Supermicro SuperBlade SBI-7125C-S3, SuperBlade SBE-710E, SuperBlade SBI-7125C-S3E, SuperBlade SBI-7125C-T3, SuperBlade SBE-710Q User Manual
...
SuperBlade
®
User’s Manual
Revison 1.1

SuperBlade User’s Manual
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and i s believed to be accurate. The
vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document, makes no
commitment to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to not ify any person or
organization of the u pdates. Plea se Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual, please see
our web site at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. ("Supermicro") reserves the right to make changes to the product described
in this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software and documentation, is the
property of Supermicro and/or its licensors, and is supplied only unde r a license. Any use or rep rodu ction
of this product is not allowed, except as expressly permitted by the terms of said license.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE
THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPERMICRO SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF
REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING, INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and cu stomer shall be governed by the laws of Santa Clara
County in the State of California, USA. The State of California, Co unty of Santa Clara shall be the
exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes. Super Micro's total liabilit y for all claims will not
exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC State ment: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction manual, may cause harmful interference with radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference,
in which case you will be required to correct the interference at your own expense.
California Best Management Practices Regulations for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning
applies only to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells. Perchlorate
Material-special handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate for further
details.
WARNING: HANDLING OF LEAD SOLDER MATERIALS USED IN THIS
PRODUCT MAY EXPOSE YOU TO LEAD, A CHEMICAL KNOWN TO THE
STATE OF CALIFORNIA TO CAUSE BIRTH DEFECTS AND OTHER
REPRODUCTIVE HARM.
Manual Revison 1.1
Release Date: July 13, 2011
Unless you request and receive written permission fr om Super Micro Computer, Inc., you may not copy
any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies referred
to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 2010 by Super Micro Computer, Inc.
All rights reserv ed .
Printed in the United States of America
ii

Preface
About this Manual
This manual is written for professional system integrators, Information Technology
professionals, service personnel and technicians. It provides information for the
installation and use of Supermicro's SuperBlade system. Installation and maintenance
should be performed by experienced professionals only.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1: Introduction
The first chapter provides a checklist of the main components included with the blade
system and describes the main features of the mainboard and enclosure. A quick start
procedure is also provided for your use.
Chapter 2: System Safety
You should familiarize yourself with this chapter for a general overview of safety
precautions that should be followed when installing and servicing the SuperBlade.
Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Refer here for details on installing the SuperBlade system into a rack.
Chapter 4: System Modules
This chapter covers modules in the SuperBladeSuperBlade system. It also covers the
CMM module and configuring double-wide bays.
Chapter 5: Power Supply Modules
This chapter covers the system power supplies and their installation.
Appendix A: System Specifications
This appendix provides a summary of system specifications.
Appendix B: LED Descriptions
This appendix provides descriptions of LEDs in the SuperBlade system for your
reference.
iii

SuperBlade User’s Manual
Notes
iv

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................................1-1
1-1 Overview.............................................................................................1-1
1-2 Quick Start Setup..............................................................................1-1
1-3 OfficeBlade and Datacen terBlade Systems..................................1-2
DataCenterBlade ....................................................................................1-2
OfficeBlade .............................................................................................1-3
T win Blades.............................................................................................1-3
Software Mode Selection........................................................................1-3
1-4 Product Checklist of Typical Components.....................................1-4
1-5 Blade Enclosure Features...............................................................1-5
Power......................................................................................................1-8
Middle Plane...........................................................................................1-8
LEDs.......................................................................................................1-8
Enclosure Cooling....................... .......................................... ..................1-8
1-6 Power Supply Features....................................................................1-9
Power Supply Modules...........................................................................1-9
Power Cord..........................................................................................1-9
Power Supply Failure.........................................................................1-10
1-7 Special Design Features................................................................1-10
Operating System Support...................................... ... ... ........................1-10
Remote Management ...........................................................................1-10
Computing Density/Power ....................................................................1-10
High-Efficiency Power Supplies............................................................1-11
1-8 Returning Merchandise for Service..............................................1-11
1-9 Contacting Supermicro...................................................................1-12
Chapter 2 System Safety..................................................................2-1
2-1 Electrical Safety Precautions ...........................................................2-1
2-2 General Safety Precautions.............................................................2-2
2-3 Electrostatic Discharge Precautions..............................................2-2
2-4 Operating Precautions......................................................................2-3
Chapter 3 Setup and Installation.................................................3-1
3-1 Overview.............................................................................................3-1
3-2 Unpacking the System .....................................................................3-1
v

SuperBlade User’s Manual
Choosing a Setup Location.....................................................................3-1
Rack Precautions....................................................................................3-2
Server Precautions .................................................................................3-2
Rack Mounting Considerations...............................................................3-2
Ambient Operating Temperature..........................................................3-2
Reduced Airflow...................................................................................3-2
Mechanical Loading.............................................................................3-3
Circuit Overloading...............................................................................3-3
Reliable Ground......................................................... .. ... .....................3-3
Installing the System Into a Rack............................................................3-3
Rack Mounting Hardware .......................................................................3-3
Installation...............................................................................................3-4
Chapter 4 System Modules.............................................................4-1
4-1 Chassis Management Module.........................................................4-2
Module Redundancy...............................................................................4-4
Master/Slave Modules.................... .......................................... .. ... .......4-4
SBM-CMM-001 or SBM-CMM-003 Module Installation..........................4-4
BMB-CMM-002 Module Installation........................................................4-5
Configuring the CMM.............................................. ... .............................4-7
CMM Functions.......................................................................................4-9
Local KVM............ ... .......................................... .................................4-10
Remote KVM over IP .........................................................................4-10
Remote Storage (Virtual Media).........................................................4-10
Serial Over LAN (SOL).......................................................................4-10
Monitoring Functions..........................................................................4-10
Power Consumption Management.....................................................4-11
CMM Switches and Buttons..................................................................4-11
USB Switch.......... ... ...........................................................................4-11
Reset Button ......................................................................................4-12
Firmware...............................................................................................4-12
Web-based Management Utility ............................................................4-12
Supported Browsers...........................................................................4-13
Network Connection/Login.................................................................4-13
Address Defaults................................................................................4-13
Home Page........................................................................................4-14
4-2 Double-Wide and Triple-Wide Modules.......................................4-15
Setting up a Double-Wide Bay..............................................................4-15
Setting up a Triple Wide Bay.................................................................4-24
vi

Chapter 5 Power Supply Modules..............................................5-1
5-1 Power Supply Modules.....................................................................5-1
Power Supply Failure..............................................................................5-6
Installing a Power Supply.................................. ......................................5-6
Removing a Power Supply......................................................................5-6
5-2 Power Supply Fans...........................................................................5-7
5-3 Power Components..........................................................................5-8
Power Cord.............................................................................................5-8
Power Cord Tie and Clamp........................................... ..........................5-9
Appendix A System Specifications...........................................A-1
A-1 Enclosure Specifications..................................................................A-1
A-2 Environmental Specifications..........................................................A-2
A-3 Address Defaults...............................................................................A-2
A-4 Power Supply Power Calculations.................................................A-3
:
Appendix B LED Descriptions......................................................B-1
B-1 Gigabit Ethernet Module LED Descriptions..................................B-1
B-2 1/10 Gigabit Ethernet Module LED Descriptions.........................B-2
B-3 SBM-XEM-X10SM 10G Ethernet Switch LED Descriptions......B-3
B-4 SBM-IBS-001 InfiniBand Switch LED Descriptions.....................B-4
B-5 SBM-IBS-Q3616M and SBM-IBS-Q3618M
InfiniBand Switch LED Descriptions
......................................................B-5
vii

SuperBlade User’s Manual
Notes
viii

List of Figures
Figure 3-1. Positioning the Enclosure Template...............................................3-4
Figure 3-2. Securing the Rails to the Rack .......................................................3-4
Figure 3-3. Attaching the Optional Handles......................................................3-5
Figure 3-4. Enclosure Installed into Rack.........................................................3-6
Figure 4-1. Typical Blade System Module Configuration: Rear View ........... ... .4-1
Figure 4-2. Chassis Management Module........................................................4-3
Figure 4-3. Stand-off Screw Holes on Module Board........................................4-5
Figure 4-4. Mini-CMM Mounted on Module Board............................................4-6
Figure 4-5. Choose Internal Protocol................................................................4-7
Figure 4-6. Manually Configure the IP Address................................................4-8
Figure 4-7. Changing Settings..........................................................................4-9
Figure 4-8. USB Switch on Rear of CMM.......................................................4-11
Figure 4-9. Home Page...................................................................................4-14
Figure 4-10. Horizontal Spacers for Single Bays............................................4-16
Figure 4-11. Modifying for a Double-Wide Module Bay (Steps 1 & 2) ............4-17
Figure 4-12. Modifying for a Double-Wide Module Bay (Steps 3 & 4) ............4-18
Figure 4-13. Modifying for an Upper Left Double-Wide Bay (Step 1)..............4-19
Figure 4-14. Modifying for an Upper Left Double-Wide Bay (Step 3)..............4-20
Figure 4-15. Modifying for an Upper Left Double-Wide Bay (Step 4)..............4-21
Figure 4-16. Modifying for an Upper Left Double-Wide Bay (Step 5)..............4-22
Figure 4-17. Modifying for an Upper Left Double-Wide Bay (Step 6)..............4-23
Figure 4-18. Modifying for a Triple Wide Bay (Step 1 & 2)..............................4-24
Figure 4-19. Modifying for a Triple Wide Bay (Step 3 & 4)..............................4-25
Figure 4-20. Modifying for a Triple Wide Bay (Step 5)....................................4-26
Figure 4-21. Modifying for a Triple Wide Bay (Step 6)....................................4-27
Figure 5-1. PWS-1K41-BR Power Supply.........................................................5-2
Figure 5-2. PWS-1K62-BR Power Supply.........................................................5-3
Figure 5-3. PWS-2K01-BR Power Supply.........................................................5-4
Figure 5-4. PWS-2K53-BR Power Supply.........................................................5-5
Figure 5-5. Power Supply Module.....................................................................5-7
Figure 5-6. Power Components........................................................................5-8
Figure 5-7. Power Cord Tie and Clamp Parts...................................................5-9
Figure 5-8. Power Cord Tie and Clamp Assembly..........................................5-10
ix

SuperBlade User’s Manual
Notes
x

List of Tables
Table 1-1. SuperBlade Enclosures ...................................................................1-5
Table 1-2. Number of Network Modules that May Be Installed
in each Enclosure..............................................................................................1-7
Table 4-1. Typical Blade System Module Configuration: Rear View.................4-1
Table 4-2. CMM Module Interface.....................................................................4-3
Table 4-3. CMM Module Features....................................................................4-3
Table 4-4. CMM Reset Settings......................................................................4-12
Table 4-5. Address Defaults............................................................................4-13
Table 4-6. Home Page Controls......................................................................4-14
Table 5-1. PWS-1K41-BR Power Supply Features........... ................................5-2
Table 5-2. PWS-1K62-BR Power Supply Features........... ................................5-3
Table 5-3. PWS-2K01-BR Power Supply Features........... ................................5-4
Table 5-4. PWS-2K53-BR Power Supply Features........... ................................5-5
Table 5-5. Power Components.........................................................................5-8
Table A-1. Enclosure Specification Features....................................................A-1
Table A-2. Environmental Specification Features.............................. ...............A-2
Table A-3. Address Defaults.............................................................................A-2
Table A-4. Power Supply: Power Calculations (PWS-2K53-BR).................. ... .A-3
Table A-5. Power Supply: Power Calculations (PWS-2K01-BR).................. ... .A-3
Table A-6. Power Supply: Power Calculations (PWS-1K62-BR).................. ... .A-4
Table A-7. Power Supply: Power Calculations (PWS-1K41-BR).................. ... .A-4
Table B-1. Gigabit Ethernet Switch LED Indicators ..........................................B-1
Table B-2. 1/10 Gigabit Ethernet Switch LED Indicators.............................. ....B-2
Table B-3. Stacking LED Activity (SBM-GEM-X2C/+ Only)..............................B-2
Table B-4. SBM-XEM-X10SM Ethernet Switch LEDs.......................................B-3
Table B-5. SBM-IBS-001 InfiniBand Switch LEDs............................................B-4
Table B-6. SBM-IBS-Q3616M and SBM-IBS-Q3618M
InfiniBand Switch LEDs.....................................................................................B-5
xi

SuperBlade User’s Manual
Notes
xii

Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
The SuperBlade is a compact self-contained server that connects to a pre-cabled
enclosure that provides power, cooling, management and networking functions. One
enclosure can hold up to either ten or fourteen blade units, depending upon the blade
enclosure used.
In this manual, “blade system” refers to the entire system (including the enclosure and
blades units), “blade” or “blade unit” refers to a single blade module and “blade
enclosure” is the unit that the blades, power supplies and modules are housed in.
Each blade unit is optimized to fit into either a specific ten-blade or fourteen-blade
enclosure.
Please refer to our web site for information on operating systems that have been
certified for use with the SuperBlade (www.supermicro.com/products/superblade/).
1-2 Quick Start Setup
This section covers how to quickly get your new SuperBlade system up and running.
Follow the procedure below to quickly setup your SuperBlade system.
1. Unpack the components of your SuperBlade system and check the packing list for
damaged or missing components.
2. Select a setup location for your system. See "Choosing a Setup Location" on
page 3-1 for details.
3. Setup any double-wide or triple-wide bays if you require any for double-wide or
triple-wide modules in your system. See Section 4-2: Double-Wide and Triple-Wide
Modules on page 4-15 for details.
4. Mount the SuperBlade chassis in your server rack. See "Installing the System Into a
Rack" on page 3-3 for details.
5. Install the power supply modules into the rear of the SuperBlade chasssis. See
"Installing a Power Supply" on page 5-6 for details.
6. Install the CMM module and any InfiniBand or Ethernet modules into the rear of the
SuperBlade chassis.
a. For the CMM module, see "SBM-CMM-001 or SBM-CMM-003 Module Installa-
tion" on page 4-4 for details.
b. For the InfiniBand and Ethernet modules, see "SBM-CMM-001 or
SBM-CMM-003 Module Installation" on page 4-4 and the SuperBlade Network
Modules User’s Manual on your system’s CD-ROM.
1-1

SuperBlade User’s Manual
c. Attach keyboard, mouse and video connections to your CMM module. See
"Local KVM" on page 4-10 for details.
d. Attach network connections for your InfiniBand or Ethernet modules. See the
SuperBlade Network Modules User’s Manual on your system’s CD-ROM for
details.
7. Setup your blade modules for use by doing the following:
a. Open the module case lids of each blade module. See your purchased blade’s
user’s manual on you system’s CD-ROM for details.
b. Install memory into each module. See the the user’s manual for your purchased
blade module from your system’s CD-ROM for details.
c. Close the module case lids when you have installed your memory for each
blade module. See the the user’s manual for your purchased blade module from
your system’s CD-ROM for details.
d. Install the hard disk drives into each module. See the the user’s manual for your
purchased blade module from your system’s CD-ROM for details.
e. Install your blade modules into your SuperBlade chassis. See the the user’s
manual for your purchased blade module from your system’s CD-ROM for
details.
8. Connect the power cords for your SuperBlade system’s power supply and plug them
into your power source ONLY after you have installed and secured all system
components.
9. Power up your SuperBlade system. Check to be sure all components are operating
right and are not showing any fault LEDs or alarms in their operation.
10. Install your selected operating system for each blade module. See the the user’s
manual for your purchased blade module from your system’s CD-ROM for details.
11. Download a BIOS update for each of your blade modules from the Supermicro
website.
1-3 OfficeBlade and DatacenterBlade Systems
DatacenterBlade™ and OfficeBlade™ are two SuperBlade system product packages
that use many of the same blades, modules and components as the standard
SuperBlade system.
DataCenterBlade
The DatacenterBlade system is a blade and enclosure that is configured for data center
and HPC applications. It has a performance and density optimized to achieve 1008
processing cores and 8TB memory, 252 2.5" SAS/SATA/SSD HDD storage per 42U
standard rack.
1-2

Chapter 1: Introduction
OfficeBlade
The OfficeBlade system is a blade and enclosure optimized for small-medium business
and personal HPC applications. With acoustically enhanced thermal and cooling
technologies, the OfficeBlade system can operate at or below 50dB with 10 DP server
blades. The OfficeBlade system is best used with Supermicro’s CSE-RACK1U mini-rack
cabinet.
Some examples of blades that are suitable for use in Office Blade mode are:
• SBI-7125C-S3
• SBI-7125C-S3E
• SBI-7125C-T3
For Office Blade Mode, it is recommended that no more than two 80W Intel Xeon 5400/
5200 series CPUs with 1333 FSB support be used in each blade module.
Twin Blades
Some blade modules for the SuperBlade system contain two (twin) nodes that allow the
blade module to function as effectively two server systems. This allows an enclosure
with these “twin” blades to function with a maximum compute capacity, density and
efficiency of up to 2880 cores, 15TB memory and 240 2.5" SATA HDD or SSD drives in
a 42U rack.
NOTE: Due to high power demands, a full enclosure of Twin-node blade
modules in an enclosure requires that you install four PWS-2K53-BR 2500W
power modules to power them.
Software Mode Selection
Using the Web-based Management Utility, you can specify your SuperBlade system to
use a different mode for quieter operation and lower fan speed. This is done by selecting
a mode in the CMM O
allows you to specify your system to run in either Office Blade Mode (for quieter
operation) or Enterprise Mode (for normal operation). See Section 4-1: Chassis
Management Module on page 4-2 for further details.
PERATION MODE section of the CMM STATUS screen. This screen
1-3

SuperBlade User’s Manual
1-4 Product Checklist of Typical Components
• Blade Enclosure (x1): SBE-710E/Q, SBE-720E, SBE-720D-R75 or SBE-720D-D50
(10-blade series); SBE-714D/E (14-blade series)
• Blade Unit (minimum of 2, 10 or 14 maximum): See the the Supermicro website
(http://www.supermicro.com/products/superblade/) for a complete list of blades that
can be mounted in your system.
• Power Supplies (x2): PWS-1K62-BR, PWS-2K01-BR or PWS-2K53-BR
• CMM Module (x1): SBM-CMM-001 (Not compatible with 720E chassis enclosure)
• KVM Cable (x1): CBL-0218L
• Dummy Blade Units: MCP-650-00004-0N (10-blade enclosure) or
MCP-650-00005-0N (14-blade enclosure)
• Dummy Power Supplies: MCP-650-00001-0N
• Dummy CMM Modules: MCP-650-00002-0N
• Dummy GbE Switches: MCP-650-00003-0N
• SuperBlade CD-ROM with other SuperBlade component manuals
Optional components include:
• InfiniBand® Switch Module: SBM-IBS-001 or SBM-IBS-Q3618M and
SBM-IBS-Q3616M (“M” models support BMB-CMM-002 Mini-CMM module)
• InfiniBand Pass-through Module: SBM-IBP-D14
• Blade IPMI Add-on Card: AOC-SIMBL
• Mezzanine Cards (required for operation with the InfiniBand Switch): AOC-IBH-002,
AOC-IBH-XDS, AOC-IBH-XDD, XOC-IBH-XQS and/or AOC-IBH-XQD
• AOC-XEH-iN2 Add-on Card (required for operation with the 10-Gbps Ethernet
Pass-Through or 10-Gbps Ethernet Switch Modules)
• Ethernet Switches: SBM-GEM-001 (1-Gbps), SBM-GEM-X2C+ (1/10-Gbps), or
SBM-XEM-X10SM (10-Gbps)
• Ethernet Pass Through Modules: SBM-GEM-002 (1-Gbps), SBM-GEP-T20
(1-Gbps) or SBM-XEM-002M (10-Gbps)
• Extra CMM Module for redundancy: SBM-CMM-001, BMB-CMM-002,
SBM-CMM-003
Additional modules will periodically become available. Please refer to http://
www.supermicro.com/products/superblade for the most current list of modules available
for the SuperBlade.
Blade systems install into standard racks. Up to six 7U blade systems may be installed
into a 19" industry standard 42U rack.
1-4
Chapter 1: Introduction
1-5 Blade Enclosure Features
Supermicro's blade enclosures are designed to house from 10 to 14 blade units. Each
accommodates either two or more power supplies. The enclosure mid-plane allows the
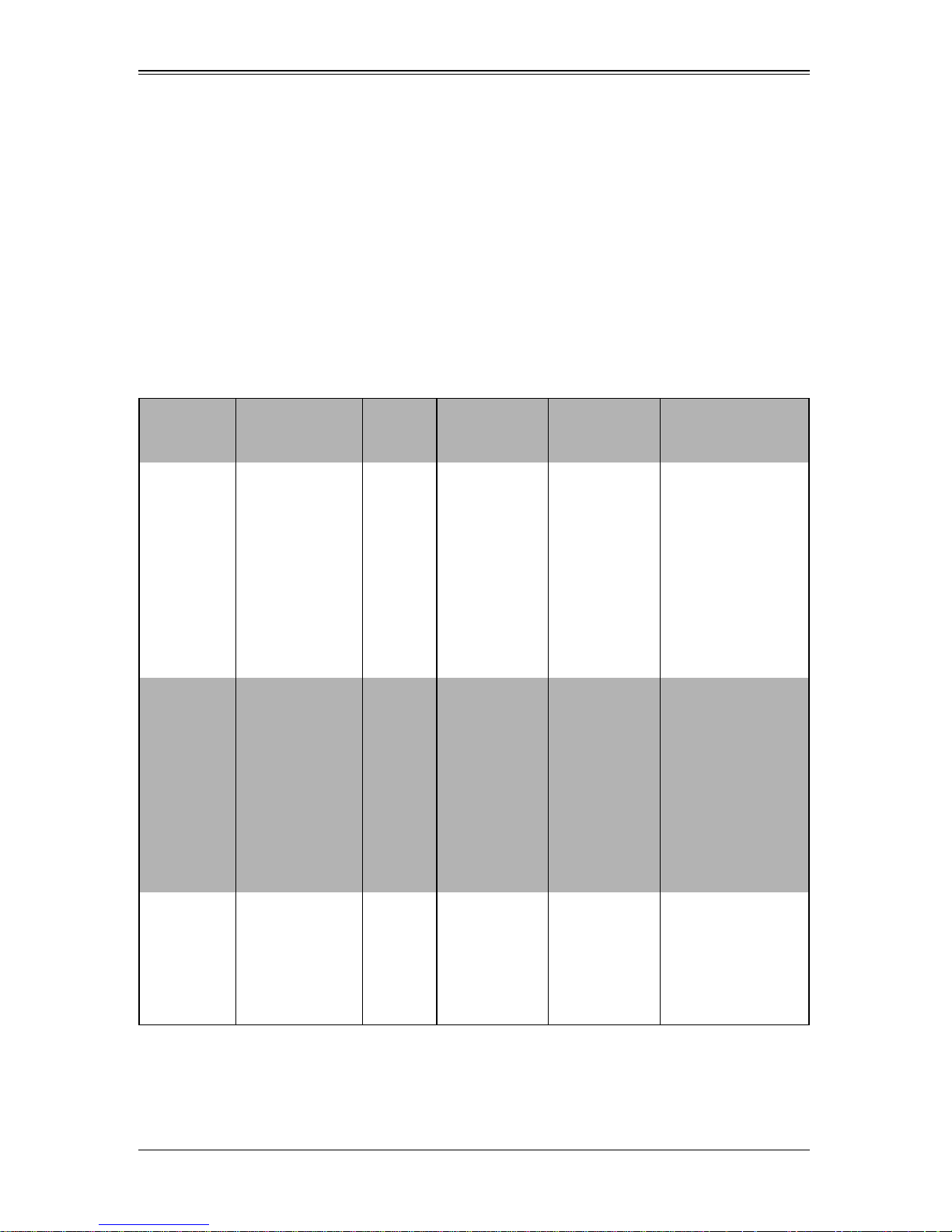
blade units to share certain functions such as power, cooling and networking. Table 1-1
below describes the various enclosures, their components and modules. Table 1-2
shows the number of each module that may be installed in the various enclosure
models.
Please check the Supermicro website for the latest module and enclosure installation
information at http://www.supermicro.com/servers/blade/networking/matrix.cfm for
further details.
Table 1-1. SuperBlade Enclosures
Enclosure
Model
SBE-710E 10-blade Modules
SBE-710Q 10-blade Modules
Blade Module
Capacity
Power
Supply
Options
1400W
1620W
2000W
1620W
2500W
Intel Blade
Options
SBI-7126TG
SBI-7126T-S6
SBI-7126T-SH
SBI-7126T-T1E
SBI-7126T-T1L
SBI-7125B-T1
SBI-7125W-S6
SBI-7125C-S3E
SBI-7125C-S3
SBI-7125C-T3
SBI-7126TG
SBI-7126T-S6
SBI-7126T-SH
SBI-7126T-T1E
SBI-7126T-T1L
SBI-7125B-T1
SBI-7125W-S6
SBI-7125C-S3E
SBI-7125C-S3
SBI-7125C-T3
AMD Blade
Options
SBA-7142G-T4
SBA-7141A-T
SBA-7141M-T
SBA-7121M-T1
SBA-7141A-T
SBA-7141M-T
SBA-7121M-T1
Module
Options
SBM-CMM-001 or
BMB-CMM-002
(Mini-CMM)
SBM-GEM-001,
SBM-GEM-002 or
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SBM-IBS-001
SBM-IBP-D14
SBM-XEM-002M
(See Note 2)
SBM-CMM-003 or
BMB-CMM-002
(Mini-CMM)
SBM-GEM-001,
SBM-GEM-002 or
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SBM-IBS-Q3616 or
SBM-IBS-Q3616M
SBM-XEM-X10SM
(See Note 1)
SBE-714D 14-blade Modules
1400W
1620W
SBI-7426T-S3
SBI-7426T-T3
SBI-7426T-SH
SBI-7425C-S3E
SBI-7425C-S3
SBI-7425C-T3
1-5
NA
SBM-CMM-001
SBM-GEM-001,
SBM-GEM-002 or
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SuperBlade User’s Manual
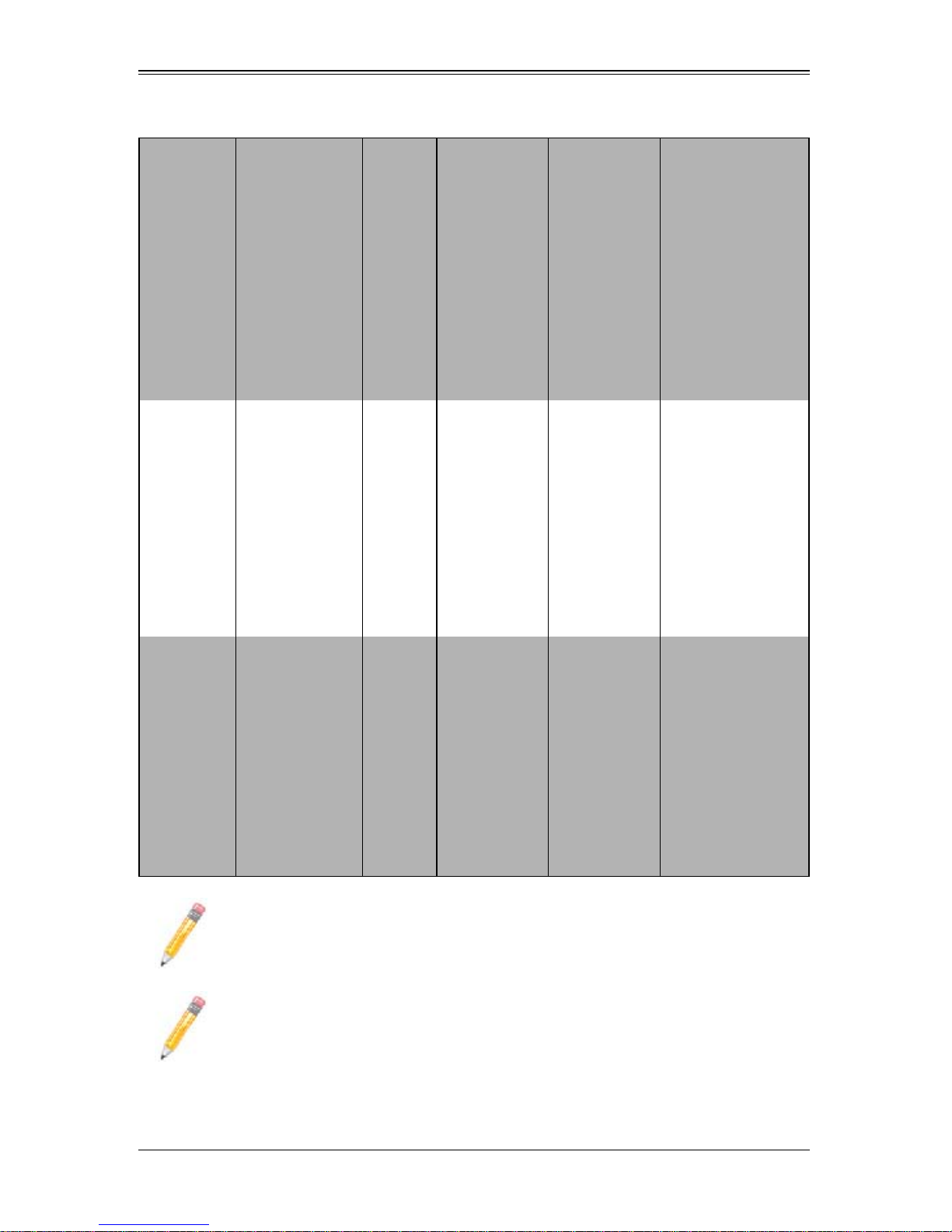
Table 1-1. SuperBlade Enclosures (Continued)
Enclosure
Model
SBE-714E 14-blade Modules
SBE-720D
Blade Module
Capacity
10-blade Modules
(20 TwinBlade
nodes)
Power
Supply
Options
1400W
1620W
2500W
(x2)
Intel Blade
Options
SBI-7426T-S3
SBI-7426T-T3
SBI-7426T-SH
SBI-7425C-S3E
SBI-7425C-S3
SBI-7425C-T3
SBI-7126TG
SBI-7226T-T2
SBI-7126T-S6
SBI-7126T-SH
SBI-7126T-T1E
SBI-7126T-T1L
SBI-7125B-T1
SBI-7125W-S6
SBI-7125C-S3E
SBI-7125C-S3
SBI-7125C-T3
AMD Blade
Options
NA
SBA-7222G-T2
SBA-7142G-T4
SBA-7141A-T
SBA-7141M-T
SBA-7121M-T1
Module
Options
SBM-CMM-001 or
BMB-CMM-002
(Mini-CMM)
SBM-GEM-001,
SBM-GEM-002 or
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SBM-IBS-001
SBM-IBP-D14
SBM-XEM-002M
(See Note 2)
SBM-CMM-003
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SBM-GEP-T20
SBE-720E
BMB-CMM-002
(Mini-CMM) or
SBM-CMM-003
SBM-GEM-X2C+
SBM-GEP-T20
SBM-IBS-Q3616 or
SBM-IBS-Q3616M
SBM-IBS-Q3618 or
SBM-IBS-Q3618M
SBM-XEM-X10SM
(See Note 1)
(See Note 3)
10-blade Modules
(20 TwinBlade
nodes)
2500W
(x4)
SBI-7126TG
SBI-7226T-T2
SBI-7126T-S6
SBI-7126T-SH
SBI-7126T-T1E
SBI-7126T-T1L
SBI-7125B-T1
SBI-7125W-S6
SBI-7125C-S3E
SBI-7125C-S3
SBI-7125C-T3
SBA-7222G-T2
SBA-7142G-T4
SBA-7141A-T
SBA-7141M-T
SBA-7121M-T1
NOTE 1: When supporting the dual InfiniBand QDR and 10-Gb switch modules
you must also use the BMB-CMM-002 Mini-CMM module.
NOTE 2: One InfiniBand DDR switch/pass-through module and one 10-Gb
pass-thru module can be supported simultaneously with the BMB-CMM-002
Mini-CMM installed in the 10-Gb pass-thru module.
1-6
Chapter 1: Introduction
NOTE 3: When the SBM-GEP-T20 is installed, one SBM-GEM-X2C+ and one
InfiniBand QDR switch or 10-Gb switch can also be supported.
NOTE: The SBE-720E and SBE-720D series enclosures support only one
CMM module. When equipped with redundant QDR IB switches or 10 Gb
Ethernet switches, one of the switches must have a BMB-CMM-002 Mini-CMM
installed. The SBE-720E and SBE-720D series enclosures do not support the
InfiniBand Pass-Through module.
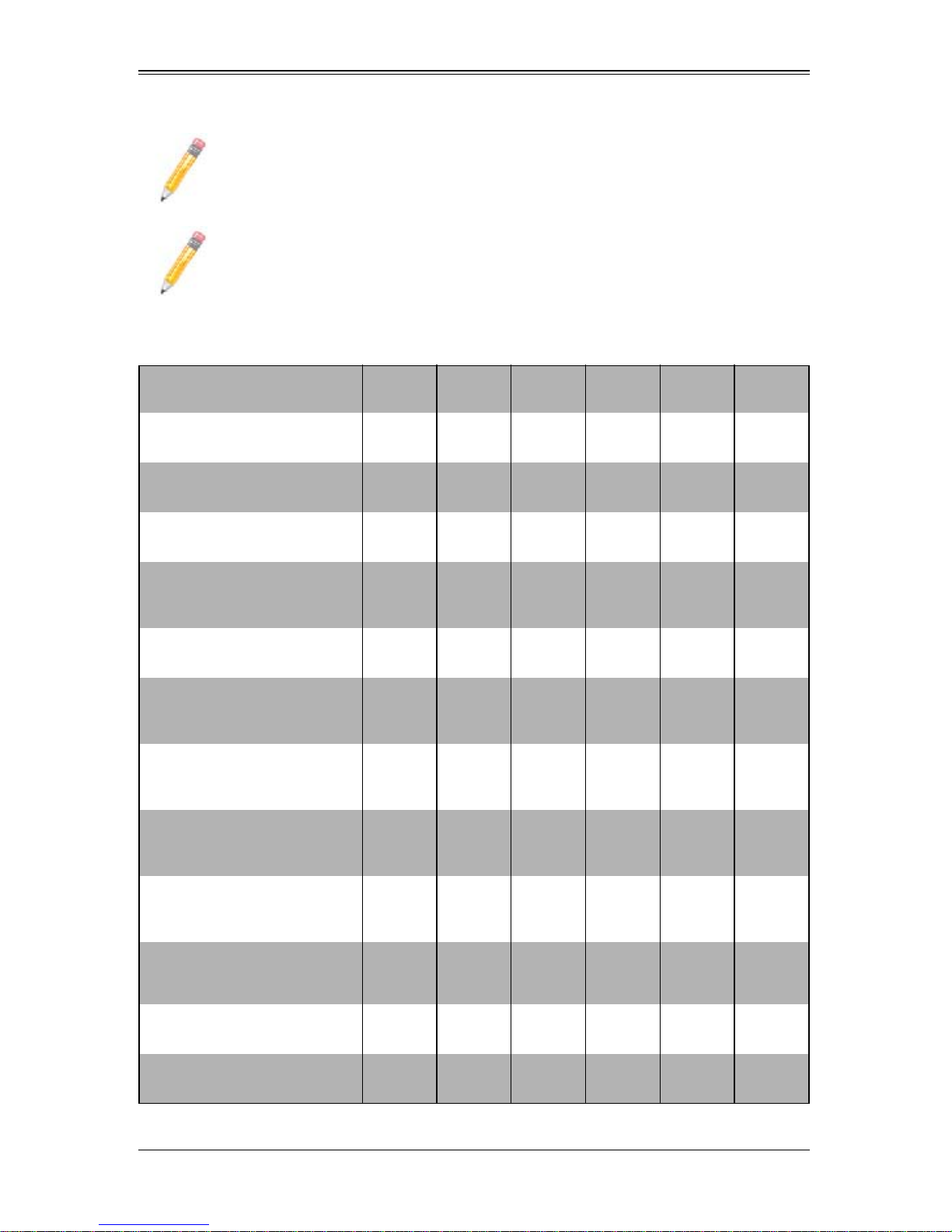
Table 1-2. Number of Network Modules that May Be Installed in each Enclosure
Name (SKU)
1G Ethernet Switch
(SBM-GEM-001)
1G Ethernet Pass-Through
(SBM-GEM-002)
1/10G Ethernet Switch
(SBM-GEM-X2C+)
10G Ethernet Switch
w/ option for Mini-CMM
(SBM-XEM-X10SM)
1G Ethernet Pass-Through
(SBM-GEP-T20)
10G Ethernet Pass-Through
w/ option for Mini-CMM
(SBM-XEM-002M )
QDR 16UL/20DL InfiniBand
Switch w/ option for Mini-CMM
(SBM-IBS-Q3616M)
QDR 16UL/20DL InfiniBand
Switch
(SBM-IBS-Q3616)
SBE
-720E
1 or 2 1 or 2 1 or 2 1 or 2 1 or 2 1
1 or 2 1 or 2
12
1 or 2 1 or 2
1 1
SBE
-720D
SBE
-710E
1 or 2 1 or 2 1 or 2 1
1 or 2 1 or 2 1 or 2 1
1 or 2 1 or 2
SBE
-710Q
SBE
-714E
SBE
-714D
QDR 18UL/18DL InfiniBand
Switch w/ option for Mini-CMM
(SBM-IBS-Q3618M)
QDR 18UL/18DL InfiniBand
Switch
(SBM-IBS-Q3618)
DDR InfiniBand Switch
(SBM-IBS-001)
DDR InfiniBand Pass-Through
(SBM-IBP-D14)
1 or 2 1 or 2
1 1
11
1 1
1-7

SuperBlade User’s Manual
The following sections provide a general outline of the main features for all blade server
enclosures.
Power
The typical blade enclosure features a 2500W, 2000W , 1620W or 1400W power system
composed of two active power supply modules. An alternate configuration (and required
for a full 10 or 14-blade system) features a total of four power supply modules for
redundancy. This power redundancy feature allows you to replace a failed power
module while the backup module takes over to keep the system running. Y ou must have
either two or four power supply modules installed in the blade enclosure (four is
recommended in a full system).
The Chassis Management Module assumes the worst case (maximum) power for any
model of blade prior to applying power. If the power supplies cannot supply that amount
of power, given the current load on the power supplies, then the CMM will not allow that
unit to power up. After a blade is powered up, the blade’s BIOS calculates the actual
power load required by the blade based upon the installed devices and informs the
CMM of its requirements. The CMM then adjust the remaining power for additional
blades based upon the actual power used by the blades th at are powered on.
Middle Plane
The middle plane connects the various capabilities of the blades, such as the Gigabit
(GbE) switch(es) to Network Interface Controller(s), the Chassis Management Module
(CMM) to the USB devices and the InfiniBand Switch to the Host Channel Adapters.
These devices all connect to the middle plane through high density connectors that
provide both signals and power. This type of configuration reduces the amount of
system cabling and simplifies the task of setting up the system. It provides an alternative
signals route to support redundant power, CMM, network and IPMI functions.
NOTE: Signaling information can NOT be physically routed from one blade to
another.
LEDs
Two LEDs are located at the right top of the enclosure above the last or right most blade.
The left LED provides Power Status information and the right LED is the Fault LED.
Enclosure Cooling
The cooling for the entire blade system is provided by the fans in the power supply
modules. For example, the 2500W and 2000W power supply modules have four fans
per module, whereas the 1600W and 1400W power supply modules have two fans per
module. If a power supply fails, its fans will continue to operate to provide continuous
cooling. For this reason, a failed power supply should remain installed in the enclosure
until a replacement unit is ready.
1-8

Chapter 1: Introduction
NOTE: You must install dummy power supplies (MCP-650-00001-0N) in any
open power supply slots in order to prevent air flow leaks that would reduce
cooling efficiency in the blade system’s enclosure.
For overheat problems, check that there are no obstructions (such as poorly routed
cables), check that all fans are operating normally and make sure the ambient room
temperature is not too warm (refer to Section A-2: Environmental Specifications on
page A-2 for the maximum operating temperature). You can also use either of the blade
management software utilities to increase the fan speed and maximize system cooling.
In the event of a power overload, you will have to add additional power supply modules
to take up the load. Otherwise, you will not be able to power up all the blade modules.
The blade BIOS plus CMM firmware calculates the load to determine if the power
supplies can adequately handle the total system configuration.
1-6 Power Supply Features
The SuperBlade enclosure comes standard with one CMM module and either two or
four power supplies. Information on the power supplies is summarized below. See
Section 4-1: Chassis Management Module on page 4-2 for details on the CMM module
and Chapter 5 for details on the power supplies.
If you install only two power supplies in the enclosure, they should be installed in the
lower rather than the upper power bays. The reason for this counter-intuitive installation
is that the power supplies in the lower bays provide increased airflow across the
memory modules within each blade module.
Power Supply Modules
Each power supply module has its own power cord. Four modules are required when
the full complement of blade units are installed into an enclosure. An LED on the back of
a power supply will be red when AC power is present and green when the power is on.
Supermicro's high-efficiency blade system power supplies deliver continuous redundant
power up to 94% peak efficiency. Each power supply module includes a management
module that monitors the power supplies and the power enclosure.
Power Cord
Each 2500W or 2000W power supply module has a C-20 type socket (IEC-60320-C20)
for AC power and the power cord must have a C-19 type connector (IEC-60320-C19) to
connect to the power supply. Each 1400W or 1620W power supply module has a C-14
type socket (IEC-60320-C14) for AC power and the power cord must have a C-13 type
connector (IEC-60320-C13) to connect to the power supply.
WARNING: Please note that ONLY the recommended power cord or an
equivalent 14 Gauge power cord should be used for the 1620W/1400W power
supply . T ypical C13/C14 cords are only 16 Gauge wiring and pose a fire hazard if
they are used.
1-9

SuperBlade User’s Manual
A plastic locking clip partially covering the socket was designed to prevent the power
supply module from being removed with the power cord still connected.
Refer to Appendix A for power/amperage calculation tables.Refer to the supermicro web
site for further details on power cords.
Power Supply Failure
If a power supply or a fan in a power supply fails, the system management software will
notify you of the situation. In either case, you will need to replace the power supply
module with another identical one. Please note that if a power supply fails, its fans will
continue to operate to provide system cooling. For this reason, a failed power supply
should remain installed in the enclosure until a replacement unit is ready.
See Chapter 5 for the procedure on replacing power supplies.
1-7 Special Design Features
Supermicro's SuperBlade offers special design features, some of which no other blade
server can duplicate. These features give you extraordinary flexibility in configuring a
blade system for your own particular needs.
Operating System Support
Both Microsoft Windows, VMWare and Linux operating systems are supported by the
SuperBlade. Furthermore, you may have different operating systems running on
different blade units within the same blade enclosure.
Remote Management
The Chassis Management Module (CMM) can manage the whole enclosure and any
individual blade module by switching around to it.
Using an optional SIMBL add-on card provides separate IPMI controls for any blade
module that has one installed in it. If your application needs to manage individual blade
units at the same time, just add a SIMBL add-on card to each blade module.
NOTE: Some Blade modules already have onboard BMC.
Computing Density/Power
Dual and quad core processors are supported in the blade module systems. Each
SuperBlade mainboard supports two or four processors and up to 256 GB of main
memory . This translates to a maximum potential of up to 40 processors and 2560 GB of
memory per 7U enclosure or 240 processors and 15 TB of memory for a full 42U rack.
1-10

Chapter 1: Introduction
High-Efficiency Power Supplies
A reliable source of power is critical in server systems and even more so in a blade
system, where up to fourteen systems (blades) share the same power source.
SuperBlade power supplies have been designed to operate at up to 94% peak efficiency
and provide redundancy. Using high-efficiency power supplies results in a measurable
reduction in wasted energy consumption and generated heat.
1-8 Returning Merchandise for Service
A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is required before
any warranty service will be rendered. Y ou can obtain service by calling your vendor for
a Returned Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number. When returning to the
manufacturer, the RMA number should be prominately displayed on the outside of the
shipping carton, and mailed prepaid or hand-carried. Shipping and handling charges will
be applied for all orders that must be mailed when service is complete.
This warranty only covers normal consumer use and does not cover damages incurred
in shipping or from failure due to the alteration, misuse, abuse or improper maintenance
of products.
During the warranty period, contact your distributor first for any product problems.
For faster service, RMA authorizations may be requested online at:
http://www. supermicro.com/support/rma/
1-11

SuperBlade User’s Manual
1-9 Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer , Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email:
Web Site: www.supermicro.com
marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
‘s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
Email:
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Asia-Pacific
Address: Super Micro Computer , Inc.
4F, No. 232-1, Liancheng Rd.
Chung-Ho 235, Taipei County
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3991
Web Site: www.supermicro.com.tw
Technical Support:
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-5990
1-12

Chapter 2
System Safety
2-1 Electrical Safety Precautions
Basic electrical safety precautions should be followed to protect yourself from harm and
the SuperBlade from damage:
• Be aware of how to power on/off the enclosure power supplies and the individual
blades as well as the room's emergency power-off switch, disconnection switch or
electrical outlet. If an electrical accident occurs, you can then quickly remove power
from the system.
• Do not work alone when working with high voltage components.
• Power should always be disconnected from the blade module when removing or
installing such system components as the mainboard, memory modules and
processors.
• When working around exposed electrical circuits, another person who is familiar
with the power-off controls should be nearby to switch off the power if necessary.
• Use only one hand when working with powered-on electrical equipment. This is to
avoid making a complete circuit, which will cause electrical shock. Use extreme
caution when using metal tools, which can easily damage any electrical components
or circuit boards they come into contact with.
• Do not use mats designed to decrease electrostatic discharge as protection from
electrical shock. Instead, use rubber mats that have been specifically designed as
electrical insulators.
• The power supply power cords must include a grounding plug and must be plugged
into grounded electrical outlets. Power input requires 110-240 V AC, depending upon
your power supply module. See Section 5-1: Power Supply Modul es on p age5-1 in
Chapter 5 for details.
• Mainboard Battery: This battery must be replaced only with the same or an
equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer (CR2032 Lithium 3V battery).
Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
WARNING: There is a danger of explosion if the onboard battery is installed
upside down, which will reverse its polarities.
WARNING: Please handle used batteries carefully. Do not damage the battery in
any way; a damaged battery may release hazardous materials into the
environment. Do not discard a used battery in the garbage or a public landfill.
Please comply with the regulations set up by your local hazardous waste
management agency to dispose of your used battery properly.
2-1

SuperBlade User’s Manual
• Mainboard replaceable soldered-in fuses: Self-resetting PTC (Positive Temperature
Coefficient) fuses on the mainboard must be replaced by trained service technicians
only. The new fuse must be the sa me or equivalent as the one replaced. Contact
technical support for details and support.
2-2 General Safety Precautions
Follow these rules to ensure general safety:
• Keep the area around the SuperBlade clean and free of clutter.
• Place the blade module cover and any system components that have been removed
away from the system or on a table so that they won't accidentally be stepped on.
• While working on the system, do not wear loose clothing such as neckties and
unbuttoned shirt sleeves, which can come into contact with electrical circuits or be
pulled into a cooling fan.
• Remove any jewelry or metal objects from your body, which are excellent metal
conductors that can create short circuits and harm you if they come into contact with
printed circuit boards or areas where power is present.
• After accessing the inside of the system, replace the blade module's cover before
installing it back into the blade enclosure.
2-3 Electrostatic Discharge Precautions
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is generated by two objects with different electrical
charges coming into contact with each other. An electrical discharge is created to
neutralize this difference, which can damage electronic components and printed circuit
boards.
The following measures are generally sufficient to neutralize this difference before
contact is made to protect your equipment from ESD:
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent static discharge.
• Keep all components and printed circuit boards (PCBs) in their antistatic bags until
ready for use.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the antistatic bag.
• Do not let components or PCBs come into contact with your clothing, which may
retain a charge even if you are wearing a wrist strap.
• Handle a board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral chips,
memory modules or contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the mainboard and peripherals back into their antistatic bags when not in use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure the blade enclosure provides excellent
conductivity between the power supplies, the blade modules and the mainboard.
WARNING: This product may be connected to an IT power system. In all cases,
make sure that the unit is also reliably connected to Earth (ground).
2-2
 Loading...
Loading...