
SBI-7126T-S6
Blade Module
User’s Manual
Revison 1.0

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and i s believed to be accurate. The
vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document, makes no
commitment to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to not ify any person or
organization of the u pdates. Plea se Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual, please see
our web site at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. (“Supermicro”) reserves the right to make changes to the product described
in this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software, if any, and documentation
may not, in whole or in part, be copied, photocop ied, re produced, translated or redu ced t o any medi um or
machine without prior written consent.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR INABILITY T O USE
THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPERMICRO SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF
REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING, INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and cu stomer shall be governed by the laws of Santa Clara
County in the State of California, USA. The S tate of California, County of Santa Clara shall be the
exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes. Super Micro's total liabilit y for all claims will not
exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC State ment: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits f or a Class A digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction manual, may cause harmful interference with radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference,
in which case you will be required to correct the interference at your own expense.
California Best Management Practices Regulations for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning
applies only to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells. Perchlorate
Material-special handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate for further
details.
WARNING: HANDLING OF LEAD SOLDER MATERIALS USED IN THIS
PRODUCT MAY EXPOSE YOU TO LEAD, A CHEMICAL KNOWN TO THE
STATE OF CALIFORNIA TO CAUSE BIRTH DEFECTS AND OTHER
REPRODUCTIVE HARM.
Manual Revison 1.0
Release Date: July 10, 2009
Unless you request and receive written permission fr om Super Micro Computer, Inc., you may not copy
any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies referred
to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 2009 by Super Micro Computer, Inc.
All rights reserv ed .
Printed in the United States of America
ii

Preface
About this Manual
This manual is written for professional system integrators, Information Technology
professionals, service personnel and technicians. It provides information for the
installation and use of Supermicro's SBI-7126T-S6 blade module. Installation and
maintenance should be performed by experienced professionals only.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1: Introduction
The first chapter provides a checklist of the main components included with the
SBI-7126T-S6 blade module and describes its main features.
Chapter 2: System Safety
You should familiarize yourself with this chapter for a general overview of safety
precautions that should be followed when installing and servicing the SBI-7126T-S6
blade module.
Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Refer to this chapter for details on installing the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module into the
Superblade chassis. Other sections cover the installation and placement of memory
modules and the installation of hard disk drives into the blade module.
Chapter 4: Blade Module Features
This chapter coves features and component information about the SBI-7126T-S6 blade
module. Included here are descriptions and information for mainboard components,
connectors, LEDs and other features of the blade module.
Chapter 5: RAID Setup Procedure
RAID setup and operations for the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module are covered in this
chapter.
Chapter 6: BIOS
BIOS setup is covered in this chapter for the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module.
Appendix A: BIOS POST Codes
BIOS POST Codes for the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module are explained in this appendix.
iii

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
iv

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................................1-1
1-1 Overview.............................................................................................1-1
1-2 Product Checklist of Typical Components.....................................1-1
1-3 Blade Module Features....................................................................1-2
Processors..............................................................................................1-2
Memory...................................................................................................1-2
Storage....................................................................................................1-3
Density....................................................................................................1-3
1-4 Contacting Supermicro.....................................................................1-4
Chapter 2 System Safety..................................................................2-1
2-1 Electrical Safety Precautions ...........................................................2-1
2-2 General Safety Precautions.............................................................2-2
2-3 Electrostatic Discharge Precautions..............................................2-2
2-4 Operating Precautions......................................................................2-2
Chapter 3 Setup and Installation.................................................3-1
3-1 Overview.............................................................................................3-1
3-2 Installing Blade Modules..................................................................3-1
Powering Up a Blade Unit.......................................................................3-1
Powering Down a Blade Unit ..................................................................3-1
Removing a Blade Unit from the Enclosure............................................3-1
Removing/Replacing th e Bl ade Cover....................................................3-2
Installing a Blade Unit into the Enclosure ...............................................3-2
3-3 Processor Installation .......................................................................3-4
3-4 Onboard Battery Installation............................................................3-5
3-5 Memory Installation...........................................................................3-6
Populating Memory Slots........................................................................3-6
DIMM Installation....................................................................................3-8
3-6 Hard Disk Drive Installation.............................................................3-9
3-7 Installing the Operating System....................................................3-11
Installing with an External USB CD-ROM Drive....................................3-11
Installing via PXE Boot..........................................................................3-11
Installing via Virtual Media (Drive Redirection) .....................................3-12
3-8 Management Software...................................................................3-12
v

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
3-9 Configuring and Setting up RAID.................................................3-12
Chapter 4 Blade Module Features..............................................4-1
4-1 Control Panel.....................................................................................4-2
Power Button ..........................................................................................4-3
KVM Button.............................................................................................4-3
LED Indicators ........................................................................................4-3
KVM Connector.......................................................................................4-3
4-2 Mainboard...........................................................................................4-4
Jumpers..................................................................................................4-6
CMOS Clear............................................................................................4-6
4-3 Blade Unit Components...................................................................4-7
Memory Support .....................................................................................4-8
Hard Disk Drives.....................................................................................4-8
Chapter 5 RAID Setup Procedure...............................................5-1
Chapter 6 BIOS.......................................................................................6-1
6-1 Introduction.........................................................................................6-1
System BIOS ..........................................................................................6-1
How To Change the Configuration Data .................................................6-1
Starting the Setup Utility.................................... ... ... ............................ ... .6-1
6-2 BIOS Updates....................................................................................6-2
Flashing BIOS.........................................................................................6-2
6-3 Running Setup...................................................................................6-3
6-4 Main BIOS Setup...............................................................................6-4
6-5 Advanced Setup................................................................................6-5
6-6 Security.............................................................................................6-15
6-7 Boot...................................................................................................6-17
6-8 Exit.....................................................................................................6-19
6-9 Hardware Health Information........................................................6-20
CPU Temperature .................................................................................6-20
System Temperature.............................................................................6-21
Voltage Monitoring ................................................................................6-21
Appendix A BIOS POST Codes....................................................A-1
A-1 BIOS POST Messages....................................................................A-1
A-2 BIOS POST Codes...........................................................................A-3
Recoverable POST Errors............................................ .. ... .....................A-4
vi

Terminal POST Errors............................... ... ............................ ... ............A-4
vii

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
viii

List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Full Rack of Blade Enclosures and Blade Servers.........................1-3
Figure 3-1. Inserting a Blade into the Enclosure...............................................3-3
Figure 3-2. Locking the Blade into Position.......................................................3-3
Figure 3-3. Installing a Processor in a Socket...................................................3-5
Figure 3-4. Installing the Onboard Battery.................. ... ... ............................... .3-6
Figure 3-5. 12-Slot DIMM Numbering...............................................................3-7
Figure 3-6. Installing a DIMM into a Memory Slot........................... ... ... ............3-8
Figure 3-7. Installing a Hard Drive in a Carrier................................................3-10
Figure 4-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module Front View........................................4-1
Figure 4-2. Blade Control Panel........................................................................4-2
Figure 4-3. B8DT6 Mainboard...........................................................................4-4
Figure 4-4. Intel 5500 Tylersburg Chipset Block Diagram................................4-5
Figure 4-5. Exploded View of SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module.............................4-7
Figure 6-1. Main Setup Menu Screen...............................................................6-4
Figure 6-2. Advanced Setup Menu...................................................................6-5
Figure 6-3. Security Setup Menu....................................................................6-15
Figure 6-4. Boot Setup Menu..........................................................................6-17
Figure 6-5. Exit Setup Menu...........................................................................6-19
ix

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
x

List of Tables
Table 1-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Specification Features ...................................1-2
Table 3-1. Populating Twelve Memory Slots for Interleaved Operation............3-6
Table 4-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module Features............................................4-1
Table 4-2. Blade Control Panel.........................................................................4-2
Table 4-3. Blade Module LED Indicators ..........................................................4-3
Table 4-4. B8DT6 Mainboard Layout................................................................4-5
Table 4-5. Main Components of SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module.........................4-7
Table 6-1. Main BIOS Setup Menu Options......................................................6-5
Table 6-2. Advanced Setup Menu Options.......................................................6-6
Table 6-3. CPU and Clock Configuration Sub-menu ........................................6-7
Table 6-4. IDE Configuration Menu...................................................................6-7
Table 6-5. PCIPnP Configuration Sub-menu....................................................6-8
Table 6-6. SuperIO Configuration Sub-menu....................................................6-9
Table 6-7. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu.....................................................6-9
Table 6-8. ACPI Configuration Sub-menu.......................................................6-11
Table 6-9. AHCI Configuration Sub-menu ......................................................6-12
Table 6-10. Event Log Configuration Sub-menu.............................................6-12
Table 6-11. IPMI Configuration Sub-menu......................................................6-12
Table 6-12. MPS Configuration Sub-menu.....................................................6-14
Table 6-13. PCI Express Configuration Sub-menu.........................................6-14
Table 6-14. SMBIOS Configuration Sub-menu...............................................6-14
Table 6-15. Remote Access Configuration Sub-menu....................................6-14
Table 6-16. System Health Monitor Sub-menu...............................................6-15
Table 6-17. Security Menu Options.................................................................6-16
Table 6-18. Boot Setup Menu Options............................................................6-17
Table 6-19. Exit Menu Options........................................................................6-19
Table A-1. BIOS POST Messages....................................................................A-1
Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors.....................................................................A-4
Table A-3. Boot Block Flash ROM Terminal POST Errors................................A-8
xi

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
xii

Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade module is a compact self-contained server that connects into a
pre-cabled enclosure that provides power, cooling, management and networking
functions. One enclosure for the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module can hold ten blade units.
In this manual, “blade system” refers to the entire system (including the enclosure and
blades units), “blade” or “blade unit” refers to a single blade module and “blade
enclosure” is the chassis that the blades, power supplies and modules are housed in.
Please refer to our web site for information on operating systems that have been
certified for use with the SuperBlade (www.supermicro.com/products/superblade/).
1-2 Product Checklist of Typical Components
Your blade module ships with its mainboard already installed in its chassis. Memory,
hard disk drives and the CPU must all be installed by the user after shipment. See
Chapter 3: "Setup and Installation" on page 3-1 for details on installation of these
components.
Aside from the blade module unit itself, the following optional Mezzanine add-on cards
(with InfiniBand Switch) may be ordered for your blade module:
• AOC-IBH-XDD
• AOC-IBH-XDS
• AOC-IBH-XQS
See the Supermicro website and the Superblade Network Modules User’s Manual on
your Superblade system’s CD-ROM for more details on these add-on cards including
instructions on how to install them.
NOTE: Some of these add-on cards may not be available at the time of this
manual’s publication. Please refer to the Supermicro website for their
availability.
1-1
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
1-3 Blade Module Features
Table 1-1 lists the main features of the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module. See the proceeding
section for components typically included in a blade system and other optional
components. Specific details on the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module is found in Chapter 4:
"Blade Module Features" on page 4-1.
Table 1-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Specification Features
Mainboard
Processors
FSB Speed 1333/1066/800 MHz front side (system) bus speed
Chipset Intel 5500 Tylersburg
Graphics Controller Hermon
BIOS 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM wiht AMI® BIOS
Memory Capacity
Drive Controller LSI SAS2 on-board controller for six SAS(2) or SATA
Hard Drive Bays Six (6) hot-swap drive bays for 2.5" SAS(2) or SATA disk drives
B8DT6 (proprietary form factor)
Chassis Dimensions (HxWxD): 11.32” x 1.67” x 18.9”
Single or dual Intel™ Xeon® 5500 Sequence processors. Please refer to
our web site for a complete listing of supported processors.
Twelve 240-pin DIMM sockets supporting up to 96 GB/24 GB of ECC
Registered/Unbuffered ECC DDR3-1333/1066/800 SDRAM.
Processors
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade module supports up to dual 1366-pin Intel Xeon 5500 series
processors.
Refer to the Supermicro web site for a complete listing of supported proce ssors (http://
www.supermicro.com/products/superblade). Please note that you will need to check the
detailed specifications of a particular blade module for a list of the CPUs it supports.
Details on installation of the processor into the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module are found in
Chapter 3: "Setup and Installation" on page 3-1.
Memory
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade module has twelve 240-pin DIMM sockets that can support up
to 96 GB/24 GB of ECC Registered/Unbuffered ECC DDR3-1333/1066/800 SDRAM.
Memory is interleaved, which requires modules of the same size and speed to be
installed in groups (of two or three).
Please refer to the Supermicro web site for a list of supported memory
(www.supermicro.com/products/superblade). The detailed specifications for a blade
module will contain a link to a list of recommended memory sizes and manufacturers.
Details on installation of memory modules into the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module are
found in Chapter 3: "Setup and Installation" on page 3-1.
1-2

Chapter 1: Introduction
Storage
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade module can have six 2.5" SAS(2) or SATA (Serial ATA) hard
disk drives in front-mounted easy removable carriers. See Chapter 3: "Setup and
Installation" on page 3-1 for storage installation details.
Density
A maximum of ten blade modules may be installed into a single blade enclosure. Each
blade enclosure is a 7U form factor, so a standard 42U rack may accommodate up to six
enclosures with sixty blade modules, or the equivalent of sixty 1U servers. With the
inclusion of six CMM modules, twelve Gigabit Ethernet switches and six InfiniBand
switches, this would occupy up to 108U space in a conventional 1U server configuration.
Figure 1-1 displays a view of a full rack with six blade enclosures in it, each with ten
blades to an enclosure.
Figure 1-1. Full Rack of Blade Enclosures and Blade Servers
1-3

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
1-4 Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer , Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email:
Web Site: www.supermicro.com
marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
‘s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
Email:
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Asia-Pacific
Address: Super Micro Computer , Inc.
4F, No. 232-1, Liancheng Rd.
Chung-Ho 235, Taipei County
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3991
Web Site: www.supermicro.com.tw
Technical Support:
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Tel: +886-2-8228-1366, ext. 132 or 139
1-4

Chapter 2
System Safety
2-1 Electrical Safety Precautions
Basic electrical safety precautions should be followed to protect yourself from harm and
the SuperBlade from damage:
• Be aware of how to power on/off the enclosure power supplies and the individual
blades as well as the room's emergency power-off switch, disconnection switch or
electrical outlet. If an electrical accident occurs, you can then quickly remove power
from the system.
• Do not work alone when working with high voltage components.
• Power should always be disconnected from the blade module when removing or
installing such system components as the mainboard, memory modules and
processors.
• When working around exposed electrical circuits, another person who is familiar
with the power-off controls should be nearby to switch off the power if necessary.
• Use only one hand when working with powered-on electrical equipment. This is to
avoid making a complete circuit, which will cause electrical shock. Use extreme
caution when using metal tools, which can easily damage any electrical components
or circuit boards they come into contact with.
• Do not use mats designed to decrease electrostatic discharge as protection from
electrical shock. Instead, use rubber mats that have been specifically designed as
electrical insulators.
• The power supply power cords must include a grounding plug and must be plugged
into grounded electrical outlets. Power input requires 110-240 V AC, depending upon
your power supply module.
• Mainboard Battery: This battery must be replaced only with the same or an
equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer (CR2032 Lithium 3V battery).
Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
WARNING: There is a danger of explosion if the onboard battery is installed
upside down, which will reverse its polarities.
• Mainboard replaceable soldered-in fuses: Self-resetting PTC (Positive Temperature
Coefficient) fuses on the mainboard must be replaced by trained service technicians
only. The new fuse must be the same or equivalent as the one replaced. Contact
technical support for details and support.
2-1

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
2-2 General Safety Precautions
Follow these rules to ensure general safety:
• Keep the area around the SuperBlade clean and free of clutter.
• Place the blade module cover and any system components that have been removed
away from the system or on a table so that they won't accidentally be stepped on.
• While working on the system, do not wear loose clothing such as neckties and
unbuttoned shirt sleeves, which can come into contact with electrical circuits or be
pulled into a cooling fan.
• Remove any jewelry or metal objects from your body, which are excellent metal
conductors that can create short circuits and harm you if they come into contact with
printed circuit boards or areas where power is present.
• After accessing the inside of the system, replace the blade module's cover before
installing it back into the blade enclosure.
2-3 Electrostatic Discharge Precautions
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is generated by two objects with different electrical
charges coming into contact with each other. An electrical discharge is created to
neutralize this difference, which can damage electronic components and printed circuit
boards.
The following measures are generally sufficient to neutralize this difference before
contact is made to protect your equipment from ESD:
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent static discharge.
• Keep all components and printed circuit boards (PCBs) in their antistatic bags until
ready for use.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the antistatic bag.
• Do not let components or PCBs come into contact with your clothing, which may
retain a charge even if you are wearing a wrist strap.
• Handle a board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral chips,
memory modules or contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the mainboard and peripherals back into their antistatic bags when not in use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure the blade enclosure provides excellent
conductivity between the power supplies, the blade modules and the mainboard.
2-4 Operating Precautions
Care must be taken to assure that the cover of the blade unit is in place when the blade
is operating to assure proper cooling. Out of warranty damage to the blade can occur if
this practice is not strictly followed.
Any drive carrier without a hard drive installed must remain fully installed in the drive bay
when the blade module is operating to ensure proper airflow.
2-2

Chapter 3
Setup and Installation
3-1 Overview
This chapter covers the setup and installation of the blade module and its components.
3-2 Installing Blade Modules
Up to ten SBI-7126T-S6 blade modules may be installed into a single blade enclosure
(depending upon your enclosure and blad). Blade modules with Windows and Linux
operating systems may be mixed together in the same blade enclosure.
Powering Up a Blade Unit
Each blade unit may be powered on and off independently from the rest of the blades
installed in the same enclosure. A blade unit may be powered up in two ways:
• Press the power button on the blade unit.
• Use IPMIView or the web-browser based management utility to apply power using
either a CMM module, or by the use of the onboard BMC chip in the blade module.
Powering Down a Blade Unit
A blade unit may be powered down in either of five ways:
• Press the power button on the blade unit.
• Use IPMIView or the web-browser based management utility to power down (if you
have Operator or Admin privileges on the CMM).
• Use IPMItool when connected to the CMM to power down (if you have Operator or
Admin privileges on the CMM).
• Use IPMIview or a browser connected to the onboard BMC chip attached to the
blade to power down.
• Use IPMItool to use a Command Line Interface (CLI) to the onboard BMC chip (if
you have Operator or Admin privileges).
Removing a Blade Unit from the Enclosure
Although the blade system may continue to run, individual blades should always be
powered down before removing them from the enclosure.
Removing a Blade Unit from the Enclosure
1. Power down the blade unit (see "Powering Down a Blade Unit" above).
2. Squeeze both handles to depress the red sections then pull out both handles
completely and use them to pull the blade unit from the enclosure.
3-1
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
NOTE: Blade Modules can be Hot-Plugged from the enclosure.
Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover
The blade cover must be removed to access the mainboard when you need to install or
remove processors, memory units, the onboard battery and so on.
Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover
1. Remove the blade unit from the enclosure (see "Removing a Blade Unit from the
Enclosure" above).
2. Depress the two buttons on the cover while pushing the cover toward the rear of the
blade unit. When it stops, lift the cover off the blade unit.
3. To replace the cover, fit the six grooves in the cover into the studs in the sides of the
blade, then slide the cover toward the front of the blade to lock it into place.
Installing a Blade Unit into the Enclosure
Make sure the cover of the blade unit has been replaced first before installing a blade
unit in the enclosure.
Installing a Blade Unit into the Enclosure
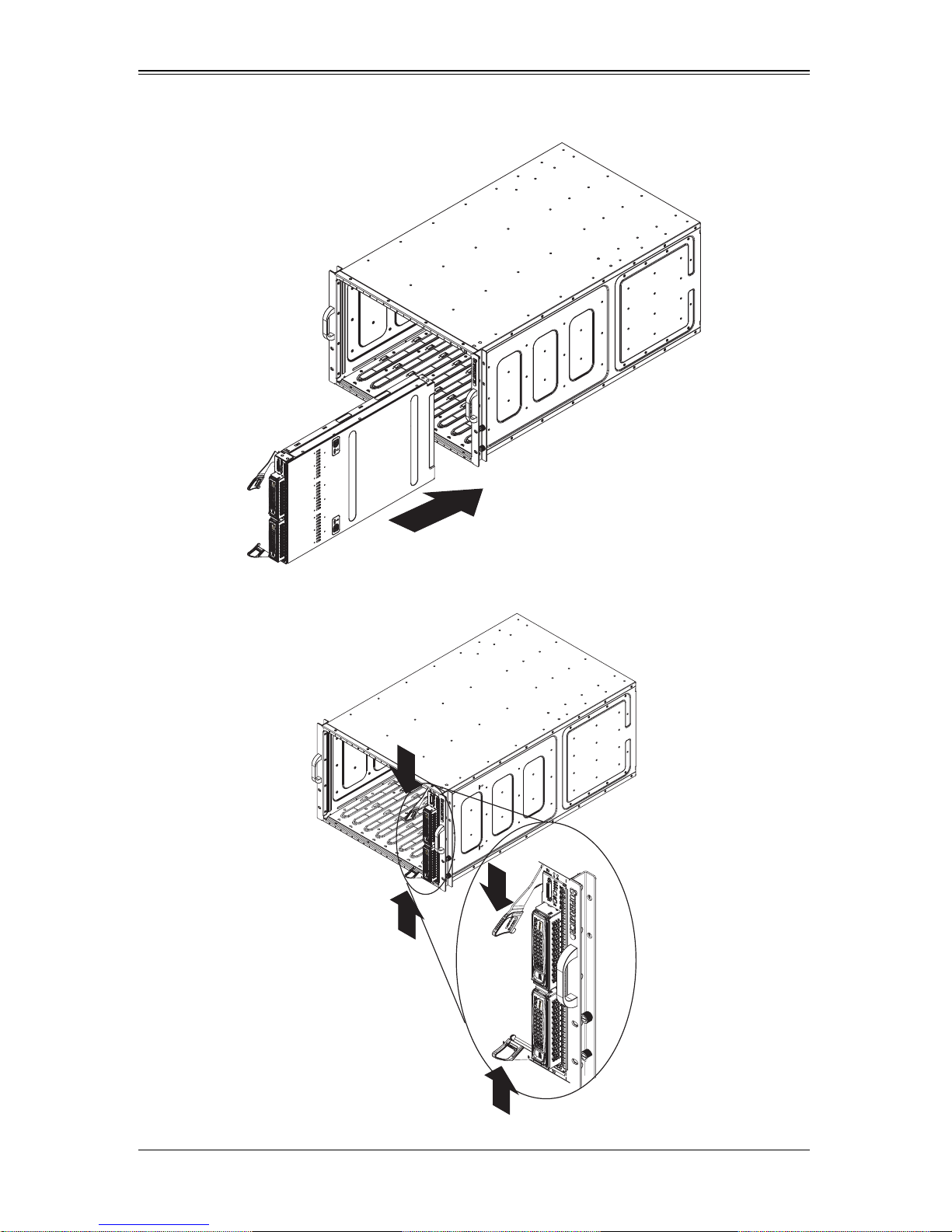
1. Slowly push the blade unit into its bay with the handles fully pulled out (see
Figure 3-1).
2. When the blade stops, push the handles back in to their locked position, making
sure the notches in both handles catch the lip of the enclosure (see Figure 3-2).
NOTE: Blade Modules can be Hot-Plugged into the enclosure.
WARNING: Use extreme caution when inserting a blade module into the
enclosure. If the blade's power connector becomes damaged, it can damage
pins on other blade bays that it is inserted into.
3-2
Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Figure 3-1. Inserting a Blade into the Enclosure
Figure 3-2. Locking the Blade into Position
3-3
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
3-3 Processor Installation
One or two processors may be installed to the mainboard of each blade unit. See
Chapter 1 for general information on the features of the blade unit and the Supermicro
web site for further details including processor, memory and operating system support.
WARNING: This action should only be performed by a trained service
technician. Allow the processor heatsink to cool before removing it.
Removing a Processor
1. Power down and remove the blade unit from the enclosure (see Section 3-2:
Installing Blade Modules on page 3-1 for details).
2. Remove the cover of the blade unit (see "Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover" on
page 3-2).
3. Loosen the four screws that secure the heatsink to the mainboard.
4. Remove the heatsink by gently rotating it back-and-forth sideways with your fingers
to release it from the processor. Set the heatsink aside and upside-down so that
nothing comes into contact with the thermal grease on its underside.
5. Raise the lever of the processor socket up until the processor is released from the
socket, then lift the silver cover plate and remove the processor.
WARNING: This action should only be performed by a trained service
technician.
Installing a Processor
1. If present, remove the protective black PnP cap from the processor socket.
2. Raise the lever of the processor socket until it reaches its upper limit.
3. Lift the silver cover plate completely up and out of the way.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the pins protruding from the CPU socket.
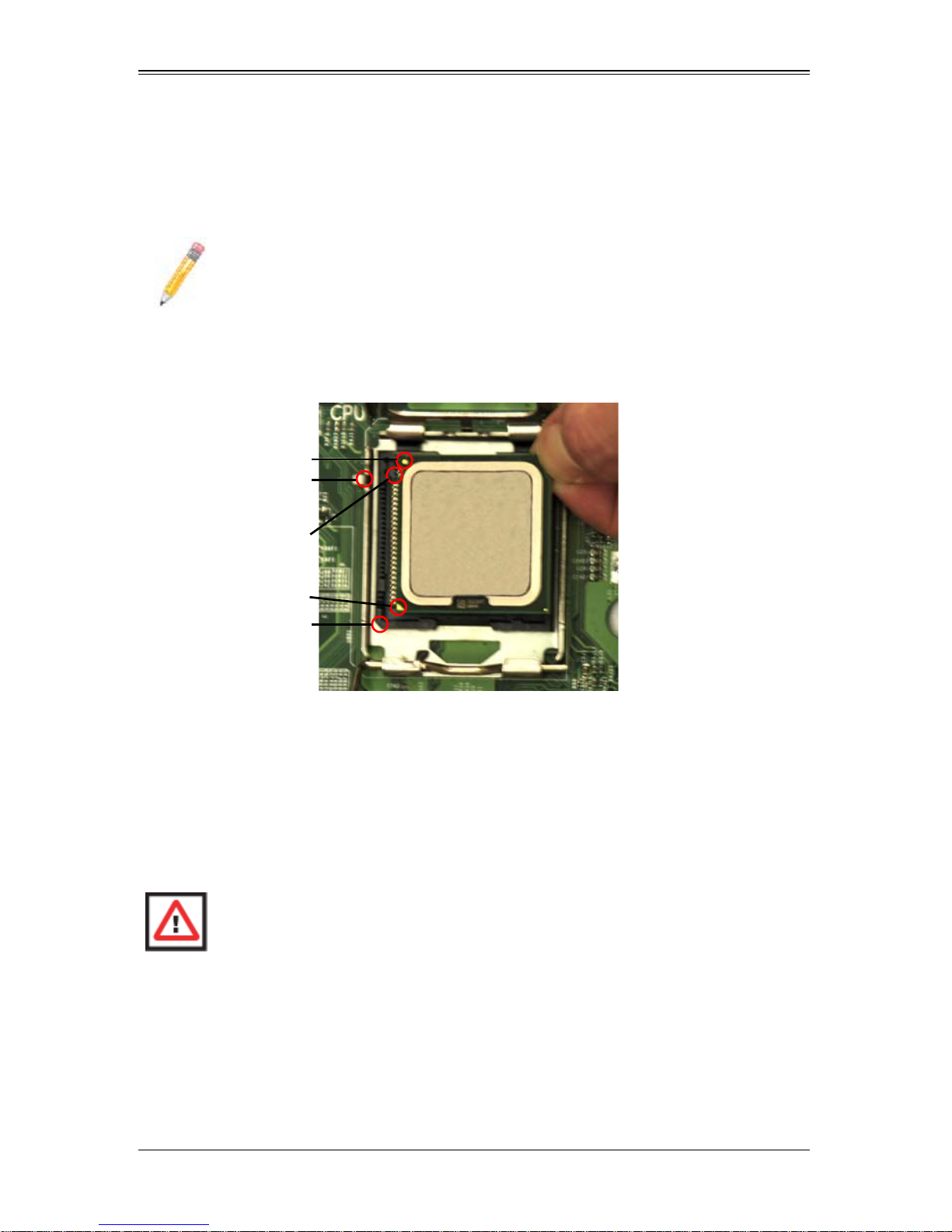
4. Align pin 1 of the processor with pin 1 of the socket (both are marked with a small
gold triangle) and gently seat the processor into the socket (Figure 3-3).
5. Check to make sure the processor is flush to the socket and fully seated.
6. Lower the socket lever until it locks.
7. To install the heatsink, apply thermal grease to the top of the processor. (If
reinstalling a heatsink, first clean off the old thermal grease with a clean, lint-free
cloth.)
3-4
Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
8. Place the heatsink on the processor then tighten two diagonal screws until snug,
then the other two screws.
9. When all four screws are snug, tighten them all to secure the heatsink to the
mainboard.
NOTE: Do not overtighten the screws as this may damage the processor or the
heatsink.
10. Replace the cover on the blade unit and finish by installing the unit back into the
blade enclosure.
Figure 3-3. Installing a Processor in a Socket
Gold dot
Socket key
CPU key
CPU pin
Notched corner
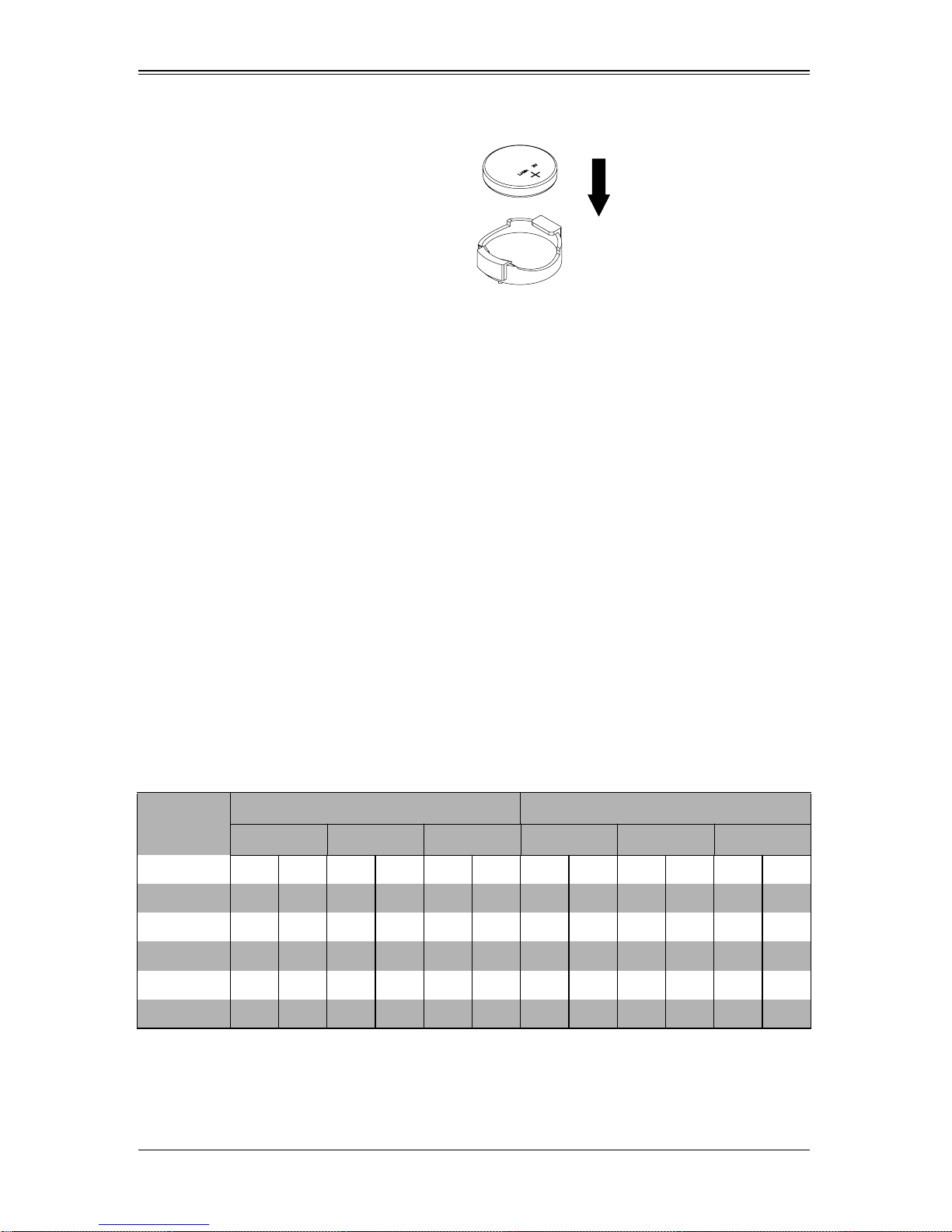
3-4 Onboard Battery Installation
A battery is included on the mainboard to supply certain volatile memory components
with power when power has been removed from the blade module. If this battery dies, it
must be replaced with an equivalent CR2032 Lithium 3V battery. Dispose of used
batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions. See Figure 3-4 for a diagram of
installing a new onboard battery.
WARNING: There is a danger of explosion if the onboard battery is installed
upside down, which reverses its polarities.
3-5
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Figure 3-4. Installing the Onboard Battery
Lithium Battery
Battery Holder
3-5 Memory Installation
The mainboard of each blade unit must be populated with DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory
Modules) to provide system memory. The DIMMs should all be of the same size and
speed and from the same manufacturer due to compatibility issues. See details
below on supported memory and our web site (www.supermicro.com/products/
superblade for recommended memory.
Populating Memory Slots
The mainboard of a SBI-7126T-S6 blade module has twelve memory slots, depending
upon the blade model. Both interleaved and non-interleaved memory are supported, so
you may populate any number of DIMM slots.
Populating three slots at a time (DIMM1A + DIMM2A+ DIMM3A, etc.) with memory
modules of the same size and of the same type will result in dual-channel, interleaved
memory, which is faster than single-channel, non-interleaved memory. See Table 3-1
and Figure 3-5 for details.
For an interleaved configuration, memory modules of the same size and speed
must be installed in pairs. You should not mix DIMMs of different sizes and
speeds.
Table 3-1. Populating Twelve Memory Slots for Interleaved Operation
Number
of DIMMs
2 DIMMs 1A 1A
4 DIMMs 1A 2A 1A 2A
6 DIMMs 1A 2A 3A 1A 2A 3A
8 DIMMs 1A 1B 2A 3A 1A 1B 2A 3A
Channel 0 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 0 Channel 1 Channel 2
Processor 1 Processor 2
10 DIMM 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A
12 DIMM 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 3B 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 3B
3-6

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
NOTE: The DIMM slot number specified in Table 3-1 equals the DIMM slot to
be populated. A “---” indicates that the DIMM slot should be left unpopulated.
NOTE: Though multiple DIMM memory module types and speeds may be
supported, you need to use DIMM memory modules of the same speed and
type.
Figure 3-5. 12-Slot DIMM Numbering
Edge of Board
DIMM3B
DIMM3A
DIMM2A
DIMM2B
DIMM1B
DIMM1A
Toward CPU
Toward CPU
DIMM1B
DIMM1A
DIMM2A
DIMM2B
DIMM3B
DIMM3A
Edge of Board
3-7

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
DIMM Installation
WARNING: Exercise extreme care when installing or removing DIMM modules
to prevent any possible damage.
Installing DIMM Memory Modules
1. Power down the blade module (see "Powering Down a Blade Unit" on page 3-1).
2. Remove the blade from the enclosure and the cover from the blade (see
"Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover" on page 3-2).
3. Remove the air shroud that covers the DIMM slots.
4. Insert each DIMM vertically into its slot, starting with slots 1A and 2A. Pay attention
to the notch along the bottom of the module to prevent inserting the DIMM
incorrectly (see Figure 3-6).
Figure 3-6. Installing a DIMM into a Memory Slot
T o Install: Insert module vertically
and press down until it snaps into
place. Pay attention to the bottom
notch.
To Remove: Use your thumbs to
gently push each release tab
outward to free the DIMM from the
slot.
5. Gently press down on the DIMM until it snaps into place in the slot. Repeat for all
modules (see Table 3-1 for installing DIMMs into the slots in the correct order).
6. Replace the air shroud and the blade cover and install the blade module back into
the enclosure.
7. Power up the blade unit (see "Powering Up a Blade Unit" on page 3-1).
3-8

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
3-6 Hard Disk Drive Installation
Hard disk drives are installed in “carriers” which are hot-swappable and can be removed
or replaced without powering down the blade unit they reside in. A blade module needs
a hard disk drive with an operating system installed to operate.
WARNING: To maintain proper airflow, both hard drive bays must have drive
carriers inserted during operation whether or not a drive is installed in the carrier.
To remove a hard drive carrier, do the following:
Removing a Hard Drive Carrier
1. Locate the colored “Open” button at the bottom of the drive carrier and press it with
your thumb. This action releases the drive carrier from the drive bay.
2. Pull the release handle out about 45-degrees, then use it to pull the drive carrier out.
To Install a hard drive, use the following procedure:
Installing a Hard Drive
1. Remove a blank drive carrier from the blade (see removal procedure above).
2. Insert a drive into the carrier with the PCB side facing down and the connector end
toward the rear of the carrier.
3. Align the drive in the carrier so that the screw holes of both line up. Note that there
are holes in the carrier marked “SAS/SATA” to aid in correct installation.
4. Secure the drive to the carrier with four screws as shown in Figure 3-7: "Installing a
Hard Drive in a Carrier" on page 3-10.
5. Insert the drive carrier into its slot keeping the Open button at the bottom. When the
carrier reaches the rear of the bay the release handle will retract.
6. Push the handle in until you hear the carrier click into its locked position.
3-9

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Figure 3-7. Installing a Hard Drive in a Carrier
3-10

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
3-7 Installing the Operating System
An operating system (OS) must be installed on each blade module. Blades with
Microsoft Windows OS and blades with Linux OS can both occupy and operate within
the same blade enclosure. Refer to the SuperMicro web site for a complete list of
supported operating systems.
There are several methods of installing an OS to the blade modules.
Installing with an External USB CD-ROM Drive
The most common method of installing the OS is with an external USB CD-ROM drive.
Take the following steps to install the OS to a blade module:
WARNING: Installing the OS from an external CD-ROM drive may take several
hours to complete.
1. Connect an SUV cable (Serial port/USB port/Video port cable) to the KVM
connector on the front of the blade module. You will then need to attach a USB hub
to the USB port on this cable to provide multiple USB ports.
2. Connect the external CD-ROM drive, a USB keyboard and a mouse to the USB hub.
You will also need to connect a monitor to the video connector on the SUV cable.
Turn on the blade module.
3. Insert the CD containing the OS into the CD-ROM drive.
4. Follow the prompts to begin the installation.
Installing via PXE Boot
PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) is used to boot a computer over a network. To
install the OS via PXE, the following conditions must be met:
1. The PXE B
2. A PXE server has been configured (this can be another blade in the system).
3. The PXE server must be connected over a network to the blade to be booted.
4. The blade has only non-partitioned/unformatted hard drives installed and no
bootable devices attached to it.
Once these conditions are met, make sure the PXE server is running. Then turn on the
blade on which you wish to boot and/or install the OS. The BIOS in the blade will look at
all bootable devices and finding none will connect to the PXE server to begin the boot/
install.
OOT option in BIOS must be enabled.
3-11

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
Installing via Virtual Media (Drive Redirection)
You can install the OS via Virtual Media through either the IPMIview (Java based client
utility), IPMItool or the Web-based Management Utility. With this method, the OS is
installed from an ISO image that resides on another system/blade.
Refer to the manuals on your Superblade CD-ROM for further details on the Virtual
Media (CD-ROM or Drive Redirection) sections of these two utility programs.
3-8 Management Software
System management may be performed with either of three software packages:
IPMIview, IPMItool or a Web-based Management Utility. These are designed to provide
an administrator with a comprehensive set of functions and monitored data to keep tabs
on the system and perform management activities.
Refer to the manuals on your Superblade CD-ROM for further details on the various
functions provided by these management programs.
3-9 Configuring and Setting up RAID
Each blade module that supports two or more hard drives may be used to create a RAID
array. The procedures for doing this vary depending upon the blade model chosen for
your SuperBlade system.
See Chapter 5 for details on how to configure and set up RAID on your blade module.
3-12

Chapter 4
Blade Module Features
Figure 4-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module Front View
This chapter describes the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module. Installation and maintenance
should be performed by experienced technicians only.
See Figure 4-1 for a front view of the blade unit and Table 4-1 for its features.
Table 4-1. SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module Features
Feature Description
Processors Supports single or dual 1366-pin Intel Xeon 5500 series processors
Memory
Storage Six 2.5" hot-plug SAS2/SATA hard disk drives
Ports KVM port (1)
Features
Power Consumption
Supports up to 96 GB/24 GB of ECC Registered/Unbuffered ECC
DDR3-1333/1066/800 SDRAM in twelve DIMM slots
Onboard Hermon graphics chip, IPMI 2.0, ATA/100, Plug and Play, APM
1.2, DMI 2.3, PCI 2.2, ACPI 1.0/2.0, SMBIO S 2.3, Real Time Clock, Watch
Dog,
Base Power Draw (~35W) / Power per CPU (60W/80W/95W) / Power per
DIMM (typically 14.5W)
4-1

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
4-1 Control Panel
Each blade has a similar control panel (Figure 4-2) with power on/off button, a KVM
connector, a KVM button and four LEDs on the top front of the unit. The numbers
mentioned in Figure 4-2are described in Table 4-2.
Figure 4-2. Blade Control Panel
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
Table 4-2. Blade Control Panel
Item Function State Description
1 Power Button N/A Turns blade module on and off
2 KVM Button N/A Initiates KVM function
3 Power LED
4 KVM/UID LED
5 Network/IB LED
System Fault
6
LED
Green Indicates power status “On”
Orange Indicates power status “Off” (with power cabl es plugged in)
Blue Indicates KVM being utilized on blade unit
Flashing Blue Indicates UID activated on blade module
Flashing Green Indicates network activity over LAN
Flashing Orange Indicates network activity over InfiniBand module
Red
Indicates a memory error, overheat, VGA error or any error
that prevents booting
7 KVM Connector N/A Connector for SUV/KV M cabl e
4-2

Chapter 4: Blade Module Features
Power Button
Each blade has its own power button so that individual blade units within the enclosure
may be turned on or off independently of the others. Press the power button (#1) to turn
on the blade server. The power LED (#3) will turn green. To turn off, press and hold the
power button for >4 seconds and the power LED will turn orange.
KVM Button
KVM stands for Keyboard/Video/Mouse. With KVM, a user can control multiple blades
with a single keyboard/video/mouse setup. Connect your keyboard, mouse and monitor
to the USB and VGA connectors on the CMM module, then push the KVM button on the
control panel of the blade module you wish to access.
LED Indicators
Blade module LEDs are described below in Table 4-3.
Table 4-3. Blade Module LED Indicators
LED State Description
Green Power On
Power LED
KVM/UID LED
(Blue)
Network LED
(Green)
System Fault
LED (Red)
Amber Standby
Red Power Failure
Steady On Indicates that KVM has been initialized on this blade module
Flashing
Flashing
Steady On
Serves as a UID indicator (the UID function is activated with a
management program)
Flashes on and off to indicate traffic (Tx and Rx data) on the LAN
connection to this blade module.
This LED illuminates red when a fatal error occurs. This may be the
result of a memory error, a VGA error or any other fatal error that
prevents the operating system from booting up .
a
a. In the event of a power failure, the N+1 Redundant Power Supply (if included in your
system's configuration) picks up the system load to provide uninterrupted operation. The
failed power supply should be replaced with a new one as soon as possible.
KVM Connector
Alternatively , you may connect a KVM cable (CBL-0218L, with a keyboard/video/mouse
attached) to the KVM connector (#7) of the blade you wish to access. To switch to
another blade, disconnect the cable then reconnect it to the new blade.
See the Web-based Management Utility User’s Manual on your Superblade system
CD-ROM for further details on using the KVM function remotely.
4-3

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
4-2 Mainboard
The mainboard of the SBI-7126T-S6 blade unit is a proprietary design, which is based
on the Intel 5500 Tylersburg chipset. See Figure 4-4 for a block diagram of this chipset,
Figure 4-3 for a view of the B8DT6 Mainboard and Figure 4-5 for an exploded view
diagram of the blade unit.
Figure 4-3. B8DT6 Mainboard
10
11
6
7
5
4
2
1
5
8
2
1
9
3
4-4
3
3
Chapter 4: Blade Module Features
Table 4-4. B8DT6 Mainboard Layout
Item Description
1 LGA 1366 CPU Sockets
2 DIMM Slots
3 6 SAS2/SATA Hard Drive Bays
4 InfiniBand Connectors (for InfiniBand cards)
5 Gbx Connectors (for power and logic to backplane)
6 ICH10R (South Bridge chip)
7 Intel 5500 Tylersburg (North Bridge chip)
8 Onboard Battery
9 KVM Module
10 BIOS Chip
11 LSI 2008 SAS2 Controller
Figure 4-4. Intel 5500 Tylersburg Chipset Block Diagram
PROCESSOR 0 PROCESSOR 1
DDR3 DIM M #1
DDR3 DIM M #2
DDR3 DIM M #3
KAWELA
MIDDLE PANE
INFINIBAND
ADAPTER
CARD
QPI
QPI QPI
IOH
TYLERSBURG
24D
PCIEx8
SAS2
CONTROLLER
LSI SAS2008
SPI
USB 3/4
SST25
VF016
DDR3 DIM M #3
SAS2/
SATA
To FRON T
SIDE
DDR3 DIM M #2
SAS2/SATA #1
SAS2/SATA #2
SAS2/SATA #3
DDR3 DIM M #1
SAS2/SATA #4
SAS2/SATA #5
SAS2/SATA #6
ICH10
DDR II
MEMORY
PCI
WINDBOND
HERMON
FRONT
VGA
To CMM
VGA
LPC
LPC I/O
83527
USB 0/1
FRONT SIDE
COM1 to
To CMM1
& CMM2
4-5

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Jumpers
The jumpers present on the mainboard are used by the manufacturer only; there are no
jumpers used to configure the operation of the mainboard.
CMOS Clear
JBT1 is used to clear CMOS and will also clear any passwords. JBT1 consists of two
contact pads located near the BIOS chip (#12 in Figure 4-5).
Clearing CMOS
1. First power down the blade and remove it from the enclosure.
2. Remove the blade cover to access the mainboard (see Section : Removing/
Replacing the Blade Cover on page 3-2 for further details). Short the CMOS pads
with a metal object such as a small screwdriver.
3. Replace the cover, install the blade back into the enclosure and power it on.
4-6
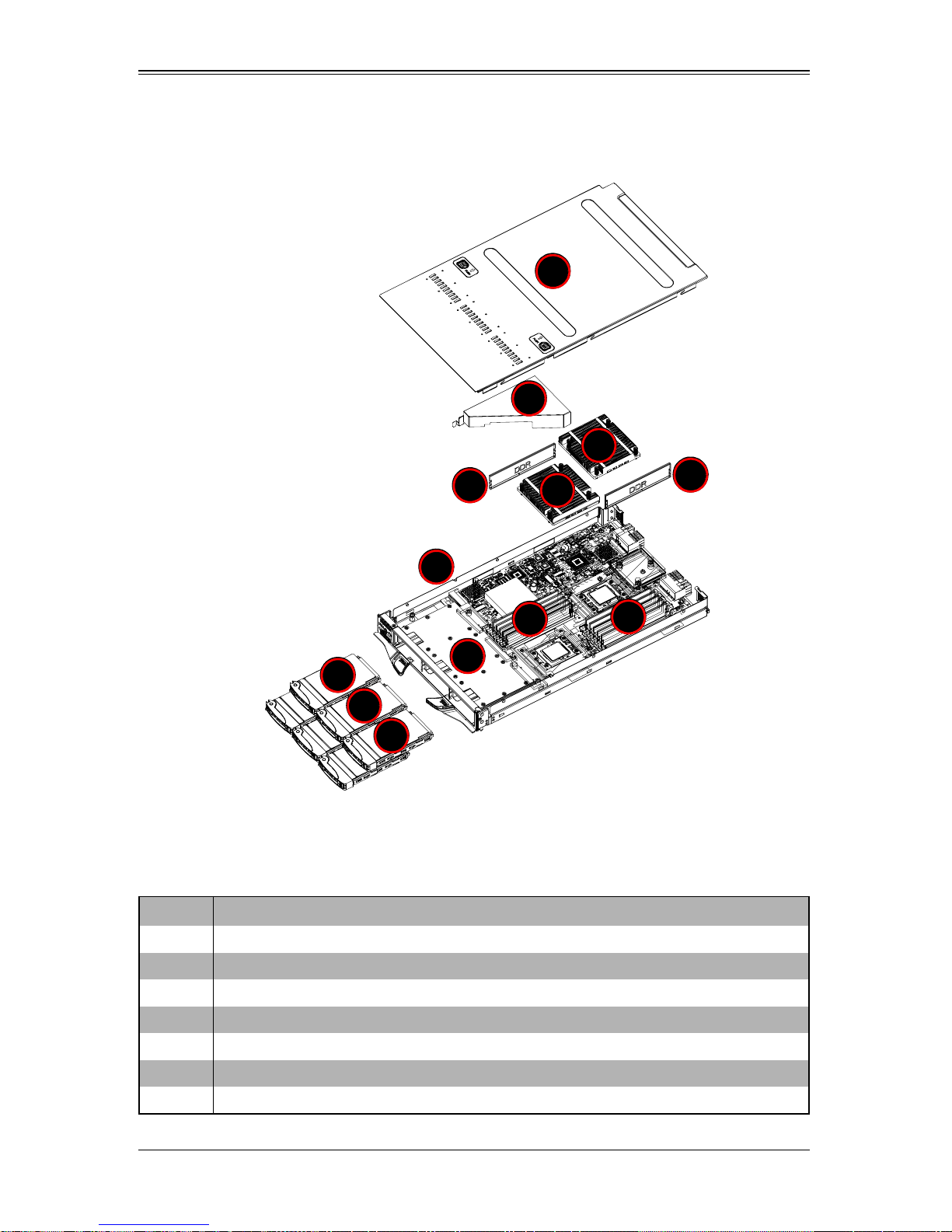
4-3 Blade Unit Components
Figure 4-5. Exploded View of SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module
Chapter 4: Blade Module Features
7
5
6
4
6
4
1
4
4
3
2
2
2
Main components of the SBI-7126T-S6 blade module are shown in Figure 4-5 and
described in Table 4-5.
Table 4-5. Main Components of SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module
Item Description
1 Blade Unit/Module
2 SAS2/SATA Hard Drives (six per blade module)
3 SAS2/SATA Hard Drive Bays
4 DIMMs (system memory)
5 Airflow Deflector
6 CPU Heatsinks
7 Top Cover
4-7

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
Memory Support
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade module supports up to 96 GB/24 GB of ECC Registered/
Unbuffered ECC DDR3-1333/1066/800 SDRAM in twelve DIMM sockets. See
Section 3-5 for further details on mainboard memory installation.
Hard Disk Drives
The SBI-7126T-S6 blade unit accommodates up to six 2.5" SAS2/SATA hard disk
drives, which are mounted in drive “carriers”. The drives are hot-swappable and can be
removed or replaced without powering down the blade unit they reside in. The six drives
can be used to set up a RAID array or JBOD. These drives use a yellow color for the
Blade HDD active LED.
WARNING: To maintain proper airflow, both hard drive bays must have drive
carriers inserted during operation whether or not a drive is installed in the carrier.
4-8

Chapter 5
RAID Setup Procedure
Each SBI-7126T-S6 blade module supports six hard drives, which may be used to
create a RAID array. Use the LSI MegaRAID Software Configuration Utility found on
your system’s CD-ROM disc for your RAID setup. Go to http://www.supermicro.com/
support/manuals/ to download the installation guide and manual for this utility.
Important Notes
Please read the following notes and warnings before setting up your RAID array.
NOTE: Before adding a new drive to an array, back up any data contained on
the new drive. Otherwise, all data will be lost.
NOTE: A RAID 1 created using the QUICK INIT option may return some data
miscompares if you later run a consistency check. This is normal and is not a
cause for concern.
NOTE: The ACU allows you to use drives of different sizes in an array.
However, during a build operation, only the smaller drive can be selected as the
source or first drive.
NOTE: When migrating from single volume to RAID 0, migrating from a larger
drive to a smaller drive is allowed. However, the destination drive must be at
least half the capacity of the source drive.
WARNING: Adaptec does not recommend that you migrate or build an array on
Windows dynamic disks (volumes), as it will result in data loss.
WARNING: Do not interrupt the creation of a RAID 0 using the MIGRATE option. If
you do, you will not be able to restart or to recover the data that was on the
source drive.
5-1

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
5-2

Chapter 6
BIOS
6-1 Introduction
This chapter describes the BIOS for Intel SuperBlade modules. The Intel Blade modules
use a AMI™ ROM BIOS that is stored in a flash chip. This BIOS can be easily upgraded
using a floppy disk-based program.
NOTE: Due to periodic changes to the BIOS, some settings may have been
added or deleted and might not yet be recorded in this manual. Please refer to
the http://www.supermicro.com/products/SuperBlade/module/ web site for
further details on BIOS setup and the BIOS menus for your SuperBlade blade
module.
System BIOS
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System. The AMI BIOS flash chip stores the system
parameters, types of disk drives, video displays, etc. in the CMOS. The CMOS memory
requires very little electrical power. When the blade unit is turned off, a backup battery
provides power to the BIOS flash chip, enabling it to retain system parameters. Each
time the blade is powered on it is configured with the values stored in the BIOS ROM by
the system BIOS, which gains control at boot up.
How To Change the Configuration Data
The CMOS information that determines the system parameters may be changed by
entering the BIOS Setup utility. This Setup utility can be accessed by pressing the
<D
ELETE> key at the appropriate time during system boot. (See "Starting the Setup
Utility" below.)
Starting the Setup Utility
Normally , the only visible POST (Power-On Self-Test) routine is the memory test. As the
memory is being tested, press the <D
Setup utility. From the main menu, you can access the other setup screens, such as the
Security and Power menus.
WARNING: To prevent possible boot failure, do not shut down or reset the
system while updating the BIOS.
ELETE> key to enter the main menu of the BIOS
6-1

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
6-2 BIOS Updates
It may be necessary to update the BIOS used in the blade modules on occasion.
However, it is recommended that you not update BIOS if you are not experiencing
problems with a blade module.
Updated BIOS files are located on our web site(www.supermicro.com/products/
superblade/). Please check the current BIOS revision and make sure it is newer than
your current BIOS before downloading.
There are several methods you may use to upgrade (flash) your BIOS. After
downloading the appropriate BIOS file (in a zip file format), follow one of the methods
described below to flash the new BIOS.
Flashing BIOS
Use the procedures below to “Flash” your BIOS with a new update using the KVM
dongle, USB ports on the CMM module or by use of a Floppy disk.
Flashing a BIOS using the KVM Dongle:
For this method, you must use a KVM “dongle” cable (CBL-0218L, included with the
system).
1. Copy the contents of the zip file to a bootable USB pen drive.
2. Connect the KVM dongle (CBL-0218L) to the KVM connector at the front of the
blade you will be flashing the BIOS to.
3. Connect your bootable USB pen drive to one of the two USB slots on the KVM
dongle.
4. Boot to the USB pen drive and go to the directory where you saved the contents of
the zip file.
5. Type flash filename.rom (replace filename.rom by the actual ROM file name).
Flashing a BIOS using the USB Ports on the CMM:
1. Copy the contents of the zip file to a bootable USB pen drive.
2. Connect your bootable USB pen drive to one of the two USB slots on the CMM
(located on the back side of the enclosure).
3. Boot to the USB pen drive and go to the directory where you saved the contents of
the zip file.
4. Type flash filename.rom (replace filename.rom by the actual ROM file name).
Flashing a BIOS using a Floppy Image File
This method must be performed remotely.
1. Copy the image file from the zip file to your desktop.
2. Use the web browser or IPMIView to access your CMM remotely using its IP
Address.
6-2

Chapter 6: BIOS
3. Go to the VIRTUAL MEDIA menu and select FLOPPY IMAGE UPLOAD.
4. BROWSE or OPEN to locate the *.img file on your desktop and select it.
5. Press the UPLOAD button and wait a few seconds for the image to upload to the
CMM.
6. Once the upload finishes, turn on the blade module and press <D
EL> to enter the
BIOS setup utility.
7. In the B
OOT MENU, bring USB LS120: PEPPCMM VIRTUAL DISC 1 to the top of
the boot priority list.
8. Exit while saving the changes. The blade module will boot to the virtual media
(floppy image) A:\>.
9. Type flash filename.rom.
NOTE: Replace filename.rom by the actual ROM file name (such as
B8DTE142.rom for example) in the command.
6-3 Running Setup
NOTE: Default settings are in bold text unless otherwise noted.
The BIOS setup options described in this section are selected by choosing the
appropriate text from the M
section, although the screen display is often all you need to understand how to set the
options.
AIN BIOS SETUP screen. All displayed text is described in this
When you first power on the computer, the BIOS is immediately activated.
While the BIOS is in control, the Setup program can be activated in one of two ways:
1. By pressing <D
ELETE> immediately after turning the system on, or
2. When the message Press the <Delete> key to enter Setup appears briefly at the
bottom of the screen during the POST, press the <D
S
ETUP menu:
ELETE> key to activate the main
6-3

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
6-4 Main BIOS Setup
All Main Setup options are described in this section.
Use the UP/DOWN arrow keys to move among the different settings in each menu. Use
the L
EFT/RIGHT arrow keys to change the options for each setting.
Press the <ESC> key to exit the CMOS SETUP menu. The next section describes in
detail how to navigate through the menus.
Items that use sub-menus are indicated with the
press the <E
Menu options found in the MAIN BIOS SETUP menu are shown in Figure 6-1 and
described in Table 6-1.
NTER> key to access the submenu.
Figure 6-1. Main Setup Menu Screen
X icon. With the item highlighted,
6-4

Table 6-1. Main BIOS Setup Menu Options
Menu Option Description
Chapter 6: BIOS
System Time
System Date
BIOS Date
To set the system date and time, key in the correct information in the ap propriat e
fields. Then press the <Enter> key to save the data.
Using the arrow keys, highlight the month, day and year fields, and enter the
correct data for the system date. Press the <Enter> key to save the data.
The BIOS Date field displays the date when this version of the BIOS was built.
This option is not configurable.
6-5 Advanced Setup
Figure 6-2. Advanced Setup Menu
Choose Advanced from the BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys to
display the A
DVANCED SETUP menu (Figure 6-2).
6-5

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
The items with a triangle beside them are sub-menus that can be accessed by
highlighting the item and pressing <E
highlighting the setting option using the arrow keys and pressing <E
Table 6-2 describes all sub-menus found in the ADVANCED SETUP menu.
Table 6-2. Advanced Setup Menu Options
Sub-menu Description
NTER>. Options for PIR settings are displayed by
NTER>.
XCPU and Clock
Configuration
XIDE Configuration See Table 6-4 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XPCIPnP
Configuration
XSuperIO
Configuration
XChipset
Configuration
XACPI Configuration See Table 6-8 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XAHCI Configuration See Table 6-9 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XEvent Log
Configuration
XIPMI Configuration See Table 6-11 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XMPS Configuration See Table 6-12 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XPCI Express
Configuration
XSMBIOS
Configuration
See Table 6-3 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
Access this submenu to make changes to settings for PCI/PnP devices. See
Table 6-5 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-6 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-7 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-10 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-13 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-14 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
XRemote Access
Configuration
XSystem Health
Monitor
See Table 6-15 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 6-16 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
6-6

Table 6-3. CPU and Clock Config uration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Sets the ratio between CPU core clock and the FSB frequency. The default
setting depends upon the type of CPU installed on the mainboard. The default
Ratio CMOS Setting
Hardware Prefetcher
setting for the CPU installed in your mainboard is 18. Press + or - on your
keyboard to change this value.
NOTE: If an invalid ratio is entered, the AMI BIOS will restore the setting to a
previous state.
If set to Enabled, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of data and
instructions from the main memory to the L2 cache in the forward or backward
manner to improve CPU performance. Options are Enabled and D
For UP platforms leave it enabled. for DP/MP servers, this setting may be used
to tune performance to the specific application.
Chapter 6: BIOS
ISABLED.
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
Max CPUID Value
Limit
Intel® Virtualization
Tech
Execute-Disable Bit
Capability
Intel HT Technology
Active Processor
Cores
The CPU fetches the cache line for 64-byte s if this option is set to D
ISABLED. The
CPU fetches both cache lines for 128-bytes as comprised if Enabled.
For UP platforms leave it enabled. for DP/MP servers, this setting may be used
to tune performance to the specific application.
This setting is Disabled for Windows systems.
Select Enabled to use this Virtual ization Technology feature to allow one platform
to run multiple operating systems and applications in independen t partitions,
creating multiple “virtual” systems in one physical computer system. The options
are Enabled and D
ISABLED. Please refer to the Intel website for further detailed
information.
NOTE: A full reset of the system is required when you change this setting.
The Execute Disable Bit allows the processor to designate areas in th e system
memory where an application code can be executed, and where it cannot. This
prevents a worm or virus from flooding illegal codes into the system to
overwhelm the processor or damage the system during an attack. The default
setting is Enabled.
Please refer to the Intel and Microsoft websites for more information .
When this setting is D
ISABLED, only one thread per enabled core is enabled. The
default for this setting is Enabled.
Sets the number of cores to enable in each processor package. Default is ALL.
Menu Option Description
SATA#1
Configuration
Configure SATA#1 as
Max Ports on SATA#1
If Compatible is selected, this sets SATA#1 to legacy compatibility mode.
Selecting Enhanced sets SATA#1 to native SATA mode. The options are
ISABLED, Compatible and ENHANCED.
D
This setting allows you to select the drive type for SATA#1. The op tions are IDE,
RAID and AHCI. Choosing the RAID or AHCI changes which further menu
options appear on the screen.
This setting allows you to specify the max ports for SATA#1 when RAID
configuration is selected for SATA#1 Configuration. The options are 4 P
6Ports.
Table 6-4. IDE Configuration Menu
ORTS or
6-7

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table 6-4. IDE Configuration Menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
This setting allows you to select either the Intel or ADAPTEC RAID Configuration
RAID ID Support
Hot Plug
Utility to be used for configuring your RAID setup. This setting is onl y available
when RAID is selected for SATA#1 Configuration.
This setting allows you to enable the Hot Plug feature when using RAID for your
SATA devices when RAID is selected for your SATA#1 Configuration. Options
include E
NABLED or Disabled.
SATA#2
Configuration
Hard Disk Write
Protect
IDE Detect Tie Out
(Sec)
ATA(PI) 80Pin Cable
Detection
Selecting Enhanced sets SATA#2 to native SATA mode. The options are
D
ISABLED and Enhanced.
This setting Enables/Disables device write protection and is effective only if the
device is accessed through BIOS. The default is Enabled.
This setting allows you to select the time out value for detecting ATA?ATAPI
devices. Press + or - on your keyboard to change this value. The default is 35.
This setting allows you to select the mechanism for detect ing 80P in ATA(PI)
cable. The default is Host & Device.
Table 6-5. PCIPnP Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Clear NVRAM
Plug & Play O/S
PCI Latency Timer
Allocate IRQ to PCI
VGA
This setting allows you to clear NVRAM during a system boot. The options are
No and Y
ES.
Selecting Y ES allows the OS to configure Pl ug & Play d evices. Select No to allow
the AMI BIOS to configure all devices in your system.
NOTE: This is not required for system boot (select No) if your system has an OS
that supports Plug & Play.
This sets the latency timer of each PCI device installed on a PCI bus. For
example, select 64 to set the PCI la tency to 6 4 PCI clock cycles. The op tions are
32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224 an 248.
Select Yes to assign IRQ to the PCI VGA card if the card requests IRQ.
Selecting N
O does not assign IRQ to the PCI VGA card e ven if the card request s
an IRQ.
Palette Snooping
PCI IDE BusMaster
Offboard PCI/ISA IDE
Card
When E
in the system so the card will function correctly. The default is Disabled.
When enabled, the BIOS uses PCI bus mastering for reading/writing to IDE
devices. The options are D
Some PCI IDE cards may require this setting to be set to the PCI slot number
that is holding the card. The default Auto setting works for most PCI IDE cards.
When each of these settings is set t o Available, the specified IRQ is available to
IRQ3 ~ IRQ11
be used by PCI/PnP devices. If set to R
lagacy ISA devices.
NABLED, this informs PCI devices that an ISA graphics device is installed
ISABLED and Enabled.
ESERVED, the IRQ is reserved for use by
6-8
Chapter 6: BIOS
Table 6-6. SuperIO Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
This option specifies the base I/O port address and the Interrupt Request
address of Serial Port 1. Select Disabled to prevent the serial port from
Serial Port1 Address
Serial Port2 Address Same as above, but options are DISABLED, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4 and 2E8/IRQ3.
accessing any system resources. When this option is Disabled, the serial port
physically becomes unavailable. Select 3F8/IRQ4 to allow the serial port to use
3F8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 4 for its interrupt address. Options are
ISABLED, 3F8/IRQ4, 3E8/IRQ4 and 2E8/IRQ3.
D
Serial Port2 Mode
This setting allows the BIOS to select the mode for Serial Port 2. Options are
Normal, IrDA and ASK IR.
Table 6-7. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
XCPU Bridge
Configuration
QPI Links Speed
QPI Frequency
QPI L0s and L1
Memory
Frequency
Memory Mode
This sub-menu configures CPU Bridge features
This option allows you to transition QPI links to Full-Speed or leave them in
S
LOW-MODE for the QPI data transfer speed.
This option selects the desired QPI frequency. Option include Auto, 4.800 GT,
5.866 GT and 6.400 GT.
This option enables the QPI power state to low power with L0s and L1
automatically selected by the mainboard. The options are Disabled and
NABLED.
E
This feature forces a DDR3 frequency slower than what the system has
detected. The available options are Auto, DDR-800, F
ORCE DDR-1333.
F
This option sets the system memory mode. Options are the following:
• Independent (default) – All DIMMs are available to the operating system.
HANNEL MIRROR – The mainboard maintains two identical copies of al l data
•C
in memory for redundancy.
•L
OCKSTEP – The mainboard uses two areas of memory to run the same set
of operations in parallel.
PARING – A preset threshold of correctable errors is used to trigger
•S
fail-over. The spare memory is put online and used as active memory in
place of the failed memory.
ORCE DDR-1066 and
Demand
Scrubbing
Patrol Scrubbing
NUMA Support
DIMM CE Event
Log
This feature is a memory error-correction scheme whereby the processor writes
corrected data back into the memory block from where it was read by the
processor. The options are E
This feature is a memory error-correction scheme that works in the background
looking for and correcting resident errors. The options are E
This feature allows you to enable NUMA support for your system. Options are
Enabled or D
This feature enables/disables a NUMA Correctable Error Event Log.The options
are E
NABLED or Disabled.
NABLED or Disabled.
ISABLED.
NABLED or Disabled.
6-9

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table 6-7. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Serial Debug
Message Level
XNorth Bridge
Configuration
Crystal Beach/
DMA
Crystal Beach/
DCA
Intel VT-d
XSouth Bridge
Configuration
USB Functions
This feature specifies what level of debug messages to display. The default
option is None.
This sub-menu configures North Bridge features
This feature works with Intel’s I/O Acceleration T echnology (A T) to accelerate the
performance of TOE devices. When this featur e is set to E
NABLED, it will enhance
overall system performance by providing direct memory access for data
transferring. Options include E
NABLED and Disabled.
NOTE: A TOE device is a speciali zed, dedicated processor that is insta lled on an
add-on card or a network card to handle some or all packet processing of the
card.
This feature allows you to enable Crystal Beach/DCA support for your system.
Options include E
Select E
NABLED to enable Intel’s Virtualization Technology support for Direct I/O
NABLED and Disabled.
VT-d by report i ng the I/O device assignments to VMM through the DMAR ACPI
Tables. This feature offers fully protected I/O resource-sharing across Intel
platforms, providing you with greater reliability, security and availability in
networking and data-sharing. Options include E
NABLED and Disabled.
This sub-menu configures South Bridge features.
This feature allows you to enable USB functions in your system. Options are
Enabled or D
ISABLED.
USB Port
Configure
XUSB
Configuration
Legacy USB
Support
USB 2.0
Controller Mode
BIOS EHCI
Hand-Off
Hotplug USB
FDD Support
SMBUS Controller
This feature allows you to configure USB ports in your system. Options include
6x6 USB Ports and 8
X4 USB PORTS.
This submenu contains further USB configuration options.
This option allows you to enable the use of Legacy USB devices. If this option is
set to A
UTO, legacy USB support will be automatically enabled if a legacy USB
device is installed on the mainboard, and vice versa. The options include
ISABLED, Enabled and AUTO.
D
This setting allows you to select the USB 2.0 Controller mode. Options include
Hi-Speed (480 Mbps) and F
ULL SPEED (12 MBPS).
This option allows you to enable BIOS Enhanced Host Controlle r Interface
support in order to provide a workaround solution for an operating system tha t
does not have EHCI Hand-Off support. When Enabled, the EHCI Interface will
be changed from the BIOS-controlled to the OS-cont rolled. Options include
Enabled and D
ISABLED.
This option allows you to create a dummy Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) that will be
associated with the hotplugged FDD later. A
if there is no USB FDD present. Options include D
UTO creates this dummy device only
ISABLED, ENABLED and Auto.
This option allows you to enable your SMBUS controller in your system. Options
include Enabled and D
ISABLED.
6-10
Table 6-7. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Chapter 6: BIOS
Restore on AC
Power Loss
Power Button
Function
This option allows you to specify what your system will do when power is
restored after an AC power loss. Options include Power Off, P
AST STATE.
L
This option allows you to specify the power button function for turning of f your
system. Options include 4 S
Table 6-8. ACPI Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
XAdvanced ACPI
Configuration
ACPI Version
Features
ACPI APIC
Support
AMI OEMB Table
Headless Mode
XChipset ACPI
Configuration
This sub-menu allows you to configure Advanced Configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI) power management setting for your system.
Please refer to ACPI’s website http://www .acpi.info/ for more information.
This option allows you to enable RSDP pointers to 64-bit fixed system
description tables. Options include ACPI v1.0, ACPI v2.0 and ACPI v3.0.
This option allows you to include an ACPI APIC tabl e pointer in t he Root System
Description Table (RSDT) pointer list. Options include Enabled and D
This option allows you to include the OEMB table pointer to R(x)SDT pointer
lists. Options include Disabled or E
This option allows you to enable your system to function without a keyboard,
monitor or mouse attached. Options include Disabled or E
This sub-menu allows you to configure Chipset ACPI configurations.
OWER ON and
ECOND OVERRIDE and Instant Off.
ISABLED.
NABLED.
NABLED.
Energy Lake
Feature
APIC ACPI SCI
IRQ
USB Device
Wakeup From S3/
S4
High Performance
Event Timer
HPET Memory
Address
This option allows you to enable the Energy Lake Feature in your system.
Options include Enabled and D
ISABLED.
This option allows you to enable the APIC ACPI SCI IRQ in your system. Options
include Enabled and D
ISABLED.
This option allows you to enable/disable USB device wakeup from S3/S4.
Options include Disabled or E
NABLED.
Select Enabled to activate the High Performance Event Timer (HPET). This
produces periodic interrupts at a much higher frequency than a Real-time Clock
(RTC) does in synchronizing multimedia streams, providing smooth playback
and reducing the dependency on other timestamp calculation devices, such as
an x86 RDTSC Instruction embedded in the CPU. The HPET is used to replace
the 8254 Programmable Interval Timer. Options include Enabled and D
ISABLED.
This option allows you to set your HPET Memory Address for your system.
Options include FED00000h, FED01000h, FED02000h and FED03000h.
6-11

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table 6-9. AHCI Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
AHCI BIOS Support
AHCI CD/DVD Boot
Time Out
XAHCI Port0~Port5
SATA Port0 ~
Port5
S.M.A.R.T.
This option enables AHCI BIOS support on your system. Options include
Enabled and D
This sets the timeout time in seconds fo r AHCI CD/DVD boot drives. Some S ATA
CD/DVD drives in AHCI mode need to wait longer than others. Options include 0
(sec), 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35.
While entering setup, BIOS auto detects the presence of IDE devices. This
setting displays the status of auto detection of IDE devices.
For this setting, select the type of device connected to the system. Select Auto
to allow the AMI BIOS to automatically detect a hard disk drive in your system.
Options include Auto and N
Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) can help predict
impending drive failures. Select D
S.M.A.R.T in your system. Selecting Enabled allows the AMI BIOS to use
S.M.A.R.T to support the hard disk drive. Option include D
ISABLED.
OT INSTALLED.
ISABLED to prevent the AMI BIOS from using
ISABLED and Enabled.
Table 6-10. Event Log Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
View Event Log Selecting this option allows you to view all unread events on the Event Log.
Mark All Events as
Read
Clear Event Log
This option makrs all events as read. Options ae OK and Cancel when selected.
This option clears the Event Log memory of all messages. Options are OK and
Cancel.
Table 6-11. IPMI Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) manages the interface between
Status of BMC
XView BMC System
Event Log
the system management software and platform hardwar e. This non-configurable
informational feature shows the status code of the BMC micro contr oller.
This feature displays the BMC System Event Lo g (SEL) . This log sho ws the t ota l
number of entries of BMC system events. To view an event, select an entry
number and press <E
This screen contains the following information:
• Total Number of Entries
• SEL Entry Number
• SEL Record ID
• SEL Record Type
• Timestamp, Generator ID
• Event Message Format User
• Event Sensor Type
• Event Sensor Number
• Event Dir Type
• Event Data
NTER> to display the information as shown in the screen.
6-12
Table 6-11. IPMI Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
This option allows you to clear the BMC system log. Select Cancel to keep the
Clear BMC System
Event Log
BMC system log and Ok with the <E
WARNING: Any cleared information is unrecoverable. Make ab solutely sure tha t
you no longer need any data stored in the log before clearing the BMC Event
Log.
Chapter 6: BIOS
NTER> key to clear the BMC system log.
XSet LAN
Configuration
Channel Number This static display shows the channel number for the S ET LAN Config command .
Channel Number
Status
IP Address
Source
XIP Address
Parameter
Selector
IP Address
Current IP
Address in
BMC
XMAC Address
This sub-menu is used to configure the IPMI LAN adapter with a network
address.
This static display shows the channel st at us for t he channel nu mber. It will either
display C
Use this option for selecting the IP Address source. Options include S
DHCP.
This sub-menu contains static displays and options for specifying the IP add ress
for your system. This should be in decimal and in dotted quad form (such as
192.168.10.253). The value of each three-dig it number sep arated by dots should
not exceed 255.
This static display shows the parameter of your IP Address configuration.
The BIOS will automatically enter the IP address of your system; however it may
be over-ridden. IP addresses are 6 two-digit hexadecimal numbers (base 16,
0~9, A, B, C, D, E and F) separated by dots (such as 00.30.48.D0 .D4.60).
This static display shows the current IP address used for your IPMI connection.
Enter the MAC address for your system using this sub-menu. This shoul d be i n
decimal and dotted quad form (such as 192.168.10.253). The value of each
three-digit number separated by dots should not exceed 255.
HANNEL NUMBER IS OK or WRONG CHANNEL NUMBER.
TATIC or
Parameter
Selector
MAC Address
Current MAC
Address in
BMC
XSubnet Mask
Parameter
Selector
Subnet Mask
Current Subnet
Mask in BMC
This static display shows the parameter of your MAC Address configuration.
The BIOS will automatically enter the MAC address of your system; however it
may be over-ridden. MAC addresses are 6 two-digit hexadecimal numbers (b ase
16, 0~9, A, B, C, D, E and F) separated by dots (such as 00.30.48.D0.D4.60).
This static display shows the current MAC address used for your IPMI
connection.
Subnet masks tell the network which subnet this system belongs. The value of
each three-digit number separated by dots should not exceed 255.
This static display shows the parameter of your Subnet Masks configuration.
This static display shows the current Subnet Mask setting for your IPMI
connection.
This static display shows the current Subnet Mask used for your IPMI
connection.
6-13
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
Table 6-12. MPS Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
MPS Revision
This option allows you to select the MPS revision used for your system. Options
include 1.1 and 1.4.
Table 6-13. PCI Express Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Active State
Power-Management
This option allows you to enable/disable PCI Express L0s and L1 link power in
your system. Options include Enabled and D
Table 6-14. SMBIOS Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
SMI Support
This option enables SMBIOS SMI Wrapper suppor t for Plug-and-Play Func
50h-54h. Options include Enabled and D
Table 6-15. Remote Access Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Remote Access
Serial Port Number
This option allows you to select your remote acce ss type. O ptions inclu de COM1
and COM2.
This option allows you to select a serial port for console redirection if the
selected port is enabled. Options include COM1 and COM2.
The Base Address IRQ is displayed statically under this option for your
reference.
ISABLED.
ISABLED.
Serial Port Mode
Flow Control
Redirection After
BIOS POST
Terminal Type
VT-UTF8 Combo Key
Support
Sredir Memory
Display Delay
Use this option to select the serial port mode setting. Options include 115200
8,n,1 / 57600 8,n,1 / 38400 8,n,1 / 19200 8,n,1 / 09600 8,n,1
This option allows you to select Flow Control for redirection. Options include
None, H
This option allows you to specify redirection after BIOS POS T. Options include
the following:
NOTE: Some operating systems may not work if set to Always.
This option allows you to select the Terminal Type for your system. Options
include ANSI, VT100 and VT-UTF8.
Use this option to enable VT-UTF8 Combina tion Key support for ANSI/VT100
terminals. Options include Enabled and D
This option gives the delay in seconds to display memory information. Options
include No Delay, D
ARDWARE or SOFTWARE.
ISABLE – Turns off the redirection after POST
•D
•B
OOT LOADER – Redirection is active during Boot Loader
• Always – Redirection is always active.
ISABLED.
ELAY IN 1 SEC, DELAY IN 2 SEC and DELAY IN 4 SEC.
6-14

Table 6-16. System Health Monitor Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
This screen displays information about your system’s health and includes the
following health information:
• CPU Temperatures (for both CPUs)
• System Temperature
• CPU Vcore (for both CPUs)
System Health
Monitor Screen
• 3.3V Vcc (V)
•+5Vin
• +12V Vcc (V)
• 5V Standby
• Battery Voltage
See Section 6-9: Hardware Health Information on page 6-20 for further details
on the health information listed above.
6-6 Security
Chapter 6: BIOS
Figure 6-3. Security Setup Menu
6-15

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Choose Security from the AMI BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys to
bring up the S
by highlighting the setting using the arrow keys and pressing <E
BIOS settings are described in Table 6-17 below.
Menu Option Description
ECURITY SETUP menu (Figure 6-3). Security setting options are displayed
NTER>. All Security
Table 6-17. Security Menu Options
Supervisor Password
User Password
Change Supervisor
Password
This displays whether a supervisor password has been entered for the system.
“Not Installed” means that a Supervisor password has not been used.
This displays whether a user password has been entered for the system. “Not
Installed” means that a User pa ssword has not been used.
Select this option and hit the <E
NTER> key to access the sub-menu and then
type in the Supervisor's password in the dialogue box to set or change the
Supervisor password, which allows access to the System’s BIOS.
Select this option and hit the <ENTER> key to access a sub-menu with the
following options;
• Full Access (default) – This grants full user read and write acces to the
BIOS Setup Utility.
•V
Change User
Password
IEW ONLY – This allows access to the BIOS Setup Utility, but does not
allow the fields to be changed.
•L
IMITED – This allows only limited fields to be changed such as DATE and
IME.
T
• No Access – This prevents User access to the BIOS Setup Utility.
NOTE: This option is only available when the Supervisor Password has been set
above.
Clear User Password This option allows you to clear a user password after it has been entered.
Password Check
Boot Sector Virus
Protection
This item allows you to check a passwor d after it has been entered. The option s
include Setup and A
When E
NABLED, the AMI BIOS displays a warning when any program or virus
LWAYS.
issues a Disk Format command or attempts to write to t he boot sector of the h ard
disk drive. Options include E
NABLED and Disabled.
6-16
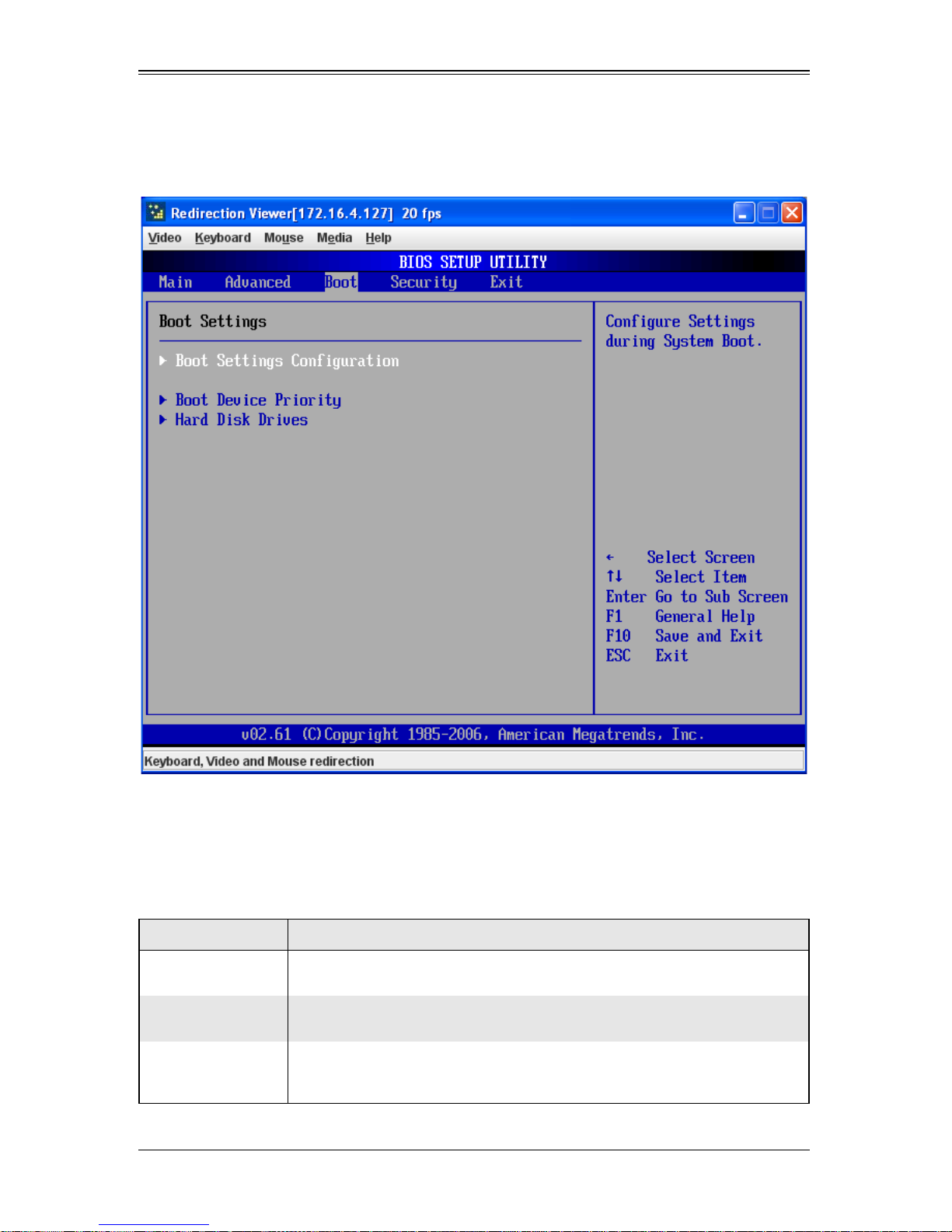
6-7 Boot
Chapter 6: BIOS
Figure 6-4. Boot Setup Menu
Choose Boot from the AMI BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys to bring
up the B
OOT SETUP menu (Figure 6-4). Security setting options are displayed by
highlighting the setting using the arrow keys and pressing <E
settings are described in Table 6-18 below.
Menu Option Description
XBoot Settings
Configuration
Quick Boot
Quiet Boot
This sub-menu allows you configure settings during system system boot.
This option allows BIOS to skip certain tests while booting . This will decrease the
time needed to boot the system. Options include Enabled or D
When E
and beeps. When Disabled, your system displays and emits normal POST
messages.
NTER>. All Security BIOS
Table 6-18. Boot Setup Menu Options
ISABLED.
NABLED, your system displa ys its OEM Logo instead of POST messages
6-17

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table 6-18. Boot Setup Menu Options (Continued)
Menu Option Description
AddOn ROM
Display Mode
Bootup Num-Lo c k
PS/2 Mouse
Support
Wait for ‘F1’ If
Error
Hit ‘Del’ Message
Display
Interrupt 19
Capture
XBoot Device Priority
XHard Disk Drives
This option allows you to set the display mode for Option ROM. Options include
Force BIOS or K
EEP CURRENT.
Use this option to select a Power-on state for Numlock during boot-up. Options
include On (Power-on state) or O
FF.
Use this option to select support for a PS/2 mouse in your system. Options
include Auto (for automatically detecting if a PS/2 mouse is present), D
NABLED.
or E
ISABLED
This option, when Enabled, causes your system to wait for the F1 key to be
pressed if an error occurs during bootup. Options include Enabled and
ISABLED.
D
When enabled, this feature displays a “Press DEL to run Setup” message in
POST. Options are Enabled and D
ISABLED.
When enabled, this feature allows option ROMs to trap Interrupt 19. Options
include Enabled and D
ISABLED.
This sub-menu feature allows you to specify the sequence of priori ty for the boot
device (such as hard disk drives, USB devices, CD-ROM drives an d so on). The
menu options are for 1
ST BOOT DEVICE, 2ND BOOT DEVICE and 3RD BOOT DEVICE.
Each numbered boot device can be set to a specific device installed in your
system or to D
ISABLED.
NOTE: A device enclo sed in parenthesis has been disabled in t he corresponding
type menu.
This sub-menu feature allows you to specif y the boot sequence from all available
hard disk drives installed on your system. The settings for each are list of all
available hard disk drives in your system that have been detected or D
ISABLED.
6-18

6-8 Exit
Chapter 6: BIOS
Figure 6-5. Exit Setup Menu
Choose EXIT from the AMI BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys to display
the E
XIT SETUP menu (Figure 6-5). All Exit BIOS settings are described in Table 6-19
below.
Menu Option Description
Save Changes and
Exit
Discard Changes and
Exit
Discard Changes
Highlight this item and hit <E
the BIOS Setup utility. The system will reboot and implement the changes you
have made to the BIOS Setup.
Highlight this item and hit <ENTER> to exit the BIOS Setup utility without saving
any changes you may have made. Any changes you have made to the BIOS
Setup will not take effect upon system bootup.
Highlight this item and hit <E
You will remain in the Setup utility.
Table 6-19. Exit Menu Options
NTER> to save any changes you made and to exit
NTER> to discard (cancel) any changes you made.
6-19

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table 6-19. Exit Menu Option s (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Load Optimal
Defaults
Load Fail Safe
Defaults
Highlight this item and hit <ENTER> to load the default set tings for all it ems in the
BIOS Setup. These are the safest settings t o use and are designed for maximum
system performance, but may not work best for all computer applications.
Highlight this item and hit <E
maximum system stability, but not for maximum performance.
NTER> to load fail-safe settings that are designed for
6-9 Hardware Health Information
This section provides further details concerning the SYSTEM HEALTH MONITOR screen
information described briefly in Table 6-16.
CPU Temperature
This feature displays current temperature readings for the CPUs installed in your
system.
The CPU’s temperature is read by the mainboard in order for it to take different actions
at different temperatures (such as increasing CPU fan speed, triggering overheat alarms
and so on). Since CPUs can have differing temperature tolerances, the installed CPU
sends information to the mainboard on what it’s ‘Temperature Tolerance’ is so
temperature management can be undertaken.
Supermicro uses this featue in its mainboard’s by assigning a temperature status to
certain thermal conditions in the processor (Low, Medium and High). This makes it
easier for you to understand the CPU’s temperature status, rather than by simply seeing
a temperature reading (such as 25° C). This CPU T emperature feature displays the CPU
temperature status as detected by the BIOS:
• Low – This level is considered as the ‘normal’ operating state. The CPU
temperature is well below the CPU ‘Temperature Tolerance’ and mainboard fans
and CPU will run normally.
• Medium – The processor is running warmer. This is a ‘precautionary’ level and
generally means that there may be factors contributing to this condition, but the
CPU is still within its normal operating state and below the CPU ‘Temperature
Tolerance’. The fans may adjust to a faster speed.
No user action is required, but you may consider checking the CPU fans and the
chassis ventalation for blockage.
• High – The processor is running hot. This is a ‘caution’ level since the CPU’s
‘Temperature Tolerance’ has been reached (or has been exceeded) and may
activate an overheat alarm.
If the system buzzer and Overheat LED has activated, take action immediately by
checking the system fans, chassis ventilation and room temperature to correct any
problems.
6-20

Chapter 6: BIOS
NOTE: The system may shut down if this high level continues for a long period
in order to prevent damage to the CPU.
System Temperature
The system temperature is displayed (in degrees Celsius and Fahrenheit) as it is
detected by the BIOS.
Voltage Monitoring
The following voltage infomation is displayed:
• CPU Vcore (for both CPUs)
• 3.3V Vcc (V)
•+5Vin
• +12V Vcc (V)
• 5V Standby
• Battery Voltage
6-21

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
6-22

Appendix A
BIOS POST Codes
A-1 BIOS POST Messages
During the Power-On Self-Test (POST), the BIOS will check for problems. If a problem is
found, the BIOS will activate an alarm or display a message. The following is a list of
such BIOS messages.
Table A-1. BIOS POST Messages
BIOS Message Description
Fixed disk is not working or not configured properly. Check to
Failure Fixed Disk
Stuck key Stuck key on keyboard.
Keyboard error Keyboard not working.
see if fixed disk is attached properl y. Run Setup. Find out if the
fixed-disk type is correctly identified.
Keyboard Controller Failed
Keyboard locked - Unlock key switch Unlock the system to proceed.
Monitor type does not match CMOS -
Run SETUP
Shadow Ram Failed at offset: nnnn
System RAM Failed at offset: nnnn
Extended RAM Failed at offset: nnnn
System battery is dead - Replace and
run SETUP
System CMOS checksum bad - Default
configuration used
System timer error The timer test failed. Requires repair of system board.
Real time clock error
Keyboard controller failed test. May require replacing keyboard
controller.
Monitor type not correctly identified in Setup
Shadow RAM failed at offset nnnn of the 64k block at which
the error was detected.
System RAM failed at offset nnnn of in the 64k block at which
the error was detected.
Extended memory not working or not configured properly at
offset nnnn.
The CMOS clock battery indicator shows the battery is dead.
Replace the battery and run Setup to reconfigure the system.
System CMOS has been corrupted or modified incorrectly,
perhaps by an application program t hat changes dat a st ored in
CMOS. The BIOS installed Default Setup Values. If you do not
want these values, enter Setup and enter your own values. If
the error persists, check the system battery or contact your
dealer.
Real-Time Clock fails BIOS hardware t est. May require board
repair.
Check date and time settings
BIOS found date or time out of range and reset the Real-Time
Clock. May require setting legal date (1991-2099).
A-1

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table A-1. BIOS POST Messages (Continued)
BIOS Message Description
Previous POST did not complete successfully. POST loads
default values and offers to run Se tup. If the f ailure was caused
by incorrect values and they are not corrected, the next boot
Previous boot incomplete - Default
configuration used
will likely fail. On systems with control of wait states, improper
Setup settings can also terminate POST and cause this error
on the next boot. Run Setup and verify that the waitstate
configuration is correct. This error is cleared the next time the
system is booted.
Memory Size found by POST differed
from CMOS
Diskette drive A error
Diskette drive B error
Incorrect Drive A type - run SETUP Type of floppy drive A: not correctly identified in Setup.
Incorrect Drive B type - run SETUP Type of floppy drive B: not correctly identified in Setup.
System cache error - Cache disabled
CPU ID: CPU socket number for Multi-Processor error.
EISA CMOS not writeable ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot write to EISA CMOS.
DMA Test Failed
Software NMI Failed
Fail-Safe Timer NMI Failed ServerBIOS2 test error: Fail-Safe Timer takes too long.
device Address Conflict Address conflict for specified device.
Allocation Error for: device
Memory size found by POST differed from CMOS.
Drive A: or B: is present but fail s the BIOS PO ST diskette test s.
Check to see that the drive is defined with the proper diskette
type in Setup and that the diskette drive is attached correctly.
RAM cache failed and BIOS disabled the cache. On older
boards, check the cache jumpers. You may have to replace the
cache. See your dealer . A disabled cache slows system
performance considerably.
ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot write to extended DMA (Direct
Memory Access) registers.
ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot generate software NMI
(Non-Maskable Interrupt).
Run ISA or EISA Configuration Utility to resolve resource
conflict for the specified device.
CD ROM Drive CD ROM Drive identified.
Entering SETUP... Starting Setup program
Failing Bits: nnnn
Fixed Disk n Fixed disk n (0-3) identified.
Invalid System Configuration Data Problem with NVRAM (CMOS) data.
I/O device IRQ conflict I/O device IRQ confl ict error.
PS/2 Mouse Boot Summary Screen: PS/2 Mouse installed.
The hex number nnnn is a map of the bit s a t the RAM addr ess
which failed the memory test. Each 1 (one) in the map
indicates a failed bit. See errors 230, 231, or 232 above for
offset address of the failure in System, Ex tended, or Shadow
memory.
A-2
Table A-1. BIOS POST Messages (Continued)
BIOS Message Description
:
nnnn kB Extended RAM Passed
nnnn Cache SRAM Passed
nnnn kB Shadow RAM Passed
nnnn kB System RAM Passed
One or more I2O Block Storage
Devices were excluded from the Setup
Boot Menu
Operating system not found
Parity Check 1 nnnn
Parity Check 2 nnnn
Where nnnn is the amount of RAM in kilobytes successfully
tested.
Where nnnn is the amount of system cache in kilobytes
successfully tested.
Where nnnn is the amount of shadow RAM in kilobytes
successfully tested.
Where nnnn is the amount of system RAM in kilobytes
successfully tested.
There was not enough room in the IPL table to display all
installed I2O block-storage devices.
Operating system cannot be located on either drive A: or drive
C:. Enter Setup and see if fixed disk and drive A: are properly
identified.
Parity error found in the system bus. BIOS attempts to locate
the address and display it on the screen. If it cannot locate the
address, it displays ????. Parity is a method for checking
errors in binary data. A parity error indicates that some data
has been corrupted.
Parity error found in the I/O bus. BIOS attempts to locate the
address and display it on the screen. If it cannot locate the
address, it displays ????.
Displayed after any recoverable error message. Press <F1> t o
Press <F1> to resume, <F2> to Setup,
<F3> for previous
Press <F2> to enter Setup
PS/2 Mouse: PS/2 mouse identified.
Run the I2O Configuration Utility
System BIOS shadowed System BIOS copied to shadow RAM.
UMB upper limit segment address:
nnnn
Video BIOS shadowed Video BIOS successfully copied to shadow RAM.
start the boot process or <F2> to enter Setup and change the
settings. Press <F3> to display the previous screen (usually an
initialization error of an Option ROM, i.e., an add-on card).
Write down and follow the information shown on the screen.
Optional message displayed durin g POST. Can be turned off in
Setup.
One or more unclaimed block storage devices have the
Configuration Request bit set in the LCT. Run an I2O
Configuration Utility (e.g. the SAC utility).
Displays the address nnnn of the upper limit of Upper
Memory Blocks, indicating released segments of the BIOS
which can be reclaimed by a virtual memory manager.
A-2 BIOS POST Codes
This section lists the POST (Power-On Self-Test) codes for the AMI BIOS. POST codes
are divided into two categories: recoverable and terminal.
A-3

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Recoverable POST Errors
When a recoverable type of error occurs during POST, the BIOS will display an POST
code that describes the problem. BIOS may also issue one of the following beep codes:
• One long and two short beeps – video configuration error
• One repetitive long beep – no memory detected
Terminal POST Errors
If a terminal type of error occurs, BIOS will shut down the system. Before doing so,
BIOS will write the error to port 80h, attempt to initialize video and write the error in the
top left corner of the screen.
The following is a list of codes that may be written to port 80h.
Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors
Post Code Description
02h Verify Real Mode
03h Disable Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI)
04h Get CPU type
06h Initialize system hardware
07h Disable shadow and execute code from the ROM.
08h Initialize chipset with initial POST values
09h Set IN POST flag
0Ah Initialize CPU registers
0Bh Enable CPU cache
0Ch Initialize caches to initial POST values
0Eh Initialize I/O component
0Fh Initialize the local bus IDE
10h Initialize Power Management
11h Load alternate registers with initial POST values
12h Restore CPU control word during warm boot
13h Initialize PCI Bus Mastering devices
14h Initialize keyboard controller
16h 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum
17h Initialize cache before memory Auto size
18h 8254 timer initialization
1Ah 8237 DMA controller initialization
1Ch Reset Programmable Interrupt Controller
20h 1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh
A-4

Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors (Continued)
Post Code Description
22h 1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller
28h Auto size DRAM
29h Initialize POST Memory Manager
2Ah Clear 512 kB base RAM
2Ch 1-3-4-1 RAM failure on address line xxxx*
2Eh 1-3-4-3 RAM failure on data bits xxxx* of low byte of memory bus
2Fh Enable cache before system BIOS shadow
32h Test CPU bus-clock frequency
33h Initialize Phoenix Dispatch Manager
36h Warm start shut down
38h Shadow system BIOS ROM
3Ah Auto size cache
3Ch Advanced configuration of chipset re gisters
:
3Dh Load alternate registers with CMOS values
41h Initialize extended memory for RomPilot
42h Initialize interrupt vectors
45h POST device initialization
46h 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice
47h Initialize I20 support
48h Check video configuration against CMOS
49h Initialize PCI bus and devices
4Ah Initialize all video adapters in system
4Bh QuietBoot start (optional)
4Ch Shadow video BIOS ROM
4Eh Display BIOS copyright notice
4Fh Initialize MultiBoot
50h Display CPU type and speed
51h Initialize EISA board
52h Test keyboard
54h Set key click if enabled
55h Enable USB devices
58h 2-2-3-1 Test f or unexpected interrupts
59h Initialize POST display service
5Ah Display prompt “Press F2 to enter SETUP”
5Bh Disable CPU cache
A-5
SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors (Continued)
Post Code Description
5Ch Test RAM between 512 and 640 kB
60h Test extended memory
62h Test extended memory address lines
64h Jump to UserPatch1
66h Configure advanced cache registers
67h Initialize Multi Processor APIC
68h Enable external and CPU caches
69h Setup System Management Mode (SMM) area
6Ah Display external L2 cache size
6Bh Load custom defaults (optional)
6Ch Display shadow-area message
6Eh Display possible high address for UMB recovery
70h Display error messages
72h Check for configuration errors
76h Check for keyboard errors
7Ch Set up hardware interrupt vectors
7Dh Initialize Intel ligent System Monitoring
7Eh Initialize coprocessor if present
80h Disable onboard Super I/O ports and IRQs
81h Late POST device initialization
82h Detect and install external RS232 ports
83h Configure non-MCD IDE controllers
84h Detect and install external parallel ports
85h Initialize PC-compatible PnP ISA devices
86h Re-initialize onboard I/O ports.
87h Configure Motherboard Configurable Devices (optional)
88h Initialize BIOS Data Area
89h Enable Non-Maskable Interrupts (NMIs)
8Ah Initialize Extended BIOS Data Area
8Bh Test and initialize PS/2 mouse
8Ch Initialize floppy controller
8Fh Determine number of ATA drives (optional)
90h Initialize hard-disk controllers
91h Initialize local-bus hard-disk controllers
92h Jump to UserPatch2
A-6

Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors (Continued)
Post Code Description
93h Build MPTABLE for multi-processor boards
95h Install CD ROM for boot
96h Clear huge ES segment register
98h 1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short beeps on check-sum failure
99h Check for SMART Drive (optional)
9Ah Shadow option ROMs
9Ch Set up Power Management
9Dh Initialize security engine (optional)
9Eh Enable hardware interrupts
9Fh Determine number of ATA and SCSI drives
A0h Set time of day
A2h Check key lock
A4h Initialize typematic rate
:
A8h Erase F2 prompt
AAh Scan for F2 key stroke
ACh Enter SETUP
AEh Clear Boot flag
B0h Check for errors
B1h Inform RomPilot about the end of POST.
B2h POST done - prepare to boot operating system
B4h 1 One short beep before boot
B5h Terminate QuietBoot (optional)
B6h Check password (optional)
B7h Initialize ACPI BIOS
B9h Prepare Boot
BAh Initialize SMBIOS
BBh Initialize PnP Option ROMs
BCh Clear parity checkers
BDh Display MultiBoot menu
BEh Clear screen (optional)
BFh Check virus and backup reminders
C0h Try to boot with INT 19
C1h Initialize POST Error Manager (PEM)
C2h Initialize error logging
C3h Initialize error display function
A-7

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Table A-2. Terminal POST Errors (Continued)
Post Code Description
C4h Initialize system error handler
C5h PnPnd dual CMOS (optional)
C6h Initialize note dock (optional)
C7h Initialize note dock late
C8h Force check (optional)
C9h Extended checksum (optional)
CAh Redirect Int 15h to enable remote keyboard
CBh
CCh Redirect Int 10h to enable remote serial video
CDh Re-map I/O and memory for PCMCIA
CEh Initialize digitizer and display message
Redirect Int 13h to Memory Technologies Devices such as ROM, RAM, PCMCIA, and
serial disk
D2h Unknown interrupt
The following are for the boot block in Flash ROM:
Table A-3. Boot Block Flash ROM Terminal POST Errors
Post Code Description
E0h Initialize the chipset
E1h Initialize the bridge
E2h Initialize the CPU
E3h Initialize system timer
E4h Initialize system I/O
E5h Check force recovery boot
E6h Checksum BIOS ROM
E7h Go to BIOS
E8h Set Huge Segment
E9h Initialize Multi Processor
EAh Initialize OEM special code
EBh Initialize PIC and DMA
ECh Initialize Memory type
EDh Initialize Memory size
EEh Shadow Boot Block
EFh System memory test
F0h Initialize interrupt vectors
F1h Initialize Run Time Clock
A-8
Table A-3. Boot Block Flash ROM Terminal POST Errors (Continued)
Post Code Description
F2h Initialize video
F3h Initialize System Management Manager
F4h Output one beep
F5h Clear Huge Segment
F6h Boot to Mini DOS
F7h Boot to Full DOS
If the BIOS detects error 2C, 2E, or 30 (base 512K RAM error), it displays an additional
word-bitmap (
xxxx) indicating the address line or bits that failed. For example, “2C 0002”
means address line 1 (bit one set) has failed. “2E 1020" means data bits 12 and 5 (bits
12 and 5 set) have failed in the lower 16 bits. The BIOS also sends the bitmap to the
port-80 LED display. It first displays the checkpoint code, followed by a delay, the
high-order byte, another delay, and then the low order byte of the error. It repeats this
sequence continuously.
:
A-9

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
Notes
A-10

Disclaimer
The products sold by Supermicro are not intended for and will not be used in life support
systems, medical equipment, nuclear facilities or systems, aircraft, aircraft devices,
aircraft/emergency communication devices or other critical systems whose failure to
perform be reasonably expected to result in significant injury or loss of life or
catastrophic property damage. Accordingly, Supermicro disclaims any and all liability,
and should buyer use or sell such products for use in such ultra-hazardous applications,
it does so entirely at its own risk. Furthermore, buyer agrees to fully indemnify, defend
and hold Supermicro harmless for and against any and all claims, demands, actions,
litigation, and proceedings of any kind arising out of or related to such ultra-hazardous
use or sale.

SBI-7126T-S6 Blade Module User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...