ST STM8AF52AA, STM8AF52A9, STM8AF52A8, STM8AF528A, STM8AF5289 User Manual
...
STM8AF5xxx STM8AF6x69/7x/8x/9x/Ax
LQFP80 14x14
LQFP48 7x7
LQFP32 7x7
VFQFPN32 5x5
LQFP64 10x10
Automotive 8-bit MCU, with up to 128 Kbytes Flash, data EEPROM,
10-bit ADC, timers, LIN, CAN, USART, SPI, I2C, 3 to 5.5 V
Datasheet − production data
Features
■ Core
–Max f
– Advanced STM8A core with Harvard
architecture and 3-stage pipeline
– Average 1.6 cycles/instruction resulting in
10 MIPS at 16 MHz f
standard benchmark
■ Memories
– Program memory: 32 to 128 Kbytes Flash
program; data retention 20 years at 55 °C
– Data memory: up to 2 Kbytes true data
EEPROM; endurance 300 kcycles
– RAM: 2 Kbytes to 6 Kbytes
■ Clock management
– Low-power crystal resonator oscillator with
external clock input
– Internal, user-trimmable 16 MHz RC and
low-power 128 kHz RC oscillators
– Clock security system with clock monitor
■ Reset and supply management
– Wait/auto-wakeup/Halt low-power modes
with user definable clock gating
– Low consumption power-on and power-
down reset
■ Interrupt management
– Nested interrupt controller with 32 vectors
– Up to 37 external interrupts on 5 vectors
■ Timers
– 2 general purpose 16-bit timers with up to 3
CAPCOM channels each (IC, OC, PWM)
– Advanced control timer: 16-bit, 4 CAPCOM
channels, 3 complementary outputs, dead-
time insertion and flexible synchronization
– 8-bit AR basic timer with 8-bit prescaler
– Auto-wakeup timer
– Window and independent watchdog timers
■ I/Os
– Up to 68 user pins (11 high sink I/Os)
– Highly robust I/O design, immune against
current injection
CPU
: 24 MHz
for industry
CPU
■ Communication interfaces
– High speed 1 Mbit/s CAN 2.0B interface
– USART with clock output for synchronous
operation - LIN master mode
– LINUART LIN 2.1 compliant, master/slave
modes with automatic resynchronization
– SPI interface up to 10 Mbit/s or f
2
–I
C interface up to 400 Kbit/s
■ Analog to digital converter (ADC)
MASTER
– 10-bit resolution, 2 LSB TUE, 1 LSB
linearity and up to 16 multiplexed channels
■ Operating temperature up to 150 °C
■ Qualification conforms to AEC-Q100 rev G
Table 1. Device summary
Part numbers: STM8AF52xx (with CAN)
STM8AF52AA, STM8AF52A9, STM8AF52A8, STM8AF528A,
STM8AF5289, STM8AF5288, STM8AF5269, STM8AF5268
Part numbers: STM8AF6269/8x/Ax
STM8AF62AA, STM8AF62A9, STM8AF62A8, STM8AF628A,
STM8AF6289, STM8AF6288, STM8AF6286, STM8AF6269,
STM8AF62A6,
Part numbers: STM8AF51xx
STM8AF51AA, STM8AF51A9, STM8AF51A8, STM8AF519A,
STM8AF5199, STM8AF5198, STM8AF518A, STM8AF5189,
STM8AF5188, STM8AF5179, STM8AF5178, STM8AF5169,
STM8AF5168
Part numbers: STM8AF6169/7x/8x/9x/Ax
STM8AF61AA, STM8AF61A9, STM8AF61A8, STM8AF619A,
STM8AF6199, STM8AF6198, STM8AF618A, STM8AF6189,
STM8AF6188, STM8AF6186, STM8AF6179, STM8AF6178,
STM8AF6176, STM8AF6169
In the order code, ‘F’ applies to devices with Flash program
1.
memory and data EEPROM while ‘H’ refers to devices with
Flash program memory only. ‘F’ is replaced by ‘P’ for devices
with FASTROM (see Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5, and Figure 52).
2. Not recommended for new design.
(with CAN)
(1)
(2)
(2)
/2
July 2012 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 1/110
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
1

Contents STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Product line-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5 Product overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1 STM8A central processing unit (CPU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.1 Architecture and registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.2 Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.3 Instruction set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2 Single wire interface module (SWIM) and debug module (DM) . . . . . . . . 16
5.2.1 SWIM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.2.2 Debug module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3 Interrupt controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4 Flash program and data EEPROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.1 Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.2 Write protection (WP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.3 Protection of user boot code (UBC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.4 Read-out protection (ROP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.5 Clock controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.2 16 MHz high-speed internal RC oscillator (HSI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.3 128 kHz low-speed internal RC oscillator (LSI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5.4 24 MHz high-speed external crystal oscillator (HSE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5.5 External clock input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5.6 Clock security system (CSS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.6 Low-power operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
5.7 Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.7.1 Watchdog timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.7.2 Auto-wakeup counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.7.3 Beeper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Contents
5.7.4 Advanced control and general purpose timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.7.5 Basic timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.8 Analog to digital converter (ADC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.9 Communication interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.9.1 Universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART) . . 23
5.9.2 Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter with LIN support
(LINUART) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.9.3 Serial peripheral interface (SPI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5.9.4 Inter integrated circuit (I
5.9.5 Controller area network interface (beCAN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2
C) interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5.10 Input/output specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6 Pinouts and pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.1 Package pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.2 Alternate function remapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7 Memory and register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.1 Memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.2 Register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8 Interrupt table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
9 Option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
10 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1 Parameter conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1.1 Minimum and maximum values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1.2 Typical values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1.3 Typical curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1.4 Loading capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.1.5 Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
10.2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
10.3 Operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
10.3.1 VCAP external capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
10.3.2 Supply current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
10.3.3 External clock sources and timing characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
10.3.4 Internal clock sources and timing characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 3/110

Contents STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
10.3.5 Memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
10.3.6 I/O port pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
10.3.7 Reset pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
10.3.8 TIM 1, 2, 3, and 4 electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
10.3.9 SPI interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
10.3.10 I
10.3.11 10-bit ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
10.3.12 EMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
2
C interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
10.4 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
10.4.1 Reference document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
10.4.2 Selecting the product temperature range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
11 Package characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
11.1 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
12 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
13 STM8 development tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
13.1 Emulation and in-circuit debugging tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
13.1.1 STice key features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
13.2 Software tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
13.2.1 STM8 toolset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
13.2.2 C and assembly toolchains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
13.3 Programming tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
14 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
4/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. STM8AF52xx product line-up with CAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 3. STM8AF62xx product line-up without CAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 4. STM8AF/H/P51xx product line-up with CAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 5. STM8AF/H/P61xx product line-up without CAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6. Peripheral clock gating bits (CLK_PCKENR1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 7. Peripheral clock gating bits (CLK_PCKENR2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. Advanced control and general purpose timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 9. TIM4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. ADC naming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 11. Communication peripheral naming correspondence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 12. Legend/abbreviation for the pin description table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 13. STM8A microcontroller family pin description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 14. Memory model 128K. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 15. I/O port hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 16. General hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 17. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 18. Temporary memory unprotection registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 19. STM8A interrupt table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 20. Option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 21. Option byte description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 22. Voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 23. Current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 24. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 25. Operating lifetime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 26. General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 27. Operating conditions at power-up/power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 28. Total current consumption in Run, Wait and Slow mode. General conditions
for V
Table 29. Total current consumption in Halt and Active-halt modes. General conditions for V
applied. TA = -40 °C to 55 °C unless otherwise stated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 30. Oscillator current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 31. Programming current consumption. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 32. Typical peripheral current consumption V
Table 33. HSE external clock characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 34. HSE oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 35. HSI oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 36. LSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 37. Flash program memory/data EEPROM memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 38. Flash program memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 39. Data memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table 40. I/O static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table 41. NRST pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table 42. TIM 1, 2, 3, and 4 electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table 43. SPI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Table 44. I
2
C characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 45. ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Table 46. ADC accuracy for V
apply, TA = -40 °C to 150 °C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
DD
DD
= 5.0 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
DD
= 5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
DDA
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 5/110

List of tables STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
Table 47. EMS data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Table 48. EMI data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Table 49. ESD absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Table 50. Electrical sensitivities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Table 51. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Table 52. LQFP 80-pin low profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Table 53. LQFP 64-pin low profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Table 54. LQFP 48-pin low profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Table 55. LQFP 32-pin low profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Table 56. VFQFPN 32-lead very thin fine pitch quad flat no-lead package
mechanical data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Table 57. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
6/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. STM8A block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 2. Flash memory organization of STM8A products. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 3. LQFP 80-pin pinout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 4. LQFP 64-pin pinout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 5. LQFP 48-pin pinout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 6. LQFP/VFQFPN 32-pin pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 7. Register and memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 8. Pin loading conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 9. Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 10. f
CPUmax
Figure 11. External capacitor C
Figure 12. Typ. I
Figure 13. Typ. I
Figure 14. Typ. I
Figure 15. Typ. I
Figure 16. Typ. I
Figure 17. Typ. I
Figure 18. HSE external clock source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 19. HSE oscillator circuit diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 20. Typical HSI frequency vs V
Figure 21. Typical LSI frequency vs V
Figure 22. Typical V
Figure 23. Typical pull-up resistance R
Figure 24. Typical pull-up current I
Figure 25. Typ. V
Figure 26. Typ. V
Figure 27. Typ. V
Figure 28. Typ. V
Figure 29. Typ. V
Figure 30. Typ. V
Figure 31. Typ. V
Figure 32. Typ. V
Figure 33. Typ. V
Figure 34. Typ. V
Figure 35. Typical NRST V
Figure 36. Typical NRST pull-up resistance R
Figure 37. Typical NRST pull-up current I
Figure 38. Recommended reset pin protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 39. SPI timing diagram in slave mode and with CPHA = 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 40. SPI timing diagram in slave mode and with CPHA = 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 41. SPI timing diagram - master mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 42. Typical application with ADC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 43. ADC accuracy characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 44. LQFP 80-pin low profile quad flat package (14 x 14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Figure 45. LQFP 64-pin low profile quad flat package (10 x 10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 46. LQFP 64-pin recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 47. LQFP 48-pin low profile quad flat package (7 x 7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 48. LQFP 48-pin recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
versus V
DD(RUN)HSE
DD(RUN)HSE
DD(RUN)HSI
DD(WFI)HSE
DD(WFI)HSE
DD(WFI)HSI
IL
@ VDD = 3.3 V (standard ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
OL
@ VDD = 5.0 V (standard ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
OL
@ VDD = 3.3 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
OL
@ VDD = 5.0 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
OL
@ VDD = 3.3 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
OL
@ VDD = 5.0 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
OL
- V
DD
- V
DD
- VOH @ VDD = 3.3 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
DD
- V
DD
DD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
vs. VDD @f
vs. f
vs. VDD @ f
vs. VDD @ f
vs. f
vs. VDD @ f
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
EXT
@ VDD = 5.0 V, peripherals = on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
@ VDD = 5.0 V, peripherals = on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
= 16 MHz, peripherals = on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
= 16 MHz, peripherals = off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
= 16 MHz, peripherals = on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
= 16 MHz, peripherals = off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CPU
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
DD
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
DD
and VIH vs VDD @ four temperatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
vs VDD @ four temperatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
PU
vs VDD @ four temperatures
pu
@ VDD = 3.3 V (standard ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
OH
@ VDD = 5.0 V (standard ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
OH
@ VDD = 5.0 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
OH
and VIH vs VDD @ four temperatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
IL
pu
vs VDD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
PU
vs VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 7/110

List of figures STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
Figure 49. LQFP 32-pin low profile quad flat package (7 x 7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Figure 50. LQFP 32-pin recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 51. VFQFPN 32-lead very thin fine pitch quad flat no-lead package (5 x 5). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure 52. Ordering information scheme
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
8/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Introduction
1 Introduction
This datasheet refers to the STM8AF52xx, STM8AF62xx, STM8AF51xx, and STM8AF61xx
products with 32 to 128 Kbytes of program memory.
In the order code, the letter ‘F’ refers to product versions with Flash and data EEPROM, ‘H’
to product versions with Flash only, and ‘P’ to product versions with FASTROM. The
identifiers ‘F’, ‘H’, and ‘P’ do not coexist in a given order code.
The datasheet contains the description of family features, pinout, electrical characteristics,
mechanical data and ordering information.
● For complete information on the STM8A microcontroller memory, registers and
peripherals, please refer to STM8S and STM8A microcontroller families reference
manual (RM0016).
● For information on programming, erasing and protection of the internal Flash memory
please refer to the STM8S and STM8A Flash programming manual (PM0051).
● For information on the debug and SWIM (single wire interface module) refer to the
STM8 SWIM communication protocol and debug module user manual (UM0470).
● For information on the STM8 core, please refer to the STM8 CPU programming manual
(PM0044).
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 9/110

Description STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
2 Description
The STM8AF52xx, STM8AF62xx, STM8AF51xx, and STM8AF61xx automotive 8-bit
microcontrollers described in this datasheet offer from 32 Kbytes to 128 Kbytes of non
volatile memory and integrated true data EEPROM. They are referred to as high density
STM8A devices in the STM8S and STM8A microcontroller families reference manual
(RM0016).
The STM8AF51xx and STM8AF52xx series feature a CAN interface.
All devices of the STM8A product line provide the following benefits: reduced system cost,
performance and robustness, short development cycles, and product longevity.
The system cost is reduced thanks to an integrated true data EEPROM for up to 300 k
write/erase cycles and a high system integration level with internal clock oscillators,
watchdog, and brown-out reset.
Device performance is ensured by 20 MIPS at 24 MHz CPU clock frequency and enhanced
characteristics which include robust I/O, independent watchdogs (with a separate clock
source), and a clock security system.
Short development cycles are guaranteed due to application scalability across a common
family product architecture with compatible pinout, memory map and and modular
peripherals. Full documentation is offered with a wide choice of development tools.
Product longevity is ensured in the STM8A family thanks to their advanced core which is
made in a state-of-the art technology for automotive applications with 3.3 V to 5.5 V
operating supply.
All STM8A and ST7 microcontrollers are supported by the same tools including
STVD/STVP development environment, the STice emulator and a low-cost, third party incircuit debugging tool.
10/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product line-up
3 Product line-up
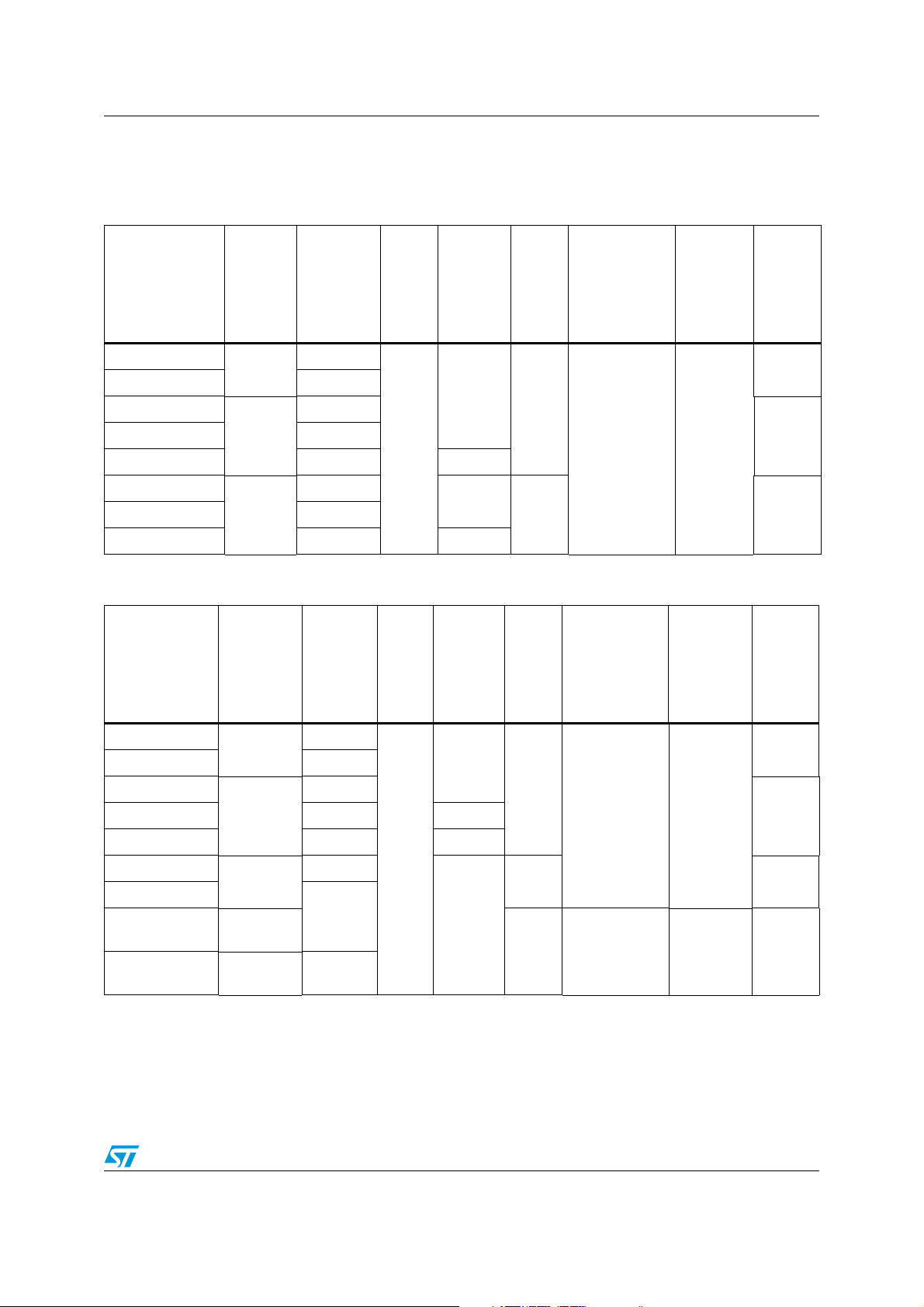
Table 2. STM8AF52xx product line-up with CAN
..
High
Order code Package
density
Flash
program
memory
RAM
(bytes)
Data
EEPROM
(bytes)
(bytes)
STM8AF/P52AA
STM8AF/P528A 64 K
LQFP80
(14x14)
128 K
2 K
STM8AF/P52A9
128 K
LQFP64
(10x10)
6 K
STM8AF/P5269 32 K 1 K
STM8AF/P52A8
LQFP48
128 K
2 K
(7x7)
STM8AF/P5268 32 K 1K
Table 3. STM8AF62xx product line-up without CAN
High
Order code Package
density
Flash
program
memory
RAM
(bytes)
Data
EEPROM
(bytes)
(bytes)
10-bit
A/D
chan.
16
10 38/35STM8AF/P5288 64 K
10-bit
A/D
chan.
Timers
(IC/OC/PWM)
1x8-bit: TIM4
3x16-bit: TIM1,
TIM2, TIM3
(9/9/9)
Timers
(IC/OC/PWM)
Serial
interfaces
CAN,
LIN(UART)
, SPI,
USART,
I²C
Serial
interfaces
I/0
wakeup
pins
68/37
52/36STM8AF/P5289 64 K
I/0
wakeup
pins
STM8AF/P62AA
STM8AF/P628A 64 K
LQFP80
(14x14)
STM8AF/P62A9
128 K
2 K
128 K
LQFP64
(10x10)
STM8AF/P6269 32 K 1 K
STM8AF/P62A8
STM8AF/P6288
STM8AF/P6286
STM8AF/P62A6
LQFP48
(7x7)
LQFP32
(7x7)
VFQFPN32
(5x5)
128 K
64 K
128 K
6 K
2 K
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 11/110
68/37
16
1x8-bit: TIM4
3x16-bit: TIM1,
TIM2, TIM3
(9/9/9)
LIN(UART),
SPI,
USART, I²C
52/36STM8AF/P6289 64 K 2 K
10 38/35
1x8-bit: TIM4
3x16-bit: TIM1,
7
TIM2, TIM3
LIN(UART),
SPI, I²C
25/23
(8/8/8)
Product line-up STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
.
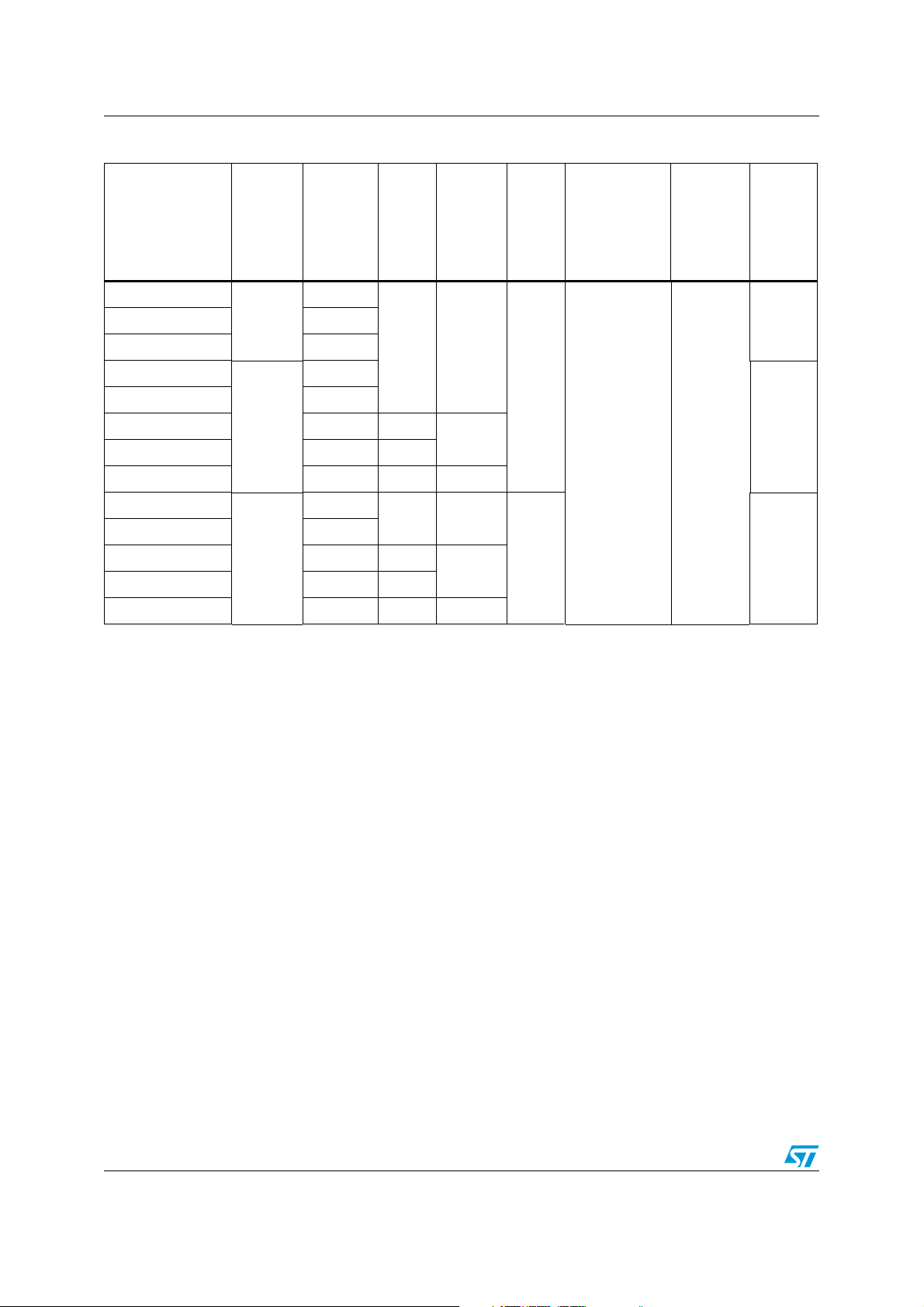
Table 4. STM8AF/H/P51xx product line-up with CAN
High
Order code Package
density
Flash
program
memory
(bytes)
RAM
(bytes)
Data
EEPROM
(bytes)
10-bit
A/D
chan.
Timers
(IC/OC/PWM)
Serial
interfaces
I/0
wakeup
pins
STM8AF/H/P51AA
128 K
LQFP80
(14x14)
STM8AF/H/P518A 64 K
STM8AF/H/P51A9
128 K
6 K 2 K
STM8AF/H/P5199 96 K
STM8AF/H/P5189 64 K 4 K
LQFP64
(10x10)
1.5 K
STM8AF/H/P5179 48 K 3 K
STM8AF/H/P5169 32 K 2 K 1 K
STM8AF/H/P51A8
128 K
6 K 2 K
STM8AF/H/P5198 96 K
STM8AF/H/P5188 64 K 4 K
LQFP48
(7x7)
1.5 K
STM8AF/H/P5178 48 K 3 K
STM8AF/H/P5168 32 K 2 K 1K
68/37STM8AF/H/P519A 96 K
16
1x8-bit: TIM4
3x16-bit: TIM1,
TIM2, TIM3
(9/9/9)
CAN,
LIN(UART)
, SPI,
USART,
I²C
52/36
10 38/35
12/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product line-up
²
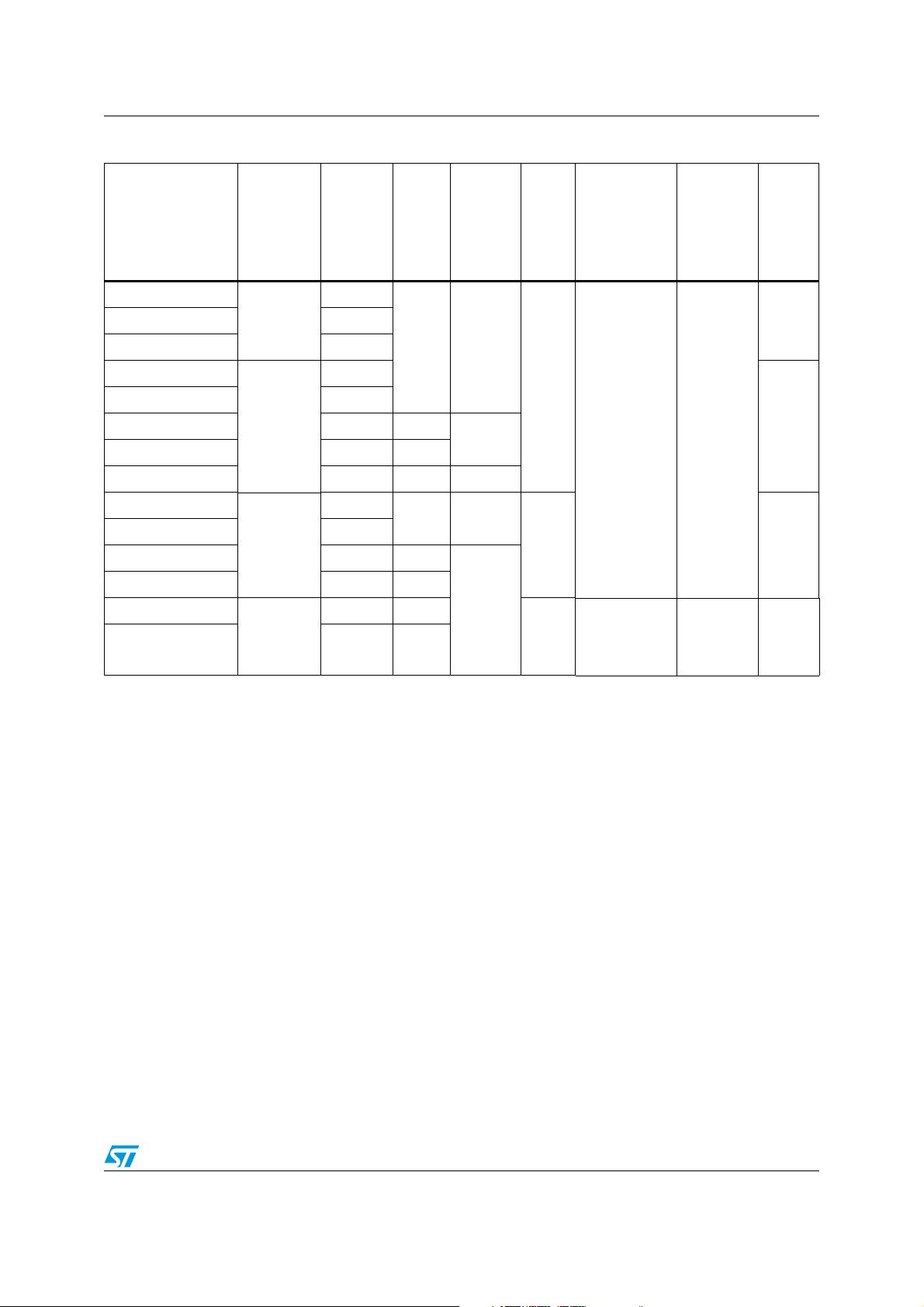
Table 5. STM8AF/H/P61xx product line-up without CAN
High
Order code Package
density
Flash
program
memory
(bytes)
RAM
(bytes)
Data
EEPROM
(bytes)
10-bit
A/D
chan.
Timers
(IC/OC/PWM)
Serial
interfaces
I/0
wakeup
pins
STM8AF/H/P61AA
128 K
LQFP80
(14x14)
STM8AF/H/P618A 64 K
STM8AF/H/P61A9
128 K
6 K 2 K
STM8AF/H/P6199 96 K
STM8AF/H/P6189 64 K 4 K
LQFP64
(10x10)
1.5 K
STM8AF/H/P6179 48 K 3 K
STM8AF/H/P6169 32 K 2 K 1 K
STM8AF/H/P61A8
128 K
6 K 2 K
STM8AF/H/P6198 96 K
STM8AF/H/P6188 64 K 4 K
LQFP48
(7x7)
STM8AF/H/P6178 48 K 3 K
STM8AF/H/P6186
64 K 4 K
1.5 K
LQFP32
STM8AF/H/P6176 48 K 3 K
(7x7)/
68/37STM8AF/H/P619A 96 K
16
1x8-bit: TIM4
3x16-bit:
TIM1, TIM2,
TIM3
LIN(UART),
SPI,
USART, I²C
52/36
(9/9/9)
10 38/35
1x8-bit: TIM4
7
3x16-bit:
TIM1, TIM2,
LIN(UART),
SPI, I²C
25/23
TIM3 (8/8/8)
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 13/110
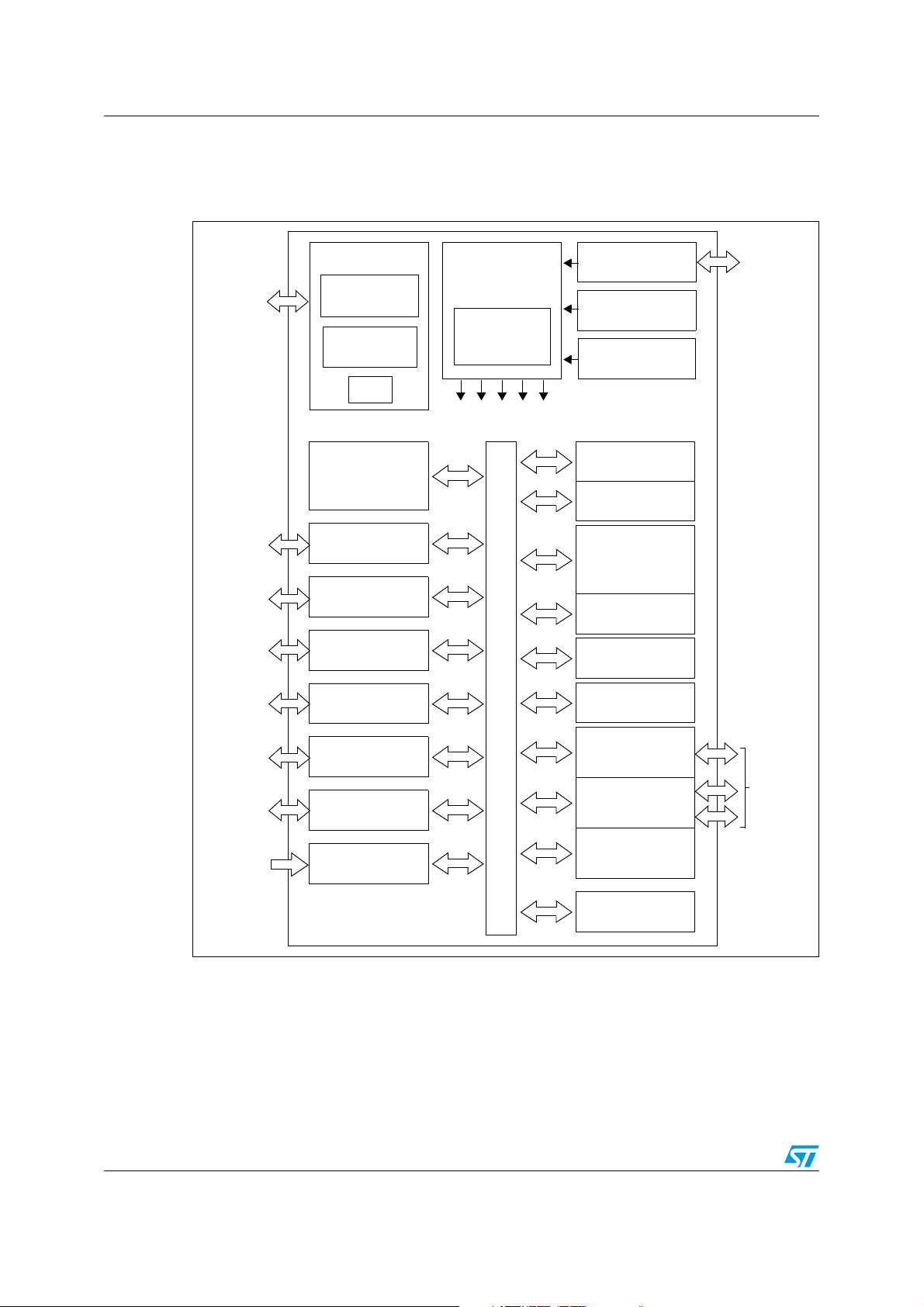
Block diagram STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
XTAL 1-24 MHz
RC int. 16 MHz
RC int. 128 kHz
STM8A CORE
Debug/SWIM
I
2
C
SPI
USART
LINUART
16-bit general purpose
AWU tim er
Reset block
Reset
Clock controller
Detector
Clock to peripherals and core
10 Mbit/s
LIN master
Up to
Window WDG
IWDG
Up to 128 Kbyte
Up to 2 Kbytes
Up to 6 Kbytes
Boot ROM
10-bit ADC
beCAN
9 CAPCOM
Reset
400 Kbit/s
1 Mbit/s
Master/slave
Single wire
automatic
debug interf.
SPI emul.
channels
high density program
Flash
16-bit advanced control
timer (TIM1)
(TIM2, TIM3)
8-bit AR timer
(TIM4)
data EEPROM
RAM
Up to
Address and data bus
16 channels
resynchronization
POR
BOR
4 Block diagram
Figure 1. STM8A block diagram
1. Legend:
ADC: Analog-to-digital converter
beCAN: Controller area network
BOR: Brownout reset
I²C: Inter-integrated circuit multimaster interface
IWDG: Independent window watchdog
LINUART: Local interconnect network universal asynchronous receiver transmitter
POR: Power on reset
SPI: Serial peripheral interface
SWIM: Single wire interface module
USART: Universal synchronous asynchronous receiver transmitter
14/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
Window WDG: Window watchdog

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
5 Product overview
This section is intended to describe the family features that are actually implemented in the
products covered by this datasheet.
For more detailed information on each feature please refer to the STM8S and STM8A
microcontroller families reference manual (RM0016).
5.1 STM8A central processing unit (CPU)
The 8-bit STM8A core is a modern CISC core and has been designed for code efficiency
and performance. It contains 21 internal registers (six directly addressable in each execution
context), 20 addressing modes including indexed indirect and relative addressing and 80
instructions.
5.1.1 Architecture and registers
● Harvard architecture
● 3-stage pipeline
● 32-bit wide program memory bus with single cycle fetching for most instructions
● X and Y 16-bit index registers, enabling indexed addressing modes with or without
offset and read-modify-write type data manipulations
● 8-bit accumulator
● 24-bit program counter with 16-Mbyte linear memory space
● 16-bit stack pointer with access to a 64 Kbyte stack
● 8-bit condition code register with seven condition flags for the result of the last
instruction.
5.1.2 Addressing
● 20 addressing modes
● Indexed indirect addressing mode for look-up tables located anywhere in the address
space
● Stack pointer relative addressing mode for efficient implementation of local variables
and parameter passing
5.1.3 Instruction set
● 80 instructions with 2-byte average instruction size
● Standard data movement and logic/arithmetic functions
● 8-bit by 8-bit multiplication
● 16-bit by 8-bit and 16-bit by 16-bit division
● Bit manipulation
● Data transfer between stack and accumulator (push/pop) with direct stack access
● Data transfer using the X and Y registers or direct memory-to-memory transfers
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 15/110

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
5.2 Single wire interface module (SWIM) and debug module (DM)
5.2.1 SWIM
The single wire interface module, SWIM, together with an integrated debug module, permits
non-intrusive, real-time in-circuit debugging and fast memory programming. The interface
can be activated in all device operation modes and can be connected to a running device
(hot plugging).The maximum data transmission speed is 145 bytes/ms.
5.2.2 Debug module
The non-intrusive debugging module features a performance close to a full-flavored
emulator. Besides memory and peripheral operation, CPU operation can also be monitored
in real-time by means of shadow registers.
● R/W of RAM and peripheral registers in real-time
● R/W for all resources when the application is stopped
● Breakpoints on all program-memory instructions (software breakpoints), except the
interrupt vector table
● Two advanced breakpoints and 23 predefined breakpoint configurations
5.3 Interrupt controller
● Nested interrupts with three software priority levels
● 24 interrupt vectors with hardware priority
● Five vectors for external interrupts (up to 37 depending on the package)
● Trap and reset interrupts
5.4 Flash program and data EEPROM
● 32 Kbytes to 128 Kbytes of high density single voltage Flash program memory
● Up to 2 Kbytes true (not emulated) data EEPROM
● Read while write: writing in the data memory is possible while executing code in the
Flash program memory.
The whole Flash program memory and data EEPROM are factory programmed with 0x00.
5.4.1 Architecture
● The memory is organized in blocks of 128 bytes each
● Read granularity: 1 word = 4 bytes
● Write/erase granularity: 1 word (4 bytes) or 1 block (128 bytes) in parallel
● Writing, erasing, word and block management is handled automatically by the memory
interface.
16/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
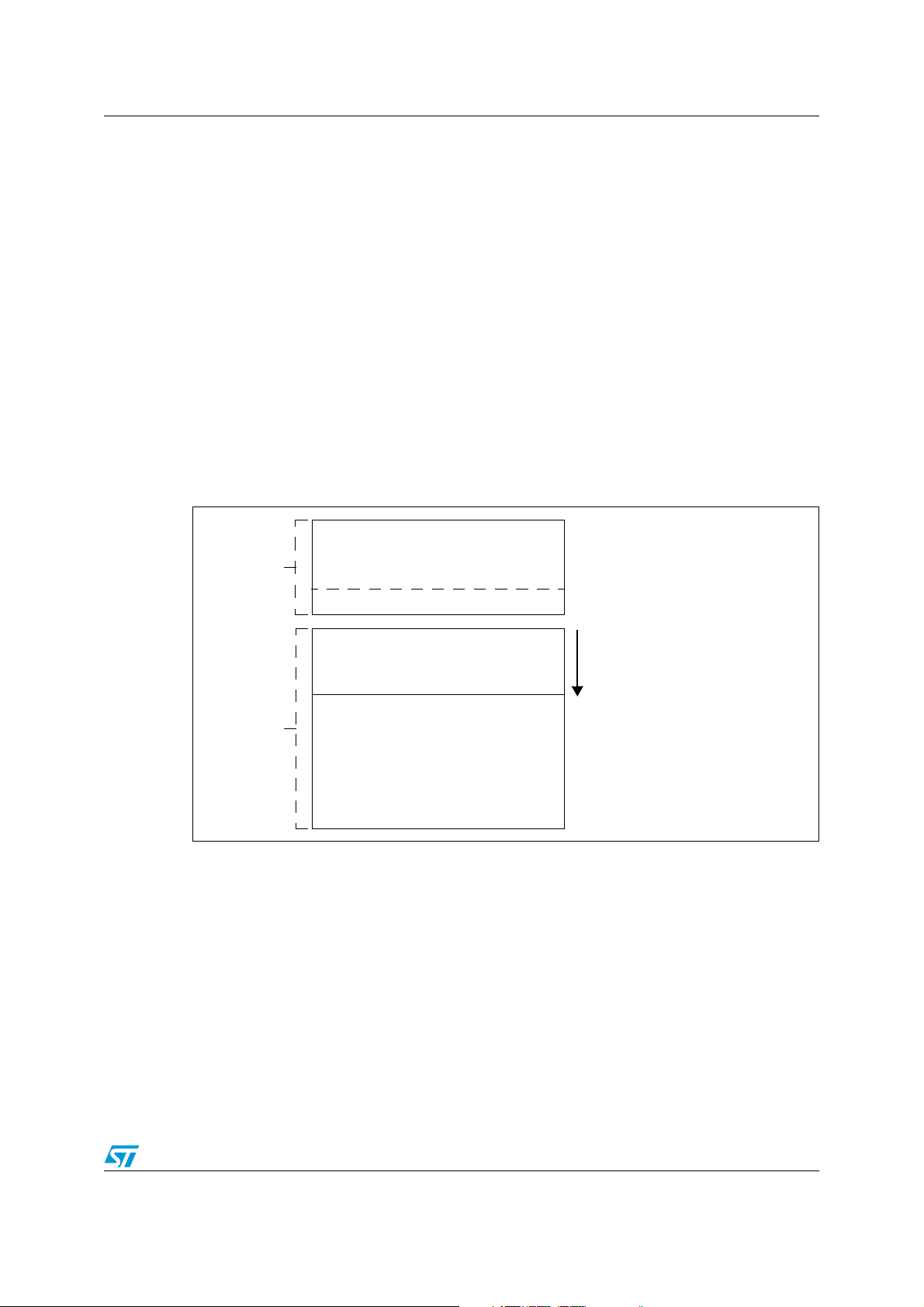
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
Programmable area from 1 Kbyte
Data
UBC area
Program memory area
Data memory area
(first two pages) up to program memory
EEPROM
Remains write protected during IAP
memory
Write access possible for IAP
Option bytes
end - maximum 128 Kbytes
Flash
program
memory
5.4.2 Write protection (WP)
Write protection in application mode is intended to avoid unintentional overwriting of the
memory. The write protection can be removed temporarily by executing a specific sequence
in the user software.
5.4.3 Protection of user boot code (UBC)
If the user chooses to update the Flash program memory using a specific boot code to
perform in application programming (IAP), this boot code needs to be protected against
unwanted modification.
In the STM8A a memory area of up to 128 Kbytes can be protected from overwriting at user
option level. Other than the standard write protection, the UBC protection can exclusively be
modified via the debug interface, the user software cannot modify the UBC protection status.
The UBC memory area contains the reset and interrupt vectors and its size can be adjusted
in increments of 512 bytes by programming the UBC and NUBC option bytes
(see Section 9: Option bytes on page 51).
Figure 2. Flash memory organization of STM8A products
5.4.4 Read-out protection (ROP)
The STM8A provides a read-out protection of the code and data memory which can be
activated by an option byte setting (see the ROP option byte in section 10).
The read-out protection prevents reading and writing Flash program memory, data memory
and option bytes via the debug module and SWIM interface. This protection is active in all
device operation modes. Any attempt to remove the protection by overwriting the ROP
option byte triggers a global erase of the program and data memory.
The ROP circuit may provide a temporary access for debugging or failure analysis. The
temporary read access is protected by a user defined, 8-byte keyword stored in the option
byte area. This keyword must be entered via the SWIM interface to temporarily unlock the
device.
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 17/110

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
If desired, the temporary unlock mechanism can be permanently disabled by the user
through OPT6/NOPT6 option bytes.
5.5 Clock controller
The clock controller distributes the system clock coming from different oscillators to the core
and the peripherals. It also manages clock gating for low-power modes and ensures clock
robustness.
5.5.1 Features
● Clock sources
– 16 MHz high-speed internal RC oscillator (HSI)
– 128 kHz low-speed internal RC (LSI)
– 1-24 MHz high-speed external crystal (HSE)
– Up to 24 MHz high-speed user-external clock (HSE user-ext)
● Reset: After reset the microcontroller restarts by default with an internal 2-MHz clock
(16 MHz/8). The clock source and speed can be changed by the application program
as soon as the code execution starts.
● Safe clock switching: Clock sources can be changed safely on the fly in Run mode
through a configuration register. The clock signal is not switched until the new clock
source is ready. The design guarantees glitch-free switching.
● Clock management: To reduce power consumption, the clock controller can stop the
clock to the core, individual peripherals or memory.
● Wakeup: In case the device wakes up from low-power modes, the internal RC
oscillator (16 MHz/8) is used for quick startup. After a stabilization time, the device
switches to the clock source that was selected before Halt mode was entered.
● Clock security system (CSS): The CSS permits monitoring of external clock sources
and automatic switching to the internal RC (16 MHz/8) in case of a clock failure.
● Configurable main clock output (CCO): This feature permits to outputs a clock signal
for use by the application.
5.5.2 16 MHz high-speed internal RC oscillator (HSI)
● Default clock after reset 2 MHz (16 MHz/8)
● Fast wakeup time
User trimming
The register CLK_HSITRIMR with two trimming bits plus one additional bit for the sign
permits frequency tuning by the application program. The adjustment range covers all
possible frequency variations versus supply voltage and temperature. This trimming does
not change the initial production setting.
18/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
5.5.3 128 kHz low-speed internal RC oscillator (LSI)
The frequency of this clock is 128 kHz and it is independent from the main clock. It drives
the independent watchdog or the AWU wakeup timer.
In systems which do not need independent clock sources for the watchdog counters, the
128 kHz signal can be used as the system clock. This configuration has to be enabled by
setting an option byte (OPT3/OPT3N, bit LSI_EN).
5.5.4 24 MHz high-speed external crystal oscillator (HSE)
The external high-speed crystal oscillator can be selected to deliver the main clock in
normal Run mode. It operates with quartz crystals and ceramic resonators.
● Frequency range: 1 MHz to 24 MHz
● Crystal oscillation mode: preferred fundamental
● I/Os: standard I/O pins multiplexed with OSCIN, OSCOUT
5.5.5 External clock input
An external clock signal can be applied to the OSCIN input pin of the crystal oscillator. The
frequency range is 0 to 24 MHz.
5.5.6 Clock security system (CSS)
The clock security system protects against a system stall in case of an external crystal clock
failure.
In case of a clock failure an interrupt is generated and the high-speed internal clock (HSI) is
automatically selected with a frequency of 2 MHz (16 MHz/8).
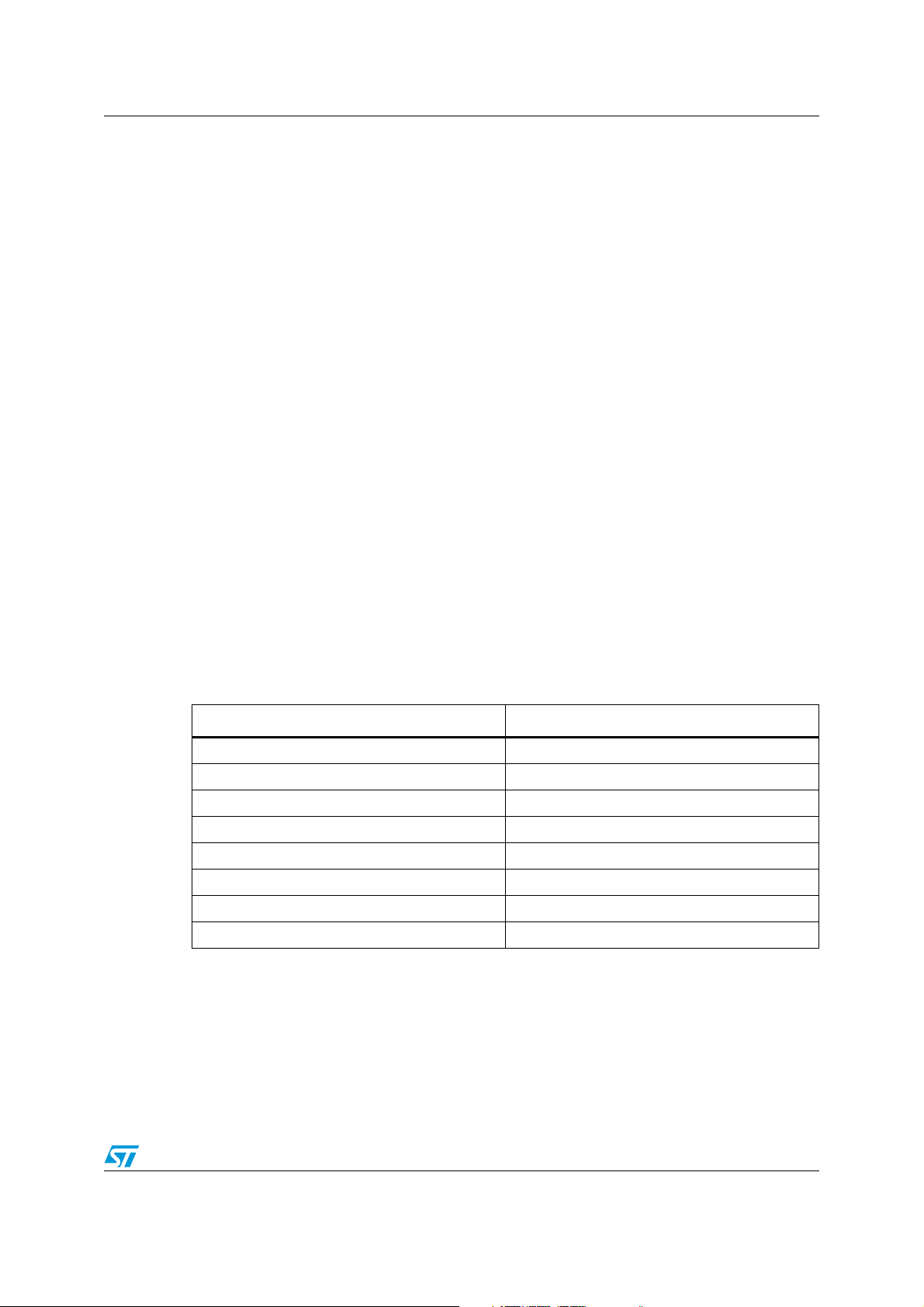
Table 6. Peripheral clock gating bits (CLK_PCKENR1)
Control bit Peripheral
PCKEN17 TIM1
PCKEN16 TIM3
PCKEN15 TIM2
PCKEN14 TIM4
PCKEN13 LINUART
PCKEN12 USART
PCKEN11 SPI
PCKEN10 I
2
C
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 19/110

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
Table 7. Peripheral clock gating bits (CLK_PCKENR2)
Control bit Peripheral
PCKEN27 CAN
PCKEN26 Reserved
PCKEN25 Reserved
PCKEN24 Reserved
PCKEN23 ADC
PCKEN22 AWU
PCKEN21 Reserved
PCKEN20 Reserved
5.6 Low-power operating modes
For efficient power management, the application can be put in one of four different lowpower modes. You can configure each mode to obtain the best compromise between lowest
power consumption, fastest start-up time and available wakeup sources.
● Wait mode
In this mode, the CPU is stopped but peripherals are kept running. The wakeup is
performed by an internal or external interrupt or reset.
● Active-halt mode with regulator on
In this mode, the CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped. An internal wakeup is
generated at programmable intervals by the auto wake up unit (AWU). The main
voltage regulator is kept powered on, so current consumption is higher than in Activehalt mode with regulator off, but the wakeup time is faster. Wakeup is triggered by the
internal AWU interrupt, external interrupt or reset.
● Active-halt mode with regulator off
This mode is the same as Active-halt with regulator on, except that the main voltage
regulator is powered off, so the wake up time is slower.
● Halt mode
CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped, the main voltage regulator is powered off.
Wakeup is triggered by external event or reset.
In all modes the CPU and peripherals remain permanently powered on, the system clock is
applied only to selected modules. The RAM content is preserved and the brown-out reset
circuit remains activated.
20/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
5.7 Timers
5.7.1 Watchdog timers
The watchdog system is based on two independent timers providing maximum security to
the applications. The watchdog timer activity is controlled by the application program or
option bytes. Once the watchdog is activated, it cannot be disabled by the user program
without going through reset.
Window watchdog timer
The window watchdog is used to detect the occurrence of a software fault, usually
generated by external interferences or by unexpected logical conditions, which cause the
application program to abandon its normal sequence.
The window function can be used to trim the watchdog behavior to match the application
timing perfectly. The application software must refresh the counter before time-out and
during a limited time window. If the counter is refreshed outside this time window, a reset is
issued.
Independent watchdog timer
The independent watchdog peripheral can be used to resolve malfunctions due to hardware
or software failures.
It is clocked by the 128 kHz LSI internal RC clock source, and thus stays active even in case
of a CPU clock failure. If the hardware watchdog feature is enabled through the device
option bits, the watchdog is automatically enabled at power-on, and generates a reset
unless the key register is written by software before the counter reaches the end of count.
5.7.2 Auto-wakeup counter
This counter is used to cyclically wakeup the device in Active-halt mode. It can be clocked by
the internal 128 kHz internal low-frequency RC oscillator or external clock.
LSI clock can be internally connected to TIM3 input capture channel 1 for calibration.
5.7.3 Beeper
This function generates a rectangular signal in the range of 1, 2 or 4 kHz which can be
output on a pin. This is useful when audible sounds without interference need to be
generated for use in the application.
5.7.4 Advanced control and general purpose timers
STM8A devices described in this datasheet, contain up to three 16-bit advanced control and
general purpose timers providing nine CAPCOM channels in total. A CAPCOM channel can
be used either as input compare, output compare or PWM channel. These timers are
named TIM1, TIM2 and TIM3.
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 21/110
Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
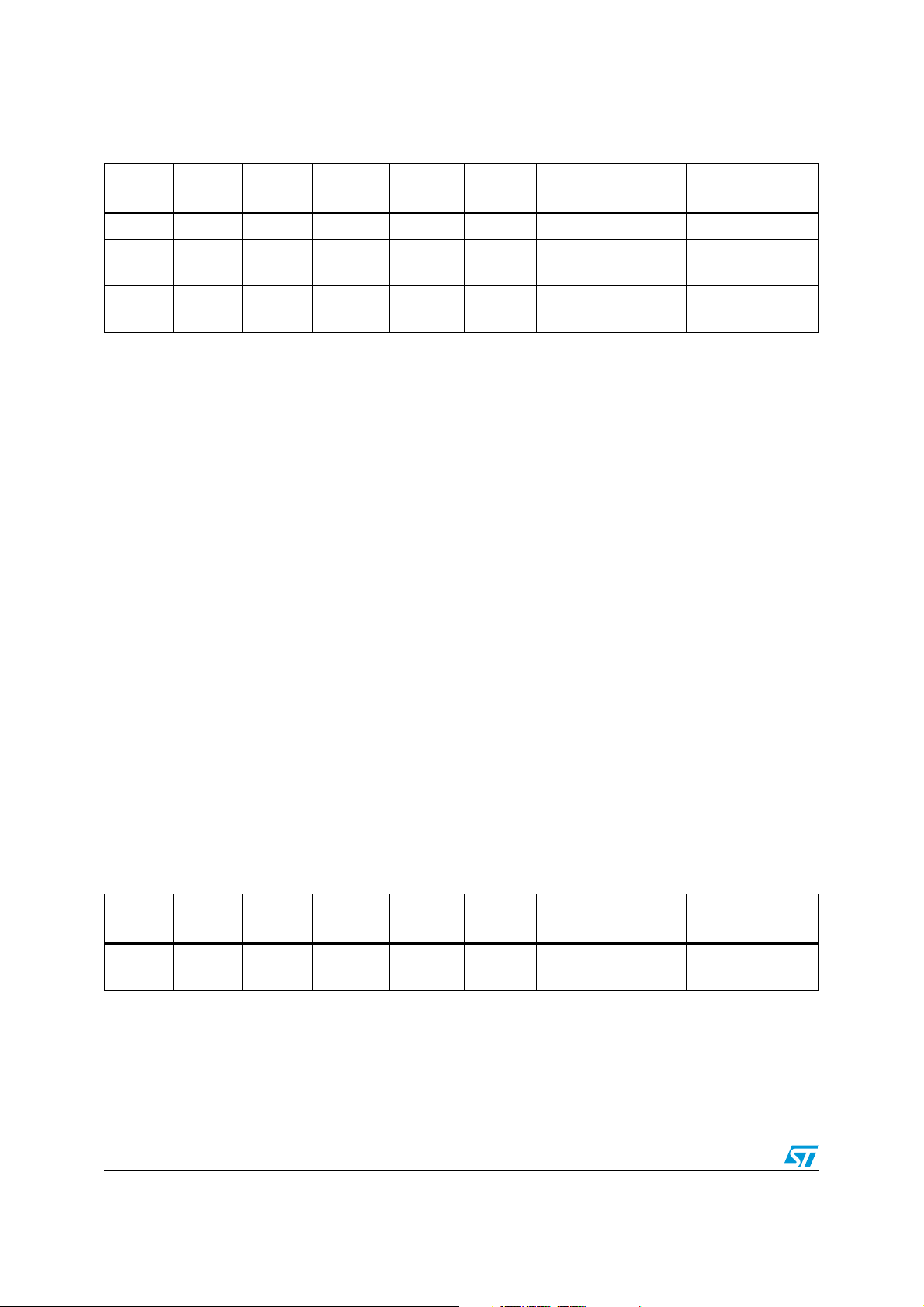
Table 8. Advanced control and general purpose timers
Timer
Counter
width
Counter
type
Prescaler
factor
Channels
Inverted
outputs
Repetition
counter
trigger
unit
External
trigger
TIM1 16-bit Up/down 1 to 65536 4 3 Yes Yes Yes Yes
n
TIM2 16-bit Up
TIM3 16-bit Up
2
n = 0 to 15
n
2
n = 0 to 15
3 None No No No No
2 None No No No No
TIM1 - advanced control timer
This is a high-end timer designed for a wide range of control applications. With its
complementary outputs, dead-time control and center-aligned PWM capability, the field of
applications is extended to motor control, lighting and bridge driver.
● 16-bit up, down and up/down AR (auto-reload) counter with 16-bit fractional prescaler.
● Four independent CAPCOM channels configurable as input capture, output compare,
PWM generation (edge and center aligned mode) and single pulse mode output
● Trigger module which allows the interaction of TIM1 with other on-chip peripherals. In
the present implementation it is possible to trigger the ADC upon a timer event.
● External trigger to change the timer behavior depending on external signals
● Break input to force the timer outputs into a defined state
● Three complementary outputs with adjustable dead time
● Interrupt sources: 4 x input capture/output compare, 1 x overflow/update, 1 x break
Break
input
TIM2, TIM3 - 16-bit general purpose timers
● 16-bit auto-reload up-counter
● 15-bit prescaler adjustable to fixed power of two ratios 1…32768
● Timers with three or two individually configurable CAPCOM channels
● Interrupt sources: 2 or 3 x input capture/output compare, 1 x overflow/update
5.7.5 Basic timer
The typical usage of this timer (TIM4) is the generation of a clock tick.
Table 9. TIM4
Timer
TIM4 8-bit Up
Counter
width
● 8-bit auto-reload, adjustable prescaler ratio to any power of two from 1 to 128
● Clock source: master clock
● Interrupt source: 1 x overflow/update
Counter
type
Prescaler
factor
n
2
n = 0 to 7
Channels
Inverted
outputs
Repetition
counter
trigger
unit
External
trigger
0 None No No No No
Break
input
22/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
5.8 Analog to digital converter (ADC)
The STM8A products described in this datasheet contain a 10-bit successive approximation
ADC with up to 16 multiplexed input channels, depending on the package.
The ADC name differs between the datasheet and the STM8A/S reference manual (see
Ta bl e 10).
Table 10. ADC naming
Peripheral name in datasheet
ADC ADC2
ADC features
● 10-bit resolution
● Single and continuous conversion modes
● Programmable prescaler: f
● Conversion trigger on timer events, and external events
● Interrupt generation at end of conversion
● Selectable alignment of 10-bit data in 2 x 8 bit result registers
● Shadow registers for data consistency
● ADC input range: V
●
Schmitt-trigger on analog inputs can be disabled to reduce power consumption
SSA
MASTER
≤ VIN ≤ V
DDA
5.9 Communication interfaces
The following sections give a brief overview of the communication peripheral. Some
peripheral names differ between the datasheet and the STM8A/S reference manual (see
Ta bl e 11).
Table 11. Communication peripheral naming correspondence
Peripheral name in reference manual
(RM0016)
divided by 2 to 18
Peripheral name in datasheet
USART UART1
LINUART UART3
Peripheral name in reference manual
(RM0016)
5.9.1 Universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART)
The devices covered by this datasheet contain one USART interface. The USART can
operate in standard SCI mode (serial communication interface, asynchronous) or in SPI
emulation mode. It is equipped with a 16 bit fractional prescaler. It features LIN master
support.
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 23/110

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
Detailed feature list:
● Full duplex, asynchronous communications
● NRZ standard format (mark/space)
● High-precision baud rate generator system
– Common programmable transmit and receive baud rates up to f
● Programmable data word length (8 or 9 bits)
● Configurable stop bits: Support for 1 or 2 stop bits
● LIN master mode:
MASTER
/16
– LIN break and delimiter generation
– LIN break and delimiter detection with separate flag and interrupt source for
readback checking.
● Transmitter clock output for synchronous communication
● Separate enable bits for transmitter and receiver
● Transfer detection flags:
– Receive buffer full
– Transmit buffer empty
– End of transmission flags
● Parity control:
– Transmits parity bit
– Checks parity of received data byte
● Four error detection flags:
– Overrun error
– Noise error
–Frame error
– Parity error
● Six interrupt sources with flags:
– Transmit data register empty
– Transmission complete
– Receive data register full
– Idle line received
– Parity error
– LIN break and delimiter detection
● Two interrupt vectors:
– Transmitter interrupt
– Receiver interrupt
● Reduced power consumption mode
● Wakeup from mute mode (by idle line detection or address mark detection)
● Two receiver wakeup modes:
– Address bit (MSB)
– Idle line
24/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
5.9.2 Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter with LIN support (LINUART)
The devices covered by this datasheet contain one LINUART interface. The interface is
available on all the supported packages. The LINUART is an asynchronous serial
communication interface which supports extensive LIN functions tailored for LIN slave
applications. In LIN mode it is compliant to the LIN standards rev 1.2 to rev 2.1.
Detailed feature list:
LIN mode
Master mode
● LIN break and delimiter generation
● LIN break and delimiter detection with separate flag and interrupt source for read back
checking.
Slave mode
● Autonomous header handling – one single interrupt per valid header
● Mute mode to filter responses
● Identifier parity error checking
● LIN automatic resynchronization, allowing operation with internal RC oscillator (HSI)
clock source
● Break detection at any time, even during a byte reception
● Header errors detection:
– Delimiter too short
– Synch field error
– Deviation error (if automatic resynchronization is enabled)
– Framing error in synch field or identifier field
– Header time-out
UART mode
● Full duplex, asynchronous communications - NRZ standard format (mark/space)
● High-precision baud rate generator
– A common programmable transmit and receive baud rates up to f
● Programmable data word length (8 or 9 bits) – 1 or 2 stop bits – parity control
● Separate enable bits for transmitter and receiver
● Error detection flags
● Reduced power consumption mode
● Multi-processor communication - enter mute mode if address match does not occur
● Wakeup from mute mode (by idle line detection or address mark detection)
● Two receiver wakeup modes:
MASTER
– Address bit (MSB)
– Idle line
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 25/110
/16

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
5.9.3 Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
The devices covered by this datasheet contain one SPI. The SPI is available on all the
supported packages.
● Maximum speed: 8 Mbit/s or f
● Full duplex synchronous transfers
● Simplex synchronous transfers on two lines with a possible bidirectional data line
● Master or slave operation - selectable by hardware or software
● CRC calculation
● 1 byte Tx and Rx buffer
● Slave mode/master mode management by hardware or software for both master and
MASTER
slave
● Programmable clock polarity and phase
● Programmable data order with MSB-first or LSB-first shifting
● Dedicated transmission and reception flags with interrupt capability
● SPI bus busy status flag
● Hardware CRC feature for reliable communication:
– CRC value can be transmitted as last byte in Tx mode
– CRC error checking for last received byte
/2 both for master and slave
5.9.4 Inter integrated circuit (I2C) interface
The devices covered by this datasheet contain one I2C interface. The interface is available
on all the supported packages.
2
● I
C master features:
– Clock generation
– Start and stop generation
2
● I
C slave features:
– Programmable I
– Stop bit detection
● Generation and detection of 7-bit/10-bit addressing and general call
● Supports different communication speeds:
– Standard speed (up to 100 kHz),
– Fast speed (up to 400 kHz)
● Status flags:
– Transmitter/receiver mode flag
– End-of-byte transmission flag
2
–I
C busy flag
● Error flags:
– Arbitration lost condition for master mode
– Acknowledgement failure after address/data transmission
– Detection of misplaced start or stop condition
– Overrun/underrun if clock stretching is disabled
2
C address detection
26/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9

STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Product overview
● Interrupt:
– Successful address/data communication
– Error condition
– Wakeup from Halt
● Wakeup from Halt on address detection in slave mode
5.9.5 Controller area network interface (beCAN)
The beCAN controller (basic enhanced CAN), interfaces the CAN network and supports the
CAN protocol version 2.0A and B. It is equipped with a receive FIFO and a very versatile
filter bank. Together with a filter match index, this allows a very efficient message handling in
today’s car network architectures. The CPU is significantly unloaded. The maximum
transmission speed is 1 Mbit/s.
Transmission
● Three transmit mailboxes
● Configurable transmit priority by identifier or order request
Reception
● 11- and 29-bit ID
● 1 receive FIFO (3 messages deep)
● Software-efficient mailbox mapping at a unique address space
● FMI (filter match index) stored with message for quick message association
● Configurable FIFO overrun
● Time stamp on SOF reception
● 6 filter banks, 2 x 32 bytes (scalable to 4 x 16-bit) each, enabling various masking
configurations, such as 12 filters for 29-bit ID or 48 filters for 11-bit ID.
● Filtering modes (mixable):
– Mask mode permitting ID range filtering
– ID list mode
Interrupt management
● Maskable interrupt
● Software-efficient mailbox mapping at a unique address space
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 27/110

Product overview STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
5.10 Input/output specifications
The product features four I/O types:
● Standard I/O 2 MHz
● Fast I/O up to 10 MHz
● High sink 8 mA, 2 MHz
● True open drain (I
To decrease EMI (electromagnetic interference), high sink I/Os have a limited maximum
slew rate. The rise and fall times are similar to those of standard I/Os.
The analog inputs are equipped with a low leakage analog switch. Additionally, the schmitttrigger input stage on the analog I/Os can be disabled in order to reduce the device standby
consumption.
STM8A I/Os are designed to withstand current injection. For a negative injection current of
4
mA, the resulting leakage current in the adjacent input does not exceed 1 µA. Thanks to
this feature, external protection diodes against current injection are no longer required.
2
C interface)
28/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx Pinouts and pin description
PD4 (HS)/TIM2_CH1/BEEP
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
9
12
14
16
18
20
11
15
13
17
19
2526282730
32
34
36
38
29
33
31
35
37
39
57
58
56
55
54
53
52
51
49
50
47
45
43
41
48
44
46
42
60
59
61
62
63
64
666865
67
69
70
71
727473
75
76
77
78
79
80
PI4
PI3
PI2
PI1
PC4 (HS)/TIM1_CH4
PC3 (HS)/TIM1_CH3
PC2 (HS)/TIM1_CH2
PC1 (HS)/TIM1_CH1
PG6
PG5
PI5
PI0
PG4
PG3
PG2
PC7/SPI_MISO
V
SSIO_2
V
DDIO_1
TIM2_CH3/PA3
USART_RX/PA4
USART_TX/PA5
AIN12/PF4
V
SSIO_1
V
SS
VCAP
V
DD
USART_CK/PA6
(HS) PH0
(HS) PH1
PH2
PH3
AIN15/PF7
AIN14/PF6
AIN13/PF5
NRST
OSCIN/PA1
OSCOUT/PA2
AIN5/PB5
AIN4/PB4
AIN1/PB1
AIN0/PB0
AIN8/PE7
V
REF-
AIN10/PF0
AIN7/PB7
AIN6/PB6
TIM1_ETR/PH4
TIM1_CH3N/PH5
TIM1_CH2N/PH6
40
AIN9/PE6
212224
23
AIN11/PF3
V
REF+
V
DDA
V
SSA
PD0 (HS)/TIM3_CH2
PE2/I 2C_SDA
PE3/TIM1_BKIN
PE4
PG7
PD7/TLI
PD6/LINUART_RX
PD5/LINUART_TX
PI7
PI6
PD2 (HS)/TIM3_CH1
PD1 (HS)/SWIM
PC5/SPI_SCK
PC6/SPI_MOSI
PG0/CAN_TX
(1)
PG1/CAN_RX
(1)
PE0/CLK_CCO
PD3 (HS)/TIM2_CH2
AIN3/PB3
AIN2/PB2
PC0/ADC_ETR
PE5/SPI_NSS
TIM1_CH1N/PH7
V
DDIO_2
PE1/I2C_SCL
6 Pinouts and pin description
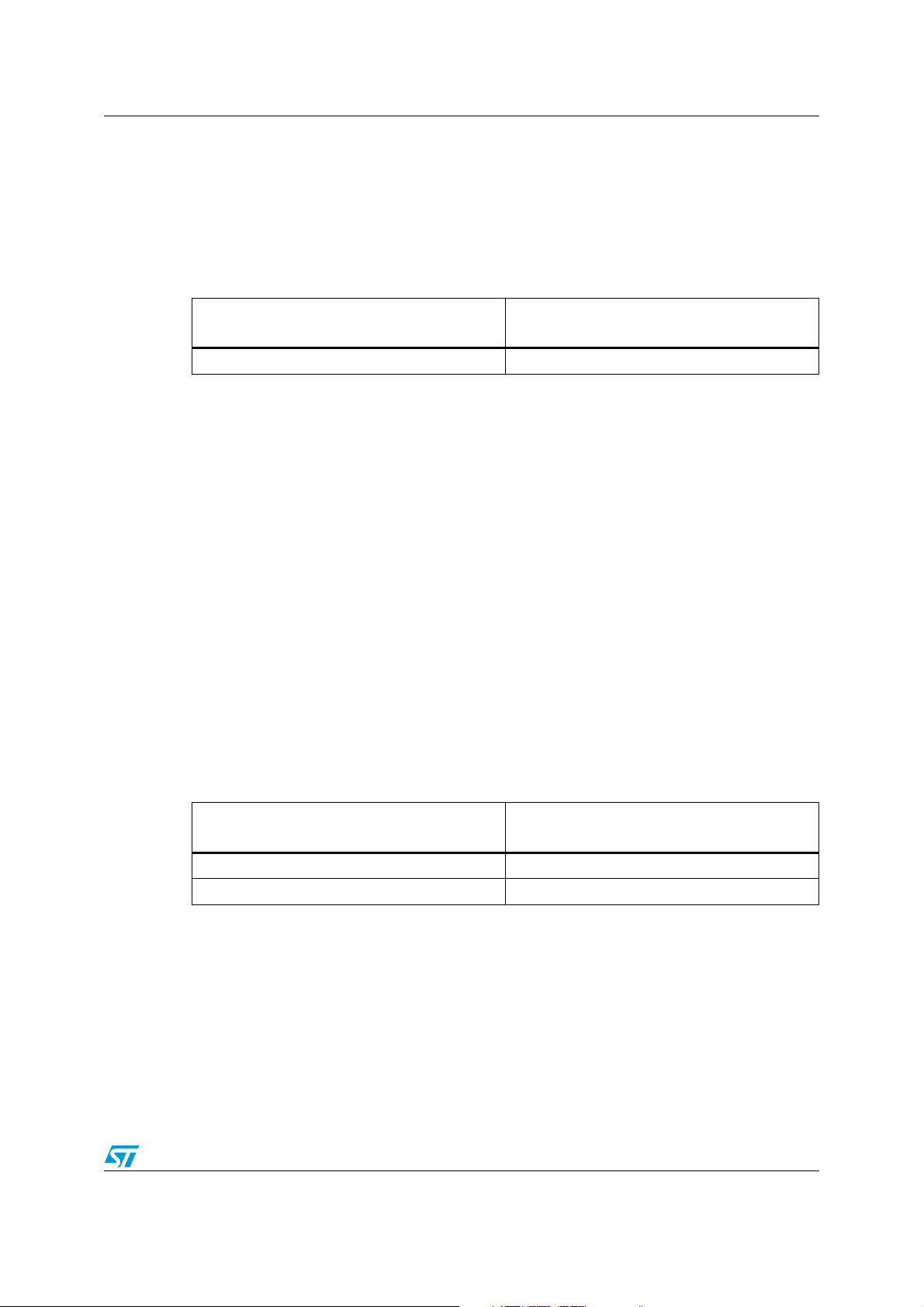
6.1 Package pinouts
Figure 3. LQFP 80-pin pinout
1. The CAN interface is only available on the STM8AF/H/P51xx and STM8AF52xx product lines.
2. (HS) stands for high sink capability.
Doc ID 14395 Rev 9 29/110
Pinouts and pin description STM8AF52/62xx, STM8AF51/61xx
V
REF-
AIN10/PF0
AIN7/PB7
AIN6/PB6
AIN5/PB5
AIN4/PB4
TIM1_ETR/AIN3/PB3
TIM1_CH3N/AIN2/PB2
TIM1_CH2N/AIN1/PB1
TIM1_CH1N/AIN0/PB0
AIN8/PE7
AIN9/PE6
AIN11/PF3
V
REF+
V
DDA
V
SSA
64 63 6261 60 5958 57 56 55 5453 52 51 50 49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
17 18 1920 2122 2324 2930 31 3225 26 2728
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
V
SS
VCAP
V
DD
V
DDIO_1
TIM2_CH3/PA3
USART_RX/PA4
USART_TX/PA5
USART_CK/PA6
AIN15/PF7
AIN14/PF6
AIN13/PF5
AIN12/PF4
NRST
OSCIN/PA1
OSCOUT/PA2
V
SSIO_1
PG1/CAN_RX
(1)
PG0/CAN_TX
(1)
PC7/SPI_MISO
PC6/SPI_MOSI
V
DDIO_2
V
SSIO_2
PC5/SPI_SCK
PC4 (HS)/TIM1_CH4
PC3 (HS)/TIM1_CH3
PC2 (HS)/TIM1_CH2
PC1 (HS)/TIM1_CH1
PE5/SPI_NSS
PI0
PG4
PG3
PG2
PD3 (HS)/TIM2_CH2/ADC_ETR
PD2 (HS)/TIM3_CH1
PD1 (HS)/SWIM
PD0 (HS)/TIM3_CH2
PE0/CLK_CCO
PE1/I2C_SCL
PE2/I2C_SDA
PE3/TIM1_BKIN
PE4
PG7
PG6
PG5
PD7/TLI
PD6/LINUART_RX
PD5/LINUART_TX
PD4 (HS)/TIM2_CH1/ BEEP
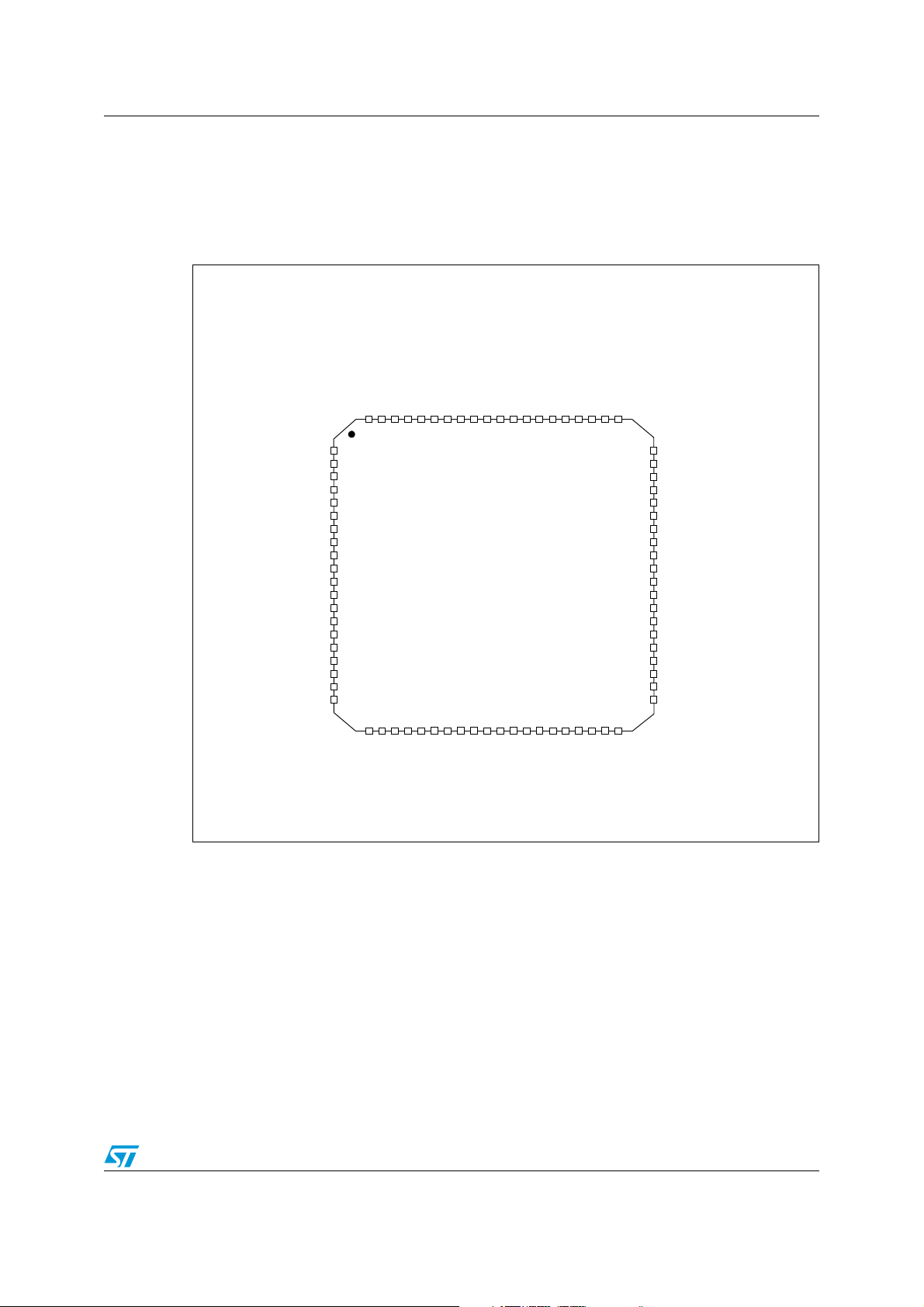
Figure 4. LQFP 64-pin pinout
1. The CAN interface is only available on the STM8AF/H/P51xx and STM8AF52xx product lines.
2. HS stands for high sink capability.
30/110 Doc ID 14395 Rev 9
 Loading...
Loading...