STMicroelectronics L6599 User Manual
Features
K
■ 50% duty cycle, variable frequency control of
resonant half-bridge
■ High-accuracy oscillator
■ Up to 500kHz operating frequency
■ Two-level OCP: frequency-shift and latched
shutdown
■ Interface with PFC controller
■ Latched disable input
■ Burst-mode operation at light load
■ Input for power-ON/OFF sequencing or
brownout protection
■ Non-linear soft-start for monotonic output
voltage rise
■ 600V-rail compatible high-side gate driver with
integrated bootstrap diode and high dV/dt
immunity
■ -300/800mA high-side and low-side gate
drivers with UVLO pull-down
■ DIP-16, SO-16N packages
L6599
High-voltage resonant controller
DIP-16 SO-16N
Order code
Part number Package Packaging
L6599D SO-16N Tube
L6599DTR SO-16N Tape and reel
L6599N DIP-16 Tube
Applications
■ LCD & PDP TV
■ Desktop PC, entry-level server
■ Telecom SMPS
■ AC-DC adapter, open frame SMPS
Block diagram
Vcc
DIS
STBY 5
RFmin
Css
CF
8
1.85V
1.25V
4
1
3
DISABLE
+
-
+
Ifmin
VCO
UVLO
12
DIS
S Q
R
STANDBY
+
2V
-
CONTROL
LOGIC
2
DELAY
17V
UV
DETECTION
UVLO
DEAD
TIME
SYNCHRONOUS
BOOTST RAP DIODE
DRIVING
LOGIC
ISEN_DIS
1.2 5V
6.3V
15
µA
7
LINE
Q S
HVG
DRIVER
LEVEL
SHIFTER
LVG DR IVER
+
-
R
UVLO
-
LINE _OK
+
ISEN_DIS
STANDBY
1.5V
+
-
0.8V
DIS
16
15
14
Vs
11
10
9
July 2006 Rev 2 1/36
6
H.V.
V
BOOT
HVG
OUT
LV G
GND
ISEN
PFC _STOP
C
BOOT
LC T AN
CIRCUIT
www.st.com
36

Contents L6599
Contents
1 Device description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Pin Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1 Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.2 Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3 Typical system block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Electrical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.1 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
5 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
6 Typical electrical performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
7 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.1 Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7.2 Operation at no load or very light load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7.3 Soft-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.4 Current sense, OCP and OLP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.5 Latched shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
7.6 Line sensing function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
7.7 Bootstrap section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7.8 Application example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
9 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2/36

L6599 Device description
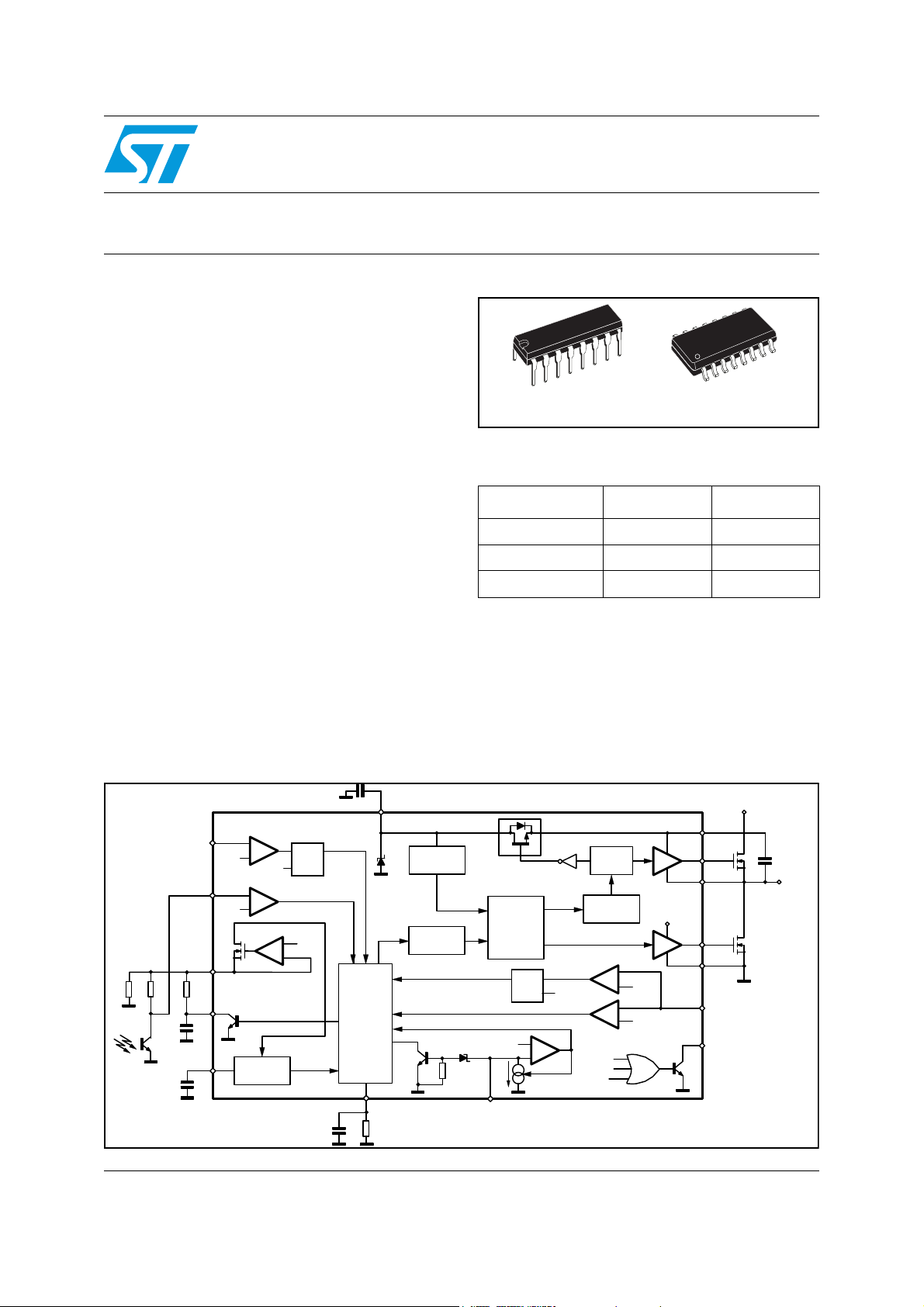
1 Device description
The L6599 is a double-ended controller specific for the resonant half-bridge topology. It
provides 50% complementary duty cycle: the high-side switch and the low-side switch are
driven ON 180° out-of-phase for exactly the same time.
Output voltage regulation is obtained by modulating the operating frequency. A fixed deadtime inserted between the turn-OFF of one switch and the turn-ON of the other one
guarantees soft-switching and enables high-frequency operation.
To drive the high-side switch with the bootstrap approach, the IC incorporates a high-voltage
floating structure able to withstand more than 600V with a synchronous-driven high-voltage
DMOS that replaces the external fast-recovery bootstrap diode.
The IC enables the designer to set the operating frequency range of the converter by means
of an externally programmable oscillator.
At start-up, to prevent uncontrolled inrush current, the switching frequency starts from a
programmable maximum value and progressively decays until it reaches the steady-state
value determined by the control loop. This frequency shift is non linear to minimize output
voltage overshoots; its duration is programmable as well.
The IC can be forced to enter a controlled burst-mode operation at light load, so as to keep
converter's input consumption to a minimum.
IC's functions include a not-latched active-low disable input with current hysteresis useful for
power sequencing or for brownout protection, a current sense input for OCP with frequency
shift and delayed shutdown with automatic restart.
A higher level OCP latches off the IC if the first-level protection is not sufficient to control the
primary current. Their combination offers complete protection against overload and short
circuits. An additional latched disable input (DIS) allows easy implementation of OTP and/or
OVP.
An interface with the PFC controller is provided that enables to switch off the pre-regulator
during fault conditions, such as OCP shutdown and DIS high, or during burst-mode
operation.
3/36
Pin Settings L6599
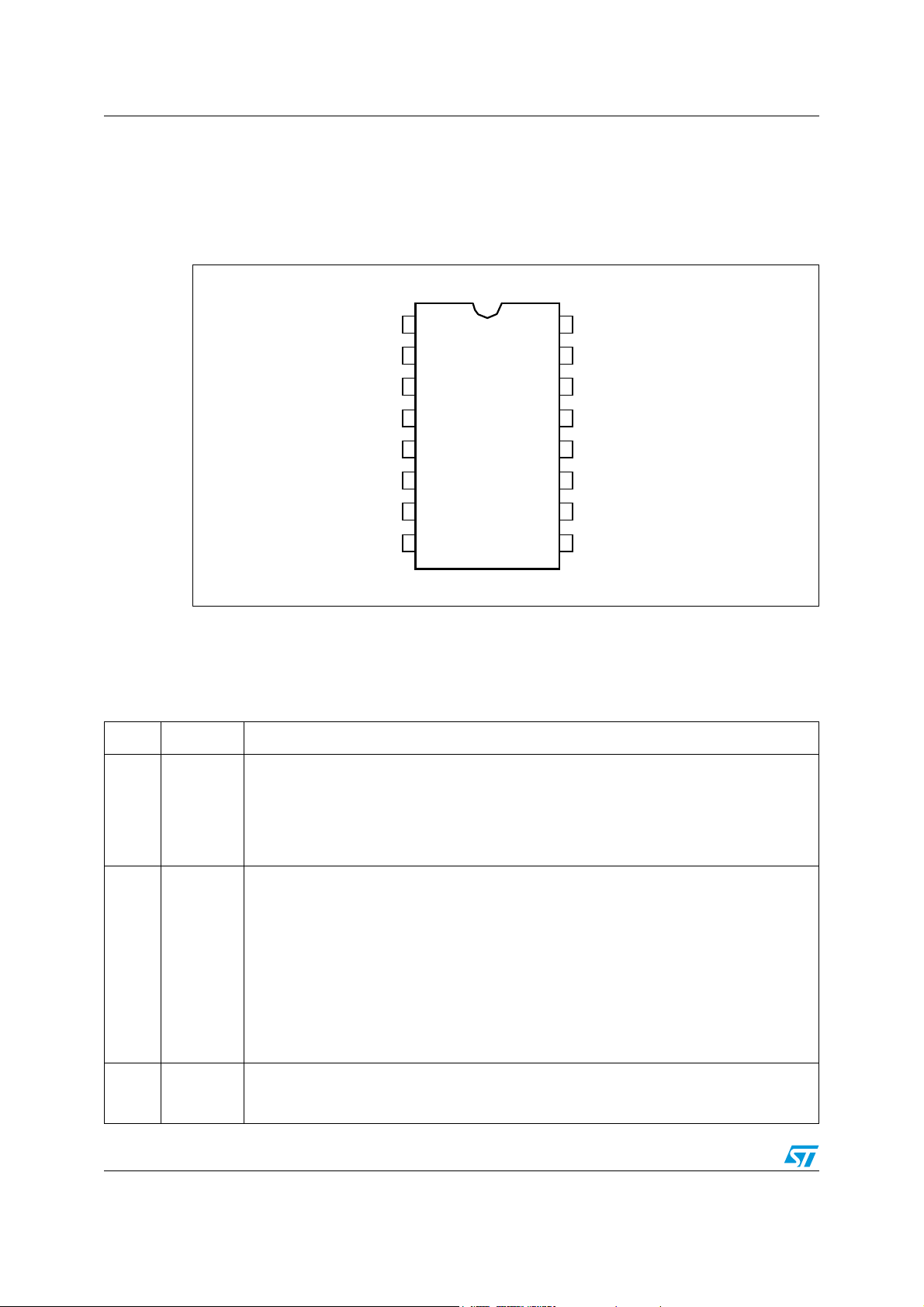
2 Pin Settings
2.1 Connection
Figure 1. Pin Connection (Top view)
Css
DELAY
CF
RFmin
STBY
ISEN
LINE
DIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2.2 Functions
Table 1. Pin functions
N. Name Function
Soft start. This pin connects an external capacitor to GND and a resistor to RFmin (pin 4)
that set both the maximum oscillator frequency and the time constant for the frequency shift
1C
2DELAY
3CF
SS
that occurs as the chip starts up (soft-start). An internal switch discharges this capacitor
every time the chip turns OFF (V
1.5V, DELAY > 3.5V) to make sure it will be soft-started next, and when the voltage on the
current sense pin (ISEN) exceeds 0.8V, as long as it stays above 0.75V.
Delayed shutdown upon overcurrent. A capacitor and a resistor are connected from this pin
to GND to set both the maximum duration of an overcurrent condition before the IC stops
switching and the delay after which the IC restarts switching. Every time the voltage on the
ISEN pin exceeds 0.8V the capacitor is charged by an internal 150µA current generator and
is slowly discharged by the external resistor. If the voltage on the pin reaches 2V, the soft
start capacitor is completely discharged so that the switching frequency is pushed to its
maximum value and the 150µA is kept always on. As the voltage on the pin exceeds 3.5V
the IC stops switching and the internal generator is turned OFF, so that the voltage on the
pin will decay because of the external resistor. The IC will be soft-restarted as the voltage
drops below 0.3V. In this way, under short circuit conditions, the converter will work
intermittently with very low input average power.
Timing capacitor. A capacitor connected from this pin to GND is charged and discharged by
internal current generators programmed by the external network connected to pin 4 (RFmin)
and determines the switching frequency of the converter.
< UVLO, LINE < 1.25V or > 6V, DIS > 1.85V, ISEN >
CC
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
VBOOT
HVG
OUT
N.C.
Vcc
LVG
GND
PFC_STOP
4/36
L6599 Pin Settings
Table 1. Pin functions
Minimum oscillator frequency setting. This pin provides a precise 2V reference and a resistor
connected from this pin to GND defines a current that is used to set the minimum oscillator
frequency. To close the feedback loop that regulates the converter output voltage by
4RFmin
5STBY
6 ISEN
7LINE
8DIS
9PFC_STOP
10 GND
modulating the oscillator frequency, the phototransistor of an optocoupler will be connected
to this pin through a resistor. The value of this resistor will set the maximum operating
frequency. An R-C series connected from this pin to GND sets frequency shift at start-up to
prevent excessive energy inrush (soft-start).
Burst-mode operation threshold. The pin senses some voltage related to the feedback
control, which is compared to an internal reference (1.25V). If the voltage on the pin is lower
than the reference, the IC enters an idle state and its quiescent current is reduced. The chip
restarts switching as the voltage exceeds the reference by 50mV. Soft-start is not invoked.
This function realizes burst-mode operation when the load falls below a level that can be
programmed by properly choosing the resistor connecting the optocoupler to pin RFmin (see
block diagram). Tie the pin to RFmin if burst-mode is not used.
Current sense input. The pin senses the primary current though a sense resistor or a
capacitive divider for lossless sensing. This input is not intended for a cycle-by-cycle control;
hence the voltage signal must be filtered to get average current information. As the voltage
exceeds a 0.8V threshold (with 50mV hysteresis), the soft-start capacitor connected to pin 1
is internally discharged: the frequency increases hence limiting the power throughput. Under
output short circuit, this normally results in a nearly constant peak primary current. This
condition is allowed for a maximum time set at pin 2. If the current keeps on building up
despite this frequency increase, a second comparator referenced at 1.5V latches the device
off and brings its consumption almost to a “before start-up” level. The information is latched
and it is necessary to recycle the supply voltage of the IC to enable it to restart: the latch is
removed as the voltage on the Vcc pin goes below the UVLO threshold. Tie the pin to GND if
the function is not used.
Line sensing input. The pin is to be connected to the high-voltage input bus with a resistor
divider to perform either AC or DC (in systems with PFC) brownout protection. A voltage
below 1.25V shuts down (not latched) the IC, lowers its consumption and discharges the
soft-start capacitor. IC’s operation is re-enabled (soft-started) as the voltage exceeds 1.25V.
The comparator is provided with current hysteresis: an internal 15µA current generator is ON
as long as the voltage applied at the pin is below 1.25V and is OFF if this value is exceeded.
Bypass the pin with a capacitor to GND to reduce noise pick-up. The voltage on the pin is
top-limited by an internal zener. Activating the zener causes the IC to shut down (not
latched). Bias the pin between 1.25 and 6V if the function is not used.
Latched device shutdown. Internally the pin connects a comparator that, when the voltage
on the pin exceeds 1.85V, shuts the IC down and brings its consumption almost to a “before
start-up” level. The information is latched and it is necessary to recycle the supply voltage of
the IC to enable it to restart: the latch is removed as the voltage on the V
the UVLO threshold. Tie the pin to GND if the function is not used.
Open-drain ON/OFF control of PFC controller. This pin, normally open, is intended for
stopping the PFC controller, for protection purpose or during burst-mode operation. It goes
low when the IC is shut down by DIS > 1.85V, ISEN > 1.5V, LINE > 6V and STBY < 1.25V.
The pin is pulled low also when the voltage on pin DELAY exceeds 2V and goes back open
as the voltage falls below 0.3V. During UVLO, it is open. Leave the pin unconnected if not
used.
Chip ground. Current return for both the low-side gate-drive current and the bias current of
the IC. All of the ground connections of the bias components should be tied to a track going
to this pin and kept separate from any pulsed current return.
pin goes below
CC
5/36
Typical system block diagram L6599
Table 1. Pin functions
Low-side gate-drive output. The driver is capable of 0.3A min. source and 0.8A min. sink
11 LVG
12 V
13 N.C.
14 OUT
15 HVG
16 VBOOT
CC
peak current to drive the lower MOSFET of the half-bridge leg. The pin is actively pulled to
GND during UVLO.
Supply Voltage of both the signal part of the IC and the low-side gate driver. Sometimes a
small bypass capacitor (0.1µF typ.) to GND might be useful to get a clean bias voltage for
the signal part of the IC.
High-voltage spacer. The pin is not internally connected to isolate the high-voltage pin and
ease compliance with safety regulations (creepage distance) on the PCB.
High-side gate-drive floating ground. Current return for the high-side gate-drive current.
Layout carefully the connection of this pin to avoid too large spikes below ground.
High-side floating gate-drive output. The driver is capable of 0.3A min. source and 0.8A min.
sink peak current to drive the upper MOSFET of the half-bridge leg. A resistor internally
connected to pin 14 (OUT) ensures that the pin is not floating during UVLO.
High-side gate-drive floating supply Voltage. The bootstrap capacitor connected between
this pin and pin 14 (OUT) is fed by an internal synchronous bootstrap diode driven in-phase
with the low-side gate-drive. This patented structure replaces the normally used external
diode.
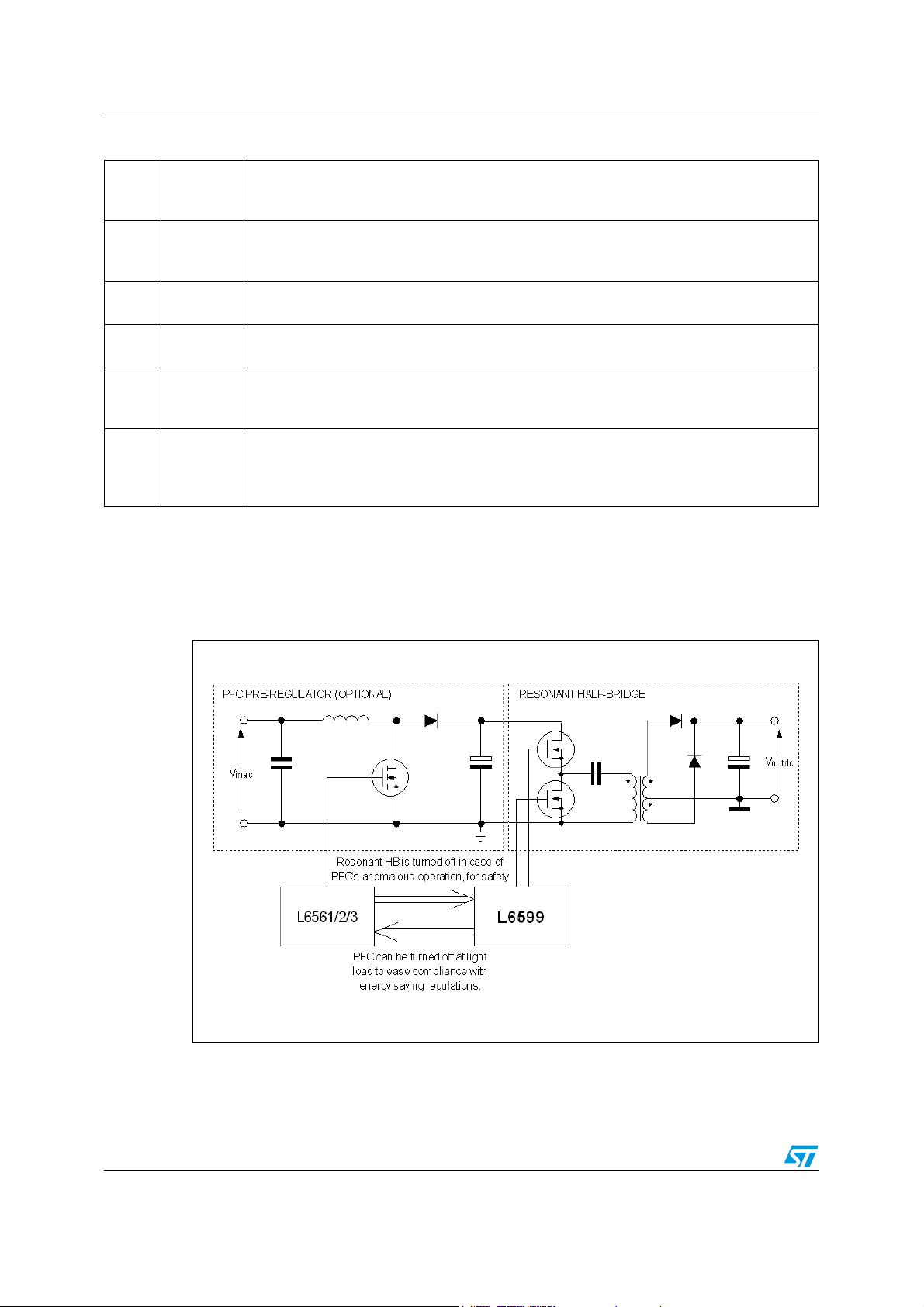
3 Typical system block diagram
Figure 2. Typical system block diagram
6/36

L6599 Electrical data
4 Electrical data
4.1 Maximum ratings
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Pin Parameter Value Unit
V
BOOT
V
OUT
dV
OUT
V
CC
V
PFC_STOP
I
PFC_STOP
V
LINEmax
I
RFmin
/dt
16 Floating supply voltage -1 to 618 V
14 Floating ground voltage
14 Floating ground max. slew rate 50 V/ns
IC Supply voltage (I
12
≤ 25 mA)
CC
9 Maximum voltage (pin open)
9 Maximum sink current (pin low) Self-limited A
7 Maximum pin voltage (Ipin ≤ 1mA) Self-limited V
4 Maximum source current 2 mA
1 to 6, 8 Analog inputs & outputs -0.3 to 5 V
Note: ESD immunity for pins 14, 15 and 16 is guaranteed up to 900V
4.2 Thermal data
Table 3. Thermal data
Symbol Description Value Unit
R
T
P
thJA
STG
T
TOT
Max. thermal resistance junction to ambient (DIP16) 80
Max. thermal resistance junction to ambient (SO16) 120
Storage temperature range -55 to 150 °C
Junction operating temperature range -40 to 150 °C
J
Recommended max. power dissipation @T
Recommended max. power dissipation @T
= 70°C (DIP16)
A
= 50°C (SO16)
A
BOOT
-18
V
-3 to V
Self-limited V
-0.3 to V
CC
V
°C/W
1
W
0.83
7/36
Electrical characteristics L6599
5 Electrical characteristics
TJ = 0 to 105°C, V
R
= 12kΩ; unless otherwise specified.
RFmin
= 15V, V
CC
BOOT
= 15V, C
HVG
= C
= 1nF; CF = 470pF;
LVG
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
IC supply voltage
V
CC
V
CC(ON)
V
CC(OFF)
Hys Hysteresis 2.55 V
V
Z
Supply current
I
start-up
I
q
I
op
I
q
Operating range After device turn-on 8.85 16 V
Turn-ON threshold Voltage rising 10 10.7 11.4 V
Turn-OFF threshold Voltage falling 7.45 8.15 8.85 V
VCC clamp voltage
Start-up current
Quiescent current
Operating current
Residual consumption
Iclamp = 10mA 16 17 17.9 V
Before device turn-ON
= V
V
CC
Device ON, V
CC(ON)
- 0.2V
STBY
= 1V
Device ON,
V
= V
STBY
V
DIS
> 3.5V or V
or V
RFmin
> 1.85V or V
LINE
= V
LINE
clamp
DELAY
< 1.25 V
200 250 µA
1.5 2 mA
3.5 5 mA
300 400 µA
High-side floating gate-drive supply
V
pin leakage
I
LKBOOT
I
LKOUT
r
DS(on)
BOOT
current
OUT pin leakage current
Synchronous bootstrap
diode ON-resistance
V
BOOT
V
OUT
V
LVG
Overcurrent comparator
I
ISEN
t
V
ISENx
LEB
Input bias current
Leading edge blanking
Frequency shift
threshold
V
ISEN
After V
low-to-high transition
Voltage rising
Hysteresis Voltage falling 50 mV
V
ISENdis
td
(H-L)
Latch OFF threshold
Voltage rising
Delay to output 300 400 ns
8/36
= 580V
= 562V
= High
= 0 to V
HVG
ISENdis
and V
(1)
(1)
LVG
5 µA
5 µA
150 Ω
-1 µA
250 ns
0.76 0.8 0.84 V
1.44 1.5 1.56 V
L6599 Electrical characteristics
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
Line sensing
Voltage rising or falling
(1)
VCC > 5V, V
I
= 1mA
LINE
LINE
= 0.3V
1.2 1.25 1.3 V
12 15 18 µA
6 8 V
I
V
V
th
Hyst
clamp
Threshold voltage
Current hysteresis
Clamp level
DIS function
I
DIS
V
Input bias current
th
Disable threshold
= 0 to Vth
V
DIS
Voltage rising
(1)
1.77 1.85 1.93 V
Oscillator
D Output duty cycle Both HVG and LVG 48 50 52 %
58.2 60 61.8
f
osc
Oscillation frequency
RFmin
= 2.7 kΩ
240 250 260
R
Maximum
recommended
V
V
V
RF
T
CFp
CFv
REF
K
D
M
MIN
Dead-time Between HVG and LVG 0.2 0.3 0.4 µs
Peak value 3.9 V
Valley value 0.9 V
Voltage reference at
pin 4
(1)
1.92 2 2.08 V
Current mirroring ratio 1 A/A
Timing resistor range 1 100 kΩ
-1 µA
kHz
500 kHz
PFC_STOP function
I
leak
V
High level leakage
current
L
Low saturation level
V
PFC_STOP
V
DIS
I
PFC_STOP
V
DIS
= 0V
= 2V
= VCC,
=1mA,
1 µA
0.2 V
Soft-start function
I
leak
R Discharge resistance
Open-state current V(Css) = 2V 0.5 µA
V
ISEN
> V
ISENx
120 Ω
Standby function
= 0 to Vth
I
DIS
V
Input Bias Current
th
Disable threshold
V
DIS
Voltage falling
(1)
-1 µA
1.2 1.25 1.3 V
Hys Hysteresis Voltage rising 50 mV
9/36
Electrical characteristics L6599
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
Delayed shutdown function
I
leak
I
CHARGE
Vth
Open-state current V(DELAY) = 0 0.5 µA
Charge current
Threshold for forced
1
V
V
Voltage rising
DELAY
ISEN
= 1V,
= 0.85V
operation at max.
frequency
Vth
Vth
Shutdown threshold
2
Restart threshold
3
Voltage rising
Voltage falling
Low - side gate driver (voltages referred to GND)
= 200mA
V
LVG L
V
LVG H
I
sourcepk
I
sinkpk
t
f
t
r
Output low voltage
Output high voltage
Peak source current -0.3 A
Peak sink current 0.8 A
Fall time 30 ns
Rise time 60 ns
UVLO saturation
I
sink
I
source
V
CC
I
sink
= 5mA
= 0 to V
= 2mA
High-side gate driver (voltages referred to OUT)
(1)
(1)
(1)
CC(ON)
100 150 200 µA
1.92 2 2.08 V
3.3 3.5 3.7 V
0.25 0.3 0.35 V
1.5 V
12.8 13.3 V
,
1.1 V
V
HVGL
V
HVGH
I
sourcepk
I
sinkpk
t
f
t
r
Output low voltage
Output high voltage
Peak source current -0.3 A
Peak sink current 0.8 A
Fall time 30 ns
Rise time 60 ns
I
sink
I
source
HVG-OUT pull-down 25 kΩ
1. Values traking each other
10/36
= 200 mA
= 5 mA
1.5 V
12.8 13.3 V
L6599 Typical electrical performance
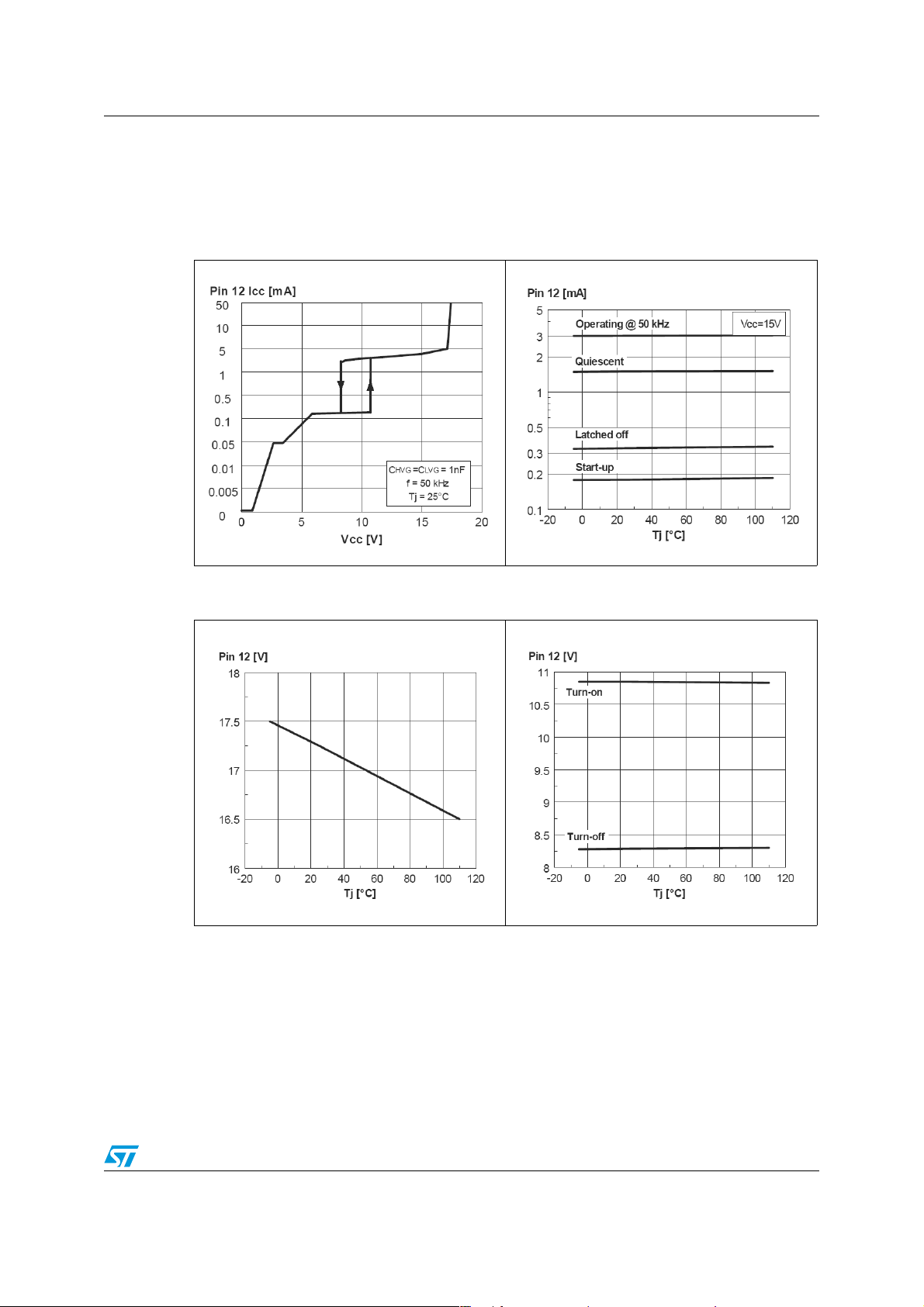
6 Typical electrical performance
Figure 3. Device consumption vs
supply voltage
Figure 5. VCC clamp voltage vs
junction temperature
Figure 4. IC consumption vs
junction temperature
Figure 6. UVLO thresholds vs
junction temperature
11/36
 Loading...
Loading...