Supermicro P5MMA2, P5MMA98, P5MMS98, P5MMS2 Reference Manual
SUPER
P5MMA98/P5MMS98
P5MMA2/P5MMS2
AMI BIOS
®
REFERENCE MANUAL
Revision 1.1
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be
accurate. The vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be
contained in this document, makes no commitment to update or to keep current the
information in this manual, or to notify any person or organization of the updates.
The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the product described in this
manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software, if any, and
documentation may not, in whole or in part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated
or reduced to any medium or machine without prior written consent.
IN NO EVENT WILL THE MANUFACTURER BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, THE VENDOR SHALL NOT HAVE
LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE
PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF THE REPAIRING, REPLACING, OR
RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Copyright © 1997 by SUPERMICRO COMPUTER INC.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Unless you request and receive written permission from the manufacturer, you may not
copy any part of this document.
All products and company names mentioned are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective holders.
Do not upgrade the BIOS unless you are notified to do so. Please call technical
support first before upgrading the boot-block BIOS.
Baud Rate: 1200-14400 bps, Data Bits: 8, Stop Bit: 1, Parity: None
SUPER BBS # (408) 895-2022 (24 hours)
SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMA2/P5MMS98/P5MMS2 User's Manual
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: AMI BIOS
1-1 Introduction
System BIOS ....................................................................................... 1-1
Configuration Data............................................................................. 1-1
How Data Is Configured................................................................... 1-1
POST Memory Test ............................................................................ 1-2
1-2 BIOS Features...................................................................................... 1-3
BIOS Configuration Summary Screen ........................................... 1-4
Chapter 2: Running Setup
2-1 Setup
2-1-1 Standard Setup.................................................................. 2-1
2-1-2 Advanced Setup ................................................................. 2-3
2-1-3 Chipset Setup .................................................................... 2-7
2-1-4 Power Management Setup............................................ 2-11
2-1-5 PCI/PnP Setup ................................................................. 2-14
2-1-6 Peripheral Setup ............................................................. 2-18
2-2 Security Setup
2-2-1 Supervisor/User ................................................................2-22
2-2-2 Anti-Virus ........................................................................... 2-22
2-3 Utility Setup
2-3-1 Detect IDE .......................................................................... 2-23
2-3-2 Language........................................................................... 2-23
2-4 Default Setting
2-4-1 Optimal Default................................................................. 2-23
2-4-2 Fail-Safe Default............................................................... 2-23
iii

Table of Contents
Appendix A: Hard Disk Error Messages ................ A-1
Appendix B: BIOS Hard Disk Drive Types.............. B-1
Appendix C: BIOS Error Beep Codes..................... C-1
Appendix D: AMI BIOS POST Diagnostic Error
Messages .......................................... D-1
Appendix E: BIOS Non-Fatal Error Messages........ E-1
iv

PRINTED IN U.S.A.

Chapter 1: AMI BIOS
Chapter 1
AMI BIOS
1-1 Introduction
This chapter describes the AMIBIOS for the Intel 430 TX chipset
which is designed for an Intel Pentium® 75/90/100/120/133/150/
166/180/200/233 MHz, Cyrix/IBM 5x86, 6x86, AMD-K5, AMD-K6 and
MMXTM processors. The AMI ROM BIOS is stored in the Flash
EEPROM and is easily upgraded using a floppy disk-based program.
System BIOS
The BIOS is the basic input output system used in all IBM® PC,
XT™, AT®, and PS/2® compatible computers. The WinBIOS is a
high-quality example of a system BIOS.
Configuration Data
AT-compatible systems, also called ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) must have a place to store system information when the
computer is turned off. The original IBM AT had 64 bytes of nonvolatile memory storage in CMOS RAM. All AT-compatible systems
have at least 64 bytes of CMOS RAM, which is usually part of the
Real Time Clock. Many systems have 128 bytes of CMOS RAM.
How Data Is Configured
AMIBIOS provides a Setup utility in ROM that is accessed by
pressing <Del> at the appropriate time during system boot. Setup
configures data in CMOS RAM.
1-1

SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
POST Memory Test
Normally, the only visible POST routine is the memory test. The
screen that appears when the system is powered on is shown
below.
An AMIBIOS Identification string is displayed at the left bottom
corner of the screen, below the copyright message.
081597 Pentium Mainboard
xxxxx KB OK
Hit <DEL> if you want to run SETUP
(C) American Megatrends Inc.,
XX-XXXX-XXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXX-XXXX-X
1-2
Chapter 1: AMI BIOS
1-2 BIOS Features
• supports Plug and Play V1.0A
• supports V1.03 of the EPA Green PC specification
• supports V1.1 of the APM (Advanced Power Management)
specification. Power management features are implemented via
the System Management Interrupt (SMI). Sleep and Suspend power
management modes are supported. Power to the hard drives and
video monitors can be managed
• supports Intel PCI 2.1 (Peripheral Component Interconnect) local bus specification
• supports pipelined burst synchronous and asynchronous SRAM
• supports FPM, EDO and SDRAM memories
• supports Flash ROM, 1 Mb flash memory
• supports DMI 2.0
• supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
1-3
SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
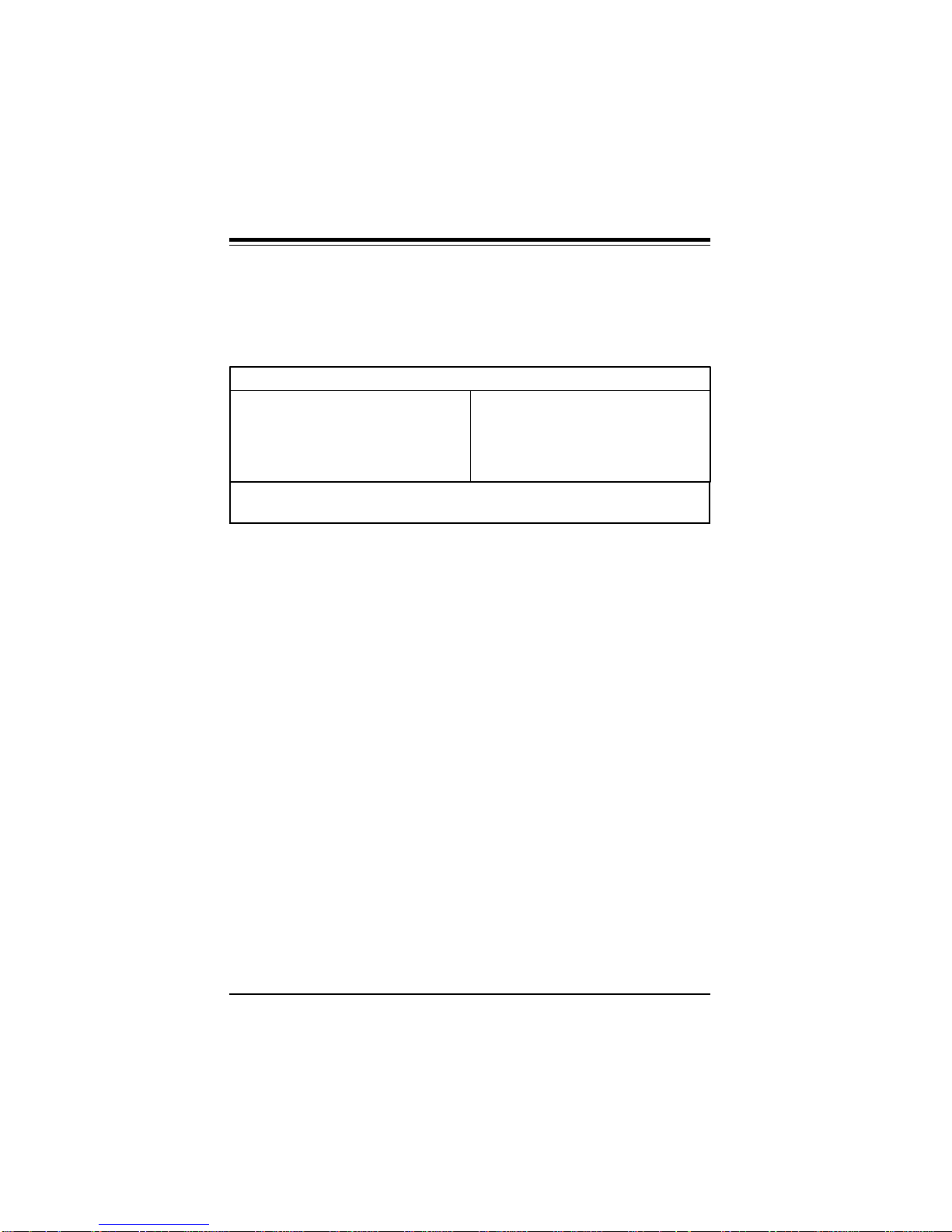
BIOS Configuration Summary Screen
AMIBIOS displays a screen that looks similar to the following when
the POST routines complete successfully.
AMIBIOS System Configuration (C) 1985-1996 American Megatrends Inc.,
Main Processor :Pentium(P54C) Base Memory Size :640 KB
Math Processor :Built-In Ext. Memory Size :31744 KB
Floppy Drive A: :1.2 MB, 5¼ Display Type :VGA/EGA
Floppy Drive B: :1.44 MB, 3½ Serial Port(s) :3F8,2F8
ROM-BIOS Date: :07/15/95 Parallel Port(s) :378
Processor Clock: :166MHz Ext Cache :512KB,Enabled
Power Management: :APM, SMI
PCI Devices:
PCI Onboard Bridge Device PCI Onboard USB Controller
PCI Onboard IDE PCI Slot 3 VGA
Current CPU Temperature 35 °C
1-4

Chapter 2: Running Setup
Chapter 2
Running Setup
The WinBIOS Setup options described in this section are selected
by choosing the appropriate high-level icon from the Standard Setup
screen. All displayed icons are described in this section, although
the screen display is often all you need to understand how to set
the option.
2-1 Setup
2-1-1 Standard Setup
Pri Master
Pri Slave
Sec Master
Sec Slave
Choose these icons to configure the hard disk drive. When you
click on an icon, the following parameters are listed: Type, LBA/
Large Mode, Block Mode, 32Bit Mode, and PIO Mode. All
parameters relate to IDE drives except Type.
If the hard disk drive to be configured is an IDE drive, select the
appropriate drive icon, choose the Type parameter and select Auto.
The BIOS will automatically detect the IDE drive parameters and
display them. Click on the OK button to accept these parameters.
Click on LBA/Large Mode and choose On to enable support for IDE
drives with capacities greater than 528MB. Click on Block Mode
and choose On to support IDE drives that use Block Mode. Click on
32Bit Mode and click on On to support IDE drives that permit 32-bit
accesses.
2-1
SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
To configure a CD-ROM drive, select the appropriate drive icon,
choose the Type parameter and select CDROM. You can boot the
computer from a CD-ROM drive. To configure a SCSI drive, select
Not Installed in the Type field.
To configure an old MFM hard disk drive, you must know the drive
parameters (number of heads, number of cylinders, number of
sectors, the starting write precompensation cylinder, and drive
capacity). Choose Type and select the hard disk drive type (1-46).
Refer to Appendix B in this manual for a list of the various hard disk
drive types. Select User in the Type field if the drive parameters on
your MFM drive do not match any of the drive type in Appendix B.
Entering Drive Parameters
You can also enter the hard disk drive parameters. The drive parameters are:
Parameter Description
Type The number for a drive with certain identification parameters.
Cylinders The number of cylinders in the disk drive.
Heads The number of heads.
Write The size of a sector gets progressively smaller as the track
Precompensation diameter diminishes. Yet each sector must still hold 512 bytes.
Landing Zone This number is the cylinder location where the heads will normally
Sectors The number of sectors per track. MFM drives have 17 sectors
Capacity The formatted capacity of the drive is (Number of heads) x
Write precompensation circuitry on the hard disk compensates for
the physical difference in sector size by boosting the write
current for sectors on inner tracks. This parameter is the track
number where write precompensation begins.
park when the system is shut down.
per track. RLL drives have 26 sectors per track. ESDI drives
have 34 sectors per track. SCSI and IDE drive may have even
more sectors per track.
(Number of cylinders) x (Number of sectors per track) x (512
bytes per sector)
2-2
Chapter 2: Running Setup
Date and Time Configuration
Select the Standard option. Select the Date/Time icon. The current
values for each category are displayed. Enter new values through
the keyboard.
Floppy A
Floppy B
Choose the Floppy Drive A or B icon to specify the floppy drive type.
The settings are 360 KB 5¼ inch, 1.2 MB 5¼ inch, 720 KB 3½ inch,
1.44 MB 3½ inch, 2.88 MB 3½ inch or Not Installed.
2-1-2 Advanced Setup
Quick Boot
Set this option to Enabled to permit AMIBIOS to boot within 5 seconds. The settings are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal default
setting is Enabled. The Fail-Safe default setting is Disabled.
Pri Master ARMD Emulated as
Pri Slave ARMD Emulated as
Sec Master ARMD Emulated as
Sec Slave ARMD Emulated as
These options are used to emulate removable drives. ARMD stands
for Atapi Removable Media Device. The settings are Floppy or Hard
Disk. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Floppy. For
IOMEGA IDE zip drive, set the emulation to Floppy. For IOMEGA
ATAPI zip drive, set the emulation to Hard Disk.
1st Boot Device
2nd Boot Device
3rd Boot Device
4th Boot Device
2-3

SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
The options for 1st Boot Device are IDE-1, IDE-2, IDE-3, Floppy,
ARMD-FDD, ARMD-HDD, CDROM or SCSI. The options for 2nd
Boot Device are Disabled, IDE-0, Floppy, ARMD-FDD, CDROM or
SCSI. The options for 3rd Boot Device are Disabled, IDE-0, Floppy,
ARMD-FDD, CDROM or SCSI. The options for 4th Boot Device are
Disabled, IDE-0, Floppy, ARMD-FDD, CDROM or SCSI.
The Disabled option means that setup will not be considered during the boot process.
IDE-0, IDE-1, IDE-2, IDE-3 are the four hard disks than can be installed by the BIOS. IDE-0 is the first hard disk installed by the
BIOS, IDE-1 is the second hard disk, and so on. For example, if the
system has a hard disk connected to Primary Slave and another
hard disk to Secondary Master, then IDE-0 will be referred to as the
hard disk connected to Primary Slave and IDE-1 will be referred to
as the hard disk connected to the Secondary Master. IDE-2 and
IDE-3 are not present. Note that the order of the initialization of the
devices connected to the primary and secondary channels are Primary Master first, Primary Slave second, Secondary Master third,
and Secondary Slave fourth.
The BIOS will attempt to read the boot record from 1st, 2nd, 3rd,
and 4th boot device in the selected order until it is successful in
reading the booting record. The BIOS will not attempt to boot from
any device which is not selected as the boot device.
S.M.A.R.T. for Hard Disks
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) is
a technology developed to manage the reliability of the hard disk by
predicting future device failures. The hard disk needs to be
S.M.A.R.T. capable. The settings for this option are Disabled or
Enabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
2-4

Chapter 2: Running Setup
Boot Up Num-Lock
When this option is set to On, the BIOS turns off the Num Lock key
when the system is powered on. This will enable the end user to
use the arrow keys on both the numeric keypad and the keyboard.
The settings are On or Off. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are On.
Floppy Drive Swap
This option allows the logical floppy drives A: and B: to be swapped.
The settings for this option are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
PS/2 Mouse Support
When this option is set to Enabled, AMIBIOS supports a PS/2-type
mouse. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
Primary Display
This option specifies the type of display adapter card installed in
the system. The settings are VGA/EGA, CGA40x25, CGA80x25,
Mono, or Absent. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are
VGA/EGA.
Password Check
This option enables the password check option every time the system boots or the end user runs WinBIOS Setup. If Always is chosen, a user password prompt appears every time the computer is
turned on. If Setup is chosen, the password prompt appears if
WinBIOS Setup is executed. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Setup.
2-5

SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
Boot to OS/2
If DRAM size is over 64M, set this option to Yes to permit AMIBIOS to
run with IBM OS/2. The settings are No or Yes. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are No.
Internal Cache
This option selects the type of caching algorithm used by AMIBIOS
and the CPU for L1 cache memory. The settings are Disabled or
Writeback. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are
Writeback.
External Cache
This option selects the type of caching algorithm used by AMIBIOS
and the CPU for L2 secondary cache memory. The settings are
Disabled or Writeback. The Optimal default setting is Writeback.
The Fail-Safe default setting is Disabled.
System BIOS Cacheable
AMIBIOS always copies the system BIOS from ROM to RAM for
faster execution. Set this option to Enabled to permit the contents
of F0000h RAM memory segment to be written to and read from
cache memory. The settings are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal default setting is Enabled. The Fail-Safe default setting is Dis-
abled.
C000, 16K Shadow
C400, 16K Shadow
These options specify how the contents of the video ROM are
handled. The settings are: Disabled, Cached or Enabled. When
set to Cached, the contents of the video ROM area from C0000hC7FFFh are not only copied from ROM to RAM, the contents of the
C0000h-C7FFFh RAM can be written to or read from cache memory.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
2-6
Chapter 2: Running Setup
C800, 16K Shadow
CC00, 16K Shadow
D000, 16K Shadow
D400, 16K Shadow
D800, 16K Shadow
DC00, 16K Shadow
These options specify how the contents of the adaptor ROM named
in the option title are handled. The ROM area that is not used by
ISA adapter cards will be allocated to PCI adapter cards. The
settings are: Disabled, Cached or Enabled. When Cached, the
contents of the ROM area are not only copied from ROM to RAM for
faster execution, the contents of the RAM area can be written to or
read from cache memory. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default
settings are Disabled.
2-1-3 Chipset Setup
USB Function
Set this option to Enabled to enable the USB (Universal Serial Bus)
functions. The settings for this option are Enabled or Disabled.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
USB KB/Mouse Legacy Support
Set this option to Enabled to enable the USB keyboard and mouse.
The settings for this option are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
SDRAM RAS# to CAS# Override
When set to Enabled, and the CAS Latency bit is "0", then a RAS# to
CAS# delay of 2 HCLKs is provided for the SDRAM. The settings for
this option are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Disabled.
2-7

SUPER P5MMA98/P5MMS98/P5MMA2/P5MMS2 User's Manual
SDRAM CAS# Latency
The settings for this option are 3 or 2. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are 2. When set to 2, a CAS# latency of 2 is used
for all SDRAM cycles. When set to 3, a CAS# latency of 3 is used for
all SDRAM cycles.
SDRAM RAS# Timing
This controls the RAS# active to precharge time. The settings for
this option are 5 or 4. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are 5.
SDRAM Speculative Read Logic
The settings for this option are Enabled or Disabled. Set this to
Enabled to allow the system to perform SDRAM read cycle base on
the expected logic specified by the chipset. The Optimal and FailSafe default settings are Disabled.
DRAM Speed
This option should be set according to the speed of the DRAM in
the system. The value of this option determines how the DRAM
timings should be programmed in the chipset. The settings for this
option are Manual, 60ns or 70ns. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default
settings are Manual.
DRAM Read Burst Timing
You can define the DRAM read burst timing by setting the DRAM
speed to Manual. This option sets the timing for system memory
burst mode read operations. The settings for this option are
x4EDO/x4FPM, x3EDO/x4FPM, or x2EDO/x3FPM. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are x4EDO/x4FPM.
2-8
Chapter 2: Running Setup
DRAM Write Burst Timing
You can define the DRAM write burst timing by setting the DRAM
speed to Manual. This option sets the timing for system memory
burst mode write operations. The settings for this option are
x4EDO/x4FPM, x3EDO/x3FPM, or x2EDO/x2FPM. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are x4EDO/x4FPM.
DRAM Leadoff Timing (DLT)
You can define the DRAM leadoff timing by setting the DRAM speed
to Manual. This option sets the leadoff timings (Read leadoff/Write
leadoff/RAS# Precharge). The settings are 11/7/3, 10/6/3, 11/7/4, or
10/6/4. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are 11/7/3.
Speculative Leadoff Timing
When set to Disabled, the DRAM controller read request is presented before the final memory target is decoded by the MTXC. This
results in a 1 hclk pull-in for all read leadoff latencies. The settings
for this option are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Disabled.
Memory Address Drive Strength
This option controls the strength of the output buffers driving the
MA, MAA, SRAS#, SCAS#, MWE# and CKE pins. The settings for
this option are 10mA/10mA, 10mA/16mA, 16mA/10mA or 16mA/
16mA. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are 10mA/10mA.
Enhanced Paging Disable
When set to Enabled, the MTXC will keep the page open until a
page/row miss. When set to Disabled, the MTXC will use additional
information to keep the DRAM page open when host may be "right
back". The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
2-9
 Loading...
Loading...