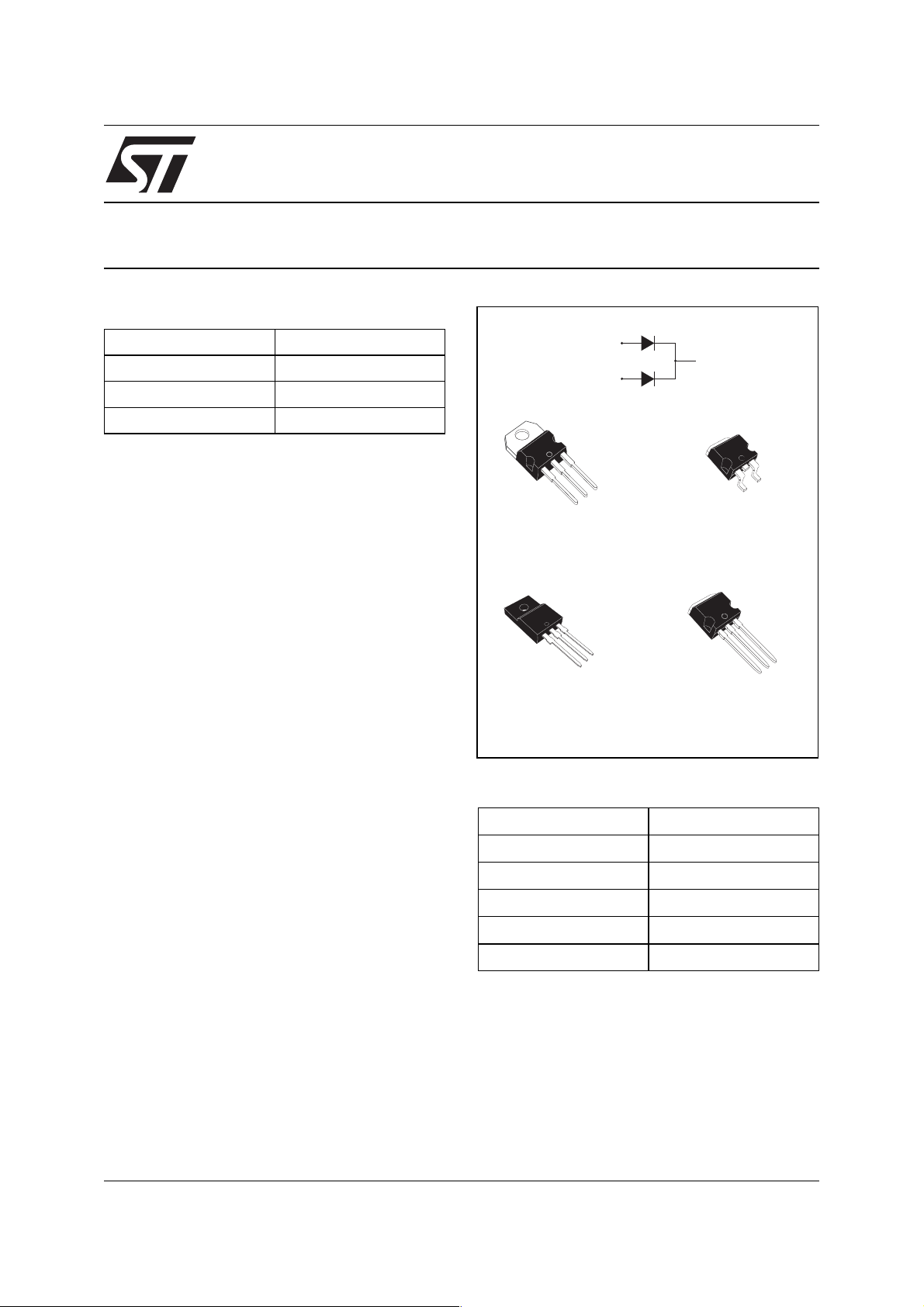
®
HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SCHOTTKY RECTIFIER
Table 1: Main Product Characteristics
V
V
F
I
F(AV)
RRM
T
j
(max)
2 x 10 A
170 V
175°C
0.75 V
STPS20170C
A1
K
A2
K
K
Features
■ High reverse voltage
■ High junction temperature capability
■ Avalanche specification with derating curves
Benefits
■ Can challenge bipolar ultrafast diodes with
better dynamic characteristics.
Description
Dual center tap Schottky rectifier diode su ited for
high frequency switched mode power supplies.
A2
K
A1
TO-220AB
STPS20170CT
A2
K
A1
TO-220FPAB
STPS20170CFP
D2PAK
STPS20170CG
K
2
I
STPS20170CR
Table 2: Order Codes
Part Numbers Marking
STPS20170CT STPS20170CT
STPS20170CFP STPS20170CFP
STPS20170CR STPS20170CR
A1
PAK
A2
A2
K
A1
June 2005
STPS20170CG STPS20170CG
STPS20170CG-TR STPS20170CG
REV. 2
1/8

STPS20170C
d
-
Table 3: Absolute Ratings (limiting values, per diod e)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
P
ARM
T
T
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage 10000 V/µs
Ptot
--------------
* : thermal runaway condition for a diode on its own heatsink
dTj
Table 4: Thermal Parameters
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 170 V
RMS forward voltage 30 A
TO-220AB /
Average forward current
2
PAK / I2PAK
D
δ = 0.5
TO-220FPAB
Surge non repetitive forward current
Repetitive peak avalanche po wer
Storage temperature range -65 to + 175 °C
stg
Maximum operating junction temperature * 175 °C
j
1
------------------------- -
<
Rth j a–()
= 155°C
T
c
Per diode
Per device
= 135°C
T
c
t
= 10ms sinusoidal
p
t
= 1µs Tj = 25°C
p
Per diode
Per device
6700 W
10
20
10
20
180 A
A
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
TO-220AB / D
R
th(j-c)
Junction to case
TO-220FPAB
R
th(c)
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously:
∆ Tj(diode 1) = P(diode 1) x R
th(j-c)
TO-220AB / D2PAK / I2PAK
TO-220FPAB 2.5
(Per diode) + P(diode 2) x R
2
PAK / I2PAK
th(c)
Per diode
Total
Per diode
Total
Coupling
2.2
1.3
4.5
3.5
0.3
°C/W
Table 5: Static Electrical Characteristics (per diode)
Symbol Parameter Tests conditions Min. Typ Max. Unit
T
= 25°C
*
I
R
V
F
Pulse test: * tp = 5 ms, δ < 2%
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation: P = 0.64 x I
Reverse leakage current
**
Forward voltage drop
** tp = 380 µs,
δ < 2%
j
= 125°C
T
j
= 25°C
T
j
= 125°C
T
j
= 25°C
T
j
= 125°C
T
j
V
R
I
F
I
F
= V
= 10A
= 20A
F(AV)
RRM
+ 0.011 I
0.69 0.75
0.79 0.86
F2(RMS)
15 µA
15 mA
0.90
V
0.99
2/8
STPS20170C
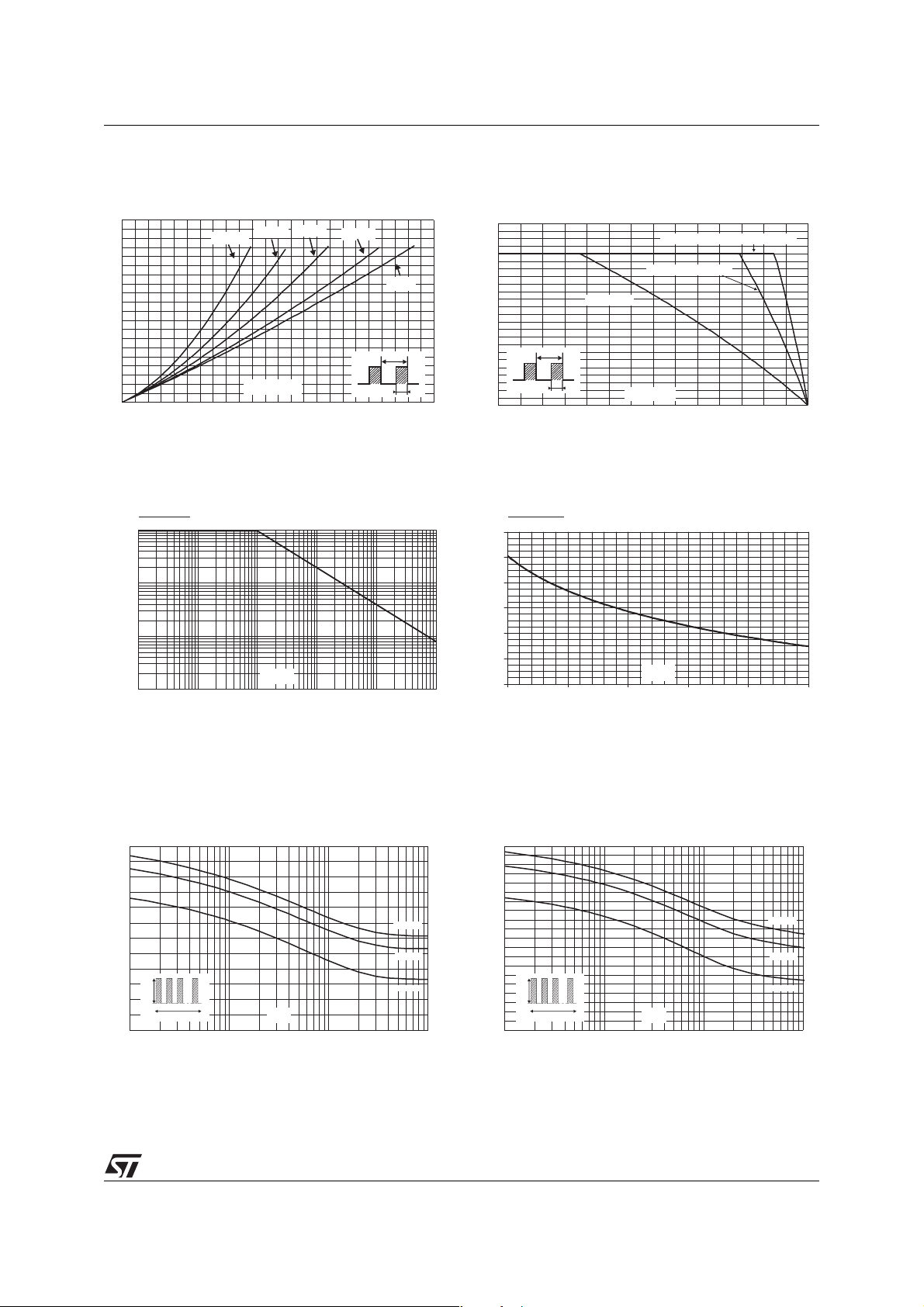
Figure 1: Average forward power dissipation
versus average forward current (per diode)
P (W)
F(AV)
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0123456789101112
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
I (A)
F(AV)
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 3: Normalized avalanche power
derating versus pulse duration
P(t)
ARM p
P (1µs)
ARM
1
0.1
0.01
t (µs)
0.001
0.10.01 1
p
10 100 1000
Figure 2: Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (δ = 0.5, per diode)
I (A)
F(AV)
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
=tp/T
1
δ
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
R =15°C/W
th(j-a)
T
tp
R=R
th(j-a) th(j-c)
T (°C)
amb
R=R
th(j-a) th(j-c)
(TO-220FPAB)
22
(TO-220AB,I PAK and D PAK)
Figure 4: Normalized avalanche power
derating versus junction temperature
P(t)
ARM p
P (25°C)
ARM
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
25 50 75 100 125 150
T (°C)
j
Figure 5: Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration (maximum
2
values, per diode) (TO-220AB, D
I (A)
M
150
125
100
75
50
IM
25
0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
t
δ
=0.5
t(s)
PAK, I2PAK)
T =50°C
C
T =75°C
C
T =125°C
C
Figure 6: Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration (maximum
values, per diode) (TO-220FPAB)
I (A)
M
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
IM
20
10
0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
t
δ
=0.5
t(s)
T =50°C
C
T =75°C
C
T =125°C
C
3/8

STPS20170C
Figure 7: Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to case versus pulse
duration
Z/R
th(j-c) th(j-c)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
Single pulse
0.1
0.0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
22
(TO-220AB,I PAK and D PAK)
(TO-220FPAB)
t (s)
p
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
Figure 9: Junction capacitance versus reverse
voltage applied (typical values, per diode)
C(pF)
1000
100
F=1MHz
V =30mV
OSC RMS
T=25°C
j
Figure 8: Reverse leakage current versus
reverse voltage applied (typical values, per
diode)
I (µA)
R
1.E+05
1.E+04
1.E+03
1.E+02
1.E+01
1.E+00
1.E-01
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
T=175°C
j
T=150°C
j
T=125°C
j
T=100°C
j
T=25°C
j
V (V)
R
Figure 10: Forward voltage drop versus
forward current (per diode)
I (A)
FM
100.0
T=125°C
j
(maximum values)
T=25°C
10.0
T=125°C
j
(typical values)
j
(maximum values)
V (V)
10
1 10 100 1000
R
Figure 11: Thermal resistance junction to ambient versus copper surface under tab (epoxy
2
printed board FR4, Cu = 35µm) (D
R (°C/W)
th(j-a)
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
S(cm²)
PAK)
1.0
V (V)
0.1
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
FM
4/8

Figure 12: D2PAK Package Mechanical Data
m
D
A
L2
E
L
L3
B2
B
G
* FLAT ZONE NO LESS THAN 2m
C2
A1
C
A2
M
R
*
V2
STPS20170C
DIMENSIONS
REF.
A 4.40 4.60 0.173 0.181
A1 2.49 2.69 0.098 0.106
A2 0.03 0.23 0.001 0.009
B 0.70 0.93 0.027 0.037
B2 1.14 1.70 0.045 0.067
C 0.45 0.60 0.017 0.024
C2 1.23 1.36 0.048 0.054
D 8.95 9.35 0.352 0.368
E 10.00 10.40 0.393 0.409
G 4.88 5.28 0.192 0.208
L 15.00 15.85 0.590 0.624
L2 1.27 1.40 0.050 0.055
L3 1.40 1.75 0.055 0.069
M 2.40 3.20 0.094 0.126
R 0.40 typ. 0.016 typ.
V2 0° 8° 0° 8°
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
Figure 13: Foot Print Dimensions (in millimeters)
16.90
10.30
8.90
3.70
5.08
1.30
5/8

STPS20170C
Figure 14: I2PAK Package Mechanical Data
A
L2
E
L1
L
b1
b
e
e1
c2
D
A1
c
DIMENSIONS
REF.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
A 4.40 4.60 0.173 0.181
A1 2.40 2.72 0.094 0.107
b 0.61 0.88 0.024 0.035
b1 1.14 1.70 0.044 0.067
c 0.49 0.70 0.019 0.028
c2 1.23 1.32 0.048 0.052
D 8.95 9.35 0.352 0.368
e 2.40 2.70 0.094 0.106
e1 4.95 5.15 0.195 0.203
E 10 10.40 0.394 0.409
L 13 14 0.512 0.551
L1 3.50 3.93 0.138 0.155
L2 1.27 1.40 0.050 0.055
Figure 15: TO-220FPAB Package Mechanical Data
A
B
Dia
L7
E
L3
L2
L4
G1
H
L6
L5
F1
F2
F
G
D
DIMENSIONS
REF.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
A 4.4 4.6 0.173 0.181
B 2.5 2.7 0.098 0.106
D 2.5 2.75 0.098 0.108
E 0.45 0.70 0.018 0.027
F 0.75 1 0.030 0.039
F1 1.15 1.70 0.045 0.067
F2 1.15 1.70 0.045 0.067
G 4.95 5.20 0.195 0.205
G1 2.4 2.7 0.094 0.106
H 10 10.4 0.393 0.409
L2 16 Typ. 0.63 Typ.
L3 28.6 30.6 1.126 1.205
L4 9.8 10.6 0.386 0.417
L5 2.9 3.6 0.114 0.142
L6 15.9 16.4 0.626 0.646
L7 9.00 9.30 0.354 0.366
Dia. 3.00 3.20 0.118 0.126
6/8

Figure 16: TO-220AB Package Mechanical Data
A
C
L7
D
M
E
L2
F2
F1
H2
Dia
L5
L6
L9
L4
F
G1
G
STPS20170C
DIMENSIONS
REF.
A 4.40 4.60 0.173 0.181
C 1.23 1.32 0.048 0.051
D 2.40 2.72 0.094 0.107
E 0.49 0.70 0.019 0.027
F 0.61 0.88 0.024 0.034
F1 1.14 1.70 0.044 0.066
F2 1.14 1.70 0.044 0.066
G 4.95 5.15 0.194 0.202
G1 2.40 2.70 0.094 0.106
H2 10 10.40 0.393 0.409
L2 16.4 typ. 0.645 typ.
L4 13 14 0.511 0.551
L5 2.65 2.95 0.104 0.116
L6 15.25 15.75 0.600 0.620
L7 6.20 6.60 0.244 0.259
L9 3.50 3.93 0.137 0.154
M 2.6 typ. 0.102 typ .
Diam. 3.75 3.85 0.147 0.151
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
Table 6: Ordering Information
Ordering type Marking Package Weight Base qty
Delivery
mode
STPS20170CT STPS20170CT TO-220AB 2.20 g 50 Tube
STPS20170CFP STPS20170CFP TO-220FPAB 2 g 50 Tube
STPS20170CR STPS20170CR
STPS20170CG STPS20170CG
STPS20170CG-TR STPS20170CG 1000 Tape & reel
■ Epoxy meets UL94, V0
■ Cooling method: by conduction (C)
■ Recommended torque value: 0.8 m.N.
■ Maximum to rque value: 1.0 m.N.
I
D
2
PAK
2
PAK
1.49 g 50 Tube
1.48 g
50 Tube
Table 7: Revision History
Date Revision Description of Changes
Mar-2004 1 First issue.
28-Jul-2005 2
TO-220FPAB, I
2
PAK and D2PAK packages added.
7/8

STPS20170C
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infri ngement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without no tice. This publication supersedes and repl aces all information previously supplied. ST Microelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
8/8
 Loading...
Loading...