperature °C = (V
– 1.8078) × 147.514
ADC
where
• V
=[(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE (5)
ADC
7.3.3.9 VM Measurement Result Conversion to Voltage
There is no internal threshold checking of this value. The expectation is that the microcontroller checks that the
value is within the appropriate range.
The value returned from an ADC conversion for this channel converts to volts by:
VVM = –2 × [(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE (6)
7.3.3.10 V5VAO, VDIG, VDD18 Measurement Result Conversion to Voltage
The value returned from an ADC conversion for these channels converts to volts by:
V
= [(2 × VREF) / 65535] × READ_ADC_VALUE (7)
ADC
There is no internal threshold checking of these values. The expectation is that the microcontroller checks that
the values are within the appropriate ranges.
7.3.3.11 Auto-Monitor
Auto-monitor periodically samples a user-defined set of channels in the AM_CHAN register. The conversion
results do not automatically transmit on the communications channel, but are available to be read by the microcontroller. Auto-monitor senses non-masked fault conditions automatically without sending convert commands.
When Auto-monitor is running, the part is fully powered and awake in the IDLE state. Auto-monitor does not
affect operation of the secondary protection comparators.
Fault detection is fully functional and operates in the same manner as when Auto-monitor mode is not enabled.
NOTE
Always disable the Auto-monitor function before initiating any new action such as
requesting ADC samples, running checksum test, and so forth.
When enabled, Auto-monitor sets the STATUS[AUTO_MON_RUN] bit during the ADC conversion only.
Start the Auto-monitor function by setting AM_PER[AUTO_MON_PER] to a non-zero value. Setting the
STATUS[AUTO_MON_RUN] bit also restarts the Auto-monitor function when AM_PER[AUTO_MON_PER] is
non-zero. This can synchronize the Auto-monitor function measurement cycles to system operations and/or
between ICs in the stack.
28
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1

bq76PL455A-Q1
www.ti.com
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
7.3.4 Thermal Shutdown
Thermal shutdown occurs when either one or both of the Thermal Shutdown (TSD) sensors on either die sense
an overtemperature condition. The sensors operate separately without interaction and are separate from the
analog and digital die sensors. Each has a separate register-status indicator flag. When a TSD fault occurs, the
part immediately enters the SHUTDOWN state. To awake the part, follow the normal WAKEUP procedure. The
bq76PL455A-Q1 does not exit SHUTDOWN automatically. It cannot be awakened until the temperature falls
below the TSD threshold. Upon waking up, either SHDN_STS[GTSD_PD_STAT] or
(SHDN_STS[ANALOG_PD_STAT]&& SHDN_STS[HTSD_PD_STAT]) bits will be set.
7.3.5 Voltage Reference (ADC)
The VREF pin receives a precise internal voltage reference for the ADC. Two parallel X7R or better filter
capacitors between pins VREF and AGND are required for the reference; see Application and Implementation for
recommended values and PCB layout considerations.
7.3.6 Voltage Reference (REF2)
The window comparators have a 4.5-V internal voltage reference provided. It does not go out to an external pin.
To check the reference, select it with the CHANNELS[CMD_REFSEL] bit.
7.3.7 Passive Balancing
Sixteen internal drivers control individual cell balancing through the pins labeled EQ1…EQ16. When the device
issues a balance command through register CBENBL, the bq76PL455A-Q1 asserts the EQ(N) output, switches
to the VSENSE(N) rail and turns on Q
VSENSEn–1 rail, turns off Q
, and reduces the balancing current to zero. The squeeze (OWD) function must
BAL
. With a de-asserted register bit, the EQn bit switches to the
BAL
be disabled for correct balancing operation by setting TSTCONFIG[EQ_SQUEEZE_EN] = 0.
If CBCONFIG[BAL_CONTINUE] is set to '0', then when there is a FAULT the bq76PL455A-Q1 disables
balancing. The CBENBL register bits clear to indicate this event. However, there is one exception. The USER
checksum fault indicated by FALUT_DEV[USER_CKSUM_FLT] does not disable balancing. The following
describes the scenarios:
• BAL_CONTINUE = 0: CBENBL is set to 0 and balancing is disabled until the fault and fault status bits are
cleared. Information about what was being balanced is discarded. No change is made to the BAL_TIME bits
in CBCONFIG. The CBENBL register must then be rewritten with the desired balancing action.
• BAL_CONTINUE = 1: There is no effect on CBENBL and CBCONFIG and any balancing in progress
continues.
Changing the CBENBL register will create a checksum fault and cause FAULT_DEV[USER_CKSUM_ERR] to be
set. This may be a result of setting bits to enable balancing for cells, or the register being reset, because of a
fault or CBTIME expiring.
The internal balancing control circuitry only powers up when any bit in CBENBL is set. See Passive Cell
Balancing Circuit section for details on selecting the external passive balancing components.
7.3.8 General Purpose Input-Outputs (GPIO)
There are six GPIO pins available in the bq76PL455A-Q1. Registers GPIO_xxx, located at addresses 0x78–7D,
control GPIO behavior. Each can be programmed to be an input or output pin.
Each GPIO pin can have an internal pull-up or pull-down resistor enabled to keep the pin in a known state when
power is not on for external circuitry. Configuration for pull-up or pull-down resistors is in the GPIO_PU and
GPIO_PD registers. The pull-up/down resistors have internal connections to supply VIO. The resistor values are
in the Digital Input/Output: Wakeup section of the Electrical Characteristics tables.
The GPIOs can also trigger a FAULT condition. Programmed GPIOs trigger a FAULT indication by setting bits in
register GPIO_FLT_IN.
The FAULT_GPI register and the DEVCONFIG[UNLATCHED_FAULT] bit controls the behavior of the device in
response to a FAULT triggered by an enabled GPIO pin. The usual pin configuration is to be an input in the
GPIO_DIR register when used to trigger faults.
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
29

bq76PL455A-Q1
SLUSC51C –APRIL 2015–REVISED NOVEMBER 2016
www.ti.com
7.3.9 UART Interface to Host Microcontroller
The UART follows the standard serial protocol of 8-N-1, where it sends information as a START bit, followed by
eight data bits, and then followed by one STOP bit. In all, 10 bits comprise a character time. Received data bits
are oversampled by 16 times to improve communication reliability.
The UART sends data on the TX pin and receives data on the RX pin. When the transmitter is idling (not sending
data), TX = 1. The RX input pin idles in the same state, RX = 1. Hold the RX line high using a pull-up to VIO, if
not used (that is, non-base device in the daisy chain). Do not allow the RX pin to float when VIO is present.
7.3.9.1 UART Transmitter
The transmitter can be configured to wait a specified amount of time after the last bit reception and start of
transmission using the TX_HOLDOFF register. The TX_HOLDOFF register specifies the number of bit periods
that the bq76PL455A-Q1 will wait to allow time for the microcontroller to switch the bus direction at the end of its
transmission.
7.3.9.2 UART Receiver
The UART interface design works in half-duplex. As a result, while the device is transmitting data on the TX pin,
it ignores RX. To avoid collisions when sending data up the daisy-chain interface, the host microcontroller should
wait until it receives all bytes of a transmission from the device to the microcontroller before attempting to send
data or commands up the daisy-chain interface. If the microcontroller starts a transaction without waiting to
receive the preceding transaction's response, the communication might hang up and the microcontroller may
need to send Communication Clear (see Communication Clear (Break) Detection) or Communication Reset (see
Communication Reset Detection) to restore normal communications.
7.3.9.3 Baud Rate Selection
The baud rate of the communications channel to the microcontroller is set in the COMCONFIG[BAUD] register
for 125k-250k-500k-1M baud rates. The default rate after a communications reset is 250k. The default rate after
a POR is the rate selected by the value stored in EEPROM for the COMCONFIG[BAUD] register.
When the value in this register changes, the new rate takes effect after the complete reception of a valid packet
containing the new setting including the CRC. This should send the next packet at the new baud rate and all
packets transmitted by the device will be at the new rate. It is possible to change the baud rate at any time and,
optionally, store the new baud rate in the EEPROM as a new POR default. After changing the baud rate, observe
a minimum wait period of 10 µs before sending the first packet at the new baud rate.
The value in the COMCONFIG[BAUD] register only affects the baud rate used in microcontroller communications
on the TX and RX pins. The daisy-chain vertical communication bus rate is at a higher fixed rate and not user
modifiable. All devices in the stack must have the same baud rate setting as the base device to read data from
stacked devices.
7.3.9.4 Communication Clear (Break) Detection
Use communications clear to reset the receiver to re-synchronize looking for the start of frame.
The receiver continuously monitors the RX line for a break (<BRK>) condition. A <BRK> is detected when the
RX line is held low for at least t
than t
COMM_BREAKmax
bit periods may result in recognition of a communication reset instead of the intended
COMM_BREAKmin
bit periods (approximately 1 character times). Sending for more
communication clear. When detected, a <BRK> will set the STATUS[COMM_CLEAR] flag.
7.3.9.5 Communication Reset Detection
Detection of a communication reset occurs when the RX line is held low for more than approximately
t
COMM_RESETmin
. The primary purpose of sending a communications reset is to recover the device in the event the
baud rate is inadvertently changed or unknown. The baud rate resets unconditionally to the FACTORY default
value of 250 kb/s, REGARDLESS of the value stored in the EEPROM COMCONFIG register. This sets the baud
rate to a known, fixed rate (250k baud), and the STATUS[COMM_RESET] flag.
30
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2015–2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq76PL455A-Q1
 Loading...
Loading...