
DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
User’s Guide
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
Digital Equipment Corporation
Maynard, Massachusetts

Second Edition, April 1998
While DIGITAL believes the information included in this publication is correct as of
the date of publication, it is subject to change without notice.
Any changes or modifications made to this equipment may void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
This equipment requires the use of shielded SCSI cables such as the Digital Equipment
Corporation BN37A-series.
StorageWorks and the DIGITAL logo are trademarks of Digital Equipment
Corporation.
Copyright © 1998 Digital Equipment Corporation All Rights Reserved
Printed in the USA

Contents
Revision Record
About This Guide
…………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….…..
1 Introducing the 16-Bit SCSI Hub
1.1 SCSI Bus Hub Functions........................................................................................ 1–1
1.2 Product Descriptions.............................................................................................. 1–2
1.2.1 DWZZH 3.5" SBB Hubs .................................................................................. 1–2
1.2.2 DWZZH 5.25" SBB Hubs................................................................................. 1–4
1.2.3 SCSI Bus Components ..................................................................................... 1–5
1.3 Product Specifications............................................................................................ 1–6
2 Using a 16-Bit SCSI Hub
2.1 Large Hub Fair Arbitration..................................................................................... 2–1
2.2 Large Hub Addressing Configurations.................................................................... 2–2
2.3 Front Panel............................................................................................................. 2–4
2.3.1 Fair ARB Disable............................................................................................. 2–4
2.3.2 Indicators......................................................................................................... 2–5
2.3.3 Narrow Addressing Setting............................................................................... 2–5
2.4 Determining the Configuration............................................................................... 2–6
2.5 Selecting the SCSI Cables...................................................................................... 2–6
Glossary
Figures
1–1 DWZZH–21 or DWZZH-03 SCSI Bus Hub............................................................ 1–2
1–2 DWZZH–21 Front Panel ........................................................................................ 1–3
1–3 DWZZH–03 Front Panel ........................................................................................ 1–3
1–4 DWZZH–05 SCSI Bus Hub....................................................................................1–4
2–1 DWZZH–05 SCSI ID Assignments ........................................................................ 2–3
2–2 DWZZH Front Panel.............................................................................................. 2–4
2–3 DWZZH–05 SCSI Narrow ID Assignments............................................................ 2–5
2–4 DWZZH–05 SCSI Narrow Addressing Jumper....................................................... 2–6
v
vii
Tables
1–1 SCSI Bus Hub Functional Specifications................................................................ 1–5
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 iii


Revision Record
The Revision Record provides a concise publication history of this guide. It lists the guide
revision levels and release dates, and summarizes the changes.
The following revision history lists all revisions of this publication and their effective
dates. The publication part number is included in the Revision Level column, with the
last entry denoting the latest revision. This publication supports the DWZZH 16-Bit
SCSI Bus Hub.
Revision Level Date Summary of Changes
EK–DWZZH–UG. A01 October 1997 Original Release.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 April 1998 Change title page;
Add Section 1.2.2 describing
DWZZH–05 hub;
Change Chapter 2 title from
“Installing” to “Using” and add
procedures for configuring a SCSI bus
using a DWZZH hub.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 v


About This Guide
This chapter tells you what this User’s Guide does, identifies the audience, describes the
structure and contents (chapter-by-chapter ) briefly, and tells you how to get support and
services from DIGITAL.
This User’s Guide describes the purpose, function, operation, and use of the DWZZH
16-Bit SCSI Bus Hub (the DWZZH Hub or the Hub). The DWZZH Hub allows the
connection of up to five ports on one logical SCSI bus.
Visit our Web Site for the Latest Information
Check our web site for the latest drivers, technical tips, and documentation. We
can be found in the technical area of our web page:
http://www.storage.digital.com/
Audience
This guide is intended for end users and for DIGITAL employees responsible for
configuring, installing, and maintaining the StorageWorks subsystem and its
components.
Related Documentation
You should be familiar with the information contained in the following
documentation:
Document Title Order Number
StorageWorks Solutions Configuration Guide
StorageWorks Solutions Shelf and SBB User’s Guide
StorageWorks SBB Shelf I/O Modules
StorageWorks UltraSCSI Configuration Guidelines
StorageWorks Solutions BA356–SB 16-bit Shelf User’s Guide
EK–BA350–CG
EK–BA350–UG
EK–SBBIO–UG
EK–ULTRA–CG
EK–BA356–UG
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 vii

DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
Document Structure
This guide contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1. Introducing the DWZZH Hub
This chapter gives brief functional and physical descriptions of the DWZZH Hub
and lists significant product specifications.
Chapter 2. Using the DWZZH Hub
This chapter gives the procedures for configuring a StorageWorks SCSI bus
using a DWZZH Hub.
Glossary
The Glossary defines terms that are used frequently with StorageWorks and SCSI
bus components.
Support and Services
Who to contact in the Americas
Information and Product Questions: Local Sales Office / StorageWorks Hotline
1-800-786-7967
Installation Support: Contact the DIGITAL Distributor where the
Storage Solution was Purchased / Local
DIGITAL Sales Office.
DIGITAL Multivendor Customer Service (MCS)
Installation Contact the DIGITAL Customer Support
Center (CSC).
Warranty Contact the DIGITAL Customer Support
Center (CSC) for warranty service after
solution is installed and operating.
Remedial Contact the DIGITAL Customer Support
Center (CSC)
Note: A Service Contract is recommended
when the equipment is out of warranty.
Contact the local DIGITAL Sales Office.
Customer Support Center (CSC) 1 800-354-9000
viii EK–DWZZH–UG. B01

About This Guide
Who to contact in Europe
Information and Product Questions, Contact the DIGITAL Distributor or reseller
Installation Support, and Installation: from whom the Storage Solution was
purchased.
For Warranty Service See the Warranty Card packaged with the
product.
For Remedial Service Contact the DIGITAL Distributor or reseller
from whom the Storage Solution was
purchased.
Note: A Service Contract is recommended
when the equipment is out of warranty.
Who to contact in Asia Pacific
For all services, contact the DIGITAL Distributor or reseller from whom the
equipment was purchased.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 ix


1
Introducing the DWZZH Hub
This chapter describes the DWZZH Hub functions and available versions, and list the
Hub functional specifications.
The series of DWZZH Hubs are SCSI–2 and draft SCSI–3
(ANSI X379.2/91–10R3) compliant 16-bit converters capable of data transfer
rates of up to 40 Mbytes per second. The series of Hubs consists of the following:
DWZZH–21 and DWZZH–03 are 3.5" SBB (small) Hubs; the DWZZH–21
•
contains two single-ended and one differential SCSI ports, while the
DWZZH–03 contains three differential SCSI ports.
DWZZH–05 is a 5.25" SBB (large) Hub that contains 5 differential SCSI
•
ports.
1.1 SCSI Bus Hub Functions
Most device SCSI buses are either 8-bit or 16-bit single-ended, physical buses.
Some controllers and hosts use differential buses and others use a single-ended
bus. Single-ended and differential physical buses are not compatible. The SCSI
protocol disables both buses when they are connected together. However, by
using a SCSI bus Hub you can accomplish the following:
Connect a differential physical bus to a single-ended physical bus.
•
Extend the maximum length of a SCSI bus.
•
Provide radial disconnect where remaining connections can continue to
•
operate.
Provide “fair” SCSI arbitration for host nodes (DWZZH-05 SCSI HUB
•
only).
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 1–1
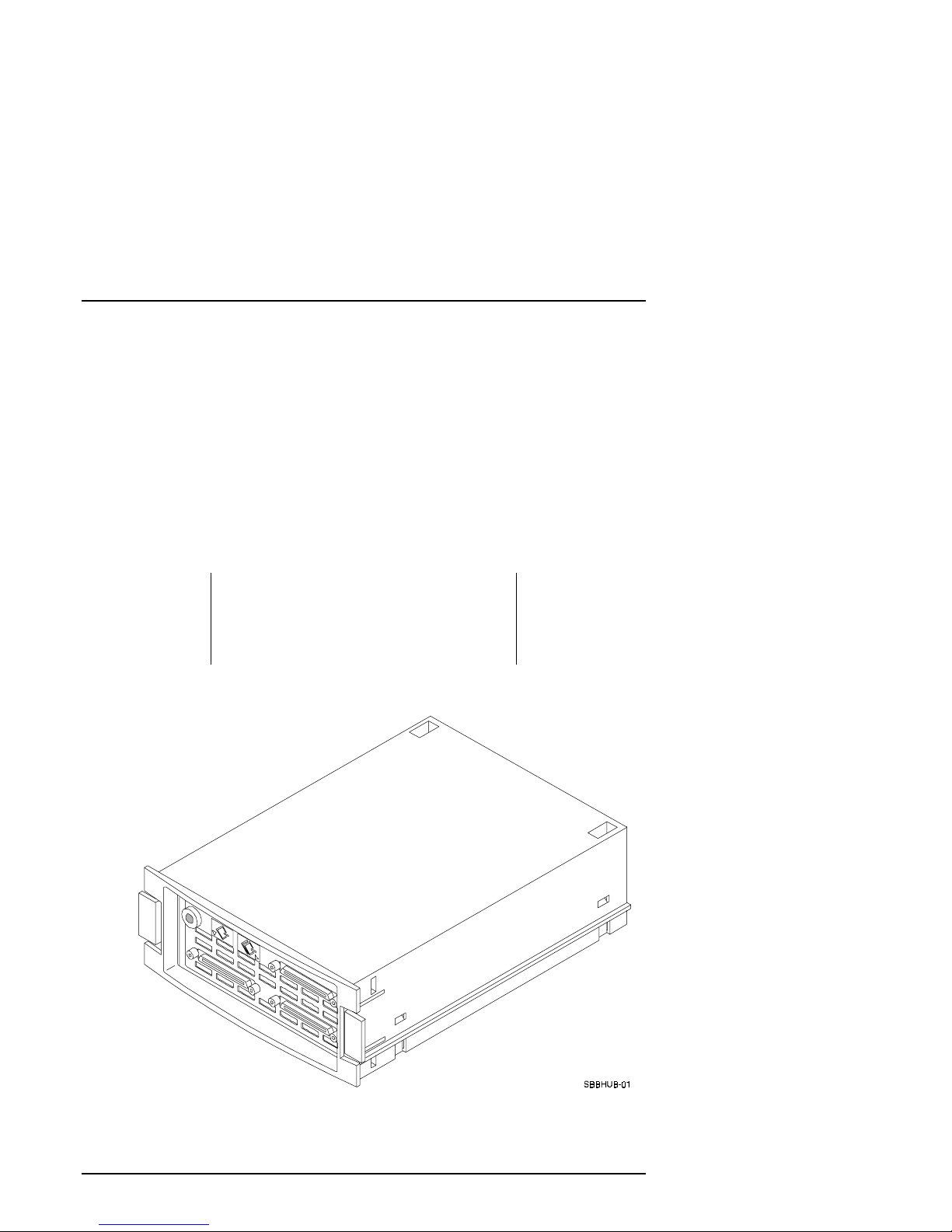
DWZZH 16-Bit SCSI Bus Hub
1.2 Product Descriptions
There are two classes of DWZZH Hubs: 3.5" SBB Hubs, and 5.25" SBB Hubs.
1.2.1 3.5" SBB Hubs
The DWZZH small SCSI Hub (Figure 1-1) comes in two versions.
DWZZH-21 contains two single–ended SCSI bus connections and one
•
differential SCSI connection; Figure 1-2 illustrates the front panel.
DWZZH-03 contains three differential SCSI bus connections; Figure 1-3
•
illustrates the front panel.
CAUTION
Connec ting a different ial bus cable to t he singleended connector , or a single- ended bus cable to
the diff erential c onnector c auses t he SCSI bus to
fail.
Figure 1–1 DWZZH–21 or DWZZH–03 3.5" SBB Hub
1–2 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
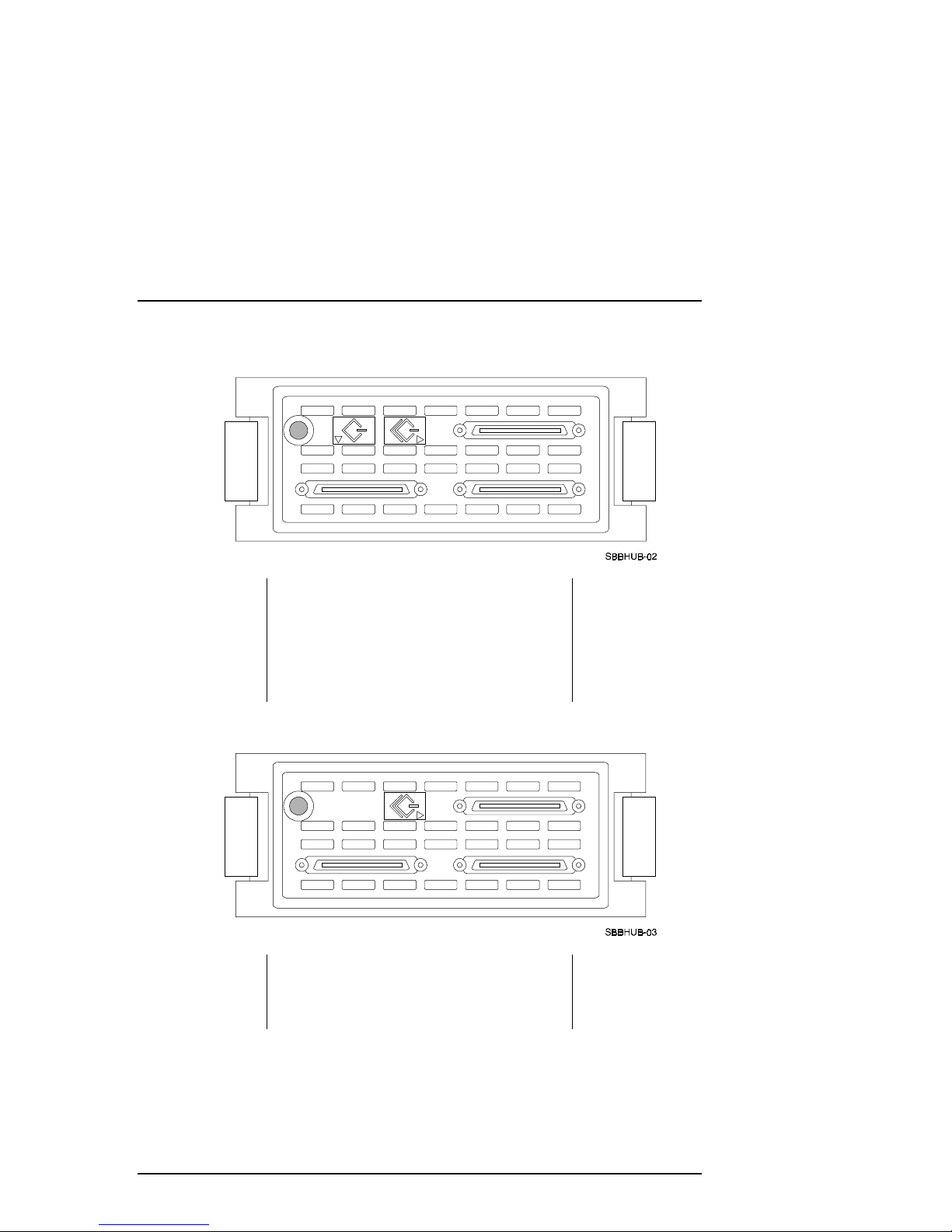
Figure 1–2 DWZZH–21 Front Panel
Chapter 1. Introducing the DWZZH Hub
The single–ended symbol with the downward–
pointing di amond in Figure 1-2 indi cates that the
lower two connectors are single–ended SCSI
connecti ons, whi le the di fferent ial sy mbol wi th t he
right–pointing diamond indicates that the top
connector is a differential SCSI connection.
Figure 1–3 DWZZH–03 Front Panel
The differential symbol with the right–pointing
diamond in Figure 1-3 indicates that the three
connectors are differential SCSI connections.
NOTE
NOTE
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 1–3

DWZZH 16-Bit SCSI Bus Hub
1.2.2 5.25” SBB Hubs
The DWZZH large SCSI Hub (Figure 1-4) comes in a single version that
contains five differential SCSI bus connections.
CAUTION
Connec ting a different ial bus cable to t he singleended connector , or a single- ended bus cable to
the diff erential c onnector c auses t he SCSI bus to
fail.
Figure 1–4 DWZZH–05 5.25" SBB Hub
1.2.3 SCSI Bus Components
To install a DWZZH SCSI bus converter you need SCSI BN37 series cables.
Refer to the StorageWorks Solutions Configuration Guide for a complete list of
the available cables.
1–4 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01

Chapter 1. Introducing the DWZZH Hub
1.3 Product Specifications
Table 1-1 lists the functional specifications for the DWZZH Hub.
Table 1–1 DWZZH Hub Functional Specifications
Feature Specification
SCSI ID
SCSI Addresses
Overload Protection
DTERMPOWER
STERMPOWER
Shielding
Enclosure &
Connectors
Power-Up Reset Automatically clears
SCSI Bus Reset Automatically clears
Single-Ended SCSI Bus
Length
Ultra (20 megatransfers per
second or 40 MB/s)
Differential SCSI Bus Length 25 meters (82 feet) per segment
Data Timing The relationship between the data and the control
Design High reliability SMT
The SCSI HUB does not use a SCSI ID (small HUB)
The large SCSI HUB uses SCSI ID 7 for arbitration.
TERMPOWER is not supplied to the external ports
of the SCSI HUB. Internal TERMPOWER is
protected via a resetable fuse. TERMPOWER must
be supplied from the remote connection to enable
each HUB port.
Shielded for ESD, EMI, and safety requirements
• Initiator detection circuit
• Target detection circuit
• BSY glitch filter
• Initiator detection circuit
• Target detection circuit
• BSY glitch filter
20 Meters (66 feet) per segment
signals is brought to SCSI compatibility before
transmission to the other SCSI bus.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 1–5

DWZZH 16-Bit SCSI Bus Hub
Table 1–1 DWZZH Hub Functional Specifications (Cont’d)
Feature Specification
Cable Fault DIFFSENSE support and port disable on cable fault
Glitch Elimination 100% glitch free operation during power-up
BUSY GLITCH trap eliminates cable length constraint
due to wired-OR glitches on the BSY line
Termination
Singled-ended Active termination for 16bit operation.
Differential Termination for 16bit operation.
Service
There are no user servicable functions on these products.
Contact Digital service personnel all service.
Agency Approvals
UL, CSA, FCC Class B, TUV
Environmental Specifications
Relative Humidity 10% to 85% non-condensing
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature (non-
10°C to 40°C (50°F to 104°F)
–40°C to 66°C (–40°F to 151°F)
operating)
Power Requirements
DWZZH +5V
Input Current:
DWZZH-03
DWZZH-05
DWZZH-21
2.3 Amp
4.3 Amp
1.8 Amp
TERMPOWER Supplied to internal terminators only.
SCSI Connectors and Cables
Single-Ended Board mounted 68pin VHDCI SCSI connector
Differential Board mounted 68pin VHDCI SCSI connector
Cables BN37A-series shielded SCSI cables
1–6 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01

2
Using the DWZZH Hub
This chapter discusses f air arbitr ation of the SCSI bus by the 5.25" SBB Hub, describes
addressing configurations, tells you how to use the large Hub front panel, and gives
guidelines for selecting the SCSI cables.
UltraSCSI Configuration guidelines are documented in EK-ULTRA-CG. These
guidelines include a list of all UltraSCSI components and the last few example
configurations include a SCSI Hub. Refer to the configuration guidelines for bus
length and SCSI bus data transmission rates.
The UltraSCSI Hubs are designed to be installed in StorageWorks Solutions
BA350 and BA356 Shelfs. The small SCSI Hub may be installed in any open
SBB slot. The large SCSI Hub may be installed in any slot that will
accommodate a 5.25 SBB. The small SCSI Hub does not consume a SCSI ID and
uses the shelf only to provide its power and mechanical support. The large SCSI
Hub uses SCSI ID 7 to control the fair arbitration of the host port IDs and uses
the shelf only to provide its power and mechanical support.
2.1 Large HUB Fair Arbitration
The large Hub configurations utilize a modified SCSI arbitration algorithm. The
normal SCSI arbitration scheme is based on the SCSI ID. The highest priority
SCSI ID will always win arbitration This will have the effect of ‘starving’ lower
priority SCSI ID requests on the bus.
In order to allow up to four ‘host’ SCSI IDs to participate on a single SCSI bus, a
fair arbitration (fair arb) scheme is employed. Fair arb works by assigning SCSI
ID 7, the highest priority ID to the Hub. When a SCSI arbitration phase occurs,
all the arbitrating IDs are captured in a register. The winning ID for this group
will be the highest priority ID. After this ID has been serviced, the ID will be
removed from the group and at the next arbitration phase, the remaining highest
ID will be serviced. This will continue until all of the IDs in the group have been
serviced once. All requests from IDs not contained in the register will be
“backed off ” using ID 7.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 2–1

DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
After all the IDs in the group have been serviced, a new group of IDs will be
captured at the next arbitration phase. The fair arbitration algorithm only applies
to host port SCSI IDs as defined by the assignment in each configuration.
2.2 Large HUB Addressing Configurations
The large SCSI Hub has a specific SCSI ID configuration. The SCSI IDs are
assigned to specific physical locations in the Hub. This allows the fair arbitration
logic in the Hub to correctly identify the SCSI IDs that are participating in a fair
arbitration cycle.
CAUTION
The SCSI ID of the HOST adapter must
correspond to the assigned ID of the Hub port.
Mismatched SCSI IDs will cause the Hub SCSI
bus to hang.
Figure 2-1 shows the physical layout of the ports and their associated SCSI ID
assignments.
2–2 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
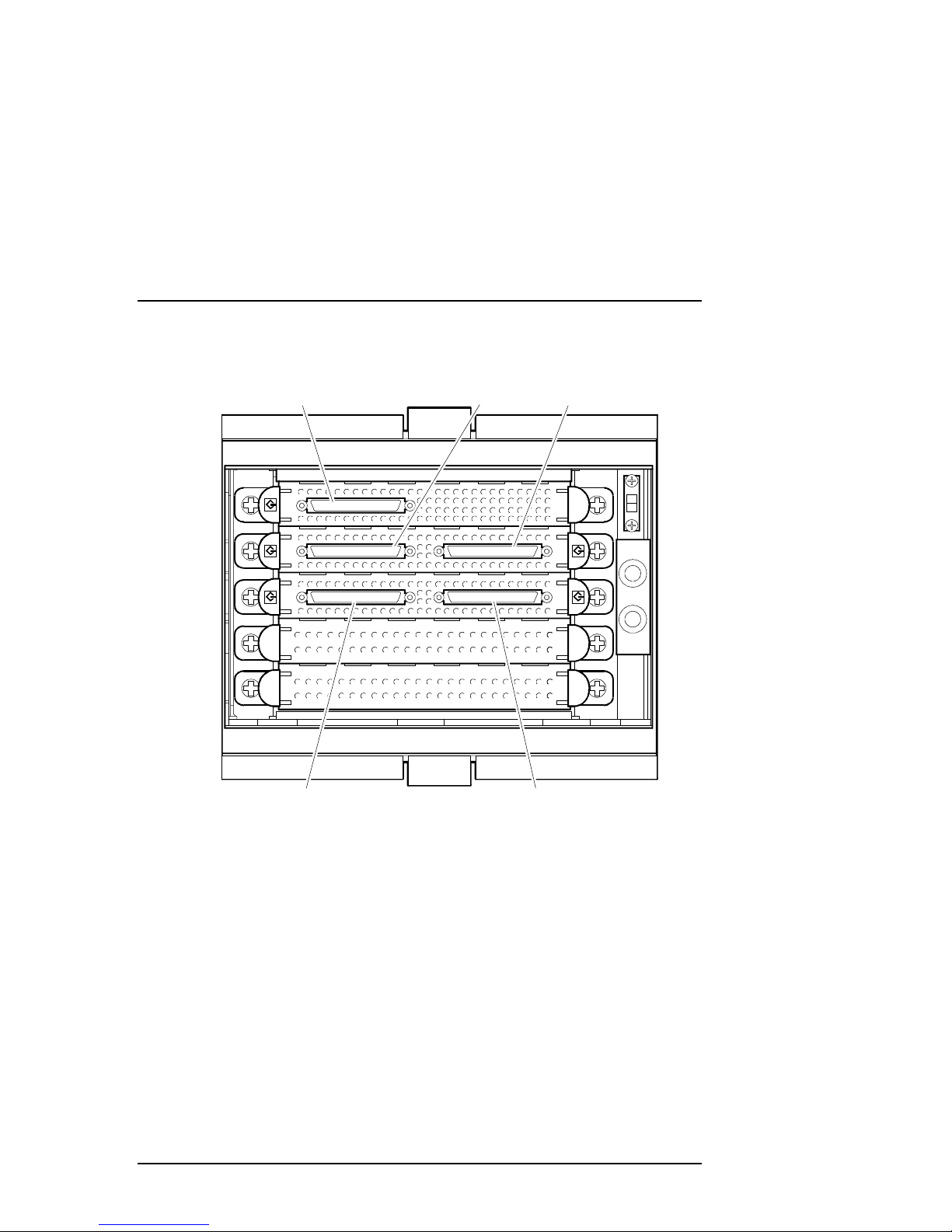
Figure 2–1 DWZZH–05 SCSI ID Assignments
C
Chapter 2. Using the DWZZH Hub
on tro ller Port
SCSI ID 6 -0
Host Port
SCSI ID 13
Host Port
SCSI ID 15
Host Port
SCSI ID 12
Host Port
SCSI ID 14
-
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 2–3

DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
2.3 Front Panel
Figure 2-2 shows the location of the front panel controls and indicators.
Figure 2–2 DWZZH–05 Front Panel
Fair Disable
Power
Busy
The black part of the switch in the diagram
indicates the position of the switch.
2.3.1 FAIR ARB Disable
The large Hub contains a switch on the front panel that allows the user to disable
the
FAIR ARB
services SCSI arbitration cycles in the conventional SCSI priority order. Host
port SCSI ID assignments are not linked to the physical port location in the Hub
when
FAIR ARB
2–4 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
feature of the Hub. When
is disabled.
NOTE
FAIR ARB
-
is disabled, the Hub

Chapter 2. Using the DWZZH Hub
C
2.3.2 Indicators
The large Hub has two indicators on the front panel. The green LED indicates
that POWER is applied to the Hub, while the yellow LED indicates that the SCSI
bus is BUSY.
2.3.3 Narrow Addressing Setting
The large Hub can be used with SCSI bus architectures that are limited to eight
ID assignments (Figure 2-3 shows narrow ID assignments). A jumper on the rear
of the Hub (Figure 2-4) must be installed to make the Hub respond to SCSI IDs
3 – 0 on the host ports.
Figure 2–3 DWZZH–05 SCSI Narrow ID Assignments
on tro ller P ort
SCSI ID 6 -4
Host Port
SCSI ID 1
Host Port
SCSI ID 3
SCSI ID 0
Host Port
SCSI ID 2
Host Port
-
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 2–5

DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
Figure 2–4 DWZZH–05 SCSI Narrow Addressing Jumper
W1 (To enable narrow addressing mode, install a jumper at W1)
2.4 Determining the Configuration
The SCSI Hub is used in end–bus SCSI bus configurations only. The SCSI bus
segments require TERMPOWER supplied from the remote connection to enable
the SCSI Hub port for that segment. Each port on the SCSI Hub has its own
terminators.
All SCSI buses are terminated at the physical ends of the bus. This is true even
when using a DWZZH SCSI Hub. DWZZH SCSI Hubs are factory set to
terminate the SCSI bus. No user configuration of the SCSI terminators is
required.
2.5 Selecting the SCSI Cables
The
StorageWorks Solutions UltraSCSI Configuration Guide
cables in detail. When selecting a cable you must consider the cable connector
clearance. Be sure to determine the type connector compatible with the controller
connector. In some cases you must use a right–angle connector because there is
not enough clearance to use a straight connector. Cables connected to the
DWZZH converters are BN37A series.
2–6 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
describes SCSI

Glossary
This Glossary includes an alphabetized listing and brief definition of the abbreviations,
acronyms, DIGITAL-specific references, and other technical terms that are used in this
manual and that may be unfamiliar to the reader.
adapter
See SCSI bus converter.
building block shelf
See SBB shelf.
controller
A hardware/firmware device that manages communications on behalf of host systems over the
SCSI bus to devices, such as the HSC-series, HSJ-series, and HSZ-series controllers. Controllers
typically differ by the type of interface to the host and provide functions beyond what the
devices support.
differential SCSI bus
A signal's level is determined by the potential difference between two wires. A differential bus
is more robust and less subject to electrical noise than is a single-ended bus.
DWZZC
A StorageWorks compatible 16-bit SCSI bus converter.
See SCSI bus converter.
DWZZH
A StorageWorks compatible 16-bit SCSI bus HUB.
electrostatic discharge
See ESD.
ESD
Electrostatic discharge is the discharge of a potentially harmful static electric voltage as a result
of improper grounding.
host
The primary or controlling computer or any such unit (in a multiple computer network) to which
storage is attached.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 Glossary–1

DWZZH 16–Bit SCSI Bus Hub
initiator
A SCSI device that requests another device on the bus to perform an operation. Any device on
the bus can be an initiator or a target.
logical bus
A single-ended, physical bus connected to a differential, physical bus by a SCSI bus converter.
personality module
The BA356 module that interfaces the SCSI-bus to the BA356 shelf.
physical bus
Two SCSI terminators separated by cables, connectors, and/or the backplane circuitry.
SBB
StorageWorks building block. The basic building block of the StorageWorks product line. Any
device conforming to shelf mechanical and electrical standards installed in either a 3½-inch or
5¼-inch carrier is considered to be an SBB, whether it is a storage device, a power supply, or
other device.
SBB shelf
The common name for any StorageWorks shelf that contains only power supply and storage
SBBs.
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface. This ANSI interface defines the physical and electrical
parameters of a parallel I/O bus used to connect computers and devices. The StorageWorks
subsystem implementation uses SCSI–2 for the transfer of data.
SCSI bus converter
Sometimes referred to as an adapter. (1) A connecting device that permits the attachment of
accessories or provides the capability to mount or link units. (2) The device that connects a
differential SCSI bus to a single-ended SCSI bus.
SCSI device
A host computer adapter, a peripheral controller, or an intelligent peripheral that can be attached
to the SCSI bus.
SCSI device ID
The bit-significant, representation of the SCSI addressing referring to one of the signal lines
numbered 0 through 15. Also referred to as target ID. For example, SCSI device ID 1 would be
represented as 00001.
SCSI mid-bus position
The physical location of a controller or a device that the SCSI bus passes through enroute to the
controller or device that contains the SCSI bus termination.
Glossary–2 EK–DWZZH–UG. B01

Glossary
SCSI cable
A 68-conductor (34 twisted pairs) cable used for differential bus connections.
single-ended SCSI bus
A bus in which each signal’s logic level is determined by the voltage of a single wire in relation
to ground.
Small Computer System Interface
See SCSI.
StorageWorks
The Digital set of enclosure products that allows customers to design and configure their own
storage subsystem. Components include power, packaging, and interconnections in a
StorageWorks shelf. SBBs and array controllers are integrated therein to form level enclosures
to house the shelves. Standard mounting devices for SBBs are also included.
StorageWorks building block
See SBB.
target
A SCSI device that performs an operation requested by an initiator. Any device on the bus can
be an initiator or a target.
target ID
See SCSI device ID.
termpower
Is an electrical current that is limited by self-resetting fuses.
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01 Glossary–3


Reader’s Comments
Manual Order Number:
EK–DWZZH–UG. B01
DIGITAL is committed to providing the best products and services. Since our manuals are
important components of our products, we value your comments, corrections, and
suggestions for improvements. Please take a few minutes to fill out and return this form.
Attach additional sheets, if necessary. Thank you.
Manual Rating
Accuracy (correct presentation of facts) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Completeness (adequate information) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Clarity (easy to understand) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Organization (logical sequence of information) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Layout (easy to follow subject matter) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Indexing (easy to locate desired information) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Errors Noted
(include page, paragraph, table or figure number)___________________
Excellent Good Fair Poor
Most-Liked Features
Least-Liked Feature
: ____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
Suggestions for Improvement
Return Address:
Digital Equipment Corporation
Customer Research
Response Center
334 South Street, SHR3-2/W3
Shrewsbury, MA 01545
_____________________________________________
Name Phone
Title
Company
Street Address
Mail Stop
City State ZIP
Country (if other than USA)

 Loading...
Loading...