Page 1

User’s Guide
!479,12
RS-232 to I
with ASCII Fast Mode Interface
with iPort Utility Pack for Windows
TM
2
C Host Adapter
www.mcc-us.com
Page 2

Introduction
The MCC iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) RS-232 to I2C Host
Adapter with ASCII Fast Mode Interface allows any PC,
Host Computer, or Data Terminal with an RS-232 port
to become an I
or receiving I
across an I
2
C Bus.
This user’s guide describes the installation and
operation of the iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) RS-232 to I
2
C Master or Slave device, transmitting
2
C messages to one or more I2C devices
2
C
Host Adapter with ASCII Fast Mode Interface and iPort
Utility Pack Software for Windows.
MCC products are licensed to use the I²C Bus.
Purchase of Philips I²C components conveys a license under the Philips I²C patent to use the
components of the I²C system, provided the system conforms to the I²C specifications defined
by Philips.
I²C is a trademark of Philips Corporation.
Page 3

Copyright© 2002 by Micro Computer Control Corporation. All rights
reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced by any means
without the prior written permission of Micro Computer Control
Corporation, PO Box 275, Hopewell, New Jersey 08525 USA.
DISCLAIMER
representations or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and
specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness
for any particular purpose. Further, Micro Computer Control Corporation
reserves the right to revise the product described in this publication and to
make changes from time to time in the content hereof without the
obligation to notify any person of such revisions or changes.
Life Support Applications
MCC Products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices,
or systems where the malfunction of a MCC Product can reasonably be
expected to result in a personal injury.
WARNING
: Micro Computer Control Corporation makes no
: This equipment can radiate levels of radio frequency energy
that may cause interference to communications equipment. Operation of
this equipment may cause interference with radio, television, or other
communications equipment. The user is responsible for correcting such
interference at the expense of the user.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 4

Table of Contents:
Part 1
RS-232 to I2C Host Adapter w/ASCII Fast Mode Interface
Overview
iPort/AFM Adapter................................................. 8
iPort Utility Pack Software ........................................... 8
Programmer’s Reference ............................................ 8
Packing Slip
System Requirements
Interconnects
DB-25 Serial Port Pinout ............................................ 10
DB-9 Serial Port Pinout ............................................. 10
+5VDC Power Jack ................................................ 10
I2C Interface Connector ............................................. 11
INT, iNterrupt Signal Control ........................................ 11
Hardware Configuration
Pull-up Resistors .................................................. 12
Connecting to a 3.3v System
Connecting to an SMBus System
Hardware Set-Up
.............................................................. 8
........................................................... 9
................................................... 9
.......................................................... 9
............................................... 12
............................................. 12
...................................................... 12
......................................... 12
Part 2
iPort Utility Pack For Windows
Introduction to Utility Pack
iPort Message Center............................................... 14
iPort Message Manager ............................................. 15
System Requirements
Software Installation
Introduction to Message Center
I2C Message Operations............................................. 18
Introduction to Message Manager
I2C Message Operations............................................. 22
Basic Set-up ................................................. 23
Advanced Set-up ............................................. 24
Diagnostic Set-up ............................................. 25
.................................................. 16
................................................... 16
............................................. 14
.......................................... 17
........................................ 21
Sending Messages
..................................................... 26
Page 5

Master Operations ................................................. 26
To Master Transmit Data ....................................... 26
To Master Receive Data ........................................ 27
Slave Operations .................................................. 28
To Slave Transmit a message.................................... 28
To Slave Receive a message .................................... 28
Uninstalling iPort Utility Pack ........................................... 28
Part 3
Programmer’s Reference ASCII Command Interface Definitions
Quick Start ........................................................... 30
ASCII Command Interface Definitions .................................... 31
Synchronous Interface Events ........................................ 32
iPort/AFM Reset ............................................. 32
Status Display ............................................... 33
RS-232 Baud Rate ............................................ 33
Close I2C Connection ......................................... 34
Set Destination I2C Slave Address................................ 34
Echo/Prompt Control ......................................... 34
Flow Control ................................................ 34
I2C General Call Control ....................................... 35
Hex Only Display Control ...................................... 35
Set iPort/AFM’s Own I2C Slave Address .......................... 36
I2C Bus Clock Rate Control ..................................... 36
Command Menu Display ....................................... 36
iNterrupt Signal Control/Status .................................. 37
Open I2C Connection .......................................... 37
Master Read Message.......................................... 38
Slave Transmit Message........................................ 39
Master Transmit Message ...................................... 40
Set I2C Bus time oUt in msec ................................... 41
Display Firmware Version...................................... 41
eXtended Commands .......................................... 41
Display Tx bYte Count ........................................ 44
Asynchronous Interface Events ....................................... 45
Slave Transmit Request ........................................ 45
Slave Receive Complete ........................................ 45
General Call Receive Complete .................................. 45
I2C Bus Time-out Detected ..................................... 46
Page 6

iNterrupt Signal Assert......................................... 46
iNterrupt Signal Release ....................................... 46
iPort/AFM Prompts ................................................ 47
iPort/AFM Ready ............................................. 47
Slave Not Acknowledging ...................................... 47
iPort/AFM Busy ............................................. 47
I2C Bus Arbitration Loss ....................................... 47
I2C Bus Error Detected ........................................ 47
I2C Bus Time-out Detected ..................................... 47
iPort/AFM Connection Closed................................... 48
Invalid Command Argument .................................... 48
Slave Transmit Request Not Active .............................. 48
Invalid iPort/AFM Command ................................... 48
iPort/AFM RS-232 Receive Buffer Overflow ...................... 48
Example Code ........................................................ 49
iPort/AFM Reset .................................................. 49
iPort/AFM Initialization ............................................ 49
Master Transmit Message ........................................... 49
Master Receive Message ............................................ 49
Communication Event Processing..................................... 49
iPort/AFM Revision Report ............................................. 53
Additional Information ................................................. 53
Software License Agreement ............................................ 54
Appendix A ........................................................... 56
Page 7

Part 1
Model MIIC-203
2
RS-232 to I
C Host Adapter
w/ASCII Fast Mode Interface
Model MIIC-203
8
Page 8

RS-232 to I2C Host Adapter
w/ASCII Fast Mode Interface
Overview
2
The MCC iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) RS-232 to I
Fast Mode Interface allows any PC, Host Computer, or Data Terminal with
2
an RS-232 port to become an I
2
receiving I
PRODUCT FEATURES
C messages to one or more I2C devices across an I2C Bus.
C Master or Slave device, transmitting or
C Host Adapter with ASCII
Turn
Supports Standard (100) and Fast (400) I2C Bus Activity.
High Performance Bus Co-Processor
Maximum Bus Throughput with Low Overhead.
19.2, 57.6, and 115.2 k selectable Baud Rates.
Supports Bus Master and Slave, Transmit and Receive, and INT Signaling .
Compatible with 3v to 5v I2C at up to 400kbit/s.
Compatible with iPort/AI applications.
ANY
Computer’s Serial Port into an I2C Port.
The iPort/AFM system consists of the following components:
1) iPort/AFM Adapter
This adapter plugs into an RS-232 Port on a host computer and
2
generates I
C Bus signals.
2) iPort Utility Pack Software
This software package, included with each iPort, includes the iPort
Message Manager and Message Center applications to easily send and
2
receive I
C Bus messages.
3) Programmer’s Reference
This section includes ASCII command interface definitions and
example code to assist in developing a custom application for the
iPort/AFM adapter.
9
Page 9

Packing Slip
This package includes the following items:
2
• iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) RS-232 to I
C Host Adapter with ASCII Fast Mode
Interface.
2
• 4 Foot I
C Interface Cable. (#CAB4)
• 1Ft. /INT-Trigger Cable (#AXM-12G)
• Serial Port Cable, 9F/25M, 1 Foot Long. (#C9F25M1)
• 1Ft. /INT-Trigger Cable (#AXM-12G)
• iPort/AFM User’s Guide.
• iPort Utility Pack for Windows Software.
• Power Supply
Standard 120VAC, 60Hz, USA Plug (#MWT-5VA)
European 220VAC, 50Hz, European Plug (#MWT-5VAE)
International 120/220/240VAC, 50-60Hz, Int.Plug selection (#MWT-5VAI)
System Requirements
a. Host computer
b. 1 free RS-232 Serial Port
Interconnects
The I2C Bus Host Adapter includes four interconnections:
1. RS-232 Serial Port Connector
RS-232 Serial Port Connector
This connector provides connection
to the serial port on the PC. Use the #C9F25M1 cable to adapt the iPort to
9-pin serial ports.
10
Page 10

DB-25 Serial Port Pinout
DB-25 Pin 2, Transmit Data from the Host Computer to the iPort
DB-25 Pin 3, Receive Data from the iPort to the Host Computer.
DB-25 Pin 4, Request to Send from the Host Computer to iPort.
DB-25 Pin 5, Clear to Send from the iPort to the Host Computer.
DB-25 Pin 7, Ground between Host Computer and iPort
DB-9 Serial Port Pinout
DB-9 Pin 3, Transmit Data from the Host Computer to the iPort
DB-9 Pin 2, Receive Data from the iPort to the Host Computer.
DB-9 Pin 7, Request to Send from the Host Computer to iPort.
DB-9 Pin 8, Clear to Send from the iPort to the Host Computer.
DB-9 Pin 5, Ground between Host Computer and iPort
Transmit Data, Receive Data, and Ground are required in all cases.
Request to Send and Clear to Send are required if RTS/CTS communication
handshaking protocol is selected. See the iPort/AFM Flow Control
command.
Communication Handshaking Protocol
iPort/AFM implements either XON/XOFF (by default) or RTS/CTS flow
control protocols. Either protocol can be selected with the iPort/AFM Flow
Control command. Flow control is used by the iPort/AFM to limit character
flow to and from the Host computer to avoid overflowing internal
communication buffers and lost data.
Communication Parameters
19,200, 57.6k, or 115.2k Baud, No Parity, 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit
The default baud rate is 19,200 until the iPort/AFM receives a Baud Change
command from the host computer.
2. +5VDC Power Jack
The iPort/AFM Host Adapter can be powered in one of two ways, from the
2
power jack, or from the I
C interface connector. If the unit is powered from
the provided +5VDC Wall Transformer, approximately 250ma of regulated
2
+5VDC is available at the I
If the iPort/AFM is powered from the I
C interface connector to power external devices.
2
C connector, the unit requires 50ma
of regulated +5VDC.
11
Page 11
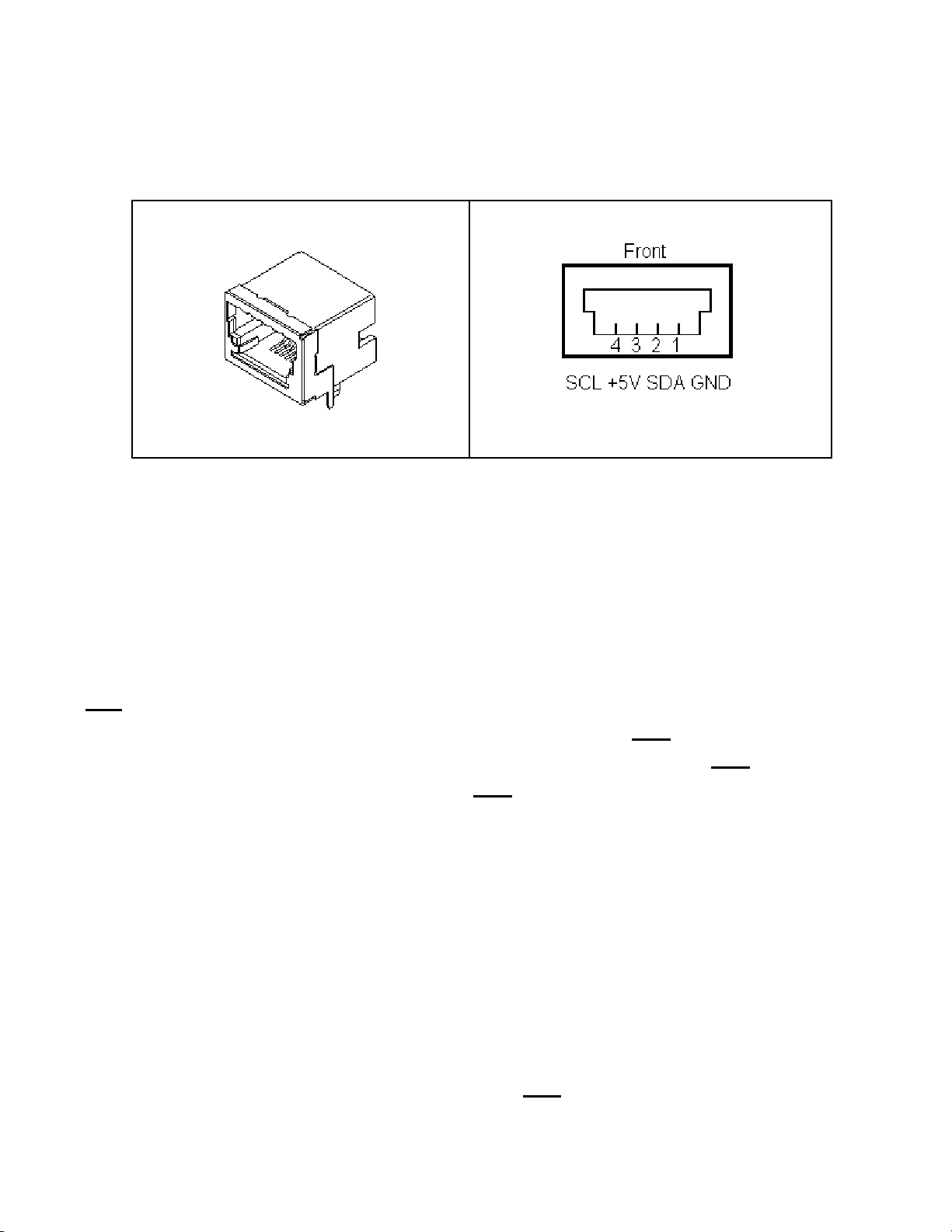
3. I2C Interface Connector
The iPort/AFM Host Adapter includes a four wire, positive locking, modular
connector (see Appendix A for more info on these parts) for interfacing to an
2
external I
C Bus. Lines provided include I2C Clock (SCL), Data (SDA),
Ground, and +5VDC.
Receptacle Connector
An I2C Interface Cable (White=SCL, Red=+5VDC, Green=SDA,
2
Black=Ground) is provided to connect to a external I
2
no standard I
C Bus connector, you may want to cut off one end of the cable
C Bus. Since there is
and add a connector compatible with your target system.
2
Additional I
C Interface Cables (4 ft., 8ft., or 16 ft.) and above mentioned
modular connectors are available from MCC. Clip Lead cables are also
available. (see Appendix A)
4. INT, Interrupt Signal Control
The iPort/AFM provides an open drain input/output (INT) which can be
connected to a corresponding pin on a master or slave. The INT Signal
allows the iPort/AFM to participate in INT master and/or slave
communications.
___
An interrupt output (INT=low) is generated upon receiving an iNterrupt
assert command from the host computer. Resetting and reactivating the
interrupt signal is achieved when a release command is received from the
host computer or data is read from or written to the iPort/AFM when
2
addressed as an I
C Bus slave.
Interrupt monitoring is enabled upon receiving an enable command from the
host computer. Interrupt monitoring causes the iPort/AFM to send
notification to the host computer when the INT signal changes state.
12
Page 12

Hardware Configuration
Pull-up Resistors
The iPort/AFM Host Adapter includes a slide switch used to enable or
disable internal 1.8K ohm Pull-Up resistors on the SCL, SDA, and INT lines.
Every I2C Bus system must have at least one Pull-Up on each line. Use this
switch to configure the iPort/AFM appropriately for your system.
Connecting to a 3.3v System
1. Shut off iPort internal pull-ups. (See Pull-up Resistor section)
2. Use external pull-ups to 3.3 volts.
The iPort uses a 5 volt device. 3.3v is high enough for the iPort to see a
Logical 1.
Connecting to an SMBus System
1. Shut off iPort internal pull-ups. (See Pull-up Resistor section)
2. Use external SMBus rated (approx. 15k ohm) pull-up resistors.
Hardware Set-Up
1. Attach your iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) to an open ComPort on your
computer. If your ComPort has a DB9 connector, use DB-9F to DB-25M
Serial Port Adapter Cable included with your iPort/AFM to connect.
2. Connect the power supply provided or see Interconnect Section +5VDC
Power Jack.
2
3. Connect I
device does not have the matching connector (#15830064) you can cut
C Interface Cable to iPort/AFM and your I2C device. If your
the end of the cable and attach the individual wires to your device or you
can purchase our clip-lead cable(#CABCL).
4. Connect INT line if used.
13
Page 13

Part 2
iPort Utility Pack for
Windows
V5
14
Page 14
iPort Utility Pack for Windows
1. Introduction to Utility Pack
This product includes two (2) Windows applications (Message Manager and
2
Message Center) that help a user get started sending and receiving I
messages quickly.
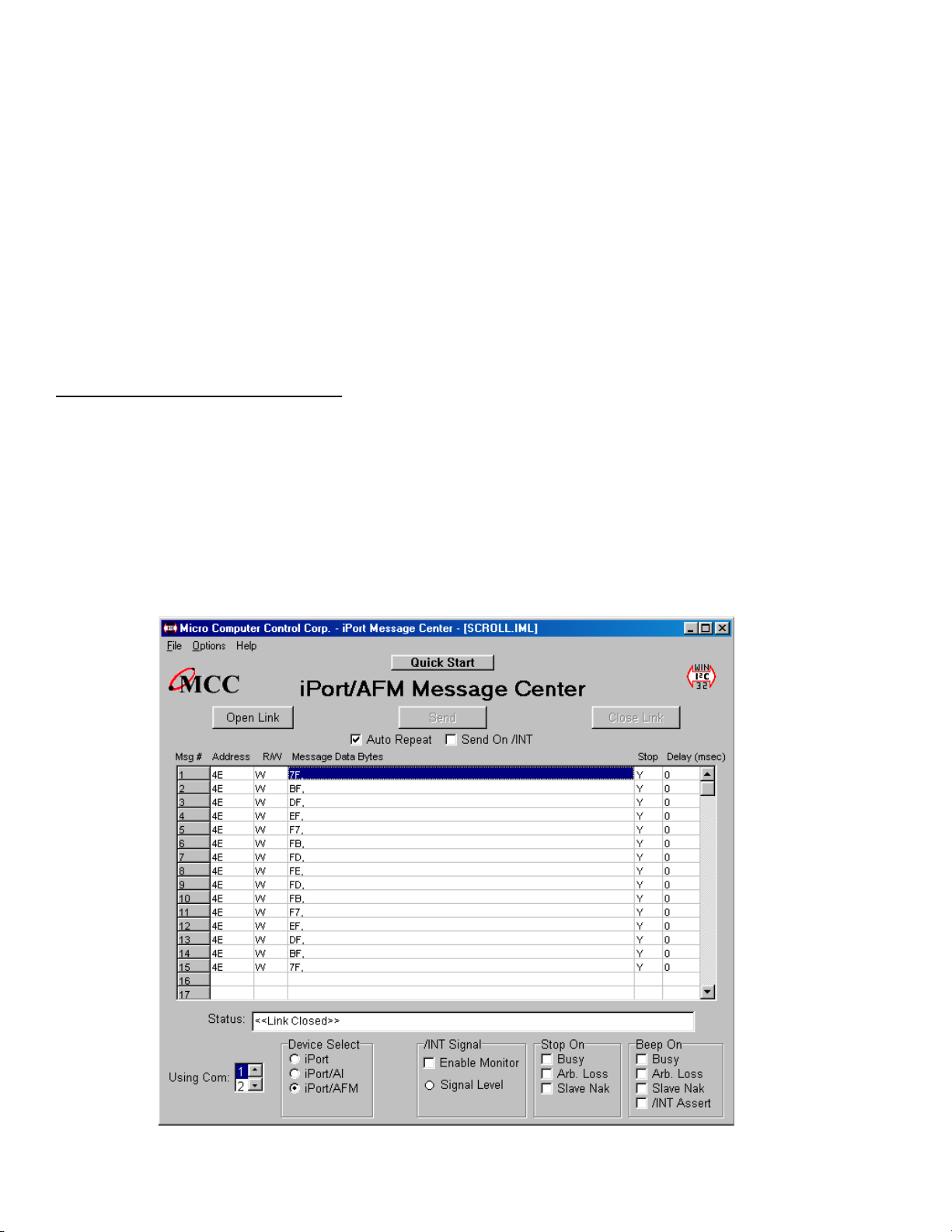
iPort Message Center
The iPort Message Center operates with all versions of the iPort I2C Bus
Host Adapter. With this program you can create, save, and execute scripts
2
of the following modes of I
C Bus message activity:
C Bus
• Master Transmit
• Master Receive
15
Page 15
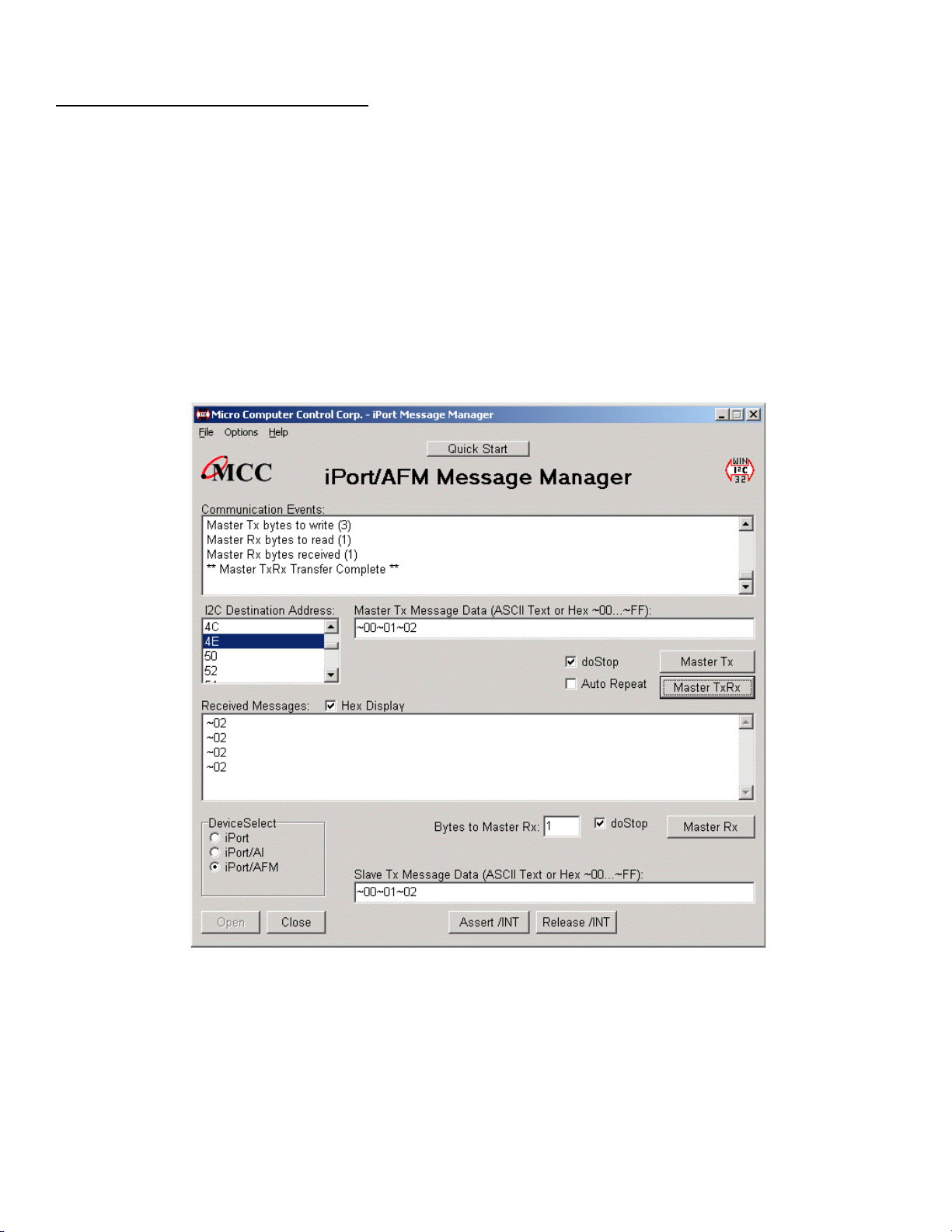
iPort Message Manager
The Message Manager operates with all versions of the iPort I2C Bus Host
2
Adapter. Using this program you can perform all four (4) modes of I
messages activity, including:
• Master Transmit
• Master Receive
• Slave Transmit
• Slave Receive
C Bus
16
Page 16

2. System Requirements
a. One of the following:
1. iPort (#MIIC-201) Windows to I
2. iPort/AI (#MIIC-202) RS-232 to I
Interface
3. iPort/AFM (#MIIC-203) RS-232 to I
Fast Mode Interface.
b. Windows 95 or higher
c. 1 free RS-232 Serial Port.
3. Software Installation
Windows 95 and Above:
2
C Bus Host Adapter.
2
C Bus Host Adapter with ASCII
2
C Bus Host Adapter with ASCII
1. Insert software distribution diskette into floppy drive.
2. Select Start
Run. Type “A:SETUP.EXE”.
3. Follow instructions on screen.
17
Page 17

iPort Message Center for Windows
Introduction to Message Center
The iPort Message Center supports I2C Master Transmit and Receive
2
activities for all versions of the iPort I
program you can create, save, and execute scripts of I
The MCC iPort Message Center Software, when used with an MCC iPort
allows a PC to become an I
2
sending I
2
an I
C Bus.
C messages between the PC and one or more I2C devices across
2
C Master transmitter or receiving device,
C Bus Host Adapter. With this
2
C Master messages.
The iPort Message Center is designed to be a simple application for
experimenting with I
1. Edit a list of I
2
2. Save and/or Load a list of I
3. Transmit the current list of I
2
C messages. It provides methods to:
C Master Transmit or Receive Messages.
2
C Master messages to/from disk.
2
C Master messages, with the option to auto
repeat upon completion, or send on INT assert (low). (iPort/AFM only)
Each iPort Message Center I
2
C message can include up to 32 bytes of 8-bit
data, with an optional time delay at the completion of each message.
18
Page 18

I2C Message Operations
In order to communicate with another I2C device, a user must take the
following steps:
1. Start
Programs iPort Utility PackiPort Message Center
2. Select which device you are operating with by choosing the
corresponding image (Opening Screen), or the correct checkbox on the
main application.
Opening Screen
Main Application
The Main Application screen is opened by selecting an image on the
Opening Screen.
19
Page 19

3. Select the PC ComPort where the iPort is connected to your computer.
2
4. Use the Options menu to override default Baud Rate and I
C Bus Clock
rate settings.
5. Establish a link to the iPort with the Open button. The iPort Message
2
Center software sets the iPort’s own I
C Slave address to 0xFE.
6. To open an existing message list, click File|Open List on the menu bar.
2
To enter or edit a message List, open the “I
C Message Editor” screen,
by double clicking on a message row in the spreadsheet.
Now you can:
2
a. Set the I
C address (i.e. 4C, 4E, etc.)
b. Set Msg Direction (Read or Write)
c. Do stop (yes or no, Repeated starts)
d. Set time delay (delay in msec, controls speed of activity).
e. Write message data (from 00 to FF) or read count.
f. Click OK.
Repeat above steps for additional messages.
20
Page 20

You can insert a new message between existing messages by clicking once
on message below where you want to insert, press the “Insert” button on
2
your keyboard, this will bring up the I
C Message Editor screen, set all
information and click OK.
2
7. On the main screen, click on Send to transmit the current list of I
C
Master messages, with the option to auto repeat upon completion, or send
on INT assert (low).
Once the link has opened successfully, you are now an active I2C node.
Messages are entered into the message spreadsheet and are transmitted
upon clicking the Send button. Data received as part of a Master Receive
message replaces the 0xFF placeholders in the message spreadsheet
control.
If you get a “Slave Not Acknowledging” message in the Communications
2
Events window, this could mean you have the wrong address in the I
C
Destination Address, or the device is not answering to its address.
21
Page 21

iPort Message Manager Software for Windows
Introduction to Message Manager
The MCC iPort Message Manager Software, when used in conjunction with
2
an MCC iPort allows a PC to become an I
2
transmitting or receiving I
2
devices across an I
C Bus.
C messages between the PC and one or more I2C
The iPort Message Manager is designed to be a simple application for
experimenting with I
2
C messages. It provides methods to:
C Master or Slave device,
1. Set the device’s I
2
C Slave address, General Call Enable, and other
operating parameters.
2. Master Transmit ASCII text or Hex [~00...~FF] data to a specified I
Slave Receiver device.
2
3. Master Receive data from a specified I
C Slave Transmitter device.
4. Perform Master Read after Write operation.
2
5. Slave Transmit data to a requesting I
C Master Receive device.
6. Display Slave Receiver data.
__
7. Assert or release the INT signal (iPort/AFM only).
2
C
2
Each iPort Message Manager I
C message can include up to 23 bytes of
8-bit ASCII binary data, although the iPort itself is capable of sending or
2
receiving I
C messages up to 64K bytes in length.
22
Page 22

I2C Message Operations
In order to communicate with another I2C device, a user must take the
following steps:
1.
Starting the program
Start
2.
Select iPort Device
Programs iPort Utility Pack
:
iPort Message Manager
Select which device you are operating with by choosing the
corresponding image (Opening Screen), or the correct checkbox on the
main application.
Opening Screen
Main Application
The Main Application screen is opened by selecting an image on the Opening Screen.
3.
Establish iPort Link
On the Message Manager main screen, click the Open button to view the
Set Up Screen. You now have three options of set-up for the Message
Manager, Basic Set-up, Advanced Set-up, and Diagnostic Set-up.
23
Page 23

Basic Set Up Screen
Basic Set-up
Select the PC ComPort attached to your iPort and the baud rate, then click
OK. The Communications Events window on the Main Screen should report
2
C Open Successful”. If this message does not appear, check the iPort
“I
connections and power.
24
Page 24

Advanced Set Up Screen
Advanced Set-up
On the Advanced Set-up screen you can set the following parameters:
1. iPort I2C Slave Address
2
Select iPort’s I
C slave address. iPort will acknowledge
messages sent to this address.
2 .iPort General Call
Enabled allows iPort to respond to the I
General call is used to broadcast an I
2
3. I
C Bus Master Bit Rate (iPort, iPort/AFM)
2
C general call address (00).
2
C message to multiple devices.
The speed of the Bus will run. 100KHz is standard mode, 400kHz is fast
mode. Use other rates if you are having trouble talking to a very slow
slave device.
2
C Bus TimeOut (Msec) (iPort, iPort/AFM)
4. I
2
Control how long iPort will wait before reporting an I
C Bus intra-message
timeout. (0=None, 1...32767 msec)
5. Enable INT monitor (iPort/AFM only)
Enables monitoring of the INT signal state. INT state changes are
reported in the main screen Communications Events window.
25
Page 25

Diagnostic Set Up Screen
Diagnostic Set-up (iPort Only)
On the Diagnostic Set-up screen you can set the following parameters:
1. iPort Log File Level
Select iPort logging level.1 gives minimal info, 4 is verbose. Use the log
file to troubleshoot communication problems.
2. Log File Name
iPort log file name if enabled.
3. Log File Size (Lines)
iPort log file length if enabled.
4. Set the Destination Slave Address
On the main screen, use the I
2
C Destination Address list control to set the
slave address of the device you want to communicate with.
Additional operating information is available by viewing the Status and Log
File. (Option available only for the iPort).
26
Page 26

Sending Messages
Master Operations
To Master Transmit Data
1.
On the main screen, set the Master Tx Message Bytes edit box to the data
you want to send by single clicking on the box. For example: To send a
0x05(hexadecimal) to the device, enter ~05 in the edit box. Click Ok and
then the Master TX button to send the message. The Communications
Events window on the main screen should report “Master TX Complete”. If
this message does not appear, check the slave device address,
connections, and power.
Example:
You have the option to Auto Repeat a transmitted message upon completion
by checking the Auto Repeat box. Also you may do a DoStop which will
perform repeated starts automatically.
to send message 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, type in ~01~02~03.
27
Page 27

2. To Master Receive Data
2
On the main screen, use the I
C Destination Address list control to set the
slave address of the device you want to communicate with.
Main Application Screen
On the lower part of the main screen, set the Bytes to MasterRx edit box to
the number of bytes you want to read. For example: Set this to 1 to read a
single byte. Click on the Master RX button to receive the message. Data
received from the slave is displayed in the Received Messages text box on
the main screen. The Communications Events window should report “Master
RX Transfer Complete”. If this message does not appear, check the slave
device address, connections, and power.
If you get a “Slave Not Acknowledging” message in the Communications
2
Events window, this could mean you have the wrong address in the I
C
Destination Address, or the device is not answering to its address.
You have the option to Auto Repeat a transmitted message upon completion
by checking the Auto Repeat box. Also you may do a DoStop which will
perform repeated starts automatically. Another option you have is to do
“DoNak”, which allows you to Ack or Nak the last byte coming from a Slave
Transmitter. Some Slave Transmitter Devices require a Nak on the final byte
going across the bus. (Option only available for the windows iPort).
28
Page 28

Slave Operations
To Slave Transmit a message:
Enter data to be transmitted in the Slave Tx Message Bytes control by single
clicking. Binary data bytes are entered using a three character
Hex-Equivalent format (~00 ... ~FF), you may also type in ASCII text. These
bytes are automatically transmitted when a Slave Transmit Request is
received from a Master device.
To Slave Receive a message:
Data bytes received from a Master Transmitter are automatically displayed in
the Received Message window. Received binary data is displayed using a
three character Hex-Equivalent format (~00 ... ~FF). By selecting the HexDisplay checkbox, the data is displayed as Hexadecimal data .
Uninstalling iPort Utility Pack
Click, Start | Programs | iPort Utility Pack | uninstall.
Follow the on screen instructions.
29
Page 29

Part 3
Programmer’s Reference
ASCII Command Interface Definitions
V2
30
Page 30

iPort/AFM
Quick Start
Follow these steps to start sending and receiving I2C messages:
1. Install iPort/AFM as directed in the “Installation Instructions” section of this
User’s Guide.
2. Use a terminal emulator program (like the Windows Terminal Program or
Windows Hyperterminal) to get started. Remember to select the correct
Com Port (COM1, COM2,…) and set the terminal emulator to 19200 Baud, 8
Data Bits, No Parity, and 1 Stop Bit.
3. Enter // to get an iPort/AFM Status Report.
Note
: All iPort/AFM commands
are terminated with a Carriage Return character. On most terminal emulators
press the Enter key.
4. Enter
/E1
to Enable the Echo/Prompt feature. This makes it easier for a
person to interact with the iPort/AFM from a terminal.
5. Enter
/F0
or
/F1
to set iPort/AFM’s communications Flow Control to match
your terminal.
6. Enter
/Ixx
(xx = 02…FE even) to set iPort/AFM’s Own I
2
C Slave Address.
7. Enter /O to Open the iPort/AFM Connection. The iPort/AFM does not need to
2
be connected to an I
8. Enter
9. Enter
/Dxx
(xx = 00…FE even) to select a Destination I
/Ttext
(text = ASCII or Hex-Equivalent ~00…~FF) to Master Transmit a
message to the current Destination I
10. Enter
Destination I
/Rn
(n = 0…32767) to Master Read a message from the current
2
C Slave device.
C Bus to open a connection.
2
C Slave device.
2
C Slave Address.
Syntax: [CR] = Carriage Return
The following sections provide detailed information on all
Commands and Prompts.
For the latest product information and application note
visit our web site at:
http://www.mcc-us.com
31
iPort/AFM
ASCII
Page 31

ASCII Text Interface Commands
Note: [CR] = Carriage Return Code or Enter Key.
Syntax: [Select], (Optional), xx = [00..FE], n = [0..32767]
Command Description
iPort/AFM
Ctrl/R,Ctrl/R,Ctrl/R
//[CR]
/B[0|1|2][CR]
/C[CR]
/Dxx[CR]
/E[0|1][CR]
/F[0|1][CR]
iPort/AFM Reset
This command resets the iPort/AFM to its default state.
Status Display
Display iPort/AFM status information.
RS-232 Baud Rate Control
Set the RS-232 Baud rate (0 = 19.2, 1 = 57.6, 2 = 115.2 Baud)
2
Close I
Disconnect from the I
Set Destination I
Set the destination I
C Connection
2
C Slave Address
2
C Slave Address for subsequent Master Transmit or
2
C Bus.
Receive operations.
Echo/Prompt Control [0 = Disable, 1 = Enable]
Enable/Disable data entry echo and prompts.
Flow Control [0 = XON/XOFF, 1 = RTS/CTS]
Select serial communication handshaking protocol.
/G[0|1][CR]
/H[0|1][CR]
/Ixx[CR]
/K[0|1|2|3][CR]
/M[CR]
2
C General Call Control [0 = Disable, 1 = Enable]
I
2
Enables/Disables iPort/AFM response to I
C Bus General Call (00)
messages.
Hex Only Display Control [0 = Disable, 1 = Enable]
Controls display format of received message data.
2
Set iPort/AFM’s Own I
Sets iPort/AFM's own I
C Slave Address
2
C Slave Address. iPort/AFM will respond to I2C
Bus messages sent to this address.
2
C Bus Clock Rate Control
I
2
Set I
C Bus Clock Rate Control (0=23, 1=86, 2=100, 3=400 KHz)
Command Menu Display
Display iPort/AFM's Command Menu
32
Page 32

/N( [0|1|A|R] )[CR]
iNterrupt Signal Monitor/Control/Status
Sets Monitor/Control/Status of INT line.
[0 = Disable, 1 = Enable, A = Assert, R = Release/CR=Status]
/O[CR]
/(*)Rn[CR]
/S(text)[CR]
/(*)T(text)[CR]
/Un[CR]
/V[CR]
2
Open I
Activates iPort/AFM as an I
C Connection
2
C device attached to the bus.
Master Read Message
Read the specified number of data bytes from the current Destination I
Slave device. * = No Stop for Repeated Start
Slave Transmit Message
2
Write the specified data bytes to a requesting I
C Master Receiver device.
Master Transmit Message
2
Master Transmit the specified data bytes to the current Destination I
C
Slave device. * = No Stop for Repeated Start
I2C
Bus Time-oUt
I2C
Set
Bus Time-oUt in msec (0=Disable)
Display Firmware Version
(Major XX.XX M inor) (R equires Version 2.0 or later)
2
C
/X[CR]
eXtended Commands
(See Prompt or User’s G uide) (R equires Version 2.0 or later)
/Y[CR]
Note:
An online version of this programmer’s reference is available at: http://www.mcc-us.com/203ug.htm
Synchronous Interface Events
Display Tx bYte Count
(Requires Version 2.0 or later)
Synchronous Events are those iPort/AFM interface activities initiated by the Host
computer.
iPort/AFM Reset
This command resets iPort/AFM to its default state.
This command consists of three (3) sequential Ctr/R characters.
Ctr/R is the character code Decimal 18 and Hexadecimal 12, and can also be
generated by holding down the Ctrl Key and pressing R.
Note: It is recommended that the Host computer turn off all serial port flow control
before sending this command. Flow control should be enabled once the response is
received.
33
Page 33

Command: Ctrl/R,Ctrl/R,Ctrl/R ‘iPort Reset
Response. * ‘iPort/AFM Ready
Default Setting: None
Status Display
This command displays current iPort/AFM status.
Command: //[CR] 'Status Display
Response:
iPort/AFM I
2
C Host Adapter w/ASCII Fast Mode Interface Vxx.xx
Copyright © xxxx, Micro Computer Control Corp.
Visit our Web Site at: http://www.mcc-us.com
RS-232 Baud Rate (19.2KHz)
Destination I
2
C Slave Address (4EH)
Echo/Prompt (Disabled)
Flow Control (XON/XOFF)
Hex Only Display (Enabled)
2
I
C Connection (Closed)
General Call (Enabled)
iPort’s own Slave Address (6EH)
I2C Bus Clock Rate (100 KHz)
iNterrupt Signal (Released)
I2C Bus Time-oUt (10000 msec)
RS-232 Baud Rate
This command sets the RS-232 Baud Rate. (0=19.2k, 1=57.6k, 2= 115.2k)
Command: /B[0|1|2][CR] 'Set RS-232 Baud Rate
Response 1: /BC0[CR] 'Baud Change Complete
Response 2: /BC1[CR] 'Baud Change Complete
Response 3: /BC2[CR] 'Baud Change Complete
Response 3: /I89[CR] 'Invalid Command Argument
Default Setting: /B0[CR]
34
Page 34

Close I2C Connection
This command disconnects iPort/AFM from the I
2
C Bus.
Command: /C[CR] 'Close I
2
C Connection
Response: /CCC[CR] 'Close Connection Complete
Default Setting: 'Closed
2
Set Destination I
This command sets the destination I
C Slave Address
2
C Slave Address (Hex 0,2...FE) for all
subsequent Master Transmit or Receive operation.
Command: /Dxx[CR] 'Set Destination I
2
C Slave Address
Response 1: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Response 2: /I89[CR] 'Invalid Command Argument
Default Setting: 00
Echo/Prompt Control
This command enables or disables data entry echo and prompts used as feedback to
manual operations from a computer terminal.
Command: /E[0|1][CR] 'Echo/Prompt Control [0 = Off, 1 = On]
Response: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Default Setting: Off
Flow Control
This command selects the serial communication handshaking protocol to be use in
communicating with the Host computer.
iPort/AFM implements either XON/XOFF (by default) or RTS/CTS flow control
protocols. Flow control is used by the iPort/AFM to limit character flow to and from
the Host computer to avoid overflowing internal communication buffers and lost
data.
The XON/XOFF protocol inserts characters directly into the ASCII data stream.
XON (Hexadecimal 11) is used to enable the flow of data. XOFF (Hexadecimal 13)
is used to stop the flow of data.
35
Page 35

The RTS/CTS protocol uses two additional wires in the cable connecting
communicating devices. The RTS wire is an output signal. It indicates that the
device generating the signal has buffer space available, and can receive. The CTS
wire is an input signal. It indicates that the other device has buffer space available,
and can receive.
In general, XON/XOFF requires a minimal three-wire connection, Ground, Transmit
Data, and Receive Data. This protocol does insert control characters into the stream
of data, and may not be appropriate for all Host systems. If supported, these control
characters are normally automatically stripped out of the data stream by Host
communication driver software, and are not visible at the application program level.
The RTS/CTS protocol requires a serial port, cabling, and Host communication
driver software that supports the additional control signals.
Command: /F[0|1][CR] Flow Control [0 = XON/XOFF, 1 = RTS/CTS]
Response: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Default Setting: XON/XOFF
2
I
C General Call Control
This command enables or disables iPort/AFM response to I
2
C Bus General Call
(Address 00) messages.
Command: /G[0|1][CR] ' I
2
C General Call [0 = Disabled, 1 = Enabled]
Response: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Default Setting: Enabled
Hex Only Display Control
This command controls Hex Only (~00...~FF) output of Master or Slave received
data.
When enabled, all received I
2
C message data bytes are displayed in Hex (~00…~FF)
form.
When disabled, received I
2
C message data bytes representing ASCII printable
characters are displayed as their ASCII printable character. Non-ASCII printable
data bytes are always displayed in Hex (~00…~FF) form.
36
Page 36

Command: /H[0|1][CR] 'Hex Only Display [0 = Disabled, 1 = Enabled]
Response: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Default Setting: Enabled
Set iPort/AFM’s Own I
This command sets iPort/AFM's own I
2
I
C messages to this address will cause iPort/AFM to become an active Slave device
2
C Slave Address
2
C Slave Address (Hex 2...FE). Subsequent
on the bus.
Command: /Ixx[CR] 'Set iPort/AFM’s Own I
2
C Slave Address
Response 1: * 'iPort/AFM Ready
Response 2: /I89[CR] 'Invalid Command Argument
Default Setting: 6E
2
I
C Bus Clock Rate Control
Set the I
2
C Bus master clock rate.
(0=23, 1=86, 2=100, 3=400KHz)
Command: /K[0|1|2|3][CR] 'Set iPort/AFM’s Clock Rate
Response 1: *
Default Setting: /K2[CR]
The iPort/AFM clock rate for standard commands is controlled by the oscillator
crystal we use on our microcontroller. This crystal has been selected to give accurate
RS-232 baud rates, as the RS-232 baud rate must exactly match the rate used by the
host computer. Master I2C clock rates are the fastest possible given the required
crystal frequency. Slave I2C clock rates are driven by the external master device,
with possible clock-stretching as required to store or retrieve message data.
Command Menu Display
This command displays iPort/AFM’s command menu.
Command: /M[CR] 'Command Menu Display
Response:
iPort/AFM Command Menu Syntax: [Select], (Optional), xx=[00..FE], n=[1..32767]
37
Page 37

// Status Display
/B[0|1|2] RS-232 Baud Rate Control (0=19.2, 1=57.6, 2=115.2KHz)
/C Close I2C Connection
/Dxx Set Destination I2C Slave Address
/E[0|1] Echo/Prompt Control (0=Disable, 1=Enable)
/F[0|1] Flow Control (0=XON/XOFF, 1=RTS/CTS)
/G[0|1] General Call Control (0=Disable, 1=Enable)
/H[0|1] Hex Only Display Control (0=Disable, 1=Enable)
/Ixx Set iPort/AFM’s Own I2C Slave Address
/K[0|1|2|3] I2C Bus Clock Rate Control (0=23, 1=86, 2=100, 3=400 KHz)
/M Menu Display
/N([0|1|A|R]) iNterrupt Signal Monitor/Control/Status
(0=Disable, 1=Enable / A=Assert, R=Release / <CR>=Status
/O Open I2C Connection
/(*)Rn Master Rx Message *=No Stop
/S(text) Slave Tx Message
/(*)T(text) Master Tx Message *=No Stop
/Un Set
/V Display Firmware Version (Major XX.XX Minor)
/X[...]... Extended Cmds (See Prompt or User’s Guide)
/Y Display Tx bYte Count
Bus Time-oUt in msec 0=Disable)
I2C
Interrupt Signal Control/Status
___
The INT signal allows the iPort/AFM to participate in INT master and/or slave
communications.
Command: /N0[CR] Disable Monitor
/N1[CR] Enable Monitor
/NA[CR] Assert INT Signal
/NR[CR] Release INT Signal
Response: *
Default Setting: /N0
Open I2C Connection
This command activates iPort/AFM as an active device on the I
, /NR
2
C Bus.
Command: /O[CR] 'Open I
2
C Connection
Response: /OCC[CR] 'Open Connection Complete
Default Setting: Closed
38
Page 38

Master Read Message
This command causes iPort/AFM to read the specified number of data bytes from
the currently selected Destination I
2
I
C Stop condition after the last byte is received.
2
C Slave Address with or without generating an
Enter Byte Count (Decimal 0...32767) then Press Enter, or ESCape to Cancel.
A Byte Count of Zero (0) represents a Variable Length message, where the first byte
read from the I
2
C Slave device indicates the number of additional trailing bytes are
available to read. iPort/AFM automatically reads the first byte, then the additional
bytes as specified by the first byte. All message bytes including the Length byte are
returned to the Host computer.
The received text is a representation of the data bytes within the Master Receive
message. The format of this data is controlled by the current setting of the Hex Only
Display Control .
If the device acknowledges its I
read from the current Destination I
2
C Slave Address, the specified number of bytes are
2
C Slave Address. iPort/AFM acknowledges all
bytes read except the last. If not disabled, the message is then terminated with an
2
I
C Stop condition.
Sending Master Receive messages with No Stop allows the Master to retain
exclusive control of the I
2
C Bus until it finally sends a Stop. During this time, the
Master can send additional (Repeated Start) Master Transmit or Master Receive
messages to the same or other I
2
C Slave devices.
Command: /(*)Rnnnn[CR] 'Master Read Message
(* = No Stop)
Response 1: /MRCtext[CR] 'Master Read Complete
Response 2: /SNA[CR] 'Slave Not Acknowledging
Response 3: /I81[CR] 'iPort/AFM is Busy, Command Ignored
Response 4: /I83[CR] ' I
2
C Arbitration Loss Detected
Response 5: /I88[CR] 'iPort Connection Not Open
Response 6: /I89[CR] 'Invalid Command Argument
Default Setting: None
39
Page 39

Slave Transmit Message
This command should be issued to iPort/AFM in response to a Slave Transmit
Request (/STR). This command causes iPort/AFM to write the specified data bytes
to the requesting I
2
C Master Receiver device.
Enter Message Bytes (1 or more Printable ASCII or Hex-equivalent ~00..~FF), then
Press Enter, or ESCape to Cancel.
Note 1
the I
initiates an I
: Upon receiving a Slave Transmit request from a Master Receiver device on
2
C Bus, iPort/AFM outputs a Slave Transmit Request to its Host device, and
2
C Clock Stretch (SCL Low) until a Slave Transmit Text command is
received from the Host computer. While clock stretching, no other messages can be
transmitted on the I
Note 2
: The tilde (~) character and the Carriage Return (CR) character are used as
2
C Bus.
special marker characters within all iPort/AFM transmit text messages. These
characters may not be used within the text of a message, but must be replaced by the
following "Hex equivalent" characters:
Tilde replaced by "~7E"
Carriage Return replaced by "~0D"
iPort/AFM automatically translates "Hex equivalent" characters to their single-byte
value for transmission across the I
2
C Bus.
All entered data bytes are transmitted to the requesting Master Receiver device.
Slave Transmit stops upon receiving the first negative acknowledgment (Nack) from
the Master Receiver.
Command: /Stext[CR] 'Slave Transmit Message
Response 1: /STC[CR] 'Slave Transmit Complete
Response 2: /I88[CR] 'iPort Connection Not Open
Response 3: /I8A[CR] ‘Slave Transmit Request Not Active, Cmd Ignored
Default Setting: None
Examples:
/Sabcd1234[CR] ‘ASCII Printable characters "abcd1234"
/S~00~01~02[CR] ‘Binary data bytes 00, 01,02
40
Page 40

/Sab~7Ecd[CR] ‘Tilde embedded in ASCII Printable characters
/S12~0D24[CR] ‘Carriage Return embedded in ASCII Printable characters
Master Transmit Message
This command causes iPort/AFM to write the specified data bytes to the currently
selected Destination I
2
C Slave Address with or without generating an I2C Stop
condition after the last byte is transmitted.
Enter Message Bytes (0 or more Printable ASCII or Hex-equivalent ~00..~FF), then
Press Enter, ESCape to Cancel.
Note: The tilde (~) character and the Carriage Return (CR) character are used as
special marker characters within all iPort/AFM transmit text messages. These
characters may not be used within the text of a message, but must be replaced by the
following "Hex-equivalent" characters:
Tilde replaced by "~7E"
Carriage Return replaced by "~0D"
iPort/AFM automatically translates "Hex equivalent" characters to their single-byte
value for transmission across the I
2
C Bus.
All entered data bytes are transmitted to the Destination I
2
C Slave Receiver device.
Master Transmit stops upon receiving the first negative acknowledgment (Nack)
from the Slave Receiver. If not disabled, the message is then terminated with an I
Stop condition.
Sending Master Transmit messages with No Stop allows the Master to retain
exclusive control of the I
2
C Bus until it finally sends a Stop. During this time, the
Master can send additional (Repeated Start) Master Transmit or Master Receive
messages to the same or other I
2
C Slave devices.
Command: /(*)Ttext[CR] 'Master Transmit Message
(* = No Stop)
Response 1: /MTC[CR] 'Master Transmit Complete
Response 2: /SNA[CR] 'Slave Not Acknowledging
Response 3: /I81[CR] 'iPort/AFM is Busy, Command Ignored
Response 4: /I83[CR] ' I
2
C Arbitration Loss Detected
2
C
Response 5: /I88[CR] 'iPort Connection Not Open
41
Page 41

Default Setting: None
Examples:
/Tabcd1234[CR] ‘ASCII Printable characters "abcd1234"
/T~00~01~02[CR] ‘Binary data bytes 00, 01,02
/*T~00~01~02[CR] ‘Binary data bytes 00, 01,02 with No Stop
/Tab~7Ecd[CR] ‘Tilde embedded in ASCII Printable characters
/T12~0D24[CR] ‘Carriage Return embedded in ASCII Printable characters
Set I
2
C Bus Time-oUt in msec
Set bus time-out in msec (0=disable)
The iPort/AFM reports a bus time-out if no bus activity for the specified time occurs
within an I
2
C Bus message.
Command: /Unnnn[CR] 'I2C Bus time-oUt
Response: *
Display Firmware Version
(requires V2.00+)
Display firmware version
Command: /V[CR] 'Firmware Version
Response: /VCCXX.XX[CR] '(Major XX.XX Minor)
eXtended Commands
(requires V2.00+)
The eXtended commands are used to generate “out-of-spec” signaling. eXtended
commands cannot use the I2C hardware to control the SCL and SDA lines, as the
I2C hardware only generates I2C compatible signals. The eXtended commands use
firmware to “bit-bang” the SCL and SDA lines. This firmware cannot operate as fast
as the hardware, and it can be interrupted at any time by internal interrupts. The
eXtended commands run directly off the command characters as they are received
on the RS-232 link. Speed of execution of eXtended commands is controlled by the
RS-232 baud rate, the execution speed of the firmware, delays caused by execution
interruptions that may occur while a command is executing, and I2C Bus clockstretching by external slave devices.
The following commands manipulate the I
2
C Clock (SCL) and data (SDA) lines.
42
Page 42

Command: /X[S|~xx|R| r|P|0|1|?|D|d|C|c|L|A| |"]..., then Press Enter or ESCape
Enter /X followed by zero or more sub-commands, the [CR]
Response: /XCC(see commands below)[CR]
High Level Sub-Commands:
S = Send Start
~xx = Send Byte (xx = 00...FF)(response = A or N)
R = Read Byte with Ack (response = ~xx)
r = Read Byte with Nak (response = ~xx)
P = Send Stop
Mid Level Sub-Commands:
0 = Send 0 Bit
1 = Send 1 Bit
? = Read Bit (response = 0 or 1)
Low Level Sub-Commands:
D = Set SDA High
d = Set SDA Low
C = Set SCL High
c = Set SCL Low
L = Read SCL (response = 0 or 1)
A = Read SDA (response = 0 or 1)
Misc Sub-Commands:
space = no action
“comment” = no action
Examples:
Master transmit three bytes to slave address 0x4e using high level, mid level, and
low level sub-commands.
High Level Command:/X S ~4e ~01 ~02 ~03 P [CR]
High Level Response: /XCCAAAA[CR]
Mid Level Command:/X S 01001110 ? 00000001 ? 00000010 ? 00000011 ? P [CR]
43
Page 43

Mid Level Response: /XCC0000[CR]
Low Level Command:/X dc dCcDCcdCcdCcDCcDCcDCcdCc DCAc
dCcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcDCc DCAcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcDCcdCc DCAc
dCcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcdCcDCc DCAc dCD[CR]
Low Level Response: /XCC0000[CR]
Master read three bytes from slave address 0x4F. First two bytes are acknowledged
by master.
Comma nd: /X S ~4f Rrr P [CR]
Response: /XCCA~xx~xx~xx[CR] ‘(xx = 00...FF)
Master transmit a Write WCR command to a Xicor X9241 at slave address 0x50.
WCR data is 0x00.
Command: /X S ~50 ~a0 ~00 P [CR]
Response: /XCCAAA[CR]
Master transmit a Write WCR command to a Xicor X9241 at slave address 0x50.
WCR data is 0x3f.
Comma nd: /X S ~50 ~a0 ~3f P [CR]
Response: /XCCAAA[CR]
Issue a Read WCR command to a Xicor X9241 at slave address 0x50.
Command: /X S ~50 ~90 ~R P [CR]
Response: /XCCAA~xx[CR] ‘(xx = 00...FF)
Issue an Increment Wiper command to a Xicor X9241 at slave address 0x50.
Comm a nd: /X S ~50 ~20 1 P [CR]
Response: /XCCAA[CR]
Issue an Decrement Wiper command to a Xicor X9241 at slave address 0x50.
Comm a nd: /X S ~50 ~20 0 P [CR]
Response: /XCCAA[CR]
44
Page 44

Display Tx bYte Count
(requires V2.00+)
Returns the number of bytes received by the slave device in the last master transmit
message.
Command: /Y[CR] 'Tx bYte Count
Response: /TBCn[CR] 'n =00000...32767
45
Page 45

Asynchronous Interface Events
Asynchronous Events are those iPort/AFM interface activities initiated by the
iPort/AFM I
2
C Host Adapter in response to activities on the I2C Bus.
Slave Transmit Request
This event is caused by the reception of an I
2
C Bus Slave Transmit message directed
at the current iPort/AFM’s own Slave address.
Prompt: /STR[CR] ‘Slave Transmit Request
Command: /Stext[CR] ‘Slave Transmit Text
The normal Host computer response is to send a Slave Transmit Text (/Stext[CR])
command.
Note
the I
initiates an I
: Upon receiving a Slave Transmit request from a Master Receiver device on
2
C Bus, iPort/AFM outputs a Slave Transmit Request to its Host device, and
2
C Clock Stretch (SCL Low) until a Slave Transmit Text command is
received from the Host computer. While clock stretching, no other messages can be
transmitted on the I
Slave Receive Complete
This event is caused by the reception of an I
2
C Bus.
2
C Bus Slave Receive message directed
at the current iPort/AFM’s own Slave address.
The received text is a representation of the data bytes within the Slave Receive
message. The format of this data is controlled by the current setting of the Hex Only
Display Control .
Prompt: /SRCtext[CR] ‘Slave Receive Complete
Command: None Required
General Call Receive Complete
This event is caused by the reception of an I
at the I
2
C General Call Address (00), when iPort/AFM’s General Call recognition is
2
C Bus Slave Receive message directed
enabled.
46
Page 46

The received text is a representation of the data bytes within the Slave Receive
message. The format of this data is controlled by the current setting of the Hex Only
Display Control .
Prompt: /GRCtext[CR] ‘General Call Receive Complete
Command: None Required
2
I
C Bus Time-out Detected
Prompt: /I85[CR] I
2
C Bus Time-out Detected
Cause: iPort/AFM issues this response when an I
2
C Bus message lasts for more than
1 second. No corrective action is taken by iPort/AFM. No Host response is required,
but this event can be used to detect bus problems.
iNterrupt Signal Assert
Prompt: /NSA[CR] iNterrupt Signal Assert (low) Detected
iNterrupt Signal Release
Prompt: /NSR[CR] iNterrupt Signal Release (high) Detected
47
Page 47

iPort/AFM Prompts
iPort/AFM Prompts are messages generated by iPort/AFM in response to Host
computer commands.
iPort/AFM Ready
Prompt: * ‘iPort/AFM Ready
Cause: iPort/AFM is ready for the next Host command.
Slave Not Acknowledging
Prompt: /SNA[CR] ‘Slave Not Acknowledging
Cause: There is no response (I
Transmit or Receive operation from an I
2
I
C Address.
iPort/AFM Busy
2
C Slave Address Acknowledgment) during a Master
2
C Slave device at the current Destination
Prompt: /I81[CR] ‘iPort/AFM Busy
Cause: Host attempted a Master operation while iPort/AFM was busy. Host should
repeat the last command.
2
I
C Bus Arbitration Loss
Prompt: /I83[CR] ‘I
Cause: iPort/AFM lost I
Receiving an I
2
C Bus Error Detected
I
2
C message. Host should repeat the last command.
Prompt: /I84[CR] ‘I
Cause: iPort/AFM has detected a error condition on the I
2
C Arbitration Loss Detected
2
C Bus Arbitration while Master Transmitting or Master
2
C Bus Error Detected
2
C Bus. Host should repeat
the last command or issue an iPort/AFM Reset command.
2
C Bus Time-out Detected
I
Prompt: /I85[CR] ‘I
Cause: iPort/AFM issues this command when an I
2
C Bus Time-out Detected
2
C Bus message lasts for more
than 1 second. No corrective action is taken by iPort/AFM. No Host response is
required, but this event can be used to detect bus problems.
48
Page 48

iPort/AFM Connection Closed
Prompt: /I88[CR] ‘iPort/AFM Connection is Closed.
Cause: Host is attempting to perform an I
iPort/AFM Connection is Closed. The Host should issue an Open I
command before attempting to perform I
Invalid Command Argument
2
C Bus message operation while the
2
C Connection
2
C Bus message operations.
Prompt: /I89[CR] ‘Invalid Command Argument Detected
Cause: This event normally indicates the value of a Host command argument was
out of range. The Host should reissue command with correct arguments.
Slave Transmit Request Not Active
Prompt: /I8A[CR] ‘Slave Transmit Request Not Active
Cause: This event indicates the Host attempted to issue a Slave Transmit Text
command when no Slave Transmit Request was present.
Invalid iPort/AFM Command
Prompt: /I8F[CR] ‘Invalid iPort/AFM Command
Cause: This event normally indicates that an invalid command was issued by the
Host. The Host should reissue the correct command.
iPort/AFM RS-232 Receive Buffer Overflow
Prompt: /I90[CR] ‘iPort/AFM RS-232 Receive Buffer Overflow
Cause: This event normally indicates that data sent to the iPort/AFM via the RS-232
serial port has been lost. Check your Host Computer Serial Port Flow Control
(XON/XOFF, or Hardware) to make sure it matches current iPort/AFM Flow
Control. Also check if Host Computer FIFO buffers in the 16550 UART are
enabled. If so, reduce Transmit Buffer level.
49
Page 49

Example Code
The following examples are written in MS Visual Basic V3 for Windows using the
serial communications control (MSCOMM.VBX). It can be used as a guide in
implementing iPort/AFM interface programs in other programming languages and
operating environments.
Note:
iPort/AFM Reset
This example code is available online at: http://www.mcc-us.com/202ug.htm#ExampleCode.
Comm1.Output = Chr$(18) 'Ctrl/R
Comm1.Output = Chr$(18) 'Ctrl/R
Comm1.Output = Chr$(18) 'Ctrl/R
iPort/AFM Initialization
Comm1.Output = "/f0" 'Set iPort/AFM XON/XOFF Flow Control
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13)
Comm1.Output = "/i70" 'Set iPort/AFM’s Own Slave Address
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13)
Comm1.Output = "/d4e" 'Set Destination Slave Address
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13)
Comm1.Output = "/o" 'Open I
2
C Connection
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13)
Master Transmit Message
Comm1.Output = "/T~00~01" 'Send Master Tx Command
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13) 'Terminate Command
Master Receive Message
Comm1.Output = "/R10" 'Send Master Rx Command
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13) 'Terminate Command
Communication Event Processing
Static Sub Comm1_OnComm ()
Static LineBuf$
While Comm1.InBufferCount
Msg$ = Comm1.Input ' Get Comm input character
CharIn$ = Msg$
50
Page 50

If Msg$ = Chr$(13) Then Msg$ = "" ' Remove CR
If Msg$ = Chr$(10) Then Msg$ = "" ' Remove LF
If Msg$ = "*" Then ' if iPort/AFM Ready
Msg$ = "****" ‘ Substitute Token
CharIn$ = Chr$(13) ‘ Terminate Line
End If
LineBuf$ = LineBuf$ + Msg$ 'Add new text to line buffer
If CharIn$ = Chr$(13) Then ' if Carriage Return detected
iPortResp$ = Left$(LineBuf$, 4) 'Isolate Response Code
' Test for iPort/AFM Synchronous Interface Events
If (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/OCC") = 0) Then
' Open Connection Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = "/OCC Open Connection Complete"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/MTC") = 0) Then
' Master Transmit Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = "/MTC Master Tx Complete"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/MRC") = 0) Then
' Master Rx Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = LineBuf$ 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/STC") = 0) Then
' Slave Tx Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = "/STC Slave Tx Complete"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/CCC") = 0) Then
' Close Connection Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = "/CCC Close Connection Complete "
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/BC0") = 0) Then
' iPort/AFM Baud Change 0 {19.2K}
TextBox.Text = "iPort/AFM Baud Change 0 {19.2K} "
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/BC1") = 0) Then
' iPort/AFM Baud Change 1 {57.6K}
TextBox.Text = "iPort/AFM Baud Change 1 {57.6K} "
51
Page 51

ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/BC2") = 0) Then
' iPort/AFM Baud Change 2 {115.2K}
TextBox.Text = "iPort/AFM Baud Change 0 {115.2K} "
' Test for iPort/AFM Asynchronous Interface Events
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/SRC") = 0) Then
' Slave Rx Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = LineBuf$ 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/GRC") = 0) Then
' General Call Rx Complete Processing
TextBox.Text = LineBuf$ 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/STR") = 0) Then
' Slave Tx Request Processing
Comm1.Output = "/S~00~01" 'Send Slave Tx Msg
Comm1.Output = Chr$(13) 'Terminate Command
TextBox.Text = LineBuf$ 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/NSA") = 0) Then
' iNterrupt Signal Assert Detected
TextBox.Text = iNterrupt Signal Assert Detected
'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/NSR") = 0) Then
' iNterrupt Signal Release Detected
TextBox.Text = iNterrupt Signal Release Detected
'Update Display
' Test for iPort/AFM Response Messages
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "****") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "* iPort/AFM Ready" 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/SNA") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/SNA Slave Not Acknowledging"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I81") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I81 iPort/AFM Busy" 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I83") = 0) Then
52
Page 52

TextBox.Text = "/I83 Arbitration Loss" 'Update Display
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I84") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I84 I2C Bus Error Detected"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I85") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I85 I2C Bus Time-out Detected"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I88") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I88 iPort/AFM Connection Closed"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I89") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I89 Invalid Command Argument"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I8A") = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I8A Slave Tx Request Not Active"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I8F") = 0) Then
LineBuf$ = ""
End If
Wend
End Sub
TextBox.Text = "/I8F Invalid iPort/AFM Command"
ElseIf (StrComp(iPortResp$, "/I90 = 0) Then
TextBox.Text = "/I90 iPort/AFM Rx Buffer Overflow”
Else
TextBox.Text = LineBuf$ 'Other Update Display
End If
53
Page 53

iPort/AFM Revision Report
This section defines revisions and changes made to the iPort/AFM interface:
Revision: 1.02
1. Initial Release
Revision: 2.00
1. Add Firmware Version Command.
2. Add eXtended Commands.
3. Add Tx bYte Count Command.
Additional Information
For additional information on the I
“The I
2
C and How to Use It”
2
C Bus, please refer to the following:
http://www.mcc-us.com/i2chowto.htm
"80C51-Based 8-Bit Microcontroller" Data Handbook.
Philips Semiconductors, Tel. (800)227-1817
2
" I
C Peripherals for Microcontrollers" Data Handbook.
Philips Semiconductors, Tel. (800)227-1817
Micro Computer Control Corporation
PO Box 275, 17 Model Avenue
Hopewell, New Jersey 08525 USA
Tel: (609)466-1751 Fax: (609)466-4116 WWW: www.mcc-us.com
7/30/2
54
203.wpd
Page 54

Software License Agreement
BY INSTALLING THIS SOFTWARE, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BECOME
BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT
AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, PROMPTLY RETURN
THE ENTIRE PRODUCT WITHIN 7 DAYS WITH ALL ITS CONTENTS TO
THE PLACE OF PURCHASE, WITH A NOTE THAT YOU RETAIN NO
COPIES OF THE SOFTWARE OR PRINTED MATERIALS, FOR A FULL
REFUND.
The computer files and materials supplied in this package are
2
non-exclusively licensed to Purchasers of the MCC iPort I
Distribution of the MCC iPort Utility Pack software (IMSGCTR.EXE) and any
other computer files supplied as part of the MCC iPort Utility Pack, is strictly
limited to employees of the Purchasing Company.
C Host Adapter.
Violation of any of the above provisions automatically terminates the
Purchaser's license.
Life Support Applications
MCC Products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices,
or systems where the malfunction of a MCC Product can reasonably be
expected to result in a personal injury.
Limited Warranty
MCC warrants, as the sole warranty, that the disks on which the Software is
furnished will be free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal
use and conditions for a period of thirty (30) days from the date of purchase.
No distributor, dealer, or any other entity or person is authorized to expand
or alter this Agreement.
MCC does not warrant that the functions contained in the Software will be
uninterrupted or error-free. Except as stated above in this paragraph, the
Software is provided as is without warranty of any kind either expressed or
55
Page 55

implied, included but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose. The Purchaser assumes entire risk as it
applies to the quality and performance of the Software. Should the Software
prove defective, the Purchaser (and not MCC, authorized MCC distributors,
or dealers) assume the entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair or
correction.
Limitation of Remedies and Damages
MCC's entire liability and remedy will be the replacement of any disks not
meeting MCC "Limited Warranty" explained above.
In no event will MCC be liable for any damages direct, indirect, incidental, or
consequential, including damages for lost profits, lost savings, or other
incidental or consequential damage arising out of the use or inability to use
such Software, even if MCC has been advised of the possibility of such
damages or for any claim by any other party. In no event will MCC's liability
of damages to the Purchaser or any other person ever exceed the amount of
the license fee paid by the Purchaser to use the Software regardless of the
form of the claim.
This Agreement is governed by the laws of the State of New Jersey USA
(except federal law governs copyrights and registered trademarks.) If a
provision of this Agreement is deemed invalid by any court having
jurisdiction, that particular provision will be deemed deleted and will not
affect the validity of any other provision of this Agreement.
TEL(609)466-1751 FAX (609)466-4116 EMAIL inf o@m cc-us.com
For the latest product infor m at ion, application notes,
and
visit our Web Site at:
http://www.mcc-us.com
software updates
free
56
Page 56

Appendix A
Interface Connector and Plug Information
MCC uses two (2) different connectors and plug assemblies. These parts are all
compatible with one another and are interchangeable.
Connectors
Molex SEMCONN ACCESS.bus Receptacle Connector
Molex Part # 15-83-0064
AMP SDL (Shielded Data Link) Connectors for ACCESS.bus
AMP Part # 4-943197-1
Plugs
Molex SEMCONN ACCESS.bus Plug
Molex Part # 15-83-1564
AMP SDL (Shielded Data Link) Plug for ACCESS.bus
Bush Amp Part # 520851-1
Ferrule Amp Part # 520433-1
SDL (Shell) Amp Part # 520461-1
SDL (Shell) Amp Part # 520460-1
SDL Amp Part # 4-520424-1
Additional Cables Available
MCC Part # CAB4 I
MCC Part # CAB8 I
MCC Part # CAB16 I
MCC Part # CABCL I
2
C Interface Cable, 48inches (4ft)
2
C Interface Cable, 96 inches (8ft)
2
C Interface Cable, 192 inches (16ft)
2
C and SMBus Clip Lead Cable
MCC Part # AXM-12G 1 Ft. INT-Trigger Cable
57
 Loading...
Loading...