
Features
■ Monochip SLIC optimized for WLL & VoIP
applications
■ Implements all Borsht function key features
■ Single supply (4.5 V to 12 V) for fly-back
configuration
■ Single supply (5.5 V to 12 V) for buck-boost
configuration
■ Built in DC/DC converter controller
■ Soft battery reversal with programmable
transition time
■ On-hook transmission
■ Programmable off-hook detector threshold
■ Metering pulse generation and filter
■ Integrated ringing
■ Integrated ring trip
■ Parallel control interface (3.3 V logic level)
■ Programmable constant current feed
■ Surface mount package
■ Integrated thermal protection
■ Dual gain value option
■ Automatic recognition flyback and buckboost
configuration
■ BCDIIIS 90V technology
■ -40 °C to +85 °C operating range
Description
The STLC3075 is a SLIC device specifically
designed for WLL (Wireless Local Loop), and
ISDN terminal adaptors and VoIP applications.
One distinctive characteristic of this device is its
ability to operate with a single supply voltage
(from +4.5 V to +12 V) and to self generate the
negative battery by means of an on-chip DC/DC
converter controller that drives an external MOS
switch.
STLC3075
Integrated POTS interface
for home access gateway and WLL
LQFP44
The battery level is properly adjusted depending
on the operating mode. A useful characteristic for
these applications is the integrated ringing
generator.
The control interface is parallel with open drain
output and 3.3 V logic levels.
The metering pulses are generated on-chip
starting from two logic signals (0 and 3.3 V): one
signal defining the metering pulse frequency, the
other signal defining the metering pulse duration.
An on-chip circuit then provides the proper
shaping and filtering. Metering pulse amplitude
and shaping (rising and decay time) can be
programmed by external components.
A dedicated cancellation circuit avoids possible
codec input saturation due to metering pulse
echo.
Constant current feed can be set from 20 mA to
40 mA. Off-hook detection threshold is
programmable from 5 mA to 9 mA.
The device, which is developed in BCDIIIS
technology (90 V process), operates in the
extended temperature range and integrates a
thermal protection that sets the device in power
down when T
Table 1. Device summary
Order code
E-STLC3075
1. ECOPACK® (see Section 9)
exceeds 140 °C.
j
Package Packing
(1)
LQFP44 Tray
March 2009 Rev 8 1/36
www.st.com
1

Contents STLC3075
Contents
1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3 Electrical specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1 Absolute maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.2 Operating range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.3 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 DC/DC converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.2 Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2.1 Power down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2.2 High impedance feeding (HI-Z) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2.3 Active . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.2.4 Ringing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.1 Layout recommendation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.2 External components list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.1 Test circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7 Over voltage protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8 Typical state diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
9 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
10 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2/36

STLC3075 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4. Operating range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 5. Thermal data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 6. SLIC operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 7. Gain set in active mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 8. SLIC states in active mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 9. CREST factor values @ 20 and 25Hz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 10. External components for buckboost configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 11. VBAT values in RING and ACTIVE modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 12. External components for flyback configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 13. Coilcraft type FA2469-AL electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 14. Coilcraft type FA2470-AL electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 15. External components @gain set = 0. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 16. External components @gain set = 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 17. Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 18. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3/36

List of figures STLC3075
List of figures
Figure 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. Pin connection (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 3. DC characteristics in HI-Z mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 4. DC characteristics in active mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 5. TIP/RING typical transition from direct to reverse polarity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 6. Metering pulse generation circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 7. TIP/RING typical ringing waveform. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 8. Application diagram with N-channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 9. Application diagram without metering pulse generation with N-channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 10. Application diagram with P-channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 11. Application diagram without metering pulse generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 12. 2W return loss 2WRL = 20Log(|Zref + Zs|/|Zref-Zs|) = 20Log(E/2Vs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 13. THL trans hybrid loss THL = 20Log|Vrx/Vtx/ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 14. G24 transmit gain G24 = 20Log|2Vtx/E| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 15. G42 receive gain G42 = 20Log|VI/Vrx| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 16. PSRRC power supply rejection VPOS to 2W port PSSRC = 20Log|Vn/Vl| . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 17. L/T longitudinal to transversal conversion L/T = 20Log|Vcm/Vl| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 18. T/L transversal to longitudinal conversion T/L = 20Log|Vrx/Vcm|. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 19. VTTX metering pulse level on line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 20. V2Wp and W4Wp: Idle channel sophometric noise at line and TX.
V2Wp = 20Log|Vl/0.774l|; V4Wp = 20Log|Vtx/0.774l| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 21. Simplified configuration for indoor over voltage protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 22. Standard over voltage protection configuration for K20 compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 23. Typical state diagram for STLC3075 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 24. LQFP44 (10 x 10 x 1.4 mm) mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4/36

STLC3075 Block diagram
1 Block diagram
Figure 1. Block diagram
PD D0 D1 D2 DET
GAIN
SETTING
TX
RX
ZAC1
ZAC
RS
ZB
CKTTX
CTTX1
CTTX2
FTTX
INPUT LOGIC AND DECODER
Status and functions
SUPERVISION
AC PROC
TTX PROC
RTTX CAC ILTF RD IREF RLIM RTH
REFERENCE
OUTPUT LOGIC
LINE
DRIVER
DC PROC
Vcc
Vss
Agnd
OUTPUT
STAGE
DC/DC
CONV.
VOLT.
REG.
AGND
BGND
TIP
RING
CREV
CSVR
CLK
RSENSE
GATE
VF
CZ
CVCC
VPOS
VBAT
Vbat
5/36

Pin description STLC3075
2 Pin description
Figure 2. Pin connection (top view)
VBAT1
CREV
N.C.
TIP
N.C.
N.C.
GAIN SET
N.C.
DET
CKTTX
CTTX1
CTTX2
RTTX
RING
N.C.
44 43 42 413940 38 37 36 35 34
1
D0
2
D1
3
D2
4
PD
5
6
7
8
9
10
12 13 14 15 16
RX
FTTX
ZAC1
171118 19 20 21 22
ZB
RS
ZAC
CAC
TXCZVF
VBAT
BGND
CSVR
N.C.
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
ILTF
RD
RTH
IREF
RLIM
AGND
CVCC
VPOS
RSENSE
GATE
CLK
D00TL488
Table 2. Pin description
N° Pin Function
1 D0 Control interface: input bit 0
2 D1 Control interface: input bit 1
3 D2 Control interface: input bit 2
4 PD Power down input. Normally connected to CVCC (or to logic level high)
5 Gain SET
6, 22, 38,
39, 40, 42
Control gain interface: 0 Level R
NC Not connected
1 Level R
xgain
xgain
= 0dB T
= +6dB T
xgain
xgain
= -12dB
= -12dB
7 DET Logic interface output of the supervision detector (active low)
8 CKTTX Metering pulse clock input (12 kHz or 16 kHz square wave)
9 CTTX1 Metering burst shaping external capacitor
10 CTTX2 Metering burst shaping external capacitor
11 RTTX
12 FTTX
Metering pulse cancellation buffer output. TTX filter network should be connected to
this point. If not used, should be left open.
Metering pulse buffer input this signal is sent to the line and used to perform TTX
filtering
4 wires input port (RX input). A 100 kΩ external resistor must be connected to AGND
13 RX
via the bias input stage. This signal refers to AGND. If connected to single supply
CODEC output it must be DC decoupled with proper capacitor.
14 ZAC1 RX buffer output (the AC impedance is connected from this node to ZAC)
15 ZAC AC impedance synthesis
6/36

STLC3075 Pin description
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
N° Pin Function
16 RS Protection resistors image (the image resistor is connected from this node to ZAC)
17 ZB
Balance network for 2 to 4 wire conversion (the balance impedance ZB is connected
from this node to AGND. ZA impedance is connected from this node to ZAC1).
18 CAC AC feedback input, AC/DC split capacitor (CAC)
19 TX
4 wire output port (TX output). The signal is referred to AGND. If connected to single
supply CODEC input it must be DC decoupled with proper capacitor.
20 CZ Flyback compensation
21 VF Feedback input for DC/DC converter controller
Power switch controller clock (typ. 125 kHz). This pin can also be connected to CVCC
23 CLK
or AGND. When the CLK pin is connected to CVCC an internal auto-oscillation is
internally generated and it is used instead of the external clock. When the CLK pin is
connected to AGND, the GATE output is disabled.
24 GATE
25 R
SENSE
Driver for external power MOS transistor (P-channel in buckboost configuration, Nchannel in flyback configuration).
Voltage input for current sensing. R
pin and V
pin (Buckboost) or GND (Flyback). The PCB layout should minimize the
POS
resistor should be connected close to this
SENSE
extra resistance introduced by the copper tracks.
26 V
POS
Positive supply input
27 CVCC Internal positive voltage supply filter
28 AGND Analog ground. Must be shorted with BGND.
29 RLIM
30 IREF
Constant current feed programming pin (via RLIM). RLIM should be connected close
to this pin and AGND pin to avoid noise injection.
Internal bias current setting pin. RREF should be connected close to this pin and
AGND pin to avoid noise injection.
31 RTH
32 RD
Off-hook threshold programming pin (via RTH). RTH should be connected close to this
pin and AGND pin to avoid noise injection.
DC feedback and ring trip input. RD should be connected close to this pin and AGND
pin to avoid noise injection.
33 ILTF Transversal line current image output
34 CSVR Battery supply filter capacitor
35 BGND Battery ground, must be shorted with AGND
36 VBAT
Regulated battery voltage self generated by the device via DC/DC converter. Must be
shorted to VBAT1.
37 RING 2 wire ports; RING wire (Ib is the current sunk into this pin)
41 TIP 2 wire ports; TIP wire (Ia is the current sourced from this pin)
Reverse polarity transition time control. A proper capacitor connected between this pin
43 CREV
and AGND is setting the reverse polarity transition time. This is the same transition
time used to shape the ’trapezoidal ringing’ during ringing injection.
44 VBAT1 Frame connection. Must be shorted to VBAT
7/36

Electrical specification STLC3075
3 Electrical specification
3.1 Absolute maximum rating
Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
POS
Positive supply voltage -0.4 to +13 V
A/BGND AGND to BGND -1 to +1 V
V
dig
T
j
(1)
V
btot
Pin D0, D1, D2, DET, CKTTX -0.4 to 5.5 V
Max. junction temperature 150 °C
Vbtot=|V
device supply pins).
Human body model ±1750 V
ESD rating
Charged device model ±500 V
1. Vbat is self generated by the on-chip DC/DC converter and can be programmed via RF1 and RF2. RF1
and RF2 must be selected in order to fulfil the a.m. limits (see components tables).
3.2 Operating range
Table 4. Operating range
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
POS
A/BGND AGND to BGND -100 to +100 mV
V
dig
T
op
(1)
V
bat
1. Vbat is self generated by the on-chip DC/DC converter and can be programmed via RF1 and RF2. RF1
and RF2 must be selected in order to fulfil the a.m. limits (see Table 10: External components for
buckboost configuration)
Positive supply voltage 4.5 to +12 V
Pin D0, D1, D2, DET, CKTTX, PD -0.25 to 5.25 V
Ambient operating temperature range -40 to +85 °C
Self generated battery voltage -74 max. V
|+|Vbat|. (Total voltage applied to the
POS
90 V
3.3 Thermal data
Table 5. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th j-amb
8/36
Thermal resistance junction to ambient typical. 60 °C/W

STLC3075 Functional description
4 Functional description
The STLC3075 is a device specifically developed for WLL VoIP and ISDN-TA applications. It
is based on a SLIC core, on purpose optimized for these applications, with the addition of a
DC/DC converter controller to meet the WLL and ISDN-TA design requirements.
The SLIC performs the standard feeding, signalling and transmission functions.
STLC3075 can be set in three different operating modes via the D0, D1, D2 pins of the
control logic interface (0 to 3.3 V logic levels). The loop status is carried out on the DET
(active low).
pin
The DET
pin is an open drain output to allow easy interfacing with both 3.3 V and 5 V logic
levels.
The four possible SLIC’s operating modes are:
– Power down
– High impedance feeding (HI-Z)
– Active
– Ringing
Ta bl e 6 shows how to set the different SLIC operating modes.
Table 6. SLIC operating modes
PD D0 D1 D2 Operating mode
000XPower down
1 0 0 X H.I. feeding (HI-Z)
1 0 1 0 Active normal polarity
1011Active reverse polarity
1 1 1 0 Active TTX injection (N.P.)
1 1 1 1 Active TTX injection (R.P.)
1 1 0 0/1 Ring (D2 bit toggles @ fring)
4.1 DC/DC converter
The DC/DC converter controller drives an external power MOS transistor N-Ch plus
transformer (Flyback configuration) or P-Ch plus inductor (Buckboost configuration), in order
to generate the negative battery voltage needed for the device operation.
The DC/DC converter controller is synchronized with an external CLK (125 kHz typ.) or with
an internal clock generated when the pin CLK is connected to CVCC. One R
to PGND supply (Flyback) or to V
input peak current.
This feature is implemented in order to avoid overload on V
transient (ex. ring trip detection). The 110 mΩ typical value guarantees an average current
consumption from V
guarantees an average current consumption from V
POS
in series
supply (Buckboost) allows to fix the maximum allowed
POS
supply in case of line
POS
SENSE
< 700 mA for buckboost configuration. The 220 mΩ typical value
< 800 mA for flyback configuration.
POS
9/36

Functional description STLC3075
The self generated battery voltage is set to a predefined value in on-hook state.
The typical value of -50 V can be adjusted via one external resistor (RF1). When RING
mode is selected this typical value is increased to -70 V.
Once the line goes in off-hook condition, the DC/DC converter automatically adjusts the
generated battery voltage in order to feed the line with a fixed DC current (programmable via
RLIM) optimizing the power dissipation.
4.2 Operating modes
4.2.1 Power down
When this mode is selected the SLIC is switched off and the TIP and RING pins are in high
impedance. The line detectors are also disabled therefore the off-hook condition cannot be
detected.
The power down mode can be selected in emergency condition when it is necessary to cut
any current delivered to the line.
The power down mode is also forced by STLC3075 in case of thermal overload
(T
> 140 °C). In this case the device goes back to the previous status as soon as the
j
junction temperature decrease under the hysteresis threshold.
No AC transmission is possible.
4.2.2 High impedance feeding (HI-Z)
This operating mode is normally selected when the telephone is in on-hook in order to
monitor the line status keeping the power consumption at the minimum.
The output voltage in on-hook condition is equal to the self generated battery voltage (-50 V
typical).
When off-hook occurs the DET
The off-hook threshold value in HI-Z mode is the same as the programmed value in ACTIVE
mode.
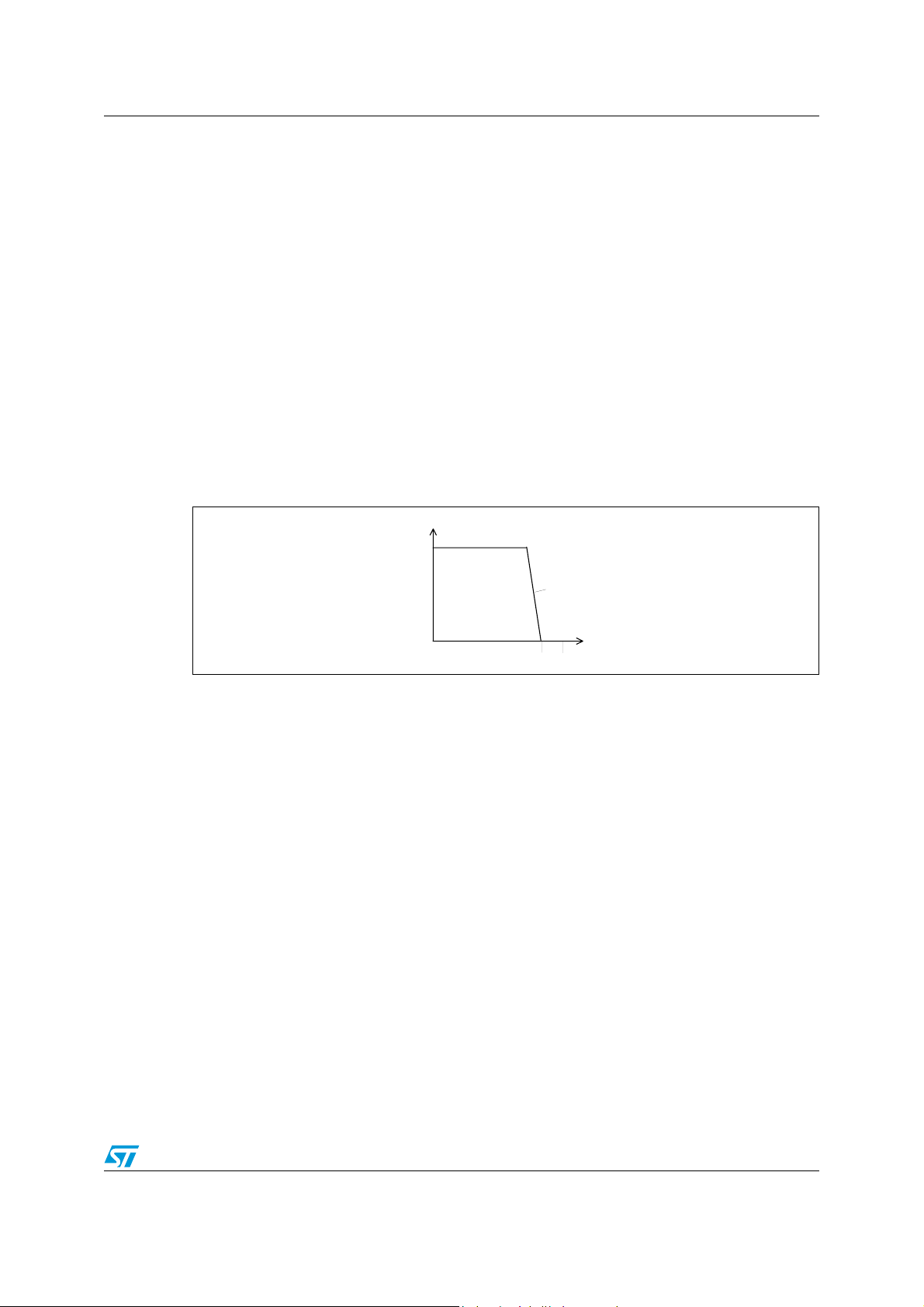
The DC characteristics in HI-Z mode are equal to the self generated battery with
2x(1600 Ω+Rp) in series (see Figure 3), where Rp is the external protection resistance.
No AC transmission is possible.
Figure 3. DC characteristics in HI-Z mode.
becomes active (low logic level).
IL
Vbat
2x(R1+Rp)
Slope: 2x(R1+Rp)
(R1=1600ohm)
10/36
VL
Vbat (-50V)
STLC3075 Functional description
4.2.3 Active
DC characteristics & supervision
When this mode is selected the STLC3075 provides both DC feeding and AC transmission.
The STLC3075 feeds the line with a constant current fixed by RLIM (20 mA to 40 mA
range). The on-hook voltage is typically 40 V allowing on-hook transmission; the self
generated Vbat is -50 V typical.
If the loop resistance is very high and the line current cannot reach the programmed
constant current feed value, the STLC3075 behaves like a 40 V voltage source with a series
impedance equal to the protection resistors 2xRp (typ. 2x50 Ω). Figure 4. shows the typical
DC characteristics in active mode.
The line status (on/off hook) is monitored by the SLIC’S supervision circuit. The off-hook
threshold can be programmed via the external resistor RTH in the range from 5mA to 9mA.
Independently on the programmed constant current value, the TIP and RING buffers have a
current source capability limited to 80mA typical.
Figure 4. DC characteristics in active mode
IL
Ilim
(20 to
40mA)
2Rp
VL
10V
Vbat (-50V)
Moreover the power available at Vbat is controlled by the DC/DC converter that limits the
peak current drawn from the V
R
SENSE
resistor.
supply. The maximum allowed current peak is set by
POS
11/36
 Loading...
Loading...