Page 1

Security Made Smarter
PLATINUM DIGITAL HD
Professional HD
Security System
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 2

2
Click for contents
Important Information
FCC Verification
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class
B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
· Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
· Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver
· Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected
· Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
These devices comply with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
· These devices may not cause harmful interference
· These devices must accept any interference received, including interfer-
ence that may cause undesired operation
Important Notice: All jurisdictions have specific laws and regulations relat-
ing to the use of cameras. Before using any camera for any purpose, it is the
buyer’s responsibility to be aware of all applicable laws and regulations that
prohibit or limit the use of cameras and to comply with the applicable laws
and regulations.
FCC Regulation (for USA): Prohibition against eavesdropping
Except for the operations of law enforcement officers conducted under lawful
authority, no person shall use, either directly or indirectly, a device operated
pursuant to the provisions of this Part for the purpose of overhearing or recording the private conversations of others unless such use is authorized by
all of the parties engaging in the conversation.
Warning: Changes or modifications made to this device not approved
expressly by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
Important Safety Instructions
· Do not operate if wires and terminals are exposed
· Do not cover vents on the side of your device and allow adequate space for
ventilation
· Only use the power adapter supplied with your NVR
About this Instruction Manual
This instruction manual is written for the NVR-7450 series and was accurate
at the time it was completed. However, because of our on-going efforts to
constantly improve our products, additional features and functions may have
been added since that time.
Important Password Information
This NVR does not have a default password. A password is created during the Startup Wizard. If password protection has been enabled and you
have forgotten your password, your NVR’s MAC address can be used to
create a new password (see page 3 - Password Recovery).
Page 3
3
Click for contents
Password Recovery
Forgotten your password? Please do the following:
1. Right-click the mouse on the Live View screen to display the Menu Bar
then click “Main Menu”.
2. At the password login screen click “Forgot Password” then click “Yes”.
3. After a short moment, you will receive a password reset request email
containing your NVR’s MAC address (if it’s not in your inbox, check your junk
or spam folder).
4. Input the MAC address including the semicolons (see left example) then
click “OK”.
5. A message will appear on-screen stating that your password has been
reset. Click “OK” to continue.
6. Enter a new password (see bottom left example). The password has to
be a minimum of six characters and can contain a mixture of numbers and
letters. Use a password that you are familiar with, but is not easily known to
others.
7. Write down your password in the space provided below for safe keeping.
8. Complete the Startup Wizard as normal (the settings that you previously
selected in the Startup Wizard will remain unchanged).
Don’t forget to write down your password: _________________________
I haven’t created an email for my NVR, what can I do? Don’t worry, we’re
here to help. Please contact Swann Helpdesk & Technical Support (phone
numbers located on page 83) for assistance.
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
CH3
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMStaircase
CH4
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMSide Gate
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
CH3
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMStaircase
CH4
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMSide Gate
Page 4
4
Contents
Important Information ����������������������������������������������������������������������������� 2
Password Recovery ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 3
Live View �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 6
Live View Mode ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 7
Live View Icons & Controls ���������������������������������������������������������������������� 8
Main Menu ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 9
Menu Layout ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 10
Camera Configuration ��������������������������������������������������������������������������� 11
Display: Live ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 12
Display: Image Control �������������������������������������������������������������������������� 14
Display: Privacy Zone ����������������������������������������������������������������������������� 17
Creating a Privacy Mask ������������������������������������������������������������������������ 18
Record: Mainstream ������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 19
Record: Substream �������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 22
Record: Mobilestream ���������������������������������������������������������������������������� 24
Alarm: Motion ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 26
Motion Detection Setup �������������������������������������������������������������������������� 28
Motion Detection Tips ���������������������������������������������������������������������������� 29
Device: PTZ ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 30
Controlling your PTZ Camera ���������������������������������������������������������������� 31
Creating a Preset ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 32
Display: IP Channel �������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 33
Recording Configuration ����������������������������������������������������������������������� 34
Record: Record ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 35
Record: Schedule ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 36
Capture: Capture ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 37
Capture: Schedule (8 channel model) ��������������������������������������������������� 38
Playback & Backup �������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 39
Search: General �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 40
Playback Interface ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 41
Search: Events ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 43
Search: QuickShot ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 44
Playing a Slideshow ������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 45
Search: QuickReview ������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 46
QuickReview Playback ��������������������������������������������������������������������������� 47
System Configuration ���������������������������������������������������������������������������� 49
Display: Output ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 50
Network: Network ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 51
Network: Switch ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 53
Network: Email �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 54
Network: Email Schedule ���������������������������������������������������������������������� 55
Network: DDNS �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 56
Network: RTSP ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 57
Alarm: Alarm ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 58
Device: HDD �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 60
Device: S.M.A.R.T. (8 channel model) ���������������������������������������������������� 61
Device: Cloud ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 62
System: General ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 63
System: DST ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 64
System: NTP ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 65
Page 5
5
Contents
System: Users ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 66
Advanced: Maintain �������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 67
Advanced: Events ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 69
Advanced: Auto Upgrade ����������������������������������������������������������������������� 70
System Status ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 71
Search: Log ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 72
System: Info �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 73
System: Channel Info ����������������������������������������������������������������������������� 74
System: Record Info ������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 75
Glossary �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 76
Frequently Asked Questions ������������������������������������������������������������������ 81
Warranty Information ����������������������������������������������������������������������������� 82
Helpdesk & Technical Support �������������������������������������������������������������� 83
Page 6
6
Click for contents
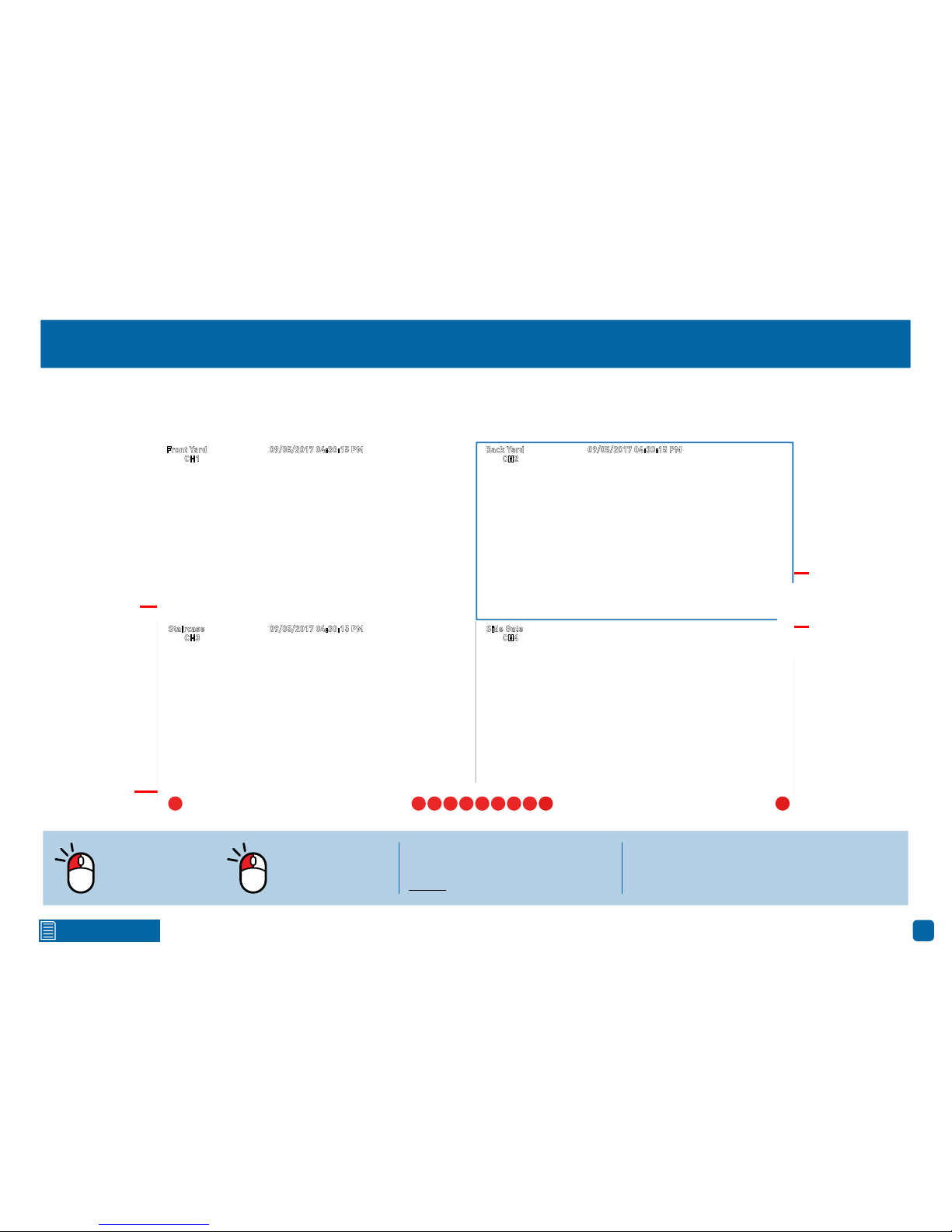
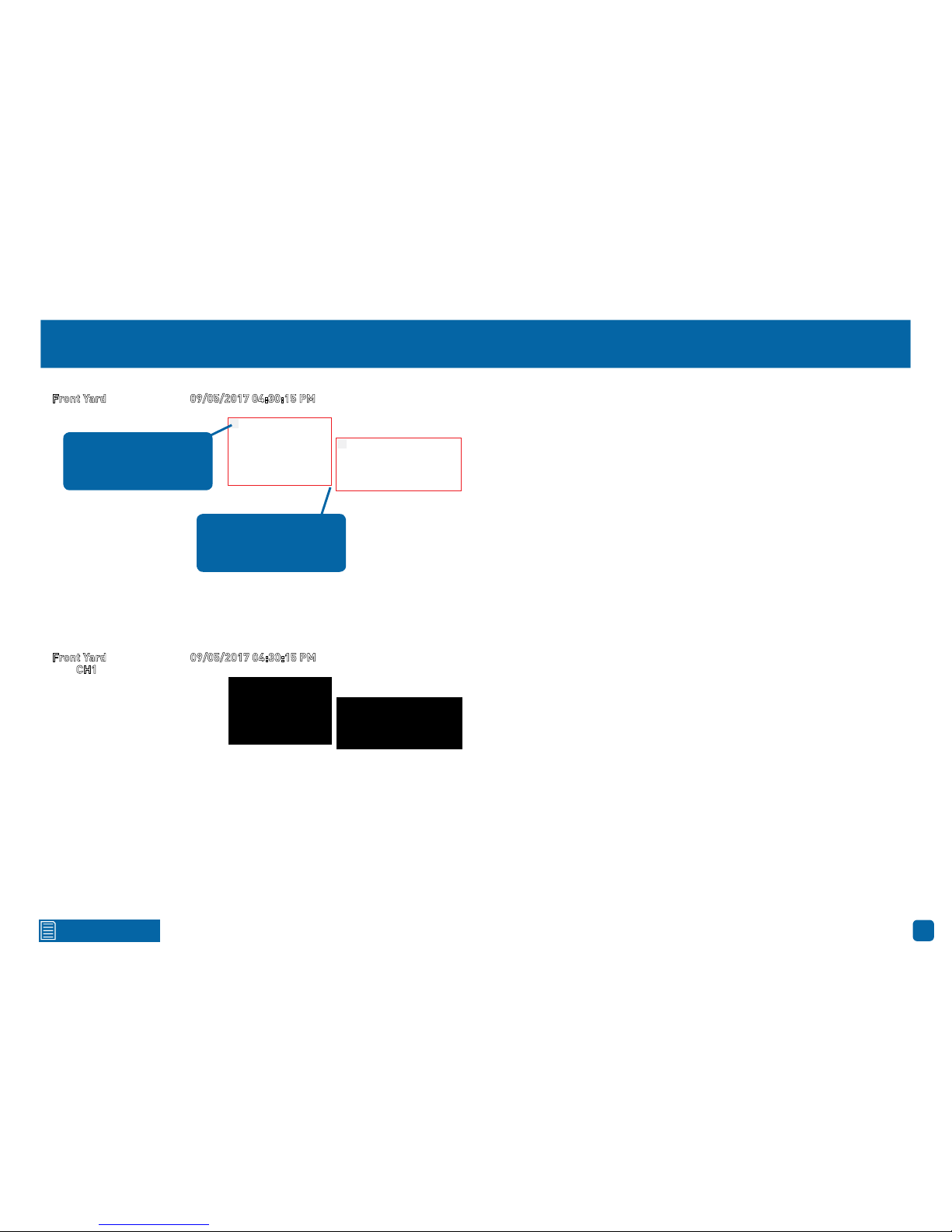
Live View
Live View is the default display mode for
your NVR. Each camera connected will
be displayed on-screen. You can check
the status or operation of your NVR and
cameras using the icons and Menu Bar
on the Live View screen. Right-click the
mouse to access the Menu Bar.
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
CH3
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMStaircase
CH4
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMSide Gate
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
Page 7
7
Click for contents
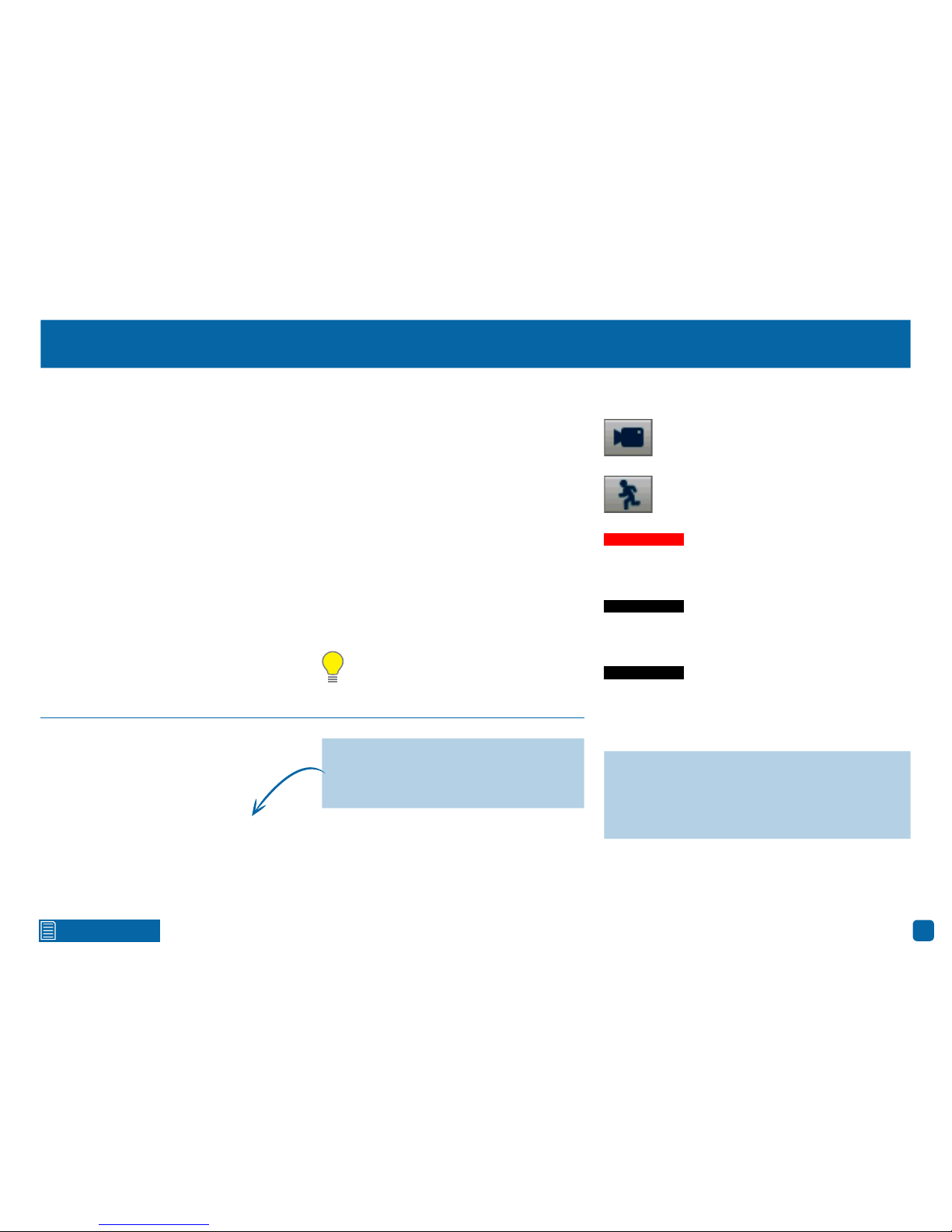
Live View Mode
Live View mode is the default display for your NVR. Each camera connected will be displayed (multiple view modes available). You can check the operation of
your NVR by using the status icons on the Live View screen. The date and time as well as the name for each camera is also displayed.
Camera Toolbar
Status Icons
Menu Bar
Camera/Group
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
CH3
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMStaircase
CH4
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMSide Gate
1 3 4 95 6 7 82
10
11
Double-click a live
video channel to
view full screen.
Click & drag a live
video channel to
reposition it.
Right-click the mouse in Live View
mode to display the Menu Bar (see
page 8 for more information).
Click a camera to access the Camera Toolbar.
This provides access to functions such as instant playback and to change image settings.
Page 8
8
Click for contents
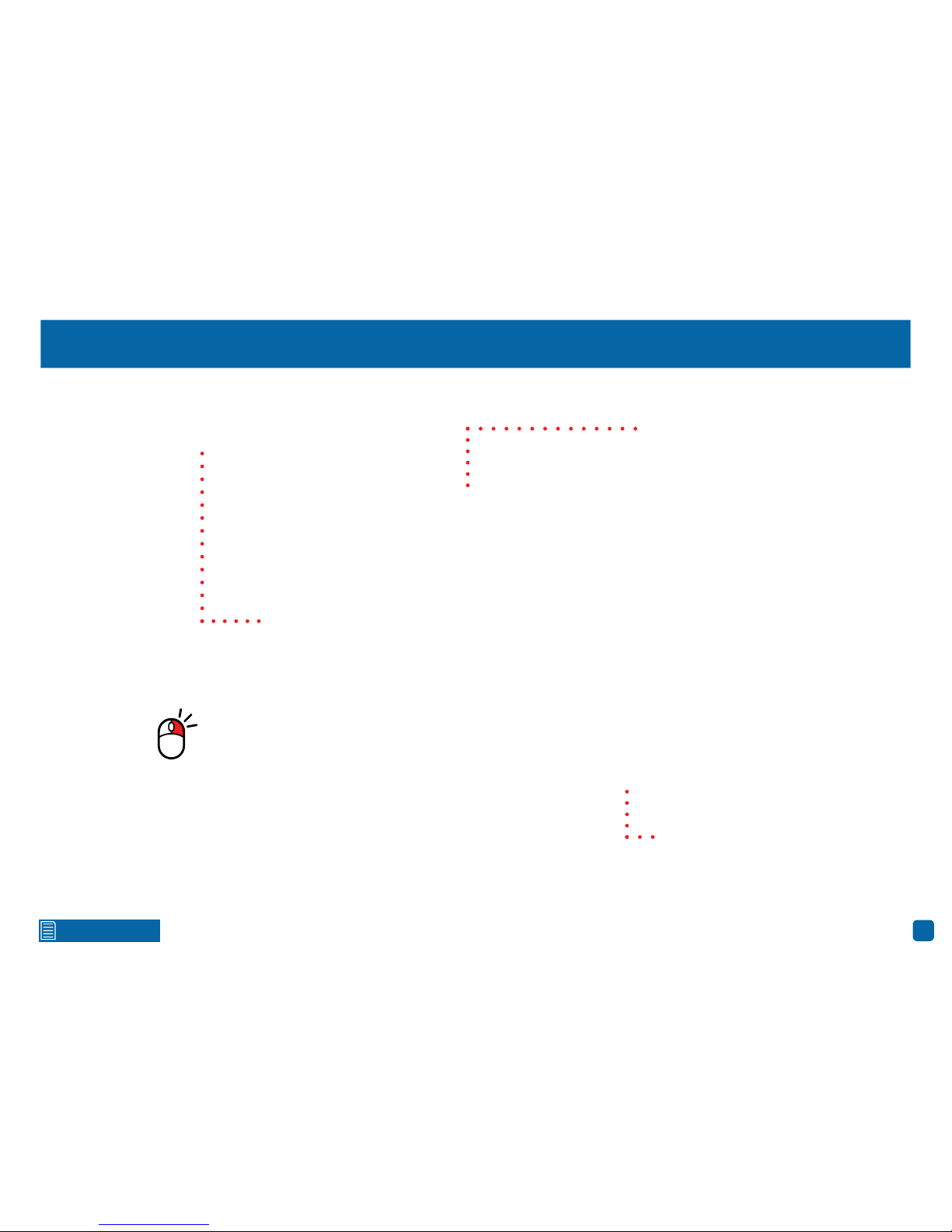
Live View Icons & Controls
Menu Bar
1. Click this to open the Main Menu.
2. Lock your NVR to prevent access to the Main
Menu when “Menu Timeouts” is turned off.
3. Four camera view.
4. Nine camera view (this will display eight
cameras on the 8 channel model).
5. Click this to select from one of the mul-
ti-screen viewing modes available.
6. Click this to change from Mainstream to Sub-
stream when viewing the cameras in Live View
mode. Click again to change to Mainstream.
7. Click this to change the bitrate and frame rate
when viewing the cameras in Live View mode.
There are three profiles available - Real-time
(high bitrate/high frame rate), Balanced (a
balance between Real-time and Smooth), and
Smooth (high frame rate/low bitrate).
8. Click this to repeatedly cycle through each
channel full screen. Each channel will be displayed for five seconds.
9. Click this to change the volume or mute the
audio (click the speaker icon to mute).
10. Click this to access the Search menu.
11. Click this to access the Startup Wizard.
Please note: The 16 channel model will
have additional camera views available
(twelve camera and sixteen camera views).
To ensure the integrity of your recordings,
enter your password and click “Shutdown”
when powering off your NVR.
Status Icons
This icon indicates that the camera is being
recorded (either manually or by motion).
This icon indicates that your NVR is detecting motion from the camera.
This message indicates that the
camera has not been configured for
that camera input or the camera input
has lost the feed from its camera.
This message indicates that your NVR
does not have a hard drive or it fails to
detect the drive that is installed.
NO HDD
VIDEO LOSS
Camera/Group: When viewing a single camera or
a group of cameras, move the mouse to the far left
or right to reveal the camera/group button. You can
cycle through each camera or group of cameras.
This message indicates that your
NVR cannot verify the camera that is
connected to that camera input.
O-line
Page 9

9
Click for contents
Main Menu
The “Main Menu” is where you control the
various actions and options that are available
on your NVR. You can also access previous-
ly recorded video for playback and to copy to
a storage device such as a USB flash drive.
To maintain system integrity, a firmware up-
grade can be performed when available and
access to the “Shutdown” menu to restart or
safely turn off your NVR.
Page 10
10
Click for contents
The various functions and options
available, are categorised on the lefthand side of the Menu.
Clicking each category will reveal a
number of tabs or sub-categories
that can be changed from their default setting.
To exit or access the
previous menu, rightclick the mouse.
Save changes that have been made
or restore default settings.
Menu Layout
Page 11

11
Click for contents
Camera Configuration
The camera configuration options are avail-
able in the “Display”, “Record”, “Alarm” and
“Device” menus that are accessible from the
Main Menu. You can change the resolution,
bitrate, OSD (on-screen display) position as
well as image settings for hue, brightness,
contrast and saturation. Your NVR has con-
trols for detecting motion, allowing you to
define specific areas to alert you to a poten-
tial threat in and around your home. You also
have the ability to create one or more zones
for privacy.
Page 12

12
Click for contents
Display: Live
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Channel Name: Enter a name for the camera you’ve selected. It can be up to
eight characters in length.
Show Name: Leave this enabled to display the camera name in Live View
mode, otherwise click the drop down menu to disable.
Record Time: It’s recommended to leave this enabled, as a timestamp will
be embedded on all video recordings. This allows you to easily identify when
events have occurred. You can disable this if you wish.
Date Format: Select a preferred display format (this is independent to the
date format selected for the NVR itself).
Time Format: Select a preferred display format (this is independent to the
time format selected for the NVR itself).
Refresh Rate: This setting correlates to the “Video Format” selection in the
Startup Wizard. When selecting “NTSC”, 60Hz will be displayed. When selecting “PAL”, 50Hz will be displayed.
OSD Position: Allows you to change the position of the on-screen display on
the Live View screen. Click the “Setup” button then use the mouse to reposition. Right-click the mouse then click “Save”.
Color: Click the “Setup” button to access the image adjustment tools:
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Hue: This changes the color mix of the image.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The configuration options
available allow you to name
each camera relevant to
where it has been installed
as well as the ability to adjust image settings such as
brightness and contrast. You
can also change how the
date and time format are displayed in Live View mode.
Page 13
13
Click for contents
Display: Live
Bright: This changes how light the image appears to be.
Contrast: This increases the difference between the blackest black and the
whitest white in the image.
Saturation: This alters how much color is displayed in the image.
Use the slider to adjust each setting. Click the “Default” button to reset all
settings. When finished, click the “Save” button then click “Close” to exit.
Please note: Any changes made to the image settings available will af-
fect your recordings.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 14

14
Click for contents
Display: Image Control
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
IR-CUT Mode: Lets you choose how the camera handles color and how it
manages the transition from daytime to night-time and vice versa:
GPIO Auto: This will instruct the camera to switch automatically from “Color
Mode” to “Black White mode” and vice versa. This setting will be suitable for
most camera locations.
Color Mode: This will instruct the camera to operate in color mode only. In
low light conditions, the color will be quite faint. Image clarity will also be
reduced in low-light conditions.
Black White Mode: This will instruct the camera to operate in black & white
mode only.
IR-Cut Delay: Controls the delay of the IR cut filter when transitioning from
daytime to night-time. The default setting will be suitable for most camera
locations but can be adjusted if needed. Click and hold the slider left or right
to change. The higher the number, the greater the delay.
Lens Flip: Lets you turn the image upside down.
Angle Flip: Lets you horizontally reverse the orientation of the image.
Back Light: Improves exposure of an object that is in front of a light source.
This may happen if an object is in front of a window or if a person is coming
in from the outside. The camera will pick up the natural light, therefore the
object or person in the foreground becomes dark. If the camera is mounted
in a location where this is required, click the drop down menu to enable.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
The functions available enable you to control the appearance and characteristics
of the image shown from
each camera. Each function
can be adjusted to obtain the
best possible image quality,
providing you the flexibility
to install the camera in the
most challenging of lighting
situations.
Page 15
15
Click for contents
Display: Image Control
BLC (Back Light Compensation) Level: If “Back Light” has been enabled, you
will see this option available. Click the drop down menu to select the level of
back light compensation that you would like to apply. Some experimentation
is recommended to select the best settings.
3D Noise Reduction: This function will reduce the overall noise content for
recordings done at night or in lower light conditions. In most circumstances,
the default selection will be suitable for most camera locations but can be
adjusted if needed:
Manual: Click the drop down menu and select “Manual”. Click and hold the
slider left or right to change. Just be aware that setting the value too high,
can result in a “trailing” effect (also known as motion blur) on moving objects
appearing on-screen.
WDR (Wide Dynamic Range): This function will balance out images that have
a large dynamic range. It does this by brightening dark areas and darkening bright areas. An example of this situation would be if an indoor camera
is pointing towards a window or building entrance. The image produced by
the camera during the day would be extremely washed out due to the high
brightness of the incoming light. If the camera is mounted in a location where
this is required, click the drop down menu to enable.
AGC (Automatic Gain Control): This function allows an increase in sensitivity,
enabling operation in lower light conditions. The camera will automatically
boost the gain control so that objects can be seen more clearly. Click the drop
down menu to select a level of control that you would like to apply.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
Page 16
16
Click for contents
Display: Image Control
White Balance: This function adjusts for lighting in order to make white ob-
jects appear white in photos. One of the factors that affect correct image reproduction is the light source which illuminates the scene. One of the indicators for an improper white balance setting are dark colors which appear
faded, shifted, or a completely different color altogether. If this is happening,
click the drop down menu and change this to “Manual”. If the colors appear
correctly, leave the default setting. You can also select “Indoor” if the camera
has been mounted inside a place of residence.
Manual: When selecting this mode, click and hold the red, green and blue
sliders left or right to change.
Shutter: This function controls the length of time a camera’s shutter is open
and the amount of light reaching the sensor. In low light situations, the shut-
ter needs to stay open longer in order for the sensor to receive enough light.
The default setting will be suitable for most camera locations.
Time Exposure: When selecting “Manual”, click the drop down menu to se-
lect a different exposure time. The lower the number, the slower the shutter
speed (this will create a motion blur effect). Some experimentation is recommended to select the best settings.
Defog Mode: This function extends visibility and improves video quality if
there is moderate to heavy fog or haze. The default setting will be suitable for
most camera locations. If selecting “Manual”, click and hold the slider left or
right to change.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
Page 17

17
Click for contents
Display: Privacy Zone
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Mask Area: To create a mask, click the drop down menu to enable.
Area Setup: Click the checkbox on the number of privacy masks that you
want to create. Up to four privacy masks can be created per camera.
Mask Area: Click the “Setup” button to create one or more masks (see page
18 - Creating a Privacy Mask).
This function can be used to
obscure all or part of your
image for privacy (up to four
privacy masks can be created per camera). You can also
use this to minimize false
triggers when motion is detected. Areas obscured by a
mask won’t be shown live or
recorded.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 18
18
Click for contents
Creating a Privacy Mask
1. Depending on the number of masks that you want to create, each mask
will be numbered. To reposition the mask, click and hold the mask number
then move the mask to the desired location.
2. To resize the mask, click and hold the bottom right corner of the mask then
resize to the desired size. You can reposition and resize each mask to overlap
each other.
In the example provided on the left, two masks have been created to block
out cars and pedestrians adjacent to the front yard of the house. This will
minimise false triggers and block movement that is not relevant to entry via
the front entrance.
3. When finished, right-click to exit then click “Save” to apply. Areas obscured
by a mask won’t be shown live or recorded (see below left).
To remove a mask, uncheck the relevant checkbox next to “Area Setup” then
click “Save” to apply.
CH1
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
1
2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMFront Yard
Click and hold here to
reposition the mask to
the desired location.
Click and hold here to
resize the mask to the
desired size.
Page 19

19
Click for contents
Record: Mainstream
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Resolution: By default the recording resolution is automatically selected to
match the capabilities of the provided cameras. Lower resolutions are available to select if required.
FPS: The number of frames per second (fps) that your NVR will record. The
default is 15fps, however you can change this if needed. In the HomeSafe
View app, you can select “Mainstream” in Live mode to view your cameras.
Lower the frame rate if you’re having issues streaming to your mobile device
(lowering the frame rate to 6fps for example, will reduce the bandwidth required without sacrificing image quality).
Video Encode Type: Your NVR utilizes two encoding methods to record vid-
eo. The default method of compression is H.265. This will result in less hard
drive space used when recording (before older videos are automatically overwritten) and will consume less bandwidth when using the remote playback
feature in the HomeSafe View app. The second method of compression is
H.264. This is a commonly used format for recording and compressing video
and is used in Blu-ray players and to broadcast TV signals. If visual quality is
of importance, change this to H.264, otherwise leave the default selection.
Bitrate Control: CBR (Constant Bitrate) utilises a fixed bitrate and band-
width to record video. This means your NVR will use the same number of bits
throughout the entire recording, regardless of what is happening on-screen.
VBR (Variable Bitrate) utilises a bitrate that will increase or decrease, depending on how complex the scene is, to record video.
(continued on next page)
The functions available allow
you to change the resolution,
frame rate and bitrate for
each camera connected. By
default the recording resolution, frame rate and bitrate
are automatically selected to
fit in with the capabilities of
the provided cameras, however you can change them if
required.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 20
20
Click for contents
Record: Mainstream
Which method should I choose? Scene complexity can vary significantly over
several hours of recorded video, and the bitrate you select for recording will
have an effect on image quality, bandwidth consumption, and hard drive storage. A complex scene with moving action, such as traffic on a city street, or a
scene with a lot of contrasting colors, will affect image quality and bandwidth
consumption more than a less complex scene with little action or movement.
CBR: This is the default method of control that your NVR will use to record
video. If you have cameras placed in high traffic areas, CBR is the recommended control method. As the bitrate is fixed, the image quality will be consistent throughout the entire recording.
VBR: If you have cameras placed in low traffic areas, VBR is the recommend-
ed control method. As the bitrate is variable, your NVR can use a lower bitrate
if there is little to no movement detected. This will result in a lower recording
size as well as a lower bandwidth requirement.
When choosing VBR, you can select the recording quality that will define the
variable bitrate used. You can select from lowest to highest.
Bitrate Mode: You have the choice of selecting a predefined or user-defined
bitrate. For most instances, the default selection will be suitable.
Bitrate: The amount of data that your NVR will use to record video. The high-
er the bitrate, the more space each recording will consume on the hard drive.
The default bitrate is 4096Kbps. Change the bitrate if you’re having issues
streaming to your mobile device via the HomeSafe View app (when selecting
“Mainstream” in Live mode to view your cameras).
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 21

21
Click for contents
Record: Mainstream
Decreasing this will consume less bandwidth when streaming.
Please note: Selecting the appropriate recording settings is dependent
on camera location, lighting conditions and the level of quality required.
Some experimentation is recommended to select the best settings.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 22

22
Click for contents
Record: Substream
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Resolution: The default resolution is 1280 x 720. You can select a lower res-
olution if you’re having issues streaming to your mobile device via the HomeSafe View app (especially when viewing multiple cameras).
FPS: The number of frames per second (fps) that your NVR will process when
streaming to your mobile device and computer via HomeSafe View. For most
instances, the default frame rate (15fps) will be suitable. This is especially
the case for cameras that monitor medium to high traffic areas and will result in smoother motion, but just be aware this will increase the bandwidth
required. You can lower this if monitoring low traffic areas.
Video Encode Type: Your NVR utilizes two encoding methods to record vid-
eo. The default method of compression is H.265. This will result in less hard
drive space used when recording (before older videos are automatically overwritten) and will consume less bandwidth when using the remote playback
feature in the HomeSafe View app. The second method of compression is
H.264. This is a commonly used format for recording and compressing video
and is used in Blu-ray players and to broadcast TV signals. If visual quality is
of importance, change this to H.264, otherwise leave the default selection.
Bitrate Control: Change this to VBR. This will result in a lower recording size
as well as a lower bandwidth requirement. You can select the recording quality that will define the variable bitrate used, from lowest to highest.
Bitrate Mode: You have the choice of selecting a predefined or user-defined
bitrate. For most instances, the default selection will be suitable.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The functions available allow you to control how video
is streamed to your mobile
device and computer using
the HomeSafe View app and
software. You can also click
“Stream switch” to change
to Substream in Live View
mode. You can change the
resolution, frame rate, bitrate control and bitrate if
you’re having issues streaming live video from your NVR.
Page 23

23
Click for contents
Record: Substream
Bitrate: The amount of data that your NVR will use to stream video to your
mobile device. For cameras that monitor medium to high traffic areas, increase the bitrate to add more detail to the camera’s image, but just be aware
this will increase the bandwidth required. Increase the bitrate in small doses
until you are satisfied with the image quality.
Please note: When streaming live video, the overall quality is dependent
on your internet connection and the Substream settings utilised. This is
important to note when streaming multiple cameras at the same time.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 24

24
Click for contents
Record: Mobilestream
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Enable: It’s strongly recommended leaving this option enabled as there is no
benefit if it is disabled (if disabled, Substream will be used to stream video).
Resolution: The default resolution is 640 x 480. You can select a lower resolu-
tion if you’re having issues streaming to your mobile device via the HomeSafe
View app (especially when viewing multiple cameras).
FPS: The number of frames per second (fps) that your NVR will process
when streaming to your mobile device via the HomeSafe View app. For most
instances, the default frame rate will be suitable. Change this to 10fps or
15fps for cameras that monitor medium to high traffic areas. This results in
smoother motion, but just be aware this will increase the bandwidth required.
Video Encode Type: Your NVR utilizes two encoding methods to record vid-
eo. The default method of compression is H.265. This will result in less hard
drive space used when recording (before older videos are automatically overwritten) and will consume less bandwidth when using the remote playback
feature in the HomeSafe View app. The second method of compression is
H.264. This is a commonly used format for recording and compressing video
and is used in Blu-ray players and to broadcast TV signals. If visual quality is
of importance, change this to H.264, otherwise leave the default selection.
Bitrate Control: Change this to VBR. This will result in a lower recording size
as well as a lower bandwidth requirement. You can select the recording quality that will define the variable bitrate used, from lowest to highest.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Mobilestream is the default control method used to
stream video to your mobile
device and computer using
the HomeSafe View app and
software. You can change
the resolution, frame rate,
bitrate control and bitrate if
you’re having issues streaming live video from your NVR.
Page 25
25
Click for contents
Record: Mobilestream
Bitrate Mode: You have the choice of selecting a predefined or user-defined
bitrate. For most instances, the default selection will be suitable.
Bitrate: The amount of data that your NVR will use to stream video to your
mobile device. For cameras that monitor medium to high traffic areas, increase the bitrate to add more detail to the camera’s image, but just be aware
this will increase the bandwidth required. Increase the bitrate in small doses
until you are satisfied with the image quality.
Please note: When streaming live video, the overall quality is dependent
on your internet connection and the Mobilestream settings utilised. This
is important to note when streaming multiple cameras at the same time.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 26

26
Click for contents
Alarm: Motion
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Enable: If for some reason motion detection is not required, you have the
option to disable it.
Buzzer: When motion has been detected, you can enable the NVR’s buzzer to
alert you for a predetermined amount of time.
Sensitivity: This option allows you to change the sensitivity level. The higher
the number, the more sensitive your NVR will be when detecting motion. For
most instances, the default selection will be suitable, however it’s recommended to conduct a test to see if the sensitivity level is correct for the camera’s location (see page 29 - Motion Detection Tips).
Area: Click the “Setup” button to change the default motion detection area.
The entire view of the camera is enabled for motion detection, however you
can select certain areas if you wish (see page 28 - Motion Detection Setup).
Post Recording: This option instructs your NVR to record for a set period of
time after an event has occurred. For most instances, the default selection
will be suitable, however you can change this if you wish.
Latch Time: If you have an alarm device connected to the alarm output (such
as a siren), you can control how long it will be active for when motion has
been detected. Click the drop down menu and adjust accordingly.
Alarm Out: Click the checkbox to enable the alarm output when motion has
been detected.
(continued on next page)
When motion has been detected by one or more cameras, your NVR will alert you
to a potential threat at your
home. It does this by sending you an email alert with an
attached snapshot from the
camera to use as a reference
and enabling the NVR’s buzzer (if enabled). You also have
the option to copy snapshots
to the cloud via Dropbox.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 27

27
Click for contents
Alarm: Motion
Show Message: When motion has been detected, the motion icon will appear
on-screen. Click the checkbox if you want to disable this.
Send Email: Click the checkbox to enable your NVR to send an email alert
when motion has been detected.
Full Screen: Click the checkbox if you would like to view the camera full
screen in Live View mode when motion has been detected.
Send to Cloud: Click the checkbox to copy snapshots to the cloud via Dropbox
(see page 62 - Device: Cloud).
Record Channel: This option instructs your NVR to trigger additional camer-
as to start recording when motion has been detected. Click the checkbox to
select all cameras or click on the individual camera number that you want to
trigger for recording.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 28

28
Click for contents
Motion Detection Setup
1. Place the mouse inside the cell or square surrounded by a yellow border (as
illustrated on the left). Press and hold the left mouse button, click and drag
to the bottom right-hand corner then release the mouse. This will delete the
default motion detection area.
2. To create a new motion detection area, select the cell or square that you
want to start at. Press and hold the left mouse button, click and drag to select
the area that you want to create then release the mouse.
3. Multiple areas can be created. Each individual cell or square can be enabled
to detect motion. The same action also applies to delete an area that has been
created.
In the example provided, a motion detection area has been created for the
front yard but excludes objects such as trees as well as cars and pedestrians
adjacent to the front yard of the house. Anyone who walks along the path via
the front entrance and approaches the front door will be detected.
Movement outside of the motion detection areas will not be detected so will
not trigger recordings or event notifications.
4. Right-click the mouse to exit. Adjust the sensitivity if required.
5. Click the “Save” button to save changes made.
To delete the default
motion detection area,
place your mouse here.
Each individual cell or
square can be enabled
to detect motion.
Page 29

29
Click for contents
Motion Detection Tips
Placement of the cameras
1. Place cameras so they are facing areas where people have to walk through to approach your home
regardless of where they are headed. A good idea is to place a camera overlooking your front door
to capture an image of anyone approaching it for later reference. This is great if you have parcels
delivered to your door or if the potential burglar knocks or rings the doorbell to see if anyone is home.
2. Walk around your house and assess where intruders are most likely to approach to enter, and what
path they would take. Most burglars enter the home through a front or back door, so it’s advisable
to place the cameras near those areas so that you get the best amount of detail of anyone who
approaches.
3. When installing cameras outside, it’s important to keep your front and backyard as well-lit as
possible for ideal night vision and the ability to detect motion. It’s common for intruders to enter a
home through an unlocked garage or by using a garage door opener in an unlocked car located in
the driveway. Positioning your cameras to overlook cars in the driveway and similar locations can be
very useful.
Avoiding False Triggers
1. A tree, shrub or foliage that is blown by the wind - angle the camera so wind-blown objects are out
of the camera’s view or use the camera motion detection area settings to exclude these areas from
detection.
2. People moving along sidewalks or streets that are close to your home, aim your cameras and use
the motion detection area settings to ensure only legitimate threats are triggering events.
3. Vehicles moving in the background - angle the camera so as to avoid movement in the background
or use the motion detection area settings to stop detection of cars in the street.
4. Movement or light reflected off smooth surfaces such as glass - adjust the sensitivity level and/or
avoid pointing the camera directly at glass surfaces.
The red cameras illustrated (see above) are your
primary locations. Place your cameras close to
the front door, back door, garage entrance and
overlooking the backyard.
The blue cameras illustrated are your secondary
locations. If your NVR includes additional cameras, place these at the front entrance inside the
home, the front of the house (this could overlook
the front garden or driveway), a side gate or if you
have multiple entrances to the backyard.
Page 30

30
Click for contents
Device: PTZ
If you have a compatible PTZ camera connected to your NVR, you can use the
PTZ controls to move the camera as well as the ability to zoom into an object
and to control the level of focus (if available). You can create multiple preset
positions, which can be recalled to focus the camera’s view to a different position. Cruise mode can also be used to move the camera to different preset
positions that have been created.
To configure your PTZ camera, consult the instruction manual included with
your device then match those settings here.
For instructions on how to control your PTZ camera and creating preset positions (see page 31 - Controlling your PTZ Camera).
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 31

31
Click for contents
Controlling your PTZ Camera
To control your PTZ camera, in Live View mode click on the channel the camera is connected to then click the “PTZ” button located on the camera toolbar. The channel will go full screen and the PTZ controls will be visible (as
shown on the left).
1. If you have multiple PTZ cameras connected, click this to select a different
camera.
2. Click this to start cruise mode (preset positions must be created first).
Cruise mode instructs your NVR to automatically move the camera according to the preset positions that have been created. Click again to stop cruise
mode.
3. Adjust the speed control to alter how fast or slow the camera will pan or
tilt. Move the slider to decrease or increase the speed.
4. Click this to access the Preset panel. This allows you to create multiple
preset positions and to access the camera’s on-screen display. Click again
to close.
5. This allows you to zoom into an object and to control the level of focus (de-
pending on the camera you have, the iris control may not be available).
6. Click the directional buttons to move the camera in the direction selected
(the middle button has no function).
For instructions on how to create a preset and to access the camera’s onscreen display (see page 32 - Creating a Preset).
To move the PTZ con-
trols, click and hold then
reposition it.
The 7450 series supports the Onvif protocol, allowing connection of nonSwann PTZ compatible cameras (some functions may not be available).
1 2 3
4
56
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
Page 32

32
Click for contents
Creating a Preset
Creating a Preset
→ To create a preset, use the PTZ controls to move the camera to the de-
sired focal position. The zoom and focus controls can also be used. Use
the speed control to alter how fast or slow the camera will move.
→ Change the length of time the camera will stay at this position.
→ Click the “Set” button to create the preset. You will notice that the preset
position will increase each time a preset is created. The total number of
presets created will also be displayed. Up to 255 different preset positions
can be created.
→ Repeat these steps to create multiple preset positions. When finished,
click the “Save” button to save. Right-click to exit.
→ Click the “Start Cruise” button to continually cycle through each preset
created. Click again to stop.
1. Each preset position will have a different number assigned to it. To recall
a particular position, click the dialogue box, input a number then click “GO
TO”. The camera will then move to that particular position. When creating
a preset position, you may want to make note which position is assigned to
each number.
2. Click the dialogue box to change the length of time (in seconds) the camera
will stay at a particular position, before moving to the next position.
3. Click this to go to a particular preset position.
4. Click this to create a preset.
5. Click this to save any changes made.
6. Click this to clear a preset.
Accessing your Camera’s On-screen Display
→ Click the preset position dialogue box (1) then click the backspace button
twice. Enter “95”, click the enter button then click the “GO TO” button.
→ To navigate the on-screen display, click the up and down directional but-
tons. The hyphen indicates which option or setting has been selected.
→ Click the right directional button to confirm selection. Click the left and
right directional buttons to change settings within sub-menus.
→ Consult the camera’s instruction manual for information about the func-
tions available in the on-screen display.
Please note: If the above instructions don’t work for your camera, try
pressing the Iris “+” button to access the on-screen display.
CH2
09/05/2017 04:30:15 PMBack Yard
56
1
2
3
4
5 6
Page 33

33
Click for contents
Display: IP Channel
This function is an advanced feature that is used to manage the cameras
connected directly to your NVR as well as compatible IP cameras connected
to your router. In most circumstances, the functions available here will not be
needed for general use of your NVR.
When adding one or more cameras connected to your router, you need to
change Switch Mode to manual (see page 53 - Network: Switch).
1. Click this button “User-defined add” to add your network connected cam-
era.
2. After a short moment, your NVR will detect the camera and it will appear
as shown in the screenshot above-right. Click the checkbox to select.
3. Input the password (if required) and click the drop down menu to select the
channel that you would like to add the camera to.
4. Click this button “Add selected” to add the camera. A green status button
will appear indicating successful connection. Click the “Close” button to finish.
Please note: If you see “Off-line” in Live View mode for the camera that
you have added, this indicates that either a setting has changed (such as
password), or it has been physically disconnected from your router.
1
2
4
3
Page 34

34
Click for contents
Recording Configuration
The recording configuration options are avail-
able in the “Record” and “Capture” menus
that are accessible from the Main Menu. From
here you can access and change the default
recording schedule (presented as a 24 hour 7
days a week grid and is color coded) for each
camera connected. You can also enable and
set a schedule for your NVR to take a snap-
shot each time an event occurs.
Page 35

35
Click for contents
Record: Record
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Record Switch: When disabled, your NVR will detect motion but it will not
record (manual record is also disabled).
Stream Mode: By default, your NVR will record both Mainstream and Sub-
stream video (known as DualStream). This is especially useful when using
“Playback” mode via the HomeSafe View app, as Substream can be selected. This requires less bandwidth to stream the video from your NVR to your
mobile device. Mainstream video is used for playback when using your NVR
directly. If remote playback is not required, you can select Mainstream recording only.
PreRecord: Allows your NVR to record for a number of seconds before an
event occurs. It’s recommended to leave this enabled.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 36

36
Click for contents
Record: Schedule
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Normal: Your NVR will constantly record for a set period of time.
Motion: Your NVR will only record when motion has been detected from one
or more cameras.
Alarm: Your NVR will only record if one or more alarm sensors (connected to
the alarm inputs on your NVR) have been triggered.
Each square represents 30 minutes. Using the mouse, select the desired recording mode then click on a particular square to change or click and drag
the mouse over the squares corresponding to your desired time period. The
same action can also be applied if Normal, Motion or Alarm recording is not
required (on one or more sections that have recording enabled).
In the above example, a Motion recording schedule has been created for
12:00 a.m. to 06:00 p.m. and a Normal recording schedule for 06:00 p.m. to
12:00 a.m. Sunday to Saturday.
To search for and play previous Normal, Motion and Alarm recordings (see
page 40 - Search: General).
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
By default, a Motion schedule
has been enabled for each
camera connected, however
you can change the schedule to suit your needs. The
schedule is presented as a
24-hour 7 days a week grid
and is color coded to represent the event type.
Page 37

37
Click for contents
Capture: Capture
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Auto Capture: When enabled, your NVR will take a snapshot each time an
event occurs.
Stream Mode: Leave the default selection. This will save each snapshot at
the camera’s native resolution.
Normal Interval: The length of time that must elapse before a snapshot is
taken. For example, when setting a Normal capture schedule, a snapshot
will be taken every 5 seconds using the default selection. Adjust accordingly.
Alarm Interval: When setting a Motion capture schedule, a snapshot will be
taken each time motion has been detected according to the interval selected.
Adjust accordingly.
Manual Capture: Enable this feature if you would like to manually take a
snapshot using the Manual Capture button on the camera toolbar.
As this is an added feature, a capture schedule is not enabled by default. To
enable this (see page 38 – Capture: Schedule).
Please note: The Capture Schedule, Normal Interval and Alarm Interval
options are not available on the 4 channel model. Snapshots will be au-
tomatically taken when enabled.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
As an added feature, you can
enable and set a schedule for
your NVR to take a snapshot
each time an event occurs.
This is particularly useful for
finding motion events quickly
and can also be used for different purposes such as time
lapse photography.
Page 38

38
Click for contents
Capture: Schedule (8 channel model)
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Each square represents 30 minutes. Using the mouse, select the desired
capture mode then click on a particular square to change or click and drag
the mouse over the squares corresponding to your desired time period. The
same action can also be applied if Normal, Motion or Alarm capture mode is
not required (on one or more sections that have been enabled).
In the above example, a Motion capture schedule has been created for 12:00
a.m. to 06:00 p.m. and a Normal capture schedule for 06:00 p.m. to 12:00
a.m. Sunday to Saturday.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 39

39
Click for contents
Playback & Backup
The Search function gives you the ability to
search for and play previously recorded vid-
eos as well as snapshots that are stored on
your NVR’s hard drive. You have the choice
of playing video that matches your record-
ing schedule, manual recordings or motion
events only. The Backup function gives you
the ability to save important events (both vid-
eo and snapshots) to a USB flash drive.
Page 40

40
Click for contents
Search: General
1. Click the drop down menu to select the month that you would like to search
on.
2. Click the drop down menu to select the year that you would like to search
on.
3. Click the drop down menu to select from one or all cameras that you would
like to search on and display for playback.
4. Click the drop down menu to select the video type that you want to search
on. In most circumstances “Motion” would be selected but you can leave this
on “All” if you want to search for all video types. Adjust accordingly.
5. Click the “Search” button to filter your search criteria.
6. The orange triangles indicate there are recordings on those particular
dates that match your search criteria. Click on a date that you want to select
for playback.
7. When selecting all cameras for playback, this will indicate the channels
that match your search (each channel will be highlighted in blue with an orange triangle). You can leave the default selection or you can select specific
cameras for playback (click the checkbox then select the channel required).
8. You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific start time.
9. You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific end time.
10. Click the “Play” button to start playing.
You will now see the playback interface (see page 41 - Playback Interface).
The orange triangles indicate there are recordings available on those
particular dates.
1098
7
6
21
3 4 5
Page 41

41
Click for contents
Calendar: You can select a different date without
exiting to the previous screen.
Playback Mode: You have the option of selecting
a different playback mode (a message will appear
on-screen when changing modes).
Camera List: Select from one or more cameras to
display for playback. The blue icon indicates which
cameras match your search criteria.
Time Period: This represents the time period that
is visible. Click on a different time period to zoom
in for precise control or to zoom out.
1. Click this to hide the playback interface so you
can maximise your viewing area. Right-click to restore.
2. From left to right, these are your reverse, slow
motion, play, pause, stop and fast forward con-
trols. Subsequent presses of the reverse, slow
motion and fast forward buttons will increase the
speed of each action.
3. Select a camera, click this button then click and
drag an area to get a close up view. Use the picture-in-picture screen to select a different area to
view. Right-click to exit.
(continued on next page)
Playback Interface
12/07/2017 04:41:04 PMFront Yard 12/07/2017 04:41:04 PMBack Yard
12/07/2017 04:41:04 PMStaircase 12/07/2017 04:41:04 PMSide Gate
Play
Click and hold the timeline
then drag left or right to
the desired time period (if
the video is playing, press
the stop button first).
Click to close
Video TypeTime Period
1 2
3
Camera List
Calendar
Playback Mode
Timeline
Click on a camera to select it (a surrounding blue
square is shown).
Page 42

42
Click for contents
4. This button allows you to edit the video by set-
ting mark in and out points on your video which
you can then copy to a USB flash drive. When you
have selected a video to play, press this button at
the mark in point and press it again at the mark
out point. Press the button again to save (a disk
icon will be shown). For the backup type, leave
the default selection or change to AVI or MP4 for
wider playback compatibility on your computer
(we recommend VLC media player software, you
can download a free copy from www.videolan.org).
Insert a USB flash drive to your NVR then click
“Save”. You have the choice of formatting the flash
drive or creating a new folder if required. Click
“OK” to save then click “Close” when finished.
5. Click this button to mute or unmute the audio.
6. Click and hold the slider left or right to change
the volume level (the cameras included with your
NVR do not record audio).
Video Type: Indicates the video type on the time-
line.
Playback Interface
Play
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMFront Yard
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMSide Gate
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMBedroom
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMBack Yard
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMBack Yard
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMLiving Room
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMStaircase
07/08/2017 10:18:44 AMCourt Yard
When selecting five or
more cameras for playback, each camera is
represented as a single
recording on the timeline.
Click to close
Video TypeTime Period
Camera List
Calendar
Playback Mode
Timeline
4
5
6
Double-click a camera
to view full screen. Double-click again to return.
Page 43

43
Click for contents
Search: Events
This function can be used to search, play and copy events to a USB flash drive.
Date: Click the calendar icon to select the month, year and date that you
would like to search on.
Time: You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific start and end time.
Channel: Click the drop down menu to select from one or all cameras that
you would like to search on.
Type: Leave the default selection or click the drop down menu to select the
event type.
Quick Backup: Click this to copy all or selected events that match your search
criteria.
Search: Click this to display a list of events that match your search criteria (as
shown above). Double-click an event to play (the event will play full screen).
Click the checkbox next to each event to select it.
Backup: Click this to copy selected events. For the backup type, leave the
default selection or change to AVI or MP4 for wider playback compatibility on
your computer (we recommend VLC media player software, you can download a free copy from www.videolan.org). Insert a USB flash drive to your NVR
then click “Save”. You have the choice of formatting the flash drive or creating
a new folder if required. Click “OK” to save then click “Close” when finished.
Close: Click this to exit.
Page 44

44
Click for contents
Search: QuickShot
This function can be used to search, play and copy snapshots to a USB flash
drive.
Date: Click the calendar icon to select the month, year and date that you
would like to search on.
Time: You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific start and end time.
Channel: Click the drop down menu to select from one or all cameras that
you would like to search on.
Type: You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
select the type of snapshot you would like to search on.
Quick Backup: Click this to copy all snapshots matching your search criteria.
Search: Click this to display a list of snapshots that match your search cri-
teria (as shown above). Double-click a snapshot to display it full screen.
You can also play a slideshow (see page 45 - Playing a Slideshow). Click the
checkbox next to each event to select it (a maximum of 5000 snapshots can
be displayed at any one time).
Backup: Click this to copy selected snapshots. Insert a USB flash drive to
your NVR then click “Save”. You have the choice of formatting the flash drive
or creating a new folder if required. Click “OK” to save then click “Close”
when finished.
Close: Click this to exit.
Page 45

45
Click for contents
1. Click this to play the slideshow in reverse.
2. Click this to play the slideshow.
3. Click this to stop the slideshow.
4. Click this to display the previous snapshot or
group of snapshots.
5. Click this to display the next snapshot or group
of snapshots.
6. Click this to view a single snapshot at a time.
7. Click this to view four snapshots at a time.
8. Click this to view eight snapshots at a time.
Right-click to exit.
Playing a Slideshow
Play
12/05/2017 10:36:44 AMFront Yard
12/05/2017 10:36:45 AMSide Gate
12/05/2017 10:36:50 AMBedroom
12/05/2017 10:36:44 AMBack Yard
12/05/2017 10:36:49 AMBack Yard
12/05/2017 10:36:50 AMLiving Room
12/05/2017 10:36:44 AMStaircase
12/05/2017 10:36:49 AMCourt Yard
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Page 46

46
Click for contents
Search: QuickReview
QuickReview allows you to play multiple normal recordings and motion
events simultaneously from a single channel. With normal and event recordings, the video is divided evenly depending on the split-screen mode that has
been selected. For example, if the video is an hour long and you have selected
Split-screens x 4, each split-screen will play for 15 minutes.
1. Click the drop down menu to select the month that you would like to search
on.
2. Click the drop down menu to select the year that you would like to search
on.
3. Click the drop down menu to select the camera that you would like to dis-
play for playback (only one camera can be selected).
4. Click the drop down menu to select the video type that you want to search
on. In most circumstances “Motion” would be selected but you can leave this
on “All” if you want to search for all video types. Adjust accordingly.
5. Click the “Search” button to filter your search criteria.
6. The orange triangles indicate there are recordings on those particular
dates that match your search criteria. Click on a date that you want to select
for playback.
7. You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific start time.
8. You can leave the default selection or you can click the dialogue box to
enter a specific end time.
9. Up to eight split-screens can be enabled for playback.
10. Click the “Play” button to start playing.
(continued on next page)
109
8
6
21
3 4 5
7
Page 47

47
Click for contents
Split-screens: Click the drop down menu to se-
lect the preferred split-screen mode for playback.
Time Period: This represents the time period that
is visible. Click on a different time period to zoom
in for precise control or to zoom out.
1. Click this to hide the playback interface so you
can maximise your viewing area. Right-click to restore.
2. From left to right, these are your reverse, slow
motion, play, pause, stop and fast forward controls. Subsequent presses of the reverse, slow
motion and fast forward buttons will increase the
speed of each action.
3. Select a particular split-screen, click this but-
ton then click and drag an area to get a close up
view. Use the picture-in-picture screen to select a
different area to view. Right-click to exit.
(continued on next page)
QuickReview Playback
12/07/2017 04:52:20 PMFront Yard 12/07/2017 05:29:41 PMFront Yard
Play
12/07/2017 05:51:13 PMFront Yard 12/07/2017 06:39:48 PMFront Yard
Within the split-screen
selected, you can select
a different time period on
the timeline.
Click to close
Video TypeTime Period
1 2
3
Timeline
Split-screens
Click on a split-screen to
select it (a surrounding
blue square is shown).
Page 48

48
Click for contents
4. This button allows you to edit the video by set-
ting mark in and out points on your video which
you can then copy to a USB flash drive. When you
have selected a video to play, press this button at
the mark in point and press it again at the mark
out point. Press the button again to save (a disk
icon will be shown). For the backup type, leave
the default selection or change to AVI or MP4 for
wider playback compatibility on your computer
(we recommend VLC media player software, you
can download a free copy from www.videolan.org).
Insert a USB flash drive to your NVR then click
“Save”. You have the choice of formatting the flash
drive or creating a new folder if required. Click
“OK” to save then click “Close” when finished.
5. Click this button to mute or unmute the audio.
6. Click and hold the slider left or right to change
the volume level (the cameras included with your
NVR do not record audio).
Video Type: Indicates the video type on the time-
line.
QuickReview Playback
12/07/2017 04:52:20 PMFront Yard 12/07/2017 05:29:41 PMFront Yard
Play
12/07/2017 05:51:13 PMFront Yard 12/07/2017 06:39:48 PMFront Yard
Click to close
Video TypeTime Period
4
5
6
Timeline
Split-screens
Page 49

49
Click for contents
System Configuration
The options available give you complete con-
trol on how your NVR is configured and how
it operates. Some of the options such as dis-
play resolution, time zone, email configura-
tion, Daylight Saving and password creation
are configured during the Startup Wizard. For
experienced network users, your NVR pro-
vides options that can be configured to suit
your particular requirements. You can also
perform a firmware upgrade when available.
Page 50

50
Click for contents
Display: Output
Video Output: This option cannot be changed.
SEQ Mode: Select how many video channels you would like to display when
your NVR is in sequence mode (select from one, four or six cameras).
SEQ Dwell Time: Enter in seconds the maximum length of time you would
like to display a video channel in sequence mode before displaying the next
video channel (300 seconds is the maximum).
VGA/HDMI Resolution: Select a display resolution that is suitable for your
TV. 1920 x 1080 will suit most TVs. If you have a 4K capable TV, you can select
either 2K (2560 x 1440) or 4K (3840 x 2160) to take advantage of the higher
resolution that your TV provides.
Transparency (8 channel model): Click and hold the slider left or right to
change how transparent the Menu Bar and Main Menu will appear on-screen.
Adjust accordingly.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 51

51
Click for contents
Network: Network
PPPoE: Allows your NVR to be directly connected to a DSL modem. When
selecting this option, you need to input the user name, password and DNS
settings for your internet service provider.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Your router will automatically
assign an IP address to each device connected to your network. This is enabled by default.
Static: All devices on your network have their IP address manually defined.
Server Port: This port number is used by your NVR to send information
through. The default number will work in most situations.
HTTP Port: This port number is used to log into your NVR from a remote lo-
cation. The default number will work in most situations.
The following five options can be changed when selecting Static:
IP Address: Each device on your network must have a unique IP address. A
typical address might be “192.168.1.24” or something similar.
Subnet Mask: This allows the flow of network traffic between hosts to be
segregated based on a network configuration. A typical address might be
“255.255.255.0” or something similar.
Gateway: This allows your NVR to connect to the internet. This is typically the
same IP address as your modem or router.
DNS (Domain Name System)1/2: Input the DNS settings for your internet
service provider.
(continued on next page)
As SwannLink Peer-to-Peer
technology is utilised to communicate with your network
and mobile device, configuration of the network settings is not required. If you
have networking expertise
and require specific settings
for your network, you do have
the ability to change them.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 52

52
Click for contents
Network: Network
UPNP: A network protocol designed to allow network connected devices to
automatically configure the router for the purposes of remote access. This is
not required when using UID to access your NVR via the HomeSafe View app.
You can enable UPNP if required.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 53

53
Click for contents
Network: Switch
Switch Mode: When adding one or more cameras connected to your router,
you need to change this to Manual Mode. Click the drop down menu and adjust accordingly.
Please note: When changing back to Auto Mode, any camera or camer-
as that you have added in Manual Mode, will be deleted.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 54

54
Click for contents
Network: Email
Email: Click “Enable” to input your email details.
Encryption: Leave this on “Auto”. This ensures your NVR will always use the
correct encryption for your email provider.
SMTP Port: Gmail input 00587. Outlook input 00587.
SMTP Server: Gmail input “smtp.gmail.com”. Outlook input “smtp.live.com”.
User Name: Input the email user name for the account you created.
Password: Input the email password for the account you created. Click the
“show” checkbox if you would like to hide your password.
Sender: Input a name for your email account, for example NVR8-7450.
Receiver1: Input the email address that you want to send email alerts to.
Interval: This is the length of time that must elapse after your NVR sends an
email alert before it will send another. Adjust accordingly.
Test Email: Click to verify the information is correct then click “OK”. A mes-
sage will appear if the test has been successful. Click “OK” to continue.
If the test email is not in your inbox, check your junk or spam folder.
Email not working? Please try the following:
1. Check that your email user name and password are correct.
2. Located at the back of your NVR, you should see one or two flashing LEDs
(above the Ethernet port). If you don’t see this, disconnect then reconnect the
Ethernet cable or try a different port on your router.
3. Search “less secure apps” at support.swann.com.
Why do I need to create an email for
my NVR? So your NVR can send you
email alerts and to send you a password reset request if you have forgotten your password.
The following email providers are supported - Gmail
gmail.com and Outlook outlook.com. On your computer
or mobile device, go to the
relevant website to create an
account. When finished, input those details here.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 55

55
Click for contents
Network: Email Schedule
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to edit.
Motion: If email alerts have been enabled for motion detection, you can
change the schedule on when your NVR can send those alerts. For example, you may only want to receive motion alerts during the day but not in the
evening. A different schedule can be created for each camera.
Alarm: Your NVR will send an email alert when it detects an alarm event. Set
a schedule for this if you have alarm sensors connected to your NVR.
Exception: There are three event types that your NVR will detect as an excep-
tion - no space left on the hard drive, a hard drive error and if one or more
channels has lost the feed from its camera (see page 69 - Advanced: Events).
It’s recommended to leave the default schedule in place in case there is an
exception that you need to be alerted to.
Each square represents 30 minutes. Using the mouse, click on a particular
square to change or click and drag the mouse over the squares corresponding to your desired time period.
In the above example, a Motion email alert schedule has been created for
08:00 a.m. to 07:00 p.m. Monday to Friday. Motion alerts outside of these
times will not be emailed. A 24/7 Alarm and Exception email alert schedule
is enabled by default.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Use the “Copy” function to
apply all settings to the other
cameras.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 56

56
Click for contents
Network: DDNS
Go to www.swanndvr.com and click the “Registration” button. Follow the
prompts to create your account.
DDNS: Click the drop down menu to enable.
Server: SWANNDVR is automatically selected.
Domain: Enter the domain name that is hosted on your account. For exam-
ple, (username.swanndvr.net).
User: Enter the username (host name) for your account.
Password: Enter the password for your account.
Test DDNS: Click this button then click “OK” to confirm your account details.
After a short moment you will see “DDNS test is successful!”. Click “OK” to
close.
Prior to developing our
SwannLink Peer-to-Peer
technology, our SwannDNS
service was used to connect
to your NVR remotely. This
service is still active and we
recommend creating an account as a means of backup.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 57

57
Click for contents
Network: RTSP
The following instructions are for the VLC media player software (you can
download a free copy from www.videolan.org). After download, double click
the file then follow the on-screen instructions for installation.
RTSP Enable: Click the drop down menu to enable.
Verify: Leave the default selection if you would like VLC to verify your us-
ername and password for access, otherwise click the drop down menu to
disable.
RTSP Port: The default port number will work in most circumstances.
1. On your computer, load the VLC media player software. Click “Media” then
click “Open Network Stream”.
2. Enter the IP address of your NVR (on your NVR click “Network” in the Main
Menu to display the IP address) into VLC. The following is an example of what
you need to enter - (rtsp://192.168.99.160:554/ch01/0).
rtsp://192.168.99.160: This is the IP address of your NVR.
554: This is the RTSP port of your NVR.
ch01: This represents channel 1. To display channel 2 enter ch02, etc.
0: This represents Mainstream. For Substream enter 1 instead.
3. Click “Play” then enter the user name and password (if required). You will
now see a live view image from the camera.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The RTSP function can be
used to stream a camera’s
live view image to your computer, using video streaming
software such as VLC media player. Multiple cameras
can be streamed at the same
time. You can also record
each stream if required.
Page 58

58
Click for contents
Alarm: Alarm
Alarm In: The connection that corresponds to the input you’ve connected the
sensor to. Click the drop down menu to select.
Alarm Type: Whether the sensor is Normally-Open or Normally-Close.
Please check the documentation that came with your sensor then click the
drop down menu to select the appropriate setting.
Latch Time: If you have an alarm device connected to the alarm output (such
as a siren), you can control how long it will be active for when one or more
alarm sensors have been triggered.
Buzzer: When one or more alarm sensors have been triggered, you can ena-
ble the NVR’s buzzer to alert you for a predetermined amount of time.
Post Recording: This option instructs your NVR to record for a set period of
time after an event has occurred. For most instances, the default selection
will be suitable, however you can change this if you wish.
Alarm Out: Click the checkbox to enable the alarm output when one or more
alarm sensors have been triggered.
Show Message: When one or more alarm sensors have been triggered, a
message will appear on-screen. Click the checkbox to disable this.
Send Email: Click the checkbox to enable your NVR to send an email alert
when one or more alarm sensors have been triggered.
Full Screen: Click the checkbox to view the camera full screen in Live View
mode when one or more alarm sensors have been triggered.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The functions available here
allow you to customize and
configure how you would like
your NVR to interpret from
and respond to the alarm
panel (up to eight alarm inputs and one alarm output
available) located at the rear
of your NVR.
Page 59

59
Click for contents
Alarm: Alarm
Push: Click the checkbox to send push notifications via the HomeSafe View
app (alarm notification has to be enabled within the app - see “Alarm Mode”
in the HomeSafe View manual for more information).
Send to Cloud: Click the checkbox to copy snapshots to the cloud via Dropbox
(see page 62 - Device: Cloud).
Record Channel: This option instructs your NVR to trigger additional camer-
as to start recording when one or more alarm sensors have been triggered.
Click the checkbox to select all cameras or click on the individual camera
number that you want to trigger for recording.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 60

60
Click for contents
Device: HDD
This function gives you the option of formatting your NVR’s hard drive, and it
will be listed here for selection.
Overwrite: This instructs your NVR to overwrite the oldest video files as the
hard drive becomes full. You also have the option of disabling this or selecting
the amount of days events are kept before they are overwritten. It’s recommended to leave the default selection as this prevents your NVR from running out of storage space.
Format HDD: Click the checkbox to select the hard drive then click this but-
ton to format. A message will appear noting that all data will be erased. Click
“OK” to continue.
Please note: From time to time, we recommend that you format the
hard drive. This ensures that your NVR maintains system integrity.
Connect a USB flash drive to copy events that you want to save. Remember,
formatting the hard drive erases all your recordings.
*If a new hard drive has been installed inside your NVR, you need to format
the drive before it can be used.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 61

61
Click for contents
Device: S.M.A.R.T. (8 channel model)
Whole Evaluation not passed, continue to use the disk: If for some reason
the hard drive has developed a fault (such as one or more bad sectors), you
can instruct your NVR to continue saving to the drive.
Self-check Type: There are three types available:
Conveyance: This is a very quick test that verifies the mechanical parts of the
hard drive are working.
Short: This test verifies major components of the hard drive such as read/
write heads, electronics and internal memory.
Long: This is a longer test that verifies the above as well as performing a
surface scan to reveal problematic areas (if any) and forces bad sector relocation.
When performing a test, your NVR will continue to work as normal.
In most circumstances, the information here will not be needed for general
use of your NVR, however one of our Swann Helpdesk & Technical Support
staff may ask you to access this if you call for assistance.
This function can be used to
display technical information
on the hard drive installed
inside your NVR. You can
also perform a test (there
are three types available) to
evaluate and detect potential
drive errors.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 62

62
Click for contents
Device: Cloud
Before activating the cloud function, we recommend that you create a Dropbox account using the same email address and password used for your NVR.
Go to www.dropbox.com, input your name, email address and password,
agree to the terms & conditions then click the sign up button.
Cloud Storage: Click the drop down menu to enable.
Channel: Select a camera that you would like to enable for cloud storage.
Activate Cloud: Click this to activate then click “OK” to confirm.
After a short moment, you will see a message on-screen. An activation link
has been sent to your email (the email address used to receive email alerts).
Check your email then click the link to activate. You will be taken to the Dropbox website. Click “Allow” to finalise the activation. Repeat these steps if you
would like to enable cloud storage for the other cameras available.
With the cloud function enabled, you need to instruct your NVR to send alerts
to the cloud:
1. In the Main Menu, click “Alarm”.
2. Click the drop down menu to select the camera that you enabled for cloud
storage.
3. Click the “Send to Cloud” checkbox then click “Save”.
Use the “Copy” function to apply cloud alerts to the other cameras available.
When browsing your files in Dropbox, you will see a “NVR4-7450” or “NVR87450” folder. Click this then click the folder for the camera that you enabled
for cloud storage. Your snapshots will be saved here. Click a snapshot to display.
When the “Capture” function
has been enabled, your NVR
has the ability to copy snapshots to the cloud via Dropbox. Dropbox is a free service
that allows you to easily store
and share snapshots and
always have them on hand
when you need them.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 63

63
Click for contents
System: General
Date: Click the calendar icon to change the date.
Time: Click the dialogue box to change the time. Click the drop down menu
to select AM or PM.
As NTP is enabled by default, the date and time should always remain accurate.
Date Format: Click the drop down menu to select the preferred date format.
Time Format: Click the drop down menu to select the preferred time format
(the playback interface will display in 24-hour time only).
Time Zone: Select a time zone relevant to your region or city.
Language: Select a language you would like the system menus to be dis-
played in. Multiple languages are available.
Video Format: Select the correct video standard for your country. USA and
Canada are NTSC. UK, Australia and New Zealand are PAL.
Menu Timeouts: Click the drop down menu to select the time your NVR will
exit the Main Menu when idle. You can also disable this by selecting “OFF”
(password protection will be temporarily disabled).
Show Wizard: Click the checkbox if you would like to display the Startup Wiz-
ard each time you turn on or reboot your NVR.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 64

64
Click for contents
System: DST
DST: If Daylight Saving applies to your time zone or region, click the drop
down menu to enable.
Time Offset: Select the amount of time that Daylight Saving has increased by
in your time zone. This refers to the difference in minutes, between Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the local time.
Daylight Saving Time: You can select how Daylight Saving starts and ends:
Week: Select the month, a particular day and time when Daylight Saving
starts and ends. For example, 2 a.m. on the first Sunday of a particular month.
Date: Select the start date (click the calendar icon), end date and time when
Daylight Saving starts and ends.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The DST (Daylight Saving
Time) function allows you to
select the amount of time
that Daylight Saving has increased by in your particular
time zone or region.
Page 65

65
Click for contents
System: NTP
NTP: This is enabled by default.
Server Address: The default time server will work in most circumstances. If
for some reason the NVR’s clock is not syncing, select a different time server.
Update Now: If for some reason the date and time are not correct, click this
button to update then click “OK” to continue.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
The NTP (Network Time Protocol) function allows your
NVR to automatically sync
its clock with a time server.
This gives it the ability to constantly have an accurate time
setting (your NVR will periodically sync automatically).
Page 66

66
Click for contents
System: Users
To change your NVR’s password, click the “Edit” button. The password has to
be a minimum of six characters and can contain a mixture of numbers and
letters. Enter your new password again to confirm.
Additional user accounts can also be enabled:
1. Select “user1” then click the “Edit” button.
2. Click the drop down menu to enable.
3. Enter a user name and password.
4. Click the “Save” button, enter the admin password then click “OK” to con-
firm.
To change permissions, click the “Permission” button then select which options you would like to enable. Click the “All” button to select all options. Click
the “Save” button then click “OK” to confirm.
Page 67

67
Click for contents
Advanced: Maintain
Default User: Admin is the default user account. If multiple user accounts
have been created, click the drop down menu to disable.
Auto Reboot: It’s recommended leaving this option enabled, as it maintains
the operational integrity of your NVR.
Reboot: Choose an appropriate day and time to reboot your NVR.
Upgrade: Click this button to upgrade the firmware from a USB flash drive.
Select the firmware file then “OK” to confirm. When the firmware upgrade
has completed, your NVR will reboot automatically.
Load Settings: Click this button to import a configuration file containing all
the settings that you have customised.
IPC Load Default: Click this button to restore the camera’s default settings.
Click the checkbox for the camera that you want to restore or click “Select
All” to select all cameras. Click “OK” to continue. A message will appear onscreen and the camera will momentarily reset. Click “Exit” to close.
Load Default: Click this button to restore your NVR’s default settings. Click
“All” then click “Save”. The Startup Wizard will appear on-screen after reboot.
Save Settings: Click this button to export a configuration file containing all
the settings that you have customised.
Reboot IPC: Click this button to reboot the camera. Click the checkbox for
the camera that you want to reboot or click “Select All” to select all cameras.
Click “OK” to continue. A message will appear on-screen and the camera will
momentarily reset. Click “Exit” to close.
(continued on next page)
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 68

68
Click for contents
Advanced: Maintain
IPC Upgrade: Click this button to upgrade the camera’s firmware from a USB
flash drive. Select the firmware file, click the checkbox for the camera that
you want to upgrade or click “All” to select all cameras then click “OK” to
confirm. When the firmware upgrade has completed, the camera will momentarily reset. Click “OK” to close. It’s recommended to reboot your NVR to
maintain operational integrity.
Please note: To restore all default settings on your NVR, you need to
restore your NVR and camera (changes to image settings are stored on
the camera).
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 69

69
Click for contents
Advanced: Events
Event Type: Select the event type that you would like to change.
Enable: Click the checkbox if you would like to disable alerts for the event
selected.
Show Message: Click the checkbox if you like to disable the on-screen mes-
sage for the event selected.
Send Email: Click the checkbox if you would like to disable email alerts for
the event selected.
Alarm Out: Click the checkbox to enable the alarm output for the event se-
lected.
Latch Time: If you have an alarm device connected to the alarm output (such
as a siren), you can control how long it will be active for when an event occurs.
Buzzer: Click the drop down menu and select the time period for the internal
buzzer to activate for the event selected.
Please note: When your NVR detects an exception, it will automatically
send an alert to the HomeSafe View app (alarm notification has to be
enabled within the app - see “Alarm Mode” in the HomeSafe View manual for
more information).
Whenever there is an event
or if your NVR displays usual
behaviour, you can be alerted
to in multiple ways such as
receiving an email, displaying
a message on-screen and
activating its internal buzzer.
There are three event types
that your NVR will detect as
an exception.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 70

70
Click for contents
Advanced: Auto Upgrade
Auto Upgrade: By default, your NVR will automatically download and install
new firmware when available. Click the drop down menu if you would like to
disable this feature.
Check for update from internet: By default, your NVR will automatical-
ly check and alert you if new firmware is available for download. Click the
checkbox if you would like to disable this feature.
Check now: Click this button to check if new firmware is available. If new
firmware is available, follow the on-screen instructions.
· Don’t forget to click “Save”
to apply settings.
· Click the “Default” button to
revert back to default settings.
· Click the “Close” button to
exit the Main Menu.
Page 71

71
Click for contents
System Status
The various status tabs give you an overview
of the various settings and options that have
been selected for your NVR to function. Each
action that your NVR performs as well as
events detected are logged, which you can
search and view. If you call our helpdesk for
assistance, our staff may ask you to access
these tabs to assist them in solving any tech-
nical issues that you may be having.
Page 72

72
Click for contents
Search: Log
Start/End Date: Click the calendar icon to select the month, year and date
that you would like to search on.
Start/End Time: You can leave the default selection or you can click the dia-
logue box to enter a specific start and end time.
Log Type: Leave the default selection or click the drop down menu to select
a specific action that you would like to search for.
Search: Click this to display a list of log files that match your search criteria.
Double-click a file to display information about that log.
Backup: Click this to copy the log files that match your search criteria. Insert
a USB flash drive to your NVR then click “Save”. You have the choice of formatting the flash drive or creating a new folder if required. Click “OK” to save
then click “Close” when finished.
Each action that your NVR
performs as well as events
detected are logged. These
log files can be searched,
viewed and copied to a USB
flash drive for safe keeping.
Page 73

73
Click for contents
System: Info
Device Name: Click the dialogue box to rename your NVR (if required).
MAC Address: You can use this as a recovery password if you have forgotten
your current password.
If you call our helpdesk for assistance, our staff may ask you to access this
tab to assist them in solving any technical issues that you may be having.
This tab displays technical
information about your NVR
as well as your device ID and
QR code. If you call our helpdesk for assistance, our staff
may ask you to access this
tab to assist them in solving
any technical issues that you
may be having.
Page 74

74
Click for contents
System: Channel Info
Displays the Mainstream, Substream and Mobilestream settings used for
each camera connected.
If you call our helpdesk for assistance, our staff may ask you to access this
tab to assist them in solving any technical issues that you may be having.
· Click the “Close” button to exit the Main Menu.
Page 75

75
Click for contents
System: Record Info
Displays the recording settings for each camera connected.
If you call our helpdesk for assistance, our staff may ask you to access this
tab to assist them in solving any technical issues that you may be having.
· Click the “Close” button to exit the Main Menu.
Page 76

76
Click for contents
Glossary
3D-Noise Filter: Is an enhanced form of digital noise reduction. The advance-
ment in technology enables noise to be filtered even more effectively from
the image, even in low light conditions.
50Hz: Is the mains frequency used in the UK, Australia and most European
countries.
60Hz: Is the mains frequency used in the United States, Canada and some
Latin American countries.
AGC (Automatic Gain Control): In low light conditions, the camera will auto-
matically boost the gain control so that people and objects can be seen more
clearly. The advantage of this technique is that your camera will produce images in much lower light conditions. The downside is that the amplification
will increase the video noise visible.
AHD: Is an analogue high definition closed-circuit television video surveil-
lance standard that uses coax cable to transmit HD video from security cameras to DVRs. AHD supports 720p and 1080p HD video resolutions.
Anti-flicker: As fluorescent lighting operates at the same frequency as your
mains power, this will cause luminance flicker when viewed through the
camera. Enabling the anti-flicker options available can reduce or eliminate
the flicker that is visible.
Anti-smearing: A smear effect means that a bright vertical line originating
from a bright light source appears in the image. This happens especially with
back lighting. Enabling this allows people and objects to be seen correctly
against a very bright background.
Auto DNS (Domain Name System): A service that stores domain names and
translates them into internet protocol addresses. For example, www.google.
com will have a DNS server address that is equivalent to 74.125.224.72. The
DNS server is automatically provided by your internet service provider.
Auto-focus: Will adjust the lens of your camera to focus on an object being
viewed.
Bandwidth: In computer networks, bandwidth is used as a synonym for data
transfer rate, the amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period (usually a second). Network bandwidth is usually
expressed in bits per second (bps).
Bitrate: The amount of data that your DVR or NVR will use to record video.
The higher the bitrate, the more space each recording will consume on the
hard drive. Increasing this will also consume more bandwidth when streaming. Unit of measurement is either Mbps (megabits per second) or kbps (kilobits per second).
BLC (Back Light Compensation): Improves exposure of an object that is in
front of a light source. It does this by splitting the whole image into different
regions, and then applying separate exposure levels to those regions.
Brightness: This changes how light the image appears to be. Its value is dif-
ferent in darkness to that in daylight. For example, the lights from car headlights appears to be brighter at night.
CDS: This allows the image to be set by the camera’s light sensor. A CDS sen-
sor is basically a resistor that changes its resistive value (in ohms) depending
on how much light is shining onto the sensor.
Cloud: Cloud computing is a model for delivering information technology ser-
vices in which resources are retrieved from the internet through web-based
tools and applications rather than a direct connection to a server. Services
such as Dropbox, Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive are just some of the
examples of cloud computing.
Page 77

77
Click for contents
Glossary
Compound Stream: Indicates that your DVR or NVR is recording video and
audio at the same time.
Contrast: This increases the difference between the blackest black and the
whitest white in the image. Without contrast you wouldn’t have an image because there wouldn’t be any differentiation between light and dark.
Covert: The camera will detect motion and trigger your DVR or NVR to re-
cord, but you will not see an image of the camera in Live View mode.
DDNS (Dynamic DNS): Is a service that converts IP addresses into host names
(a host name is a lot easier than trying to remember an IP address). It also
supports dynamic IP addresses, such as those assigned by a DHCP server.
This makes DDNS a good fit for home networks, which normally receives an
IP address from the ISP that will change occasionally.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Uses an appropriate server
or router to enable dynamic assignment of an IP address to a device connected to the network.
Display Resolution: Is the number of pixels supported by your TV or VGA
monitor or the output signal of a viewing device, e.g. your DVR or NVR.
DNS Server: Is a standard technology for managing public names of web
sites and other internet domains. DNS technology allows you to type names
into your web browser which your computer will automatically find the address on the internet.
DST (Daylight Saving Time): Is the period of the year when clocks are moved
one hour ahead.
DualStream: A process where your DVR or NVR will record both Mainstream
and Substream video at the same time.
Format: Is a command that prepares a storage device such as a USB flash
drive or hard drive to hold data.
Firmware: The software that operates a discrete device (e.g. your smart-
phone). It is referred to in this way rather than software as it is integral to the
operation of the device.
Frame Rate: The measurement of the rate that pictures are displayed to cre-
ate a video feed. The unit of measurement is frames per second (fps).
Gateway: Is a node or router that routes traffic from a device on your home
network to the outside network that is providing access to the internet.
H.264+: Mass video data requires increased storage capacity. To resolve this
issue, video compression technologies are used to reduce the data while
maintaining image quality. H.264+ is an innovative encoding technology
aimed at surveillance video.
H.265: Is a video compression standard and one of several potential succes-
sors to the widely used H.264. It offers double the data compression ratio at
the same level of video quality.
Hardware: A physical device such as your DVR or NVR.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Is a storage device located inside your DVR or NVR. It
is where all data is kept, saved and stored.
HTTP Port (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): This port is used to log into the
web browser interface of your DVR or NVR (if available) using a web client,
such as Internet Explorer.
Hue: Is somewhat synonymous to what is usually referred to as colors. By
altering the hue, you can change the color mix of the image.
IP Address: The address of a device attached to the network. Each device on
the network must use a unique address.
Page 78

78
Click for contents
Glossary
Live View: Is the default display mode for your DVR or NVR. Each camera
connected will be displayed on-screen.
MAC Address: Is a unique identifier for network hardware. Can also be used
as a super password if you have forgotten your current password.
Mainstream: Is the video stream that your DVR or NVR will display and re-
cord.
Mask: Is used to obscure part of your image for privacy. It can also be used
to minimise false triggers when your DVR or NVR detects motion. Any area
obscured won’t be shown live or recorded.
Menu: Is where you control the various actions and options that are available
on your DVR or NVR.
Motion Detection: Is the main method used by your DVR or NVR to detect
motion and is an essential part of your security system. It does this by comparing one frame of video with the next. A certain amount of difference between these two frames is interpreted as motion.
NAS (Network Attached Storage): A network device with one or more HDDs
that other network devices can use as if the storage was connected directly.
NIC (Network Interface Controller): The hardware component that allows a
device to connect to a network. Both wired and wireless NICs exist for these
respective purposes.
NTP (Network Time Protocol): Is used to synchronize your DVR or NVR’s
clock automatically with a network time server. Most time servers are on the
internet.
NTSC: Is the video system used in North America, Canada and some Latin
American countries. In NTSC, 30 frames are transmitted each second.
Optical Zoom: Is a true zoom feature. It allows you to zoom in (or out) on an
object to get a closer view by using the camera’s lens.
OSD (On-screen Display): Display information from the camera such as time,
date and camera name on-screen.
Overscan: Is mainly used on older television sets to display the entire view-
able area correctly on-screen. It does this by cutting off the edges of the picture. This is not required for modern Plasma and LCD TVs as the image is
digitally processed to display the correct aspect ratio.
Pack Duration: Instructs your DVR or NVR to split recordings into discrete
units. Each unit can be a maximum of 60 minutes in length. Your DVR or NVR
will play these as one continual video.
PAL: Is the video system used in the United Kingdom, Australia and most
European countries. In PAL, 25 frames are transmitted each second.
Post-record: Instructs your DVR or NVR to record for a set period of time
after an event has occurred.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet): Is the most common meth-
od that your router uses to login to your ISP to enable your internet connection. This setting also exists on the DVR or NVR, but is only for advanced
users as the configuration required is difficult to complete and requires a
modem-only device (or a modem/router set to modem-only).
Pre-record: Allows your DVR or NVR to record for a number of seconds be-
fore an event occurs.
Privacy Zone: See Mask for information.
Resolution: The measure of detail that can be seen in an image. The higher
the number, the greater the detail available.
Page 79

79
Click for contents
Glossary
RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol): A network protocol designed to trans-
mit video and audio information over networks and the internet in real time.
Saturation: This alters how much color is displayed in the image. The higher
the saturation, the more bright and vivid colors will appear.
Server Port: Is a logical connection place and specifically, using the internet
protocol TCP/IP, the way a client program specifies a particular server program on a computer in a network.
SEQ: Puts the DVR or NVR in sequence mode. This will repeatedly cycle
through each video channel for a predetermined time in Live View mode.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis & Reporting Technology): This is an
automatic system on modern HDDs and SSDs to detect potential drive errors
before they occur.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): This is used to send an outbound
email (e.g. from you DVR or NVR to an email address).
SMTP Port: Is the port number used by a SMTP server to listen for email
send requests. This is specified by your email provider.
SMTP Server: This is the address of the server used for SMTP. Usually in the
form of a web address (e.g. smtp.gmail.com).
Software: A set of instructions that runs on a computing device.
SSID: Is the technical term for a wireless network name. When you setup a
wireless network, you give it a name to distinguish it from other networks in
your neighbourhood.
SSL (Secure Socket Layer): A secure method for connecting to servers. In
the context of the DVR or NVR, primarily used for email server connections.
Static: When referring to IP addresses, this is where a device’s IP address
has been manually entered. Sometimes used on older devices without UIDs
to prepare for internet access.
Static DNS: In some circumstances, your internet service provider may re-
quire you to use a static DNS instead of an auto DNS on your router.
Substream: Is the video stream that your DVR or NVR will send to remote
devices via the network or internet. Video quality is reduced to make it easier
to send.
Subnet Mask: Used to define which part of the IP address refers to the net-
work location.
Time Server: Is a server that reads the actual time from a reference clock
and distributes the information to its clients on the network.
Time Zone: Is a region that observes a uniform standard time for legal, com-
mercial, and social purposes. It is convenient for areas in close communication to keep the same time.
Timestamp: Is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying
when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second.
TVI: Is a digital signal processing and transport technology for video used in
HD security cameras. TVI cameras currently support 1080p video resolution
using the same coaxial cabling techniques used by traditional analogue CCTV
cameras.
UID (Unique Identifier): Is an alphanumeric string that is associated with a
single entity within a given system. By entering your UID into the mobile app
or computer software, this allows you to communicate with your DVR or NVR
without having to remember IP addresses or port numbers.
Page 80

80
Click for contents
Glossary
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play): A network protocol designed to allow net-
work connected devices to automatically configure the router for the purposes of remote access. Not required to be enabled when using UID.
VCA (Video Content Analysis): Is a new method for triggering recording and
events. This uses the image processing system of the DVR or NVR & camera
to set specific triggers for recording (such as line crossing or intrusion). This
system does use more processing power, therefore it may not be available on
all devices.
Video Loss: Is regarded as a potential alarm event and is considered to occur
any time your DVR or NVR doesn’t receive an active video signal from any one
of its video inputs.
Video Quality Diagnostics: Enables your DVR or NVR to alert you if the cam-
era has a blurred image, abnormal brightness or unwanted tint in the image
due to the lighting and white balance of the camera (known as Color Cast).
Video Stream: Indicates that your DVR or NVR is recording a video stream
only.
WDR (Wide Dynamic Range): Is technology to balance out images that have
a large dynamic range. An example of this situation would be if an indoor
camera were pointing towards a window or building entrance. The image
produced by the camera during the day would be extremely washed out due
to the high brightness of the incoming light.
Page 81

81
Click for contents
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I play video(s) on my NVR that I have copied to a USB flash drive?
No, your NVR doesn’t have the option to play video(s) from a USB flash drive.
You will have to play them on your computer or mobile device.
What is the largest hard drive that I can install inside my NVR?
The largest hard drive you can install is 6TB (terabyte). We recommend that
you purchase a drive that is surveillance rated such as the Western Digital
Purple™ and Seagate Skyhawk™ range of drives.
Can I connect and record to a portable USB hard drive?
No, your NVR will only record to the internal hard drive that is installed.
Can I connect and copy videos to a portable USB hard drive?
Due to the nature of how portable USB hard drives operate, there is no guarantee that your drive, when connected to the NVR’s USB port, will work. You’ll
have to give it a try. For backup purposes, we recommend using a USB flash
drive.
How do I save video recordings that are on my NVR?
To copy video recordings to a USB flash drive, use the Search: Events function
(see page 43).
Can I use my own email address and server instead of creating a new one?
You can providing you have the settings required for the SMTP port and server. If you don’t have this, you will have to contact your internet service provider to get this information.
One or more cameras display “Off-line” in Live View mode.
The reason this is happening is because your NVR cannot verify the camera
that is connected to the camera input. Either a setting has changed (such as
password) or if you have added a camera that is connected to your router, it
may have been accidentally disconnected from your router. Try the following:
1. Right-click the mouse in Live View mode then click “Main Menu”.
2. On the “IP Channel” tab, click the “Edit” button for the channel that is dis-
playing the “Off-line” message.
3. You will see the following screen:
4. Make sure the settings highlighted above match what you see on-screen.
Input the default password - admin then click the “OK” button.
5. A green status button will appear indicating successful connection.
For cameras connected directly to your router, check cables and connections
to make sure they are not disconnected.
Can I change the camera’s default password?
Yes you can, go to our support center support.swann.com to download our
camera configuration software. Search for - 7450 Camera Configuration.
Page 82

82
Click for contents
Warranty Information
USA
Swann Communications USA Inc.
12636 Clark Street
Santa Fe Springs CA 90670
USA
Australia
Swann Communications
Unit 13, 331 Ingles Street
Port Melbourne Vic 3207
Australia
United Kingdom
Swann Communications LTD.
Stag Gates House 63/64 The Avenue
SO171XS
United Kingdom
Warranty Terms & Conditions
Swann Communications warrants this product against defects in workmanship and material for a period of one (1) year from its original purchase date. You
must present your receipt as proof of date of purchase for warranty validation. Any unit which proves defective during the stated period will be repaired without charge for parts or labour or replaced at the sole discretion of Swann. The end user is responsible for all freight charges incurred to send the product to
Swann’s repair centres. The end user is responsible for all shipping costs incurred when shipping from and to any country other than the country of origin.
The warranty does not cover any incidental, accidental or consequential damages arising from the use of or the inability to use this product. Any costs associated with the fitting or removal of this product by a tradesman or other person or any other costs associated with its use are the responsibility of the end user.
This warranty applies to the original purchaser of the product only and is not transferable to any third party. Unauthorized end user or third party modifications
to any component or evidence of misuse or abuse of your device will render all warranties void.
By law some countries do not allow limitations on certain exclusions in this warranty. Where applicable by local laws, regulations and legal rights will take
precedence.
For Australia: Our goods come with guarantees which cannot be excluded under Australian Consumer Law. You are entitled to a replacement or refund for
a major failure and for compensation for any other reasonably foreseeable loss or damage. You are also entitled to have the goods repaired or replaced if the
goods fail to be of acceptable quality and the failure does not amount to major failure.
Page 83

Helpdesk & Technical Support
Technical Support E-mail: tech@swann.com
Technical Support Website: support.swann.com
Telephone Helpdesk
USA Toll Free 1-800-627-2799
USA Parts & Warranty 1-800-627-2799
(M-F, 9am-5pm US PT)
AUSTRALIA 1800 788 210
NEW ZEALAND Toll Free 0800 479 266
UK 0808 168 9031
M7450_VER1E070717 | © Swann 2017
Security Made Smarter
Tell us what you think!
We are constantly working to improve
the quality of our documentation, and
we would appreciate your feedback.
Click here to complete a short survey.
Firmware Version: V7.1.0-20170525
 Loading...
Loading...