SUMMIT S24022PI-2.7, S24022PI-2.7T, S24022PI-A, S24022PI-AT, S24022PI-B Datasheet
...
SUMMIT MICROELECTRONICS, Inc. • 300 Orchard City Drive, Suite 131 • Campbell, CA 95008 • Telephone 408-378-6461 • Fax 408-378-6586 • www.summitmicro.com
1
© SUMMIT MICROELECTRONICS, Inc. 1998
2010 1.4 5/3/98
Characteristics subject to change without notice
SUMMIT
MICROELECTRONICS, Inc.
FEATURES
• Precision Supply Voltage Monitor
— Dual reset outputs for complex
microcontroller systems
— Integrated memory write lockout
• Guaranteed RESET (
RESETRESET
RESETRESET
RESET) assertion
to VCC=1V
• Power-Fail Accuracy Guaranteed
• No External Components
• 3 and 5 Volt system versions
• Low Power CMOS
— Active current less than 3mA
— Standby current less than 25µA
• Memory Internally Organized 256 X 8
— Two Wire Serial Interface (I2C™)
– Bidirectional data transfer protocol
– Standard 100KHz and Fast 400KHz
Precision RESET Controller and 2K I2C Memory
With Both RESET and
RESETRESET
RESETRESET
RESET Outputs
S24022/S24023
• High Reliability
— Endurance: 1,000,000 erase/write cycles
— Data retention: 100 years
• 8-Pin PDIP or SOIC Packages
OVERVIEW
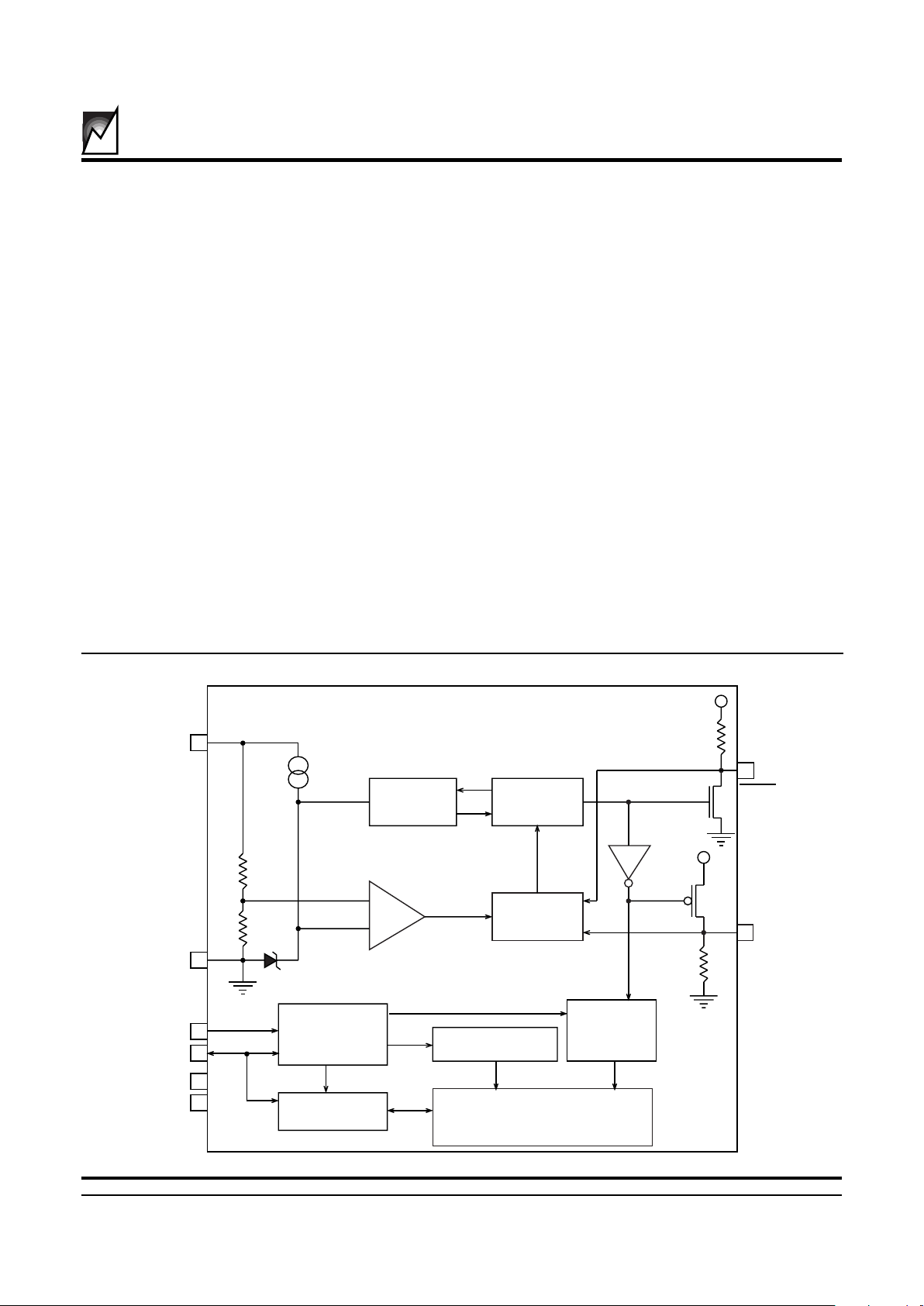
The S24022 and S24023 are power supervisory devices
with 2,048 bits of serial E2PROM. They are fabricated
using SUMMIT's advanced CMOS E2PROM technology
and are suitable for both 3 and 5 volt systems.
The memory is internally organized as 256 x 8. It features
the I2C serial interface and software protocol allowing
operation on a simple two-wire bus.
The S24022 provides a precision VCC sense circuit and
two open drain outputs: one (RESET) drives high and the
other (RESET) drives low whenever VCC falls below
V
TRIP
. The S24023 is identical to the S24022 with the
exception being RESET is not bonded out on pin 7.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
3 and 5 Volt Systems
+
-
1.26V
7
RESET
2
RESET
8
NC
SDA
NC
SCL16
3
4
5
GND
WRITE
CONTROL
MODE
DECODE
DATA I/O
ADDRESS
DECODER
E
2
PROM
MEMORY
ARRAY
5KHz
Oscillator
RESET
PULSE
GENERATOR
2010 ILL2 1.3
RESET
CONTROL
V
TRIP
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
2
S24022/S24023
2010 1.4 5/3/98
RESETRESET
RESETRESET
RESET -
RESETRESET
RESETRESET
RESET is an active low open drain output. It is
driven low whenever VCC is below V
TRIP
. RESET is also
an input and can be used to debounce a switch input or
perform signal conditioning. The RESET pin does have
an internal pull-up and should be left unconnected if the
signal is not used in the system. However, when the pin
is tied to a system RESET line an external pull-up resistor
should be employed.
RESET - RESET is an active high open drain output. It is
driven high whenever VCC is below V
TRIP
. RESET is also
an input and can be used to debounce a switch input or
perform signal conditioning. The RESET pin does have
an internal pull-down and should be left unconnected if
the signal is not used in the system. However, when the
pin is tied to a system reset line an external pull-down
resistor should be employed.
ENDURANCE AND DATA RETENTION
The S24022/23 is designed for applications requiring
1,000,000 erase/write cycles and unlimited read cycles.
It provides 100 years of secure data retention, with or
without power applied, after the execution of 1,000,000
erase/write cycles.
APPLICATIONS
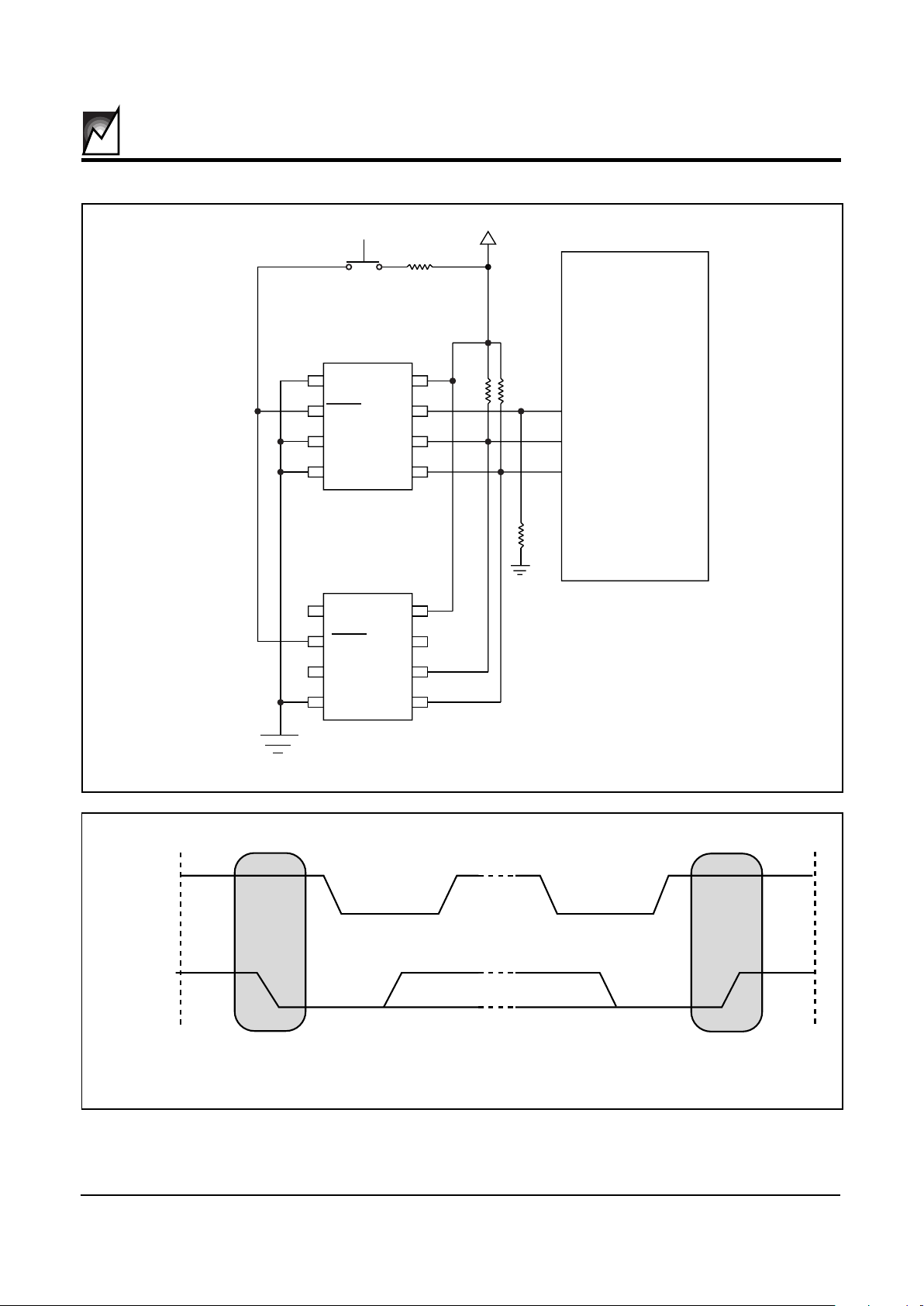
Reset Controller Description
The S24022/23 provides a precision RESET controller
that ensures correct system operation during brown-out
and power-up/-down conditions. It is configured with two
open drain RESET outputs; pin 7 is an active high output
and pin 2 is an active low output.
During power-up, the RESET outputs remain active until
VCC reaches the V
TRIP
threshold and will continue driving
the outputs for approximately 200ms after reaching
V
TRIP
. The RESET outputs will be valid so long as VCC is
> 1.0V. During power-down, the RESET outputs will
begin driving active when VCC falls below V
TRIP
.
The RESET pins are I/Os; therefore, the S24022/23 can
act as a signal conditioning circuit for an externally
applied reset. The inputs are edge triggered; that is, the
RESET input will initiate a reset timeout after detecting a
low to high transition and the RESET input will initiate a
reset timeout after detecting a high to low transition. Refer
to the applications Information section for more details on
device operation as a reset conditioning circuit.
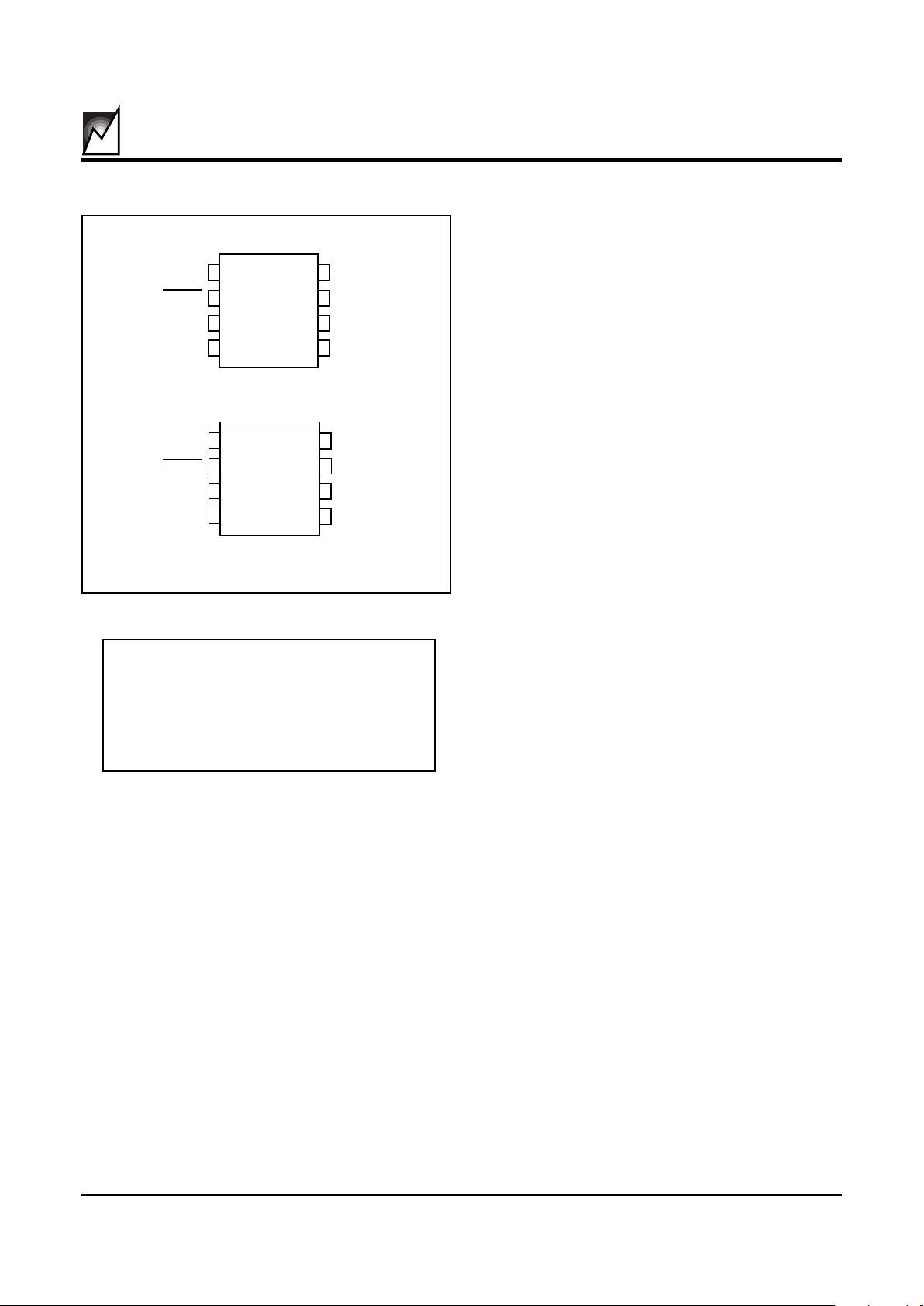
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Serial Clock (SCL) - The SCL input is used to clock data
into and out of the device. In the WRITE mode, data must
remain stable while SCL is HIGH. In the READ mode, data
is clocked out on the falling edge of SCL.
Serial Data (SDA) - The SDA pin is a bidirectional pin
used to transfer data into and out of the device. Data may
change only when SCL is LOW, except START and STOP
conditions. It is an open-drain output and may be wireORed with any number of open-drain or open-collector
outputs.
No Connects (NC) the no connect pins may be left
floating or tied to ground. They cannot be tied high.
PIN NAMES
SDA Serial Data I/O
SCL Serial Clock Input
RESET & RESET Reset Output
V
SS
Ground
V
CC
Supply Voltage
NC No Connect
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
NC
RESET
NC
V
SS
V
CC
NC
SCL
SDA
NC
RESET
NC
V
SS
V
CC
RESET
SCL
SDA
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
S24023
S24022
2010 ILL1 1.1
S24022/S24023
3
2010 1.4 5/3/98
FIGURE 1. TYPICAL SYSTEM CONFIGURATION FOR DUAL RESET
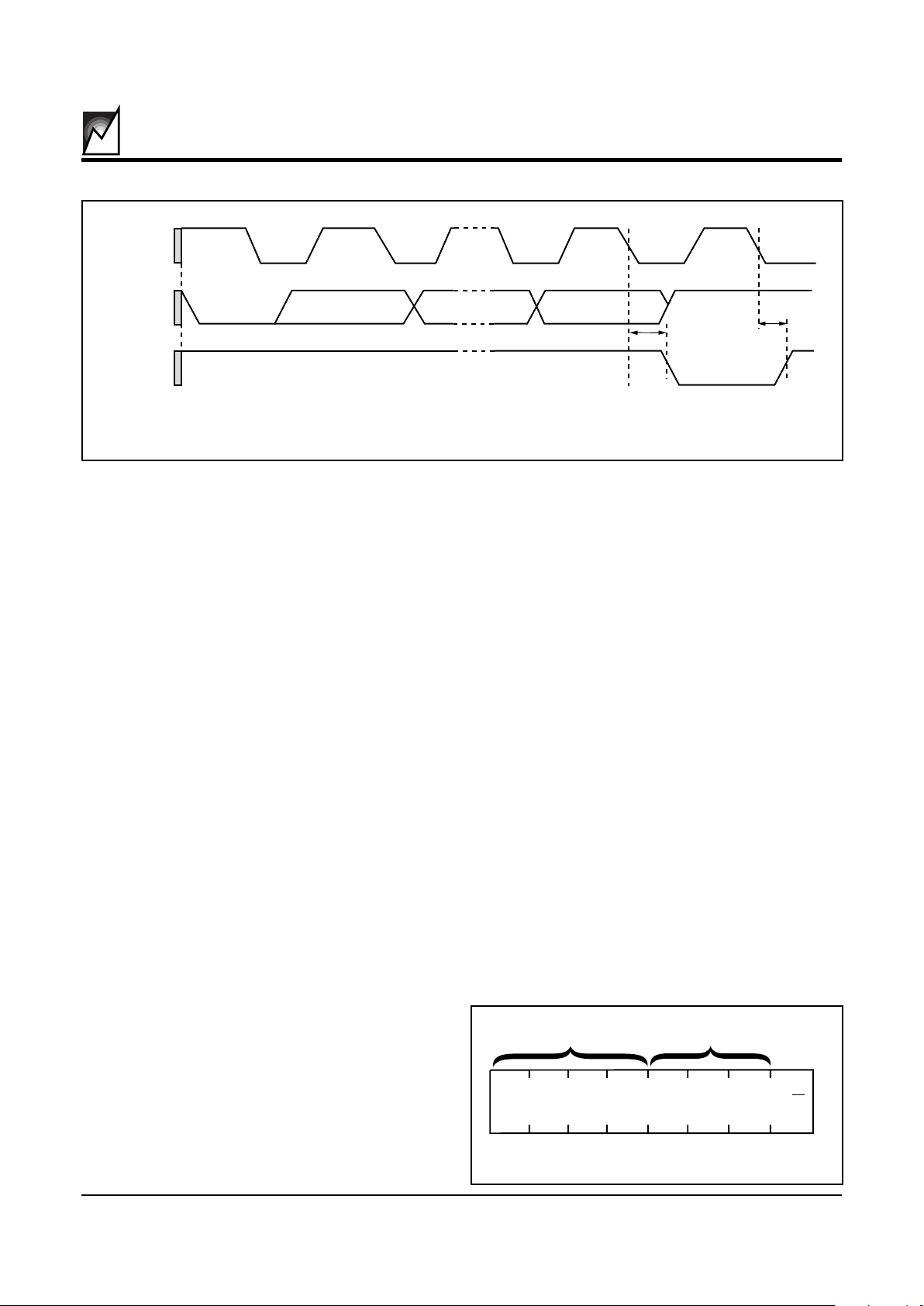
FIGURE 2. START AND STOP CONDITIONS
SCL
SDA In
START
Condition
STOP
Condition
2010 ILL5 1.0
RESET
SCL
SDA
Vcc
RESET
SCL
SDA
RESET
Vss
SCL
SDA
RESET
VCC = 3.0 0r 5.0
8051 Type MCU
S24022
I C
Peripheral
2
2
1
3
4
7
8
6
5
2010 ILL3 1.2
4
S24022/S24023
2010 1.4 5/3/98
FIGURE 3. ACKNOWLEDGE RESPONSE FROM RECEIVER
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C BUS
General Description
The I2C bus was designed for two-way, two-line serial
communication between different integrated circuits. The
two lines are: a serial data line (SDA), and a serial clock
line (SCL). The SDA line must be connected to a positive
supply by a pull-up resistor, located somewhere on the
bus (See Figure 1). Data transfer between devices may
be initiated with a START condition only when SCL and
SDA are HIGH (bus is not busy).
Input Data Protocol
One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The
data on the SDA line must remain stable during clock
HIGH time, because changes on the data line while SCL
is HIGH will be interpreted as start or stop condition, refer
to Figure 10.
START and STOP Conditions
When both the data and clock lines are HIGH, the bus is
said to be not busy. A HIGH-to-LOW transition on the data
line, while the clock is HIGH, is defined as the “START”
condition. A LOW-to-HIGH transition on the data line,
while the clock is HIGH, is defined as the “STOP” condition (See Figure 2).
DEVICE OPERATION
The S24022/23 is a 2,048-bit serial E2PROM. The device
supports the I2C bidirectional data transmission protocol.
The protocol defines any device that sends data onto the
bus as a “transmitter” and any device which receives data
as a “receiver.” The device controlling data transmission
is called the “master” and the controlled device is called
the “slave.” In all cases, the S24022/23 will be a “slave”
device, since it never initiates any data transfers.
FIGURE 4. SLAVE ADDRESS BYTE
Acknowledge (ACK)
Acknowledge is a software convention used to indicate
successful data transfers. The transmitting device, either
the master or the slave, will release the bus after transmitting eight bits. During the ninth clock cycle, the receiver
will pull the SDA line LOW to ACKnowledge that it received the eight bits of data (See Figure 3).
The S24022/23 will respond with an ACKnowledge after
recognition of a START condition and its slave address
byte. If both the device and a write operation are selected,
the S24022/23 will respond with an ACKnowledge after
the receipt of each subsequent 8-bit word.
In the READ mode, the S24022/23 transmits eight bits of
data, then releases the SDA line, and monitors the line for
an ACKnowledge signal. If an ACKnowledge is detected,
and no STOP condition is generated by the master, the
S24022/23 will continue to transmit data. If an
ACKnowledge is not detected, the S24022/23 will terminate further data transmissions and awaits a STOP condition before returning to the standby power mode.
Device Addressing
Following a start condition the master must output the
address of the slave it is accessing. The most significant
four bits of the slave address are the device type identifier
(see figure 4). For the S24022/23 this is fixed as 1010[B].
The next three bits are don’t care.
SCL from
Master
Data Output
from
Transmitter
Data Output
from
Receiver
Start
Condition
ACKnowledge
t
AA
t
AA
1
8
9
2010 ILL6 1.0
1 0 1 0
X X X R/W
DEVICE
IDENTIFIER
DON’T CARE
2010 ILL7 1.0
S24022/S24023
5
2010 1.4 5/3/98
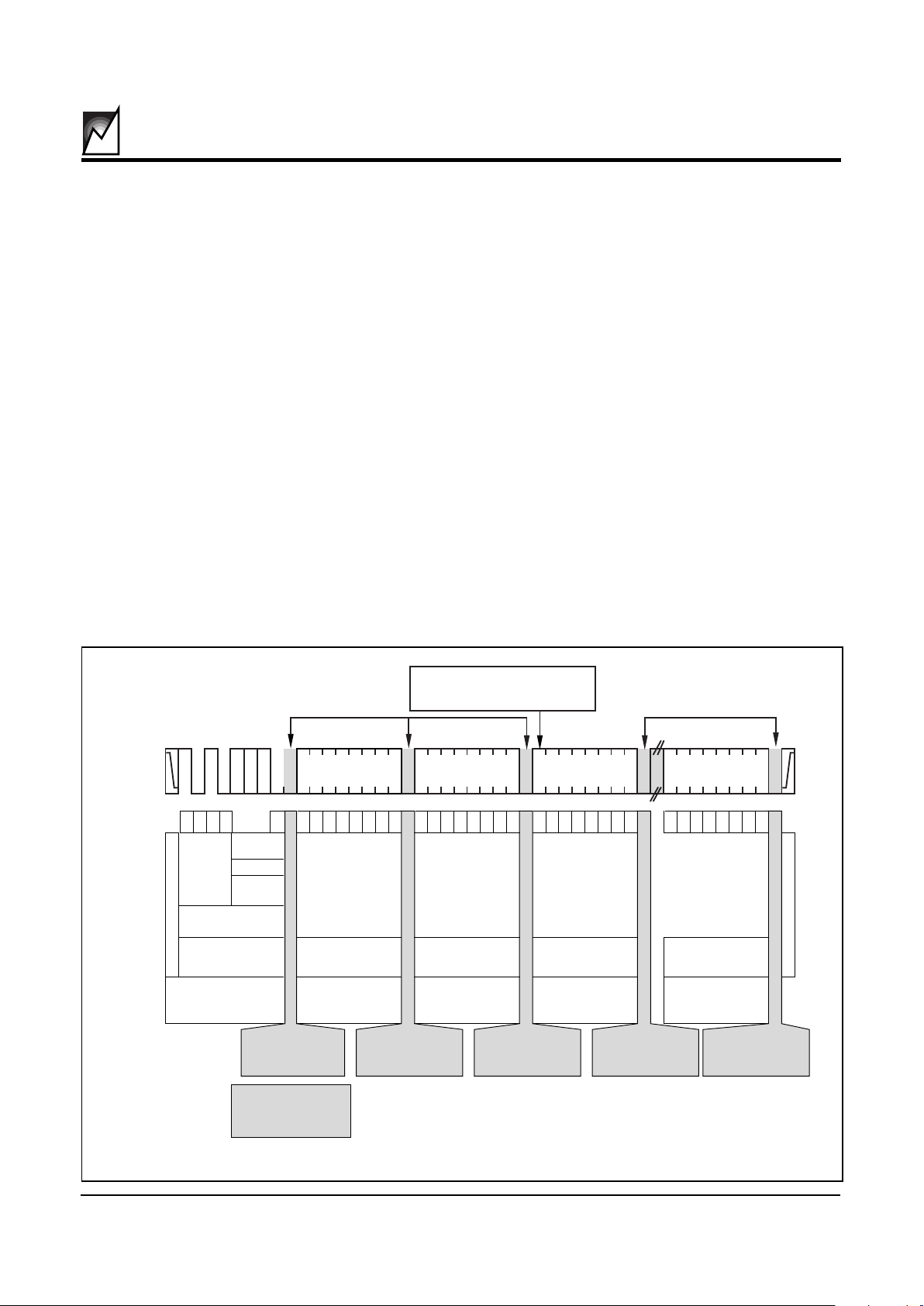
FIGURE 5. PAGE/BYTE WRITE MODE
WRITE OPERATIONS
The S24022/23 allows two types of write operations: byte
write and page write. The byte write operation writes a
single byte during the nonvolatile write period (tWR). The
page write operation allows up to 16 bytes in the same
page to be written during tWR.
Byte WRITE
After the slave address is sent (to identify the slave
device, and a read or write operation), a second byte is
transmitted which contains the 8 bit address of any one of
the 256 words in the array.
Upon receipt of the word address, the S24022/23 responds with an ACKnowledge. After receiving the next
byte of data, it again responds with an ACKnowledge. The
master then terminates the transfer by generating a
STOP condition, at which time the S24022/23 begins the
internal write cycle.
While the internal write cycle is in progress, the S24022/
23 inputs are disabled, and the device will not respond to
any requests from the master. Refer to Figure 5 for the
address, ACKnowledge and data transfer sequence.
Page WRITE
The S24022/23 is capable of a 16-byte page write operation. It is initiated in the same manner as the byte-write
operation, but instead of terminating the write cycle after
the first data word, the master can transmit up to 15 more
bytes of data. After the receipt of each byte, the S24022/
23 will respond with an ACKnowledge.
The S24022/23 automatically increments the address for
subsequent data words. After the receipt of each word,
the low order address bits are internally incremented by
one. The high order bits of the address byte remain
constant. Should the master transmit more than 16 bytes,
prior to generating the STOP condition, the address
counter will “roll over,” and the previously written data will
be overwritten. As with the byte-write operation, all inputs
are disabled during the internal write cycle. Refer to
Figure 5 for the address, ACKnowledge and data transfer
sequence.
Read/Write Bit
The last bit of the data stream defines the operation to be
performed. When set to “1,” a read operation is selected;
when set to “0,” a write operation is selected.
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D
0
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D
0
A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0D7D5D6D
4
D
0
D3D2D
1
S
T
A
R
T
Data Byte n Data Byte n+15
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
Acknowledges Transmitted from
24022/23 to Master Receiver
Slave Address
Device
Type
Address
Read/Write
0= Write
SDA
Bus
Activity
A
C
K
A
C
K
Master Sends Read
Request to Slave
Master Writes Word
Address to Slave
1 0 1 0
0
Data Byte n+1
A
C
K
Master Writes
Data to Slave
Master Transmitter
to
Slave Receiver
Slave Transmitter
to
Master Receiver
Slave Transmitter
to
Master Receiver
Master Transmitter
to
Slave Receiver
Master Transmitter
to
Slave Receiver
Shading Denotes
24022/23
SDA Output Active
Master Transmitter
to
Slave Receiver
Slave Transmitter
to
Master Receiver
Slave Transmitter
to
Master Receiver
Master Transmitter
to
Slave Receiver
Slave Transmitter
to
Master Receiver
Master Writes
Data to Slave
Master Writes
Data to Slave
Acknowledges Transmitted from
24022/23 to Master Receiver
If single byte-write only,
Stop bit issued here.
XX
R
W
A
C
K
X
2010 ILL8 1.2
 Loading...
Loading...