Page 1

STMPE2403
24-bit Enhanced port expander with Keypad and PWM controller
Xpander logic
Features
■ 24 GPIOs
■ Operating voltage 1.8V
■ Hardware key pad controller (8*12 matrix ma x)
■ 8 Special Function Key support
■ 3 PWM (8 bit) output for LED brightness control
and blinking
■ Interrupt output (open drain) pin
■ Configurable hotkey feature on each GPIO
■ Ul tr a-l ow St an db y- mo de cu rr ent
■ Package TFBGA - 36 pins 3.6x3.6mm, pitch
0.5mm
Description
TFBGA
The STMPE2403 is a GPIO (General Purpose
Input / Output) port expander able to interface a
Main Digital ASIC via the two-line bidirectional
2
bus (I
C); separate GPIO Expander IC is often
used in Mobile-Multimedia platforms to solve the
problems of the limited amounts of GPIOs usually
available on the Digital Engine.
The STMPE2403 offers great flexibility as each
I/Os is configurable as input, output or specific
functions; it's able to scan a keyboard, also
provides PWM outputs for brightness control in
backlight, rotator decoder interface and GPIO.
This device has been designed very low
quiescent current, and is including a wake up
feature for each I/O, to optimize the power
consumption of the IC.
Potential application of the STMPE2403 includes
portable media player, game console, mobile
phone, smart phone
Table 1. Device summary
Part Number Package Packaging
STMPE2403TBR TFBGA36 Tape and reel
June 2007 Rev 1 1/63
www.st.com
63
Page 2

Contents STMPE2403
Contents
1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Pin settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.1 Pin connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Pin assignment and TFBGA ball location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.3 GPIO Pin functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.4 Pin mapping to TFBGA ( bottom view, balls up) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1 Absolute maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Electrical specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.1 DC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.2 I/O DC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.3 DC input specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4 DC output specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.5 AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 I2C Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1 Start condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.2 Stop condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.3 Acknowledge bit (ACK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.4 Data input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.5 Slave device address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.6 Memory addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.7 Operation modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6.8 General call address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2/63
Page 3

STMPE2403 Contents
7 System controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7.1 Identification register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7.2 System control register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
7.3 System control register 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7.4 States of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.5 Autosleep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.6 Keypress detect in the hibernate mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
8 Clocking system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8.1 Clock source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8.2 Power mode programming sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9 Interrupt system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
9.1 Register map of interrupt system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
9.2 Interrupt Control Register (ICR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.3 Interrupt Enable Mask Register (IER) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
9.4 Interrupt Status Register (ISR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.5 Interrupt Enable GPIO Mask Register (IEGPIOR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.6 Interrupt Status GPIO Register (ISGPIOR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
9.7 Programming sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
10 GPIO controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
10.1 GPIO control registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
10.2 GPIO Alternate Function Register (GPAFR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
10.3 Hot key feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
10.3.1 Programming sequence for Hot Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
10.3.2 Minimum pulse width . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
10.4 MUX Control Register (MCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
10.5 STMPE2401 Pin Compatibility Register (COMPAT2401) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3/63
Page 4

Contents STMPE2403
11 PWM controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
11.1 Registers in the PWM controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
11.2 PWM Control and Status Register (PWMCS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.3 PWM Instruction Channel x (PWMICx) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
11.4 PWM commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
12 Keypad controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
12.1 Keypad configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
12.2 Registers in keypad controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
12.3 KPC_col register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
12.4 KPC_row_msb register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
12.5 KPC_row_lsb register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
12.6 KPC_ctrl_msb register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
12.7 KPC_ctrl_lsb register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
12.8 Data registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
12.8.1 Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.8.2 Using the keypad controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.8.3 Ghost Key Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.8.4 Priority of Key detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
12.8.5 Keypad Wake-Up from sleep and hibernate modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
13 Rotator controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
14 Miscellaneous features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
14.1 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
14.2 Under Voltage Lockout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
14.3 Clock output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
14.4 Crystal oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
15 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
16 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
4/63
Page 5

STMPE2403 Block diagram
1 Block diagram
Figure 1. Block diagram
Keypad
Keypad
INT
INT
Keypad
Controller
Controller
Controller
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
0-7
0-7
0-7
Main FSM
Main FSM
Main FSM
+ PWM
+ PWM
+ PWM
+ Rotator Control
+ Rotator Control
+ Rotator Control
+ GPIO Control
+ GPIO Control
+ GPIO Control
Keypad
Keypad
Keypad
Inputs
Inputs
Inputs
Keypad
Keypad
Keypad
Outputs
Outputs
Outputs
Function
Function
Function
Select
Select
Select
Function
Function
Function
Select
Select
Select
&
&
&
MUX 1, 2
MUX 1, 2
MUX 1, 2
Control
Control
Control
Keypad Input 0-7 /
Keypad Input 0-7 /
Keypad Input 0-7 /
GPIO 0-7
GPIO 0-7
GPIO 0-7
Keypad Output 0-11
Keypad Output 0-11
Keypad Output 0-11
/ GPIO 8-14, 16-20
/ GPIO 8-14, 16-20
/ GPIO 8-14, 16-20
/ Digital MUX 1, 2
/ Digital MUX 1, 2
/ Digital MUX 1, 2
/ Rotator
/ Rotator
/ Rotator
SCLK
SCLK
SDAT
SDAT
I2C
I2C
I2C
Interface
Interface
Interface
A0
A0
A0
A1
A1
A1
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
15
15
15
PWM
PWM
PWM
O/P
O/P
O/P
POR
POR
POR
RC OSC
RC OSC
RC OSC
Clock
Clock
Clock
Controller
Controller
Controller
XTAL2OUTXTAL1INGND
XTAL2OUTXTAL1INGND
XTAL2OUTXTAL1INGND
GPIO 15
GPIO 15
GPIO 15
ADDR0
ADDR0
ADDR0
Trigger I/O
Trigger I/O
Trigger I/O
PWM1,2,3
PWM1,2,3
PWM1,2,3
/ ADDR1
/ ADDR1
/ ADDR1
/ GPIO 21-23
/ GPIO 21-23
/ GPIO 21-23
Reset_N
Reset_N
Reset_N
VCC1
VCC1
VCC1
VCC2
VCC2
VCC2
5/63
Page 6

Pin settings STMPE2403
2 Pin settings
2.1 Pin connection
Figure 2. Pin connection
TFBGA
2.2 Pin assignment and TFBGA ball location
Table 2. Pin assignment
Ball Name Type Description
C3 GND1 -
A6 KP_X0 IO GPIO
C1 Reset_N I External reset input, active LOW
A5 KP_X1 IO GPIO
F1 KP_X2 IO GPIO
F2 KP_X3 IO GPIO
A2 KP_X4 IO GPIO
B3 KP_X5 IO GPIO
A3 KP_X6 IO GPIO
D3 GND2 -
A4 VCC1 - 1.8V Input
6/63
Page 7

STMPE2403 Pin settings
Table 2. Pin assignment (continued)
Ball Name Type Description
B4 KP_X7 IO GPIO
A1 KP_Y5 IO GPIO
B2 KP_Y4 IO GPIO
B5 KP_Y3 IO GPIO
B6 KP_Y2 IO GPIO
C5 KP_Y1 IO GPIO
C6 KP_Y0 IO GPIO
C4 GND3 -
D6 ADDR0 IO GPIO and I2C ADDR 0 (in reset)
D5 KP_Y9 A/IO GPIO/MUX
E6 KP_Y10 A/IO GPIO/MUX
F6 KP_Y11 A/IO GPIO/MUX
E5 PWM3 A/IO GPIO and I2C ADDR 1 (in reset) /MUX
F5 PWM2 A/IO GPIO/MUX
E4 PWM1 A/IO GPIO/MUX
F4 VCC2 - 1.8V Input
D4 GND4 -
F3 INT O Open drain interrupt output pin
E3 KP_Y8 IO GPIO
C2 KP_Y7 IO GPIO
B1 KP_Y6 IO GPIO
E2 SDATA A I2C DATA
E1 SCLK A I2C Clock
D2 XTALIN A XTAL Oscillator or External 32KHz input.
be left floating.
D1 XTALOUT A XTAL Oscillator
7/63
Page 8

Pin settings STMPE2403
2.3 GPIO Pin functions
Table 3. GPIO Pin functions
Name Primary Function Alternate Function 1 Alternate Function 2 Alternate Function 3
KP_X0 GPIO 0 Keypad input 0
KP_X1 GPIO 1 Keypad input 1
KP_X2 GPIO 2 Keypad input 2
KP_X3 GPIO 3 Keypad input 3
KP_X4 GPIO 4 Keypad input 4
KP_X5 GPIO 5 Keypad input 5
KP_X6 GPIO 6 Keypad input 6
KP_X7 GPIO 7 Keypad input 7
KP_Y5 GPIO 13 Keypad Output 5
KP_Y4 GPIO 12 Keypad Output 4
KP_Y3 GPIO 11 Keypad Output 3
KP_Y2 GPIO 10 Keypad Output 2
KP_Y1 GPIO 9 Keypad Output 1
KP_Y0 GPIO 8 Keypad Output 0
ADDR0 GPIO 15
KP_Y9 GPIO 18 Keypad Output 9 Rotator 0 Mux1_In_1
KP_Y10 GPIO 19 Keypad Output 10 Rotator 1 Mux1_In_2
KP_Y11 GPIO 20 Keypad Output 11 Rotator 2 Mux1_Out
PWM3 GPIO 23 Mux2_Out
PWM2 GPIO 22 Mux2_In_2
PWM1 GPIO 21 Mux2_In_1
KP_Y8 GPIO 17 Keypad Output 8 ClkOut
KP_Y7 GPIO 16 Keypad Output 7
KP_Y6 GPIO 14 Keypad Output 6
8/63
Page 9

STMPE2403 Pin settings
2.4 Pin mapping to TFBGA ( bottom view, balls up)
Table 4. Pin mapping to TFBGA ( bottom view, balls up)
ABCDEF
1 KP_Y5 KP_Y6 RESET XTALOUT SCLK KP_X2
2 KP_X4 KP_Y4 KP_Y7 XTALIN SDATA KP_X3
3 KP_X6 KP_X5 GND1 GND2 KP_Y8 INT
4 VCC1 KP_X7 GND3 GND4 PWM-1 VCC2
5 KP_X1 KP_Y3 KP_Y1 KP_Y9 PWM-3 PWM-2
6 KP_X0 KP_Y2 KP_Y0 ADDR0 KP_Y10 KP_Y11
9/63
Page 10
Maximum rating STMPE2403
3 Maximum rating
Stressing the device above the rating listed in the “Absolute Maximum Ratings” table may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE
Program and other relevant quality documents.
3.1 Absolute maximum rating
Table 5. Absolute maximum rating
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CC
V
Input voltage on GPIO pin 2.5 V
IN
V
I2C Input voltage on I2C pin 4.5 V
IN
VESD (HBM) ESD protection on each GPIO pin 2 KV
Supply voltage 2.5 V
3.2 Thermal data
Table 6. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
R
thJA
T
A
T
J
Thermal resistance junction-ambient 100 °C/W
Operating ambient temperature -40 25 85 °C
Operating junction temperature -40 25 125 °C
10/63
Page 11

STMPE2403 Electrical specification
4 Electrical specification
4.1 DC electrical characteristics
Table 7. DC electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
VCC1,2 Supply voltage 1.65 1.8 1.95 V
I
HIBERNATE1
HIBERNATE mode
current
XTALIN not floating
Min. Typ. Max.
Val ue
Unit
15 20 uA
I
HIBERNATE2
I
SLEEP1
I
SLEEP2
Icc
INT
HIBERNATE mode
current
SLEEP mode current
SLEEP mode current
Operating current
(FSM working – No
peripheral activity)
Open drain output
current
XTALIN floating
XTALIN not floating
XTALIN floating
4.2 I/O DC electrical characteristics
The 1.8V I/O complies to the EIA/JEDEC standard JESD8-7.
Table 8. I/O DC electrical characteristic
Symbol Parameter
Vil Low level input voltage
Vih High level input voltage
35 40 uA
55 100 uA
75 120 uA
1.2 1.6 mA
4mA
Val u e
Min. Typ. Max.
0.35*Vcc
0.65*Vcc
= 1.17
= 0.63
Unit
V
V
Vhyst Schmitt trigger hysteresis 0.10 V
11/63
Page 12

Electrical specification STMPE2403
4.3 DC input specification
(1.55V < VDD < 1.95V)
Table 9. DC input specification
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
Min. Typ. Max.
Vol Low level output voltage Iol = 4mA 0.45 V
Val ue
Unit
Voh High level output voltage Ioh = 4mA
Vol_PWM Low level output voltage Iol = 16mA 0.45 V
Voh_PWM High level output voltage Ioh = 16mA
4.4 DC output specification
(1.55V < vdd < 1.95V)
Table 10. DC output specification
Symbol Parameter
Ipu Pull-up current Vi = 0V 15 35 65 uA
Ipd Pull-down current Vi = vdd 14 35 60 uA
Rup Equivalent pull-up resistance Vi = 0V 30 50 103.3 KΩ
Rpd Equivalent pull-down resistance Vi = vdd 32.5 50 110.7 KΩ
Ron_1 Ron when the MUX is ON Vsignal = 0V 5 10 Ω
Ron_2 Ron when the MUX is ON Vsignal = 0.9V 5 20 Ω
Ron_3 Ron when the MUX is ON Vsignal = 1.8V 10 10 Ω
Test
conditions
Vcc - 0.45
= 1.35
Vcc - 0.45
= 1.35
Val ue
Min. Typ. Max.
V
V
Unit
Ron Ron when the MUX is ON Vsignal < 1.8V 20 35 Ω
Note: Pull-up and Pull-down characteristics
4.5 AC characteristics
Table 11. AC characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Int_32KHz Internally generated 32KHz clock 22 28 41.6 KHz
12/63
Val ue
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
Page 13

STMPE2403 Register map
5 Register map
All registers have the size of 8-bit. For each of the module, their registers are residing within
the given address range.
Table 12. Register map
Address Module registers Description
0x00 – 0x07
0x80 – 0x81
0x10 – 0x1F
0x30 – 0x37 PWM controller module PWM Controller register range Yes
0x38 – 0x3F PWM Controller register range No
Clock and power
Manager module
Interrupt controller
module
Clock and Power Manager register
range.
Interrupt Controller register range Yes
Auto-Increment
(during read/write)
Ye s
0x60 – 0x6F
0x70 – 0x77
0x82 – 0xBF GPIO Controller Module GPIO Controller register range Yes
Keypad controller
module
Rotator controller
module
Keypad Controller register range Yes
Rotator Controller register range Yes
13/63
Page 14

I2C Interface STMPE2403
6 I2C Interface
The features that are supported by the I2C interface are as below:
2
● I
C Slave device
● Operates at 1.8V
● Compliant to Philip I
● Supports Standard (up to 100kbps) and Fast (up to 400kbps) modes.
● 7-bit and 10-bit device addressing modes
● General Call
● Start/Restart/Stop
● Address up to 4 STMPE2403 devices via I
The address is selected by the state of two pins. The state of the pins will be read upon
reset and then the pins can be configured for normal operation. The pins will have a pull-up
or down to set the address. The I
access the registers in the STMPE2403.
6.1 Start condition
2
C specification version 2.1
2
C
2
C interface module allows the connected host system to
A Start condition is identified by a falling edge of SDATA while SCLK is stable at high state.
A Start condition must precede any data/command transfer. The device continuously
monitors for a Start condition and will not respond to any transaction unless one is
encountered.
6.2 Stop condition
A Stop condition is identified by a rising edge of SDATA while SCLK is stable at high state.
A Stop condition terminates communication between the slave device and bus master. A
read command that is followed by NoAck can be followed by a Stop condition to force the
slave device into idle mode. When the slave device is in idle mode, it is ready to receive the
2
next I
C transaction. A Stop condition at the end of a write command stops the write
operation to registers.
6.3 Acknowledge bit (ACK)
The acknowledge bit is used to indicate a successful byte transfer. The bus transmitter
releases the SDATA after sending eight bits of data. During the ninth bit, the receiver pulls
the SDATA low to acknowledge the receipt of the eight bits of data. The receiver may leave
the SDATA in high state if it would to not acknowledge the receipt of the data.
6.4 Data input
The device samples the data input on SDATA on the rising edge of the SCLK. The SDATA
signal must be stable during the rising edge of SCLK and the SDATA signal must change
only when SCLK is driven low.
14/63
Page 15

STMPE2403 I2C Interface
6.5 Slave device address
The slave device address is a 7 or 10-bit address, where the least significant 2-bit are
programmable. These 2-bit values will be loaded in once upon reset and after that these 2
pins no longer be needed with the exception during General Call. Up to 4 STMPE2403
devices can be connected on a single I
2
C bus.
Table 13. Slave device address
ADDR 1 ADDR 0 Address
0 0 0x84
0 1 0x86
1 0 0x88
11 0x8A
6.6 Memory addressing
For the bus master to communicate to the slave device, the bus master must initiate a Start
condition and followed by the slave device address. Accompanying the slave device
address, there is a Read/Write
operation.
bit (R/W). The bit is set to 1 for Read and 0 for Write
If a match occurs on the slave device address, the corresponding device gives an
acknowledgement on the SDA during the 9
th
bit time. If there is no match, it deselects itself
from the bus by not responding to the transaction.
15/63
Page 16

I2C Interface STMPE2403
R
W
0
k
A
k
k
N
A
k
S
R
W
0
k
A
k
k
A
kAck
R
W
0
k
A
k
A
k
S
M
R
W
0
k
A
k
A
kAckAck
S
Da
ad
2
6.7 Operation modes
Table 14. Operation modes
Mode Bytes Programming Sequence
Read ≥1 START, Device Address, R/W
reSTART, Device Address, R/W
If no STOP is issued, the Data Read can be continuously preformed. If
the register address falls within the range that allows address autoincrement, then register address auto-increments internally after every
byte of data being read. For register address that falls within a nonincremental address range, the address will be kept static throughout
the entire read operations. Refer to the Memory Map table for the
address ranges that are auto and non-increment. An example of such
a non-increment address is FIFO.
Write ≥1 START, Device Address, R/W
Write, STOP
If no STOP is issued, the Data Write can be continuously performed. If
the register address falls within the range that allows address autoincrement, then register address auto-increments internally after every
byte of data being written in. For register address that falls within a
non-incremental address range, the address will be kept static
throughout the entire write operations. Refer to the Memory Map table
for the address ranges that are auto and non-increment. An example of
a non-increment address is Data Port for initializing the PWM
commands.
Figure 3. Master/slave operation modes
One Byte
Read
Dev
Addr
Start
=
n
Reg
Addr
Ac
= 0, Register Address to be read
= 1, Data Read, STOP
= 0, Register Address to be written, Data
c
Dev
Addr
reStart
RnW=1Ac
Dat a
Read
c
o
top
Mor e t han
One Byte
Read
One Byte
Write
or e than
One Byte
Write
Dev
Addr
Start
Dev
Addr
Start
Dev
Addr
Start
=
n
=
n
=
n
Reg
Addr
Ac
Reg
Addr
Ac
Reg
Addr
Ac
Mast er
16/63
c
c
c
Dev
Addr
reStart
Dat a to
be
Written
Dat a to
Write
RnW=1Ac
c
top
Dat a to
c
Write + 1
Dat a
Read
c
Dat a to
Write +
Dat a
Read + 1
Re
top
Page 17

STMPE2403 I2C Interface
6.8 General call address
A general call address is a transaction with the slave address of 0x00 and R/W = 0. When a
general call address is made, STMPE2403 responds to this transaction with an
acknowledgement and behaves as a slave-receiver mode. The meaning of a general call
address is defined in the second byte sent by the master-transmitter.
Table 15.
R/W Second byte value Definition
0 0x06 2-byte transaction in which the second byte tells the slave device to
reset and write (or latch in) the 2-bit programmable part of the slave
address.
0 0x04 2-byte transaction in which the second byte tells the slave device not
to reset and write (or latch in) the 2-bit programmable part of the
slave address.
0 0x00 Not allowed as second byte.
Note: All other second byte value will be ignored.
17/63
Page 18

System controller STMPE2403
7 System controller
The system controller is the heart of the STMPE2403. It contains the registers for power
control, and the registers for chip identification.
The system registers are:
Table 16. System controller
Address Register_Name
0x00 Reserved (Reads 0x00)
0x01 Reserved (Reads 0x00)
0x02 SYSCON
0x03 SYSCON2
0x80 CHIP_ID
0x81 VERSION_ID
0x82 Reserved (Reads 0x00)
7.1 Identification register
Table 17. CHIP_ID
Bit 76543210
Read/Write(IIC) RRRRRRRR
Reset Value 00000001
Table 18. VERSION_ID
Bit 76543210
Read/Write(IIC) R R R R R R R R
Reset Value 00000010
8-bit LSB of Chip ID
8-bit Version ID
18/63
Page 19

STMPE2403 System controller
7.2 System control register
Table 19. System control register
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Soft_Reset Clock_Source Disable_32KHz Sleep Enable_GPIO Enable_PWM Enable_KPC Enable_ROT
Read/
Write (IIC)
Reset
Val ue
WRW RWRWRW RWRWRW
00 001 1 11
Table 20. System control register writing
Bits Name Description
0 Enable_ROT Writing a ‘0’ to this bit will gate off the clock to the Rotator module, thus
stopping its operation
1 Enable_KPC Writing a ‘0’ to this bit will gate off the clock to the Keypad Controller module,
thus stopping its operation
2 Enable_PWM Writing a ‘0’ to this bit will gate off the clock to the PWM module, thus
stopping its operation
3 Enable_GPIO Writing a ‘0’ to this bit will gate off the clock to the GPIO module, thus
stopping its operation
4 Sleep Writing a ‘1’ to this bit will put the device in sleep mode. When in sleep
mode, all the units will work on 32KHz (typical) clock frequency.
5 Disable_32KHz Set this bit to disable the 32KHz OSC, thus putting the device in hibernate
mode. Only a Reset or a wakeup on IIC will reset this bit
6 Clock_Source Set to ‘1’ if external 32KHz clock were to be used. ‘0’ by default.
7 Soft_Reset Writing a ‘1’ to this bit will do a soft reset of the device. Once the reset is
done, this bit will be cleared to ‘0’ by the HW.
19/63
Page 20

System controller STMPE2403
7.3 System control register 2
Table 21. System control register 2
Bit76543 210
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved AutoSleepEN Sleep_2 Sleep_1 Sleep_0
Read/
Write (IIC)
Reset
Value
R R R R RW RWRWRW
00000 000
Table 22. System control register 2
Bits Name Description
0 Sleep_0 “000” for 4mS delay
1 Sleep_1
2 Sleep_2
3 AutoSleepEN “1” to enable auto-sleep feature. “0” to disable auto-sleep.
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7 Reserved
“001” for 16mS delay
“010” for 32mS delay
“011” for 64mS delay
“100” for 128mS delay
“101” for 256mS delay
“110” for 512mS delay
“111” for 1024mS delay
20/63
Page 21

STMPE2403 System controller
7.4 States of operation
The device has three main modes of operation:
● Operational Mode: This is the mode, whereby normal operation of the device takes
place. In this mode, the RC clock is available and the Main FSM Unit routes this clock
and the 32 KHz clock to all the device blocks that are enabled. In this mode, individual
blocks that need not be working can be turned off by the master by programming the
bits 3 to 0 of the SYSCON register.
● Sleep Mode: In this low-power mode, individual blocks can be turned off by the master
by programming the bits 3 to 0 of the SYSCON register. However, the master needs to
program the SYSCON register before coming into this mode, as in the sleep mode, the
IIC interface is not active except to detect traffic for wakeup. Any activity on the I2C port
(intended I2C transaction for the device) or Wakeup pin or Hotkey activity will cause the
device to leave this mode and go into the Operational mode. When leaving this mode,
the I2C will need to hold the SCLK till the RC clock is ready.
● Hibernate Mode: This mode is entered when the system writes a '1' to bit 5 of the
SYSCON register. In this mode, the device is completely inactive as there is absolutely
no clock. Only a Reset or a wakeup on IIC will bring back the System to operational
mode. A keypress detect will bring the system to Sleep mode, in which the debounce of
the key will take place.
Note: 32KHz clock mentioned in this section could be (1) External clock from connected XTAL, (2)
Externally fed 32KHz clock, or (3) internally generated (from RC OSC) clock. In the case
that internal clock is used, it has a range of 25KHz to 45KHz.
Caution: Hotkey detection is not possible in hibernate mode.
Figure 4. States of operation
OPERATIONAL
OPERATIONAL
32K: ON;
Set Sleep
Set Sleep
bit or
bit or
autosleep
autosleep
SLEEP
SLEEP
32K: ON
32K: ON
4MRC :ONFF
4MRC :ONFF
32K: ON;
4MRC: ON;
4MRC: ON;
Keypad,
Keypad,
Interrupts & I
Interrupts & I
transaction
transaction
Valid Key press
Valid Key press
detect
detect
2
2
C
C
2
2
I
I
C
C
transaction
transaction
Reset
Reset
Set Disable_32K bit
Set Disable_32K bit
HIBERNATE
HIBERNATE
32K: OFF;
32K: OFF;
4MRC: OFF;
4MRC: OFF;
21/63
Page 22

System controller STMPE2403
7.5 Autosleep
Host system may configure the STMPE2403 to go into sleep mode automatically whenever
there is a period of inactivity following a complete I2C transaction with the STMPE2403.
This inactivity means there is no intended I2C transaction for the device. For example, if
there is I2C transaction sent by the host to other slave devices, the STMPE2403 device will
still be counting down for the auto-sleep. The STMPE2403 device resets the autosleep
time-out counter only when it receives an I2C transaction meant for the device itself. This
autosleep feature is controlled by the System Control Register 2.
All events that trigger an interrupt (KPC, Rotator controller, Hot-Key) would result in a
transition from SLEEP state to OPERATIONAL state automatically. The wake up can also
be performed through I2C transaction intended for the device.
7.6 Keypress detect in the hibernate mode
When in hibernate mode, a keypress detect will cause the system to go into sleep mode.
The sleep clock (32KHz) will then be used to debounce the key to detect a valid key. If the
keypress is detected to be valid, the system staty in the sleep mode. If the key is detected to
be invalid, the system will go back into hibernate mode.
22/63
Page 23
STMPE2403 Clocking system
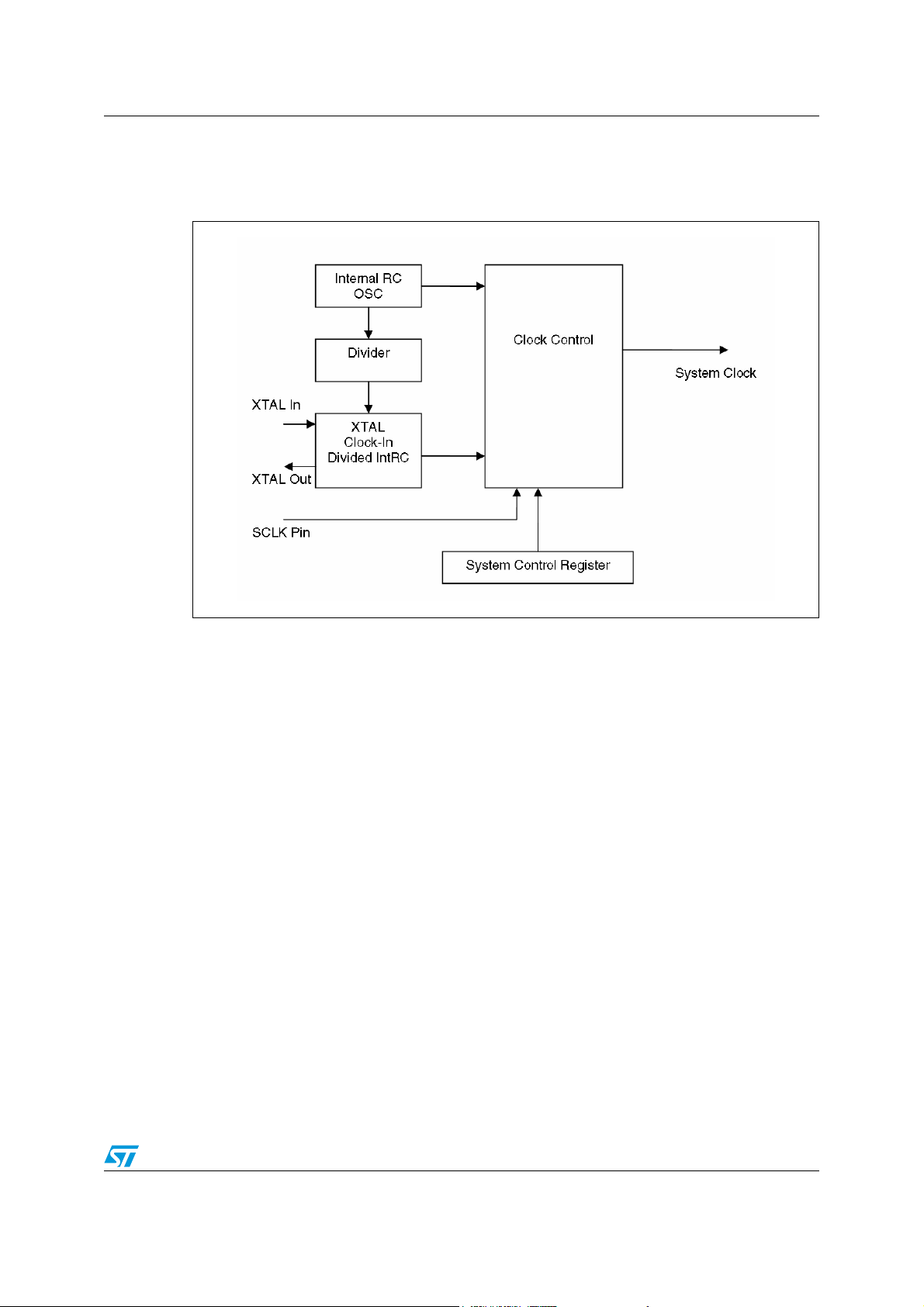
8 Clocking system
Figure 5. Clocking system
The decision on clocks is based on the bits written into SYSCON registers. Bits 0 to 4 of the
SYSCON register control the gating of clocks to the Rotator, Keypad Controller, PWM and
GPIO respectively in the operational mode.
8.1 Clock source
By default, when the STMPE2403 powers up, it derives a 32KHz clock from the internal RC
oscillator for it's operation. If external 32KHz crystal or clock source is available, it must be
configured to accept external clock through the SYSCON register.
In the case where the STMPE2403 is powered and configured to use external clock, and the
XTALIN is left floating, there will be an additional leakage current of approximately 20µA
drawn from the V
CC
.
23/63
Page 24

Clocking system STMPE2403
8.2 Power mode programming sequence
To put the device in sleep mode, the following needs to be done by the host:
Write a '1' to bit 4 of the SYSCON register.
To wakeup the device, the following needs to be done by the host:
Assert a wakeup routine on the I2C bus by sending the Start Bit, followed by the device
address and the Write bit. Subsequently, proceed with sending the Base Register address
and continue with a normal I2C transaction. The device wakes up upon receiving the
correct device address and in Write direction. In other words, the procedure of waking up
the device is performed by just sending an I2C transaction to the device. This procedure
can be extended to wake up the device that is in hibernate mode.
To do a soft reset to the device, the host needs to do the following:
Write a '1' to bit 7 of the SYSCON register.
This bit is automatically cleared upon reset.
To go into Hibernate mode, the following needs to be done by the host:
Set the Disable_32K bit to '1'
To come out of the Hibernate mode, the following needs to be done by the host:
Assert a system reset or
Put a wakeup on the I2C
24/63
Page 25

STMPE2403 Interrupt system
9 Interrupt system
STMPE2403 uses a highly flexible interrupt system. It allows host system to configure the
type of system events that should result in an interrupt, and pinpoints the source of interrupt
by status register. The INT pin could be configured as ACTIVE HIGH, or ACTIVE LOW.
Once asserted, the INT pin would de-assert only if the corresponding bit in the Interrupt
Status register is cleared.
Figure 6. Interrupt system
25/63
Page 26

Interrupt system STMPE2403
9.1 Register map of interrupt system
Table 23. Register map of interrupt system
Auto-Increment
Address Register name Description
0x10 ICR_msb
Interrupt Control Register
0x11 ICR_lsb Yes
0x12 IER_msb
Interrupt Enable Mask Register
0x13 IER_lsb Yes
(during sequential
R/W)
Ye s
Ye s
0x14 ISR_msb
Interrupt Status Register
0x15 ISR_lsb Yes
0x16 IEGPIOR_msb Interrupt Enable GPIO Mask Register Yes
0x17 IEGPIOR_csb Yes
0x18 IEGPIOR_lsb Yes
0x19 ISGPIOR_msb Interrupt Status GPIO Register Yes
0x1A ISGPIOR_csb Yes
0x1B ISGPIOR_lsb Yes
Ye s
26/63
Page 27

STMPE2403 Interrupt system
9.2 Interrupt Control Register (ICR)
ICR register is used to configure the Interrupt Controller. It has a global enable interrupt
mask bit that controls the interruption to the host.
ICR_msb ICR_lsb
Bit1514131211109876543 2 1 0
Reserved IC2 IC1 IC0
R/WRRRRRRRRRRRRRRW RW RW
Reset
Val ue
0000000000000 0 0 0
Table 24. Register description
Bit Name Description
Global Interrupt Mask bit
0IC[0]
1IC[1]
2IC[2]
When this bit is written a ‘1’, it will allow interruption to the host. If it is written with
a ‘0’, then, it disables all interruption to the host. Writing to this bit does not affect
the IER value.
Output Interrupt Type
‘0’ = Level interrupt
‘1’ = Edge interrupt
Output Interrupt Polarity
‘0’ = Active Low / Falling Edge
‘1’ = Active High / Rising Edge
27/63
Page 28

Interrupt system STMPE2403
9.3 Interrupt Enable Mask Register (IER)
IER register is used to enable the interruption from a particular interrupt source to the host.
IER_msb IER_lsb
Bit1514131211109876543210
Reserved IE8 IE7 IE6 IE5 IE4 IE3 IE2 IE1 IE0
R/WR R R R R R RRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val ue
0000000000000000
Table 25. Register description
Bits Name Description
Interrupt Enable Mask (where x = 8 to 0)
IE0 = Wake-up Interrupt Mask
IE1 = Keypad Controller Interrupt Mask
IE2 = Keypad Controller FIFO Overflow Interrupt Mask
IE3 = Rotator Controller Interrupt Mask
8:0 IE[x]
IE4 = Rotator Controller Buffer Overflow Interrupt Mask
IE5 = PWM Channel 0 Interrupt Mask
IE6 = PWM Channel 1 Interrupt Mask
IE7 = PWM Channel 2 Interrupt Mask
IE8 = GPIO Controller Interrupt Mask
Writing a ‘1’ to the IE[x] bit will enable the interruption to the host.
28/63
Page 29

STMPE2403 Interrupt system
9.4 Interrupt Status Register (ISR)
ISR register monitors the status of the interruption from a particular interrupt source to the
host. Regardless whether the IER bits are enabled or not, the ISR bits are still updated.
ISR_msb ISR_lsb
Bit1514131211109876543210
Reserved IS8 IS7 IS6 IS5 IS4 IS3 IS2 IS1 IS0
R/W R R R R R R R RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Reset
Val ue
0000000000000000
Table 26. Register description
Bits Name Description
Interrupt Status (where x = 8 to 0)
Read:
IS0 = Wake-up Interrupt Status
IS1 = Keypad Controller Interrupt Status
IS2 = Keypad Controller FIFO Overflow Interrupt Status
IS3 = Rotator Controller Interrupt Status
8:0 IS[x]
IS4 = Rotator Controller Buffer Overflow Interrupt Status
IS5 = PWM Channel 0 Interrupt Status
IS6 = PWM Channel 1 Interrupt Status
IS7= PWM Channel 2 Interrupt Status
IS8 = GPIO Controller Interrupt Status
Write:
A write to a IS[x] bit with a value of ‘1’ will clear the interrupt and a write with a
value of ‘0’ has no effect on the IS[x] bit.
9.5 Interrupt Enable GPIO Mask Register (IEGPIOR)
IEGPIOR register is used to enable the interruption from a particular GPIO interrupt source
to the host. The IEG[23:0] bits are the interrupt enable mask bits correspond to the
GPIO[23:0] pins.
Table 27. IEGPIOR register
Bit 76543210
IEGPIOR_msb IEG-23 IEG -22 IEG -21 IEG -20 IEG -19 IEG -18 IEG -17 IEG -16
IEGPIOR _csb IEG -15 IEG -14 IEG -13 IEG -12 IEG -11 IEG -10 IEG -9 IEG -8
IEGPIOR _lsb IEG -7 IEG -6 IEG -5 IEG -4 IEG -3 IEG -2 IEG -1 IEG -0
Table 28. Register description
Name Description
IEG[x] Interrupt Enable GPIO Mask (where x = 23 to 0)
Writing a ‘1’ to the IE[x] bit will enable the interruption to the host.
29/63
Page 30

Interrupt system STMPE2403
9.6 Interrupt Status GPIO Register (ISGPIOR)
ISGPIOR register monitors the status of the interruption from a particular GPIO pin interrupt
source to the host. Regardless whether the IEGPIOR bits are enabled or not, the ISGPIOR
bits are still updated. The ISG[23:0] bits are the interrupt status bits correspond to the
GPIO[23:0] pins.
Table 29. ISGPIOR register
Bit 76543210
ISGPIOR_msb ISG-23 ISG -22 ISG -21 ISG -20 ISG -19 ISG -18 ISG -17 ISG -16
ISGPIOR _csb ISG -15 ISG -14 ISG -13 ISG -12 ISG -11 ISG -10 ISG -9 ISG -8
ISGPIOR _lsb ISG -7 ISG -6 ISG -5 ISG -4 ISG -3 ISG -2 ISG -1 ISG -0
Table 30. Register description
Name Description
Interrupt Status GPIO (where x = 23 to 0)
Read:
ISG[x]
Interrupt Status of the GPIO[x].
Write:
A write to a ISG[x] bit with a value of ‘1’ will clear the interrupt and a write with a value of
‘0’ has no effect on the ISG[x] bit.
30/63
Page 31

STMPE2403 Interrupt system
9.7 Programming sequence
To configure and initialize the Interrupt Controller to allow interruption to host, observe the
following steps:
● Set the IER and IEGPIOR registers to the desired values to enable the interrupt
sources that are to be expected to receive from.
● Configure the output interrupt type and polarity and enable the global interrupt mask by
writing to the ICR.
● Wait for interrupt.
● Upon receiving an interrupt, the INT pin is asserted.
● The host comes to read the ISR through I2C interface. A ‘1’ in the ISR bits indicates
that the corresponding interrupt source is triggered.
● If the IS8 bit in ISR is set, the interrupt is coming from the GPIO Controller. Then, a
subsequent read is performed on the ISGPIOR to obtain the interrupt status of all 24
GPIOs to locate the GPIO that triggers the interrupt. This is a feature so-called ‘Hot
Key’.
● After obtaining the interrupt source that triggers the interrupt, the host performs the
necessary processing and operations related to the interrupt source.
● If the interrupt source is from the GPIO Controller, two write operations with value of ‘1’
are performed to the ISG[x] bit (ISGPIOR) and the IS[8] (ISR) to clear the
corresponding GPIO interrupt.
● If the interrupt source is from other module, a write operation with value of ‘1’ is
performed to the IS[x] (ISR) to clear the corresponding interrupt.
● Once the interrupt is being cleared, the INT pin will also be de-asserted if the interrupt
type is level interrupt. An edge interrupt will only assert a pulse width of 250ns.
● When the interrupt is no longer required, the IC0 bit in ICR may be set to ‘0’ to disable
the global interrupt mask bit.
31/63
Page 32

GPIO controller STMPE2403
10 GPIO controller
A total of 24 GPIOs are available in the STMPE2403 port expander IC. Most of the GPIOs
are sharing physical pins with some alternate functions. The GPIO controller contains the
registers that allow the host system to configure each of the pins into either a GPIO, or one
of the alternate functions. Unused GPIOs should be configured as outputs to minimize the
power consumption.
Table 31. GPIO controller
Address Register Name Description
Auto-Increment
(during sequential R/W)
0xA2 GPMR_msb
0xA3 GPMR_csb Yes
0xA4 GPMR_lsb Yes
0x83 GPSR_msb
0x84 GPSR_csb Yes
0x85 GPSR_lsb Yes
0x86 GPCR_msb
0x87 GPCR_csb Yes
0x88 GPCR_lsb Yes
0x89 GPDR_msb
0x8A GPDR_csb Yes
0x8B GPDR_lsb Yes
0x8C GPEDR_msb
0x8D GPEDR_csb Yes
0x8E GPEDR_lsb Yes
0x8F GPRER_msb
0x90 GPRER_csb Yes
0x91 GPRER_lsb Yes
0x92 GPFER_msb
0x93 GPFER_csb Yes
GPIO Monitor Pin State Register
GPIO Set Pin State Register
GPIO Clear Pin State Register
GPIO Set Pin Direction Register
GPIO Edge Detect Status Register
GPIO Rising Edge Register
GPIO Falling Edge Register
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
0x94 GPFER_lsb Yes
0x95 GPPUR_msb
0x96 GPPUR_csb Yes
0x97 GPPUR_lsb Yes
0x98 GPPDR_msb
0x99 GPPDR_csb Yes
0x9A GPPDR_lsb Yes
32/63
GPIO Pull Up Register
GPIO Pull Down Register
Ye s
Ye s
Page 33

STMPE2403 GPIO controller
Table 31. GPIO controller (continued)
Address Register Name Description
0x9B GPAFR_U_msb
0x9C GPAFR_U_csb Yes
0x9D GPAFR_U_lsb Yes
0x9E GPAFR_L_msb
0x9F GPAFR_L_csb Yes
0xA0 GPAFR_L_lsb Yes
0xA1 MUX_CTRL MUX Control Register Yes
0xA5 COMPAT2401 STMPE2401 Pin Compatibility Register Yes
0xA6 – 0xAF RESERVED Reserved Yes
GPIO Alternate Function Register (Upper Bit)
GPIO Alternate Function Register (Lower Bit)
Auto-Increment
(during sequential R/W)
Ye s
Ye s
10.1 GPIO control registers
A group of registers are used to control the exact function of each of the 24 GPIO. All GPIO
registers are named as GPxxx_yyy, where
Xxx represents the functional group
Yyy represents the byte position of the GPIO
Lsb registers controls GPIO[7:0]
Csb registers controls GPIO[15:8]
Msb registers controls GPIO[23:16]
Table 32. GPIO control registers
Bit 76543210
GPxxx_msb IO-23 IO-22 IO-21 IO-20 IO-19 IO-18 IO-17 IO-16
GPxxx_csb IO-15 IO-14 IO-13 IO-12 IO-11 IO-10 IO-9 IO-8
GPxxx_lsb IO-7 IO-6 IO-5 IO-4 IO-3 IO-2 IO-1 IO-0
Note: This convention does not apply to the GPIO Alternate Function Registers
33/63
Page 34

GPIO controller STMPE2403
The function of each bit is shown in the following table:
Table 33. Bit function
Register Name Function
GPIO Monitor Pin State
GPIO Set Pin State
Reading this bit yields the current state of the bit. Writing has no
effect.
Writing ‘1’ to this bit causes the corresponding GPIO to go to ‘1’
state. Writing ‘0’ has no effect.
GPIO Clear Pin State
GPIO Set Pin Direction
GPIO Edge Detect Status
GPIO Rising Edge
GPIO Falling Edge
GPIO Pull Up Set to ‘1’ to enable internal pull-up resistor
GPIO Pull Down Set to ‘1’ to enable internal pull-down resistor
Writing ‘1’ to this bit causes the corresponding GPIO to go to ‘0’
state. Writing ‘0’ has no effect.
‘0’ sets the corresponding GPIO to input state, and ‘1’ sets it to
output state
Set to ‘1’ by hardware when there is a rising/falling edge on the
corresponding GPIO. Writing ‘1’ clears the bit. Writing ‘0’ has no
effect.
Set to ‘1’ to enable rising edge detection on the corresponding
GPIO.
Set to ‘1’ to enable falling edge detection on the corresponding
GPIO.
34/63
Page 35

STMPE2403 GPIO controller
10.2 GPIO Alternate Function Register (GPAFR)
GPAFR is to select the functionality of the GPIO pin. To select a function for a GPIO pin, a
bit-pair in the register (GPAFR_U or GPAFR_L) has to be set.
GPAFR_U_msb
Bit2322212019181716
AF23 AF22 AF21 AF20
R/WRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val u e
Bit151413121110 9 8
R/WRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val u e
00000000
GPAFR_U_csb
AF19 AF18 AF17 AF16
00000000
GPAFR_U_lsb
Bit76543210
AF15 AF14 AF13 AF12
R/WRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val u e
00000000
Table 34. Bit description
Bits Name Description
GPIO Pin ‘x’ Alternate Function Select (where x = 23 to 12).
‘00’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Primary Function.
23:0 AF[x]
‘01’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 1.
‘10’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 2.
‘11’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 3.
35/63
Page 36

GPIO controller STMPE2403
GPAFR_L_msb
Bit23 22212019181716
AF11 AF10 AF9 AF8
R/WRW RWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val u e
Bit15 1413121110 9 8
R/WRW RWRWRWRWRWRWRW
00000000
GPAFR_L_csb
AF7 AF6 AF5 AF4
Reset
00000000
Val u e
GPAFR_L_lsb
Bit76543210
AF3 AF2 AF1 AF0
R/WRW RWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset
00000000
Val u e
Table 35. Bit description
Bits Name Description
GPIO Pin ‘x’ Alternate Function Select (where x = 11 to 0).
‘00’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Primary Function.
23:0 AF[x]
‘01’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 1.
‘10’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 2.
‘11’ – The corresponding GPIO pin (GPIO[x]) is configured to Alternate Function 3.
36/63
Page 37

STMPE2403 GPIO controller
10.3 Hot key feature
A GPIO is known as ‘Hot Key’ when it is configured to trigger an interruption to the host
whenever the GPIO input is being asserted. This feature is applicable in Operational mode
,as well as Sleep mode.
10.3.1 Programming sequence for Hot Key
1. Configures the GPIO pin into GPIO mode by setting the corresponding bits in the
GPAFR.
2. Configures the GPIO pin into input direction by setting the corresponding bit in GPDR.
3. Set the GPRER and GPFER to the desired values to enable the rising edge or falling
edge detection.
4. Configures and enables the interrupt controller to allow the interruption to the host.
5. Now, the GPIO Expander may be put into Sleep mode if it is desired.
6. Upon any Hot Key being asserted, the device will wake-up and issue an interrupt to the
host.
Below are the conditions to be fulfilled in order to configure a Hot Key:
1. The pin is configured into GPIO mode and as input pin.
2. The global interrupt mask bit is enabled.
3. The corresponding GPIO interrupt mask bit is enabled.
10.3.2 Minimum pulse width
The minimum pulse width of the assertion of the Hot Key must be at least 62.5us. Any pulse
width less than the stated value may not be registered.
37/63
Page 38

GPIO controller STMPE2403
10.4 MUX Control Register (MCR)
STMPE2403 is integrated with 2 SPDT bi-directional signal multiplexer. The Ron of the
multiplexer is 5 OHM (Typical). Signal level is 1.8V (MAX). The MUX are controlled by the
MUX Control register.
MCR is to control the two analog multiplexers operation.
MCR
Bit7 6 543210
RESERVED M1C1 M2C1 M1C1 M1C0
R/WRRRRRWRWRWRW
Reset
Val u e
Table 36. Bit description
Bits Name Description
0 M1C0 MUX 1 Control 0 bit selects whether Mux1In_0 or Mux1In_1 connects to
1 M1C1 MUX 1 Control 1 bit enables the MUX 1.
2 M2C0 MUX 2 Control 0 bit selects whether Mux2In_0 or Mux2In_1 connects to
3 M2C1 MUX 2 Control 1 bit enables the MUX 2.
0 0 000000
Mux1Out.
‘0’ – Mux1In_0 is connected to the Mux1Out.
‘1’ – Mux1In_1 is connected to the Mux1Out.
‘0’ – Enables the MUX 1.
‘1’ – Disables the MUX 1.
Mux2Out.
‘0’ – Mux1In_0 is connected to the Mux1Out.
‘1’ – Mux1In_1 is connected to the Mux1Out.
‘0’ – Enables the MUX 2.
‘1’ – Disables the MUX 2.
38/63
Page 39

STMPE2403 GPIO controller
10.5 STMPE2401 Pin Compatibility Register (COMPAT2401)
STMPE2403 is an enhanced version of the other port expander device, STMPE2401.
However, the pin configuration of STMPE2403 is different from that of STMPE2401. For
backward pin compatibility to STMPE2401, COMPAT2401 register provides a control bit that
allows STMPEE2403 to have the same pin configuration as in STMPE2401.
COMPAT2401
Bit7 6 543210
RESERVED PIN2401
R/WRRRRRRRRW
Reset
Val ue
Table 37. Bit description
Bits Name Description
0 PIN2401This control bit selects pin configuration to be used.
0 0 000000
‘0’ – STMPE2401 pin configuration as defined in sections 1.1 and 1.3.
‘1’ – Pin configuration compatible to STMPE2401.
The pin locations for the following eight IO ports are different from those shown in section
1.3: KP_X0, KP_X1, KP_X2, KP_X3, KP_Y4, KP_Y5, KP_Y6 and KP_Y7. When ‘PIN2401’
bit is set to ‘1’, the eight IO ports are assigned to the pin locations as defined by the following
diagram.
Table 38. Pin location
ABCDEF
1 KP_X2 KP_X1 RESET XTALOUT SCLK KP_Y6
2 KP_X4 KP_X3 KP_X0 XTALIN SDATA KP_Y7
3 KP_X6 KP_X5 GND1 GND2 KP_Y8 INT
4 VCC1 KP_X7 GND3 GND4 PWM-1 VCC2
5 KP_Y5 KP_Y3 KP_Y1 KP_Y9 PWM-3 PWM-2
6 KP_Y4 KP_Y2 KP_Y0 ADDR0 KP_Y10 KP_Y11
39/63
Page 40

PWM controller STMPE2403
11 PWM controller
The STMPE2403 PWM controller provides 3 independent PWM outputs used to generate
light effect; if the PWM outputs are not used, these pins can be used as GPIO.
Figure 7. PWM controller
Divide by “Step Time”
(Up/Down by “Step
Sign”)
64Hz-2KHz
Prescaler
(Divide by 16 or 512)
32KHz
Primary Clock
PWM Ref
Counts from 0-255
repeatedly
1Hz-2KHz
Instruction
Processor
PWM Output
Increment
Counter
Comparator
Instruction Word 0
Instruction Word 1
Instruction Word 2
Instruction Word 63
Trigger Bus
INT
PWM Count
Count from 0-255
based on instructions
Instructions are downloaded into the memory via the I2C connection.
40/63
Page 41

STMPE2403 PWM controller
11.1 Registers in the PWM controller
The main system registers are:
Table 39. Main system registers
Address Register name Description
0x30 PWMCS PWM Control and Status register Yes
PWM instructions are initialized through this
data port. Every instruction is 16-bit width and
0x38 PWMIC0
0x39 PWMIC1
0x3A PWMIC2
therefore, the MSB of the first word is written
first, then, followed by LSB of the first word.
Subsequently, MSB of second word and LSB of
second word and so on.
PWM instructions are initialized through this
data port. Every instruction is 16-bit width and
therefore, the MSB of the first word is written
first, then, followed by LSB of the first word.
Subsequently, MSB of second word and LSB of
second word and so on.
PWM instructions are initialized through this
data port. Every instruction is 16-bit width and
therefore, the MSB of the first word is written
first, then, followed by LSB of the first word.
Subsequently, MSB of second word and LSB of
second word and so on.
Auto-Increment
(during Read/Write)
No
No
No
41/63
Page 42

PWM controller STMPE2403
11.2 PWM Control and Status Register (PWMCS)
Bit 76543210
ExtSel ExtEn II2 II1 II0 EN2 EN1 EN0
Read/Write RW RW R R R RW RW RW
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 40. Bit description
Bits Name Description
PWM Channel 0 Enable bit.
‘1’ – Enable the PWM Channel 0
0EN0
1EN1
‘0’ – Reset the PWM Channel 0. Only when the PWM channel is in reset state,
the stream of commands can be written into its data port, which in this case is
PWM_Command_Channel_0.
PWM Channel 1 Enable bit.
‘1’ – Enable the PWM Channel 1
‘0’ – Reset the PWM Channel 1. Only when the PWM channel is in reset state,
the stream of commands can be written into its data port, which in this case is
PWM_Command_Channel_1.
PWM Channel 2 Enable bit.
‘1’ – Enable the PWM Channel 2
2EN2
‘0’ – Reset the PWM Channel 2. Only when the PWM channel is in reset state,
the stream of commands can be written into its data port, which in this case is
PWM_Command_Channel_2.
PWM Invalid Instruction Status bit for PWM Channel 0
3II0
‘0’ – No invalid command encountered during the instruction execution.
‘1’ – Invalid command encountered and this puts the PWM Channel 0 into reset
state.
PWM Invalid Instruction Status bit for PWM Channel 1
4II1
‘0’ – No invalid command encountered during the instruction execution.
‘1’ – Invalid command encountered and this puts the PWM Channel 1 into reset
state.
PWM Invalid Instruction Status bit for PWM Channel 2
5II2
‘0’ – No invalid command encountered during the instruction execution.
‘1’ – Invalid command encountered and this puts the PWM Channel 2 into reset
state.
External Trigger Enable
6ExtEn
‘0’ – External triggering function is disabled
‘1’ – External triggering function is enabled
If enabled, GPIO-15 is used as trigger input/output
External Trigger Direction Selection
7ExtSel
‘0’ – Active high external trigger input
‘1’ – Active low external trigger output
42/63
Page 43

STMPE2403 PWM controller
11.3 PWM Instruction Channel x (PWMICx)
This PWMICx is the dataport that allows the instructions to be loaded into the PWM
channel. The loading of the instructions is achieved by continuously writing to this dataport.
As this dataport address falls on the non-auto increment region, continuous write operation
2
on I
C will write into the same dataport address. The ‘x’ value is from 0 to 2 as there are 3
independent PWM channels. To access these dataports, the corresponding ENx in the
PWMCS register must be set to 0 first to put the PWM channel in reset state.
Bit 76543210
IB7 IB6 IB5 IB4 IB3 IB2 IB1 IB0
Read/Write RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Reset Value00000000
Table 41. Bit description
Bits Name Description
7:0 IB[y] PWM Instruction Channel x, where y is 7 to 0
As an instruction is 16-bit width, writing the instruction into this 8-bit PWMICx
dataport requires two 8-bit data write. The most significant byte of the 16-bit
instruction is to be written in first and followed by the least significant byte of the
instruction. The same effect applies to the read operation.
11.4 PWM commands
The STMPE2403 PWM Controller works as a simple MCU, with program space of 64
instructions and a simple instruction set. The instructions are all 16 bits in length. The 3
most significant bits are used to identify the commands.
Table 42. PWM commands
Instruction Description
RAMP This instruction starts the PWM counters and set the pwm_x_out with the result
from the counting.
Prescale: (0 or 1)
‘0’ - divide 32KHz clock by 16
‘1’ – divide 32KHz clock by 512
Step Time: (1-63)
One ramp increment done in (step time) x (clock after prescale)
Sign: (0 or 1)
“0” – increase PWM output
‘1’ – decrease PWM output
Increment: (0-127)
The number of increment/decrement cycles
43/63
Page 44

PWM controller STMPE2403
Table 42. PWM commands (continued)
Instruction Description
LOAD Load the PWM counter with a value between 0x0 and 0xFF.
PWM value: (0-255)
Loads an absolute value between 0-255 into PWM count
Go to Start (GTS) Branch to the address 0x0 and execute from 0x0 and onwards.
BRANCH This instruction loads the Step Number into the instruction counter
Loop Count: (0-63)
Number of loops to repeat. 0 means infinite loop
Addr: (0 or 1)
0 – Absolute addressing
1 – Relative addressing
Step Size: (0-63)
The step number to be loaded to instruction counter
END End the instruction execution by resetting and interrupting to the host.
Trigger (TRIG) Capable of waiting as well as sending triggers to another PWM channel. Can be
configured to send/receive external trigger
Wait For Trigger
Bit 7: Channel 0
Bit 8: Channel 1
Bit 9: Channel 2
Bit 12: External Trigger Input
Send Trigger
Bit 1: Channel 0
Bit 2: Channel 1
Bit 3: Channel 2
Bit 6: External Trigger Output
Table 43. Identification of Instructions
Instruction Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13
Ramp 0 - -
LOAD 0 1 -
GoToStart 0 0 -
Branch101
End110
Trigger111
Reserved100
44/63
Page 45

STMPE2403 PWM controller
Table 44. Instruction bit
Instruction
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RAMP 0 Prescale
0=16
1=512
Step Time
0 - 63
0 = immediate action
LOAD 0 1 0 PWM Value 0-255
GTS 0 0 0 0 0
BRANCH 1 01 Loop Count 0-63 Addr Step Size
END 1 10 Interrupt
to host
Reset
instructio
n counter
and
output
level to
zero
TRIG 1 11 Wait for Trigger
on channel 0 – 2 and external Trigger
Continues if all selected triggers present.
Each bit signifies wait for the corresponding
channel.
reserved 1 00 RESERVED
1. Don’t care
Bit
RESERVED
Sign
0=step-up
1=step-down
Increment
1 – 126
0 – 63*
Send Trigger
on channel 0 – 2 and
external Trigger
Continues if no Wait for
Trigger in this
instruction.
(1)
x
In order to enable a PWM channel, the programming sequence below should be observed.
● The ENx of the PWMCS register should be kept in ‘0’. By default, it has a value of ‘0’.
● Loads the instructions into the PWM channel x by writing the corresponding PWMICx.
● The PWM channel x has a 64-word depth (16-bit width). Any instructions of size less
than or equal to 64 words can be loaded into the channel. Any attempt to load beyond
64 words will result in internal address pointer to roll-over (0x1f ◊ 0x00) and the excess
instructions to be over-written into the first address location of the channel and
onwards.
● After the instructions are loaded in, then, the PWM channel x can be enabled by setting
a ‘1’ to the ENx bit.
● Enables the corresponding interrupt mask bit to allow interruption to the host.
45/63
Page 46

Keypad controller STMPE2403
12 Keypad controller
The keypad controller consists of: 1) four dedicated key controllers that support up to four
simultaneous dedicated key presses; 2) a key scan controller and two normal key controllers
that support a maximum of 12x8 key matrix with detection of three simultaneous key
presses; 3) eight special function key controllers that support up to eight simultaneous
special function key presses.
Four of the column inputs can be configured as dedicated keys through the setting of
Dkey0~3 bits of KPC_ctrl register.
The normal key matrix size is configurable through the setting of KPC_row and KPC_col
registers. The scanning of each individual row output and column input can be enabled or
masked to support a key matrix of variable size from 1x1 to 12x8. It is allowed to have
another eight special function keys incorporated in the key matrix.
The operation of the keypad controller is enabled by the SCAN bit of KPC_ctrl register.
Every key activity detected will be de-bounced for a period set by the DB_0~7 bits of
KPC_ctrl register before a key press or key release is confirmed and updated into the output
FIFO. The key data, indicating the key coordinates and its status (up or down), is loaded into
the FIFO at the end of a specified number of scanning cycles (set by ScanCount0~3 bits of
KPC_row_msb register). An interrupt will be generated when a new set of key data is
loaded. The FIFO has a capacity for ten sets of key data. Each set of key data consists of 5
bytes of information when any of the four dedicated keys is enabled. It is reduced to 4 bytes
when no dedicated key is involved. When the FIFO is full before its content is read, an
overflow signal will be generated while the FIFO will continue to hold its content but forbid
loading of new key data set.
Figure 8. Keypad controller
Input 0-7
Keypad Matrix
Output 0-11
46/63
Page 47

STMPE2403 Keypad controller
y
The keypad column inputs enabled by the KPC_col register are normally 'HIGH', with the
corresponding input pins pulled up by resistors internally. After reset, all the keypad row
outputs enabled by the KPC_row register are driven 'LOW'. If a key is pressed, its
corresponding column input will become 'LOW' after making contact with the 'LOW' voltage
on its corresponding row output.
Once the key scan controller senses a 'LOW' input on any of the column inputs, the
scanning cycles will then start to determine the exact key that has been pressed. The twelve
row outputs will be driven 'LOW' one by one during each scanning cycle. While one row is
driven 'LOW', all other rows are in tri-state and pulled up. If there is any column input sensed
as 'LOW' when a row is driven 'LOW', the key scan controller will then decode the key
coordinates (its corresponding row number and column number), save the key data into a
de-bounce buffer if available, confirm if it is a valid key press after de-bouncing, and update
the key data into output data FIFO if valid.
12.1 Keypad configurations
The keypad controller supports the following types of keys
– Up to 8 Input *12 Output Matrix Keys
– Up to 8 Special Function Keys
– Up to 4 Dedicated Keys
Figure 9. Maximum configuration
STMPE2403 Matrix Keypad
Output 0-11
Input 0-7
Special Function Keys
8*12 (96) Matrix Keys
8 Special Function Keys
0 Dedicated Ke
s
(8*12)
47/63
Page 48

Keypad controller STMPE2403
y
Figure 10. Dedicated key configuration
STMPE240 3 Matrix Keypad
Output 00-11
(4*12)
Input 0-3
4*1212 (9648) Matrix Keys
4 Special Function Keys
04 Dedicated Ke
Input 4-7
Special FunctionDedicated
Keys
s
12.2 Registers in keypad controller
Table 45. Registers in keypad controller
Address Register Name Description
0x60 KPC_col Keypad column scanning register Yes
Special Function Keys
Auto-Increment
(during sequential R/W)
0x61 KPC_row_msb
Keypad row scanning register
0x62 KPC_row_lsb Yes
0x63 KPC_ctrl_msb
0x64 KPC_ctrl_lsb Yes
0x68 KPC_data_byte0
0x69 KPC_data_byte1 Yes
0x6A KPC_data_byte2 Yes
0x6B KPC_data_byte3 Yes
0x6C KPC_data_byte4 Yes
48/63
Ye s
Ye s
Keypad control register
Ye s
Keypad data register
Page 49

STMPE2403 Keypad controller
12.3 KPC_col register
Bit 76543210
Name Input Column 0 ~ 7
Read/Write RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 46. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 Input Column 7 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 7; ‘0’ to turn off
6 Input Column 6 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 6; ‘0’ to turn off
5 Input Column 5 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 5; ‘0’ to turn off
4 Input Column 4 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 4; ‘0’ to turn off
3 Input Column 3 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 3; ‘0’ to turn off
2 Input Column 2 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 2; ‘0’ to turn off
1 Input Column 1 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 1; ‘0’ to turn off
0 Input Column 0 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of column 0; ‘0’ to turn off
12.4 KPC_row_msb register
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ScanPW1 ScanPW0 Hib_Wk - Output Row 8 ~ 11
Read/Write RW RW RW R RW RW RW RW
Reset Value 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 47. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 ScanPW1 Pulse width setting of keypad scanning. Use “11” at all
6 ScanPW0
5 Hib_Wk ‘1’ to enable keypad wake-up from hibernate mode; ‘0’ to
4--
3 Output Row 11 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 11; ‘0’ to turn off
2 Output Row 10 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 10; ‘0’ to turn off
1 Output Row 9 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 9; ‘0’ to turn off
0 Output Row 8 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 8; ‘0’ to turn off
times
disable
49/63
Page 50

Keypad controller STMPE2403
12.5 KPC_row_lsb register
Bit 76543210
Name Output Row 0 ~ 7
Read/Write RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 48. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 Output Row 7 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 7; ‘0’ to turn off
6 Output Row 6 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 6; ‘0’ to turn off
5 Output Row 5 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 5; ‘0’ to turn off
4 Output Row 4 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 4; ‘0’ to turn off
3 Output Row 3 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 3; ‘0’ to turn off
2 Output Row 2 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 2; ‘0’ to turn off
1 Output Row 1 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 1; ‘0’ to turn off
0 Output Row 0 ‘1’ to turn on scanning of row 0; ‘0’ to turn off
12.6 KPC_ctrl_msb register
Bit 76543210
Name ScanCount0 ~ 3 DKey_0 ~ 3
Read/WriteRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Reset Value00000000
Table 49. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 ScanCount3
6 ScanCount2
5 ScanCount1
4 ScanCount0
3 DKey_3 Set ‘1’ to use Input Column 3 as dedicated key
2 DKey_2 Set ‘1’ to use Input Column 2 as dedicated key
1 DKey_1 Set ‘1’ to use Input Column 1 as dedicated key
0 DKey_0 Set ‘1’ to use Input Column 0 as dedicated key
Number of key scanning cycles elapsed before a confirmed
key data is updated into output data FIFO (0 ~ 15 cycles)
50/63
Page 51
STMPE2403 Keypad controller
12.7 KPC_ctrl_lsb register
Bit 76543210
Name DB_0 ~ 5 SCAN
Read/Write RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 50. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7DB_6
6DB_5
5DB_4
4DB_3
3DB_2
2DB_1
1DB_0
0 SCAN ‘1’ to start scanning; ‘0’ to stop
0-128ms of de-bounce time
12.8 Data registers
The KPC_DATA register contains three bytes of information. The first two bytes store the key
coordinates and status of any two keys from the normal key matrix, while the third byte store
the status of dedicated keys.
KPC_data_byte0 Register
Bit 7 6543210
NameUp/DownR3R2R1R0C2C1C0
Read/WriteR RRRRRRR
Reset Value1 1111000
Table 51. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 Up/Down ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
6R3
5R2
4R1
3R0
2C2
0C0
row number of key 1 (valid range : 0-11)
0x1111 for No Key
column number of key 1 (valid range : 0-7)1C1
51/63
Page 52

Keypad controller STMPE2403
KPC_data_byte1 Register
Bit 7 6543210
NameUp/DownR3R2R1R0C2C1C0
Read/WriteR RRRRRRR
Reset Value1 1111000
Table 52. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 Up/Down ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
6R3
5R2
4R1
3R0
2C2
0C0
row number of key 2 (valid range : 0-11)
0x1111 for No Key
column number of key 2 (valid range : 0-7)1C1
KPC_data_byte2 Register
Bit 7 6543210
NameUp/DownR3R2R1R0C2C1C0
Read/WriteR RRRRRRR
Reset Value1 1111000
Table 53. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 Up/Down ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
6 R3 row number of key 3 (valid range : 0-11)
0x1111 for No Key
5R2
4R1
3R0
2 C2 column number of key 3 (valid range : 0-7)
1C1
0C0
52/63
Page 53
STMPE2403 Keypad controller
KPC_data_byte3 Register
Bit 76 543210
Name SF7 SF6 SF5 SF4 SF3 SF2 SF1 SF0
Read/WriteRR RRRRRR
Reset
11 111111
Val ue
Table 54. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7 SF7 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
6 SF6 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
5 SF5 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
4 SF4 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
3 SF3 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
2 SF2 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
1 SF1 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
0 SF0 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
KPC_data_byte4 Register
Bit 76 543210
Name - - - - Dedicated Key 0 ~ 3
Read/WriteRR RRRRRR
Reset
00 001111
Val ue
Table 55. Bit description
Bit Name Description
7--
6--
5--
4--
3 Dedicated Key 3 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
2 Dedicated Key 2 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
1 Dedicated Key 1 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
0 Dedicated Key 0 ‘0’ for key-down, ‘1’ for key-up
53/63
Page 54

Keypad controller STMPE2403
12.8.1 Resistance
Maximum resistance between keypad output and keypad input, inclusive of switch
resistance, protection circuit resistance and connection, must be less than 3.2 KΩ
12.8.2 Using the keypad controller
It is not necessary to explicitly enable the internal pull-up and direction by configuring the GPIO control
registers. Once a GPIO is enabled for keypad function, its internal pull-up and direction is controlled
automatically.
The scanning of column inputs should then be enabled for those GPIO ports that are
configured as keypad inputs by writing ‘1’s to the corresponding bits in the KPC_col register.
If any of the first three column inputs is to be used as dedicated key input, the corresponding
bits in the KPC_ctrl_msb register should be set to ‘1’. The bits in the KPC_row_msb and
KPC_row_lsb registers should also be set correctly to enable the row output scanning for
the corresponding GPIO ports programmed as keypad outputs.
The scan count and de-bounce count should also be programmed into the keypad control
registers before enabling the keypad controller operation. To enable the keypad controller
operation, the Enable_KPC bit in the system control register must be set to ‘1’ to provide the
required clock signals. The keypad controller will then start its operation by setting the
SCAN bit in the KPC_ctrl_lsb register to ‘1’.
The keypad controller operation can be disabled by setting the SCAN bit back to ‘0’. To
further reduce the power consumption, the clock signals can be cut off from the keypad
controller by setting the Enable_KPC bit to ‘0’.
As long as there is any un-read key-press in the keypad controller buffer, the KPC interrupt
will always be asserted.
12.8.3 Ghost Key Handling
Ghost key is an inherent in keypad matrix that is not equipped with a diode at each of the
keys. While it is not possible to avoid ghost key occurrence, the STMPE2403 allow the
detection of possible ghost key by the capability of detecting 3 simultaneous key-presses in
the key matrix.
Ghost key is only possible if 3 keys are pressed and held down together in a keypad matrix.
If 3 keys are reported by STMPE2403 keypad controller, it indicates a potential ghost key
situation. The system may check for possibility of ghost key by analyzing the coordinates of
the 3 keys. If the 3 keys form 3 corners of a rectangle, it could be a ghost key situation.
Ghost key may also occur in the Special Function Keys. The keypad controller does not
attempt to avoid the occurrence of ghost keys. However, the system should be aware that if
more than one special function key is reported, then there is a possibility of ghost key.
54/63
Page 55

STMPE2403 Keypad controller
12.8.4 Priority of Key detection
Dedicated key will always be detected, if it is enabled.
When a Special Function key is detected, the matrix key scanning on the same input line will
be disabled.
Up to 3 matrix keys will be detected. Matrix keys that fall on activated Special Function keys
will not be counted.
As a result of these rules of priority, a matrix key will be ignored by the keypad controller
when the special function key on the same input line is detected, even if the matrix key is
being pressed down before the special function key. Hence, when a matrix is reported “keydown” and it is being held down while the corresponding special function is being pressed, a
“no-key” status will be reported for the matrix key when the special function key is reported
“key-down”. If the matrix key is released while the special function key is still being held
down, no “key-up” will be reported for the matrix key. On the other hand, if the matrix key is
released after the special function key is reported “key-up”, then a new “key-down” will be
reported for the matrix key, followed by “key-up”.
12.8.5 Keypad Wake-Up from sleep and hibernate modes
The keypad controller is functional in sleep mode as long as it is enabled before entering sleep mode.
It will then wake the system up into operational mode if a valid key press is detected.
In the case of hibernate mode, the ‘Hib_Wk’ bit in ‘KPC_row_msb’ register must be set to ‘1’ in order to
enable system wake-up by valid key press. When this is enabled, asynchronous detection of keypad
column input activity will be turned on during hibernate mode. If any key activity is detected, the
system is expected to enter sleep mode temporarily to allow de-bouncing of key press to take place. If
a valid key is detected, the system will then wake up into operational mode; otherwise, the device will
go back into hibernate mode.
55/63
Page 56

Rotator controller STMPE2403
C
13 Rotator controller
Rotator controller consists of 3 terminal, each capable of becoming an input with internal
pull-up, or and output. At any moment, 2 terminals are inputs and one terminal is output.
Figure 11. Rotator controller
A
Rotator Controller
B
The Rotator Controller is responsible for the detection of the direction of rotator and the
reporting of these direction sequences. The direction of a rotator can be either up or down.
A rotator has 3 contacts and detection of shorts on these contacts is used to determine the
direction of rotation. Following diagram shows the definition of the direction of rotation and
how the FSM states and driven outputs correspond to rotation.
3 possible conditions: A-B short, B-C short, C-A short.
Table 56. Possible conditions
LO
Input
C1 ABC2BACUp
B1ABC3CABDown
A2BAC3CABDown
C2 BAC1ABCUp
A3CAB2BACUp
B3CAB1ABCDown
State Output Input Input State Output Input Input
Current State Next State
Result
Figure 12. Rotator direction detection
56/63
Page 57

STMPE2403 Rotator controller
Figure 13. Registers for rotator control
Address Register name Register size
0x70 Rotator_Control 8
0x72 Rotator_Buffer 8
Rotator_Control
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Start_FSM Reserved
Read/Write RW R R R R R R R
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 57. Bit description
Bits Name Description
7 Start_FSM Rotator FSM start bit.
‘1’ – Activate the FSM
‘0’ – Stop sampling rotator symbols
Rotator_Buffer
Bit 7 6543210
Symbol_Type Symbol_Count
Read/Write R R R R R R R R
Reset Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 58. Bit description
Bits Name Description
7 Symbol_Type Symbol type to be reported
‘1’ – Down
‘0’ – Up
6~0 Symbol_Count Number of symbols of the type specified by bit 7
Minimum of 0 (b’0000000) to
Maximum of 127 (b’1111111)
The host should do the following on the I2C bus to start the Rotator controller:
1. The host writes to GPIO Controller to select the Rotator Bits on the relevant IO.
2. Write Rotator_Control data register to start the rotator controller. A maximum of 2
rotations later, the correct initial state on the rotator FSM is obtained. Scanning for
rotator movement continues.
3. The host waits for interrupt from the rotator controller.
4. The host reads Rotator_Buffer
5. The host can stop rotator controller operation by writing to Rotator_Control register.
57/63
Page 58

Miscellaneous features STMPE2403
14 Miscellaneous features
14.1 Reset
STMPE2403 is equipped with an internal POR circuit that holds the device in reset state,
until the clock is steady and VCC input is valid. Host system may choose to reset the
STMPE2403 by asserting Reset_N pin.
14.2 Under Voltage Lockout
STMPE2403 is equipped with an internal UVLO circuit that generates a RESET signal,
when the main supply voltage falls below the allowed threshold.
14.3 Clock output
STMPE2403 provides a buffered 32KHz clock output at one of the GPIO as alternate
function. This clock could be used for cascading of multiple port expander devices, using
just 1 XTAL unit.
14.4 Crystal oscillator
STMPE2403 provides the option to use a crystal oscillator to provide the 32KHz clock.
Figure 14. Recommended schematics if external XTAL is used
STMPE2403
XTAL OUT
XTAL IN
32KHz
27pF
27pF
GND
58/63
Page 59

STMPE2403 Package mechanical data
15 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect . The category of
second level interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com
59/63
Page 60

Package mechanical data STMPE2403
Table 59. TFBGA Mechanical data
mm. inch
Dim.
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
A 1.1 1 1.16 0.043 0.039 0.046
A1 0.25 0.010
A2 0.78 0.86 0.031 0.034
b 0.30 0.25 0.35 0.012 0.010 0.014
D 3.60 3.50 3.70 0.142 0.138 0.146
D1 3.50 0.138
E 3.50 3.60 3.70 0.142 0.138 0.146
E1 2.50 0.098
e 0.50 0.020
F 0.55 0.022
Figure 15. Package dimensions
60/63
Page 61

STMPE2403 Package mechanical data
Figure 16. Recommended footprint
Figure 17. Tape and reel information
61/63
Page 62

Revision history STMPE2403
16 Revision history
Table 60. Revision history
Date Revision Changes
08-Jun-2007 1 Initial release
62/63
Page 63

STMPE2403
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2007 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
63/63
 Loading...
Loading...