Telwin Tecnica 152, Tecnica 170, Tecnica 150, Tecnica 168GE Troubleshooting And Repair Manual

cod. 988666
TECNICA 150-152-170-168
GE
TECNICA 140.1 - 142
inverter
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
AND REPAIR MANUAL
AND
AND REPAIR MANUAL
AND REPAIR MANUAL
CONTENTS PAGE
OPERATION AND WIRING DIAGRAMS................ 2
Block diagram 2
Analysis of the block diagram 3
Illustrations 5
Wiring diagrams 6
REPAIR GUIDE.......................................................10
Equipment required 10
General repair instructions 11
Troubleshooting and remedies 11
Testing the machine 14
Illustrations 17
REPAIR MANUAL
SPARE PARTS LIST...............................................18
REPAIR SHEET......................................................20
“reparation no problem !”
TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
OPERATION AND WIRING DIAGRAMSOPERATION AND WIRING DIAGRAMS
OPERATION AND WIRING DIAGRAMSOPERATION AND WIRING DIAGRAMS
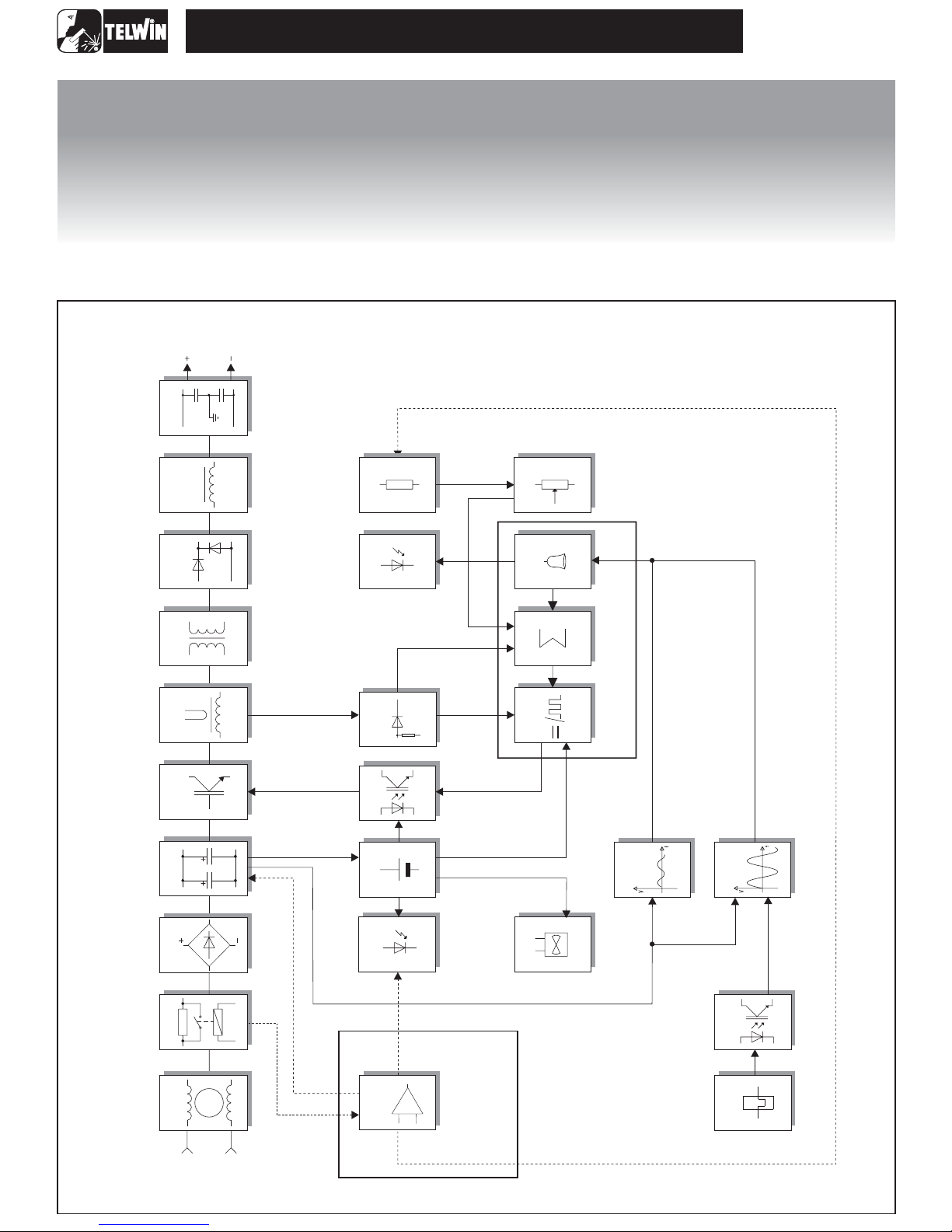
BLOCK DIAGRAM
OUTPUT
EMC FILTER II°
INDUCTANCE
DIODES
SECONDARY
POWER
TRANSFORMER
CURRENT
TRANSFORMER
CHOPPER
10
MAXIMUM
9
8
7
CURRENT ADJUST.
ALARM LED
19
17
CURRENT
POTENTIOMETER
ALARM BLOCK
ADDER
18
16
15
CONTROLLO
DUTY CYCLE
6
5
PRIMARY CURRENT
READER AND LIMITER
DRIVER
13
12
MAKER
14
FILTER
RECTIFIER BRIDGE
PRE-CHARGE
PRIMARY
EMC FILTER
INPUT
4
3
2
1
FLY-BACKPOWER
POWER SUPPLY
POWER SUPPLY
SUPPLY
LED
IDENTIFICATION
115/230V
+ |
11
25
24
CHANGE
VOLTAGE
(only for Tecnica 152)
-2-
OVERVOLATGE
UNDERVOLTAGE
SAFEGUARD
FAN
26
SEFEGUARD
23
GALVANIC
SEPARATOR
POWER
TRANSFORMER
THERMOSTAT
22
21
20

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
ANALYSIS OF THE BLOCK DIAGRAM
NOTE: Unless indicated otherwise, it should be assumed that
the components are assembledon thepower board.
Block 1
EMC Filter
Consisting of: C1, C2,C3, L1.
Prevents noise from the machinefrom beingtransmitted along
the main power lineand viceversa.
Block 2
Pre-charge
Consisting of: K1, R1.
Prevents the formation of high transitory currents that could
damage the main power switch, the rectifier bridge and the
electrolytic capacitors.
When the power source is switched on the relay K1 is deenergised, capacitors C4, C5, C6, C7, C8 are then charged
by R1. When the capacitors are charged the relay is
energised.
Block 3
Rectifier bridge
Consisting of: D1.
Converts the mains alternating voltage into continuous pulsed
voltage.
Block 4
Filter
Consisting of: C4, C5,C6, C7.
Converts the pulsed voltage from the rectifier bridge into
continuous voltage .
(C7 fitted on Tecnica 152 only)
Block 5
Chopper
Consisting of: Q1, Q2,Q3, Q4.
Converts the continuous voltage from the filter into a high
frequency square wave capable of piloting the power
transformer.
Regulates the power according to the required welding
current/voltage.
Block 6
Current transformer
Consisting of: T2.
The C.T. is used to measure the current circulating in the
power transformer primary and transmit the information to
block 14 (primary currentreader andlimiter).
Block 7
Power transformer
Consisting of: T3.
Adjusts the voltage and current to values required for the
welding procedure. Also forms galvanic separation of the
primary from the secondary (welding circuit from the power
supply line).
Block 8
Secondary diodes
Consisting of: D20, D21,D22, D23.
D20, D21 converts the current circulating in the transformer to
a single direction, preventingsaturation ofthe nucleus.
D22, D23 recirculate the inductance output current (block 9)
when the IGBT's are not conducting, bypassing the power
transformer (block 7).
Block 9
Inductance
Consisting of: L2.
Levels the secondary board diodes’ output current making it
practically continuous.
Block 10
Secondary EMC Filter
Consisting of: C21, C22.
Prevents noise from the power source from being transmitted
through the welding cablesand viceversa.
Block 11
Flyback power supply
Consisting of: T1, U2.
Uses switching methods to transform and stabilise the voltage
obtained from block 4 (filter) and supplies auxiliary voltage to
power block 12 (driver)and thecontrol board correctly.
Block 12
Driver
Consisting of: ISO2, ISO3.
Takes the signal from block 11 (flyback power supply) and,
controlled by block 14 (duty cycle maker), makes the signal
suitable for piloting block6 (chopper).
Block 13
Primary current reader andlimiter
Consisting of: R63, R64, R65 and partof thecontrol section.
Reads the signal from block 6 (current transformer) and scales
it down so it can be processed and compared in blocks 14 and
15.
Block 14
Duty cycle maker
Consisting of: U2 (controlboard).
Processes the information from block 15 (adder) and block 13
(primary current reader and limiter) and produces a square
wave with variable duty cycle limiting the primary current to a
maximum pre-set value underall circumstances.
Block 15
Adder
Consisting of: U1C (controlboard).
Gathers all the information from block 13 (primary current
reader and limiter), from block 16 (alarms) and from block 18
(current potentiometer), and produces a signal with a suitable
voltage for processing byblock 14(duty cycle maker).
Block 16
Alarm Block
Consisting of: U1A, U1B(control board).
When an alarm is detected the power source output current is
drastically reduced by making direct adjustments to block 14
(duty cycle maker) and directly changing the reference signal
obtained from block 18(current potentiometer).
Block 17
Alarm LED
Consisting of: D14.
It is switched onby block16 (alarms) in the eventof:
1) Triggering of thermostatic capsule/thermostat on power
transformer.
2) Triggering dueto undervoltage.
3) Triggering dueto overvoltage.
4) Short circuit at output (electrode holder clamp and earth
cable connected to one another or electrode stuck to piece
being welded).
-3-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Block 18
Current potentiometer
Consisting of: R52.
This is used to set the reference voltage needed to adjust the
output current: when the potentiometer knob is turned the
cursor voltage varies, thus varying the current from the
minimum to the maximumvalue.
Block 19
Maximum current adjustment
Consisting of: R56, R57,R58.
Used to adjust the maximum cutting current to be supplied by
the power source.
Block 20
Power transformer thermostat
Consisting of: ST1.
When the temperature of the power transformer is too high,
the thermostat transmit the information to block 21 (galvanic
separation). It is reset automatically after the alarm condition
has ceased.
Block 21
Galvanic separator
Consisting of: ISO1.
The signal arriving from blocks 20 and 21 (power transformer
thermostat and secondary diodes) is separated galvanically
and sent to block 16 (alarms) for detection of a possible alarm
event.
Block 26
Fan
Consisting of: V1.
Powered directly by block 13 (power supply) and cools the
power components.
Block 22
Overvoltage safeguard
Consisting of: R71, R73and partof the control section.
If the main supply voltage exceeds the maximum value this
safeguard triggers (a tolerance of approx. ±15% of the power
supply voltage is allowed: outside this range the safeguard
triggers).
Block 23
Undervoltage safeguard
Consisting of: R72, R70and partof control board.
If the main supply voltage falls below the minimum allowed
value this safeguard triggers (a tolerance of approx. ±15% of
the power supply voltage is allowed: outside this range the
safeguard triggers).
Block 24
Power supply identification 115/230V
Consisting of: U1A, Q2,Q1 (voltagechange board).
This is only present on machines with the automatic
identification function.
Identifies the power supply voltage level (115V or 230V) and
compares the values with a reference signal. The comparison
causes enabling of block 5 (filter) for operation in standard
mode (230V) or as voltage duplicator (115V). This block also
adjusts for the correct maximum current in relation to the
different operatingmodes.
Block 25
Power supply LED
Consisting of: D12 (D13for Tecnica 152).
Indicates when the power source is correctly powered and
ready for use.
On machines operating exclusively at 230V it is green. On
machines with automatic voltage identification (Tecnica 152) it
is green for operation at 230V and orange for operation at
115V.
-4-
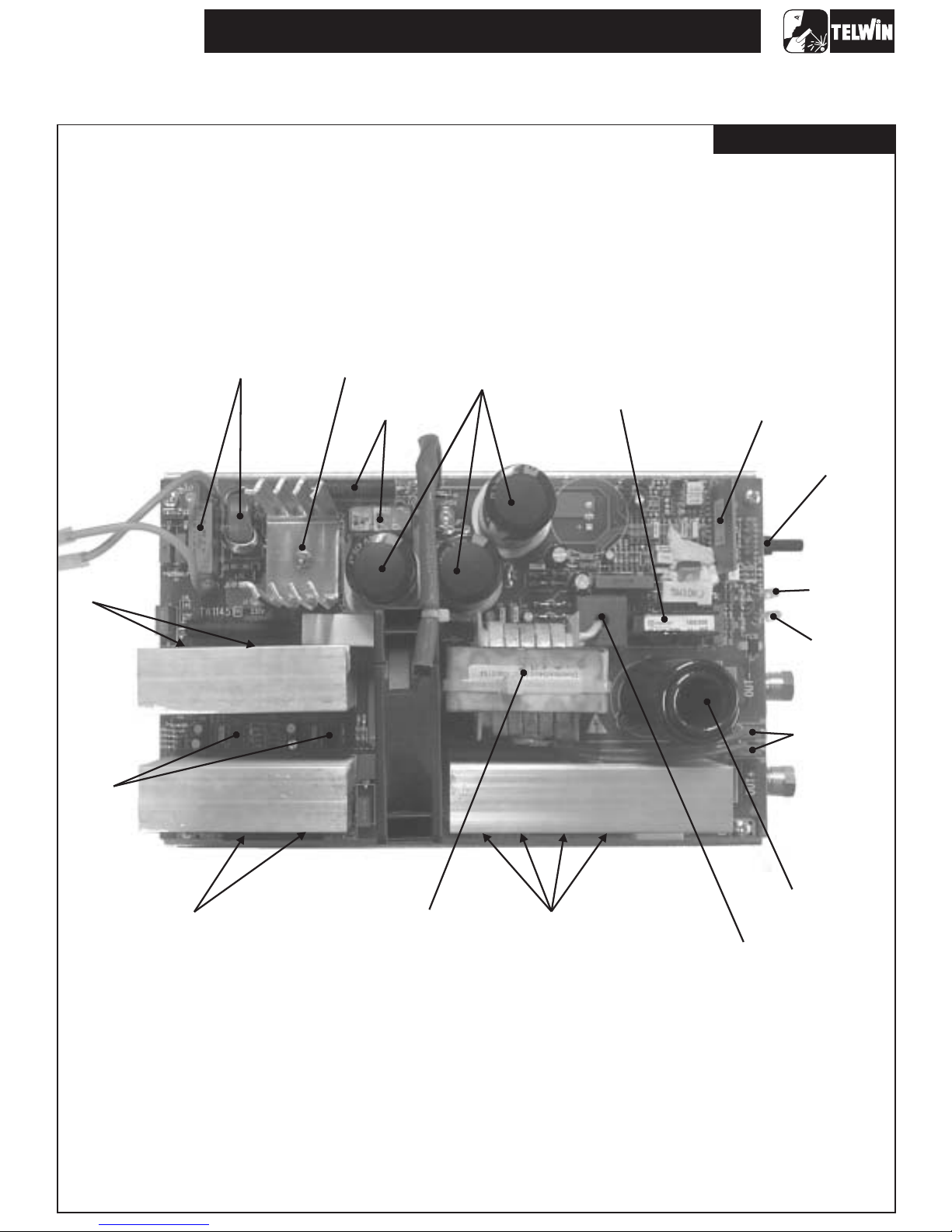
ILLUSTRATIONS
TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Power board
(5)
CHOPPER
(12)
DRIVER
(1)
PRIMARY EMC
FILTRE
(3)
RECTIFIER
BRIDGE
PRE-CHARGE
(2)
(4)
FILTER
(11)
FLY-BACK
POWER SUPPLY
CONTROL
BOARD
(18)
CURRENT
POTENTIOMETER
(25)
POWER
SUPPLY
LED
(17)
ALARM
LED
(10)
SECONDARY
FILTER EMC
(5)
CHOPPER
(7)
POWER
TRANSFORMER
-5-
(8)
SECONDARY
DIODES
(9)
INDUCTANCE
(6)
CURRENT
TRANSFORMER
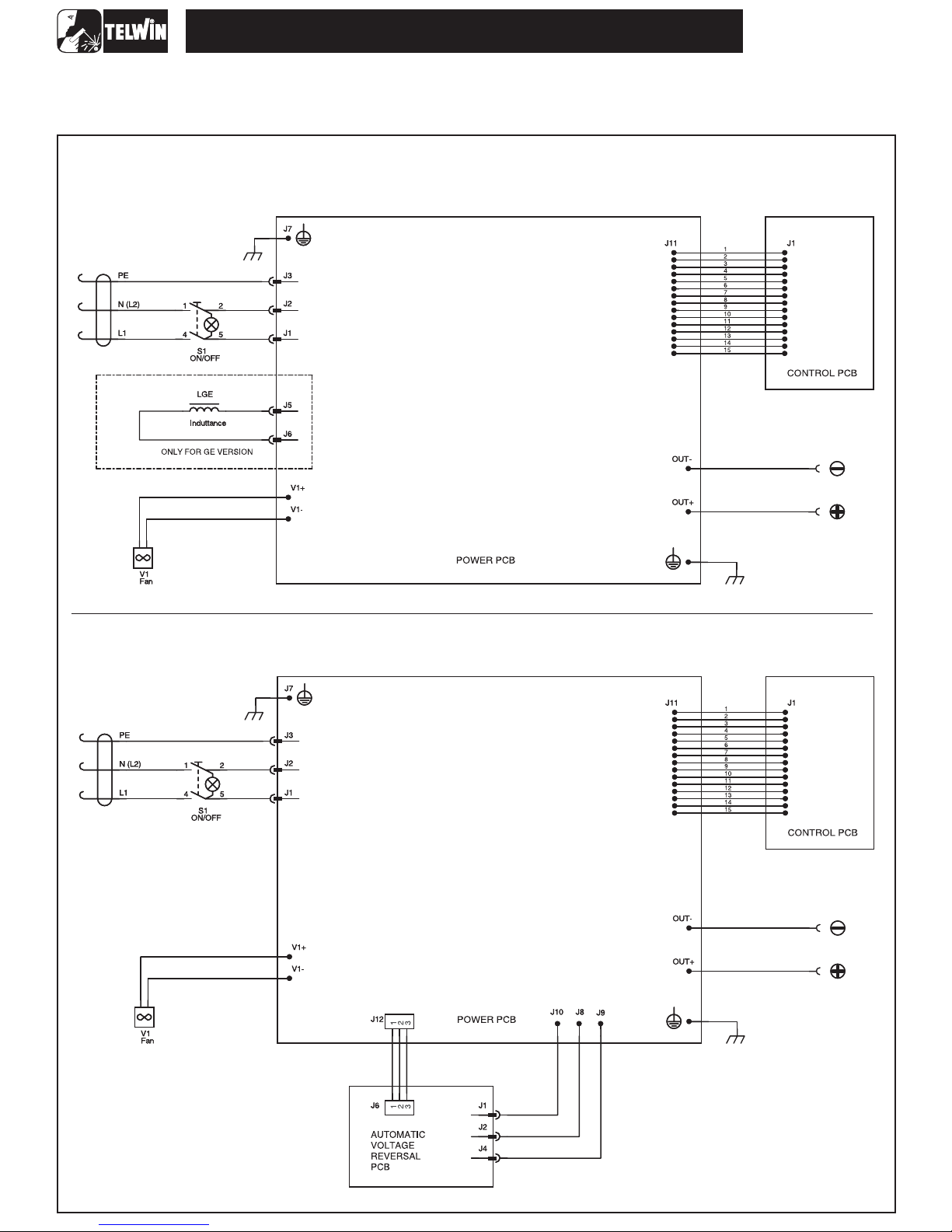
TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
WIRING DIAGRAMS
Wiring diagram
general -TECNICA 150 - 170 - 168GE
Wiring diagramgeneral TECNICA 152-
-6-
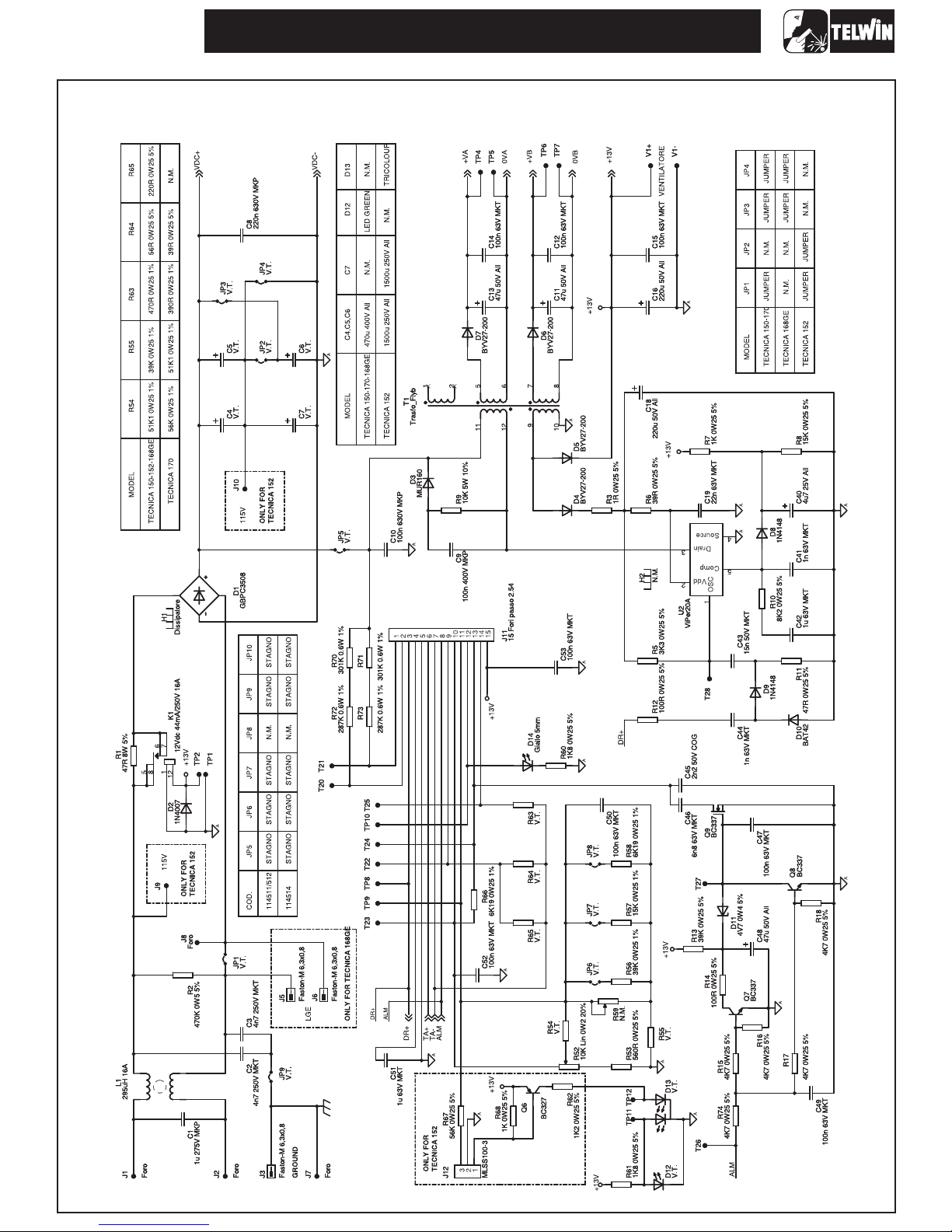
TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Wiring diagram power board - power supply / control
-7-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Wiring diagram power board - power / driver
-8-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Wiring diagram - control board
Wiring diagram - change voltage board 115/230V (only forTECNICA)
-9-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
4 2513
REPAIR GUIDEREPAIR GUIDE
REPAIR GUIDEREPAIR GUIDE
ESSENTIAL INSTRUMENTS
1 Dual trace oscilloscope cod. 802401 (*)
2 Static load generator cod. 802110 (*)
3 Variac 0 - 300v 1500 VA cod. 802402 (*)
4 Digital multimeter
USEFUL INSTRUMENTS
5 Unsoldering station
6 Miscellaneous tools
(*)The instruments with codes can be supplied by Telwin. The sale price is available on request.
6
-10-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
TROUBLESHOOTING AND REMEDIES
WARNING:
BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH REPAIRS TO
THE MACHINE READ THE INSTRUCTION
MANUAL CAREFULLY.
WARNING:
EXTRAORDINARY MAINTENANCE SHOULD
BE CARRIED OUT ONLY AND EXCLUSIVELY
BY EXPERT OR SKILLED ELECTRICALMECHANICAL PERSONNEL.
WARNING:
ANY CHECKS CARRIED OUT INSIDE THE
MACHINE WHEN IT IS POWERED MAY
CAUSE SERIOUS ELECTRIC SHOCK DUE TO
DIRECT CONTACT WITH LIVE PARTS.
GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
The following is a list of practical rules which must be strictly
adhered to if repairsare to be carried out correctly.
A) When handlingthe activeelectronic components,the IGBT's
and Power DIODES in particular, take elementary antistatic
precautions (use antistatic footwear or wrist straps, antistatic
working surfaces etc.).
B) To ensure the heat flow between the electronic components
and the dissipator, place a thin layer of thermo-conductive
grease (e.g. COMPOUND GREASIL MS12) between the
contact zones.
C) The power resistors (should they require replacement)
should always be solderedat least 3 mm above theboard.
D) If silicone is removed from some points on the boards, it
should be re-applied.
Use only non-conducting neutral or oximic reticulating
N.B.
silicones (e.g. DOW CORNING 7093). Otherwise, silicone
that is placed in contact with points at different potential
(rheophores of IGBT's, etc.) should be left to reticulate
before the machine istested.
E) When the semiconductor devices are soldered the
maximum temperature limits should be respected (normally
°
300 C for no more than 10seconds).
F) It is essential to take the greatest care at each disassembly
and assembly stage forthe various machine parts.
G) Take care to keep the small parts and other pieces that are
dismantled from the machine so as to be able to position
them in the reverse order when re-assembling (damaged
parts should never be omitted but should be replaced,
referring to the spare parts list given at the end of this
manual).
H) The boards (repairedwhen necessary)and the wiringshould
never be modified withoutprior authorisation from Telwin.
I) For further information on machine specifications and
operation, refer to theInstruction Manual.
J) When the machine is in operation there are
WARNING!
dangerously high voltages on its internal parts so do not
touch the boards whenthe machine is live.
1.0 Disassembling themachine
Every operation should be carried out in complete safety with the
power supply cable disconnected from the mains outlet and
should only by done by expert or skilled electrical-mechanical
personnel.
- remove the current adjustment knob on the front panel of the
machine ;
- undo the 4 screws attaching the handle to the top cover( ).
-
undo the 8 screwsfasteningthe back and front plastic panels;
4forthecap( ).
- undothe2screwsattachingthetopcovertothebase:1 screw
oneachside ).
- undo the 2 screws fastening the top cover to the metal
structure.
- slide out the top cover upwards
After completing the repairs, proceed in the reverse order to reassemble the cover anddo not forgetto insertthe toothed washer
on the ground screw.
(fig. 1)
fig. 1
fig.1
(fig.1
2.0 Cleaning theinside of the machine
Using suitably dried compressed air, carefully clean the
components of the power source since dirt is a danger to parts
subject to high voltages and can damage the galvanic separation
between the primary andsecondary.
To clean the electronic boards we advise decreasing the air
pressure to prevent damageto the components.
It is therefore important to take special care when cleaning the
following parts
Fan fig. 2A
()
Check whether dirt has been deposited on the front and back air
vents or has damaged the correct rotation of the blades, if there is
still damage after cleaningreplace the fan.
Power board figs. 2Aand 2B
- rheofores ofIGBT's Q1, Q2, Q3,Q4;
- rheofores ofrecirculating diodes D40, D41;
- rheofores ofsecondary power diodes D21, D22, D23;
- thermostat ST1on power transformer;
- opto couplersISO1;
- control board.
():
3.0 Visual inspection of the machine
Make sure there is no mechanical deformation, dent, or
damaged and/or disconnected connector.
Make sure the power supply cable has not been damaged or
disconnected internally and that the fan works with the
machine switched on. Inspect the components and cables for
signs of burning or breaks that may endanger operation of the
power source. Check thefollowing elements:
Main power supply switch fig. 2A
Use the multimeter to check whether the contacts are stuck
together or open. Probablecause:
- mechanical or electric shock (e.g. bridge rectifier or IGBT
in short circuit, handlingunder load).
Current potentiometer R52 fig. 3
Probable cause:
- mechanical shock.
Relay K1 fig. 3
Probable cause:
- see main power supply switch. If the relay contacts
Electrolytic capacitors C4,C5, C6,C7 fig. 3
Probable cause :
- mechanical shock;
- machine connected to power supply voltage much higher
()
are stuck together or dirty, do not attempt to separate them
and clean them, justreplace therelay.
(C7 fitted on Tecnica 152only)
than the rated value;
()
()
N.B.
()
-11-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
- broken rheophore on one or more capacitor: the
remainder will be overstressed and become damaged by
overheating;
- ageing aftera considerablenumber of working hours;
- overheating causedby thermostaticcapsule failure.
IGBT's Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 fig. 4
()
Probable cause:
- discontinuation in snubber network;
- fault in driver circuit;
- poorly functioning thermal contact between IGBT and
dissipator (e.g. loosened attachmentscrews: check);
- excessive overheating related tofaulty operation.
Primary diodes D40, D41 fig. 4
()
Probable cause:
- excessive overheating related tofaulty operation.
Secondary diodes D20, D21,D22, D23 fig. 4
()
Probable cause:
- discontinuation in snubber network;
- poorly functioning thermal contact between IGBT and
dissipator (e.g. loosened attachmentscrews: check);
- faulty output connection.
Power transformer and filterreactance (fig.2A)
Inspect the windings forcolour changes.Probable causes:
- power source connectedto ahigher voltage than 280Vac;
- ageing after asubstantial numberof working hours;
- excessive overheating relatedto faultyoperation.
4.0 Checking the power and signal wiring
It is important to check that all the connections are in good
condition and the connectors are inserted and/or attached
correctly. To do this, take the cables between finger and
thumb (as close as possible to the fastons or connectors) and
pull outwards gently: the cables should not come away from
the fastons or connectors. N.B. If the power cables are not
tight enough this couldcause dangerousoverheating.
6.0 Electrical measurements with the machine in
operation
WARNING!
remind you that during these tests the power source is
powered and therefore the operator is exposed to the danger
of electric shock.
The tests describedbelow canbe usedto check the operation
of the power andcontrol partsof the power source.
6.1 Preparation for testing
A) Set up the oscilloscope with the voltage probe x100
connected between pin 3 of U2 and the earth on the anode of
diode D2 ( ).
B) Set up the multimeterin DCmode and connect the prods to
the OUT+ and OUT- bumpcontacts.
C) Position the potentiometer R52 on maximum (turn
clockwise as far asit willgo).
D) Connect the power supply cable to a single-phase variac
with variable output 0-300Vac.
6.2 Tests forthe TECNICA 150 -170 -168GE
A) Switch on the variac (initially set to the value 0 V), switch off
the main switch on the power source and increase the variac
voltage gradually to 230Vac and makesure:
- the green powersupply LED D12 lights up( ),
- the fan forthe power transformer starts upcorrectly,
- the pre-charge relayK1 commutes ( ),
- for voltages close to the rated power supply value (230Vac
±15%) the power source is not in alarm status (yellow LED
D14 off).
NB.
if the power source stays in alarm status permanently,
there could be a fault in the control board (in any case,
proceed to make theother tests)
B) Make sure the waveform shown on the oscilloscope
resembles .
FIGURE A
Before proceeding with faultfinding, we should
fig. 3
fig. 3
fig. 3
Fig. A
5.0 Electrical measurements with the machine
switched off
A) With the multimeter set in mode check the
following components (junction voltagesnot lessthan 0.2V):
- rectifier bridge D1 ( );
fig. 3
- IGBT's Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 (absence of short circuits between
collector-gate and between emitter-collector );
- secondary board diodes D20, D21, D22, D23 between
anode and cathode ( ). The secondary diodes can be
checked without removing the power board: with one prod
on the secondary board dissipator diodes and the other in
sequence on the twopower transformeroutlets;
- viper U2 (absence of short circuits between pin 3 - pin 4
and between pin 4 pin 2, )
B) With the multimeter set in ohm mode check the following
components:
- resistor R1: 47ohm (pre-charge );
- resistors R44, R45: 22ohm (primary snubber );
- resistor R20: 10ohm (secondary snubber );
- thermostat continuity test on the power transformer: clean
the resin from the bump contacts of ST1 (A,B) and
measure the resistancebetween thetwo bump contacts, it
should be approx. 0ohm ( ).
diode testing
fig. 4
fig. 4
fig. 3 .
fig. 3
fig. 3
fig. 3
fig. 2B
SETTINGS:
PROBE CH1
- x100;
- 100V/Div;
- 4 sec/Div.
µ
VERIFICARE CHE:
- FREQUENCY IS
65KHz ±10%;
AMPLITUD IS
450V ±10%.
N.B.
if no signal is present, it may be necessary to replace the
integrated circuit U2 ( ).
C) With the multimeter set in mode make sure that
fig. 3
():
Set up a multimeter in volt mode and make sure that
-
fig. 3
volt
(fig.
3):
- the voltage over the anode of D2 (-) and the cathode of D2
(+) is equal to+13V ±5%;
- the voltage over the anode of D30 (-) and the cathode of
D7 (+) is equalto +29V±5%;
- the voltage over the anode of D31 (-) and the cathode of
D6 (+) is equalto +29V±5%;
D) Set up the dual trace oscilloscope. Connect the probe
CH1(x100) to the Q1 collector and probe CH2(x10) to the
-12-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
gate, also of Q1. The earth connections are both made to the
emitter of Q1.
E) Make sure the waveform displayed on the oscilloscope
resembles
fig. B.
FIGURE B
RepeatthistestalsoforQ2, Q3.Q4(forQ3 and Q4 use the
F)
differentialprobe).
if the signal is not present there could be a fault in the
N.B.
IGBT driver circuit ( ) or in the control board ( in
fig. 3 fig. 2A,
thiscasewe recommendreplacingtheboard).
Set up the dual trace oscilloscope. Connect probe CH1
G)
(x100) to the collector of Q1 and probe CH2 (x10) to pin 9 on strip
J11. The earth terminals are connected together to the emitter of
Q1.
H) Make sure the waveform displayed on the oscilloscope
resembles and that the output voltage over OUT+ and
fig. C
OUT -is equalto +80Vdc±10%.
FIGURE C
I) Switch the power source on again and make sure that,
following the brief start up time, the machine is not in alarm
status (the yellow alarm LED D14 is off, ). If the
machine remains in alarm status (and this is not due to a fault
in the control board) there could be a fault in the photocoupler
ISO1 ( ).
fig. 3
6.3 Tests for the TECNICA161
In this case the tests are just the same and can be carried out
with either a 115V or 230V power supply:
- with a power supply of 115V±15% (LED D13 on and
orange) the voltage change board enables voltage
duplication by the inputfilter.
- with a power supply of 230V±15% (LED D13 on and
SETTINGS:
PROBE
- CH1 x100;
- 100 V/Div;
PROBE
- CH2 x10;
- 10V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
-
AMPLITUDE ON CH1
320V ±10%;
IS
- POSITIVE
AMPLITUDE ON
IS +16V ±10%;
- NEGATIVE
AMPLITUDE ON
SIA -10V ±10%.
SETTINGS:
PROBE
- CH1 x100
- 100V/Div;
PROBE
- CH2 x10;
- 500mV/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
AMPLITUDE ON
CH1IS
320V ±10%;
AMPLITUDE ON CH2
IS
500mV ±10%.
fig. 3 N.B.
green) the voltage change board disables voltage
duplication by the inputfilter.
NOTE:
The intermediate band with a power supply between
115V±15% and 230V±15% will be considered incompatible
so the machine willshow alarmstatus (yellow LED D14 litup).
7.0 Repairs, replacing the boards
If repairing the board is complicated or impossible, it should
be completely replaced. The board is identified by a 6-digit
code (printed in white on the component side after the initials
TW). This is the reference code for requesting a replacement:
:
CH2
CH2
Telwin may supply boards that are compatible but with
different codes.
Warning:
before inserting a new board check it carefully for
damage that may have occurred in transit. When we supply a
board it has already been tested and so if the fault is still
present after it has been replaced correctly, check the other
machine components. Unless specifically required by the
procedure, never alter theboard trimmers.
7.1 Removing the powerboard fig. 2A()
If the fault is in the power board remove it from the bottom as
follows:
- with the machine disconnected from the main supply,
disconnect all the wiringconnected tothe board;
- remove the current adjustment knob on the front panel of
the machine ( );
fig. 1
- remove any bands constraining the board (e.g. on the
power supply cable andconnections toprimary);
- undo the 3 screws fastening the board to the bottom (
2B
);
- remove the board from the metal structure, lifting it
upwards.
for assembly proceed in the reverse order and
N.B.
remember to insert thetoothed washeron the earth screw.
A) Please read the procedure for replacing the IGBT's
carefully: (fig. 4).
The 4 IGBT's are attached to 2 different dissipators and
whenever a replacement is required, both IGBT's should be
all replaced.
- undo the screws attaching the dissipator to the board to
replace Q1, Q3 ( );
fig. 2B
- undo the screws attaching the dissipator to the board to
replace Q2, Q4 ( );
fig. 2B
- remove the 4 IGBT's and the 2 diodes D40, D41 by
unsoldering the rheofores and then clean the solder from
the printed circuit bumpcontacts;
- remove the 2 dissipatorsfrom the board;
- undo the screws lockingthe 4 IGBT's.
Before making the replacement make sure the components
piloting the IGBT's arenot also damaged:
- with the multimeter set in mode make sure there is no
short circuit on the PCB between the 1 and 3 bump
ohm
st rd
contacts (between gate and emitter) corresponding to
each component;
- alternatively, resistors R40, R41, R42, R43 could have
burst and/or diodes D32, D33, D34 and D35 may be
unable to function at the correct Zener voltage (this should
have shown up inthe preliminarytests);
- clean any irregularity or dirt from the dissipators. If the
IGBT's have burst the dissipators may have been
irreversibly damaged: in this case they should be
replaced;
- apply thermo-conductive grease following the general
-13-
fig.

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
instructions.- Insert the new IGBT's between the
dissipator and the spring, taking care not to damage the
component during assembly (the spring should be
inserted under pressure on the dissipator so as to lock the
component);
- place the dissipators with the new IGBT's and primary
diodes D40 and D41 ( Make sure there is
WARNING!
insulation between the case of diode D41 and the
dissipator) in the PCB bump contacts, placing 4 spacers
between the dissipator and thePCB (2for eachdissipator)
and fasten them down with the screws (torque wrench
setting for screws 1Nm ±20%);
- solder the terminals taking care not to let the solder run
along them;
- on the welding side cut away the protruding part of the
rheofores and check they are not shorted (between the
gate and emitter inparticular).
B) Please read the procedure for replacing the
secondary board diodes carefully(fig. 4):
The 4 SECONDARY DIODES are attached to the same
dissipator, and when a replacement is required, all of them
should be replaced:
- undo the screws attaching the dissipator to the board, to
replace diodes D20, D21,D22 andD23;
- remove the 4 secondary diodes unsoldering the rheofores
and cleaning any solder from the bump contacts on the
board;
- removethe dissipatorfrom the board;
- removethe springlocking the 4 diodes;
- clean any irregularity or dirt from the dissipator. If the
diodes have burst the dissipator may have been
irreversibly damaged: in thiscase itshould be replaced;
- apply thermo-conductive grease following the general
instructions;
- insert the new diodes between the dissipator and the
spring, taking care not to damage the component during
assembly (the screw should be inserted under pressure
on the dissipator soas tolock the component);
- place the dissipator with the new components in the PCB
bump contacts and fasten them down with the screws
(torque wrench setting forscrews 1Nm ±20%);
- solder the terminals taking care not to let the solder run
along them;
- on the soldering side cut away the protruding part of the
rheofores and check they are not shorted (between
cathode and anode);
N.B.
make sure resistor (R20) and capacitor (C20) on the
snubber have been solderedto thePCB correctly ( ).
fig. 3
powered and therefore the operator is exposed to the danger
of electric shock.
The tests given below are used to verify power source
operation under load.
1.1 Preparation for testing
.
A) Connect the power source to the static load generator
using cables fitted with the appropriate dinse connectors
(code 802110).
B)
Set up the dual trace oscilloscope, connecting probe CH1
(x100) to the collector on Q1 and probe CH2 (x10) to pin 9 on strip
J11 (plasma control board). The earth terminals are connected
together to the emitterof Q1.
C) Set up the multimeter in DC mode and connect the prods
to the OUT+ andOUT- bump contacts.
D) Connect the power supply cable to the 230Vac power
supply.
WARNING!
During tests the operator must avoid contact with
the metal parts of the torch because of the presence of
dangerous, high voltage.
1.2 Tests for the TECNICA150 - 170 -168GE
A) Minimum
load test:
- set up the static load generator with the switch settings as
in the table in ;
Fig. D
- on the front panel position the current potentiometer R23
at (approx.) half way.
- switchon themain switch;
- activatethe staticoload generator and make surethat:
- the waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope resemble
those in ;
Fig. D
- the output current is +5Adc±20%, and the output
voltage is +20.2Vdc±20%.
- deactivate the static load generator and switch off the
main switch.
FIGURE D
SETTINGS:
- CH1 x100
PROBE
- 100V/Div;
- CH2 x10;
PROBE
- 500mV/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
-
-
:
AMPLITUDE ON CH1
320V ±10%.
IS
AMPLITUDE ON CH2
1V ±10%.
IS
C) Please read the procedure for replacing the control
board (fig. 3):
Whatever fault occurs in the control board, we strongly
recommend its replacement without attempts at repair. To
remove it, cut and then unsolder from the power board the
connector keeping it fixed perpendicularto thePCB, replaceit
and re-solder the connector.
TESTING THE MACHINE
Tests should be carried out on the assembled machine before
closing it with the top cover. During tests with the machine in
operation never commute the selectors or activate the ohmic
load contactor.
WARNING!
should remind you that during these tests the power source is
Before proceeding to test the machine, we
1
12030405060
Switch number
Position number
B) Intermediate load test:
- set up the ohmic load with the switch settings as in the
table in ;
fig. E
- on the front panel turn the current potentiometer to 75A
(approx. half-way);
- startup the ohmic load andmake surethat:
- the waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope resemble
those in ;
Fig. E
- the output current is equal to +75Adc ±10% and the
output voltage is equalto +24Vdc±10%.
- switch offthe ohmic load.
-14-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
FIGURE E
SETTINGS:
PROBE
- CH1 x100
- 100V/Div;
PROBE
- CH2 x10;
- 2V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
AMPLITUDE ON CH1
IS
320V ±10%.
AMPLITUDE CH2
IS
5V ±10%.
1
22232425261
Switch number
Position number
C) Rated load test for TECNICA150-186GE:
- set up the ohmic load with the switch settings as in the
table in ;
fig. F
- on the front panel turn the current potentiometer to
maximum (turn clockwise asfar asit will go);
- start up the ohmicload andmake sure that:
- the waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope
resemble those in ;
fig. F
- the output current is equal to +130Adc ±5% and the
output voltage is equal to +25.2Vdc ±5%; if the output
current reading is not 130A ±5%, adjust the current
using jumpers JP6, JP7and JP8( ).
fig. 7
- switch off the ohmicload.
FIGURE F
SETTINGS:
- CH1 x100
PROBE
- 100V/Div;
- CH2 x10;
PROBE
- 5V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
:
AMPLITUDE ON
320V ±10%;
CH1 IS
AMPLITUDE ON
8V ±10%.
CH2 IS
1
32333425262
Number switch
Position switch
VERIFY THAT
-
-
current reading is not 150A ±5%, adjust the current
using jumpers JP6, JP7and JP8( ).
fig. 7
- switch off the ohmicload.
FIGURE G
SETTINGS:
PROBE
- CH1 x100
- 100V/Div;
- SONDA CH2 x10;
- 5V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
AMPLITUDE ON
CH1 IS
320V ±10%;
AMPLITUDE ON
CH2 IS
8V ±10%.
1
32333435261
Switch number
Position number
E) Checking the secondary diode voltages:
- set up the dual trace oscilloscope, connecting probe CH1
x 100 to the anode of diode D21 and probe CH2x100 to the
anode of diode D22. Earth connections are both made to
the secondary dissipator;
- remove the multimeter from the OUT+ and OUT- bump
contacts;
- set up the static load generator with the switch settings as
in the table in
fig. F, G or I;
- on the front panel position the current potentiometer to the
maximum (turn the knob clockwise as far as it will go) and
switch on the mainswitch;
- activate the static load generator and make sure that the
waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope resemble those
in
fig. H;
- deactivate the static load generator and switch off the
main switch.
FIGURE H
SETTINGS:
PROBE
- CH1 x100
- 50V/Div;
PROBE
- CH2 x100;
- 50V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
- REVERSE
:
AMPLIDUTE ON CH1
AND CH2 DOES NOT
EXCEED 250V.
D) Rated load test for TECNICA170:
- set up the ohmic load with the switch settings as in the
table in ;
fig. G
- on the front panel turn the current potentiometer to
maximum (turn clockwise asfar asit will go);
- start up the ohmicload andmake sure that:
- the waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope
resemble those in ;
fig. G
- the output current is equal to +150Adc ±5% and the
output voltage is equal to +26Vdc ±5%; if the output
F) Running timecheck and closing the machine
With the load status as in and the current
fig. F or G
adjustment potentiometer on maximum, switch on the power
source and leave it in operation until the thermostatic
capsules trigger (machine in alarm status). Check the correct
positioning of the internal wiring and finally re-assemble the
machine.
-15-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
G) Welding test
With the power source set up according to the instructions in
the handbook makea testweld at80A (electrode diameter 2.5
mm). Check the dynamicbehaviour ofthe power source.
1.3 Scheduled testsfor the TECNICA 152
In this case it makes no difference whether the tests are
carried out with a115V or a230V powersupply:
- with a 230V power supply (LED D13 on and green) the
tests are exactly the same as those described for the
TECNICA 150-168GE.
- with a 115V power supply (LED D13 on and orange) the
tests are exactly the same as those described for the
TECNICA 150-168GE with the exception ofthe ratedload
test at point 1.2 C). To carry out the rated load test at 115V
see point 1.3 A).
A) Rated load test:
- set up the ohmic load with the switch settings as in the
table in ;
- on the front panel turn the current potentiometer to
maximum (turn clockwise asfar asit will go);
- switch on at the mainswitch;
- start up the ohmic loadand makesure that:
- the waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope resemble
those in
- the outputcurrent is equal to +100Adc ±5% and the output
voltage is equal to 24Vdc ±5%; if the output current
reading is not 100A ±5%, adjust the current using jumpers
JP6, JP7 and JP8 ( ).
- switch off theohmic loadand switch offthe main switch.
fig. I
fig. I;
fig. 5
FIGURE I
1
322324252
SETTINGS:
- CH1 x100
PROBE
- 100V/Div;
- CH2 x10;
PROBE
- 5V/Div;
- 5 sec/Div.
µ
TIME TOLLERANCES
±20%.
VERIFY THAT
-
-
6
2
Number switch
Position switch
:
AMPLITUDE ON
320V ±10%;
CH1 IS
AMPLITUDE ON
7V ±10%.
CH2 IS
-16-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
ILLUSTRATIONS
FIG. 1
SCREWS FASTENING
BACK PANEL
SCREWS FASTENING
TOP COVER
FIG. 2A
POWER SUPPLY
INTERRUPTOR
SCREWS FASTENING
HANDLE
DIODES BRIDGE
DISSIPATOR
FILTER
CAPACITORS
FASTENING FRONT PANEL
SCREWS
FAN WIRE
CONTROL
BOARD
SCREWS FASTENING
HANDLE
FIG. 2B
NUTS
FASTENING
METALLIC
STRUCTURE
JP6, JP7, JP8
JUMPER
CURRENT REGULATION
POTENTIOMETER
BUMP
CONTACTS
THERMOSTAT
ST1
BUMP
CONTACTS
POWER SUPPLY LED
ALARM LED
DINSE SOCKET
RHEOFORES
FAN
V1
Q1, Q4
NUTS
FASTENING
METALLIC
STRUCTURE
BOTTOM
FIG. 3
R44
DISSIPAT.
FOR
IGBT
PRIMARY
DISSIPATORS
D1
Q2, Q4
DISSIPATOR
SCREWS
FASTENING
Q1, Q3
DISSIPATOR
SCREWS
FASTENING
FAN
POWER
TRANSFORMER
THERMOSTAT
ON POWER
TRANSFORMER
R1
K1
SECONDARY
DISSIPATORS
D7
D6
INDUCTANCE
FLY BACK
TRANSFORMER
U2
J11
R52
D12
D14
ISO1
FIG. 4
IGBT
Q2, Q4
SECONDARY
DISSIPATOR
SCREWS
FASTENING
PRIMARY
DIODE
D40
RHEOFORES
Q1, Q4
NUTS FASTENING
METALLIC STRUCTURE
DRIVER
D30, D31
R45
R20, C20
DISSIPATORS
DIODES
FOR
-17-
PRIMARY
DIODE
D41
IGBT
Q1, Q3
D21
D20, D22
SECONDARY DIODES
D23

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO - LISTE PIECES DETACHEES
SPARE PARTS LIST - ERSATZTEILLISTE - PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
Esploso macchina, Dessin appareil, Machine drawing, Explosions Zeichnung des Geräts, Diseño seccionado maquina.
20
22
1
19
23
121114924625151657
10
21
18
24
Per richiedere i pezzidi ricambio senza codice precisare: codice del modello;il numero di matricola; numero di riferimento delparticolare sull'elenco ricambi.
Pour avoir les pieces detachees, dont manquela reference, il faudra preciser:modele, logo et tension de I'appareil; denomination de lapiece; numero de matricule.
When requesting spare parts without any reference,pls specify: model-brand and voltageof machine; list reference number of theitem; registration number.
Wenn Sie einen Ersatzteil,der ohne Artikel Nummer ist, benoetigen, bestimmenSie bitte Folgendes: Modell-zeichen und Spannungdes Geraetes; Teilliste Nuemmer;
13 17 3 8
-18-

TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO
PIECES DETACHEES
REF. REF. REF. REF. REF.
SPARE PARTS LIST
ERSATZTEILLISTE
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
Potenziometro
Potentiometre
Potentiometer
1
Potentiometer
Potenciometro
Resistenza
Resistance
Resistor
2
Wiederstand
Resistencia
Diodo
Diode
Diode
3
Diode
Diodo
Rele'
Relais
Relais
4
Relais
Relais
Pwm Controller
Pwm Controller
Pwm Controller
5
Pwm Controller
Pwm Controller
Condensatore
Condensateur
Capacitor
6
Kondensator
Condensador
Scheda Controllo
Platine De Control
Control Pcb
7
Steurungskarte
Tarjeta De Controlo
Opto-accoppiatore
Opto-accoupler
Opto-coupler
8
Opto-koppler
Opto-acoplador
Raddrizzatore
Redresseur
Rectifier
9
Gleichrichter
Rectificador
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO
PIECES DETACHEES
SPARE PARTS LIST
ERSATZTEILLISTE
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
Manopola Potenziometro
Poignee Pour Potentiometre
Knob For Potentiometer
10
Potentiometergriff
Malja Por Resist.electr.variable
Interruttore
Interrupteur
Switch
11
Schalter
Interruptor
Cavo Alim.
Cable Alim.
Mains Cable
12
Netzkabel
Cable Alim.
Ventilatore
Ventilateur
Fan
13
Ventilator
Ventilador
Induttanza Filtro
Inductance Filter
Filter Inductance
14
Filter Drossel
Induccion Filtro
Induttanza
Inductance
Inductance
15
Drossel
Induccion
Trasformatore
Transformateur
Transformer
16
Transformator
Transformador
Trasformatore Potenza
Transformateur Puissance
Power Transformer
17
Leistungstransformator
Transformador De Potencia
Frontale
Partie Frontal
Front Panel
18
Geraetefront
Frontal
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO
PIECES DETACHEES
SPARE PARTS LIST
ERSATZTEILLISTE
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
Retro
Partie Arriere
Back Panel
19
Rueckseite
Trasera
Manico
Poignee
Handle
20
Handgriff
Manija
Presa Dinse
Prise Dix
Dinse Socket
21
Dinse Steckdose
Enchufe Dinse
Kit Mantello
Kit Capot
Cover Kit
22
Deckel Kit
Kit Panel De Cobertura
Kit Fondo
Kit Chassis
Bottom Kit
23
Bodenteil Kit
Kit Fondo
Kit Igbt + Diodo
Kit Igbt + Diode
Kit Igbt + Diode
24
Kit Igbt + Diode
Kit Igbt + Diodo
Kit Scheda Completa
Kit Platine Complete
Complete Control Pcb Kit
25
Komplette Steurungskarte Kit
Kit Tarjeta De Controlo Completa
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO
PIECES DETACHEES
SPARE PARTS LIST
ERSATZTEILLISTE
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
ELENCO PEZZI DI RICAMBIO
PIECES DETACHEES
SPARE PARTS LIST
ERSATZTEILLISTE
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
TECHNICAL REPAIR CARD.
In order to improve the service, each servicing centre is requested to fill in the technical card on the following page at the end of every repair
job. Please fill inthis sheet as accurately as possibleand send itto Telwin. Thank you in advancefor yourco-operation!
-19-

Date:
TECNICA 150-152-170-168GE
Official servicing centers
Repairing sheet
Inverter :
Serial number:
Company:
Technician:
In which place has the inverter been used?
Supply:
Mechanichal stresses the machine has undergone to
model
Building yard
Workshop
Others:
Power supply
From mains without extension
:From mains with extension m
cription:Des
Dirty grade
Dirty inside the machine
Description:
Kind of failure
Rectifier bridge
Electrolytic capacitors
Relais
In-rush limiter resistance
IGBT
Snubber
Secondary diodes
Potentiometer
Component ref.
Substitution of primary power board: yes no
Troubles evinced during repair :
Others
-20-

TELWIN S.p.A.
36030 VILLAVERLA (Vicenza) Italy
Tel. +39 - 0445 - 858811
Fax +39 - 0445 - 858 / 858
E-mail: telwin@telwin.com http://www.telwin.com
- Via della Tecnica, 3
800 801
 Loading...
Loading...