Texas Instruments BQ2014HSN-A309TR, BQ2014HSN-A309 Datasheet
Features
➤
Accurate measurement of avail
able capacity in NiCd or NiMH
batteries
➤
Low-cost battery management so
-
lution for pack integration
-
As little as
1
2
square inch of
PCB for complete circuit
-
Low operating current (120µA
typical)
-
Less than 100nA of data
retention current
➤
High-speed (5kb/s) single-wire
communication interface (HDQ
bus) for critical battery
parameters
➤ Communication with an external
charge controller such as the
bq2004
➤ Direct drive of remaining capacity
LEDs
➤ Automatic rate and temperature
compensation of measurements
➤ 16-pin narrow SOIC
General Description
The bq2014H NiCd/NiMH Gas
Gauge IC is intended for batterypack or in-system installation to
maintain an accurate record of
available battery capacity. The IC
monitors a voltage drop across a
sense resistor connected in series
between the negative battery termi
nal and ground to determine
charge and discharge activity of
the battery. Compensations for bat
tery temperature, self-discharge,
and rate of discharge are applied to
the charge counter to provide avail
able capacity information across a
wide range of operating conditions.
Battery capacity is automatically re
calibrated, or “learned,” in the
course of a discharge cycle from full
to empty.
Nominal available capacity may be
directly indicated using a fivesegment LED display. The bq2014H
also supports a simple single-line
bidirectional serial link to an exter
nal processor (common ground). The
5kb/s HDQ bus interface reduces
communications overhead in the
external microcontroller.
Internal registers include available
capacity and energy, temperature,
voltage and current, and battery
status. The external processor may
also overwrite some of the bq2014H
gas gauge data registers.
The bq2014H can operate from the
batteries in the pack. The REF out
put and an external transistor allow
a simple, inexpensive voltage regu
lator to supply power to the circuit
from the cells.
1
Preliminary
bq2014H
LCOM LED common output
SEG
1
/PROG1LED segment 1/
program 1 input
SEG
2
/PROG2LED segment 2/
program 2 input
SEG
3
/PROG3LED segment 3/
program 3 input
SEG
4
/PROG4LED segment 4/
program 4 input
SEG
5
/PROG5LED segment 5/
program 5 input
DONE Charge complete
input
1
PN20140H..eps
16-Pin Narrow SOIC
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
LCOM
SEG1/PROG
1
SEG2/PROG
2
SEG3/PROG
3
SEG4/PROG
4
SEG5/PROG
5
DONE
V
SS
V
CC
REF
NC
HDQ
RBI
SB
DISP
SR
V
SS
System ground
SR Sense resistor input
DISP
Display control input
SB Battery sense input
RBI Register backup input
HDQ Serial communications
input/output
NC No connect
REF Voltage reference output
V
CC
Supply voltage
Pin Connections
SLUS030–JUNE 1999
Low-Cost NiCd/NiMH Gas Gauge IC
Pin Names

Pin Descriptions
LCOM
LED common output
Open-drain output that switches V
CC
to
source current for the LEDs. The switch is
off during initialization to allow reading of
the soft pull-up or pull-down program resis
tors. LCOM is also high impedance when the
display is off.
SEG
1
–
SEG
5
LED display segment outputs (dual func
tion with PROG
1
–PROG5)
Outputs that each may activate an LED to
sink the current sourced from LCOM.
PROG
1
–
PROG
2
Programmed full count selection inputs
(dual function with SEG
1
–SEG2)
Three-level input pins that define the pro
grammed full count (PFC) thresholds de
scribed in Table 2.
PROG
3
–
PROG
4
Power gauge scale selection inputs (dual
function with SEG
3
–SEG4)
Three-level input pins that define the scale
factor described in Table 2.
PROG
5
Self-discharge rate selection (dual function with SEG
5
)
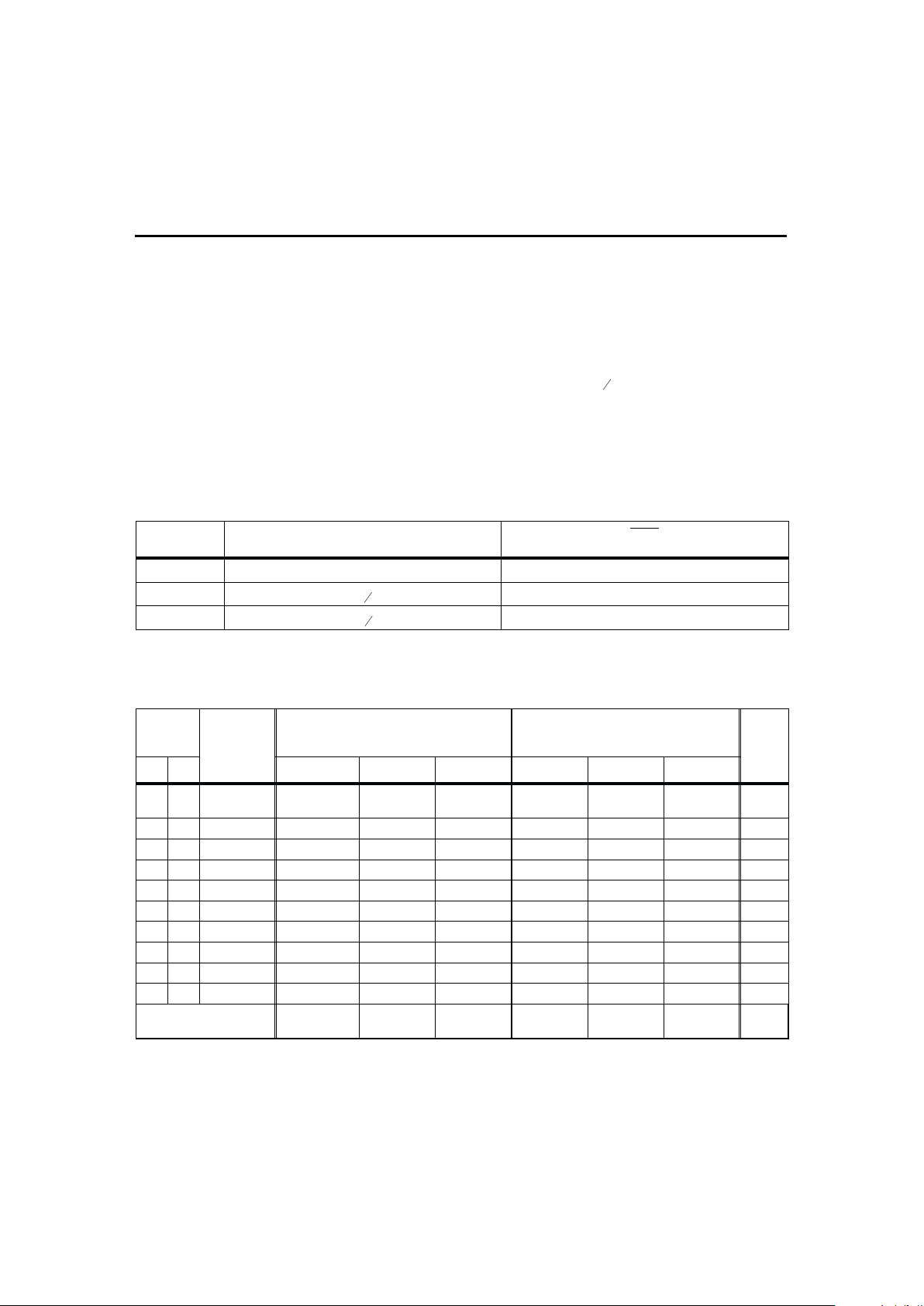
Three-level input pin that defines the
self-discharge and battery-compensation fac
tors as shown in Table 1.
DONE
Charge complete input
Communicates the status of an external
charge-controller such as the bq2004 FastCharge IC to the bq2014H. Note: This pin
must be pulled down to V
SS
using a 200kΩ
resistor.
V
SS
Ground
SR
Sense resistor input
The voltage drop (V
SR
) across the sense re
sistor R
S
is monitored and integrated over
time to interpret charge and discharge activ
ity. V
SR<VSS
indicates discharge, and VSR>
V
SS
indicates charge. The effective voltage
drop, V
SRO
, as seen by the bq2014H is VSR+
V
OS
.
DISP
Display control input
DISP high disables the LED display. DISP
tied to VCCallows PROGXto connect di
-
rectly to V
CC
or VSSinstead of through a
pull-up or pull-down resistor. DISP
floating
allows the LED display to be active during
charge. DISP
low activates the display. See
Table 1.
SB
Secondary battery input
Monitors the battery cell-voltage potential
through a high-impedance resistive divider
network for end-of-discharge voltage (EDV)
thresholds and for battery-removed
detection.
RBI
Register backup input
Provides backup potential to the bq2014H reg
-
isters while V
CC
≤
3V. A storage capacitor or
a battery can be connected to RBI.
HDQ
Serial communication input/output
This is the open-drain bidirectional communications port.
NC
No connect
REF
Voltage reference output
REF provides a voltage reference output for
an optional microregulator.
V
CC
Supply voltage input
2
bq2014H
Preliminary
Functional Description
General Operation
The bq2014H determines battery capacity by moni
toring the amount of current input to or removed
from a rechargeable battery. The bq2014H mea
sures discharge and charge currents, measures bat
tery voltage, estimates self-discharge, monitors the
battery for low battery-voltage thresholds, and com
pensates for temperature and charge/discharge rate.
Current measurement is made by monitoring the
voltage across a small-value series sense resistor be
tween the negative battery terminal and ground.
The bq2014H compensates the nominal available
capacity register for discharge rate and tempera
ture and reports the compensated available
capacity. The bq2014H uses the compensated available
capacity to drive the LED display. In addition, the
bq2014H estimates the available energy using the aver
-
age battery voltage during the discharge cycle and re
-
maining compensated available capacity.
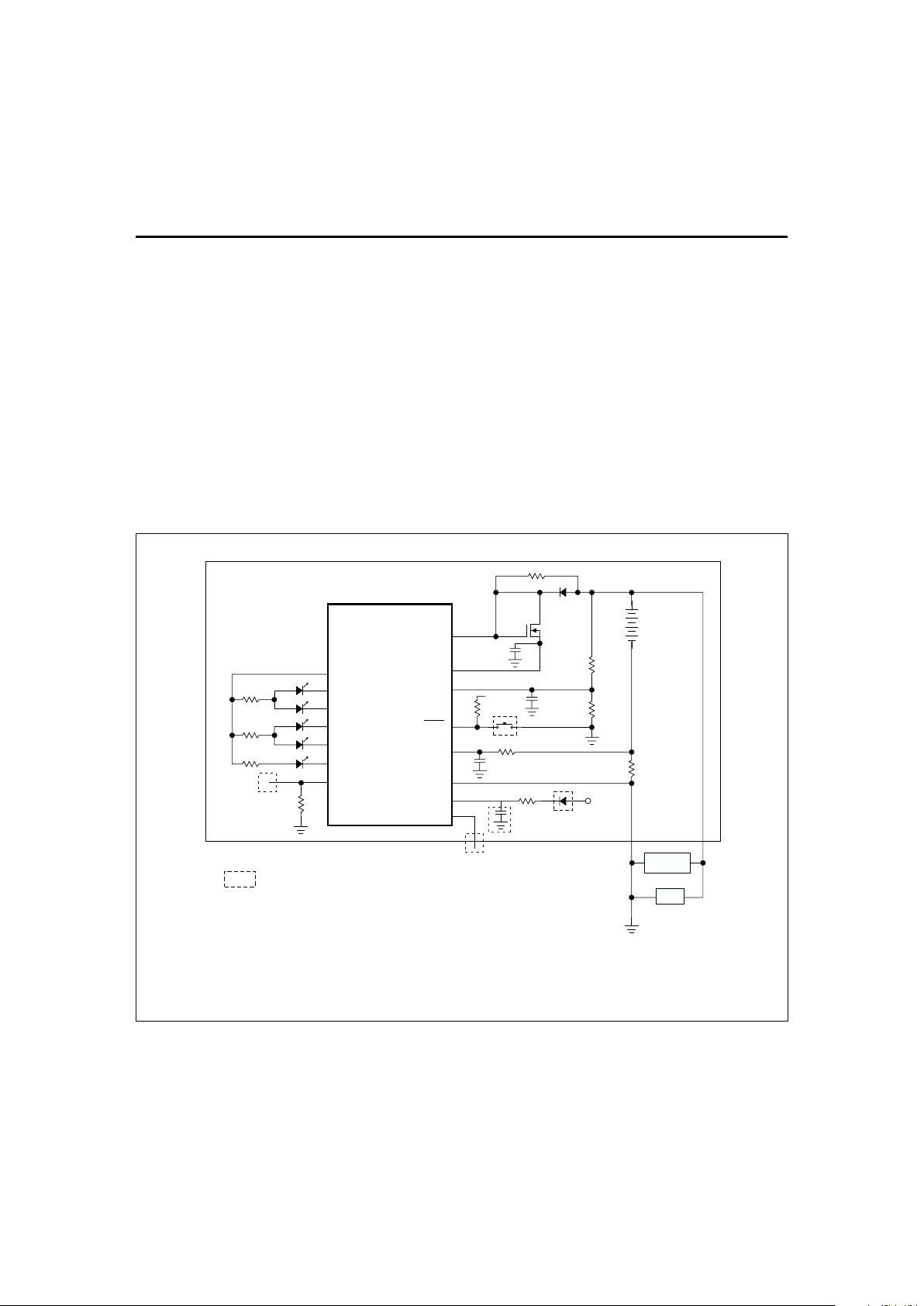
Figure 1 shows a typical battery pack application of the
bq2014H using the LED display capability as a chargestate indicator. The bq2014H is configured to display
capacity in relative display mode. The relative display
mode uses the last measured discharge capacity of the
battery as the battery “full” reference. A push-button
display feature is available for momentarily enabling
the LED display.
The bq2014H monitors the charge and discharge cur
-
rents as a voltage across a sense resistor. (See R
S
in Fig
ure 1.) A filter between the negative battery terminal
and the SR pin is required.
3
F2014HBP.eps
DONE
SEG5/PROG
5
SEG4/PROG
4
SEG3/PROG
3
SEG2/PROG
2
SEG1/PROG
1
SR
DISP
SB
V
CC
REF
bq2014H
Gas-Gauge IC
LCOM
V
SS
RBI
HDQ
V
CC
100K
0.1µF
C1
Q1
ZVNL110A
R
S
1M
RB
1
R
1
RB
2
See note 4
Load
Charger
1. Indicates optional.
2. Programming resistors (5 max.) and ESD-protection diodes are not shown.
3. RC on SR is required.
4. A series diode is required on RBI if the bottom series cell is used as the backup source.
If the cell is used, the backup capacitor is not required, and the anode is connected to the
positive terminal of the cell.
V
CC
C2
Notes:
Figure 1. Battery Pack Application Diagram—LED Display
Preliminary
bq2014H
Voltage Thresholds
In conjunction with monitoring VSRfor charge/discharge
currents, the bq2014H monitors the battery potential
through the SB pin for the end-of-discharge voltage (EDV)
thresholds.
The EDV threshold levels are used to determine when
the battery has reached an “empty”state.
The EDV thresholds for the bq2014H are programmable
with the default values fixed as follows:
EDV1 (first) = 0.76V
EDVF (final) = EDV1 - 0.025V = 0.735V
The battery voltage divider (RB1 and RB2 in Figure 1) is
used to scale these values to the desired threshold.
If V
SB
is below either of the two EDV thresholds, the as
-
sociated flag is latched and remains latched, independ
-
ent of V
SB
, until the next valid charge.
EDV monitoring is disabled if the discharge rate is
greater than 2C (OVLD Flag = 1) and resumes
1
2
second
after the rate falls below 2C. The V
SB
value is available
over the serial port.
RBI Input
The RBI input pin is used with a storage capacitor or external supply to provide backup potential to the internal
bq2014H registers when V
CC
drops below 3.0V. VCCis
output on RBI when V
CC
is above 3.0V. If using an external supply (such as the bottom series cell) as the backup
source, an external diode is required for isolation.
Reset
The bq2014H can be reset by removing VCCand ground
ing the RBI pin for 15 seconds or by commands over the
serial port. The serial port reset command sequence re
quires writing 00h to register PPFC (address = 1Eh) and
then writing 00h to register LMD (address = 05h).
Temperature
The bq2014H internally determines the temperature in
10°C steps centered from approximately -35°C to +85°C.
The temperature steps are used to adapt charge and dis
charge rate compensations, self-discharge counting, and
available charge display translation.
The temperature range is available over the serial port
in 10°C increments, as shown in the following table
Layout Considerations
The bq2014H measures the voltage differential between
the SR and V
SS
pins. VOS(the offset voltage at the SR
pin) is greatly affected by PC board layout. For optimal
results, the PC board layout should follow the strict rule
of a single-point ground return. Sharing high-current
ground with small-signal ground causes undesirable
noise on the small-signal nodes. Additionally:
■
The capacitors (C1 and C2) should be placed as
close as possible to the V
CC
and SB pins,
respectively, and their paths to V
SS
should be as
short as possible. A high-quality ceramic capacitor
of 0.1µF is recommended for V
CC
.
■
The sense-resistor capacitor should be placed as close
as possible to the SR pin.
■
The sense resistor (RS) should be as close as possible to
the bq2014H.
4
TMP (hex) Temperature Range
0x < -30°C
1x -30°C to -20°C
2x -20°C to -10°C
3x -10°C to 0°C
4x 0°C to 10°C
5x 10°C to 20°C
6x 20°C to 30°C
7x 30°C to 40°C
8x 40°C to 50°C
9x 50°C to 60°C
Ax 60°C to 70°C
Bx 70°C to 80°C
Cx > 80°C
bq2014H
Preliminary
Gas Gauge Operation
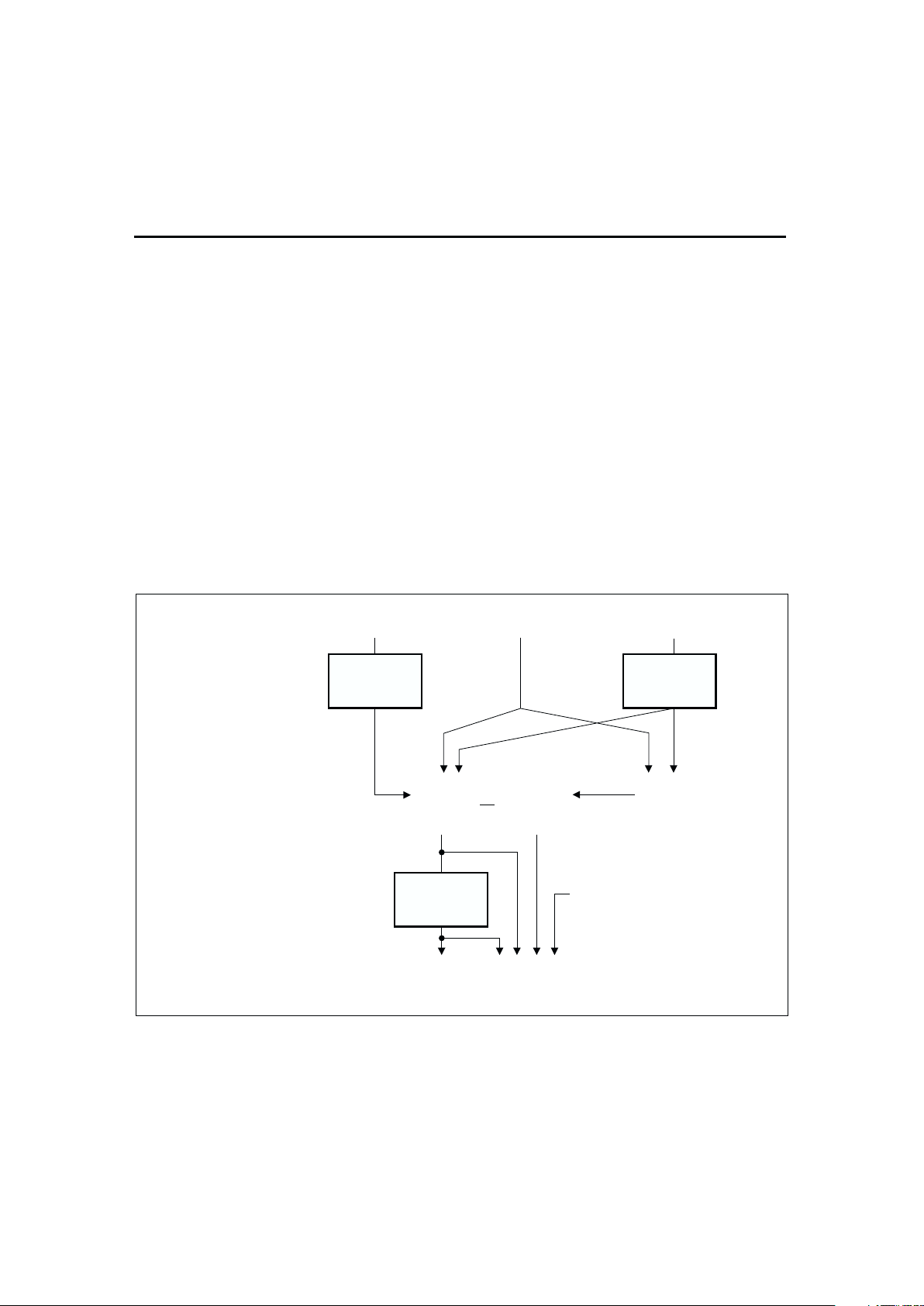
The operational overview diagram in Figure 2 illustrates
the operation of the bq2014H. The bq2014H accumu
lates a measure of charge and discharge currents, as
well as an estimation of self-discharge. The accumu
lated charge and discharge currents are adjusted for
temperature and rate to provide the indication of com
pensated available capacity to the host system or user.
The main counter, Nominal Available Capacity (NAC),
represents the available battery capacity at any given
time. Battery charging increments the NAC register,
while battery discharging and self-discharge decrement
the NAC register and increment the DCR (Discharge
Count Register).
The Discharge Count Register is used to update the Last
Measured Discharge (LMD) register only if a complete
battery discharge from full to empty occurs without any
partial battery charges. Therefore, the bq2014H adapts
its capacity determination based on the actual condi
tions of discharge.
The battery's initial capacity equals the Programmed
Full Count (PFC) shown in Table 2. Until LMD is up
dated, NAC counts up to but not beyond this threshold
during subsequent charges. This approach allows the
gas gauge to be charger-independent and compatible
with any type of charge regime.
1. Last Measured Discharge (LMD) or learned
battery capacity:
LMD is the last measured discharge capacity of the
battery. On initialization (application of V
CC
or bat
-
tery replacement), LMD = PFC. During subsequent
discharges, the LMD is updated with the latest
measured capacity in the Discharge Count Register
representing a discharge from full to below EDV1.
A qualified discharge is necessary for a capacity
transfer from the DCR to the LMD register. The
LMD also serves as the 100% reference threshold
used by the relative display mode.
5
F2014HOO.eps
Temperature
Compensation
Charge
Current
Discharge
Current
Self-Discharge
Timer
Nominal
Available
Charge
(NAC)
Last
Measured
Discharged
(LMD)
Discharge
Count
Register
(DCR)
<
Qualified
Transfer
+
Temperature Step,
Other Data
+
--
+
Inputs
Main Counters
and Capacity
Reference (LMD)
Outputs
Serial
Port
Compensated
Available Charge
LED Display, etc.
Rate and
Temperature
Compensation
Rate and
Temperature
Compensation
Figure 2. Operational Overview
Preliminary
bq2014H
2. Programmed Full Count (PFC) or initial bat
-
tery capacity:
The initial LMD and gas gauge rate values are pro
-
grammed by using PROG
1
–PROG4. The bq2014H
is configured for a given application by selecting a
PFC value from Table 2. The correct PFC may be
determined by multiplying the rated battery capac
-
ity in mAh by the sense resistor value:
Battery capacity (mAh)*sense resistor (Ω) =
PFC (mVh)
Selecting a PFC slightly less than the rated capac
ity provides a conservative capacity reference until
the bq2014H “learns” a new capacity reference.
Example: Selecting a PFC Value
Given:
Sense resistor = 0.05
Ω
Number of cells = 10
Capacity = 3500mAh, NiMH
Current range = 50mA to 1A
Relative display mode
Self-discharge =
NAC
47
per day @ 25°C
Voltage drop over sense resistor = 2.5mV to 50mV
Nominal discharge voltage = 1.2V
Therefore:
3500mAh*0.05Ω= 175mVh
6
PROG
x
Pro-
grammed
Full
Count
(PFC)
PROG
4
= L PROG4= Z or H
Units
12
PROG
3
= H PROG3= Z PROG3= L PROG3= H PROG3= Z PROG3= L
-- -
SCALE =
1/80
SCALE =
1/160
SCALE =
1/320
SCALE =
1/640
SCALE =
1/1280
SCALE =
1/2560
mVh/
count
H H 49152 614 307 154 76.8 38.4 19.2 mVh
H Z 45056 563 282 141 70.4 35.2 17.6 mVh
H L 40960 512 256 128 64.0 32.0 16.0 mVh
Z H 36864 461 230 115 57.6 28.8 14.4 mVh
Z Z 33792 422 211 106 53.0 26.4 13.2 mVh
Z L 30720 384 192 96.0 48.0 24.0 12.0 mVh
L H 27648 346 173 86.4 43.2 21.6 10.8 mVh
L Z 25600 320 160 80.0 40.0 20.0 10.0 mVh
L L 22528 282 141 70.4 35.2 17.6 8.8 mVh
V
SR
equivalent to 2
counts/s (nom.)
90 45 22.5 11.25 5.6 2.8 mV
Table 2. bq2014H Programmed Full Count mVh, VSRGain Selections
Pin
Connection
PROG
5
Self-Discharge Rate
DISP
Display State
H Disabled LEDs disabled
Z
NAC
64
LEDs on when charging
L
NAC
47
LEDs on for 4s
Table 1. Self-Discharge and Capacity Compensation
bq2014H
Preliminary

Select:
PFC = 27648 counts or 173mVh
PROG
1
= low
PROG
2
= high
PROG
3
= float
PROG
4
= low
PROG
5
= low
The initial full battery capacity is 173mVh
(3460mAh) until the bq2014H “learns” a new capac
-
ity with a qualified discharge from full to EDV1.
3. Nominal Available Capacity (NAC):
NAC counts up during charge to a maximum value
of LMD and down during discharge and self-dis
charge to 0. NAC is reset to 0 on initialization and
on the first valid charge following discharge to
EDV1. To prevent overstatement of charge during
periods of overcharge, NAC stops incrementing
when NAC = LMD or 0.94 ∗ LMDifT<0°C.
4. Discharge Count Register (DCR):
The DCR counts up during discharge independent
of NAC and could continue increasing after NAC
has decremented to 0. Prior to NAC = 0 (empty
battery), both discharge and self-discharge increment the DCR. After NAC = 0, only discharge
increments the DCR. The DCR resets to 0 when
NAC ≥ 0.94 ∗ LMD and a discharge is detected. The
DCR does not roll over but stops counting when it
reaches FFh.
The DCR value becomes the new LMD value on the
first charge after a valid discharge to V
EDV1
if all
the following conditions are met:
■
No valid charge initiations (charges greater than
2 NAC updates where V
SRO>VSRQ
) occurred
during the period between NAC ≥ 0.94 ∗ LMD and
EDV1.
■
The self-discharge is less than 6.25% of NAC.
■
The temperature is≥0°C when the EDV1 level
is reached during discharge.
■
The discharge begins when NAC ≥ 0.94 ∗ LMD.
■
VDQ is set.
The valid discharge flag (VDQ) indicates whether
the present discharge is valid for LMD update. If
the DCR update value is less than 0.94 ∗ LMD,
LMD will only be modified by 0.94 ∗ LMD. This pre
-
vents invalid DCR values from corrupting LMD.
5. Scaled Available Energy (SAE):
SAE is useful in determining the available energy
within the battery, and may provide a more useful
capacity reference in battery chemistries with
sloped voltage profiles during discharge. SAE may
be converted to an mWh value using the following
formula:
E(mWh) =
(SAEH SAEL)∗+ ∗256
12. ∗∗
∗
SCALE (R + R )
RR
B1 B2
SB2
where RB1,RB2, and RSare resistor values in
ohms, as shown in Figure 1. SCALE is the selected
scale from Table 2.
6. Compensated Available Capacity (CACT)
CACT counts similarly to NAC, but contains the
available capacity compensated for discharge rate
and temperature.
Charge Counting
Charge activity is detected based on a positive voltage
on the SR input. If charge activity is detected, the
bq2014H increments NAC at a rate proportional to V
SR
and, if enabled, activates the LED display.
The bq2014H counts charge activity when the voltage at
theSRinput(V
SRO
) exceeds the minimum charge
threshold (V
SRQ
). A valid charge is detected when NAC
has been updated twice without discharging or reaching
the digital magnitude filter time-out. Once a valid
charge is detected, charge counting continues until V
SR
,
including offset,falls below V
SRQ
.
Discharge Counting
Discharge activity is indicated by a negative voltage on
the SR input. All discharge counts where V
SRO
is less
than the minimum discharge threshold (V
SRD
) cause
the NAC register to decrement and the DCR to
increment.
Self-Discharge Counting
The bq2014H continuously decrements NAC and incre
-
ments DCR for self-discharge on the basis of time and tem
-
perature.
Charge/Discharge Current
The bq2014H current-scale registers, VSRH and VSRL,
can be used to determine the battery charge or dis
-
charge current. See the Current Scale Register descrip
-
tion for details.
7
Preliminary
bq2014H
 Loading...
Loading...