Page 1
查询BQ2000供应商
bq2000
Programmable Multi-Chemistry
Fast-Charge Management IC
Features
Safe management of fast
➤
charge for NiCd, NiMH, or LiIon battery packs
High-frequency switching con
➤
troller for efficient and simple
charger design
Pre-charge qualification for
➤
detecting shorted, damaged, or
overheated cells
Fast-charge termination by
➤
peak voltage (PVD), minimum
current (Li-Ion), maximum
temperature, and maximum
charge time
➤ Selectable top-off mode for
achieving maximum capacity in
NiMH batteries
➤ Programmable trickle-charge
mode for reviving deeply discharged batteries and for postcharge maintenance
➤ Built-in battery removal and
insertion detection
➤
Sleep mode for low power
consumption
General Description
The bq2000 is a programmable,
monolithic IC for fast-charge manage
ment of nickel cadmium (NiCd),
nickel metal-hydride (NiMH), or lith
-
ium-ion (Li-Ion) batteries in single- or
multi-chemistry applications. The
bq2000 detects the battery chemistry
and proceeds with the optimal charg
ing and termination algorithms. This
process eliminates undesirable under
charged or overcharged conditions
and allows accurate and safe termi
nation of fast charge.
Depending on the chemistry, the
bq2000 provides a number of charge
termination criteria:
Peak voltage, PVD (for NiCd and
n
NiMH)
n Minimum charging current (f or
Li-Ion)
n
Maximum temperature
n
Maximum charge time
For safety, the bq2000 inhibits fast
charge until the battery voltage and
temperature are within user-defined
-
limits. If the battery voltage is
below the low-voltage threshold, the
-
bq2000 uses trickle-charge to
condition the battery. For NiMH
batteries, the bq2000 provides an
optional top-off charge to maximize
-
the battery capacity.
The integrated high-frequency com
parator allows the bq2000 to be the
basis for a complete, high-efficiency
power-conversion circuit for both
nickel-based and lithium-based
chemistries.
-
Pin Connections
or TSSOP
8
7
6
5
PN-2000.eps
SNS
V
LED
BAT
SLUS138B–FEBRUARY 2001 F
1
2
SS
3
4
8-Pin DIP or Narrow SOIC
MOD
V
CC
RC
TS
Pin Names
SNS Current-sense input
V
SS
LED
BAT Battery-voltage
System ground
Charge-status
output
input
1
TS Temperature-sense
RC Timer-program input
V
CC
MOD Modulation-control
input
Supply-voltage input
output
Page 2
bq2000
Pin Descriptions
SNS
V
SS
LED
BAT
TS
Current-sense input
Enables the bq2000 to sense the battery cur
rent via the voltage developed on this pin by
an external sense-resistor connected in se
ries with the battery pack
System Ground
Charge-status output
Open-drain output that indicates the charg
ing status by turning on, turning off, or
flashing an external LED
Battery-voltage input
Battery-voltage sense input. A simple resistive
divider, across the battery terminals, generates
this input.
T emperature-senseinput
Input for an external battery-temperature
monitoring circuit. An external resistive divider network with a negative temperature-coefficient thermistor sets the lower
and upper temperature thresholds.
RC
Timer-program input
RC input used to program the maximum
charge-time, hold-off period, and trickle
-
-
V
CC
MOD
rate during the charge cycle, and to disable
or enable top-off charge
Supply-voltage input
Modulation-control output
Push-pull output that controls the charging
current to the battery. MOD switches high
-
to enable charging current to flow and low to
inhibit charging- current flow .
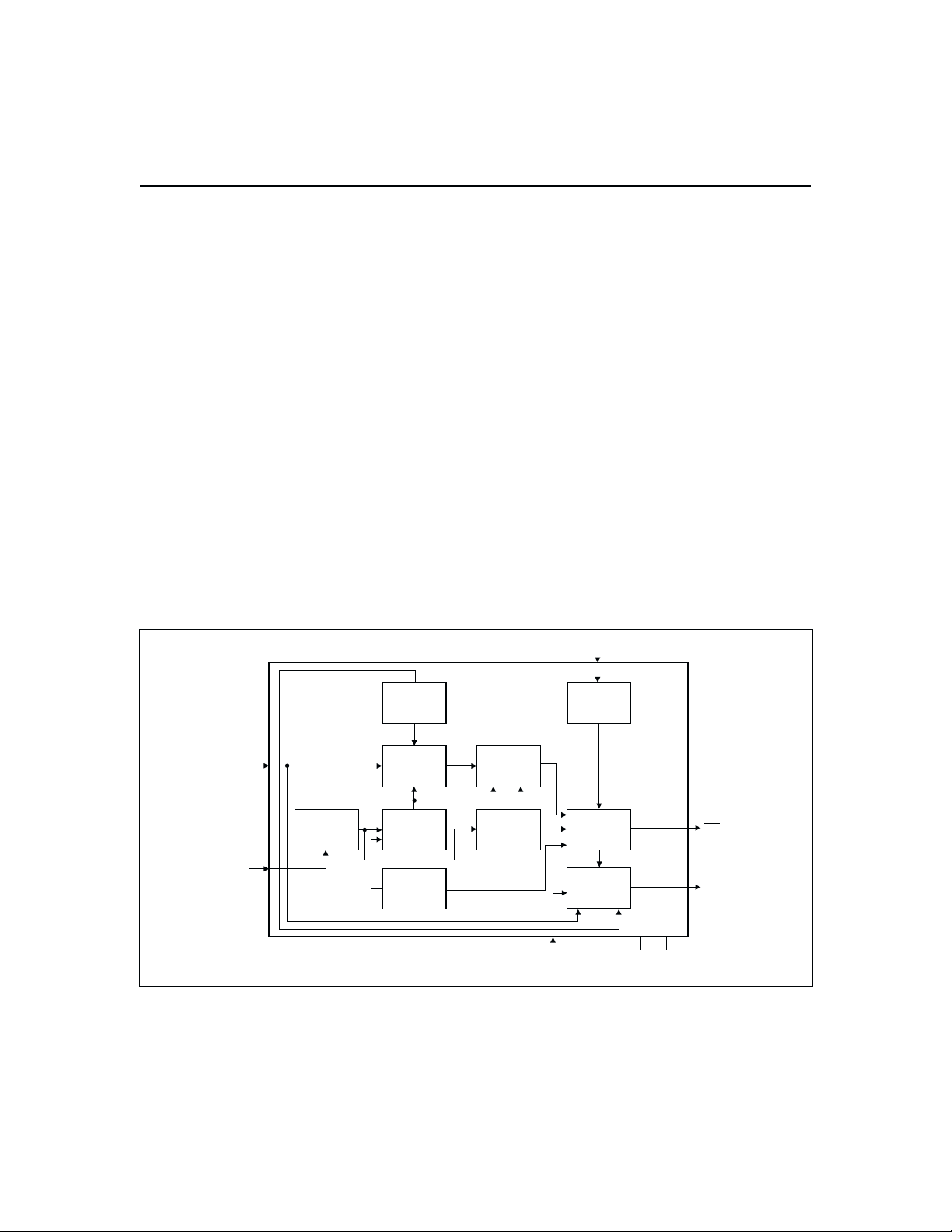
Functional Description
The bq2000 is a versatile, multi-chemistry batterycharge control device. See Figure 1 for a functional block
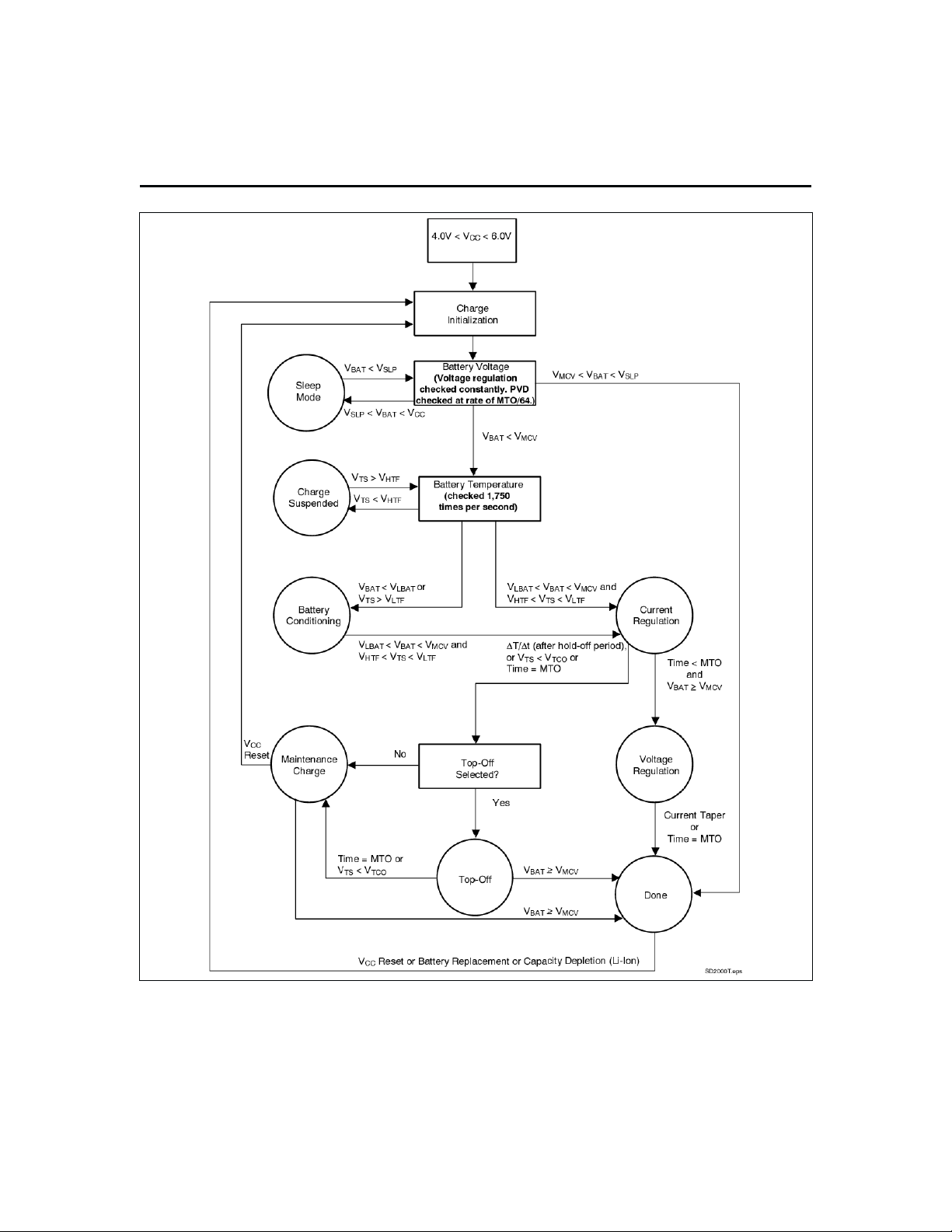
diagram and Figure 2 for a state diagram.
TS
BAT
RC
Voltage
Reference
PVD
ALU
Timer
OSC
ADC
Clock
Phase
Generator
Internal
OSC
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram
2
SNS
Voltage
Comparator
Charge
Control
Voltage
Comparator
V
CCVSS
LED
MOD
bq2000BD.eps
Page 3
bq2000
Figure 2. State Diagram
3
Page 4
bq2000
Initiation and ChargeQualification
The bq2000 initiates a charge cycle when it detects
Application of power to V
n
Battery replacement
n
Exit from sleep mode
n
Capacity depletion (Li-Ion only)
n
Immediately following initiation, the IC enters a
charge-qualification mode. The bq2000 charge qualifica
tion is based on battery voltage and temperature. If
voltage on pin BAT is less than the internal threshold,
V
, the bq2000 enters the charge-pending state. This
LBAT
condition indicates the possiblility of a defective or
shorted battery pack. In an attempt to revive a fully
depleted pack, the bq2000 enables the MOD pin to
trickle-charge at a rate of once every 1.0s. As explained
in the section “Top-Off and Pulse-Trickle Charge,” the
trickle pulse-width is user-selectable and is set by the
value of the resistance connected to pin RC.
During this period, the LED
indicating the pending status of the charger.
Similarly, the bq2000 suspends fast charge if the battery
temperature is outside the V
4.) For safety reasons, however, it disables the pulse
trickle, in the case of a battery over-temperature condition
(i.e., V
TS<VHTF
). Fast charge begins when the battery
temperature and voltage are valid.
CC
pin blinks at a 1Hz rate,
LTF
to V
range. (See Table
HTF
Battery Chemistry
The bq2000 detects the battery chemistry by monitoring
the battery-voltage profile during the initial stage of the
fast charge. If the voltage on BAT input rises to the in
ternal V
reference, the IC assumes a Li-Ion battery.
MCV
Otherwise the bq2000 assumes NiCd/NiMH chemistry.
As shown in Figure 6, a resistor voltage-divider between
the battery pack’s positive terminal and V
scales the
SS
battery voltage measured at pin BAT. In a
mixed-chemistry design, a common voltage-divider is
used as long as the maximum charge voltage of the
nickel-based pack is below that of the Li-Ion pack. Oth
erwise, different scaling is required.
Once the chemistry is determined, the bq2000 completes
the fast charge with the appropriate charge algorithm
(Table 1). The user can customize the algorithm by
programming the device using an external resistor and
a capacitor connected to the RC pin, as discussed in
later sections.
NiCd and NiMHBatteries
Following qualification, the bq2000 fast-charges NiCd or
NiMH batteries using a current-limited algorithm. During the fast-charge period, it monitors charge time, temperature, and voltage for adherence to the termination
criteria. This monitoring is further explained in later
sections. Following fast charge, the battery is topped off,
if top-off is selected. The charging cycle ends with a
trickle maintenance-charge that continues as long as
the voltage on pin BATremainsbelowV
MCV
.
-
-
I
MAX
Trickle
I
MIN
Current
Voltage
Qualification
Fast Charge
Phase 1 Phase 2
Current
Time
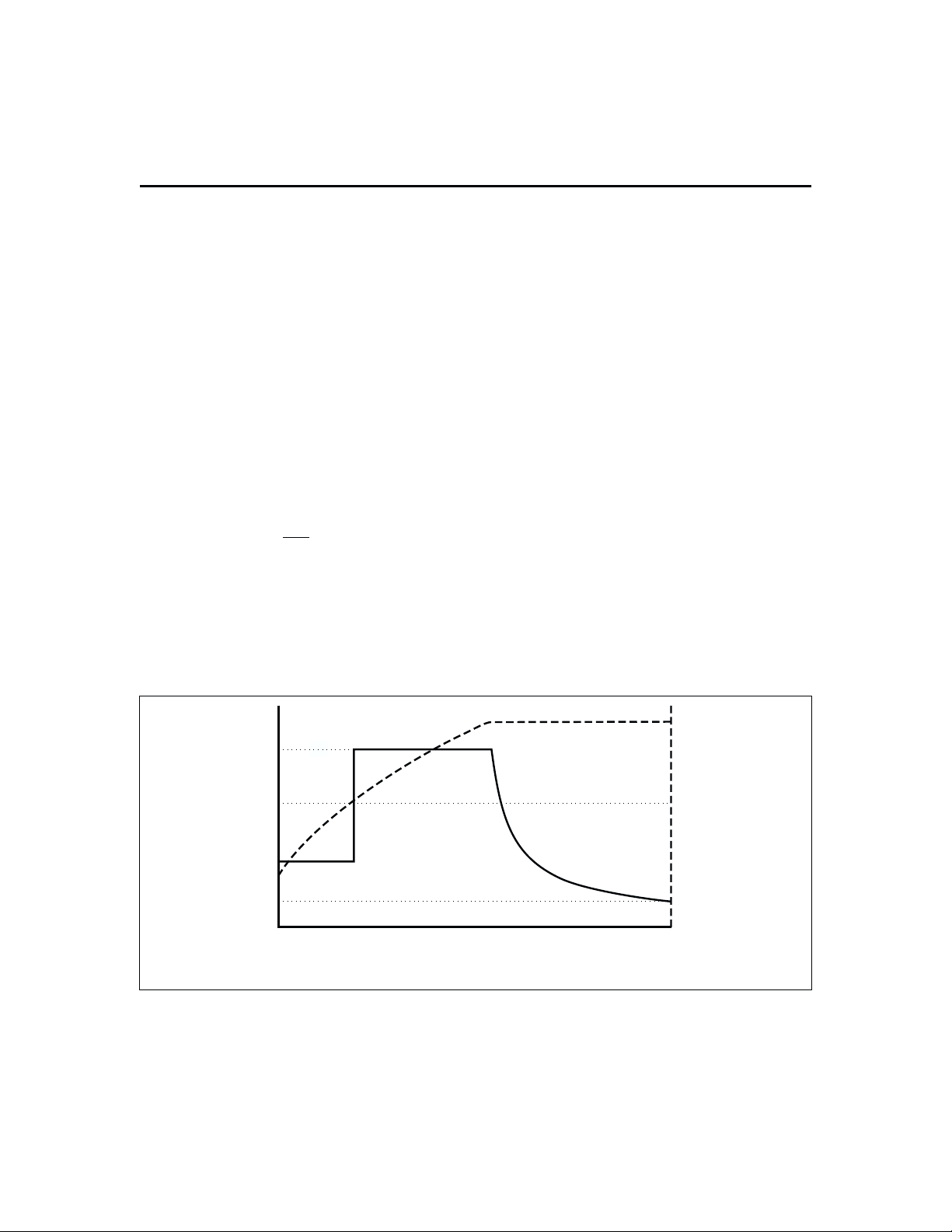
Figure 3. Lithium-Ion Charge Algorithm
4
GR2000CA.eps
V
MCV
V
LBAT
Voltage
Page 5
Table 1. Charge Algorithm
Battery Chemistry Charge Algorithm
1. Charge qualification
2. Trickle charge, if required
NiCd or NiMH
Li-Ion
3. Fast charge (constant current)
4. Charge termination (peak voltage, maximum charge time)
5. Top-off (optional)
6. Trickle charge
1. Charge qualification
2. Trickle charge, if required
3. Two-step fast charge (constant current followed by constant voltage)
4. Charge termination (minimum current, maximum charge time)
bq2000
Lithium-Ion Batteries
The bq2000 uses a two-phase fast-charge algorithm for
Li-Ion batteries (Figure 3). In phase one, the bq2000
regulates constant current until V
BAT
rises to V
MCV
. The
bq2000 then moves to phase two, regulates the battery
with constant voltage of V
charging current falls below the I
, and terminates when the
MCV
threshold. A new
MIN
charge cycle is started if the cell voltage falls below the
V
threshold.
RCH
During the current-regulation phase, the bq2000
monitors charge time, battery temperature, and battery
voltage for adherence to the termination criteria. During
the final constant-voltage stage, in addition to the
charge time and temperature, it monitors the charge
current as a termination criterion. There is no
post-charge maintenance mode for Li-Ion batteries.
Charge Termination
Maximum Charge Time (NiCD, NiMH, and
Li-Ion)
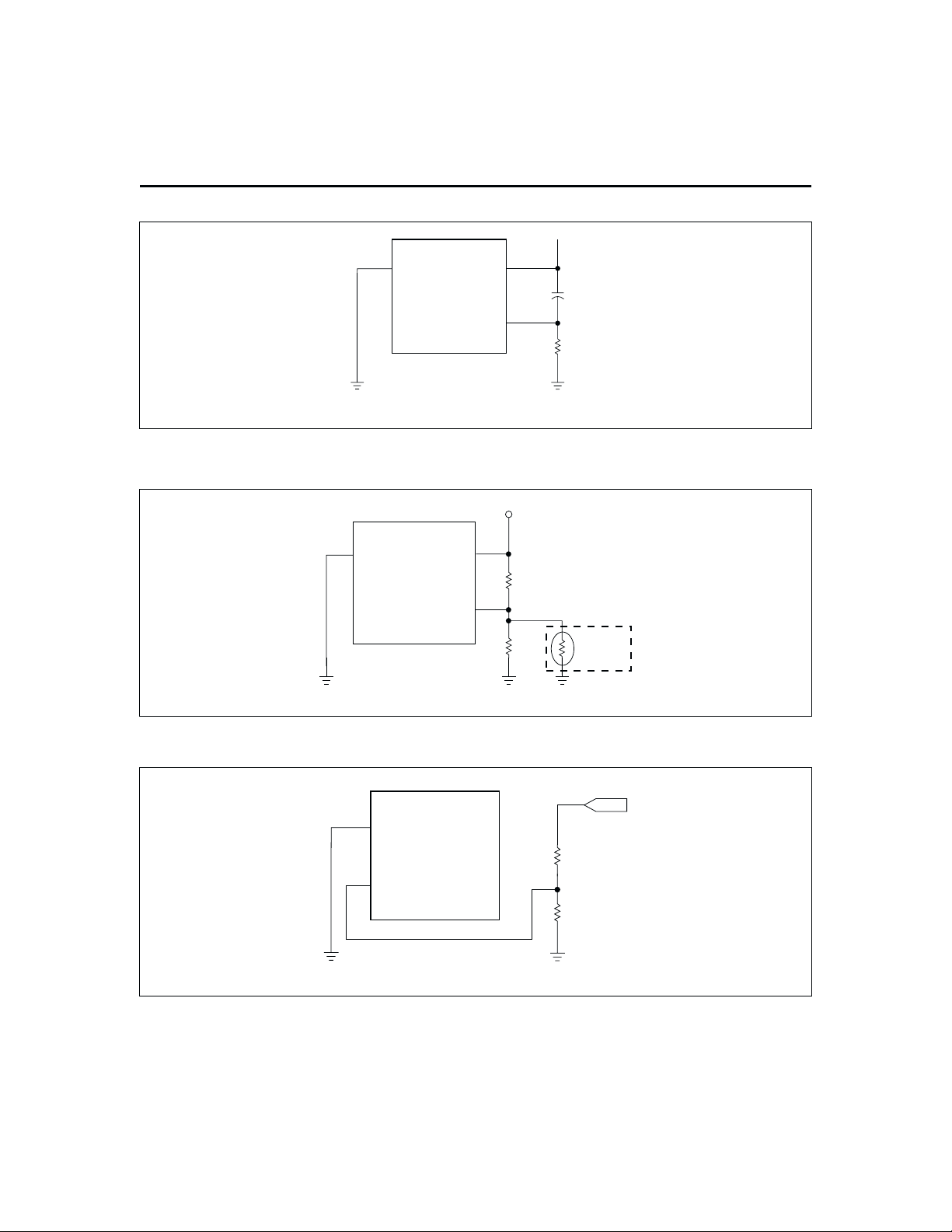
The bq2000 sets the maximum charge-time through pin
RC. With the proper selection of external resistor and
capacitor, various time-out values may be achieved. Fig
ure 4 shows a typical connection.
The following equation shows the relationship between
the R
time (MTO) for the bq2000:
MTO is measured in minutes, R
in farads. (Note: R
other features of the device. See Tables 2 and 3 for de
tails.)
For Li-Ion cells, the bq2000 resets the MTO when the
battery reaches the constant-voltage phase of the
MTO
and C
MTO=R
values and the maximum charge
MTO
∗ C
∗ 35,988
MTO
in ohms, and C
MTO
values also determine
MTO
MTO
MTO
and C
MTO
charge. This feature provides the additional charge time
required for Li-Ion cells.
Maximum Temperature(NiCd, NiMH, Li-Ion)
A negative-coefficient thermistor, referenced to VSSand
placed in thermal contact with the battery, may be used
as a temperature-sensing device. Figure 5 shows a typical temperature-sensing circuit.
During fast charge, the bq2000 compares the battery
temperature to an internal high-temperature cutoff
threshold, V
. As shown in Table 4, high-temperature
TCO
termination occurs when voltage at pin TS is less than
this threshold.
Peak Voltage(NiCd, NiMH)
The bq2000 uses a peak-voltage detection (PVD) scheme
to terminate fast charge for NiCd and NiMH batteries.
The bq2000 continuously samples the voltage on the
BAT pin, representing the battery voltage, and triggers
the peak detection feature if this value falls below the
maximum sampled value by as much as 3.8mV (PVD).
As shown in Figure 6, a resistor voltage-divider between
the battery pack’s positive terminal and V
battery voltage measured at pin BAT.
-
For Li-Ion battery packs, the resistor values R
R
are calculated by the following equation:
B2
R
B1
B2
R
V
N
=∗
V
CELL
MCV
where N is the number of cells in series and V
manufacturer-specified charging voltage. The end-toend input impedance of this resistive divider network
should be at least 200kΩ and no more than 1MΩ.
-
A NiCd or NiMH battery pack consisting of N seriescells may benefit by the selection of the R
N-1 times larger than the R
B2
value.
In a mixed-chemistry design, a common voltage-divider
is used as long as the maximum charge voltage of the
− 1
SS
CELL
value to be
B1
scales the
and
B1
is the
5
Page 6
bq2000
2
V
SS
bq2000
7
V
CC
C
MTO
6
RC
R
MTO
F2000 RCI.eps
Figure 4. Typical Connection for the RC Input
V
CC
2
V
SS
bq2000
7
V
CC
R
T1
5
TS
N
R
T2
Battery
T
C
F2000TMC.eps
Pack
Figure 5. Temperature Monitoring Configuration
R
B1
R
B2
BAT+
F2000BVD.eps
2
V
SS
bq2000
4
BAT
Figure 6. Battery Voltage Divider
6
Page 7

bq2000
nickel-based pack is below that of the Li-Ion pack. Oth
erwise, different scaling is required.
Minimum Current (Li-IonOnly)
The bq2000 monitors the charging current during the
voltage-regulation phase of Li-Ion batteries. Fast charge
is terminated when the current is tapered off to 14% of
the maximum charging current.
Initial Hold-Off Period
The values of the external resistor and capacitor
connected to pin RC set the initial hold-off period.
During this period, the bq2000 avoids early termination
due to an initial rise in the battery voltage by disabling
the peak voltage-detection feature. This period is fixed
at the programmed value of the maximum charge time
divided by 32.
hold-off period =
maximum time -out
32
Top-Off andPulse-TrickleCharge
An optional top-off charge is available for NiCd or NiMH
batteries. Top-off may be desirable on batteries that
have a tendency to terminate charge before reaching full
capacity. To enable this option, the capacitance value of
C
connected to pin RC (Figure 4) should be greater
MTO
than 0.13µF, and the value of the resistor connected to
this pin should be less than 15kΩ. To disable top-off, the
capacitance value should be less than 0.07µF. The tolerance of the capacitor needs to be taken into account in
component selection.
-
Once enabled, the top-off is performed over a period
equal to the maximum charge time at a rate of
of fast charge.
Following top-off, the bq2000 trickle-charges the battery
by enabling the MOD to charge at a rate of once every
1.0 second. The trickle pulse-width is user-selectable
and is set by the value of the resistor R
, connected to
MTO
pin RC. Figure 7 shows the relationship between the
trickle pulse-width and the value of R
. The typical
MTO
tolerance of the pulsewidth below 150kΩ is ±10%.
During top-off and trickle-charge, the bq2000 monitors
battery voltage and temperature. These charging func
tions are suspended if the battery voltage rises above
the maximum cell voltage (V
) or if the temperature
MCV
exceeds the high-temperature fault threshold (V
Charge Current Control
The bq2000 controls the charge current through the
MOD output pin. The current-control circuit supports a
switching-current regulator with frequencies up to
500kHz. The bq2000 monitors charge current at the
SNS input by the voltage drop across a sense-resistor,
R
, in series with the battery pack. See Figure 9 for a
SNS
typical current-sensing circuit. R
the desired fast-charge current (I
0.05
=
I
MAX
R
If the voltage at the SNS pin is greater than V
less than V
, the bq2000 switches the MOD output
SNSHI
high to pass charge current to the battery. When the
is sized to provide
SNS
):
MAX
SNS
1
16
HTF
SNSLO
that
-
).
or
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
Pulsewidth—ms
4
3
2
1
246810 50 100 150 200 250
R
MTO
Shows Tolerance
—kΩ
2000PNvB3.eps
Figure 7. Relationship Between Trickle Pulse-Width and Value of R
7
MTO
Page 8

bq2000
DC+
D6
BZT52-C5V1
MMSD914LT
R2
2K
D1
RED
1000PF
R5
20K
FMMT718
C9
Q1
R12
120 OHMS
Q3
MMBT3904LT1
R11
220 OHMS
D4
R8
6.81K
Q2
MMBT3904LT1
D5
MMSD914LT
R4
12.4K
R10
1K
S1A
VCC
C3
10UF
C2
0.1
R13
1.1K
D3
1
2
3
4
C4
0.0022UF
U1
SNS
VSS
LED
BAT
bq2000
C6
47UF
C7
4.7PF
MOD
VCC
RC
TS
R1
100K
C8
0.33UF
8
7
6
5
C1
0.1
L1
47UH
D2
ZHCS1000
R6
210K
R7
200K
10UF
C5
221K
R9
THERM
R3
0.05 OHM
BAT+
CHEMISTRY
-
BAT
NOTES: 1. For Li-Ion, the CHEMISTRY is left floating.
For NiCd/NiMH, the CHEMISTRY is tied to BAT-
2. DC input voltage: 9–16V
3. Charge current: 1A
4. L1: 3L Global P/N PKSMD-1005-470K-1A
Figure 8. Single-Cell Li-Ion, Three-Cell NiCd/NiMH 1A Charger
Pn1031a01.eos
8
Page 9

Table 2. Summary of NiCd or NiMH Charging Characteristics
Parameter Value*
Maximum cell voltage (V
Minimum pre-charge qualification voltage (V
High-temperature cutoff voltage (V
High-temperature fault voltage (V
Low-temperature fault voltage (V
bq2000 fast-charge maximum time out (MTO)
Fast-charge charging current (I
Hold-off period MTO/32
Top-off charging current (optional) I
Top-off period (optional) MTO
Trickle-charge frequency 1Hz
Trickle-charge pulse-width See Figure 7
*Please refertoDC Thresholds Specification for details.
)2V
MCV
) 950mV
LBAT
)
TCO
)
HTF
)
LTF
) 0.05/R
MAX
0.225 ∗ V
0.25 ∗ V
0.5 ∗ V
CC
∗ C
R
MTO
SNS
/16
MAX
CC
CC
MTO
bq2000
∗ 35,988
SNS voltage is less than V
the bq2000 switches the MOD output low to shut off
charging current to the battery. Figure 8 shows a typical
multi-chemistry charge circuit.
Temperature Monitoring
or greater than V
SNSLO
SNSHI
,
ative-temperature-coefficient thermistor. The bq2000
compares this voltage against its internal threshold
voltages to determine if charging is safe. These
thresholds are the following:
n
High-temperature cutoff voltage: V
This voltage corresponds to the maximum
temperature (TCO) at which fast charging is allowed.
The bq2000 measures the temperature by the voltage at
the TS pin. This voltage is typically generated by a neg-
The bq2000 terminates fast charge if the voltage on
pin TS falls below V
TCO
.
Table 3. Summary of Li-Ion Charging Characteristics
Parameter Value*
Maximum cell voltage (V
Minimum pre-charge qualification voltage (V
High-temperature cutoff voltage (V
High-temperature fault voltage (V
Low-temperature fault voltage (V
bq2000 fast-charge maximum time-out (MTO)
Fast-charge charging current (I
Hold-off period MTO/32
Minimum current (for fast-charge termination) I
Trickle-charge frequency (before fast charge only) 1Hz
Trickle-charge pulse-width (before fast charge only) See Figure 7
*Please refer to DC Thresholds Specification for details.
)2V
MCV
) 950mV
LBAT
LTF
MAX)
TCO
HTF
)
)
)
0.225 ∗ V
0.25 ∗ V
0.5 ∗ V
CC
2 ∗ R
MTO
0.05/R
SNS
/7
MAX
CC
CC
∗ C
MTO
= 0.225 ∗ V
TCO
∗ 35,988
CC
9
Page 10

bq2000
Table 4. Temperature-Monitoring Conditions
Temperature Condition Action
V
TS>VLTF
V
HTF<VTS<VLTF
V
TS<VHTF
V
TS<VTCO
Cold battery—checked at all times
Optimal operating range Allows charging
Hot battery—checked during charge quali
fication and top-off and trickle-charge
Battery exceeding maximum allowable
temperature—checked at all times
Suspends fast charge or top-off and timer
Allows trickle charge—LED flashes at 1Hz rate
during pre-charge qualification and fast charge
Suspends fast-charge initiation, does not allow
-
trickle charge—LED flashes at 1Hz rate during
pre-charge qualification and fast charge
Terminates fast charge or top-off
High-temperature fault voltage: V
n
= 0.25 ∗ VCCThis
HTF
voltage corresponds to the temperature (HTF) at which
fast charging is allowed to begin.
Low-temperature fault voltage: V
n
LTF
= 0.5 ∗ V
CC
This voltage corresponds to the minimum temperature
(LTF) at which fast charging or top-off is allowed. If the
voltage on pin TS rises above V
LTF,
the bq2000
suspends fast charge or top-off but does not terminate
charge. When the voltage falls back below V
LTF,
fast
charge or top-off resumes from the point where
suspended. Trickle-charge is allowed during this
condition.
Table4 summarizes these various conditions.
Charge Status Display
The charge status is indicated by open-drain output
LED. Table 5 summarizes the display output of the
bq2000.
Table 5. Charge Status Display
Charge Action State LED Status
Battery absent High impedance
Pre-charge qualification 1Hz flash
Trickle charge (before fast charge) 1Hz flash
Fast charging Low
Top-off or trickle (after fast charge,
NiCd, NiMH only)
Charge complete High impedance
Sleep mode High impedance
Charge suspended (V
TS>VLTF
High impedance
) 1Hz flash
Sleep Mode
The bq2000 features a sleep mode for low power con
sumption. This mode is enabled when the voltage at pin
BAT is above the low-power-mode threshold, V
ing sleep mode, the bq2000 shuts down all internal circuits, drives the LED output to high-impedance state,
and drives pin MOD to low. Restoring BAT below the
V
threshold initiates the IC and starts a fast-charge
MCV
cycle.
R
BAT-
Power Supply ground
bq2000 ground
f
R
SNS
1
SNS
C
f
2
V
SS
Figure 9. Current-Sensing Circuit
bq2000
2000CS.eps
SLP
. Dur
-
-
10
Page 11

bq2000
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
CC
V
T
T
OPR
T
STG
T
SOLDER
VCCrelative to V
DC voltage applied on any pin, ex
cluding V
relative to V
CC
SS
-
SS
Operating ambient temperature -20 +70 °C
Storage temperature -40 +125 °C
Soldering temperature - +260 °C 10s max.
Note: Permanent device damage may occur if Absolute Maximum Ratings are exceeded. Functional operation
should be limited to the Recommended DC Operating Conditions detailed in this data sheet. Exposure to
conditions beyond the operational limits for extended periods of time may affect device reliability.
-0.3 +7.0 V
-0.3 +7.0 V
DC Thresholds (T
A=TOPR;VCC
=5V±20% unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Rating Tolerance Unit Notes
V
TCO
V
HTF
V
LTF
V
MCV
V
LBAT
PVD BAT input change for PVD detection 3.8
V
SNSHI
V
SNSLO
V
SLP
V
RCH
Temperature cutoff 0.225*V
High-temperature fault 0.25 * V
Low-temperature fault 0.5*V
Maximum cell voltage 2.00
Minimum cell voltage 950
High threshold at SNS, resulting in
MOD-low
Low threshold at SNS, resulting in
MOD-high
Sleep-mode input threshold
Recharge threshold
V
V
MCV
CC
50
-50
-1
- 0.1
CC
CC
CC
5% V Voltage at pin TS
±
5% V Voltage at pin TS
±
5% V Voltage at pin TS
±
V
0.75%
±
5% mV Voltage at pin BAT
±
20% mV
±
±10
±10
mV Voltage at pin SNS
mV Voltage at pin SNS
±0.5
±0.02
BAT>VMCV
V
fast charge
V Applied to pin BAT
V At pin BAT
inhibits
11
Page 12

bq2000
Recommended DC Operating Conditions (T
A=TOPR)
Symbol Condition Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Notes
V
I
I
V
V
V
I
I
R
C
CC
CC
CCS
TS
OH
OL
OZ
snk
MTO
MTO
Supply voltage 4.0 5.0 6.0 V
Supply current - 0.5 1 mA Exclusive of external loads
Sleep current - - 5
Thermistor input 0.5 - V
CC
V
µA
BAT=VSLP
VVTS< 0.5V prohibited
Output high VCC- 0.6 - - V MOD, IOH= 10mA
Output low - - 0.2 V MOD, LED, IOL= 10mA
High-impedance leakage
current
--5µALED
Sink current - - 20 mA MOD, LED
Charge timer resistor 2 - 250 k
Charge timer capacitor 0.001 - 1.0
Ω
µF
Note: All voltages relative to VSSexcept as noted.
Impedance
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
R
BAT
R
TS
R
SNS
Timing (T
Battery input impedance 10 - - M
TS input impedance 10 - - M
SNS input impedance 10 - - M
A=TOPR;VCC
=5V±20% unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
d
MTO
f
TRKL
MTO time-base variation -5 - +5 %
Pulse-trickle frequency 0.9 1.0 1.1 Hz
12
Ω
Ω
Ω
Page 13

bq2000
8-Pin DIP(PN
E1
E
e
)
D
L
C
8-Pin SOIC Narrow (SN)
8-Pin PN(0.300" DIP
Dimension
A 0.160 0.180 4.06 4.57
A1 0.015 0.040 0.38 1.02
B 0.015 0.022 0.38 0.56
B1 0.055 0.065 1.40 1.65
A
A1
S
B1
B
G
C 0.008 0.013 0.20 0.33
D 0.350 0.380 8.89 9.65
E 0.300 0.325 7.62 8.26
E1 0.230 0.280 5.84 7.11
e 0.300 0.370 7.62 9.40
G 0.090 0.110 2.29 2.79
L 0.115 0.150 2.92 3.81
S 0.020 0.040 0.51 1.02
Min. Max. Min. Max.
)
Inches Millimeters
13
8-Pin SN(0.150" SOIC
Inches Millimeters
Dimension
A 0.060 0.070 1.52 1.78
A1 0.004 0.010 0.10 0.25
B 0.013 0.020 0.33 0.51
C 0.007 0.010 0.18 0.25
D 0.185 0.200 4.70 5.08
E 0.150 0.160 3.81 4.06
e 0.045 0.055 1.14 1.40
H 0.225 0.245 5.72 6.22
L 0.015 0.035 0.38 0.89
Min. Max. Min. Max.
)
Page 14

bq2000
8-Pin TSSOP (PW)
14
Page 15

Data Sheet Revision History
Change No. Page No. Description Nature of Change
1 4 MTO equation
16
Trickle-pulse width
equation
1 7 Figure 7 Schematic updated
110V
111R
28V
TCO,VHTF,VLTF
MTO,CMTO
LBAT
3 1, 13 Package option Added TSSOP
3 3 State diagram Added
3 8 Schematic updated
311V
TSO,VHTF,VLTF
3 7 Top-off charge Updatedrequirement for enabling top-off
4 7 Figure 7 Updated tolerance on the curve
412
412
V
OH
V
OL
5 3 Figure 2
5 3 Figure 2
6 14 Change package
515
Change ordering
information
Note: Change 1 = Jan. 1999 B changes to Final from Sept. 1998 Preliminary data sheet.
Change 2 = Mar. 1999 C changes from Jan. 1999 B.
Change 3 = May 1999 D changes from Mar.1999 C.
Change 4 = February 2000 E changes from May 1999 D.
Change 5 = February 2001 F changes from February 2000 E
Was:MTO = R ∗ C ∗ 71,976
Is: MTO = R
MTO
∗ C
MTO
∗ 35,988
Replaced equation with Figure 6
Tolerance updated
Values updated
Corrected values in Tables 2 and 3
Tolerance updated
Was:Minimum VOH=VCC- 0.2 at IOH= 20mA
Is: Minimum V
OH=VCC
- 0.6 at IOH= 10mA
Was:IOH= 20mA
Is: I
= 10mA
OH
Battery voltage detail was: (checked at all times)
Is: Voltage regulation checked constantly. PVD checked at rate
of MTO/64.
Battery temperature detail was: (checked at all times)
Is: (checked 1,750 times per second)
Was:8-Pin TSSOP ∼ TS Package Suffix
Is: 8-Pin PSOP
Was:TS = 8-pin TSSOP
Is: PW = 8-pin TSSOP
bq2000
15
Page 16

bq2000
Ordering Information
bq2000
Package Option:
PN = 8-pin narrow plastic DIP
SN = 8-pin narrow SOIC
PW = 8-pin TSSOP
Device:
bq2000 Multi-Chemistry Fast-Charge IC with Peak Voltage
Detection
16
Page 17

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
4-Mar-2005
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
BQ2000PN-B5 ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Pb-Free
BQ2000PW ACTIVE TSSOP PW 8 150 None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM
BQ2000PWR ACTIVE TSSOP PW 8 2000 None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM
BQ2000SN-B5 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 None CUSNPB Level-1-220C-UNLIM
BQ2000SN-B5TR ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 None CUSNPB Level-1-220C-UNLIM
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - May not be currently available - please check http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional
product content details.
None: Not yet available Lead (Pb-Free).
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean "Pb-Free" and in addition, uses package materials that do not contain halogens,
including bromine (Br) or antimony (Sb) above 0.1% of total product weight.
(RoHS)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU SNPB Level-NC-NC-NC
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDECindustry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 18

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2005, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...