Page 1

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <1> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Table of Contents
Title Page
Overview --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2
Unpacking Inspection -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2
Safety Information ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2
Rules for Safe Operation -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3
International Electrical Symbols ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4
The Meter Structure --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4
Rotary Switch ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
Functional Buttons --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
The Effectiveness of Functional Buttons ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
Display Symbols ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6
Measurement Operation --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7
A. DC/AC Voltage Measurement ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 7
B. Measuring Resistance -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7
C. Testing Diodes ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8
D. Testing for Continuity ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 8
E. Frequency Measurement ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9
F. Duty Cycle Measurement ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9
G. DC/AC Current Measurement ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 10
Sleep Mode ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10
Specifications --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11
A. General Specifications ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11
B. Environmental Requirements ------------------------------------------------------------------ 11
Accuracy Specifications ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
A. DC Voltage ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
B. AC Voltage ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
C. Resistance ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
D. Diode Test ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
E. Continuity Test ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
F. Frequency ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
G. Duty Cycle ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
H. DC Current ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
I. AC Current ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
Maintenance ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
A. General Service -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
B. Replacing the Battery ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
Page 2

Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <2> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Overview
This Operating Manual covers information on safety and cautions. Please read the relevant information carefully and observe all the
Warnings and Notes strictly.
Warning
To avoid electric shock or personal injury, read the “Safety Information” and “Rules for Safe Operation” carefully before
using the Meter.
Digital Multimeter Model UT204 (hereafter referred to as “the Meter”) are 3 3/4 digits with steady operations, fashionable
structure and highly reliable measuring instrument. The Meter uses large scale of integrated circuit with double integrated A/D
converter as its core and has full range overload protection.
The Meter can not only measure AC/DC Voltage, AC/DC Current, Frequency, Duty Cycle, Resistance, Diodes, Continuity but also it
has Data Hold, Sleep Mode and Relative Mode features.
UT204 has an extra True RMS feature.
Unpacking Inspection
Open the package case and take out the Meter. Check the following items carefully to see any missing or damaged part:
Item Description Quantity
1 English Operating Manual 1 piece
2 Test Lead
1 pair
3 Carrying Bag 1 piece
4 9V Battery (NEDA1604, 6F22 or 006P) 1 piece
In the event you find any missing or damage, please contact your dealer immediately.
Safety Information
This Meter complies with the standards IEC61010: in pollution degree 2, overvoltage category (CAT. II 600V, CAT. III 300V) and
double insulation.
CAT. II: Local level, appliance, PORTABLE EQUIPMENT etc., with smaller transient overvoltages than CAT. III. CAT.
III: Distribution level, fixed installation, with smaller transient overvoltages than
CAT. IV
Use the Meter only as specified in this operating manual, otherwise the protection provided by the Meter may be impaired.
In this manual, a Warning identifies conditions and actions that pose hazards to the user, or may damage the Meter or the equipment
under test.
A Note identifies the information that user should pay attention to.
International electrical symbols used on the Meter and in this Operating Manual are explained on page 4.
Page 3
Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <3> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Rules For Safe Operation
Warning
To avoid possible electric shock or personal injury, and to avoid possible damage to the Meter or to the equipment under test, adhere
to the following rules:
••
Before using the Meter inspect the case. Do not use the Meter if it is damaged or the case (or part of the case) is removed. Look
for cracks or missing plastic. Pay attention to the Insulation around the connectors.
••
Inspect the test leads for damaged insulation or exposed metal. Check the test leads for continuity. Replace damaged test leads
with identical model number or electrical specifications before using the Meter.
••
Do not apply more than the rated voltage, as marked on the Meter, between the terminals or between any terminal and grounding.
If the value to be measured is unknown, use the maximum measurement position and reduce the range step by step until a
satisfactory reading is obtained.
••
When measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection between the test leads and the circuit under test, remove the
testing leads away from the input terminals of the Meter and turn the Meter power off.
••
The rotary switch should be placed in the right position and no any changeover of range shall be made during measurement is
conducted to prevent damage of the Meter.
••
Do not carry out the measurement when the Meter’s back case and battery compartment are not closed to avoid electric shock.
••
Do not input higher than 600V between the two Meter’s input terminal to avoid electric shock and damages to the Meter.
••
When the Meter working at an effective voltage over 60V in DC or 30V rms in AC, special care should be taken for there is danger
of electric shock.
••
Use the proper terminals, function, and range for your measurements.
••
Do not use or store the Meter in an environment of high temperature, humidity, explosive, inflammable and strong magnetic field.
The performance of the Meter may deteriorate after dampened.
••
When using the test leads, keep your fingers behind the finger guards.
••
Disconnect circuit power and discharge all high -voltage capacitors before testing resistance, continuity and diode.
••
Replace the battery as soon as the battery indicator appears. With a low battery, the Meter might produce false readings
that can lead to electric shock and personal injury.
••
When servicing the Meter, use only the same model number or identical electrical specifications replacement parts.
••
The internal circuit of the Meter shall not be altered at will to avoid damage of the Meter and any accident.
••
Soft cloth and mild detergent should be used to clean the surface of the Meter when servicing. No abrasive and solvent should be
used to prevent the surface of the Meter from corrosion, damage and accident.
Page 4
Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <4> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
••
The Meter is suitable for indoor use.
••
Turn the Meter off when it is not in use and take out the battery when not using for a long time.
••
Constantly check the battery as it may leak when it has been using for some time, replace the battery as soon as leaking appears.
A leaking battery will damage the Meter.
International Electrical Symbols
AC (Alternating Current).
DC (Direct Current).
AC or DC.
Grounding.
Double Insulated.
Warning. Refer to the Operating Manual.
Deficiency of Built-In Battery
Continuity Test.
Diode.
Fuse.
Application around and removal from HAZARDOUS LIVE conductors is permitted.
Conforms to Standards of European Union.
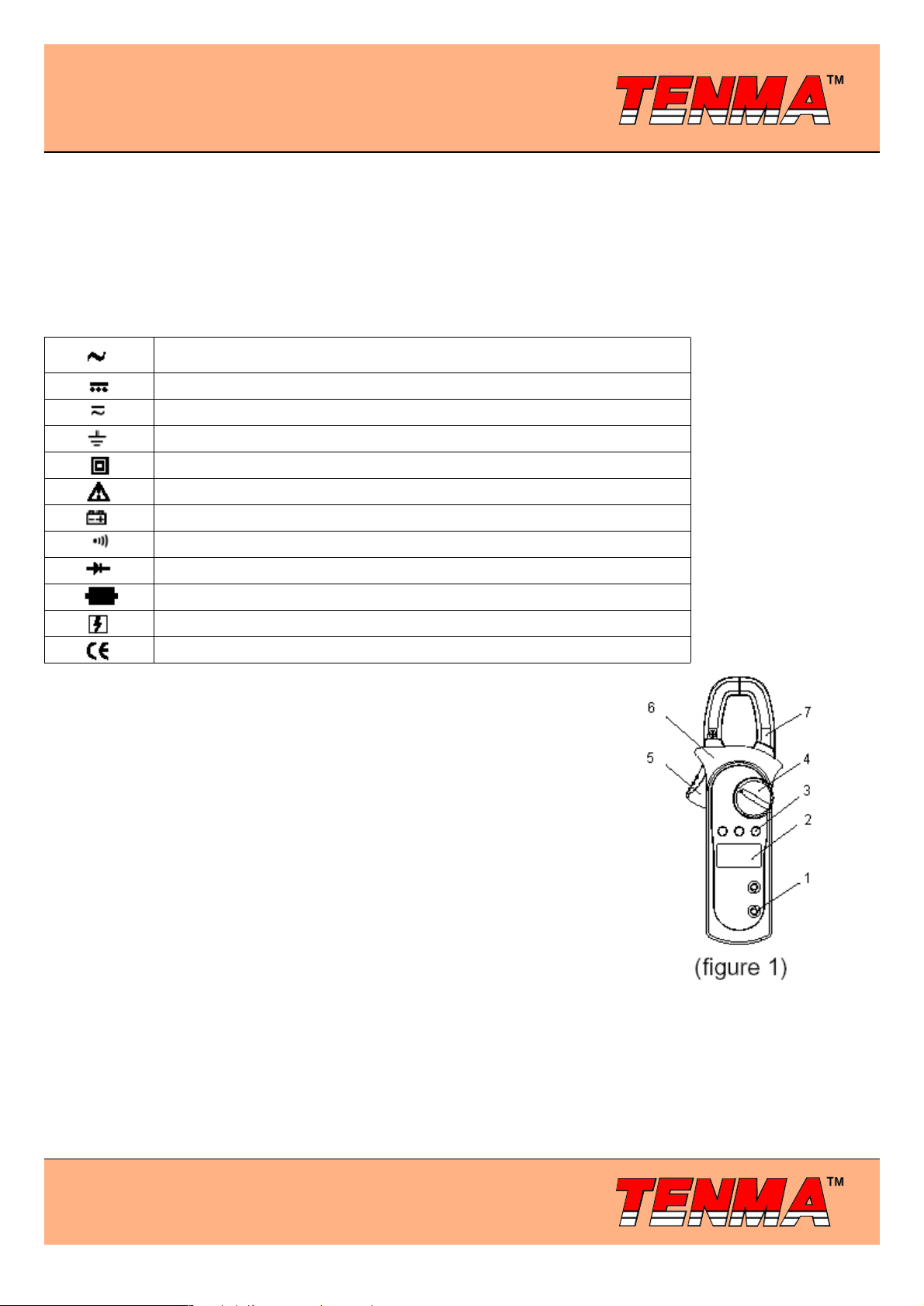
The Meter Structure (see figure 1)
1. Input Terminals
2. LCD Display
3. Functional Buttons
4. Rotary Switch
5. Trigger: press the lever to open the transformer jaws. When the pressure on the
lever is released, the jaws will close.
6. Hand Guards: to protect user’s hand from touching the dangerous area.
7. Transformer Jaw: designed to pick up the AC and DC current flowing through the
conductor. It could transfer current to voltage. The tested conductor must vertically
go through the Jaw center.
Page 5

Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <5> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Functional Buttons
Below table indicated for information about the functional button operations.
Rotary Switch Position Function
OFF Power is turned off.
AC/DC voltage measurement.
ΩΩ
Resistance measurement.
: Diode
: Continuity Test
Frequency Measurement and Duty Measurement
AC and DC current measurement range
Button Operation Performed
HOLD
••
Press HOLD to enter the Hold mode in any mode, the Meter beeps.
••
Press HOLD again to exit the Hold mode, the Meter beeps.
REL∆
••
Press to select manual ranging measurement mode. The meter is default to auto ranging
measurement mode.
••
When the Meter is at manual ranging measurement mode, press to step down the range.
At range:
••
Press to enter the REL mode.
••
It subtracts a stored value from the present measurement value and displays a result.
At Hz/Duty% range:
••
Press to switch between Hz measurement mode and Duty % measurement mode.
SELECT
••
Press SELECT button to select the alternate functions marked in blue colour on the Meter’s faceplate
including
••
After the Meter entering Sleep Mode, press and hold SELECT to
turn the Meter on, it will disable the Sleep Mode feature.
The Effectiveness of Functional Buttons
Not every functional buttons can be used on every rotary switch positions. Below two tables describe which functional buttons can be
used on which rotary switch positions
Model: UT201
Rotary Switch
Positions
Functional Buttons
SELECT
REL∆
HOLD
• • •
N/A
• •
•
N/A
•
N/A
• •
• • •
• • •
Rotary Switch
Below table indicated for information about the rotary switch positions.
At and
ΩΩ
range
::
Page 6

Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <6> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Display Symbols (see figure 2)
Number Symbol Meaning
1 AC Indicator for AC voltage or current
2 DC Indicator for DC voltage
3
The battery is low.
Warning: To avoid false readings, which could lead to possible electric shock or personal injury,
replace the battery as soon as the battery indicator appears.
4
The Meter is in the auto range mode in which the Meter automatically selects the range with the
best resolution.
5 Test of diode
6 The continuity buzzer is on
7 Indicator for Duty.
8 Data hold is active
9 Indicator for REL mode
10
Ohm. The unit of resistance.
Kilohm. 1x103or 1000 ohms
Megohm. 1x10
6
or 1,000,000 ohms
11 Hz The unit of Frequency
12 A Amperes (amps). The unit of current.
13 mV, V
Volts. The unit of voltage.
mV: Millivolt. 1x10
-3
or 0.001 volts
14 Indicates negative reading
15 TRMS Indicator for TRMS mode
16 OL The input value is too large for the selected range
Page 7

Clamp Meter
Trms
Page <7> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Measurement Operation
A. DC/AC Voltage Measurement (see figure 3)
Warning
To avoid harms to you or damages to the Meter from eletric shock, do not attempt to measure voltages higher than 600V AC/DC,
although readings may be obtained.
The DC Voltage ranges are: 400mV, 4V, 40V, 400V and 600V.
The AC Voltage ranges are: 4V, 40V, 400V and 600V.
To measure DC voltage, connect the Meter as follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz Duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to
. DC measurement mode and auto ranging is a default.
Press SELECT to switch to AC measurement mode or press REL∆ to switch to
manual ranging measurement mode.
3. Connect the test leads across with the object being measured. The measured
value shows on the display.
Note
• When DC/AC voltage measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection between the testing leads and the circuit under
test and remove testing leads from the input terminals.
B. Measuring Resistance (see figure 4).
To avoid damages to the Meter or to the devices under test, disconnect circuit power and discharge all the high-voltage capacitors
before measuring resistance.
The resistance ranges are: 400Ω, 4kΩ, 40kΩ, 400kΩ, 4MΩ and 40MΩ .
To measure resistance, connect the meter as follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the
COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to Ω. Resistance measurement is default to auto range mode, press
REL∆ to switch to manual ranging measurement mode.
3. Connect the test leads across with the object being measured. The measured value shows
on the display.
Warning
Note
••
To obtain a more precise reading, you could remove the objects being tested from the circuit when measuring.
••
When resistance measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection between the testing leads and the circuit under test
and remove testing leads from the input terminals.
Figure 4
Page 8

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <8> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Warning
C. Testing Diodes (see figure 5)
(Figure 5)
To avoid damages to the Meter or to the devices under test, is connect circuit power and
discharge all the high-voltage capacitors before testing diodes.
Use the diode test to check diodes, transistors, and other semiconductor devices. The diode
test sends a current through the semiconductor junction, then measure the voltage drop
across the junction. A good silicon junction drops between 0.5V and 0.8V.
To test the diode out of a circuit, connect the meter as follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz Duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to
. Diode measurement mode is a default or press SELECT to select
measurement mode.
3. For forward voltage drop readings on any semiconductor component, place the red test lead
on the component’s anode and place the black test lead on the component’s cathode
.
••
To obtain a more precise reading, you could remove the objects being tested from the circuit when measuring.
••
When diode testing has been completed, disconnect the connection between the testing leads and the circuit under test and
remove testing leads from the input terminals.
Note
D. Testing for Continuity (see figure 6)
Warning
To avoid damages to the Meter or to the devices under test, disconnect circuit power
and discharge all the high-voltage capacitors before measuring continuity.
To test for continuity, connect the meter as follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz Duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to
and press SELECT button to select
measurement mode.
3. The buzzer sounds if the resistance of a circuit under test is less than 50Ω.
4. The buzzer may or may not sounds if the resistance of a circuit under test is between
50Ω to 100Ω.
5. The buzzer does not sound if the resistance of a circuit under test is higher than
100Ω.
Note
••
When continuity testing has been completed, disconnect the connection between the testing leads and the circuit under test and
remove testing leads from the input terminals.
Page 9

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <9> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
E. Frequency Measurement (see figure 7)
Warning
To avoid harms to you or damages to the Meter from electric shock, do not attempt to
measure voltages higher than 600V AC/DC, although readings may be obtained.
The resistance ranges are: 10Hz, 100Hz, 1kHz, 10kHz, 100kHz, 1MHz and 10MHz.
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz Duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to Hz.
3. Connect the test leads across with the object being measured. The measured value
shows on the display.
To measure frequency, connect the Meter as follows:
Note
When frequency measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection
between the testing leads and the circuit under test, and remove the testing leads away
from the input terminals of the meter.
F. Duty Cycle Measurement (see figure 8)
Warning
To avoid harms to you or damages to the meter from electric shock, do not attempt
to measure voltages higher than 600V AC/DC, although readings may be obtained.
The duty cycle range is: 0.1% to 99.9%.
To measure duty cycle, connect the Meter as follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the Hz Duty%
terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to Hz and press REL∆ to select Duty Cycle
measurement mode.
3. Connect the test leads across with the object being measured.
The measured value shows on the display.
Note
••
When duty cycle measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection
between the testing leads and the circuit under test, and remove the testing leads
away from the input terminals of the meter.
Figure 8
Figure 7
Page 10

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <10> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
G. DC/AC Current Measurement (see figure 9)
The measurement ranges of current are: 40.00 and 400.0
To measure current, do the following:
1. Set the rotary switch to 40 or 400
DC measurement mode is a
default. Press SELECT to switch between DC and AC measurement mode.
2. Hold the meter tight, don’t release. The hall components are very sensitive not
only to the magnet but also to heat and machines reaction force. Any shock will
cause the changing in reading in the short time.
3. Press the lever to open the transformer jaw.
4. Center the conductor within the transformer jaw, then release the meter slowly
until the transformer jaw is completely closed, Make sure the conductor to be
tested is placed at the center of the transformer jaw, otherwise it will casue
deviation. The Meter can only measure one conductor at a time, to measure
more than one conductor at a time will cause deviation.
Figure 9
Note
••
Press REL∆ to subtracts a stored value from the present measurement value and displays a result.
••
When current measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection between the conductor under test and the jaw, and
remove the conductor away from the transformer jaw of the meter.
Sleep Mode
To preserve battery life, the Meter automatically turns off if you do not turn the rotary switch or press any button for around
15 minutes.
The Meter can be activated by turning the rotary switch or pressing the button based on “The Effectiveness of Functional
Buttons” on page 14. Press SELECT to activate the Meter will disable the Sleep Mode feature.
The Meter beeps 5 times in about 1 minute before entering Sleep Mode and it will have a 1 long beep just before entering
Sleep Mode.
To disable the Sleep Mode function, press and hold SELECT button while turning on the Meter.
Page 11

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <11> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Specifications
A. General Specifications:
••
Maximum Voltage between any Terminals and grounding: Refer to different range input protection voltage.
••
Display: 3 3/4 digits LCD display, Maximum display 3999
••
Polarity: Automatically display.
••
Overloading: Display OL or –OL
••
Measurement Speed: Updates 3 times/second.
••
Measurement Deviation: The conductor being meaured is not placed in the center of the jawt during AC/DC current measurement, it
will cause extra 1% deviation based on the stated accuracy.
••
Drop Test: 1 meter drop test passed.
••
Max. Jaw Size: 28mm diameter.
••
Projected Max. Current conductor size: 26mm diameter.
••
Electro-Magnetic: When carrying out measurement near the electro-magnetic, it may cause unstable or wrong reading.
••
Power: 1 x 9V battery (NEDA1604 or 6F22 or 006P)
••
Battery Life: typically 150hours (alkaline battery)
••
Sleep Mode (can be disabled)
••
Dimensions (H x W x L): 208mm x 76mm x 30mm.
••
Weight: Approximate 260g (battery included)
B. Environmental Requirements
••
The Meter is suitable for indoor use.
••
Altitude: Operating: 2000m
Storage: 10000m
••
Safety/ Compliances: IEC 61010 CAT.II 600V, CAT.III 300V over voltage and double insulation standard.
••
Temperature and humidity: Operating: 0ºC to 30ºC ( 85%R.H); 30ºC to 40ºC ( 75%R.H); 40ºC to 50ºC ( 45%R.H);
Storage: -20ºC to +60ºC ( 85%R.H)
••
Battery Deficiency: Display
Page 12

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <12> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Accurate Specifications
Accuracy : ±(a% reading + b digits), guarantee for 1 year.
Operating temperature : 23ºC ± 5ºC
Relative humidity : ≤85%R.H
Temperature coefficient : 0.1x(specified accuracy)/1ºC
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
400.0mV 0.1mV ±(0.8%+3)
600V DC/AC
4.000V 1mV
±(0.8%+1)
40.00V 10mV
400.0V 100mV
600V 1V ±(1%+3)
A. DC Voltage
Remarks: Input impedance: 10MΩ.
B. AC Voltage
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
4.000V 1mV
±(1%+5)
600V DC/AC
40.00V 10mV
400.0V 100mV
600V 1V ± (1.2%+5)
Remarks:
••
Input impedance: 10MΩ // less than 100pF
••
Frequency response: 40Hz to 400Hz.
••
Change to AC:
UT204:
Combine AC and True RMS response method. Input sine wave to adjust. Non sine wave must follow the below data to adjust:
Peak factor: 1.4 to 2.0, add 1.0% on the stated accuracy
Peak factor: 2.0 to 2.5, add 2.5% on the stated accuracy
Peak factor: 2.5 to 3.0, add 4.0% on the stated accuracy.
Page 13

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <13> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
C. Resistance
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
400.0Ω 100mΩ ±(1.2%+2)
600Vp
4.000kΩ 1Ω
±(1%+2)
40.00kΩ 10Ω
400.0kΩ 100Ω
4.000MΩ
1kΩ
±(1.2%+2)
40.00MΩ 10kΩ ±(1.5%+2)
D. Diode Test
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
1mV Display forward voltage
drop nearest value
600Vp
Remark: Open circuit voltage approximate 1.48V.
E. Continuity Test
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
100mΩ Around ≤ 50Ω,
the buzzer beeps
600Vp
Remark:
••
Open circuit voltage approximate 0.45V.
••
The buzzer may or may not beeps when the resistance of a circuit under test is between 50Ω to 100Ω
••
The buzzer will not beep when the resistance of a circuit under test is >100Ω.
Page 14

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <14> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
10Hz 0.001Hz
±(0.1%+3)
600Vp
100Hz 0.01Hz
1kHz 0.1Hz
10kHz 1Hz
100kHz
10Hz
1MHz 100Hz
10MHz 1kHz For reference only
F. Frequency
Remark:
Input Sensitivity as follows:
When ≤ 100kHz: ≥ 300mV rms;
When > 100kHz: ≥ 600mV rms
When > 1MHz: ≥ 800mV rms
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
0.1% to 99.9% 0.1% For reference only 600Vp
G. Duty Cycle
H. DC Current
Range Resolution Accuracy Overload Protection
40.00A 0.01A ±(2%+5)
400A DC/AC
400.0A 0.1A ±(2%+3)
Page 15

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <15> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Warning
The operating temperature must be 0ºC to 40ºC when measuring current.
Remark:
••
If the reading is positive, the current direction is from bottom to up. See figure 10, the front case face up while the bottom case
face down. Hold the Meter tight, do now release. The Hall components are very sensitive not only to the magnet but also to heat
and machines reaction force. Any shock will cause the changing in reading in the short time. Follow the below procedure to
measure current will be more precise:
••
Hold the Meter tight and press the lever to open the transformer jaw. Center the conductor within the transformer jaws, then
release the Meter slowly until the transformer jaw is completely closed. Make sure the conductor to be tested is placed at the
center of the transformer jaw, otherwise it will cause +1.0% deviation based on the stated accuracy.
••
Remove the transformer jaw.
••
Press REL
∆∆
to display zero.
••
Repeat the above 1. procedure.
••
The obtained reading will be more precise.
I. AC Current
Range Resolution Accuracy Frequency Response Overload Protection
40.00A 0.01A ±(2.5%+8)
50Hz to 60Hz
400A DC/AC
400.0A 0.1A ±(2.5%+5)
Warning
The operating temperature must be 0ºC to 40ºC when measuring current.
Remark:
••
It may have 10 digits or less unstable or wrong digits, it will not affect measurement result.
••
Hold the Meter tight, do now release. The Hall components are very sensitive not only to the magnet but also to heat and
machines reaction force. Any shock will cause the changing in reading in the short time. Follow the below procedure to measure
current will be more precise:
1. Hold the Meter tight and press the lever to open the transformer jaw. Center the conductor within the transformer jaws, then
release the Meter slowly until the transformer jaw is completely closed. Make sure the conductor to be tested is placed at the
center of the transformer jaw, otherwise it will cause +1.0% deviation based on the stated accuracy.
2. Remove the transformer jaw.
3. Press REL
∆∆
to display zero.
4. Repeat the above 1. procedure.
5. The obtained reading will be more precise.
••
Change to AC:
UT204:
Combine AC and True RMS response method. Input sine wave to adjust. Non sine wave must follow the below data to adjust:
Peak factor: 1.4 to 2.0, add 1.0% on the stated accuracy
Peak factor: 2.0 to 2.5, add 2.5% on the stated accuracy
Peak factor: 2.5 to 3.0, add 4.0% on the stated accuracy.
Page 16

Clamp Meter
TRMS
Page <16> 20/09/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
MAINTENANCE
This section provides basic maintenance information including battery replacement instruction.
Warning
Do not attempt to repair or service your Meter unless you are qualified to do so and have the relevant calibration, performance test,
and service information.
To avoid electrical shock or damage to the Meter, do not get water inside the case.
A. General Service
••
Periodically wipe the case with a damp cloth and mild detergent. Do not use abrasives or solvents.
••
To clean the terminals with cotton bar with detergent, as dirt or moisture in the terminals can affect readings.
••
Turn the Meter power off when it is not in use.
••
Take out the battery when it is not using for a long time.
••
Do not use or store the Meter in a place of humidity, high temperature, explosive, inflammable and strong magnetic field.
B. Replacing the Battery (see figure 10)
Warning
To avoid false readings, which could lead to possible electric shock or personal injury,
replace the battery as soon as the battery indicator appears.
Make sure the transformer jaw and the tets leads are disconected from the circuit being
tested before opening the case bottom.
To replace the battery:
1. Turn the Meter off and remove all the connections from the input terminals
2. Turn the Meter’s front case down.
3. Remove the screw from the battery compartment, and separate the battery compartment
from the case bottom.
4.Take out the old battery and replace with a new 9V battery (NEDA1604, 6F22 or 006P).
5. Rejoin the case bottom and the battery compartment, and reinstall the screw.
Disclaimer This data sheet and its contents (the "Information") belong to the Premier Farnell Group (the "Group") or are licensed to it. No licence is granted for the use of it other than for information purposes
in connection with the products to which it relates. No licence of any intellectual property rights is granted. The Information is subject to change without notice and replaces all data sheets previously supplied.
The Information supplied is believed to be accurate but the Group assumes no responsibility for its accuracy or completeness, any error in or omission from it or for any use made of it. Users of this data
sheet should check for themselves the Information and the suitability of the products for their purpose and not make any assumptions based on information included or omitted. Liability for loss or damage
resulting from any reliance on the Information or use of it (including liability resulting from negligence or where the Group was aware of the possibility of such loss or damage arising) is excluded.
This will not operate to limit or restrict the Group's liability for death or personal injury resulting from its negligence. TENMA is the registered trademark of the Group. © Premier Farnell plc 2010.
Part Number Table
Description Part Number
Clamp Meter, TRMS UT-204
 Loading...
Loading...