Page 1

P H A S E R S H A R E
Setup guide
®
N E T W O R K I N G
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/
®
Page 2

Page 3

PhaserShare
®
Networking Setup Guide
V2 January 1999
063-3116-00
Page 4

x
x
*
*
Copyright
©
Tektronix, Inc.
Unpublished rights reserved under the copyright laws of the United States. Contents of this publication may not be
reproduced in any form without permission of Tektronix, Inc.
Tektronix
®
, Phaser
®
, PhaserShare
®
, ColorStix
®
, ColorCoat
®
, and Made For Each Other
®
are registered trademarks of
Tektronix, Inc. TekColor™, Finepoint™, PhaserLink™, and PhaserPrint™ are trademarks of Tektronix, Inc.
Adobe
Apple
®
and PostScript
®
, AppleTalk
®
are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated which may be registered in certain jurisdictions.
®
, LocalTalk
®
, EtherTalk
®
, TokenTalk
®
, and Macintosh
®
are registered trademarks of Apple Computer,
Inc.
SGI™ is a trademark of Silicon Graphics, Inc.
®
SPARC
is a registered trademark of SPARC International, Incorporated. SPARCstation™ is a trademark of SPARC
International, Inc., licensed exclusively to Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Tektronix Phaser 740, Phaser 780, and Phaser 360 printers are certified as NetWare print server devices, on
both 3.12 and 4.1
NetWare systems. NetWare NDS is certified on 4.1
NetWare systems. Bindery mode is also certified to comply on both 3.12 and 4.1 x
NetWare systems.
Novell® and NetWare® are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc.
®
is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through
UNIX
X/Open Company, Ltd.
Times™, Helvetica™ and Palatino™ are trademarks of Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiaries.
Other marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of the companies with which they are associated.
PANTONE
®
Colors generated by Phaser Color Printers are four- and/or three-color process simulations and may not match
PANTONE-identified solid color standards. Use current PANTONE Color Reference Manuals for accurate colors.
PANTONE Color simulations are only obtainable on these products when driven by qualified Pantone-licensed software
packages. Contact Pantone, Inc. for a current list of qualified licensees.
Pantone, Inc.’s check-standard trademark for color reproduction and color reproduction materials.
© Pantone, Inc., 1988.
Page 5

Contents
1 Introduction
Before you begin network configuration 2
Printing a Configuration Page 2
Printer management 3
If you need more information 4
2 Connecting Your Printer to a Network
PhaserShare Series B Ethernet interface 5
PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card 9
PhaserShare Series B LocalTalk card 19
3 EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and TokenTalk Configuration
Configuration overview 21
Finding the printer’s name in the Chooser 22
4 Novell NetWare Configuration
Installing the PhaserShare Administrator 23
Using the Quick Configuration Wizard 24
Setting IPX frame types from the front panel 28
5 TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Adding the printer to the host table 31
Assigning a print queue to the printer 31
Example installation for a typical BSD UNIX system 33
Printer configuration 35
Extracting files from unix.tar 36
6 Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
TCP/IP configuration for the PC 37
Setting the printer’s IP address 38
PhaserPort software installation 38
Adding a port for a new printer 40
Adding a port to an existing printer 41
Changing a port’s IP address 42
Setup Guide
iii
Page 6

iv
7 Windows NT
Setting the printer’s IP address 43
Adding a Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 4.0 server or workstation 43
Adding a Windows NT 4.0 driver on an NT 3.51 server 46
Adding a Windows NT 3.x driver 48
8 Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
General information: setting IP parameters from the front panel 52
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 740 printer front panel 53
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 780 printer front panel 55
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 360 printer front panel 58
Setting IP parameters: RARP or BOOTP 61
Setting IP parameters: DHCP 62
Supported BOOTP/DHCP fields 64
Setting IP parameters: PostScript utility file (UNIX only) 64
Setting IP parameters: PhaserLink software 67
DNS (Phaser 740 and 780 printers only) 67
9 PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s Information Link
Accessing printer information from a browser 69
PhaserLink software help files 70
Setting printer parameters: PhaserLink software pages 71
Information Forwarding 71
Index
PhaserShare Networking
Page 7

Chapter
1
Introduction
This guide provides information to help you quickly install Tektronix
Phaser 740, Phaser 780, and Phaser 360 color printers in the following
environments:
■
EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and TokenTalk
■
Novell NetWare
■
UNIX
■
Windows 95 and Windows 98
■
Windows NT
For detailed networking information, including troubleshooting, see the online
manual on your printer’s CD-ROM, or see the PhaserShare Networking Manual in
PDF format on your printer’s CD-ROM.
For information on installing Tektronix printers in DOS environments, see the
printer’s CD-ROM or network utilities diskettes. They contain PostScript utility
files that can be sent to the printer for network configuration in DOS
environments. They also contain a DOS application, NWSET, for printer
configuration on NetWare networks.
For information on how to use the DOS configuration files, see the README
files on the printer’s CD-ROM and network utilities diskettes. PC users: the
README file for PostScript utility files is in the UTILS directory; the README
file for NWSET is in the NETWARE directory. (Macintosh users: the ReadMe file
for PostScript utility files is in the Network Utilities folder).
For information on installing into OS/2 environments, see the online manual on
your printer’s CD-ROM, or see the PhaserShare Networking Manual in PDF format
on your printer’s CD-ROM.
Setup Guide
1
Page 8

2
1
Introduction
Before you begin network configuration
■
Set up your printer and connect it to the network. See your printer’s user
documentation for information about setting up the printer. For
information about connecting the printer to the network, see Chapter 2 of
this manual, “Connecting Your Printer to a Network”.
■
Install the Tektronix driver for your printer on every Macintosh and PC
that will send print jobs to the printer. For details on driver
installation, see your printer’s user documentation.
For NetWare environments. To speed the setup process and avoid
■
conflicts, familiarize yourself with the components of your network.
You should know which version(s) of NetWare are installed, which
versions of client software are used, and the network topology (frame
types, routers, hubs, and cabling).
Printing a Configuration Page
Your printer’s Configuration Page supplies useful information for installing and
configuring the printer on a network.
Printing a Configuration Page: Phaser 740 and 360 front panels
While the Ready message is displayed, press Menu . The printer
1.
displays the first item in the menu:
Help Pages
<---- ----> Menu
Press Menu to access the Help Pages; the following message appears:
2.
Menu Map
<---- ----> Print
Press <---- or ----> until the following message appears:
3.
Configuration Page
<---- ----> Print
Press Print .
4.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 9

Printing a Configuration Page: Phaser 780 front panel
1.
While Ready is displayed, press Select ; the Printer menu is
displayed:
Printer Menu
Help Pages Menu
2.
Press Menu ; the Help Pages menu is displayed:
Help Pages
Configuration Page Print
3.
Press Print .
Printer management
After your printer is up and running on the network, you can take advantage of
the following features that aid you in managing your printer over the network:
■
Job accounting. The printer stores a log file containing information
about jobs printed. The file is a list of job accounting records. Each
record contains fields such as user name, job name, pages printed, job
times, and toner used. Job accounting is available through the
PhaserShare Administrator and PhaserLink software.
Introduction
1
■
Email notification. PhaserLink software provides email notification,
which allows the printer to automatically send email to the system
administrator and others when the printer requires attention (for
example, when printer errors, warnings, and alerts occur, or when
service is required).
■
Usage Profile reports. The printer can generate reports detailing
printer usage. These Usage Profile reports include information on many
aspects of printer usage, including ink or toner used, number of pages
printed, and media types used. You can print these reports from the
front panel or PhaserLink, or you can obtain them automatically via
email.
For more information on these features, see the PhaserShare Networking Manual
on the printer’s CD-ROM.
Setup Guide
3
Page 10

1
4
Introduction
If you need more information
You may need more information about troubleshooting your network
installation or using the printer. The following sources are available:
PhaserShare networking manual. Provides detailed networking information
for system administrators, including troubleshooting; available in PDF format
on the printer’s CD-ROM. A printed copy of this manual can be ordered from
Tektronix (part number 071-0180-00).
Online user manual . Provides complete information on using your printer,
including printer care, printer features, and networking; provided in HTML
format on the printer’s CD-ROM. It is also available on the Tektronix web site.
PhaserShare Administrator online help. Provides detailed descriptions of all
program functions and dialog boxes.
PhaserLink online help . HTML files supplied on the printer’s CD-ROM. See
“PhaserLink software help files” on page 70.
Readme files . Provided on the printer’s CD-ROM and diskettes. They contain
information about PostScript utility files and DOS applications that can be used
for configuring and using your printer in DOS environments. Some utility files
for Macintosh are also provided.
World Wide Web. User documentation and other printer information is
available from the Tektronix web site:
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/support/colcare.html
Technical support hotline. In the U. S. and Canada, call 1-800-835-6100,
Monday through Friday, 6:00 am to 5:00 pm PST. For international numbers, see
the printer’s user guide or visit:
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/cgi-bin/CPIDlocProcessor
PhaserShare Networking
Page 11

Chapter
2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
PhaserShare Series B Ethernet interface
The PhaserShare Series B Ethernet interface conforms to the IEEE 802.3 and
Ethernet II standards. With the printer’s built-in Ethernet interface, you can
connect the printer directly to an Ethernet network using twisted pair (10BaseT)
cables. With the PhaserShare Series B Ethernet card, you can connect the printer
directly to an Ethernet network using twisted pair (10BaseT or 100BaseTx) or
thin coax (10Base2) cables. Connecting the printer using thick coax (10Base5)
requires an adapter; contact your dealer to obtain adapters, cables, and
terminators.
When a PhaserShare Series B Ethernet card is installed, the printer’s built-in
Ethernet connector is disabled; use the connectors on the card.
When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased initially with the printer, it is
installed at the factory. When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased later as
an upgrade kit, follow the instructions that are shipped with the card.
C A U T I O
N
To av oid damaging the network interf ace, turn off the printer before making an y
Ethernet connections.
Setup Guide
5
Page 12
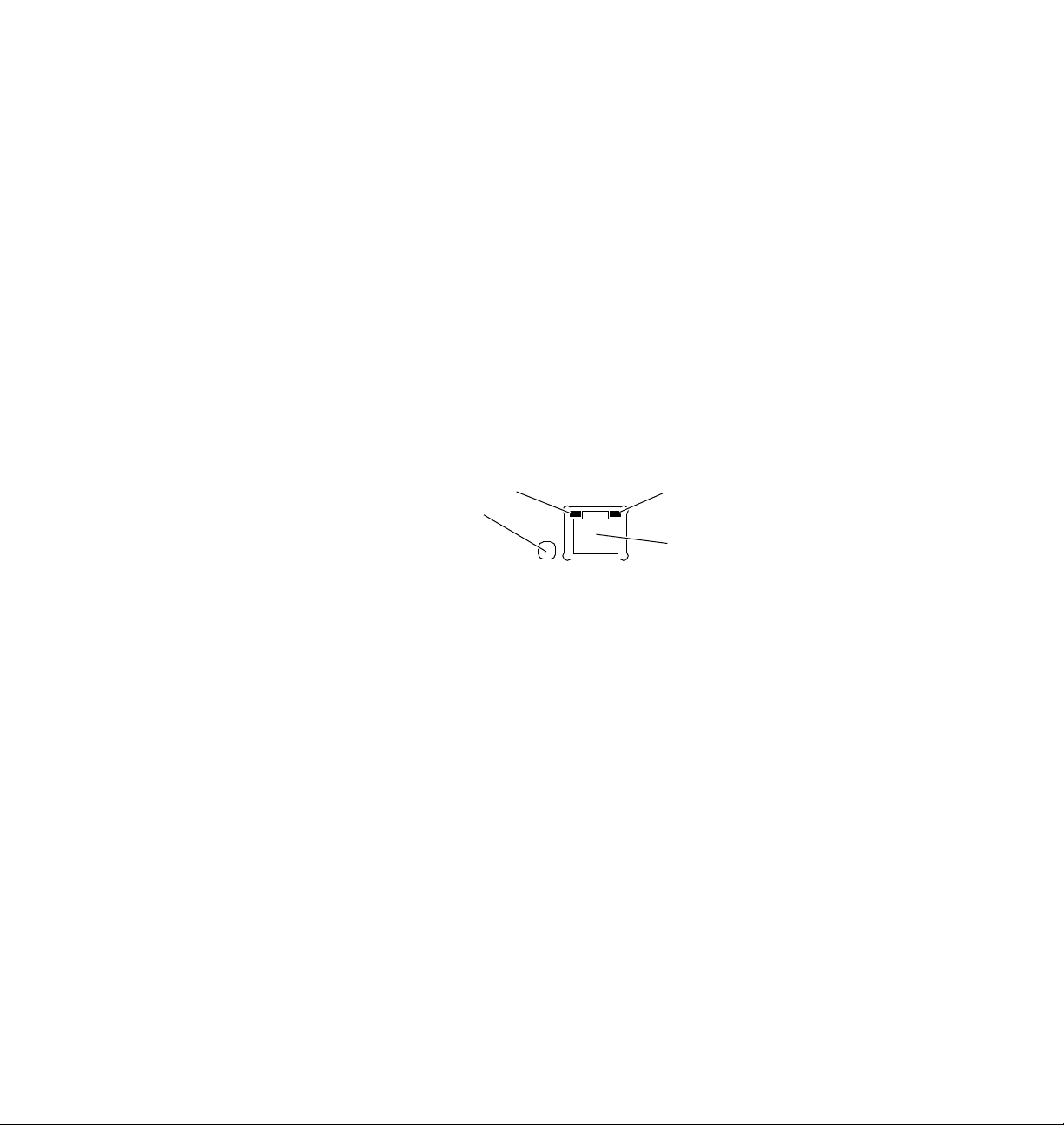
2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Ethernet connections and indicators
Built-in Ethernet connector
The printer’s built-in Ethernet connector has the following connections and
indicators:
1.
LINK indicator (Phaser 360 printer only); on indicates a working
connection to a hub; off indicates no connection to a hub.
2.
RCV indicator (green); blinks while the network interface is receiving.
3.
XMT indicator (yellow); blinks while the network interface is
transmitting.
4.
Twisted pair (10BaseT) connector.
2
1
RCV XMT
LNK
Ethernet
3
4
0180-01
6
PhaserShare Networking
Page 13
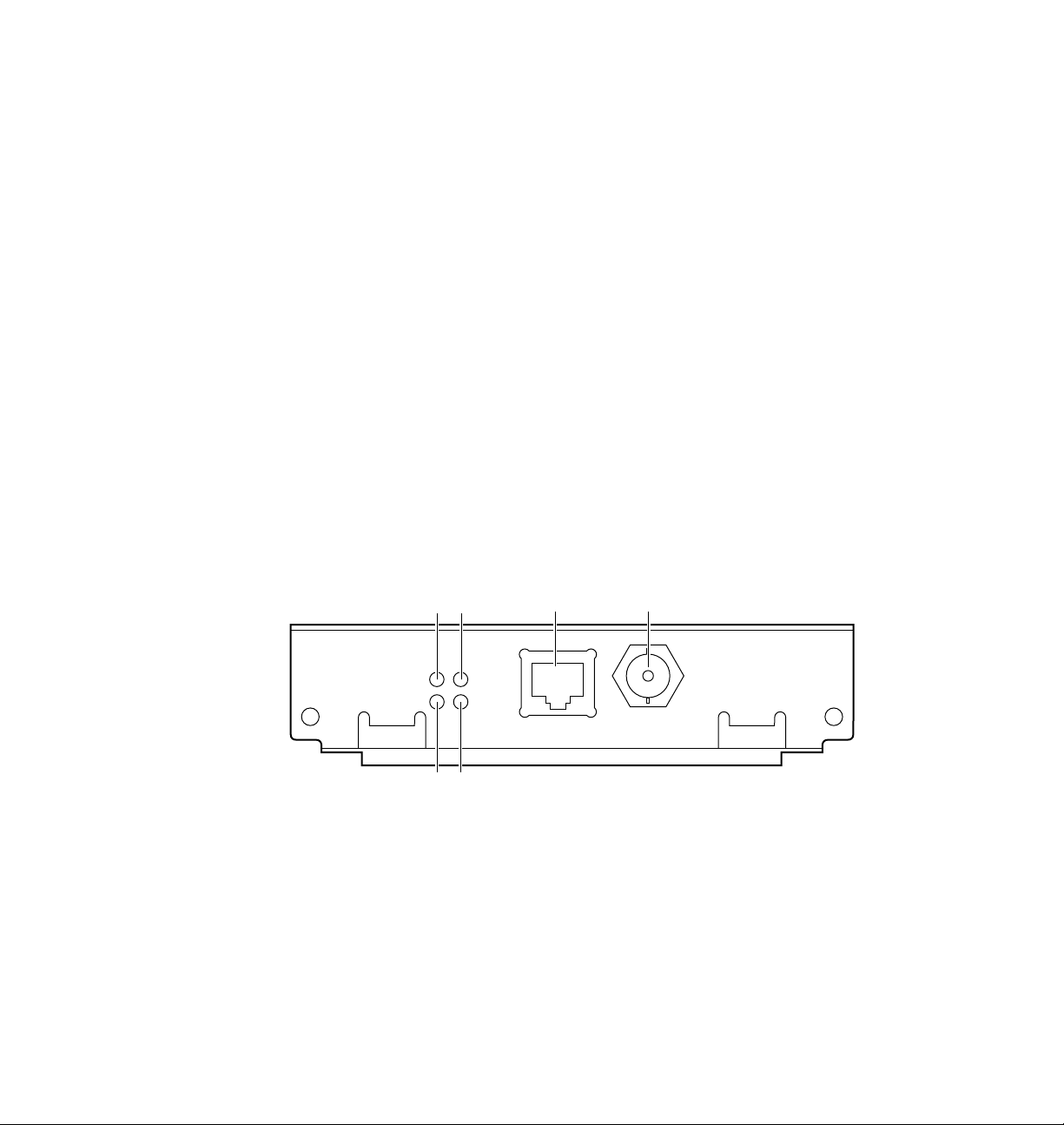
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
PhaserShare Series B Ethernet card
The PhaserShare Series B Ethernet card has the following connections and
indicators:
1.
TX indicator (yellow); blinks while the network interface is
transmitting.
2.
RX Link indicator (green); blinks while the network interface is
receiving.
3.
Speed indicator (yellow); on indicates 100 Mbps; off indicates
10 Mbps.
4.
Twisted pair connection indicator; on indicates a working connection
to a hub; off indicates no connection to a hub. If the 10Base2 connector
(6) is used, this indicator is off.
5.
Twisted pair (10BaseT or 100BaseTx) connector.
6.
Thin coax (10Base2) connector.
2
PhaserShareTM
Series B
Ethernet Card
13 5 6
100
24
Mbs
TP
LINK
10/100Base-TX
TX
RX
10Base2
Setup Guide
9789-05
7
Page 14

2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Ethernet cables and termination
N O T
E
To fully comply with EMI (electro-magnetic interference) specifications , the use
of shielded or screened cables may be required. “Shielded” describes
IBM-defined cables used with the DB-9 connector. “Screened” describes
cables that are electrically similar to Category 4 UTP (Unshielded Twisted P air),
but with an added shield or screen.
10BaseT or 100BaseTx (Twisted Pair)
100BaseTx requires Category 5 (100-Ohm UTP) cabling.
The Ethernet standard does not allow a direct 10BaseT connection between a
single computer and a single printer. Use 10Base2 (Thin Ethernet) to connect a
single computer to a single printer.
C A U T I O
N
Do not use “silver satin” telephone extension cables for 10BaseT networks,
either as drop cords or as patch cables in the wiring closet. (Silv er satin cab les
are flat, usually silver or gra y, with 28-gauge stranded or tinsel conductors .) Do
not use shielded twisted pair cable intended for IBM Token Ring networks or
voice-grade (level 1 or 2) unshielded twisted pair cable for wiring runs. These
cables do not meet the requirements for 10BaseT and will lead to
unreliable operation.
10Base2 (Thin Ethernet)
Depending on the type of Ethernet cables you use and your network
configuration, you may need to use terminators at certain points in the
installation. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for your Ethernet
adapters and cables for details.
10Base5 (Thick Ethernet)
Connecting the printer using thick coax (10Base5) requires an adapter; contact
your dealer to obtain adapters, cables, and terminators.
8
PhaserShare Networking
Page 15

Connecting Your Printer to a Network
PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card
The PhaserShare Series B Token Ring port conforms to the IEEE 802.5 standard.
With the PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card, you can connect the printer
directly to a Token Ring network using shielded twisted pair (STP; IBM Type 1)
or unshielded twisted pair (UTP; IBM Type 3) cables. Contact your dealer to
obtain adapters and cables.
N O T
E
To fully comply with EMI specifications, the use of shielded or screened cables
may be required. “Shielded” describes IBM-defined cab les used with the DB-9
connector. “Screened” describes cables that are electrically similar to Category
4 UTP, but with an added shield or screen.
When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased initially with the printer, it is
installed at the factory. When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased later as
an upgrade kit, follow the installation instructions that are shipped with the
card.
When a PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card is installed in the printer, the
printer’s built-in Ethernet connector is disabled.
2
C A U T I O
N
To av oid damaging the network interf ace, turn off the printer before making an y
Token Ring connections.
Setup Guide
9
Page 16
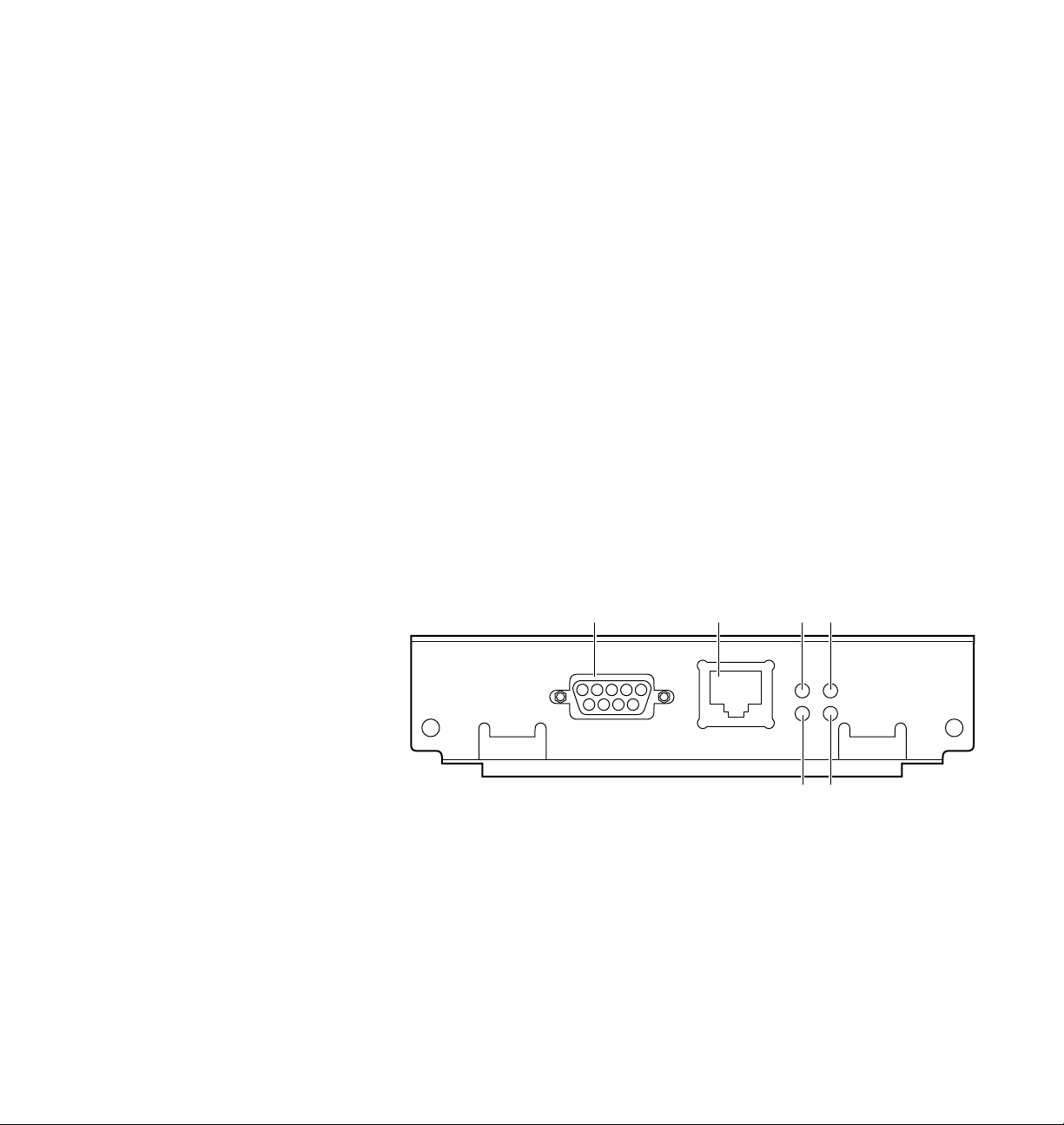
2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Token Ring connections and indicators
The PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card has the following connections and
indicators on the rear panel:
1.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP; IBM Type 1) connector (DB-9).
N O T
E
The STP port on the PhaserShare Token Ring card supports cable lengths up
to 150 meters (492 feet) from the interface to the MAU (Medium Access Unit),
including lobe and patch cables.
2.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP; IBM Type 3) connector (RJ-45).
3.
Ring speed indicator (yellow); on indicates 16 Mbps, off indicates
4 Mbps.
4.
TX indicator (yellow); blinks while the interface is transmitting.
5.
Connection indicator (green); on indicates that the card is asserting its
ring insertion control signal.
6.
RX indicator (green); blinks while the interface is receiving.
1234
PhaserShareTM
Series B
Token Ring Card
STP
UTP
Mbs
INS
16
56
TX
RX
9789-06
10
PhaserShare Networking
Page 17
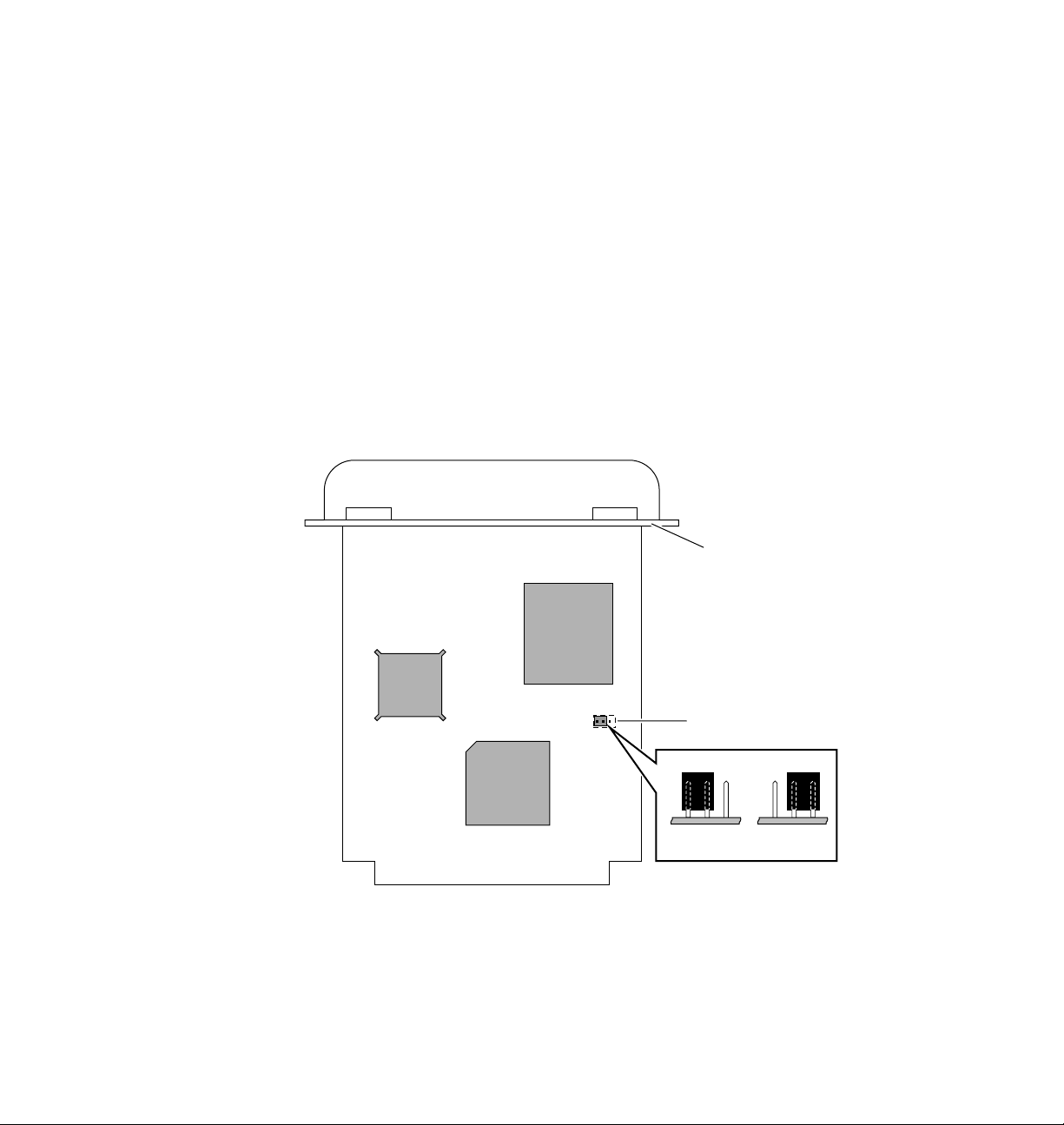
Ring speed jumper
The Token Ring card is equipped with a single three-pin jumper to set the ring
speed. There are two settings: 4 Mbps and 16 Mbps.
N O T
The following illustration shows a top view of the card and the location of the
jumper.
1.
2.
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
E
If you received your printer with the Token Ring card already installed, you must
turn off the printer and remove the card before you change the jumper setting.
Rear panel
Jumper
1
2
2
16 Mbps 4 Mbps
9789-03
Setup Guide
11
Page 18

2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Token Ring configuration
You can set the Token Ring Frame Routing from the printer’s front panel. When
you have the Frame Routing set, you may want to set other Token Ring
parameters. See “Configuring Token Ring parameters” on page 16. See the table
“Token Ring parameters” on page 15 for a list of Token Ring parameters.
Setting Frame Routing from the Phaser 740 and 360 front panels
N O T
E
If you are attempting to perform any front panel procedure and you don’t see
the expected menu choices, the front panel may be locked. For information on
how to unlock it, see the
CD-ROM.
1.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Help Pages.
N O T
E
When you are in the menu, if the front panel is not used for 5 minutes, the
printer returns to the Ready state.
PhaserShare Networking Manual
on the printer’s
12
2.
Press ----> or <---- until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
3.
Access the Frame Routing menu:
a.
b.
4.
Select the desired Frame Routing: Transparent or Source Route:
a.
b.
PhaserShare Networking
Press Menu until the front panel displays Token Ring.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the first of two Frame Routing
choices.
Press ----> until the Frame Routing choice you want is displayed.
Press OK to enter your choice into the printer; the front panel
briefly displays Selected, then returns to the Token Ring
display.
Page 19

Connecting Your Printer to a Network
5.
Return the printer to normal operation:
a.
Press Exit until the front panel displays Network Settings.
b.
Press Exit again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset
to take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you
press Reset, the printer resets. If you press Resume, the front
panel displays Network Settings. Press Exit; the printer
returns to normal operation, but the changes you have made
will not take effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset to take effect, the front panel displays Ready.
Setting Frame Routing from the Phaser 780 front panel
When the Token Ring card is installed in the printer, you can set the Frame
Routing from the printer’s front panel. The choices are Transparent (no source
routing) or Source Route (use source routing).
2
1.
While Ready is displayed, press Select; the Printer menu is
displayed:
Printer Menu
Help Pages Menu
2.
Press or until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
Printer Menu
Network Settings Menu
3.
Press Menu to enter the Network Settings menu; the front panel
displays:
Network Settings
Token Ring Menu
4.
Press Menu again; the front panel displays the first of two Frame
Routing choices.
Setup Guide
13
Page 20
2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
5.
Select the desired Frame Routing: Transparent or Source Route:
a.
b.
6.
Return the printer to normal operation:
a.
b.
Press until the Frame Routing choice you want is displayed.
Press Select to enter your choice into the printer; the front panel
briefly displays Selected, then displays the selected Frame
Routing choice again.
Press until the front panel displays:
Network Settings
Token Ring Menu
Press again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset to
take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you press
Confirm, the printer resets. To return to normal operation without
resetting the printer, press
top line of the display. Press again; the printer returns to
normal operation, but the changes you have made will not take
effect until the next time the printer is reset.
; Printer Menu appears on the
14
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset, press again; the front panel displays Ready.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 21

Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Token Ring parameters
Parameter Description Choices
Network Address Tok en Ring Address. You can supply a Locally
Speed Read-only parameter; reports the ring speed
Early T ok en
Release
Route Cache
Size
Route Cache
Timeout
Broadcast For broadcasting to all network nodes.
Adapter Status Read-only parameter; reports the Token Ring
Administered Address.
set by the jumper on the card.
Printer releases the token at the end of the last
byte transmitted (not applicable at 4 Mbps).
Number of entries in the source route table. 10 to 300.
Time in seconds that an entry remains in the
source route table before being updated.
Changes the default frame type for source
route broadcasts. Broadcast is ignored if
Frame Routing is set to Transparent. Some
protocols (for example, IP and ARP) are not
affected by this parameter.
card status.
Report is in two parts, separated by a comma:
Adapter status, Details
Adapter status
Token Ring card.
information.
Unknown Route Printer is searching for a route to a specific
network node. Changes the def ault fr ame type
for source route broadcasts. Unknown Route
is ignored if Frame Routing is set to
Transparent. Some protocols (f or e xample, IP
and ARP) are not affected by this parameter.
reports the condition of the
Details
reports additional
Any valid Token Ring address between
40.
xx.xx.xx.xx.xx
4 Mbps or 16 Mbps.
Enabled (default) or Disabled.
5 to 65535.
Single Route. The printer uses single-route
broadcasts for most source-route broadcasts.
All Routes. The printer uses all-routes
broadcasts for all broadcasts.
Adapter status:
Adapter Initializing. Card is starting up.
Adaptor Open. Card is connected to the
network.
Adapter Closed. Card is not connected to
the network.
Adapter Fault. Card is defective.
Details:
Ring OK. Ready for network communication.
Fault. Internal error; the card is defective.
Cable Disconnected. Cable is not
connected to the card.
Ring Error. Network problem.
Removed by network management. The
network administrator has disabled the
connection.
Single Route. Printer uses single-route
broadcasts for most source-route broadcasts.
All Routes. Printer uses all-routes broadcasts
for all broadcasts.
and 7F.
xx.xx.xx.xx.xx
2
.
Setup Guide
15
Page 22

2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Configuring Token Ring parameters
■ On UNIX systems, you can use the script config-TokenRing, provided
with the printer’s network utilities software. See the next topic, “Using
the config-TokenRing script”.
■ On PCs, you can edit the PostScript utility file TOKNCFG.PS and send
it to the printer. See the README file in the UTILS directory on the
printer’s network utilities diskettes or CD-ROM for details.
■ On a Macintosh, you can edit the PostScript utility file Configure Token
Ring and send it to the printer. See the ReadMe file in the Network
Utilities folder on the printer’s network utilities diskettes or CD-ROM
for details.
■ Windows users on NetWare networks can use the PhaserShare
Administrator. See “Using the PhaserShare Administrator to configure
Token Ring” on page 18.
■ With a TCP/IP connection and a World Wide Web browser, you can
use PhaserLink. “Using PhaserLink software to configure Token Ring”
on page 18.
16
Whichever method you use, reset the printer to make the changes take effect.
Using the
The UNIX shell script config-TokenRing is provided with the printer’s network
utilities software. The script creates a PostScript file containing the Token Ring
parameters. Set the Token Ring parameters by sending the PostScript file to the
printer.
Before performing this procedure, install the script on your host computer. If
you have not already installed the file, see “Extracting files from unix.tar” on
page 36. Your host spooling system must also be configured (see Chapter 5,
“TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)”).
1.
Connect the printer to the network. ARP (Address Resolution
Protocol) requires that the printer be connected on the same physical
network segment as the host. You will be using the arp command later
in this procedure.
2.
Log in.
PhaserShare Networking
config-TokenRing
script
Page 23

Connecting Your Printer to a Network
3.
Run the script config-TokenRing:
a.
In the directory where you placed your printer’s network utilities,
change (cd) to the bin subdirectory.
b.
Type the name of the script, redirecting the output to a file. Type:
config-TokenRing > filename
4.
When prompted by the script, enter the Token Ring parameters.
5.
When the script is finished, log in as root.
6.
Make an entry into the host’s ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table
defining the printer’s Printer Name/Token Ring address pair. In
general, this requires a command corresponding to one of the
following syntax examples:
arp -s printer-name Token-Ring-address (for BSD systems)
or
arp -s ether printer-name Token-Ring-address (for System V)
See the documentation for your host system for specifics of this
command.
2
7.
Turn on the printer.
8.
Use the host spooling system (for example, lpr or lp) to send to the
printer the file you created in Step 3b; this stores the Token Ring
information in the printer’s memory, where it is retained over a reset or
power cycle.
9.
Reset the printer to make the changes take effect.
Setup Guide
17
Page 24

2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
Using the PhaserShare Administrator to configure Token Ring
1.
In the PhaserShare Administrator Main window, select the desired
printer from the Printer List.
2.
Click Configure Printer; this displays the Configure Printer dialog
box.
3.
In the Configure Printer dialog box, click the Token Ring tab.
4.
In the Token Ring tab, set the Token Ring parameters as desired.
5.
Click OK.
6.
You are prompted to reset the printer. Reset the printer to make the
changes take effect.
For more information on the PhaserShare Administrator, see the PhaserShare
Networking Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM.
Using PhaserLink software to configure Token Ring
For information on connecting to your printer via PhaserLink, see “Accessing
printer information from a browser” on page 69. For general information on
PhaserLink software, see Chapter 9, “PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s
Information Link”.
18
1.
From the printer’s home page, click Configuration; this displays the
View and Configure Settings page.
2.
From the View and Configure Settings page, click View and
Configure Interface Settings; this displays the View and Configure
Interface Settings page.
3.
From the View and Configure Interface Settings page, click View and
Configure PhaserShare Settings (Token Ring card); this displays the
View and Configure PhaserShare Settings page for Token Ring.
4.
Enter your settings into the fields for Token Ring Address, Speed, and
Bridging. If you make an error, click Restore Initial Form Values and
start again.
5.
When you are finished entering the settings, enter the Validation
Password and click Do/Apply. If you are not sure of the password,
contact your system administrator.
6.
Reset the printer to make the changes take effect.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 25
PhaserShare Series B LocalTalk card
When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased initially with the printer, it is
installed at the factory. When a PhaserShare Series B card is purchased later as
an upgrade kit, follow the installation instructions that are shipped with the
card. Both the LocalTalk connection on the card and the Ethernet connector on
the printer’s rear panel are simultaneously active.
LocalTalk connection
N O T
E
LocalTalk is sometimes referred to as AppleTalk. LocalTalk refers to the
physical connection; AppleTalk is the protocol.
You can make LocalTalk connections between the printer and a single computer
or a LocalTalk network. If your LocalTalk installation is complex, or if you need
assistance, contact your network system administrator.
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
2
C A U T I O
N
Connect your printer to a LocalTalk network before you turn on the printer.
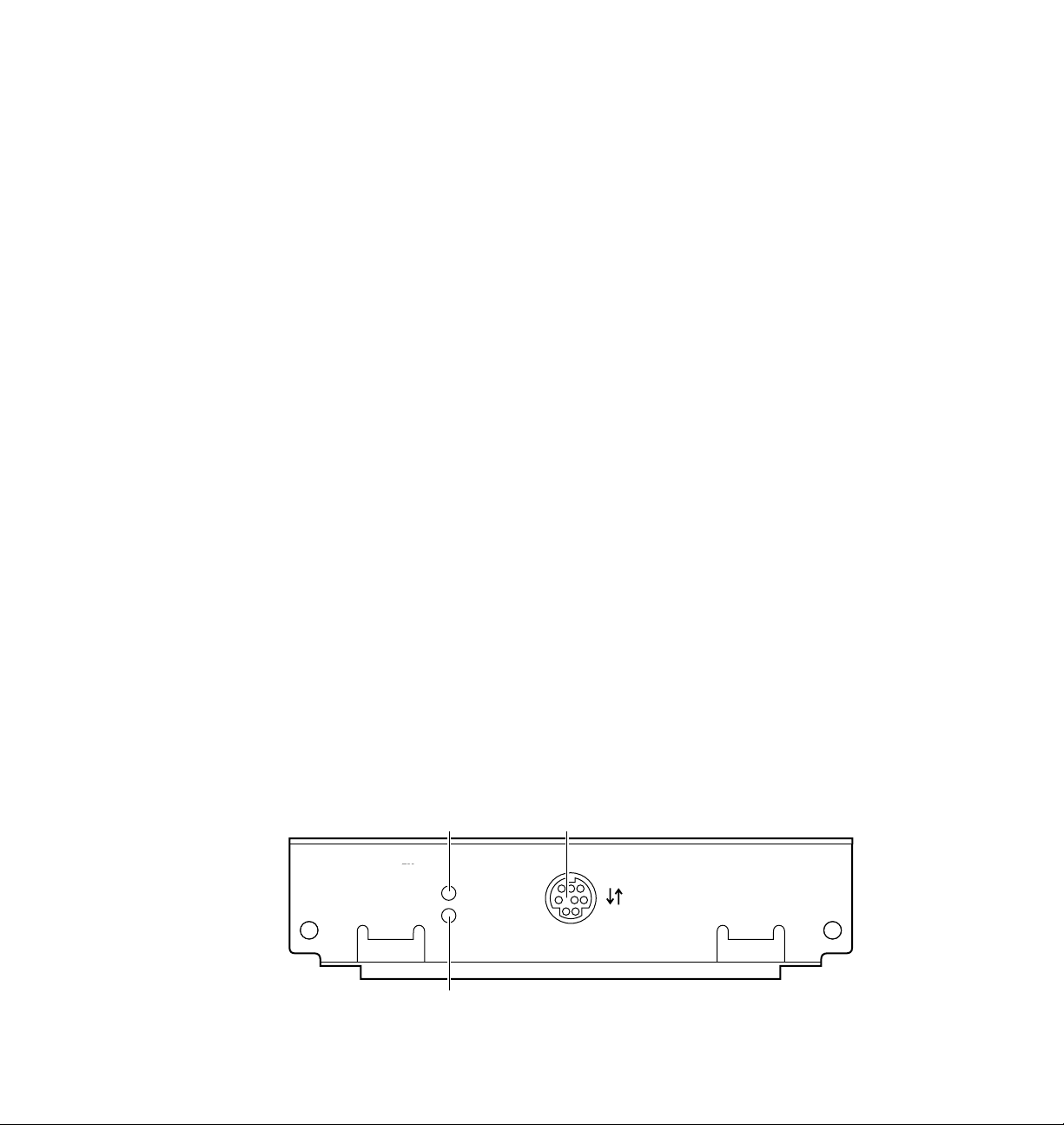
LocalTalk card connections and indicators
1.
TX indicator (yellow); blinks while the interface is transmitting.
2.
RX indicator (green); blinks while the interface is receiving.
3.
LocalTalk connector; 8-pin, circular DIN.
N O T
E
Both indicators flashing together indicates a fatal software error. Turn the
printer off, then on again; if the problem persists, replace the card.
13
PhaserShareTM
Series B
LocalTalk Card
TX
RX
2
LocalTalk®
9789-07
Setup Guide
19
Page 26

2
Connecting Your Printer to a Network
LocalTalk connectors, cables, and terminators
LocalTalk connectors and cables are available through your local reseller.
Depending on the type of LocalTalk cables you use and your network
configuration, you might need to use terminators at certain points in the
installation. Refer to the documentation for your LocalTalk connectors and
cables for details.
Connecting to a single computer
To avoid damaging the network interface, turn off the printer before making any
LocalTalk connections.
1.
Connect the short cable of a LocalTalk connector to the PhaserShare
LocalTalk port.
2.
Connect the short cable of another LocalTalk connector to your
computer’s LocalTalk port.
3.
Connect a LocalTalk cable from the LocalTalk connector that you have
just attached to your computer to the printer’s LocalTalk connector.
20
Depending on the type of LocalTalk connectors you use and your network
configuration, you might need to use external terminators. Refer to the
documentation for your LocalTalk connectors and cables for details.
For configuration details, see Chapter 3, “EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and TokenTalk
Configuration”.
PhaserShare Networking
TX
LocalTalk®
RX
TM
PhaserShare
Series B LocalTalk Card
1
2
3
9789-08
Page 27

Chapter
3
EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and TokenTalk Configuration
Configuration overview
N O T
E
The printer’s AppleTalk connection works with Macintosh system software 7.0,
7.1, 7.5, 7.6, 8.0, 8.1, and 8.2.
The configuration procedure for LocalTalk, EtherTalk, and TokenTalk consists of
two simple steps:
1.
Print the Configuration Page. It reports the printer’s default name,
which you need for EtherTalk and TokenTalk configurations. For
information on printing a Configuration Page, see “Printing a
Configuration Page” on page 2.
2.
Verify that the printer is in the Chooser. See “Finding the printer’s
name in the Chooser” on page 22.
■ If the printer is not in the Chooser, see the PhaserShare Networking
Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM.
■ If the printer is in the Chooser, you may want to change the
printer’s name or zone. For information on these procedures, see
the PhaserShare Networking Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM.
Setup Guide
21
Page 28

3
EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and TokenTalk Configuration
Finding the printer’s name in the Chooser
1.
From the Apple menu, select Chooser.
2.
In the upper-left corner of the Chooser, find the driver icon. (If the
driver icon is not in the Chooser, you need to install the printer driver.)
Click the driver icon.
3.
If a list of zones appears in the lower-left portion of the Chooser, select
the proper zone.
N O T
E
The printer’s default zone is listed on the Configuration Page in the EtherTalk
or TokenTalk field. For more information on the Configuration Page, see
“Printing a Configuration Page” on page 2.
4.
A list of printers appears in the right portion of the Chooser; find your
printer’s name. The printer’s default name is listed on the
Configuration Page (see “Printing a Configuration Page” on page 2). If
the name does not appear, check the cable connection between your
printer and the network.
22
N O T
E
It is possible for the Printer Name field on the Configuration Page to be blank.
When the printer is powered up, it uses a def ault name and then checks to see
that no other printer on the network has the same name. If enough printers
with the same default name are present, it can take several minutes for the
printer to establish a unique name. If the Printer Name field on the
Configuration Page is blank, wait a short time and reprint the Configuration
Page.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 29

Chapter
4
Novell NetWare Configuration
This chapter provides a quick configuration procedure for Windows
environments using the Tektronix PhaserShare Administrator. For detailed
information on the PhaserShare Administrator functions, see the PhaserShare
Administrator on-line help.
The printer’s CD-ROM and network utilities diskettes also contain a DOS
application, NWSET, that can be used for configuration in DOS environments.
For information on how to use NWSET, see the README file in the NETWARE
directory on the printer’s CD-ROM and network utilities diskettes.
Installing the PhaserShare Administrator
Your printer’s software CD-ROM contains the files necessary for installing the
PhaserShare Administrator. A single integrated installer is used to install printer
drivers, the PhaserShare Administrator, and other software.
Installation for Phaser 740 and Phaser 780 printers
1.
Put the printer’s software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
■ If the Windows autorun feature is enabled, the CD-ROM launches
automatically.
■ If the Windows autorun feature is disabled, double-click My
Computer, then double click the CD icon to launch the CD-ROM.
2.
View the brief introductory information, then click Install Drivers to
launch the installer.
3.
When you are prompted to select Easy Install or Custom Install, select
Custom Install.
4.
During custom installation, a dialog box is displayed enabling you to
install the PhaserShare Administrator. Follow the on-screen prompts
to complete the installation.
Setup Guide
23
Page 30

4
Novell NetWare Configuration
Installation for Phaser 360 printers
1.
Locate and run the file SETUP.EXE on the printer’s CD-ROM or
on printer software diskette 1.
2.
When you are prompted to select Easy Install or Custom Install,
select Custom Install.
3.
During the custom installation, a dialog box is displayed enabling
you to install the PhaserShare Administrator.
prompts to complete the installation.
Using the Quick Configuration Wizard
Log on to the file server
N O T
E
Many of the operations performed using the PhaserShare Administrator require
SUPERVISOR privileges (for example, creating queues).
Follow the on-screen
24
NetWare 3.x. Log on to the default NetWare file server as SUPERVISOR or
SUPERVISOR equivalent.
NetWare 4.x, Bindery mode. Log on to the default NetWare file server as
SUPERVISOR, SUPERVISOR equivalent, or ADMIN /B.
NetWare 4.x, NDS (NetWare Directory Services) mode. Log on to the default
NetWare file server as ADMIN or ADMIN equivalent.
N O T
E
While not required, it is recommended that you log in only to the file servers to
be configured with this printer.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 31

Start the PhaserShare Administrator
Double-click the PhaserShare Administrator icon. Refer to your Windows
documentation for complete information on how to start applications.
When you start the PhaserShare Administrator, the Main window is displayed.
Select a print server
In the Main window Printer List, click the print server name/printer name.
N O T
E
If the printer is not in the list of available printers, there could be a network
hardware problem, an incorrect frame type, or incorrect search options settings
(see the
PhaserShare Networking Manual
Launch the Quick Configuration Wizard
Click Quick Configuration to launch the Quick Configuration Wizard.
Novell NetWare Configuration
on the printer’s CD-ROM).
4
Configure the printer and set up queues
1.
If desired, change the Print Server Name or Printer Name.
2.
Select connection mode(s) by checking the box(es) for Bindery
Services, NDS Services, or both (the Phaser 780, 740, and 360 printers
support both).
Setup Guide
25
Page 32

4
Novell NetWare Configuration
3.
Click Next; the dialogs that follow allow you to configure Bindery
connections, NDS connections, or both. You need to supply the
following information for these connections:
Information needed for Bindery connections
Select either the configuration file server or the preferred file server
from the drop-down list; click Next.
If the file server you want is not on the list, proceed with these steps:
a.
Click File Servers to display the File Servers Browse dialog box.
b.
Select the server you want. Click OK. You are returned to the File
Server Selection dialog box.
c.
Select either the configuration file server or the preferred file server
from the drop-down list. Click Next.
Create and select a new queue, or select an existing queue. Click Finish.
Information needed for NDS connections
■ Specify the current Directory Services Tree (the tree where the
print server will reside).
26
■ Specify the current Directory Services Context (the location in the
directory services tree where the print server will reside).
■ Create and select a new queue, or select an existing queue. Click
Finish.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 33

Novell NetWare Configuration
Verify information and finish the configuration
After you have entered the configuration information, the Quick Configuration
Wizard displays the Configured Printer Information dialog box, which reports
the information you have entered.
1.
Verify that the information is correct.
■ If the information is correct, click Apply Changes.
■ If the information is not correct, click Back to return to previous
dialog boxes and correct the information. Click Next to return to
the Configured Printer Information dialog box. Click Apply
Changes.
■ To exit the wizard and return to the Main window without making
any changes, click Cancel.
2.
After you click Apply Changes, the printer resets; the changes take
effect when the reset is complete.
For more information on NetWare configuration and troubleshooting, see the
PhaserShare Networking Manual on your printer’s CD-ROM.
4
Setup Guide
27
Page 34

4
Novell NetWare Configuration
Setting IPX frame types from the front panel
Setting IPX frame types: Phaser 740 and Phaser 360 front panels
1.
Enter the Network Settings menu:
a.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Help Pages.
b.
Press ----> or <---- until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
c.
Press Menu; the front panel displays TCP/IP.
2.
Access the menu of frame types:
a.
Press ----> until the front panel displays NetWare.
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Enable Interface.
c.
Press ---->; the front panel displays IPX Frame Type.
d.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the first in a menu of frame types.
3.
Enable or disable the frame type:
28
a.
b.
c.
d.
4.
You can set more than one frame type; to set other frame types, repeat
Step 3.
PhaserShare Networking
Press ----> until the frame type you want is displayed.
Press Menu to display the current status of the frame type:
Enabled or Disabled.
Press ----> until the frame type is either Enabled or Disabled,
as desired.
Press OK to enter your choice into the printer. The front panel
briefly displays Selected, then returns to the display of the frame
type name.
Page 35

5.
Return the printer to normal operation:
a.
Press (Exit) until the front panel displays Network Settings.
b.
Press (Exit) again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset
to take effect, you are prompted to reset the printer. If you press
Reset, the printer resets. If you press Resume, the front panel
displays Network Settings. Press (Exit); the printer
returns to normal operation, but the changes you have made do
take effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset to take effect, the front panel displays Ready.
Setting IPX frame types: Phaser 780 printer
1.
Enter the Network Settings menu:
a.
While Ready is displayed, press Select; the Printer menu is
displayed:
Novell NetWare Configuration
4
Printer Menu
Help Pages Menu
b.
Press or until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
Printer Menu
Network Settings Menu
c.
Press Menu to enter the Network Settings menu; Network
Settings appears on the top line of the display.
2.
Access the menu of frame types:
a.
Press until the front panel displays NetWare.
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Interface.
c.
Press until the front panel displays IPX Frame Type.
d.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the first in a menu of frame types.
Setup Guide
29
Page 36

4
Novell NetWare Configuration
3.
Enable or disable the frame type:
a.
Press until the frame type you want is displayed.
b.
Press Menu to display the current status of the frame type: On or Off.
c.
Press until the frame type is either On or Off, as desired.
d.
Press Select to enter your choice into the printer. The front panel
briefly displays Selected, then returns to the display of the frame
type name.
e.
Press to return to the menu of frame types.
4.
You can set more than one frame type; to set other frame types, repeat
Step 3.
5.
Return the printer to normal operation:
a.
Press until Network Settings appears on the top line of the
display.
b.
Press again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset to
take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you press
Confirm, the printer resets. To return to normal operation without
resetting the printer, press ; Printer Menu appears on the
top line of the display. Press again; the printer returns to
normal operation, but the changes you have made will not take
effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset, press again; the front panel displays Ready.
30
PhaserShare Networking
Page 37

Chapter
5
TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Adding the printer to the host table
Add the printer’s name to the host table and assign an IP address to the printer’s
name. Depending on your host system, you may do this one of three ways:
■ Use NIS (Name Information Server, formerly Yellow Pages).
■ Use DNS (Domain Name Server).
■ Edit a file (for example, /etc/hosts). For an example, see “Example
installation for a typical BSD UNIX system” on page 33.
Assigning a print queue to the printer
■ For BSD systems, edit the /etc/printcap file and add a spool directory
(for example, to /usr/spool/lpd).
■ For System V hosts, configure the queue as a remote BSD print queue
(support for TCP/IP LPR is required). Specific instructions for the
following System V hosts are provided in the PhaserShare Networking
Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM:
■ Sun Solaris
■ SGI IRIX 5.3 and 6.x
■ IBM AIX 3.x and 4.x
■ Hewlett-Packard HP-UX 9.x and 10.x.
N O T
E
Some UNIX hosts report an error when you configure a print queue that is not
currently on the network; ignore this message.
Setup Guide
31
Page 38

5
TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Assigning print queues with PhaserPrint for UNIX
For UNIX environments, Tektronix offers PhaserPrint for UNIX software, which
provides fast raster printing and a graphical user interface with push-button
control of printer features. For more information on PhaserPrint software, see
the PhaserShare Networking Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM.
If you want to print using PhaserPrint for UNIX software, you must use
PhaserPrint software to configure your host. Refer to the PhaserPrint for UNIX
user manual or the instructions provided with the PhaserPrint for UNIX
CD-ROM for configuration information. PostScript and PDF versions of the
manual are available from the Tektronix ftp site:
ftp.tek.com/cpid/UNIX/phaserprint2.1/demo/MANUALS
Required remote printer queue names
The printer’s internal LPR queue uses the BSD protocol; its known queues are
listed in the following table. These are the only remote queue names that the
printer recognizes. If you use another name, the printer automatically defaults
to AUTO.
Queue name Language
PS PostScript
HPGL HP-GL (Hewlett-Packard Graphics Language)
PCL PCL (Printer Control Language)
AUTO Automatic Language Selection (the printer automatically senses
N O T
E
Your printer model may not support all languages listed in the table. See your
printer’s user documentation for information on the supported languages.
the language of the print job and processes it accordingly)
Using PostScript utility files to control printer features from queues
As you set up a spool queue, you can use the PostScript utility files provided
with your printer’s software to control printer features (for example, selecting
upper or lower paper trays, or selecting print quality modes). See your printer’s
user documentation for more information on these utility files.
32
PhaserShare Networking
Page 39

TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Example installation for a typical BSD UNIX system
The following procedure is an example spooler configuration that will work for
many BSD systems, including SunOS 4.x and 5.x (Solaris 1.x and 2.x) and Digital
UNIX.
Modify the /etc/hosts file to identify the printer to the workstation and modify the
/etc/printcap file to describe the printer to the workstation:
1.
Log on to your system as root.
2.
Make a backup copy of the /etc/hosts file.
N O T
E
You need superuser privileges to edit this file.
3.
Edit /etc/hosts and add a line that defines the printer's IP address and its
name. The IP address you enter here for the printer must be the same
address you specified as the printer's IP address when it was
configured. The name is the name by which your workstation identifies
the printer (you will enter this same remote name in your /etc/printcap
file in the next step). For example:
5
134.62.33.138 Phaser740
In this example, 134.62.33.138 is the printer’s IP address and
Phaser740 is the printer’s remote name.
4.
Make a backup copy of the /etc/printcap file.
5.
Edit /etc/printcap and add an entry for your printer. Refer to the
following example and the table “Descriptions of printcap parameters”
on page 34 to create your entry.
Setup Guide
33
Page 40

5
TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Sample printcap file
# Printer: Tektronix Phaser740
# Print queue name: colorprinter
# Remote machine name: Phaser740
# Remote printer queue name: PS
# Spool directory: /usr/spool/lpd/colorprinter
colorprinter:\
:lp=:\
:rm=Phaser740:\
:rp=PS:\
:mx#0:\
:lf=/usr/spool/lpd/ERRORLOG:\
:sd=/usr/spool/lpd/colorprinter:
#
Descriptions of
Parameter Description
lp Name of the device to open; this parameter must be left empty or set to
rm Remote machine name. The name by which the workstation identifies the printer; must match the
rp Remote printer queue name. The queue name that the printer recognizes; must be one of the
mx Maximum file size. Set this parameter to 0 for unlimited file size; this allows the print command to
lf Log file where print command error messages are collected. Some systems have a log file for
sd Host spool directory. Make a separate spool directory for each queue.
printcap
name in the
following:
PS for PostScript
PCL for Printer Control Language
HPGL for Hewlett-Packard Graphics Language
AUTO for Automatic Language Selection (the printer automatically senses the language of the
print job and processes it accordingly)
If you specify any other remote printer queue name, the printer defaults to AUTO.
Your printer model may not support all languages listed here. See your printer’s user
documentation for information on the supported languages.
handle large PostScript or image files.
each print queue. Refer to your workstation’s documentation for more information.
parameters
/etc/hosts
file.
/dev/null
.
34
PhaserShare Networking
Page 41

6.
Set up spool directories. After you have edited the /etc/hosts and
/etc/printcap files, create and set permissions for the spool directory you
specified. For example:
cd /usr/spool/lpd
mkdir colorprinter
chown daemon colorprinter
chgrp daemon colorprinter
chmod 770 colorprinter
Refer to your UNIX documentation for the correct command syntax for
your workstation.
Printer configuration
There are two steps to printer configuration:
1.
Set the printer’s IP address and other addressing information. The
Phaser 740 and 780 printers support the use of IP host name as well as
an IP address. See Chapter 8, “Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing
Parameters” for more information.
TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
5
2.
Set the printer’s other TCP/IP parameters (optional):
■ Set host access and control-character filtering for each port.
■ Receiving printer status (Syslog, SNMP, or email notification).
For information on setting these TCP/IP parameters, see the
PhaserShare Networking Manual on the printer’s CD-ROM.
Setup Guide
35
Page 42

5
TCP/IP Configuration (UNIX)
Extracting files from
The file unix.tar contains all shell scripts and other files needed for network
configuration in UNIX environments. The file is in UNIX tar format. The file is
included on your printer’s software CD-ROM.
Listing the contents of
Type this command:
Where directory-name is the mount point or the directory that contains the file.
For example:
unix.tar
unix.tar
tar tvf /directory-name/unix.tar
tar tvf /mnt/unix.tar
Extracting the files
1.
Change (cd) to the directory on your workstation where you want the
files to reside.
2.
Type this command:
tar xvf /directory-name/unix.tar
36
Where directory-name is the mount point or the directory that contains the file.
For example:
tar xvf /mnt/unix.tar
PhaserShare Networking
Page 43

Chapter
6
Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
The Tektronix PhaserPort software is a port monitor that allows you to print
directly from Windows 95 and Windows 98 to a networked Tektronix printer via
TCP/IP. There is no need for third-party software or a third-party interface
attached to the parallel port. PhaserPort gives your printer increased
throughput without sacrificing connectivity.
TCP/IP configuration for the PC
If you don't already have a TCP/IP address configured for your PC, contact your
system administrator to ensure that the configuration is made according to your
company guidelines. If there is no TCP/IP network already in place, configure
your PC with a unique address such as 192.1.1.1.
To check the IP address for your PC, follow these steps:
1.
From the Start menu, click Run.
2.
Enter:
winipcfg
3.
Click OK.
4.
Choose your network adapter from the pulldown list.
5.
The IP address is listed in the IP Address field.
For more information on installing and configuring TCP/IP in Windows
environments, see your Microsoft Windows documentation.
Setup Guide
37
Page 44

6
Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
Setting the printer’s IP address
There are three ways to assign the printer’s IP address:
■ Use the printer’s front panel. For more information, see “General
information: setting IP parameters from the front panel” on page 52.
■ Use DHCP. For more information, see “Setting IP parameters: DHCP”
on page 62.
■ Download a PostScript utility file. For more information, see the
README files on the printer’s CD-ROM. PC users will find the README
file for the PostScript utility files in the UTILS directory. Macintosh users
will find the ReadMe file to the PostScript utility files in the Network Utilities
folder.
PhaserPort software installation
Using the installer
38
You can install PhaserPort software using the installer on your printer’s software
CD-ROM. A single integrated installer is used to install printer drivers,
PhaserPort, and other software.
1.
Put the printer’s software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
■ If the Windows autorun feature is enabled, the CD-ROM launches
■ If the Windows autorun feature is disabled, double-click My
2.
View the brief introductory information, then click Install Drivers to
launch the installer.
3.
When you are prompted to select Easy Install or Custom Install, select
Custom Install.
4.
During custom installation, a dialog is displayed enabling you to select
the options you want to install. Check the box for PhaserPort. To
install the drivers and PPD files for your printer, check the box for
Drivers/PPDs (this is recommended for first-time installations).
Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation. For details,
see “Create your first port and install the printer” on page 39.
PhaserShare Networking
automatically.
Computer, then double-click the CD icon to launch the CD-ROM.
Page 45

Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
Create your first port and install the printer
1.
After the PhaserPort software is installed, the Add PhaserPort dialog is
displayed. Create your first port:
a.
In the Description field, enter a name for the port (this can be the
printer name/model, location, or any other descriptive name of
your choice), such as Phaser 740.
b.
In the Name/Address field, enter the IP address or DNS name of
the printer (for example, 192.1.1.2).
If you don’t know the printer’s IP address or DNS name, click Browse
to display a list of printers on the network. Double-click the printer
you want; PhaserPort automatically enters the information into the
Add PhaserPort dialog. To search the network again, click Refresh; to
narrow down the search by using subnets, click Advanced.
c.
Click OK.
2.
If you have NetWare software installed on your computer, you are
asked if you want to install the PhaserShare Administrator software. If
you also want to print using NetWare, choose Yes , then click Next.
6
3.
If you chose to install drivers and PPD files earlier in the installation,
the Finish Installation dialog displays information about the Add
Printer Wizard. Read the information, then click Next to start the Add
Printer Wizard, which allows you to install the driver for your printer.
The drivers are on your printer’s CD-ROM.
If you did not choose to install drivers and PPD files earlier in the
installation, go to Step 5.
4.
Install the printer.
a.
In the Add Printer Wizard, click Next. Choose Local printer, then
click Next.
b.
Click Have Disk, type the drive letter for the CD-ROM, and click
OK.
c.
Select your printer from the list, then click Next.
d.
In the Available ports list, select the port you created during the
first part of the installation and click Next.
Setup Guide
39
Page 46

6
Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
e.
If desired, change the printer’s name (the name that will show in
your Printers window). You can also choose to make this printer
your default Windows printer. Click Finish.
f.
If you are prompted to send a test page to the printer, choose No.
Click Finish.
5.
Complete the installation.
a.
In the Installation Completed dialog, click Finish.
b.
When prompted, finish the setup by registering your printer and
restarting your computer.
The following topics provide instructions for using PhaserPort after the initial
installation:
■ The next topic: “Adding a port for a new printer”
■ “Adding a port to an existing printer” on page 41
■ “Changing a port’s IP address” on page 42
Adding a port for a new printer
Use this procedure to install a new printer and add a port for it.
1.
Start the Add Printer Wizard:
a.
From the Start menu, select Settings, then click Printers.
b.
From the Printers window, open Add Printer.
2.
Use the Add Printer Wizard to install the printer. When prompted,
make the following choices:
■ When prompted to specify how the printer is attached, chose Local
Printer.
■ Chose LPT1 as the connection port.
If you are prompted to send a test page to the printer, choose No.
3.
When you are finished with Add Printer Wizard, follow the directions
in the next topic, “Adding a port to an existing printer”.
40
PhaserShare Networking
Page 47

Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
Adding a port to an existing printer
Use this procedure to add a port after you have installed the printer.
1.
Select your printer:
a.
From the Start menu, select Settings, then click Printers.
b
In the Printers window, right-mouse click on your printer.
2.
From the pop-up menu, choose Properties.
3.
When the properties dialog for the printer is displayed, click Details.
4.
Click Add Port, then select Other.
5.
Highlight PhaserPort and click OK; this displays the Add PhaserPort
dialog.
a.
In the Description field, enter a name for the port (this can be the
printer name/model, location, or any other descriptive name of
your choice), such as Phaser 740.
b.
In the Name/Address field, enter the IP address or DNS name of
the printer (for example, 192.1.1.2).
6
If you don’t know the printer’s IP address or DNS name, click Browse
to display a list of printers on the network. Double-click the printer
you want; PhaserPort automatically enters the information into the
Add PhaserPort dialog. To search the network again, click Refresh; to
narrow down the search by using subnets, click Advanced.
c.
Click OK.
6.
Click OK again to apply the changes; the printer driver is now
configured to use your new PhaserPort.
Setup Guide
41
Page 48

6
Windows 95 and Windows 98: PhaserPort Software
Changing a port’s IP address
If the IP address of the printer is changed, change the IP address of the
corresponding port:
1.
Select your printer:
a.
From the Start menu, select Settings, then click Printers.
b.
In the Printers window, right-mouse click your printer, then click
Properties.
2.
In the Properties dialog, click Details.
3.
Verify that PhaserPort appears in the Print to the following port field
and click Port Settings.
4.
In the Configure PhaserPort dialog, enter the correct IP address or
DNS name for the printer.
If you don’t know the printer’s IP address or DNS name, click Browse to
display a list of printers on the network. Double-click the printer you
want; PhaserPort automatically enters the information into the Add
PhaserPort dialog. To search the network again, click Refresh; to narrow
down the search by using subnets, click Advanced.
42
5.
Click OK.
6.
Click OK again to apply the changes.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 49

Chapter
7
Windows NT
The procedures in this chapter are valid for Windows NT version 3.x and 4.x.
For information about driver installation for later versions of Windows NT, visit
the Tektronix web site:
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/support
Setting the printer’s IP address
Set the printer’s IP address by any of the methods described in Chapter 8,
“Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters”.
Adding a Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 4.0 server
or workstation
The Windows NT 4.0 PostScript driver is a PPD-based driver. Follow these
instructions to add or update the Tektronix Phaser PPD file for use with
Windows NT 4.0. Adding this support gives your printer access to Tektronix
page sizes, tray selection, TekColor color corrections, and resident fonts.
This update procedure provides printer page-size information for Windows NT
applications. These instructions assume a basic familiarity with Windows NT
operation and terminology. For additional information about Windows NT,
refer to your Microsoft Windows NT documentation.
N O T
E
You may need the Windows NT 4.0 CD-ROM or diskettes to complete this
procedure.
Setup Guide
43
Page 50

7
Windows NT
Add the printer
1.
Log in as Administrator or a user with administrator privileges.
2.
Click Start, Settings, and Printers.
3.
In the Printers dialog box, double-click Add Printer.
■ If you intend to do your printer management from this computer,
click My Computer.
■ If you intend to do your printer management from another
computer, click Network Print Server.
4.
Click Next.
5.
If the printer is connected directly to the computer, select the port the
printer is connected to:
a.
LPTx is for a parallel-printer connection.
b.
COM is for a serial-connected printer.
6.
If this printer is connected to the network, click Add Port. Tektronix
printers support two types of network ports, LPR and AppleTalk.
The next topic covers LPR ports; for information on AppleTalk ports,
see “Creating an AppleTalk port” on page 45.
44
Creating an LPR port
1.
To connect via TCP/IP, double-click LPR Port in the Printer Ports
dialog box. If the LPR port is not listed in this box, the Microsoft
TCP/IP Printing Service needs to be added to the NT machine:
a.
b.
c.
PhaserShare Networking
Click Start, Settings, Control Panel, and Network.
Click Services, then click Add.
Select Microsoft TCP/IP Printing, then click OK and install this
service. The original Windows NT distribution CD-ROM is
needed during installation. If Microsoft TCP/IP Printing Services
is not listed in the options box, install the TCP/IP protocol on the
server. See your Windows NT documentation for details.
Page 51

Windows NT
2.
In the Add LPR compatible printer dialog box, enter the printer's IP
address in the box labeled Name or address of server providing lpd.
In the box marked Name of printer or print queue on that server, enter
PS in uppercase. Click OK.
3.
When returned to the Printer Ports box, click Close.
4.
At the Add Printer Wizard dialog box, click the box next to this new
port; a check mark is added. Click Next.
Creating an AppleTalk port
1.
In the Printer Port dialog box, double-click AppleTalk Printing
Devices.
2.
In the Available AppleTalk Printing Devices dialog box, select the
zone where the printer resides. If no zone name appears, double-click
the zone icon.
3.
Windows NT searches for all AppleTalk devices in that zone and
displays a list; double-click your printer.
4.
Windows NT prompts you to capture the printer; click No. (Capturing
the printer causes it to disappear from the Chooser.)
7
5.
After adding the printer port, click the box next to the new port to
select it; click Next.
Install the driver
1.
In the Add Printer Wizard dialog box, click Have Disk to add a new
Tektronix driver.
2.
Type the path name to the driver files. This can be A:\ if the files are
on a diskette. If these files were downloaded from an on-line service,
type the path name where they were saved. Click OK.
3.
Select the printer model and click Next.
4.
If prompted that a driver is already installed for this printer, select
Replace existing driver. Click Next.
Setup Guide
45
Page 52

7
Windows NT
Name the printer and set up sharing
1.
Type the printer's name; this can be any name you want. If the
Windows-based applications are to use this printer as the default
printer, click the appropriate box. Click Next.
2.
If this printer is to be shared on a network, click Shared and click all
applicable platforms that may be printing to this printer. If the printer
is a local printer only, click Not shared. Click Next.
Windows NT creates the printer
1.
If you want Windows NT to print a test page after installing the printer
driver, click Yes (recommended). If you do not want the Windows NT
test page, click No. When finished, click Finish.
2.
At this point, Windows NT is ready to create the printer. You may need
the original Windows NT distribution CD-ROM to complete this step.
Once the Windows NT medium is installed, type the path name to the
files requested. The files are usually in the I386 directory for
Intel-based Windows NT servers. Click OK.
3.
If you chose to have a test page printed in Step 1, check to see if it
printed. If the test page printed, click OK.
Adding a Windows NT 4.0 driver on an NT 3.51 server
N O T
E
For proper installation, use the latest Windows NT 3.51 drivers and
Windows NT 4.0 drivers, available from the Tektronix web site:
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/support/software.html
The following procedure describes how to set up the Windows NT 3.51 server to
automatically load a Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 4.0 client.
N O T
E
You must have Administrator access on the Windows NT 3.51 server.
46
PhaserShare Networking
Page 53

Add the printer
1.
From a Windows NT 4.0 client, click the right-mouse button on
Network Neighborhood. Select Find Computer.
2.
Type the name of the Windows NT 3.51 server. Press Enter.
3.
Double-click the Windows NT 3.51 server icon.
4.
Double-click the Windows NT 3.51 server's Printers folder.
5.
In the Windows NT 3.51 server's Printers folder, double-click
Add Printer.
N O T
E
If you do not have an Add Printer icon, then you are not logged on with an
account that has Administrator access on the Windows NT 3.51 server.
The first Add Printer Wizard dialog box should say Remote print
server <3.51 server name>.
6.
Select the port where the printer is connected.
N O T
E
You cannot create a port on the Windows 3.51 server from the Windows 4.0
client; create the port on the Windows 3.51 server. After the port is created,
you can specify that port from the Windows 4.0 client.
Windows NT
7
Install the driver
1.
In the Add Printer Wizard dialog box, click Have Disk to add a new
Tektronix driver.
2.
Type the path name to the driver files. This can be A:\ if the files are
on a diskette. If these files were downloaded from an on-line service,
type the path name where they were saved. Click OK.
3.
Select the printer model and click Next.
Enter the printer’s name and set up sharing
1.
Type the printer's name; this can be any name you want. Click Next.
2.
If this printer is to be shared on the network, click Shared and
highlight all applicable platforms that may be connecting to this
server (Windows NT 4.0 x86 should be one).
Setup Guide
47
Page 54

7
Windows NT
Windows NT creates the printer
1.
If you want Windows NT to print a test page after installing the printer
driver, click Yes (recommended). If you do not want the Windows NT
test page, click No. When finished, click Finish.
2.
When prompted for the Windows NT 3.51 CD-ROM, insert it into your
computer’s CD-ROM drive and click OK.
3.
Type the path name to the driver.
N O T
E
For proper installation, you must use the latest Windows NT 3.51 drivers and
Windows NT 4.0 drivers are available from the Tektronix web site:
www.tek.com/Color_Printers/support/software.html
The printer should now exist on the Windows NT 3.51 server and have
Windows NT 4.0 drivers available. Now any Windows 4.0 client can use that
shared printer, and the driver is installed automatically.
Adding a Windows NT 3.x driver
This update procedure provides printer page size information for Windows NT
applications. However, TekColor color corrections and other PostScript Level 2
features are not supported by the Windows NT driver. Refer to your printer’s
user documentation for instructions on other ways of selecting color corrections.
Refer to your Microsoft Windows NT documentation for details on features in
the Windows NT driver.
These instructions assume a basic familiarity with Windows NT operation and
terminology. For additional information about Windows NT, refer to your
Microsoft Windows NT documentation.
1.
Start your system with Windows NT.
2.
From the Main window, double-click the Print Manager icon.
3.
Install the Tektronix printer. From the Printer menu, select Create
Printer; the Create Printer dialog box appears.
4.
Under Driver, scroll to the end of the list and select Other; the Install
Driver dialog box appears.
48
PhaserShare Networking
Page 55

Windows NT
5.
When prompted, do one of the following.
■ If you are using the printer’s CD-ROM: Type the CD-ROM drive
location. Click OK; the Select Driver dialog box appears.
■ If you are using the printer’s software for Windows diskette:
Type the diskette drive location. Click OK; the Select Driver
dialog box appears.
6.
Under Printer Driver, choose your printer from the list, then click OK.
N O T
E
If you are using older drivers, you get a series of Noncritical Errors stating
that Windows NT is unable to open the
PSCRIPT.DRV
7.
Under Print to, scroll to the end of the list and select Other; the Printer
port dialog box appears. Tektronix printers support two types of
network ports in Windows NT: LPR and AppleTalk. The next topic
covers LPR ports; for information on creating an AppleTalk port, see
“Creating an AppleTalk port” on page 50.
files. Click Ignore or update your driver.
PSCRIPT.DLL
file and the
7
Creating an LPR port
1.
In the Printer Port dialog box, click the LPR port. If the LPR port is not
listed in the Printer Port dialog box, the Microsoft TCP/IP Printing
Service needs to be added to the Windows NT machine:
a.
In Control Panel, double-click Network; the Network Settings
dialog box appears.
b.
In Network Settings, click Add Software; the Add Network
Software dialog box appears.
c.
In the Add Network Software dialog box, click the drop-down
menu for Network Software. In the list, select TCP/IP Protocol
and Related Components, then click Continue; the TCP/IP
Installation dialog box appears.
d.
In the TCP/IP Installation dialog box, select TCP/IP Network
Printing Support. (Consult your Windows NT documentation for
information on other TCP/IP options.)
e.
Click Continue to install this service. The original Windows NT
distribution diskettes are needed during installation. To apply
these changes, restart Windows NT.
Setup Guide
49
Page 56

7
Windows NT
2.
In the Add LPR compatible printer dialog box, enter your printer’s IP
address in the field named Name or address of server providing lpd.
In the field named Name of printer or print queue on that server, enter
PS or AUTO in UPPERCASE letters.
Creating an AppleTalk port
1.
In the Printer Port dialog box, double-click the AppleTalk Printing
Devices port. If the AppleTalk Printing Devices port is not listed in
the Printer Port dialog box, the Microsoft Services for Macintosh needs
to be added to the Windows NT machine:
a.
In the Control Panel, double-click Network; the Network Settings
dialog box appears.
b.
In the Network Settings dialog box, click Add Software; the Add
Network Software dialog box appears.
c.
In the Add Network Software dialog box, click the drop down
menu for Network Software. In the list, select Services for
Macintosh, then click OK to install the service. The original
Windows NT distribution diskettes are needed during installation.
To apply these changes, restart Windows NT.
50
2.
In the Available AppleTalk Printing Devices dialog box, select the
zone where the printer resides. If no zone name appears, double-click
the zone icon.
3.
Windows NT searches for all AppleTalk devices in that zone and
displays a list; double-click your printer.
4.
Windows NT prompts you to capture the printer; click No. (Capturing
the printer causes it to disappear from the Chooser.)
Set up sharing
If this printer is to be shared on the network, perform the following steps:
1.
In the Create Printer dialog box, check the option Share this printer on
the network.
2.
Enter any name you want for the Share Name.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 57

Chapter
8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
You can set the printer’s IP address and other IP parameters by any of the
following methods:
■ Use the printer’s front panel. See “General information: setting IP
parameters from the front panel” on page 52.
■ Server-based printer configuration. Uses RARP (Reverse Address
Resolution Protocol), BOOTP (Boot Parameter Protocol), or DHCP.
When turned on or reset, the printer receives its IP addressing
information from a boot server. See “Setting IP parameters: RARP or
BOOTP” on page 61 or “Setting IP parameters: DHCP” on page 62.
■ Printer-based printer configuration (using a downloaded
configuration file). Can be used on hosts that do not have RARP,
BOOTP, or DHCP. For UNIX, use a Tektronix-provided shell script to
prepare a configuration file. When you send the file to the printer, you
store the IP addressing information in the printer’s internal memory,
where the printer reads it when reset. See “Setting IP parameters:
PostScript utility file (UNIX only)” on page 64.
■ PC and Macintosh users can also set IP parameters using PostScript
utility files; see the README files on the printer’s CD-ROM or
diskettes. The PC README file is in the UTILS directory; the
Macintosh README file is in the Network Utilities folder.
■ Printer-based printer configuration (using PhaserLink software).
After setting the printer’s IP address by one of the other methods listed
here, you can perform the rest of the TCP/IP configuration using
PhaserLink software, if you have a World Wide Web browser. See
“Setting IP parameters: PhaserLink software” on page 67.
N O T
E
When two or more IP addressing methods are used simultaneously, the printer
uses the first address that it successfully obtains.
Setup Guide
51
Page 58

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Obtain the information listed in the following table. It might be helpful to write
down this information so you can refer to it during the configuration procedure.
Information for TCP/IP configuration
Information Comments
Internet (IP) address for
the printer
Network mask If you are unsure, leave this blank; the printer will choose
Broadcast address If you are unsure, leave this blank; the printer computes
Gateway IP address Router address. You need this address if you want to
Format is x.x.x.x, where x represents a decimal number
from 0 - 255.
an appropriate mask.
an appropriate broadcast address.
The address the printer uses to send broadcast packets.
Regardless of how this parameter is set, the printer
accepts broadcast packets from any of the commonly
used broadcast address conventions.
communicate with the printer from anywhere other than
the local network segment.
General information: setting IP parameters
from the front panel
You can set IP address, network mask, gateway address, and broadcast address
from the front panel. For procedures, see the following topics:
■ See “Setting IP parameters: Phaser 740 printer front panel” on page 53.
■ See “Setting IP parameters: Phaser 780 printer front panel” on page 55.
52
■ See “Setting IP parameters: Phaser 360 printer front panel” on page 58.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 59

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 740 printer front panel
N O T
E
When you set the IP addressing parameters from the front panel, the selections
for DHCP/BOOTP and RARP are automatically set to Disabled.
1.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Help Pages.
2.
Press ----> or <---- until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
3.
Press Menu until the front panel displays TCP/IP.
4.
To set the IP address:
a.
Press Menu again; the front panel displays Interface.
b.
Press ----> to display TCP/IP Address.
c.
Press Select to display the IP address. For example:
192.2.194.101
+ ----> Set
8
N O T
E
Setting the IP address to 000.000.000.000 causes the printer to use Dynamic
Address Resolution to set its IP address (see “Setting IP parameters: RARP or
BOOTP” on page 61).
d.
Press + to set the left-most digit of the address.
e.
Press ----> to advance to the next digit. Press + to set this digit.
f.
Use ----> and + as described in Step e to set the remaining digits.
g.
When the address is correctly set, press Set to enter your settings
into the printer; the front panel displays:
Confirm Selection
Confirm
h.
Press Confirm; the front panel briefly displays Selected, then
returns to TCP/IP Address. The IP address is now set in the
printer.
Setup Guide
53
Page 60

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
5.
To set the network mask:
a.
Press ----> until Network Mask is displayed.
b.
Press Select; the front panel displays the network mask.
c.
Use + and ----> as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
network mask.
d.
When the network mask is set, use Set and Confirm as described
in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the network mask into the printer.
6.
To set the gateway address:
a.
Press ----> until Gateway Address is displayed.
b.
Press Select; the front panel displays the gateway address.
c.
Use + and ----> as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
gateway address.
d.
When the gateway address is set, use Set and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the gateway address into the
printer.
54
7.
The printer calculates the broadcast address based on the IP address
and the network mask. However, the broadcast address can be viewed
and set using the following procedure:
a.
b.
c.
d.
PhaserShare Networking
Press ----> until Broadcast Address is displayed.
Press Select; the front panel displays the broadcast address.
Use + and ----> as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
broadcast address.
When the broadcast address is set, use Set and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the broadcast address into the
printer.
Page 61

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
8.
Return the printer to normal operation.
a.
Press until the front panel displays Network Settings.
b.
Press again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset
to take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you
press Reset, the printer resets. If you press Resume, the front
panel displays Network Settings. Press ; the printer
returns to normal operation, but the changes you have made
will not take effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset to take effect, the front panel displays Ready.
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 780 printer front panel
N O T
E
When you set the IP addressing parameters from the front panel, the front
panel selections for DHCP/BOOTP and RARP are automatically set to
Disabled.
8
1.
While Ready is displayed, press Select; the Printer menu is
displayed:
Printer Menu
Help Pages Menu
2.
Press or until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
Printer Menu
Network Settings Menu
3.
Press Menu to enter the Network Settings menu; Network
Settings appears on the top line of the display.
4.
If TCP/IP is not already displayed, press until the front panel
displays TCP/IP.
5.
To set the IP address:
a.
Press Menu again; the front panel displays Interface.
b.
Press until the front panel displays IP Address.
Setup Guide
55
Page 62

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
c.
Press Menu to display the IP address. For example:
IP Address
192.2.194.101 Select
N O T
E
Setting the IP address to 000.000.000.000 causes the printer to use Dynamic
Address Resolution to set its IP address (see “Setting IP parameters: RARP or
BOOTP” on page 61).
d.
Press to set the left-most digit of the address.
e.
Press to advance to the next digit. Press to set this digit.
f.
Use and as described in Step e to set the remaining digits.
g.
When the address is correctly set, press Select; the front panel
displays the IP Address with a Confirm button.
h.
Press Confirm; the front panel briefly displays Selected, then
displays the IP address again. The IP address is now set in the
printer.
i.
Press ; the front panel displays:
56
6.
To set the network mask:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
PhaserShare Networking
TCP/IP
IP Address Menu
Press until Network Mask is displayed.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the network mask.
Use and as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
network mask.
When the network mask is set, use Select and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the network mask into the
printer.
Press ; the front panel displays:
TCP/IP
Network Mask Menu
Page 63

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
7.
To set the gateway address:
a.
Press until Gateway Address is displayed.
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the gateway address.
c.
Use and as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
gateway address.
d.
When the gateway address is set, use Set and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the gateway address into the
printer.
e.
Press ; the front panel displays:
TCP/IP
Gateway Address Menu
8.
The printer calculates the broadcast address based on the IP address
and the network mask. However, the broadcast address can be viewed
and set using the following procedure:
a.
Press until Broadcast Address is displayed.
8
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the broadcast address.
c.
Use and as described in Steps 4d through 4f to set the
broadcast address.
d.
When the broadcast address is set, use Select and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the broadcast address into the
printer.
e.
Press ; the front panel displays:
TCP/IP
Broadcast Address Menu
Setup Guide
57
Page 64

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
9.
Return the printer to normal operation:
a.
Press until Network Settings appears on the top line of the
display.
b.
Press again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset to
take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you press
Confirm, the printer resets. To return to normal operation without
resetting the printer, press ; Printer Menu appears on the
top line of the display. Press again; the printer returns to
normal operation, but the changes you have made will not take
effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset, press again; the front panel displays Ready.
Setting IP parameters: Phaser 360 printer front panel
N O T
E
When you set the IP addressing parameters from the front panel, the selections
for DHCP/BOOTP and RARP are automatically set to Disabled.
58
1.
Press Menu; the front panel displays Help Pages.
2.
Press ----> or <---- until the front panel displays Network
Settings.
3.
Press Menu until the front panel displays TCP/IP.
4.
To set the IP address:
a.
b.
c.
N O T
E
Setting the IP address to 000.000.000.000 causes the printer to use Dynamic
Address Resolution to set its IP address (see “Setting IP parameters: RARP or
BOOTP” on page 61).
PhaserShare Networking
Press Menu again; the front panel displays Enable Interface.
Press ----> until the front panel displays TCP/IP Address.
Press Menu to display the IP address. For example:
192.2.194.101
Increment Shift Select
Page 65

d.
Press Increment to set the left-most digit of the address.
e.
Press Shift to advance to the next digit. Press Increment to set
this digit.
f.
Use Shift and Increment as described in Step e to set the
remaining digits.
g.
When the address is correctly set, press Select to enter your
settings into the printer; the front panel displays:
Confirm Selection
Confirm
h.
Press Confirm; the front panel briefly displays Selected, then
displays the IP address again. The IP address is now set in the
printer.
i.
Press Exit to return to the menu of IP addressing parameters.
5.
To set the network mask:
a.
Press ----> until Network Mask is displayed.
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
8
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the network mask.
c.
Use Increment and Shift as described in Step 4d through 4f to
set the network mask.
d.
When the network mask is set, use Select and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the network mask into the
printer.
e.
Press Exit to return to the menu of IP addressing parameters.
6.
To set the gateway address:
a.
Press ----> until Gateway Address is displayed.
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the gateway address.
c.
Use Increment and Shift as described in 4d through 4f to set
the gateway address.
d.
When the gateway address is set, use Select and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the gateway address into the
printer.
Setup Guide
59
Page 66

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
7.
The printer calculates the broadcast address based on the IP address
and the network mask. In most cases, this calculated value is correct
and there is no need to set the broadcast address. However, the
broadcast address can be viewed and set using the following
procedure:
a.
Press ----> until Broadcast Address is displayed.
b.
Press Menu; the front panel displays the broadcast address.
c.
Use Increment and Shift as described in 4d through 4f to set
the broadcast address.
d.
When the broadcast address is set, use Select and Confirm as
described in Steps 4g and 4h to enter the broadcast address into the
printer.
8.
Return the printer to normal operation.
a.
Press Exit until the front panel displays Network Settings.
b.
Press Exit again.
■ If you have changed any parameters that require a printer reset
to take effect, you will be prompted to reset the printer. If you
press Reset, the printer resets. If you press Resume, the front
panel displays Network Settings. Press Exit; the printer
returns to normal operation, but the changes you have made
will not take effect until the next time the printer is reset.
■ If you have not changed any parameters that require a printer
reset to take effect, the front panel displays Ready.
60
PhaserShare Networking
Page 67

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Setting IP parameters: RARP or BOOTP
With this method, configuration information is sent to the printer over the
Ethernet or Token Ring connection via RARP or BOOTP, depending on which
protocol your host supports. This is called Dynamic Address Resolution.
You store the printer’s configuration information in a configuration file such as
an ethers or bootptab file on a boot server. On power-up, the printer issues RARP
and BOOTP requests and receives the configuration information from the server
in the RARP or BOOTP response.
The RARP response contains only IP address information. After the printer has
its address information, you can set other TCP/IP parameters by either of two
methods:
■ With a TCP/IP connection and a World Wide Web browser, you can
use PhaserLink software; see “Setting IP parameters: PhaserLink
software” on page 67.
■ Send PostScript files to the printer using your host spooler. UNIX shell
scripts for creating the PostScript files are provided with your printer’s
network utilities software. See “Setting IP parameters: PostScript
utility file (UNIX only)” on page 64. For PC environments, the
PostScript file IPCONFIG.PS is in the UTILS directory on your printer’s
CD-ROM or network utilities diskettes.
8
N O T
E
The printer’s BOOTP and RARP implementations do not support booting
across a router. The BOOTP or RARP server (host) and client (printer) must be
connected to the same Token Ring or Ethernet segment, or to segments
interconnected only by repeaters and/or bridges. However, with certain hosts
(such as OS/2) on Token Ring networks, the server and the client must be on
the same Token Ring. Furthermore, the printer’s BOOTP and RARP
implementations do not support booting between Token Ring and Ethernet
segments.
1.
Store the printer’s configuration information in an etc/ethers or
/etc/bootptab file.
2.
Connect the printer to the network.
3.
Turn on the printer. At power up, the printer issues RARP and BOOTP
requests and receives the configuration information from the host in
the RARP or BOOTP response.
Setup Guide
61
Page 68

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Setting IP parameters: DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a system in which
Windows NT servers can allocate IP addresses dynamically. Under DHCP, the
server gives the printer (called a DHCP client) an IP address when the printer is
reset.
Installing the DHCP server
1.
In Control Panel:Network, select Add Software.
2.
Select TCP/IP components.
3.
In the second window that is displayed, select DHCP server.
Setting up a DHCP server
1.
Go to the Network Administration Common Program Group and
select DHCP Server.
2.
Configure DHCP with a scope; a scope is a range of IP addresses
available for allocation to DHCP clients. For example, the scope could
be the IP addresses 192.2.194.101 through 192.2.194.254.
Defining a scope in Windows NT 4.x
a.
Click Start, Programs, Administrative Tools, DHCP Manager.
b.
Double-click Local Machine.
c.
Click Scope, Create.
d.
Enter the IP information to define the scope.
Defining a scope in Windows NT 3.5.x
a.
Open the Network Administration group.
b.
Double-click DHCP Manager.
c.
Double-click Local Machine.
d.
Click Scope, Create.
e.
Enter the IP information to define the scope.
62
PhaserShare Networking
Page 69

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
3.
Define the lease. A lease is a pre-determined time that the printer holds
the IP address. When the lease time expires, the printer queries the
DHCP server again for another IP address. It is recommended that you
set the lease to Unlimited.
4.
Define a name for the scope. You are prompted to activate the newly
created scope; answer Yes .
5.
Restart the DHCP server:
a.
In Control Panel:Services, scroll to DHCP Server.
b.
Click Stop; click Start.
c.
Click Close.
6.
Turn on the printer. The printer receives its IP address from the server.
Print a Configuration Page to obtain the IP address (“Printing a
Configuration Page” on page 2).
7.
Set up Print Manager to point to the printer’s IP address. See
Chapter 7, “Windows NT” for more information.
8
8.
DHCP transactions
■ On power up or reset, the printer sends a DHCP discover packet,
■ The DHCP server responds to the discover packet with a DHCP offer
■ The printer examines the DHCP offer packet and decides whether to
N O T
■ The DHCP server sends an acknowledgment packet to the printer, which
Configure the printer’s DHCP client software.
indicating its Ethernet address and requesting an IP address.
packet, which contains an IP address from within the assigned scope
and the assigned lease.
accept the lease. The printer sends a request packet, accepting the IP
address and the lease.
E
There can be multiple DHCP servers on the same network, each defining its
own scopes and leases; the printer selects the offer with the longest lease.
completes the transaction.
Setup Guide
63
Page 70

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Supported BOOTP/DHCP fields
The printer recognizes the BOOTP/DHCP fields listed in the following table.
Field Description Values
gw Gateway address list List of IP addresses separated by spaces.
ha Hardware address Hexadecimal; the
ht Hardware type (see Assigned
Numbers RFC)
ip IP address Single IP address.
lg Log host address(es) List of IP addresses separated by spaces.
sm Subnet mask Single IP address.
dn IP domain name Single domain name.
ds DNS server IP address Printer recognizes up to two IP addresses, separated by spaces.
Unsigned decimal, octal, or hexadecimal integer, or one of the
following symbolic names:
For UNIX Ethernet:
ethernet
ieee802
For UNIX Token Ring:
token ring
For OS/2 Ethernet or Token Ring:
ether
or
for IEEE 802 Ethernet (SNAP encapsulation).
ha
tag must be preceded by the ht tag.
ether
for 10-Mbit Ethernet (DIX encapsulation);
Setting IP parameters: PostScript utility file (UNIX only)
Use the config-IP script to create a PostScript file that sets the printer’s IP
addressing parameters. The config-IP script is provided with your printer’s
network utilities software.
■ The output of the script is PostScript code, which you must send to the
printer. When you run the script, redirect the output to a file. Then
send the file to the printer.
■ The script prompts you to provide certain information. For information
about these prompts, see the next table “IP parameters”.
The advantage of this method is that each printer has a permanent setup stored
in memory and is not dependent on a boot server for boot information. The
disadvantage is that you must configure each printer individually.
64
PhaserShare Networking
Page 71

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Before performing this procedure, install the files from your printer’s network
utilities software on to your host computer. If you have not already installed the
files, see “Extracting files from unix.tar” on page 36.
The IP parameters are listed in the following table. For the procedure, see the
next topic, “Running the config-IP script”.
IP parameters
Parameter Description
Use RARP Yes/no. Specifies whether the printer should get its IP address from a RARP response at
Use BOOTP/DHCP Yes/no. Specifies whether the printer should get its IP address from a BOOTP or DHCP
IP address Printer’s address on a network. Format is x.x.x.x, where x represents a decimal number
Network mask Needed in networks that use sub-netting. If you are not using sub-netting, leave this
Broadcast address Address the printer uses to send broadcast packets. Format is
Default gateway (router) Address the printer uses to communicate with devices not on the same network
power-up (default is yes). Answer no for a printer-based configuration; this prevents
RARP packets from appearing on the network when the printer is turned on or reset.
response at power-up (default is yes). Answer no for a printer-based configuration; this
prevents BOOTP or DHCP packets from appearing on the network when the printer is
turned on or reset.
from 0 - 255. Must be a valid IP address and not 0.0.0.0, 255.0.0.0, any address starting
with 127, or any address ending with 255.
blank; the printer will choose an appropriate mask. Format is
a decimal number from 0 - 255.
represents a decimal number from 0 - 255. If you are unsure, leav e this blank; the printer
chooses an appropriate address.
segment. Format is
x.x.x.x,
where
x
represents a decimal number from 0 - 255.
x.x.x.x,
x.x.x.x,
where
where
x
represents
x
8
Running the
1.
Connect the printer to a network. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
config-IP
script
requires that the printer be connected on the same physical network
segment as the host.
2.
Run the script config-IP:
a.
In the directory where you placed your printer’s network utilities,
change (cd) to the bin subdirectory.
b.
Type the name of the script, redirecting the output to a file. Type:
config-IP > filename
Setup Guide
65
Page 72

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
3.
Enter the information when prompted by the script.
N O T
E
The script accepts IP addresses that have empty fields (for example,
123..40.10). The script does not detect this error. Double-check the IP
addresses you enter.
4.
Log in as root.
5.
Make an entry into the host’s ARP table defining the printer’s
IP/hardware address pair. In general, this requires a command
corresponding to one of the following examples:
arp -s printer-IP-address hardware-address (for BSD systems)
or
arp -s ether printer-IP-address hardware-address (for System V)
See your host system documentation for specifics of this command.
N O T
E
The hardware address in the arp command example is the printer’s Ethernet
Address for PhaserShare Ethernet interfaces or the Token Ring Address for
PhaserShare Token Ring cards.
66
6.
Turn on the printer.
7.
Execute the ping command from the host:
8.
Use the host spooling system (for example, lpr or lp) to send to the
printer the file you created in Step 2b. This stores the IP addressing
information in the printer’s internal memory, where it is retained over
a reset or power cycle. (For more information on setting up queues, see
“Assigning a print queue to the printer” on page 31.)
9.
Reset the printer.
PhaserShare Networking
ping printer-IP-address
Page 73

Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
Setting IP parameters: PhaserLink software
After setting the printer’s IP address by one of the methods described
previously in this chapter, you can perform the rest of the TCP/IP configuration
using PhaserLink software, if you have a World Wide Web browser. For more
information on PhaserLink software, see Chapter 9, “PhaserLink Software: the
Printer’s Information Link”.
1.
From the printer’s home page, click Configuration; this displays the
View and Configure Settings page.
2.
From the View and Configure Settings page, click View and
Configure Interface Settings; this displays the View and Configure
Interface Settings page.
3.
From the View and Configure Interface Settings page, click View and
Configure TCP/IP Settings; this displays the View and Configure
TCP/IP Settings page.
4.
Enter your printer’s settings. If you make an error, click Restore Initial
Form Values and start again.
8
5.
When you are finished entering the settings, enter the Validation
Password (if one has been set) and click Do/Apply.
6.
The printer responds by displaying a dialog box that allows you to
reset the printer. The new parameters will not take effect until the
printer is reset.
DNS (Phaser 740 and 780 printers only)
The printers support Domain Name Services (DNS) through an embedded DNS
stub resolver. The DNS resolver protocol communicates with one or more DNS
servers to request the IP address for a given host name or the host name for a
given IP address.
To use an IP host name for the printer, the system administrator must have
already configured one or more DNS servers and a local DNS domain name
space data base.
Setup Guide
67
Page 74

8
Setting the Printer’s IP Addressing Parameters
To set up the printer for DNS, supply an IP domain name and up to two DNS
name server IP addresses. There are three ways to set up the printer:
■ BOOTP (UNIX). See “Setting IP parameters: RARP or BOOTP” on
page 61.
■ DHCP (Windows). See “Setting IP parameters: DHCP” on page 62.
■ With TCP/IP, you can use PhaserLink. See the next topic, “Setting up
the printer for DNS using PhaserLink software”.
Setting up the printer for DNS using PhaserLink software
After setting the printer’s IP address by one of the methods described
previously in this chapter, you can set up the printer for DNS using PhaserLink
software, if you have a World Wide Web browser. For more information on
PhaserLink software, see Chapter 9, “PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s
Information Link”.
1.
From the printer’s home page, click Configuration; this displays the
View and Configure Settings page.
2.
From the View and Configure Settings page, click View and
Configure Interface Settings; this displays the View and Configure
Interface Settings page.
3.
From the View and Configure Interface Settings page, click View and
Configure TCP/IP Settings; this displays the View and Configure
TCP/IP Settings page.
4.
Set the Domain Name Service Resolver Enabled field to Yes.
5.
Enter the following information:
■ Primary Name Server IP Address (required)
■ Second Name Server IP Address (optional)
■ IP Domain Name (required)
■ Additional Search Domain Name(s) (optional)
6.
When you are finished entering the settings, enter the Validation
Password and click Do/Apply.
7.
The printer displays a dialog box that allows you to reset the printer.
New parameters will not take effect until the printer is reset.
68
PhaserShare Networking
Page 75

Chapter
9
PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s Information Link
PhaserLink software is a printer administration and support tool using World
Wide Web technology. With PhaserLink software, you can access printer status
and manage your printer over a TCP/IP network using a web browser.
PhaserLink software gives you the following capabilities:
■ Receive printer status and manage your printer over the network using
a standard web browser.
■ Define a link to your local web server’s support page.
■ Access on-line manuals and technical support information by using
built-in links to the Tektronix web site.
PhaserLink software provides an easy-to-use, consistent interface that you can
use for most of the configuration tasks described throughout this guide.
Accessing printer information from a browser
Once a TCP/IP connection to the printer has been established and the printer’s
IP address is set, you can visit the printer’s home page from your web browser
by entering the printer’s URL (Uniform Resource Locator), just as you would to
visit any web site. The printer’s default URL is listed here:
http://printer’s-IP-address/
where printer’s-IP-address is the IP address you set during TCP/IP configuration.
N O T
E
Some platforms and browsers allow you to set a name/IP address pair in the
UNIX host table (or equivalent name-server database on a non-UNIX host); the
printer’s name can be used in place of the IP address in the URL. For example:
http://Phaser740-Marketing/
Setup Guide
69
Page 76

9
PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s Information Link
PhaserLink software help files
Most PhaserLink pages allow you to view and set printer parameters through
fields. HTML files containing descriptions of the fields are supplied on the
printer’s CD-ROM in the PHLINK directory, where the file PLHOME.HTM is the
home page for the help files. These files can be viewed using any browser that
supports HTML 3.0.
If you copy these PhaserLink software help files to your local web server, then
define that server as your local link, PhaserLink users can access the help files
from the printer’s PhaserLink Help page.
Configuring PhaserLink Help
1.
Copy the PhaserLink help files from the printer’s CD-ROM to your
local web server. Note the URL for the PhaserLink Help home page,
PLHOME.HTM.
2.
Access the printer’s Status page by entering the printer’s URL into
your browser. See “Accessing printer information from a browser” on
page 69 for more information.
70
3.
Click Configure; this displays the View and Configure Settings page.
4.
Click Define Local HTTP Link; this displays the Define Local HTTP
Link page.
5.
Enter the URL that you have set up for the PhaserLink Help home
page. If you have configured PhaserLink to require a password, enter
it into the Password field. Then click Do/Apply.
N O T
E
PhaserLink passwords are not encrypted.
Accessing PhaserLink Help
When the PhaserLink Help home page has been defined as a local link, as
described in the previous procedure, users can access PhaserLink Help this way:
1.
Click Help; this displays the Help page.
2.
On the Help page, click local HTTP link; this displays the PhaserLink
Help home page.
PhaserShare Networking
Page 77

PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s Information Link
Setting printer parameters: PhaserLink software pages
If there are read-write parameters on the page, there is a field at the bottom of
the page for a validation password. By default, the password is a NULL string
(no characters). The password is common across all PhaserLink software pages.
N O T
E
PhaserLink passwords are not encrypted.
■ If you enter an invalid password, the printer reports an error. The
Validation Password link displays the Set Administrator Password
page, which you can use to change the password.
■ Click Restore Initial Form Values to restore all values on the page to
their previous settings.
■ To transmit changes to the printer, click Do/Apply.
Information Forwarding
9
When you click a link that connects you to the Tektronix web server, the
Information Forwarding feature causes the printer to send the following printer
status information back to the Tektronix server:
■ Printer model
■ Firmware version
■ Printer ID number
■ Page count
■ Language
■ Serial Number
Transmitting this information back to the Tektronix server ensures the quickest
connection to relevant product and update information. Tektronix may store
this information to serve you better in the future.
Setup Guide
71
Page 78

9
PhaserLink Software: the Printer’s Information Link
Disabling Information Forwarding
1.
Display the View and Configure Information Forwarding page.
2.
Select No from the Information Forwarding Enabled menu button.
3.
If a validation password has been assigned, enter the password to
make the change to take effect.
N O T
E
PhaserLink passwords are not encrypted.
4.
Click the Do/Apply button.
72
PhaserShare Networking
Page 79

Index
A
Adapter Status 15
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
with config-IP script 65
with config-TokenRing script 16
B
BOOTP 51
Broadcast 15
Broadcast address 52
C
cables 8
Chooser 22
config-IP 65
config-TokenRing 17
Configuration Page
front panel (Phaser 780) 3
front panel (Phaser 740 and 360) 2
D
DHCP 62
DNS
printer configuration 67
UNIX host configuration 31
DOS 1
E
Early Token Release 15
email notification 3
etc/hosts file
etc/printcap file 34
Ethernet
adapters 5
cables 8
terminators 8
EtherTalk 21
33
F
Frame Routing (Phaser 740 and 360) 12
Frame Routing (Phaser 780) 13
front panel
printing Configuration Page (Phaser 780) 3
printing Configuration Page
(Phaser 740 and 360) 2
setting IPX frame type (Phaser 780) 29
setting IPX frame type (Phaser 740 and 360) 28
setting printer’s IP addressing parameters
(Phaser 360 printer) 58
setting printer’s IP addressing parameters
(Phaser 740 printer) 53
setting printer’s IP addressing parameters
(Phaser 780 printer) 55
setting Token Ring Frame Routing (Phaser
780) 13
setting Token Ring Frame Routing
(Phaser 740 and 360) 12
G
Gateway IP address 52
H
hosts file 33
I
information forwarding 71
installation
PhaserShare software 23
IP addressing parameters
62
DHCP
general information on setting 52
setting from Phaser 360 front panel 58
setting from Phaser 740 front panel 53
setting from Phaser 780 front panel 55
setting using a PostScript utility file (UNIX) 64
setting using PhaserLink software 67
setting using RARP or BOOTP 61
Setup Guide
73
Page 80

J
Job accounting 3
remote printer queue names
Route Cache Size 15
Route Cache Timeout 15
32
L
LocalTalk 21
N
NetWare 23
Network Address 15
Network mask 52
NIS 31
P
PhaserLink software
general information 69
information forwarding 71
URL, printer 69
PhaserShare software
installation procedure 23
Quick Configuration Wizard 24
PhaserShare Series B Ethernet card 7
PhaserShare Series B LocalTalk card 19
PhaserShare Series B Token Ring card 12
print queue (UNIX) 31
printcap file 34
printer management 3
S
Speed 15
T
TCP/IP
extracting files from unix.tar 36
UNIX 31
Windows NT procedures 43
Windows 95 37
terminators
Ethernet 8
LocalTalk 20
Token Ring
cables 9
configuration 12
TokenTalk 21
U
Unknown Route 15
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
for the printer 69
Usage Profile reports 3
Q
queue names (UNIX remote printer) 32
queues
NetWare
UNIX 31
UNIX remote printer queue names 32
Windows NT 3.x driver 49
Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 4.0
25
server or workstation 44
R
RARP 51
74
PhaserShare Networking
V
View and Configure Information
Forwarding page 71
W
Windows 95 and Windows 98 37
Windows NT 43
Windows NT 3.x driver 48
Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 3.51
server 46
Windows NT 4.0 driver on a Windows NT 4.0
server or workstation 43
World Wide Web 69
Page 81

Page 82

®
Printed on recycled paper
063-3116-00
 Loading...
Loading...