Page 1

User's Guide
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous
Switch-Mode Charger
Contents
1 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 2
1.1 EVM Features ...................................................................................................... 2
1.2 General Description ................................................................................................ 2
1.3 I/O Description ...................................................................................................... 2
1.4 1.4 Controls and Key Parameters Setting ...................................................................... 3
1.5 Recommended Operating Conditions ........................................................................... 3
2 Test Summary ............................................................................................................... 4
2.1 Definitions ........................................................................................................... 4
2.2 Equipment ........................................................................................................... 4
2.3 Equipment Setup ................................................................................................... 5
2.4 Procedure ........................................................................................................... 6
3 PCB Layout Guideline ...................................................................................................... 7
4 Bill of Materials, Board Layout and Schematics ........................................................................ 8
4.1 Bill of Materials ..................................................................................................... 8
5 Board Layout ............................................................................................................... 11
6 Schematics ................................................................................................................. 19
List of Figures
1 Original Test Setup for HPA422 (bq2461x/bq2463x EVM)............................................................ 5
2 Top Layer................................................................................................................... 11
3 2
4 3
5 Bottom Layer............................................................................................................... 14
6 Top Assembly.............................................................................................................. 15
7 Bottom Assembly.......................................................................................................... 16
8 Top Silkscreen............................................................................................................. 17
9 Bottom Silkscreen ......................................................................................................... 18
10 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM Schematic ..................................................................................... 19
1 I/O Description............................................................................................................... 2
2 Controls and Key Parameters Setting.................................................................................... 3
3 Recommended Operating Conditions.................................................................................... 3
4 Bill of Materials.............................................................................................................. 8
nd
Layer .................................................................................................................... 12
rd
Layer..................................................................................................................... 13
List of Tables
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
Page 2
Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 EVM Features
• Evaluation Module For bq2461x/bq2463x
• High Efficiency Synchronous Buck Charger
• User-programmable up to 26V Battery Voltage
• AC Adapter Operating Range 5 V–28 V
• LED Indication for Control and Status Signals.
• Test Points for Key Signals Available for Testing Purpose. Easy Probe Hook-up.
• Jumpers Available. Easy to Change Connections.
1.2 General Description
The bq2461x is highly integrated Li-ion or Li-polymer switch-mode battery charge controllers. The
bq2463x is highly integrated switch-mode battery charge controllers designed specifically to charge
Lithium Phosphate battery chemistries.
They offer a constant-frequency synchronous PWM controller with high accuracy charge current and
voltage regulation, adapter current regulation, termination, charge preconditioning, and charge status
monitoring,
The bq2461x/bq2463x charges the battery in three phases: preconditioning, constant current, and
constant voltage. Charge is terminated when the current reches a minimum user-selectable level. A
programmable charge timer provides a safety backup for charge termination. The bq2461x/bq2463x
automatically restarts the charge cycle if the battery voltage falls below an internal threshold, and enters a
low-quiescent current sleep mode when the input voltage falls below the battery voltage.
The dynamic power management (DPM) function modifies the charge current depending on system load
conditions, avoiding ac adapter overload.
High accuracy current sense amplifiers enable accurate measurement of the ac adapter current, allowing
monitoring of overall system power.
For details, see bq24610 and bq24617 (SLUS892), bq24616 (SLUSA49) and bq2463x (SLUS894) data
sheets.
www.ti.com
1.3 I/O Description
Jack Description
J1–DCIN AC adapter, positive output
J1–GND AC adapter, negative output
J2–VEXT External power supply, positive output
J2–GND External power supply, negative output
J2–TTC Timer capacitor pin
J3–ACSET Input current program pin
J3–ISET1 Charge Current Program Pin
J3–ISET2 Pre-charge/Termination program pin
J3–GND Ground
J–PG Power Good (active low)
J4–CHGEN Charge enable
J4–VREF IC reference voltage VREF
J4–TS Temperature Qualification Voltage Input
J5–VSYS Connected to system
J5–VBAT Connected to battery pack
2
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Table 1. I/O Description
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 3
www.ti.com
Table 1. I/O Description (continued)
Jack Description
J5–GND Ground
JP1–LOW Ground
JP1–TTC Timer capacitor pin
JP1–HI Pull-up voltage source
JP2–HI Pull-up voltage source
JP2–LEDPWR LED Pull-up power line
JP3–VREF IC reference voltage VREF
JP3–VPULLUP Pull-up voltage source
JP3–EXT External voltage supply from J2
JP4–VCC Pull-up voltage source of ACDRV and BATDRV LED logic circuit
JP4–VCOM Q7 and Q11 common source
JP5–HI Pull-up voltage source
JP5–CHGEN Charge enable
1.4 1.4 Controls and Key Parameters Setting
Table 2. Controls and Key Parameters Setting
Jack Description Factory Setting
TTC setting
JP1 Jumper on 2-3 (TTC and VPULLUP)
JP2 Jumper On
JP3 1-2 : Connect VPULLUP to VREF
JP4 The pull-up voltage source of ACDRV and BATDRV LED logic circuit. Jumper on
JP5 Jumper on: CHGEN to VPULLUP Jumper Off
1-2 : Connect TTC to GROUND (Disable termination and the safety timer)
2-3 : Connect TTC to VPULLUP (Allow termination, but disable the safety time)
2 floating: Allow termination, CTTC sets the safety timer
The pull-up power source supplies the LEDs when on.
LED has no power source when off.
VPULLUP setting
2-3 : Connect VPULLUP to VEXT
CHGEN setting
Jumper off: CHGEN is set to low by pull down resistor.
Introduction
Jumper On 1-2 (VPULLUP and
VREF)
1.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 3. Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
Supply voltage, V
Battery voltage, V
Supply current, I
Charge current, I
Operating junction
temperature range, T
IN
BAT
AC
chrg
J
Input voltage from ac adapter input 5 24 28 V
Voltage applied at VBAT terminal of J5 V
Maximum input current from ac adapter
input
Battery charge current 2 3 8 A
2.1 (61x) 21 (61x)
1.8 (63x) 18 (63x)
0 4.5 A
0 125 °C
The bq2461x/bq2463x EVM board requires a regulated supply approximately 0.5 V minimum above the
regulated voltage of the battery pack to a maximum input voltage of 28 VDC.
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
24(617)
(610/616/63x)
3
Page 4

Test Summary
R25 and R28 can be changed to regulate output.
V
= 2.1V × [1+ R25/R28]; for bq2461x;
BAT
V
= 1.8V × [1+ R25/R28]; for bq2463x;
BAT
Adjust the input voltage as required. Output set to operate at 21V (bq2461x) or 18V (bq2463x) from the
factory.
2 Test Summary
2.1 Definitions
This procedure details how to configure the HPA422 evaluation board. On the test procedure the following
naming conventions are followed. See the HPA422 schematic for details.
VXXX: External voltage supply name (VADP, VBT, VSBT)
LOADW: External load name (LOADR, LOADI)
V(TPyyy): Voltage at internal test point TPyyy. For example, V(TP12) means the voltage at TP12
V(Jxx): Voltage at jack terminal Jxx.
V(TP(XXX)): Voltage at test point "XXX". For example, V(ACDET) means the voltage at the test
V(XXX, YYY): Voltage across point XXX and YYY.
I(JXX(YYY)): Current going out from the YYY terminal of jack XX.
Jxx(BBB): Terminal or pin BBB of jack xx
Jxx ON: Internal jumper Jxx terminals are shorted
Jxx OFF: Internal jumper Jxx terminals are open
Jxx (-YY-) ON: Internal jumper Jxx adjacent terminals marked as "YY" are shorted
Measure:→ A,B Check specified parameters A, B. If measured values are not within specified limits the
Observe → A,B Observe if A, B occur. If they do not occur, the unit under test has failed.
www.ti.com
point which is marked as "ACDET".
unit under test has failed.
Assembly drawings have location for jumpers, test points and individual components.
2.2 Equipment
2.2.1 Power Supplies
Power Supply #1 (PS#1): a power supply capable of supplying 30-V at 5-A is required.
Power Supply #2 (PS#2): a power supply capable of supplying 5-V at 1-A is required.
Power Supply #3 (PS#3): a power supply capable of supplying 5-V at 1-A is required.
2.2.2 LOAD #1
A 30V (or above), 5A (or above) electronic load that can operate at constant current mode
2.2.3 LOAD #2
A Kepco bipolar operational power supply/amplifier, 0 ±30V (or above), 0 ±6A (or above).
2.2.4 Oscilloscope
Tektronix TDS3054 scope or equivalent, 10X voltage probe.
4
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 5
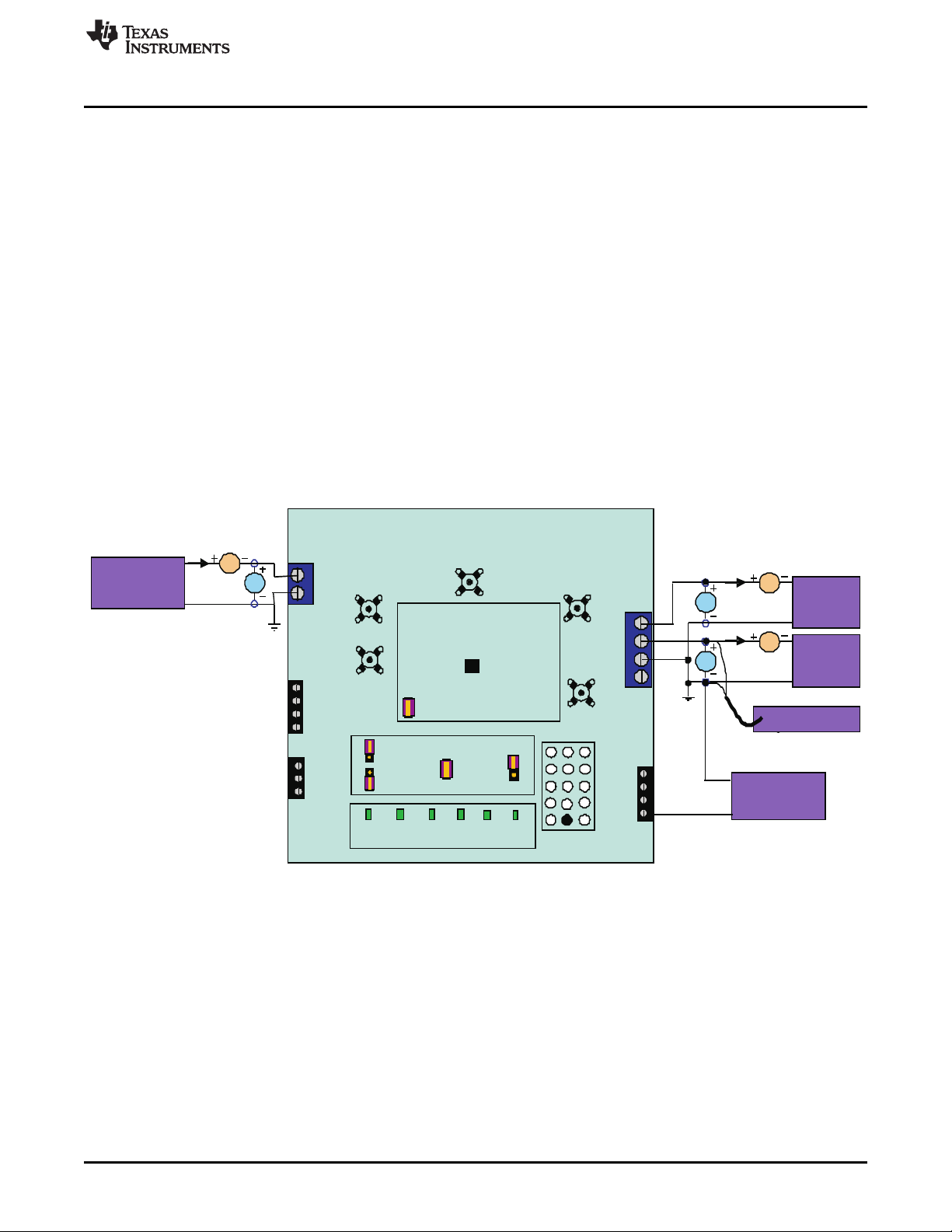
bq24610/616/617/30EVM
HPA422
ACPWR
J1
PGND
SYS
J5
PGND
BAT
VREF
JP3
PG
TS
APPLICATIONCIRCUIT
PH
TP12
SYS
VBAT
TP1
ACPWR
STAT1
J
3
J2
JP1
U1
JP5
J4
V
Iin
I
Power
supply#1
Isys
V
Ibat
V
I
Load
#1
Load
#2
I
TP2
JP2
GND
VEXT
TTC
ISET1
ACSET
ISET2
VEXT
GND
VREF
HI
L
O
Power
sup ply#2
I
/ACDRV
/BATDRV
CE PG /STAT1 /STAT2
VCC
TP9
JP4
Oscilloscope
www.ti.com
2.2.5 METERS
Seven Fluke 75 multimeters, (equivalent or better)
Or: Four equivalent voltage meters and three equivalent current meters.
The current meters must be capable of measuring 5A+ current
2.3 Equipment Setup
1. Set the power supply #1 for 0V ± 100mVDC, 5.0 ± 0.1A current limit and then turn off supply.
2. Connect the output of power supply #1 in series with a current meter (multimeter) to J1 (VIN, GND).
3. Connect a voltage meter across J1 (VIN, GND).
4. Set the power supply #2 for 0V ± 100mVDC, 1.0 ± 0.1A current limit and then turn off supply.
5. Connect the output of the power supply #2 to J4 and J5 (TS, GND).
6. Connect Load #1 in series with a current meter to J5 (SYS, GND). Turn off Load #1
7. Connect Load #2 in series with a current meter to J5 (BAT, GND). Turn off Load #2.
8. Connect a voltage meter across J5 (BAT, GND).
9. Connect an oscilloscope's probe across J5 (BAT, GND)
10. Connect a voltage meter across J5 (SYS, GND).
11. JP1 (TTC and HI): ON, JP2: ON, JP3 (VPULLUP and VREF): ON, JP4: ON, JP5: OFF.
After the above steps, the test setup for HPA422 is shown in Figure 1.
Test Summary
Figure 1. Original Test Setup for HPA422 (bq2461x/bq2463x EVM)
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
Page 6

Test Summary
2.4 Procedure
2.4.1 AC Adapter Detection Threshold
1. Make sure EQUIPMENT SETUP steps are followed. Turn on PS#2.
2. Turn on PS#1
Measure → V(J5(SYS)) = 0 ± 500mV
Measure → V(TP(VREF)) = 0V ± 1000mV
Measure → V(TP(REGN)) = 0V ± 500mV
3. Increase the output voltage on PS#1 until D5 (PG) on but do not exceed 5V. Set the power supply #2
to 1.8V ± 100mVDC
Measure → V(J1(VIN)) = 4.5V ± 0.5V
Measure → V(J5(SYS)) = 4.5V ± 0.5V
Measure → V(TP(VREF)) = 3.3V ± 200mV
Measure → V(TP(REGN)) = 0V ± 500mV
Measure → D4 (/ACDRV) on, D5 (PG) on
2.4.2 Charger Regulation Voltage
1. Increase the voltage of PS#1 until V(J1(VIN)) = 24V ± 0.1V.
Measure → V(J5(BAT, GND)) = 0V ± 1V
2. Put JP5 on (Enable the charging).
Observe → D3 (CE) on.
Measure → Peak V(J5(BAT)) = 21.0V ± 1V (bq2461x)
Measure → Peak V(J5(BAT)) = 18.0V ± 1V (bq2463x)
Measure → V(TP(REGN)) = 6V ± 500mV
www.ti.com
2.4.3 Charge Current and AC Current Regultion (DPM)
1. Take off JP5 (Disable the charging).
2. Connect the Load #2 in series with a current meter (multimeter) to J5 (BAT, GND). Make sure a
voltage meter is connected across J5 (BAT, GND). Turn on the Load #2. Set the output voltage to 12V
(bq2461x) or 2V (bq2463x).
3. Connect the output of the Load #1 in series with a current meter (multimeter) to J5 (SYS, GND). Make
sure a voltage meter is connected across J5 (SYS, GND). Turn on the power of the Load #1. Set the
load current to 3.0A ± 50mA but disable the load #1. The setup is now like Figure 1 for HPA422. Make
sure Ibat = 0A ± 10mA and Isys = 0A ± 10mA.
4. Put JP5 on (Enable the charging).
Observe → D3 (CE) on
Measure → Ibat = 300mA ± 200mA (bq2461x)
Measure → Ibat = 125mA ± 60mA (bq2463x)
Observe → D7 (STAT1) on; D8 (STAT2) off.
5. Set the Load #2 output voltage to 16.5V.
Measure → Ibat = 3000mA ± 300mA
Observe → D7 (STAT1) on; D8 (STAT2) off.
6. Enable the output of the Load #1
Measure → Isys = 3000mA ± 200mA, Ibat = 1400mA ± 500mA, Iin = 4000mA ± 500mA
7. Turn off the Load #1.
Measure → Isys = 0 ± 100mA, Ibat = 3000mA ± 300mA.
8. Increase the Load #2 output voltage from 16.5V to 22V (61x) or 19V (63x).
Measure → Isys = 0 ± 100mA, Ibat = 0mA ± 100mA.
Observe → D7 (STAT1) off; D8 (STAT2) on.
9. Decrease the Load #2 output voltage back to 16.5V.
Observe → D7 (STAT1) on; D8 (STAT2) off.
6
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 7
www.ti.com
2.4.4 Charger Cut-Off by Thermistor
1. Slowly increase the output voltage of PS2 until Ibat = 0 ± 10mA.
Measure → V(J4(TS)) = 2.44V ± 200mV
Observe → D7 (STAT1) off; D8 (STAT2) off.
2. Slowly decrease the output voltage of PS2 to 1.4V ± 0.1V.
Measure → V(J4(TS)) = 1.4V ± 100mV
Measure → Ibat = 3000mA ± 300mA (bq24610/617)
Measure → Ibat = 0mA ± 100mA (bq24616)
Measure → Ibat = 375mA ± 150mA (bq2463x)
Observe → D7 (STAT1) on; D8 (STAT2) off (bq24610/617/630)
Observe → D7 (STAT1) off; D8 (STAT2) off (bq24616)
3. Slowly decrease the output voltage of PS2.
Charge will resume. Continue to decrease the output voltage of PS2 slowly until Ibat = 0 ±10mA.
Measure → V(J4(TS)) = 1.14V ± 200mV
Observe → D7 (STAT1) off; D8 (STAT2) off.
4. Slowly increase the output voltage of PS2 to 1.8V ± 100mV.
Measure → Ibat = 3000mA ± 200mA
Observe → D7 (STAT1) on; D8 (STAT2) off.
2.4.5 Power Path Selection
1. Take off JP5 (Disable the charging)
Observe → D3 (CE) off; D7 (STAT1) off.
2. Set JP3 Jumper On 2-3 (VPULLUP and VEXT). Connect the output of the power supply #3 to
J2(VEXT, GND). Set the power supply #3 for 3.3V ± 200mVDC, 1.0 ± 0.1A current limit.
3. Set the Load #2 output voltage to 16.5V ± 500mV.
4. Measure → V(J5(SYS)) = 24V ± 1V (adapter connected to system)
Observe → D4 (ACDRV) on, D6 (BATDRV) off, D5 (PG) on, D7 (STAT1) off, D8 (STAT2) off.
5. Turn off PS#1.
6. Measure → V(J5(SYS)) = 16.5V ± 0.5V (battery connected to system)
7. Observe → D4 (ACDRV) off, D6 (BATDRV) on, D5 (PG) off, D7 (STAT1) off, D8 (STAT2) off.
8. Turn off power supply #2 and #3. Set JP3 on 1-2 (VPULLUP and VREF).
PCB Layout Guideline
3 PCB Layout Guideline
1. It is critical that the exposed power pad on the backside of the bq2461x/bq2463x package be soldered
to the PCB ground. Make sure there are sufficient thermal vias right underneath the IC, connecting to
the ground plane on the other layers.
2. The control stage and the power stage should be routed separately. At each layer, the signal ground
and the power ground are connected only at the power pad.
3. AC current sense resistor must be connected to ACP and ACN with a Kelvin contact. The area of this
loop must be minimized. The decoupling capacitors for these pins should be placed as close to the IC
as possible.
4. Charge current sense resistor must be connected to SRP, SRN with a Kelvin contact. The area of this
loop must be minimized. The decoupling capacitors for these pins should be placed as close to the IC
as possible.
5. Decoupling capacitors for DCIN, VREF, VCC, REGN should make the interconnections to the IC as
short as possible.
6. Decoupling capacitors for BAT must be placed close to the corresponding IC pins and make the
interconnections to the IC as short as possible.
7. Decoupling capacitor(s) for the charger input must be placed close to top buck FET's drain and bottom
buck FET’s source.
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
Page 8

Bill of Materials, Board Layout and Schematics
www.ti.com
4 Bill of Materials, Board Layout and Schematics
4.1 Bill of Materials
Table 4. Bill of Materials
bq24610-001 bq24617-002 Bq24630-003 bq24616-004 Value RefDes Description Size Part Number Mfr
1 0 0 0 bq24610RGE U1 Charger Controller IC QFN-24 (RGE) bq24610RGE TI
0 1 0 0 bq24617RGE U1 Charger Controller IC QFN-24 (RGE) bq24617RGE TI
0 0 1 0 bq24630RGE U1 Charger Controller IC QFN-24 (RGE) bq24630RGE TI
0 0 0 1 bq24616RGE U1 Charger Controller IC QFN-24 (RGE) bq24616RGE TI
1 1 1 1 0.1uF C3 Capacitor, Ceramic, 16V, X7R, 5%, 603 STD STD
6 6 6 6 0.1uF C7,C8,C13,C1 Capacitor, Ceramic, 16V, X7R, 10% 603 STD STD
6 6 6 6 0.1uF C4,C5,C16,C1 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 10% 603 STD STD
1 1 1 1 22p C22 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 10% 603 STD STD
0 0 0 0 C9,C21,C30,C Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 10% 603 STD STD
3 3 3 3 1.0uF C1,C6,C15 Capacitor, Ceramic, 16V, X7R, 20% 805 STD STD
0 0 0 0 C34 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 10% 805 STD STD
2 2 2 2 1.0uF/50V C12,C14 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X5R, 20% 1206 STD STD
1 1 1 1 2.2uF/50V C2 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 20% 1206 STD STD
0 0 0 0 C32 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X7R, 20% 1206 STD STD
6 6 6 6 10uF/50V C10,C11,C20, Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, Y5V, 1812 STD STD
0 0 0 0 C25,C27 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, X5R, 20% 1812 STD STD
0 0 0 0 D11 Diode, Zener, 7.5V, 350-mW SOT-23 BZX84C7V5 Diodes
0 0 0 0 D10 Diode, Schottky, 200-mA, 30-V SOT23 BAT54 Vishay-Liteon
0 0 0 0 D9 Diode, Zener, 7.5V, 350-mW SOT-23 BZX84C7V5 Diodes
6 6 6 6 Green D3,D4,D5,D6, Diode, LED, Green, 2.1V, 20mA, 6mcd 603 LTST- Lite On
0 0 0 0 D2 Diode, Schottky, 1A, 40V DO-214AA MBRS140 Fairchild
1 1 1 1 ZLLS350 D1 Diode, Schottky, 1.16A, 40-V SOD-523 ZLLS350 Zetex
1 1 0 1 6.8uH L1 Inductor, SMT, 9A, 19.8milliohm 0.520 sq inch IHLP5050CEE Vishay
0 0 1 0 8.2uH L1 Inductor, SMT, 9.5A, 18.3milliohm 0.520 sq inch IHLP5050CEE Vishay
3 3 3 3 PEC02SAAN JP2,JP4,JP5 Header, 2 pin, 100mil spacing, 0.100 inch x 2 PEC02SAAN Sullins
8,C19,C33
7,C24,C26
31
C23,C28,C29 -20/+80%
D7,D8 C190GKT
R6R8M01
R8R2M01
8
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 9

www.ti.com
Bill of Materials, Board Layout and Schematics
Table 4. Bill of Materials (continued)
bq24610-001 bq24617-002 Bq24630-003 bq24616-004 Value RefDes Description Size Part Number Mfr
2 2 2 2 PEC03SAAN JP1,JP3 Header, 3 pin, 100mil spacing, 0.100 inch x 3 PEC03SAAN Sullins
4 4 4 4 0 R10,R19,R26, Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
1 1 1 1 10 R22 Resistor, Chip, 1/4W, 1% 1206 Std Std
1 1 0 0 9.31k R4 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
0 0 1 1 2.2k R4 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
3 3 3 3 1k R21,R24,R27 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
1 1 1 1 100 R8 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
1 1 0 0 430k R5 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
0 0 1 1 6.8k R5 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 402 Std Std
1 1 1 1 0 R17 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 603 Std Std
6 6 6 6 2.21k R31,R34,R35, Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 603 Std Std
1 1 1 1 10 R14 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 603 Std Std
2 2 2 2 10k R29,R30 Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 603 Std Std
6 6 6 6 100k R3, Resistor, Chip, 1/16W, 1% 603 Std Std
1 1 1 1 10k R16 Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
1 1 1 1 100k R15 Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
1 1 1 1 22.1k R12 Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
1 1 1 1 32.4k R7 Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
4 4 4 4 100k R6,R11,R23,R Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
1 1 1 1 909k R25 Resistor, Chip, 1/10W, 1% 805 Std Std
2 2 2 2 3.9 R1,R2 Resistor, Chip, 1/8W, 5% 1206 Std Std
2 2 2 2 0.01 R9,R18 Resistor, Chip, 1/2W, 1% 2010 WSL2010R01 Vishay
1 1 1 1 ED1515 J2 Terminal Block, 3 pin, 6A, 3.5mm 0.41 x 0.25 ED555\3DS OST
2 2 2 2 ED1516 J3,J4 Terminal Block, 4 pin, 6A, 3.5mm 0.55 x 0.25 ED555\4DS OST
1 1 1 1 ED120/2DS J1 Terminal Block, 2 pin, 15A, 5.1mm 0.40 x 0.35 ED120/2DS OST
1 1 1 1 ED120/4DS J5 Terminal Block, 4 pin, 15A, 5.1mm 0.80 x 0.35 ED120/4DS OST
R13
R36,R39,R40
R20,R32,R33,
R37,R38
28
00FEA
inch
inch
inch
inch
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9
Page 10

Bill of Materials, Board Layout and Schematics
www.ti.com
Table 4. Bill of Materials (continued)
bq24610-001 bq24617-002 Bq24630-003 bq24616-004 Value RefDes Description Size Part Number Mfr
1 1 1 1 5001 GND Test Point, Black, Thru Hole Color 0.100 x 0.100 5001 Keystone
14 14 14 14 5002 /ACDRV,/BAT Test Point, White, Thru Hole Color 0.100 x 0.100 5002 Keystone
DRV,/PG, Keyed inch
ACSET,CHGE
N,ISET1,ISET
2, REGN,
STAT1,STAT2
,TS,TTC,
VCC,VREF
5 5 5 5 131-4244-00 TP1,TP2,TP8, Adaptor, 3.5-mm probe clip ( or 0.200 inch 131-4244-00 Tektronix
TP9,TP12 131-5031-00)
3 3 3 3 2N7002DICT Q6,Q8,Q9 MOSFET, N-ch, 60V, 115mA, SOT23 2N7002DICT Vishay-Liteon
3 3 3 3 SI4401BDY- Q1,Q2,Q5 MOSFET, PChan, -40V, -18A, S0-8 SI4401BDY Vishay-
T1-GE (Note 5) 9.2millohm FDS4141 Siliconxi
FDS4141 Fairchild
2 2 2 2 FDS8447 Q3,Q4 MOSFET, NChan, 40V, 50A, 4.5 S0-8 FDS8447 Vishay-
2 2 2 2 TP0610K Q7,Q10 Mosfet, P-Ch, 60V, Rds 6 ohms, Id SOT-23 TP0610K Vishay-
1 1 1 1 PCB 4 layer 2oz. PCB HPA422
5 5 5 5 929950-00 Shorting jumpers, 2-pin, 100mil 929950-00 3M/ESD
4 4 4 4 STANDOFF M/F HEX 6-32 NYL .500" 4816 Keystone
4 4 4 4 6-32 NYL Hex nuts NY HN 632 Building
Keyed inch
1.2Ohms
millohm Siliconix
185 mA Siliconix
spacing
Fasteners
10
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 11

www.ti.com
5 Board Layout
Board Layout
Figure 2. Top Layer
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
11
Page 12

Board Layout
www.ti.com
12
Figure 3. 2ndLayer
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 13

www.ti.com
Board Layout
Figure 4. 3rdLayer
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
13
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 14

Board Layout
www.ti.com
14
Figure 5. Bottom Layer
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 15

www.ti.com
Board Layout
Figure 6. Top Assembly
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
Page 16

Board Layout
www.ti.com
16
Figure 7. Bottom Assembly
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 17

www.ti.com
Board Layout
Figure 8. Top Silkscreen
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17
Page 18

Board Layout
www.ti.com
18
Figure 9. Bottom Silkscreen
bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 19

www.ti.com
6 Schematics
Schematics
Figure 10. bq2461x/bq2463x EVM Schematic
SLUU396A–January 2010–Revised July 2010 bq2461x/bq2463x EVM (HPA422) Multi-Cell Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
19
Page 20

Evaluation Board/Kit Important Notice
Texas Instruments (TI) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following conditions:
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. Persons handling the
product(s) must have electronics training and observe good engineering practice standards. As such, the goods being provided are
not intended to be complete in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective considerations,
including product safety and environmental measures typically found in end products that incorporate such semiconductor
components or circuit boards. This evaluation board/kit does not fall within the scope of the European Union directives regarding
electromagnetic compatibility, restricted substances (RoHS), recycling (WEEE), FCC, CE or UL, and therefore may not meet the
technical requirements of these directives or other related directives.
Should this evaluation board/kit not meet the specifications indicated in the User’s Guide, the board/kit may be returned within 30
days from the date of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY
SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING
ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user indemnifies TI from all
claims arising from the handling or use of the goods. Due to the open construction of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to
take any and all appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic discharge.
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THE INDEMNITY SET FORTH ABOVE, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER
FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
TI currently deals with a variety of customers for products, and therefore our arrangement with the user is not exclusive.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software performance, or infringement of
patents or services described herein.
Please read the User’s Guide and, specifically, the Warnings and Restrictions notice in the User’s Guide prior to handling the
product. This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and voltages. For additional information on TI’s
environmental and/or safety programs, please contact the TI application engineer or visit www.ti.com/esh.
No license is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any machine, process, or
combination in which such TI products or services might be or are used.
FCC Warning
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. It generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and has not been tested for compliance with the limits of computing devices pursuant to part 15
of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against radio frequency interference. Operation of this
equipment in other environments may cause interference with radio communications, in which case the user at his own expense
will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct this interference.
EVM Warnings and Restrictions
It is important to operate this EVM within the input voltage range of 5 V to 28 V and the output voltage range of 0 V to 26 V .
Exceeding the specified input range may cause unexpected operation and/or irreversible damage to the EVM. If there are
questions concerning the input range, please contact a TI field representative prior to connecting the input power.
Applying loads outside of the specified output range may result in unintended operation and/or possible permanent damage to the
EVM. Please consult the EVM User's Guide prior to connecting any load to the EVM output. If there is uncertainty as to the load
specification, please contact a TI field representative.
During normal operation, some circuit components may have case temperatures greater than 60° C. The EVM is designed to
operate properly with certain components above 125° C as long as the input and output ranges are maintained. These components
include but are not limited to linear regulators, switching transistors, pass transistors, and current sense resistors. These types of
devices can be identified using the EVM schematic located in the EVM User's Guide. When placing measurement probes near
these devices during operation, please be aware that these devices may be very warm to the touch.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 21

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Communications and www.ti.com/communications
DSP dsp.ti.com Computers and www.ti.com/computers
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
Interface interface.ti.com Energy www.ti.com/energy
Logic logic.ti.com Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Space, Avionics & www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Telecom
Peripherals
Defense
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless-apps
 Loading...
Loading...