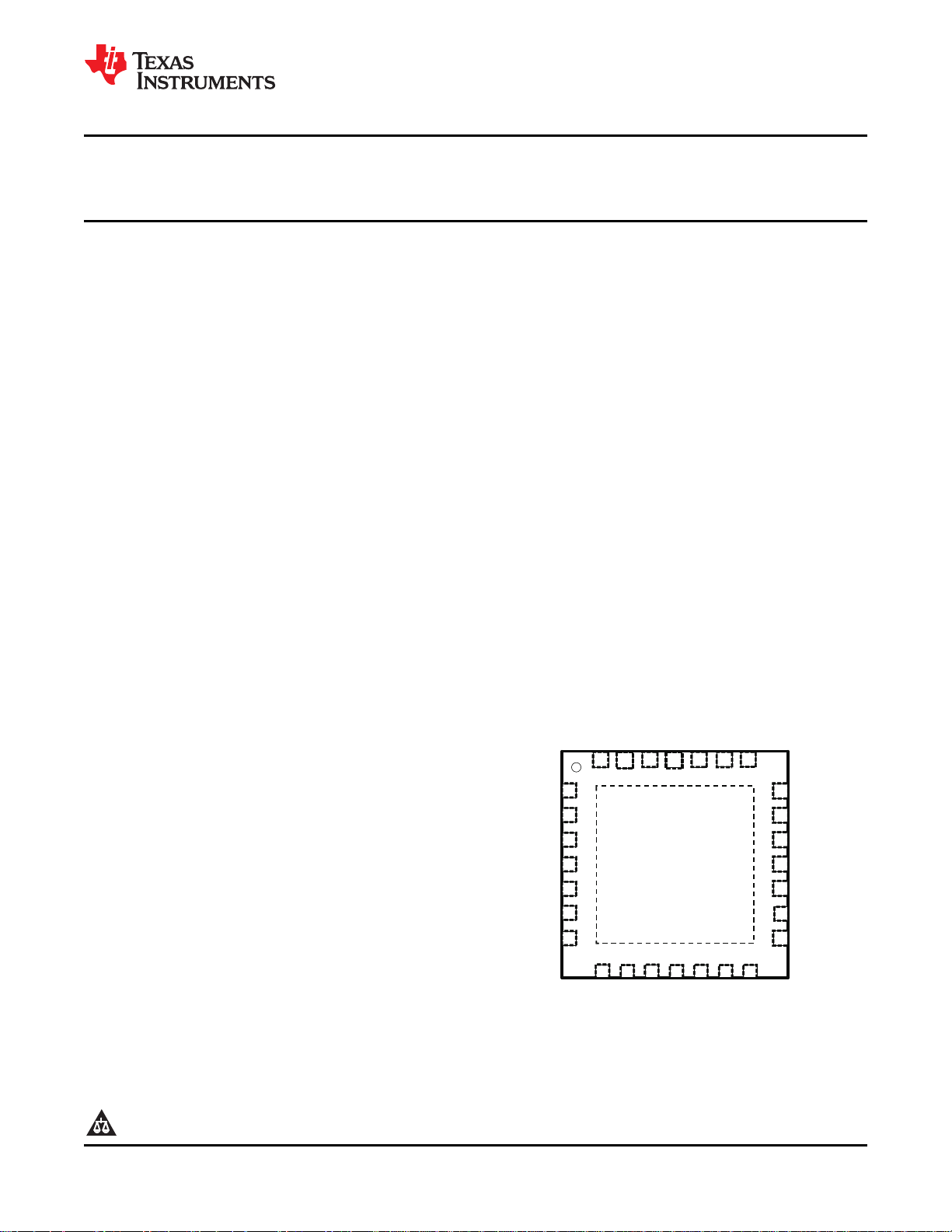
EAO
ICREF
EAI
FBO
CE
VDDP
LGATE
PGND
CSOP
CSON
bq24745
28LDQFN
TOP VIEW
ACIN
VREF
NC
VFB
1
28
7
21
15
22
2
3
4
5
6
20
19
18
17
16
27 26 25 24
8 149 10 11 12 13
23
VICM
SDA
SCL
VDDSMB
GND
ACOK
NC
CSSP
CSSN
ICOUT
BOOT
UGAT
PHAS
DCIN
www.ti.com
SMBus-Controlled Multi-Chemistry Battery Charger With Input
Current Detect Comparator and Charge Enable Pin
1
FEATURES
• NMOS-NMOS Synchronous Buck Converter
with 300-kHz Frequency and >95% Efficiency
• 30-ns Minimum Driver Dead-Time and 99.5%
Maximum Effective Duty Cycle
• High-Accuracy Voltage and Current Regulation
– ±0.5% Charge Voltage Accuracy
– ±3% Charge Current Accuracy
– ±3% Adapter Current Accuracy
– ±2% Input Current Sense Amp Accuracy
• Integration
– Input Current Comparator, With Adjustable
Threshold and Hysteresis
– Internal Soft-Start
• Safety
– Dynamic Power Management (DPM)
• Up to 19.2-V Battery Voltage
• 7-V–24-V AC/DC-Adapter Operating Range
• Simplified SMBus Control Interface
– Charge Voltage DAC (1.024 V–19.2 V)
– Charge Current DAC (128 mA–8.064 A)
– Adapter Current Limit DPM DAC (256
mA–11.008 A)
• Status and Monitoring Outputs
– AC/DC Adapter Present With Adjustable
Voltage Threshold
– Input Current Comparator With Adjustable
Threshold and Hysteresis
– Current Sense Amplifier for Current Drawn
From Input Source
• Charge Any Battery Chemistry: Li+, NiCd,
NiMH, Lead Acid, Etc.
• Charge Enable Pin
• < 10-μA Battery Current With Adapter
Removed
1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Check for Samples: bq24745
• < 1-mA Input DCIN Current With Adapter
Present and Charge Disabled
• 28-Pin, 5-mm × 5-mm QFN Package
APPLICATIONS
• Notebook and Ultra-Mobile Computers
• Portable Data-Capture Terminals
• Portable Printers
• Medical Diagnostics Equipment
• Battery Bay Chargers
• Battery Backup Systems
DESCRIPTION
The bq24745 is a high-efficiency, synchronous
battery charger with an integrated input-current
comparator, offering low component count for
space-constrained, multi-chemistry battery-charging
applications. The input-current, charge-current, and
charge-voltage DACs allow very high regulation
accuracies that can be easily programmed by the
system power-management microcontroller using the
SMBus interface. The bq24745 charges two, three, or
four series Li+ cells, and is available in a 28-pin,
5-mm × 5 mm QFN package.
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
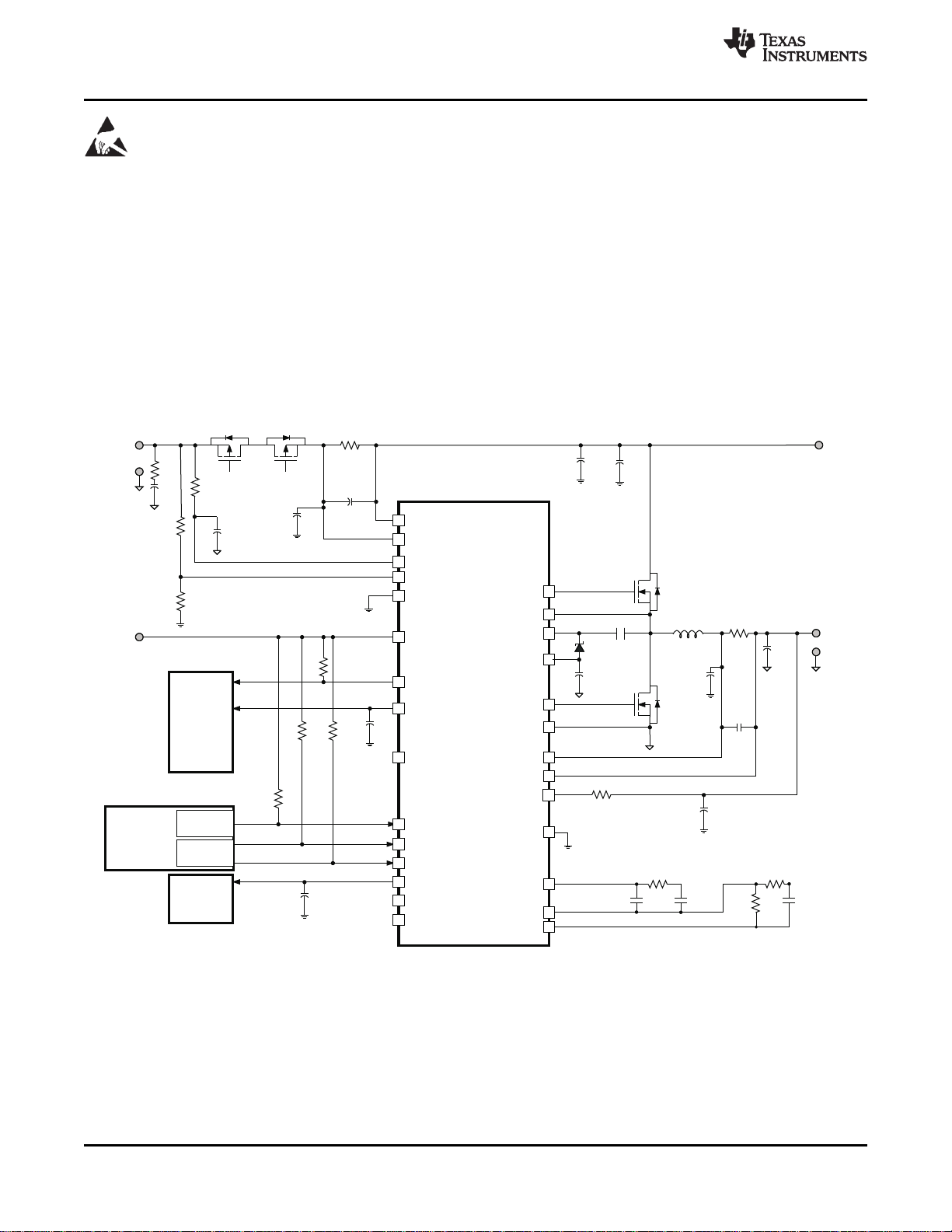
(1) Pullup rail could be either VREF or other system rail.
RAC
0.010
RSR
0.010
Q1 (ACFET)
SI4835BDY
N
PP
CSSN
CSSP
ACIN
VREF
CE
SDA
SCL
SMBus
VICM
HOST
(EC)
UGATE
N
PHASE
BOOT
VDDP
LGATE
PGND
CSOP
CSON
PACK+
PACK-
CHRG_IN
ADAPTER +
ADAPTER -
GND
bq24745
309k
1%
49.9k
1%
R1
R2
1uFC4
C2
0.1u
C3
0.1u
100pFC5
C6
1u
Q3
FDS6680A
Q4
FDS6680A
0.1uF
C7
L1
5.6uH
D1 BAT54
C8
1u
C9
0.1uF
C10
0.1uF
C13
2x10u
C15
10uF
VFB
ICOUT
ICREF
Q2 (RBFET)
SI4835BDY
Controlled by
HOST
C14
10uF
C17
0.1uF
R10
10k
R11
10k
EAI
FBO
NC
NC
EAO
27
28
2
12
3
26
7
9
10
8
14
16
4
5
6
1
15
17
18
19
20
25
21
23
24
DCIN
VDDSMB
11
ACOK
10k
R3
13
DISCRETE
LOGIC
RC6
10Ω
Dig I/O
+3.3V_ALWAYS
OR
+5V_ALWAYS
R12
10k
22
100 Ω
R22
C1
2.2u
RC
1
2.2Ω
DISCRETE
LOGIC
R20
20k
R21
200k
R19
7.5k
C21
2000pF
C22
130pF
C23
51pF
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam
during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED)
The bq24745 features dynamic power management (DPM) and input power limiting. These features reduce
battery-charge current when the input power limit is reached to avoid overloading the ac adaptor when supplying
the load and the battery charger simultaneously. A highly accurate current-sense amplifier enables precise
measurement of input current from the ac adapter, allowing monitoring the overall system power. If the adapter
current is above the programmed low-power threshold, a signal is sent to host so that the system optimizes its
performance to the power available from the adapter. An integrated comparator monitors the input current
through the current-sense amplifier, and indicates when the input current exceeds a programmable threshold
limit.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
VIN= 20 V, V
= 4-cell Li-Ion, I
BAT
CHARGE
= 4.5 A
www.ti.com
Internal Comparator
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
Figure 1. Typical System Schematic Using External Input-Current Comparator (Discrete Logic) Instead of
2 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated

RAC
0.010
RSR
0.010
(1) Pullup rail could be either VREF or other system rail.
Q1 (ACFET)
SI4435
N
PP
CSSN
CSSP
ACIN
VREF
CE
SDA
SCL
SMBus
DISCRETE
LOGIC
VICM
HOST
(EC)
UGATE
N
PHASE
BOOT
VDDP
LGATE
PGND
CSOP
CSON
PACK+
PACK-
CHRG_IN
ADAPTER +
ADAPTER -
GND
bq24745
464k
1%
33.2k
1%
R1
R2
1uFC4
0.1uFC20.1uF
C3
100pFC5
1uF
C6
Q3
FDS6680A
Q4
FDS6680A
0.1uF
C7
L1
5.6uH
D1 BAT54
1uF
C8
C9
0.1uF
C10
0.1uF
C13
2x10uF
VFB
R4
10k
ICOUT
VREF
ICREF
R22
100Ω
R8
200k
R18
1400k
Q2 (RBFET)
SI4435
Controlled by
HOST
C14
10uF
C15
10uF
C17
0.1uF
R10
10k
R11
10k
EAI
FBO
NC
NC
EAO
27
28
2
12
3
26
7
9
10
8
14
16
4
5
6
1
15
17
18
19
20
25
21
23
24
DCIN
22
VDDSMB
11
ACOK
10k
R3
13
Dig I/O
+3.3V_ALWAYS
OR
+5V_ALWAYS
R12
10k
RC6
10Ω
C16
1u
C1
2.2u
2.2Ω
1
RC
R7
200k
DISCRETE
LOGIC
R20
20k
R21
200k
R19
7.5k
C21
2000pF
C22
130pF
C23
51pF
www.ti.com
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
VIN= 20 V, V
= 4-cell Li-Ion, I
BAT
CHARGE
= 4.5 A, VICM
= 6 A, for ICOUT Input Current comparator.
er_limit
Figure 2. Typical System Schematic Using Internal Input-Current Comparator
PART NUMBER PACKAGE QUANTITY
bq24745 28-pin 5-mm × 5-mm QFN
PACKAGE THERMAL DATA
(1) For the most current package and ordering information, see the Package Option Addendum at the end of this document, or see the TI
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 3
PACKAGE θ
(1)
QFN – RHD
Web site at www.ti.com.
JA
36°C/W 2.36 W 0.028 W/°C
ORDERING INFORMATION
ORDERING NUMBER
TA= 40°C DERATING FACTOR
POWER RATING ABOVE TA= 25°C
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
(Tape and Reel)
bq24745RHDR 3000
bq24745RHDT 250
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Table 1. PIN FUNCTIONS – 28-PIN QFN
PIN
NO. NAME
1 ICREF Input-current comparator voltage reference input. Connect a resistor divider from VREF to ICREF and from ICREF to
GND to program the reference for the ICOUT comparator. The ICREF pin voltage is compared to the VICM pin
voltage and the logic output is given on the ICOUT open-drain pin. Connecting a positive feedback resistor from the
ICREF pin to the ICOUT pin programs the hysteresis.
2 ACIN Adapter-detected voltage-set input. Program the adapter-detect threshold by connecting a resistor divider from the
adapter input to ACIN pin to GND. Adapter voltage is detected if the ACIN-pin voltage is greater than 2.4 V. The VICM
current-sense amplifier, ICOUT comparator, and ACOK output are active when the ACIN pin voltage is greater than
0.6 V.
3 VREF 3.3-V regulated voltage output. Place a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VREF to the GND pin close to the IC. This
voltage could be used for ratiometric programming of voltage and current regulation and for programming the ICREF
threshold.
4 EAO Error amplifier output for compensation. Connect the feedback-compensation components from EAO to EAI. Typically,
a capacitor in parallel with a series resistor and capacitor. This node is internally compared to the PWM sawtooth
oscillator signal.
5 EAI Error amplifier input for compensation. Connect the feedback compensation components from EAI to EAO. Connect
the input compensation from FBO to EAI.
6 FBO Feedback output for compensation. Connect the input compensation from FBO to EAI. Typically, a resistor in parallel
with a series resistor and capacitor.
7 CE Charge enable active-high logic input. HI enables charge. LO disables charge.
8 VICM Adapter current-sense-amplifier output. The VICM voltage is 20 times the differential voltage across CSSP-CSSN.
Place a 100-pF (max) or less ceramic decoupling capacitor from VICM to GND.
9 SDA SMBus data input. Connect to the SMBus data line from the host controller. A 10-kΩ pullup resistor to the host
controller power rail is needed.
10 SCL SMBus clock input. Connect to the SMBus clock line from the host controller. A 10-kΩ pullup resistor to the host
controller power rail is needed.
11 VDDSMB Input voltage for SMBus logic. Connect a 3.3-V supply rail or 5-V rail to the VDDSMB pin. Connect a 0.1-μF ceramic
capacitor from VDDSMB to GND for decoupling.
12 GND Analog ground. On PCB layout, connect to the analog ground plane, and only connect to PGND through the thermal
pad underneath the IC.
13 ACOK Valid adapter active-high detect logic open-drain output. Pulled HI when Input voltage is above the ACIN programmed
threshold. Connect a 10-kΩ pullup resistor from the ACOK pin to pull up the supply rail.
14 NC No connect. Pin floating internally.
15 VFB Battery-voltage remote sense. Directly connect a Kelvin sense trace from the battery-pack positive terminal to the VFB
pin to sense the battery pack voltage accurately. Place a 0.1-μF capacitor from VFB to GND close to the IC to filter
high-frequency noise.
16 NC No Connect. Pin floating internally.
17 CSON Charge-current sense resistor, negative input. An optional 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the CSON pin to
GND for common-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from CSON to CSOP to provide
differential-mode filtering.
18 CSOP Charge-current sense resistor, positive input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from CSOP pin to GND for
common-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from CSON to CSOP to provide differential-mode
filtering.
19 PGND Power ground. On PCB layout, connect directly to the source of the low-side power MOSFET, and to the to ground
connection of the input and output capacitors of the charger. Only connect to GND through the thermal pad
underneath the IC.
20 LGATE PWM low-side driver output. Connect to the gate of the low-side power MOSFET with a short trace.
21 VDDP PWM low-side driver positive 6-V supply output. Connect a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VDDP to the PGND pin, close
to the IC. Use for high-side driver bootstrap voltage by connecting a small signal Schottky diode from VDDP to BOOT.
22 DCIN IC-power positive supply. Connect to the common-source (diode-OR) point: source of high-side P-channel MOSFET
and source of reverse blocking power P-channel MOSFET. Place a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from DCIN to the GND pin
close to the IC. Place a 10-Ω resistor from the adapter input to the DCIN pin to limit inrush current.
23 PHASE PWM high-side driver negative supply. Connect to the phase-switching node (junction of the low-side power MOSFET
drain, high-side power MOSFET source, and output inductor). Connect the 0.1-μF bootstrap capacitor from PHASE to
BOOT.
24 UGATE PWM high-side driver output. Connect to the gate of the high-side power MOSFET with a short trace.
FUNCTION
www.ti.com
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
www.ti.com
Table 1. PIN FUNCTIONS – 28-PIN QFN (continued)
PIN
NO. NAME
25 BOOT PWM high-side driver positive supply. Connect a 0.1-μF bootstrap ceramic capacitor from BOOT to PHASE. Connect
a small bootstrap Schottky diode from VDDP to BOOT.
26 ICOUT Input-current comparator active-high open-drain logic output. Place a 10-kΩ pullup resistor from the ICOUT pin to the
pullup voltage rail. Place a positive-feedback resistor from the ICOUT pin to the ICREF pin for programming
hysteresis. The output is HI when the VICM pin voltage is lower than the ICREF pin voltage. The output is LO when
VICM pin voltage is higher than ICREF pin voltage.
27 CSSN Adapter current-sense resistor, negative input. An optional 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the CSSN pin to
GND for common-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from CSSN to CSSP to provide
differential-mode filtering.
28 CSSP Adapter current-sense resistor, positive input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the CSSP pin to GND for
common-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from CSSN to CSSP to provide differential-mode
filtering.
FUNCTION
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
DCIN, CSOP, CSON, CSSP, CSSN, VFB, ACOK –0.3 to 30
PHASE –1 to 30
Voltage range V
Maximum difference voltage: CSOP–CSON, CSSP–CSSN –0.5 to 0.5
Junction temperature range –40 to 155 °C
Storage temperature range –55 to 155 °C
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating
Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to GND if not specified. Currents are positive into, and negative out of the specified terminal. Consult
Packaging Section of the data book for thermal limitations and considerations of packages.
EAI, EAO, FBO, VDDP, LGATE, ACIN, VICM, ICOUT, ICREF, CE –0.3 to 7
VDDSMB, SDA, SCL –0.3 to 6
VREF –0.3 to 3.6
BOOT, UGATE with respect to GND and PGND –0.3 to 36
(1) (2)
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
VALUE UNIT
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
PHASE –0.7 24
DCIN, CSOP, CSON, CSSP, CSSN, VFB, ACOK 0 24
VDDP, LGATE 0 6.5
Voltage range VREF 3.3
EAI, EAO, FBO, ACIN, VICM, ICOUT, ICREF, CE 0 5.5
BOOT, UGATE with respect to GND and PGND 0 30
VDDSMB, SDA, SCL 0 5.5
Maximum difference voltage: CSOP–CSON, CSSP–CSSN –0.3 0.3
Junction temperature range –40 125 °C
Storage temperature range –55 150 °C
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 5
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
V

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
7 V ≤ V
OPERATING CONDITIONS
V
DCIN_OP
CHARGE VOLTAGE REGULATION
V
VFB_OP
V
VFB_REG _ACC
V
VFB_REG_ RNG
CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION
V
IREG_CHG_RNG
I
CHRG_REG_ACC
INPUT CURRENT REGULATION
V
IREG_DPM_RNG
I
INPUT_REG_ACC
VREF REGULATOR
V
VREF_REG
I
VREF_LIM
VDDP REGULATOR
V
VDDP_REG
I
VDDP_LIM
≤ 24 V, 0°C < TJ< 125°C, typical values are at TA= 25°C, with respect to AGND (unless otherwise noted)
DCIN
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
DCIN input-voltage operating range 7 24 V
VFB input-voltage range 0 DCIN V
VFB charge-voltage regulation accuracy
Charge-voltage regulation range 1.024 19.2 V
Charge-current regulation differential-voltage V
range is 80.64 mV
Charge-current regulation accuracy
Adapter-current regulation differential-voltage V
range is 110.084 mV
Input-current regulation accuracy
VREF regulator voltage V
VREF current limit V
VDDP regulator voltage V
VDDP current limit mA
ChargeVoltage() = 0x41A0
ChargeVoltage() = 0x3130
ChargeVoltage() = 0x20D0
ChargeVoltage() = 0x1060
16.716 16.8 16.884 V
–0.5% 0.5%
12.529 12.592 12.655 V
–0.5% 0.5%
8.350 8.4 8.450 V
–0.6% 0.6%
4.154 4.192 4.230 V
–0.9% 0.9%
TJ= 0 to 125°C, 1.024 V–19.2 V, Max DAC
value is 19.2 V
= V
– V
IREG_CHG
CSOP
ChargeCurrent() = 0x0F80
ChargeCurrent() = 0x0800
ChargeCurrent() = 0x0200
ChargeCurrent() = 0x0080
= V
IREG_DPM
CSSP
InputCurrent() ≥ 0x0800
InputCurrent() = 0x0400
InputCurrent() = 0x0100
InputCurrent() = 0x0080
> 0.6 V, 0 – 30 mA 3.267 3.3 3.333 V
ACIN
= 0 V, V
V
V
VREF
ACIN
VDDP
VDDP
ACIN
> 0.6 V, 0 – 50 mA 5.7 6 6.3 V
= 0 V, V
ACIN
= 5 V, V
ACIN
, max. DAC value
CSON
0 80.64 mV
3968 mA
–3% 3%
2048 mA
–5% 5%
512 mA
–25% 25%
128 mA
–33% 33%
– V
, max. DAC value
CSSN
0 110.1 mV
4096 mA
–3% 3%
2048 mA
–5% 5%
512 mA
–25% 25%
256 mA
–33% 33%
> 0.6 V 35 80 mA
> 0.6 V 90 135
> 0.6 V 80
www.ti.com
6 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
www.ti.com
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
7 V ≤ V
ADAPTER CURRENT SENSE AMPLIFIER
V
CSSP/N_OP
V
VICM
I
VICM
A
VICM
I
VICM_LIM
C
VICM_MAX
ACIN COMPARATOR INPUT UNDERVOLTAGE)
V
DCIN_VFB_OP
V
ACIN_CHG
V
ACIN_CHG_HYS
V
ACIN_BIAS
V
ACIN_BIAS_HYS
DCIN / VFB COMPARATOR (REVERSE DISCHARGING PROTECTION)
V
DCIN-VFB_FALL
V
DCIN-VFB__HYS
VFB OVERVOLTAGE COMPARATOR
V
OV_RISE
V
OV_FALL
VFB SHORT (UNDERVOLTAGE and TRICKLE CHARGE) COMPARATOR
V
VFB_SHORT_RISE
V
VFB_SHORT_HYS
I
TRKL_REG_ACC
I
LOW_MAX_REG
CHARGE OVERCURRENT COMPARATOR
V
OC
INPUT UNDERVOLTAGE LOCK-OUT COMPARATOR (UVLO)
UVLO AC undervoltage rising threshold Measure on DCIN pin 3.5 4 4.5 V
V
UVLO_HYS
INPUT CURRENT COMPARATOR
V
ICCOMP_OFFSET
(1) Verified by design.
≤ 24 V, 0°C < TJ< 125°C, typical values are at TA= 25°C, with respect to AGND (unless otherwise noted)
DCIN
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input common-mode range Voltage on CSSP/CSSN 0 24 V
VICM output-voltage range 0 2.25 V
VICM output current 0 1 mA
Current-sense amplifier voltage gain A
Adapter-current sense accuracy
Output-current limit V
= V
VICM
V
IREG_DPM
V
IREG_DPM
V
IREG_DPM
V
IREG_DPM
VICM
/ V
VICM
IREG_DPM
= V(CSSP–CSSN) ≥ 40 mV –2% 2%
= V(CSSP–CSSN) = 20 mV –3% 3%
= V(CSSP–CSSN) = 5 mV –25% 25%
= V(CSSP–CSSN) = 1.5 mV –33% 33%
= 0 V 1 mA
Maximum output load capacitance For stability with 0-mA to 1-mA load 100 pF
Differential voltage from DCIN to VFB –20 24 V
ACIN rising threshold Min. voltage to enable charging, V
ACIN falling hysteresis V
ACIN rising deglitch
(1)
ACIN falling deglitch V
falling 40 mV
ACIN
V
rising 50 100 150 μs
ACIN
falling 1 μs
ACIN
Adapter present rising threshold Min voltage to enable all bias, V
Adapter present falling hysteresis V
ACIN rising deglitch
(1)
ACIN falling deglitch V
DCIN to VFB falling threshold V
falling 20 mV
ACIN
V
rising 200
ACIN
falling 1
ACIN
– V
DCIN
to turn off ACFET 140 185 240 mV
VFB
DCIN to VFB hysteresis 50 mV
DCIN to VFB rising deglitch V
DCIN to VFB falling deglitch V
Overvoltage rising threshold As percentage of V
Overvoltage falling threshold As percentage of V
DCIN
DCIN
– V
– V
VFB
VFB
> V
DCIN-VFB_RISE
< V
DCIN-VFB_FALL
VFB_REG
VFB_REG
VFB short rising threshold 2.6 2.7 2.9 V
VFB short falling hysteresis 215 mV
V
> V
VFB
VFB short rising deglitch 1.5 μs
VFB short falling deglitch V
Trickle-charge current-regulation accuracy in V
BATSHORT
Maximum charge current regulation at low V
voltage (<4 V)
VFB_SHORT
Detection delay
< V
VFB
VFB_SHORT
< V
VFB
VFB_SHORT
VFB_SHORT
Charge overcurrent falling threshold As percentage of I
+ V
VFB_SHORT_HYS
< V
< 4 3
VFB
REG_CHG
Minimum current limit (CSOP–CSON) 50 mV
Internal filter pole frequency 160 kHz
AC undervoltage hysteresis, falling 260 mV
Input current-comparator offset voltage -6.8 0.12 6.8 mV
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
20 V/V
rising 2.376 2.4 2.424 V
ACIN
rising 0.56 0.62 0.68 V
ACIN
1 ms
3.3 μs
104
102
3.3 μs
60 200 300
145%
μs
%
mA
A
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 7
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
7 V ≤ V
THERMAL SHUTDOWN COMPARATOR
T
SHUT
T
SHUT_HYS
PWM HIGH SIDE DRIVER (UGATE)
R
DS_HI_ON
R
DS_HI_OFF
V
BOOT_REFRESH
I
BOOT_LEAK
PWM LOW SIDE DRIVER (LGATE)
R
DS_LO_ON
R
DS_LO_OFF
PWM DRIVERS TIMING
PWM OSCILLATOR
F
SW
V
RAMP_HEIGHT
QUIESCENT CURRENT
I
OFF_STATE
I
BAT_ON
I
BAT_LOAD_CD
I
BAT_LOAD_CE
I
AC
I
AC_SWITCH
INTERNAL SOFT START (8 Steps to Regulation Current ICHG)
CHARGER SECTION POWER-UP SEQUENCING
CHARGE UNDERCURRENT COMPARATOR (CYCLE-BY-CYCLE SYNCHRONOUS TO NON-SYNCHRONOUS)
V
UCP
LOGIC INPUT PIN CHARACTERISTICS (CE)
V
IN_LO
V
IN_HI
V
BIAS
OPEN-DRAIN LOGIC OUTPUT PIN CHARACTERISTICS (ACOK, ICOUT)
V
OUT_LO
VDDSMB INPUT SUPPLY FOR SMBus
V
VDDSMB_RANGE
V
VDDSMB_UVLO_
Threshold_Rising
V
VDDSMB_UVLO_
Hyst_Rising
≤ 24 V, 0°C < TJ< 125°C, typical values are at TA= 25°C, with respect to AGND (unless otherwise noted)
DCIN
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Thermal shutdown rising temperature Temperature Increasing 155
Thermal shutdown hysteresis, falling 20
High-side driver (HSD) turnon resistance V
High-side driver turnoff resistance V
Bootstrap refresh comparator threshold V
voltage is requested
BOOT
BOOT
BOOT
– V
= 5.5 V 6 Ω
PHASE
– V
= 5.5 V 1 Ω
PHASE
– V
when low-side refresh pulse
PHASE
BOOT leakage current when charge enabled High side is on; charge enabled 200 μA
Low-side driver (LSD) turnon resistance 6 Ω
Low-side driver turnoff resistance 1 Ω
Driver dead time 30 ns
Dead time when switching between LGATE
and UGATE , no load at LGATE and UGATE
PWM switching frequency 240 360 kHz
PWM ramp height As percentage of DCIN 6.67 %DCIN
Total off-state battery current from CSOP, V
CSON, VFB, DCIN, BOOT, PHASE, etc V
Battery on-state quiescent current 0.7 1 mA
Internal battery load current, charge disabled 0.7 1 mA
Internal battery load current, charge enabled 6 10 12 mA
Adapter quiescent current Charge disabled, V
Adapter switching quiescent current 25 mA
= 16.8 V, V
VFB
> 5 V, 0°C ≤ TJ≤ 85°C
DCIN
V
= 16.8 V, 0.6V < V
VFB
V
> 5 V
DCIN
ACIN
Charge is disabled: V
V
> 2.4 V, V
ACIN
DCIN
Charge is enabled: V
V
> 2.4 V, V
ACIN
Charge enabled, V
running
DCIN
DCIN
< 0.6 V,
< 2.4 V,
ACIN
= 16.8 V,
VFB
> 5 V
= 16.8 V,
VFB
> 5 V
= 20 V 0.7 1 mA
DCIN
= 20 V, converter
Soft-start steps 8 step
Soft-start step time 1.5 ms
Charge-enable delay after power up 1.5 ms
Cycle-by-cycle synchronous to
non-synchronous transition threshold
Delay from when adapter is detected to when
the charger is allowed to turn on
Cycle-by-cycle, (CSOP-CSON) voltage,
falling, LGATE turns off and latches off until 5 10 15 mV
next cycle
Blankout time after LGATE turns on Blankout comparator after LGATE turns on 100 ns
(2)
Pull-up CE with ≥2.2 kΩ resistor or directly to VREF.
Input low-threshold voltage 0.8 V
Input high-threshold voltage 2.1
Input bias current V = 0 TO V
VDDP
Output low saturation voltage Sink current = 5 mA 0.5 V
VDDSMB input voltage range 2.7 5.5 V
VDDSMB undervoltage lockout threshold
voltage, rising
VDDSMB undervoltage lockout hysteresis
voltage, falling
V
rising 2.4 2.5 2.6 V
VDDSMB
V
falling 100 150 200 V
VDDSMB
www.ti.com
°C
4 V
7 10 μA
1 μA
(2) Pull up CE with ≥ 2-kΩ resistor, or connect directly to VREF.
8 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
www.ti.com
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
7 V ≤ V
IVDDSMB_Iq VDDSMB quiescent current V
≤ 24 V, 0°C < TJ< 125°C, typical values are at TA= 25°C, with respect to AGND (unless otherwise noted)
DCIN
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= SCL = SDA = 5.5 V, 0°C ≤ TJ≤ 20 27 μA
VDDSMB
85°C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
7 Vdc ≤ V
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX UNIT
[SMB TIMING SPECIFICATION (VDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V) (see Figures 4 and 5)]
SMBus TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
t
R
t
F
t
W(H)
t
W(L)
t
SU(STA)
t
H(STA)
t
SU(DAT)
t
H(DAT)
t
SU(STOP)
t
(BUF)
F
S(CL)
HOST COMMUNICATION FAILURE
t
timeout
t
WDI
OUTPUT BUFFER CHARACTERISTICS
V
(SDAL)
(1) Devices participating in a transfer time out when any clock low exceeds the 2- ms minimum time-out period. Devices that have detected
a time-out condition must reset the communication no later than the 35-ms maximum timeout period. Both a master and a slave must
adhere to the maximum value specified, as it incorporates the cumulative stretch limit for both a master (10 ms) and a slave (25 ms).
≤ 24 Vdc, –20°C<TJ<125°C, ref = AGND (unless otherwise noted)
(VCC)
SCLK/SDATA rise time 1 μs
SCLK/SDATA fall time 300 ns
SCLK pulse duration high 4 50 μs
SCLK pulse duration low 4.7 μs
Setup time for START condition 4.7 μs
START condition hold time after which first clock pulse is generated 4 μs
Data setup time 250 ns
Data hold time 300 ns
Setup time for STOP condition 4 μs
Bus free time between START and STOP condition 4.7 μs
Clock frequency 10 100 kHz
SMBus bus release timeout 22 25 35 ms
Watchdog timeout period 140 170 210 s
Output LO voltage at SDA, I
= 3 mA 0.4 V
(SDA)
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
(1)
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 9
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

-3
-2
-1
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
DCIN=10V
DCIN=20V
V -Error-%
DDP
I -LoadCurrent-mA
L
-1
-0.80
-0.60
-0.40
-0.20
0
0.20
0.40
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
I -LoadCurrent-mA
L
DCIN=10V
DCIN=20V
V -Error-%
REF
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
www.ti.com
Figure 3. SMBus Communication Timing Waveforms
VREF LOAD AND LINE REGULATION VDDP LOAD AND LINE REGULATION
LOAD CURRENT LOAD CURRENT
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 4. Figure 5.
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
vs vs
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

-3
-2
-1
0
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
BatteryChargeCurrent- A
BatteryVoltage Accuracy-%
3CELL @12.592V,
ICHG@8.064 A,
DCIN=20V
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000
VFBprogrammedSetpoint-mV
BatteryVoltageRegulation Accuracy-%
DCIN=20V
3CELL @12.592V,
ICHG@4.096 A,
DCIN=20V
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
BatteryVoltage-V
BatteryChargeCurrent- A
-16
-14
-12
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000
ICHGDACProgrammedSetpoint-mA
ChargeCurrent Accuracy-%
DCIN=20V,
VFB=9V
www.ti.com
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
VFB (BATTERY) VOLTAGE REGULATION ACCURACY VFB (BATTERY) VOLTAGE REGULATION ACCURACY
vs vs
CHARGE CURRENT DAC VBAT SETPOINT
Figure 6. Figure 7.
CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION ACCURACY CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION ACCURACY
vs vs
DAC ICHRG SETPOINT VFB (BATTERY) VOLTAGE
Figure 8. Figure 9.
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

DCIN=20V,
VFB=9V
-2
-1.8
-1.6
-1.4
-1.2
-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000
DPMProgramValue-mA
VICM Accuracy-%
DPMProgrammedSetpoint-mA
InputCurrentRegulation Accuracy-%
VFB=9V,
DCIN=20V
6000
-2.5
2000 120004000 8000 100000
0
-3
-2
-1.5
-1
-0.5
t − Time=1ms/div
Ch1
2 A/div
Ch2
2 A/div
I
(DCIN)
I
LOAD
I
(SYS)
VICM
Ch4
500mV/div
Ch3
2 A/div
DCIN=20V
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
SystemCurrent- A
ChargeCurrent- A
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
InputCurrent- A
ChargeCurrent
InputCurrent
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
INPUT CURRENT REGULATION (DPM) ACCURACY
vs VICM INPUT CURRENT-SENSE AMPLIFIER ACCURACY
DAC IDPM SETPOINT INPUT CHARGE CURRENT
Figure 10. Figure 11.
INPUT CURRENT REGULATION (DPM)
AND CHARGE CURRENT
vs SYSTEM LOAD RESPONSE
SYSTEM CURRENT CCM TO CCM
www.ti.com
INPUT CURRENT REGULATION (DPM) TRANSIENT
Figure 12. Figure 13.
12 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

t − Time=1ms/div
Ch1
2 A/div
Ch2
5 A/div
I
(DCIN)
I
LOAD
I
(SYS)
VICM
Ch4
500mV/div
Ch3
2 A/div
4 5 6 9
0
13
BatteryVoltage-V
-0.5
-1
-2
0.5
-3
-1.5
-2.5
7 8 10 11 12
BatteryChargeCurrent Accuracy-%
3-Cellat12.592V,
ICHGat4.096A
withDCIN=20V
Ch4
2 V/div
t − Time=4ms/div
Ch2
10 V/div
VFB
PH
I
(IND)
Ch1
2 A/div
0 1 2 5
96
9
BatteryChargeCurrent- A
Efficiency-%
94
92
90
86
98
84
80
88
82
3 4 6 7 8
1-4Cell
ICHGat8.064A
withDCIN=20V
4-Cell
1-Cell
3-Cell
2-Cell
Ch4
2 V/div
t − Time=4ms/div
Ch1
5 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
DCIN
VREF
ACOK
PH
Ch3
2 V/div
Ch4
2 V/div
t − Time=4ms/div
Ch1
5 V/div
Ch2
2 V/div
DCIN
VREF
ACOK
ACIN
Ch3
2 V/div
www.ti.com
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
INPUT CURRENT REGULATION (DPM) TRANSIENT
SYSTEM LOAD RESPONSE CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION ACCURACY
CCM TO DCM VFB (BATTERY) VOLTAGE
Figure 14. Figure 15.
EFFICIENCY
BATTERY CHARGE CURRENT BATTERY REMOVAL (From Constant-Current Mode)
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 13
Figure 16. Figure 17.
CHARGER WHEN ADAPTER INSERTED ADAPTER REMOVED WHILE CHARGING
Figure 18. Figure 19.
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

Ch3
1 V/div
t − Time=10ms/div
Ch1
2 V/div
Ch4
5 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
ACGOOD
PH
CE
VDDP
t − Time=1ms/div
Ch1
1 A/div
Ch4
1 A/div
I
(IND)
I
LOAD
Ch4
5 V/div
t − Time=10ms/div
Ch1
2 V/div
Ch3
1 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
SDA
VDDP
PH
ACGOOD
Ch4
5 V/div
t − Time=10ms/div
Ch1
2 V/div
Ch3
1 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
SDA
VDDP
ACGOOD
Ch4
10 V/div
t − Time=40ns/div
Ch1
2 A/div
Math1
5 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
Ch3
5 V/div
UGATE
I
(IND)
LGATE
PH
UGATE-PH
Ch4
10 V/div
t − Time=40ns/div
Ch1
2 A/div
Math1
5 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
Ch3
5 V/div
UGATE
I
(IND)
LGATE
PH
UGATE-PH
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
CHARGE ENABLE/DISABLE AND CHARGE CURRENT
Figure 20. Figure 21.
CHARGE ENABLED BY SMBus CHARGE DISABLED BY SMBus
www.ti.com
SOFT-START, INDUCTOR CURRENT
Figure 22. Figure 23.
DEAD-TIME BETWEEN DEAD-TIME BETWEEN
UGATE OFF AND LGATE ON LGATE OFF AND UGATE ON
Figure 24. Figure 25.
14 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

Ch4
5 V/div
t − Time=400 s/divm
Ch1
10 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
Ch3
2 A/div
UGATE
I
(IND)
LGATE
PHASE
t − Time=400 s/divm
Ch2
10 V/div
Ch3
2 A/div
VFB
I
(IND)
Ch4
10 V/div
t − Time=1 s/divm
Ch1
2 A/div
Math1
5 V/div
Ch2
10 V/div
Ch3
5 V/div
UGATE
I
(IND)
LGATE
PH
UGATE-PH
Ch4
10 V/div
t − Time=1 s/divm
Ch1
500 mA/div
Math1
5 V/div
Ch3
5 V/div
UGATE
I
(IND)
LGATE
PH
UGATE-PH
Ch2
10 V/div
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
0 5 10 15 20 25
VFB-Voltage-V
5
I Off-StateCurrent − A
(DCIN)
m−
Includingcurrentfrom:
DCIN,CSSP/N,VFB,
CSOP/N,BOOT,PHASE
-100
0
100
200
300
500
600
700
0 5 10 15 20 25
DCIN-Voltage-V
400
StandbyDCINCurrent − Am
AdapterConnected
ACIN>2.4V,
ChargeDisabledbyCEpin
CE=Low
www.ti.com
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
BATTERY SHORTED CHARGER RESPONSE,
NEAR 100% DUTY CYCLE BOOTSTRAP RECHARGE
PULSE CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION
Figure 26. Figure 27.
CONTINUOUS CONDUCTION MODE (CCM) DISCONTINUOUS CONDUCTION MODE (DCM)
SWITCHING WAVEFORMS, ICHARGE = 3986 mA SWITCHING WAVEFORMS, ICHARGE = 256 mA
OVERCURRENT PROTECTION (OCP) AND
bq24745
Figure 28. Figure 29.
OFF-STATE BATTERY CURRENT (LOW Iq) OFF-STATE DCIN CURRENT (LOW Iq)
VFB (BATTERY) VOLTAGE DCIN INPUT VOLTAGE (With Adapter Connected)
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 15
Figure 30. Figure 31.
vs vs
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

Ch3
100 mV/div
t − Time=4 s/divm
Ch2
5 V/div
Ch4
1 V/div
I
IN
I
COUT
I
CREF
V
ICM
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
HYSTERESIS INPUT CURRENT COMPARATOR (With Pulsed Current)
www.ti.com
PROGRAMMABLE REFERENCE AND
Figure 32.
16 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
VICM
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
VDDP
LGATE
PGND
CSSP
CSSN
VFB
CSOP
6VLDO
20xV(CSSP-CSSN)
+
-
20xV(CSOP-CSON)
COMP
ERROR
AMPLIFIER
1x
20xV(CSSP-CSSN)
20uA
IIN_ER
BAT_ER
ICH_ER
1V
20uA
IIN_REG
VBAT_REG
IBAT_ REG
CSON
DC-DC
CONVERTER
PWMLOGIC
DCIN
4V
+
_
V(BTST-PHASE)
REFRESH
CBTST
CHRG_ENA
155degC
ICTj
TSHUT
LEVEL
SHIFTER
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
20xV(CSOP-CSON)
CHG_OCP
+
-
145% XIBAT_REG
SDA
SCL
VDDSMB
`
VBAT_REG
IBAT_REG
IIN_REG
SMBus
Logic
CHRG_V
(11 bitDAC)
CHRG_I
(6 bitDAC)
INPUT_I
(6 bitDAC)
20X
VFB_DIV
BAT_OVP
+
-
104% XVBAT_REG
DCIN
3.3V
LDO
VREF
ACOK
DCIN_UVLO
+
-
DCIN
+
-
4V
ICREF
-
+VICM
ICOUT
GND
FBO
ACIN
NC
FBO
EAI
EAO
0.6V
+
-
WAKEUP
ACOK
2.4V
CE
NC
EAI
EAO
VREF
+
-
VDDSMB_UVLO
ENA
CHRG_ENA
20X
DCIN_UVLO
DCIN_UVLO
CHG_UCP
V(CSOP-CSON)
10mV
+
-
+
-
+
-
VDDSMB
+
-
2.5V
ENA
ENA
ACOK
CE
ENA
ENA
VFB
BAT_SHORT
+
-
2.5V
+
-
VFB_DIV
+
-
+
-
+
-
bq24745
www.ti.com
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 17
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
SMBus Interface
The bq24745 operates as a slave, receiving control inputs from the embedded controller host through the SMBus
interface.
Battery-Charger Commands
The bq24745 supports five battery-charger commands that use either Write-Word or Read-Word protocols, as
summarized in Table 2. ManufacturerID() and DeviceID() can be used to identify the bq24745. On the bq24745,
the ManufacturerID() command always returns 0x0040 and the DeviceID() command always returns 0x0006.
Table 2. Battery Charger SMBus Registers
REGISTER ADDRESS REGISTER NAME READ/WRITE DESCRIPTION POR STATE POR
Voltage/Current
0x14 ChargeCurrent() Read or write 6-bit charge-current setting 0x0000 0 mV
0x15 ChargeVoltage() Read or write 11-bit charge-voltage 0x0000 0 mA
setting
0x3F InputCurrent() Read or write 6-bit input-current setting 0x0080 256 mA (10-mΩ RAC)
0xFE ManufacturerID() Read-only Manufacturer ID 0x0040 –
0xFF DeviceID() Read-only Device ID 0x0006 –
www.ti.com
SMBus
The bq24745 receives control inputs from the SMBus interface. The bq24745 uses a simplified subset of the
commands documented in System Management Bus Specification V1.1, which can be downloaded from
www.smbus.org. The bq24745 uses the SMBus Read-Word and Write-Word protocols (Figure 33) to
communicate with the smart battery. The bq24745 performs only as an SMBus slave device with address
0b0001 001_ (0x12) and does not initiate communication on the bus. In addition, the bq24745 has two
identification (ID) registers (0xFE): a 16-bit device ID register and a 16-bit manufacturer ID register (0xFF).
The data (SDA) and clock (SCL) pins have Schmitt-trigger inputs that can accommodate slow edges. Choose
pullup resistors (10 kΩ, typ.) for SDA and SCL to achieve rise times according to the SMBus specifications.
Communication starts when the master signals a START condition, which is a high-to-low transition on SDA,
while SCL is high. When the master has finished communicating, the master issues a STOP condition, which is a
low-to-high transition on SDA, while SCL is high. The bus is then free for another transmission. Figure 34 and
Figure 35 show the timing diagram for signals on the SMBus interface. The address byte, command byte, and
data bytes are transmitted between the START and STOP conditions. The SDA state changes only while SCL is
low, except for the START and STOP conditions. Data is transmitted in 8-bit bytes and is sampled on the rising
edge of SCL. Nine clock cycles are required to transfer each byte in or out of the bq24745 because either the
master or the slave acknowledges the receipt of the correct byte during the ninth clock cycle.
18 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

a) Write-Word Format
S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
W
ACK
COMMAND
BYTE
ACK
LOWDATA
BYTE
ACK
HIGHDATA
BYTE
ACK P
7BITS 1b 1b 8BITS 1b 8BITS 1b 8BITS 1b
MSB LSB 0 0 MSB LSB 0 MSB LSB 0 MSB LSB 0
Preset to0b0001001 D7D0
ChargeCurrent()= 0x14
D15D8
ChargeVoltage()=0x15
InputCurrent() = 0x3F
b)Read-WordFormat
S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
W ACK
COMMAND
BYTE
ACK S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
R ACK
LOWDATA
BYTE
ACK
HIGHDATA
BYTE
NACK P
7BITS 1b 1b 8BITS 1b 7BITS 1b 1b 8BITS 1b 8BITS 1b
MSB LSB 0 0 MSB LSB 0 MSB LSB 1 0 MSB LSB 0 MSB LSB 1
Presetto0b0001001 Register Presetto D7D0 D15D8
0b0001010
ChargeMode()=0x15
ChargeMode()=0x3F
LEGEND:
S=START CONDITIONORREPEATEDSTART CONDITION
ACK= ACKNOWLEDGE(LOGIC-LOW)
W=WRITEBIT (LOGIC-LOW)
MASTER TOSLAV
E
SLAVE TOMASTER
P =STOP CONDITION
NACK=NOT ACKNOWLEDGE(LOGIC-HIGH)
R=READBIT (LOGIC-HIGH)
ChargeMode()=0x14
www.ti.com
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Figure 33. SMBus Write-Word and Read-Word Protocols
Figure 34. SMBus Write Timing
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 19
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

A B C D E F G H I J K
tLOW tHIGH
SMBCLK
SMBDATA
A =START CONDITION
B=MSBOF ADDRESSCLOCKEDINTOSLAVE
C=LSBOF ADDRESSCLOCKEDINTOSLAVE
D=R/WBIT CLOCKEDINTOSLAVE
E=SLAVEPULLSSMBDATA LINELOWI= ACKNOWLEDGECLOCKPULSE
F= ACKNOWLEDGEBIT CLOCKEDINTOMASTERJ=STOP CONDITION
G=MSBOFDATA CLOCKEDINTOMASTERK=NEWSTART CONDITION
H=LSBOFDATA CLOCKEDINTOMASTER
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Figure 35. SMBus Read Timing
BATTERY VOLTAGE REGULATION
The bq24745 uses a high-accuracy voltage regulator for charging voltage. The battery voltage regulation setting
is programmed by the host microcontroller (µC), through the SMBus interface that sets an 11-bit DAC. The
battery termination voltage is a function of the battery chemistry. Consult the battery manufacturer to determine
this voltage.
The VFB pin is used to sense the battery voltage for voltage regulation and should be connected as close to the
battery as possible, or directly on the output capacitor. A 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from VFB to GND is
recommended to be as close to the VFB pin as possible to decouple high-frequency noise.
To set the output charge-voltage regulation limit, use the SMBus to write a 16-bit ChargeVoltage() command
using the data format listed in Table 3. The ChargeVoltage() command uses the Write-Word protocol (see
Figure 33). The command code for ChargeVoltage() is 0x15 (0b0001 0101). The bq24745 provides a 1.024-V to
19.200-V charge voltage range, with 16-mV resolution. Setting ChargeVoltage() below 1.024 V or above 19.2 V
clears the DAC and terminates charge.
On reset, the ChargeVoltage() and ChargeCurrent() values are cleared (0) and the charger remains off until both
the ChargeVoltage() and the ChargeCurrent() commands are sent. During reset, both high-side and low-side
FETs remain off until the charger is started.
www.ti.com
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
0 – Not used
1 – Not used
2 – Not used
3 – Not used
4 Charge voltage, DACV 0 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
5 Charge voltage, DACV 1 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
6 Charge voltage, DACV 2 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
7 Charge voltage, DACV 3 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
8 Charge voltage, DACV 4 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
9 Charge voltage, DACV 5 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
10 Charge voltage, DACV 6 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
(1) Must be used in conjunction with other bits for a minimum output of 1024 mV
20 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Table 3. Charge Voltage Register (0x15)
1 = Adds 16 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 32 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 64 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 128 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 256 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 512 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 1,024 mV of charger voltage
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)

bq24745
www.ti.com
Table 3. Charge Voltage Register (0x15) (continued)
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
11 Charge voltage, DACV 7 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 2,048 mV of charger voltage
12 Charge voltage, DACV 8 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 4,096 mV of charger voltage
13 Charge voltage, DACV 9 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 8,192 mV of charger voltage
14 Charge voltage, DACV 10 0 = Adds 0 mV of charger voltage
1 = Adds 16,384 mV of charger voltage
15 – Not used
CHARGE CURRENT REGULATION
The ChargeCurrent() SMBus 6-bit DAC register sets the maximum charging current. Battery current is sensed by
resistor RSRconnected between the CSOP and CSON pins. The maximum full-scale differential voltage between
CSOP and CSON is 80.64 mV. Thus, for a 0.010-Ω sense resistor, the maximum charging current is 8.064 A.
The CSOP and CSON pins are used to measure the voltage across RSR, which has a default value of 10 mΩ.
However, resistors of other values can also be used. A larger sense resistor results in a larger sense voltage and
higher regulation accuracy, but at the expense of higher conduction loss.
To set the charge current, use the SMBus to write a 16-bit ChargeCurrent() command using the data format
listed in Table 4. The ChargeCurrent() command uses the Write-Word protocol (see Figure 33). The command
code for ChargeCurrent() is 0x14 (0b0001 0100). When using a 10-mΩ sense resistor, the bq24745 provides a
charge current range of 128 mA to 8.064 A, with 128-mA resolution. Set ChargeCurrent() to 0 to terminate
charging. Setting ChargeCurrent() below 128 mA, or above 8.064 A, clears DAC and terminates charge.
The bq24745 includes a foldback current limit when the battery voltage is low. If the battery voltage is less than
3.6 V but above 2.5 V, any charge current limit above 3 A is clamped at 3 A. If the battery voltage is less than
2.5 V, the charge current is set to 220 mA until that voltage rises above 2.7 V. The ChargeCurrent() register is
preserved and becomes active again when the battery voltage is higher than 2.7 V. This function effectively
provides a fold-back current limit, which protects the charger during short circuit and overload.
On reset, the ChargeVoltage() and ChargeCurrent() values are cleared (0) and the charger remains off until both
the ChargeVoltage() and the ChargeCurrent() commands are sent. During reset, both high-side and low-side
FETs remain off until the charger is started.
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Table 4. Charge Current Register (0x14), Using 10-mΩ Sense Resistor
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
0 – Not used
1 – Not used
2 – Not used
3 – Not used
4 – Not used
5 – Not used
6 – Not used
7 Charge current, DACI 0 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
8 Charge current, DACI 1 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
9 Charge current, DACI 2 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
10 Charge current, DACI 3 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
11 Charge current, DACI 4 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 21
1 = Adds 128 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 256 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 512 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 1,024 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 2,048 mA of charger current
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

LOAD BATTER Y
INP UT SYST EM BIAS
IN
I V
I = I + + I
V
é ù´
ê ú
´
ë û
h
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Table 4. Charge Current Register (0x14), Using 10-mΩ Sense Resistor (continued)
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
12 Charge current, DACI 5 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 4,096 mA of charger current
13 – Not used
14 – Not used
15 – Not used
INPUT ADAPTER CURRENT REGULATION
The total input current from an ac adapter or other dc source is a function of the system supply current and the
battery charging current. System current normally fluctuates as portions of the system are powered up or down.
Without dynamic power management (DPM), the source must be able to supply the maximum system current
and the maximum charger input current simultaneously. By using DPM, the input current regulator reduces the
charging current to keep the input current from exceeding the limit set by the Input Current SMBus 6-bit DAC
register. With high-accuracy limiting, the current capability of the ac adaptor can be lowered, reducing system
cost.
The CSSP and CSSN pins are used to sense RACwith a default value of 10 mΩ. However, resistors of other
values can also be used. A larger a sense resistor results in a larger sense voltage and a higher regulation
accuracy, but at the expense of higher conduction loss.
The total input current, from a wall cube or other dc source, is the sum of the system supply current and the
current required by the charger. When the input current exceeds the set input current limit, the bq24745
decreases the charge current to provide priority to system load current. As the system supply rises, the available
charge current drops linearly to zero.
www.ti.com
(1)
where η is the efficiency of the dc-dc converter (typically 85% to 95%).
To set the input current limit, use the SMBus to write a 16-bit InputCurrent() command using the data format
listed in Table 5. The InputCurrent() command uses the Write-Word protocol (see Figure 33). The command
code for InputCurrent() is 0x3F (0b0011 1111). When using a 10-mΩ sense resistor, the bq24745 provides an
input-current limit range of 256 mA to 11.008 A, with 256-mA resolution. InputCurrent() settings from 1 mA to
256 mA clears DAC and terminates charge. On reset the input current limit is 256 mA.
Table 5. Input Current Register (0x3F), Using 10-mΩ Sense Resistor.
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
0 – Not used
1 – Not used
2 – Not used
3 – Not used
4 – Not used
5 – Not used
6 – Not used
7 Charge current, DACS 0 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
8 Charge current, DACS 1 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
9 Charge current, DACS 2 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
10 Charge current, DACS 3 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
11 Charge current, DACS 4 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 256 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 512 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 1,024 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 2,048 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 4,096 mA of charger current
22 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
www.ti.com
Table 5. Input Current Register (0x3F), Using 10-mΩ Sense Resistor. (continued)
BIT BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
12 Charge current, DACS 5 0 = Adds 0 mA of charger current
1 = Adds 8,192 mA of charger current; 11,008 mA max
13 – Not used
14 – Not used
15 – Not used
ADAPTER DETECT AND POWER UP
An external resistor voltage divider attenuates the adapter voltage before it goes to ACIN. The adapter-detect
threshold should typically be programmed to a value greater than the maximum battery voltage and lower than
the minimum allowed adapter voltage. The ACIN divider should be placed before the input power path selector in
order to sense the true adapter input voltage.
If DCIN is below 4 V, the charger is disabled.
If ACIN is below 0.6 V but DCIN is above 4.5 V, AC and VICM are disabled and pulled down to GND. The total
quiescent current is less than 10 µA.
Once ACIN rises above 0.6 V and DCIN is above 4.5 V, VREF goes to 3.3 V and all the bias circuits are
enabled. ACOK low indicates ACIN still below 2.4 V, and the valid adaptor is not available. VICM becomes valid
to reflect the adapter current.
When ACIN keeps rising and passes 2.4 V, a valid ac adapter is present. 100 µs later, the following occurs:
• ACOK becomes high through an external pullup resistor to the host digital voltage rail.
• The charger turns on if all the conditions are satisfied. (see Enable and Disable Charging )
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
ENABLE AND DISABLE CHARGING
The following conditions must be valid before charging is enabled:
• Not in UVLO (DCIN > 4.5 V, and VDDSMB >2.5 V)
• Adapter is detected (ACIN > 2.4 V).
• Adapter – Battery voltage is higher than the V
DCIN-VFB
comparator threshold.
• 200-μs delay is complete after adapter detection.
• SMBus ChargeVoltage(),ChargeCurrent() and InputCurrent() DAC registers are inside the valid range.
• CE is HIGH.
• 2-ms delay is complete after adapter is detected and CE goes HIGH.
• VDDP and VREF are valid.
• Not in thermal shutdown (TSHUT)
Any of the following conditions stops ongoing charging:
• SMBus ChargeVoltage(), ChargeCurrent(), or InputCurrent() DAC register is outside the valid range.
• CE is LOW.
• Adapter is removed (DCIN <4 V).
• VDDSMB supply is removed. (VDDSMB <2.35 V)
• Adapter – Battery voltage is less than V
DCIN-VFB
comparator threshold.
• Battery is over voltage.
• In thermal shutdown: TSHUT IC temperature threshold is above 155°C.
AUTOMATIC INTERNAL SOFT-START CHARGER CURRENT
The charger automatically soft-starts the output regulation current every time the charger is enabled to ensure
there is no overshoot or stress on the output capacitors or the power converter. The soft-start consists of
stepping up the charge regulation current in eight evenly divided steps up to the programmed charge current.
Each step lasts around 1.6 ms, for a typical rise time of 12.8 ms. No external components are needed for this
function. The regulation limits can be changed in the middle of charging without soft start.
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 23
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

f
o
+
1
2p LoC
o
Ǹ
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
CONVERTER OPERATION
The synchronous buck PWM converter uses a fixe- frequency (300 kHz) voltage mode with feed-forward control
scheme. A type-III compensation network allows using ceramic capacitors at the output of the converter. The
compensation input stage is connected between the feedback output (FBO) and the error amplifier input (EAI).
The feedback compensation stage is connected between the error amplifier input (EAI) and error amplifier output
(EAO). The LC output filter selected gives a characteristic resonant frequency that is used to determine the
compensation to ensure there is sufficient phase margin for the target bandwidth.
The resonant frequency, fo, is given by:
An internal sawtooth ramp is compared to the internal EAO error control signal to vary the duty cycle of the
converter. The ramp height is one-fifteenth of the input adapter voltage, making it always directly proportional to
the input adapter voltage. This cancels out any loop gain variation due to a change in input voltage, and
simplifies the loop compensation. The ramp is offset by 200 mV in order to allow zero-percent duty cycle when
the EAO signal is below the ramp. The EAO signal is also allowed to exceed the sawtooth ramp signal in order to
get a 100% duty-cycle PWM request. Internal gate-drive logic allows achieving 99.98% duty cycle while ensuring
the N-channel upper device always has enough voltage to stay fully on. If the BOOT pin to PHASE pin voltage
falls below 4 V for more than three cycles, then the high-side n-channel power MOSFET is turned off and the
low-side n-channel power MOSFET is turned on to pull the PHASE node down and recharge the BOOT
capacitor. Then the high-side driver returns to 100% duty-cycle operation until the (BOOT-PHASE) voltage is
detected to fall low again due to leakage current discharging the BOOT capacitor below 4 V, and the recharge
pulse is reissued.
The fixed-frequency oscillator keeps tight control of the switching frequency under all conditions of input voltage,
battery voltage, charge current, and temperature, simplifying output filter design and keeping the frequency out of
the audible noise region. The type-III compensation provides phase boost near the cross-over frequency, giving
sufficient phase margin.
www.ti.com
CONTINUOUS AND DISCONTINUOUS CONDUCTION MODES
In continuous-conduction mode (CCM), the inductor current always flows to charge the battery, and the charger
always operates in synchronized mode. At the beginning of each clock cycle, the high-side n-channel power
MOSFET turns on, and the turnon time is set by the voltage on EAO pin. After the high-side power MOSFET
turns off, the low-side n-channel power MOSFET turns on. During CCM, the low-side n-channel power MOSFET
stays on until the end of the clock cycle. The internal gate-drive logic ensures there is break-before-make
switching to prevent shoot-through currents. During the 25-ns dead time where both FETs are off, the back diode
of the low-side power MOSFET conducts the inductor current. Having the low-side FET turn on keeps the power
dissipation low, and allows safely charging at high currents. With type-III compensation, the loop has a fixed
2-pole system.
Before the ripple valley current gets close to zero, the low-side FET must turn off before current goes negative,
or flows from the battery to the PHASE node, to avoid battery boosting the system. After the high-side n-channel
power MOSFET turns off, and after the break-before-make dead-time, the low-side n-channel power MOSFET
turns on for a blank-out time. After the blank-out time is over, if the V
CSOP-CSON
threshold (typical 10 mV), the low-side power MOSFET turns off and stays off until the beginning of the next
cycle, where the high-side power MOSFET is turned on again. After the low-side MOSFET turns off, the inductor
current flows through back-gate diode until it reaches zero. The negative inductor current is blocked by the diode,
and the inductor current becomes discontinuous. This mode is called discontinuous-conduction mode (DCM).
During the DCM mode, the loop response automatically changes and has a single-pole system at which the pole
is proportional to the load current, because the converter does not sink current, and only the load provides a
current sink. This means at very low currents the loop response is slower, as there is less sinking current
available to discharge the output voltage. At very low currents during non-synchronous operation, there may be a
small amount of negative inductor current during the 40-ns recharge pulse. The charge should be low enough to
be absorbed by the input capacitance.
Whenever the converter goes into zero percent duty-cycle, the high-side MOSFET does not turn on, and the
low-side MOSFET does not turn on (no 40-ns recharge pulse) either, and there is no discharge from the battery
unless the BOOT to PHASE voltage discharges below 4 V. In that case, it pulses once to recharge the bootstrap
capacitor.
voltage falls below the UCP
24 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

( )
RIPPLE
DCM
BAT
IN BAT
IN S
RIPPLE
out
I
I <
2
V
1
V -V
V f
and I =
L
æ ö
æ ö
´ ´
ç ÷
ç ÷
è ø
è ø
bq24745
www.ti.com
REFRESH BTST CAPACITOR
If the BOOT pin to PHASE pin voltage falls below 4 V for more than three cycles, then the high-side n-channel
power MOSFET is turned off and the low-side n-channel power MOSFET is turned on for 40 ns to pull the
PHASE node down and recharge the BOOT capacitor. The 40-ns low-side MOSFET on-time is required protect
from ringing noise, and to ensure the bootstrap capacitor is always recharged and able to keep the high-side
power MOSFET on during the next cycle.
UCP (CHARGE UNDERCURRENT), USING SENSE RESISTOR
In the bq24745, the cycle-by-cycle UCP allows using very small inductors seamlessly, even if they have large
ripple current. Every cycle when the low-side MOSFET turns-on, if the CSOP-CSON voltage falls below 10 mV
(inductor current falls below 1 A if using a 10-mΩ sense resistor), the low-side MOSFET is latched off until the
next cycle begins and resets the latch.
The converter automatically detects when to turn off the low-side MOSFET every cycle. The converter goes into
discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) when the current falls below 1/2 the inductor peak-to-peak current ripple.
The inductor current ripple is given by
where
VIN: adapter voltage = DCIN voltage
V
: output voltage = VFB voltage
VFB
fS: switching frequency = 300 kHz
L
: output inductor
OUT
For proper cycle-by-cycle UCP sensing, the output filter capacitor should sit on CSON. Only a 0.1-µF capacitor is
on CSOP, close to the device input.
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
(2)
AVERAGE CHARGE OVERCURRENT, USING SENSE AMPLIFIER
The charger has average overcurrent protection using the V
resistor. It monitors the charge current, and prevents the current from exceeding 145% of the programmed
regulated charge current. If the charge current limit falls below 3.3 A (on 10 mΩ), the overcurrent limit is fixed at
5 A. The high-side gate drive turns off when the overcurrent is detected, and automatically resumes when the
current falls below the overcurrent threshold. There is an internal 160-kHz filter pole, to filter the switching
frequency and prevent false tripping. This adds a small delay, depending on the amount of overdrive over the
threshold.
BATTERY OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION, USING REMOTE SENSING VFB
The converter does not allow switching when the battery voltage at VFB exceeds 104% of the regulation voltage
set-point. Once the VFB voltage returns below 102% of the regulation voltage, switching resumes. This allows
quick response to an overvoltage condition, such as occurs when the load is removed or the battery is
disconnected. A current sink from CSOP and CSON to GND is on only during charging and allows discharging
the stored output inductor energy that is transferred to the output capacitors.
BATTERY TRICKLE CHARGING
The bq24745 automatically reduces the charge current limit to a fixed 220 mA to trickle-charge the battery when
the voltage on the VFB pin falls below 2.5 V. The charge current returns to the value programmed on the
ChargeCurrent(0x14) register when the VFB pin voltage rises above 2.7 V.
This function provides a safe trickle charge to close deeply discharged open packs.
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 25
CSON-CSOP
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745
voltage across the charge-current sense

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
HIGH-ACCURACY VICM USING CURRENT-SENSE AMPLIFIER (CSA)
An industry standard, high-accuracy current-sense amplifier (CSA) is used to monitor the input current by the
host or some discrete logic through the analog voltage output of the VICM pin. The CSA amplifies the input
sensed voltage of CSSP-CSSN by 20× through the VICM pin. The VICM output is a voltage source 20 times the
input differential voltage. Once DCIN is above 4.5 V and ACIN is above 0.6 V, VICM no longer stays at ground,
but becomes active. A user wanting to lower the voltage could use a resistor divider from VICM to GND and still
achieve accuracy over temperature.
A 100-pF capacitor connected on the output is recommended for decoupling high-frequency noise.
VDDSMB INPUT SUPPLY
The VDDSMB input provides bias power to the SMBus interface logic. Connect VDDSMB to an external 3.3-V or
5-V supply rail. SMBus communication can start between host and charger when the VDDSMB voltage is above
2.5 V and the VREF voltage is at 3.3 V. Bypass VDDSMB to GND with a 0.1-µF or greater ceramic capacitor.
INPUT UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT (UVLO)
The system must have a minimum 4.5-V DCIN voltage to allow proper operation. When the DCIN voltage is
below 4 V, VREF LDO stays inactive, even with ACIN above 0.6 V. VREF turns on when DCIN > 4.5 V and ACIN
> 0.6 V. To enable VDDP requires DCIN > 4.5 V, ACIN > 2.4 V, and CE = HIGH.
VDDP GATE DRIVE REGULATOR
An integrated low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator provides a 6-V supply derived from DCIN for high efficiency,
and delivers over 90 mA of load current. The LDO powers the gate drivers of the n-channel switching MOSFETs.
Bypass VDDP to PGND with a 1-µF or greater ceramic capacitor. During thermal shutdown, the VDDP LDO is
disabled.
www.ti.com
INPUT CURRENT COMPARATOR TRIP DETECTION
In order to optimize the system performance, the host monitors the adapter current. Once the adapter current is
above a threshold set via ICREF, the ICOUT pin sends a signal to the HOST. The signal alarms the host that
input power has exceeded the programmed limit, allowing the host to throttle back system power by reducing
clock frequency, lowering rail voltages, or disabling certain parts of the system. The ICOUT pin is an open-drain
output. Connect a pullup resistor to ICOUT. The output is logic HI when the VICM output voltage (VICM = 20 ×
V
CSSP-CSSN
using VREF. The hysteresis can be programmed by a positive feedback resistor from the ICOUT pin to the
ICREF pin.
) is lower than the ICREF input voltage. The ICREF threshold is set by an external resistor divider
26 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

20k
1k
VICM
CurrentSense
Amplifier
VICM
Error
Amplifier
Disable
+
-
ACOK
Comparator
ACOK
2.4V
ACIN
+
-
InputCurrent
Comparator
+
-
VICM
ICREF
ICOUT
+
-
CSSP
CSSN
ACOK
ProgramHysteresisof
comparator
byputtingaresistorinfeedback
fromICOUT pintoICREFpin
.
VICM
Disable
www.ti.com
bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Figure 36. ACOK, ICREF, and ICOUT Logic
OPEN-DRAIN STATUS OUTPUTS (ACOK, ICOUT PINS)
Two status outputs are available; both require external pullup resistors to pull the pins to the system digital rail for
a high level.
The ACOK open-drain output goes high when ACIN is above 2.4 V. It indicates that a functional adapter is
providing a valid input voltage.
The ICOUT open-drain output goes low when the input current is higher than the threshold programmed via the
ICREF pin. Hysteresis can be programmed by adding a resistor from the ICREF pin to the ICOUT pin.
THERMAL SHUTDOWN PROTECTION
The QFN package has low thermal impedance, which provides good thermal conduction from the silicon to the
ambient, to keep the junction temperature low. As an added level of protection, the charger converter turns off
and self-protects whenever the junction temperature exceeds the TSHUT threshold of 155°C. VDDP LDO is
disabled as well during thermal shutdown. The charger stays off until the junction temperature falls below 135°C.
Once the temperature drops below 135°C, the VDDP LDO is enabled. If all the conditions described in the
Enable and Disable Charging section are valid, charge soft-starts again.
CHARGER TIME-OUT
The bq24745 includes a timer to terminate charging if the charger does not receive a ChargeVoltage() or
ChargeCurrent() command within 170 s. If a time-out occurs, both ChargeVoltage() and ChargeCurrent()
commands must be resent to re-enable charging.
CHARGE TERMINATION FOR Li-Ion OR Li-Polymer
The primary termination method for Li-Ion and Li-Polymer is minimum current. Secondary temperature
termination (see the Charge Current Regulation section) also provides additional safety. The host controls the
charge initiation and the termination. A battery pack gas gauge assists the hosts on setting the voltages and
determining when to terminate based on the battery-pack state of charge.
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 27
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
REMOTE SENSE
The bq24745 has a dedicated remote sense pin, VFB, which allows the rejection of board resistance and
selector resistance. To use remote sensing fully, connect VFB directly to the battery interface through an
unshared battery-sense Kelvin trace, and place a 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor near the VFB pin to GND (see
Figure 1).
Remote Kelvin sensing provides higher regulation accuracy by eliminating parasitic voltage drops. Remote
sensing cancels the effect of impedance in series with the battery. This impedance normally causes the battery
charger to enter constant-voltage mode prematurely.
Component List for Typical System Circuit of Figure 2
Part Designator Qty Description
Q1, Q2, 3 P-channel MOSFET, –30-V, –7.5-A, SO-8, Vishay-Siliconix, Si4435
Q3, Q4 2 N-channel MOSFET, 30-V, 12.5-A, SO-8, Fairchild, FDS6680A
RAC, RSR 2 Sense resistor, 10-mW, 2010, Vishay-Dale, WSL2010R0100F
L1 1 Inductor, 5.6-uH, 7-A, 31-mΩ Vishay, IHLP2525CZ01-2R
D1 1 Diode, dual Schottky, 30-V, 200-mA, SOT23, Fairchild, BAT54C
C1 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 2.2-µF, 35-V, 10%, X7R
C6 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 1-µF, 35-V, 10%, X7R
2xC13, C14, C15 4 Capacitor, ceramic, 10-µF, 35-V, 20%, X5R, 1206, Panasonic, ECJ-3YB1E106M
C6, C16, C4, C8 4 Capacitor, ceramic, 1-µF, 25-V, 10%, X7R, 2012, TDK, C2012X7R1E105K
C2, C3, C7, C9, C10, C17 6 Capacitor, ceramic, 0.1-µF, 50-V, 10%, X7R, 0805, Kemet, C0805C104K5RACTU
C5 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 100- pF, 25-V, 10%, X7R, 0805, Kemet
C23 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 51-pF, 25-V, 10%, X7R, 0805, Kemet
C21 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 2000-pF, 25-V, 10%, X7R, 0805, Kemet
C22 1 Capacitor, ceramic, 130-pF, 25-V, 10%, X7R, 0805, Kemet
R3, R4, R10, R11, R12 5 Resistor, chip, 10-kΩ, 1/16-W, 5%, 0402
R1 1 Resistor, chip, 309-kΩ, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
R2 1 Resistor, chip, 49.9-kΩ, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
RC1 1 Resistor, thick film chip paralleling, 2× 3.9-Ω, 25-V, 1210
RC6 1 Resistor, thick film chip , 10-Ω, 1206
R19 1 Resistor, chip, 7.5-kΩ, 1/16-W, 5%, 0402
R20 1 Resistor, chip, 20-kΩ, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
R21 1 Resistor, chip, 200-kΩ, 1/16-W, 5%, 0402
R22 1 Resistor, chip, 100-Ω, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
R7, R8 2 Resistor, chip, 200-kΩ, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
R18 1 Resistor, chip, 1.4-MΩ, 1/16-W, 1%, 0402
www.ti.com
28 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

www.ti.com
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
GLOSSARY
VICM Output Voltage of Input Current Monitor
ICREF Input Current Reference - sets the threshold for the input current limit
DPM Dynamic Power Management
CSOP, CSON Current Sense Output of battery positive and negative
These pins are used with an external low-value series resistor to monitor the current to and
from the battery pack.
CSSP, CSSN Current Sense Supply positive and negative
These pins are used with an external low-value series resistor to monitor the current from
the adapter supply.
POR Power-on reset
bq24745
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 29
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
REVISION HISTORY
NOTE: Page numbers of previous versions may differ from the current version.
Changes from Original (December 2007) to Revision A Page
• Changed The data sheet title From: SMBus-Controlled Multi-Chemistry Battery Charger With Input Current Detect
Comparator To: SMBus-Controlled Multi-Chemistry Battery Charger With Input Current Detect Comparator and
Charge Enable Pin ................................................................................................................................................................ 1
• Deleted Features Bullet: Cells Pin Supports Two to Four Li-Ion Cells ................................................................................. 1
• Deleted Condition above Figure 1: VICM
• Added text to the condition above Figure 2: "for ICOUT Input Current comparator" ........................................................... 3
• Changed ICREF text in the PIN FUNCTIONS table From: Input current comparator voltage reference input. Connect
a resistor-divider from VREF to ICREF, and GND to program the reference for the LOPWR comparator To: Input
current comparator voltage reference input. Connect a resistor-divider from VREF to ICREF, and GND to program
the reference for the ICOUT comparator .............................................................................................................................. 4
Changes from Revision A (October 2008) to Revision B Page
• Deleted "Level 2" from title ................................................................................................................................................... 1
• Deleted "Input Overvoltage Protection (OVP)" Features bullet ............................................................................................ 1
• Changed Feature bullet from "6 V-24 V" to "7 V-24 V" ........................................................................................................ 1
• Changed "10-μ" to "10-μA" Battery Current .......................................................................................................................... 1
• Changed last sentence of first paragraph of DESCRIPTION by deleting "one," from the text string. .................................. 1
• Changed Figure 1 graphic entity ........................................................................................................................................... 2
• Changed Figure 2 graphic entity ........................................................................................................................................... 3
• Changed TAfrom "70°C" to "40°C" in the Package Thermal Data table. ............................................................................. 3
• Changed θJAfrom "39°C/W" to "36°C/W" in the Package Thermal Data table. .................................................................... 3
• Changed "ACOUT" to "ICOUT" and deleted "ICREF input" from Pin 2 functional description. ........................................... 4
• Deleted "optional" from Pins 17, 18, 27, and 28 functional description in the Pin Functions table. ..................................... 4
• Added text to Pin 22 functional description. ......................................................................................................................... 4
• Changed Pin 22 functional description from "100-Ω" resistor to "10-Ω" resistor in the Pin Functions table. ....................... 4
• Added "ACOK" specification to first row of Absolute Maximum Ratings table. .................................................................... 5
• Added "SDA" and "SCL" specification to fourth row of Absolute Maximum Ratings table, and changed maximum
voltage from "7 V" to "6 V" .................................................................................................................................................... 5
• Deleted "GND" and "PGND" specification from Absolute Maximum Ratings table .............................................................. 5
• Added "ACOK" specification to Recommended Operating Conditions table ........................................................................ 5
• Added "VDDSMB", "SDA", and "SCL" specifications to Recommended Operating Conditions table .................................. 5
• Changed VFB SHORT (....) COMPARATOR specification parameter text from ""VFB short rising hysteresis" to "VFB
short falling hysteresis" ......................................................................................................................................................... 7
• Changed Functional Block Diagram graphic entity ............................................................................................................. 17
• Changed Detailed Description -- re-write for clarification ................................................................................................... 18
• Changed Figure 33 graphic entity ....................................................................................................................................... 19
• Changed Figure 34 graphic entity legend ........................................................................................................................... 19
• Changed Figure 35 graphic entity legend ........................................................................................................................... 20
• Changed Figure 36 graphic entity ....................................................................................................................................... 27
• Deleted "Q5" from Component List table. ........................................................................................................................... 28
• Added description for C1 and C6 in the Component List table. ......................................................................................... 28
• Changed "R9" to "R19" in Component List ......................................................................................................................... 28
• Added R20 to Component List ............................................................................................................................................ 28
= 6 A ............................................................................................................ 2
er_limit
www.ti.com
30 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

bq24745
www.ti.com
• Changed "R11" to "R21" in Component List ....................................................................................................................... 28
• Added R22 to Component List ............................................................................................................................................ 28
Changes from Revision B (April 2010) to Revision C Page
• Changed Table 5 , Bit 7 description from "128mA" to "256mA"; Bit 8 description from "256mA" to "512mA"; Bit 9
description from "512mA" to "1024mA"; Bit 10 description from "1024mA" to "2048mA"; Bit 11 description from
"2048mA" to "4096mA"; and Bit 12 description from "4096mA" to "8192 mA". .................................................................. 22
Changes from Revision C (April 2011) to Revision D Page
• Corrected pin numbers on pins CSSN, CSSP, CSON, and CSOP in Figure 1 .................................................................... 2
• Corrected pin numbers on pins CSSN, CSSP, CSON, and CSOP in Figure 2 .................................................................... 3
SLUS761D –DECEMBER 2007– REVISED OCTOBER 2011
Copyright © 2007–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 31
Product Folder Link(s) :bq24745

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
11-Apr-2013
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
BQ24745RHDR ACTIVE VQFN RHD 28 3000 Green (RoHS
BQ24745RHDRG4 ACTIVE VQFN RHD 28 3000 Green (RoHS
BQ24745RHDT ACTIVE VQFN RHD 28 250 Green (RoHS
BQ24745RHDTG4 ACTIVE VQFN RHD 28 250 Green (RoHS
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
Package Type Package
(1)
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
(3)
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR 0 to 125 BQ
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR 0 to 125 BQ
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR 0 to 125 BQ
CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR 0 to 125 BQ
Op Temp (°C) Top-Side Markings
(4)
24745
24745
24745
24745
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability
information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that
lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between
the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight
in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature.
(4)
Multiple Top-Side Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Top-Side Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a
continuation of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Top-Side Marking for that device.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information
provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and
continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals.
TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis.
Samples
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
11-Apr-2013
Addendum-Page 2

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 18-Aug-2014
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
BQ24745RHDR VQFN RHD 28 3000 330.0 12.4 5.3 5.3 1.1 8.0 12.0 Q2
BQ24745RHDT VQFN RHD 28 250 180.0 12.4 5.3 5.3 1.1 8.0 12.0 Q2
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0
(mm)B0(mm)K0(mm)P1(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 18-Aug-2014
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
BQ24745RHDR VQFN RHD 28 3000 367.0 367.0 35.0
BQ24745RHDT VQFN RHD 28 250 210.0 185.0 35.0
Pack Materials-Page 2




IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other
changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest
issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and
complete. All semiconductor products (also referred to herein as “components”) are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its components to the specifications applicable at the time of sale, in accordance with the warranty in TI’s terms
and conditions of sale of semiconductor products. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary
to support this warranty. Except where mandated by applicable law, testing of all parameters of each component is not necessarily
performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or
other intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI components or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license to use such products or services or a warranty or
endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property of the
third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of significant portions of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration
and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered
documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional restrictions.
Resale of TI components or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that component or service
voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI component or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice.
TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Buyer acknowledges and agrees that it is solely responsible for compliance with all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements
concerning its products, and any use of TI components in its applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support
that may be provided by TI. Buyer represents and agrees that it has all the necessary expertise to create and implement safeguards which
anticipate dangerous consequences of failures, monitor failures and their consequences, lessen the likelihood of failures that might cause
harm and take appropriate remedial actions. Buyer will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use
of any TI components in safety-critical applications.
In some cases, TI components may be promoted specifically to facilitate safety-related applications. With such components, TI’s goal is to
help enable customers to design and create their own end-product solutions that meet applicable functional safety standards and
requirements. Nonetheless, such components are subject to these terms.
No TI components are authorized for use in FDA Class III (or similar life-critical medical equipment) unless authorized officers of the parties
have executed a special agreement specifically governing such use.
Only those TI components which TI has specifically designated as military grade or “enhanced plastic” are designed and intended for use in
military/aerospace applications or environments. Buyer acknowledges and agrees that any military or aerospace use of TI components
which have not been so designated is solely at the Buyer's risk, and that Buyer is solely responsible for compliance with all legal and
regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI has specifically designated certain components as meeting ISO/TS16949 requirements, mainly for automotive use. In any case of use of
non-designated products, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet ISO/TS16949.
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Automotive and Transportation www.ti.com/automotive
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DSP dsp.ti.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com
OMAP Applications Processors www.ti.com/omap TI E2E Community e2e.ti.com
Wireless Connectivity www.ti.com/wirelessconnectivity
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...