Page 1

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H
MicroBlade Module
User’s Manual
Revison 1.0b
Page 2

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be accurate. The
vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document, makes no
commitment to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to notify any person or
organization of the updates. P lease Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual, please see
our web site at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. ("Supermicro") reserves the right to make changes to the product described
in this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software and documentation, is the
property of Supermicro and/or its licensors, and is supplied only under a license. Any u se or rep rodu ction
of this product is not allowed, except as expressly permitted by the terms of said license.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIA L DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE
THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPERMICRO SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF
REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING, INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and customer shall be governe d by the laws of Santa Clara
County in the State of Californ i a, USA. The State of California, County of Sant a Clara shall be the
exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes. Super Micro's total liability for all claims will not
exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction manual, may cause harmful interference with radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference,
in which case you will be required to correct the interference at your own expense.
California Best Management Practices Regulat ions for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning
applies only to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells. Perchlorate
Material-special handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate for further
details.
WARNING: HANDLING OF LEAD SOLDER MATERIALS USED IN THIS PRODUCT MAY
EXPOSE YOU TO LEAD, A CHEMICAL KNOWN TO THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA TO
CAUSE BIRTH DEFECTS AND OTHER REPRODUCTIVE HARM.
Manual Revison 1.0b
Release Date: November 25, 2014
Unless you request and receive written permission from Super Micro Computer, Inc., you may not copy
any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies referred
to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 2014 by Super Micro Computer, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America
ii
Page 3

Preface
About this Manual
This manual is written for professional system integrators, Information Technology
professionals, service personnel and technicians. It provides information for the
installation and use of the Supermicro MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module.
Installation and maintenance should be performed by experienced professionals only.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1: Introduction
The first chapter provides a checklist of the main components included with
MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module and describes their main features.
Chapter 2: System Safety
You should familiarize yourself with this chapter for a general overview of safety
precautions that should be followed when installing and servicing MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H
MicroBlade module.
Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Refer to this chapter for details on installing the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade
module into the MicroBlade chassis. Other sections cover the installation and placement
of memory modules and the installation of hard disk drives into the blade module.
Chapter 4: Blade Module Features
This chapter coves features and component information about MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H
MicroBlade module. Included here are descriptions and information for mainboard
components, connectors, LEDs and other features of the blade module.
Chapter 5: BIOS
BIOS setup is covered in this chapter for MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module.
Appendix A: BIOS POST Codes
BIOS POST Codes for MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module are explained in this
appendix.
iii
Page 4

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Notes
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................................1-1
1-1 Overview.............................................................................................1-1
1-2 Blade Module Features....................................................................1-2
Processors..............................................................................................1-2
Memory...................................................................................................1-2
Storage....................................................................................................1-3
RAID .......................................................................................................1-3
Density....................................................................................................1-3
1-3 Contacting Supermicro.....................................................................1-4
Chapter 2 Standardized Warning Statements.....................2-1
2-1 About Standardized Warning Statements......................................2-1
Warning Definition...................................................................................2-1
Installation Instructions ...........................................................................2-3
Circuit Breaker........................................................................................2-4
Power Disconnection Warning................................................................2-5
Equipment Installation................................................... ..........................2-6
Restricted Area.......................................................................................2-7
Battery Handling .....................................................................................2-9
Redundant Power Supplies ..................................................................2-10
Backplane Voltage................................................................................2-11
Comply with Local and National Electrical Codes.................................2-12
Product Disposal...................................................................................2-13
Hot Swap Fan Warning .........................................................................2-14
Power Cable and AC Adapter ..............................................................2-15
Chapter 3 Setup and Installation.................................................3-1
3-1 Overview.............................................................................................3-1
3-2 Installing MicroBlade Modules ........................................................ 3-1
Powering Up a MicroBlade Module Unit .................................................3-1
Powering Down a MicroBlade Module Unit.............................................3-1
Removing a MicroBlade Module Unit from the Enclosure ......................3-2
Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover....................................................3-2
Installing a Blade Unit into the Enclosure ...............................................3-2
3-3 Onboard Battery Installation............................................................3-3
3-4 Memory Installation...........................................................................3-4
v
Page 6

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Populating Memory Slots........................................................................3-4
Memory Support .....................................................................................3-4
DIMM Installation....................................................................................3-6
3-5 Hard Disk Drive Installation.............................................................3-7
3-6 Installing the Operating System......................................................3-7
Installing with a SATA-DOM Module................................................... ....3-7
Installing via PXE Boot............................................................................3-8
Installing via Virtual Media (Drive Redirection).......................................3-8
Chapter 4 MicroBlade module Features.................................4-1
4-1 Control Panel..................................................................................... 4-2
Power Button ..........................................................................................4-3
LED Indicators ........................................................................................4-3
4-2 Serverboard.......................................................................................4-4
Jumpers..................................................................................................4-5
CMOS Clear............................................................................................4-6
4-3 Blade Unit Components...................................................................4-7
Memory Support .....................................................................................4-7
Hard Disk Drives.....................................................................................4-8
Chapter 5 BIOS.......................................................................................5-1
5-1 Introduction.........................................................................................5-1
System BIOS ..........................................................................................5-1
How To Change the Configuration Data .................................................5-1
Starting the Setup Utilit y.................... .. ... .......................................... ... ... .5-1
5-2 BIOS Updates....................................................................................5-2
Flashing BIOS.........................................................................................5-2
5-3 Running Setup...................................................................................5-3
5-4 Main BIOS Setup...............................................................................5-4
5-5 Advanced Setup................................................................................5-5
5-6 IPMI Setup........................................................................................5-20
5-7 Event Logs Setup............................................................................5-20
5-8 Boot...................................................................................................5-22
5-9 Security.............................................................................................5-22
5-10 Save & Exit.....................................................................................5-25
vi
Page 7

Table of Contents
Appendix A AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes..............................A-1
A-1 Checkpoint Ranges..........................................................................A-1
A-2 Standard Checkpoints......................................................................A-2
A-3 OEM-Reserved Checkpoint Ranges.............................................A-9
vii
Page 8

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Notes
viii
Page 9

Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
This user’s manual covers the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module. This
MicroBlade module is a compact self-contained server that connects into a pre-cabled
enclosure that provides power, cooling, management and networking functions. One
enclosure for the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module can hold twenty-eight blade
units. The only difference between the MBI-6418A-T5H and the MBI-6418A-T7H is the
processor. The MBI-6418A-T5H uses the Atom™ C2550 processor, while the
MBI-6418A-T7H uses the Atom C2750 processor instead.
In this manual, “blade system” refers to the entire system (including the enclosure and
blades units), “blade”, “MicroBlade” or “blade unit” refers to a single MicroBlade module
and “blade enclosure” is the chassis that the MicroBlades, power supplies and
MicroBlade modules are housed within.
Please refer to our web site for information on operating systems that have been
certified for use with the MicroBlade (http://www.supermicro.com/products/nfo/
microblade.cfm).
Note: For your system to work properly, please follow the links below to download all
necessary drivers/utilities and the user’s manual for your server.
• Supermicro product manuals: http://www.MicroBlade.com/support/manuals/
• Product drivers and utilities: ftp://ftp.supermicro.com
• Product safety information: http://super-dev/about/policies/safety_information.cfm
• If you have any questions, please contact our support team at:
support@supermicor.com
Note: A complete list of safety warnings is provided on the Supermicro web site at
http://www.supermicro.com/about/policies/safety_information.cfm.
1-1
Page 10
MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
1-2 Blade Module Features
Table 1-1 lists the main features of the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module. See
the proceeding section for components typically included in a blade system and other
optional components. Specific details for the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module
are found in Chapter 4: "MicroBlade module Features" on page 4-1.
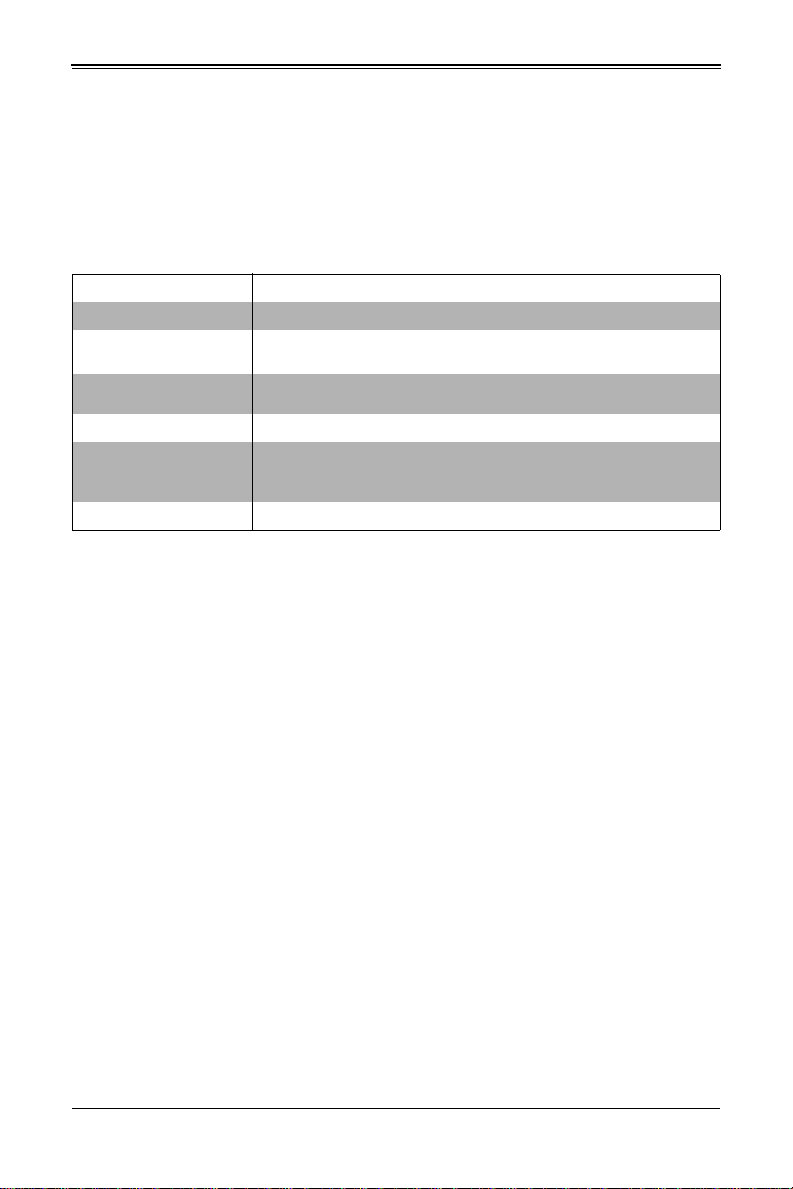
Table 1-1. MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module Specification Features
Serverboard B1SA4-2750F (proprietary form factor)
Enclosures MBE-628L-416/816
Chassis Specifications
Processors
BIOS 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI® BIOS
Memory Capacity
Hard Drive Bays Each node (4 total) supports one 2.5" SATA3
Processors
Each node of the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module supports a single BGA1283
Intel ATOM C2750/C2550 series processors in a BGA1283 socket embedded in the
motherboard.
Refer to the Supermicro web site for a complete listing of supported processors (http://
www.supermicro.com/products/microblade). Please note that you will need to check the
detailed specifications of a particular blade module for a list of the CPUs it supports.
Details on installation of the processor into the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module
are found in Chapter 3: " Setup and Installation" on page 3-1.
Chassis Dimensions (HxWxD): 1.2" x 4.94" x 23.2" (30.48-mm x
125.476-mm x 589.28-mm), Gross Weight: 7.5 lbs (3.4 kg)
One Intel ATOM C2750/C2550 per node (four nodes total) embedded in
BGA1283 sockets on the serverboard
Supports up to 32 GB of DDR3 1600/1333 MHz speed and 16GB, 8GB,
4GB, 2GB and 1GB size SODIMM memory in two (2) 204-pin DIMM
sockets
HDD/SSD disk drive
Memory
Each of the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module’s nodes has two (2) 204-pin
DIMM sockets that can support up to 32 GB of DDR3 1600/1333 MHz speed, 16GB,
8GB, 4GB, 2GB and 1GB size SODIMM memory. Memory is interleaved, which requires
both modules to be of the same size and speed.
Please refer to the Supermicro web site for a list of supported memory http://
www.supermicro.com/products/microblade The detailed specifications for a blade
module will contain a link to a list of recommended memory sizes and manufacturers.
Details on installation of memory modules into the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade
module are found in Chapter 3: " Setup and Installation" on page 3-1.
1-2
Page 11

Chapter 1: Introduction
Storage
Each node in the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module has one 2.5" SATA3 HDD/
SSD internally mounted and one SATA-DOM drive that it can also use for storage or for
installation of the node’s operating system. See Chapter 3: " Setup and Installation" on
page 3-1 for storage installation details.
RAID
The MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module has only one hard drive assigned per
node, so no RAID array is possible.
Density
A maximum of twenty-eight blade modules may be installed into a single blade
enclosure. Each blade enclosure is a 6U form factor, so a standard 42U rack may
accommodate up to seven enclosures with 196 blade modules, each with four nodes or
the equivalent of 784 1U servers. With the inclusion of up to fourteen CMM modules and
up to twenty-eight Gigabit Ethernet switches this would occupy up to 826U space in a
conventional 1U server configuration.
1-3
Page 12

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
1-3 Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email:
Web Site: www.supermicro.com
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
Email:
Asia-Pacific
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3992
Web Site: www.supermicro.com.tw
Technical Support:
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Tel: +886-(2)-8226-3990
marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
‘s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
3F, No. 150, Jian 1st Rd.
Zhonghe Dist., New Taipei City 23511
Taiwan (R.O.C)
1-4
Page 13

Chapter 2
Standardized Warning Statements
2-1 About Standardized Warning Statements
The following statements are industry standard warnings, provided to warn the user of
situations which have the potential for bodily injury. Should you have questions or
experience difficulty, cont act Supermicro's Technical Support department for assistance.
Only certified technicians should attempt to install or configure components.
Read this appendix in its entirety before installing or configuring components in the
Supermicro chassis
These warnings may also be found on our web site at http://
www.supermicro.com/about/policies/safety_information.cfm.
Warning Definition
Warning!
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause
bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing
accidents.
警告の定義
この警告サインは危険を意味します。
人身事故につながる可能性がありますので、いずれの機器でも動作させる前に、
電気回路に含まれる危険性に注意して、標準的な事故防止策に精通して下さい。
此警告符号代表危险。
您正处于可能受到严重伤害的工作环境中。在您使用设备开始工作之前,必须充分意识到
触电的危险,并熟练掌握防止事故发生的标准工作程序。请根据每项警告结尾的声明号码
找到此设备的安全性警告说明的翻译文本。
此警告符號代表危險。
您正處於可能身體可能會受損傷的工作環境中。在您使用任何設備之前,請注意觸電的危
險,並且要熟悉預防事故發生的標準工作程序。請依照每一注意事項後的號碼找到相關的
翻譯說明內容。
2-1
Page 14

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
. ﻲﻓ ﻚﻧا نأ ﻦﻜﻤﯾ ﺔﻟﺎﺣ ﻲﻓ ﺐﺒﺴﺘﺗ ﺔﺑﺎﺻا ﺔﯾﺪﺴﺟ ﺰﻣﺮﻟا اﺬھ ﻲﻨﻌﯾ ﺮﻄﺧ !ﺮﯾﺬﺤﺗ
نأ ﻞﺒﻗ يأ ﻰﻠﻋ ﻞﻤﻌﺗ تاﺪﻌﻣ،ﻛﻢﻠﻋ ﻰﻠﻋ ﻦ ﻦﻋ ﺔﻤﺟﺎﻨﻟا ﺮطﺎﺨﻤﻟﺎﺑ ﺮﺋاوﺪﻟا
ﺔﯿﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا
ﻛوﺔﯾارد ﻰﻠﻋ ﻦ رﺎﻤﻤﻟﺎﺑتﺎﺳ ﺔﯿﺋﺎﻗﻮﻟا ﻟ ﻊﻨﻤعﻮﻗو يأثداﻮﺣ
ﻢﻗر مﺪﺨﺘﺳا نﺎﯿﺒﻟا صﻮﺼﻨﻤﻟا ﺔﯾﺎﮭﻧ ﻲﻓ ﺮﯾﺬﺤﺗ ﻞﻛ رﻮﺜﻌﻠﻟ ﺎﮭﺘﻤﺟﺮﺗ
Warnung
WICHTIGE SICHERHEITSHINWEISE
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu
Verletzungen führen kann. Machen Sie sich vor der Arbeit mit Geräten mit den Gefahren
elektrischer Schaltungen und den üblichen Verfahren zur Vorbeugung vor Unfällen
vertraut. Suchen Sie mit der am Ende jeder Warnung angegebenen
Anweisungsnummer nach der jeweiligen Übersetzung in den übersetzten
Sicherheitshinweisen, die zusammen mit diesem Gerät ausgeliefert wurden.
BEWAHREN SIE DIESE HINWEISE GUT AUF.
INSTRUCCIONES IMPORTANTES DE SEGURIDAD
Este símbolo de aviso indica peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de
manipular cualquier equipo, considere los riesgos de la corriente eléctrica y
familiarícese con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. Al final de
cada advertencia encontrará el número que le ayudará a encontrar el texto traducido en
el apartado de traducciones que acompaña a este dispositivo.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES.
IMPORTANTES INFORMATIONS DE SÉCURITÉ
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation
pouvant entraîner des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un
équipement, soyez conscient des dangers liés aux circuits électriques et
familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées pour éviter les accidents.
Pour prendre connaissance des traductions des avertissements figurant dans les
consignes de sécurité traduites qui accompagnent cet appareil, référez-vous au numéro
de l'instruction situé à la fin de chaque avertissement.
CONSERVEZ CES INFORMATIONS.
안전을 위한 주의사항
경고 !
2-2
Page 15

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
אורקל שי רוקמל תכרעמה רוביח ינפל הנקתה תוארוה תאחתמ.
이 경고 기호는 위험이 있음을 알려 줍니다 . 작업자의 신체에 부상을 야기 할 수 있는
상태에 있게 됩니다 . 모든 장비에 대한 작업을 수행하기 전에 전기회로와 관련된 위험
요소들을 확인하시고 사전에 사고를 방지할 수 있도록 표준 작업절차를 준수해 주시기
바랍니다 .
해당 번역문을 찾기 위해 각 경고의 마지막 부분에 제공된 경고문 번호를 참조하십시오
BELANGRIJKE VEILIGHEIDSINSTRUCTIES
Dit waarschuwings symbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk
letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich
bewust te zijn van de bij een elektrische installatie betrokken risico's en dient u op de
hoogte te zijn van de standaard procedures om ongelukken te voorkomen. Gebruik de
nummers aan het eind van elke waarschuwing om deze te herleiden naar de
desbetreffende locatie.
BEWAAR DEZE INSTRUCTIES
Installation Instructions
Warning!
Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power
source.
設置手順書
システムを電源に接続する前に、設置手順書をお読み下さい。
警告
将此系统连接电源前 , 请先阅读安装说明。
警告
將系統與電源連接前,請先閱讀安裝說明。
Warnung
Vor dem Anschließen des Systems an die Stromquelle die Installationsanweisungen
lesen.
¡Advertencia!
Lea las instrucciones de instalación antes de conectar el sistema a la red de
alimentación.
Attention
Avant de brancher le système sur la source d'alimentation, consulter les directives
d'installation.
2-3
Page 16

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
ﻟا تادﺎﺷرإ ﺮﻗاﺐﯿﻛﺮﺘ ﻞﯿﺻﻮﺗ ﻞﺒﻗ ﻰﻟإ مﺎﻈﻨﻟا ﺔﻗﺎﻄﻠﻟ رﺪﺼﻣ
לע ךמתסמ הז רצומנגהה תעינמל םינבמב תנקתומה יכ אדוול שי .ילמשח רצק
רצקה ינפמ ןגמה רישכמה ילמשחהמ רתוי אל אוה-250 V, 20 A
시스템을 전원에 연결하기 전에 설치 안내를 읽어주십시오 .
Waarschuwing
Raadpleeg de installatie-instructies voordat u het systeem op de voedingsbron aansluit.
Circuit Breaker
Warning!
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent)
protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than: 250 V,
20 A.
サーキット・ブレーカー
この製品は、短絡(過電流)保護装置がある建物での設置を前提としています。
保護装置の定格が 250V、20A を超えないことを確認下さい。
警告
此产品的短路 ( 过载电流 ) 保护由建筑物的供电系统提供 , 确保短路保护设备的额定电流
不大于 250V,20A。
警告
此產品的短路 ( 過載電流 ) 保護由建築物的供電系統提供 , 確保短路保護設備的額定電
流不大於 250V,20A。
Warnung
Dieses Produkt ist darauf angewiesen, dass im Gebäude ein Kurzschluss- bzw.
Überstromschutz installiert ist. Stellen Sie sicher, dass der Nennwert der
Schutzvorrichtung nicht mehr als: 250 V, 20 A beträgt.
¡Advertencia!
Este equipo utiliza el sistema de protección contra cortocircuitos (o sobrecorrientes) del
edificio. Asegúrese de que el dispositivo de protección no sea superior a: 250 V, 20 A.
Attention
Pour ce qui est de la protection contre les courts-circuits (surtension), ce produit dépend
de l'installation électrique du local. Vérifiez que le courant nominal du dispositif de
protection n'est pas supérieur à :250 V, 20 A.
2-4
Page 17

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
ﺞﺘﻨﻤﻟا اﺬھ ﻰﻠﻋ ﺪﻤﺘﻌﯾ تاﺪﻌﻣ ﺔﯾﺎﻤﺤﻟا ةﺮﯿﺼﻘﻟاﺮﺋاوﺪﻟا ﻦﻣ ﺎﮭﺘﯿﺒﺜﺗ ﻢﺗ ﻲﺘﻟا ﻲﻓ
ﻰﻨﺒﻤﻟا
20A, 250V : ﻦﻣ ﺪﻛﺄﺗ نأ ﻢﯿﯿﻘﺗ زﺎﮭﺠﻟا ﻟاﻲﺋﺎﻗﻮ ﺲﯿﻟ ﻦﻣ ﺮﺜﻛأ
경고 !
이 제품은 전원의 단락 ( 과전류 ) 방지에 대해서 전적으로 건물의 관련 설비에 의존합니
다 . 보호장치의 정격이 반드시 250V( 볼트 ), 20A( 암페어 ) 를 초과하지 않도록 해야
합니다 .
Waarschuwing
Dit product is afhankelijk van de kortsluitbeveiliging (overspanning) van uw electrische
installatie. Controleer of het beveiligde aparaat niet groter gedimensioneerd is dan
220V, 20A.
Power Disconnection Warning
Warning!
The system must be disconnected from all sources of power and the power
cord removed from the power supply module(s) before accessing the chassis
interior to install or remove system components.
電源切断の警告
システムコンポーネントの取り付けまたは取り外しのために、シャーシー内部にアクセ
スするには、
システムの電源はすべてのソースから切断され、電源コードは電源モジュールから取り
外す必要があります。
警告
在你打开机箱并安装或移除内部器件前 , 必须将系统完全断电 , 并移除电源线。
警告
在您打開機殼安裝或移除內部元件前,必須將系統完全斷電,並移除電源線。
Warnung
Das System muss von allen Quellen der Energie und vom Netzanschlusskabel getrennt
sein, das von den Spg.Versorgungsteilmodulen entfernt wird, bevor es auf den
Chassisinnenraum zurückgreift, um Systemsbestandteile anzubringen oder zu
entfernen.
2-5
Page 18

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
יילמשח קותינ ינפמ הרהזא
!הרהזא
למשחה תורוקמ לכמ תכרעמה תא קתנל שי ריסהל שיו קפסהמ ילמשחה לבכ תא
נקתה ךרוצל זראמה לש ימינפה קלחל השיג ינפלת רסה ואת .םיביכר
ﻞﺼﻓ ﺐﺠﯾ مﺎﻈﻨﻟا ﻊﯿﻤﺟ ﻦﻣردﺎﺼﻣ ﺔﻗﺎﻄﻟا ﺔﻟازإو ءﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا ﻚﻠﺳ ﻦﻣ ةﺪﺣو داﺪﻣا
ﺔﻗﺎﻄﻟا ﻞﺒﻗ
ﻰﻟإ لﻮﺻﻮﻟا ﺔﯿﻠﺧاﺪﻟا ﻖطﺎﻨﻤﻟا ﻟﻞﻜﯿﮭﻠ ﺔﻟازإ وأ ﺖﯿﺒﺜﺘﻟ تﺎﻧﻮﻜﻣ زﺎﮭﺠﻟا
¡Advertencia!
El sistema debe ser disconnected de todas las fuentes de energía y del cable eléctrico
quitado de los módulos de fuente de alimentación antes de tener acceso el interior del
chasis para instalar o para quitar componentes de sistema.
Attention
Le système doit être débranché de toutes les sources de puissance ainsi que de son
cordon d'alimentation secteur avant d'accéder à l'intérieur du chassis pour installer ou
enlever des composants de systéme.
경고 !
시스템에 부품들을 장착하거나 제거하기 위해서는 섀시 내부에 접근하기 전에 반드시
전원 공급장치로부터 연결되어있는 모든 전원과 전기코드를 분리해주어야 합니다 .
Waarschuwing
Voordat u toegang neemt tot het binnenwerk van de behuizing voor het installeren of
verwijderen van systeem onderdelen, dient u alle spanningsbronnen en alle
stroomkabels aangesloten op de voeding(en) van de behuizing te verwijderen.
Equipment Installation
Warning!
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or
service this equipment.
機器の設置
トレーニングを受け認定された人だけがこの装置の設置、交換、またはサービスを許
可されています。
警告
只有经过培训且具有资格的人员才能进行此设备的安装、更换和维修。
警告
只有經過受訓且具資格人員才可安裝、更換與維修此設備。
2-6
Page 19

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
!הרהזא
שר דבלב ךמסומ תווצתא ףילחהל ,ןיקתהל יא .דויצה רובע תוריש תתל וא דויצה
ﻦﯿﺑرﺪﻤﻟاو و ﺐﯿﻛﺮﺘﻟلاﺪﺒﺘﺳا وأ ﺔﻣﺪﺧ زﺎﮭﺠﻟا اﺬھ ﺢﻤﺴﯾ نأ ﺐﺠﯾ ﻂﻘﻓ ﻦﯿﻠھﺆﻤﻟا ﻦﯿﻔظﻮﻤﻠﻟ
Warnung
Das Installieren, Ersetzen oder Bedienen dieser Ausrüstung sollte nur geschultem,
qualifiziertem Personal gestattet werden.
¡Advertencia!
Solamente el personal calificado debe instalar, reemplazar o utilizar este equipo.
Attention
Il est vivement recommandé de confier l'installation, le remplacement et la maintenance
de ces équipements à des personnels qualifiés et expérimentés.
경고 !
훈련을 받고 공인된 기술자만이 이 장비의 설치 , 교체 또는 서비스를 수행할 수 있습니
다.
Waarschuwing
Deze apparatuur mag alleen worden geïnstalleerd, vervangen of hersteld door
geschoold en gekwalificeerd personeel.
Restricted Area
Warning!
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted
access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and
key, or other means of security. (This warning does not apply to workstations).
アクセス制限区域
このユニットは、アクセス制限区域に設置されることを想定しています。
アクセス制限区域は、特別なツール、鍵と錠前、その他のセキュリティの手段を用い
てのみ出入りが可能です。
警告
此部件应安装在限制进出的场所,限制进出的场所指只能通过使用特殊工具、锁和钥匙或
其它安全手段进出的场所。
警告
此裝置僅限安裝於進出管制區域,進出管制區域係指僅能以特殊工具、鎖頭及鑰匙或其
他安全方式才能進入的區域。
2-7
Page 20

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
תתלבגומ השיג םע רוזא
!הרהזא
תרזעב תנתינ השיגה .השיג תלבגה םהב שיש םירוזאב הדיחיה תא ןיקתהל שי
.('דכו לוענמ ,חתפמ) דבלב החטבא ילכ
. ﺺﯿﺼﺨﺗ ةﺪﺣﻮﻟا هﺬھ ﻲﻓ ﺎﮭﺒﯿﻛﺮﺘﻟ ﻖطﺎﻨﻣ ةرﻮﻈﺤﻣ ﻢﺗ
ﺻﻮﻟا ﻦﻜﻤﯾﻰﻟإ لﻮ ﺔﻘﻄﻨﻣ ةرﻮﻈﺤﻣ ﻂﻘﻓ ماﺪﺨﺘﺳا لﻼﺧ ﻦﻣ ،ﺔﺻﺎﺧ ةادأ
وأ يأ ﻼﻟ ىﺮﺧأ ﺔﻠﯿﺳونﺎﻣﻷ حﺎﺘﻔﻣو ﻞﻔﻗ
Warnung
Diese Einheit ist zur Installation in Bereichen mit beschränktem Zutritt vorgesehen. Der
Zutritt zu derartigen Bereichen ist nur mit einem Spezialwerkzeug, Schloss und
Schlüssel oder einer sonstigen Sicherheitsvorkehrung möglich.
¡Advertencia!
Esta unidad ha sido diseñada para instalación en áreas de acceso restringido. Sólo
puede obtenerse acceso a una de estas áreas mediante la utilización de una
herramienta especial, cerradura con llave u otro medio de seguridad.
Attention
Cet appareil doit être installée dans des zones d'accès réservés. L'accès à une zone
d'accès réservé n'est possible qu'en utilisant un outil spécial, un mécanisme de
verrouillage et une clé, ou tout autre moyen de sécurité.
경고 !
이 장치는 접근이 제한된 구역에 설치하도록 되어있습니다 . 특수도구 , 잠금 장치 및 키
, 또는 기타 보안 수단을 통해서만 접근 제한 구역에 들어갈 수 있습니다 .
Waarschuwing
Dit apparaat is bedoeld voor installatie in gebieden met een beperkte toegang. Toegang
tot dergelijke gebieden kunnen alleen verkregen worden door gebruik te maken van
speciaal gereedschap, slot en sleutel of andere veiligheidsmaatregelen.
2-8
Page 21

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
!הרהזא
תנכס תמייקץוציפ .הניקת אל ךרדב הפלחוהו הדימב הללוסה לש ףילחהל שי
גוסב הללוסה תא מ םאותה תרבחלמומ ןרציתצ.
תוללוסה קוליס תושמושמה עצבל שי .ןרציה תוארוה יפל
ﺮﻄﺧ كﺎﻨھ ﻦﻣ لاﺪﺒﺘﺳا ﺔﻟﺎﺣ ﻲﻓ رﺎﺠﻔﻧا ﺔﯾرﺎﻄﺒﻟا ﺔﺤﯿﺤﺻ ﺮﯿﻏ ﺔﻘﯾﺮﻄﺑ ﻚﯿﻠﻌﻓ
ﺔﯾرﺎﻄﺒﻟا لاﺪﺒﺘﺳا
ﻂﻘﻓ عﻮﻨﻟا ﺲﻔﻨﺑ ﺎﮭﻟدﺎﻌﯾ ﺎﻣ وأ ﺎﻤﻛﺖﺻوأ ﺔﻌﻨﺼﻤﻟا ﺔﻛﺮﺸﻟا ﮫﺑ
تﺎﯾرﺎﻄﺒﻟا ﻦﻣ ﺺﻠﺨﺗ ﻟ ﺎﻘﻓو ﺔﻠﻤﻌﺘﺴﻤﻟاﺔﻌﻧﺎﺼﻟا ﺔﻛﺮﺸﻟا تﺎﻤﯿﻠﻌﺘ
Battery Handling
Warning!
There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace
the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
電池の取り扱い
電池交換が正しく行われなかった場合、破裂の危険性があります。交換する電池は
メーカーが推奨する型、または同等のものを使用下さい。使用済電池は製造元の指示
に従って処分して下さい。
警告
电池更换不当会有爆炸危险。请只使用同类电池或制造商推荐的功能相当的电池更换原有
电池。请按制造商的说明处理废旧电池。
警告
電池更換不當會有爆炸危險。請使用製造商建議之相同或功能相當的電池更換原有電
池。請按照製造商的說明指示處理廢棄舊電池。
Warnung
Bei Einsetzen einer falschen Batterie besteht Explosionsgefahr. Ersetzen Sie die
Batterie nur durch den gleichen oder vom Hersteller empfohlenen Batterietyp.
Entsorgen Sie die benutzten Batterien nach den Anweisungen des Herstellers.
Attention
Danger d'explosion si la pile n'est pas remplacée correctement. Ne la remplacer que par
une pile de type semblable ou équivalent, recommandée par le fabricant. Jeter les piles
usagées conformément aux instructions du fabricant.
¡Advertencia!
Existe peligro de explosión si la batería se reemplaza de manera incorrecta.
Reemplazar la batería exclusivamente con el mismo tipo o el equivalente recomendado
por el fabricante. Desechar las baterías gastadas según las instrucciones del fabricante.
경고 !
2-9
Page 22

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
דדחא קפסמ רתוי םייק םא
!הרהזא
.קפס לש דחא רוביחמ רתוי שי הדחיל תא ריסהל שי ןקורל תנמ לע םירוביחה לכ
חיה תאי.הד
배터리가 올바르게 교체되지 않으면 폭발의 위험이 있습니다 . 기존 배터리와 동일하거
나 제조사에서 권장하는 동등한 종류의 배터리로만 교체해야 합니다 . 제조사의 안내에
따라 사용된 배터리를 처리하여 주십시오 .
Waarschuwing
Er is ontploffingsgevaar indien de batterij verkeerd vervangen wordt. Vervang de batterij
slechts met hetzelfde of een equivalent type die door de fabrikant aanbevolen wordt.
Gebruikte batterijen dienen overeenkomstig fabrieksvoorschriften afgevoerd te worden.
Redundant Power Supplies
Warning!
This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections
must be removed to de-energize the unit.
冗長電源装置
このユニットは複数の電源装置が接続されている場合があります。
ユニットの電源を切るためには、すべての接続を取り外さなければなりません。
警告
此部件连接的电源可能不止一个,必须将所有电源断开才能停止给该部件供电。
警告
此裝置連接的電源可能不只一個,必須切斷所有電源才能停止對該裝置的供電。
Warnung
Dieses Gerät kann mehr als eine Stromzufuhr haben. Um sicherzustellen, dass der
Einheit kein trom zugeführt wird, müssen alle Verbindungen entfernt werden.
¡Advertencia!
Puede que esta unidad tenga más de una conexión para fuentes de alimentación. Para
cortar por completo el suministro de energía, deben desconectarse todas las
conexiones.
Attention
Cette unité peut avoir plus d'une connexion d'alimentation. Pour supprimer toute tension
et tout courant électrique de l'unité, toutes les connexions d'alimentation doivent être
débranchées.
2-10
Page 23

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
. ﺪﻗ اﺬﮭﻟ نﻮﻜﯾ ﻟازﺎﮭﺠ تﻻﺎﺼﺗا ةﺪﻋ تاﺪﺣﻮﺑ ﺔﻗﺎﻄﻟا داﺪﻣا
ﺔﻟازإ ﺐﺠﯾ تﻻﺎﺼﺗﻻا ﺔﻓﺎﻛ لﺰﻌﻟ ﻟاةﺪﺣﻮ ﻦﻋ ءﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا
יירוחאה לנפב חתמ
זא!הרה
ךלהמב רהזיהל שי .תכרעמה לועפת ןמזב ירוחאה לנפב חתמ תנכס תמייק
.הדובעה
경고 !
이 장치에는 한 개 이상의 전원 공급 단자가 연결되어 있을 수 있습니다 . 이 장치에 전
원을 차단하기 위해서는 모든 연결 단자를 제거해야만 합니다 .
Waarschuwing
Deze eenheid kan meer dan één stroomtoevoeraansluiting bevatten. Alle aansluitingen
dienen verwijderd te worden om het apparaat stroomloos te maken
Backplane Voltage
Warning!
Hazardous voltage or energy is present on the backplane when the system is
operating. Use caution when servicing.
バックプレーンの電圧
システムの稼働中は危険な電圧または電力が、バックプレーン上にかかっています。
修理する際には注意ください。
警告
当系统正在进行时,背板上有很危险的电压或能量,进行维修时务必小心。
警告
當系統正在進行時,背板上有危險的電壓或能量,進行維修時務必小心。
Warnung
Wenn das System in Betrieb ist, treten auf der Rückwandplatine gefährliche
Spannungen oder Energien auf. Vorsicht bei der Wartung.
¡Advertencia!
Cuando el sistema está en funcionamiento, el voltaje del plano trasero es peligroso.
Tenga cuidado cuando lo revise.
Attention
Lorsque le système est en fonctionnement, des tensions électriques circulent sur le fond
de panier. Prendre des précautions lors de la maintenance.
2-11
Page 24

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
كﺎﻨھ ﺮﻄﺧ ﻦﻣ ﻲﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا رﺎﯿﺘﻟا ﻰﻠﻋ ةدﻮﺟﻮﻤﻟا ﺔﻗﺎﻄﻟاوأ ﺔﺣﻮﻠﻟا
نﻮﻜﯾ ﺎﻣﺪﻨﻋمﺎﻈﻨﻟا ﻞﻤﻌﯾ ﺪﻨﻋ ارﺬﺣ ﻦﻛ ﺔﻣﺪﺧ زﺎﮭﺠﻟا اﺬھ
יצראה למשחה יקוח םואית
!הרהזא
תנקתה םייצראהו םיימוקמה למשחה יקוחל תמאות תויהל תבייח דויצה.
تاﺪﻌﻤﻟا ﺐﯿﻛﺮﺗ ﺔﯿﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا ﻠﻟ ﻞﺜﺘﻤﯾ نأ ﺐﺠﯾ ﻦﯿﻧاﻮﻘﺔﯿﻨطﻮﻟاو ﺔﯿﻠﺤﻤﻟا ﺔﻘﻠﻌﺘﻤﻟا
ءﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟﺎﺑ
경고 !
시스템이 동작 중일 때 후면판 (Backplane) 에는 위험한 전압이나 에너지가 발생 합니
다 . 서비스 작업 시 주의하십시오 .
Waarschuwing
Een gevaarlijke spanning of energie is aanwezig op de backplane wanneer het systeem
in gebruik is. Voorzichtigheid is geboden tijdens het onderhoud.
Comply with Local and National Electrical Codes
Warning!
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical
codes.
地方および国の電気規格に準拠
機器の取り付けはその地方および国の電気規格に準拠する必要があります。
警告
设备安装必须符合本地与本国电气法规。
警告
設備安裝必須符合本地與本國電氣法規。
Warnung
Die Installation der Geräte muss den Sicherheitsstandards entsprechen.
¡Advertencia!
La instalacion del equipo debe cumplir con las normas de electricidad locales y
nacionales.
Attention
L'équipement doit être installé conformément aux normes électriques nationales et
locales.
2-12
Page 25

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
ררצומה קוליס
!הרהזא
ו תויחנהל םאתהב תויהל בייח הז רצומ לש יפוס קוליס.הנידמה יקוח
ﻲﺋﺎﮭﻨﻟا ﺺﻠﺨﺘﻟا ﻦﻣ ﺞﺘﻨﻤﻟا اﺬھ ﮫﻌﻣ ﻞﻣﺎﻌﺘﻟا ﻲﻐﺒﻨﯾ ﻟ ﺎﻘﻓو ﻊﯿﻤﺠﺔﯿﻨطﻮﻟا ﺢﺋاﻮﻠﻟاو ﻦﯿﻧاﻮﻘﻟا ﺪﻨﻋ
경고 !
현 지역 및 국가의 전기 규정에 따라 장비를 설치해야 합니다 .
Waarschuwing
Bij installatie van de apparatuur moet worden voldaan aan de lokale en nationale
elektriciteitsvoorschriften.
Product Disposal
Warning!
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national
laws and regulations.
製品の廃棄
この製品を廃棄処分する場合、国の関係する全ての法律・条例に従い処理する必要が
あります。
警告
本产品的废弃处理应根据所有国家的法律和规章进行。
警告
本產品的廢棄處理應根據所有國家的法律和規章進行。
Warnung
Die Entsorgung dieses Produkts sollte gemäß allen Bestimmungen und Gesetzen des
Landes erfolgen.
¡Advertencia!
Al deshacerse por completo de este producto debe seguir todas las leyes y reglamentos
nacionales.
Attention
La mise au rebut ou le recyclage de ce produit sont généralement soumis à des lois et/
ou directives de respect de l'environnement. Renseignez-vous auprès de l'organisme
compétent.
2-13
Page 26

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
!הרהזא
יקלח תא םיריסמ רשאכ שי .םידבוע ןיידע םיררוואמהו ןכתי ,זראמהמ ררוואמה
קיחרהללררוואמה ךותב םיחתפהמ םינוש הדובע ילכו תועבצאה תא חוטב קחרמ
경고 !
이 제품은 해당 국가의 관련 법규 및 규정에 따라 폐기되어야 합니다 .
Waarschuwing
De uiteindelijke verwijdering van dit product dient te geschieden in overeenstemming
met alle nationale wetten en reglementen.
Hot Swap Fan Warning
Warning!
The fans might still be turning when you remove the fan assembly from the
chassis. Keep fingers, screwdrivers, and other objects away from the
openings in the fan assembly's housing.
ファン・ホットスワップの警告
シャーシから冷却ファン装置を取り外した際、ファンがまだ回転している可能性があ
ります。ファンの開口部に、指、ドライバー、およびその他のものを近づけないで下
さい。
警告
当您从机架移除风扇装置,风扇可能仍在转动。小心不要将手指、螺丝起子和其他物品太
靠近风扇
警告
當您從機架移除風扇裝置,風扇可能仍在轉動。小心不要將手指、螺絲起子和其他物品
太靠近風扇。
Warnung
Die Lüfter drehen sich u. U. noch, wenn die Lüfterbaugruppe aus dem Chassis
genommen wird. Halten Sie Finger, Schraubendreher und andere Gegenstände von
den Öffnungen des Lüftergehäuses entfernt.
¡Advertencia!
Los ventiladores podran dar vuelta cuando usted quite ell montaje del ventilador del
chasis. Mandtenga los dedos, los destornilladores y todos los objetos lejos de las
aberturas del ventilador
Attention
Il est possible que les ventilateurs soient toujours en rotation lorsque vous retirerez le
bloc ventilateur du châssis. Prenez garde à ce que doigts, tournevis et autres objets
soient éloignés du logement du bloc ventilateur.
2-14
Page 27

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
ﻦﻜﻤﻤﻟا ﻦﻣ حواﺮﻤﻟا نأ لاﺰﺗ ﻻ ﺔﻟازإ ﺪﻨﻋروﺪﺗ ﺔﻠﺘﻛ ﺔﺣوﺮﻤﻟا ﻞﻜﯿﮭﻟا ﻦﻣ ﺐﺠﯾ ءﺎﻘﺑإ
ﻊﺑﺎﺻﻷا وﻲﻏاﺮﺒﻟا تﺎﻜﻔﻣ
. ءﺎﯿﺷﻷا ﻦﻣ ﺎھﺮﯿﻏو اﺪﯿﻌﺑ ﻦﻋ تﺎﺤﺘﻔﻟا ﻲﻓ ﺔﻠﺘﻛ ﺔﺣوﺮﻤﻟا
경고 !
섀시로부터 팬 조립품을 제거할 때 팬은 여전히 회전하고 있을 수 있습니다 . 팬 조림품
외관의 열려있는 부분들로부터 손가락 및 스크류드라이버 , 다른 물체들이 가까이 하지
않도록 배치해 주십시오 .
Waarschuwing
Het is mogelijk dat de ventilator nog draait tijdens het verwijderen van het
ventilatorsamenstel uit het chassis. Houd uw vingers, schroevendraaiers en eventuele
andere voorwerpen uit de buurt van de openingen in de ventilatorbehuizing.
Power Cable and AC Adapter
Warning!
When installing the product, use the provided or designated connection
could cause a malfunction or a fire. Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law
prohibits the use of UL or CSA -certified cables (that have UL/CSA shown on the code)
for any other electrical devices than products designated by Supermicro only.
電源コードと AC アダプター
cables, power cables and AC adaptors. Using any other cables and adaptors
製品を設置する場合、提供または指定された接続ケーブル、電源コードと AC アダプ
ターを使用下さい。他のケーブルやアダプタを使用すると故障や火災の原因になるこ
とがあります。電気用品安全法は、UL または CSA 認定のケーブル (UL/CSE マークが
コードに表記 ) をSupermicro が指定する製品以外に使用することを禁止しています。
警告
安装此产品时,请使用本身提供的或指定的连接线,电源线和电源适配器.使用其它线材或
适配器可能会引起故障或火灾。除了 Supermicro 所指定的产品 , 电气用品和材料安全法
律规定禁止使用未经 UL 或 CSA 认证的线材。( 线材上会显示 UL/CSA 符号 )。
警告
安裝此產品時 , 請使用本身提供的或指定的連接線 , 電源線和電源適配器 . 使用其它線
材或適配器可能會引起故障或火災。除了 Supermicro 所指定的產品 , 電氣用品和材料安
全法律規定禁止使用未經 UL 或 CSA 認證的線材。( 線材上會顯示 UL/CSA 符號 )。
2-15
Page 28

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
אאתמו םיילמשחמ יAC
!הרהזא
םימאתמו םיקפס ,םילבכב שמתשהל שי ,רצומה תא םיניקתמ רשאכAC רשא
וא הלקתל םורגל לוכי רחא םאתמ וא לבכ לכב שומיש .ךכ םשל וקפוסו ודעונ
טב יקוחו למשח ירישכמב שומיש יקוח יפ לע .ילמשח רצק רוסיא םייק ,תוחי
ב םיכמסומה םילבכב שמתשהל-
UL ב וא- CSA לש דוק םהילע עיפומ ראשכ)
UL/CSA( רחא ילמשח רצומ לכ רובע.דבלב ורקימקרפוס ידי לע ןיוצ אלש
ﺐﯿﻛﺮﺗ ﺪﻨﻋ ماﺪﺨﺘﺳا ﺐﺠﯾ زﺎﮭﺠﻟا و،ﻞﯿﺻﻮﺘﻟا تﻼﺑﺎﻛ ﺔﯿﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا تﻼﺑﺎﻜﻟا
تﻻﻮﺤﻣو ددﺮﺘﻤﻟا رﺎﯿﺘﻟا
. نأ يأ ماﺪﺨﺘﺳا تﻼﺑﺎﻛ تﻻﻮﺤﻣو ىﺮﺧأ ﺐﺒﺴﺘﯾ ﻲﻓ ﻞﻄﻋ ثوﺪﺣ ﻖﯾﺮﺣ وأ . ﻲﺘﻟا
ﻚﻟ ﺎھﺮﯿﻓﻮﺗ ﻢﺗ ﺞﺘﻨﻤﻟا ﻊﻣ
UL وأ CSA ﺔﯿﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻜﻟا ةﺰﮭﺟﻷا داﻮﻣو نﻮﻧﺎﻗ ﺔﻣﻼﺴﻟا ماﺪﺨﺘﺳا ﺮﻈﺤﯾ تﻼﺑﺎﻜﻟا
ﻞﺒﻗ ﻦﻣ ةﺪﻤﺘﻌﻣ
Supermicro ةﺰﮭﺟأ ىﺮﺧأ ﺔﯿﺋﺎﺑﺮﮭﻛ ﺮﯿﻏ تﺎﺠﺘﻨﻤﻟا ﺔﻨﯿﻌﻤﻟا ﻞﺒﻗ ﻦﻣ يﻷ
(UL/CSA ﻞﻤﺤﺗ ﻲﺘﻟاﺔﻣﻼﻋ )
Warnung
Bei der Installation des Produkts, die zur Verfügung gestellten oder benannt
Anschlusskabel, Stromkabel und Netzteile. Verwendung anderer Kabel und Adapter
kann zu einer Fehlfunktion oder ein Brand entstehen. Elektrische Geräte und Material
Safety Law verbietet die Verwendung von UL-oder CSA-zertifizierte Kabel, UL oder
CSA auf der Code für alle anderen elektrischen Geräte als Produkte von Supermicro
nur bezeichnet gezeigt haben.
¡Advertencia!
Al instalar el producto, utilice los cables de conexión previstos o designados, los cables
y adaptadores de CA. La utilización de otros cables y adaptadores podría ocasionar un
mal funcionamiento o un incendio. Aparatos Eléctricos y la Ley de Seguridad del
Material prohíbe el uso de UL o CSA cables certificados que tienen UL o CSA se
muestra en el código de otros dispositivos eléctricos que los productos designados por
Supermicro solamente.
Attention
Lors de l'installation du produit, utilisez les bables de connection fournis ou désigné.
L'utilisation d'autres cables et adaptateurs peut provoquer un dysfonctionnement ou un
incendie. Appareils électroménagers et de loi sur la sécurité Matériel interdit l'utilisation
de UL ou CSA câbles certifiés qui ont UL ou CSA indiqué sur le code pour tous les
autres appareils électriques que les produits désignés par Supermicro seulement.
2-16
Page 29

Chapter 2: Standardized Warning Statements
경고 !
제품을 설치할 때에는 제공되거나 지정된 연결케이블과 전원케이블 , AC 어댑터를 사용
해야 합니다 . 그 밖의 다른 케이블들이나 어댑터들은 고장 또는 화재의 원인이 될 수 있
습니다 . 전기용품안전법 (Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law) 은 슈퍼마
이크로에서 지정한 제품들 외에는 그 밖의 다른 전기 장치들을 위한 UL 또는 CSA 에서
인증한 케이블 ( 전선 위에 UL/CSA 가 표시 ) 들의 사용을 금지합니다 .
Waarschuwing
Bij het installeren van het product, gebruik de meegeleverde of aangewezen kabels,
stroomkabels en adapters. Het gebruik van andere kabels en adapters kan leiden tot
een storing of een brand. Elektrisch apparaat en veiligheidsinformatiebladen wet
verbiedt het gebruik van UL of CSA gecertificeerde kabels die UL of CSA die op de code
voor andere elektrische apparaten dan de producten die door Supermicro alleen.
2-17
Page 30

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Notes
2-18
Page 31

Chapter 3
Setup and Installation
3-1 Overview
This chapter covers the setup and installation of the MicroBlade module and its
components.
3-2 Installing MicroBlade Modules
Up to twenty-eight MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module may be installed into a
single MBE-628L-416/816 MicroBlade module enclosure. MicroBlade modules with
Windows and Linux operating systems may be mixed together in the same blade
enclosure.
Powering Up a MicroBlade Module Unit
Each MicroBlade module unit may be powered on and off independently from the rest of
the MicroBlade modules installed in the same enclosure. A MicroBlade module unit may
be powered up in two ways:
• Press the power button on the MicroBlade module unit.
• Use IPMIView or the web-browser based management utility to apply power using
the CMM MicroBlade module.
Powering Down a MicroBlade Module Unit
A MicroBlade module unit may be powered down in either of the following ways:
• Press the power button on the MicroBlade module unit.
• Use IPMIView or the web-browser based management utility to power down (if you
have Operator or Admin privileges on the CMM).
• Use IPMItool when connected to the CMM to power down (if you have Operator or
Admin privileges on the CMM).
3-1
Page 32

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Removing a MicroBlade Module Unit from the Enclosure
Although the MicroBlade module system may continue to run, individual MicroBlade
modules should always be powered down before removing them from the enclosure.
Removing a MicroBlade Module Unit from the Enclosure
1. Power down the MicroBlade module unit (see "Powering Down a MicroBlade
Module Unit" above).
2. Squeeze both handles to depress the red sections then pull out both handles
completely and use them to pull the MicroBlade module unit from the enclosure.
Note: MicroBlade modules can be hot-plugged from the enclosure.
Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover
The MicroBlade module cover must be removed to access the serverboard when you
need to install or remove processors, memory units, the onboard battery and so on.
Removing/Replacing the Blade Cover
1. Remove the MicroBlade module unit from the enclosure (see "Removing a
MicroBlade Module Unit from the Enclosure" above).
2. Depress the two buttons on the cover while pushing the cover toward the rear of the
MicroBlade module unit. When it stops, lift the cover off the MicroBlade module unit.
Installing a Blade Unit into the Enclosure
Make sure the cover of the MicroBlade module unit has been replaced first before
installing a MicroBlade module unit in the enclosure.
Installing a MicroBlade Module Unit into the Enclosure
1. Slowly push the MicroBlade module unit into its bay with the handles fully pulled out
(see Figure 3-1).
2. When the MicroBlade module stops, push the handles back in to their locked
position, making sure the notches in both handles catch the lip of the enclosure.
Note: MicroBlade modules can be Hot-Plugged into the enclosure.
Caution: Use extreme caution when inserting a MicroBlade module into the
enclosure. If the MicroBlade module's power connector becomes damaged, it can damage
pins on other MicroBlade module bays that it is inserted into.
3-2
Page 33

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Lithium Battery
Battery Holder
Figure 3-1. Inserting a MicroBlade Module into the Enclosure
3-3 Onboard Battery Installation
A battery is included on the serverboard to supply certain volatile memory components
with power when power has been removed from the MicroBlade module. If this battery
dies, it must be replaced with an equivalent CR2032 Lithium 3V battery. Dispose of used
batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions. See Figure 3-2 for a diagram of
installing a new onboard battery.
Caution: There is a danger of explosion if the onboard battery is installed upside down,
which reverses its polarities.
Figure 3-2. Installing the Onboard Battery
3-3
Page 34

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
3-4 Memory Installation
The serverboard of each MicroBlade module unit must be populated with DIMMs (Dual
In-line Memory Modules) to provide system memory. The DIMMs should all be of the
same size and speed and from the same Super Micro authorized manufacturer
due to compatibility issues. See details below on supported memory and our web site
(www.superblade.com/products/microblade for recommended memory.
Populating Memory Slots
The mainboard of a MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module has two (2) memory slots
for each processor of a node, four nodes total for a total of 8 memory slots per
MicroBlade module. Both interleaved and non-interleaved memory are supported, so
you may populate any number of DIMM slots.
Each of the four nodes has its own memory bank. Populate Channel A first, the Channel
B. In this example, Channel A of Node 1 is designated as P1-DIMMA1 and Channel B is
P1-DIMMB1. Be sure to populate the sockets with SODIMM memory with the same
speed.
For an interleaved configuration, memory modules of the same size and speed
must be installed in pairs. You should not mix DIMMs of different sizes and
speeds.
Note: Check the Supermicro website for a list of memory modules that have been
validated with the B1SA4-2750F/B1SA4-2550F motherboard.
Note: Though multiple DIMM memory module types and speeds may be supported, you
need to use DIMM memory modules of the same speed and type.
Note: For an optimized memory bandwidth, it is recommended that you populate the
memory modules in a set of two (2) DIMMs for the CPU.
Memory Support
Each node on the B1SA4-2750F/B1SA4-2550F motherboard supports up to 32GB and
up to 1600MHz of ECC DDR3 SODIMM memory in two SODIMM slots (see Figure 3-3).
3-4
Page 35

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
1
P1-DIMMA1
P2-DIMMA1
P3-DIMMA1
P4-DIMMA1
P1-DIMMB1
P2-DIMMB1
P3-DIMMB1
P4-DIMMB1
Figure 3-3. SO DIMM Sideways View
Table 3-1. Memory Population Guidelines
P1/P2/P3/P4-DIMMA1 P1/P2/P3/P4-DIMMB1 Total System Memory
2GB 2GB
2GB 2GB 4GB
4GB 4GB
4GB 4GB 8GB
8GB 8GB
8GB 8GB 16GB
16GB 16GB
16GB 16GB 32GB
3-5
Page 36

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Align
Press down until
the module locks
into place.
Insert this end first
DIMM Installation
Caution: Exercise extreme care when installing or removing SODIMM modules to prevent
any possible damage.
Installing/Removing SODIMM Memory Modules
1. Power down the MicroBlade module (see "Powering Down a MicroBlade Module
Unit" on page 3-1).
2. Remove the MicroBlade module from the enclosure.
3. Position the SODIMM module's bottom key so it aligns with the receptive point on
the slot (Figure 3-4).
Figure 3-4. Aligning the SO DIMM
4. Insert the SODIMM module vertically at about a 45 degree angle (Figure 3-5).
Figure 3-5. Inserting the SO DIMM
5. Press down until the module locks into place. The side clips will automatically
secure the SODIMM module, locking it into place (Figure 3-6).
3-6
Page 37

Chapter 3: Setup and Installation
Locking Clip
Locking Clip
Figure 3-6. Securing the SO DIMM in Place
6. Power up the blade unit (see "Powering Up a MicroBlade Module Unit" on
page 3-1).
7. To Remove: Use your thumbs to gently push the side clips near both ends away
from the module. This should release it from the slot. Pull the SODIMM module
upwards.
3-5 Hard Disk Drive Installation
A single SATA3 HDD/SSD can be installed in the MicroBlade module for each node
(four nodes/drives total) and cannot be removed or replaced without powering down the
blade unit they reside in. A blade module needs a hard disk drive with an operating
system installed to operate.
3-6 Installing the Operating System
An operating system (OS) must be installed on each MicroBlade module. Blades with
Microsoft Windows OS and blades with Linux OS can both occupy and operate within
the same blade enclosure. Refer to the SuperMicro web site for a complete list of
supported operating systems.
There are several methods of installing an OS to the blade modules.
Installing with a SATA-DOM Module
The MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module contains a SATA-DOM socket for each
node on the serverboard. The operating system can be installed separately onto the
SATA-DOM module, which when plugged into the SATA-DOM socket of a node of the
MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module, can be used as the system’s operating
system just as if it was a hard disk drive of the system.
3-7
Page 38

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Installing via PXE Boot
PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) is used to boot a computer over a network. To
install the OS via PXE, the following conditions must be met:
1. The PXE B
2. A PXE server has been configured (this can be another blade in the system).
3. The PXE server must be connected over a network to the blade to be booted.
4. The blade has only non-partitioned/unformatted hard drives installed and no
bootable devices attached to it.
Once these conditions are met, make sure the PXE server is running. Then turn on the
blade on which you wish to boot and/or install the OS. The BIOS in the blade will look at
all bootable devices and finding none will connect to the PXE server to begin the boot/
install.
OOT option in BIOS must be enabled.
Installing via Virtual Media (Drive Redirection)
You can install the OS via Virtual Media through either the IPMIview (Java based client
utility), IPMItool or the Web-based Management Utility. With this method, the OS is
installed from an ISO image that resides on another system/blade.
3-8
Page 39

Chapter 4
MicroBlade module Features
Figure 4-1. MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H Blade Unit Front View
This chapter describes the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module unit. Installation
and maintenance should be performed by experienced technicians only.
See Figure 4-1 for a front view of the blade unit and Table 4-1 for its features.
Table 4-1. MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H Blade Unit Features
Feature Description
Processors
Memory
Storage
BIOS 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI® BIOS
Ports One SATA3 HDD/SSD and one SATA3 DOM port per node (four nodes)
Supports single Intel ATOM C2750/C2550 processors embedded in a
BGA1283 socket on the serverboard
Supports up to 32 GB of DDR3 1600/1333 MHz speed and 16GB, 8GB,
4GB, 2GB and 1GB size SODIMM memory in two (2) 204-pin SODIMM
sockets per node
Each node (4 total) supports one 2.5" SATA 3
SATA DOM
4-1
HDD/SSD disk drive and one
Page 40

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
1
2
3
4
5
4-1 Control Panel
Each MicroBlade module has a similar control panel (Figure 4-2) with power on/off
button, reset button and LEDs on the front left side of the module. The numbers
mentioned in Figure 4-2 are described in Table 4-2.
Figure 4-2. Blade Control Panel
Table 4-2. Blade Control Panel
Item Function State Description
1 Power Button N/A Turns MicroBlade module on and off
Green Indicates power status “On”
2 Power LED
KVM/UID LED
3
(Blue)
Network LED
(Green)
4
Network LED
(Orange)
System Fault
5
LED (Red)
Amber
Red Power Failure
Steady On Indicates that KVM has been initialized on this blade module
Flashing
Flashing Green
Flashing Orange
Steady On
Before the BMC is ready, the Amber LED will blink until the
last node out of the four is ready.
Serves as a UID indicator (the UID function is activated with
a management program)
Flashes on and off to indicate traffic (Tx and RX data) on the
LAN connection to this blade module.
Flashes on and off to indicate traffic over the InfiniBand
module (when present in the system)
This LED illuminates red when a fatal error occurs. This may
be the result of a memory error, a VGA error or any other
fatal error that prevents the operating system from booting
up.
4-2
Page 41

Chapter 4: MicroBlade module Features
Power Button
Each MicroBlade module has its own power button so that individual blade units within
the enclosure may be turned on or off independently of the others. Press the power
button (#1) to turn on the blade server. The power LED (#3) will turn green. To turn off,
press and hold the power button for >4 seconds and the power LED will turn orange.
LED Indicators
Blade module LEDs are described below in Table 4-3.
Table 4-3. Blade Module LED Indicators
LED State Description
Green Power On
Power LED
System Fault
LED (Red)
a. In the event of a power failure, the N+1 Redundant Power Supply (if included in your
system's configuration) automatically turns on and picks up the system load to provide
uninterrupted operation. The failed power supply should be replaced with a new one as
soon as possible.
Amber Standby
Red Power Failure
Steady On
This LED illuminates red when a fatal error occurs. This may be the
result of a memory error, a VGA error or any other f atal error that
prevents the operating system from booting up.
a
4-3
Page 42

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
4-2 Serverboard
The serverboard of the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module unit is a proprietary
design, which is based on the Intel Intel ATOM C2750/C2550 processor. See Figure 4-4
for a block diagram of this chipset, Figure 4-3 for a view of the B1SA4-2750F
serverboard and Figure 4-5 for an exploded view diagram of the MicroBlade module
unit.
4-4
Page 43

Chapter 4: MicroBlade module Features
3
3
3
3
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
4
4
5
6
Figure 4-3. B1SA4-2750F Serverboad
Table 4-4. B1SA4-2750F Mainboard Layout
Item Description
1
2 One SATA3 SATA-DOM connector for each node (4 total)
One Intel AT OM C2750 /C25 50 processor embe dded in a BGA12 83 socket fo r each node (4
total)
4-5
Page 44

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Avoton
CPU1
2 x SATA 3.0
6.0 Gbit/s
2 x SerDes Ethernet
1 Gbit/s
KVM
Connector
PCIE 2.0 x1
5.0 GT/s
USB 1.0 HID
12 Mbit/s
USB 2.0 Virtual Media
480 Mbit/s
LPC Interface
NCSI
ASPEED
ASP2400
RGMII
2 x USB 2.0
480 Mbit/s
RGB
REALTEK
RTL8211E-VB-CG
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
DDR3 (CHA)
1600/1333 MHz
DDR3 (CHB)
1600/1333 MHz
MDI
CPU1_BMC_LAN
Avoton
CPU2
2 x SATA 3.0
6.0 Gbit/s
2 x SerDes Ethernet
1 Gbit/s
KVM
Connector
PCIE 2.0 x1
5.0 GT/s
USB 1.0 HID
12 Mbit/s
USB 2.0 Virtual Media
480 Mbit/s
LPC Interface
NCSI
ASPEED
ASP2400
RGMII
2 x USB 2.0
480 Mbit/s
RGB
REALTEK
RTL8211E-VB-CG
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
DDR3 (CHA)
1600/1333 MHz
DDR3 (CHB)
1600/1333 MHz
MDI
CPU2_BMC_LAN
CPU1_SATA
CPU1_SerDes_LAN
REALTEK
RTL8367MB
MDI
MDI
RGMII
RGMII
CPU1_BMC_LAN
SerDes
CPU2_BMC_LAN
CPU3_BMC_LAN
CPU4_BMC_LAN
2 x SATA 3.0
2 x SATA 3.0
2 x SATA 3.0
2 x SATA 3.0
SerDes
CPU1_SATA
CPU2_SATA
CPU3_SATA
CPU4_SATA
2 x SerDes
Gold
Finger
2 x SerDes
2 x SerDes
2 x SerDes
CPU1_SerDes_LAN
CPU2_SerDes_LAN
CPU3_SerDes_LAN
CPU4_SerDes_LAN
Avoton
CPU3
2 x SATA 3.0
6.0 Gbit/s
2 x SerDes Ethernet
1 Gbit/s
KVM
Connector
PCIE 2.0 x1
5.0 GT/s
USB 1.0 HID
12 Mbit/s
USB 2.0 Virtual Media
480 Mbit/s
LPC Interface
NCSI
ASPEED
ASP2400
RGMII
2 x USB 2.0
480 Mbit/s
RGB
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
DDR3 (CHA)
1600/1333 MHz
DDR3 (CHB)
1600/1333 MHz
CPU3_SerDes_LAN
Avoton
CPU4
2 x SerDes Ethernet
1 Gbit/s
KVM
Connector
PCIE 2.0 x1
5.0 GT/s
USB 1.0 HID
12 Mbit/s
USB 2.0 Virtual Media
480 Mbit/s
LPC Interface
NCSI
ASPEED
ASP2400
2 x USB 2.0
480 Mbit/s
RGB
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
DDR3 (CHA)
1600/1333 MHz
DDR3 (CHB)
1600/1333 MHz
CPU4_SerDes_LAN
CPU3_SATA
PI2EQX6804
CPU3_BMC_LAN
CPU4_SATA
PI2EQX6804
2 x SATA 3.0
6.0 Gbit/s
CPU4_BMC_LAN
RGMII
Gold
Finger
BackPlane
nip 73x2nip 04x2
CPU2_SATA
CPU2_SerDes_LAN
T able 4-4. B1SA4-2750F Mainboard Layout (Continued)
Item Description
3 Two SODIMM slots for each node (8 total) for SODIMM memory modules
4 One 2.5" SATA3 HDD/SSD for each node (two not shown, 4 total)
5 Onboard Battery
6 CMOS Clear
Figure 4-4. Intel B1SA4-2750F Block Diagram
4-6
Jumpers
Any jumpers present on the mainboard are used by the manufacturer only; there are no
jumpers used to configure the operation of the mainboard.
CMOS Clear
JBT1 is used to clear CMOS and will also clear any passwords. JBT1 consists of two
contact pads located near the BIOS chip.
Page 45

Chapter 4: MicroBlade module Features
Clearing CMOS
1. First power down the blade and remove it from the enclosure.
2. Remove the blade cover to access the mainboard (see "Removing/Replacing the
Blade Cover" on page 3-2 for further details). Short the CMOS pads with a metal
object such as a small screwdriver.
3. Replace the cover, install the blade back into the enclosure and power it on.
4-7
Page 46

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
1
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
5
5
5
5
3
6
4-3 Blade Unit Components
Figure 4-5. Exploded View of a MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H Blade Module
T able 4-5. Main Components of a MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H Blade Module
Item Description
1 Blade Unit/Module
2 2.5" Hard Drives (4)
3 Front Top Cover
4 DIMM slots (8)
5 CPU/Heatsinks (4)
6 Hard Drive Backplane
Memory Support
The MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module supports up to 32 GB of DDR3 1600/
1333 MHz speed, 16GB, 8GB, 4GB, 2GB and 1GB size SODIMM memory in two (2)
204-pin SODIMM sockets. See Section 3-4: Memory Installation on page 3-4 for further
details on serverboard memory installation.
4-8
Page 47

Chapter 4: MicroBlade module Features
Hard Disk Drives
The MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module accommodates one 2.5" SATA3 HDD/
SSD drives. The drives cannot be removed or replaced without powering down the
blade unit they reside in. See Chapter 1 for information on RAID Setup.
WARNING: Enterprise level hard disk drives are recommended for use in Supermicro
chassis and servers. For information on recommended HDDs, visit the Supermicro Web site
at http://www.supermicro.com/products/nfo/storage.cfm
4-9
Page 48

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
4-10
Page 49

Chapter 5
BIOS
5-1 Introduction
This chapter describes the BIOS for the MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade module. This
MicroBlade module uses a 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI® BIOS™ that is stored
in a flash chip. This BIOS can be easily upgraded using a floppy disk-based program.
Note: Due to periodic changes to the BIOS, some settings may have been added or
deleted and might not yet be recorded in this manual. Please refer to the http://
www.supermicro.com/products/microblade/module/ web site for further details on BIOS
setup and the BIOS menus for your MicroBlade module.
System BIOS
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System. The 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI®
BIOS BIOS flash chip stores the system parameters, types of disk drives, video
displays, in the CMOS. The CMOS memory requires very little electrical power. When
the blade unit is turned off, a backup battery provides power to the BIOS flash chip,
enabling it to retain system parameters. Each time the blade is powered on it is
configured with the values stored in the BIOS ROM by the system BIOS, which gains
control at boot up.
How To Change the Configuration Data
The CMOS information that determines the system parameters may be changed by
entering the BIOS Setup utility. This Setup utility can be accessed by pressing the
<D
ELETE> key at the appropriate time during system boot. (See "Starting the Setup
Utility" below.)
Starting the Setup Utility
Normally, the only visible POST (Power-On Self-Test) routine is the memory test. As the
memory is being tested, press the <D
Setup utility. From the main menu, you can access the other setup screens, such as the
Security and Power menus.
Caution: To prevent possible boot failure, do not shut down or reset the system while
updating the BIOS.
ELETE> key to enter the main menu of the BIOS
5-1
Page 50

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
5-2 BIOS Updates
It may be necessary to update the BIOS used in the blade modules on occasion.
However, it is recommended that you not update BIOS if you are not experiencing
problems with a blade module.
Updated BIOS files are located on our web site (http://www.supermicro.com/products/
microblade). Please check the current BIOS revision and make sure it is newer than
your current BIOS before downloading.
There are several methods you may use to upgrade (flash) your BIOS. After
downloading the appropriate BIOS file (in a zip file format), follow one of the methods
described below to flash the new BIOS.
Flashing BIOS
Use the procedures below to “Flash” your BIOS with a new update using the USB ports
on the CMM module or by use of a Floppy Image file.
Flashing a BIOS using the USB Ports on the CMM:
1. Copy the contents of the zip file to a bootable USB pen drive.
2. Connect your bootable USB pen drive to one of the two USB slots on the CMM
(located on the back side of the enclosure).
3. Boot to the USB pen drive and go to the directory where you saved the contents of
the zip file.
4. Type flash filename.rom (replace filename.rom by the actual ROM file name).
Flashing a BIOS using a Floppy Image File
This method must be performed remotely.
1. Copy the image file from the zip file to your desktop.
2. Use the web browser or IPMIView to access your CMM remotely using its IP
Address.
3. Go to the V
4. BROWSE or OPEN to locate the *.img file on your desktop and select it.
5. Press the UPLOAD button and wait a few seconds for the image to upload to the
CMM.
6. Once the upload finishes, turn on the blade module and press <D
BIOS setup utility.
7. In the B
the boot priority list.
8. Exit while saving the changes. The blade module will boot to the virtual media
(floppy image) A:\>.
9. Type flash filename.rom.
IRTUAL MEDIA menu and select FLOPPY IMAGE UPLOAD.
EL> to enter the
OOT MENU, bring USB LS120: PEPPCMM VIRTUAL DISC 1 to the top of
5-2
Page 51

Chapter 5: BIOS
Note: Replace filename.rom by the actual ROM file name (such as B8DTE142.rom for
example) in the command.
5-3 Running Setup
Note: Default settings are in bold text unless otherwise noted.
The BIOS setup options described in this section are selected by choosing the
appropriate text from the M
section, although the screen display is often all you need to understand how to set the
options.
When you first power on the computer, the BIOS is immediately activated.
While the BIOS is in control, the Setup program can be activated in one of two ways:
1. By pressing <D
2. When the message Press the <Delete> key to enter Setup appears briefly at the
bottom of the screen during the POST, press the <D
S
ETUP menu:
AIN BIOS SETUP screen. All displayed text is described in this
ELETE> immediately after turning the system on, or
ELETE> key to activate the main
5-3
Page 52

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
5-4 Main BIOS Setup
Figure 5-1. BIOS Setup Screen
All Main Setup options are described in this section. Use the UP/DOWN arrow keys to
move among the different settings in each menu. Use the L
change the options for each setting. Press the <E
SC> key to exit the CMOS SETUP
EFT/RIGHT arrow keys to
menu. The next section describes in detail how to navigate through the menus. Items
that use sub-menus are indicated with the
<E
NTER> key to access the submenu.
icon. With the item highlighted, press the
Menu options found in the MAIN BIOS SETUP menu are described in Table 5-1.
Table 5-1. Main BIOS Setup Menu Options
Menu Option Description
System Date
System Time
BIOS Information
Using the arrow keys, highlight the month, day and year fields, and enter the
correct data for the system date. Press the <Enter> key to save the data.
T o set the syst em date an d time, key in the correct i nformat ion in the ap propriate
fields. Then press the <Enter> key to save the data.
BIOS static display information including the serverboardserverboard number,
SMC version, SMC Build Date and Total Memory is also shown on the screen.
5-4
Page 53

Chapter 5: BIOS
5-5 Advanced Setup
Choose Advanced from the BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys to
display the A
sub-menus that can be accessed by highlighting the item and pressing <E
Options for PIR settings are displayed by highlighting the setting option using the arrow
keys and pressing <E
Table 5-2 describes all sub-menus found in the ADVANCED SETUP menu.
Sub-menu Description
Boot Feature See Table 5-3 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
CPU Configuration See Table 5-4 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
Chipset
Configuration
SATA Configuration See Table 5-6 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
PCIe/PCI/PnP
Configuration
ACPI Settings See Table 5-8 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
Super IO
Configuration
Serial Port Console
Redirection
DVANCED SETUP menu. The items with a triangle beside them are
NTER>.
NTER>.
Table 5-2. Advanced Setup Menu Options
See Table 5-5 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 5-7 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 5-9 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
See Table 5-10 for a description of BIOS setup menu options in this sub-menu.
Table 5-3. Boot Feature Submenu
Menu Option Description
Use this feature to select the screen display between the POST messages and
Quiet Boot
CSM Support
AddOn ROM Display
Mode
Bootup NUM-Lock
Wait for ‘F1’ If Error
the OEM logo upon bootup. Select Disabled to display the POST messages.
Select Enabled to display the OEM logo instead of the normal PO ST messages.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This setting enables or disables CSM support. Options include Enabled or
Disabled.
Use this feature to set the display mode for the Option ROM. Select Keep
Current to display the current AddOn ROM setting. Select Force BIOS to use the
Option ROM display set by the system BIOS. The options are Force BIOS and
Keep Current.
Use this feature to set the Power-on state for the <Numlock> key. The options
are Off and On.
Use this feature to force the system to wait until the 'F1' key is pressed if an error
occurs. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
5-5
Page 54

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-3. Boot Feature Subme nu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Interrupt 19 is the software interrupt that handles the boot disk function. When
this item is set to Enabled, the ROM BIOS of the host adaptors will "capture"
Interrupt 19 Capture
Watch Dog Function
Power Button
Function
Restore on AC Power
Loss
WOL Support
Interrupt 19 at bootup and allow the drives that are att ached to these host
adaptors to function as bootable disks. If this item is set to Disabled, the ROM
BIOS of the host adaptors will not capture Interrupt 19, and the drives attached
to these adaptors will not function as bootable devices. The options are
Immediately and Postponed.
If enabled, the Watch Dog Timer will allow the system to reboot when it is
inactive for more than 5 minutes. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This feature controls how the system shuts down when the power button is
pressed. Select 4_Seconds_Override for the user to power off the system after
pressing and holding the power button for 4 seconds or longer. Select Instant Off
to instantly power off the system as soon as the user presses the power button.
The options are 4 Seconds Override and Instant Off.
Use this feature to set the power state after a power outage. Select Stay-Off for
the system power to remain off after a power loss. Select Power-On for the
system power to be turned on after a power loss. Select Last State to allow the
system to resume its last power state before a power loss. The options are
Power-On, Stay-Of f and Last State.
Select Enabled to enable WOL support which will allow the system to "wake-up"
when a device connected to a LAN port receives a signal. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Ta bl e 5-4. CPU Configuration Submenu
Menu Option Description
Processor
Information
Clock Spread
Spectrum
EIST (GV3)
P-state Coordination
TM1
Static processor information i s displayed at the top of the menu for P rocessor ID,
Processor Frequency , Micro code Revision, L1 Cache RAM, L2 Cach e RAM and
Processor Version.
If this feature is set to Enabled, the BIOS utility will monitor the level of
Electromagnetic Interference caused by the components and will attempt to
reduce the interference whenever needed. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
EIST (Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology) GV3 allows the system to
automatically adjust processor voltage and core frequency in an effort to reduce
power consumption and heat dissipation. Select Auto to enable 80 CPU stepping
support automatically and disabled other functions. The options are Disabled,
Enabled, and Auto.
Please refer to Intel’s web site for detailed information.
This feature selects the type of coordination for the P-State of the processor.
P-State is a processo r operational st ate that reduces the pro cessor's voltage and
frequency to enhance CPU energy efficiency. The options are Hardware,
Package, and Module.
This setting is only available when supported by the CPU. Select Enable to
activate TM1 support for system thermal monitoring. TM1 allows the CPU to
regulate its power consumption based upon the modulation of the CPU Internal
clock when the CPU temperature reaches a pre-defined overheating threshold.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
5-6
Page 55

Table 5-4. CPU Configuration Submenu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
TM2 Mode
CPU C State
Enhanced Halt State
(C1E)
ACPI C2
Monitor/Mwait
L1 Prefetcher
L2 Prefetcher
ACPI 3.0 T-States
Fast String
Machine Check
Max CPUID Value
Limit
Execute Disable Bit
VMX
BIST Selection
This setting is only available when supported by the CPU. Use this feature to
select the throttling mode for TM2. The options are LEM Throttling and Adaptive
Throttling.
C-States architecture, a processor power management platform developed by
Intel, can further reduce power consumption from the basic C1 (Halt S tate) state
that blocks clock cycles to the CPU. Select Enabled for CPU C-Sates support.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled to support Enhanced C1 Power State to boost system
performance. Please reboot the system for the new setting to take ef fect. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled for ACPI C2 support to determine how the processor will report
the CPU-C state to the operating system. The options are Disabled, C6 NS, and
C6 FS.
Select Enabled to implement the Mwait instruction along with the Monitor
instruction to allow the processor to specify the location for the BIOS to monitor
activities and to issue the instruction to put the operation on hold (Mwait).
If enabled, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of dat a and i nstructions
from the main memory to the L1 cache to improve CPU performance. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
If enabled, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of dat a and i nstructions
from the main memory to the L2 cache to improve CPU performance. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to support ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
3.0 T-States to determine how the processor will report to the operating system
during CPU-Throttling states. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled to enable Fast String support for REP MOVS/STOS, which will
carry out Repeat-String Operation instructions to move a string of commands to
another location (MOVS) or to add a string of commands to an existing
instruction code (STOS). The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to use Intel's machine check mechanism to detect and report
hardware (machine) errors. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Use this feature to set the maximum CPU ID value. Enable this feature to boot
the legacy operating systems that cannot support processors with extended
CPUID functions. The options are Enabled and Disabled (for the Windows OS.)
Set to Enabled to enable the Execute Disable Bit which will allow the processor
to designate areas in the system memory where an application code can
execute and where it cannot, thus preventing a worm or a virus from flooding
illegal codes to overwhelm the processor and damage the system during an
attack. The default is Enabled. (Refer to Intel and Microsoft Web Sites for more
information.)
Select Enabled to enable Intel Vanderpool Technology support which will allow
one platform to run multiple operating systems and applications in independent
partitions, creating multiple "virtual" systems in one physical computer. The
options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled to set a BIST (Built-In-Self-Test) point selection to enhance
system performance. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-7
Page 56

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-4. CPU Configuration Submenu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
MTRR Default As
Unccacheable
Extended APIC
AES-NI
PECI Enable
PECI Trusted
PECI SMBus Speed
Turbo
RAPL This is a static setting that is enabled in the system.
MSR 606
PKG_POWER_SKU_
UNIT
MSR 610
PKG_TURBO_PWR_
LIM
MSR 670
PKG_TURBO_CFG1
MSR 672
TURBO_WKLD_
CFG2
Active Processor
Cores
CPU Flex Ratio
Override
CPU Core Ratio This is a static setting that is set to 24 in the system.
If this feature is set to Enabled, the default setting will be set t o "Uncacheable" in
the Memory-Type-Range Table to protect the data stored in the MTRR table from
being cached. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to enable Extended APIC (Advanced Programmable Int errupt
Control) support to enhance power management. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
Select Enabled to use the Advanced Encryption Standard in the processor. The
options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled to enable PECI (Platform Environment Control Interface)
support, which will enhance CPU thermal management to achieve power
efficiency. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to support Trusted Platform Environment Control Interface to
improve CPU thermal management. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Use this feature to set the speed for the physical bus to operat e. The opt ions are
Standard (80 kHz), Standard (100 kHz), Fast Mode (400 kHz), and Fast Mode
Plus (1 MHz).
This feature allows processor cores to run faster than marked frequency in
specific conditions. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Use the keyboard to enter the number of the computer units that are
SKU-specific in terms of power, energy, and time are concerned.
Use this feature to specify the processor power consumption limits during short
and long duration.
This setting specifies various parameters used for Turbo, Min Energy (28:16),
SoC TDP Policy (11:9), ICCMax Control (4:3), Turbo Mode (2:0) and others.
This setting specifies ICCMax Throttle Ratio for C6 exits when
PKG_TURBO_CFG1 (4:3).
This setting selects the number of cores to enable in the SoC package. Options
include All, 4 and 2.
Select Enabled to support CPU Flex Ratio Programming. The options are
Disabled, and Enabled.
5-8
Page 57

Table 5-5. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
North Bridge
Configuration
Memory
Information
Pass Gate
Setup
Pass Gate
Feature
Enable
2x Refresh
Rate
Pass Gate
Test
Pass Gate
Refresh
Pass Gate
Test Direction
Pass Gate
Test Repetition
Pass Gate
Test Iterations
Pass Gate
Swizzle
Pass Gate
Pattern
Pass Gate
Target Pattern
Pass Gate
Speed
Channel 0/1
Rank 0~3
Pass Gate
MonteCarlo
This sub-menu configures North Bridge features and shows configuration
information.
Memory information for MRC Version, Total Memory and Memory Frequency is
static displayed at the top of the screen.
This sub-menu provides pass gate feature configuration settings.
Select Enabled to support Pass Gate features. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
Select Enabled to force the BIOS setup utility to use the x2 refresh rate in
Pass-Gate operation regardless the temperatures of the processor and the
motherboard. Refresh Rate is the total number of rows needed to refresh the
entire DRAM array. x2 Refresh Rate will take 2000 rows of memory to refresh the
entire DRAM array. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to use the Pass Gate test. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
This setting will enables a refresh period during the pass gate test, however the
test will become non-deterministic. Options include Disabled and Enabled.
This feature specifies how the BIOS setup utility should perform the Pass Gate
test (from the lowest memory to the highest or from the highest memory to the
lowest.) The options are Lowest to Highest and Highest to Lowest.
This sets the pass gate test repetition count range over the same r ow (1000x).
Pressing the “-” key on your keyboard decreases th e count while pressi ng the “+”
key increases. Default is “900”.
This sets the pass gate test iterations on the row (repeats the pass gat e test
repetion). Pressing the “-” key on your keyboard decreases the count while
pressing the “+” key increases. Default is “1”.
Select Enabled to use the Pass Gate Test Swizzle mode to support Samsung
products. Select Auto for the system to automatically switch to the Pass Gate
Test Swizzle mode when a Samsung device is detected. The options are Auto
and Enabled.
This setting selects between Pattern 1’s or 0’s agressor. Options include 0’s or
1’s.
This selects between Pattern 1’s or 0’s for the target pattern. Options include 0’s
or 1’s.
This setting, when selecting the Auto option, will select 4x speed available
according to the pass gate counter , otherwise it will run at 1x speed. Selecting
the 1x Only option will run it at 1x speed only.
These settings allow Channel 0 or 1 Rank 0~3 to each be tested. Options
include Enabled and Disabled.
This setting enables or disables the search algorithm in order to find the PG Max.
Options include Disabled and Enabled.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-9
Page 58

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-5. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Pass Gate
Information
Fast Boot
SMM Size (MB)
Force Memory
Map Ax
Memory
Frequency
Memory Channels
MRC Debug
Messages
DDR Voltage
Mmio High
CKE Power Down
ECC Support
Faulty Part
Tracking
On Correctable
Faulty Part
Patrol Scrub
Enable
Patrol Scrub
Period
Static displayed information for Pass Gate Max Failures, Pass Gate Max
Repetition and Pass Gate Min Repetition is displayed at the botto m of the
screen.
This setting enables or disables fast boot, which skips memory training and
attempts to boot using the last know good configuration. Options include
Enabled and Disabled.
This setting specifies the size of the SMM/TSEG region 1 MB aligned. Options
include 2, 4, 8 or 16.
Select Enabled to force the BIOS setup utility to specify the total number of Kb
(or an error) of memory errors detected by the BIOS upon OS initialization. The
options are Enabled and Auto.
This setting selects the DDR3 memory frequency. Options include Auto,
DDR3-1333 and DDR3-1600.
This setting enables the DDR3 memory channels. Options include Auto and
Single Channel.
This setting enables the system to display the volume of debug output into the
Maximal Ratio Combining (MRC). Options include Disabled, Minimum, Medium
and Maximum.
This setting selects the desired DDR voltage. Options include Auto, 1.25V,
1.35V and 1.50V.
This selects between -100 to 100 mV in steps of 5mV. Pressing the “-” key on
your keyboard decreases the count by 5 while pressing the “+” key increases it
by 5. Default is “100”.
Select Enabled to enable CKE Power Down support which controls the low
power mode for RAM in the active power standby mode. The options are
Enabled, and Disabled.
This selects whether to enable or disable ECC support. Options include Enabled
and Disabled.
This setting allows you to enable or disable faulty part tracking. Options include
Enabled and Disabled.
Unless the Faulty Part Tracking setting is enabled, this setting is static with the
Halt option selected. This sets whether upon detecting a correctable Faulty
DIMM issue (single bit) the system will Halt or Continue.
Patrol Scrubbing is a process that allows the CPU to correct corre ctable memory
errors detected on a memory module and send the correction to the requestor
(the original source). When this item is set to Enabled, North Bridge will read and
write back one cache line every 16K cycles, if there is no delay caused by
internal processing. By using this method, roughly 64 GB of memory behind
North Bridge will be scrubbed every day. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Use this item to specify how often Patrol Scrubbing should be performed. Select
24 hours to allow Patrol Scrubbing to be performed every 24 hours. The options
are 24 hours, 10 hours, 4 hours, and 1 hour.
5-10
Page 59

Table 5-5. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Demand Scrubbing is a process that allows the CPU to correct correctable
memory errors found on a memory module. When the CPU or I/O issues a
Demand Scrub
Enable
AB Segments in
DRAM
E Segment in
DRAM
F Segment in
DRAM
ZQ Calibration
Propagate Errors
to Cores
(BMCMODE)
CMD Rate
Out of Order
Memory
Processing
Out of Order
Aging Threshold
New Request
Bypass
Dynamic Self
Refresh
PMOP Value for
PCO
demand-read command, and the read data from memory turns out to be a
correctable error, the error will be corrected and sent to the requestor (the
original source). Memory will be updated at the same time. Select Enabled to
use Demand Scrubbing for ECC memory correction. The options are Enabled
and Disabled.
This setting allows you to configure AB segments in DRAM. When this bit is set it
reads and writes the targeting A or B segments that are routed to DRAM.
Options include Disabled and Enabled.
This setting allows you to configure the E segment in DRAM. When this bit is set
it reads and writes the targeting E segment that are routed to DRAM. Options
include Enabled and Disabled.
This setting allows you to configure the F segment in DRAM. When this bit is set
it reads and writes the targeting F segment that are routed to DRAM. Options
include Enabled and Disabled.
When this feature is set to Enabled, commands to calibrate DRAM output drivers
will be issued so that ZQ Calibration will be performed during a system boot or
system reset. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This setting allows you to configure the Bunit machine check mode to pro p agat e
errors to cores. Options include Disabled and Enabled.
Use this feature to set the CMD rate, wh ich is the number of clock cycles n eeded
for the memory to send data. The options are Auto, 1N, 2N and 3N.
Select Enabled to support Out-of-Order Memory Processing, which is a process
used by a computer to retrieve instructions from its memory to improve CPU
performance. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
In a multi-core architecture, the DRAM system in a computer processes multiple
threads or streams of requests from the In_Order (FIFO: First_In_First_Out)
queue and the Out_of_Order queue in the interleaved/interconnect mode. This
feature allows the user to specify the maximum number of requests to be
processed for the same order before the system moves on and process the next
thread of requests in the "Out_Of_Order" queue while in the "Out_of_Order"
cycle. Once the "Out_of_Order" cycle expires, the system will move to the
"In_Order" cycle and starts to process t he requests in the "In-Order" queue.
Pressing the “-” key on your keyboard decreases the count by 1 while pressing
the “+” key increases it by 1. Default is “31”, which is the maximum number for
this field.
This setting enables new memory requests to be processed immediately,
skipping the In-Progress queue if the queue is empty. Options include Enabled
and Disabled.
This setting enables or disables dynamic self refresh in the memory controller.
Options include Enabled and Disabled.
This sets the power mode Opcode for PCO. Pressing the “-” key on your
keyboard decreases the count by 1 while pressing the “+” key increases it by 1.
Default is “4”, which is the maximum number for this field.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-11
Page 60

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-5. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
PMOP Value for
PCX
Per-Bit Margins
Open Page Policy
Timer
Memory Thermal
Scrambler
Slow Power Down
Exit
VREF Override
Enable
Timing
Configuration
tCL Sets tCL to Auto, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or 13 DRAM clocks.
tRCD Sets tRCD to Auto, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or 13 DRAM clocks.
tRp Sets tRp to Auto, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or 13 DRAM clocks.
tRAS Sets tRAS to Auto, 14 ~ 34 DRAM clocks.
tRTP Sets tRTP to Auto, 4, 5, 6 or 7 DRAM clocks.
tRRD Sets tRRD to Auto, 4, 5, 6 or 7 DRAM clocks.
tFAW Sets tFAW to Auto, 16 ~ 36 DRAM clocks.
tCCD Sets tCCD to Auto, 4, 12 or 18 DRAM clocks.
tWTP Sets tWTP to Auto, 15 ~ 30 DRAM clocks.
tWCL Sets tWCL to Auto, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 DRAM clocks.
South Bridge
Configuration
USB
Configuration
USB
Configuration
Information
Legacy USB
Support
This sets power mode Opcode for PCX. Pressing the “-” key on your keyboard
decreases the count by 1 while pressing the “+” key increases it by 1. Default is
“7”, which is the maximum number for this field.
This setting enables the system to show per-bit margins in MRC training.
Options include Disabled and Enabled.
Use the feature to set the Page_Closure timer, which will specify how long a
DRAM memory page should remain open. The options are Disabled, Immediate,
30-60 ns, 60-120 ns, 120-240 ns, 240-480 ns, 480-960 ns, and 1-2 us.
This setting enables or disables memory thermal management mode in your
system. Options include Disabled and Enabled.
This setting enables or disables the scrambler. Options include Enabled and
Disabled.
This setting enables or disables slow power down exit form pre-charge. Options
include Enabled and Disabled.
This setting enables or disables VREF override enable. Options include
Disabled and Enabled.
This sub-menu is used for configuring timing for the memory.
This sub-menu static displays PCH Information (chipset Name, Stepping and
USB Devices), and allows you to configure other South Bridge features.
This sub-menu sets USB configuration parameters.
This static display shows information regarding the USB Version and the
system’s USB Devices.
This setting allows you to enable the use of Legacy USB devices. If t his option is
set to Auto, legacy USB support will be automatically disabled if no USB device
is connected. The Disable option will keep USB devices available only for EFI
applications. Options include Auto, Disabled and Enabled.
5-12
Page 61

Table 5-5. Chipset Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
USB3.0
Support
XHCI Hand-off
EHCI Hand-off
USB Mass
Storage Driver
Support
Port 60/64
Emulation
USB Transfer
Time-out
Device Reset
Time-out
Device
Power-up
Delay
Device
power-up
delay in
seconds
This setting enables or disables USB 3.0 (XHCI) controller support. Options
include Enabled or Disabled.
This item is a work-around solution for operating systems that do not support
XHCI (Extensible Host Controller Interface) hand-off. The XHCI ownership
change should be claimed by the XHCI driver. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
This item is for the Operating Systems that do not support Enhanced Host
Controller Interface (EHCI) hand-off. When this it em is enabled, EHCI ownershi p
change will be claimed by the EHCI driver. The settings are Enabled and
Disabled.
This setting enables or disables USB mass storage driver support. Options
include Enabled or Disabled.
This feature enables or disables I/O port 60h/64h emulation support. This feature
should be enabled for complete USB keyboard legacy support for operating
systems that cannot detect the presence of USB devices . Options include
Enabled or Disabled.
This sets the time-out value for Control, Bulk and Interrupt transfers. Pressing
the “-” key on your keyboard decreases the count by increments while pressing
the “+” key increases it. Default is “20”, which is the maximum number for this
field. Other available values you can increase or decrease to are 1, 5 and 10
only.
This sets the USB mass storage device start unit command time-out. Pressing
the “-” key on your keyboard decreases the count by increments while pressing
the “+” key increases it. Default is “20”, while other available values you can
increase or decrease to are 10, 30 and 40 only.
This is the maximum time the device will take before it properly reports itself to
the host controller. Auto use the default value (for Root port it is 100 ms and for
Hub port the delay is taken from the Hub descriptor). If yo u select Manual for this
setting, then the setting “Device power-up delay in seconds” appears for you to
configure.
This setting is only available if you select the Manual option from the Device
Power-up Delay setting above. Pressing the “-” key on your keyboard decreases
the count by increments while pressing the “+” key increases it. Default is “5”.
Chapter 5: BIOS
Table 5-6. SATA Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
SATA 3 Controller This feature allows the user to configure the settings of SATA 3.0 devices.
SATA 3 Controller
SATA Mode This item sets SATA device mode. The options are IDE and AHCI.
LPM (Link Power
Management)
Select Enabled to enable the onboard SATA 3.0 controller. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled to support Link Power Management to improve system power
management. The options are Disabled, and Enabled.
5-13
Page 62

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-6. SATA Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
ALPM
(Aggressive Link
Power
Management)
Overwrite SIR Values Select Enabled to overwrite SIR values. The options are Enabled, and Disabled.
SATA Port 0/SATA
Port 1
Spin Up
Hot Plug
External Device
Mechanical Switch
Select Enabled to support Aggressive Link Power Management to enhance
system power performance. The options are Disabled, and Enabled.
The submenu below allows the user to configure the following settings for SATA
Port 0 or SATA Port 1.
On an edge detect from 0 to 1, use this feature to set a COMRESET initialization
sequence for a device. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This feature designates this port for hot plugging. Set this item to Enabled for
hot-plugging support, which will allow the user to replace a SATA drive without
shutting down the system. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Enabled for external SATA device support. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
Select Enabled for mechanical switch support. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Table 5-7. PCIe/PCI/PnP Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Use this feature to set the latency Timer of each PCI device inst alled on a PCI
PCI Latency Timer
VGA Palette Snoop
PERR# Generation
SERR# Generation
System Error Logging
Maximum Payload
Maximum Read
Request
bus. Select 32 to set the PCI latency to 32 PCI clock cycles. The options are 32
PCI Bus Clocks, 64 PCI Bus Clocks, 96 PCI Bus Clocks, 128 PCI Bus Clocks,
160 PCI Bus Clocks, 192 PCI Bus Clocks, 224 PCI Bus Clocks and 248 PCI Bus
Clocks.
Select Enabled to support VGA palette regist er snooping which will all ow the PCI
cards that do not contain their own VGA color palettes to examine th e video
cards palette to mimic it for proper color display. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Select Enabled to allow a PCI device to generate a PERR number for a PCI Bus
Signal Error Event. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled to allow a PCI device to generate an SERR number for a PCI
Bus Signal Error Event. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
If this item is set to enabled, an error log will be created when a system error
occurs. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Select Auto to allow the system BIOS to automatically set the maximum payload
value for a PCI-E device to enhance system performance. The options are Auto,
128 Bytes, 256 Bytes, 512 Bytes, 1024 Bytes, 2048 Bytes, and 4096 Bytes.
Select Auto to allow the system BIOS to automatically set the maximum Read
Request size for a PCI-E device to enhance system performance. The optio ns
are Auto, 128 Bytes, 256 Bytes, 512 Bytes, 1024 Bytes, 2048 Bytes, and 4096
Bytes.
5-14
Page 63

Table 5-7. PCIe/PCI/PnP Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
This feature allows the user to set the Active State Power Management (ASPM)
level for a PCI-E device. Select Force L0 to force all PCI-E links to operat e at L0
ASPM Support
Above 4G Decoding
(Available if the
system supports
64-bit PCI decoding)
Launch Storage
OPROM Policy
PCIe Slot 1 OPROM
Launch Video
OPROM Policy
VGA Priority
Launch Network
OPROM Policy
Onboard LAN Option
ROM Select
Load Onboard LAN1
OPROM / Load
Onboard LAN2
OPROM
state. Select Auto to allow the system BIOS to automatically set the ASPM level
for the system. Select Disabled to disable ASPM support. The options are
Disabled, Force L0, and Auto.
Enabling ASPM support may cause some PCI-E devices to fail!
Select Enabled to decode a 64-bit PCI device in the space above 4G Address.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This feature controls how the system executes UEFI (Unified
Extensible Firmware Interface), and legacy storage OPROM. Select
Legacy Only to boot the system 4-20 B1SA4-2750F/B1SA4-2550F
Motherboard User’s Manual
using a legacy storage device. The options are Do Not Use, UEFI Only Legacy
Only, Legacy First, UEFI First.
Select Enabled to enable Option ROM support to boot the computer using a
network interface device install in the slot specified above. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
This feature controls how the system executes UEFI (Unified Extensible
Firmware Interface) and video device OPROM. Select Legacy Only to boot the
system using a legacy device installed in a video port. The options are Do Not
Use, UEFI Only Legacy Only, Legacy First, UEFI First.
This feature allows the user to select the graphics adapter to be used as the
primary boot device. The options are Onboard, and Offboard.
This feature controls how the system executes UEFI (Unified Extensible
Firmware Interface) and LAN device OPROM. Select Legacy Only to boot the
system using a legacy device installed in a LAN port. The options are Do Not
Use, UEFI Only Legacy Only, Legacy First, UEFI First.
Select iSCSI to use the iSCSI Option ROM to boot the co mputer using a network
device. Select PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) to use an PXE Option
ROM to boot the computer using a network device. The options are iSCSI and
PXE.
Select Enabled to enable the onboard LAN1 Option ROM~LAN4 Option ROM.
This is to boot the computer using a network device. The default setti ng for LAN1
Option ROM is Enabled, and the default settings for LAN2 Option ROM/LAN3
Option ROM/LAN4 Option ROM are Disabled.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-15
Page 64

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-8. ACPI Settings Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Select Enabled to activate the High Performance Event T imer (HPET) that
produces periodic interrupts at a much higher frequency than a Real-time Clock
High Precision Event
Timer
WHEA Support
(RTC) does in synchronizing multimedia streams, providing smooth playback
and reducing the dependency on other timestamp calculation devices, such as
an x86 RDTSC Instruction embedded in the CPU. The High Performance Event
Timer is used to replace the 8254 Programmable Inter val Timer. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
This feature Enables the Windows Hardware Error Architect ure (WHEA) sup port
for the Windows 2008 (or a later vision) operating system. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
Table 5-9. SuperIO Device Configuration Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
Super IO Chip
Serial Port 0/1
Configuration
Serial Port
Device Settings This item displays the status of a serial part specified by the user.
Change Settings
Device Mode
Serial Port 2
Attribute
(Available for
Serial Port 1 only)
Serial Port 2
Configuration
submenu
Serial Port This setting allows you to Enable or Disable the Serial Port.
Device Settings This static display shows device settings for serial port 2 configuration.
This static display shows the name of the Super IO chip installed for your
system.
This submenu allows the user the configure settings of Serial Port 1 or Serial
Port 2.
Select Enabled to enable the a selected onboard serial port. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
This feature specifies the base I/O port address and the Interrupt Request
address of a serial port specified by the user. Select Auto to allow the BIOS to
automatically assign the base I/O and IRQ address.
The options for Serial Port 1 are Auto, (IO=3F8h; IRQ=4), (IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11 , 12), (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12), (IO=3E8h;
IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12) and (IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12).
The options for Serial Port 2 are Auto, (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3), (IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11 , 12), (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12), (IO=3E8h;
IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12) and (IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12).
Use this feature to set the optimal setti ng for a super I/O device. The o pti ons ar e
24MHz/13 and 24MHz.
This feature specifies the attribute of Serial Port 1. The options are SOL and
COM.
This submenu allows you to configure Serial Port 2.
5-16
Page 65

Table 5-9. Su perIO Device Configuration Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Change Settings
Serial Port Mode
Use this setting to select an optimal setting for the Super IO device to use for the
Serial Port. Options include Auto, IO=3F8h/IRQ=4, IO=3F8h/IRQ=3~12,
IO=2F8h/IRQ=3~12, IO=3E8h/IRQ=3~12 and IO=2E8h/IRQ=3~12
This setting allows you to set the Serial Port Mode to either Normal or High
Speed.
Table 5-10. Serial Port Console Redirection Sub-menu
Menu Option Description
COM1 Console Redirection, COM2/SOL Console Redirection
Console Redirection
Console
Redirection Settings
Terminal Type
Bits Per second
Data Bits
Parity
Stop Bits
Flow Control
VT-UTF8 Combo
Key Support
Select Enabled to enable console redirection support for a serial port sp ecified
by the user. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This feature allows the user to specify how the host computer will exchange data
with the client computer, which is the remote computer used by the user.
This feature allows the user to select the target terminal emulation type for
Console Redirection. Select VT100 to use the ASCII Character set. Select
VT100+ to add color and function key support. Select ANSI to use the
Extended ASCII Character Set. Select VT-UTF8 to use UTF8 encoding to
map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The options are ANSI,
VT100, VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
Use this feature to set the transmission speed for a serial port used in
Console Redirection. Make sure that the same speed is used in the host
computer and the client computer. A lower transmission spee d may be
required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600
and 115200 (bits per second).
Use this feature to set the data transmission size for Console Redirection.
The options are 7 Bits and 8 Bits.
A parity bit can be sent along with regular data bits to detect data
transmission errors. Select Even if the parity bit is set to 0, and the numbe r of
1's in data bits is even. Select Odd if the p arity bi t is set to 0, a nd the nu mber
of 1's in data bits is odd. Select None if you do not want to send a parity bit
with your data bits in transmission. Select Mark to add a mark as a parity bit
to be sent along with the data bi ts. Sele ct S p ace to add a S pace a s a pa rity bit
to be sent with your data bits. The options are None, Even, Odd, Mark and
Space.
A stop bit indicates the end of a serial data packet. Select 1 Stop Bit for
standard serial data communication. Select 2 Stop Bits if slower devices are
used. The options are 1 and 2.
Use this feature to set the flow control for Console Redirection to prevent
data loss caused by buffer overflow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop sending
data when the receiving buffer is full. Send a "Start" signal to start sending
data when the receiving buffer is empty. The options are None and Har dware
RTS/CTS.
Select Enabled to enable VT-UTF8 Combination Key support for ANSI/
VT100 terminals. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-17
Page 66

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-10. Serial Port Console Redirection Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Recorder Mode
Resolution
100x31
Legacy OS
Redirection
Resolution
Putty KeyPad
Redirection After
BIOS Post
Serial Port for
Out-of-Band
Management/
Windows Emergency
Management
Services (EMS)
Console Redirection
(for EMS)
Console
Redirection Settings
(for EMS)
Out-of-Band
Management Port
Terminal Type
Bits Per Second
Select Enabled to capture the data displayed on a terminal and send it as text
messages to a remote server. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Select Enabled for extended-terminal resolution support. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Use this feature to select the number of rows and columns used in Console
Redirection for legacy OS support. The options are 80x24 and 80x25.
This feature selects the settings for Function Keys and KeyPad used for
Putty, which is a ter minal emulator designed for the Windows OS. The
options are VT100, LINUX, XTERMR6, SC0, ESCN, and VT400.
Use this feature to enable or disable legacy console redirection after BIOS
POST. When set to Bootloader , le gacy console re direct ion i s disa bled before
booting the OS. When set to Always Enable, legacy console redirection
remains enabled when booting the OS. The options are Always Enable and
Bootloader.
The submenu allows the user to configure Console Redirection settings to
support Out-of-Band Serial Port management.
Select Enabled to use a COM Port selected by the user for Console Redire ction .
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This feature allows the user to specify how the host computer will
exchange data with the client computer, which is the remote computer
used by the user.
The feature selects a serial port used by the Microsoft Windows Emergency
Management Services (EMS) to communicate with a remote server. The
options are COM1 Console Redirection and COM2/SOL Console
Redirection.
This feature allows the user to select the target terminal emulation type for
Console Redirection. Select VT100 to use the ASCII character set. Select
VT100+ to add color and function key support. Select ANSI to use the
extended ASCII character set. Select VT -UTF8 to use UTF8 encoding to map
Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The options are ANSI, VT100,
VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
This item sets the transmission speed for a serial port used in Console
Redirection. Make sure that the same speed is used in the host computer
and the client computer. A lower transmission speed may be required for long
and busy lines. The options are 9600, 19200, 57600, and 115200 (bits per
second).
5-18
Page 67

Chapter 5: BIOS
Table 5-10. Serial Port Console Redirection Sub-menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
This feature allows the user to set the flow control for Console Redirection to
Flow Control
Data Bits, Parity,
Stop Bits
prevent data loss caused by buffer overflow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop
sending data when the receiving buffer is full. Send a "Start" signal to start
sending data when the receiving buffer is empty. The options are None,
Hardware RTS/CTS, and Software Xon/Xoff.
The status of each item above is displayed.
5-19
Page 68

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
5-6 IPMI Setup
T a ble 5-11. IPMI Menu
Menu Option Description
IPMI Information This item indicates the IPMI firmware revision used in your system.
Status BMC
(Baseboard
Management Cont
BMC Network
Configuration
Update IPMI LAN
Configuration
Configuration
Address Source
Station IP Address
Subnet Mask
Station MAC Address
Router IP Address
Router MAC Address
This item indicates the status of the IPMI firmware installed in your system.
Use this submenu to configure BMC network parameters.
This setting updates the IPMI LAN Configuration. BIOS will be set to the other
settings specified and changed in this screen to the IPMI on the next boot.
Options include No or Yes.
This feature allows the user to select the source of the IP address for this
computer. If Static is selected, you will need to know the IP address of this
computer and enter it to the system manually in the field. If DHCP is selected,
the BIOS will search for a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server
in the network that is attached to and request the next available IP address for
this computer. Option s include Static or DHCP. The following items are assigned
IP addresses automatically if DHCP is selected.
This item displays the Station IP address for this computer. This should be in
decimal and in dotted quad form (i.e., 192.168.10.253).
This item displays the sub-network that this computer belongs to. The val ue of
each three-digit number separated by dots should not exceed 255.
This item displays the Station MAC addr ess for this computer. Mac addresses
are 6 two-digit hexadecimal numbers.
This item displays the Router IP address for this computer. This should be in
decimal and in dotted quad form (i.e., 192.168.10.253).
This item displays the Router MAC address for this computer. Mac addresses
are 6 two-digit hexadecimal numbers.
5-7 Event Logs Setup
Table 5-12. Event Logs Menu
Menu Option Description
Change SMBIOS
Event Log Settings
SMBIOS Event Log
Erase Event Log
This submenu allows you to change the SMBIOS Event Log configuration
settings.
Change this item to enable or disable all features of the SMBIOS
Event Logging during system boot. The options are Enabled and
Disabled.
If No is selected, data stored in the event log will not be erased. Select
Yes, Next Reset, data in the event log will be erased upon next system
reboot. Select Yes, Every Reset, data in the event log will be erased
upon every system reboot. The options are No, Yes, Next reset, and
Yes, Every reset.
5-20
Page 69

Table 5-12. Event Logs Menu (Continued)
Menu Option Description
When Log is Full
Log System Boot
Event
MECI
METW
Log OEM Codes
Convert OEM Codes
View SMBIOS
Event Log
Select Erase Immediately for all messages to be automatically erased from the
event log when the event log memory is full. The options are Do Nothing and
Erase Immediately.
This option toggles the System Boot Event logging to enabled or disabled. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
The Multiple Event Count Increment (MECI) counter counts the number of
occurences that a duplicate event must happen before the MECI counter is
incremented. This is a numeric value. The default value is 1.
The Multiple Event Time Window (METW) defines numbe r of minutes must p ass
between duplicate log events before MECI is incremented. This is in minutes,
from 0 to 99. The default value is 60.
Select Enabled to log the status of OEM EFI codes. The options are Enabled
and Disabled.
Select Enabled to convert the OEM Status codes to the standard SMBIOS
codes. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
This section displays the contents of the SMBIOS Event Log.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-21
Page 70

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
5-8 Boot
Choose Boot from the 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI® BIOS BIOS Setup Utility
main menu with the arrow keys to bring up the B
OOT SETUP menu. Security setting
options are displayed by highlighting the setting using the arrow keys and pressing
<E
NTER>. All Security BIOS settings are described in Table 5-13 below.
Table 5-13. Boot Setup Menu Options
Menu Option Description
This feature allows you to specify the sequence of priority for the boot device
(such as hard disk drives, USB devices, CD-ROM drives, Network drives and so
Boot Priority
Option 1/2/3
Hard Drive BBS
Priorities
Network Device
BBS Priorities
Delete Boot Option This submenu allows you to remove an EFI boot option form the boot order.
Delete Driver
Option
on). The menu options are for 1st Boot Device, 2nd Boot Device and 3rd Boot
device. Each numbered boot device can be set to a specific device installed in
your system or to Disabled.
NOTE: A device enclosed in parent hesis has been disabled in the corresponding
type menu.
This submenu allows you to set the order of the legacy devices in this group for
setting the boot order.
This submenu allows you to set the order of the legacy devices in this group for
setting the boot order.
This submenu allows you to remove an EFI driver option form the boot order.
5-9 Security
Choose Security from the BIOS Setup main menu with the arrow keys to bring up the
S
ECURITY SETUP menu. Security setting options are displayed by highlighting the setting
using the arrow keys and pressing <E
Table 5-14 below.
NTER>. All Security BIOS settings are described in
Table 5-14. Security Menu Options
Menu Option Description
Administrator
Password
User Password
Secure Boot Menu This section displays the contents of the following secure boot features:
Secure Boot
Mode
Secure Boot
Mode
Key
Management
This allows you to create an administrator password for the system.
Use this feature to set a User Password which is required to log into the system
and to enter the BIOS setup utility. The length of the password should be from 3
characters to 20 characters long.
Use this item to select the secure boot mode. The options are Standard and
Custom.
This is a Secure Boot Mode selector. Custom mode enables you to change the
image execution policy and manage secure boot keys.
This submenu allows the user to configure the following Key Management
settings.
5-22
Page 71

Table 5-14. Security Menu Options (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Default Key
Provision
Delete All
Secure Boot
Variables
Save All
Secure Boot
Variables
Platform Key
(PK)
Delete
PK
(Platform
Keys)
Set New
PK
Key Exchange
Key (KEK)
Delete
KEK
Set New
KEK
Append
KEK
Authorized
Signatures
Delete DBThis feature deletes the variable from NVRAM. Removing PK will reset the
Set New
DB
Append DBSelect Yes to add the KEK from the manufacturer's defaults list to the existing
Authorized
Timestamps
Delete
DBT
Set New
DBT
Select Enabled to install the default Secure-Boot keys set by the manufacturer.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Selecting this option forces the system to Setup mode and clear all secure boot
variables (PK, KEK, db, Dbx and dbt). This change takes effect after the reboot.
This feature allows you to decide if all secure boot variables should be saved.
This feature allows the user to configure the settings of the Platform Keys.
This feature allows you to delete the variable from NVRAM. Removing PK will
reset the system to Setup mode. Select Yes to delete. The options are Yes and
No.
Select Yes to load new platform keys or set them from the manufacturer's
defaults. Select No to load the platform keys from a f ile. The options are Yes and
No.
This feature allows the user to configure the settings of the Key Exchange Keys.
This feature deletes the variable from NVRAM. Removing PK will reset the
system to Setup Mode.Select Yes to delete. The options are Yes and No.
Select Yes to load new platform keys or set them from the manufacturer's
defaults. Select No to load the platform keys from a f ile. The options are Yes and
No.
Select Yes to add the KEK from the manufacturer's defaults list to the existing
KEK. Select No to load the KEK from a file. The options are Yes and No.
This feature allows the user to configure the Authorized Signatures settings.
system to Setup Mode.Select Yes to delete. The options are Yes and No.
Select Yes to load new platform keys or set them from the manufacturer's
defaults. Select No to load the platform keys from a f ile. The options are Yes and
No.
KEK. Select No to load the KEK from a file. The options are Yes and No.
This feature deletes the variable from NVRAM. Removing PK will reset the
system to Setup Mode.Select Yes to delete. The options are Yes and No.
Select Yes to load new platform keys or set them from the manufacturer's
defaults. Select No to load the platform keys from a f ile. The options are Yes and
No.
Chapter 5: BIOS
5-23
Page 72

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table 5-14. Security Menu Options (Continued)
Menu Option Description
Append
DBT
Forbidden
Signatures
Delete
DBX
Set New
DBX
Append
DBX
Select Yes to add the KEK from the manufacturer's defaults list to the existing
KEK. Select No to load the KEK from a file. The options are Yes and No.
This feature allows the user to configure the Forbidden Signatures settings.
This feature deletes the variable from NVRAM. Removing PK will reset the
system to Setup Mode.Select Yes to delete. The options are Yes and No.
Select Yes to load new platform keys or set them from the manufacturer's
defaults. Select No to load the platfor m keys from a f ile. The options are Yes and
No.
Select Yes to add the KEK from the manufacturer's defaults list to the existing
KEK. Select No to load the KEK from a file. The options are Yes and No.
5-24
Page 73

Chapter 5: BIOS
5-10 Save & Exit
Choose SAVE & EXIT from the 32 MB SPI Flash EEPROM with AMI® BIOS BIOS Setup
Utility main menu with the arrow keys to display the S
BIOS settings are described in Table 5-15 below.
Table 5-15. Exit Menu Options
Menu Option Description
Discard Changes and
Exit
Save Changes and
Reset
Save Changes
Discard Changes
Restore Defaults
Save as Users
Defaults
Restore User
Defaults
Boot Override
Highlight this item and hit <E
any changes you may have made. Any changes you have made to the BIOS
Setup will not take effect upon system bootup.
Highlight this item and hit <ENTER> to save any changes you made and to exit
the BIOS Setup utility. The system will reboot and implement the changes you
have made to the BIOS Setup.
Highlight this item and hit <E
setup options.
Highlight this item and hit <ENTER> to discard (cancel) any changes you made.
You will remain in the Setup utility.
Highlight this item and hit <E
BIOS Setup. These are the safest settings to use and are designe d for maximum
system performance, but may not work best for all computer applications.
Highlight this item and hit <ENTER> to save changes done so far as user
defaults.
Highlight this item and hit <E
options.
For each boot device you have the option of saving the configuration for it and
exiting.
NTER> to exit the BIOS Setup utility without saving
NTER> to save changes done so far to any of the
NTER> to load the default settings for all items in the
NTER> to restore the user defaults to all the setup
AVE & EXIT SETUP menu. All Exit
5-25
Page 74

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Notes
5-26
Page 75

Appendix A
AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes
A status code is a data value used to indicate progress during the boot phase. A subset
of these status codes, known commonly as checkpoints, indicate common phases of the
BIOS boot process.
Checkpoints are typically output to I/O port 80h, but Aptio 4.x core can be configured to
send status codes to a variety of sources. Aptio 4.x core outputs checkpoints throughout
the boot process to indicate the task the system is currently executing. Checkpoints are
very useful in aiding software developers or technicians in debugging problems that
occur during the pre-boot process.
A-1 Checkpoint Ranges
Table A-1. Checkpoint Ranges
Status Code Range Description
0x01 – 0x0B SEC execution
0x0C – 0x0F SEC errors
0x10 – 0x2F PEI execution up to and including memory detection
0x30 – 0x4F PEI execution after memory detection
0x50 – 0x5F PEI errors
0x60 – 0x8F DXE execution up to BDS
0x90 – 0xCF BDS execution
0xD0 – 0xDF DXE errors
0xE0 – 0xE8 S3 Resume (PEI)
0xE9 – 0xEF S3 Resume errors (PEI)
0xF0 – 0xF8 Recovery (PEI)
0xF9 – 0xFF Recovery errors (PEI)
A-1
Page 76

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
A-2 Standard Checkpoints
Table A-2. SEC Phase
Codes Description
Status Code
0x00 Not Used
Progress Codes
0x01 Power on. Reset type detection (soft/hard).
0x02 AP initialization before microcode loading
0x03 North Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x04 South Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x05 OEM initialization before microcode loading
0x06 Microcode loading
0x07 AP initialization after microcode loading
0x08 North Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0x09 South Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0x0A OEM initialization after microcode loading
0x0B Cache initialization
0x0C – 0x0D Reserved for future AMI SEC error codes
0x0E Microcode not found
0x0F Microcode not loaded
Table A-3. PEI Phase
Status Codes Description
Progress Codes
0x10 PEI Core is started
0x11 Pre-memory CPU initialization is started
0x12 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x13 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x14 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x15 Pre-memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x16 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x17 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x18 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
A-2
Page 77

Appendix A: AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes
Table A-3. PEI Phase
Status Codes Description
0x19 Pre-memory South Bridge initialization is started
0x1A Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1B Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1C Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initialization codes
0x2B Memory initialization. Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data reading
0x2C Memory initialization. Memory presence detection
0x2D Memory initialization. Programming memory timing information
0x2E Memory initialization. Configuring memory
0x2F Memory initialization (other).
0x30 Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0x31 Memory Installed
0x32 CPU post-memory initialization is started
0x33 CPU post-memory initialization. Cache initialization
0x34 CPU post-memory initialization. Application Processor (s) (AP) initia lization
0x35 CPU post-memory initialization. Boot Strap Processor (BSP) selection
0x36
0x37 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x38 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x39 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3A Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3B Post-Memory South Bridge initialization is started
0x3C Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3D Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3E Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3F-0x4E OEM post memory initialization codes
0x4F DXE IPL is started
PEI Error Codes
0x50
0x51 Memory initialization error. SPD reading has failed
0x52
CPU post-memory initialization. System Management Mode (SMM)
initialization
Memory initialization error. Invalid memory type or incompatible memory
speed
Memory initialization error. Invali d memory size or memory modules do no t
match.
A-3
Page 78

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table A-3. PEI Phase
Status Codes Description
0x53 Memory initialization error. No usable memory detected
0x54 Unspecified memory initialization error.
0x55 Memory not installed
0x56 Invalid CPU type or Speed
0x57 CPU mismatch
0x58 CPU self test failed or possible CPU cache error
0x59 CPU micro-code is not found or micro-code update is failed
0x5A Internal CPU error
0x5B reset PPI is not available
0x5C-0x5F Reserved for future AMI error codes
S3 Resume Progress Codes
0xE0 S3 Resume is stared (S3 Resume PPI is called by the DXE IPL)
0xE1 S3 Boot Script execution
0xE2 Video repost
0xE3 OS S3 wake vector call
0xE4-0xE7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
S3 Resume Error Codes
0xE8 S3 Resume Failed
0xE9 S3 Resume PPI not Found
0xEA S3 Resume Boot Script Error
0xEB S3 OS Wake Error
0xEC-0xEF Reserved for future AMI error codes
Recovery Progress Codes
0xF0 Recovery condition triggered by firmware (Auto recovery)
0xF1 Recovery condition triggered by user (Forced recovery)
0xF2 Recovery process started
0xF3 Recovery firmware image is found
0xF4 Recovery firmware image is loaded
0xF5-0xF7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
Recovery Error Codes
0xF8 Recovery PPI is not available
0xF9 Recovery capsule is not found
A-4
Page 79
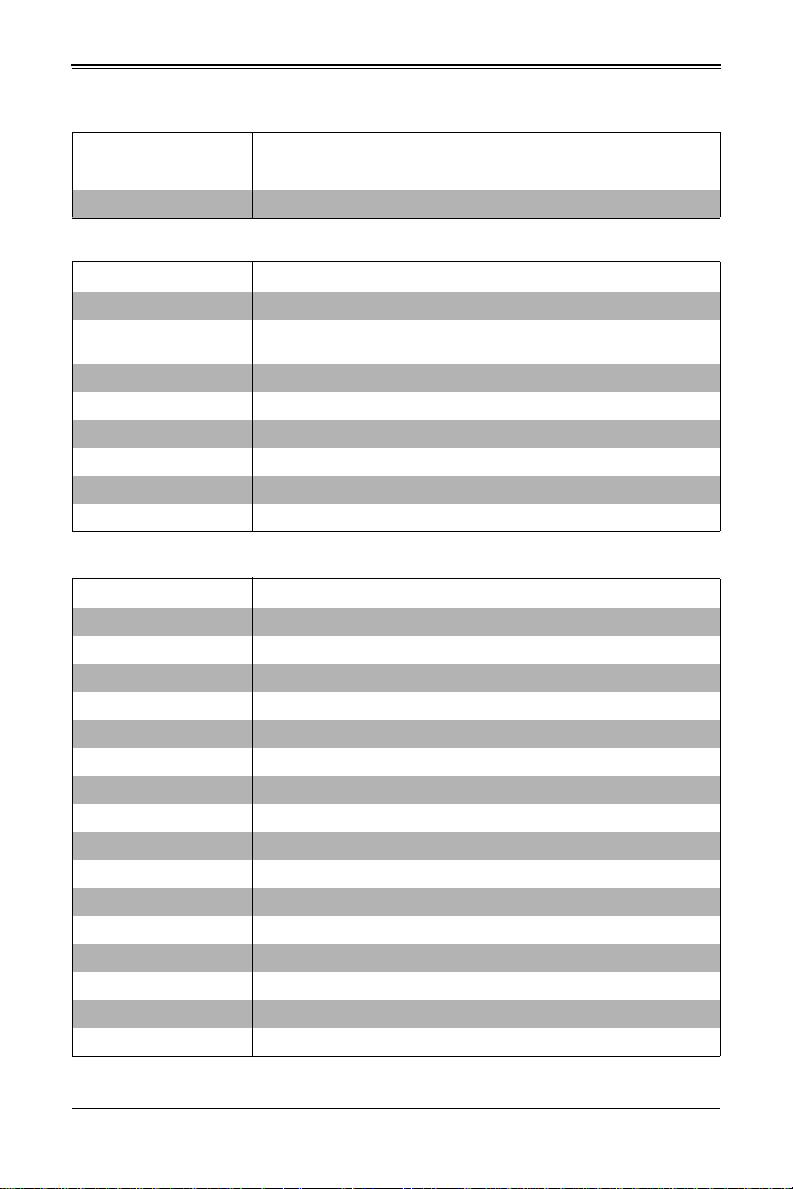
Appendix A: AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes
Table A-3. PEI Phase
Status Codes Description
0xFA Invalid recovery capsule
0xFB – 0xFF Reserved for future AMI error codes
Table A-4. PEI Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
1 Memory not Installed
1
2 Recovery started
3 DXEIPL was not found
3 DXE Core Firmware Volume was not found
4 Recovery failed
4 S3 Resume failed
7 Reset PPI is not available
Memory was installed twice (InstallPeiMemory routine in PEI Core called
twice)
Table A-5. DXE Phase
Status Codes Description
0x60 DXE Core is started
0x61 NVRAM initialization
0x62 Installation of the South Bridge Runtime Services
0x63 CPU DXE initialization is started
0x64 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x65 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x66 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x67 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x68 PCI host bridge initialization
0x69 North Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x6A North Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x6B North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6C North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6D North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6E North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6F North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
A-5
Page 80

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table A-5. DXE Phase
Status Codes Description
0x70 South Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x71 South Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x72 South Bridge devices initialization
0x73 South Bridge DXE Initialization ( South Bridge module specific)
0x74 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x75 South Bridge DXE Initialization ( South Bridge module specific)
0x76 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x77 South Bridge DXE Initialization ( South Bridge module specific)
0x78 ACPI module initialization
0x79 CSM initialization
0x7A – 0x7F Reserved for future AMI DXE codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0x90 Boot Device Selection (BDS) phase is started
0x91 Driver connecting is started
0x92 PCI Bus initialization is started
0x93 PCI Bus Hot Plug Controller Initialization
0x94 PCI Bus Enumeration
0x95 PCI Bus Request Resources
0x96 PCI Bus Assign Resources
0x97 Console Output devices connect
0x98 Console input devices connect
0x99 Super IO Initialization
0x9A USB initialization is started
0x9B USB Reset
0x9C USB Detect
0x9D USB Enable
0x9E – 0x9F Reserved for future AMI codes
0xA0 IDE initialization is started
0xA1 IDE Reset
0xA2 IDE Detect
0xA3 IDE Enable
0xA4 SCSI initialization is started
A-6
Page 81

Appendix A: AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes
Table A-5. DXE Phase
Status Codes Description
0xA5 SCSI Reset
0xA6 SCSI Detect
0xA7 SCSI Enable
0xA8 Setup Verifying Password
0xA9 Start of Setup
0xAA Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0xAB Setup Input Wait
0xAC Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0xAD Ready To Boot event
0xAE Legacy Boot event
0xAF Exit Boot Services event
0xB0 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP Begin
0xB1 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP End
0xB2 Legacy Option ROM Initialization
0xB3 System Reset
0xB4 USB hot plug
0xB5 PCI bus hot plug
0xB6 Clean-up of NVRAM
0xB7 Configuration Reset (reset of NVRAM settings)
0xB8 – 0xBF Reserved for future AMI codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
DXE Error Codes
0xD0 CPU initialization error
0xD1 North Bridge initialization error
0xD2 South Bridge initialization error
0xD3 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
0xD4 PCI resource allocation error. Out of Resources
0xD5 No Space for Legacy Option ROM
0xD6 No Console Output Devices are found
0xD7 No Console Input Devices are found
0xD8 Invalid password
0xD9 Error loading Boot Option (LoadImage returned error)
A-7
Page 82

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Table A-5. DXE Phase
Status Codes Description
0xDA Boot Option is failed (StartImage returned error)
0xDB Flash update is failed
0xDC Reset protocol is not available
Table A-6. DXE Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
1 Invalid password
4 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
5 No Console Output Devices are found
5 No Console Input Devices are found
6 Flash update is failed
7 Reset protocol is not available
8 Platform PCI resource requirements cannot be met
T able A-7. ACPI/ASL Checkpoints
Status Codes Description
0x01 System is entering S1 sleep state
0x02 System is entering S2 sleep state
0x03 System is entering S3 sleep state
0x04 System is entering S4 sleep state
0x05 System is entering S5 sleep state
0x10 System is waking up from the S1 sleep state
0x20 System is waking up from the S2 sleep state
0x30 System is waking up from the S3 sleep state
0x40 System is waking up from the S4 sleep state
0xAC
0xAA
System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in PIC
mode.
System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in APIC
mode.
A-8
Page 83

Appendix A: AMI UEFI BIOS POST Codes
A-3 OEM-Reserved Checkpoint Ranges
Table A-8. OEM-Reserved Checkpoint Range s
Status Codes Description
0x05 OEM SEC initialization before microcode loading
0x0A OEM SEC initialization after microcode loading
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initia lization codes
0x3F – 0x4E OEM PEI post memory initialization codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
A-9
Page 84

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
Notes
A-10
Page 85

Disclaimer
The products sold by Supermicro are not intended for and will not be used in life support
systems, medical equipment, nuclear facilities or systems, aircraft, aircraft devices,
aircraft/emergency communication devices or other critical systems whose failure to
perform be reasonably expected to result in significant injury or loss of life or
catastrophic property damage. Accordingly, Supermicro disclaims any and all liability,
and should buyer use or sell such products for use in such ultra-hazardous applications,
it does so entirely at its own risk. Furthermore, buyer agrees to fully indemnify, defend
and hold Supermicro harmless for and against any and all claims, demands, actions,
litigation, and proceedings of any kind arising out of or related to such ultra-hazardous
use or sale.
0-1
Page 86

MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H MicroBlade Module User’s Manual
MBI-6418A-T5H/T7H
0-2
 Loading...
Loading...