Page 1

Operator's
Manual
WaveSurfer 10
Oscilloscopes
Page 2

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes Operator's Manual
© 2014 Teledyne LeCroy, Inc. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized duplication of Teledyne LeCroy documentation materials other than for internal sales and
distribution purposes is strictly prohibited. However, clients are encouraged to distribute and duplicate
Teledyne LeCroy documentation for their own internal educational purposes.
WaveSurfer 10 and Teledyne LeCroy are trademarks of Teledyne LeCroy, Inc. Other product or brand names
are trademarks or requested trademarks of their respective holders. Information in this publication
supersedes all earlier versions. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
924609 Rev A
October 2014
Page 3

Operator's Manual
Contents
Safety Instructions 1
Symbols 1
Precautions 1
Operating Environment 2
Cooling 2
Power 2
Start Up 3
Carrying and Placing the Oscilloscope 3
Positioning the Feet 3
Powering On/Off 3
Software Activation 4
Front Input/Output Panel 4
Analog Inputs 5
Probes 5
Digital Inputs 5
Side Input/Output Panel 6
Connecting to Other Devices/Systems 7
Touch Screen 8
Menu Bar 8
Grid Area 9
Descriptor Boxes 10
Dialogs 12
Turning On/Off Traces 13
Annotating Traces 14
Entering/Selecting Data 15
Printing/Screen Capture 16
Oscilloscope Application Window 17
Language Selection 17
Screen Saver 17
Front Panel 18
Top Row Buttons 18
Trigger Controls 18
Horizontal Controls 19
Vertical Controls 19
Measure, Zoom, and Mem(ory) Buttons 19
Cursor Controls 19
Adjust 20
Zooming Waveforms 21
i
Page 4

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Creating Zooms 21
Zoom Controls 22
Vertical 24
Channel Settings 24
Probe Settings 25
Auto Setup 26
Restore Default Setup 26
Viewing Status 27
Timebase 28
Timebase Settings 28
Sampling Modes 29
History Mode 32
Trigger 34
Trigger Modes 34
Trigger Types 35
Setting UpTriggers 36
Trigger Holdoff 47
Display 49
Display Settings 49
Persistence 50
Cursors 52
Cursor Types 52
Cursor Settings 53
Measure 54
Set Up Measurements 54
List of Standard Measurements 56
Calculating Measurements 58
Math 60
Single vs. Dual Operator Functions 60
Set Up Math Function 61
List of Standard Operators 62
Advanced Debut Toolkit Math Functions 63
FFT 64
Averaging Waveforms 66
Enhanced Resolution 67
Rescaling and Assigning Units 70
Trend 72
Memory 73
Save Waveform to Memory 73
ii
Page 5

Operator's Manual
Save Waveform Files to Memory 73
Restore Memory 74
Analysis 75
WaveScan 75
Pass/Fail Testing 79
Utilities 82
Utilities 82
System Status 82
Remote Control Settings 83
Hardcopy (Print) Settings 85
Auxiliary Output Settings 88
Date/Time Settings 89
Options 89
Disk Utilities 90
Preferences Settings 91
Acquisition Settings 92
E-Mail 93
Miscellaneous Settings 94
Save/Recall 95
Save/Recall Setups 95
Save/Recall Waveforms 97
Save Table Data 100
LabNotebook 101
Create Notebook Entry 101
LabNotebook Drawing Toolbar 102
Manage Notebook Entries 103
Print to Notebook Entry 105
Flashback Recall 105
Manage Notebooks 106
Customize Reports 107
Configure LabNotebook Preferences 108
Maintenance 109
Cleaning 109
Calibration 109
Touch Screen Calibration 109
Reboot Oscilloscope 110
Adding an Option Key 110
X-Stream Firmware Update 111
System Recovery 112
Technical Support 114
iii
Page 6

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Returning a Product for Service 115
Certifications 117
EMC Compliance 117
Safety Compliance 118
Environmental Compliance 119
ISO Certification 119
Warranty 120
Windows License Agreement 120
iv
Page 7

Operator's Manual
Welcome
Thank you for purchasing a Teledyne LeCroy WaveSurfer Oscilloscope. We're certain you'll be pleased with
the detailed features unique to our instruments.
The manual is arranged in the following manner:
l Safety contains important precautions and information relating to power and cooling.
l The sections from Start Up through Maintenance cover everything you need to know about the
operation and care of the oscilloscope.
Documentation for software options is available from the Teledyne LeCroy website at teledynelecroy.com.
Our website maintains the most current product specifications and should be checked for frequent updates.
Remember...
When your product is delivered, verify that all items on the packing list or invoice copy have been shipped to
you. Contact your nearest Teledyne LeCroy customer service center or national distributor if anything is
missing or damaged. We can only be responsible for replacement if you contact us immediately.
Thank You
We truly hope you enjoy using Teledyne LeCroy's fine products.
Sincerely,
David C. Graef
Teledyne LeCroy
Vice President and Chief Technology Officer
v
Page 8

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
vi
Page 9
Operator's Manual
Safety Instructions
Observe these instructions to keep the instrument operating in a correct and safe condition. You are required
to follow generally accepted safety procedures in addition to the precautions specified in this section. The
overall safety of any system incorporating this instrument is the responsibility of the assembler of the
system.
Symbols
These symbols appear on the instrument's front and rear panels or in its documentation to alert you to
important safety considerations:
CAUTION of potential damage to instrument, or WARNING of potential bodily injury. Do not proceed
until the information is fully understood and conditions are met.
High voltage. Risk of electric shock or burn.
Ground connection.
Alternating current.
Standby power (front of instrument).
Precautions
Use only the proper power cord shipped with this instrument and certified for the country of use.
Maintain ground. This product is grounded through the power cord grounding conductor. To avoid electric
shock, connect only to a grounded mating outlet.
Connect and disconnect properly. Do not connect/disconnect probes or test leads while they are connected
to a voltage source.
Observe all terminal ratings. Do not apply a voltage to any input (C1-C4 or EXT) that exceeds the maximum
rating of that input. Refer to the front of the oscilloscope for maximum input ratings.
Use only within operational environment listed. Do not use in wet or explosive atmospheres.
Use indoors only.
Keep product surfaces clean and dry. See Cleaning in the Maintenance section.
Do not block the cooling vents. Leave a minimum six-inch (15 cm) gap between the instrument and the
nearest object. Keep the underside clear of papers and other objects.
Do not remove the covers or inside parts. Refer all maintenance to qualified service personnel.
1
Page 10

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Do not operate with suspected failures. Do not use the product if any part is damaged. Obviously incorrect
measurement behaviors (such as failure to calibrate) might indicate impairment due to hazardous live
electrical quantities. Cease operation immediately and sequester the instrument from inadvertent use.
Operating Environment
Temperature: 5 to 40° C.
Humidity: Maximum relative humidity 80 % for temperatures up to 31° C, decreasing linearly to 50% relative
humidity at 40° C.
Altitude: Up to 3,000 m at or below 25° C.
Cooling
The instrument relies on forced air cooling with internal fans and vents. Take care to avoid restricting the
airflow to any part. Around the sides and rear, leave a minimum of 15 cm (6 inches) between the instrument
and the nearest object. The feet provide adequate bottom clearance.
CAUTION. Do not block cooling vents. Always keep the area beneath the instrument clear of paper
and other items.
The instrument also has internal fan control circuitry that regulates the fan speed based on the ambient
temperature. This is performed automatically after start-up.
Power
AC Power
The instrument operates from a single-phase, 100-240 Vrms (± 10%) AC power source at 50/60 Hz (± 5%) or a
100-120 Vrms (± 10%) AC power source at 400 Hz (± 5%). Manual voltage selection is not required because
the instrument automatically adapts to the line voltage.
Power Consumption
Maximum power consumption with all accessories installed (e.g., active probes, USB peripherals) is 340 W
(340 VA). Power consumption in standby mode is 10 W.
Ground
The AC inlet ground is connected directly to the frame of the instrument. For adequate protection again
electric shock, connect to a mating outlet with a safety ground contact.
WARNING. Only use the power cord provided with your instrument. Interrupting the protective
conductor inside or outside the oscilloscope, or disconnecting the safety ground terminal, creates
a hazardous situation. Intentional interruption is prohibited.
2
Page 11

Operator's Manual
Start Up
Carrying and Placing the Oscilloscope
The oscilloscope’s case contains a built-in carrying handle. Lift the handle away from the oscilloscope body,
grasp firmly and lift the instrument. Always unplug the instrument from the power source before moving it.
Place the instrument where it will have a minimum 15 cm (6 inch) clearance from the nearest object. Be
sure there are no papers or other debris beneath the oscilloscope or blocking the cooling vents.
CAUTION. Do not place the instrument so that it is difficult to reach the power cord in case you
need to quickly disconnect from power.
Positioning the Feet
To tilt the body back slightly for easier bench top viewing, pull the small flaps on the
bottom of the feet away from the body of the oscilloscope.
Powering On/Off
Press the Power button at the lower, left front of the oscilloscope to switch on the instrument; press it
again to switch into Standby mode (reduced power). The oscilloscope application software loads
automatically when you use the Power button.
CAUTION. Do not change the instrument’s Windows® Power Options setting from the default Never
to System Standby or System Hibernate. Doing so can cause the system to fail.
CAUTION. Do not power on or calibrate the oscilloscope with a signal attached.
Always use the Power button or the File > Shutdown menu option to execute a proper shut down process and
preserve settings before powering down. Do not power off by pulling the power cord from the socket or
shutting off a connected power strip without first shutting down properly.
The Power button does not disconnect the oscilloscope from the AC power supply. The only way to fully
power down the instrument is to unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
We recommend unplugging the instrument if it will remain unused for a long period of time.
3
Page 12

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Software Activation
The oscilloscope operating software (firmware and standard applications) is active upon delivery. At powerup, the oscilloscope loads the software automatically.
Firmware
Free firmware updates are available periodically from the Teledyne LeCroy website at:
teledynelecroy.com/support/softwaredownload.
Registered users can receive an email notification when a new update is released. Follow the instructions
on the website to download and install the software.
Purchased Options
If you decide to purchase an option, you will receive a license key via email that activates the optional
features on the oscilloscope. See Adding an Option Key for instructions on activating optional software
packages.
Front Input/Output Panel
A. Power button.
B. Channel inputs 1-4 for analog signals.
C. EXT to input an external trigger.
D. Front-mounted host USB port for transferring data or connecting peripherals such as a mouse or
keyboard.
E. Ground and calibration output terminal used to compensate passive probes.
4
Page 13

Operator's Manual
Analog Inputs
A series of BNC connectors arranged on the front of the are used to input analog signal on Channels 1-4.
Channel connectors use the ProBus interface. The ProBus interface contains a 6-pin power and
communication connection and a BNC signal connection to the probe. It includes sense rings for detecting
passive probes and accepts a BNC cable connected directly to it. ProBus offers 50 Ω and 1 MΩ input
impedance and control for a wide range of probes.
The interfaces power probes and completely integrate the probe with the oscilloscope channel. Upon
connection, the probe type is recognized and some setup information, such as input coupling and
attenuation, is performed automatically. This information is displayed on the Probe Dialog, behind the
Channel (Cx) dialog. System (probe plus oscilloscope) gain settings are automatically calculated and
displayed based on the probe attenuation.
Probes
WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes are compatible with the included passive probes and all Teledyne LeCroy
ProBus active probes that are rated for the oscilloscope’s bandwidth. Probe specifications and
documentation are available at teledynelecroy.com/probes.
The passive probes supplied with your oscilloscope are matched to the input impedance of the instrument
but may need further compensation. Follow the directions in the probe instruction manual to compensate the
frequency response of the probes.
Digital Inputs
The WaveSurfer 10 is compatible with the MS-250 and MS-500 Mixed Signal hardware options for input of upto-36 lines of digital data. For instructions, see the product documentation available from
teledynelecroy.com.
5
Page 14
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
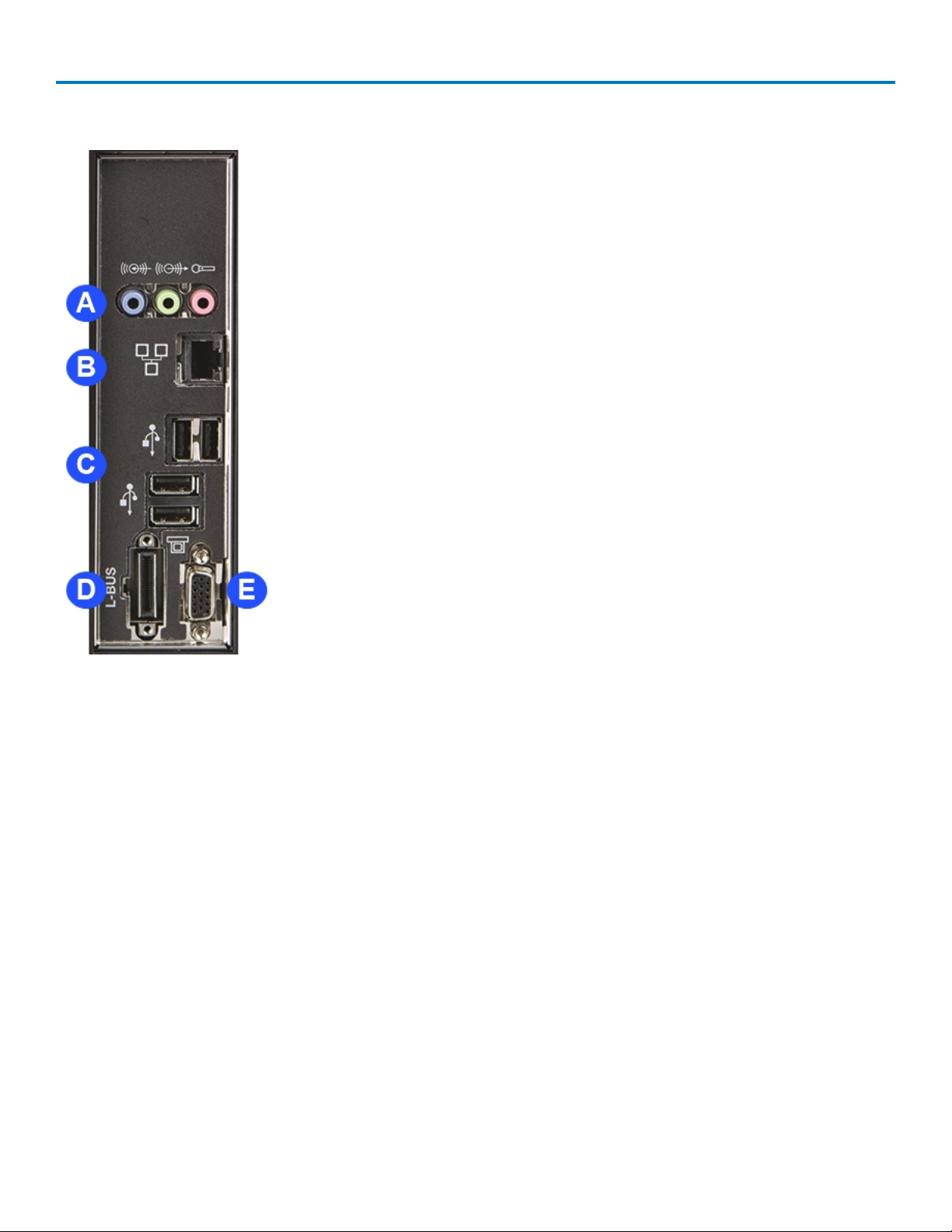
Side Input/Output Panel
A. Audio Input/Output Line-In, Speaker, and Mic jacks connect the
oscilloscope to external audio devices.
B. Ethernet Port connects the oscilloscope to networks.
C. USB Ports (4) allow you to connect external USB devices, such as
storage drives.
D. L-BUS connector interfaces the oscilloscope with the MS-250 or MS-500
external MSO module.
E. VGAconnector sends video output to external monitors.
6
Page 15

Operator's Manual
Connecting to Other Devices/Systems
Make all desired cable connections. After start up, configure the connections using the menu options listed
below. More detailed instructions are provided later in this manual.
POWER
Connect the line cord rated for your country to the AC power inlet on the back of the instrument, then plug it
into a grounded AC power outlet. (See Power and Ground Connections in General Safety Information.)
LAN
The instrument accepts DHCP network addressing. Connect a cable from the Ethernet port on the side panel
to a network access device.
To assign the oscilloscope a static IP address, go to Utilities > Utilities Setup > Remote and choose Net
Connections from the Remote dialog. Use the standard Windows networking dialogs to configure the device
address.
Go to Utilities > Preference Setup > Email to configure email settings.
USB PERIPHERALS
Connect the device to a USB port on the front or side of the instrument.
PRINTER
The oscilloscope supports USB printers compatible with the oscilloscope's Windows OS. Connect the printer
to any host USB port. Go to Utilities > Utilities Setup > Hardcopy to configure printer settings.
EXTERNAL MONITOR
Connect the monitor cable to the VGA output on the sideof the instrument. Minimize the oscilloscope
application and use the Windows controls to configure the display. Configure the oscilloscope as the primary
monitor and be sure to extend, not duplicate, the display.
EXTERNAL CONTROLLER
Connect a USB-A/B cable from the instrument to the controller, or connect both to the same network using
an Ethernet connection. Go to Utilities > Preference Setup > Remote to configure remote control.
OTHER AUXILIARY DEVICE
Connect a BNC cable from Aux Out on the back of the instrument to the other device. Go to Utilities >
Utilities Setup > Aux Output to configure the output.
7
Page 16
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Touch Screen
The touch screen is the principal viewing and control center of the oscilloscope. The entire display area is
active: use your finger or the stylus to touch, double-touch, touch-and-drag, or draw a selection box. Many
controls that display information also work as “buttons” to access other functions.
If you have a mouse installed, you can click anywhere you can touch to activate a control; in fact, you can
alternate between clicking and touching, whichever is convenient for you.
The touch screen is divided into the following major control groups:
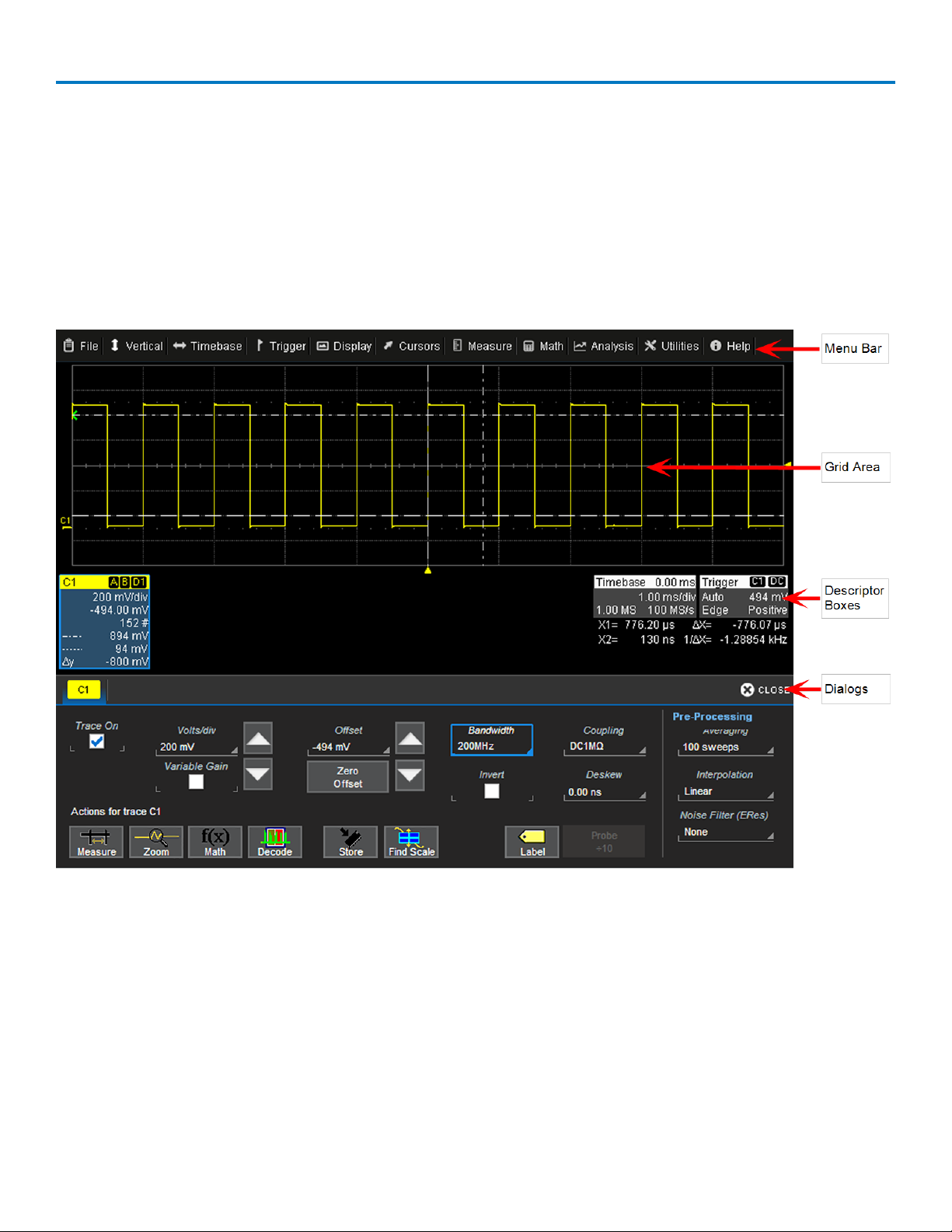
Menu Bar
The top of the window contains a complete menu of oscilloscope functions. Making a selection here
changes the dialogs displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Many common oscilloscope operations can also be performed from the front panel or launched via the
Descriptor Boxes. However, the menu bar is the best way to access dialogs for Save/Recall (File) functions,
Display functions, Status, LabNotebook, Pass/Fail setup, and Utilities/Preferences setup.
8
Page 17
Operator's Manual
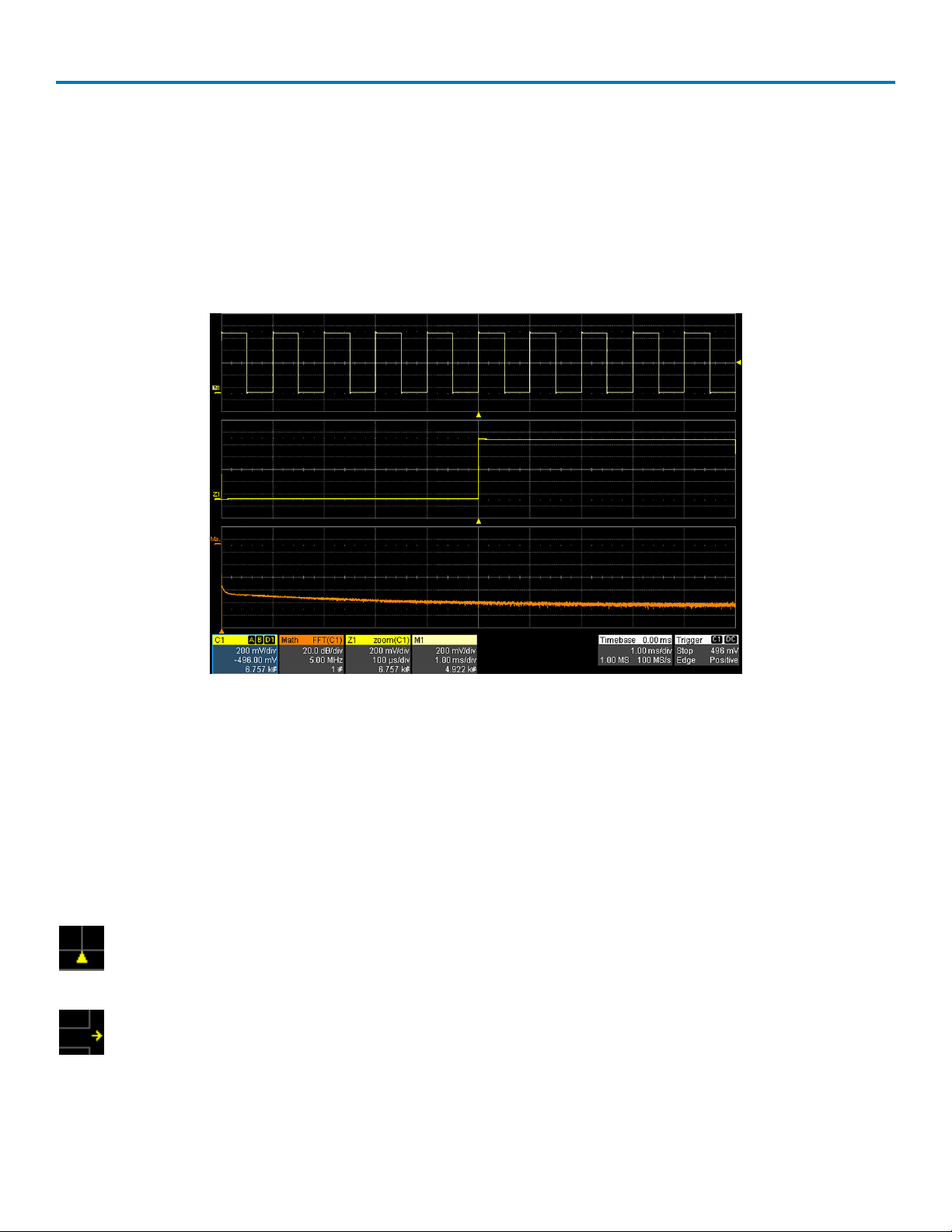
Grid Area
The grid area displays the waveform traces. Every grid is 8 Vertical divisions and 10 Horizontal divisions. The
value of Vertical and Horizontal divisions depends on the Vertical and Horizontal scale of the traces that
appear on the grid.
By default (Auto Grid mode), the grid area will automatically divide up to three times to display channel, zoom
and math traces on different grids. Regardless of the number of grids, every grid always shows the same
number of Vertical levels. Therefore, absolute Vertical measurement precision is maintained.
Different types of traces opening in a multi-grid display.
Adjusting Grid Brightness
You can adjust the brightness of the grid lines. Go to Display > Display Setup and enter a new Grid Intensity
percentage. The higher the number, the brighter and bolder the grid lines.
Grid Indicators
These indicators appear around or on the grid to mark important points on the display. They are matched to
the color of the trace to which they apply.
Trigger Position, a small triangle along the bottom (horizontal) edge of the grid, shows the time
the oscilloscope is set to trigger an acquisition. Unless Delay is set, this indicator is at the zero
(center) point of the grid. Trigger Delay is shown at the top right of the Timebase descriptor box.
Pre/Post-trigger Delay, a small arrow to the bottom left or right of the grid, indicates that a pre- or
post-trigger Delay has shifted the Trigger Position indicator to a point in time not displayed on the
grid. All trigger Delay values are shown on the Timebase Descriptor Box.
9
Page 18

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Trigger Level at the right edge of the grid tracks the trigger voltage level. If you change the trigger
level when in Stop trigger mode, or in Normal or Single mode without a valid trigger, a hollow
triangle of the same color appears at the new trigger level. The trigger level indicator is not shown
if the triggering channel is not displayed.
Zero Volts Level is located at the left edge of the grid. One appears for each open trace on the
grid, sharing the number and color of the trace.
Various Cursor lines appear over the grid to indicate specific voltage and time values on the
waveform. Touch-and-drag cursor indicators to quickly reposition them.
Grid Context Menu
Quickly touch a trace, or touch-and-hold the trace descriptor box, to open a pop-up menu
with various actions such as turning on/off the trace, placing a label, or applying math
and measurements.
Descriptor Boxes
Trace descriptor boxes appear just beneath the grid whenever a trace is turned on. They function to:
l Inform—descriptors summarize the current trace settings and its activity status.
l Navigate—touch the descriptor box once to activate the trace; the box will be highlighted. Touch it a
second time to open the trace setup dialog.
Besides trace descriptor boxes, there are also Timebase and Trigger descriptor boxes summarizing the
acquisition settings shared by all channels, which also open the corresponding setup dialogs.
Channel Descriptor Box
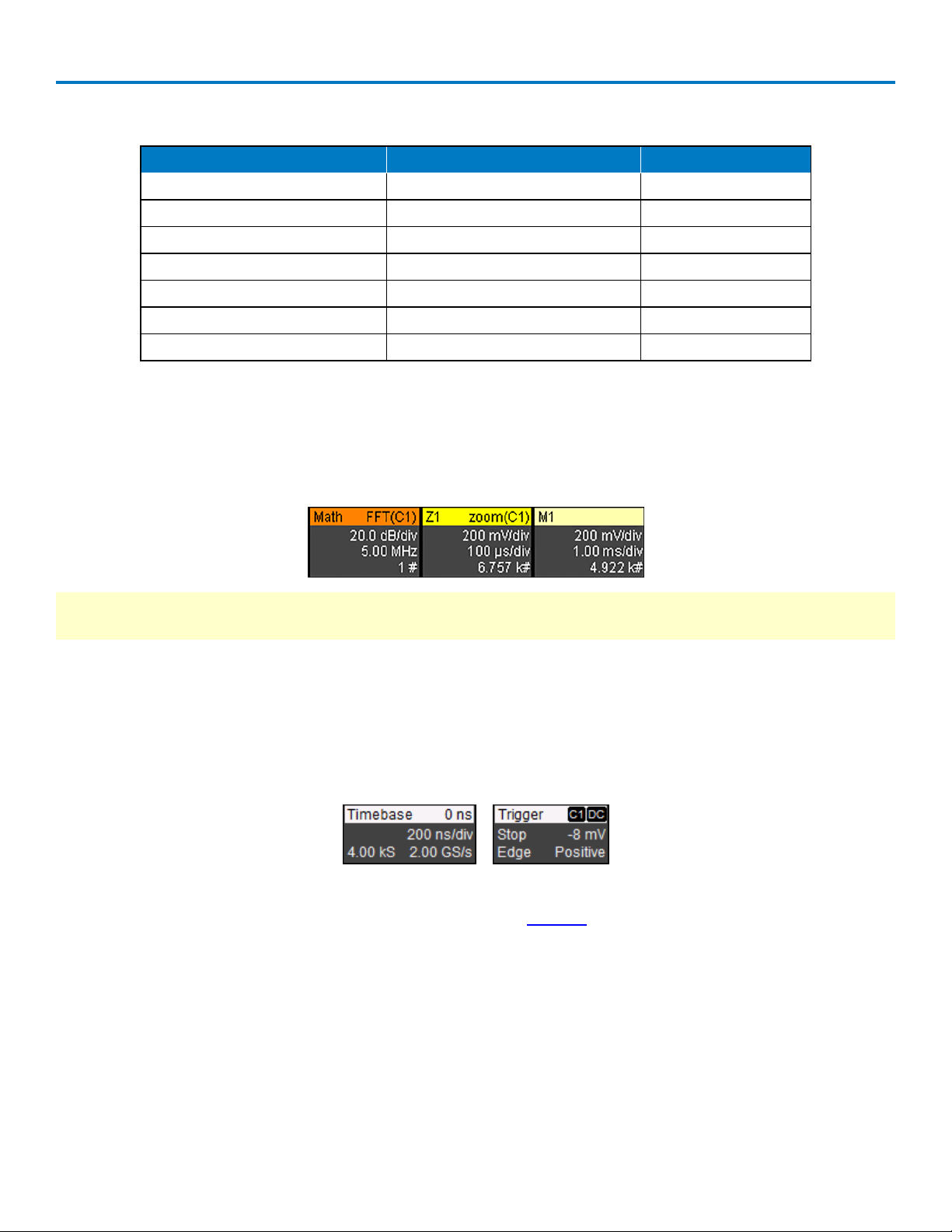
Channel trace descriptor boxes correspond to analog signal inputs. They show (clockwise
from top left): Channel Number, Pre-Processing List, Coupling, Gain Setting, Offset Setting,
Sweeps Count (when Averaging), and Vertical Cursor positions. Codes are used to indicate
pre-processing that has been applied to the input. The short form is used when several
processes are in effect.
10
Page 19
Operator's Manual
Preprocessing Symbols on Descriptor Boxes
Pre-Processing Type Long Form Short Form
Sin X Interpolation SINX S
Averaging AVG A
Inversion INV I
Deskew DSQ DQ
Coupling DC50, DC1M or AC1M D50, D1, or A1
Ground GND G
Bandwidth Limiting BWL B
Other Trace Descriptor Boxes
Similar descriptor boxes appear for math, zoom (Zx), and memory (Mx) traces. These descriptor boxes show
any Horizontal scaling that differs from the signal Timebase. Units will be automatically adjusted for the
type of trace.
NOTE: On WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed, there will be two math functions,
labeled F1 and F2 on the descriptor boxes and on the Math setup dialogs.
Timebase and Trigger Descriptor Box
The Timebase descriptor box shows: (clockwise from top right) Trigger Delay (position), Time/div, Sample
Rate, Number of Samples, and Sampling Mode (blank when in real-time mode).
Trigger descriptor box shows: (clockwise from top right) Trigger Source and Coupling, Trigger Level (V),
Slope, Trigger Type, Trigger Mode.
Setup information for Horizontal cursors, including the time between cursors and the frequency, is shown
beneath the TimeBase and Trigger descriptor boxes. See the Cursors section for more information.
11
Page 20
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
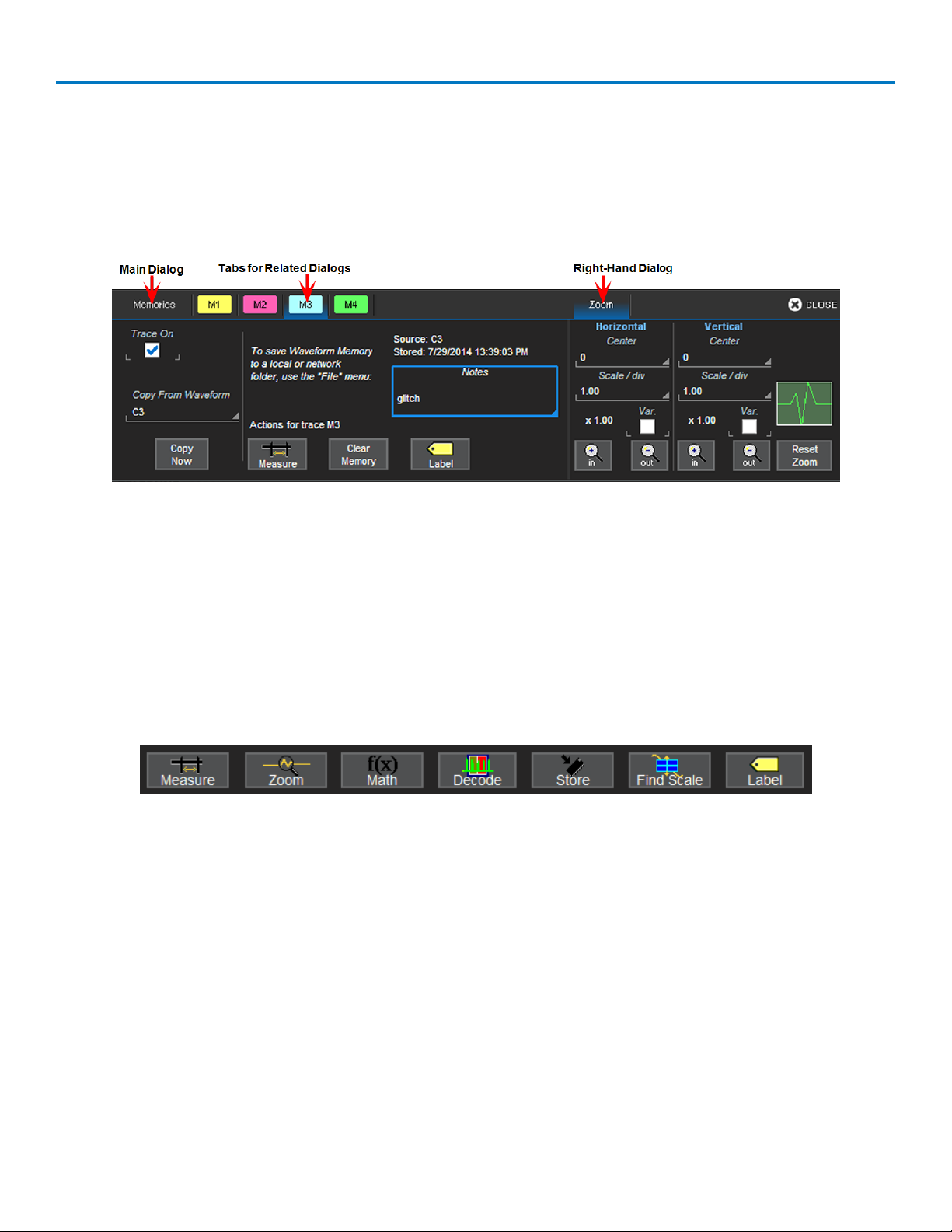
Dialogs
Dialogs appear at the bottom of the display for entering setup data. The top dialog will be the main entry
point for the selected setup option. For convenience, related dialogs appear as a series of tabs behind the
main dialog. Touch the tab to open the dialog.
Right-Hand Dialogs
At times, your selections will require more settings than normally appear (or can fit) on a dialog, or the task
commonly invites further action, such as zooming a new trace. In that case, sub-dialogs will appear to the
right-side of the main dialog. These right-hand dialog settings always apply to the object that is being
configured on the left-hand dialog.
Action Toolbar
Several setup dialogs contain a toolbar at the bottom of the dialog. These buttons apply common actions
without having to leave the underlying set up dialog. They always apply to the active trace.
Measure opens the Measure pop-up to set measurement parameters on the active trace.
Zoom creates a zoom trace of the active trace.
Math opens the Math pop-up to apply math functions to the active trace and create a new math trace.
Decode opens the main Serial Decode dialog where serial data decoders can be configured and applied. This
button is only active if you have decoder software options installed.
Store loads the active trace into the corresponding memory location (C1, F1 and Z1 to M1; C2, F2 and Z2 to
M2, etc.).
Find Scale automatically performs a vertical scaling that fits the waveform into the grid.
Label opens the Label pop-up to annotate the active trace.
12
Page 21

Operator's Manual
Turning On/Off Traces
Analog Traces
From the menu bar, choose Vertical > Channel <#> Setup to turn on the trace. To turn it off, clear the Trace
On checkbox on the corresponding Channel dialog, or touch-and-hold (right-click) on the descriptor box and
choose Off.
From the front panel, press the Channel button (1-4) to turn on the trace; press again to turn it off.
NOTE: The default is to display each trace type in its own grid (e.g., Channels together, Zooms together, etc.).
Use the Display menu to change how traces are arranged.
Other Traces
Quickly create zoom or math traces by touching the Zoom or Math action toolbar button.
Activate Trace
Although several traces may be open and appear on the grid, only one at a time is active. Touch the trace
descriptor box to activate the trace. A highlighted descriptor box indicates the trace is active. All actions now
apply to that trace until you activate another.
Active trace descriptor (left), inactive trace descriptor (right).
Whenever you activate a trace, the dialog at the bottom of the screen automatically switches to the
appropriate setup dialog. The tab at the top of the dialog shows to which trace it belongs.
Channel descriptor label matches Channel dialog tab.
13
Page 22
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Annotating Traces
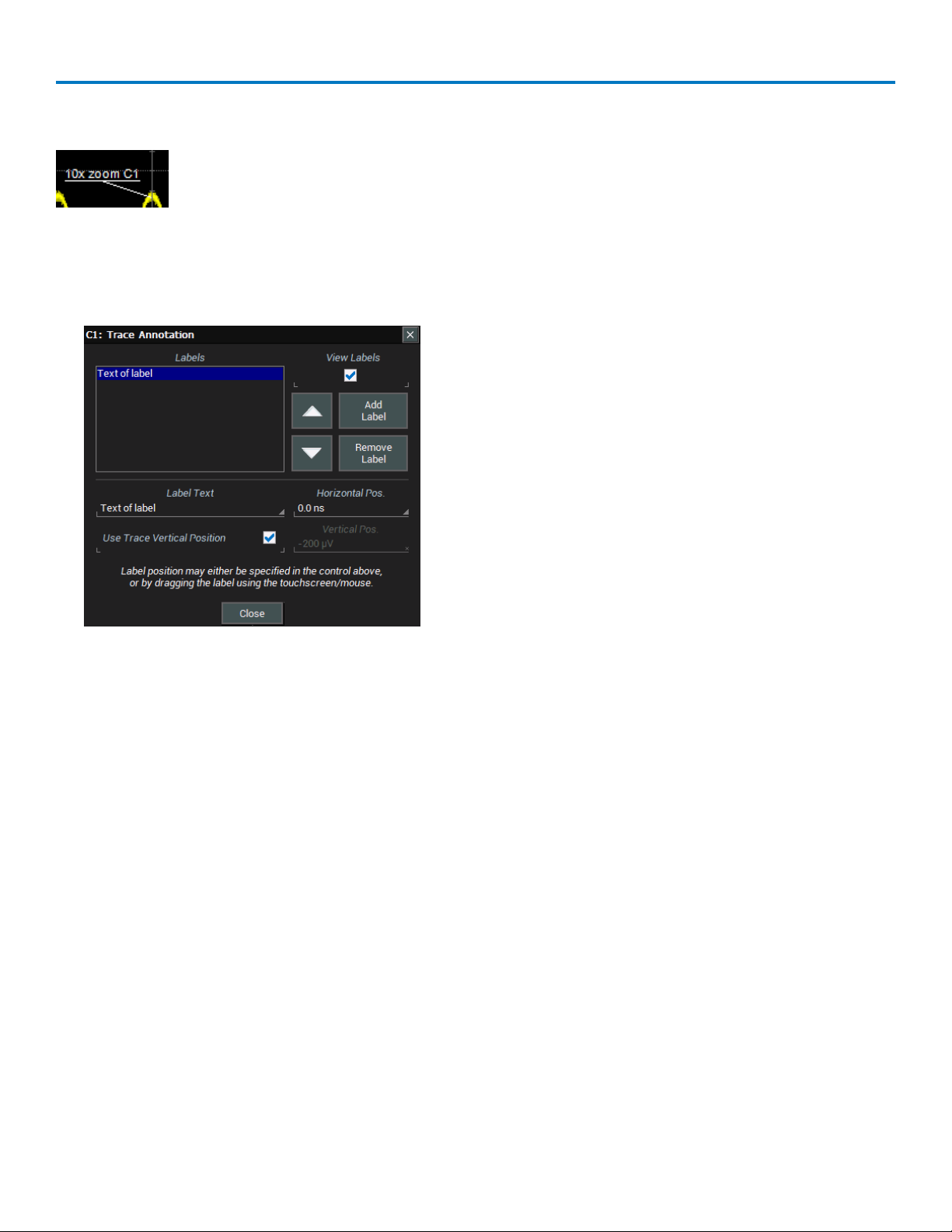
The Label function gives you the ability to add custom annotations to traces that are shown
on the display. Labels are numbered sequentially in the order they were created. Once
placed, labels can be moved to new positions or turned off.
Create Label
1. Touch the trace and choose Set label... from the context menu, or touch the trace descriptor box twice
and touch the Label toolbar button on the setup dialog.
2. On the Trace Annotation pop-up, touch Add Label.
3. Enter the Label Text.
4. Optionally, enter the Horizontal Pos. and Vertical Pos. (in same units as the trace) at which to place the
label. The default position is 0 ns horizontal. You can optionally check Use Trace Vertical Position
instead of entering a Vertical Pos.
Reposition Label
Once placed, drag-and-drop labels to a new position on the grid, or reopen the Trace Annotation pop-up and
enter a new Horizontal Pos. and Vertical Pos.
Edit/Remove Label
Open the Trace Annotation pop-up and select the Label. You can use the Up/Down arrow keys to scroll the
list. Change the Label Text or Horizontal and Vertical Pos.(itions). Touch Remove Label to delete it.
Turn On/Off Labels
After labels have been placed, you can turn on/off all labels at once by opening the Trace Annotation dialog
and selecting/deselecting the View labels checkbox.
14
Page 23
Entering/Selecting Data
Touch
Touch once to activate a control. In some cases, you’ll immediately see a pop-up menu of
options. Touch one to select it.
TIP: You can touch the Icon or List buttons where they appear on larger
pop-ups to change how menu options are displayed.
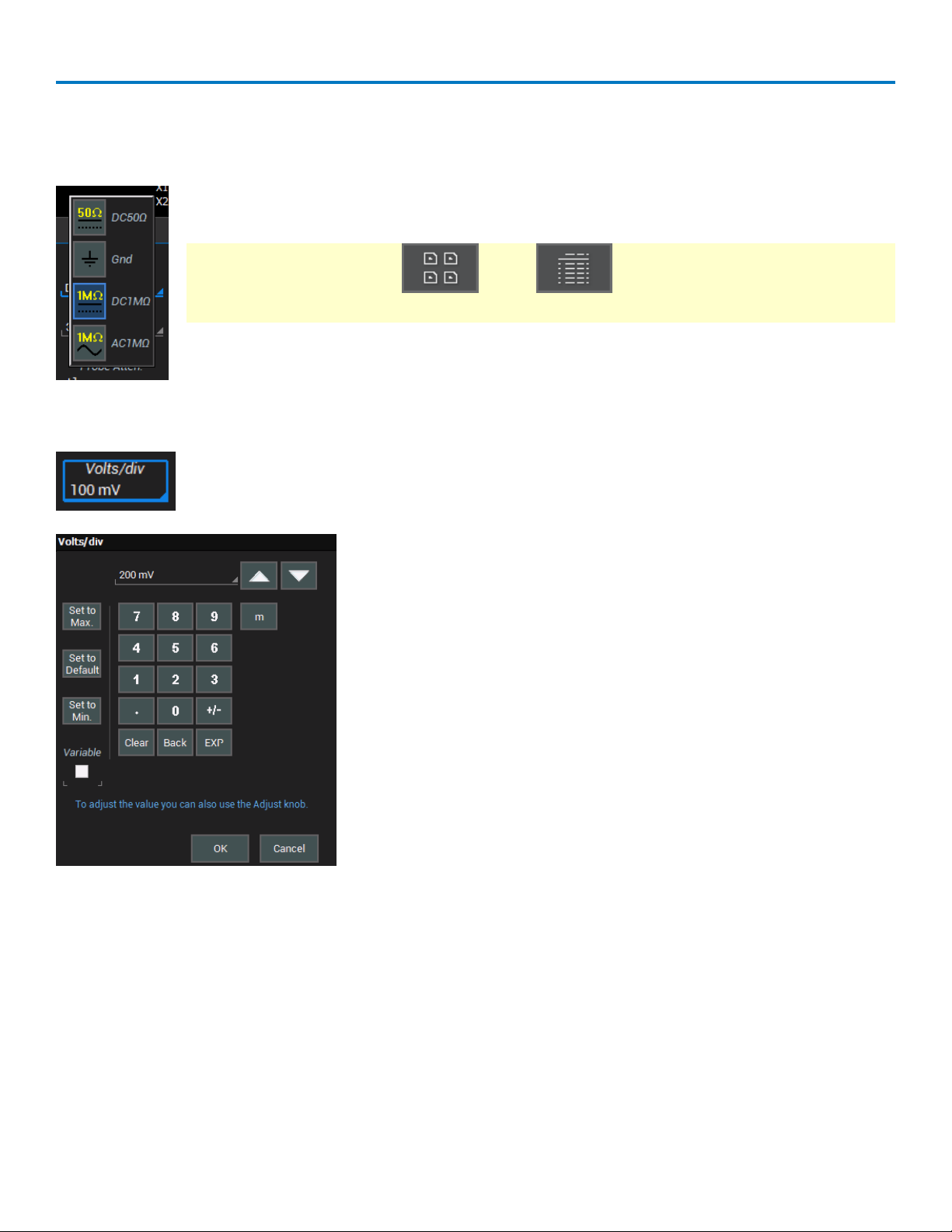
Touch & Type
In other cases, data entry fields appear highlighted in blue when you touch them. When a
data entry field is highlighted, it is active and can be modified by using the front panel
Adjust knob. Or, touch it again and use the pop-up menu or keypad to make an entry.
Operator's Manual
You’ll see a pop-up keypad when you touch twice on a numerical data
entry field. Use it exactly as you would a calculator. When you touch
OK, the calculated value is entered in the field.
The Set to... buttons quickly enter the maximum, default or minimum
value for that field.
The Up and Down arrow buttons increment/decrement the displayed
value.
The Variable checkbox allows you to make fine increment changes
when using the Up and Down arrow buttons.
15
Page 24
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Touch & Drag
Touch-and-drag cursor lines and annotation labels to
reposition them on the grid; this is the same as setting the
values on the dialog.
Touch-and-drag to draw a selection box around part of a trace
to quickly zoom that portion.
Printing/Screen Capture
The Print function captures an image of the display and outputs it according to your Hardcopy settings.
There are three ways to print a capture of the screen:
l Touch the front panel Print button.
l Choose File > Print.
l Choose Utilities > Utilities Setup > Hardcopy tab and touch the Print button to the far right of the
dialog.
NOTE: When the front panel Print button is configured to capture the screen as a LabNotebook entry, only the
File and Utilities menu print options will function according to your Hardcopy setup.
16
Page 25

Operator's Manual
Oscilloscope Application Window
The oscilloscope application runs on a Windows operating system and functions exactly as do other
Windows applications.
To minimize the application window and show the Windows desktop, choose File > Minimize. To restore the
window after minimizing, touch the oscilloscope display icon in the lower right corner of the desktop.
To exit the application window, choose File > Exit. When you exit the application, the oscilloscope operating
system continues to run. To reload the application after exiting, touch the Start DSO desktop shortcut.
Language Selection
To change the language that appears on the touch screen:
1. Go to Utilities > Preference Setup > Preferences and make your Language selection.
2. Follow the prompt to restart the oscilloscope application.
To also change the language of the Windows operating system dialogs:
1. Choose File > Minimize to hide the oscilloscope display and show the Windows Desktop.
2. From the Windows task bar, choose Start > Control Panel > Clock, Language and Region.
3. Under Region and Language select Change Display Language.
4. Touch the Install/Uninstall Languages button.
5. Select Install Language and Browse Computer or Network.
6. Touch the Browse button, navigate to D:\Lang Packs\ and select the language you want to install. The
available languages are: German, Spanish, French, Italian, and Japanese. Follow the installer prompts.
NOTE: Other language packs are available from Microsoft’s website.
7. Reboot the oscilloscope after changing the language.
Screen Saver
As on any Windows PC, a screen saver can be enabled to begin after a preset idle time, or disabled:
1. Minimize the oscilloscope application by choosing File > Minimize from the menu bar.
2. Open the Windows ControlPanel to change Appearance and Personalization settings.
3. Touch the oscilloscope icon at the bottom right of the desktop to restore the instrument display.
17
Page 26
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Front Panel
Most front panel controls duplicate functionality available through the
touch screen display and are described on the following pages.
Many knobs on the front panel function one way if turned and another
if pushed like a button. When a knob is multi-plexed, the top label
describes the knob’s “turn” action, the bottom label its “push” action.
Front panel buttons light up to indicate which traces and functions are
active. Actions performed from the front panel always apply to the
active trace.
Top Row Buttons
Auto Setup performs an Auto Setup. After the first press, you will be
prompted for a confirmation. Press the button again or use the touch
screen to confirm.
Clear Sweeps resets the acquisition counter and any cumulative
measurements.
Print captures the entire screen and outputs it according to your
Hardcopy settings. It can also be configured to output a LabNotebook
entry.
When you push the Intensity knob, the oscilloscope switches into
WaveStream acquisition mode. The WaveStream indicator lights to
show it is on.
Trigger Controls
Level knob changes the trigger threshold level (V). The number is
shown on the Trigger descriptor box. Pushing the knob sets the trigger level to the 50% point of the input
signal.
READY indicator lights when the trigger is armed. TRIG'D is lit momentarily when a trigger occurs. A fast
trigger rate causes the light to stay lit continuously.
Setup corresponds to the menu selection Trigger > Trigger Setup. Press it once to open the Trigger Setup
dialog and again to close the dialog.
Auto sets Auto trigger mode, which triggers the oscilloscope after a time-out, even if the trigger conditions
are not met.
Normal sets Normal trigger mode, which triggers the oscilloscope each time a signal is present that meets
the conditions set for the type of trigger selected.
18
Page 27

Operator's Manual
Single sets Single trigger mode, which arms the oscilloscope to trigger once (single-shot acquisition) when
the input signal meets the trigger conditions set for the type of trigger selected. If the scope is already
armed, it will force a trigger.
Stop prevents the oscilloscope from triggering on a signal. If you boot up the instrument with the trigger in
Stop mode, a "No trace available" message is shown. Press the Auto button to display a trace.
Horizontal Controls
The Delay knob changes the Trigger Delay value (S) when turned. Push the knob to reset Delay to zero.
The Horizontal Adjust knob sets the Time/division (S) of the oscilloscope acquisition system when the trace
source is an input channel. The Time/div value is shown on the Timebase descriptor box. When using this
control, the oscilloscope allocates memory as needed to maintain the highest sample rate possible for the
timebase setting. When the trace is a zoom, memory or math function, turn the knob to change the horizontal
scale of the trace, effectively "zooming" in or out. By default, the knob adjusts values in 1, 2, 5, 10 step
increments. Push the knob to change the action to fine increments; push it again to return to stepped
increments.
Vertical Controls
Channel buttons turn on a channel that is off, or activate a channel that is already on. When the channel is
active, pushing its channel button turns it off. A lit button shows the active channel.
Offset knob adjusts the zero level of the trace (this makes it appear to move up or down relative to the
center axis of the grid). The value appears on the trace descriptor box. Push it to reset Offset to zero.
Gain knob sets Vertical Gain (V/div). The value appears on the trace descriptor box. By default, the knob
adjusts values in 1, 2, 5, 10 step increments. Push the knob to change the action to fine increments; push it
again to return to stepped increments.
Measure, Zoom, and Mem(ory) Buttons
The Zoom button creates a quick zoom for each open channel trace. Touch the zoom trace descriptor box to
display the zoom controls.
The Measure and Mem(ory) buttons open the corresponding setup dialogs.
Cursor Controls
Cursors identify specific voltage and time values on the waveform. The white cursor lines help make these
points more visible, while a readout of the values appears on the trace descriptor box. There are three preset
cursor types, each with a unique appearance on the display. These are described in more detail in the
Cursors section.
Type selects the cursor type. Continue pressing to cycle through all cursor types until the desired type is
found. The type "no cursors" turns off the cursor display.
19
Page 28

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Cursor knobs reposition the selected cursor line when turned. Each knob controls one line. Push the knob
resets the cursor to the default position. When both Horizontal and Vertical cursors are displayed, each knob
controls two lines, and pushing the knob switches the line that is being controlled.
Adjust
The Adjust knob changes the value in any highlighted data entry field when turned. Pushing the Adjust knob
toggles between coarse (large increment) or fine (small increment) adjustments when the knob is turned.
The Touch Screen button enables/disables the touch screen controls.
20
Page 29
Operator's Manual
Zooming Waveforms
The Zoom function magnifies a selected region of a trace. On WaveSurfer 10 model oscilloscopes, you can
display up to four zoom traces (Z1-Z4) taken from any channel, math, or memory trace.
Creating Zooms
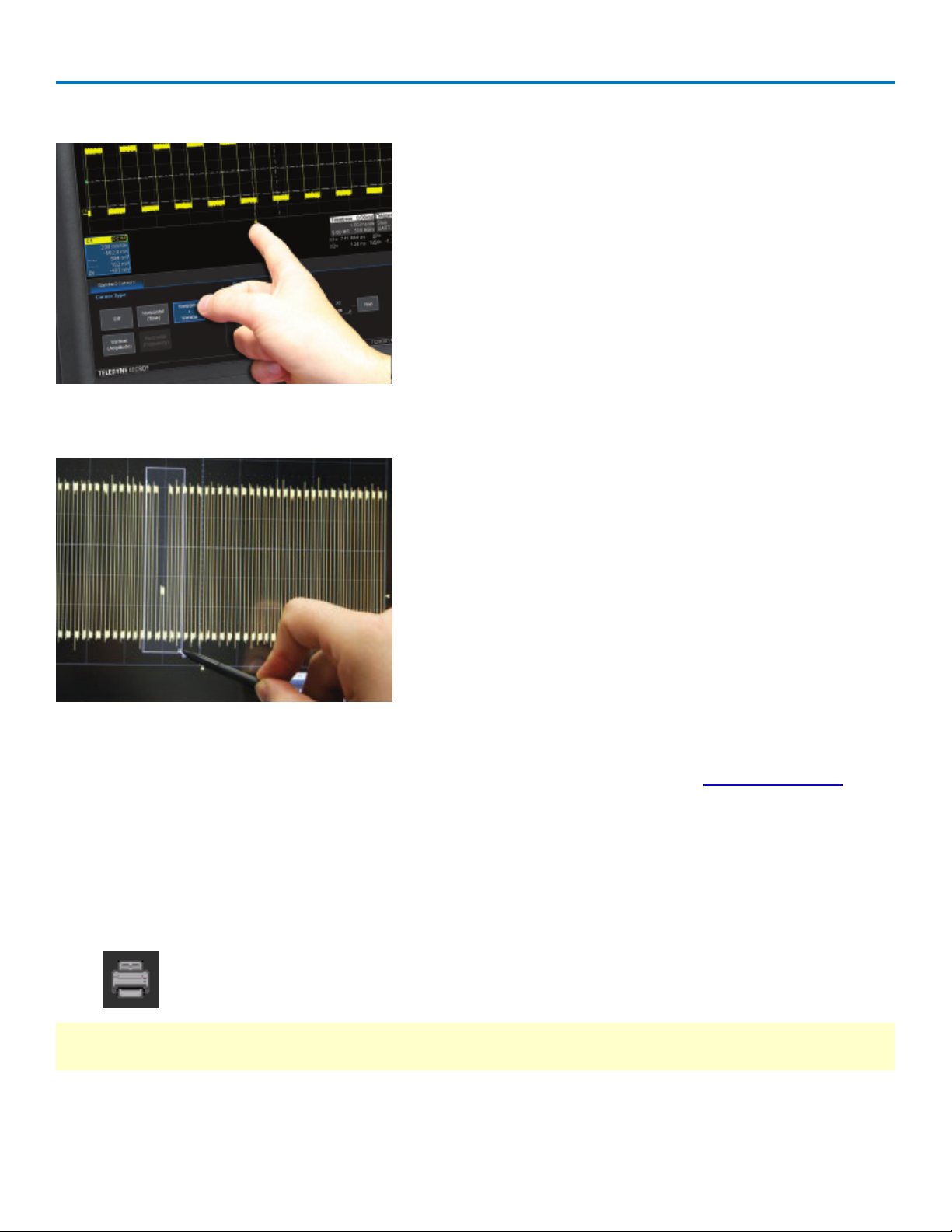
To create a zoom, touch -and-drag to draw a selection box around any part of the source waveform.
Selection box over trace.
The zoom will resize the selected portion to fit the full width of the grid. The degree of vertical and horizontal
magnification, therefore, depends on the size of the rectangle that you draw.
The zoom opens in a new grid, with the zoomed portion of the source trace highlighted. New zooms are
turned on and visible by default. However, you can turn off a particular zoom if the display becomes too
crowded, and the zoom settings are saved in its Zx location, ready to be turned on again when desired.
21
Page 30
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Adjust Zoom
The zoom's Horizontal units will differ from the signal timebase because the zoom is showing a calculated
scale, not a measured level. This allows you to adjust the zoom factor using the front panel knobs or the
Zoom dialog controls however you like without affecting the timebase (a characteristic shared with math
and memory traces).
Turn off Zoom
To close the zoom, either touch the zoom descriptor box twice to open the Zoom dialog and deselect Trace
On, or touch the zoom trace to open the context menu and choose Off.
Zoom Controls
To open the Zoom dialog, touch twice on any zoom descriptor box, or choose Math > Zoom Setup from the
menu bar.
Trace Controls
Trace On shows/hides the zoom trace. It is selected by default when the zoom is created.
Source lets you change the source for this zoom to any channel, math, or memory trace while maintaining all
other settings.
Segment Controls
These controls are used in Sequence Sampling Mode. They are only displayed on WaveSurfer 10
oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
Zoom Factor Controls
These controls on the Zx dialogs appear throughout the oscilloscope software:
l Out and In buttons increase or decrease the magnification of the zoom, and consequently change the
Horizontal andVertical Scale settings. Continue to touch either button until you've achieved the desired
level of zoom.
22
Page 31

Operator's Manual
l Var. checkbox enables variable zooming in increments finer than the default 1, 2, 5, 10 step
increments. When checked, each touch of the zoom control buttons changes the degree of
magnification by a single increment.
l Horizontal Scale/div sets the amount of time represented by each horizontal division of the grid. It is
the equivalent of Time/div, only unlike the Timebase setting, it may be set differently for each zoom,
math function, or memory trace.
l Vertical Scale/div sets the voltage level represented by each vertical division of the grid; it's the
equivalent of V/div used for channel settings.
l Horizontal/Vertical Center sets the voltage or time that is to be at the center of the screen on the zoom
trace. The horizontal center is the same for all zoom traces.
l Reset Zoom returns the zoom to x1 magnification.
23
Page 32

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Vertical
Vertical, also called Channel, settings usually relate to voltage level and control the trace along the Y axis.
The amount of voltage displayed by one vertical division of the grid, or Vertical Scale (V/div), is most quickly
adjusted by using the front panel Vertical knob. The Channel descriptor box always shows the current
Vertical Scale setting.
Vertical settings are made on the Channel dialog, labeled Cx after the corresponding channel. To access the
Channel dialog, choose Vertical > Channel <#> Setup from the menu bar, or touch the Channel descriptor box.
The Cx dialog contains:
l Channel Settings for scale, offset, coupling, bandwidth, and probe attenuation.
l Pre-Processing Settings to set up pre-acquisition processes that will affect the waveform, such as
noise filtering and interpolation.
If a Teledyne LeCroy probe is connected to the channel, a Probe dialog appears behind the Cx dialog.
Channel Settings
Volts/div sets the vertical scale (aka gain or sensitivity). Select Variable Gain adjustment or leave the
checkbox clear for fixed adjustment.
Offset adds a defined value of DC offset to the signal as acquired by the input channel. This may helpful in
order to display a signal on the oscilloscope grid while maximizing the vertical height (or gain) of the signal.
A negative value of offset will "subtract" a DC voltage value from the acquired signal (and move the trace
down on the grid") whereas a positive value will do the opposite. Touch Zero Offset to return to zero.
A variety of Bandwidth filters are available at a variety of fixed settings. The exact settings vary by model. To
limit bandwidth, select a filter from this field.
Invert inverts the waveform for the selected channel.
Coupling may be set to DC 50 Ω, DC1M, AC1M or GROUND (Gnd).
CAUTION. The maximum input voltage depends on the input used. Limits are displayed on the front
of the oscilloscope. Whenever the voltage exceeds this limit, the coupling mode automatically
24
Page 33

Operator's Manual
switches to GROUND. You then have to manually reset the coupling to its previous state. While the
unit does provide this protection, damage can still occur if extreme voltages are applied.
Deskew adjusts the amount of horizontal time offset to compensate for propagation delays caused by
different probes or cable lengths. The valid range depends on the current timebase setting. The Math
deskew function performs the same activity.
Probe Settings
When a Teledyne LeCroy-compatible probe is connected to the oscilloscope input, the probe is automatically
identified and the model name displayed on the Channel dialog under the "Probe" heading. Also, the Probe
dialog bearing the probe name is added to the right of the Channel dialog. When a probe is not connected, the
Channel dialog shows only the Cx tab for vertical setup.
When third-party probes are connected, an Attenuation field appears on the Cx dialog, with a default value of
/1, allowing you to enter attenuation and rescale values manually.
Channel dialog with tab for connected probe.
The Probe Dialog displays probe attributes and (depending on the probe type) allows you to AutoZero or
DeGauss probes from the oscilloscope touch screen. Other settings may appear, as well, depending on the
probe model.
Probe dialog showing the connected probe's control attributes.
25
Page 34

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Auto Zero Probe
Auto Zero corrects for DC offset drifts that naturally occur from thermal effects in the amplifier of active
probes. Teledyne LeCroy probes incorporate Auto Zero capability to remove the DC offset from the probe's
amplifier output to improve the measurement accuracy.
CAUTION. Remove the probe from the circuit under test before initializing AutoZero.
DeGauss Probe
The Degauss control is activated for some types of probes (e.g., current probes). Degaussing eliminates
residual magnetization from the probe core caused by external magnetic fields or by excessive input. It is
recommended to always degauss probes prior to taking a measurement.
CAUTION. Remove the probe from the circuit under test before initializing DeGauss.
Auto Setup
Auto Setup quickly configures the essential oscilloscope settings based on the first input signal it finds,
starting with Channel 1. If nothing is connected to Channel 1, it searches Channel 2 and so forth until it finds
a signal. Vertical Scale (V/div), Offset, Timebase (Time/div), and Trigger are set to an Edge trigger on the
first, non-zero-level amplitude, with the entire waveform visible for at least 10 cycles over 10 horizontal
divisions.
To run Auto Setup:
1. Either press the Auto Setup button on the front panel, or choose Auto Setup from the Vertical, Timebase,
or Trigger menus. All these options perform the same function.
2. Press the Auto Setup button again or use the touch screen display to confirm Auto Setup.
Restore Default Setup
Restore the oscilloscope to its factory default state by pressing the front panel Default Setup button. You
can also restore default settings by choosing File > Recall Setup > Recall Default.
Default settings for your oscilloscope include the following:
Channel/Vertical C1-C2 on at 50 mV/div Scale, 0 V Offset
Timebase Real Time Sampling at 50 ns/div, 0 Delay, 2.0 kS at 4 GS/s, 100 kS Memory
Trigger C1 with an Auto Positive Edge, DC Coupling, 0 V Level
Display Auto Grid
Cursors Off
Measurements Cleared
Math Cleared
26
Page 35

Operator's Manual
Viewing Status
All oscilloscope settings can be viewed through the various Status dialogs. These show all existing
acquisition, trigger, channel, math function, measurement and parameter configurations, as well as which
are currently active.
Access the Status dialogs by choosing the Status option from the Vertical, Timebase, Math menus (e.g.,
Channel Status, Acquisition Status).
27
Page 36

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Timebase
Timebase, also known as Horizontal, settings control the trace along the X axis. The timebase is shared by
all channels.
The time represented by each horizontal division of the grid, or Time/Division, is most easily adjusted using
the front panel Horizontal knob. Full Timebase set up, including sampling mode selection, is done on the
Timebase dialog, which can be accessed by either choosing Timebase > Horizontal Setup from the menu bar,
or touching the Timebase descriptor box.
The Timebase dialog contains settings for Sampling Mode, Timebase Mode, Real Time Memory, and Active
Channels.
Timebase Settings
Sampling Mode
Choose fromWaveStream, Real Time, Sequence,RIS, orRoll mode.
NOTE: Sequence mode available only on oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
Timebase Mode
Time/Division is the time represented by one horizontal division of the grid. Touch the Up/Down Arrow
buttons on the Timebase dialog or turn the front panel Horizontal knob to adjust this value.
Delay is the amount of time relative to the trigger event to display on the grid. In Real Time sampling mode,
the trigger event is placed at time zero on the grid. Delay may be time pre-trigger, entered as a negative
value, or post-trigger, entered as a positive value. Raising/lowering the Delay value has the effect of shifting
the trace to the right/left, enabling you to focus on the relevant portion of longer acquisitions.
Set to Zero returns Delay to zero.
Real Time Memory
Max. Sample Points is the maximum number of samples taken per acquisition. The actual number of
samples acquired can be lower due to the current Sample Rate and Time/Division settings.
28
Page 37
Operator's Manual
Active Channels
These settings enable you to control the distribution of memory to achieve longer acquisitions through a
single channel if needed.
4 (or 2 in 2 channel scopes) utilizes the per channel maximum memory (10 Mpts/ch standard, 16 Mpts/ch
with the WS10-ADT option).
2 (or 1 in 2 channel scopes) distributes the total maximum memory across only two channels (20 Mpts/ch
standard, 32 Mpts/ch with the WS10-ADT option) . Channels 2 and 3 (in 4 channel scopes) and Channel 2 (in
2 channel scopes) are available for use.
Auto allows the scope to make this decision based on which channels are currently in use.
Sampling Modes
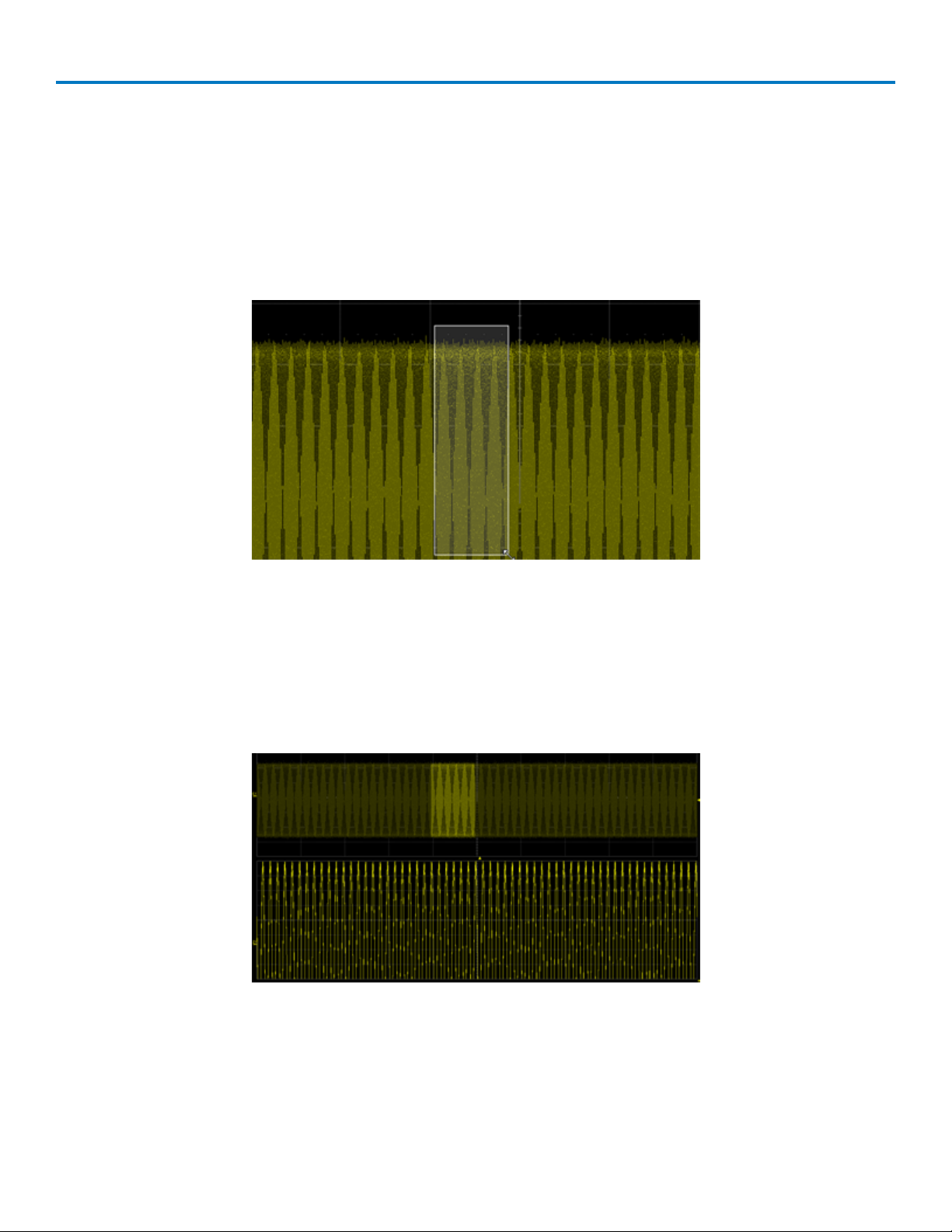
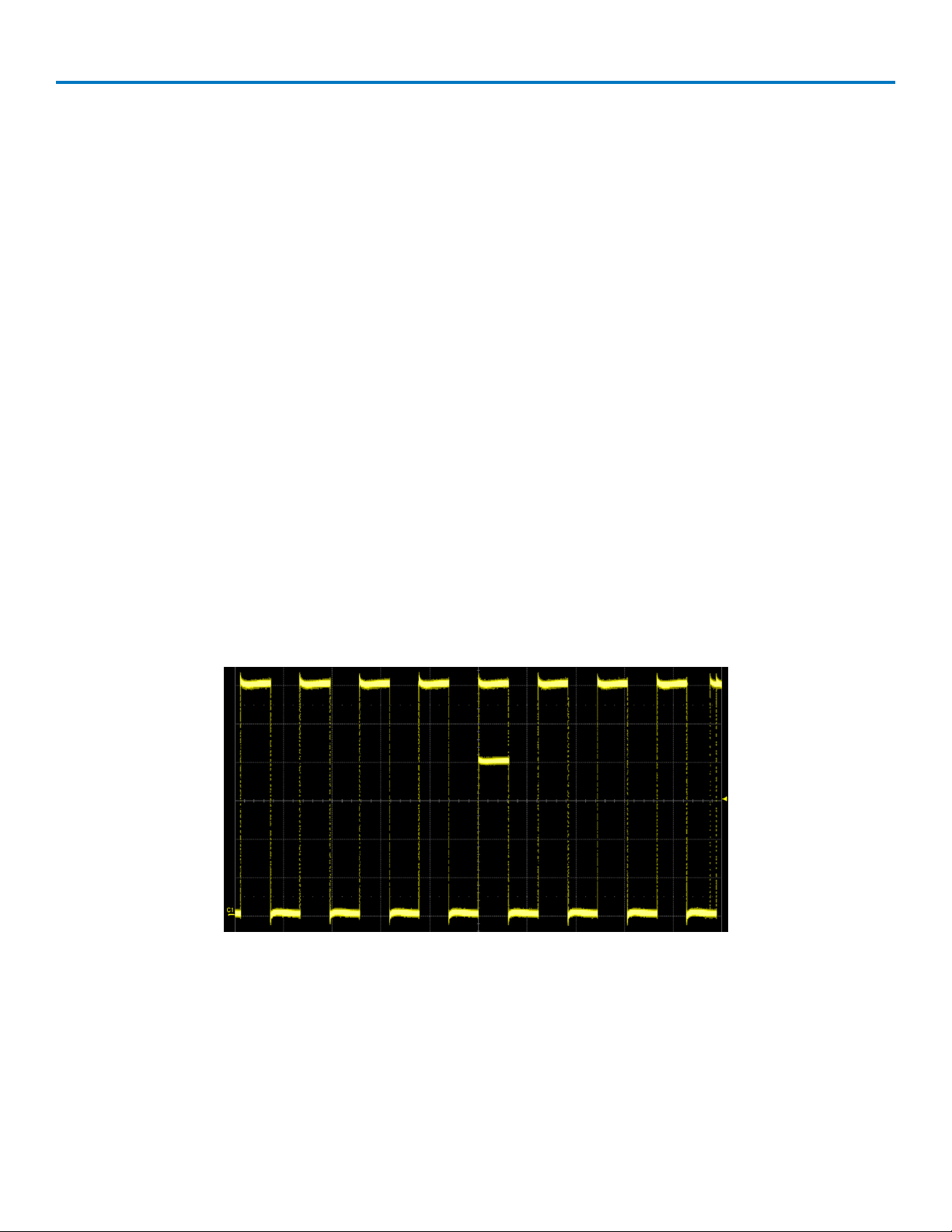
WaveStream Sampling Mode
WaveStream provides a vibrant, intensity graded display with a fast update rate to closely simulate the look
and feel of an analog oscilloscope. WaveStream is most helpful in viewing signals that have signal jitter or
signal anomalies, or for applying a visual check before creating an advanced trigger or WaveScan setup to
locate an unusual event.
WaveStream mode operates at up to 80 GS/s with an update rate of up to several thousand
waveforms/second for better capture of higher frequency abnormal events. Time/div must be set to 50 ms or
faster to use WaveStream.
Waveform captured in WaveStream sampling mode, showing hard-to-find runt.
To use WaveStream, select it as the Sampling Mode when making other settings on the Timebase dialog, or
press the front panel Intensity knob. The WaveStream (ACQ) indicator next to the knob will light to show you
are now in WaveStream mode. Press the knob again to exit WaveStream Mode.
29
Page 38

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Real Time Sampling Mode
Real Time sampling mode is a series of digitized voltage values sampled on the input signal at a uniform
rate. These samples are displayed as a series of measured data values associated with a single trigger
event. By default, the waveform is horizontally positioned so that the trigger event is time zero on the grid.
The relationship between sample rate, memory, and time can be expressed as:
Capture Interval = 1/Sample Rate X Memory
Capture Interval/10 = Time Per Division
In Real Time sampling mode, the acquisition can be displayed for a specific period of time (or number of
samples) either before or after the trigger event occurs, known as trigger delay. This allows you to isolate
and display a time/event of interest that occurs before or after the trigger event.
l Pre-trigger delay displays the time prior to the trigger event. This can be set from a time well before
the trigger event to the moment the event occurs, up to the oscilloscope's maximum sample record
length. How much actual time this represents depends on your timebase setting. When set to the
maximum allowed pre-trigger delay, the trigger position (and zero point) is off the grid (indicated by the
trigger delay arrow at the lower right corner), and everything you see represents pre-trigger time.
l Post-trigger delay displays time following the trigger event. Post-trigger delay can cover a much
greater lapse of time than pre-trigger delay, up to the equivalent of 10,000 time divisions after the
trigger event occurred. When set to the maximum allowed post-trigger delay, the trigger point may
actually be off the grid far to the left of the time displayed.
Usually, on fast timebase settings, the maximum sample rate is used when in Real Time mode. For slower
timebase settings, the sample rate is decreased so that the maximum number of data samples is
maintained over time.
Sequence Sampling Mode
Sequence sampling mode is available on WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
In Sequence Mode, the complete waveform consists of a number of fixed-size segments (see the instrument
specifications at teledynelecroy.com for the limits). The oscilloscope uses the sequence timebase setting
to determine the capture duration of each segment as 10 x time/div. With this setting, the oscilloscope uses
the desired number of segments, maximum segment length, and total available memory to determine the
actual number of samples or segments, and time or points.
Sequence Mode is ideal when capturing many fast pulses in quick succession or when capturing few events
separated by long time periods. The instrument can capture complicated sequences of events over large
time intervals in fine detail, while ignoring the uninteresting periods between the events. You can also make
time measurements between events on selected segments using the full precision of the acquisition
timebase.
30
Page 39

Operator's Manual
SET UP SEQUENCE MODE
When setting up Sequence Mode, you define the number of fixed-size segments acquired in single-shot mode
(see the instrument specifications for the limits). The oscilloscope uses the sequence timebase setting to
determine the capture duration of each segment. Along with this setting, the oscilloscope uses the number
of segments, maximum segment length, and total available memory to determine the actual number of
samples or segments, and time or points.
1. From the menu bar, choose Timebase > Horizontal Setup....
2. Choose Sequence Sampling Mode.
3. On the Sequence tab under Acquisition Settings, touch Number of Segments and enter a value.
4. To stop acquisition in case no valid trigger event occurs within a certain timeframe, check the Enable
Timeout box, then touch Timeout and provide a timeout value.
NOTE: While optional, Timeout ensures that the acquisition will complete in a reasonable amount of time
and control of the oscilloscope will return to the operator/controller without having to manually stop the
acquisition.
5. Touch the one of the front panel Trigger buttons to begin acquisition.
NOTE: Once acquisition has started, you can interrupt it at any time by pressing the Stop front panel
button. In this case, the segments already acquired will be retained in memory.
VIEW SEGMENTS IN SEQUENCE MODE
When in Sequence Mode, you can view individual segments easily using the Zoom dialog. The Zoom trace
defaults to Segment 1. You can move to later segments by changing the values in First segment to display
and Num(ber) of segments to display at once.
TIP: By changing the Num field value to 1, you can use the front panel Adjust knob to scroll through each
segment in order.
Channel descriptor boxes indicate the total number of segments acquired. Zoom descriptor boxes show the .
As with all other Zoom traces, the zoomed segments are highlighted on the source trace.
Use the to change the scale factors of the trace.
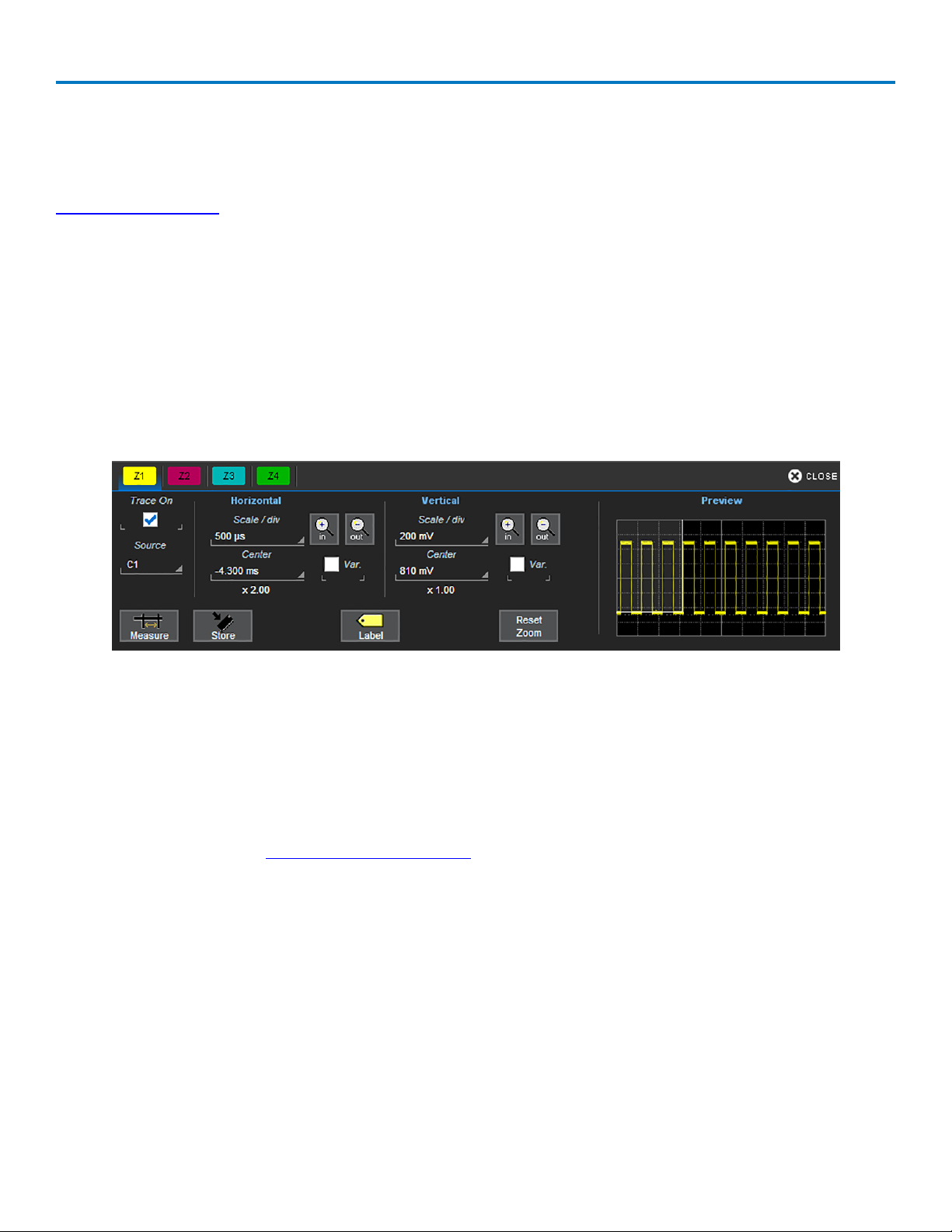
RIS Sampling Mode
RIS (Random Interleaved Sampling) allows effective sampling rates higher than the maximum single-shot
sampling rate. It is used on repetitive waveforms with a stable trigger. The maximum effective RIS sampling
rate is achieved by making multiple single-shot acquisitions at maximum real-time sample rate. The bins
thus acquired are positioned approximately 20 ps (50 GS/s) apart. The process of acquiring these bins and
satisfying the time constraint is a random one. The relative time between ADC sampling instants and the
event trigger provides the necessary variation.
31
Page 40

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
The instrument requires multiple triggers to complete an acquisition. The number depends on the sample
rate: the higher the sample rate, the more triggers are required. It then interleaves these segments (as
shown in the following illustration) to provide a waveform covering a time interval that is a multiple of the
maximum single-shot sampling rate. However, the real-time interval over which the instrument collects the
waveform data is much longer, and depends on the trigger rate and the amount of interleaving required.
Interleaving of sample in RIS sampling mode.
Roll Mode
Roll mode displays, in real time, incoming points in single-shot acquisitions that appear to "roll" continuously
across the screen from right to left until a trigger event is detected and the acquisition is complete. The
parameters or math functions connected to each channel are updated every time the roll mode buffer is
updated, as if new data is available. This resets statistics on every step of Roll mode that is valid because of
new data.
Timebase must be set to 100 ms/div or slower to enable Roll mode selection. Roll mode samples at ≤ 5
MS/s.
NOTE: If the processing time is greater than the acquire time, the data in memory is overwritten. In this case,
the instrument issues the warning, "Channel data is not continuous in ROLL mode!!!" and rolling starts again.
History Mode
History Mode is available on WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
History Mode allows you to review any acquisition saved in the oscilloscope's history buffer, which
automatically stores all acquisition records until full. Not only can individual acquisitions be restored to the
grid, you can "scroll" backward and forward through the history at varying speeds to capture individual details
or changes in the waveforms over time.
Each record is indexed and time-stamped, and you can choose to view the absolute time of acquisition or the
time relative to when you entered History Mode. In the latter case, the last acquisition is time zero, and all
others are stamped with a negative time. The maximum number of records stored depends on your
acquisition settings and the size of the oscilloscope memory.
To view history:
32
Page 41

Operator's Manual
1. Choose Timebase > History Mode.
2. Press the front panel History Mode button, or choose Timebase > History Mode.
3. Select View History to enable the history display, and View Table to display the index of records.
Optionally, select to show Relative Times on the table.
4. Choose a single acquisition to view by entering its Index number on the dialog or selecting it from the
table of acquisitions.
OR
Use the Navigation buttons to "scroll" the history of acquisitions.
l The top row of buttons scrolls continuously and are (left to right): Fast Backward, Slow Backward,
Pause, Slow Forward, Fast Forward.
l The bottom row of buttons steps one record at a time and are (left to right): Back to Start, Back
One, Go to Index (#), Forward One, Forward to End.
5. Entering History Mode automatically stops new acquisitions. To leave History Mode, restart acquisition
by pressing one of the front panel Trigger Mode buttons.
33
Page 42

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Trigger
While the oscilloscope is continuously sampling signal when it is turned on, it can only display up to its
maximum memory in data samples. Triggers select an exact event/time in the waveform to display on the
oscilloscope screen so that memory is not wasted on insignificant periods of the signal. For all trigger types,
you can set:
l Pre-trigger or post-trigger delay—time relative to the trigger event displayed on screen (although the
trigger itself may not be visible).
l Time between sweeps—how often the display is refreshed.
Unless modified by a pre- or post-trigger delay, the trigger event occurs at point zero at the center of the grid,
and an equal period of time before and after this point is shown to the left and right of it.
In addition to the trigger type, the trigger mode determines how the oscilloscope behaves in the presence or
absence of a trigger event.
Trigger capabilities include:
l Simple Triggers activated by basic waveform features such as an edge with a positive or negative
slope or width.
l Pattern Triggers that fire when a pattern condition occurs on selected input channels.
l SMART Triggers, sophisticated triggers that enable you to create basic or complex trigger conditions.
Use SMART Triggers for signals with rare features, like glitches.
Trigger Modes
The trigger mode determines how the oscilloscope sweeps, or refreshes, the display. This can be set from
the Trigger menu or from the front panel Trigger control group.
Auto mode causes the oscilloscope to sweep without a set trigger. An internal timer triggers the sweep after
a preset timeout period so that the display refreshes continuously. Otherwise, Auto functions the same as
Normal when a trigger condition is found.
In Normal mode, the oscilloscope sweeps only if the input signal reaches the set trigger point. Otherwise it
continues to display the last acquired waveform.
In Single mode, one sweep occurs each time you choose Trigger >Single or press the front panel Single
button.
Stop pauses sweeps until you select one of the other three modes.
34
Page 43

Operator's Manual
Trigger Types
These are the trigger types available for selection. If the trigger is part of a subgroup (e.g., Smart), first
choose the subgroup from among the basic types to display all the trigger options.
Basic Triggers
Edge triggers upon a achieving a certain voltage level in the positive or negative slope of the waveform.
Width triggers upon finding a positive- or negative-going pulse width when measured at the specified voltage
level.
Pattern triggers upon a user-defined pattern of concurrent high and low voltage levels on selected inputs. In
Mixed-Signal oscilloscopes, it may be a digital logic pattern relative to high and low voltage levels on analog
channels, or just a digital logic pattern omitting any analog inputs. Likewise, if your oscilloscope does not
have digital input capability, the pattern can be set using voltage levels on analog channels alone. You can
stipulate the voltage level/logic threshold for each analog or digital input independently.
TV triggers on a specified line and field in standard (PAL, SECAM, NTSC, HDTV) or custom composite video
signals.
Qualified arms the trigger on the A event, then fires on the B event. In Normal trigger mode, it automatically
resets after the B event. The A event can be an Edge, State, Pattern, or PatState (a pattern that persists over
a user-defined number of events or time). The options for the B event depend on the type of A event. If A is a
digital Pattern or PatState, B can only be an Edge.
NOTE:This functionality is identical to Teledyne LeCroy's previous Qualify and State triggers, but presented
through a different user interface.
Smart Triggers
The Smart subgroup triggers allow you to apply Boolean logic conditions to the basic signal characteristics
of level, slope, and polarity to determine when to fire the trigger.
Interval triggers upon finding a specific interval, the time (period) between two consecutive edges of the
same polarity: positive to positive or negative to negative. Use the interval trigger to capture intervals that
fall short of, or exceed, a specified range.
Glitch triggers upon finding a pulse-width that is less than a specified time or within a specified range of
times.
Dropout triggers when a signal loss is detected. The trigger is generated at the end of the timeout period
following the last trigger source transition. It is used primarily in single-shot applications with a pre-trigger
delay.
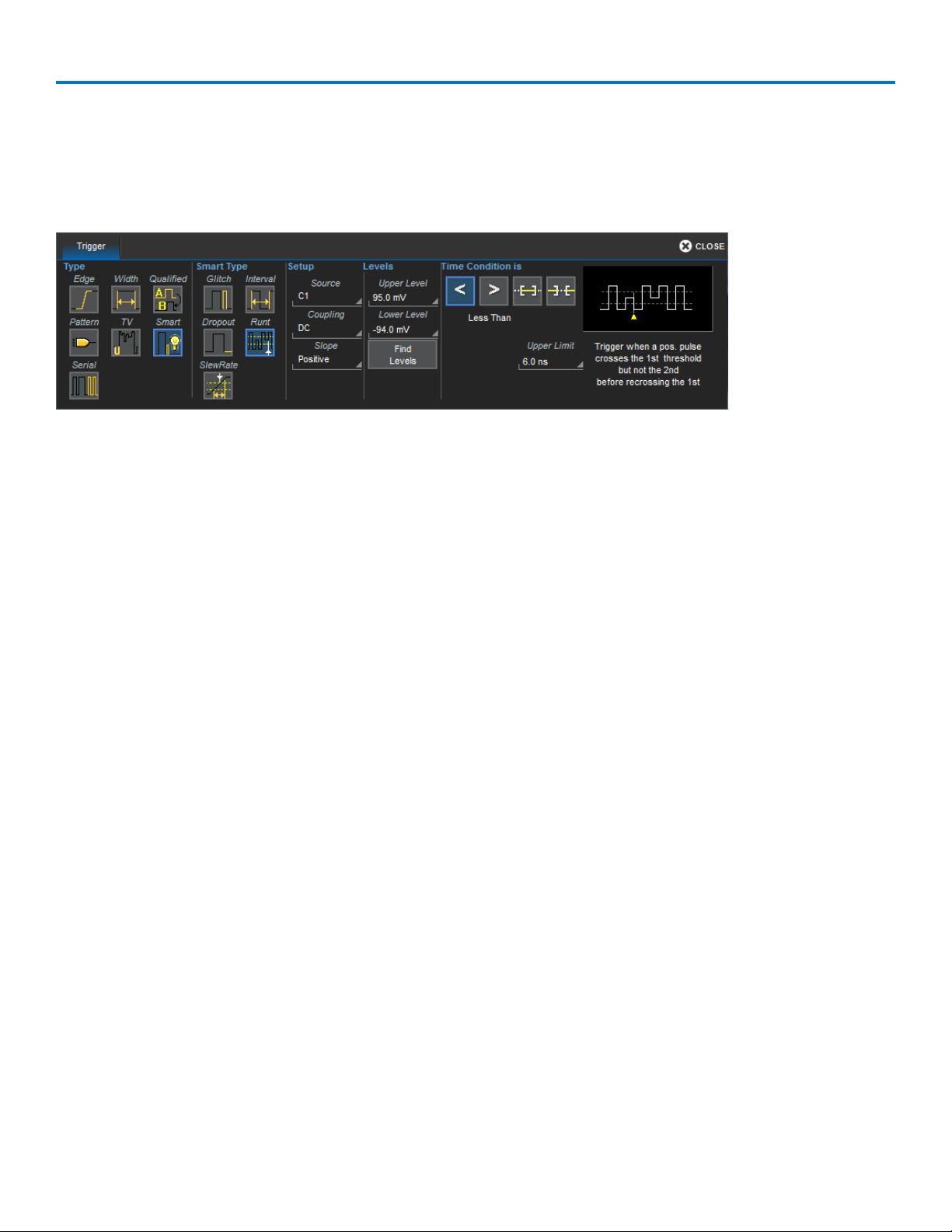
Runt triggers when a pulse crosses a first threshold, but fails to cross a second threshold before re-crossing
the first. Other defining conditions for this trigger are the edge (triggers on the slope opposite to that
selected) and runt width.
35
Page 44

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
SlewRate triggers when the rising or falling edge of a pulse crosses an upper and a lower level. The pulse
edge must cross the thresholds faster or slower than a selected period of time.
Serial Triggers
The Serial trigger type will appear if you have installed protocol-specific serial data trigger and decode
options. Select this type to open the serial trigger setup dialogs. Instructions for using all serial data options
are available from our website at teledynelecroy.com/serialdata.
Setting UpTriggers
To access the Trigger setup dialogs, do one of the following:
l Choose Trigger > Trigger Setup from the menu bar
l Press the front panel Trigger Setup button
l Touch the Trigger descriptor box
The main Trigger dialog contains the trigger type selections. On oscilloscopes with the Mixed Signal option,
many trigger types can be set on either analog channels, including the External Trigger input, or digital lines.
For digital triggering instructions, see the Operator's Manual for your Mixed Signal accessory.
Other controls will appear depending on the trigger type selection (e.g., Slope for Edge triggers). These are
described in the set up procedures for each trigger.
The trigger condition is summarized in a preview window at the far right of the Trigger dialog. Refer to this to
confirm your selections are producing the trigger you want.
36
Page 45

Operator's Manual
Edge Trigger
Edge triggers upon a achieving a certain voltage level in the positive or negative slope of the waveform. It is
the default trigger selection on standard oscilloscopes.
NOTE: Alternatively, you may choose a Slope of Window and enter the Upper Level and Lower Level voltage
that define the window. The trigger fires when the signal leaves the widow.
On the Trigger dialog, select Edge trigger type to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source signal input.
2. Enter the voltage Level upon which to trigger.
The Find Level button sets the Level to the signal mean.
3. Choose the Slope (edge) of the wave on which to trigger.
4. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
37
Page 46

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Width Trigger
Width triggers upon finding a positive- or negative-going pulse width when measured at the specified voltage
level.
On the Trigger dialog, select Width trigger type to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. Best used for stable triggering on medium to high
frequency signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz. Best used for triggering on low frequencies.
3. Choose the Polarity at which to measure pulse width.
4. Enter the voltage Level at which to measure pulse width. The Find Level button sets the level to the
signal mean.
5. Use Width Condition is settings to create an expression describing the triggering pulse width. This may
be:
l Any width Less Than an Upper Value.
l Any width Greater Than a Lower Value.
l Any width In Range or Out Range of values. You may describe the range using either:
l Limits, an absolute Upper Value and Lower Value.
38
l Delta, any Nominal width plus or minus a Delta width.
Page 47

Operator's Manual
Qualified Trigger
Qualified arms the trigger on the A event, then fires on the B event. In Normal trigger mode, it automatically
resets after the B event. The options for the B event depend on the type of A event. You may apply additional
Holdoff by time or number of events.
On the Trigger dialog, select Qualified trigger type to display the controls.
Besides an Edge or Pattern trigger, two special conditions may be selected as the arming ("A") event:
l State, any voltage measured above or below a threshold Level.
l PatState, a pattern that persists over a user-defined number of events or time. Like Pattern triggers,
PatState events may be analog voltage patterns, digital logic patterns, or a mix of both, depending on
the oscilloscope's capabilities.
NOTE: On a standard oscilloscope, Pattern and PatState events will default to the analog pattern setup
dialog. On a Mixed-Signal oscilloscope, Pattern and PatState events will default to the digital pattern setup
dialog.
Once you've selected the A and B events on the Qualified dialog, set up the conditions on the respective subdialogs exactly as you would a single-stage trigger.
39
Page 48

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Pattern Trigger
Pattern is the default trigger when the Mixed Signal option is connected to the oscilloscope, as these users
generally wish to find and trigger upon digital logic patterns.
However, a Pattern trigger can also be set on a user-defined pattern of High or Low voltage levels in analog
channels (including the External Trigger input), or a combination of digital and analog patterns when Mixed
Signal capabilities are available.
See the MS-250 Operator's Manual or MS-500 Operator's Manual delivered with your Mixed Signal option for
instructions on setting up a digital pattern trigger.
To set up an analog pattern trigger, on the Trigger dialog, select Pattern trigger type.
The standard dialog for setting up an analog Pattern trigger includes all the controls for setting the pattern
and the voltage threshold on the same dialog.
1. Select the Boolean Operator (AND, NAND, OR, or NOR) that describes the relationship among analog
inputs (e.g., C1 must be High NAND C2 must be Low).
2. For each input to be included in the trigger pattern, and select what State it must be in (High, Low, or
Don't Care) compared to the threshold Level you will set. Leave "Don't Care" selected for any input you
wish to exclude.
3. For each input included in the trigger, enter the voltage threshold Level.
4. If you've included EXTERNAL as an input, open the Ext tab and enter the Attenuation.
40
Page 49

Operator's Manual
TV Trigger
TV triggers on a specified line and field in standard (PAL, SECAM, NTSC, HDTV) or custom composite video
signals.
On the Trigger dialog, select TV trigger type to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source signal input.
2. Choose the signal TV Standard. To use a custom signal, also enter the:
l Frame Rate
l # of Fields per line
l # of Lines
l Interlace ratio
3. Choose the Line and Field upon which to trigger.
41
Page 50

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Glitch Trigger
Glitch triggers upon finding a pulse-width that is less than a specified time or within a specified range of
times.
On the Trigger dialog, select Smart trigger type, then Glitch to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source signal input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
3. Choose the Polarity on which to trigger.
4. Enter the voltage Level at which to measure. The Find Level button sets the Level to the signal mean.
5. Use Glitch Condition is settings to create an expression describing the glitch width. This may be:
l Any width Less Than an Upper Value.
l Any width In Range of values marked by the specified Upper Value and Lower Value.
42
Page 51

Operator's Manual
Interval Trigger
Interval triggers upon finding a specific interval, the time (period) between two consecutive edges of the
same polarity: positive to positive or negative to negative. Use the interval trigger to capture intervals that
fall short of, or exceed, a specified range.
On the Trigger dialog, select Smart trigger type, then Interval to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
3. Choose the Slope (edge) from which to measure.
4. Enter the voltage Level at which to measure interval width. Where available, the Find Level button sets
the level to the signal mean.
5. Use Interval Condition is settings to create an expression describing the triggering interval. This may be:
l Any width Less Than an Upper Value.
l Any width Greater Than a Lower Value.
l Any width In Range or Out Range of values. You may describe the range using either:
l Limits, an absolute Upper Value and Lower Value.
l Delta, any Nominal width plus or minus a Delta width.
43
Page 52

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Dropout Trigger
Dropout triggers when a signal loss is detected. The trigger is generated at the end of the timeout period
following the last edge transition that meets the trigger conditions. It is used primarily in single-shot
applications with a pre-trigger delay.
On the Trigger dialog, select Smart trigger type, then Dropout to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source signal input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
3. Choose the Slope (edge) and enter the voltage Level to watch for transitions. Where available, the Find
Level button sets the Level to the signal mean.
4. Under Dropout Condition is..., enter the time interval after which to trigger if no transition occurs at that
Slope and Level.
44
Page 53
Operator's Manual
Runt Trigger
Runt triggers when a pulse crosses a first threshold, but fails to cross a second threshold before re-crossing
the first. Other defining conditions for this trigger are the polarity and runt interval (width).
On the Trigger dialog, select Smart trigger type, then choose Runt to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
3. Choose the Polarity on which to measure.
4. Enter the voltage crossing Upper Level and Lower Level. Where available, the Find Level button sets the
levels to the positive and negative signal mean.
5. Use Time Condition is settings to create an expression describing the runt interval (width). This condition
is in addition to (AND) the voltage crossing levels. The interval may be:
l Any width Less Than an Upper Interval.
l Any width Greater Than a Lower Interval.
l Any width In Range or Out Range of values. You may describe the range using either:
l Limits, an absolute Upper Interval and Lower Interval.
l Delta, any Nominal width plus or minus a Delta width.
45
Page 54

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
SlewRate Trigger
SlewRate triggers when the rising or falling edge of a pulse crosses an upper and a lower level. The pulse
edge must cross the thresholds faster or slower than a selected period of time.
On the Trigger dialog, select Smart trigger type, then Slew Rate to display the controls.
1. Choose the Source input.
2. Choose the type of signal Coupling at the input. Choices are:
l DC - All the signal’s frequency components are coupled to the trigger circuit for high frequency
bursts or where the use of AC coupling would shift the effective trigger level.
l AC - The signal is capacitively coupled. DC levels are rejected, and frequencies below 50 Hz are
attenuated.
l LFREJ - The signal is coupled through a capacitive high-pass filter network, DC is rejected and
signal frequencies below 50 kHz are attenuated. For stable triggering on medium to high frequency
signals.
l HFREJ - Signals are DC coupled to the trigger circuit, and a low-pass filter network attenuates
frequencies above 50 kHz (used for triggering on low frequencies).
3. Choose the Slope (edge) from which to measure.
4. Enter the voltage crossing Upper Level and Lower Level. Where available, the Find Level button sets the
level to the positive and negative signal mean.
5. Use Time Condition is settings to create an expression describing the interval within which both levels
must be crossed. This may be:
l Any time Less Than an Upper Value.
l Any time Greater Than a Lower Value.
l Any time In Range or Out Range of values. You may describe the range using either:
l Limits, an absolute Upper Value and Lower Value.
46
l Delta, any Nominal width plus or minus a Delta width.
Page 55

Operator's Manual
Trigger Holdoff
The trigger holdoff function is available on WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
Holdoff is an additional condition that may be set for Edge and Pattern triggers. It can be expressed either as
a period of time or an event count. Holdoff disables the trigger temporarily, even if the trigger conditions are
met, until the holdoff conditions are also met. The trigger fires when the holdoff has elapsed.
Use holdoff to obtain a stable trigger for repetitive, composite waveforms. For example, if the number or
duration of sub-signals is known, you can disable them by choosing an appropriate holdoff value. Qualified
triggers operate using conditions similar to holdoff.
Hold Off by Time
This is a period of time to wait to fire the trigger, either since the beginning of the acquisition or since the
trigger conditions were met.
Sometimes you can achieve a stable display of complex, repetitive waveforms by placing a holdoff condition
on the time between each successive Edge trigger event. This time would otherwise be limited only by the
input signal, the coupling, and the instrument's bandwidth. Select a positive or negative slope, and a
minimum time between triggers.
In the figure below, the bold edges on the trigger source indicate that a positive slope has been selected. The
broken upward-pointing arrows indicate potential triggers, which would occur if other conditions are met. The
bold arrows indicate where the triggers actually occur when the holdoff time has been exceeded.
Edge trigger with holdoff by time.
Hold Off by Events
For purposes of Hold Off, Events refers to the number of times the trigger conditions have been met, counted
either from the beginning of the acquisition or since the last trigger. For example, if the hold-off number of
Events is 2 counted from the beginning of the acquisition, the trigger fires on the third event.
47
Page 56

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
In the figure below, the bold edges on the trigger source indicate that a positive slope has been selected. The
broken, upward-pointing arrows indicate potential triggers, while the bold ones show where triggers actually
occur after the holdoff expires.
Edge trigger with holdoff by events.
Holdoff Settings
To access the Trigger Holdoff dialog, choose Triggers > Trigger Setup from the menu bar or press the front
panel Trigger Setup button, then touch the Holdoff tab.
Choose to Holdoff by Time (clock) or Event. None disables Holdoff.
l If using Holdoff by Time, enter the Time in S to wait before triggering.
l If using Holdoff by Events, enter the number of Events to count before triggering.
Choose to Start Holdoff Counter On either:
l Acquisition Start, best for single-shot acquisitions.
l Last Trigger Time, best for acquiring repetitive waveforms.
48
Page 57
Operator's Manual
Display
Display settings affect the number and style of grids that appear on screen and some of the visual
characteristics of traces, such as persistence.
By default, the oscilloscope has Auto Grid enabled. This divides the screen into a maximum of three grids,
one each for channels/memories, math functions, and zooms. All traces of the same type appear on the
same grid.
To display all types of traces on a single grid, choose Single Grid from the Display dialog.
Two special grid layouts are available: XY Grid, which puts the oscilloscope in XY mode, and XY Single Grid,
which creates one XY grid and one single grid for the rest of your traces.
Display Settings
To access the Display dialogs, choose Display > Display Setup or Display > Persistence Setup.
Grid
Select one of the grid types:
Auto, the default, automatically adds or deletes grids as you open or close traces, up to the maximum
number supported.
Single displays a single grid shared by all traces.
XY displays an XY type trace instead of a traditional voltage/time trace.
XY Single displays a single grid with an XY trace next to it.
To dim or brighten the background grid lines, touch Grid Intensity and enter a value from 0 to 100.
Grid on top superimposes the grid over the waveform.
Check Axis labels to display the voltage values associated with the top and bottom grid lines (calculated
from Volts/div) and the time associated with the extreme left and right grid lines (calculated from the
Time/div).
Trace
Choose a line style for your traces: solid Line or a disconnected series of sample Points.
49
Page 58

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
XY
XY displays plot the phase shift between otherwise identical signals. They can be used to display either
voltage or frequency on both axes, each axis now corresponding to a different signal input, rather than a
different parameter. The shape of the resulting pattern reveals information about phase difference and
frequency ratio.
NOTE: The inputs can be any combination of channels, math functions, or memories, but both sources must
have the same X-axis scale.
If you choose to display an XY grid, select the source channels to Input X and Input Y.
Persistence
The Persistence feature retains waveform traces on the display for a set amount of time before allowing
them to gradually "decay," similar to the display of old phosphor screen oscilloscopes. Use Persistence to
accumulate on-screen points from many acquisitions to see your signal change over time. The persistence
modes show the most frequent signal path in three-dimensional intensities of the same color (Analog), or
graded in a spectrum of colors (Color). You can show persistence for any channel, math function, or memory.
Access the Persistence dialog by choosing Display > Persistence Setup. Check Persistence On to shown
persistence, then select the mode, saturation level, persistence time, and last trace display.
Persistence Mode
The Persistence display is generated by repeated sampling of the amplitudes of events over time, and the
accumulation of the sampled data into display maps. These maps create an analog-style display. Statistical
integrity is preserved because the duration (decay) is proportional to the persistence population for each
amplitude or time combination in the data.
In Analog Mode, as a persistence data map develops, different intensities of the
same color are assigned to the range between a minimum and a maximum
population. The maximum population automatically gets the highest intensity, the
minimum population gets the lowest intensity, and intermediate populations get
intensities in between these extremes. The information in the lower populations (for
50
Page 59

Operator's Manual
example, down at the noise level) could be of greater interest to you than the rest. The Analog persistence
view highlights the distribution of data so that you can examine it in detail.
Color Mode persistence works on the same principle as Analog persistence, but
instead uses the entire color spectrum to map signal intensity: violet for minimum
population, red for maximum population. In this mode, all traces use all colors, which
is helpful for comparing amplitudes by seeking like colors among the traces.
Other Persistence Settings
Besides the different modes, you can select a Saturation level as a percentage of the maximum population.
All populations above the saturation population are then assigned the highest color intensity: that is, they are
saturated. At the same time, all populations below the saturation level are assigned the remaining
intensities. Data populations are dynamically updated as data from new acquisitions is accumulated. A
saturation level of 100% spreads the intensity variation across the entire distribution; at lower saturation
levels the intensity will saturate (become brighter) at the percentage value specified. Lowering this
percentage causes the pixels to be saturated at a lower population and makes visible those events rarely
seen at higher saturation levels.
Persistence Time is the duration of time (in seconds) after which persistence data is erased from the
display.
Choose to superimpose the last waveform over the persistence display by selecting Show Last Trace .
51
Page 60

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Cursors
Cursors are markers (lines or cross-hairs) that identify specific voltage and time values on the waveform.
Use cursors to make fast, accurate measurements of specific points in the waveform. There are three,
standard cursor types available.
Vertical (amplitude) cursor readouts appear the descriptor box for the trace; Horizontal (time) cursor
readouts appear below the Timbebase descriptor box.
Horizontal and vertical cursors.
Cursor Types
Standard Cursors
These cursors can be placed on most any Channel, Memory, Math or Zoom trace.
Horizontal (Time) cursors place vertical lines through a desired point along the horizontal axis.
Vertical (Amplitude) cursors place horizontal lines through a point on the vertical axis.
An option exists to place Horizontal + Vertical cursors together.
Special Cursors
Some cursors are offered only in special circumstances. Horizontal (Frequency) cursors look the same as
Horizontal (Time) cursors except that they are placed on waveforms that have frequency on the x-axis, such
as FFTs.
In addition, some optional software packages provide cursors and help markers that are specific to the
application.
52
Page 61

Operator's Manual
Cursor Settings
Display Cursors
To quickly turn on/off cursors, either:
l From the menu bar, choose Cursors then select the desired cursor type from the drop-down list.
l On the front panel, press the Cursor Type button repeatedly to cycle through all the cursor types. Stop
when the desired type is displayed.
Position Cursors
Te easiest way to position a cursor is to touch and drag the cursor line to a new position.
Alternatively, with the cursor on, turn the front panel Cursors knob. If there is more than one cursor line, push
the Cursor knob until the correct line is selected, then turn the knob to move it.
Use the Position data entry controls on the Standard Cursors dialog to place cursors precisely.
Standard Cursors Dialog
These controls can be used instead of the front panel controls to set cursors or to refine the cursor setup.
Access the dialog by choosing Cursors > Cursors Setup from the menu bar.
Cursor Type buttons select the type of cursor displayed on the grid.
The Position controls at the right-side of the Standard Cursors dialog display the current cursor location and
can be used to set a new location. The options available depend on the Cursor Type settings.
l X 1 (negative) and X 2 (positive) time from the zero point.
l Y 1 (negative) and Y 2 (positive) number of divisions from the zero level. May be a fraction of a
division.
l Track locks cursor lines so they move together, maintaining their same relative distance from each
other.
53
Page 62

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Measure
Measurement parameters are tools that give you access to a wide range of waveform properties. Use them
to analyze many attributes of your waveform such as rise-time, rms voltage, and peak-to-peak voltage.
You can create a custom set of up to six parameters drawn from all the standard measurements, as well as
specialized measurements installed with optional software packages.
Measurement readouts appear in a table below the grid. Readouts can be individually turned on/off. To
quickly access the Measure Setup dialog if it is closed, touch any cell of the readout table.
Measurement readout table open below grid showing statistics and histicons.
(Histicons available with the WS10-ADT option.)
Set Up Measurements
To configure custom measurements to add to the table of parameter readouts:
1. From the menu bar, choose Measure > Measure Setup.
2. Check Show Table to display the readout on screen.
3. Touch the Measure button next to an unused Px location (or one that you want to change), then choose
the measurement from the pop-up window.
54
Page 63

Operator's Manual
4. For each input required by the measurement, touch Source and select the waveform to be measured.
5. Optionally, set a measurement gate by entering the Gate Start and Stop divisions or dragging the gate
posts from the far left and right edges of the grid to reposition them.
6. Choose to display Statistics orHisticons (WS10-ADT only) on the measurement readout table.
Gating Measurements
By using gates, you can narrow the span of the waveform on which to perform parameter measurements,
allowing you to focus on the area of greatest interest. For example, if you "gate" five rising edges of the
waveform, the parameter calculations for rise time are performed only on the five pulses bounded by the
gate posts.
The default starting positions of the gate posts are 0 div and 10 div, which coincide with the left and right
ends of the grid. The gate, therefore, initially encloses the entire waveform.
The quickest way to set a gate is to drag the gate posts located at the far left and right of the grid to the
desired positions. You can refine this setting by specifying a position down to hundredths of a division in the
Gate Start and Stop fields on the Measure dialog dialog. All parameters share the same gate.
Touch the Default button to return gates to the width of the trace.
Viewing Statistics
You can add the statistical measures value(last), mean, min., max., sdev, and num(ber of measurements
computed) to the measurement parameter readout table by checking Statistics On.You can also choose
Measure > Statistics from the menu bar.
The num statistic is the number of measurements computed. For any parameter that computes on an entire
waveform (like amplitude, mean, minimum, maximum, etc.) the value displayed represents the number of
sweeps.
For any parameter that computes on every event, the value displayed is equal to the number of events per
acquired waveform. If x waveforms were acquired, the value represents x times the number of cycles per
waveform. The value(last) statistic is equal to the measurement of the last cycle on the last acquisition.
To reset the statistics counter, touch Clear Sweeps on the display or front panel.
Viewing Histicons
The histicon capability is available on WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the WS10-ADT option installed.
Histicons are miniature histograms of measurement parameters that appear on the measurement table.
These thumbnail histograms let you see at a glance the statistical distribution of each parameter. Select the
Histicons checkbox to turn on histicons.
55
Page 64

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
List of Standard Measurements
Measurements included standard with the oscilloscope are listed below alphabetically.
NOTE: There may be additional parameters available depending on the software options installed on the
oscilloscope.
Measurement Description
Measures the difference between upper and lower levels in two-level signals. Differs from pkpk in that noise,
Amplitude
(ampl)
overshoot, undershoot, and ringing do not affect the measurement. Amplitude is calculated by using the
formula Top – Base. On signals not having two major levels (such as triangle or saw-tooth waves), the
amplitude parameter returns the same value as peak-to-peak.
Area
Base
Delay
Duty Cycle Percent of period for which data are above or below the 50% level of the signal.
Fall 80-20%
(fall8020)
Fall time
(fall)
Frequency
(freq)
Maximum
(max)
Mean
Integral of data: Computes area of the waveform relative to zero level. Values greater than zero contribute
positively to the area; values less than zero, negatively.
Lower of two most probable states (higher is top). Measures lower level in two-level signals. Differs from min in
that noise, overshoot, undershoot, and ringing do not affect measurement. On signals not having two major
levels (such as triangle or saw-tooth waves), the amplitude parameter returns the same value as minimum.
Time from trigger to transition: Measures time between trigger and first 50% crossing of specifies signal. Delay
can be used to measure the propagation delay between two signals by triggering on one and determining
delay of other.
Duration of pulse waveform's falling transition from 80% to 20% of the amplitude averaged for all falling
transitions between the measurement gates. On signals not having two major levels (triangle or saw-tooth
waves, for example), top and base can default to maximum and minimum, giving less predictable results.
Duration of pulse waveform's falling transition from 90% to 10% of the amplitude averaged for all falling
transitions between the measurement gates. On signals not having two major levels (triangle or saw-tooth
waves, for example), top and base can default to maximum and minimum, giving less predictable results.
Period of cyclic signal measured as time between every other pair of 50% crossings. Starting with first
transition after left measurement gate. The period is measured for each transition pair. The reciprocal of each
period measurement is calculated as the frequency.
Measures highest point in waveform. Unlike top, does not assume waveform has two levels.
Average of data for time domain waveform. Computed as centroid of distribution for a histogram of the data
values.
Minimum
(min)
None Disables parameter calculation
Overshoot-
Overshoot+
Peak to Peak
(pkpk)
Measures the lowest point in a waveform. Unlike base, does not assume waveform has two levels.
Amount of overshoot following a falling edge. This is represented as percentage of amplitude. Overshoot- is
calculated using the formula (base - min.)/ampl x 100. On signals not having two major levels (triangle or saw-
tooth waves, for example), may not give predictable results.
Amount of overshoot following a rising edge specified This is represented as a percentage of amplitude.
Overshoot+ is calculated using the formula (max. - top)/ampl x 100. On signals not having two major levels
(triangle or saw-tooth waves, for example), may not give predictable results.
Difference between highest and lowest points in waveform. Unlike ampl, does not assume the waveform has
two levels. Peak to peak is calculated using the formula maximum – minimum.
56
Page 65
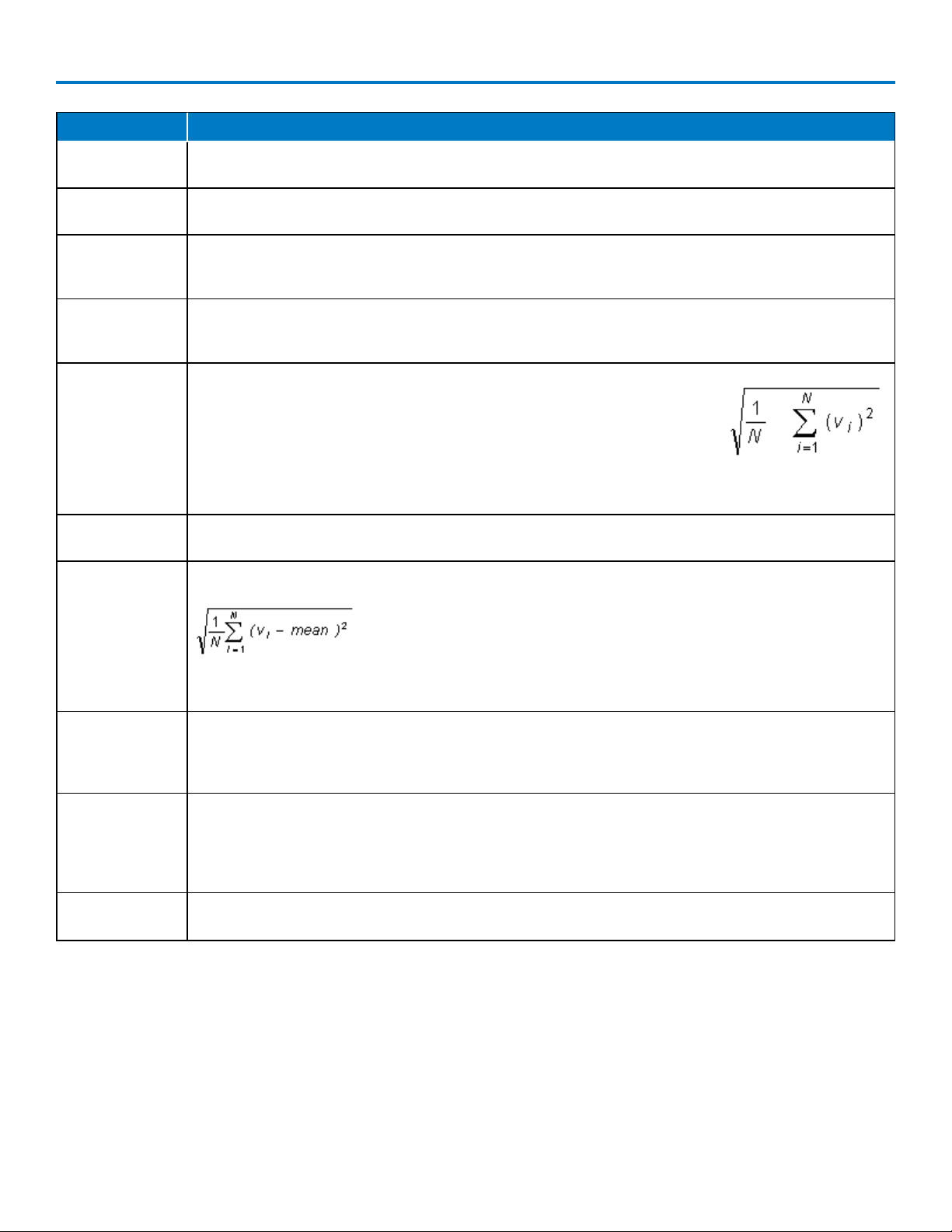
Measurement Description
Operator's Manual
Period
Phase
Rise 20-80%
(rise2080)
Rise Time
RMS
Skew
The time between every other pair of 50% crossings. Starting with first transition after left measurement gate,
period is measured for each transition pair, with values averaged to give final result.
Phase difference between signal analyzed and signal used as reference. Both signals are measured from the
50% point of their rising edges.
Duration of pulse waveform's rising transition from 20% to 80% of the amplitude averaged for all rising
transitions between the measurement gates. On signals not having two major levels (triangle or saw-tooth
waves, for example), top and base can default to maximum and minimum, giving less predictable results.
Duration of pulse waveform's rising transition from 10% to 90% of the amplitude averaged for all rising
transitions between the measurement gates. On signals not having two major levels (triangle or saw-tooth
waves, for example), top and base can default to maximum and minimum, giving less predictable results.
Root Mean Square of data between the measure gates calculated using the formula:
Where: vi denotes measured sample values, and N = number of data points within the periods found up to
maximum of 100 periods.
Time of clock1 edge minus time of nearest clock2 edge. Both signals are measured from the 50% point of their
rising edges.
Standard deviation of the data between the measure gates using the formula:
Std Dev
(sdev)
Top
Width
WidthN
(widn)
Where: vi denotes measured sample values, and N = number of data points within the periods found up to
maximum of 100 periods. This is equivalent to the rms for a zero-mean waveform. Also referred to as AC RMS
Higher of two most probable states (base is lower). Measures higher level in two-level signals. Differs from
max in that noise, overshoot, undershoot, and ringing do not affect measurement. On signals not having two
major levels (such as triangle or saw-tooth waves), the amplitude parameter returns the same value as
minimum.
Width of cyclic signal determined by examining 50% crossings in data input. If first transition after left cursor is
a rising edge, waveform is considered to consist of positive pulses and width the time between adjacent rising
and falling edges. Conversely, if falling edge, pulses are considered negative and width the time between
adjacent falling and rising edges. For both cases, widths of all waveform pulses are averaged for the final
result.
Time of cyclic signal determined by examining 50% crossings in data input. The widthN is measured from
falling edge to rising edge.
57
Page 66

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Calculating Measurements
Determining Top and Base Lines
Proper determination of the top and base reference lines is fundamental for ensuring correct parameter
calculations. The analysis begins by computing a histogram of the waveform data over the time interval
spanned by the left and right measurement gates. For example, the histogram of a waveform transitioning in
two states will contain two peaks (see figure). The analysis will attempt to identify the two clusters that
contain the largest data density. Then the most probable state (centroids) associated with these two
clusters will be computed to determine the top and base reference levels: the top line corresponds to the top
and the base line to the bottom centroid.
Determining Rise and Fall Times
Once top and base are estimated, calculation of the rise and fall times is easily done (see figure). The
appropriate threshold levels are automatically determined by the instrument, using the amplitude (ampl)
parameter.
Rising Edge Duration
Falling Edge Duration
58
Page 67

Operator's Manual
Where Mr is the number of leading edges found, Mf the number of trailing edges found, the time when
rising edge i crosses the x% level, and the time when falling edge i crosses the x% level.
Determining Time Parameters
Time parameter measurements such as width, period and delay are carried out with respect to the mesial
reference level, located halfway (50%) between the top and base reference lines.
59
Page 68

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Math
Math traces ) display the result of applying a mathematical operation to a source trace. The output of a math
function is always another trace, whereas the output of a measurement parameter is a tabular readout of the
measurement.
Math can be applied to any channel (Cx), zoom (Zx), or memory (Mx) trace. On oscilloscopes with the WS10ADT option, it can even be applied to another math trace (Fx), allowing you to chain operations (for example,
trace F1 can show the average of C1, while trace F2 provides the integral of F1). Functions such as Trend
can be applied to measurement parameters (Px) to plot the history of the measurement.
In addition to the extensive math capabilities that are standard with every oscilloscope, enhanced math
analysis tools customized for various industries and applications are offered through optional software
packages. To learn about math tools available in each optional package, see the datasheets on the Teledyne
LeCroy website at teledynelecroy.com. If you have installed software options, these capabilities are
accessed through the oscilloscope Analysis menu, rather than the Math menu, although special measure
parameters and math functions will be available when using Measure and Math dialogs.
Single vs. Dual Operator Functions
Single functions perform one operation on one or two input sources.
Dual functions chain two operations to arrive at a single result. This saves you the effort of having to chain
two separate math functions. As with single functions, the number of sources required will vary based on the
operation. You may need only one source for Operator1, but two for Operator2 (the result of the first operation
counts as one source).
60
Page 69

Operator's Manual
Set Up Math Function
This procedure explains how to set up math function (Fx) traces. Function traces take as input one or more
channel, zoom, memory or math traces and output a new math trace.
NOTE: You can set up two, single- or dual-operator math functions on WaveSurfer 10 oscilloscopes with the
WS10-ADT option installed. Use the F1 and F2 dialogs to configure the functions; use the Math dialog to
enable/disable them.
1. From the menu bar, choose Math > Math Setup.
TIP: If you know which function number you'll be using, select Fx Setup right from the Math menu.
2. If you have the WS10-ADT option installed, choose a location by touching one of the Fx tabs.
3. Choose a single f(x) or dual g(f(x) operator function.
4. In Operator1, choose the math operation to perform.
5. The choice of operator drives the number of Source fields you will see displayed. Make a selection in
each field.
A Summary of the function you are building appears on the dialog. Refer to this to be sure your sources
are in the proper order to yield the function you want (e.g., C1-C2 vs. C2-C1).
6. If the operator you've selected has any other configurable settings, you'll see a right-hand dialog of the
same name as the operator. Touch the tab to open the dialog and make any further settings. These are
explained on the dialog.
61
Page 70

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
There will also be a Zoom dialog where you can adjust the math trace Vertical range. This does not
affect the scale of any other traces.
List of Standard Operators
The math operators included standard with your oscilloscope are listed below alphabetically.
NOTE: There may be additional operators available depending on the software options installed on the
oscilloscope.
Operator Definition
Absolute For every point in the waveform the distance away from zero is calculated. For values greater than
zero this is the same as the value. For values less than zero, the magnitude of this value without
regard to its sign is used.
Average Calculates either a summed or continuous average of a selected number of sweeps. See
Averaging Waveforms. The maximum number of sweeps is determined by the oscilloscope model
and memory. See the specifications at teledynelecroy.com.
Derivative Calculates the derivative of adjacent samples using the formula:
(next sample value – current sample value) / (horizontal sample interval)
DIfference For every point in the waveform, the value of Source2 is subtracted from the value of Source1.
Source1 and Source2 must have the same horizontal units and scale and the same vertical units.
Envelope Calculates highest and lowest vertical values of a waveform at each horizontal value for a specified
number of sweeps.
ERes Applies a noise reduction and smoothing filter by adding a specified number of bits. See Enhanced
Resolution.
FFT Computes a frequency spectrum with optional Rectangular, Von Hann, Flat Topp, Hamming,
Blackman-Harris, and Hanning windows. Calculates up to 1 Mpts. Also allows FFT Averaging
through use of a second math operator. See FFT.
Floor Calculates the lowest vertical values of a waveform at each horizontal value for a specified number
of sweeps.
Integral Calculates the linearly rescaled integral (with multiplier and adder) of a waveform input starting
from the left edge of the screen using the formula:
(current sample value + next sample value) * (horizontal sample interval)
Each calculated area is summed with the previous sum of areas. The multiplier and adder are
applied before the integration function.
Invert For every point in the waveform, the inverse of that point is calculated.
Product For every point in the waveform, the value of Source1 is multiplied by the value of Source 2.
Source1 and Source2 must have the same horizontal units and scale.
Ratio For every point in the waveform, the value of Source1 is divided by the value of Source2. Source1
and Source2 must have the same horizontal units and scale.
Reciprocal For every point in the waveform the inverse is calculated using the formula:
1 / (sample value)
Rescale For every point in the waveform the sample value is multiplied by the specified multiplier and then
add to with the specified adder. See Rescaling and Assigning Units.
62
Page 71

Operator's Manual
Operator Definition
Roof Calculates the highest vertical values of a waveform at each horizontal value for a specified
number of sweeps.
Square For every point in the waveform, the square of the sample value is calculated.
Square Root For every point in the waveform, the square root of the sample value is calculated.
Sum For every point in the waveform, the value of Source1 is added to the value of Source 2.Source1
and Source2 must have the same horizontal units and scale and the same vertical units.
Trend Produces a waveform composed of a series of parameter measurements in the order the
measurements were taken. The vertical units are those of the source parameter, the horizontal unit
is measurement number. The trend contains a single value for each measurement.
Zoom Produces a magnified trace of a selected portion of the input waveform. See Zooming Traces.
Advanced Debut Toolkit Math Functions
These operators are added with the WS10-ADT option.
Operator Definition
Average Calculates either a summed or continuous average of a selected number of sweeps. See
Averaging Waveforms. The maximum number of sweeps is determined by the oscilloscope model
and memory. See the specifications at teledynelecroy.com.
ERes Applies a noise reduction and smoothing filter by adding a specified number of bits. See Enhanced
Resolution.
Exp Calculates the antilog to the base e of the source; that is, e raised to the power equal to the source.
Exp10 Same as Exp, using base 10.
Invert For every point in the waveform, the inverse of that point is calculated.
Ln Peforms a natural log of a waveform. Values less than or equal to zero are set to underflow.
Log10 Performs a log base 10 of a waveform. Values less than or equal to zero are set to underflow.
Rescale For every point in the waveform the sample value is multiplied by the specified multiplier and then
add to with the specified adder. See Rescaling and Assigning Units.
Trend Produces a waveform composed of a series of parameter measurements in the order the
measurements were taken. The vertical units are those of the source parameter, the horizontal unit
is measurement number. The trend contains a single value for each measurement. See Trend.
63
Page 72

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
FFT
For a large class of signals, you can gain greater insight by looking at spectral representation rather than
time description. Signals encountered in the frequency response of amplifiers, oscillator phase noise and
those in mechanical vibration analysis, for example, are easier to observe in the frequency domain.
If sampling is done at a rate fast enough to faithfully approximate the original waveform (usually five times
the highest frequency component in the signal), the resulting discrete data series will uniquely describe the
analog signal. This is of particular value when dealing with transient signals because, unlike FFT,
conventional swept spectrum analyzers cannot handle them.
Because of its versatility, FFT analysis has become a popular analysis tool. However, some care must be
taken with it. In most instances, incorrect positioning of the signal within the display grid will significantly
alter the spectrum, producing effects such as leakage and aliasing that distort the spectrum.
An effective way to reduce these effects is to maximize the acquisition record length. Record length directly
conditions the effective sampling rate of the oscilloscope and therefore determines the frequency resolution
and span at which spectral analysis can be carried out.
Set Up FFT
1. Follow the usual steps to set up a math function, selecting FFT from the Frequency Analysis submenu.
2. Open the FFT right-hand dialog.
3. Choose an Output type.
4. Optionally, choose a weighting Window. See below for more information about FFT weighting windows.
5. Depending on your Output Type selection, you may also make selections for Line Impedence. By default,
the FFT function assumes that the oscilloscope is terminated in 50 Ohms. If an external terminator is
being used, this setting can be changed to properly calculate the FFT based on the new termination
value.
6. Check the Suppress DC box to make the DC bin go to zero. Otherwise, leave it unchecked.
64
Page 73
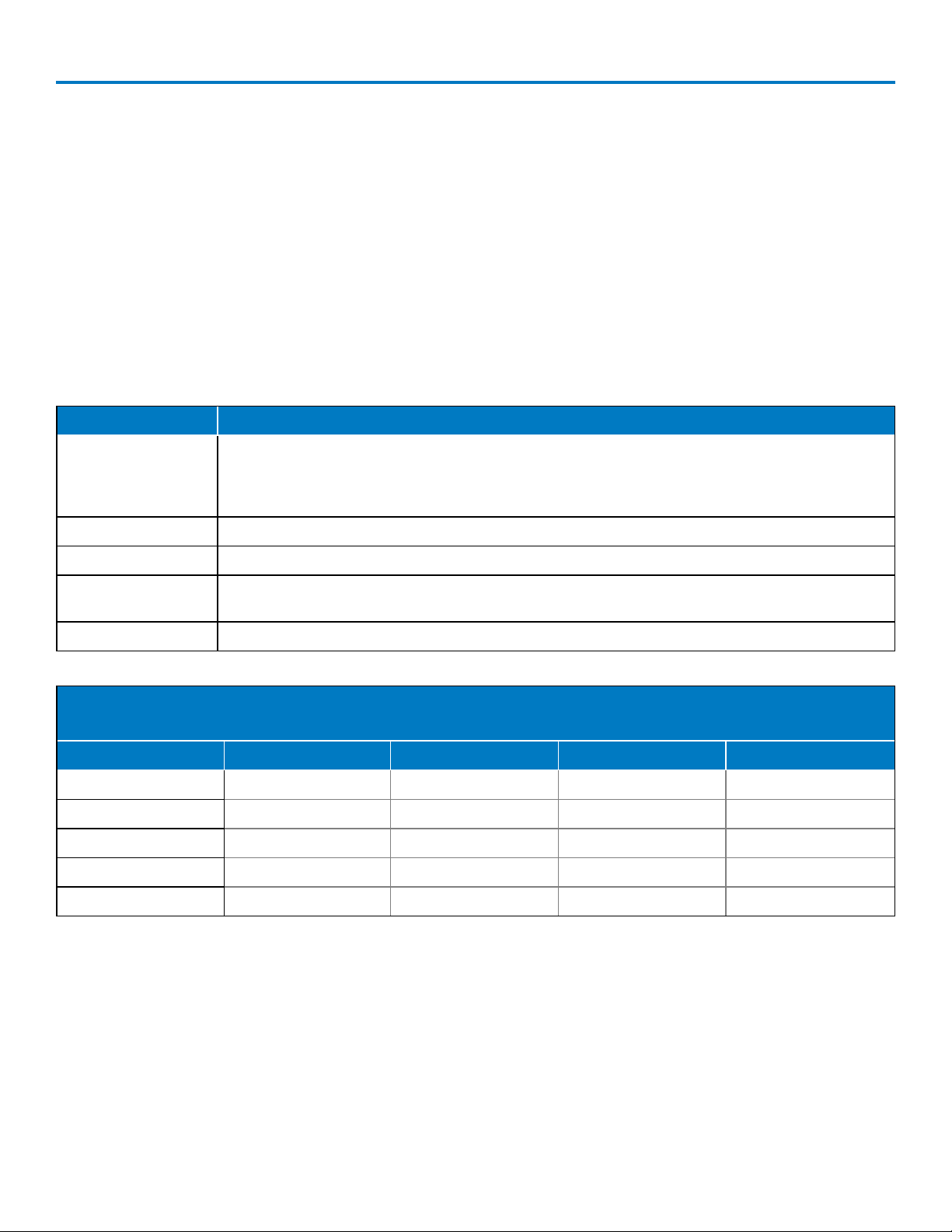
Operator's Manual
Choosing a Window
The choice of a spectral window is dictated by the signal's characteristics. Weighting functions control the
filter response shape, and affect noise bandwidth as well as side lobe levels. Ideally, the main lobe should be
as narrow and flat as possible to effectively discriminate all spectral components, while all side lobes
should be infinitely attenuated. The window type defines the bandwidth and shape of the equivalent filter to
be used in the FFT processing.
Rectangular windows provide the highest frequency resolution and are useful for estimating the type of
harmonics present in the signal. Because the rectangular window decays as a (sinx)/x function in the
spectral domain, slight attenuation will be induced. Functions with less attenuation (Flat Top and BlackmanHarris) provide maximum amplitude at the expense of frequency resolution, whereas Hamming and Von Hann
are good for general purpose use with continuous waveforms.
Window Type Applications and Limitations
Rectangular These are normally used when the signal is transient (completely contained in the time-domain window)
or known to have a fundamental frequency component that is an integer multiple of the fundamental
frequency of the window. Signals other than these types will show varying amounts of spectral leakage
and scallop loss, which can be corrected by selecting another type of window.
Hanning (Von Hann) These reduce leakage and improve amplitude accuracy. However, frequency resolution is also reduced.
Hamming These reduce leakage and improve amplitude accuracy. However, frequency resolution is also reduced.
Flat Top This window provides excellent amplitude accuracy with moderate reduction of leakage, but with reduced
frequency resolution.
Blackman-Harris It reduces the leakage to a minimum, but with reduced frequency resolution.
FFT Window Filter Parameters
Window Type Highest Side Lobe (dB) Scallop Loss (dB) ENBW (bins) Coherent Gain (dB)
Rectangular -13 3.92 1.0 0.0
Von Hann -32 1.42 1.5 -6.02
Hamming -43 1.78 1.37 -5.35
Flat Top -44 0.01 3.43 -11.05
Blackman-Harris -67 1.13 1.71 -7.53
65
Page 74

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Averaging Waveforms
Summed Averaging
Summed Averaging is the repeated addition, with equal weight, of successive source waveform records. If a
stable trigger is available, the resulting average has a random noise component lower than that of a singleshot record. Whenever the maximum number of sweeps is reached, the averaging process stops. In Summed
averaging, you specify the number of acquisitions to be averaged. The averaged data is updated at regular
intervals.
An even larger number of records can be accumulated simply by changing the number in the dialog. However,
the other parameters must be left unchanged or a new averaging calculation will be started. You can pause
the averaging by changing the trigger mode from NORM/AUTO to STOP. The instrument resumes averaging
when you change the trigger mode back to NORM/AUTO.
You can reset the accumulated average by pushing the CLEAR SWEEPS button or by changing an acquisition
parameter such as input gain, offset, coupling, trigger condition, timebase, or bandwidth limit. The number of
current averaged waveforms of the function, or its zoom, is shown in the acquisition status dialog. When
summed averaging is performed, the display is updated at a reduced rate to increase the averaging speed
(points and events per second).
Continuous Averaging
Continuous Averaging, the default setting, is the repeated addition, with unequal weight, of successive
source waveforms. It is particularly useful for reducing noise on signals that drift very slowly in time or
amplitude. The most recently acquired waveform has more weight than all the previously acquired ones: the
continuous average is dominated by the statistical fluctuations of the most recently acquired waveform. The
weight of ‘old' waveforms in the continuous average tends to zero (following an exponential rule) at a rate
that decreases as the weight increases.
You determine the importance of new data vs. old data by assigning a weighting factor. Continuous
averaging allows you to make adjustments to a system under test and to see the results immediately. The
formula for both summed and continuous averaging is:
new average = (new data + weight * old average)/(weight + 1)
However, by setting a "sweeps" value, you establish a fixed weight that is assigned to the old average once
the number of "sweeps" is reached. For example, for a sweeps (weight) value of 4:
1stsweep (no old average yet): new average = (new data +0 * old average)/(0 + 1) = new data only
2ndsweep: new average = (new data + 1*old average)/(1 + 1) = 1/2 new data +1/2 old average
3rdsweep: new average = (new data + 2 * old average)/(2 + 1) = 1/3 new data + 2/3 old average
4thsweep: new average = (new data + 3 * old average)/(3 + 1) = 1/4 new data + 3/4 old average
5thsweep: new average = (new data + 4 * old average)/(4 + 1) = 1/5 new data + 4/5 old average
66
Page 75

Operator's Manual
6thsweep: new average = (new data + 4 * old average)/(4 + 1) = 1/5 new data + 4/5 old average
7thsweep: new average = (new data + 4 * old average)/(4 + 1) = 1/5 new data + 4/5 old average
In this way, for sweeps > 4 the importance of the old average begins to decrease exponentially.
NOTE: The number of sweeps used to compute the average is displayed at the bottom of the trace descriptor
box.
Set Up Averaging
To quickly set up Continuous Averaging (only), access the Channel setup dialog and enter the number of
sweeps to average in Averaging. The valid range is 1 to 1,000,000 sweeps.
To apply Continuous or Summed Averaging as a Math function:
1. Follow the usual steps to set up a math fuction, selecting Average from the Basic Math submenu.
2. On the Average right-hand dialog, choose Summed or Continuous.
3. Touch Sweeps and provide a value. The valid range is 1 to 1,000,000 sweeps.
Enhanced Resolution
ERes (Enhanced Resolution) filtering increases vertical resolution, allowing you to distinguish closely
spaced voltage levels. The instrument's ERes function is similar to smoothing the signal with a simple,
moving-average filter. However, it is more efficient concerning bandwidth and pass-band filtering.
Use ERes:
l On single-shot acquisitions, or where the data record is slowly repetitive (cases where you cannot use
averaging).
l To reduce noise on noticeably noisy signals when you do not need to perform noise measurements.
l When performing high-precision voltage measurements (e.g., zooming with high vertical gain).
ERes can be applied as a form of Pre-Processing, or as a Math function.
Set Up Enhanced Resolution (ERes)
To quickly set up ERes, open the Channel setup dialog and in the Pre-Processing section select a Noise
Filter (ERes) bit size .
To apply ERes as a Math function:
1. Follow the usual steps to set up a math function, selecting ERes from the Filter submenu.
2. Touch the Trace On checkbox.
3. Touch the ERes right-hand dialog tab , then touch bits and make a selection from the pop-up menu.
67
Page 76

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
How the Instrument Enhances Resolution
The instrument's enhanced resolution feature improves vertical resolution by a fixed amount for each filter.
This real increase in resolution occurs whether or not the signal is noisy, or your signal is single-shot or
repetitive. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) improvement you gain is dependent on the form of the noise in the
original signal. The enhanced resolution filtering decreases the bandwidth of the signal, filtering out some of
the noise.
The instrument's constant phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters provide fast computation, excellent
step response in 0.5 bit steps, and minimum bandwidth reduction for resolution improvements of between
0.5 and 3 bits. Each step corresponds to a bandwidth reduction factor of two, allowing easy control of the
bandwidth resolution trade-off. The parameters of the six filters are given in the following table.
Resolution increased by
0.5 0.5 2
1.0 0.241 5
1.5 0.121 10
2.0 0.058 24
2.5 0.029 51
3.0 0.016 117
-3 dB Bandwidth
(x Nyquist)
Filter Length
(Samples)
With low-pass filters, the actual SNR increase obtained in any particular situation depends on the power
spectral density of the noise on the signal.
The improvement in SNR corresponds to the improvement in resolution if the noise in the signal is white
(evenly distributed across the frequency spectrum). If the noise power is biased towards high frequencies,
the SNR improvement will be better than the resolution improvement.
The opposite may be true if the noise is mostly at lower frequencies. SNR improvement due to the removal
of coherent noise signals - feed-through of clock signals, for example - is determined by the fall of the
dominant frequency components of the signal in the passband. This is easily ascertained using spectral
analysis. The filters have a precisely constant zero-phase response. This has two benefits. First, the filters
do not distort the relative position of different events in the waveform, even if the events' frequency content
is different. Second, because the waveforms are stored, the delay normally associated with filtering
(between the input and output waveforms) can be exactly compensated during the computation of the
filtered waveform.
The filters have been given exact unity gain at low frequency. Enhanced resolution should therefore not
cause overflow if the source data is not overflowed. If part of the source trace were to overflow, filtering
would be allowed, but the results in the vicinity of the overflowed data -- the filter impulse response length -
68
Page 77

Operator's Manual
would be incorrect. This is because in some circumstances an overflow may be a spike of only one or two
samples, and the energy in this spike may not be enough to significantly affect the results. It would then be
undesirable to disallow the whole trace.
Example ERes Applications
The following examples illustrate how you might use the instrument's enhanced resolution function.
Graph Function
In low-pass filtering: The spectrum of a square signal before (left top) and after (left
bottom) enhanced resolution processing. The result clearly illustrates how the filter rejects
high-frequency components from the signal. The higher the bit enhancement, the lower the
resulting bandwidth.
To increase vertical resolution: In the example at left, the lower (inner) trace has been
significantly enhanced by a three-bit enhanced resolution function.
To reduce noise: The example at left shows enhanced resolution of a noisy signal. The
original trace (left top) has been processed by a 2-bit enhanced resolution filter. The result
(left bottom) shows a smooth trace, where most of the noise has been eliminated.
NOTE: While enhanced resolution can only improve the resolution of a trace, it cannot improve the accuracy
or linearity of the original quantization. The pass-band causes signal attenuation for signals near the cut-off
frequency. The highest frequencies passed may be slightly attenuated. Perform the filtering on finite record
69
Page 78

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
lengths. Data is lost at the start and end of the waveform and the trace ends up slightly shorter after
filtering. The number of samples lost is exactly equal to the length of the impulse response of the filter used:
between 2 and 117 samples. Normally this loss (just 0.2 % of a 50,000 point trace) is not noticed. However,
you might filter a record so short that no data is output. In that case, however, the instrument would not allow
you to use the ERes feature.
Rescaling and Assigning Units
The rescale function allows you to apply a multiplication factor (a) and additive constant (b) to your
waveform: aX + b. You can do it in the unit of your choice, depending on the type of application.
Set Up Rescaling
1. Follow the usual steps to set up a math function, selecting Rescale from the Functions submenu.
2. Touch the Rescale right-hand dialog tab.
3. To apply a multiplication factor:
l Check the First multiply by: box and enter a value for a, the multiplication factor.
l Touch then add: and enter a value for b, the additive constant.
4. To change the output unit of measure from that of the source waveform:
l Check Override units.
l In Output enter the abbreviation for the unit the measure you wish to use.
You can also enter combinations of the unit abbreviations following these rules:
l For the quotient of two units, use the character ":/"
l For the product of two units, use the character "."
l For exponents, append the digit to the unit without a space: S2 = seconds squared.
NOTE: Some units may be converted to simple units (e.g., V.A will display as W).
70
Page 79

Abbreviated Units of Measure
Abbreviation Measure Abbreviation Measure
(blank) No units N Newton
A Ampere OHM Ohm
C Coulomb PAL Pascal
CYCLE Cycles PCT Percent
DB Decibel POISE Poise
DBC Decibel referred to carrier PPM Parts per million
DBM Decibel Milliwatt RAD Radian
DBV Decibel Volts DEG Degree (of arc)
DBUZ Decibel Microamp MNT Minute (of arc)
DEC Decade SAMPLE Sample
DIV Divisions SWEEP Sweeps
Event Events SEC Second (of arc)
Operator's Manual
F Farad S Second
G Gram SIE Siemens
H Henry T Tesla
HZ Hertz UI Unit interval
J Joule V Volt
K Degree Kelvin VA Volt amps
CEL Degree Celsius W Watt
FAR Degree Fahrenheit WB Weber
L Liter MIN Min
M Meter HOUR Hour
FT Foot DAY Day
IN Inch WEEK Week
YARD Yard
MILE Mile
71
Page 80

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Trend
A Trend is a plot composed of a series of parameter measurements in the order the measurements were
taken. The vertical units are those of the source parameter, the horizontal unit is measurement number. The
Trend contains a single value for each measurement. Trends are especially useful for visualizing the history
of a parameter over an extended period of time or over multiple acquisitions.
1. Follow the usual steps to set up a math function, selecting Trend from the submenu.
2. Open the Trend right-hand dialog.
3. Choose a computation Mode of All (plots multiple points per acquisition) or Average (plots one point per
acquisition).
4. To rescale the Trend plot, uncheck Auto Find Scale and enter the new Center and Height/div values. You
can also use Find Scale to automatically find suitable values.
72
Page 81

Operator's Manual
Memory
The oscilloscope is equipped with fourinternal memory slots (Mx) to which you can copy any channel, math,
zoom or other special waveform that is active on the grid. This is a convenient way to store an acquisition
for later viewing and analysis.
Memories are created at the same scale as the source trace, but they can be adjusted independent of the
original by using the Zoom controls that appear next to the Mx dialogs.
Save Waveform to Memory
1. With the source waveform displayed on the grid, press the front panel Mem button or choose Math >
Memory Setup to open the Memories dialog.
2. Touch the Mx tab corresponding to the memory slot you wish to use.
NOTE: Try to choose an empty slot, as anything currently stored in that location will be overwritten. All
memories will state if they are empty or an acquisition is stored there.
3. In Copy from Waveform, choose the source trace to copy to memory.
4. Touch Copy Now.
5. Optionally, check Trace On to immediately display the memory. Use the Zoom controls to adjust the
scale of the memory while it is turned on.
Save Waveform Files to Memory
Trace (.trc) files saved on other Teledyne LeCroy oscilloscopes can also be stored to internal memory. Use
the Recall Waveform function to save external files to memory. Then, you can use the Memories dialog to
enable them from the oscilloscope.
73
Page 82
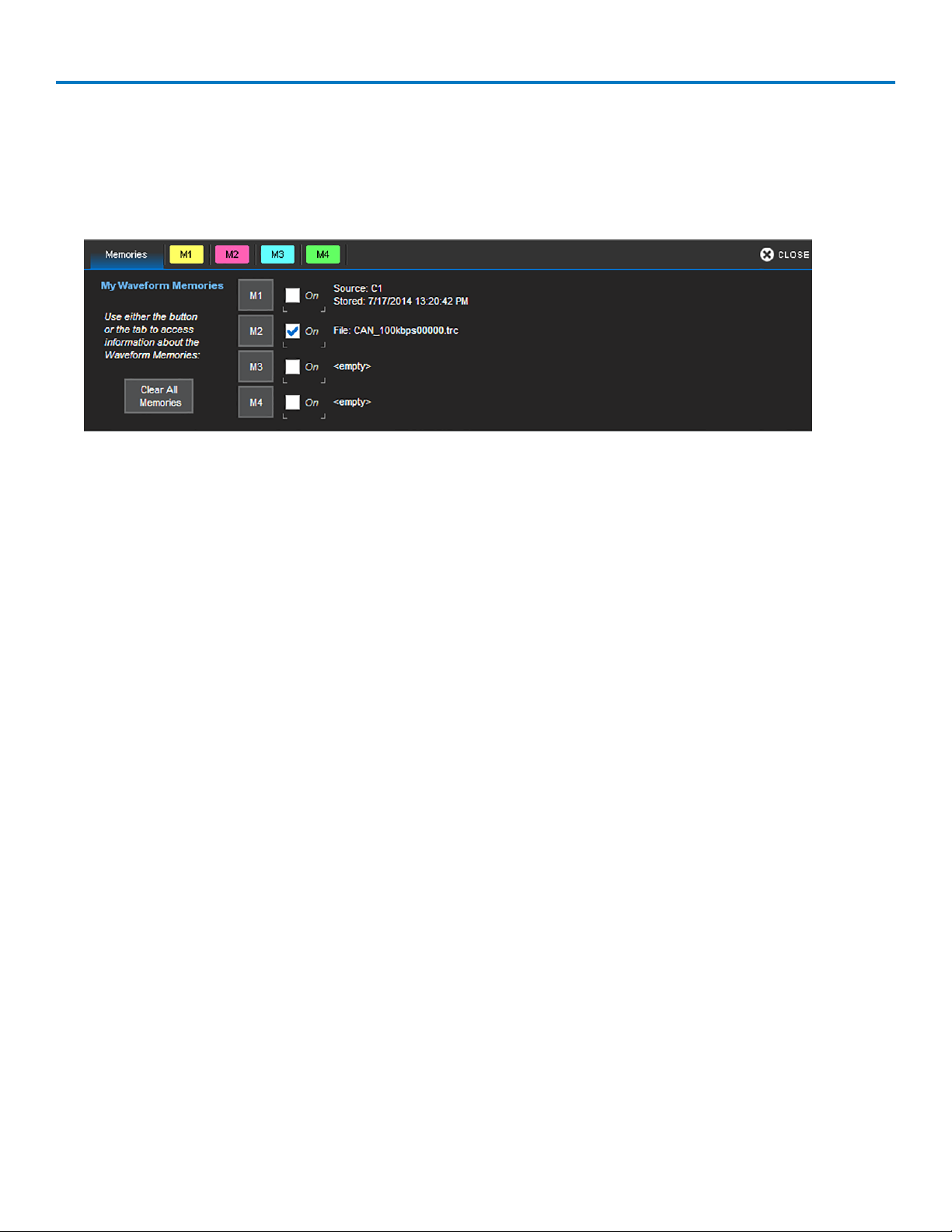
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Restore Memory
1. Access the Memories dialog by pressing the front panel Mem button or choosing Math > MemorySetup.
2. Check On next to the memory you wish to display. A description of the memory showing the source
channel and creation time appears next to each Mx on the dialog.
74
Page 83

Operator's Manual
Analysis
Most Teledyne LeCroy oscilloscopes calculate measurements for all instances in the acquisition, enabling
you to rapidly and thoroughly analyze a long memory acquisition of thousands or millions of parameter
values, or to apply a variety of mathematical functions to the waveform trace.
WaveScan searches a single acquisition for events that meet specific criteria, enabling you to zoom in on
anomalies in the waveform, or scans multiple acquisitions with allowable trigger actions when conditions
are met. It can also be used to filter measurements. A variety of views help you understand the behavior of
waveforms.
Pass/Fail Testing indicates whether or not waveforms meet a set of defined criteria.
Optional software packages may be purchased that simplify specialized analysis, such as various Serial
Data Decode options. These add new functionality to the oscilloscope Analysis menu.
WaveScan
The WaveScan®Search and Find tool enables you to search for unusual events in a single capture, or to
scan for a particular event in many acquisitions over a long period of time. Each Scan Mode is optimized to
find a different type of event. Results are time stamped, tabulated, and can be selected individually.
WaveScan window with different scan "views" turned on.
75
Page 84

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Customize the presentation by choosing different WaveScan display features, or Scan Views. Optionally, set
Actions to occur automatically when unusual events are found, such as stopping the acquisition or sounding
an alarm.
NOTE: Whenever WaveScan is enabled, the instrument reverts to Real-time sampling mode.
Scan Modes
The scan mode determines the type of search to be performed. Select the Mode along with the Source trace
to be searched on the main WaveScan dialog. For each mode, different controls appear on the WaveScan
dialog, providing additional inputs to the search criteria. Make the appropriate entries in these fields before
starting the search.
EDGE MODE
Edge Mode is used for detecting the occurrence of edges. Events that meet the threshold level are captured
and tabulated. When the acquisition is stopped, scan filters can be applied to the edges to find specific
characteristics. Additional settings for Edge Mode are:
l Slope. Choose Pos, Neg, or Both.
l Level is (set in...). Choose Percent or Absolute.
l Percent/Absolute Level. Enter a threshold value as a percentage of Top to Base or voltage level. A
marker displayed over the source trace indicates the level.
NON-MONOTONIC MODE
Non-monotonic Mode looks for edges that cross a threshold more than once between high and low levels. All
events that meet the criteria of slope, hysteresis, and level are presented in a table and highlighted in the
source trace. The value displayed in the table is the difference of the max. and min. of the non-monotonicity.
This can be confirmed with cursors. The hysteresis value is used to eliminate noise. A non-monotonicity is
detected only when its amplitude is greater than the hysteresis. Therefore, when setting a hysteresis level,
set a value that is greater than the amplitude of the noise. Additional settings for Non-monotonic Mode are:
l Slope. Choose Pos, Neg, or Both.
l Hysteresis is (set in...). Choose Division, Percent, Absolute.
l Division/Percent/Absolute. Enter the hysteresis level in the units you selected.
l Levels are (set in...). Choose Percent, Absolute, or Pk-Pk%.
l High Level and Low Level. Enter the top and bottom thresholds in the units you selected.
RUNT MODE
Runt Mode looks for pulses that fail to cross a specified threshhold. You can search for positive-going or
negative-going runts, or both. An adjustable hysteresis band is provided to eliminate noise.
76
Page 85

Operator's Manual
In the case of negative-going runt pulses, the value displayed in the table is the difference (delta) of the high
level of the signal and the runt amplitude (i.e., where the runt bottoms out). This can be confirmed by placing
cursors on the runt pulse and reading the delta Y value in the trace labels. In the case of positive-going runt
pulses, the value displayed in the table is the absolute value of the amplitude of the runt pulse. Additional
settings for Runt Mode are:
l Runt Type. Choose Both, Pos, or Neg.
l Hysteresis. Enter the hysteresis level as a percentage or voltage.
l Low Threshold and High Threshold. Enter the levels as a percentage or voltage.
l Absolute Levels. Check this box to enter levels as absolute voltage instead of percentage.
MEASUREMENT MODE
Measurement Mode is used for applying filters to measurements to find those that meet your defined
criteria, helping to isolate particular events within many samples. Markers appear over the source trace to
indicate the location of measurement, while the table displays values for the selected parameter that meet
the criteria. Additional Settings for Measurement Mode are:
l Measurement. Choose the measurement parameter you wish to search.
l Filter Method. Choose the operator that indicates the desired relationship to the Filter Limit. Only
measurements that meet this criteria are returned.
l Filter Limit. Enter the value that completes the filter criteria.
Alternatively, you can use the Filter Wizard to create the filter criteria.
BUS PATTERN MODE
Bus Pattern Mode ( only) is used for finding 2- to 16-bit patterns across the digital lines. Additional settings
for Bus Pattern Mode are:
l Viewing. Choose to enter the pattern as Binary or Hex(adecimal).
l Binary/Hex. Enter the pattern.
l Num. Patterns to detect. Enter a whole number.
Scan Views
Scan Views are different ways to view your WaveScan results. You can choose to display views
simultaneously or visit them sequentially. Just check the boxes at the bottom of the WaveScan dialog for
those views you wish to display. Uncheck the box to turn off the view.
By default, the Source Trace is displayed in the top grid, with markers indicating points in the trace that meet
the search criteria.
Table view displays a table of measurements relevant to your chosen Search Mode next to the source trace.
Times view adds columns to the table showing Start and Stop Times for each event.
77
Page 86

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Zoom view works exactly as it does elsewhere in the oscilloscope software, opening a close-up of the
source trace in a new grid that you can adjust vertically and horizontally. A Zx tab appears by default when
you launch WaveScan; see Zoom Controls for an explanation of the remainder of the controls found on this
dialog.
A unique feature of the WaveScan Zoom is that you can automatically zoom the events captured from the
source trace by touching the Prev/Next buttons on the Zx dialog. You can also select the event from the
Table display, and you are automatically relocated to that event on the zoom trace.
Setting Up WaveScan
This procedure explains how to set up WaveScan to search an acquisition for events of interest. Set up your
source channel and triggers before setting up the scan.
1. Press the front panel Stop button to stop acquisition.
2. Choose Analysis > WaveScan.
3. Check Enable.
4. Choose the Source waveform.
5. Choose the Scan Mode and enter values for any additional settings that appear at the right of the dialog
based on your selection.
6. If you're using Measurement Mode, set up the filter in one of the following ways:
l Touch Filter and choose an operator, then enter the Filter Limit.
l Touch Filter Wizard and choose one of the pre-set filters. The Filter and Filter Limit are
automatically set based on your selection.
7. Select each Scan View in which you wish to display results by checking the box at the bottom of the
dialog. Each view selected is displayed simultaneously.
8. Optionally, choose an Action to trigger when an event that meets your scan criteria is found.
9. Restart acquisition.
10. When using the Zoom view, use the Zx tab to adjust the zoom.
78
Page 87
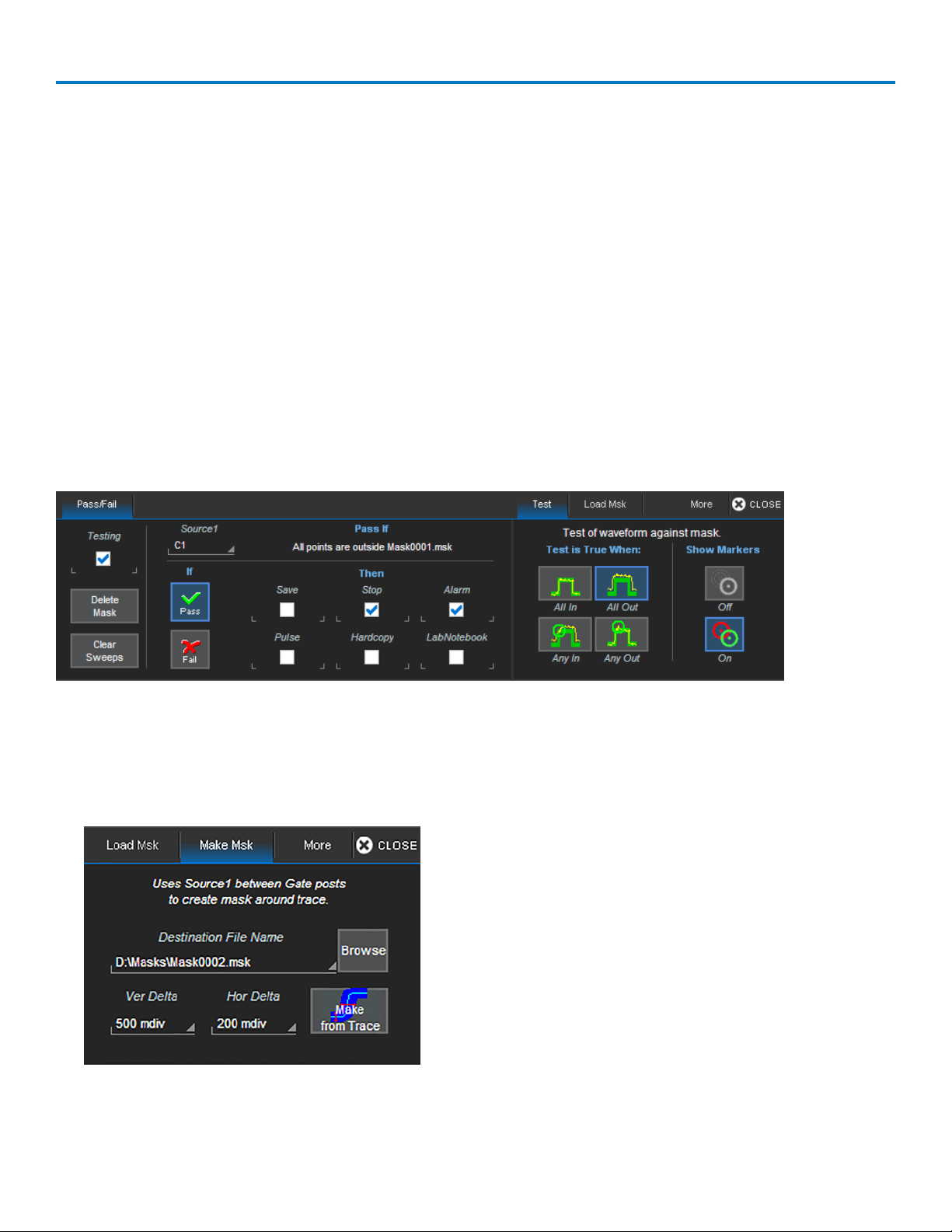
Operator's Manual
Pass/Fail Testing
Pass/Fail testing is a type of mask testing that is particularly useful for comparing newly acquired signals to
a previously acquired "golden standard" waveform.
A mask defines an area of the grid against which a source Channel, Zoom, or Math trace is compared. Test
conditions are associated with the mask, defining how the waveform is to be compared to the masked area
(e.g., some/all values fall within, some/all values fall outside), and a Pass or Fail result is returned indicating
the condition was found to be true or false.
Mask testing can be done using a pre-defined mask or a mask created from a waveform with user-defined
vertical and horizontal tolerances. The mask test can be confined to just a portion of the trace by the use of
a measure gate.
Access Pass/Fail Test Dialogs
Choose Analysis > Pass/Fail to display the Pass/Fail dialog.
Make Mask
Use this procedure to create a new mask based on a live waveform. The mask will cover the area of the
waveform, plus the boundary values you enter.
1. Touch the Make Mask tab to display the dialog.
79
Page 88
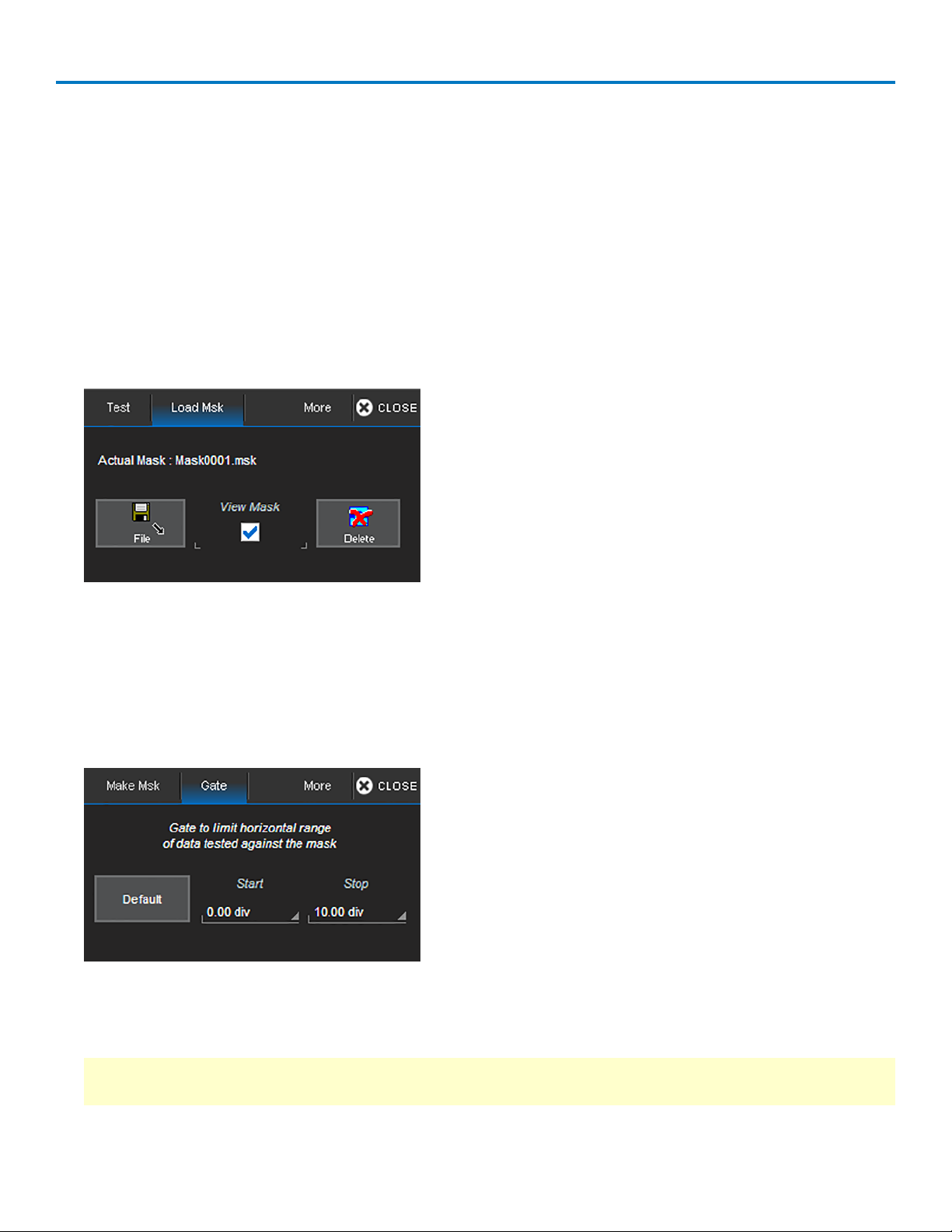
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
2. If desired, enter a new DestinationFile Name and path, or touch Browse and select a previous file to
overwrite. The file name should end with the .msk extension.
3. Touch the Ver Delta and Hor Delta fields and enter boundary values using the pop-up numeric keypad or
the front panel Adjust knob.
4. Touch Make from Trace.
Load Mask
Use this procedure in lieu of Make Mask if you have a pre-defined mask file, or wish to recall a mask you
previously created and saved.
1. Touch the Load Mask tab to display the dialog.
2. To use a saved .msk file, touch File and select the mask.
3. Check ViewMask to display the mask over the trace.
Set Gates
Optionally, set gates to limit the portion of the waveform that is compared to the mask.
1. Touch More to display the Gate tab, then open the Gate dialog.
2. Enter the Start and Stop horizontal divisions that mark the segment of the waveform to be tested with
this mask. This can be a whole division or a fraction of a division. Divisions are numbered 1-n left to
right.
Tip: A quick way to position the gate is to drag the gate posts initially placed at the extreme left and right
ends of the grid to the desired points.
80
Page 89

Operator's Manual
Define Test
1. Touch More to display the Test tab, then open the Test dialog.
2. Select one of the conditions that, when True (yes), result in a Pass.
3. Optionally, turn Off/On markers. Markers visually indicate where on the waveform mask violations have
occurred.
Run Test
1. On the main Pass/Fail dialog, select the Source trace to test.
2. Select any additional actions for the oscilloscope to take in the event of a Pass or Fail.
Save the waveform to a file.
Stop the test.
Sound an Alarm.
Send a Pulse via the Aux Out connector.
Capture the screen and process it according to your Hardcopy setting (print, email, or save it to file).
3. Select the Testing checkbox to start the test.
A test counter showing the number of sweeps and the number that Passed or Failed appears below the
grid area. If you have turned on markers, the source waveform samples that Failed the mask test are
overlaid in red on the grid; the samples that Passed the test are overlaid in green.
Removing a Mask from the Display
1. Access the Pass Fail dialogs.
2. Touch the Delete Mask button.
81
Page 90

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Utilities
Utilities
Utilities settings primarily control the instrument's interaction with other devices/systems. Preferences, on
the other hand, tend to control the appearance and performance of the oscilloscope application.
To access the Utilities dialog, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup... from the menu bar.
HardCopy Setup, Date/Time Setup, and System Status buttons open their corresponding dialogs, as do the
tabs.
There are also tabs linking to Remote Control, Auxilliary Output, and Options settings.
Touch-Screen Calibration launches a sequence of display calibration screens. You will be prompted through
a series of actions to improve the precision and accuracy of the touch screen.
The Service button to the far right of the dialog launches a section of the application reserved for qualified
Teledyne LeCroy service personnel. An access code is required to enter this section.
System Status
The Utilities Status dialog displays information about your instrument including model number, serial
number, firmware version, and installed hardware and software options.
Choose Utilities > Utilities Setup from the menu bar, then touch the Status tab.
OR
Choose Support > About from the menu bar.
The Utilities Status is not the same as the Status feature accessed through various menus (e.g., Vertical >
Channels Status). That feature displays the current state of the oscilloscope configurations —such as
acquisition, channel, measurement parameter, math function, and memory settings.
82
Page 91

Operator's Manual
Remote Control Settings
The Remote dialog contains settings to configure remote control of the instrument. Supported protocols are:
l TCPIP (Ethernet). If you choose this option, also install Teledyne LeCroy's VICP drivers on the
controller. These are included in the VICP Passport plug-in, available free from teledynelecroy.com.
The instrument uses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) as its default addressing protocol.
You can assign a static IP address using the standard Windows network setup menus.
l LXI (Ethernet)
l GPIB. To activate this option, connect the GPIB-USB adapter to any host USB port.
Assign Static IP Address/Name Server
Before starting, consult with your Network Administrator regaring the oscilloscope's network address,
subnet, default gateway.
NOTE: You can also use this procedure to assign a name server if your network uses DHCP addressing.
1. Connect a keyboard to the front panel USB port.
2. From the menu bar, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup, then touch the Remote tab.
3. On the Remote dialog, touch Net Connections.
4. Touch the SMSC icon.
5. On the Ethernet Driver Settings dialog, choose Specify an IP Address.
If assigning a Name server, leave Obtain an IP address via DHCP.
6. Touch the IP Address field, and use the keyboard to enter the address. Repeat for Subnet Mask and
Default Gateway.
Alternatively, touch the Name Server tab and enter the DNS server address.
7. Touch the window close boxes to return to the oscillosocpe application.
83
Page 92

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Set Up Remote Control
1. From the menu bar, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup, then touch the Remote tab.
2. On the Remote dialog, make a Control From selection.
3. If using TCPIP or LXI, touch the Net Connections button and select a network from the pop-up.
4. If using TCPIP and wish to restrict control of the oscilloscope to specific network clients, touch Yes.
Enter the IP addresses or DNS names of the authorized controllers in a comma-delimited list.
Configure the Remote Control Assistant Event Log
The Remote Control Assistant monitors communication between the controller and oscilloscope when you
are operating the instrument remotely. You can log all events or errors only. The log can be output to an
ASCII file and is invaluable when you are creating and debugging remote control programs.
1. From the menu bar, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup, then touch the Remote tab.
2. Under Remote Control Assistant, touch Log Mode and choose Off, Errors Only, or Full Dialog.
3. To always clear the log at startup, check Reset to Errors Only and clear at startup.
Export Contents of the Event Log
1. From the menu bar, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup, then touch the Remote tab.
2. Touch the Show Remote Control Log button. The Event Logs pop-up is shown.
3. Enter a log file name in DestFilename, or touch Browse and navigate to an existing file.
NOTE:New contents will overwrite the existing content; it is not appended.
4. Touch Export to Text File.
84
Page 93

Operator's Manual
Hardcopy (Print) Settings
Hardcopy settings control how the oscilloscope Print function behaves. Print captures an image of the
oscilloscope display, but there are several options as to what it does with the image next:
l Send to a hardcopy printer
l "Print" to a file that can be saved to an internal or external drive
l Send to E-Mail
l Copy to the Windows clipboard for you to paste elsewhere
Each option is set up on the Utilities Hardcopy dialog. You can further set up a default print color scheme
and capture area. A preview of your hardcopy setup appears to the right of the dialog.
NOTE: You can configure the front panel Print button to create a new Notebook Entry to be included in a
LabNotebook report. This is not done in Utilities Hardcopy, but in LabNotebook itself. See Print to Notebook
Entry. However, the File menu Print option will continue to use your Hardcopy setting.
From the menu bar, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup > Hardcopy to display the Hardcopy dialog.
Send to Printer
ADD PRINTER
NOTE: Any printer compatible with the oscilloscope's Windows OS is supported. Minimize the oscilloscope
application and use the Windows controls to install printer drivers. Connect printers via LAN (Ethernet) or
USB.
1. On the Utilities Hardcopy dialog, choose Printer.
2. Touch the Add Printer button that appears. A Microsoft Windows Devices and Printers window opens
where you can configure a new printer.
3. To make the printer the instrument default, select it from the Select Printer list.
85
Page 94

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
PRINT SETUP
1. On the Hardcopy dialog, choose Printer.
2. Touch Select Printer and choose a printer from the list. If you don't see the printer you want, first follow
steps to Add Printer.
3. Choose a page Orientation: portrait or landscape.
4. Optionally, choose a color scheme and hardcopy (print) area.
5. Optionally, touch Properties to open the Windows print dialog and adjust printer properties.
Print to File
Image files can be saved to any folder on the oscilloscope hard drive, or to an external drive connected to a
USB port.
1. On the Hardcopy dialog, choose File.
2. Choose the output File Format.
3. Enter a File Name. This will form the basis of all print filenames, until you change it.
NOTE: Numbers at the end of the filename will be truncated, as the instrument appends numbers to this
name with each new file. If you wish to add your own identifying numbers, place them at the front of the
name.
4. Optionally, enter the path to a new save Directory, or touch the Browse button and navigate to the folder.
NOTE: The default print folder is C:\...\XStream\Hardcopy. Other types of files that may be saved using
other oscilloscope functions, such as masks and scripts, have their own XStream subfolders.
5. Optionally, choose a color scheme and hardcopy (print) area.
Copy to Clipboard
This procedure copies the screen to the clipboard so you can paste it into another application (Microsoft
Word, for example).
1. On the Hardcopy dialog, choose Clipboard.
2. Optionally, choose a color scheme and hardcopy (print) area.
86
Page 95

Operator's Manual
Send to E-Mail
Follow this procedure to e-mail capture files to a preset address. The e-mail connection is set up in Utilities
> Preferences Setup > E-Mail.
1. On the Hardcopy dialog, choose E-Mail.
2. Choose the output File Format.
3. If you wish to be able to include messages with the files as they are sent, check Prompt for message to
send with mail.
4. Optionally, choose a color scheme and hardcopy (print) area.
5. To go on and set up the e-mail connection, touch Configure E-Mail Server and recipient.
Choose Print Color Scheme
To change the color of your print output, touch the Color button on the Hardcopy dialog and choose from:
l Standard(default) - prints objects on a black background, as they appear on the display.
l Print - prints objects on a white background using your chosen colors. This option saves ink.
l Black & White - prints objects in grayscale.
Set Print Area
To limit which part of the touch screen is captured, touch Hardcopy Area on the Hardcopy dialog and choose
from:
l Grid Area Only - omits dialogs and menus and prints only the grids.
l DSO Window - prints the dialogs with the grids.
l Full Screen - prints the entire touch screen.
87
Page 96
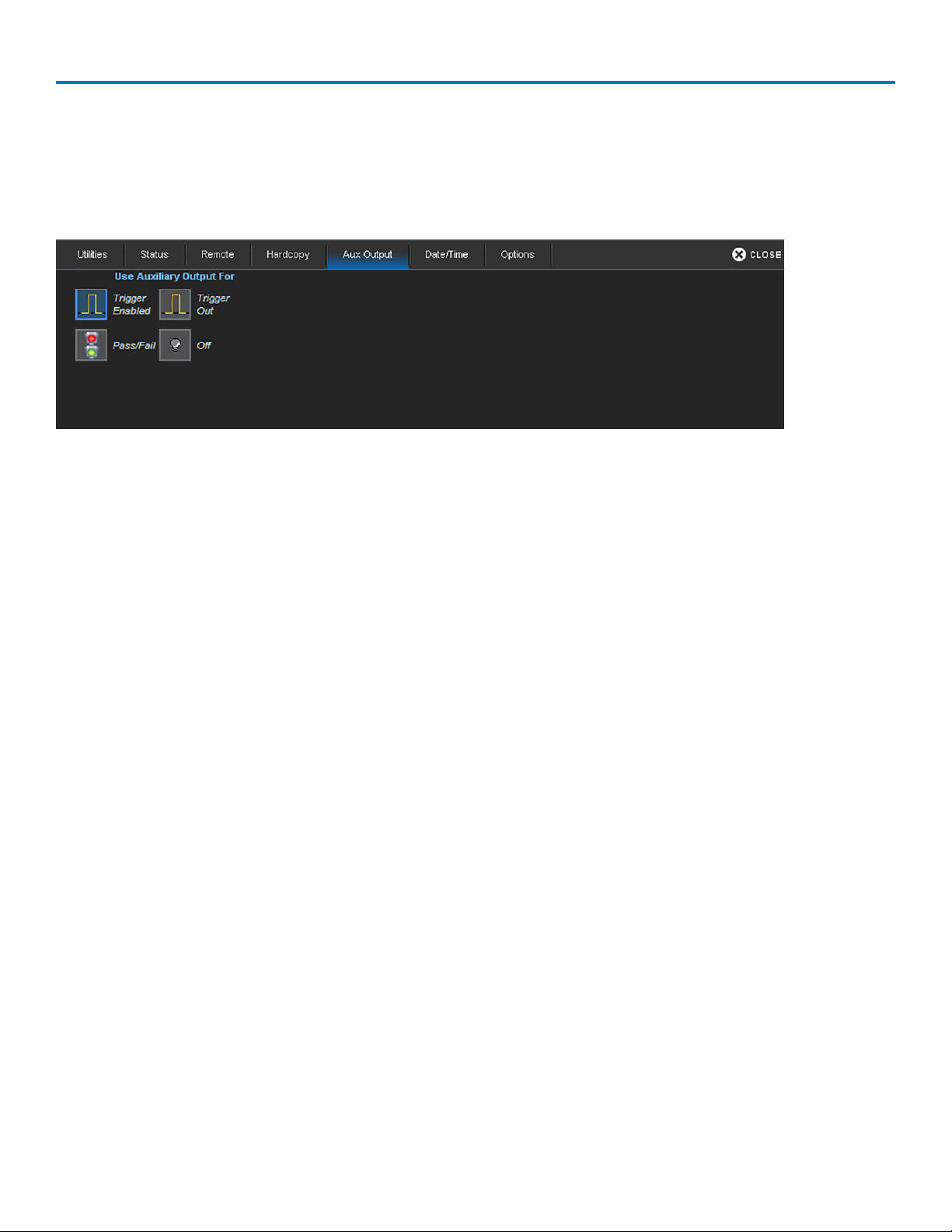
WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Auxiliary Output Settings
Use the Aux Output dialog to configure the output of the Aux Out and Cal Out ports.
Use the Aux Output dialog to configure the output of the Aux Out port. The port outputs a 1.0 V TTL pulse
following the selected event.
l Trigger Enabled sends a pulse when the oscilloscope trigger is ready (Ready indicator lit), but not
necessarily fired. It can be used as a gating function to trigger another instrument when the
oscilloscope is ready.
l Trigger Out sends a pulse when the oscilloscope trigger fires (Trig'd Indicator lit). It can be used to
trigger an external oscilloscope off the instrument's state.
l Pass/Fail generates a pulse when Pass/Fail testing is active and conditions are met. With this
selection, a Pulse Duration data entry control appears. Provide a value within your instrument's
specified range, which varies by model. Refer to datasheet specifications at teledynelecroy.com.
Off disables auxiliary input/output.
88
Page 97

Operator's Manual
Date/Time Settings
Date/Time settings control the oscilloscope's timestamp. These numbers appear in the oscilloscope
message bar and on tables/records internal to the oscilloscope application, such as History Mode and
WaveScan.
NOTE: This is not the same as the Timebase reference clock used to synchronize traces.
To access the Date/Time dialog, choose Utilities > Utilities Setup from the menu bar, then touch the
Date/Time tab.
Manual Method
Enter the Hour, Minute, Second, Day, Month, and Year, then touch the Validate Changes button.
Internet Method
This method uses the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) to read the time from time-a.nist.gov. The
oscilloscope must be connected to an internet access device through the LAN (Ethernet) port on your
instrument's I/O panel. .
If your connection is active, touch the Set from Internet button.
Windows Method
To set date and time using the internal Windows system clock, touch the Windows Date/Time button. This
displays the standard Windows DateTime Properties pop-up dialog, where you can further configure these
settings. If you are satisfied with the setup, just touch OK.
Options
The Options dialog is used to add or remove software options. This dialog also displays the ScopeID and
Serial #. See Adding an Option Key for instructions on using this dialog.
89
Page 98

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Disk Utilities
Use the Disk Utilities dialog to manage files and folders on your instrument's hard drive. Disk Space
information is shown at the far right of the dialog for convenience.
NOTE: These tasks can also be accomplished using the standard Microsoft Windows file management tools.
Choose File > Minimize to access the Windows desktop and task bar.
Access the Disk Utilities dialog by selecting Utilities > Disk Utilities from the menu bar, or choose any of the
Save/Recall functions and open the Disk Utilities tab.
Delete a Single File
1. Touch the Delete button.
2. Browse to the current folder containing the file.
3. Browse to the file to be deleted, or use the Upand Down arrow buttons to scroll through the files in the
folder.
4. With the desired file selected, touch Delete File.
Delete All Files in a Folder
1. Touch the Delete button.
2. Browse to the current folder containing the file.
3. With the desired folder selected, touch Empty Folder.
Create a New Folder
1. Touch Create.
2. Touch Current folder and provide the full path to the new folder, including the folder name.
3. Touch Create Folder.
90
Page 99

Operator's Manual
Preferences Settings
Preference settings have mostly to do with the appearance and performance of the oscilloscope itself, rather
than the oscilloscope's interaction with other devices/systems.
Access the Preferences dialog by choosing Utilities > Preference Setup... from the menu bar.
Audible Feedback controls the instrument's audio output. Select this box to hear a beep each time you touch
a screen or front panel control.
Automatic Calibration enables or disables the temperature dependent calibration feature. When enabled, the
instrument will offer you a choice of calibrations to perform whenever there is a significant change in
ambient temperature.
NOTE: If you do not enable this option, the oscilloscope re-calibrates only at startup and whenever you
change certain operating conditions.
Language sets the language used on the display.
There are also tabs linking to Acquisition, E-Mail, and Miscellaneous settings.
91
Page 100

WaveSurfer 10 Oscilloscopes
Acquisition Settings
The Acquisition settings determine how traces behave on screen as gain or timebase changes.
Offset Setting constant in:
l Volts moves the vertical offset level indicator with the actual voltage level.
l Div(isions) keeps the vertical offset level indicator stationary. The waveform remains on the grid as
you increase the gain; whereas, if Volts is selected, the waveform could move off the grid.
Delay Setting constant in:
l Time moves the horizontal offset level indicator with the trigger point.
l Div(isions) keeps the horizontal offset indicator stationary. The trigger point remains on the grid as you
increase the timebase; whereas, if Time is selected, the trigger point could move off the grid.
NOTE: The Offset is always in volts, and the Delay is always in time. However, whenever Div is selected,
these are scaled proportional to the change in gain or timebase, thereby keeping the division of the grid
constant.
Checking Reset trigger counter before starting a new acquisition clears the trigger counter each time the
oscilloscope issues an acquisition command. It is only available when trigger Holdoff is set.
92
 Loading...
Loading...