TDA7266SA
7W+7W DUAL BRIDGE AMPLIFIER
■ WIDE SUPPLY VOLTAGE RA NGE (3 .5 - 1 8 V)
■ MINIMUM EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
– NO SWR CAPACITOR
– NO BOOTSTRAP
– NO BOUCHEROT CELLS
– INTERNALLY FIXED GAIN
■ STAND-BY & MUTE FUNCTIONS
■ SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
■ THERMAL OVERLOAD PROTECTION
DESCRIPTION
The TDA7266SA is a dual bridge amplifier specially
designed for LCD Monitor, PC Motherboard, TV and
Portable Radio applications.
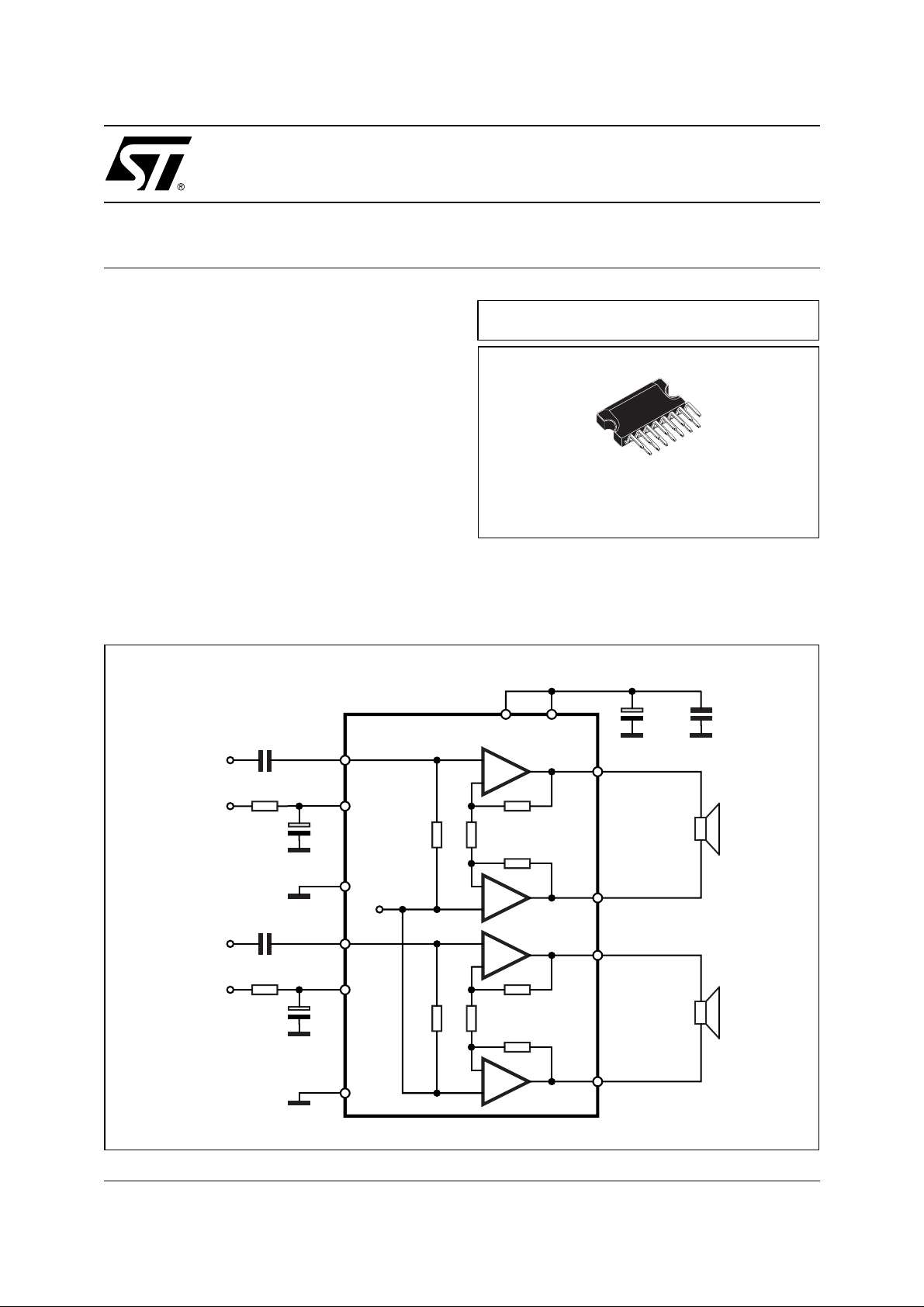
BLOCK AND APPLICATION DIAGRAM
0.22µF
IN1
ST-BY 7
4
TECHNOLOGY BI20II
CLIPWATT15
ORDERING NUMBER: TDA7266SA
Pin to pin compatible with: TDA7266S, TDA7266,
TDA7266M, TDA7266MA, TDA7266B, TDA7297SA
& TDA7297.
V
CC
133
+
-
1
470µF 100nF
OUT1+
IN2
MUTE 6
September 2003
0.22µF
S-GND
PW-GND
9
12
8
Vref
OUT1-
15
14
2
OUT2+
OUT2-
D94AU175B
1/11
-
+
+
-
-
+
TDA7266SA
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
I
O
P
tot
T
op
T
stg, Tj
THERMAL DATA
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th j-case
R
th j-amb
Supply Voltage 20 V
s
Output Peak Current (internally limited) 2 A
Total Power Dissipation (T
= 70°C) 20 W
amb
Operating Temperature 0 to 70 °C
Storage and Junction Temperature -40 to 150 °C
Thermal Resistance Junction-case Typ = 1.8; Max. = 2.5 °C/W
Thermal Resistance Junction-ambient 48 °C/W
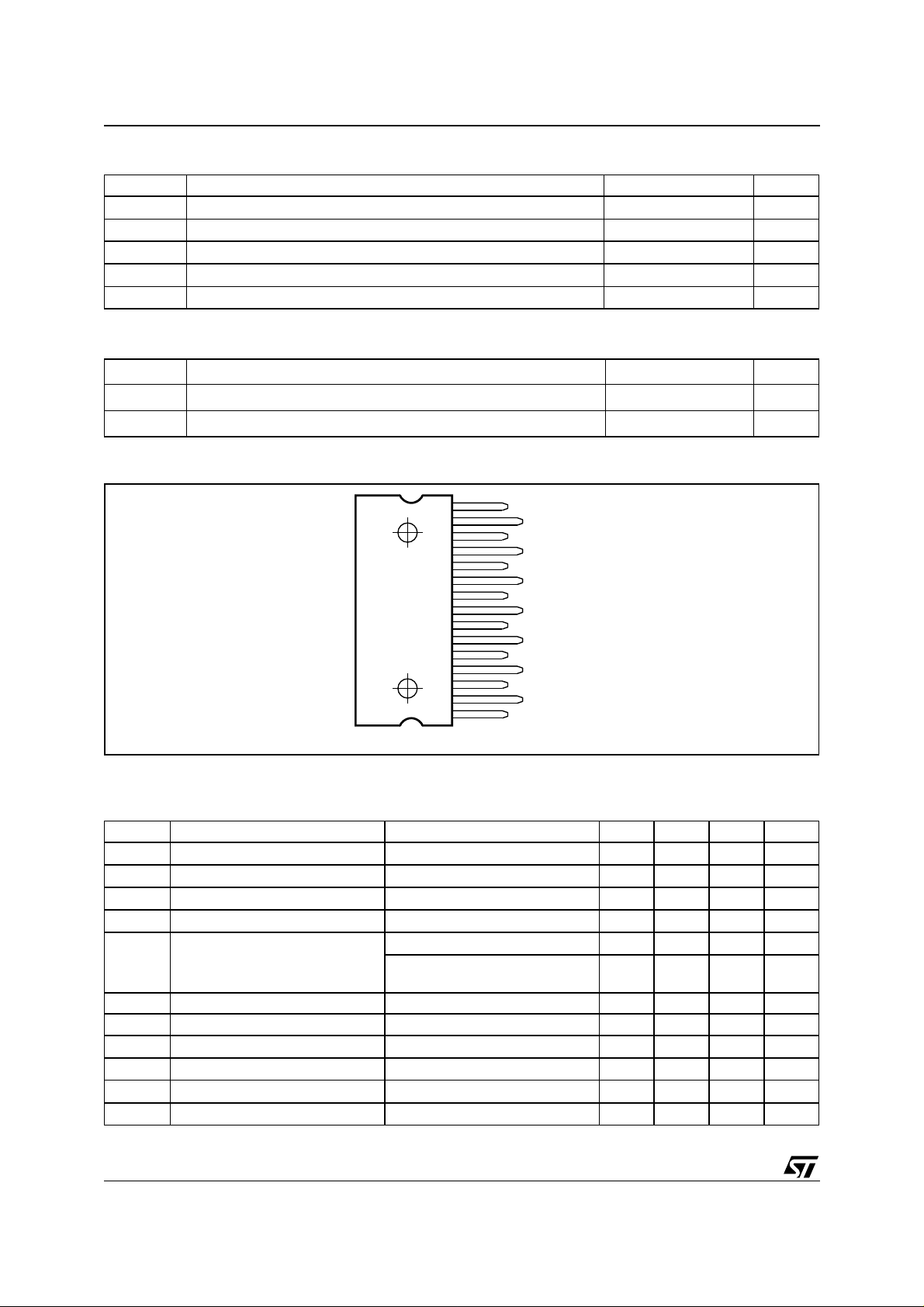
PIN CONNECTION
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTCS
(V
= 11V, RL = 8Ω, f = 1KHz, T
CC
(Top view)
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
D03AU1463
= 25°C unless otherwise specified)
amb
OUT2+
OUT2VCC
IN2
N.C.
N.C.
S-GND
PW-GND
ST-BY
MUTE
N.C.
IN1
V
CC
OUT1OUT1+
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
V
P
THD Total Harmonic Distortion P
Supply Range 3 11 18 V
CC
I
Total Quiescent Current 50 65 mA
q
Output Offset Voltage 120 mV
OS
Output Power THD 10% 6.3 7 W
O
= 1W 0.05 0.2 %
O
= 0.1W to 2W
P
O
1%
f = 100Hz to 15KHz
SVR Supply Voltage Rejection f = 100Hz, VR =0.5V 40 56 dB
CT Crosstalk 46 60 dB
A
MUTE
∆G
T
G
Mute Attenuation 60 80 dB
Thermal Threshold 150 °C
w
Closed Loop Voltage Gain 25 26 27 dB
V
Voltage Gain Matching 0.5 dB
V
2/11
TDA7266SA
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTCS
(V
= 11V, RL = 8Ω, f = 1KHz, T
CC
(continued)
= 25°C unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
R
Input Resistance 25 30 KΩ
i
VT
VT
I
MUTE
ST-BY
e
Mute Threshold for VCC > 6.4V; Vo = -30dB 2.3 2.9 4.1 V
< 6.4V; Vo = -30dB VCC/2-1VCC/2
for V
CC
-075
St-by Threshold 0.8 1.3 1.8 V
ST-BY
St-by Current V6 = GND 100 µA
Total Output Voltage A Curve; f = 20Hzto 20KHz 150 µV
N
VCC/2
-0.5
V
APPLICATION SUGGESTION
STAND-BY AND MUTE FUNCTIONS
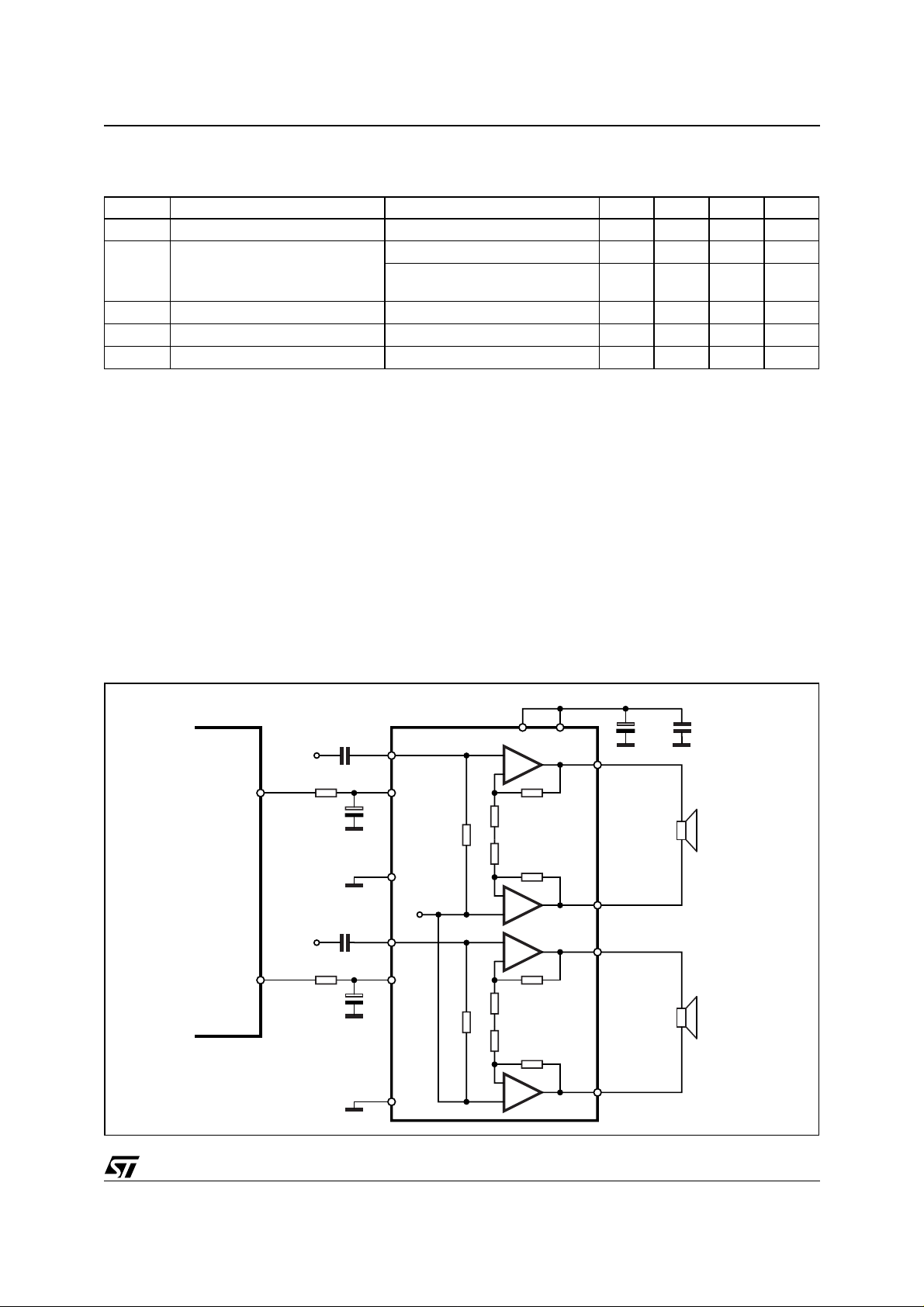
(A) Microprocessor Application
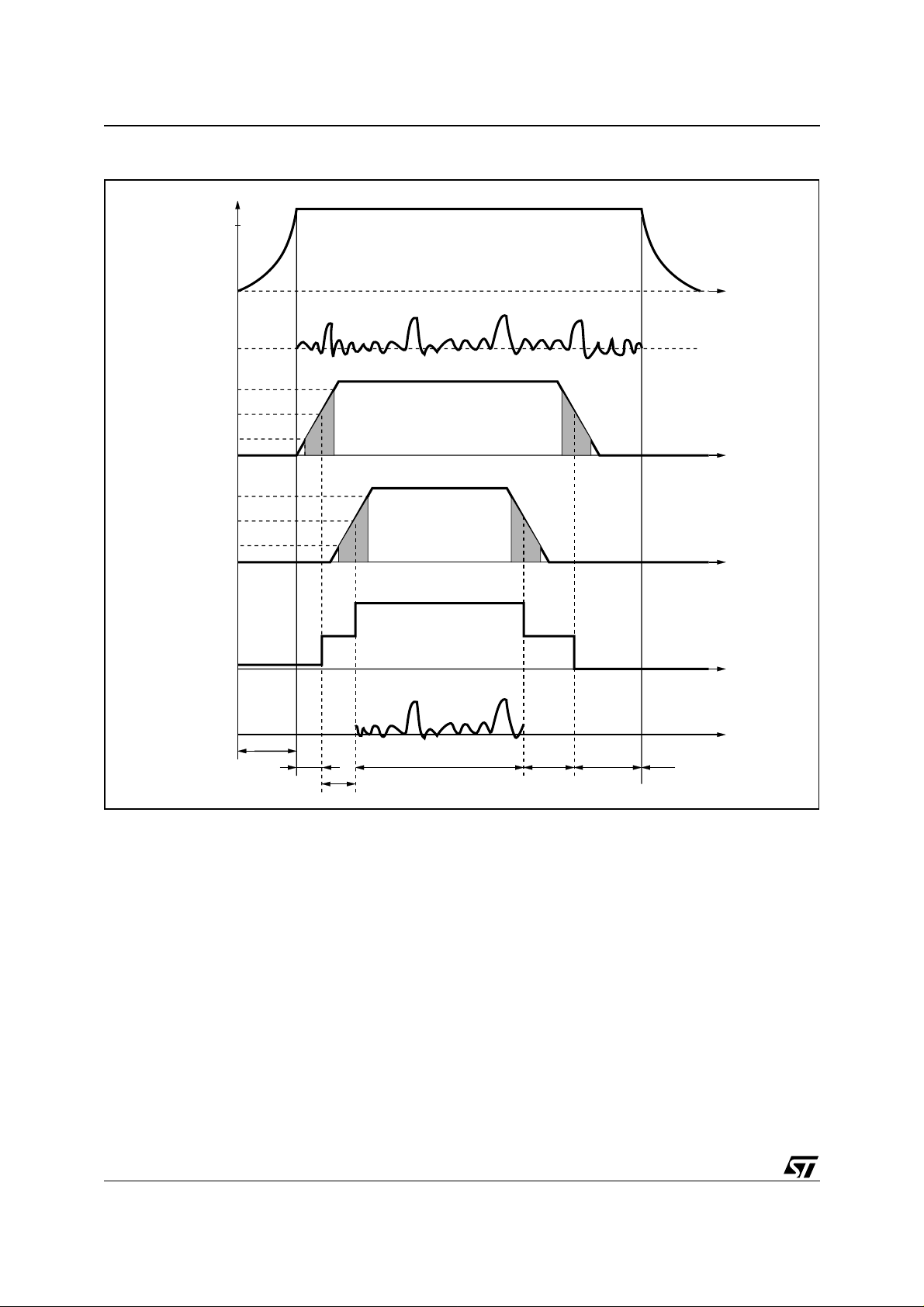
In order to avoid annoying "Pop-Noise" during Turn-On/Off transients, it is necessary to guarantee the right Stby and mute signals sequence. It is quite simple to obtain this function using a microprocessor (Fig. 1 and 2).
At first St-by signal (from
µ
P) goes high and the voltage across the St-by terminal (Pin 7) starts to increase exponentially. The external RC network is intended to turn-on slowly the biasing circuits of the amplifier, this to
avoid "POP" and "CLICK" on the outputs.
When this voltage reaches the St-by threshold level, the amplifier is switched-on and the external capacitors in
series to the input terminals (C3, C53) start to charge.
It's necessary to mantain the mute signal low until the capacitors are fully charged, this to avoid that the device
goes in play mode causing a loud "Pop Noise" on the speakers.
A delay of 100-200ms between St-by and mute signals is suitable for a proper operation.
Figure 1. Microprocessor Application
C1 0.22µF
IN1
R1 10K
ST-BY
C2
10µF
µP
IN2
MUTE
S-GND
C3 0.22µF
R2 10K
C4
1µF
PW-GND
V
CC
4
7
9
Vref
12
6
8
+
+
+
+
133
1
-
-
-
-
2
15
14
C5
470µFC6100nF
OUT1+
OUT1-
OUT2+
OUT2-
D95AU258A
3/11
TDA7266SA
Figure 2. Microprocessor Dri ving Sig nals
+VS(V)
V
IN
(mV)
V
ST-BY
pin 7
1.8
1.3
0.8
V
MUTE
pin 6
4.1
2.9
2.3
I
q
(mA)
V
OUT
(V)
OFF
ST-BY
PLAY MUTE ST-BY
MUTE
OFF
D96AU259mod
B) Low Cost Application
In low cost applications where the µP is not present, the suggested circuit is shown in fig.3.
The St-by and mute terminals are tied together and they are connected to the supply l ine via an external v oltage
divider.
The device is switched-on/off from the supply line and the external capacitor C4 is intended to delay the St-by
and mute threshold exceeding, avoiding "Popping" problems.
4/11

Figure 3. Stand-alone low-cost Application
TDA7266SA
V
CC
R1
47K
R2
47K
C4
10µF
IN1
C3 0.22µF
C5 0.22µF
IN2
PW-GND
ST-BY
S-GND
MUTE
4
7
9
12
6
8
Vref
133
+
1
470µFC2100nF
OUT1+
-
C1
OUT1-
-
2
+
+
15
OUT2+
-
-
14
OUT2-
+
D95AU260A
Figure 4. Disto rti on v s Frequency Figure 5. Gain vs Frequency
THD(%)
10
Vcc = 11 V
1
0.1
0.010
Rl = 8 ohm
Pou t = 100mW
Pout = 2W
100 1k 10k 20k
fr equency (H z)
Leve l (d Br )
5.0000
4.0000
3.0000
2.0000
1.0000
0.0
-1.000
-2.000
-3.000
-4.000
-5.000
Vcc = 11V
Rl = 8 ohm
Pout = 1 W
10 100 1k 10k 100k
frequency (Hz)
5/11

TDA7266SA
Fig u re 6. M ute Attenuation vs Vpin.8
At tenua t ion ( dB )
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
11.522.533.544.55
Vpin .6(V)
Figure 7. Sta nd- By attenuati on vs Vpin 9
At t e nua t ion ( dB )
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1. 2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4
Vpin.7 (V)
Figure 8. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Iq (mA)
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
3456789101112131415161718
Vsupply(V)
6/11

Figure 9. PC Board Component Layout
Figure 10. Evaluation Board Top Layer Layout
TDA7266SA
Figure 11. Evaluation Board Bottom Layer Layout
7/11

TDA7266SA
HEAT SINK DIMENSIONING:
In order to avoid the thermal protection intervention, that is placed approximati vely at Tj = 150°C, it is important
the dimensioning of the Heat Sinker R
The parameters that influence the dimensioning are:
– Maximum dissipated powe r for the device (P
– Max thermal resistance Junction to case (R
– Max. ambient temperature T
amb max
– Quiescent current Iq (mA)
Example:
= 11V, R
V
CC
= (N° channels) ·
P
dmax
= 2 · ( 3.0 ) + 0.5 = 6.5 W
P
dmax
(Heat Sinker)
= 8ohm, R
load
R
Th c-a
= 2.5 °C/W , T
Th j-c
2
V
cc
-------------------------- - I
R
2
load
--------------
⋅
Π
2
150 T
–
----------------------------------------- R
P
d max
Th
qVcc
amb max
(°C/W).
⋅+
–
Th j-c
dmax
)
Th j-c
amb max
)
= 50°C
150 50–
---------------------- 2.5– 12.8°C/W===
6.5
In figure 12 is shown the Power derating curve for the device.
Figure 12. Power derating curve
25
25
20
20
(a)
15
15
(b)
(c)
(c)
(b)
Tamb (°C)
Tamb (°C)
Pd (W)
Pd (W)
10
10
5
5
0
0
0 40 80 120 160
0 40 80 120 160
(a)
a) Infinite Heatsink
a) Infinite Heatsink
b) 7 °C/ W
b) 7 °C/ W
c) 10 °C/ W
c) 10 °C/ W
8/11
TDA7266SA
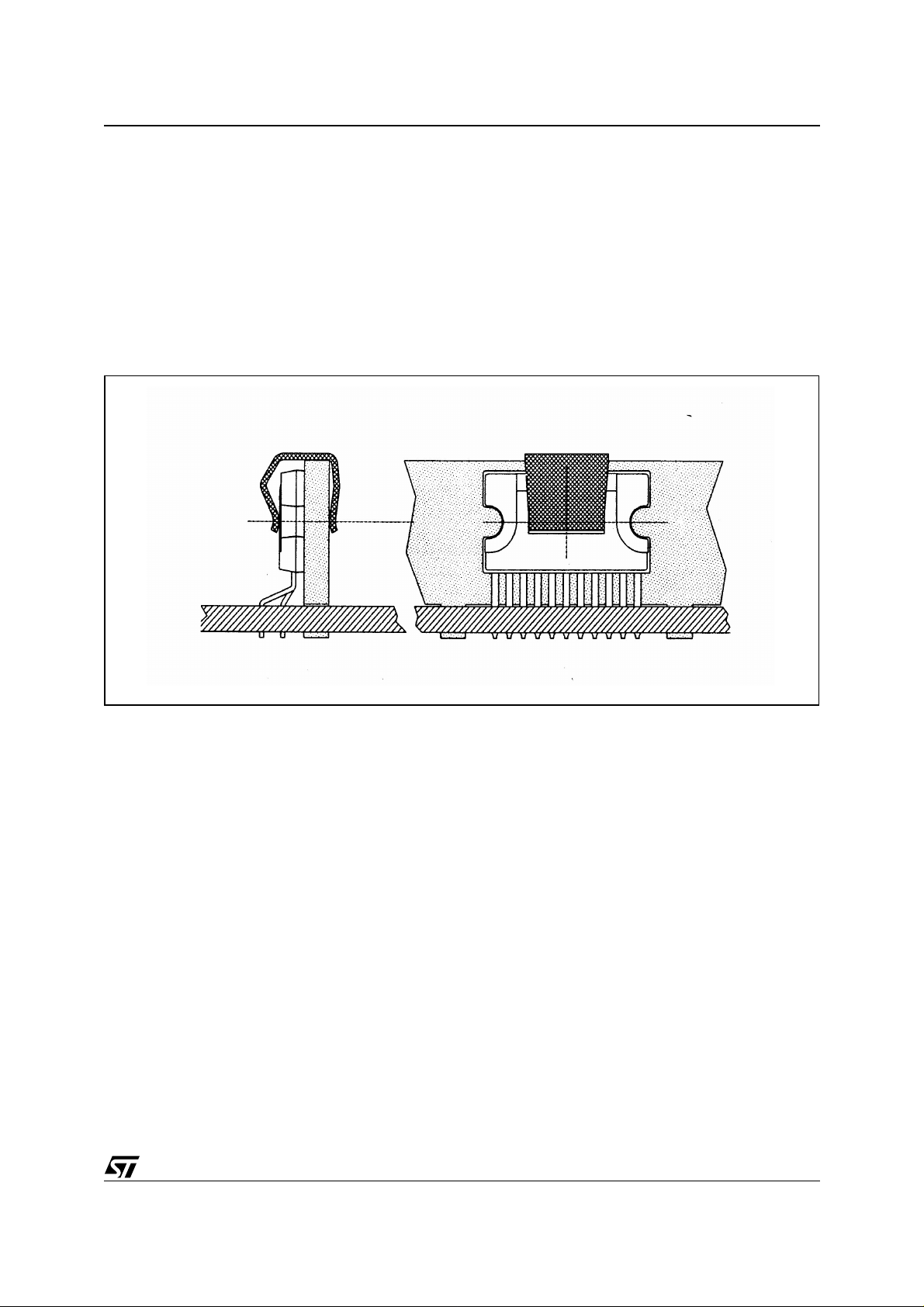
Clipwatt Assembling Suggestions
The suggested mounting method of Clipwatt on external heat sink, requires the use of a clip placed as much
as possible in the plastic body center, as indicated in the example of figure 13.
A thermal grease can be used in order to reduce the additio nal thermal resistance of the contact betw een package and heatsink.
A pressing force of 7 - 10 Kg gives a good contact and the clip mus t be designed in order to avoid a maxi mum
contact pressure of 15 Kg/mm2 between it and the plastic body case.
As example , if a 15Kg force is applied by the clip on the package , the clip must have a contact area of 1mm2
at least.
Figure 13. Example of right placement of the clip
9/11

TDA7266SA
DIM.
mm inch
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 3.2 0.126
B 1.05 0.041
C 0.15 0.006
D 1.55 0.061
E 0.49 0.55 0.019 0.022
F 0.67 0.73 0.026 0.029
G 1.14 1.27 1.4 0.045 0.050 0.055
G1 17.57 17.78 17.91 0.692 0.700 0.705
H1 12 0.480
H2 18.6 0.732
H3 19.85 0.781
L 17.95 0.707
L1 14.45 0.569
L2 10.7 11 11.2 0.421 0.433 0.441
L3 5.5 0.217
M 2.54 0.100
M1 2.54 0.100
OUTLINE AN D
MECHAN ICAL DATA
Weight:
1.92gr
Clipwatt15
10/11
0044538

TDA7266SA
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implic ation or otherwise under any patent or patent r i ght s of STMi croelectr oni cs. Spec i fications mentioned i n this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics product s are not
authorized for use as cri tical comp onents in lif e support devi ces or systems without express written approva l of STMicroel ectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectr oni cs.
All other n am es are the property of th ei r respectiv e owners
© 2003 STMi croelectronics - All rights reserved
Australi a - B elgium - Brazil - Canada - China - C zech Republi c - Finland - F rance - Germ any - Hong Kong - India - Is rael - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
www.st.com
11/11
 Loading...
Loading...