
LE920
Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.9 - 2016-03-29

PRODUCT
LE920-EUG (cs1550f-B)
LE920-NAG (cs1550f-A)
LE920-EU (cs1647c)
LE920-NA (cs1701)
LE920-CN (cs1648D)
LE920-NA AUTO S (cs1717)
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
APPLICABILITY TABLE
APPLICABILITY TABLE 1
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 2 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Telit assumes
no liability resulting from any inaccuracies or omissions in this document, or from use of the
information obtained herein. The information in this document has been carefully checked and
is believed to be entirely reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies or
omissions. Telit reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein and
reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes from time to time in content
hereof with no obligation to notify any person of revisions or changes. Telit does not assume
any liability arising out of the application or use of any product, software, or circuit described
herein; neither does it convey license under its patent rights or the rights of others.
It is possible that this publication may contain references to, or information about Telit products
(machines and programs), programming, or services that are not announced in your country.
Such references or information must not be construed to mean that Telit intends to announce
such Telit products, programming, or services in your country.
Copyrights
This instruction manual and the Telit products described in this instruction manual may be,
include or describe copyrighted Telit material, such as computer programs stored in
semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the Italy and other countries preserve for Telit
and its licensors certain exclusive rights for copyrighted material, including the exclusive right
to copy, reproduce in any form, distribute and make derivative works of the copyrighted
material. Accordingly, any copyrighted material of Telit and its licensors contained herein or
in the Telit products described in this instruction manual may not be copied, reproduced,
distributed, merged or modified in any manner without the express written permission of Telit.
Furthermore, the purchase of Telit products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by
implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license under the copyrights, patents or patent
applications of Telit, as arises by operation of law in the sale of a product.
Computer Software Copyrights
The Telit and 3rd Party supplied Software (SW) products described in this instruction manual
may include copyrighted Telit and other 3rd Party supplied computer programs stored in
semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the Italy and other countries preserve for Telit
and other 3rd Party supplied SW certain exclusive rights for copyrighted computer programs,
including the exclusive right to copy or reproduce in any form the copyrighted computer
program. Accordingly, any copyrighted Telit or other 3rd Party supplied SW computer
programs contained in the Telit products described in this instruction manual may not be copied
(reverse engineered) or reproduced in any manner without the express written permission of
Telit or the 3rd Party SW supplier. Furthermore, the purchase of Telit products shall not be
deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license under the
copyrights, patents or patent applications of Telit or other 3rd Party supplied SW, except for
the normal non-exclusive, royalty free license to use that arises by operation of law in the sale
of a product.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 3 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Usage and Disclosure Restrictions
License Agreements
The software described in this document is the property of Telit and its licensors. It is furnished
by express license agreement only and may be used only in accordance with the terms of such
an agreement.
Copyrighted Materials
Software and documentation are copyrighted materials. Making unauthorized copies is
prohibited by law. No part of the software or documentation may be reproduced, transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer language,
in any form or by any means, without prior written permission of Telit
High Risk Materials
Components, units, or third-party products used in the product described herein are NOT faulttolerant and are NOT designed, manufactured, or intended for use as on-line control equipment
in the following hazardous environments requiring fail-safe controls: the operation of Nuclear
Facilities, Aircraft Navigation or Aircraft Communication Systems, Air Traffic Control, Life
Support, or Weapons Systems (“High Risk Activities"). Telit and its supplier(s) specifically
disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of fitness for such High Risk Activities.
Trademarks
TELIT and the Stylized T Logo are registered in Trademark Office. All other product or
service names are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © Telit Communications S.p.A. 2015.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 4 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Contents
1. Introduction ................................................. 9
1.1. Scope ..................................................... 9
1.2. Audience .................................................. 9
1.3. Contact Information, Support .............................. 9
1.4. Document Organization .................................... 10
1.5. Text Conventions ......................................... 11
1.6. Related Documents ........................................ 11
2. General Product Description ................................. 12
2.1. Overview ................................................. 12
2.2. LE920 Mechanical Dimensions .............................. 13
2.3. Weight ................................................... 13
2.4. Environmental requirements ............................... 14
2.4.1. Temperature range .......................................... 14
2.4.2. RoHS compliance ............................................ 14
2.5. Operating Frequency ...................................... 15
2.5.1. LE920-EUG(cs1550f-B), LE920-EU (cs1647c) ................... 15
2.5.2. LE920-NAG (cs1550f-A) ...................................... 15
2.5.3. LE920-NA (cs1701), LE920-NA AUTO S (cs1717) ................ 16
2.5.4. LE920-CN (cs1648D) ......................................... 17
2.6. Sensitivity .............................................. 18
2.7. Conformity assessment issues .............................. 18
2.7.1. FCC/IC Regulatory notices .................................. 18
2.7.1.1. Modification statement .................................. 18
2.7.1.2. Interference statement .................................. 18
2.7.1.3. RF exposure ............................................. 18
2.7.1.4. FCC Class B digital device notice ....................... 19
2.7.1.5. Labelling Requirements for the Host device .............. 19
3. LE920 Module Connections .................................... 21
3.1. PIN-OUT .................................................. 21
3.1.1. LGA Pads Layout ............................................ 28
4. Hardware Commands ........................................... 29
4.1. Turning ON the LE920 ..................................... 29
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 5 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.2. Initialization and Activation state ...................... 29
4.3. Turning OFF the LE920 .................................... 30
4.3.1. Shutdown by Software Command ............................... 31
4.3.2. Hardware Shutdown .......................................... 32
4.3.3. Hardware Unconditional Restart (RESET) ..................... 33
4.3.4. Hardware Unconditional Shutdown ............................ 34
4.4. Summary of Turning ON and OFF the module ................. 35
5. Power Supply ................................................ 36
5.1. Power Supply Requirements ................................ 36
5.2. General Design Rules ..................................... 38
5.2.1. Electrical Design Guidelines ............................... 38
5.2.1.1. + 5V Input Source Power Supply Design Guidelines ........ 38
5.2.1.2. + 12V Input Source Power Supply Design Guidelines ....... 39
5.2.1.3. Battery Source Power Supply Design Guidelines ........... 41
5.2.2. Thermal Design Guidelines .................................. 42
5.2.3. Power Supply PCB Layout Guidelines ......................... 43
6. Antenna(s) .................................................. 45
6.1. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna Requirements ....................... 45
6.2. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – PCB line Guidelines .............. 46
6.3. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – Installation Guidelines .......... 47
6.4. Antenna Diversity Requirements ........................... 47
6.5. GPS/GNSS Antenna Requirements ............................ 48
6.5.1. Combined GPS/GNSS Antenna .................................. 49
6.5.2. Linear and Patch GPS/GNSS Antenna .......................... 49
6.5.3. Front End Design Considerations ............................ 49
6.5.4. GPS/GNSS Antenna - PCB Line Guidelines ..................... 50
6.5.5. GPS/GNSS Antenna – Installation Guidelines ................. 50
7. Logic Level Specifications .................................. 51
8. USB Port .................................................... 52
9. Serial Ports ................................................ 53
9.1. Modem Serial Port 1 ...................................... 54
9.2. Modem Serial Port 2 ...................................... 55
9.3. RS232 Level Translation .................................. 55
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 6 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
10. Peripheral Ports ............................................ 57
10.1. SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface ...................... 57
10.2. I2C - Inter-integrated circuit ......................... 58
10.3. SDIO – Secure Digital I/O .............................. 58
10.4. Wi-Fi (SDIO) control Interface ......................... 60
11. Audio Section Overview ...................................... 61
11.1. Analog Audio ........................................... 61
11.2. Digital Audio .......................................... 61
12. General Purpose I/O ......................................... 63
12.1. Logic Level Specifications ............................. 64
12.2. Using a GPIO Pad as Input .............................. 64
12.3. Using a GPIO Pad as Output ............................. 65
12.4. Using the Temperature Monitor Function ................. 65
12.4.1. Short Description ........................................ 65
12.5. Indication of Network Service Availability ............. 66
12.6. RTC Bypass ............................................. 67
12.7. VAUX Power Output ...................................... 67
13. ADC section ................................................. 68
13.1. ADC Converter .......................................... 68
13.1.1. Description .............................................. 68
13.1.2. Using ADC Converter ...................................... 68
14. Mounting the module on your board ........................... 69
14.1. General ................................................ 69
14.2. Finishing & Dimensions ................................. 69
14.3. Recommended foot print for the application ............. 70
14.4. Stencil ................................................ 71
14.5. PCB Pad Design ......................................... 71
14.6. Recommendations for PCB Pad Dimensions (mm) ............ 72
14.7. Solder Paste ........................................... 73
14.7.1. Solder Reflow ............................................ 73
15. Application guide ........................................... 75
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 7 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
15.1. Debug of the LE920 in production ....................... 75
15.2. Bypass capacitor on Power supplies ..................... 76
15.3. SIM interface .......................................... 77
15.3.1. SIM schematic example .................................... 77
15.3.2. eSIM interface guidelines ................................ 78
15.4. EMC recommendations .................................... 80
15.5. Download and Debug Port ................................ 81
16. Packing system .............................................. 82
16.1. Tray Drawing ........................................... 84
16.2. Moisture Sensitivity ................................... 85
17. Safety Recommendations ...................................... 86
18. Document History ............................................ 87
- Adding section 2.7 Conformity assessment issues ............................. 88
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 8 of 88

1. Introduction
1.1. Scope
The aim of this document is to present possible and recommended hardware solutions useful
for developing a product with the Telit LE920 module. All the features and solutions detailed
are applicable to all LE920, where “LE920” refers to the modules listed in the applicability
table.
If a specific feature is applicable to a specific product, it will be clearly highlighted.
NOTICE:
The description text “LE920” refers to all modules listed in the APPLICABILITY TABLE 1.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
1.2. Audience
This document is intended for Telit customers, especially system integrators, about to
implement their applications using our LE920 module.
1.3. Contact Information, Support
For general contact, technical support, to report documentation errors and to order manuals,
contact Telit’s Technical Support Center (TTSC) at:
TS-EMEA@telit.com
TS-NORTHAMERICA@telit.com
TS-LATINAMERICA@telit.com
TS-APAC@telit.com
Alternatively, use:
http://www.telit.com/en/products/technical-support-center/contact.php
For detailed information about where you can buy the Telit modules or for recommendations
on accessories and components visit:
http://www.telit.com
To register for product news and announcements or for product questions contact Telit’s
Technical Support Center (TTSC).
Our aim is to make this guide as helpful as possible. Keep us informed of your comments and
suggestions for improvements.
Telit appreciates feedback from the users of our information.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 9 of 88
1.4. Document Organization
This document contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1: “Introduction” provides a scope for this document, target audience, contact and
support information, and text conventions.
Chapter 2: “General Product Description” gives an overview of the features of the product.
Chapter 3: “LE920 Module Connections” deals with the pin out configuration and layout.
Chapter 4: “Hardware Commands” instructs how to control the module via hardware
Chapter 5: “Power Supply” deals with supply and consumption.
Chapter 6: “Antenna” The antenna connection and board layout design are the most important
parts in the full product design
Chapter 7: “Logic Level specifications” Specific values adopted in the implementation of
logic levels for this module.
Chapter 8: “USB Port”
Chapter 9: “Serial Ports”
Chapter 10: “Peripheral Ports”
Chapter 11: “Audio Section Overview”
Chapter 12: “General Purpose I/O” How the general purpose I/O pads can be configured.
Chapter 13 “DAC and ADC Section” Deals with these two kind of analog converters.
Chapter 14: “Mounting the module on your board”
Chapter 15: “Application Guides”
Chapter 16: “Packing System”
Chapter 17: “Safety Recommendations”
Chapter 18: “Document History”
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 10 of 88
1.5. Text Conventions
Danger – This information MUST be followed or catastrophic equipment failure or bodily
injury may occur.
Caution or Warning – Alerts the user to important points about integrating the module, if
these points are not followed, the module and end user equipment may fail or malfunction.
Tip or Information – Provides advice and suggestions that may be useful when integrating
the module.
All dates are in ISO 8601 format, i.e. YYYY-MM-DD.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
1.6. Related Documents
LE920-EUG/NAG Product Description, 80407ST10118A
LE920-EUG/NAG AT command reference guide, 80407ST10116A
Telit EVK2 User Guide, 1vv0300704
Telit xE920 Audio Settings Application Note, 80404NT10095A
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 11 of 88
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2. General Product Description
2.1. Overview
The aim of this document is to present possible and recommended hardware solutions useful
for developing a product with the Telit LE920 module.
In this document all the basic functions of a wireless module will be taken into account; for
each one of them a valid hardware solution will be suggested and usually incorrect solutions
and common errors to be avoided will be highlighted. Obviously this document cannot
embrace every hardware solution or every product that may be designed. Obviously avoiding
invalid solutions must be considered as mandatory. Whereas the suggested hardware
configurations need not be considered mandatory, the information given should be used as a
guide and a starting point for properly developing your product with the Telit LE920 module.
.
NOTICE:
The integration of the GSM/GPRS/EGPRS/WCDMA/HSPA+/LTE LE920 cellular module
within user application must be done according to the design rules described in this manual.
The information presented in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable. However,
no responsibility is assumed by Telit Communication S.p.A. for its use, such as any
infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent rights of Telit Communication
S.p.A. other than for circuitry embodied in Telit products. This document is subject to change
without notice.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 12 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2.2. LE920 Mechanical Dimensions
The Telit LE920 module overall dimensions are:
• Length: 34 mm , +/- 0.15 mm Tolerance
• Width: 40 mm , +/- 0.15 mm Tolerance
• Thickness: 2.9 mm , +/- 0.13 mm Tolerance
2.3. Weight
The module weight of LE920 is about 9.0 gram.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 13 of 88
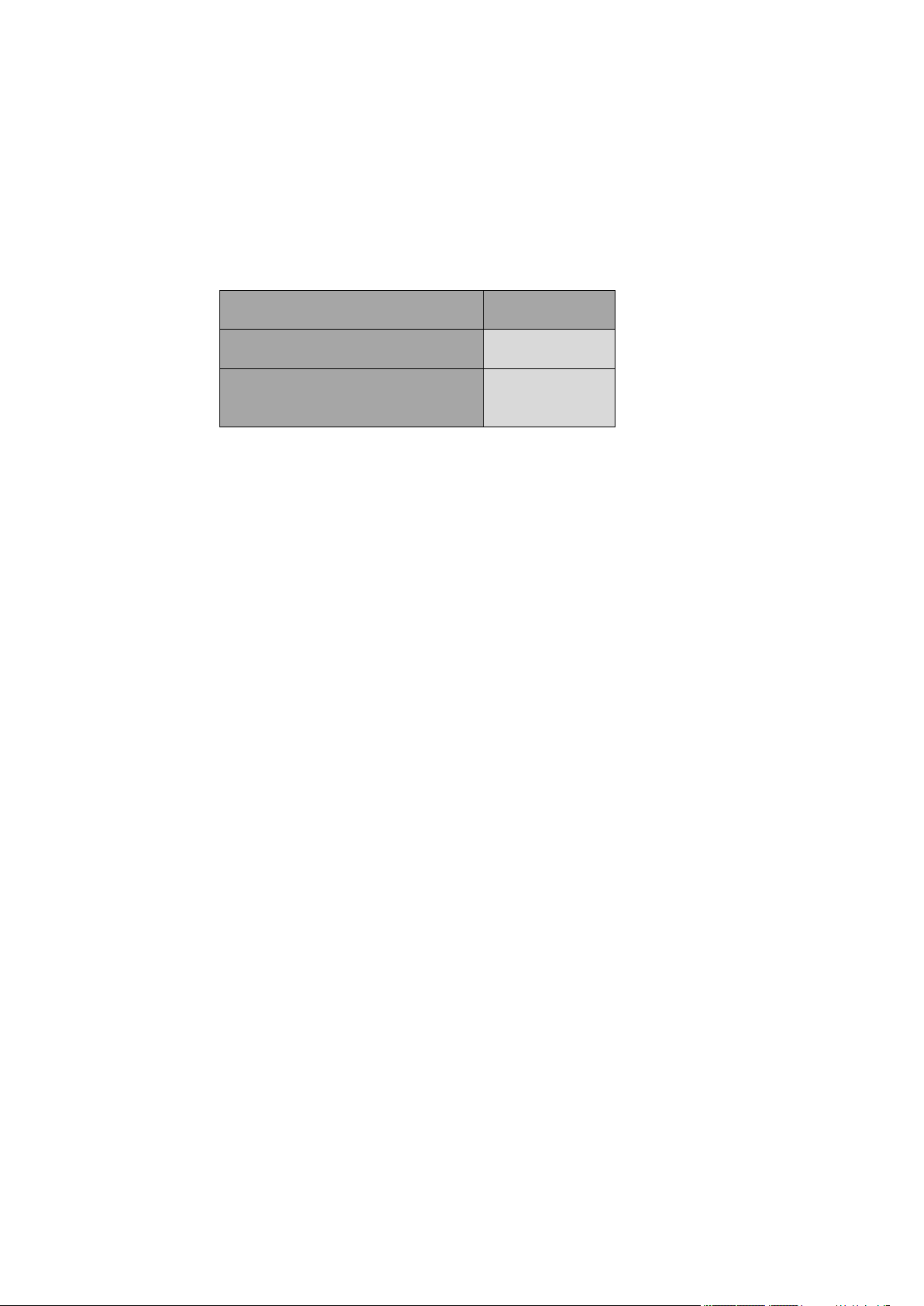
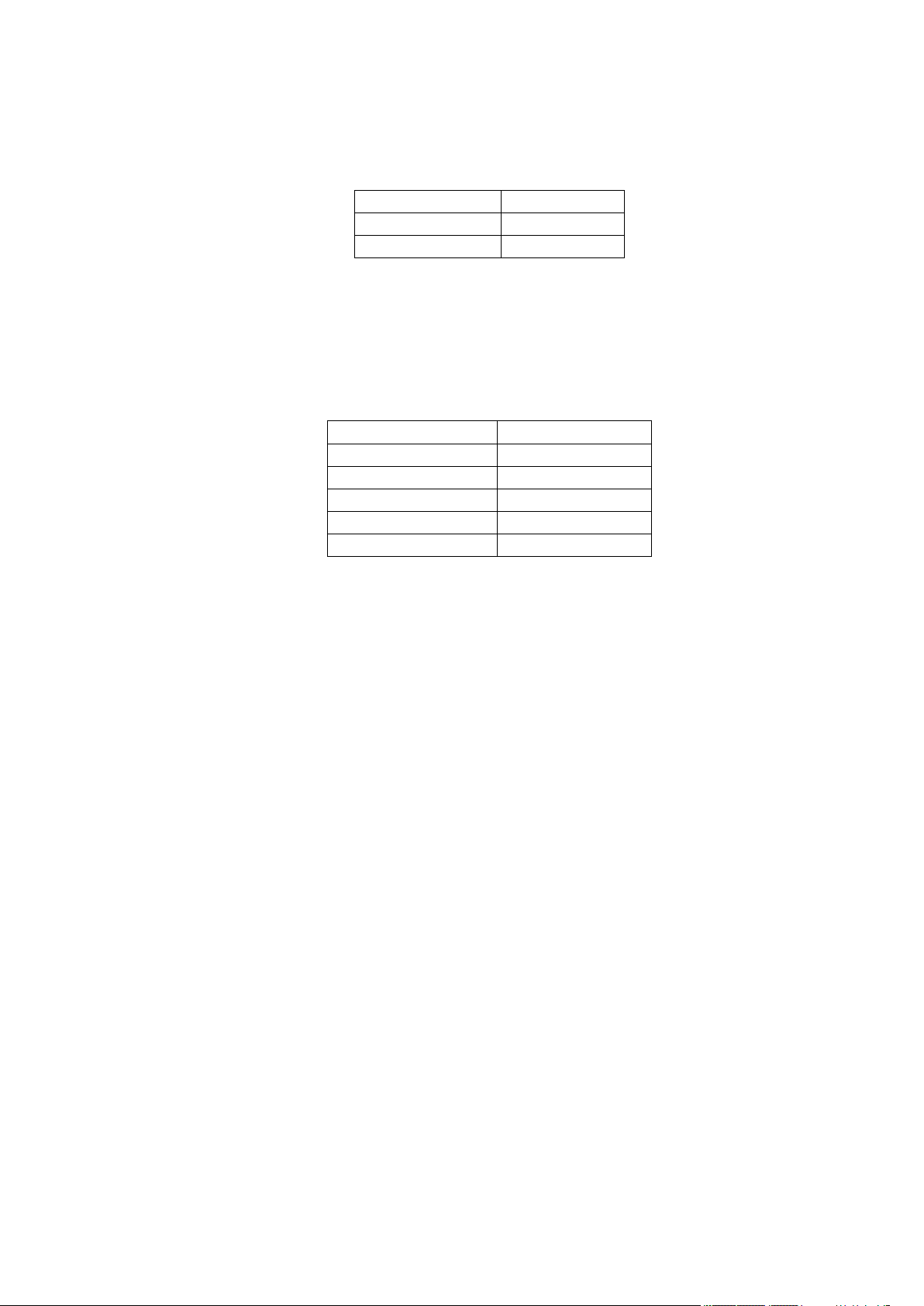
Operating Temperature Range
–40°C ~ +85°C
Storage and non-operating
Temperature Range
–40°C ~ +85°C
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2.4. Environmental requirements
2.4.1. Temperature range
2.4.2. RoHS compliance
LE920 Hardware User Guide
As a part of Telit corporate policy of environmental protection, the LE920 complies with the
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive of the European Union (EU directive
2011/65/EU).
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 14 of 88
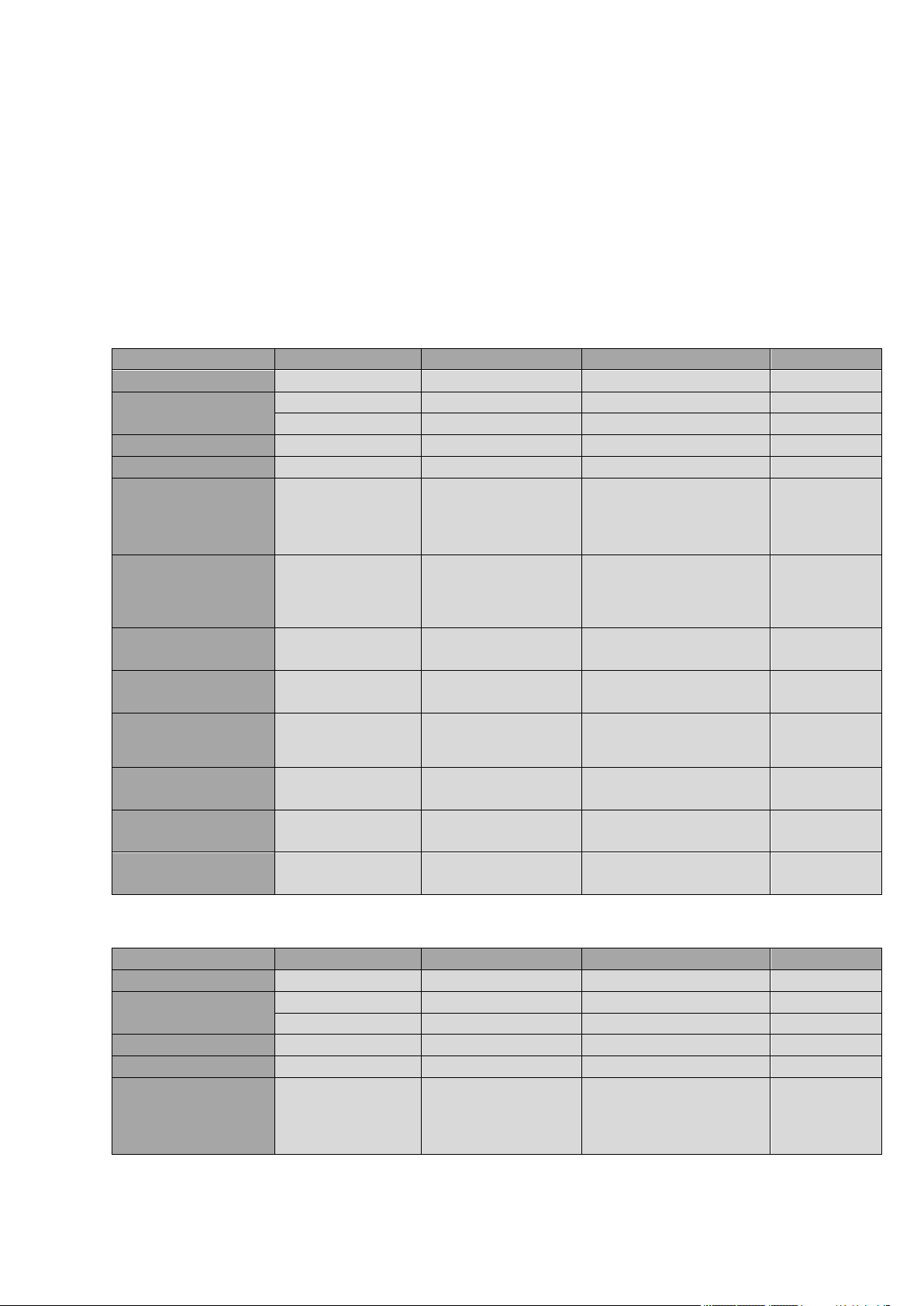
Mode
Freq. TX (MHz)
Freq. RX (MHz)
Channels
TX - RX offset
GSM850
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
128 ~ 251
45 MHz
EGSM900
890 ~ 915
935 ~ 960
0 ~ 124
45 MHz
880 ~ 890
925 ~ 935
975 ~ 1023
45 MHz
DCS1800
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
512 ~ 885
95MHz
PCS1900
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
512 ~ 810
80MHz
WCDMA2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 9612 ~ 9888
Rx: 10562 ~ 10838
190MHz
WCDMA1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 937 ~ 1288
Rx: 1162 ~ 1513
95MHz
WCDMA900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 2712 ~ 2863
Rx: 2937 ~ 3088
45MHz
LTE2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 18000 ~ 18599
Rx: 0 ~ 599
190MHz
LTE1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 19200 ~ 19949
Rx: 1200 ~ 1949
95MHz
LTE2600 – B7
2500 ~ 2570
2620 ~ 2690
Tx: 20750 ~ 21449
Rx: 2750 ~ 3449
120MHz
LTE900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 21450 ~ 21799
Rx: 3450 ~ 3799
45MHz
LTE800 – B20
832 ~ 862
791 ~ 821
Tx: 24150 ~ 24449
Rx: 6150 ~ 6449
-41MHz
Mode
Freq. TX (MHz)
Freq. RX (MHz)
Channels
TX - RX offset
GSM850
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
128 ~ 251
45 MHz
EGSM900
890 ~ 915
935 ~ 960
0 ~ 124
45 MHz
880 ~ 890
925 ~ 935
975 ~ 1023
45 MHz
DCS1800
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
512 ~ 885
95MHz
PCS1900
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
512 ~ 810
80MHz
WCDMA2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 9612 ~ 9888
Rx: 10562 ~ 10838
190MHz
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2.5. Operating Frequency
The operating frequencies in GSM850, EGSM900, DCS1800, PCS1900, WCDMA & LTE
modes are conformed to the 3GPP specifications.
2.5.1. LE920-EUG(cs1550f-B), LE920-EU (cs1647c)
2.5.2. LE920-NAG (cs1550f-A)
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 15 of 88
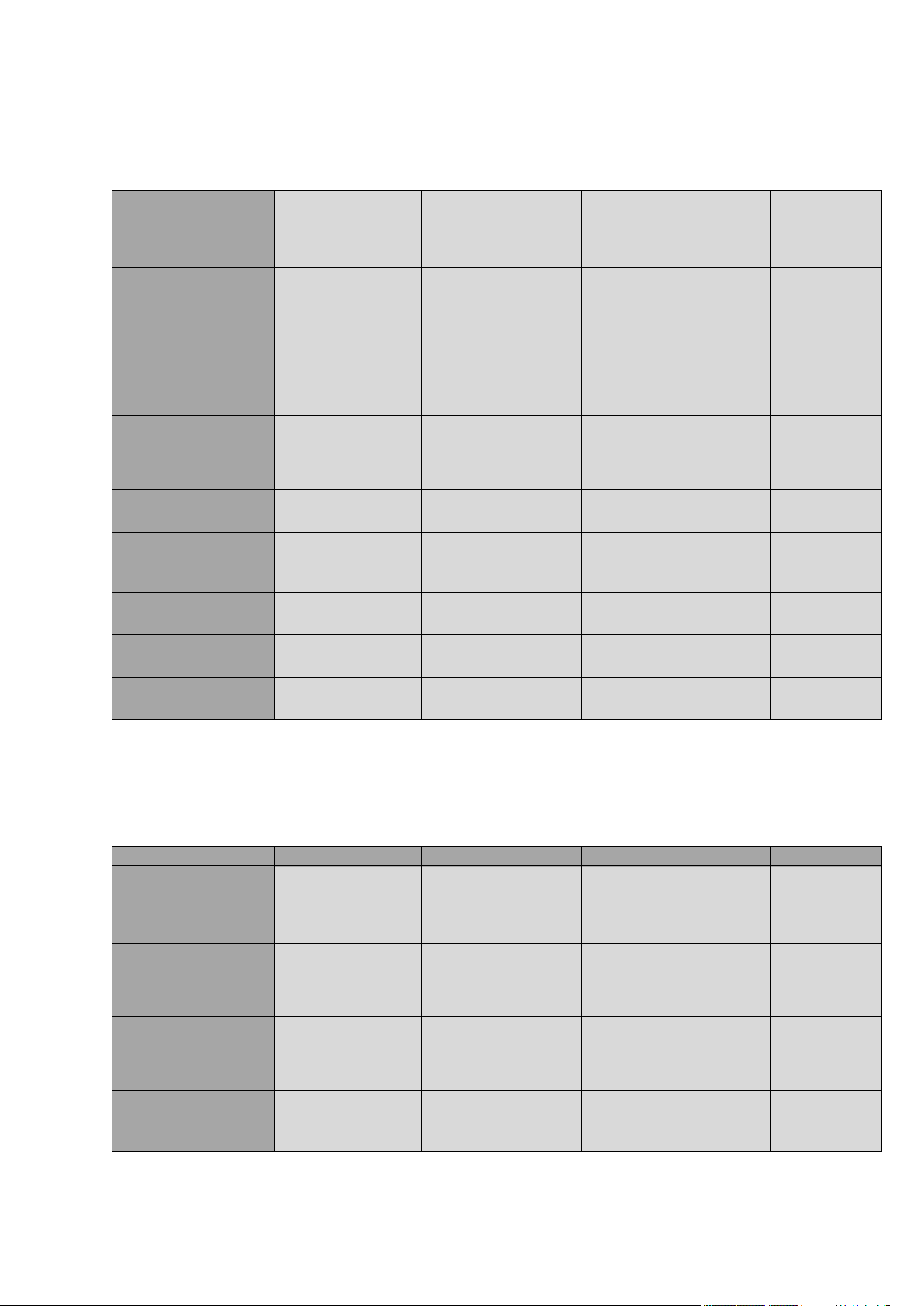
LE920 Hardware User Guide
WCDMA1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 9262 ~ 9538
Rx: 9662 ~ 9938
80MHz
WCDMA1700 – B4
1710 ~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 1312 ~ 1513
Rx: 1537 ~ 1738
400 MHz
WCDMA850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 4132 ~ 4233
Rx: 4357 ~ 4458
45MHz
WCDMA800 – B6
830 ~ 840
875 ~ 885
Tx: 4162 ~ 4188
Rx: 4387 ~ 4413
45MHz
LTE2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 18000 ~ 18599
Rx: 0 ~ 599
190MHz
LTE1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 18600 ~ 19199
Rx: 600 ~ 1199
80MHz
LTE1700 – B4
1710~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 19950 ~ 20399
Rx: 1950 ~ 2399
400MHz
LTE850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 20400 ~ 20649
Rx: 2400 ~ 2649
45MHz
LTE700 – B17
704 ~ 716
734 ~ 746
Tx: 23730 ~ 23849
Rx: 5730 ~ 5849
30MHz
WCDMA1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 9262 ~ 9538
Rx: 9662 ~ 9938
80MHz
WCDMA1700 – B4
1710 ~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 1312 ~ 1513
Rx: 1537 ~ 1738
400 MHz
WCDMA850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 4132 ~ 4233
Rx: 4357 ~ 4458
45MHz
LTE1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 18600 ~ 19199
Rx: 600 ~ 1199
80MHz
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2.5.3. LE920-NA (cs1701), LE920-NA AUTO S (cs1717)
Mode Freq. TX (MHz) Freq. RX (MHz) Channels TX - RX offset
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 16 of 88
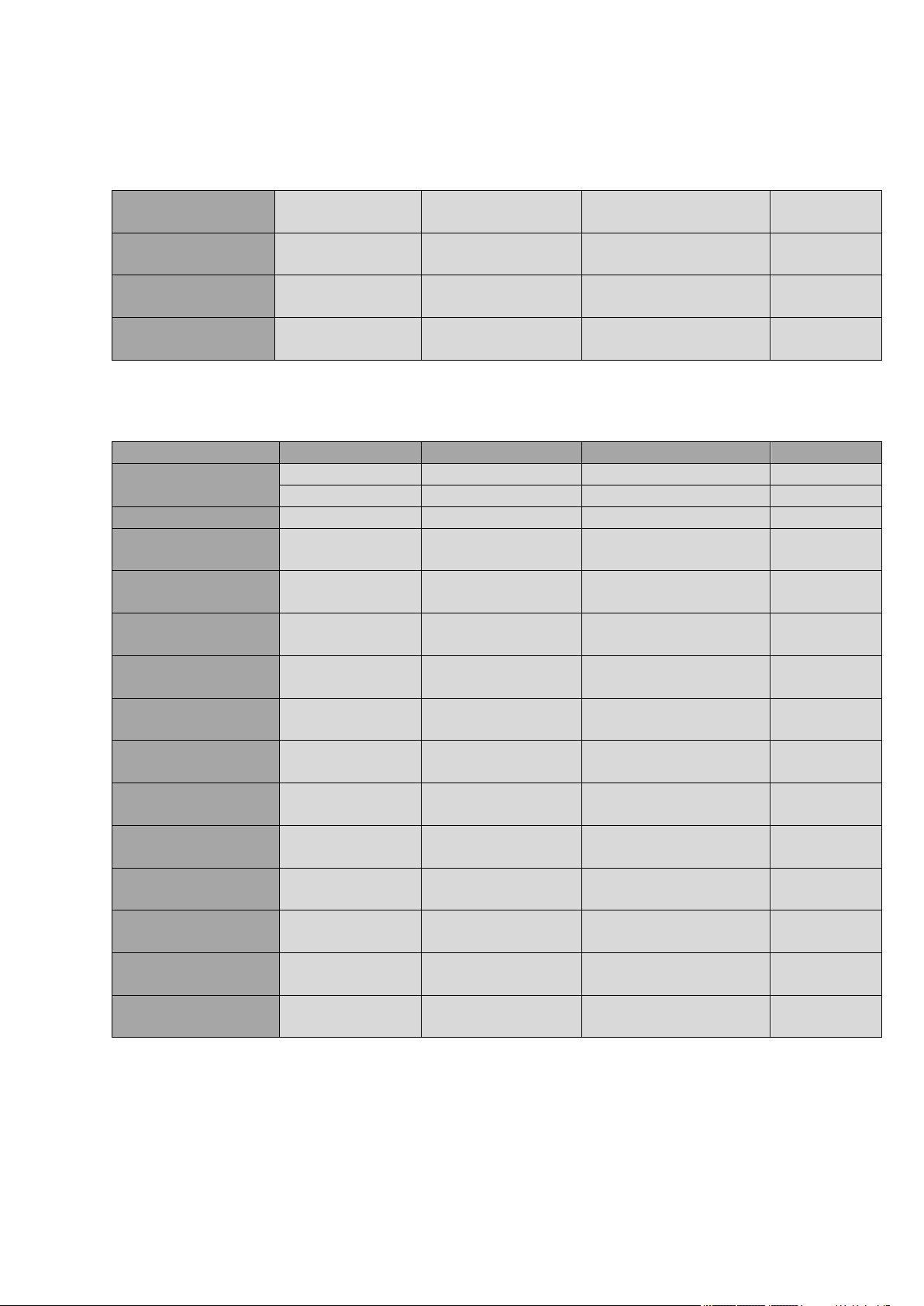
LE920 Hardware User Guide
LTE1700 – B4
1710~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 19950 ~ 20399
Rx: 1950 ~ 2399
400MHz
LTE850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 20400 ~ 20649
Rx: 2400 ~ 2649
45MHz
LTE2600 – B7
2500 ~ 2570
2620 ~ 2690
Tx: 20750 ~ 21449
Rx: 2750 ~ 3449
120MHz
30MHz
Mode
Freq. TX (MHz)
Freq. RX (MHz)
Channels
TX - RX offset
EGSM900
890 ~ 915
935 ~ 960
0 ~ 124
45 MHz
880 ~ 890
925 ~ 935
975 ~ 1023
45 MHz
DCS1800
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
512 ~ 885
95MHz
WCDMA2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 9612 ~ 9888
Rx: 10562 ~ 10838
190MHz
WCDMA1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 937 ~ 1288
Rx: 1162 ~ 1513
95MHz
WCDMA900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 2712 ~ 2863
Rx: 2937 ~ 3088
45MHz
LTE2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 18000 ~ 18599
Rx: 0 ~ 599
190MHz
LTE1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 19200 ~ 19949
Rx: 1200 ~ 1949
95MHz
LTE900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 21450 ~ 21799
Rx: 3450 ~ 3799
45MHz
LTE TDD 2600 – B38
2570 ~ 2620
2570 ~ 2620
Tx: 37750 ~ 38250
Rx: 37750 ~ 38250
0MHz
LTE TDD 1900 – B39
1880 ~ 1920
1880 ~ 1920
Tx: 38250 ~ 38650
Rx: 38250 ~ 38650
0MHz
LTE TDD 2300 – B40
2300 ~ 2400
2300 ~ 2400
Tx: 38650 ~ 39650
Rx: 38650 ~ 39650
0MHz
LTE TDD 2500 – B41
2496 ~ 2690
2496 ~ 2690
Tx: 39650 ~ 41590
Rx: 39650 ~ 41590
0MHz
TDSCDMA2000 – B34
2010 ~ 2025
2010 ~ 2025
Tx: 10054 ~ 10121
Rx: 10054 ~ 10121
0MHz
TDSCDMA1900 – B39
1880 ~ 1920
1880 ~ 1920
Tx: 9404 ~ 9596
Rx: 9404 ~ 9596
0MHz
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
LTE700 – B17 704 ~ 716 734 ~ 746
2.5.4. LE920-CN (cs1648D)
Tx: 23730 ~ 23849
Rx: 5730 ~ 5849
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 17 of 88
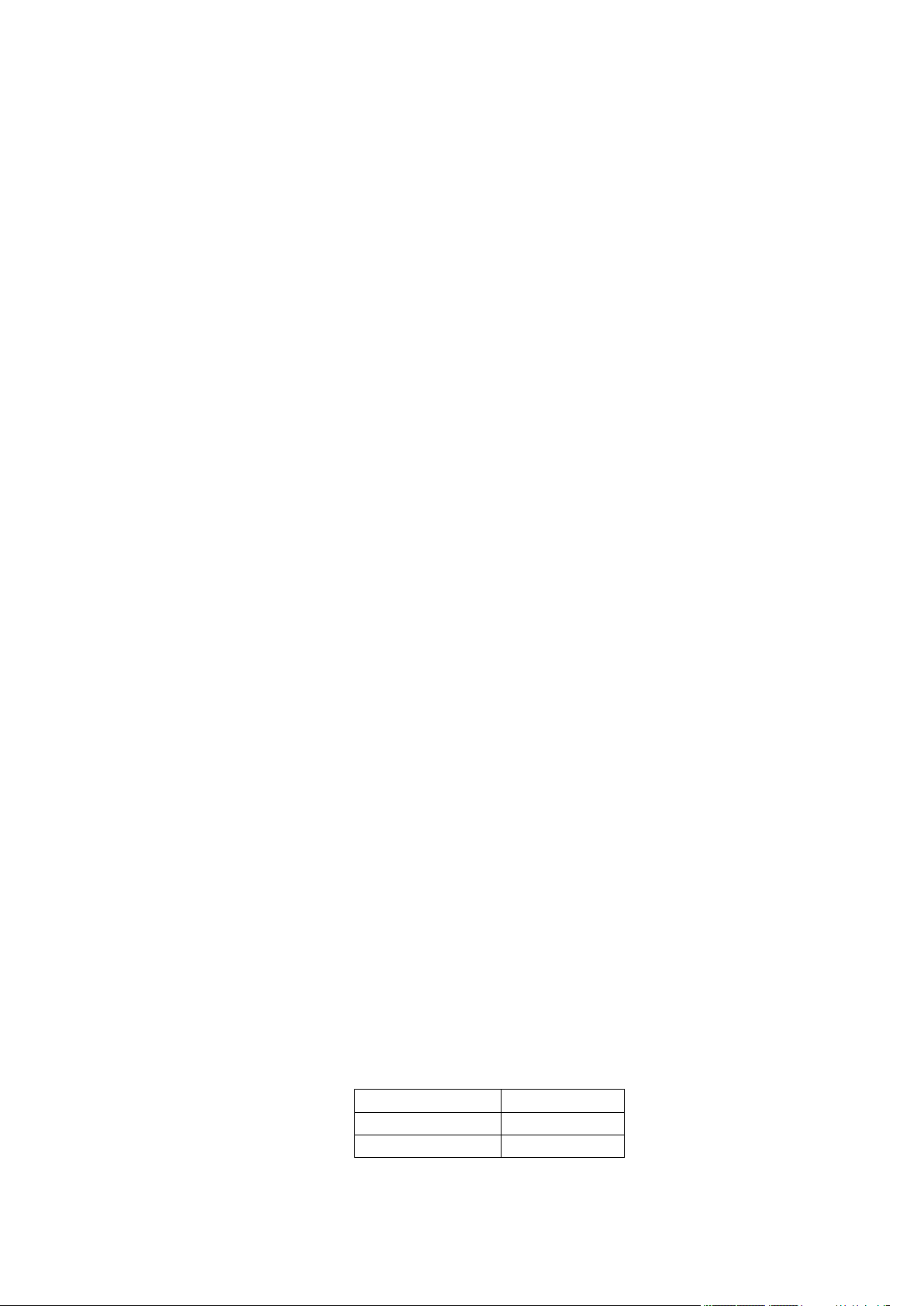
Frequency band
Antenna gain
700 MHz
5,66 dBi
850 MHz
6,13 dBi
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
2.6. Sensitivity
LE920 maximum sensitivity levels are as follow:
-113 dBm @ 2G
-112 dBm @ 3G
-111 dBm @ TD-SCDMA (BW=1.6MHz)
-102 dBm @ 4G FDD (BW=5MHz)
-101 dBm @ 4G TDD (BW=5MHz)
2.7. Conformity assessment issues
2.7.1. FCC/IC Regulatory notices
2.7.1.1. Modification statement
Telit has not approved any changes or modifications to this device by the user. Any changes or modifications
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Telit n’approuve aucune modification apportée à l’appareil par l’utilisateur, quelle qu’en soit la nature. Tout
changement ou modification peuvent annuler le droit d’utilisation de l’appareil par l’utilisateur.
2.7.1.2. Interference statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s).
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de
licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de
brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
2.7.1.3. RF exposure
This equipment complies with FCC and IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. The antenna should be installed and operated with minimum distance of 20 cm between
the radiator and your body.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 18 of 88
Antenna gain must be below:
1700 MHz
5,00 dBi
1900 MHz
8,01 dBi
2600 MHz
8,01 dBi
Bande de fréquence
Gain de l'antenne
700 MHz
5,66 dBi
850 MHz
6,13 dBi
1700 MHz
5,00 dBi
1900 MHz
8,01 dBi
2600 MHz
8,01 dBi
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Cet appareil est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux rayonnements de la IC pour un environnement non
contrôlé. L'antenne doit être installé de façon à garder une distance minimale de 20 centimètres entre la source
de rayonnements et votre corps. Gain de l'antenne doit être ci-dessous:
L'émetteur ne doit pas être colocalisé ni fonctionner conjointement avec à autre antenne ou autre émetteur.
2.7.1.4. FCC Class B digital device notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
2.7.1.5. Labelling Requirements for the Host device
The host device shall be properly labelled to identify the modules within the host device. The certification label
of the module shall be clearly visible at all times when installed in the host device, otherwise the host device
must be labelled to display the FCC ID and IC of the module, preceded by the words "Contains transmitter
module", or the word "Contains", or similar wording expressing the same meaning, as follows:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 19 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Contains FCC ID: RI7LE920NA1
Contains IC: 5131A-LE920NA1
L'appareil hôte doit être étiqueté comme il faut pour permettre l'identification des modules qui s'y trouvent.
L'étiquette de certification du module donné doit être posée sur l'appareil hôte à un endroit bien en vue en tout
temps. En l'absence d'étiquette, l'appareil hôte doit porter une étiquette donnant le FCC ID et le IC du module,
précédé des mots « Contient un module d'émission », du mot « Contient » ou d'une formulation similaire
exprimant le même sens, comme suit:
Contains FCC ID: RI7LE920NA1
Contains IC: 5131A-LE920NA1
CAN ICES-3 (B) / NMB-3 (B)
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de classe B est conforme à la norme canadienne ICES-003.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 20 of 88
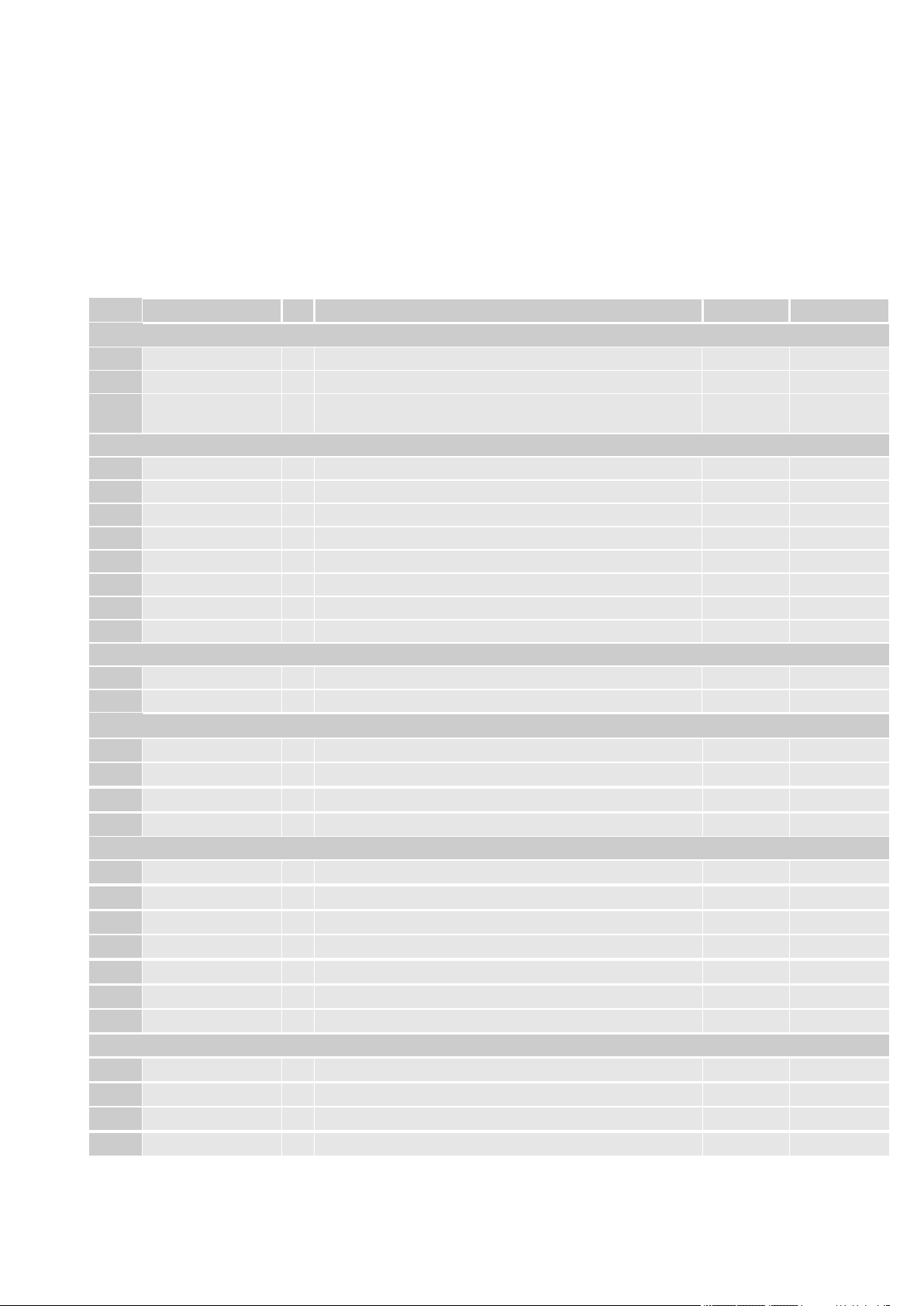
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
USB HS 2.0 Communication Port
D19
USB_D+
I/O
USB differential Data(+)
F19
USB_D-
I/O
USB differential Data(-)
A18
USB_VBUS
AI
Power sense for the internal USB transceiver
Power
2.2V – 5.25V
@ max 5mA
Asynchronous UART – Prog. / data +HW Flow Control
AH19
C103/TXD
I
Serial data input (TXD) from DTE
1.8V
AF19
C104/RXD
O
Serial data output to DTE
1.8V
AC18
C108/DTR
I
Input for Data terminal ready signal (DTR) from DTE
1.8V
AA18
C105/RTS
I
Input for Request to send signal (RTS) from DTE
1.8V
AK19
C106/CTS
O
Output for Clear to send signal (CTS) to DTE
1.8V
AE18
C109/DCD
O
Output for Data carrier detect signal (DCD) to DTE
1.8V
AG18
C107/DSR
O
Output for Data set ready signal (DSR) to DTE
1.8V
AJ18
C125/RING
O
Output for Ring indicator signal (RI) to DTE
1.8V
Asynchronous Auxiliary UART
AB19
TXD_AUX
O
Auxiliary UART (TX Data to DTE)
1.8V
AD19
RXD_AUX
I
Auxiliary UART (RX Data from DTE)
1.8V
SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
P19
SPI_CLK
O
SPI Clock output
1.8V
M19
SPI_MISO
I
SPI data Master Input Slave output
1.8V
K19
SPI_MOSI
O
SPI data Master Output Slave input
1.8V
N18
SPI_CS
O
SPI Chip select output
1.8V
SDIO – Secure Digital I/O
AH17
SD/MMC_CMD
O
SD Command
1.8/2.95V
AD17
SD/MMC_CLK
O
SD Card Clock
1.8/2.95V
Y17
SD/MMC_DATA0
I/O
SD Serial Data 0
1.8/2.95V
AF17
SD/MMC_DATA1
I/O
SD Serial Data 1
1.8/2.95V
AB17
SD/MMC_DATA2
I/O
SD Serial Data 2
1.8/2.95V
W17
SD/MMC_DATA3
I/O
SD Serial Data 3
1.8/2.95V
U17
SD/MMC_CD
I
SD card detect input
1.8V
Active Low
Wi-Fi (SDIO) control Interface
AB3
WiFi_SD_CMD
O
Wi-Fi SD Command
1.8V
AM3
WiFi_SD_CLK
O
Wi-Fi SD Clock
1.8V
AD3
WiFi_SD _DATA0
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 0
1.8V
AF3
WiFi_SD _DATA1
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 1
1.8V
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
3. LE920 Module Connections
3.1. PIN-OUT
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 21 of 88
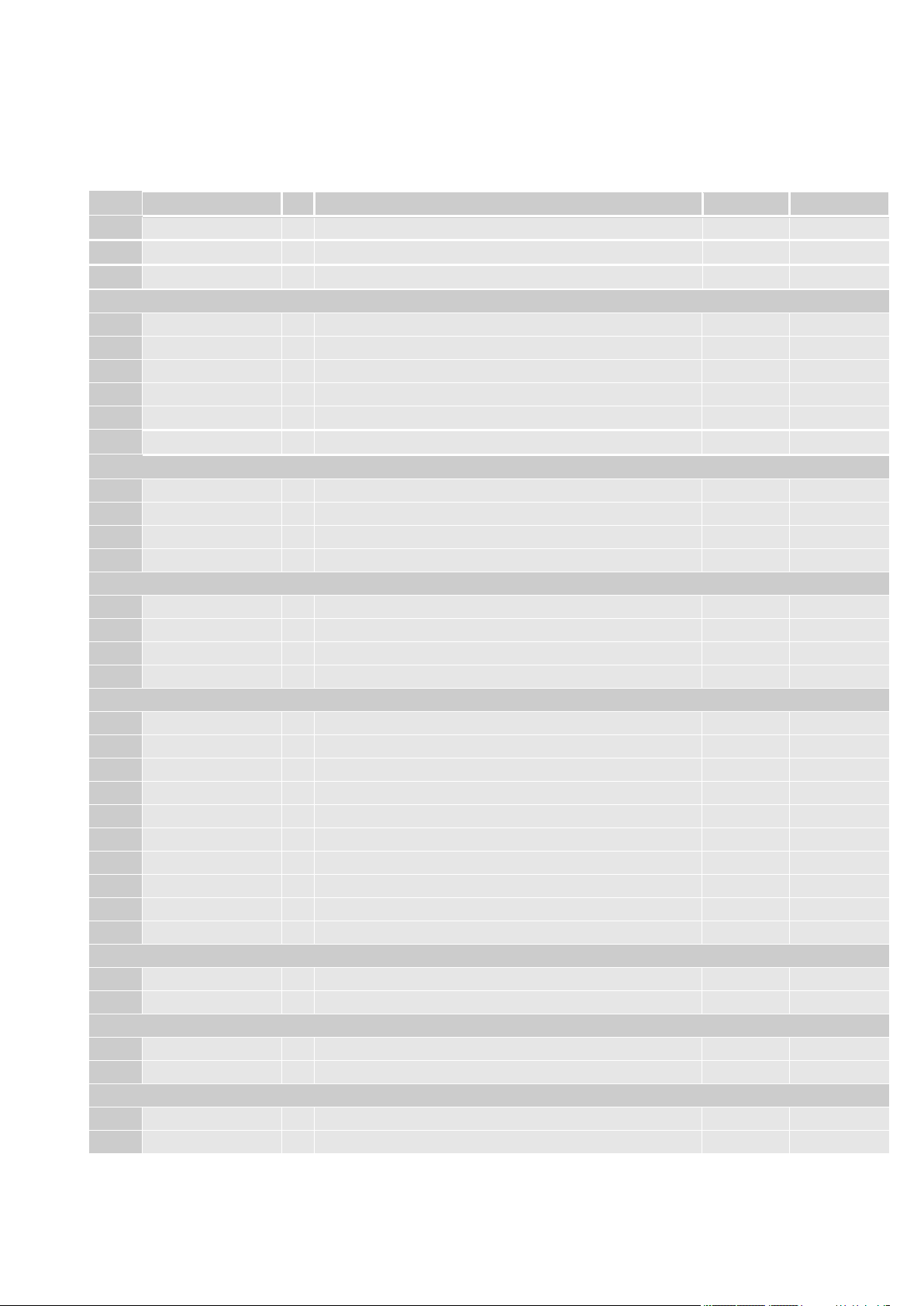
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AH3
WiFi_SD _DATA2
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 2
1.8V
AK3
WiFi_SD _DATA3
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 3
1.8V
Y3
WiFi_RST_Ctr
O
Wi-Fi Reset output control / Power enable control
1.8V
Active Low
SIM Card Interface 1
A10
SIMCLK1
O
External SIM signal – Clock
1.8/2.85V
B11
SIMRST1
O
External SIM signal – Reset
1.8/2.85V
B9
SIMIO1
I/O
External SIM signal - Data I/O
1.8/2.85V
B7
SIMIN1
I
External SIM signal - Presence (active low)
1.8V
A8
SIMVCC1
-
External SIM signal – Power supply for the SIM
1.8/2.85V
E8
ESIM_RST
-
Internal eSIM signal – Reset
1.8/2.85V
Analog Audio interface
B5
EAR1_MT+
AO
Earphone signal output1, phase +
Audio
A4
EAR1_MT-
AO
Earphone signal output1, phase -
Audio
B3
MIC1_MT+
AI
Mic signal input1, phase +
Audio
A2
MIC1_MT-
AI
Mic signal input1, phase -
Audio
Digital Voice interface (DVI)
D11
DVI_WA0
O
Digital Voice interface (WA0 master output)
1.8V
C8
DVI_RX
I
Digital Voice interface (RX)
1.8V
D9
DVI_TX
O
Digital Voice interface (TX)
1.8V
C10
DVI_CLK
O
Digital Voice interface (CLK master output)
1.8V
Digital I/O
F9
GPIO_01
I/O
GPIO_01
1.8V
I2C alternate
E10
GPIO_02
I/O
GPIO_02
1.8V
I2C alternate
F11
GPIO_03
I/O
GPIO_03
1.8V
I2C alternate
E12
GPIO_04
I/O
GPIO_04
1.8V
I2C alternate
F13
GPIO_05
I/O
GPIO_05
1.8V
I2C alternate
E14
GPIO_06
I/O
GPIO_06
1.8V
I2C alternate
R18
GPIO_07
I/O
GPIO_07
1.8V
I2C alternate
S19
GPIO_08
I/O
GPIO_08
1.8V
I2C alternate
U19
GPIO_09
I/O
GPIO_09
1.8V
I2C alternate
W19
GPIO_10
I/O
GPIO_10
1.8V
I2C alternate
RF Section
AD1
Antenna
I/O
GSM/EDGE/UMTS/LTE Antenna (50 Ohm)
RF
AU9
ANT_DIV
I
UMTS/LTE Antenna Diversity Input (50 Ohm)
RF
GPS Section
S1
ANT_GPS
I
GPS Antenna (50 Ohm)
RF
V2
GPS_LNA_EN
O
Enable the external regulator for GPS LNA
1.8V
Miscellaneous Function
AP1
RESET#
I
Reset Input
Active Low
AS1
ON_OFF#
I
Input Command for Power ON
Active Low
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 22 of 88
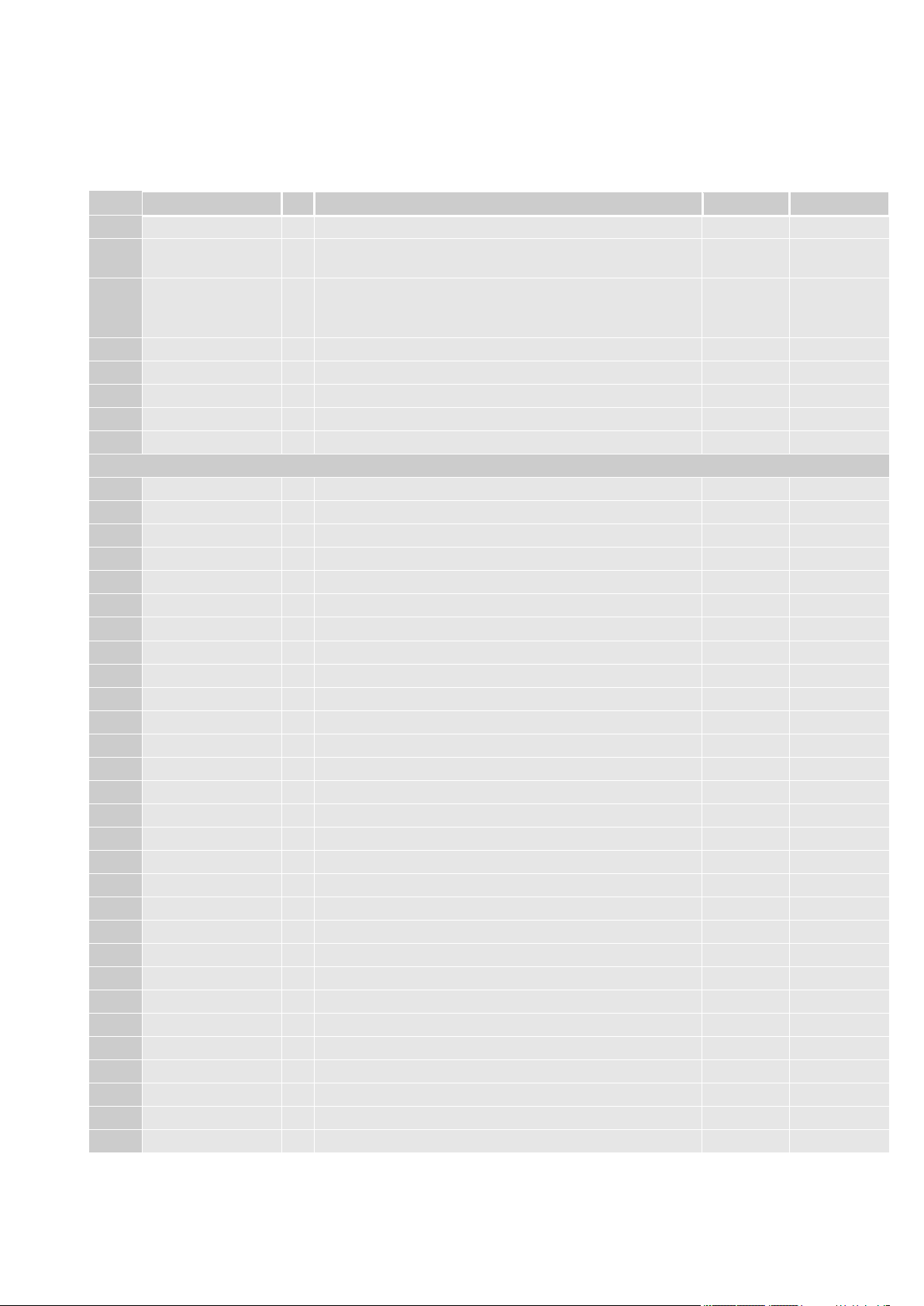
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AN12
SHDN_N
I
Unconditional Shut down Input
Active Low
P17
VAUX/PWRMON
O
Supply Output for External Accessories / Power ON
Monitor
1.8V
F17
VRTC
AI/
AO
VRTC Backup Capacitor
Power
To be used to
back up the
RTC section
D5
ADC_IN1
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input 1
Analog
E6
ADC_IN2
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input 2
Analog
F7
ADC_IN3
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input 3
Analog
AU3
STAT_LED
O
Status Indicator LED
1.8V
AN10
SW_RDY
O
Indicates that the boot sequence completed successfully
1.8V
Power Supply
AP17
VBATT
-
Main Power Supply (Digital Section)
Power
AP19
VBATT
-
Main Power Supply (Digital Section)
Power
AR18
VBATT
-
Main Power Supply (Digital Section)
Power
AS17
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF Transmit Power Section)
Power
AS19
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF Transmit Power Section)
Power
AT18
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF Transmit Power Section)
Power
AU17
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF Transmit Power Section)
Power
AU19
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF Transmit Power Section)
Power
A6
GND
-
Ground
A12
GND
-
Ground
B13
GND
-
Ground
B15
GND
-
Ground
B17
GND
-
Ground
C4
GND
-
Ground
C6
GND
-
Ground
D3
GND
-
Ground
D7
GND
-
Ground
E18
GND
-
Ground
F1
GND
-
Ground
G18
GND
-
Ground
H19
GND
-
Ground
M1
GND
-
Ground
N2
GND
-
Ground
P1
GND
-
Ground
P3
GND
-
Ground
R2
GND
Ground
T2
GND
Ground
T18
GND
-
Ground
U1
GND
-
Ground
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 23 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
V18
GND
-
Ground
W1
GND
-
Ground
X2
GND
-
Ground
X18
GND
-
Ground
Y1
GND
-
Ground
Y19
GND
Ground
AA2
GND
-
Ground
AB1
GND
-
Ground
AC2
GND
-
Ground
AE2
GND
-
Ground
AF1
GND
-
Ground
AG2
GND
-
Ground
AH1
GND
-
Ground
AJ2
GND
-
Ground
AK1
GND
-
Ground
AK17
GND
-
Ground
AL18
GND
-
Ground
AM17
GND
-
Ground
AM19
GND
-
Ground
AN16
GND
-
Ground
AN18
GND
-
Ground
AP3
GND
-
Ground
AP5
GND
-
Ground
AP7
GND
-
Ground
AP9
GND
-
Ground
AP11
GND
-
Ground
AP13
GND
-
Ground
AP15
GND
-
Ground
AR2
GND
-
Ground
AR4
GND
-
Ground
AR6
GND
-
Ground
AR8
GND
-
Ground
AR10
GND
-
Ground
AR12
GND
-
Ground
AR14
GND
-
Ground
AR16
GND
-
Ground
AS5
GND
-
Ground
AS7
GND
-
Ground
AS9
GND
-
Ground
AS11
GND
-
Ground
AS13
GND
-
Ground
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 24 of 88
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AS15
GND
-
Ground
AT4
GND
-
Ground
AT6
GND
-
Ground
AT8
GND
-
Ground
AT10
GND
-
Ground
AT12
GND
-
Ground
AT14
GND
-
Ground
AT16
GND
-
Ground
AU1
GND
-
Ground
AU5
GND
-
Ground
AU7
GND
-
Ground
AU11
GND
-
Ground
AU15
GND
-
Ground
Reserved
C12
Reserved
-
Reserved
A14
Reserved
-
Reserved
A16
Reserved
-
Reserved
M17
Reserved
-
Reserved
AN6
Reserved
-
Reserved
C14
Reserved
-
Reserved
D13
Reserved
-
Reserved
C16
Reserved
-
Reserved
D17
Reserved
-
Reserved
E16
Reserved
-
Reserved
C18
Reserved
-
Reserved
D15
Reserved
-
Reserved
F15
Reserved
-
Reserved
E4
Reserved
-
Reserved
F3
Reserved
-
Reserved
F5
Reserved
-
Reserved
G2
Reserved
-
Reserved
H1
Reserved
-
Reserved
H3
Reserved
-
Reserved
H17
Reserved
-
Reserved
J2
Reserved
-
Reserved
J18
Reserved
-
Reserved
K1
Reserved
-
Reserved
K3
Reserved
-
Reserved
K17
Reserved
-
Reserved
L2
Reserved
-
Reserved
L18
Reserved
-
Reserved
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 25 of 88
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
M3
Reserved
-
Reserved
S3
Reserved
-
Reserved
S17
Reserved
-
Reserved
U3
Reserved
-
Reserved
W3
Reserved
-
Reserved
AL2
Reserved
-
Reserved
AM1
Reserved
-
Reserved
AN2
Reserved
-
Reserved
AN4
Reserved
-
Reserved
AN8
Reserved
-
Reserved
AN14
Reserved
-
Reserved
AS3
Reserved
-
Reserved
AT2
Reserved
-
Reserved
B19
Reserved
-
Reserved
AU13
Reserved
-
Reserved
E2
Reserved
-
Reserved
D1
Reserved
-
Reserved
C2
Reserved
-
Reserved
B1
Reserved
-
Reserved
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
When the UART signals are used as the communication port between the Host and the
Modem:
- DTR pin must be connected in order to enter LE920’s power saving mode.
- RI pin must be connected in order to wake the host when a call is coming during sleep
mode of host.
- RTS must be connected to GND (on the module side) if flow control is not used
In case UART port isn’t used, all UART signals may be left disconnected
NOTE:
E8 port – eSIM Reset signal is available for LE920-NA AUTO S model only. For other
models, E8 is internally disconnected.
NOTE:
Unless otherwise specified, RESERVED pins must be left unconnected (Floating).
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 26 of 88
PAD
Signal
Notes
AP17,AP19,AR18,AS17,AS19,AT18,AU17,AU19
VBATT &
VBATT_PA
A6,A12,B13,B15,B17,C4,C6,D3,D7,E18,F1,G18,H19,
M1,N2,P1,P3,R2,T2,T18,U1,V18,W1,X2,X18,Y1,Y19,
AA2,AB1,AC2,AE2,AF1,AG2,AH1,AJ2,AK1,AK17,
AL18,AM17,AM19,AN16,AN18,AP3,AP5,AP7,AP9,
AP11,AP13,AP15,AR2,AR4AR6,AR8,AR10,AR12,
AR14,AR16,AS5,AS7,AS9,AS11,AS13,AS15,AT4,
AT6,AT8,AT10,AT12,AT14,AT16,AU1,AU5,AU7,
AU11,AU15
GND
AS1
ON/OFF*
AN12
SHDN_N
D19
USB_D+
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point or an USB connector
F19
USB_D-
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point or an USB connector
A18
USB_VBUS
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point or an USB connector
AH19
C103/TXD
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
AF19
C104/RXD
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
AA18
C105/RTS
If the flow control is not used it
should be connected to GND
AK19
C106/CTS
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
AB19
TXD_AUX
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
AD19
RXD_AUX
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
AD1
Antenna
AU9
ANT_DIV
S1
ANT_GPS
G2, J2, L2, F3, H3, K3, E4, AN14
Reserved
If not used should be connected to
a Test Point
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
The table below specifies the LE920A4 signals that must be connected even if not used by
end application:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 27 of 88

3.1.1. LGA Pads Layout
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 28 of 88

4. Hardware Commands
4.1. Turning ON the LE920
To turn on LE920, the pad ON# must be tied low for at least 1 second and then released.
The maximum current that can be drained from the ON# pad is 0.1 mA.
A simple circuit to power on the module is illustrated below:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.2. Initialization and Activation state
Upon turning on LE920 module, The LE920 is not activated yet because the boot sequence of
LE920 is still going on internally. It takes about 10 seconds to complete the initializing the
module internally.
For this reason, it would be useless to try to access LE920 during the Initialization state, as
shown below. To reach full stability, The LE920 needs at least 15 seconds after the
PWRMON goes High to become operational by reaching the activation state.
During the Initialization state, any kind of AT-command is not available. DTE must wait for
the Activation state before communicating with LE920.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 29 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
To check if the LE920 has powered on, the hardware line PWRMON must be monitored.
When PWRMON goes high, the module has powered on.
NOTE:
Do not use any pull up resistor on the ON# line, it is internally pulled up. Using pull up
resistor may cause latch-up problems on the LE920 power regulator and improper powering
on/off of the module. The line ON# must be connected only in an open collector
configuration.
NOTE:
In this document all the lines are inverted. Active low signals are labeled with a name that
ends with "#" or with a bar over the name.
NOTE:
In order to avoid a back-powering effect it is recommended to avoid having any HIGH logic
level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is powered OFF or during an
ON/OFF transition.
4.3. Turning OFF the LE920
Turning off the device can be done in four different ways:
by Software command AT#SHDN
by Hardware Shutdown using pad ON/OFF#
by Hardware Unconditional Reset using the RESET#
by Hardware Unconditional Shutdown using the SHDN#
When the device is shut down by software command or by hardware shutdown, it issues to
the network a detach request that informs the network that the device will not be reachable
any more.
TIP:
To check if the device has powered off, hardware line PWRMON must be monitored. When
PWRMON goes low it can be considered the device has powered off.
NOTE:
In order to avoid a back-powering effect it is recommended to avoid having any HIGH logic
level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is powered OFF or during an
ON/OFF transition.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 30 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.3.1. Shutdown by Software Command
LE920 can be shut down by a software command.
When a shutdown command is sent, LE920 goes into the finalization state and finally will
shut down PWRMON at the end of this state.
The duration of the finalization state can differ according to the situation in which the LE920
is, so a value cannot be defined.
Normally it will be more than15 seconds after sending a shutdown command, DTE should
monitor the status of PWRMON to observe the actual power off.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
TIP:
To check if the device has powered off, hardware line PWRMON must be monitored. When
PWRMON goes low, the device has powered off.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 31 of 88

4.3.2. Hardware Shutdown
To turn OFF LE920 the pad ON/OFF# must be tied low for at least 2 seconds and then
released. The same circuitry and timing for the power on must be used.
When the hold time of ON/OFF# is above 2.5 seconds, LE920 goes into the finalization state
and finally will shut down PWRMON at the end of this state.
The period of the finalization state can differ according to the situation in which the LE920 is,
so it cannot be fixed definitely.
. Normally it will be more than15 seconds after sending a shutdown command ; DTE should
monitor the status of PWRMON to see observe the actual power off.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
TIP:
To check if the device has powered off, hardware line PWRMON must be monitored. When
PWRMON goes low, the device has powered off.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 32 of 88

NOTE:
Do not use any pull up resistor on the RESET# line or any totem pole digital output. Using
pull up resistor may cause latch-up problems on the LE920 power regulator and improper
functioning of the module. The line RESET# must be connected only in open collector
configuration.
NOTE:
Asserting tRESET low for period greater than 2000 milliseconds will cause the module to
shut down.
TIP:
The unconditional hardware Restart must always be implemented on the boards and the
software must use it only as an emergency exit procedure, and not as a normal power-off
operation
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.3.3. Hardware Unconditional Restart (RESET)
To unconditionally restart LE920, the pad RESET# must be tied low for period between 500 2000 milliseconds and then released.
A simple circuit to do it is:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 33 of 88

NOTE:
Do not use any pull up resistor on the SHDN_N line or any totem pole digital output. Using
pull up resistor may cause latch-up problems on the LE920 power regulator and improper
functioning of the module. The line SHDN_N must be connected only in open collector
configuration.
NOTE:
The unconditional hardware SHDN_N must always be implemented on the boards. The
software must use it as an emergency exit procedure only, and not as a normal power-off
operation.
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.3.4. Hardware Unconditional Shutdown
To unconditionally Shutdown LE920, the pad SHDN_N must be tied low for at least 200
milliseconds and then released.
A simple circuit to do it is:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 34 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
4.4. Summary of Turning ON and OFF the module
The chart below describes the overall sequences for Turning ON and OFF.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 35 of 88

Power Supply
Nominal Supply Voltage
3.8V
Max Supply Voltage
4.2V
Supply Voltage Range
3.3V– 4.2V
LE920 current consumption
Mode
Average(mA)
Mode Description
SWITCHED OFF
Module supplied but switched Off
Switched Off
40 uA
IDLE mode
Standby mode; no call in progress
AT+CFUN=1
WCDMA
16
Normal mode; full functionality of the module
GSM
19
LTE
20
AT+CFUN=4
10
Disabled TX and RX; modules is not registered on the
network
AT+CFUN=5
GSM
4.4
DRx2
3.3
DRx3
2.8
DRx4
2.5
DRx5
2.3
DRx6
2.1
DRx7
2.0
DRx8
1.9
DRx9
WCDMA
3.0
DRx6
2.2
DRx7
1.8
DRx8
1.4
DRx9
LTE
6.3
Paging cycle #32 frames (0.32 sec DRx cycle)
3.8
Paging cycle #64 frames (0.64 sec DRx cycle)
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
5. Power Supply
The power supply circuitry and board layout are a very important part in the full product
design and they strongly reflect on the overall product performance. Reading carefully the
requirements and the guidelines that follow will ensure a good and proper design.
5.1. Power Supply Requirements
The LE920 power requirements are:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 36 of 88

2.5
Paging cycle #128 frames (1.28 sec DRx cycle)
1.9
Paging cycle #256 frames (2.56 sec DRx cycle)
Operative mode (LTE)
LTE (0dBm)
203
LTE data call channel BW 5MHz,RB=1, TX = 0dBm)
LTE (22dBm)
540
LTE data call (channel BW 5MHz,RB=1, TX = 22dBm)
Operative mode (WCDMA)
WCDMA Voice
185
WCDMA voice call (TX = 10dBm)
WCDMA HSDPA (0dBm)
170
WCDMA data call (Cat 14, TX = 0dBm, Max Throughput)
WCDMA HSDPA (22dBm)
470
WCDMA data call (Cat 14, TX = 22dBm, Max Throughput)
Operative mode (GSM)
GSM TX and RX mode
GSM900 PL5
290
GSM Voice Call
DCS1800 PL0
170
GPRS 4TX + 1RX
GSM900 PL5
410
GPRS Sending data mode
DCS1800 PL0
320
EDGE 4TX + 1RX
GSM900 PL5
255
EDGE Sending data mode
DCS1800 PL0
240
NOTE:
In GSM/GPRS mode, RF transmission is not continuous and is packed into bursts at a base
frequency of about 216 Hz with relative current peaks as high as about 2A. Therefore the
power supply must be designed to withstand these current peaks without big voltage drops;
this means that both the electrical design and the board layout must be designed for this
current flow. If the layout of the PCB is not well designed, a strong noise floor is generated
on the ground. This will reflect on all the audio paths producing an audible annoying noise at
216 Hz; if the voltage drops during the peaks, current absorption is too high. The device may
even shut down as a consequence of the supply voltage drop.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
* Worst/best case depends on network configuration and is not under module control.
TIP:
The electrical design for the Power supply must be made ensuring that it will be capable of a
peak current output of at least 2A.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 37 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
5.2. General Design Rules
The principal guidelines for the Power Supply Design embrace three different design steps:
the electrical design
the thermal design
the PCB layout
5.2.1. Electrical Design Guidelines
The electrical design of the power supply depends strongly on the power source where this
power is drained. We will distinguish them into three categories:
+5V input (typically PC internal regulator output)
+12V input (typically automotive)
battery
LE920 Hardware User Guide
5.2.1.1. + 5V Input Source Power Supply Design Guidelines
The desired output for the power supply is 3.8V, hence there is not a big
difference between the input source and the desired output and a linear regulator
can be used. A switching power supply will not be suitable because of the low
drop-out requirements.
When using a linear regulator, a proper heat sink must be provided in order to
dissipate the power generated.
A Bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided in order to
cut the current absorption peaks close to LE920, a 100μF tantalum capacitor is
usually suitable (on both VBATT and VBATT_PA together)..
Make sure the low ESR capacitor on the power supply output (usually a tantalum
one) is rated at least 10V.
A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input, in order to protect
LE920 from power polarity inversion.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 38 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
An example of linear regulator with 5V input is:
5.2.1.2. + 12V Input Source Power Supply Design Guidelines
The desired output for the power supply is 3.8V, hence due to the big difference
between the input source and the desired output, a linear regulator is unsuitable
and must not be used. A switching power supply will be preferable because of its
better efficiency especially with the 2A peak current load represented by LE920.
When using a switching regulator, a 500 kHz or more switching frequency
regulator is preferable because of its smaller inductor size and its faster transient
response. This allows the regulator to respond quickly to the current peaks
absorption.
In any case, the frequency and switching design selection is related to the
application to be developed due to the fact the switching frequency could also
generate EMC interference.
For car batteries (lead-acid accumulators) the input voltage can rise up to 15.8V
and this must be kept in mind when choosing components: all components in the
power supply must withstand this voltage.
A bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided in order to
cut the current absorption peaks. A 100μF tantalum capacitor is usually suitable
(on both VBATT and VBATT_PA together).
Make sure the low ESR capacitor on the power supply output (usually a tantalum
one) is rated at least 10V.
For automotive applications a spike protection diode must be inserted close to the
power input, in order to clean the supply of spikes.
A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input, in order to protect
LE920 from power polarity inversion. This can be the same diode as for spike
protection.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 39 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
An example of switching regulator with 12V input is in the below schematic (it is split in 2
parts):
Switching regulator
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 40 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
5.2.1.3. Battery Source Power Supply Design Guidelines
The desired nominal output for the power supply is 3.8V and the maximum allowed
voltage is 4.2V, hence a single 3.7V Li-Ion cell battery type is suited for supplying
the power to the Telit LE920 module.
NOTE:
Do not use any Ni-Cd, Ni-MH, and Pb battery types directly connected with LE920. Their use
can lead to overvoltage on LE920 and damage it. Use only Li-Ion battery types.
A bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided in order to
cut the current absorption peaks; a 100μF tantalum capacitor is usually suitable
(on both VBATT and VBATT_PA together).
Make sure the low ESR capacitor (usually a tantalum one) is rated at least 10V.
A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input, in order to protect
LE920 from power polarity inversion. Otherwise the battery connector must be
done in a way to avoid polarity inversions when connecting the battery.
The battery capacity must be at least 900mAh in order to withstand the current
peaks of 2A.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 41 of 88

5.2.2. Thermal Design Guidelines
The thermal design for the power supply heat sink must be done with the following
specifications:
Average current consumption during HSPA transmission @PWR level max in
LE920: 640mA (TBD)
Average current consumption during class12 GPRS transmission @PWR level
max: 680mA (TBD)
Average GPS current during GPS ON (Power Saving disabled) : 65mA (TBD)
NOTE:
The average consumption during transmissions depends on the power level at which the
device is requested to transmit via the network. The average current consumption hence varies
significantly.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
The thermal design for the Power supply must be made keeping an average consumption at
the max transmitting level during calls of 640mA(HSPA)/680mA(GPRS) rms plus 65mA rms
for GPS in tracking mode.
Considering the very low current during idle, especially if Power Saving function is enabled,
it is possible to consider from the thermal point of view that the device absorbs significant
current only during calls.
If we assume that the device stays in transmission for short periods of time (let us say few
minutes) and then remains for quite a long time in idle (let us say one hour), then the power
supply always has time to cool down between calls and the heat sink could be smaller than the
calculated for 640mA (HSPA)/680mA (GPRS) maximum RMS current. There could even be
a simple chip package (no heat sink).
Moreover in average network conditions the device is requested to transmit at a lower power
level than the maximum and hence the current consumption will be less than 640mA (HSPA)
/680mA (GPRS) (being usually around 250mA).
For these reasons the thermal design is rarely a concern and the simple ground plane where
the power supply chip is placed can be enough to ensure a good thermal condition and avoid
overheating.
For the heat generated by the LE920, you can consider it to be during transmission 2W max
during class12 GPRS upload. This generated heat will be mostly conducted to the ground
plane under the LE920; you must ensure that your application can dissipate heat.
In the WCDMA/HSPA mode, since LE920 emits RF signals continuously during
transmission, you must pay special attention how to dissipate the heat generated.
The current consumption will be up to about 640mA in HSPA (630mA in WCDMA)
continuously at the maximum TX output power (23dBm). Thus you must arrange on the PCB
used to mount LE920, that the area under LE920 is as large as possible. You must mount
LE920 on the large ground area of your application board and make many ground vias to
dissipate the heat.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 42 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Even though peak current consumption in GSM mode is higher than in WCDMA,
consideration for the heat sink is more important in the case of WCDMA.
As mentioned before, a GSM signal is bursty, thus, the temperature drift is more insensitive
than WCDMA. Consequently, if you successfully manage heat dissipation in WCDMA mode,
you don’t need to think more about GSM mode.
5.2.3. Power Supply PCB Layout Guidelines
As seen in the electrical design guidelines, the power supply must have a low ESR capacitor
on the output to cut the current peaks and a protection diode on the input to protect the supply
from spikes and polarity inversion. The placement of these components is crucial for the
correct working of the circuitry. A misplaced component can be useless or can even decrease
the power supply performances.
The bypass low ESR capacitor must be placed close to the Telit LE920 power
input pads, or in the case the power supply is a switching type, it can be placed
close to the inductor to cut the ripple as long as the PCB trace from the capacitor
to LE920 is wide enough to ensure a drop-less connection even during the 2A
current peaks.
The protection diode must be placed close to the input connector where the power
source is drained.
The PCB traces from the input connector to the power regulator IC must be wide
enough to ensure no voltage drops occur during the 2A current peaks. Note that
this is not done to save power loss but especially to avoid the voltage drops on the
power line at the current peaks frequency of 216 Hz that will reflect on all the
components connected to that supply (also introducing the noise floor at the burst
base frequency.) For this reason while a voltage drop of 300-400 mV may be
acceptable from the power loss point of view, the same voltage drop may not be
acceptable from the noise point of view. If your application does not have audio
interface but only uses the data feature of the Telit LE920, then this noise is not
so disturbing and power supply layout design can be more forgiving.
The PCB traces to LE920 and the bypass capacitor must be wide enough to
ensure no significant voltage drops occur when the 2A current peaks are
absorbed. This is needed for the same above-mentioned reasons. Try to keep this
trace as short as possible.
The PCB traces connecting the switching output to the inductor and the switching
diode must be kept as short as possible by placing the inductor and the diode very
close to the power switching IC (only for switching power supply). This is done
in order to reduce the radiated field (noise) at the switching frequency (usually
100-500 kHz).
The use of a good common ground plane is suggested.
The placement of the power supply on the board must be done in a way to
guarantee that the high current return paths in the ground plane are not
overlapping any noise sensitive circuitry such as the microphone amplifier/buffer
or earphone amplifier.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 43 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
The power supply input cables must be kept separate from noise sensitive lines
such as microphone/earphone cables.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 44 of 88

Antenna Line on PCB Requirements
GSM / WCDMA/ LTE Antenna Requirements
Frequency
range
Depending on frequency band(s) provided by the network operator, the customer must use the most suitable antenna for
that/those band(s)
Bandwidth
LE920-EU
LE920-NAG
LE920-NA
GSM850 : 70 MHz
GSM900 : 80 MHz
GSM1800(DCS) : 170 MHz
GSM1900(PCS) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band I(2100) : 250 MHz
WCDMA band III(1800) : 170 MHz
WCDMA band VIII(900) : 80 MHz
LTE Band I(2100) : 250 MHz
LTE band III(1800) : 170 MHz
LTE Band VII(2600) : 190 MHz
LTE Band VIII(900) : 80 MHz
LTE Band XX(800) : 71 MHz
GSM850 : 70 MHz
GSM900 : 80 MHz
GSM1800(DCS) : 170 MHz
GSM1900(PCS) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band I(2100) : 250 MHz
WCDMA band II(1900) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band IV(1700) : 445 MHz
WCDMA band V(850) : 70 MHz
WDCMA band VI(800): 70MHz
LTE Band I(2100) : 250 MHz
LTE Band II(1900) : 140 MHz
LTE Band IV(1700) : 445 MHz
LTE Band V (850) : 70 MHz
LTE Band XVII(700) : 42 MHz
GSM850 : 70 MHz
GSM1900(PCS) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band II(1900) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band IV(1700) : 445 MHz
WCDMA band V(850) : 70 MHz
LTE Band II(1900) : 140 MHz
LTE Band IV(1700) : 445 MHz
LTE Band V (850) : 70 MHz
LTE Band VII(2600) : 190 MHz
LTE Band XVII(700) : 42 MHz
LTE Band XII(700) : 42 MHz
Gain
Gain < 3dBi
Impedance
50 Ohm
Input power
> 33dBm(2 W) peak power in GSM
> 24dBm Average power in WCDMA & LTE
VSWR
absolute max
<= 10:1
VSWR
recommended
<= 2:1
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
6. Antenna(s)
The antenna connection and board layout design are the most important parts in the full
product design and they strongly reflect on the product’s overall performance. Read carefully
and follow the requirements and the guidelines for a good and proper design.
6.1. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna Requirements
The antenna for a Telit LE920 device must fulfill the following requirements:
When using the Telit LE920, since there’s no antenna connector on the module, the antenna
must be connected to the LE920 antenna pad (AD1) by means of a transmission line
implemented on the PCB.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 45 of 88
In the case that the antenna is not directly connected to the antenna pad of the LE920, then a
PCB line is required in order to connect with it or with its connector.
This transmission line shall fulfill the following requirements:

Characteristic Impedance
50Ohm
Max Attenuation
0.3dB
Coupling with other signals shall be avoided
Cold End (Ground Plane) of antenna shall be equipotential to the LE920 ground pads
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Furthermore if the device is developed for the US and/or Canada market, it must comply with
the FCC and/or IC approval requirements:
This device is to be used only for mobile and fixed application. The antenna(s) used for this
transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all
persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter. End-Users must be provided with transmitter operation conditions for satisfying
RF exposure compliance. OEM integrators must ensure that the end user has no manual
instructions to remove or install the LE920 module. Antennas used for this OEM module must
not exceed 3dBi gain for mobile and fixed operating configurations.
6.2. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – PCB line Guidelines
Make sure that the transmission line’s characteristic impedance is 50ohm.
Keep the line on the PCB as short as possible since the antenna line loss should be less
than around 0.3dB.
Line geometry should have uniform characteristics, constant cross section, avoid
meanders and abrupt curves.
Any suitable geometry/structure can be used for implementing the printed transmission
line affecting the antenna.
If a Ground plane is required in the line geometry, that plane must be continuous and
sufficiently extended so the geometry can be as similar as possible to the related canonical
model.
Keep, if possible, at least one layer of the PCB used only for the Ground plane; if possible,
use this layer as reference Ground plane for the transmission line.
It is wise to surround (on both sides) the PCB transmission line with Ground. Avoid
having other signal tracks facing directly the antenna line track.
Avoid crossing any un-shielded transmission line footprint with other tracks on different
layers.
The Ground surrounding the antenna line on the PCB must be strictly connected to the
main Ground plane by means of via-holes (once per 2mm at least) placed close to the
ground edges facing the line track.
Place EM-noisy devices as far as possible from LE920 antenna line.
Keep the antenna line far away from the LE920 power supply lines.
If EM-noisy devices are present on the PCB hosting the LE920, such as fast switching
ICs, take care to shield them with a metal frame cover.
If EM-noisy devices are not present around the line, using geometries like Micro strip or
Grounded Coplanar Waveguide is preferred since they typically ensure less attenuation
compared to a Strip line having the same length.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 46 of 88

ANTENNA REQUIREMENTS
Frequency range
Depending on frequency band(s) provided by the network operator, the
customer shall use the most suitable antenna for that/those band(s)
Bandwidth
LE920-EU
LE920-NA
WCDMA band I(2100) : 250 MHz
WCDMA band III(1800) : 170 MHz
WCDMA band VIII(900) : 80 MHz
LTE Band I(2100) : 250 MHz
LTE band III(1800) : 170 MHz
LTE Band VII(2600) : 190 MHz
LTE Band VIII(900) : 80 MHz
LTE Band XX(800) : 71 MHz
WCDMA band I(2100) : 250 MHz
WCDMA band II(1900) : 140 MHz
WCDMA band IV(AWS) : 445 MHz
WCDMA band IV(850) : 445 MHz
WCDMA band V(850) : 70 MHz
WDCMA band VI(800): 55MHz
LTE Band I(2100) : 250 MHz
LTE Band II(1900) : 140 MHz
LTE Band IV(1700) : 445 MHz
LTE Band V (850) : 70 MHz
Band XVII(700) : 42 MHz
Band XII(700) : 42 MHz
Impedance
50Ω
VSWR recommended
≤ 2:1
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
6.3. GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – Installation
Guidelines
Install the antenna in a location with access to the network radio signal.
The antenna must be installed such that it provides a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter;
The antenna must not be installed inside metal cases;
The antenna must also be installed according to the antenna manufacturer’s
instructions.
6.4. Antenna Diversity Requirements
This product includes an input for a second RX antenna to improve the radio sensitivity. The
function is called Antenna Diversity.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 47 of 88
When using the Telit LE920, since there’s no antenna connector on the module, the antenna
must be connected to the LE920 antenna pad (AU9) by means of a transmission line
implemented on the PCB.

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
In the case that the antenna is not directly connected at the antenna pad of the LE920, then a
PCB line is required in order to connect with it or with its connector.
The second Rx antenna should not be located in the close vicinity of the main antenna. In order
to improve Diversity Gain, Isolation and reduce mutual interaction, the two antennas should be
located at the maximum reciprocal distance possible, taking into consideration the available
space within the application.
NOTE:
If the RX Diversity is not used/connected, disable the Diversity functionality using the
AT#RXDIV command (refer to the AT User guide) and leave the Diversity pad AU9
unconnected.
6.5. GPS/GNSS Antenna Requirements
LE920 supports an active antenna.
It is recommended to use antennas as follow:
An external active antenna (GPS only).
An external active antenna, GNSS pre-filter.
NOTE:
Released models LE920-NA cs1550f-A & LE920-EU cs1550f-B include internal LNA
(13.5dB gain typ.).
For LE920-NA cs1550f-A & LE920-EU cs1550f-B models it is recommended to use:
• An external passive antenna (GPS only).
• An external passive antenna, GNSS pre-filter.
NOTE:
The external GNSS pre-Filter shall be required for GLONASS application.
GNSS pre-Filter requirement shall fulfill the following requirements.
Source and Load Impedance = 50Ohm
Insertion Loss (1575.42 – 1576.42MHz) = 1.4dB (Max)
Insertion Loss (1565.42 – 1585.42MHz) = 2.0dB (Max)
Insertion Loss (1597.5515 – 1605.886MHZ) = 2.0dB (Max)
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 48 of 88

Antenna Line on PCB Requirements
Characteristic Impedance
50Ohm
Max Attenuation
0.3dB
Coupling with other signals shall be avoided
Cold End (Ground Plane) of antenna shall be equipotential to the LE920 ground pads
NOTE:
It is recommended to add a DC block to the customer’s GPS application in order to prevent
damage to the LE920 due to unwanted DC voltage
WARNING:
The LE920 software is implemented differently depending on the configurations of an external
device. Please refer to the AT command User Guide in detail.
6.5.1. Combined GPS/GNSS Antenna
The use of combined RF/GPS/GNSS antenna is NOT recommended. This solution could
generate extremely poor GPS/GNSS reception. In addition, the combination of antennas
requires an additional diplexer, which adds significant power losses in the RF path.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
6.5.2. Linear and Patch GPS/GNSS Antenna
Using this type of antenna introduces at least 3dB of loss compared to a circularly polarized
(CP) antenna. Having a spherical gain response instead of a hemispherical gain response could
aggravate the multipath behaviour & create poor position accuracy.
6.5.3. Front End Design Considerations
When using the Telit LE920, since there’s no antenna connector on the module, the antenna
must be connected to the LE920 through the PCB to the antenna pad.
In the case that the antenna is not directly connected at the antenna pad of the LE920, then a
PCB line is required.
This line of transmission shall fulfill the following requirements:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 49 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Furthermore if the device is developed for the US and/or Canada market, it must comply with
the FCC and/or IC requirements.
This device is to be used only for mobile and fixed application.
6.5.4. GPS/GNSS Antenna - PCB Line Guidelines
Ensure that the antenna line impedance is 50ohm.
Keep the line on the PCB as short as possible to reduce the loss.
The antenna line must have uniform characteristics, constant cross section, avoiding
meanders and abrupt curves.
Keep one layer of the PCB used only for the Ground plane; if possible.
Surround (on the sides, over and under) the antenna line on the PCB with Ground. Avoid
having other signal tracks directly facing the antenna line track.
The Ground around the antenna line on the PCB must be strictly connected to the main
Ground plane by placing vias at least once per 2mm.
Place EM-noisy devices as far as possible from LE920 antenna line.
Keep the antenna line far away from the LE920 power supply lines.
If EM-noisy devices are around the PCB hosting the LE920, such as fast switching ICs,
ensure shielding the antenna line by burying it inside the layers of PCB and surrounding
it with Ground planes; or shield it with a metal frame cover.
If you do not have EM-noisy devices around the PCB of LE920, use a Micro strip line
on the surface copper layer for the antenna line. The line attenuation will be lower than a
buried one.
6.5.5. GPS/GNSS Antenna – Installation Guidelines
The LE920, due to its sensitivity characteristics, is capable of performing a fix inside
buildings. (In any case the sensitivity could be affected by the building characteristics i.e.
shielding)
The antenna must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
The antenna shall not be installed inside metal cases.
The antenna shall also be installed according to the antenna manufacturer’s instructions.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 50 of 88

Parameter
LE920
Min
Max
Input level on any
digital pin when on
-0.3V
+2.16V
Input voltage on
analog pins when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
Level
LE920
Min
Max
Input high level
1.5V
2.1V
Input low level
-0.3V
0.5V
Output high level
1.35V
1.8V
Output low level
0V
0.45V
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
7. Logic Level Specifications
Where not specifically stated, all the interface circuits work at 1.8V CMOS logic levels.
The following table shows the logic level specifications used in the Telit LE920 interface
circuits:
NOTE:
Do not connect LE920’s digital logic signal directly to OEM’s digital logic signal with a level
higher than 2.7V for 1.8V CMOS signals.
For 1.8V CMOS signals:
Absolute Maximum Ratings - Not Functional
Operating Range - Interface levels (1.8V CMOS)
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 51 of 88

Signal
LE920
Pad No.
Usage
USB_VBUS
A18
Power sense for the internal USB transceiver.
Acceptable input voltage range 2.2V – 5.25V @ max 5mA consumption
USB_D-
F19
Minus (-) line of the differential, bi-directional USB signal to/from the
peripheral device
USB D+
D19
Plus (+) line of the differential, bi-directional USB signal to/from the
peripheral device
8. USB Port
The LE920 module includes a Universal Serial Bus (USB) transceiver, which operates at
USB high-speed (480Mbits/sec). It can also work with USB full-speed (12Mbits/sec) hosts
It is compliant with the USB 2.0 specification and can be used control and data transfers as
well as for diagnostic monitoring and firmware update. In fact firmware update by the host is
only possible via USB and not possible via UART. The reason is that Telit consider it
impractical to transfer firmware binaries exceeding 100Mb via UART.
The USB port on the Telit LE920 is typically the main interface between the module and
OEM hardware.
The USB_DPLUS and USB_DMINUS signals have a clock rate of 480MHz. The signal traces
should be routed carefully. Trace lengths, number of vias and capacitive loading should be
minimized. The impedance value should be as close as possible to 90 Ohms differential.
The table below describes the USB interface signals:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
- USB_VBUS input power is internally used to detect the USB port and start enumeration
process. It isn’t used for supplying internal LE920 USB HW block. Therefore, only
maximum of 5mA is required.
- The USB_VBUS is internally pulled-down by 10k ohm resistor. Customer host
application must take into account voltage divider with the internal pull down resistor
meeting the minimum of 2.2V input, in case that a serial resistor is placed on
USB_VBUS signal.
NOTE:
In the case of not using USB communication, it is still highly recommended to place an
optional USB connector in the application board.
USB physical communication is needed in the case of SW update
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 52 of 88

Parameter
LE920
Min
Max
Input level on any
digital pin when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
Input voltage on
analog pins when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
Level
LE920
Min
Max
Input high level
1.5V
2.1V
Input low level
-0.3V
0.5V
Output high level
1.35V
1.8V
Output low level
0V
0.45V
9. Serial Ports
The serial port on the Telit LE920 is typically a secondary interface between the module and
OEM hardware.
Two serial ports are available on the module:
MODEM SERIAL PORT 1(Main)
MODEM SERIAL PORT 2 (Auxiliary)
Several configurations can be designed for the serial port on the OEM hardware.
The most common are:
RS232 PC com port;
Microcontroller UART @ 1.8V (Universal Asynchronous Receive Transmit) ;
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Microcontroller UART @ 5V or other voltages different from 1.8V.
Depending on the type of serial port on the OEM hardware, a level translator circuit may be
needed to make the system work. The only configuration that does not need a level translation
is the 1.8V UART.
The serial port 1 on LE920 is a +1.8V UART with all the 7 RS232 signals. It differs from the
PC-RS232 in signal polarity (RS232 is reversed) and levels.
The Serial port 2 is a +1.8V Auxiliary UART.
The levels for LE920 UART are the CMOS levels:
Absolute Maximum Ratings -Not Functional
Operating Range - Interface levels
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 53 of 88

RS232
Pin
Number
Signal
LE920
Pad Number
Name
Usage
1
DCD -
dcd_uart
AE18
Data Carrier
Detect
Output from the LE920 that indicates the carrier
presence
2
RXD -
Tx_uart
AF19
Transmit line
*see Note
Output transmit line of the LE920 UART
3
TXD -
Rx_uart
AH19
Receive line
*see Note
Input receive of the LE920 UART
4
DTR -
dtr_uart
AC18
Data Terminal
Ready
Input to the LE920 that controls the DTE READY
condition
5
GND
A6, A12, B13, B15….
Ground
ground
6
DSR -
dsr_uart
AG18
Data Set Ready
Output from the LE920 that indicates the module is
ready
7
RTS -
rts_uart
AA18
Request to Send
Input to the LE920 that controls the Hardware flow
control
8
CTS -
cts_uart
AK19
Clear to Send
Output from the LE920 that controls the Hardware flow
control
9
RI -
ri_uart
AJ18
Ring Indicator
Output from the LE920 that indicates the Incoming call
condition
9.1. Modem Serial Port 1
Serial port 1 on the LE920 is a +1.8V UART with all 7 RS232 signals.
It differs from the PC-RS232 in the signal polarity (RS232 is reversed) and levels.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
In order to avoid a back-powering effect it is recommended to avoid having any HIGH logic
level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is powered OFF or during an
ON/OFF transition.
TIP:
For minimum implementations, only the TXD and RXD lines need be connected, the other
lines can be left open provided a software flow control is implemented.
NOTE:
According to V.24, RX/TX signal names are referred to the application side, therefore on the
LE920 side these signal are in the opposite direction: TXD on the application side will be
connected to the receive line (here named TXD/ rx_uart ) of the LE920 serial port and vice
versa for RX.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 54 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AB19
TXD_AUX
O
Auxiliary UART (TX Data to DTE)
1.8V
AD19
RXD_AUX
I
Auxiliary UART (RX Data to DTE)
1.8V
9.2. Modem Serial Port 2
Serial port 2 on the LE920 is a +1.8V UART with only the RX and TX signals.
The signals of the LE920 serial port are:
NOTE:
In order to avoid a back-powering effect it is recommended to avoid having any HIGH logic
level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is powered OFF or during an
ON/OFF transition.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
9.3. RS232 Level Translation
In order to interface the Telit LE920 with a PC com port or a RS232 (EIA/TIA-232)
application a level translator is required. This level translator must:
Invert the electrical signal in both directions;
Change the level from 0/1.8V to +15/-15V.
Actually, the RS232 UART 16450, 16550, 16650 & 16750 chipsets accept signals with lower
levels on the RS232 side (EIA/TIA-562), allowing a lower voltage-multiplying ratio on the
level translator. Note that the negative signal voltage must be less than 0V and hence some
sort of level translation is always required.
The simplest way to translate the levels and invert the signal is by using a single chip level
translator. There are a multitude of them, differing in the number of drivers and receivers and
in the levels (be sure to get a true RS232 level translator not a RS485 or other standards).
By convention the driver is the level translator from the 0-1.8V UART to the RS232 level.
The receiver is the translator from the RS232 level to 0-1.8V UART.
In order to translate the whole set of control lines of the UART you will need:
5 drivers
3 receivers
NOTE:
The digital input lines working at 1.8V CMOS have an absolute maximum input voltage of
2.7V; therefore the level translator IC shall not be powered by the +3.8V supply of the
module. Instead, it must be powered from a +1.8V (dedicated) power supply.
This is because in this way the level translator IC outputs on the module side (i.e. LE920
inputs) will work at +3.8V interface levels, damaging the module inputs.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 55 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
An example of RS232 level adaption circuitry could be accomplished using a MAXIM
transceiver (MAX218).
In this case the chipset is capable of translating directly from 1.8V to the RS232 levels (Example
on 4 signals only).
NOTE:
In this case the length of the lines on the application must be taken into account to avoid
problems in the case of High-speed rates on RS232.
The RS232 serial port lines are usually connected to a DB9 connector with the following
layout: signal names and directions are named and defined from the DTE point of view
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 56 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
P19
SPI_CLK
O
SPI Clock output
1.8V
M19
SPI_MISO
I
SPI data Master Input Slave output
1.8V
K19
SPI_MOSI
O
SPI data Master Output Slave input
1.8V
N18
SPI_CS
O
SPI Chip select output
1.8V
LE920 (Master)
SPI_CS
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
SPI_MISO
Host (Slave)
SPI_CS
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
SPI_MISO
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
10. Peripheral Ports
In addition to Telit LE920 serial ports, the LE920 supports the following peripheral ports:
SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
I2C - Inter-integrated circuit
2 x SDIO – Secure Digital I/O
10.1. SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
The LE920 SPI supports the following:
Master Mode only
1.8V CMOS level
Up to 26MHz clock rate
NOTE:
SPI is supported only on the Linux side.
LE920 can support Master mode only, and can’t be configured as slave mode.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 57 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AH17
SD/MMC_CMD
O
SD Command
1.8/2.95V
AD17
SD/MMC_CLK
O
SD Card Clock
1.8/2.95V
Y17
SD/MMC_DATA0
I/O
SD Serial Data 0
1.8/2.95V
AF17
SD/MMC_DATA1
I/O
SD Serial Data 1
1.8/2.95V
AB17
SD/MMC_DATA2
I/O
SD Serial Data 2
1.8/2.95V
W17
SD/MMC_DATA3
I/O
SD Serial Data 3
1.8/2.95V
U17
SD/MMC_CD
I
SD card detect input
1.8V
Active Low
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
10.2. I2C - Inter-integrated circuit
The LE920 I2C is an alternate function of our GPIO 1-10 pins.
Any GPIO can be configured as SCL and SDA
Available only from Modem side as SW emulation of I2C on GPIO lines.
LE920 supports I2C Master Mode only.
NOTE:
I2C is supported only on from Modem side as SW emulation of I2C on GPIO lines.
Refer to LE920 AT SW manual for command settings
10.3. SDIO – Secure Digital I/O
The LE920 is used to support standard SD/MMC memory cards with the following:
Interface with SD/MMC memory cards up to 2 TB
Max clock: 50 MHz SDR at 1.8 V, Max Data: 25MB/s, MMC standard: MMC 4.4
type 3 SDR at 1.8 V; SD standard: UHS-SDR25 at 1.8 V
Max clock: 50 MHz SDR at 2.95 V, Max Data: 25MB/s, MMC standard: MMC
4.4 type 3 SDR at 2.95 V; SD standard: DS, HS at 2.95
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 58 of 88

SD/MMC_DATA2
SD/MMC_DATA3
SD/MMC_CMD
SD/MMC_CLK
SD/MMC_DATA0
SD/MMC_DATA1
LE920
SDIO Interface
SD/MMC_CD
Ext, Card supply
DATA2
DATA3
CMD
VDD
CLK
VSS
DATA0
DATA1
microSD
SW1
SW2
GND
GND
10K
10K
10K
10K
10K
C=100nF
GND
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Connection diagram of the SD interface is shown below:
NOTE:
1. SDIO is supported only on the Linux side.
2. SD/MMC card supply shall be provided by the Host application board. LE920 doesn’t
provide a dedicated SD/MMC card supply.
3. Pull-up resistors should be place on the application host board
4. Card detection input has an internal pull-up resistor
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 59 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
AB3
WiFi_SD_CMD
O
Wi-Fi SD Command
1.8V
AM3
WiFi_SD_CLK
O
Wi-Fi SD Clock
1.8V
AD3
WiFi_SD _DATA0
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 0
1.8V
AF3
WiFi_SD _DATA1
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 1
1.8V
AH3
WiFi_SD _DATA2
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 2
1.8V
AK3
WiFi_SD _DATA3
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 3
1.8V
Y3
WiFi_RST_Ctr
O
Wi-Fi Reset output control / Power enable control
1.8V
Active Low
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
10.4. Wi-Fi (SDIO) control Interface
The LE920 has an integrated SW driver for supporting Qualcomm QCA6053 Wi-Fi chipset via
a 2nd dedicated SD bus interface.
The secondary SD bus interface can be used only with the QCA6053 chipset, and can’t be used
as external SD/MMC card connection.
For detailed explanation, refer to Telit 80407NT11289A - xE920 - Wi-Fi interface Application
Note
WARNING:
Wi-Fi (SDIO) control interface is fully supported in LE920-EU and LE920-NA.
However, in some cases isn’t supported in LE920-EUG and LE920-NAG.
If Wi-Fi control is required for LE920-NAG or LE920-NAG, please contact your local Telit
rep. or contact customer support for specific ordering info.
NOTE:
‘Wifi_RST_Ctr’ should have an optional Pull-up resistor to 1.8V on the host
application, to disable Wi-Fi reset function if needed
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 60 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
COMMENT
D11
DVI_WA0
O
Digital Audio Interface (WA0)
B-PD
1.8V
PCM_SYNC
C8
DVI_RX
I
Digital Audio Interface (RX)
B-PD
1.8V
PCM_DIN
D9
DVI_TX
O
Digital Audio Interface (TX)
B-PD
1.8V
PCM_DOUT
C10
DVI_CLK
O
Digital Audio Interface (CLK)
B-PD
1.8V
PCM_CLK
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
11. Audio Section Overview
The LE920 module support analog and digital audio interfaces.
11.1. Analog Audio
The LE920 module provides single analog audio path transmitting and receiving.
Please refer to the xE920_Audio_Settings_Application_Note, 80404NT10095A
WARNING:
LE920 Analog audio implementation uses an internal CODEC.
LE920 internal codec uses the same external LE920 digital Audio interface signals
Therefore, applications that are using analog audio, must make sure that the digital audio
interface shall be either not connected, or Hi-Z, or ‘input’ to Host application.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
11.2. Digital Audio
LE920 can be connected to an external codec through the digital interface.
The product provides one Digital Audio Interface (DVI) on the following Pins:
LE920 DVI supports PCM master 2048khz short frame
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 61 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 62 of 88

PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Drive Strength
F9
GPIO_01
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
E10
GPIO_02
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
F11
GPIO_03
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
E12
GPIO_04
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
F13
GPIO_05
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
E14
GPIO_06
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
R18
GPIO_07
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
S19
GPIO_08
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
U19
GPIO_09
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
W19
GPIO_10
I/O
Configurable GPIO
CMOS 1.8V
2mA
12. General Purpose I/O
The general-purpose I/O pads can be configured to act in three different ways:
input
output
alternate function (internally controlled)
Input pads can only be read and report the digital value (high or low) present on the pad at the
read time; output pads can only be written or queried and set the value of the pad output; an
alternate function pad is internally controlled by the LE920 firmware and acts depending on
the function implemented.
The following GPIOs are available on the LE920.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
In order to avoid a back-powering effect it is recommended to avoid having any HIGH logic
level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is powered OFF or during an
ON/OFF transition.
NOTE:
LE920 GPIO can also be used as alternate I2C function.
Refer to I2C section
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 63 of 88

Parameter
LE920
Min
Max
Input level on any
digital pin when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
Input voltage on
analog pins when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
Level
LE920
Min
Max
Input high level
1.5V
2.1V
Input low level
-0.3V
0.5V
Output high level
1.35V
1.8V
Output low level
0V
0.45V
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
12.1. Logic Level Specifications
Where not specifically stated, all the interface circuits work at 1.8V CMOS logic levels.
The following table shows the logic level specifications used in the LE920 interface circuits:
For 1,8V signals:
Absolute Maximum Ratings -Not Functional
LE920 Hardware User Guide
Operating Range - Interface levels (1.8V CMOS)
12.2. Using a GPIO Pad as Input
The GPIO pads, when used as inputs, can be connected to a digital output of another device
and report its status, provided this device has interface levels compatible with the 1.8V
CMOS levels of the GPIO.
If the digital output of the device is connected with the GPIO input, the pad has interface
levels different from the 1.8V CMOS. It can be buffered with an open collector transistor with
a 47KΩ pull-up resistor to 1.8V.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 64 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
12.3. Using a GPIO Pad as Output
The GPIO pads, when used as outputs, can drive 1.8V CMOS digital devices or compatible
hardware. When set as outputs, the pads have a push-pull output and therefore the pull-up
resistor may be omitted.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
12.4. Using the Temperature Monitor Function
12.4.1. Short Description
The Temperature Monitor is a function of the module that permits to control its internal
temperature and if properly set (see the #TEMPMON command on AT Interface guide) it
raises to High Logic level a GPIO when the maximum temperature is reached.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 65 of 88

LED status
Device Status
Permanently off
Device off
Fast blinking
(Period 1s, Ton 0,5s)
Net search / Not registered /
turning off
Slow blinking
(Period 3s, Ton 0,3s)
Registered full service
Permanently on
a call is active
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
12.5. Indication of Network Service Availability
The STAT_LED pin status shows information on the network service availability and call
status. In the LE920 modules, the STAT_LED usually needs an external transistor to drive an
external LED. Because of the above, the status indicated in the following table is reversed
with respect to the pin status:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 66 of 88

Min
Typical
Max
Output voltage
1.75V
1.80V
1.85V
Output current
100mA
Output bypass capacitor
(Inside the module)
1μF
12.6. RTC Bypass
The VRTC pin brings out the Real Time Clock supply, which is separate from the rest of the
digital part, allowing having only the RTC operating when all the other parts of the device are
turned off.
If maintaining internal RTC block is needed, it recommended to connect a backup capacitor
or a coin cell to this pin (valid range from 2.5V to 3.2V), otherwise, it can be left unconnected
Operating Modes:
1. LE920 has a valid VBAT supply, and the unit is turned ON – RTC block supply will be
generated from main VBAT supply, and the VRTC pin will output the VRTC supply,
charging external coin cell or capacitor.
2. LE920 has no VBAT connected – The External coin cell or capacitor will maintain
VRTC supply, keeping the internal RTC unit block operational.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
NO devices may be powered from this pin.
12.7. VAUX Power Output
A regulated power supply output is provided in order to supply small devices from the
module. This output is active when the module is ON and goes OFF when the module is shut
down. The operating range characteristics of the supply are:
Operating Range – VAUX power supply
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 67 of 88

Min
Max
Units
Input Voltage range
0
1.7
Volt
AD conversion
- 8 bits
Resolution
-
< 6.6
mV
13. ADC section
13.1. ADC Converter
13.1.1. Description
The on board ADCs are 8-bit converters. They are able to read a voltage level in the range of
0-2 volts applied on the ADC pin input and store and convert it into 8 bit word.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
The LE920 module provides 3 Analog to Digital Converters.
13.1.2. Using ADC Converter
An AT command is available to use the ADC function.
The command is AT#ADC=1,2. The read value is expressed in mV
Refer to SW User Guide or AT Commands Reference Guide for the full description of this
function.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 68 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
14. Mounting the module on your board
14.1. General
The LE920 modules have been designed to be compliant with a standard lead-free SMT
process.
14.2. Finishing & Dimensions
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 69 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
14.3. Recommended foot print for the application
198 pads
Top View
In order to easily rework the LE920 it is suggested to consider that the application has a 1.5
mm placement inhibit area around the module.
It is also suggested, as a common rule for an SMT component, to avoid having a mechanical
part of the application in direct contact with the module.
NOTE:
In the customer application, the region under WIRING INHIBIT (see figure above) must be
clear from signal or ground paths.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 70 of 88

14.4. Stencil
Stencil’s apertures layout can be the same as the recommended footprint (1:1). A suggested
thickness of stencil foil is greater than 120 µm.
14.5. PCB Pad Design
Non solder mask defined (NSMD) type is recommended for the solder pads on the PCB.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 71 of 88

Finish
Layer thickness (um)
Properties
Electro-less Ni / Immersion Au
3 –7 / 0.05 – 0.15
good solder ability protection,
high shear force values
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
14.6. Recommendations for PCB Pad Dimensions (mm)
It is not recommended to place via or micro-via not covered by solder resist in an area of 0,3
mm around the pads unless it carries the same signal of the pad itself (see following figure).
Holes in pad are allowed only for blind holes and not for through holes.
Recommendations for PCB Pad Surfaces:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 72 of 88
The PCB must be able to resist the higher temperatures which occur during the lead-free
process. This issue should be discussed with the PCB-supplier. Generally, the wettability of tinlead solder paste on the described surface plating is better compared to lead-free solder paste.

Solder Paste
Lead free
Sn/Ag/Cu
14.7. Solder Paste
We recommend using only “no clean” solder paste in order to avoid the cleaning of the modules
after assembly.
14.7.1. Solder Reflow
Recommended solder reflow profile:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 73 of 88

Profile Feature
Pb-Free Assembly
Average ramp-up rate (TL to TP)
3°C/second max
Preheat
– Temperature Min (Tsmin)
– Temperature Max (Tsmax)
– Time (min to max) (ts)
150°C
200°C
60-180 seconds
Tsmax to TL
– Ramp-up Rate
3°C/second max
Time maintained above:
– Temperature (TL)
– Time (tL)
217°C
60-150 seconds
Peak Temperature (Tp)
245 +0/-5°C
Time within 5°C of actual Peak
Temperature (tp)
10-30 seconds
Ramp-down Rate
6°C/second max.
Time 25°C to Peak Temperature
8 minutes max.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE:
All temperatures refer to topside of the package, measured on the package body surface.
WARNING:
The LE920 module withstands one reflow process only.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 74 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
15. Application guide
15.1. Debug of the LE920 in production
To test and debug the mounting of LE920, we strongly recommend foreseeing test pads on
the host PCB, in order to check the connection between the LE920 itself and the application
and to test the performance of the module by connecting it with an external computer.
Depending on the customer application, these pads include, but are not limited to the
following signals:
TXD
RXD
ON/OFF
SHUTDOWN
RESET
GND
VBATT
TXD_AUX
RXD_AUX
USB_VBUS
USB_D+
USB_D-
In addition the below signal are also recommended (but not must)
PWRMON
STAT_LED
SW_RDY
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 75 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
15.2. Bypass capacitor on Power supplies
When a sudden voltage is asserted to or cut from the power supplies, the steep transition
makes some reactions such as overshoot and undershoot.
This abrupt voltage transition can affect the device causing it to not work or make it
malfunction.
Bypass capacitors are needed to alleviate this behavior. The behavior can be affected
differently according to the various applications. Customers must pay special attention to this
when they design their application board.
The length and width of the power lines need to be considered carefully and the capacitance
of the capacitors need to be selected accordingly.
The capacitor will also prevent ripple of the power supplies and the switching noise caused in
TDMA systems like GSM.
Especially, a suitable bypass capacitor must be mounted on the Vbatt & Vbatt_PA (Pads
AP17,AP19,AR18,AS17,AS19,AT18,AU17,AU19) and USB_VBUS (Pad A18) lines in the
application board.
The recommended values can be presented as:
100uF for Vbatt
4.7uF for USB_VBUS (including the 1uF capacitor inside the module).
Customers must still consider that the capacitance mainly depends on the conditions of their
application board.
Generally more capacitance is required when the power line is longer.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 76 of 88

Product P/N
C1 range (nF)
LE920-EU/NA
100 nF
15.3. SIM interface
This section deals with the recommended schematics for the design of SIM interfaces on the
application boards.
15.3.1. SIM schematic example
Figure 1 illustrates in particular how the application side should be designed, and what values
the components should have.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
NOTE FOR R1:
The resistor value on SIMIO pulled up to SIMVCC should be defined accordingly in order to
be compliant with 3GPP specification for USIM electrical testing.
LE920 contains an internal pull-up resistor of 20KΩ on SIMIO.
However, the un-mounted option in the application design can be recommended in order to
tune R1 if necessary.
The following Table lists the values of C1 to be adopted with the LE920 product:
Refer to the following document for the detail:
80000NT10026A - SIM Interface And ESD Protection Application Note Rev.2
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 77 of 88

SIMCLK1
SIMRST1
SIMVCC1
LE920-NA AUTO S module
SIMIN1
ESIM_RST
A8
E8
SIMIO1
B7
GND
A10
B11
B9
15.3.2. eSIM interface guidelines
NOTE:
eSIM feature available with LE920-NA AUTO S model only.
LE920-NA AUTO S model designed to operate either with internal build-in eSIM, external
SIM card or with both options, switching SIM cards using following setups:
For using internal eSIM configuration only, connect E8 pin “ESIM_RST” to B11
“SIMRST1”.
Connect B7 SIMIN1 to GND, leave all other SIM card ports disconnected:
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 78 of 88

C1
R2
Not mounted
R1
B11
A10
SIMCLK1
SIMRST1
SIMVCC1
LE920-NA AUTO S module
SIMIN1
8
7
SIMIN
1
2 3 4
5
ESIM_RST
A8
E8
SIMIO1
6
External SIM card
SPDT switch 1
SPDT switch 2
SW1
SW2
8.2K
GND
GND
GND
GND
200k
GND
B9
B7
C2
C3
C4
100nF
33pF
33pF
33pF
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
For external SIM configuration only, leave E8 open (or set to GND) and follow 15.3.1
section guidelines.
For configuration with both internal eSIM and external SIM cards use following
approach:
1) Both eSIM and external SIM share the same lines except SIMRST1 and SIMIN1
lines that should be switched between them, either electronically or manually. For
SIMRST1 switching, it is mandatory to keep second output of SW1 in high Z state
when connected to the first one, therefore analog relay (for example DG9431
Single SPDT Analog Switch) / mechanical relay / 3 state buffer with separate
enable for each output is recommended.
2) Connect 200kΩ pulldown resistor (R2) to external SIM Reset line for keeping
external SIM in high Z state during internal eSIM use, whenever SIMRST1 signal
routed to E8 ESIM_RST path. This method prevents interference between the SIM
cards enabling only one of them by SW1 selection.
3) For SIMIN1 card detection mechanism, similar approach to SIMRST1
recommended. Manual selection with 0Ω resistors is another option.
NOTE FOR R1:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 79 of 88
The resistor value on SIMIO pulled up to SIMVCC should be defined accordingly in order to
be compliant with 3GPP specification.
LE920-NA AUTO S contains an internal pull-up resistor on SIMIO1.
However, the un-mounted option in the application design can be recommended in order to
tune R1 if necessary.

Pad
Signal
I/O
Function
Contact
Air
All Pins
All
± 4KV
± 8KV
Antenna
AD1,AU9,S1
Antenna
Pads
AI
Antenna pad
± 8KV
± 15KV
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
15.4. EMC recommendations
All LE920 signals are provided with some EMC protection. Nevertheless the accepted level
differs according to which pin. The characteristics are described in the following Table:
Appropriate series resistors must be considered to protect the input lines from overvoltage.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 80 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
15.5. Download and Debug Port
One of the following options should be chosen in the design of host system in order to download
or upgrade the Telit software and debug LE920 when LE920 is already mounted on a host
system.
Users who use both UART and USB interfaces to communicate with LE920
- Must implement a USB download method in a host system for upgrading LE920 when it is
mounted.
Users who use USB interface only to communicate with LE920
- Must arrange for a USB port in a host system for debugging or upgrading LE920 when it is
mounted.
Users who use UART interface only to communicate with LE920
LE920 Hardware User Guide
- Must arrange for a USB port in a host system for debugging or upgrading LE920 when
it is mounted.
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 81 of 88

Tray
in each
tray
inside each
envelope
inside each
carton box
Modules/tray
Description
modules/
tray
trays/
envelope
modules/
envelope
envelopes/
carton box
modules/
box
xE920
packaging
JEDEC Tray
24
5+ 1 empty
120 4 480
Qty
Minimum Order
Quantity (MOQ)
120
Standard Packing
Quantity (SPQ)
480
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
16. Packing system
The Telit LE920 is packaged on trays. The tray is JEDEC compliant, injection molded antistatic Modified
Polyphenylene ether (MPPO). It has good thermal characteristics and can withstand a the standard baking
temperature up to 125°C, thereby avoiding handling the modules if baking is required. The trays are rigid, thus
providing more mechanical protection against transport stress. Additionally they are re-usable and so
environmentally sustainable.
There are 2 (two) antistatic rubber bands that enclose each envelope.
The carton box is rigid, thus offering mechanical protection. The carton box has one flap across the whole top
surface. It is sealed with tape along the edges of the box.
Each tray contains 24 pieces as shown in the following picture:
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 82 of 88

LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 83 of 88

16.1. Tray Drawing
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 84 of 88

16.2. Moisture Sensitivity
The LE920 is a Moisture Sensitive Device level 3, in accordance with standard IPC/JEDEC JSTD-020. Observe all of the requirements for using this kind of components.
Calculated shelf life in sealed bag: 4 months at <40°C and <90% relative humidity (RH).
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 85 of 88

1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
17. Safety Recommendations
READ CAREFULLY
Be sure that the use of this product is allowed in your country and in the environment
required. The use of this product may be dangerous and must be avoided in the following
areas:
Where it can interfere with other electronic devices in environments such as
hospitals, airports, aircrafts, etc.
Where there is risk of explosion such as gasoline stations, oil refineries, etc.
It is the responsibility of the user to enforce the country regulations and the specific
environment regulations.
Do not disassemble the product; any mark of tampering will compromise the warranty
validity.
LE920 Hardware User Guide
We recommend following the instructions of the hardware user guides for correct wiring of
the product. The product must be supplied with a stabilized voltage source and the wiring
conform to the security and fire prevention regulations.
The product must be handled with care, avoiding any contact with the pins because
electrostatic discharges may damage the product itself. The same caution must be taken for
the SIM, checking carefully the instructions for its use. Do not insert or remove the SIM when
the product is in power saving mode.
The system integrator is responsible for the functioning of the final product; therefore, care
must be taken of the external components of the module, as well as of any project or
installation issue, because of the risk of disturbing the GSM network or external devices or
having any impact on safety. Should there be any doubt, please refer to the technical
documentation and the regulations in force.
Every module must be equipped with a proper antenna with the specified characteristics. The
antenna must be installed with care in order to avoid any interference with other electronic
devices and must be installed with the guarantee of a minimum 20 cm distance from a human
body. In case this requirement cannot be satisfied, the system integrator must assess the final
product against the SAR regulation.
The European Community provides some Directives for electronic equipment introduced on
the market. All the relevant information is available on the European Community website:
http://europa.eu.int/comm/enterprise/rtte/dir99-5.htm
The text of the Directive 99/05 regarding telecommunication equipment is available, while
the applicable Directives (Low Voltage and EMC) are available at:
http://europa.eu.int/comm/enterprise/rtte/dir99-5.htm
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 86 of 88

Revision
Date
Changes
0-draft1
2012-10-03
First issue
0-draft2
2012-12-11
- Remove SIM2 interface
- Remove external GPS LNA support
0-draft3
2013-03-12
Updated pin-out
0-draft4
2013-05-21
- Update DVI
- Adding Current consumption
- Adding SHDN_N section
- Update Mechanical drawings
0-draft5
2013-10-08
- Remove VRTC support
- Section 2.2, update tolerance value
- Section 3.1, remove VRTC and 2nd analog audio signals
- Section 4.2, update PWRMON turn on to 100mSec
- Section 4.3.2, update Hold Time min to 2.5 seconds
- Section 4.3.3, update RESET control timing details
- Section 5.1, update table
- Section 6.5, update insertion Loss value
- Section 8, remove USB Low speed support
- Section 10, adding Analog Audio support.
- Section 14.4, update table
1
2014-02-04
Initial ‘official’ Release
- Added LE920-NV support
- Added VRTC support
- Added Section 2.6, sensitivity
- Section 8, added note
- Section 13.3, update figure
- Section 14.3, update description
2
2014-04-02
General editorial update
- Update 8, Firmware update
- Update 14.5, Firmware update
3
2014-09-26
- Removed LE920-NV support
- Section 8, update USB_VBUS notes
- Section 15, update packing drawing and text
4
2015-03-19
- Add Section 10, Peripheral Ports
- Section 6.4, added note for diversity antenna connection
- Section 5.1, added additional CFUN=5 measurements
- Section 12, remove ‘high voltage tolerate’
- Section 3.1, Update pinout
- Section 12.6 update
- Section 15.3 update
5
2015-04-27
- Section 3.1, correct SPI_CS LGA pad
- Section 3.1.1 update figure
- Section 10.1, correct SPI_CS LGA pad
- Added differences NAG and NA (removing name NAA)
- Section 2.5, changed to 3 discrete figures
18. Document History
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 87 of 88

6
2015-06-25
- Section 3.1 correct pad F19 Function description
7
2015-09-21
- APPLICABILITY TABLE 1 – adding LE920-CN, LE920-
NA AUTO S models. Added cs numbers per model.
- Section 1.4 Document Organization links fixed.
- Section 2.5 - Added cs numbers per model.
- Added section 2.5.4 – LE920-CN model bands.
- LE920-NA AUTO S added to section 2.5.3
- Section 2.6 - added sensitivity levels for TD-SCDMA & 4G
TDD.
- Section 3.1, 3.1.1, 15.4 – added ESIM_RST signal for
LE920-NA AUTO S model.
- Section 6.5 modified according to GPS active / passive
antenna configuration changes.
- Added section 15.3.2 – eSim schematic example.
- Section 10.4 LE920-EUA changed to LE920-EU
8
2016-02-02
- Section 3.1, 3.11 – Pad V2 GPS_LNA_EN functionality
declared to customer.
Pads G2, J2, L2, F3, H3, K3, E4, and AN14 must be routed
to TP for Telit debugging purpose.
- Section 2.5.3 - Changing B17 support to B12.
- Sections 6.1 , 6.4 – Adding B12 support to
GSM/WCDMA/LTE & Diversity Antenna requirements.
- Section 2.5.2 , 2.5.3 channels corrected for WCDMA B4.
- Section 5.2.1.3 – Battery recommendations updated.
- Section 15.1 – Recommended signals for debug updated.
- Section 15.2 – Recommended USB_VBUS decupling
capacitor value updated.
- Section 15.4 – EMC recommendations updated.
9
2016-03-29
- Adding section 2.7 Conformity assessment issues
LE920 Hardware User Guide
1vv0301026 Rev.8 2015-01-03
Reproduction forbidden without written authorization from Telit Communications S.p.A. - All Rights
Reserved. Page 88 of 88
 Loading...
Loading...