STMicroelectronics TS1871, TS1872, TS1874 Technical data
TS1871-TS1872-TS1874
1.8V Input/Output Rail-to-Rail
Low Power Operational Amplifiers
■ Operating at VCC = 1.8V to 6V
■ Rail-to-rail input & output
■ Extended Vicm (V
- 0.2V to VCC + 0.2V)
DD
■ Low supply current (400µA)
■ Gain bandwidth product (1.6MHz)
■ High stability
■ ESD tolerance (2kV)
■ Latch-up immunity
■ Available in SOT23-5 micropackage
Description
The TS187x (single, dual & quad) is an
operational amplifier family able to operate with
voltage as low as 1.8V and features both I/O railto-rail.
The common mode input voltage extends 200mV
at 25°C beyond the supply voltages while the
output voltage swing is within 100mV of each rail
with 600 Ohm load resistor. This device consumes
typically 400µA per channel while offering 1.6Mhz
of gain-bandwidth product. The amplifier provides
high output drive capability typically at 65mA-load.
These performances make the TS187X family
ideal for sensor interface, battery-supplied and
portable applications.
Pin Connections (top view)
TS1871ILT
VCC
Outp ut
Outp ut
1
1
VDD
VDD
2
2
Non Inverting I nput Inverting In put
Non Inverting I nput Inverting In put
3
3
TS1871ID-TS1871IDT
1
1
N.C.
N.C.
2
VDD
VDD
2
3
3
Inverting I nput
Inverting I nput
Non Inverting Input
Non Inverting Input
TS1872IST-TS1872IN-TS1872ID-TS1872IPT
Output 1
Output 1
1
1
_
Inverting Input 1
Inverting Input 1
Non Inverting Input 1
Non Inverting Input 1
VDD
VDD
_
2
2
+
+
3
3
TS1874IN-TS1874ID-TS1874IDT-TS1874IPT
1
1
Output 1
Output 1
Inverting Input 1
Inverting Input 1
Non Inverting Input 1
Non Inverting Input 1
Non Inverting Input 2
Non Inverting Input 2
Inverting Input 2
Inverting Input 2
Output 2
Output 2
VCC
VCC
_
_
2
2
+
+
3
3
5
5
+
+
_
_
6
6
7
7
5
5
4
4
_
_
+
+
_
_
+
+
14
14
_
_
13
13
+
+
12
12
114
114
10
10
+
+
_
_
9
9
8
8
VCC
8
8
7
7
6
6
54
54
8
8
VCC
VCC
7
7
Output 2
Output 2
6
6
Inverting Input 2
Inverting Input 2
Non Inverting Input 2
Non Inverting Input 2
54
54
Output 4
Output 4
Inverting Input 4
Inverting Input 4
Non Inverting Input 4
Non Inverting Input 4
VDD
VDD
Non Inverting Input 3
Non Inverting Input 3
Inverting Input 3
Inverting Input 3
Output 3
Output 3
N.C.
N.C.
VCC
VCC
Output
Output
N.C.
N.C.
Applications
■ Battery-powered applications (toys)
■ Portable communication devices (cell
phone)
■ Audio driver (headphone driver)
■ Laptop/notebook computers
Order Codes
Part Number
TS1871ID/IDT/AID/AIDT
TS1871ILT/AILT SOT23-5L Tape & Reel K171/K172
TS1872IN/AIN DIP Tube
TS1872ID/IDT/AID/AIDT SO Tube or Tape & Reel
TS1872IPT/AIPT TSSOP
TS1872IST/AIST mini SO Tape & Reel K171/K172
TS1874IN/AIN DIP Tube
TS1874ID/IDT/AID/AIDT SO Tube or Tape & Reel
TS1874IPT/AIPT TSSOP
May 2005 Revision 2 1/22
Temperature
Range
-40°C, +125°C
Package Packaging Marking
SO Tube or Tape & Reel
(Thin Shrink Outline Package)
(Thin Shrink Outline Package)
Tape & Reel
Tape & Reel
TS1871-TS1872-TS1874 Absolute Maximum Ratings
1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 1: Key parametes and their absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
T
R
Supply voltage
CC
V
Differential Input Voltage
id
V
Input Voltage
i
Storage Temperature
stg
T
Maximum Junction Temperature
j
Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient
thja
SOT23-5
SO8
SO14
TSSOP8
TSSOP14
miniSO8
HBM: Human Body Model
ESD
MM: Machine Model
CDM: Charged Device Model 1.5 kV
Latch-up Immunity 200 mA
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10sec) 250 °C
Output Short Circuit Duration
1) All voltages values, except differential voltage are with respect to network terminal.
2) Differential voltages are the non-inverting input terminal with respect to the inverting input terminal. If Vid > ±1V, the maximum input current must not exceed ±1mA. In this case (Vid > ±1V) an input serie resistor must be added to limit input current.
3) Short-circuits can cause excessive heating. Destructive dissipation can result from simultaneous short-circuit on all amplifiers
4) Human body model, 100pF discharged through a 1.5kΩ resistor into pin of device.
5) Machine model ESD, a 200pF cap is charged to the specified voltage, then discharged directly into the IC with no external series resistor
(internal resistor < 5
6) Short-circuits from the output to V
the magnitude of V
1
2
V
DD
3
4
5
Ω), into pin to pin of device.
can cause excessive heating. The maximum output current is approximately 80mA, independent of
. Destructive dissipation can result from simultaneous short-circuits on all amplifiers.
cc
cc
7V
±1 V
-0.3 to VCC +0.3
V
-65 to +150 °C
150 °C
250
°C/W
125
103
120
100
190
2kV
200 V
see note
6
Table 2: Operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
VCC Supply Voltage 1.8 to 6 V
Vicm
Vicm
T
1) At 25°C, for 1.8 ≤ VCC ≤ 6V, V
2) In full temperature range, both Rails can be reached when VCC does not exceed 5.5V.
Common Mode Input Voltage Range
Common Mode Input Voltage Range
Operating Free Air Temperature Range
oper
is extended to VDD - 0.2V, VCC + 0.2V.
icm
1
2
2/22
VDD - 0.2 to VCC + 0.2
VDD to V
CC
-40 to + 125 °C
V
V
Electrical Characteristics TS1871-TS1872-TS1874
2 Electrical Characteristics
Tab le 3: VCC = +1.8V, VDD = 0V, RL, CL connected to VCC/2, T
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Input Offset Voltage
V
= V
= V
= V
= V
CC
CC
CC
/2
TS1871/2/4
TS1871A/2A/4A
1
/2
1)
/2
= V
CC
/2
= 0.5V to 1.3V
V
out
R
= 2kΩ
L
out
RL = 600Ω
icm
icm
icm
≤ V
= V
= V
icm
out
out
out
≤ VCC, V
V
io
∆V
I
io
I
ib
CMR
Input Offset Voltage Drift
io
Input Offset Current
V
Input Bias Current
V
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
0
SVR Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio 70 80 dB
Large Signal Voltage Gain
A
vd
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
0.1 3
1
2
330nA
40 125 nA
55 77
77
70
92
85
mV
µV/°C
dB
dB
High Level Output Voltage
V
= 100mV
V
OH
id
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
1.65
1.62
1.77
1.74
Low Level Output Voltage
= -100mV
V
V
OL
id
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
88
115
100
150
mV
Output Source Current
V
I
o
I
CC
GBP
SR
φm
= 100mV, VO = V
ID
DD
Output Sink Current
V
= -100mV, VO = V
ID
CC
Supply Current (per amplifier), Vout = Vcc/2
A
= 1, no load
VCL
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, f = 100kHz
L
Slew Rate
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, AV = 1
L
Phase Margin
C
= 100pF
L
20
20
65
65
mA
400 560
0.9 1.6 MHz
0.38 0.54 V/
53 Degrees
en Input Voltage Noise 27 nV/
THD Total Harmonic Distortion 0.01 %
V
µA
µs
√Hz
1) Maximum values including unavoidable inaccuracies of the industrial test.
3/22
TS1871-TS1872-TS1874 Electrical Characteristics
Table 4: VCC = +3V, VDD = 0V, RL, CL connected to VCC/2, T
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Input Offset Voltage
V
= V
= V
= V
= V
CC
CC
CC
/2
TS1871/2/4
TS1871A/2A/4A
1
/2
1)
/2
= V
CC
/2
out
60 80
0.1 3
1
2
µV/°C
330nA
4 125 nA
V
io
∆V
I
io
I
ib
CMR
icm
out
Input Offset Voltage Drift
io
Input Offset Current
V
= V
icm
out
Input Bias Current
V
= V
icm
out
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
0
≤ V
≤ VCC, V
icm
SVR Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio 70 85 dB
Large Signal Voltage Gain
V
= 0.5V to 2.5V
A
out
vd
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
80
74
92
95
High Level Output Voltage
V
= 100mV
V
OH
id
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
2.82
2.80
2.95
2.95
mV
dB
dB
V
Low Level Output Voltage
V
= -100mV
V
OL
id
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
88
115
L120
160
Output Source Current
V
I
o
I
CC
GBP
SR
φm
= 100mV, VO = V
ID
DD
Output Sink Current
V
= -100mV, VO = V
ID
CC
Supply Current (per amplifier), Vout = Vcc/2
= 1, no load
A
VCL
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, f = 100kHz
L
Slew Rate
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, AV = 1
L
Phase Margin
C
= 100pF
L
20
20
80
80
450 650
11.7 MHz
0.42 0.6 V/
53 Degrees
en Input Voltage Noise 27 nV/
THD Total Harmonic Distortion 0.01 %
1) Maximum values including unavoidable inaccuracies of the industrial test.
mV
mA
µA
µs
√Hz
4/22
Electrical Characteristics TS1871-TS1872-TS1874
Table 5: V
= +5V, VDD = 0V, CL & RL connected to VCC/2, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise
amb
specified)
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Input Offset Voltage
V
= V
= V
= V
= V
/2
CC
1
/2
CC
1)
/2
CC
different of V
out
CC
TS1871/2/4
TS1871A/2A/4A
/2
R
RL = 600Ω
R
RL = 600Ω
= 2kΩ
L
= 2kΩ
L
0.1 3
1
2
µV/°C
330nA
70 130 nA
65 85 dB
83
77
4.80
4.75
92
85
4.95
4.90
icm
icm
icm
≤ V
= V
= V
icm
out
out
out
≤ VCC, V
V
io
∆V
I
io
I
ib
CMR
Input Offset Voltage Drift
io
Input Offset Current
V
Input Bias Current
V
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
0
SVR Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio 70 90 dB
Large Signal Voltage Gain
V
= 1V to 4V
A
out
vd
High Level Output Voltage
V
= 100mV
V
OH
id
mV
dB
V
Low Level Output Voltage
V
= -100mV
V
OL
id
R
= 2kΩ
L
RL = 600Ω
88
115
130
188
Output Source Current
I
o
I
CC
GBP
SR
φm
V
ID
DD
Output Sink Current
V
= -100mV, VO = V
ID
CC
Supply Current (per amplifier), Vout = Vcc/2
A
= 1, no load
VCL
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, f = 100kHz
L
Slew Rate
R
= 10kΩ, CL = 100pF, AV = 1
L
Phase Margin
C
= 100pF
L
20
20
80
80
500 835
11.8 MHz
0.42 0.6 V/
55 Degrees
= 100mV, VO = V
en Input Voltage Noise 27 nV/
THD Total Harmonic Distortion 0.01 %
1) Maximum values including unavoidable inaccuracies of the industrial test.
mV
mA
µA
µs
√Hz
5/22
TS1871-TS1872-TS1874 Electrical Characteristics
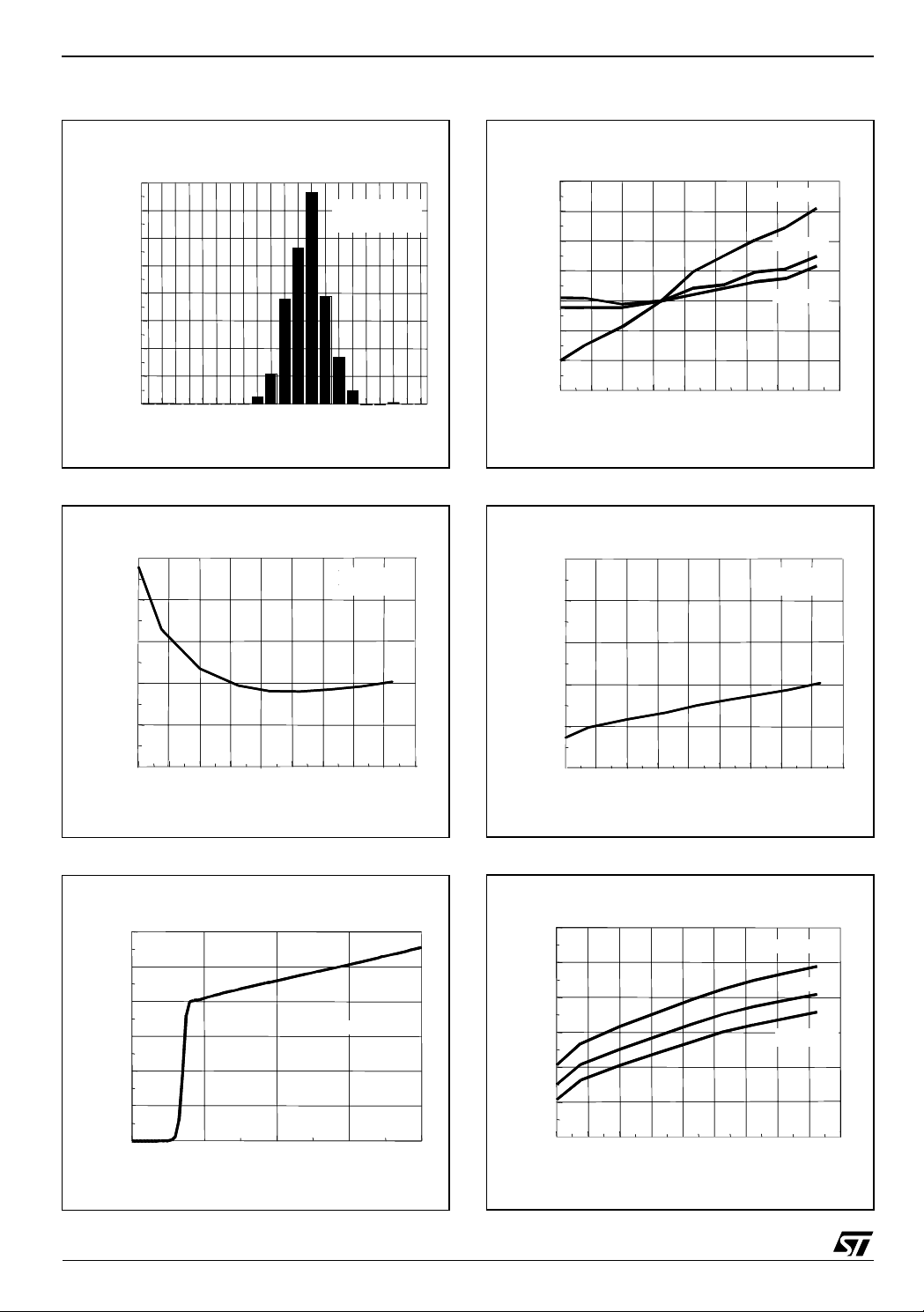
Figure 1 :
160
160
140
140
120
120
100
100
80
80
60
60
Quantity of pieces
Quantity of pieces
40
40
20
20
0
0
Figure 2 :
10.0
10.0
0.0
0.0
Input Offset Voltage Distribution
Input Offset Voltage Distribution
492 pieces tested
492 pieces tested
492 pieces tested
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Temp = +25°C
Temp = +25°C
Temp = +25°C
-2. -1.6 -1.2 -.8 -.4 0 .4 .8 1.2 1.6 2
-2. -1.6 -1.2 -.8 -.4 0 .4 .8 1.2 1.6 2
Input Offset Voltage (mV)
Input Offset Voltage (mV)
Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vicm = 0.9V
Vicm = 0.9V
Figure 4 :
200
200
150
150
100
100
50
50
0
0
-50
-50
Input Voltage Drift (µV)
Input Voltage Drift (µV)
-100
-100
-150
-150
-40 -20 0 20 4 0 60 80 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 20 4 0 60 80 100 120 140
Figure 5 :
10.0
10.0
0.0
0.0
Input Offset Voltage Drift vs. Temperature
Input Offset Voltage Drift vs. Temperature
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Tempe rature ( °C)
Tempe rature ( °C)
Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 3V
Vicm = 1.5V
Vicm = 1.5V
-10.0
-10.0
-20.0
-20.0
Input bias current (nA)
Input bias current (nA)
-30.0
-30.0
-40.0
-40.0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Figure 3 :
600
600
500
500
400
400
300
300
200
200
Supply Current (µA)
Supply Current (µA)
100
100
0
0
02468
02468
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Supply Current / Amplifier vs. Supply Voltage
Supply Current / Amplifier vs. Supply Voltage
Tamb = 25°C
Tamb = 25°C
Supply Voltage (V)
Supply Voltage (V)
-10.0
-10.0
-20.0
-20.0
Input bias current (nA)
Input bias current (nA)
-30.0
-30.0
-40.0
-40.0
Figure 6 :
550
550
500
500
450
450
400
400
350
350
Supply Current (µA)
Supply Current (µA)
300
300
250
250
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 12 0 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 12 0 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Supply Current / Amplifier vs. Temperature
Supply Current / Amplifier vs. Temperature
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
6/22
Electrical Characteristics TS1871-TS1872-TS1874
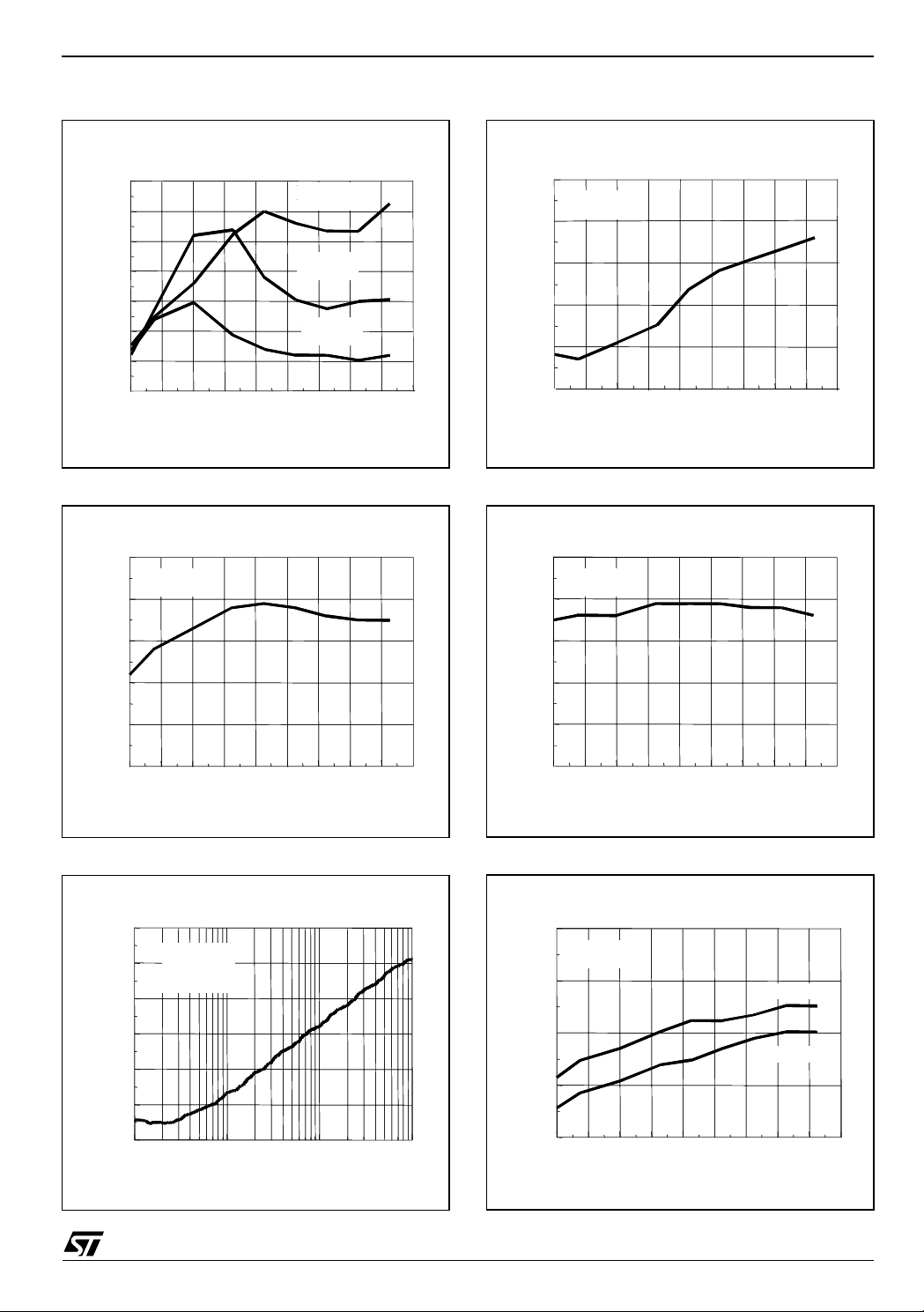
Figure 7 :
120
120
115
115
110
110
105
105
100
100
95
95
Common Mode Rejection (dB)
Common Mode Rejection (dB)
90
90
85
85
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 8 0 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 8 0 100 120 140
Figure 8 :
110
110
100
100
Common Mode Rejection vs. Temperature
Common Mode Rejection vs. Temperature
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 3V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
Vcc = 3V
Vcc = 3V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
Figure 10 :
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
110
110
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
100
100
90
90
80
80
70
70
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
60
60
-40-200 2040 6080100120140
-40-200 2040 6080100120140
Figure 11 :
110
110
Vcc = 5V
Vcc = 5V
Vicm = 0V
Vicm = 0V
100
100
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Temperature
90
90
80
80
70
70
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
60
60
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
Figure 9 :
Power Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Frequency
Power Supply Voltage Rejection vs. Frequency
-20
-20
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
-30
-30
Vicm = 0.7V
Vicm = 0.7V
Gain = 10
Gain = 10
-40
-40
-50
-50
-60
-60
-70
-70
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
Supply Voltage Rejection (dB)
-80
-80
100 1000 10000 100000
100 1000 10000 100000
Frequency (H z)
Frequency (H z)
90
90
80
80
70
70
Supply V oltage Rejection (dB)
Supply V oltage Rejection (dB)
60
60
-40 -20 0 2 0 4 0 60 80 100 120 140
-40 -20 0 2 0 4 0 60 80 100 120 140
Figure 12 :
110
110
100
100
90
90
Open Loop Gain (dB)
Open Loop Gain (dB)
80
80
70
70
-40-200 20406080100120140
-40-200 20406080100120140
Temperatu re (°C)
Temperatu re (°C)
Open Loop Gain vs. Temperature
Open Loop Gain vs. Temperature
Vcc = 1.8V
Vcc = 1.8V
Vicm = 0.9V
Vicm = 0.9V
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°C)
RL = 2 kOhms
RL = 2 kOhms
RL = 600 Ohm s
RL = 600 Ohm s
7/22
 Loading...
Loading...