Page 1

2403 Walsh Avenue, Santa Clara, CA 95051-1302 Tel:
+1/408.727.6600 Fax: +1/408.727.6622
IBTracer
Verification Script Engine
User Manual
IBTracer VSE Manual Version 1.0
For IBTracer Software Version 2.2 or Higher
1 November, 2002
Page 2

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................................. 4
2. Verification Script Structure....................................................................................... 4
3. Interaction between IBTracer and verification script ............................................... 7
4. Running verification scripts from IBTracer............................................................... 9
4.1 R
4.2 E
5. Verification Script Engine Input Context members................................................ 12
5.1 T
5.2 T
6. Verification Script Engine Output Context members............................................. 14
7. Verification Script Engine events ............................................................................ 14
7.1 P
7.2 N
8. Sending functions ..................................................................................................... 15
8.1 SENDCHANNEL()...................................................................................................................... 15
8.2 S
8.3 S
8.4 S
9. Timer functions ......................................................................................................... 19
9.1 VSE TIME OBJECT .................................................................................................................... 19
9.2 S
9.3 K
9.4 G
10. Time construction functions .................................................................................... 20
10.1 TIME() ...................................................................................................................................... 20
10.2 T
11. Time calculation functions ....................................................................................... 21
11.1 ADDTIME()............................................................................................................................... 21
11.2 S
11.3 M
11.4 D
12. Time logical functions............................................................................................... 23
12.1 ISEQUALTIME()........................................................................................................................ 23
12.2 I
12.3 I
13. Time text functions ................................................................................................... 25
13.1 TIMETOTEXT()......................................................................................................................... 25
14. Output functions ....................................................................................................... 25
14.1 REPORTTEXT() ......................................................................................................................... 25
14.2 E
14.3 D
15. Common Retrieving functions ................................................................................. 26
15.1 RETRIEVEPKTPAYLOAD() ........................................................................................................26
15.2 I
16. Packet Header retrieving functions ......................................................................... 27
UNNING VERIFICATION SCRIPTS.............................................................................................. 10
DITOR SETTINGS..................................................................................................................... 12
RACE EVENT-INDEPENDENT SET OF MEMBERS........................................................................ 13
RACE EVENT-DEPENDENT SET OF MEMBERS. .......................................................................... 13
ACKET EVENTS. ......................................................................................................................14
OTIFICATION EVENTS. ............................................................................................................ 15
ENDEVENT ().......................................................................................................................... 16
ENDLINKPKT () ......................................................................................................................17
ENDMAD () ........................................................................................................................... 17
ETTIMER().............................................................................................................................. 19
ILLTIMER() ............................................................................................................................ 19
ETTIMERTIME() ..................................................................................................................... 20
IMEFROMSYMBOLS() ............................................................................................................. 21
UBTRACTTIME() ..................................................................................................................... 22
ULTIMEBYINT().................................................................................................................... 22
IVTIMEBYINT() ..................................................................................................................... 23
SLESSTIME() ........................................................................................................................... 24
SGREATERTIME().................................................................................................................... 24
NABLEOUTPUT() .................................................................................................................... 26
ISABLEOUTPUT() ................................................................................................................... 26
SMAD() ................................................................................................................................... 27
Page 2 of 35
Page 3

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
16.1 GETLRHFIELD() ...................................................................................................................... 27
16.2 G
16.3 G
16.4 G
16.5 G
16.6 G
16.7 G
16.8 G
16.9 G
16.10 G
ETBTHFIELD() ...................................................................................................................... 28
ETGRHFIELD()...................................................................................................................... 28
ETDETHFIELD() ................................................................................................................... 29
ETRETHFIELD().................................................................................................................... 29
ETATOMICETHFIELD() .........................................................................................................30
ETATOMICACKETHFIELD() .................................................................................................. 30
ETRDETHFIELD()................................................................................................................. 31
ETRWHFIELD()..................................................................................................................... 31
ETPOSTHDRFIELD()........................................................................................................... 31
17. MAD decoded fields retrieving functions................................................................ 32
17.1 G
17.2 G
ETDECODEDMADFIELD() ..................................................................................................... 32
ETHEXMADFIELD().............................................................................................................. 33
18. Miscellaneous functions........................................................................................... 34
18.1 S
18.2 S
CRIPTFORDISPLAYONLY() ..................................................................................................... 34
LEEP()..................................................................................................................................... 34
19. The VSE important script files ................................................................................. 34
APPENDIX A How to Contact CATC ................................................................................................ 35
Page 3 of 35
Page 4

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
1. Introduction
This document contains a description of the CATC’s Verification Script Engine (VSE) – a new
feature in the IBTracer software that allows users to create custom tests on Infiniband(IB) traffic,
recorded on CATC’s Infiniband protocol analyzers.
The VSE conveniently allows users to ask the IBTracer application to send some of desired
“events” ( packets and some predefined notifications ) that occurred in the recorded IB trace to a
special verification script written using CATC script language. The script then evaluates the sequence
of events (timing, data or both) in accordance with user-defined conditions.
Using the VSE API, users can easily retrieve information about any field in IB packet headers,
Link packets and MADs, make very complex timing calculations between different events in recorded
trace, filter data in or out of the trace with dynamically changing filtering conditions, and display all
interesting information in the special output window.
2. Verification Script Structure.
A varification script file should have extension *.dec, and be located in the subfolder
..\Scripts\VFScripts of the main IBTracer folder. Some other files might be included in the main script
file using directive %include. (see CATC Script Language (CSL) manual for details)
The following schema can present the common structure of verification script:
#
#
# VS1.dec
#
# Verification script
#
# Brief Description:
# Verify something…
#
############################################################################################
# Module info
#
############################################################################################
# Filling of this block is necessary for proper verification script operation...
#
############################################################################################
set ModuleType = "Verification Script"; # Should be set for all verification scripts
set OutputType = "VS"; # Should be set for all verification scripts
set InputType = "VS"; # Should be set for all verification scripts
Page 4 of 35
Page 5

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
set DecoderType = "<Your VScript name>"; # Should be set for all verification scripts
set DecoderDesc = "<Your Verification Script description>"; # Optional
############################################################################################
##########
#
# include main Verification Script Engine definitions
#
%include "VSTools.inc" # Should be set for all verification scripts
######################################################################################
# Global Variables and Constants #
######################################################################################
# Define your verification script-specific global variables and constant in this section...
# (Optional)
const MY_GLOBAL_CONSTANT = 10;
set g_MyGlobalVariable = 0;
######################################################################################
######################################################################################
# OnStartScript() #
######################################################################################
# #
# It is a main intialization routine for setting up all necessary #
# script parameters before running the script. #
# #
######################################################################################
OnStartScript()
{
######################################################################################
# Specify in the body of this function initial values for global variables #
# and what kind of packets or trace events should be passed to the script. #
# ( By default, only MAD packets and Link state change events from both channels #
# will be passed to the script. #
# #
# For details – how to specify what kind of events should be passed to the script #
# please see the topic ‘sending functions’. #
# #
# OPTIONAL. #
######################################################################################
# Uncomment the line below - if you want to disable output from
# ReportText()-functions.
#
# DisableOutput();
}
Page 5 of 35
Page 6

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
######################################################################################
# ProcessData() #
######################################################################################
#
# #
######################################################################################
# It is a main script function called by the application when the next waited event #
# occured in the evaluated trace. #
# #
# !!! REQUIRED !!! – MUST BE IMPLEMENTED IN VERIFICATION SCRIPT #
######################################################################################
# #
ProcessData()
{
#
# The function below will show specified message only one time # no matter how many times ProcessData is called.
#
ShowStartPrompt("ShowStartPrompt\n");
# Write the body of this function depending on your needs …
return Complete();
}
######################################################################################
# OnFinishScript() #
######################################################################################
#
######################################################################################
# It is a main script function called by the application when the script completed #
# running. Specify in this function some resetting procedures for a successive run #
# of this script. #
# #
# OPTIONAL. #
######################################################################################
OnFinishScript()
{
return 0;
}
######################################################################################
######################################################################################
# Additional script functions. #
######################################################################################
# #
# Write your own script-specific functions here... #
# #
######################################################################################
MyFunction( arg )
{
if( arg == “Blah” ) return 1;
Page 6 of 35
Page 7

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
return 0;
}
3. Interaction between IBTracer and verification script
The following describes how IBTracer interacts with a verification script to test an open trace:
1. When a verification script is run, VSE looks for the function OnStartScript() and calls it if it is
found. In the OnStartScript() function, setup routines can be created that can perform tasks such
as specifying what kind of trace events should be passed to the script, and setting up initial
values of global script-specific global variables.
2. VSE then goes through the recorded trace and checks if the current packet in the trace meets
specified sending criteria – if the criteria are met, VSE calls the script’s main processing
function ProcessData() and provides input context variables to the script about the current
event. (Please refer to the topic “Input context variables” below in this document for full
description of verification script input context variables )
3. The ProcessData() function, which is present in all verification scripts, then processes whatever
event has been sent to the script and verifies that the information in the event is appropriate for
the current stage of the verification process. At the completion of each stage, the ProcessData()
function determines if VSE should continue running the script or not. If the result for any given
stage of the script is clear, the script tells VSE to complete execution of the script.
The decision to terminate the test prior to evaluating the entire trace is controlled by the
output context variable: out.Result = _VERIFICATION_PASSED or
_VERIFICATION_FAILED.
(Please refer to the topic “Output context variables” below in this document for full description
of verification script output context variables)
4. When script running is finished, VSE looks for the function OnFinishScript() and calls it if it is
found. In this function some resetting procedures can be done.
The following picture describes the interaction between the IBTracer application and the running
verification script:
Page 7 of 35
Page 8
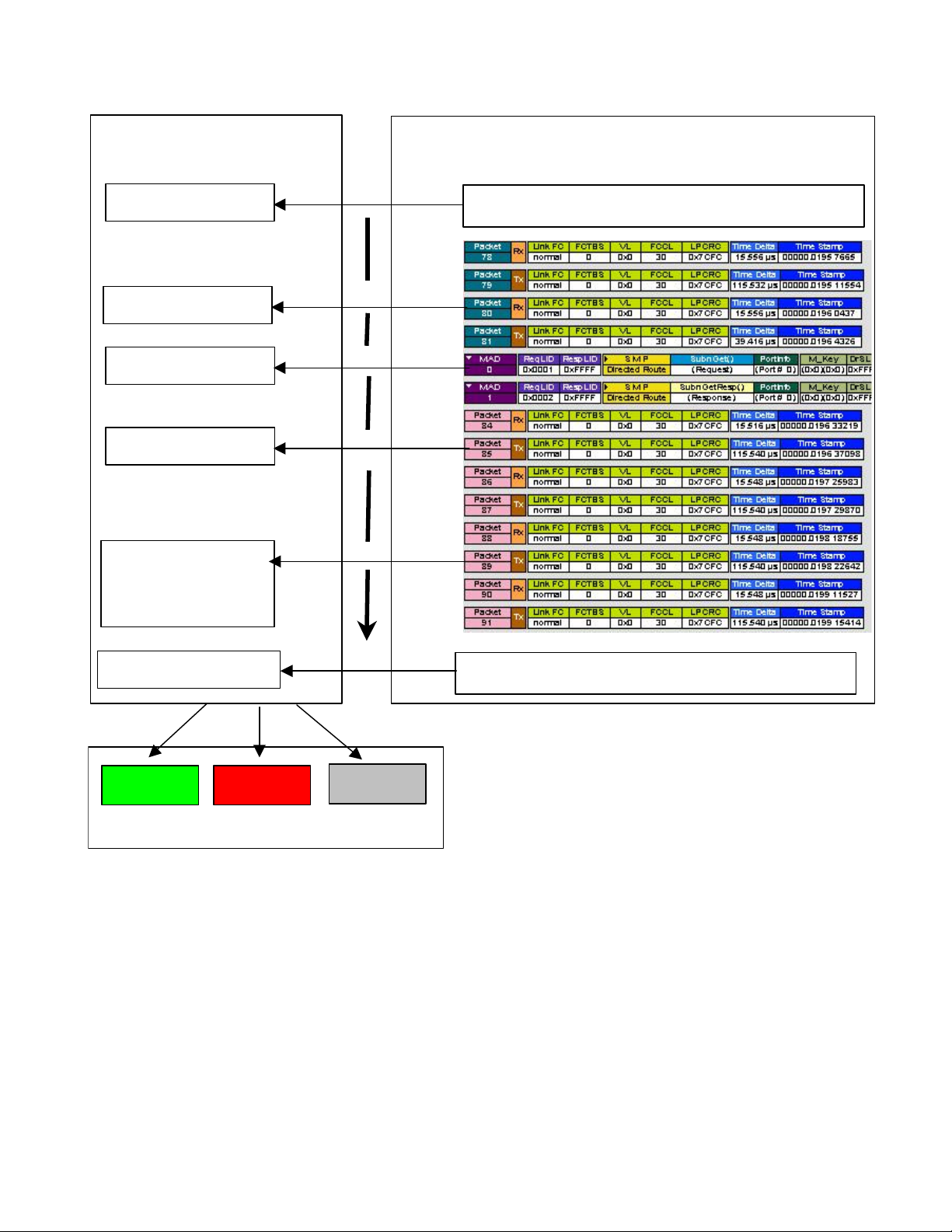
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
V
_
r
_
p
V
erification Script
IBTracer Application
(Run verification script)
OnStartScript()
ProcessData()
ProcessData()
ProcessData()
ProcessData()
Set out.Result =
VERIFICATION_PASSED o
VERIFICATION_FAILED
will com
lete the script run.
Call
Call..
Call..(If expected event )
Call..(If expected event )
Call..(If expected event )
..(If expected event )
Starting VSE running …
OnFinishScript()
PASSED
FAILED
Call..
DONE
Finishing VSE running … …
erification Script results
NOTE: Verification script result : <DONE> means that the script is intended solely for
extracting and displaying some information from recorded traces and that the user does not
care about the result . To specify that your script is intented only for the purposes of
displaying information, call somewhere in your script ( in OnStartScript() – for instance )
function ScriptForDisplayOnly() )
Page 8 of 35
Page 9
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
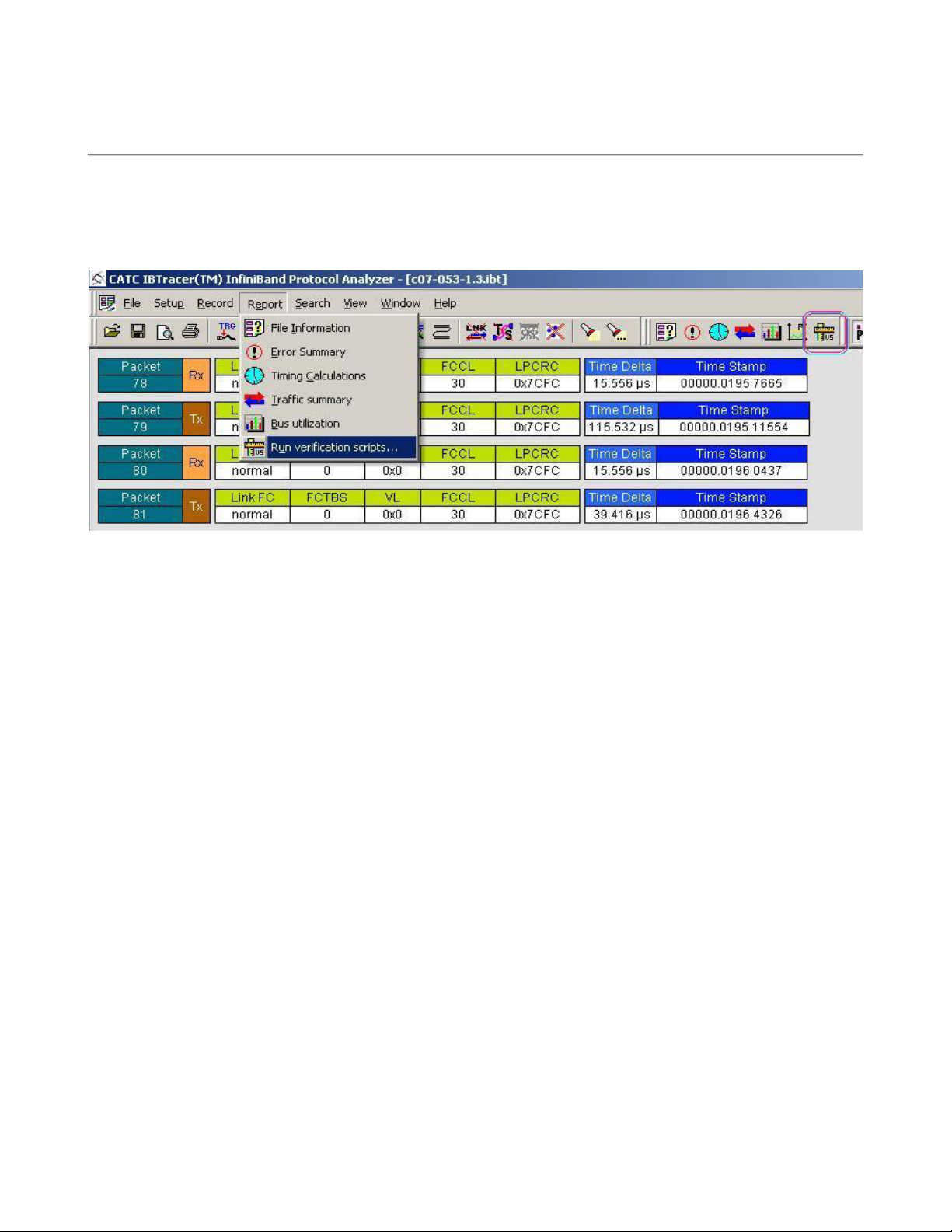
4. Running verification scripts from IBTracer
To run a verification script over a trace –run the command Report>Run verification scripts…
from the menu or push the button shown below on the main toolbar ( if it is not hidden ):
The special dialog will open inviting to choose and run one or several verification scripts:
Page 9 of 35
Page 10
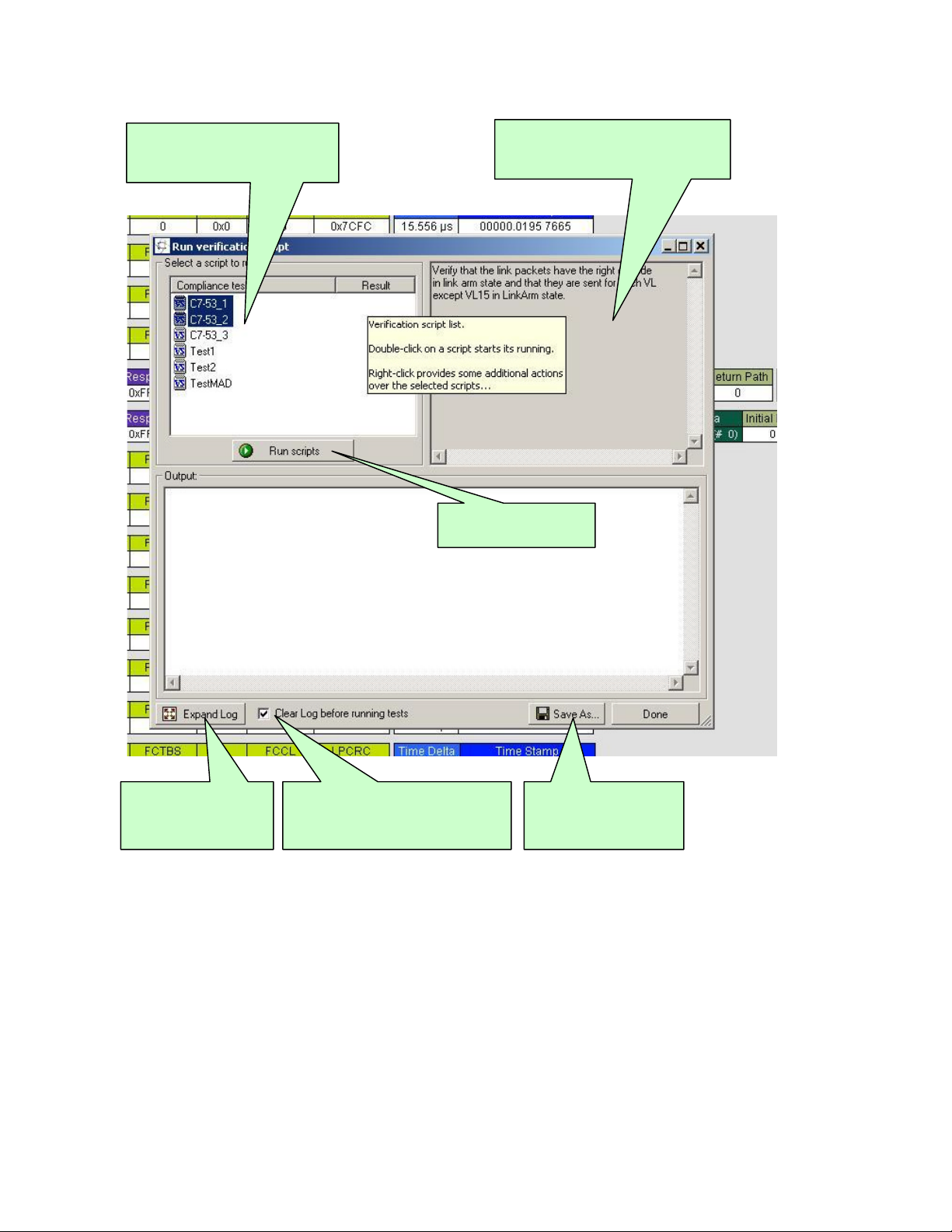
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Verification Script List.
Name for scripts are defined in
set DecoderType = "MyName";
Verification Script description.
Descriptions for scripts are defined in
set DecoderDesc= "MyDescription";
Start running selected
verification scripts
Maximize dialog and
expand output window
This option( if set ) clears up the
contents of the output window when
'Run scripts' button is pressed.
Save contents of output
window in a text file
4.1 Running verification scripts.
Push the button ‘Run scripts’ after you selected desired scripts to run. VSE will start the
selected verification scripts, show script report information in the output window and present
results of verification in the script list:
Page 10 of 35
Page 11
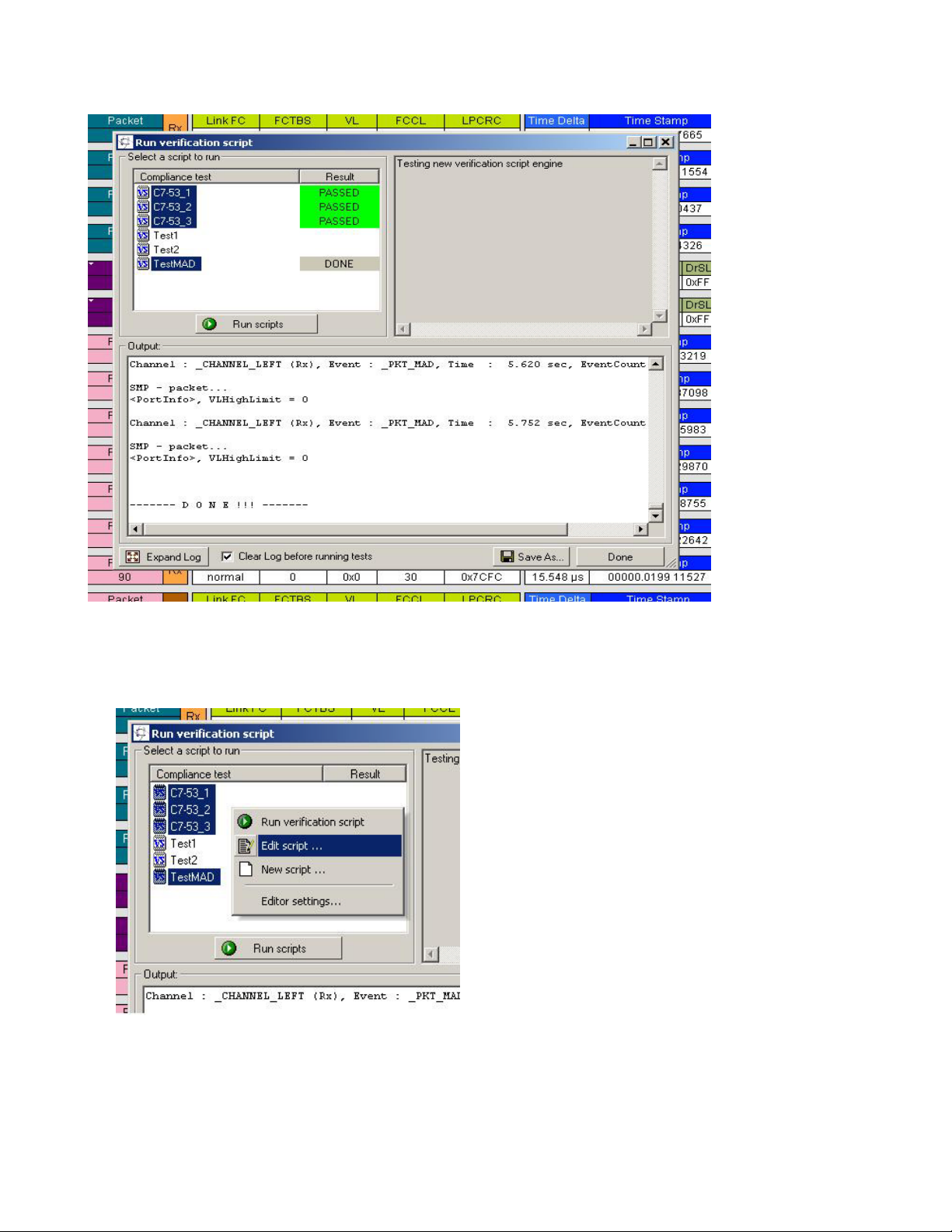
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Right-click in script list to open a pop-up menu with options for performing additional operations
over selected scripts:
Run verification script – starts running selected script.
-
Page 11 of 35
Page 12

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Edit script – allows you to edit selected scripts using whatever editor application has been
specified in ‘Editor settings’.
New script – creates a new script file using the template specified in ‘Editor settings’.
-
Editor settings – allows to specify some settings for editing scripts and creating new ones.
-
4.2 Editor settings.
After choosing ‘Editor settings’ the following dialog will appear:
This option (if set) allows editor
applications supporting multi-document
interface (MDI) to edit all script files
related to the selected scripts in one
application instance.
Otherwise, a new application instance
will be launched for each script file.
This option (if set) allows editor
applications to edit all included files
(extension : *.inc) along with main
verification script files (extension : *.dec )
Otherwise, only main verification script
files will be open for editing.
Launches editor application in
full screen mode.
Full path to the file to be used
as a template for a new script.
5. Verification Script Engine Input Context members
All verification scripts have input contexts –special structures whose members are set by the script
and can be used inside of the application. ( For more details about input contexts – please refer to the
CATC Script Language(CSL) Manual ). The verification script input contexts have two sets of
members:
- Trace event-independent set of members.
- Trace event -dependent set of members.
Page 12 of 35
Page 13

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
5.1 Trace event-independent set of members.
This set of members is defined and can be used for any event passed to script:
in.Time - time of the event( type : list, having format : 2 sec 125 ns -> [2 , 125])
in.Channel - channel where the event occured. ( can be _CHANNEL_LEFT or _CHANNEL_RIGHT
indicating on which channel event occurred )
in.TraceEvent - type of trace events( application predefined constants are used. See list of possible
events below )
5.2 Trace event-dependent set of members.
This set of members is defined and can be used only for a specific events or after calling some
functions filling out some of variables:
5.2.1 All packet-specific set of members.
( valid for any packets - but only after RetrievePktPayload()-function was called – see description of
this function for details )
in.Payload - bit source of the packet payload ( you can extract any necessary
information using GetNBits(), NextNBits() or PeekNBits() functions – please refer to CSL Manual for
details about these functions )
in.PayloadLength - the length( in bytes of the retrieved packet payload )
5.2.2 Link packet-specific set of members.
(valid for link packets only, undefined for other events )
in.Opcode
in.VL
in.FCCL
in.FCTBS
in.LPCRC
5.2.3 Link state change notification-specific set of members.
(valid for Link State Change notifications only, undefined for other events )
in.LinkStatePrev - previous link state(Opcode)
Page 13 of 35
Page 14

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
in.LinkStateCurr - current link state(Opcode)
6. Verification Script Engine Output Context members
All verification scripts have output contexts –special structures whose members are set by the
script and can be used inside of the application ( For more details about output contexts – please refer
to the CATC Script Language(CSL) Manual ). The verification script output contexts have only one
member:
out.Result - the result of the whole verification program defined in the verification script.
This member is supposed to have 3 values:
_VERIFICATION_PROGRESS,( is set by default when script starts running )
_VERIFICATION_PASSED,
_VERIFICATION_FAILED
The last two values should be set if you decide that recorded trace does ( or not ) satisfy the
imposed verification conditions. In both cases the verification script will stop running.
If you don't specify any of those values - the result of script execution will be set as
VERIFICATION_FAILED at exit.
7. Verification Script Engine events
VSE defines a large group of trace “events” – packets or special notifications – that can be
passed to a verification script for evaluation or retrieving and displaying some contained information.
The information about the type of event can be seen in in.TraceEvent. Please refer to the topic
“Sending functions” in this manual for details about how to send events to scripts.
7.1 Packet events.
The table below shows current list of packet events and value of in.TraceEvent:
Packet in.TraceEvent
TS1 _PKT_TS1
TS2 _PKT_TS2
Link Packet _PKT_LINK
MAD packets _PKT_MAD
Reliable Connection packets _PKT_RC
Reliable Datagram packets _PKT_RD
Unreliable Connection packets _PKT_UC
Unreliable Datagram packets _PKT_UD
Page 14 of 35
Page 15

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Skips _PKT_SKIPS
7.2 Notification events.
VSE defines a group of notification events that can be passed to a verification script for
evaluation or for retrieving and displaying some contained information. The information about the type
of event can be seen in in.TraceEvent. Please refer to the topic “Sending functions” in this manual for
details about how to send events in scripts. The notification events are not the same as packets – they
basically indicate that something changed in current stream of evaluated data.
The table below shows current list of packet events and value of in.TraceEvent:
Notification event in.TraceEvent
Physical link woke up from silence _EVNT_CONNECT
Physical link came to silence (no physical signal) _EVNT_DISCONNECT
Changing of Opcode in series of link packets _EVNT_LINKSTATE_CHANGE
8. Sending functions
This topic contains information about the special group of VSE functions designed to specify
what kind of event verification script expects to receive.
8.1 SendChannel()
This function specifies that events occurred only on specified channel should be sent to script.
Format : SendChannel( channel )
Parameters:
_CHANNEL_RIGHT – send events only from right channel
_CHANNEL_BOTH – send events from both channels
Example:
SendChannel( _CHANNEL_LEFT ); # - send events from left channel
channel – This parameter can be one of following values:
_CHANNEL_LEFT – send events only from left channel
Page 15 of 35
Page 16

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
8.2 SendEvent ()
This function specifies what kind of events should be sent to script.
Format : SendEvent( event )
Parameters:
event – This parameter can be combination of the following values:
event value Description
_PKT_TS1 TS1
_PKT_TS2 TS2
_PKT_LINK Link Packet
_PKT_MAD MAD packets
_PKT_RC Reliable Connection packets
_PKT_RD Reliable Datagram packets
_PKT_UC Unreliable Connection packets
_PKT_UD Unreliable Datagram packets
_PKT_SKIPS Skips
_EVNT_CONNECT Physical link woke up from silence
_EVNT_DISCONNECT Physical link came to silence (no physical signal)
_EVNT_LINKSTATE_CHANGE Changing of Opcode in series of link packets
Some special values can be used covering large groups of events:
_ALL_PACKETS All possible packets
_ALL_EVENTS All possible notification events
_ALL All possible packets and notification events
Example:
SendEvent( _PKT_LINK ); # - send link packets
SendEvent( _PKT_LINK | _PKT_MAD ); # - send link packets and MADs
SendEvent(_ALL_PACKETS | _EVNT_DISCONNECT );
# - send all possible packets and Disconnect notification
Page 16 of 35
Page 17

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
8.3 SendLinkPkt ()
This function specifies more precise tuning for sending link packets.
Format : SendLinkPkt( opcode = _ALL, vl = _ALL )
Parameters:
opcode – This parameter specifies that only link packets with this Opcode will be sent
( _ALL – means that link packets with all opcodes will be sent )
vl – This parameter specifies that only link packets with this VL will be sent
( _ALL – means that link packets with for all VLs will be sent )
Example:
SendLinkPkt(); # - send all link packets – equal to SendEvent( _PKT_LINK );
SendLinkPkt( 0x1 ); # - send all link packets with Opcode = 0x1
SendLinkPkt( 0x1 , 0x7 ); # - send all link packets with Opcode = 0x1 and VL = 0x7
SendLinkPkt( _ALL, 0x7 ); # - send all link packets with VL = 0x7
8.4 SendMAD ()
This function specifies more precise tuning for MAD packets.
Format : SendMAD( mgmtclass = _ALL,
attrId = _ALL,
method = _ALL,
field_name = “” , # means no care about field_name
field_value =0)
Parameters:
mgmtclass – This parameter specifies that only MADs with this management class will be sent
( _ALL – means that MADs with all management classes will be sent )
attrId – This parameter specifies that only MADs having AttributeId equal to attrId will be
sent
( _ALL – means that MADs with any AttributeIds will be sent )
method – This parameter specifies that only MADs having Method equal to method will be
sent
( _ALL – means that MADs with any Method will be sent )
field_name – This parameter specifies that only MADs having a field with field_name (how it is
Page 17 of 35
Page 18

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
shown in CATC trace) and value equal to
field_value will be sent ( This field
makes sense only if one of the previous parameters are not equal to _ALL )
field_value – This parameter specifies that only MADs having a field with field_name (how it is
shown in CATC trace) and value equal to
field_value will be sent ( This field
makes sense only if one of the previous parameters are not equal to _ALL )
NOTE: For fields having size more than 32 bits use raw binary values
( like : ‘0011223344556677FF’) For more information about raw binary
values please refer to CSL Manual.
Example:
# SendEvent(
SendMAD() # - send all MAD packets – equal to
_PKT_MAD );
SendMAD (SMP_LIDROUTED); # - send SMP LID routed MADs
SendMAD ( _ALL , PORT_INFO); # - send PortInfo for all classes
SendMAD( SMP_DIRROUTED, PORT_INFO, GET_RESP, "GIDPrefix",
'FE80000000000000' );
#
# - send SMP Directed routed GetResp() MADs with PortInfo: GIDPrefix =
FE80000000000000'
SendMAD (SMP_LIDROUTED, PORT_INFO, GET_RESP, “PortState”, PS_ARMED);
#
# - send SMP LID routed GetResp() MADs with PortInfo:PortState = PS_ARMED
NOTE : SMP_LIDROUTED, PORT_INFO,…areconstantdefinedinfileVS_constants.inc
in ..\Scripts\VFScripts subfolder of main IBTracer folder.
Page 18 of 35
Page 19

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
9. Timer functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to work with timers -an internal routines that
repeatedly measures a timing intervals between different events.
9.1 VSE time object
A VSE time object – is a special object that presents time intervals in verification scripts.
From point of view of CSL - the verification script time object is a “list”-object of two elements :
( Please see CSL Manual for more details about CSL types )
[seconds, nanoseconds]
NOTE: The best way to construct VSE time object is to use Time() function (see
below )
9.2 SetTimer()
Format : SendTimer( timer_id =0)
Parameters:
Example:
SetTimer(23); # - start timing for timer with id = 23;
Remark :
If this function is called second time for the same timer id – it resets timer and starts timing
calculation again from the point where it was called.
9.3 KillTimer()
Format : KillTimer( timer_id =0)
Parameters:
.
Starts timing calculation from the event where this function was called.
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
SetTimer(); # - start timing for timer with id = 0;
Stops timing calculation for a specific timer and frees related resources.
Page 19 of 35
Page 20

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
Example:
KillTimer(23); # - stop timing for timer with id = 23;
KillTimer(); # - stop timing for timer with id = 0;
9.4 GetTimerTime()
Retrieve timing interval from the specific timer
Format : GetTimerTime ( timer_id =0)
Parameters:
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
Return values:
Returns VSE time object from timer with id = timer_id.
Example:
GetTimerTime (23); # - Retrieve timing interval
GetTimerTime (); # - Retrieve timing interval for timer with id = 0;
for timer with id = 23;
Remark :
This function, when called, doesn’t reset timer.
10. Time construction functions
This group of functions is used to construct VSE time objects.
10.1 Time()
Constructs verification script time object.
Format : Time(nanoseconds)
Time(seconds, nanoseconds)
Return values:
First function returns
[0, nanoseconds], second one returns [seconds, nanoseconds]
Page 20 of 35
Page 21

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Parameters:
nanoseconds – number of nanoseconds in specified time
seconds – number of seconds in specified time
Example:
Time ( 50 * 1000 ); # - create time object of 50 microseconds
Time (3, 100); # - create time object of 3 seconds and 100 nanoseconds
Time( 3 * MICRO_SECS ); # - create time object of 3 microseconds
Time( 4 * MILLI_SECS ); # - create time object of 4 milliseconds
NOTE: MICRO_SECS and MILLI_SECS are constants defined in
“VS_constants.inc”.
10.2 TimeFromSymbols()
Constructs VSE time object by integer value presenting number of IB symbols
Format : TimeFromSymbols (symbols)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object presenting time equal to
symbols number of IB symbols.
Parameters:
symbols – number of IB symbols
Example:
TimeFromSymbols(300) # - create time object equal to 300 IB symbols
11. Time calculation functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to work with “time” – VSE time objects.
11.1 AddTime()
Adds two VSE time objects
Format : AddTime(time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object presenting time interval equal to sum of time_1 and time_2
Page 21 of 35
Page 22

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object presenting first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object presenting second time interval
Example:
t1 = Time(100);
t2 = Time(2, 200);
t3 = AddTime( t1, t2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 2 sec 300 ns.
11.2 SubtractTime()
Subtract two VSE time objects
Format : SubtractTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object presenting time interval equal to subtraction of time_1 and time_2
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object presenting first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object presenting second time interval
Example:
t1 = Time(100);
t2 = Time(2, 200);
t3 = SubtractTime ( t2, t1 ) # - returns VSE time object = 2 sec 100 ns.
11.3 MulTimeByInt()
Multiplies VSE time object by integer value
Format : MulTimeByInt (time, mult)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object presenting time interval equal to time * mult
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
mult - multiplier, integer value
Example:
t = Time(2, 200);
t1 = MulTimeByInt ( t, 2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 4 sec 400 ns.
Page 22 of 35
Page 23

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
11.4 DivTimeByInt()
Divides VSE time object by integer value
Format : DivTimeByInt (time, div)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object presenting time interval equal to time / div
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
div - divider, integer value
Example:
t = Time(2, 200);
t1 = DivTimeByInt ( t, 2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 1 sec 100 ns.
12. Time logical functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to compare VSE time objects
12.1 IsEqualTime()
Verifies that one VSE time object is equal to the other VSE time object
Format : IsEqualTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns 1 if time_1 is equal to time_2,
returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object presenting first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object presenting second time interval
Example:
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
Page 23 of 35
Page 24

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
If( IsEqualTime( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
12.2 IsLessTime()
Verifies that one VSE time object is less than the other VSE time object
Format : IsLessTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns 1 if time_1 is less than time_2,
returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object presenting first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object presenting second time interval
Example:
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
If( IsLessTime ( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
12.3 IsGreaterTime()
Verifies that one VSE time object is greater than the other VSE time object
Format : IsGreaterTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns 1 if time_1 is greater than time_2,
returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object presenting first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object presenting second time interval
Example:
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
If( IsGreaterTime ( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
Page 24 of 35
Page 25

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
13. Time text functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to convert VSE time objects into text strings.
13.1 TimeToText()
Converts a VSE time object into text.
Format : TimeToText (time)
Return values:
Returns text representation of VSE time object
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
Example:
ReportText( TimeToText(t) ); # see below details for ReportText() function
t = Time(100);
14. Output functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to present information in the output window.
14.1 ReportText()
Outputs text in the output window if output is enabled
Format : ReportText (time)
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
Example:
t = Time(100)
ReportText ( t );
Page 25 of 35
Page 26

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
14.2 EnableOutput()
Enables showing information in the output window.
Format : EnableOutput ()
Example:
EnableOutput ( );
14.3 DisableOutput()
Disables showing information in the output window.
Format : DisableOutput ()
Example:
DisableOutput ();
15. Common Retrieving functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to retrieve information from the recorded trace.
15.1 RetrievePktPayload()
Retrieves the packet payload inside the script and makes valid two input context members :
in.Payload - the bit source of the packet payload and
in.PayloadLength - the length(in bytes of the retrieved packet payload)
Format : RetrievePktPayload ()
Example:
RetrievePktPayload ( ); # actualize input context packet payload related members
val = GetNBits( in.Payload, 128, 8 ); # retrieve one byte from packet payload starting
# from offset 16 bytes
Remark :
Page 26 of 35
Page 27
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Before calling this function - in.Payload and in.PayloadLength are empty but some other
retrieving functions can be used to receive all information about fields in link packets, packet headers
and MAD decoded fields.
15.2 IsMad()
Verifies that current event is MAD
Format : IsMad()
Example:
if( IsMad() ) DoSomething();
16. Packet Header retrieving functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to extract information about IB packet header fields.
If the header is not present in the packet – all of those functions will return null-value ( see CSL
Manual –for details about null-value ).
16.1 GetLRHField()
Extracts information about LRH header field
Format : GetLRHField ( lrh_fld )
Parameters:
lrh_fld - LRH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_VL
_LVER
_SL
_DLID
_SLID
_PLEN
_LNH
Virtual Lane
Link version
Service Level
Destination LID
Source LID
Packet length
Link next header field
Example:
val = GetLRHField (
_VL ); # extract VL field from LRH header
Page 27 of 35
Page 28

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
16.2 GetBTHField()
Extracts information about BTH header field
Format : GetBTHField ( bth_fld )
Parameters:
bth_fld - BTH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_OPCODE
_SE
_M
_PAD
_THVER
_P_KEY
_DESTQP
_A
_PSN
Operation Code
Solicit Event
Migration State
Length of pad
Transport version
Partition Key
Destination QP
Answer bit
Packet Sequence Number
Example:
val = GetBTHField (
_DESTQP); # extract DestQP field from BTH header
16.3 GetGRHField()
Extracts information about GRH header field
Format : GetGRHField ( grh_fld )
Parameters:
grh_fld - GRH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_IPVER
_TCLASS
_FLOWLABEL
_PAYLEN
_NXTHDR
_HOPLMT
_SGID_0_3
_SGID_4_7
_SGID_8_11
_SGID_12_15
IP Version
Traffic Class
Flow Label
Payload length
Next Header
Hop Limit
Source GID (bytes 0-3)
Source GID (bytes 4-7)
Source GID (bytes 8-11)
Source GID (bytes 12-15)
Page 28 of 35
Page 29
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
_DGID_0_3
_DGID_4_7
_DGID_8_11
_DGID_12_15
Destination GID (bytes 0-3)
Destination GID (bytes 4-7)
Destination GID (bytes 8-11)
Destination GID (bytes 12-15)
Example:
val = GetGRHField (
_IPVER ); # extract IPVersion field from GTH header
16.4 GetDETHField()
Extracts information about DETH header field
Format : GetDETHField ( deth_fld )
Parameters:
deth_fld - DETH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_Q_KEY
_SRCQP
Queue Key
Source QP
Example:
val = GetDETHField (
_Q_KEY); # extract QKey field from DETH header
16.5 GetRETHField()
Extracts information about RETH header field
Format : GetRETHField ( reth_fld )
Parameters:
reth_fld - RETH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_VA_0_3
_VA_4_7
_R_KEY
_DMALEN
Virtual Address (bytes 0-3)
Virtual Address (bytes 4-7)
Remote Key
DMA Length
Example:
val = GetRETHField (_DMALEN); # extract DMALen field from RETH header
Page 29 of 35
Page 30

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
16.6 GetAtomicETHField()
Extracts information about AtomicETH header field
Format : GetAtomicETHField ( aeth_fld )
Parameters:
aeth_fld - AtomicETH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_VA_0_3
_VA_4_7
_R_KEY
_SWAPADDDATA_0_3
_SWAPADDDATA_4_7
_COMPAREDATA_0_3
_COMPAREDATA_4_7
Virtual Address (bytes 0-3)
Virtual Address (bytes 4-7)
Remote Key
Swap (or Add) Data (bytes 0-3)
Swap (or Add) Data (bytes 4-7)
Compare Data (bytes 0-3)
Compare Data (bytes 4-7)
Example:
val = GetAtomicETHField (
_COMPAREDATA_0_3); # extract first word of
CompareData field from AtomicETH header.
16.7 GetAtomicAckETHField()
Extracts information about AtomicAckETH header field
Format : GetAtomicAckETHField ( aeth_fld )
Parameters:
aeth_fld - AtomicAckETH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_ORIGREMDATA_0_3
_ORIGREMDATA_4_7
Original Remote Data (bytes 0-3)
Original Remote Data (bytes 4-7)
Example:
val = GetAtomicAckETHField (
_ORIGREMDATA_0_3);
Page 30 of 35
Page 31
Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
16.8 GetRDETHField()
Extracts information about AtomicAckETH header field
Format : GetRDETHField ( rdeth_fld )
Parameters:
rdeth_fld - RDETH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_ EECONTEXT
EE-Context
Example:
val = GetRDETHField (
_EECONTEXT );
16.9 GetRWHField()
Extracts information about RWH header field
Format : GetRWHField ( rwh_fld )
Parameters:
rwh_fld - RWH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
Identifier Meaning
_ ETHERTYPE
EtherType
Example:
val = GetRWHField( _ETHERTYPE ); # extract EtherType field from
16.10 GetPostHdrField()
Extracts information going after headers
Format : GetPostHdrField ( posthdr_fld )
Parameters:
posthdr_fld - RWH field identifier that can be one of the following values:
RWH header
Page 31 of 35
Page 32

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Identifier Meaning
_IMMDT
_VCRC
_ICRC
Immediate Data
VCRC
ICRC
Example:
val = GetPostHdrField (
_VCRC); # extract VCRC field
NOTE : If there are some reserved fields in headers – they can be retrieved by using
some special keywords in header retrieving functions :
Keyword Length
_RES_1
_RES_2
_RES_5
_RES_7
_RES_8
_RES_16
1 bit field
2 bit field
5 bit field
7 bit field
8 bit field
16 bit field
Example:
val = GetLRHField ( _RES_2 ); # extract reserved 2-bit field from LRH header
17. MAD decoded fields retrieving functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to extract information about MAD decoded fields.
17.1 GetDecodedMADField()
Extracts information about MAD decoded field how it is shown in IBTracer trace view or
“View MAD” dialog.
Format : GetDecodedMADField ( mad_fld_name )
Parameters:
mad_fld_name - name of the MAD field supposedly existing in the MAD being processed:
Return Values:
The text value of the decoded field how it is seen in the trace if field name asked is present in
current MAD, empty string otherwise.
Example:
Page 32 of 35
Page 33

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
str = GetDecodedMADField (“PortState”); # extract the decoded value of PortState
# field.
Remark:
The name of field should be exactly the same as it seen in the trace ( case included )
17.2 GetHexMADField()
Extracts raw hexadecimal information about MAD decoded field.
Format : GetHexMADField ( mad_fld_name )
Parameters:
mad_fld_name - name of the MAD field supposedly existing in the MAD being processed:
Return Values:
If the field with the name asked is present in the current MAD - function returns the hex value
of the decoded field ( integer value- if the length of field is less than 32 bits or raw binary value
(list of bytes) - if the length of field is greater than 32 bits ), null-value if field was not found.
Example:
val = GetHexMADField (
“PortState”); # extract the hex value of PortState field.
# extract the hex value of GIDPrefix field.
if( GetHexMADField ( "GIDPrefix" ) == 'FE80000000000000' )
ReportText( "GIDPrefix = FE80-0000-0000-0000");
Remark:
The name of field should be exactly the same as it seen in the trace ( case included )
Page 33 of 35
Page 34

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
18. Miscellaneous functions
18.1 ScriptForDisplayOnly()
Specifies that the script is designed for displaying information only and that its author doesn’t
care about verification script result. Such a script will have a result <DONE> after execution.
Format : ScriptForDisplayOnly ()
Example:
ScriptForDisplayOnly();
18.2 Sleep()
Asks VSE not to send any events to a script until the timestamp of the next event is greater than
timestamp of current event plus sleeping time.
Format : Sleep( time )
Parameters:
time - VSE time object specifying sleep time
Example:
Sleep ( Time(1000) ); # Don’t send any event occurred during 1 microsecond from the current
event
NOTE : Some other useful miscellaneous functions can be found in the
file : VSTools.inc
19. The VSE important script files
The VSE working files are located in ..\Scripts\VFScripts subfolder of the main IBTracer
folder. The current version of VSE includes following files:
File Description
VSTools.inc
VS_constants.inc
VSTemplate.de_
VSTemplateSimple.de_
VSUser_globals.inc
main VSE file containing definitions of VSE script functions
file containing definitions of some important VSE global constants
template file for new verification scripts with detailed comments
template file for new verification scripts with just a few comments
file of user global variables and constants definitions
Page 34 of 35
Page 35

Computer Access Technology Corporation IBTracer Verification Script Engine Manual, version 1.0
Appendix A
How to Contact CATC
TYPE OF SERVICE
Call for technical support… US and Canada: 1 (800) 909-2282
Fax your questions… Worldwide: 1 (408) 727-6622
Write a letter … Computer Access Technology
Send e-mail… support@CATC.com
Visit CATC’s web site… http://www.CATC.com/
CONTRACT
Worldwide: 1 (408) 727-6600
Corporation
Customer Support
2403 Walsh Avenue
Santa Clara, CA 95051-1302
Warranty and License
Computer Access Technology Corporation (hereafter CATC) warrants this
product to be free from defects in material, content, and workmanship, and
agrees to repair or replace any part of the enclosed unit that proves defective
under these terms and conditions. Parts and labor are warranted for one year
from the date of first purchase.
The CATC software is licensed for use on a single personal computer. The
software may be copied for backup purposes only.
This warranty covers all defects in material or workmanship. It does not cover accidents, misuse,
neglect, unauthorized product modification, or acts of nature. Except as expressly provided above,
CATC makes no warranties or conditions, express, implied, or statutory, including without limitation
the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
CATC shall not be liable for damage to other property caused by any defects in this product,
damages based upon inconvenience, loss of use of the product, loss of time or data, commercial loss, or
any other damages, whether special, incidental, consequential, or otherwise, whether under theory of
contract, tort (including negligence), indemnity, product liability, or otherwise. In no event shall
CATC's liability exceed the total amount paid to CATC for this product.
CATC reserves the right to revise these specifications without notice or penalty.
Page 35 of 35
 Loading...
Loading...