Page 1

DIRECTV COM1000
Integrator's Manual
Software Version
ST02.08.07
REV. 2.72
Page 2

Contents
1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................... 10
2 COM1000 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION .................................................... 13
3 MECHANICAL OVERVIEW .................................................................. 17
3.1 COM200 Front View ................................................................................................ 17
3.2 COM200 Rear View ................................................................................................. 18
3.3 COM24 Card ............................................................................................................ 19
3.4 COM24FLX Card ...................................................................................................... 20
3.5 GbE Card ................................................................................................................. 21
3.6 XDR24 Card ............................................................................................................. 21
3.7 QAM24 Board ......................................................................................................... 21
4 GETTING STARTED ........................................................................... 24
4.1 Setting up Multiple Chassis ...................................................................................... 24
4.2 Installation Requirement Guidelines ........................................................................ 27
4.2.1 General System Guidelines ......................................................................................... 27
4.2.2 System Integrator Guidelines ..................................................................................... 28
4.2.3 System Operator Guidelines ....................................................................................... 28
5 CONFIGURING THE SYSTEM ................................................................ 30
5.1 Useful tools ............................................................................................................. 30
5.1.1 Configuration tool ...................................................................................................... 30
5.1.2 DHCP Server ................................................................................................................ 30
5.1.3 Video Playback ........................................................................................................... 31
5.1.4 System Logging ........................................................................................................... 31
5.1.5 TFTP/FTP Server .......................................................................................................... 31
5.1.6 IP Address Discovery ................................................................................................... 32
5.2 Connecting to the COM1000 .................................................................................... 33
©2011, 2012 Technicolor. All rights reserved.
Page 3

3
5.2.1 Preparing Your Computer’s Network Connections ..................................................... 33
5.2.2 Avoiding IP Address conflicts ...................................................................................... 35
5.3 Using a TFTP Server ................................................................................................. 35
5.3.1 Determining Your IP Address ...................................................................................... 35
5.3.2 Configuring Your TFTP Server ..................................................................................... 37
6 USING THE COM1000 WEB INTERFACE ............................................... 43
6.1 Discovery of COM24 and COM24FLX Cards ............................................................. 43
6.1.1 Fields prior to ST02.05.05 no longer present ............................................................. 47
6.1.2 Fields present after ST02.05.05 .................................................................................. 47
6.2 Scanning for COM24 Cards ...................................................................................... 49
6.3 Refreshing the COM1000 Display ............................................................................. 51
6.4 Displaying COM1000 Status ..................................................................................... 52
6.5 Evaluating COM24 Authorization Status .................................................................. 54
6.6 Evaluating COM1000 System Status ......................................................................... 58
6.7 Evaluating COM1000 Health Status ......................................................................... 60
6.8 The Tune Command ................................................................................................ 63
6.8.1 Tuning the COM24 Cards ........................................................................................... 64
6.8.2 Evaluating COM24 Informational Status ................................................................... 68
6.8.3 Using the COM24 “Direct Tune” Feature ................................................................... 70
6.8.4 Using the COM24 LED Control Feature ...................................................................... 71
6.8.5 Using the COM24 File Transfer Utility ........................................................................ 72
6.8.6 Setting the COM24 User Configuration Options ........................................................ 74
6.8.7 Reading the COM24 CAM Log Data ........................................................................... 75
6.8.8 Using the COM24 Software Reset Feature ................................................................. 79
6.9 Using the COM1000 TuneAll Command ................................................................... 80
6.10 Using the DIRECTV Electronic Program Guide (EPG) ................................................. 83
6.10.1 Starting Out .............................................................................................................. 85
6.10.2 Configuring the EPG ................................................................................................. 89
6.10.3 Adding a Logo to the EPG ......................................................................................... 92
Page 4

4
6.11 Using the COM24 Syslog Command ......................................................................... 93
6.12 Using the COM24 ATSC Command ........................................................................... 94
6.13 Using the COM24 401 Command ............................................................................. 95
6.14 Using the COM24 QAM Command ........................................................................... 96
6.15 Using the COM24 Help Command ............................................................................ 99
7 COM1000 FIRMWARE UPGRADE PROCEDURES ................................... 100
7.1 Preparing for a Firmware Upgrade ......................................................................... 100
7.2 Upgrading COM24 Firmware ................................................................................. 100
7.3 Upgrading a FLX24 from SD to HD .......................................................................... 103
7.4 Upgrading QAM24 Firmware ................................................................................. 104
8 COM1000 DIAGNOSTIC CAPABILITIES ............................................... 107
8.1 Indicator lights ...................................................................................................... 107
8.1.1 Power Supply Issues.................................................................................................. 107
8.1.2 System Startup ......................................................................................................... 108
8.1.3 Normal Operation .................................................................................................... 109
8.1.4 Software Upgrade .................................................................................................... 110
8.2 Network Connectivity Indicators ........................................................................... 112
9 DIRECTV AUTHORIZATION ............................................................. 113
10 GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS .................................................... 114
10.1 Testing Video without Pro:Idiom Encryption .......................................................... 114
10.1.1 Streaming Video to a Standard Television ............................................................. 114
10.1.2 Streaming Video to your PC .................................................................................... 115
10.2 Preventing Pro:Idiom key loss ............................................................................... 117
10.3 Changing the Input ................................................................................................ 118
10.4 Verifying Card Authorization ................................................................................. 118
Appendix A COM24 IP CONFIGURATION CONSIDERATIONS .................... 119
Appendix B RF SANITY CHECK .......................................................... 124
Page 5

5
Appendix C TROUBLESHOOTING THE COM1000 .................................. 125
List of Figures
Figure 1 – COM1000 System Overview ...................................................................................... 14
Figure 2 – COM200 Front View ................................................................................................... 17
Figure 3 – COM200 Rear View .................................................................................................... 18
Figure 4 - COM24 Card ................................................................................................................ 19
Figure 5 - COM24FLX Card ........................................................................................................ 21
Figure 6 – QAM24 Board installed in Chassis ............................................................................. 22
Figure 7 – QAM24 Front View .................................................................................................... 23
Figure 8 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration Switch Location ................................................. 25
Figure 9 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration Switch Closeup .................................................. 25
Figure 10 - COM24FLX to SWM Module connections ............................................................... 29
Figure 10 – Results from the COM24 Discovery Tool................................................................. 32
Figure 11 – Network Connections Window ................................................................................. 33
Figure 12 – Internet Protocol Configuration ................................................................................. 34
Figure 14 – Accessing the Command Prompt window ................................................................ 36
Figure 15 – Running ipconfig ....................................................................................................... 36
Figure 16 – Tftpd32 Startup Screen .............................................................................................. 38
Figure 17 – Tftpd32 Settings Window (Global Settings).............................................................. 39
Figure 18 – Tftpd32 Settings Window (TFTP Settings) ............................................................... 40
Figure 19– Tftpd32 Settings Window (Syslog Settings) .............................................................. 41
Figure 20 – Tftpd32 File Transfer Progress Screen ...................................................................... 42
Figure 21 – Tftpd32 Completed Transfer Screen .......................................................................... 42
Figure 22 - COM1000 Web Based User Interface Introduction Page .......................................... 43
Figure 23 - COM24 Discover Page .............................................................................................. 44
Figure 24 - Discover Page w. COM24FLX .................................................................................. 45
Figure 25 – COM1000 Discover Page (showing colors) .............................................................. 46
Page 6

6
Figure 26 – COM1000 Scan Page ................................................................................................ 50
Figure 27 – COM1000 Refresh Page ............................................................................................ 52
Figure 28 – COM1000 Display Page ............................................................................................ 53
Figure 29 – COM1000 Pairing Info Page ..................................................................................... 54
Figure 30 – COM24 Multi-card Upgrade Feature ........................................................................ 56
Figure 31 – COM24 Multi-card Upgrade Results Page................................................................ 57
Figure 32 – COM1000 SysInfo Page ............................................................................................ 58
Figure 33 – COM1000 HealthInfo Page ....................................................................................... 60
Figure 34 – COM24 Basic Tune Screen ....................................................................................... 63
Figure 35 – Advanced Tune screen portion of Advanced Edit page ............................................ 65
Figure 36 – “Info” Section on Advanced Edit Page. .................................................................... 68
Figure 37 – “Direct Tune” Interface on Advanced Edit page ....................................................... 70
Figure 38 – “LED Control” Interface on Advanced Edit page ..................................................... 71
Figure 39 – “File Transfer” Interface on Advanced Edit page ..................................................... 72
Figure 40 – “User Config” Interface on Advanced Edit page ...................................................... 74
Figure 41 – “CAM Log” Interface on Advanced Edit page ......................................................... 76
Figure 42 – CAM Log Report ....................................................................................................... 77
Figure 43 – “Reset” Interface on Advanced Edit page ................................................................. 79
Figure 44 – COM1000 TuneAll Page............................................................................................ 80
Figure 45 – COM1000 EPG Page ................................................................................................ 85
Figure 46 – COM1000 EPG Page (Configured) ........................................................................... 88
Figure 47 – COM24 EPGLoad Result .......................................................................................... 89
Figure 48 – Guide Channel (EPG) ................................................................................................ 91
Figure 49 – EPG Logo Adjustments ............................................................................................. 92
Figure 50 – Guide Channel (EPG) with Custom Logo ................................................................. 92
Figure 51 – COM24 Syslog Report .............................................................................................. 93
Figure 53 – QAM24 Command Screen (bottom portion) ............................................................. 97
Figure 54 – COM24 Help Command............................................................................................ 99
Figure 55 – Multi-card COM24 SW Upgrade ............................................................................ 101
Figure 56 – Multi-card COM24 SW Upgrade Results ............................................................... 102
Page 7

7
Figure 58 – QAM24 SW Upgrade .............................................................................................. 105
Figure 59 – QAM24 SW Upgrade Results ................................................................................. 106
Figure 60 – Network Connectivity Indicator LEDs .................................................................... 112
Figure 61 – Configuring VLC Media Player .............................................................................. 115
Figure 62 – Opening a Network Stream ..................................................................................... 116
Figure 63 – Streaming Video from a COM24 Card ................................................................... 117
List of Tables
Table 1 – Definition of Terms ...................................................................................................... 10
Table 2 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration ............................................................................. 27
Table 3 – LED States .................................................................................................................. 107
Table 4 – LED Startup Behavior ................................................................................................ 108
Table 5 – LED Behavior during Normal Upgrade...................................................................... 110
Table 6 – RF Spot Check Values ................................................................................................ 124
Page 8

8
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY
BLANK
Page 9

9
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY
BLANK
Page 10
10
1 INTRODUCTION
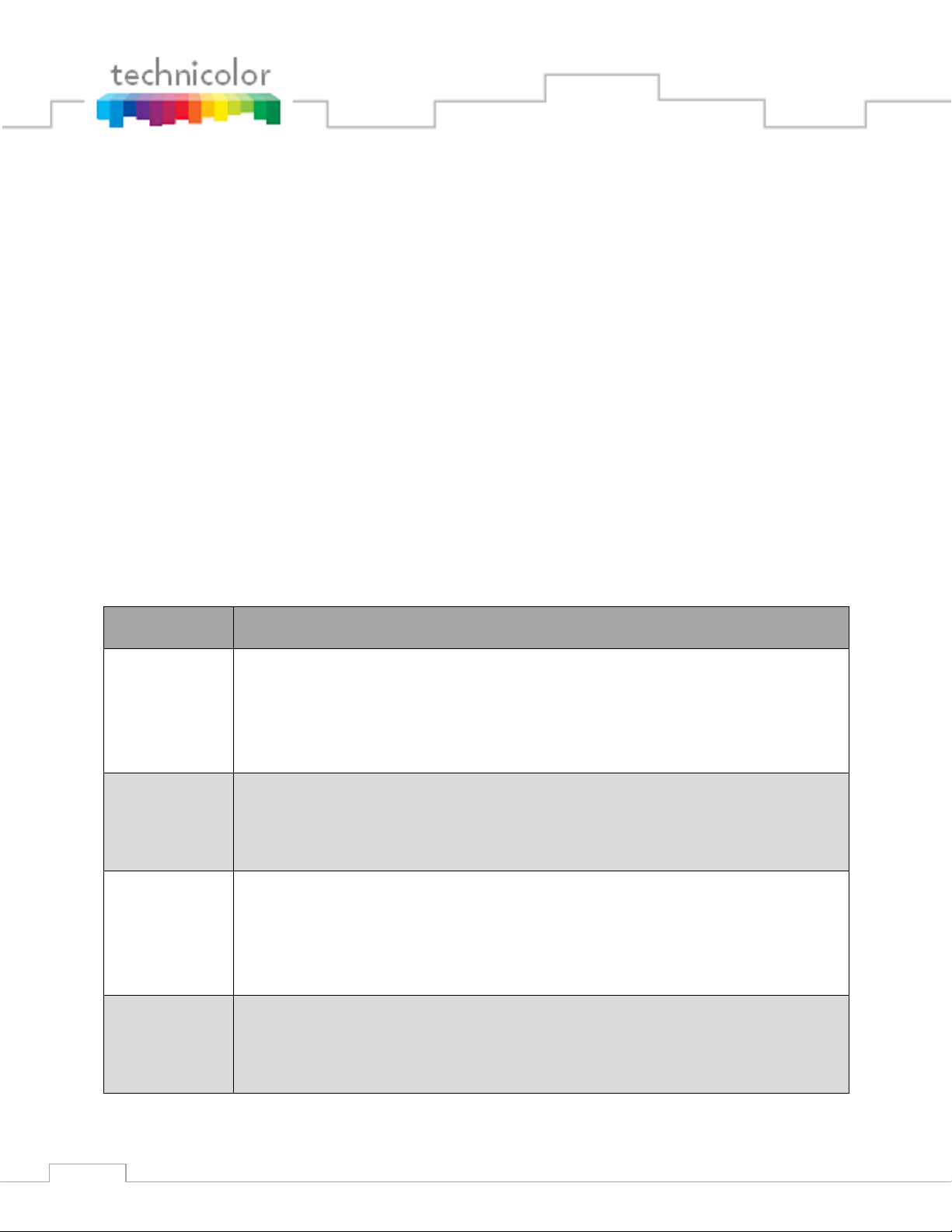
Term
Definition
COM1000
This is the complete system, consisting of the following: one or more COM100
(now discontinued) or COM200 chassis, COM120 or SWM units, an optional
gigabit Ethernet switch, and QAM24 cards or alternatively comercial edge
QAMs.
COM120
A RF (radio frequency) distribution panel, which is necessary to enable Ka B
band signal delivery. The manual will use this device as a reference, but it may
be replaced with a similar device of your choosing.
COM200
A chassis that can support up to 12 receiver cards. This chassis contains an
integrated gigabit Ethernet switch and Ethernet Card, but does not include
other necessary equipment such as an edge QAM device, Ethernet switches, or
RF distribution and signaling electronics.
COM100
The first-generation chassis of the COM1000 series chassis, similar in structure
to the COM200 but lacking backplane Ethernet connections. This product was
discontinued in 2010.
This document describes the processes and procedures for configuring a COM1000 system. The
following sections will provide a brief overview of the system hardware, an in-depth guide to the
COM24 user interface, and descriptions of certain system processes. Also included are several
indices that cover common troubleshooting problems.
It is recommended that you read through the entirety of the manual, or at least review the main
sections before working with the system, as it contains some important pointers that may come in
handy during setup and maintenance.
The table below provides an explanation of some useful terms and device names that will be
referred to throughout the manual. You should use these terms to familiarize yourself with the
different aspects of the system before proceeding any further.
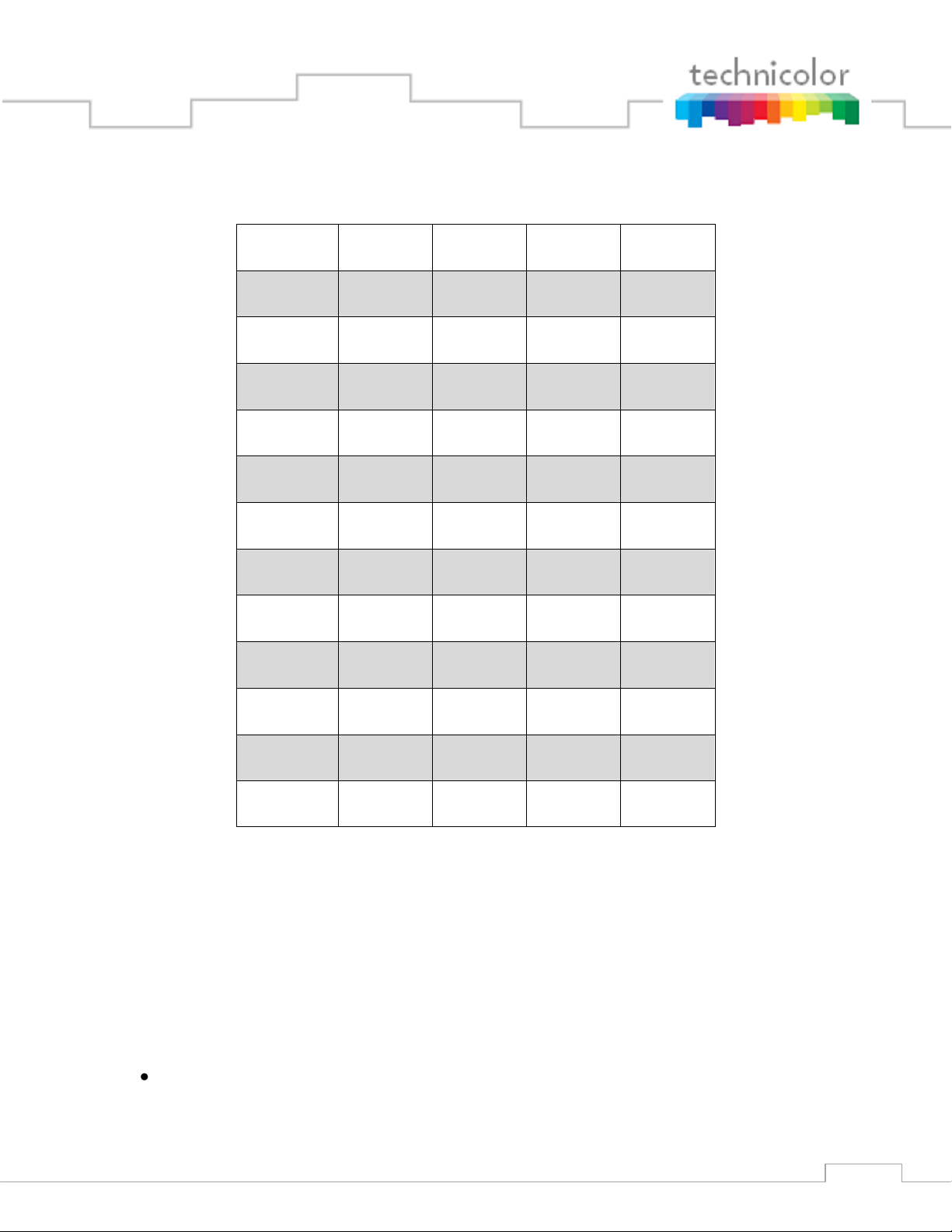
Table 1 – Definition of Terms
Page 11

11
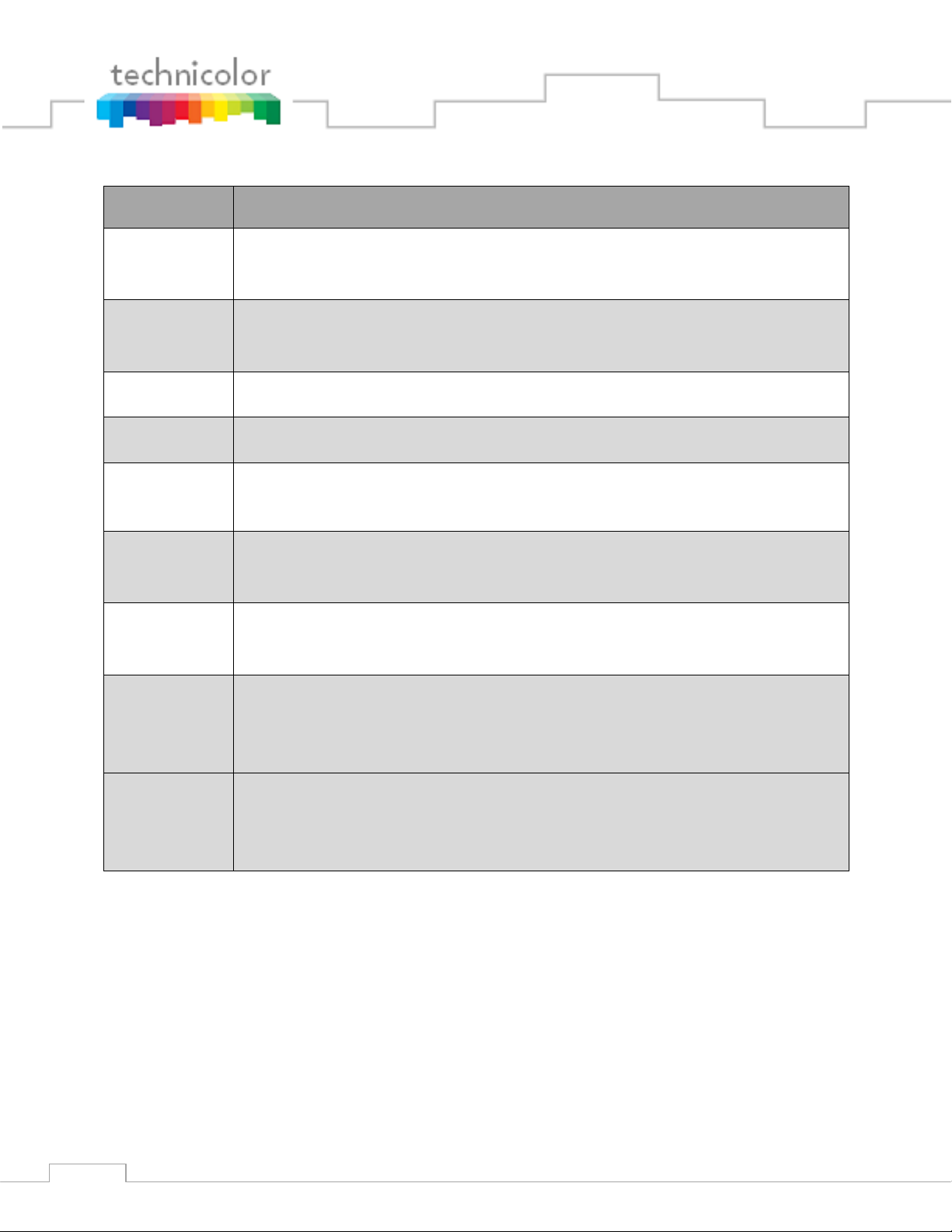
Term
Definition
COM24
Individual DIRECTV receiver card that fits within a COM200 chassis and is
capable of sourcing 2 DIRECTV HD or SD channels.
COM24FLX
Individual DIRECTV receiver card that fits within a COM200 chassis and is
capable of sourcing 3 DIRECTV SD channels. Software upgradeable to 2 HD
channels with a software upgrade license purchase.
QAM6
The QAM6 is an optional circuit board (i.e., internal Edge QAM) that replaces
the Ethernet Card in the upper left side of a COM200 Chassis. The board
provides 6 QAM channels in addition to a system management Ethernet port.
Each QAM channel can carry 2 HD or 8 SD video channels. The QAM6 can be
expanded up to 12 QAM channels, 2 at a time, by purchasing a SWQAM2.
SWQAM2
The SWQAM2 is a software key that will enable 2 QAM channels per key on a
QAM6 card. By pruchasing 3 SWQAM2 keys a QAM6 can be expanded to 12
QAM channels.
QAM24
An optional circuit board (i.e., internal Edge QAM) that replaces the Ethernet
Card in the upper left side of a COM200 Chassis. The board provides 12 QAM
channels in addition to a system management Ethernet port. Each QAM
channel can carry 2 HD or 8 SD video channels. This product has been replaced
by the QAM6 and the SWQAM2.
ATSC8
An optional eight channel off-air ATSC receiver that may be connected to and
configured from a COM1000 system.
Edge QAM
QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) is the format by which digital cable
channels are encoded and transmitted. An edge QAM is a device built to carry
both video-on-demand and switched digital video streams. Makers include
Technicolor, Arris, Harmonic Inc., Motorola, and Scientific-Atlanta/Cisco.
Pro:Idiom
An encryption technology used in the hospitality industry for the delivery of
digital television signals of which Zenith Electronics LLC is the license holder.
This is the encryption standard around which the COM1000 system is
designed.
Page 12
12
Term
Definition
Transcryption
The process by which the COM 1000 system converts content streaming from
DIRECTV’s conditional access system to Pro:Idiom encrypted video.
“Hot-
swappable”
The unit or device this term describes may be added to, removed from, or
replaced within the system it is a part of without powering anything down.
SD
Standard Definition
HD
High Definition
System
Integrator
The person or company that performs the onsite installation.
System
Operator
The company or organization that typically holds the “right of entry” and is
responsible for installation and all onsite support on a daily basis.
SWM
a.k.a. SWiM
“Single Wire Multiswitch” - DirecTV Module used for selecting up to 8 satellite
transponders for TV programs and 1 network transponder.
Pseudo code
The first five characters of the COM200 Chassis serial number (e.g., BC009).
Identifies the version of the chassis. The serial number is found on the label
on the rear of the COM200 chassis (see Figure 3).
GbE
The Gigabit Ethernet card (GbE) is a card that when installed in slot 1 of a
COM200 chassis provides a gigabit speed Ethernet port for use in stacking
multiple chassis or for injecting ATSC signals into a QAM24 or QAM6.
Page 13

13
2 COM1000 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
A fully populated COM200 chassis is capable of tuning and transcrypting up to 24 DIRECTV
HD channels or 36 SD channels. The satellite signal is tuned and demodulated resulting in a
DIRECTV Legacy or MPEG-2 transport stream. This transport stream is then IP-encapsulated
using standard Internet protocols and RFCs and is sent out via the Ethernet interface. The data
leaving the system is in a format suitable for input to an edge QAM device or for distribution on
an IPTV network. The original DIRECTV broadcast video encoding format (MPEG-2 or MPEG4 compression) is preserved and the output transport stream is encrypted with the Pro:Idiom
encryption standard.
Multiple COM200 chassis can be “stacked” in order to provide more than 24 HD or 36 SD
output channels. While there is no technical limit to the number of COM200 chassis than can be
configured in this manner, the DIP switches used for setting individual chassis IDs are only
capable of providing 12 unique identifiers. Refer to Section 4.1 for more information on this
topic.
The COM24 receiver cards are controlled and managed via an Ethernet connection and do not
contain an internal video decoder for viewing the currently tuned channels. The COM24 card
does not operate like a traditional DIRECTV receiver. Specifically, COM24 cards do not
perform any MPEG video or audio decoding. They do not provide a traditional Middleware
based User Interface, and do not require a remote control device. The COM24 card includes a
built-in web interface and must be configured using a web browser. The video output of a
COM24 receiver can be viewed on a properly equipped commercial Pro:Idiom television or
Pro:Idiom capable set-top box. Manufacturers of this equipment include but are not limited to
LG, Phillips, Samsung, Sony, Enseo, and Technicolor.
Page 14
14
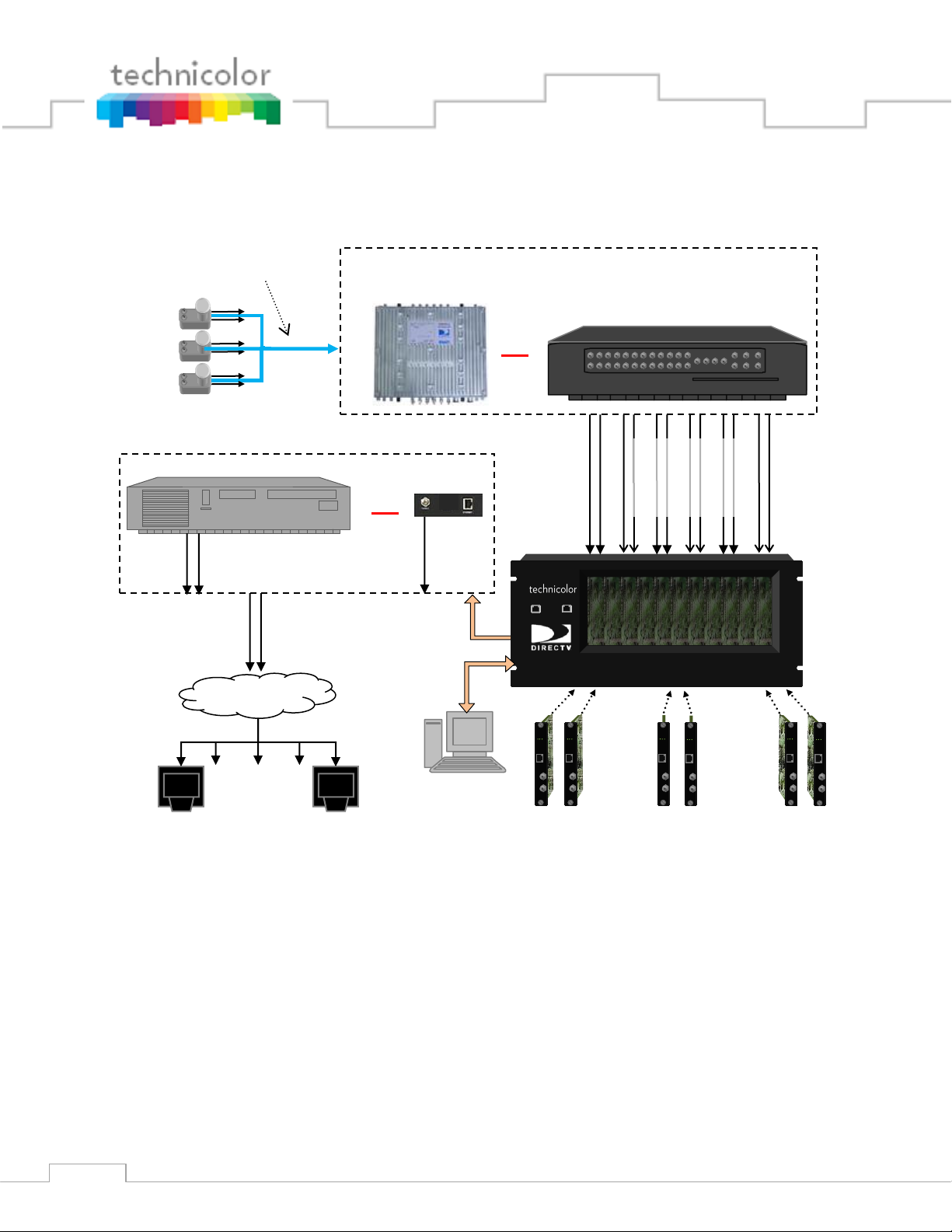
Refer to Figure 1 below for a diagram illustrating a complete COM1000 system.
TV TV
COM120
(RF Distribution Panel)
External Edge QAM
. . .
COM200
Chassis
Up to… 12 COM24 cards
. . .
. . .
Admin PC
(Optional)
Series of any number of Pro:Idiom
enabled Digital TVs with tuners
QAM24
OR
LNB 3
LNB 2
LNB 1
OR
SWM32
(Single Wire Multi-switch)
RF Distribution
RF Signal Level:
-50dBm to -30dBm
per Transponder
RF Signal Level:
-55dBm to
-25dBm per
Transponder
COM1000 System – This describes the entire video distribution system setup as seen above,
including all devices and connections that work together to stream DIRECTV HD video
programming.
LNB (Low-Noise Block) – This is a device that acts as the antenna of your satellite dish. It
receives incoming signals and sends them to the RF distribution panel. Each one is
capable of providing two outputs.
Figure 1 – COM1000 System Overview
Page 15

15
COM120 (RF Distribution Panel) – This device receives the incoming satellite feed via your
dish receiver and distributes the signals using a series of multiswitches. It then sends
these signals into the COM24 cards via the RF Inputs (labeled “Tuner 1” and “Tuner 2”).
COM200 Chassis – This device houses the COM24 and COM24FLX cards. All video traffic is
routed through the Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) port on the rear of the chassis or to the
QAM24. System management and control can be done by connecting a computer to one
of the management ports on the Ethernet Card or QAM24 card (i.e., front of the chassis).
Admin PC – This is an optional device and is nonessential to normal system operation. It is
recommended, however, as it can be useful in maintaining desired programming and
monitoring system function. This can be a desktop or laptop computer equipped with an
Ethernet port (or a USB port with Ethernet adapter), any of the recommended
applications listed in Section 5.1, and a web browser of your choice.
COM24 and COM24FLX Cards – The bulk of this manual is dedicated to these cards. They
are the means by which the property will be able to receive the desired television
programming for their network and control the entire COM1000 system.
QAM24 or QAM6 Cards – An optional board that replaces the Ethernet Card in the upper left
side of a COM200 Chassis. The board provides up to 12 QAM modulator channels in
addition to a 10/100 Ethernet port to an Edge QAM. Each QAM modulator can carry two
HD or eight SD video channels.
Edge QAM – In a typical installation, the COM24 cards will be configured to stream to this
device. It converts the COM24‟s IP-packetized streams to QAM-modulated RF for
distribution throughout a property.
Property Distribution Network – This network, set up and maintained by the System Operator,
will distribute any channels provided by the property. It may consist of any configuration
of devices as defined by the System Operator.
Pro:Idiom Enabled Televisions – It is important to note that some Pro:Idiom compliant
televisions only support MPEG-2 video compression. The COM24 card is agnostic to the
Page 16

16
content compression type and it will stream either MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 encoded
transport streams.
Page 17
17
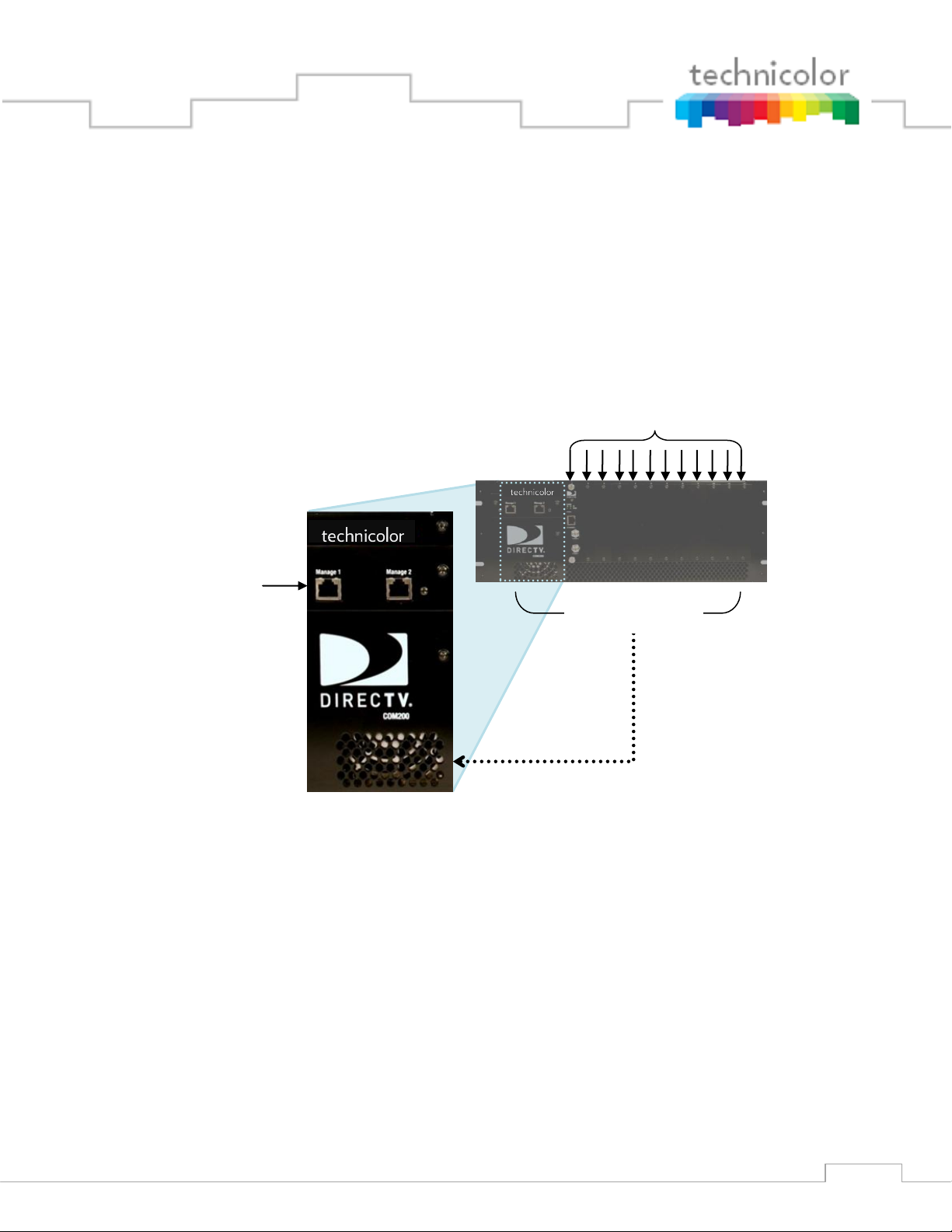
3 MECHANICAL OVERVIEW
Ethernet Ports
(Management)
Card Slots #1 – 12
Ventilation Grate
The following sections contain a brief overview of the devices that you will be interacting with
along with the associated hardware. The intent is to give you a working knowledge of how the
system operates under normal circumstances so that you will be able to recognize it when
something goes wrong.
3.1 COM200 Front View
Figure 2 above shows the faceplate of the COM200 chassis.
The two Ethernet ports on the far left, combined with the Gigabit Ethernet port in the rear (see
Figure 3) allow for direct connections to other devices such as an edge QAM, Ethernet switch,
and/or a management PC (optional) and allows any additional chassis in the system to be
interconnected. If the chassis is using the QAM24 modulator, it replaces the Ethernet Card (See
Section 3.7).
Along the bottom edge is the ventilation grate, which, combined with the exhaust fans in the
back, allow air to flow over the internal system, cooling it.
The majority of the face shows the 12 available card slots, each corresponding to a unique Slot
ID, capable of supporting 12 individual cards.
Figure 2 – COM200 Front View
Page 18

18
3.2 COM200 Rear View
Exhaust Fan 1
Rear Mounting
Bracket
Gigabit
Ethernet
Port
AC Input 1
AC Input 2
Power
Supply Fans
Exhaust Fan 2
Figure 3 – COM200 Rear View
Figure 3 above shows the rear of the COM200 chassis.
The two AC input connections shown at the bottom right provide power to the COM200 chassis.
Only a single AC input connection is required in order for the system to operate. However,
utilizing both AC input connections creates a DMR (Dual Modular Redundant) system. In other
words, the second power unit acts as a backup in case the first power module fails, providing a
seamless transition to a functioning power supply. In the case of such an event, the rear
mounting bracket just below the power supply fans must be removed in order to replace the
failed module. It should be noted that the power supplies are hot-swappable.
The COM200 chassis also contains two 5-inch exhaust fans to provide cooling to the system.
Airflow is pulled through the ventilation grate on the front of the COM200 chassis across the
COM24 cards and out the back. In the case of an equipment failure, the COM200 chassis can
run with just one fan without overheating, but it is recommended that the broken fan is serviced
and/or replaced as soon as possible.
The COM200 chassis also contains an integrated Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) port. This port provides
the means of routing all COM200 traffic an external edge QAM. If a QAM24 card is installed
the external GbE port will NOT available for use as that port will be used to route traffic to the
QAM24 card.
Page 19
19
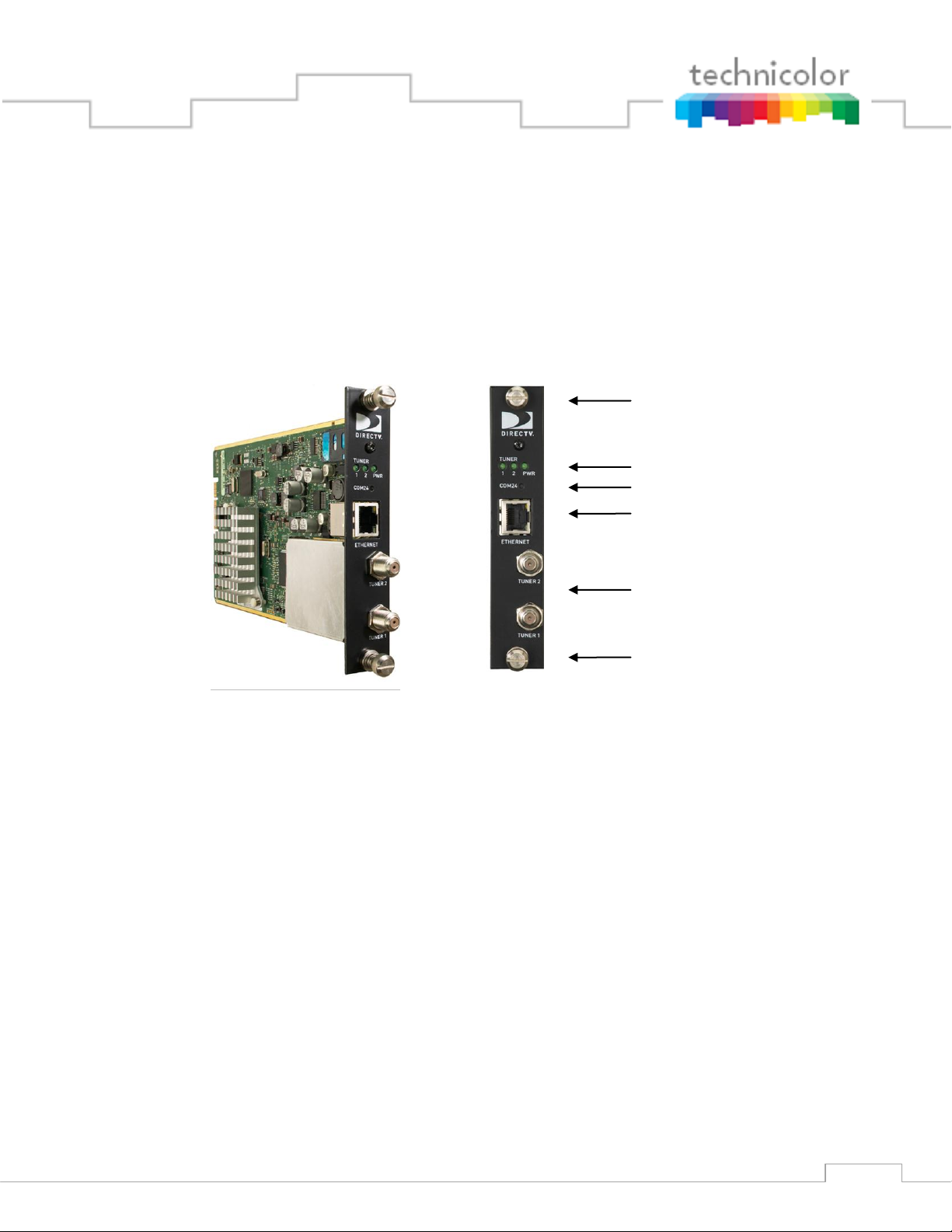
3.3 COM24 Card
Upper Thumbscrew
Indicator Lights
Reset Button
Ethernet Port
RF Inputs
Lower Thumbscrew
Figure 4 - COM24 Card
The COM24 card is a customized DIRECTV receiver with a built-in smart card and has been
specifically designed to meet the unique requirements of the Lodging and Hospitality market.
below shows a detailed picture of the COM24 card.
Each COM24 card contains two RF inputs, a 10/100Mbps Ethernet port, three indicator lights, a
recessed reset button, and thumbscrews on either end. The cards are hot-swappable, allowing
one card to be serviced independently of the other cards. In order to remove a card, simply
loosen the thumbscrews that secure the card in place and pull it straight out of its slot.
Each RF input on a COM24 card feeds a dedicated DIRECTV tuner capable of supporting one
channel of transcryption. When both RF inputs are connected, the card is capable of streaming
two Pro:Idiom encrypted HD channels simultaneously via the Ethernet port. The COM24 is
designed such that each tuner on a card only needs to be set once. Once configured, the cards
should remain locked unless there is a disruption in the signal due to weather, dish misalignment,
or other RF distribution issues. However, the cards will automatically recover when the
disruption to the RF is removed.
The COM24 card only works with DIRECTV input signals in the range of 950 - 2150 MHz
(when used in conjunction with the required B band converters). Software version ST02.05.11
Page 20

20
or newer supports SWM (Single-Wire Multiswitch) inputs. A RF distribution panel is required
to support the COM200 to enable delivery of Ka B band signals.
If using a SWM, the SWM must be connected to the Tuner1 F connector (lower) and must be
powered up at the time that the COM24 is booted since the COM24 only detects a SWM at
power on. If the first tuner is receiving HD channels from satellite 103 and a multi-switch is
being used, then satellite 119 must also be received for background guide monitoring. However,
if using a SWM and receiving HD channels from satellite 103, then satellite 119 reception is not
required since satellite 101 will be used for background guide monitoring instead whenever in
SWM mode.
See Section 8.1 for an explanation of indicator light diagnostic capabilities.
3.4 COM24FLX Card
The COM24FLX card is a variant of the standard COM24 card that only supports SWM
connections. It is configurable as a three channel standard definition or two channel high
definition satellite receiver. The COM24FLX as purchased is only capable of receiving SD
programming. To upgrade a FLX card to receive two HD channels, a license key must be
purchased from Technicolor.
Almost all of the information regarding identification and configuration of the COM24 cards
applies to the COM24FLX. The two exceptions are the number of configurable tuners and the
upgrade of a COM24FLX from SD to HD. The COM24FLX tuners are configured exactly the
same way as the COM24 tuners although if an HD channel is selected the card will return a
channel number of 0 in the Discovery page. See Section 6.8 for tuning instructions. See
Section7.3 for upgrade instructions.
Page 21
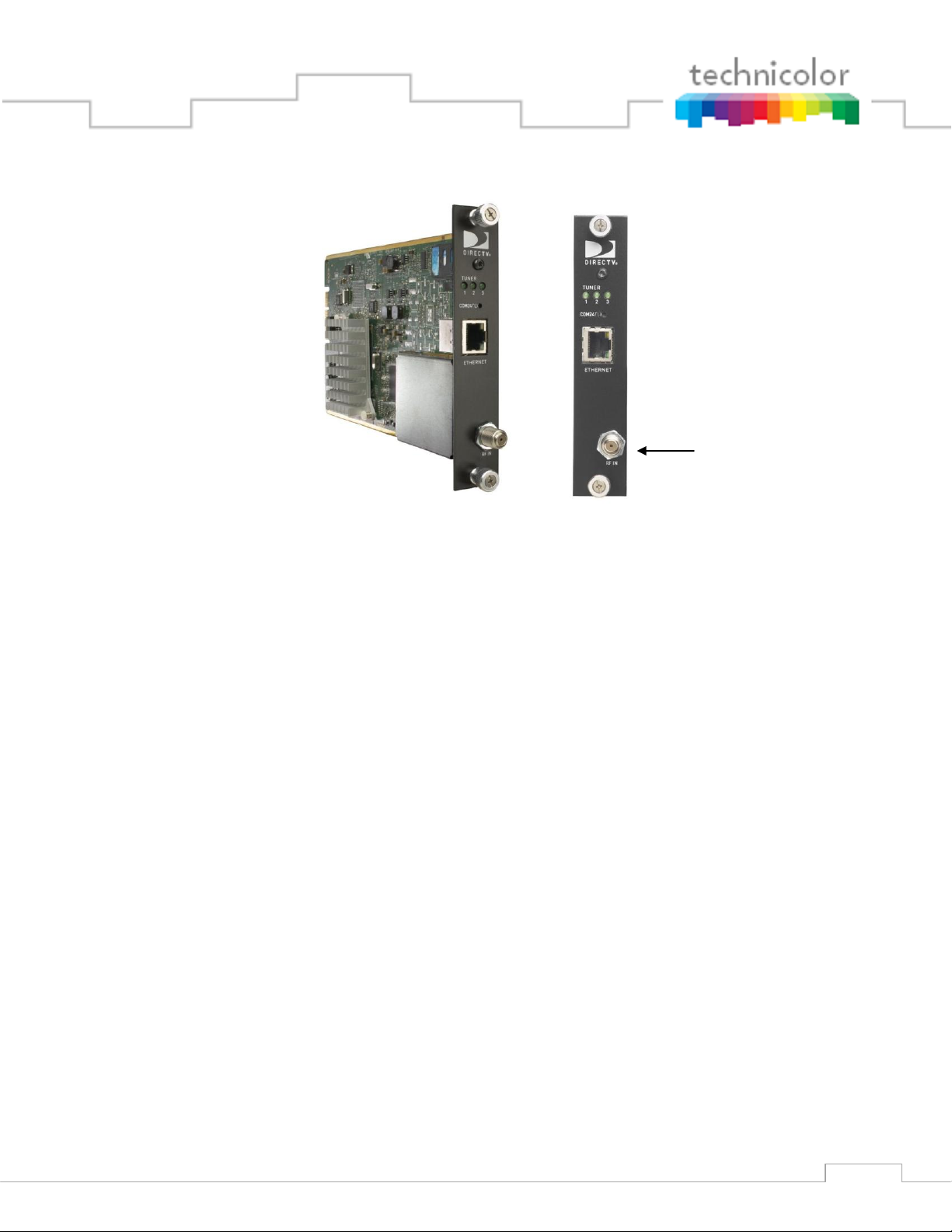
21
SWM Input
Figure 5 - COM24FLX Card
3.5 GbE Card
The COM200 chassis has an integrated Ethernet switch on the backplane. This switch provides
gigabit speed on two ports. One of those is the port on the back of the chassis the other is card
slot number one. The gigabit port that is available on the back of the chassis is the port that the
QAM24 card uses when it is installed. In order to daisy chain chassis or to inject large amounts
of data to the QAM24 in a Colony system you would need another gigabit port and that is where
the GbE card comes in. By replacing the card in slot one with the GbE card you now have
another gigabit speed Ethernet port that can be used to route data to the QAM24 card in that
chassis. This card is also required for use of the ATSC8 receiver in the system if the QAM24 or
QAM6 modulator is used.
3.6 XDR24 Card
The XDR24 card is currently being deprecated. For additional support contact your equipment
vendor or Technicolor.
3.7 QAM24 Board
The QAM24 card is an Edge QAM that is installed directly into the COM200 chassis. It connects
to the COM24 cards via a GigE connection on the back edge of the card. This optional card
replaces the Ethernet Card in the upper left side of a COM200 Chassis. The board provides 12
QAM modulators in addition to the front Ethernet port, which can be used to manage the
Page 22
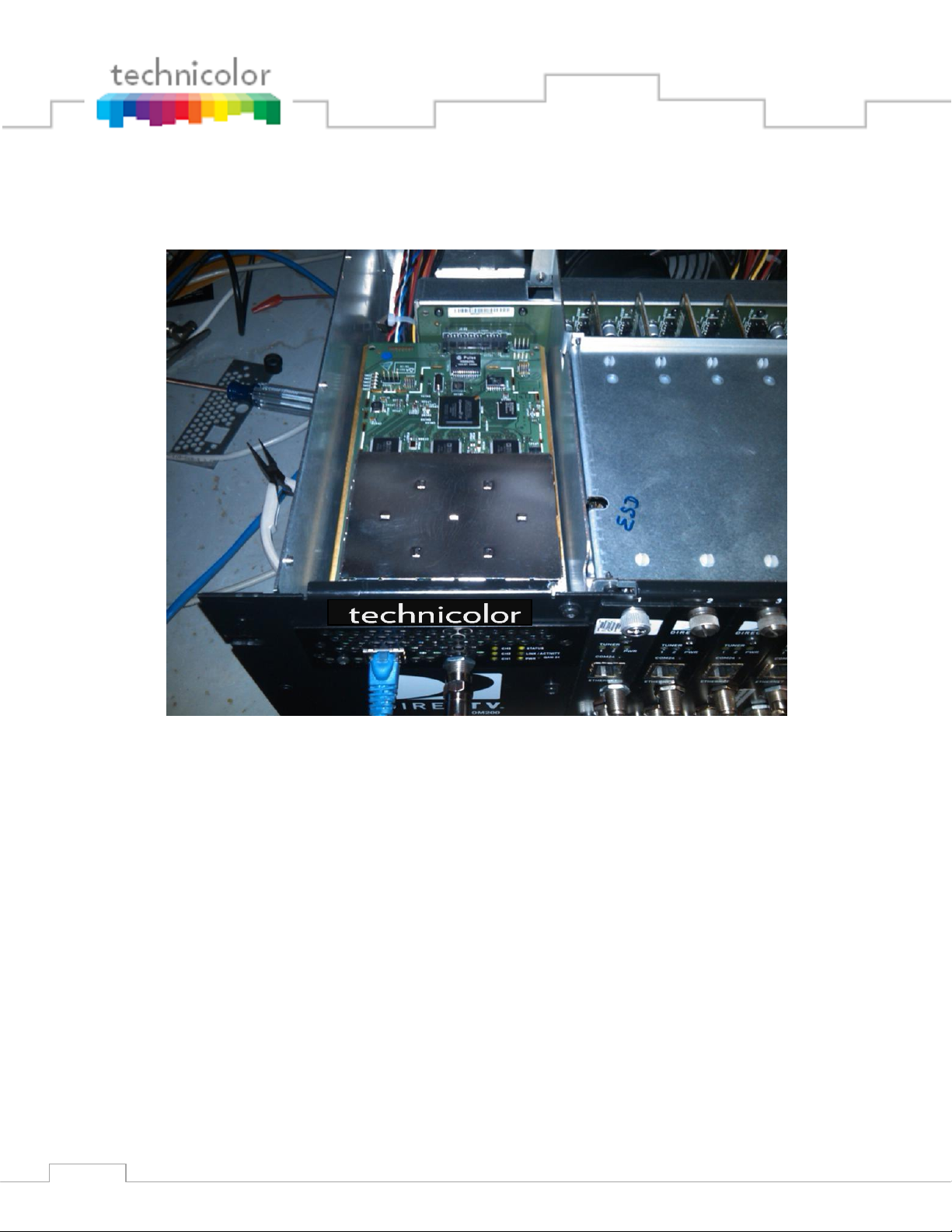
22
COM1000 system. Each QAM channel can carry 2 HD or 8 SD video channels. The QAM24
can be configured from any COM24 running version ST02.05.05 or higher.
Figure 6 – QAM24 Board installed in Chassis
The QAM24 board plugs into the Ethernet Card slot and therefore replaces that card. There are
no card guides in the chassis; the board is retained by front panel screws, which MUST be
installed.
Install the QAM24 Board as follows:
1. Remove power from the chassis. Remember to unplug BOTH power cables.
2. Remove the chassis top cover to gain access to the slot connector and rear panel GbE port
cable.
3. Unplug the rear panel Ethernet cable
4. Remove the switch access board.
5. Install the QAM24.
6. Tighten front panel retaining screws.
7. Plug power cables back into the chassis.
A front view of the QAM24 can be seen in Figure 7.
Page 23

23
Card Edge Connector
Ethernet Port
RF Output
LEDs
Figure 7 – QAM24 Front View
The QAM24 outputs three unique channel-grouping of four channels each according to the EIA
North American Cable Television Frequency Plan (see EIA-542B) from the front RF connector.
The four channels within each channel-grouping must be adjacent to one another and within the
same band.
The QAM24 card contains six (6) green LEDs on its front panel that indicate power, GbE Link/
Activity, and QAM status, as well as the link-status for each channel group.
The QAM24 card‟s bottom-right LED represents the board‟s power (PWR) state, lighting
up once all on-board power regulators report the “good” state, and going dark when power
is removed from the chassis or when a problem is detected on one of the regulators.
The QAM24 card‟s middle- right LED represents the link and activity of the GbE interface
on the back of the card.
The QAM24 card contains a recessed button on its front panel to be used as a dedicated
hardware reset for the FPGA processor. To complete an upgrade of the FPGA firmware a power
The QAM24 card‟s top- right LED represents the status of the QAM24 card. It is solidly-lit
when the card is performing a software update. It is flashing if an over-temperature
condition is detected on the card.
The QAM24 card‟s left LEDs represent the link-status for each of the 3 channel groupings.
Page 24

24
cycle is required.
The 10/100 Ethernet Interface on the front can be used to manage the COM1000 System.
4 GETTING STARTED
The COM1000 System is quite a bit different from the DIRECTV set-top box (STB) receiver
traditionally used in these installations. This is because the COM1000 does not natively decode
any audio or video, instead relying upon other devices in the system to decode and display the
MPEG streams it produces. Furthermore, the COM1000 does not have any native user interface.
Controlling and monitoring the COM1000 requires a Windows- based PC, and a web browser of
your choice.
4.1 Setting up Multiple Chassis
For installations that require more than one COM200 chassis each chassis will need to be
assigned a unique chassis ID. This can be done by removing the top cover of the COM200 and
setting the DIP switches located on the backplane as shown in Figure 8.
Page 25
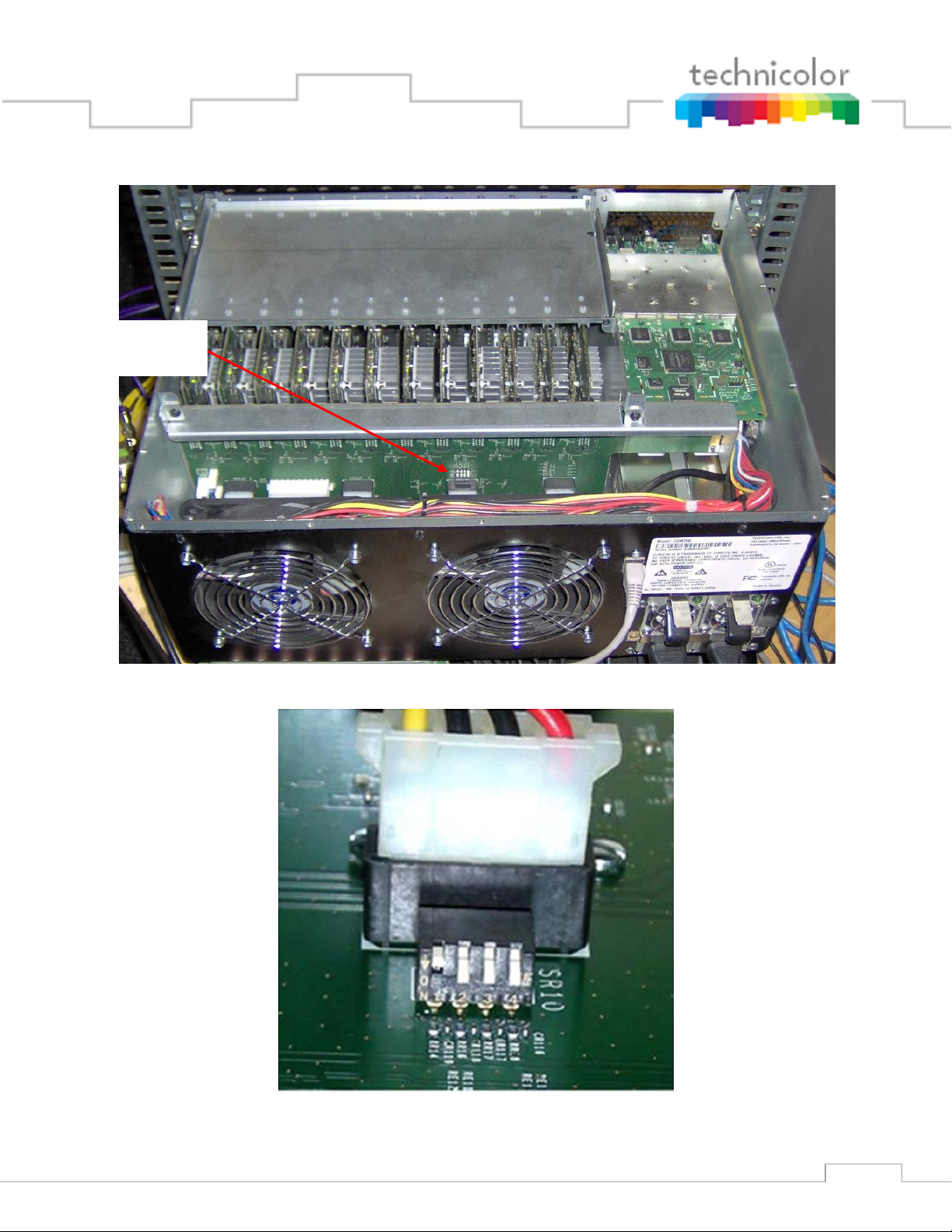
25
Figure 8 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration Switch Location
Chassis ID
Configuration
Figure 9 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration Switch Closeup
Page 26

26
The DIP switch pictured above will allow you to assign the chassis a unique ID between 1 and
12 by setting the switches as described in Table 2.
Note: The photo above and the table below are written as if you are standing with the front of
COM200 facing you and are looking down on the rear side of the backplane.
Page 27
27
Table 2 – COM200 Chassis ID Configuration
Chassis ID
Switch #1
Switch #2
Switch #3
Switch #4
1
UP
DOWN
DOWN
DOWN
2
DOWN
UP
DOWN
DOWN
3
UP
UP
DOWN
DOWN
4
DOWN
DOWN
UP
DOWN
5
UP
DOWN
UP
DOWN
6
DOWN
UP
UP
DOWN
7
UP
UP
UP
DOWN
8
DOWN
DOWN
DOWN
UP
9
UP
DOWN
DOWN
UP
10
DOWN
UP
DOWN
UP
11
UP
UP
DOWN
UP
12
DOWN
DOWN
UP
UP
4.2 Installation Requirement Guidelines
Here are a few guidelines to keep in mind when installing the COM1000 system that will
minimize the potential problems that the system could be expected to encounter.
4.2.1 General System Guidelines
The optimum RF levels at the input of a COM120 or SWM are -30 to -50 dBm per
transponder.
Page 28

28
The optimum RF input levels for the COM24 cards are -25 to -55 dBm per transponder.
COM24FLX cards can only be connected to a SWM module, they will not support a
multiswitch.
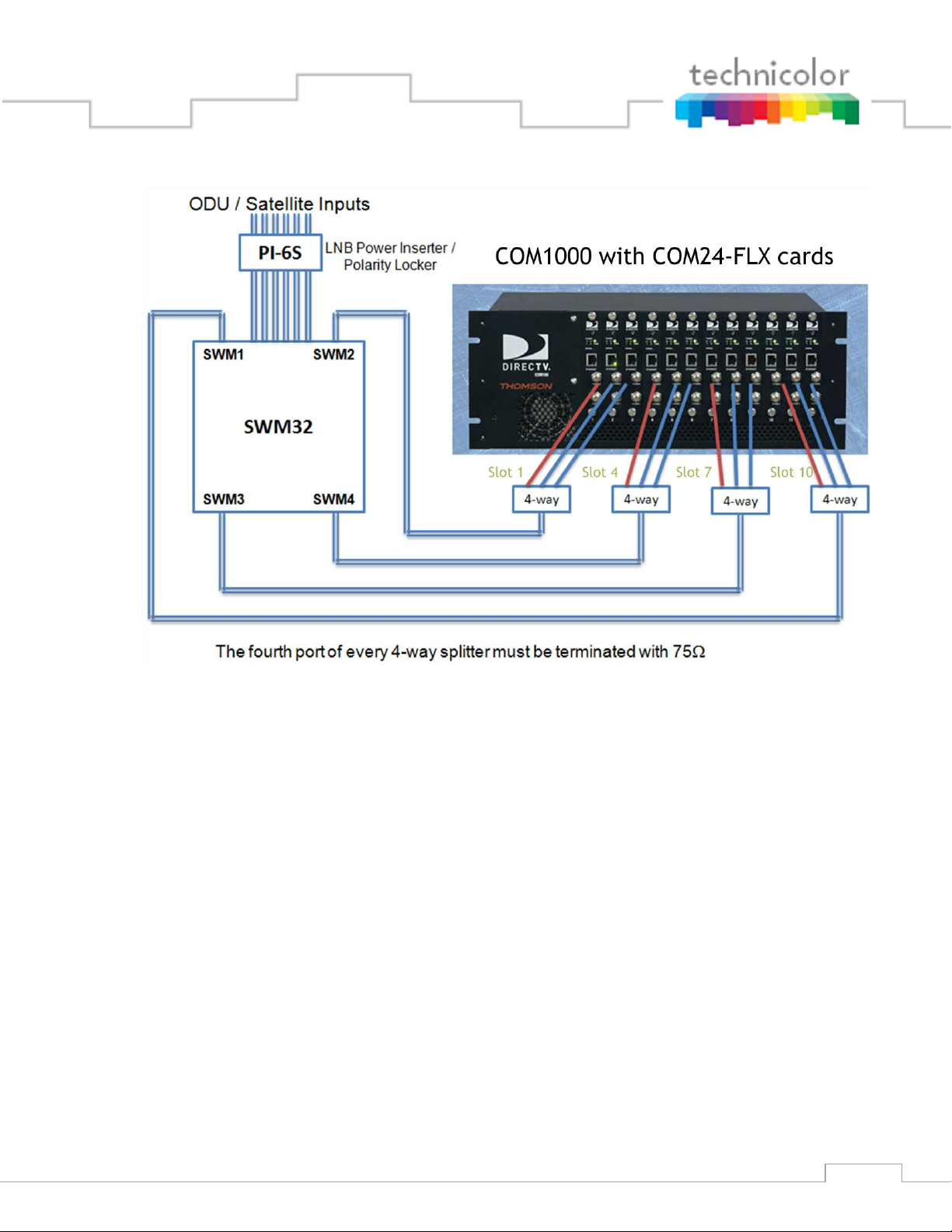
The RF connections from the COM24FLX to the SWM module MUST be as shown in
Figure 10 or some channels will not be received properly. Cards in slots 1, 4, 7, and 10
MUST be on separate SWM outputs.
Normal operational behavior of the COM200 chassis is achieved in ambient
environments of 95°F (35°C) or less.
The system will not be capable of streaming any video on any channel besides 100 until
the COM24 cards have been authorized by DIRECTV.
4.2.2 System Integrator Guidelines
The system integrator must provide a mapping of TV channels to COM24 slots and
tuners.
The COM1000 will generally be preconfigured, including the appropriate RF and IP
connections to an edge QAM device, which most likely is the QAM24.
A COM120 RF Distribution panel, consisting of DIRECTV-approved multiswitches and
Ka B band converters, or a DirecTV SWM-32 unit, shall be supplied by the System
Integrator.
4.2.3 System Operator Guidelines
It is recommended to use the StarRoute SRSN4 Normalizer within the property‟s RF
plant before the COM120 RF distribution panel in order to normalize the B band Ka
signals with the traditional Ku satellite signal levels. B band signals are generally higherpowered and tend to saturate the converters unless the installer is very careful regarding
input signal levels going into the COM120 panel.
The operator must take care not to block the front and rear air passageways of the
COM200 chassis. Racks containing doors and/or rear panels are not recommended.
Page 29
29
Figure 10 - COM24FLX to SWM Module connections
Page 30

30
5 CONFIGURING THE SYSTEM
This section will guide the integrator through the process of configuring a COM1000 to meet the
needs of the system operator.
5.1 Useful tools
You should be aware that the firewall on your PC might prevent some of the following tools
from working correctly. This is particularly true when attempting to execute file transfers to a
COM24 card via a TFTP server.
5.1.1 Configuration tool
Each COM24 card contains an embedded web-based user interface that can be used to configure
all key parameters for all the components of the system, as well as providing access to crucial
operating conditions like RF levels and authorization status. These controls can be accessed
using your choice of web browser. Details on accessing the user interface are included in
Section 5.1.6 below.
5.1.2 DHCP Server
Because the COM24 cards have the ability to remember their settings, once the system has been
properly configured, the cards will retain whichever IP addresses were used last and will not
need to obtain new ones from a DHCP server.
Even if the cards are assigned new IP addresses, they will continue to operate normally, but
communicating with them after this happens can become somewhat problematic, especially if
you are used to interfacing with a card at a specific IP address. Refer to Section 5.1.6 below for
recommendations on how to avoid this particular difficulty.
If you find that you need a DHCP server in your system, a useful multi-function tool that also
provides access to a TFTP server and a syslogger is Tftpd32, which can be found at the
following URL: http://tftpd32.jounin.net/.
See Appendix A for more information on IP settings.
Page 31

31
5.1.3 Video Playback
During the configuration and installation process, it may be necessary to verify the COM24
video streams in the absence of a Pro:Idiom enabled television.
The COM24 card can facilitate this type of debug activity by allowing the user to bypass the
Pro:Idiom encryption process temporarily. It should be noted that this feature is only available
when tuning to DIRECTV channel 100. Please refer to Section 6.8.1 (“Security_Mode” setting)
for additional information on this feature.
If you wish to take advantage of this feature, you will need a video player on the PC that is
capable of decoding MPEG video transferred via IP Packets. VLC Media Player, which is a free
download, can decode MPEG video and can be found at the following URL:
http://www.videolan.org/vlc/.
5.1.4 System Logging
The COM24 cards have the ability to send logging data to a remote destination. This is
especially useful in situations where a management PC will remain with the COM1000 systems
at all times, but it can also prove helpful when setting up and troubleshooting a system.
One simple solution is the syslog feature of the previously referenced Tftpd32, but it is limited in
terms of features. A more feature-rich option might be considered for a more robust debugging
capability. One alternative solution is an offering from Kiwi Enterprises (available at
http://www.kiwisyslog.com/), but this option carries a licensing fee for a full version of the
software, so it may not be a viable option for the casual user.
Furthermore, for software releases ST02.00.03 and above, each COM24 card provides a limited
syslog capability. The cards are only capable of displaying 500 lines worth of log-data, so this
may not be an appropriate tool for long-term system troubleshooting. However, the syslog
feature can be quite useful if the system operator is able to access it within that window of time
after a card begins to exhibit some unexpected behavior.
5.1.5 TFTP/FTP Server
The COM24 cards have the ability to transfer data to and from an external source via either an
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server. The data
transferred will typically take the form of software upgrades, but it is also possible to configure
the system to log system status messages remotely for troubleshooting.
Page 32

32
As mentioned previously, the multi-function tool Tftpd32 is very effective at handling the file
transfer needs for a log file or a software update to the COM24 card.
Because the COM1000 is field-upgradable, it is important that everyone working with the system
in the field understands how to perform this function, so a brief overview of how to set up the
TFTP server will be provided in Section 5.3.
5.1.6 IP Address Discovery
One potential complication inherent to interacting with the COM24 cards is that you must know
the IP address of any card that you wish to interact with. In the case that you do know the IP
address of the card you are trying to access, simply type the IP into your web browser‟s address
bar. An alternative to typing a card‟s IP address directly into your web browser is to use an
application designed by Technicolor specifically to combat this issue, called COM24.exe. Some
PCs require that only one Ethernet cable be connected in order to reliably discover the cards.
Technicolor will make this application available to anyone who wants it. An example can be
seen in Figure 11 below.
Figure 11 – Results from the COM24 Discovery Tool
Page 33

33
5.2 Connecting to the COM1000
5.2.1 Preparing Your Computer’s Network Connections
As mentioned previously, interaction with the COM24 cards can only be achieved by providing a
computer interface via one of the cards‟ Ethernet ports. However, this can only be achieved if
the computer to be used for this purpose has been configured correctly. The directions below are
intended to help you through this task step-by-step.
In order to locate the screen shown in Figure 12 below, you will first need to open the Control
Panel, typically located on the right-hand side of the Start Menu. Double-click on the icon
labeled Network Connections.
Figure 12 – Network Connections Window
From there you will need to identify the network interface that will communicate with the
COM24 cards. In this example, our system is utilizing the connection that is linked to the PC via
an USB/Ethernet adapter. You will need to right-click the connection, and then select
Properties.
At this point, you should have a window titled something similar to “Local Area Connection
Properties”. From here, you will need to scroll through the list of available items and select the
last one, “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” and click the Properties button (see Figure 13).
Page 34

34
Figure 13 – Internet Protocol Configuration
In the window that you have just opened, you will see that there are two options available for
defining an IP address for your PC. If your system has a DHCP server, you may select the first
option, “Obtain an IP address automatically.” The benefit of this option is that it greatly
minimizes the chances that you will have duplicate IP addresses in your network. One potential
downfall of this choice, however, is that there is a chance that everything in your system could
be assigned new IP addresses at the next reboot. Unless you are using something like the
COM24.exe tool to resolve those addresses for you automatically, controlling the cards may
prove difficult once this happens. Refer to Section 5.1.6 above on how to resolve this issue.
If you wish to manually configure your network and ensure that you will never have to worry
about IP addresses changing on you, however, then select the second option, “Use the following
IP address,” taking care to assign a unique IP address to your PC. Also configure the subnet
mask to 255.255.0.0.You may not know the cards‟ IP addresses at this point, but it is very likely
that they will be using the factory default range of 192.168.3.18 to 192.168.3.29, so any IP with
the same prefix should work. If, for example, you select an address of 192.168.3.249 for your
PC, you should generally be able to find the cards with a minimum of difficulty.
In addition, in order to successfully perform file transfers to your system (as required for
software upgrades), it is recommended that you give your computer an IP address that is in the
same subnet as your COM24 cards when using the manual configuration method. Configure
subnet route to 255.255.0.0.
Page 35

35
5.2.2 Avoiding IP Address conflicts
When building a system that is comprised of a mixture of cards from different sources, there is a
possibility that some of the cards will have duplicate IP addresses, thereby making
communication with these cards unreliable.
There are two recommendations for addressing this problem. The first is to use a DHCP server
to ensure that each card gets a unique address. The second is to use the web interface on the
COM24 cards to change the IP address of one of the duplicate cards (refer to Section 6.8.1 for
more information).
It should also be noted that, depending upon your computer‟s network configuration, attempting
to access a property‟s wireless network at the same time you are accessing the COM24 cards
could also give the undesirable result of not being able to navigate to your COM24 cards with
the web browser. If you are suddenly unable to even see your COM24 cards in a system that was
not previously exhibiting any IP address conflicts, you may wish to disable the wireless interface
temporarily and see if that helps.
5.3 Using a TFTP Server
While you do have the option of using your choice of either FTP or TFTP to transfer data
between the management PC and the COM1000 system, it is recommended that you use a TFTP
program.
The reason is that TFTP is greatly simplified over FTP, the biggest difference being that it does
not require user/password authentication, which are not necessary to access the COM1000
system in the first place.
Note: This section will be describing procedures specific to the previously mentioned Tftpd32.
5.3.1 Determining Your IP Address
In order to configure your TFTP server properly, you first need to know the IP address that your
computer is using to communicate with the COM24 cards.
The following steps describe a fairly simple process that will be useful in determining where to
send file transfers containing software upgrades (see Section 7) and also where to direct
streaming video to test your system (see Section 6.8.1).
As seen in Figure 14, you will first need to access the Start Menu and select the “Run…” option.
Type “cmd” in the small window that comes up and press the OK button.
Page 36

36
Figure 14 – Accessing the Command Prompt window
In the program window that appears, you will be prompted to enter a command. Type in
“ipconfig” and press Enter (see Figure 15 below).
Figure 15 – Running ipconfig
Page 37

37
In the example above, the computer is communicating with the COM1000 system over the
“Local Area Connection” via an Ethernet adapter. In this case, the management PC has been
assigned the IP address 192.168.1.137. This is the IP you will be using with the TFTP server
and possibly later on with a program like VLC Multimedia Player (covered in Sections 5.1.3
and 10.1.2) when testing the system configuration.
5.3.2 Configuring Your TFTP Server
This section offers examples specific to the previously mentioned application Tftpd32. The
primary function of this tool for most COM1000 systems will be to serve as a TFTP server to
facilitate software upgrades.
The DHCP server may also be used if a particular installation needs that functionality, but you
should be aware of the effect that it will have on the system, as there is a possibility that it could
pass out new IP addresses to the COM24 cards every time one of them reboots.
The syslog server may also be used, if desired, although the version offered here is not as
feature-rich as the Kiwi syslog daemon discussed in the previous section.
Tftpd32 has proven useful for performing file transfers to the COM24 cards, but some important
limitations must be kept in mind when using it:
A successful file transfer could be prevented by any third-party firewalls or anti-virus
tools running on your computer, so you should disable them temporarily.
You must be sure that your computer and the COM24 are on the same subnet (e.g.
192.168.3.xxx with subnet mask 255.255.0.0)
Be sure to configure your TFTP server so that it points to the correct directory where the
file is saved.
The size of the file should be 10 MB or less.
The COM24‟s file-transfer mechanism has a limit of 200 total characters, so it is
suggested that you save the file to a location with a short path (e.g. C:\tftp\transfers)
instead of embedding it deep within the system.
Also, be sure that the directory and file names contain no spaces, as these will not be
recognized by the COM24‟s file-transfer mechanism (Use C:\tftp\software_upgrades
rather than C:\tftp\Software Upgrades, for example)
Be sure that the “Server Interface” field shows the IP address of your PC.
When you initially launch Tftpd32, you will see a screen similar to the one shown in Figure 16.
Page 38

38
From here, you may fine-tune the settings by clicking the “Settings” button at the bottom of the
screen.
Figure 16 – Tftpd32 Startup Screen
The window that comes up should look like the one below in Figure 17. At times, things like
firewall setting and improper IP address configurations can interfere with the file transfers
between your computer and the COM24 cards.
Page 39
39
Figure 17 – Tftpd32 Settings Window (Global Settings)
Page 40

40
Figure 18 – Tftpd32 Settings Window (TFTP Settings)
Page 41

41
Figure 19– Tftpd32 Settings Window (Syslog Settings)
If you do not see a progress-bar (shown in Figure 20) within 30 seconds after hitting the Submit
Query button on the upgrade page (see Section 7 on upgrading your system), then the file
transfer will not happen. In that case, it is advised that you review your setup.
Page 42

42
Figure 20 – Tftpd32 File Transfer Progress Screen
On rare occasions, the progress bar shown above in Figure 20 will appear, but you will find that
the requested file has not successfully transferred to the COM24 card. In order to get a better
understanding of what happened, you should be sure to review the “Log Viewer” tab of the
Tftpd32 interface. If the file transferred successfully, you should see a statement similar to the
last line shown in Figure 21 for each file you attempted to upload.
Figure 21 – Tftpd32 Completed Transfer Screen
Page 43

43
6 USING THE COM1000 WEB INTERFACE
Each COM24 card contains a basic web-based application that provides an easy means to control
and configure the COM1000 system. This tool can be accessed by entering the IP address of one
of the COM24 cards in the system into any web browser‟s address bar or by using the card
discovery tool discussed in Section 5.1.6.
Figure 22 - COM1000 Web Based User Interface Introduction Page
The COM24 card issues a discovery call for all other COM24 cards in the system, and then
populates a table with some basic information on current tuning parameters and RF signal levels.
Once this information is complete, for version ST02.05.05 and later, the Discover Web Page
illustrated in Figure 22 is automatically displayed. For SW versions earlier than ST02.05.05, the
Discover Web Page is reached by clicking the company logo on the Home Page.
6.1 Discovery of COM24 and COM24FLX Cards
Figure 25 is the result obtained after the COM24 web interface‟s home page times out or by
Page 44

44
clicking the Discover link at the top of any other page1.
Figure 23 - COM24 Discover Page
Figure 25 shows a basic data summary that is also similar to the pages you will get by clicking
on the Scan, Refresh, or Display hyperlinks at the top of any COM1000 web interface page. The
differences will be discussed in later sections. Figure 24 shows the Discover page for systems
containing COM24FLX cards. Note that the slots containing COM24FLX cards (in SD mode)
will contain entries for three tuners instead of two.
1
Prior to ST02.05.05, the company logo needed to be clicked to transition from to .
Page 45
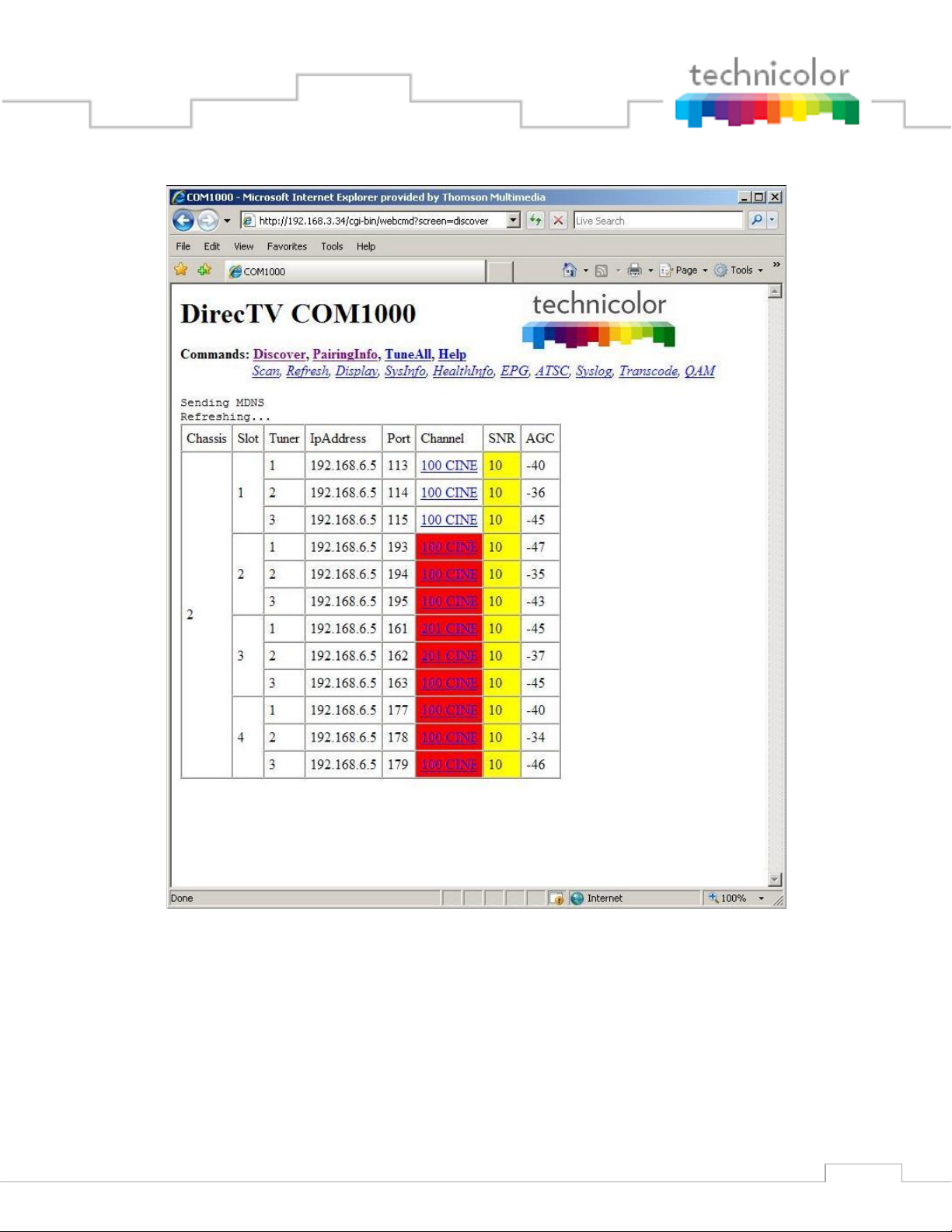
45
Figure 24 - Discover Page w. COM24FLX
Page 46

46
There are several changes from the old discovery page to this new one:
• Color coded problem areas have been added
• Network name and channel are now both displayed
• “Clickable” channel name results in tune
• Card IP address no longer shown
• RF output channel and subchannel if directed to internal QAM24 port are shown
• Destination IP address and IP port if directed to an external device is shown
• Program bit rate if directed to an internal QAM24 port (static snapshot)
• Clickable Slot_ID link shows CAM log if there are authorization problems
Issues for some of the tuners are shown color coded in Figure 25 below.
Figure 25 – COM1000 Discover Page (showing colors)
Page 47

47
The following is a detailed list of the information found on these pages.
6.1.1 Fields prior to ST02.05.05 no longer present
Edit – Clicking the Tune hyperlink is the method by which you access the “Channel Tune”
interface of the COM24 cards (covered in Section 6.8.1). Each tuner in the system is
independently controllable (two per card). (Field removed in ST02.05.05.)
CardIP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card that resides in the chassis and slot
combination to its left. (Field removed in ST02.05.05.)
6.1.2 Fields present after ST02.05.05
Chassis – This field reports a unique identifier for the chassis. In systems that contain multiple
chassis, this can be used to identify each card in the system. See Section 4.1 on how to assign
unique identifiers to multiple chassis within a system.
Slot – This field identifies the card‟s location within a chassis, numbered 1 through 12. If this
field is grey, the slot number is a link to messages in the CAM Log.
Tuner – There are two entries per CardIP for this column. This represents the two tuners
available on each COM24 card. Version ST02.05.05 changed the tuner numbers to start at one
instead of zero to match the card‟s faceplate.
QAM or IPAddress – Prior to SW version ST02.05.05, this column header was “IPAddress.” In
SW version ST02.05.05 and later, if some of the programs are streaming to a QAM24, then
“QAM” is displayed as the column header. If all signals are routed out of the system, then
“IPAddress” will display as the column header instead. In SW version ST02.05.05 or later, if the
card is sending video to a QAM24, this field shows the output QAM frequency and QAM subchannel number. If a card is streaming video to outside of the chassis, this field will contain the
destination IP address. Typically, this will be the IP address of an external edge QAM. Both
unicast and multicast addresses are supported. However, older COM200 Chassis (pseudo codes
BC004 and NC004) require that multicast streams be sent out the front port and an external
Ethernet switch be used. Newer COM200 chassis route multicast traffic only to the two gigabit
Ethernet ports (the QAM24 slot and slot 1).
Bitrate or Port – Prior to SW version ST02.05.05, this column header was “Port.” . In SW
version ST02.05.05 and later, if some of the programs are streaming to a QAM24, then “Bitrate”
is displayed as the column header. If all signals are routed out of the system, then “Port” will
display as the column header instead. In SW version ST02.05.05 or later, if the card is sending
video to a QAM24, this field shows the instantaneous bitrate of the channels being sent out of the
QAM24. Otherwise this field contains the destination port associated with the destination IP
address described above. You must have a unique port number for each individual channel you
Page 48

48
wish to stream.
Channel – This field shows the Channel Name and the DIRECTV channel number you tune to
on a typical DIRECTV tuner. This field is also a link that permits the user to change channels.
If the smart card has not been authorized or paired then the channel will be highlighted in red.
SNR – This field returns the Signal-to-Noise Ratio associated with the selected tuners. In
ST02.05.05, if the SNR is low, it will be highlighted in yellow and if the SNR is very low, it will
be highlighted in red.
Note: For optimum performance of the COM200, this value should be 11 or higher.
AGC2 – This value provides a value corresponding to the internal Automatic Gain Control
setting in the COM24. In ST02.05.05 and later, if the AGC is low, it will be highlighted in
yellow and if the AGC is very low, it will be highlighted in red.
Note: For optimum performance of the COM200, this value should
be somewhere between -25 and -55.
2
Although named AGC, this value is essentially the power level at the input of the COM24 card.
Page 49

49
6.2 Scanning for COM24 Cards
Using the Scan link is not recommended. Figure 26 below is the result obtained by clicking the
Scan link at the top of any COM1000 web interface page. You may suppress the status messages
at the top by the clicking the Display link.
It should be noted that the more chassis a property has, the longer the Scan command will take.
There are cases where the scan can take an hour or more. As a result, the Discover command is a
better choice in nearly all cases, unless you have found that it does not work for you.
The Scan operation is limited in its capabilities. The COM24 card will scan through four full
subnets including and following the current one, looking for other COM24 cards. For example,
if the card‟s IP is 192.168.3.100, it will scan for cards in the range of 192.168.3.1 through
192.168.6.254. If your network topology is such that the IP Addresses of your COM24 cards lie
outside of this range, the Scan command will not return any data.
Page 50

50
Figure 26 – COM1000 Scan Page
The Scan function displays a limited amount of information in the same format as was covered in
Section 6.1. It primarily displays all IPs found within an area in numerical order. The
information can be resolved into a more useable format (i.e. COM24 card information only) by
clicking the Refresh link.
Page 51

51
6.3 Refreshing the COM1000 Display
Figure 27 below is the result obtained by clicking the Refresh link at the top of any COM1000
web interface page. Please note that this table is filled in with data obtained during execution of
either the Discover or Scan commands, so if it appears to be empty, simply perform one of these
operations first and then come back to this screen.
Page 52

52
Figure 27 – COM1000 Refresh Page
6.4 Displaying COM1000 Status
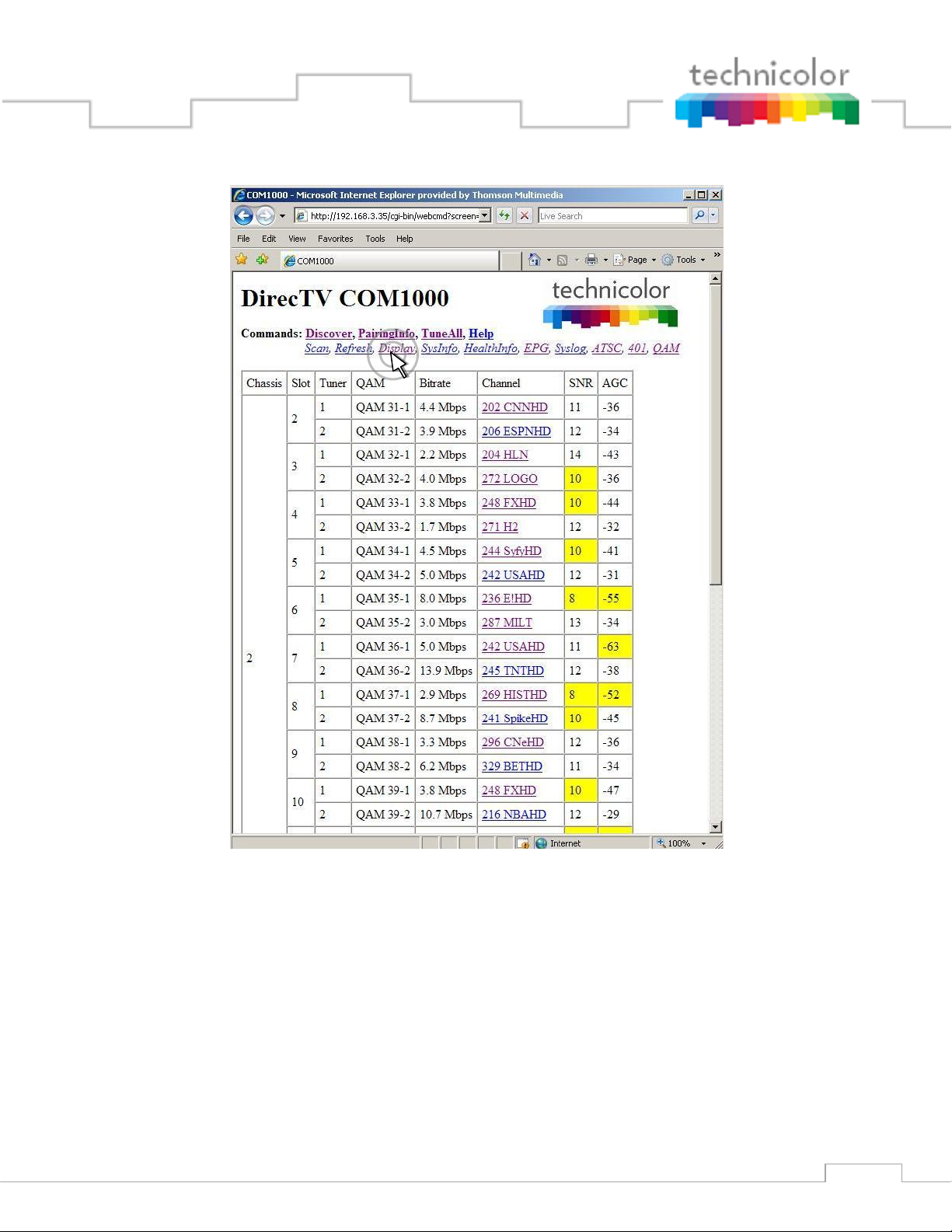
By clicking the Display hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page, you can see
the information last obtained from a Discover or Refresh with the signal status of all cards in the
system as shown in Figure 28 below.
Page 53
53
Figure 28 – COM1000 Display Page
When used in conjunction with the Scan and Refresh commands, it simply filters the table so that
all discovered COM24 cards are shown at the top of the table and removes any system status
messages that may appear when running the previously covered functions.
Page 54

54
6.5 Evaluating COM24 Authorization Status
By clicking the PairingInfo hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page, you can
quickly evaluate the authorization status of all cards in the system as shown in Figure 29 below.
For details on how to obtain more in-depth information on this topic, please refer to Section 7.
This page also provides direct access to a card‟s internal syslog and CAM log and the ability to
upgrade multiple cards. These can be reached by clicking the hyperlinks that represent the card‟s
IP address and CAM_ID, as can be seen below.
Figure 29 – COM1000 Pairing Info Page
Page 55

55
Following is a detailed list of information available on the PairingInfo page.
Chassis – This field reports a unique identifier for the chassis. In systems that contain multiple
chassis, this can be used to identify each card in the system. See Section 4.1 on how to assign
unique identifiers to multiple chassis within a system.
Slot – This field identifies the card‟s location within a chassis, numbered 1 through 12.
CardIP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card that resides in the chassis and slot
combination to its left. This field is also a link to see the Syslog for that card.
RID –This field reports the DIRECTV Receiver ID, or RID. This value is the first of two
parameters required to obtain authorization on the DIRECTV network.
CAM_ID – This field reports the DIRECTV CAM ID. This value is the second parameter
required to obtain authorization on the DIRECTV network. For any card running a software
version above ST02.00.09, you can click on the hyperlink in this column to be taken directly to
that card‟s CAM Log (see Section 6.8.7 for more information on reading a card‟s CAM log).
Authorized – This field reports whether the COM24 card‟s CAM has been authorized. A value
of „1‟ indicates that the card has been authorized, thereby enabling the card to receive DIRECTV
programming. A value of „0‟ indicates that the card has not been authorized.
Paired – This field reports the pairing status of the CAM card. In order to be capable of
receiving an authorization to the DIRECTV network, the RID and CAM data must first be
paired. If this has not happened, then the card cannot be authorized until the pairing is resolved.
A value of „1‟ indicates that the RID and CAM are successfully paired; a value of „0‟ indicates
that they are not.
Note: Refer to Section 10.4 for more information if you notice a
card that has a value of „1‟ under both the “Authorized” and
“Paired” columns but is not streaming video properly.
SW_Version – This field reports the software version that currently resides on the COM24 card.
All cards that have a similar web interface to the one described in this document will have a
version number of at least ST01.00.25. The examples given have been taken from cards that are
running the ST02.05.11 software release.
Up_Time – This field gives an indication of how much time has elapsed since the card was last
rebooted or powered up.
Upgrade – By checking this box for a particular card, you will make each of the fields at the
bottom of the screen active for that card. This allows you to upgrade multiple cards at a time.
Page 56

56
Software Upgrade –The fields in this section are covered on the next page.
Figure 30 below shows in detail the upgrade section available on the PairingInfo page.
Figure 30 – COM24 Multi-card Upgrade Feature
Following is a brief description of the relevant fields on this page.
Upgrade – By checking this box for a particular card, you will make each of the fields under
“Software Upgrade” heading active for that card. This method is more efficient in that it allows
you to update multiple cards to the latest software in one easy step.
Usage – This field allows you to select which type of file transfer you wish to undertake for a
particular card. The available options are shown below. It should be noted that when selecting
any option other than „2‟, the card will appear to go through the usual software update cycle, but
that it will revert to the current build of code once it has rebooted.
0 = Set_Log_IP – This option allows you to identify the IP address to which you wish to
send COM24 logging for monitoring by a syslog utility.
1 = NA – This option is not available to new users and only exists in order to support
backward-compatibility with older builds of code.
2 = SW_Upgrade – This is the only user-accessible means of updating the software in a
COM24 card.
3 = Log – This option allows you to copy a COM24 card‟s internal log files to a PC.
Page 57

57
Note: Options 4 through 7 are not available to users and are for development purposes only.
Figure 31 – COM24 Multi-card Upgrade Results Page
See Section 7 for more information on upgrading your system.
Page 58

58
6.6 Evaluating COM1000 System Status
By clicking the SysInfo hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page, you will
access the page shown below in Figure 32. This table gives you the ability to select from one of
a number of different unique identifiers for every COM24 card if your system needs such
capability.
Figure 32 – COM1000 SysInfo Page
Page 59

59
Following is a detailed list of the information available on the SysInfo (System Info) page.
Chassis – This field reports a unique identifier for the chassis. In systems that contain multiple
chassis, this can be used to identify each card in the system. See Section 4.1 on how to assign
unique identifiers to multiple chassis within a system.
Slot – This field identifies the card‟s location within a chassis, numbered 1 through 12.
CardIP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card that resides in the chassis and slot
combination to its left.
System_Integrator_ID – This is a user-defined field that can be used in conjunction with the
Property_ID below to create a unique identity for every chassis you distribute. Unfortunately,
the ability to load this data is not supported by the web interface at this time. Entering this
information requires a more advanced tool that will give access to the complete set of
instructions contained within the COM24 cards.
Property_ID – This is a user-defined field that can be used in conjunction with the
System_Integrator_ID above to create a unique identity for every chassis you distribute.
Unfortunately, the ability to load this data is not supported by the web interface at this time.
Entering this information requires a more advanced tool that will give access to the complete set
of instructions contained within the COM24 cards. The string „:EPG‟ indicates that the card is
generating the EPG guide channel.
MAC_Address – This value is loaded during the manufacturing process and is unique to every
COM24 card. Every IP-enabled device contains a similar address, which is used to ensure that
all Ethernet traffic is routed to the correct destinations.
Serial_Number – This value is loaded during the manufacturing process and is unique to every
COM24 card. This number is assigned by DIRECTV, and is used to track the COM24 receivers
in their database.
Note: In keeping up-to-date with software upgrades, you may be able to resolve the issues
discussed above in future versions of the user interface.
Page 60

60
6.7 Evaluating COM1000 Health Status
By clicking the HealthInfo hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page, you will
access the page shown in Figure 33 below. The data available here gives you an impression of
the overall health of the COM1000 system, and can be used to identify potential problem areas at
a glance.
Figure 33 – COM1000 HealthInfo Page
Page 61

61
Following is a detailed list of the information available on the HealthInfo page.
Chassis – This field reports a unique identifier for the chassis. In systems that contain multiple
chassis, this can be used to identify each card in the system. See Section 4.1 on how to assign
unique identifiers to multiple chassis within a system.
Slot – This field identifies the card‟s location within a chassis, numbered 1 through 12.
CardIP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card that resides in the chassis and slot
combination to its left.
Card_Temperature – This field reports the temperature of the COM24 card, as measured on its
surface. This essentially gives the ambient temperature inside the COM200 chassis.
IC_Temperature – This field reports the internal temperature of the main processor chip on the
COM24 card. An elevated temperature here and nowhere else could mean that this chip is
defective.
PS0 Health – This field reports the health for Power Supply 0. If the power supply is connected
and operating properly, the value should return “OK”. If there is a problem with either of these
things, the value will return “Fault”.
Note: Newer chassis will only have a single power supply instead of a dual power supply. These
power supplies do not provide health indicators so the PS0 and PS1 Health indicators will report
Fault, which should be ignored.
*See device labeled “AC Input 1” in Figure 3 in Section 3.2.
PS1 Health – This field reports the health for Power Supply 1. If the power supply is connected
and operating properly, the value should return “OK”. If there is a problem with either of these
things, the value will return “Fault”.
*See device labeled “AC Input 2” in Figure 3 in Section 3.2.
Fan0 Health – This field reports the health for Fan 0. If the fan is connected and operating
properly, the value should return “OK”. If there is a problem with either of these things, the
value will return “Fault”.
*See device labeled “Exhaust Fan 1” in Figure 3 in Section 3.2.
Fan1 Health – This field reports the health for Fan 1. If the fan is connected and operating
properly, the value should return “OK”. If there is a problem with either of these things, the
value will return “Fault”.
Page 62

62
*See device labeled “Exhaust Fan 2” in Figure 3 in Section 3.2.
Page 63

63
6.8 The Tune Command
The Basic Tune screen shown in Figure 34 can be accessed by clicking the ChannelNumber link
in the Channel column of the Discovery page (see Figure 25 ). There was no equivalent to this
screen in SW versions earlier than ST02.05.05. You can also access the Basic Tune screen of
any given COM24 card and tuner combination by clicking the channel name/number hyperlink
in the Channel column on the Refresh or Display pages.
Figure 34 – COM24 Basic Tune Screen
This form permits two different ways of tuning DIRECTV channels with Pro:Idiom encryption.
The first way specifies the destination IP address and port along with the DIRECTV channel
number.
Page 64

64
Dest_IP_Address – In this field, you will enter the IP address of the device you wish to stream
video content to (i.e. an edge QAM).
Dest_Port_Number – This field represents the port of the IP address you wish to stream video
to. Depending upon the destination, this value may not be freely chosen.
Major_Number – This field is equivalent to the DIRECTV channel number you tune to on a
typical DIRECTV tuner.
The second way is used if a QAM24 is in the chassis. The QAM major and minor numbers are
set along with the DIRECTV channel number. The IP address will be set to
192.168.6.(chassisId+1) and the port will be set the QAM_Index * 16 + QAM_subchannel.
QamMajor – The QAM24 output QAM major channel number. This corresponds to the
channel number from the North American Cable Television Frequency Plan (see EIA-542B or
http://www.jneuhaus.com/fccindex/cablech.html ).
QamMinor – The QAM24 output QAM minor channel number. This corresponds to the
subchannel number (e.g., 2 in the channel number 13.2 or 13-2 is the subchannel number).
Major_Number – This field is equivalent to the DIRECTV channel number you tune to on a
typical DIRECTV tuner.
Use the link Advanced Edit to access the Advanced Tune page (Figure 35) described below.
For software versions before ST02.05.05, by clicking the Tune hyperlink from the Edit
column on the old Discovery page, you will access the old Tune screen, which is similar
to the new Advanced Tune screen shown in Figure 35.
There are many different functions available under the heading of the Advanced Tune screen.
Each of these functions will be detailed in the subsections that follow.
6.8.1 Tuning the COM24 Cards
The Basic Tune page can be used to change the main tuning parameters of a channel. Additional
tune parameters can be accesses by clicking the Advanced Edit hyperlink at the bottom of the
Basic Tune screen (Figure 34), which brings one to the Advanced Tune screen (Figure 35). A
quicker method of executing a mass tune for any number of cards is available under the TuneAll
command (see Section 6.9).
Page 65

65
Figure 35 – Advanced Tune screen portion of Advanced Edit page
Information identify the tuner currently being tuned is displayed at the top of the web page below
the command links. A unique tuner can be identified by chassis number, slot number, tuner
number, and IP Address.
Chassis – This value shows the Chassis number of the COM200 that holds the COM24 card you
are currently tuning.
Slot – This value shows the Slot number within the COM200 chassis that holds the COM24 card
you are currently tuning.
Tuner – This value indicates which tuner on the COM24 card you are controlling. It is
important to note that Tuner 0 („lower‟) in the web interface is the same as the coaxial hub
labeled Tuner 1 on the COM24 card faceplate, and Tuner 1 („upper‟) in the interface is labeled
Tuner 2 on the faceplate.
IP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card you are currently interacting with.
Page 66

66
A detailed description of each advanced tuning field on the Advanced Edit page follows:
Dest_IP_Address – In this field, you will enter the IP address of the device you wish to stream
video content to (e.g. an edge QAM). The COM24 will stream to any valid unicast or multicast
IP address entered with no additional steps necessary. However, older COM200 Chassis (pseudo
codes BC004 and NC004) require that multicast streams be sent out the front port and an
external Ethernet switch be used. The default value is 192.168.0.0.
Dest_Port_Number – This field represents the port of the IP address you wish to stream video
to. Depending upon the destination, this value may not be freely chosen. The default value is 0.
Protocol_Type – This field is used to control whether the COM24 streams the data in UDP or
RTP packet structures. The default value is UDP.
Channel_Object_ID – This field is the data that the COM24 actually uses for tuning purposes.
It will be automatically filled in when a valid DIRECTV channel number is entered into the
“Major_Number” field. Before the card has been successfully tuned, the default value is 0.
For some local markets, there are multiple DIRECTV channels with the same channel numbers.
To resolve this issue, the Major_Number and Minor_Number should be set to zero and the
correct Channel_Object_ID must be entered. Contact Technicolor to convert the television call
letters to the Channel_Object_ID. Major_Number – This field is equivalent to the DIRECTV
channel number you tune to on a typical DIRECTV tuner. The default value is 0.
Minor_Number – This field is automatically filled in by the COM24 card, with a default value
of 65535. If the DIRECTV channel has a minor channel number then the Minor_Number value
must be entered.
Many DIRECTV channels have both a high-definition and standard-definition channels with the
same Major and Minor numbers. The COM24 will prefer the high-definition channels in this
case. To prefer the standard-definition channels instead, add 100000 to the Minor_Number. In
most cases, this would cause the Minor_Number to be 165535 if the standard-definition channel
is desired.
Stream_ID – This field is optional, and allows a unique identifier to be applied to every video
stream produced by the COM1000 system. The allowable values for this field are any whole
number between 1 and 65535. The default value is 111.
To enable a second audio stream set the Stream_ID to 54000.
Security_Mode – Typically, this field will not need to be changed. The only settings most
should be concerned with are „0 = None‟, „1 = Pro_Idiom‟, and „4 = Transcode‟ (See Section 1.1
for more on transcoding). The „0‟ (“off”) setting will only work on DIRECTV channel 100.
Page 67

67
This allows you to turn Pro:Idiom encryption off so that a standard HDTV or PC-based utility
like VLC Media Player can be used for troubleshooting. The value should be set to „1‟ at any
other time. The default value is 0.
Persistent – Setting this value to „1‟ tells the COM24 to retain all channel and IP-destination
settings in memory (i.e., data entered into the card is “persistent”). This eliminates the need to
reprogram the COM24 cards after every power-cycle or reboot. Persistent is on by default (i.e.,
1). It should be on for most installations. Otherwise, all settings will be lost in the event of a
power interruption.
Page 68

68
6.8.2 Evaluating COM24 Informational Status
The information shown in Figure 36 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 36 – “Info” Section on Advanced Edit Page.
This section provides a selection of many key indicators to the operation of the COM24 card. It
acts as a concise index to the characteristics of each individual COM24 card according to its
status and user-defined settings.
Following is a brief explanation of each field shown above.
Page 69

69
Chassis_ID – This field represents which COM200 chassis the card resides in when there are
multiple chassis in the system.
Slot_ID – This field identifies the card‟s location within a chassis, numbered 1 through 12.
Tuner – This field identifies the tuner‟s location on the COM24 card (0 or 1).
Card_IP – This field shows the IP address of the COM24 card you are currently interacting
with.
Receiver_ID – This field reports the DIRECTV Receiver ID, or RID. This value is the first of
two parameters required to obtain authorization on the DIRECTV network.
CAM_ID – This field reports the DIRECTV CAM ID. This value is the second of the two
parameters required to obtain authorization on the DIRECTV network.
Network_ID – This field reports the DIRECTV network that the tuner is currently tuned to. The
value recorded here corresponds to the satellite being used to transmit the channel as is
determined by the most recent DIRECTV broadcast settings.
Frequency_Index – This field reports the frequency index corresponding to the channel the
tuner is currently set to.
Authorized – This field provides feedback on whether the card has been authorized within the
DIRECTV network. The card needs to be paired and authorized in order to receive DIRECTV
programming. A value of „1‟ means that the card has been successfully authorized; „0‟ means
that it has not yet been authorized, or has lost its authorization.
Paired – This field provides feedback on whether the smart card has been successfully paired
with the COM24 card. The card needs to be paired and authorized in order to receive DIRECTV
programming. A value of „1‟ means that the card has been successfully paired; „0‟ means that it
has not yet been paired, or has lost its pairing.
Blackout – This field can be used to determine whether DIRECTV has issued a blackout of the
content on a particular channel. This is a good thing to investigate if the video suddenly stops
playing on any channel, but it is particularly likely to happen with nationally televised sporting
events. A value of „0‟ means that the channel should be functioning properly; „1‟ means that the
programming on the selected channel is not currently available to you. TVs will display a
blackout message on screen in the event of a blackout.
SW_Version – This field reports the software version that currently resides in the COM24 card.
All cards that have a similar web interface to the one described in this document will have a
version number of at least ST01.00.25.
Page 70

70
Using the COM24 “Direct Tune” Feature
The information shown in Figure 37 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 37 – “Direct Tune” Interface on Advanced Edit page
This section gives you a method to force a tuner to a particular satellite and transponder pair.
This ability can especially useful when attempting to track and isolate RF problems with the
COM1000 system. The data required to perform this operation can be gathered from the basic
“Tune” interface shown in Figure 34 above. A brief explanation of each field follows.
Network_ID – This field displays the DIRECTV network of the currently tuned channel. This
number correlates to a specific satellite, and can be used in conjunction with the
“Frequency_Index” field below to determine whether the card is locked to the correct channel
version (as of this version of the manual, all SD content resides on Network 0, and the HD
content is spread across Networks 10 and 15).
Frequency_Index – This field displays the DIRECTV frequency index of the currently tuned
channel. This number correlates to a specific transponder, and can be used in conjunction with
the “Network_ID” field above to determine whether the card is locked to the correct channel.
Page 71
71
6.8.4 Using the COM24 LED Control Feature
The information shown in Figure 38 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 38 – “LED Control” Interface on Advanced Edit page
This section gives you the ability to assume control of the PWR LED temporarily. This feature
can help you easily identify a specific card within a chassis if there is ever any doubt about
which card you are accessing. A brief explanation of each field shown above is as follows:
LED_State – This field allows you to control the PWR LED. This may be used as a simple
means to identify a particular card within a chassis at a remote location. The allowed values are:
0 = Off
1 = On
2 = Flashing
Page 72

72
6.8.5 Using the COM24 File Transfer Utility
The information shown in Figure 39 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 39 – “File Transfer” Interface on Advanced Edit page
Similar in function to the upgrade section found on the PairingInfo page, this section provides
you with a method of transferring software updates to or transferring log data from individual
COM24 cards.
See Section 7 for more information on upgrading your COM24 cards.
Following is a brief explanation of each field shown above.
Page 73

73
Usage – This field is used to tell the COM24 which type of transfer to execute. Only two values
are available for customer use (all others are for development purposes only):
2 = Software Upgrade – This option is used to update the COM24 software. In this case,
the file is downloaded to the COM24 card specified by the earlier Card IP address.
3 = Log – This option tells the COM24 to transfer its log file to the destination entered in
the “IP_Address” field (i.e., log file is uploaded to PC).
Server_IP_Address – This field tells the COM24 card where to retrieve the software update or
where to send the log file, based upon the “Usage” setting above. The default value for this field
is 192.168.1.254.
Filename – This value entered in this field tells the COM24 which file to download (in the case
of software updates), or what name you want to give the log file being transferred from the card.
Mode – This field is used to tell the COM24 card which file-transfer protocol to use for the file
transfers. The supported modes are TFTP (option „0‟) and FTP (option „1‟), allowing you to
select the mode that best works with the software you use for the transfer. The default setting is
0.
See Section 5.3 for more information on using FTP vs. TFTP.
The card will automatically reset after completing an upgrade.
Page 74

74
6.8.6 Setting the COM24 User Configuration Options
The information shown in Figure 40 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 40 – “User Config” Interface on Advanced Edit page
This section gives you the ability customize select features of the COM24 cards to better suit
your application. The cards actually support a few more features than shown here, but the two
most useful features have been made available here. You have the ability to change the
mechanism the cards use to obtain IP addresses and the ability to send log data to a PC or other
monitoring mechanism.
Following is a brief explanation of each field shown above.
CardIP – This field represents the IP address of the COM24 card that you are currently
interacting with. The value is filled in automatically.
IP_Config – This field allows for one of 9 methods of IP address assignments to be chosen.
When changing the value in this field, you must also enter a valid address in the “Base_IP” field
below, as the parameters are used to create a new IP address for the cards. The default setting is
0.
0 = Default
1 = DHCP_Persistent
2 = NA
3 = NA
Page 75

75
4 = Fixed
5 = NA
6 = NA
7 = NA
8 = NoChange
Base_IP – This field gives the COM24 card a starting point for defining its IP address in several
of the modes listed above.
Subnet – This field allows you to give a subnet mask of your choosing to the COM24 card.
Clear this field to use a default subnet.
Gateway – This field allows you to set a default gateway of your choosing for the COM24 card.
Clear this field to remove the gateway value.
Time-to-Live – Time to Live field in IP protocol header.
Log_IP – This field allows you to direct the COM24 card to send its log files to an external
destination automatically. This is very useful for monitoring the health of the system over an
extended period. After entering the IP address of the destination, the log files will start being
forwarded to this address after a short delay. You may then run a system-logging utility like
Kiwi on the destination computer to capture this information.
Log_Level – This field allows you to define the level of detail that will be captured in the
resulting log files. Due to the complexity of this setting, it is strongly advised that it be left blank
unless someone from support has asked to change the value.
UtilConfig – This field is for development purposes only, and should be left blank unless you
have been asked to modify the value by someone from support.
Please refer to Appendix A for more information on using these settings.
6.8.7 Reading the COM24 CAM Log Data
The information shown in Figure 41 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Page 76

76
Figure 41 – “CAM Log” Interface on Advanced Edit page
This section gives you the ability to read the log files generated by any COM24 card‟s
Conditional Access Module (CAM), also known as its smart card. The messages reported here
match the ones that may be seen on a normal set-top box, and can be used to determine whether
the card has been properly authorized and paired.
Page 77

77
Under normal circumstances, an authorized card will produce a very short CAM log file that
looks like the image shown in Figure 42 below.
Figure 42 – CAM Log Report
If, however, there are issues with the card‟s authorization, you will see messages that look more
like this:
0 0 0: CARD_INSERTED
1 9 727: 727 - Program Not Available in Your Area (Service Blacked Out)
[GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
2 0 0: Can't view [GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
3 0 0: Blackout [GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
4 9 727: 727 - Program Not Available in Your Area (Service Blacked Out)
[GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
5 0 0: Can't view [GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
6 0 0: Blackout [GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
7 9 727: 727 - Program Not Available in Your Area (Service Blacked Out)
[GMT=Thu May 12 00:00:00 2011]
The 3-digit values starting with a “7” are the DIRECTV support extension numbers associated
with the error condition.
Other things that you may see reported here include messages about access card not being active,
wrong or missing RID number, card not paired, and programming information for audio-only
channels. Many commercial TVs won‟t play audio-only channels.
Page 78

78
There are a few fields as described below:
Refresh – Refreshes this display.
Clear_CAM_Log – Clears all current entries in that card‟s CAM log.
Page 79

79
6.8.8 Using the COM24 Software Reset Feature
The information shown in Figure 43 below is one of the subsections available on the Advanced
Edit page.
Figure 43 – “Reset” Interface on Advanced Edit page
This section allows you to initiate a software reset on the card identified in the “CardIP” field.
This is sometimes helpful in situations where a card has become non-responsive. Activating this
feature is the equivalent to pushing the recessed reset button on the face of the COM24 card, and
has a similar effect as pressing the small reset button on a traditional set-top box.
Page 80

80
6.9 Using the COM1000 TuneAll Command
The information shown in Figure 44 below is the result of clicking the TuneAll hyperlink at the
top of any COM1000 web interface page.
Figure 44 – COM1000 TuneAll Page
Page 81

81
This section provides a practical way to configure an entire COM1000 system with minimal
effort. In order to use this feature, you can start by copying and pasting the information provided
at the bottom of the browser page (below the Submit Query button) either directly into the text
field provided or into your text editor of choice, and then modifying it as indicated by the guide
comments located above the text field. Examples are provided below to help you understand
how to utilize this feature.
Note: Saving a copy of the tuning table for your entire system in the form of a text file is
recommended, just in case the settings are not fully restored after a system reset.
The lines in the tuning table take the following form (see Section 6.8.1 for more on tuning):
Chassis-Slot-Tuner, IP_Address:Port_Number, Major_Number-Minor_Number-Security_Mode;
The sample line below indicates the upper tuner of a card residing in Slot #4 of Chassis #2. It is
targeting Port 301 of the device residing at the IP address 192.168.4.245, and tuned to the HD
broadcast of channel 242 with Pro:Idiom encryption set.
2-4-1, 192.168.4.245:301, 242-65535-1;
Upon initial system startup, your table might look something like this:
Current Tuning Table
1-1-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-1-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-2-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-2-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-3-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-3-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-4-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-4-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-5-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-5-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-7-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-7-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-9-0, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
1-9-1, 192.168.0.0:0, 0-0-0;
After modifying the data to meet your system needs, it might look something like this:
Current Tuning Table
1-1-0, 192.168.4.245:6401, 3-65535-1;
1-1-1, 192.168.4.245:6402, 10-65535-1;
1-2-0, 192.168.4.245:6403, 29-65535-1;
1-2-1, 192.168.4.245:6657, 6-65535-1;
Page 82

82
1-3-0, 192.168.4.245:6658, 17-65535-1;
1-3-1, 192.168.4.245:6659, 259-65535-1;
1-4-0, 192.168.4.245:6913, 209-65535-1;
1-4-1, 192.168.4.245:6914, 276-65535-1;
1-5-0, 192.168.4.245:6915, 280-65535-4;
1-5-1, 192.168.4.245:7169, 306-65535-4;
1-7-0, 192.168.4.245:7170, 501-65535-4;
1-7-1, 192.168.4.245:7171, 218-65535-4;
1-9-0, 192.168.4.245:7426, 206-65535-4;
1-9-1, 192.168.4.245:7427, 545-65535-4;
After editing the tuning table, you simply need to copy and paste this information into the large
field provided by the TuneAll command, and then click Submit Query.
If you are using a QAM24 Card, you can also use the syntax of
Channel[hd|sd] -> QamMajor-QamMinor
For example, to tune the first unused tuner to the HD Science channel so that will it will be QAM
modulated at channel 50-1 use:
284hd -> 50-1
Page 83

83
6.10 Using the DIRECTV Electronic Program Guide (EPG)
Each COM24 card gives you access to an integrated Electronic Program Guide (EPG) that can
be used to create a user-defined guide channel of all programming offered at your location. The
setup is done through the same web interface as is used for the normal system setup. The guide
can be expanded to include all channels being offered at the property, whether the source is the
COM1000, an analog SMATV system, or over-the-air signals. The only limitation to what
channels can be added to the EPG is that they must also exist in DIRECTV‟s channel lineup.
There are some important items to note when working with the EPG:
1. The EPG information can only be contained within a single card. You cannot access
your EPG settings when logging in to any other card. Therefore, it is important to keep
track of which card contains your guide information. It is also recommended to keep a
text file containing the EPG listing in case you lose access to that particular card. The
SysInfo page will show „:EPG‟ in the Property_ID field if a card is transmitting the EPG
channel.
2. The EPG is created in such a way that it provides the viewer with what appears to be an
auto-scrolling channel listing. It is essentially a dynamic MPEG video stream made up of
still images of the current programming. It moves down the list of assigned channels
every 2.5 seconds, creating a constant cycle, showing nine channels at a time. As such,
the guide is not interactive, so the viewer must manually tune to their channel of choice.
3. If the number of channels in the EPG fits in one screen (nine or less) the channel listing
will not scroll. This permits the installer to have multiple cards generating a different
EPG channel listing nine channels each. This will create the user experience that
channeling up or down will page up or down nine channels in the guide.
4. The SysInfo tab will show which cards are generating an EPG by placing the string
“:EPG” in the Property_ID field.
5. The EPG can also convert the DIRECTV guide information into PSIP guide information
that is decodable by many televisions. Most commercial televisions appear to ignore
PSIP guide information. PSIP permits the channel number to be remapped, the channel
name can be displayed, the current time displayed, and the current and next program titles
displayed. To generate PSIP guide information, the last two numbers for each channel
must list the QAM24 chassis number and QAM24 destination port number. This
information is automatically filled in when EpgLoad it clicked. To disable PSIP guide
generation for a channel, set the port number to -1. If the DestIP is a valid IP address but
the DestPort is 0, then the EPG channel is disabled but PSIP guide generation is still
enabled.
Page 84

84
6. It is possible to add non-DIRECTV channels to the EPG. This is done by adding an entry
where instead of a DIRECTV channel number, the capital letter „N‟ appears followed by
the channel name, and program information separated by underscore characters. For
example:
10-1 NLobby_The_lobby_channel 1 17
7. Each channel in the EPG is comprised of a still image and it can take up to 10 seconds to
produce the image for every channel being offered when the EPG is first loaded. For
example, a location offering a list of 18 channels can expect to wait up to 3 minutes for a
first-time EPG configuration.
8. Due to the combination of the auto-scroll programming and the constant addition of new
channels, you can expect the EPG to exhibit some odd behavior during the initial image
creation. It may appear to skip around at random, but it can be expected to settle back
into a normal operational state once it has finished generating all the necessary images.
9. The EPG is a video-only channel, and you cannot set audio to play in the background.
10. A COM24 card that is set to transcode cannot support an EPG. This means that any
COM24 that has been paired with an XDR24 is incapable of storing and displaying an
EPG.
11. Because the EPG is generated from the DIRECTV program guide data, you can only add
channels that are active in the DIRECTV channel lineup. For example, you cannot add
an independent local channel to your EPG unless it is also offered on DIRECTV.
12. You must remember to reprogram the EPG anytime your location‟s channel offering is
remapped.
Page 85

85
6.10.1 Starting Out
In order to access the EPG setup screen shown in Figure 45 below, simply click the EPG
hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page.
Figure 45 – COM1000 EPG Page
Following is a brief explanation of each field available on the EPG page as shown above.
Page 86

86
DestIP – This field represents the IP address of the device you wish to send the EPG data to. In
a typical installation, this will be the address of the edge QAM device. The default value is
0.0.0.0.
Note: the default value of 0.0.0.0 can be entered at any time to disable the EPG channel.
DestPort – This field represents the port number that is to be used to map the EPG to a specific
QAM channel. The default value is 0.
TimeZoneOffset – This field is used to tell the COM24 to shift the guide data by the appropriate
amount of time to account for the property‟s time zone. Example values can be seen to the right
of the field. The default value is 0.
IgnoreDST – This field is used to tell the COM24 to ignore Daylight Savings Time, if needed.
This is accomplished by entering a value of „1‟ here. The default value is 0.
LogoTftpServerIP – This field is used to tell the COM24 where to find the custom logo for the
property. This will be the IP address of the PC containing the TFTP server.
LogoFileName – This field is used to tell the COM24 the name of the file that is to be used for
the logo.
See Section 0 for more information on selecting and uploading
a custom logo for your EPG.
The EPG‟s channel lineup is created in the large textbox on the lower half of the screen, using
the following format:
displayNumber majorNumber-[minorNumber]-[hd|sd] chassis port
displayNumber – This is the TV channel that the viewer will find the program on.
majorNumber – This is the same as the “Major_Number” field in the Channel Tune interface.
minorNumber – This is the same as the “Minor_Number” field in the Channel Tune interface.
Please note that on submission, the EPG will default to „65535‟ if this value is not provided.
hd|sd – This tells the guide whether to pull the data for the HD or the SD version of a particular
channel. The default behavior for the COM1000 is to look for HD channels, so this setting
allows you to add SD channels to the EPG if needed. Please note that on submission, the EPG
will default to „hd‟ if this value is not provided.
Page 87

87
chassis – This tells the guide which chassis the QAM24 is in so that it knows the QAM24‟s IP
address for sending PSIP guide data. If not using PSIP this field can be set to -1.
port – This tells the guide which QAM24 UDP port is being used for sending PSIP guide data.
If not using PSIP this field can be set to -1.
Examples:
10 501-65535-hd ➔ TV channel 10 carries HBOHD (from COM1000)
23 209-65535-hd ➔ TV channel 23 carries ESPN2HD (from COM1000)
45 202-65535-sd ➔ TV channel 45 carries CNN (from SMATV or COM1000)
37 8-65535-hd ➔ TV channel 37 carries local channel 8 (from OTA, SMATV, or COM1000)
10-1 NLocal_Program_Info 1 71 ➔ Non-DIRECTV channel (channel name Local)
Note: The actual content could come from the COM1000, a separate analog SMATV system, or
even from on-air, as long as the channel is available in DIRECTV‟s lineup.
The first time you access the EPG page, it will be blank, as shown in Figure 45 above. Note
that, as mentioned previously, this page applies to the card that you are currently logged in to,
and that an EPG can only exist on one card. If you have previously completed an EPG
configuration and instead see a blank page like the one shown above, you are probably logged in
to the wrong COM24 card. After a successful configuration, the screen should look similar to
the one shown below in Figure 46.
Page 88

88
Figure 46 – COM1000 EPG Page (Configured)
Page 89

89
6.10.2 Configuring the EPG
The screen shown in Figure 47 below is the result of clicking the EpgLoad button located at the
bottom of the EPG screen. Doing this provides a convenient starting point for building an EPG
for your system.
Figure 47 – COM24 EPGLoad Result
Page 90

90
The results shown on this page contain the programming information for all COM24 cards in
your system based on the current tuning table. The function builds a channel lineup starting with
channel 10. It then assigns channel information starting from the first tuner on the leftmost card
in the lowest-numbered chassis and steps up one channel for every successive tuner. This
information will automatically be loaded into the appropriate text field the next time you visit the
EPG page.
Note: In the submission results shown above, a „0‟ at the end of a
channel line refers to a submission of „sd‟ and „1‟ refers to „hd‟.
Page 91

91
In order to customize the EPG to match the property‟s lineup, you will need to go back to the
main EPG screen by clicking the EPG link at the top of the page. From this screen, you will
need to tell the COM24 card where to send the EPG data (an edge QAM, for instance), define a
time zone offset, and modify the lineup as needed. You may also upload a logo for the property
that will be displayed in the upper right corner of the EPG. See Section 6.10.3 for instructions
on selecting and uploading a logo.
When modifying the EPG channel lineup, the channels can be entered in any order, as the
COM24 card will automatically sort them by channel number when it builds the guide. As with
the tuning table on the TuneAll page, you may edit the EPG information in its text field on the
page, but it is recommended that you make all changes in a separate text editor and save a copy
of the text file for easy retrieval in the case of any information loss.
Once you are finished entering all of the information necessary to build your EPG, simply click
the “Submit Query” button at the bottom of the screen. Doing so will provide you with a screen
that reports all of the data the COM24 card has been sent. This screen will look similar to the
resulting screen after clicking the EPGLoad button. Once the EPG has had enough time to
configure, the resulting guide channel should look like Figure 48 below.
Figure 48 – Guide Channel (EPG)
Page 92

92
6.10.3 Adding a Logo to the EPG
Original Image
Modified Image
On-screen Appearance
The COM24 has a built-in facility for superimposing a property‟s logo into the upper right
corner of the EPG. Should the System Operator express an interest in providing such a logo, it is
entirely up to the property to employ someone to do so. It is recommended that you work with
someone in either the property‟s Branding or Corporate Identity department or with a graphics
professional in order to obtain an image that is in the proper format to be added to the EPG.
In order to work properly with the EPG, the logo must be saved as a 24-bit bitmap (*.bmp) file,
and can be no larger than 170x60 pixels in size (170 pixels wide and 60 pixels long). In
addition, the image‟s background can be made to render as transparent by changing the color to
magenta (RGB values of 251-0-255). An example of this can be found in Figure 49 below.
Figure 49 – EPG Logo Adjustments
Once the image has been properly uploaded (see Section 5.3 on using TFTP) by using the
“LogoTftpServerIP” and “LogoFileName” fields on the EPG page, you should see the logo
appear in the upper right corner of the guide channel screen, as can be seen in Figure 50 below.
Figure 50 – Guide Channel (EPG) with Custom Logo
Page 93

93
6.11 Using the COM24 Syslog Command
The information shown in Figure 51 below is the result of clicking the Syslog hyperlink at the
top of any COM1000 web interface page. Note that this method of displaying the syslog will
only show the last 500 lines of messages from the card you are currently logged into.
Figure 51 – COM24 Syslog Report
Page 94

94
In addition to clicking the Syslog hyperlink at the top of any COM1000 web interface page, the
syslog data may also be accessed directly from the PairingInfo screen as discussed in Section 6.5
by clicking directly on the hyperlinks for each card‟s IP address, as seen in Figure 29.
It should be noted, however, that this particular feature will only give the results shown above if
the card you are logged into and the card you wish to access are both running a firmware version
higher than ST02.00.03. If a target card is not carrying the correct firmware, you will be
redirected to that card‟s Help page.
6.12 Using the COM24 ATSC Command
The ATSC command can control Technicolor ATSC tuner boards. There are eight tuners in each
board that can receive an ATSC channel and forward the transport stream to a QAM24. There is
a different IP address per every two tuners. This results in four different IP addresses per board.
First, the four IP addresses must be set. Specify the desired base IP address (such as
192.168.4.1) and click IP_Discover_and_Set. This will discover all of the ATSC tuners and set
their IP addresses starting with the base IP address.
Next, enter one line per tuner using this format:
HomeRun_IP Tuner_Index RF_Index Major.Minor Dest_IP Dest_Port
For example, to tune to WFYI 20-1, 20-2, and 20-3 with
ATSC Base IP address = 192.168.4.1
The Tuner_Index is either 0 or 1 for each IP address.
WFYI is carried on ATSC frequency 21.
QAM24 address is 192.168.6.2
Therefore enter the following three lines:
192.168.4.1 0 21 20.1 192.168.6.2 17
192.168.4.1 1 21 20.2 192.168.6.2 18
192.168.4.2 0 21 20.3 192.168.6.2 19
Page 95

95
6.13 Using the COM24 401 Command
The 401 tab can send control messages to DCI401MCS Digital Security Terminator devices
(DSTs). The DCI401 can receive Pro:Idiom encrypted QAM channels and output HDMI video
to a TV. Each message can be sent to either a single DCI401 based on its unique Receive ID
(RID) or to all DCI401s by setting the Receiver_ID to 0xffffffff.
The Messages are:
0 = Download new DCI401MCS software
3 = Feature enable/disable
4 = Reset DTA user settings (ratings locks, …)
5 = Tune to a specified Major_Number – Minor_Number channel
6 = Scan for new channels
7 = Display text for a few seconds on the TV
9 = Set which channel is the EPG channel
10 = Set site specific error messages indicating who to call for support
11 = Send logo file for use in the user interface
The DCI401MCS will only decrypt Pro:Idiom channels if the channel was Pro:Idiom encrypted
by a COM24.
Page 96

96
6.14 Using the COM24 QAM Command
The QAM24 link will display the page below:
Figure 52 – QAM24 Command Screen (top portion)
The QAM24 card is controlled by any of the COM24 cards via Ethernet. The QAM24 card has a
fixed IP address = 192.168.6.“Chassis ID” + 1. An arbitrary alternate address can be assigned.
Page 97

97
QAM output channels have a destination port of QamChannel *16 + subchannel number.
The top screen shows the status of each channel. The RF groups are labeled Qam1-Qam12.
Each RF channel can have up to 8 subchannels or programs. If a subchannel is active, its bit rate
will be shown. Bitrates are static snapshots.
Figure 53 – QAM24 Command Screen (bottom portion)
The bottom screen controls the RF output configuration and provides SW upgrade capability. 12
RF output channels are defined in 3 groups of 4. Each group of 4 is in a fixed channel sequence
starting with the base channel. Each group‟s base channel can be set according to the North
American Cable Television Frequency plan. Each RF channel can be individually turned on or
off. Each channel must be frequency adjacent and within the same band per the North American
Cable Television Frequency Plan (See EIA-542B or
http://www.jneuhaus.com/fccindex/cablech.html).
The QAM24 supports an emergency broadcast override. If a video stream is sent to port 25600 it
will override all of the channels.
The “tftpIP” address field sets the address of the file server for SW upgrades. “tftpFilename”
sets the name of the new SW image.
DO NOT turn off power or unplug a card that is updating its SW image. YOU WILL
create a doorstop.
The reset field executes a SW reset of the QAM24. It is almost user transparent.
Page 98

98
The alternateIp field will configure the QAM24 to have a second IP address. This IP address can
be a multicast IP address. However, the QAM24 does not notify a managed switch that it wants
this multicast IP address via IGMP.
Some QAM24 boards have an RF spur that can interfere with analog television channels. The
spur is 1176 MHz minus the desired center RF frequency for each group of four channels. For
channels 23 through 94 this means that the spur will be at (1086 – 6 * channel) MHz. Change
the frequency plan to minimize the impact of the RF spurs.
New reduced cost QAM-6 boards will only permit six QAM carriers to be active at a time. To
increase the number of QAM carriers, additional licenses must be purchased from Technicolor
and downloaded to the QAM24.
When debugging QAM24 issues, click on the qamLog button to see the QAM24 system log.
This log is mainly for Technicolor technical analysis but a short summary is:
A = Arp reply
bad(#) = Discarded # number of unexpected Ethernet packets.
C = Command and control message received
c## = Continuity counter error. May indicate multiple channels to same port.
PMT## = PMT changed on a channel
T = PCR discontinuity
Page 99

99
6.15 Using the COM24 Help Command
The help command can be reached by clicking “Help” at the top of any COM1000 page. It
briefly describes all of the other commands.
Figure 54 – COM24 Help Command
Page 100

100
7 COM1000 FIRMWARE UPGRADE PROCEDURES
When you first receive your COM1000 system, your distributor should have already installed the
most recent firmware on every COM24 card. However, since we are continuing to improve
upon the software associated with the system, you may find it useful to stay up-to-date as future
versions are released.
Note: The latest firmware release covered in this manual is ST02.07.05.
The following sections will explain in detail the upgrade options that were touched upon earlier
within the file transfer utility located under the Tune command and on the PairingInfo page
(Advanced Tune for SW version ST02.05.05 and later).
7.1 Preparing for a Firmware Upgrade
Before proceeding any further, it is recommended that you first visit Section 5.2.1 on setting up
your network connections and Sections 5.1.5 and 5.3 on using FTP/TFTP and configuring your
server in order to ensure that everything is properly configured to perform this operation.
7.2 Upgrading COM24 Firmware
WARNING: DO NOT download old software versions (before ST02.07.05) if the RID does
not start with 0330. This will cause all three LEDs to blink once a second and the card will not
work.
This section will guide you through the procedure for upgrading your COM24 cards. There are
two different ways you can go about doing this. The first method is a single-card upgrade, which
requires the use of the file transfer utility located on the Advanced Edit page (see Section 6.8.5).
The second and preferred method is a multi-card upgrade, the controls for which are located at
the bottom of the PairingInfo page (see Section 6.5).
For both of these options, the “Usage” option should be on „2 = SW_Upgrade.‟ The
“IP_Address” will be the device that contains the upgrade file (your PC). The “Filename” will
be the name of the upgrade file (e.g. “imageB020113.bin”). It is recommended that you retain
the original filename of the update file you have been issued to avoid confusion later on. The
mode determines whether the card tries to contact a FTP or TFTP server.
The fields that apply to the COM24 Multi-card upgrade are listed in Section 6.5 “Evaluating
COM24 Authorization Status.”
 Loading...
Loading...