32 Mbit (4Mb x8 or 2Mb x16, Boot Block)
FEATURES SUMMARY
■ SUPPLY VOLTAGE
–V
–V
■ ACCESS TIMES: 70, 90ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
– 10µs per Byte/Word typical
– Double Word/ Quadruple Byte Program
■ MEMORY BLOCKS
– Memory Array: 63 Main Blocks
– 8 Parameter Blocks (Top or Bottom
■ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUME MODES
– Read and Program another Block during
■ UNLOCK BYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– Faster Production/Batch Programming
■ V
PP
WRITE PROTECT
■ TEMPORARY BLOCK UNPROTECTION
MODE
■ COMMON FLASH INTERFACE
– 64 bit Security Code
■ EXTENDED MEMORY BLOCK
– Extra block used as security block or to
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 0020h
– Top Device Code M29W320ET: 2256h
– Bottom Device Code M29W320EB: 2257h
2.7V to 3.6V for Program, Erase
CC =
and Read
=12V for Fast Program (optional)
PP
Location)
Erase Suspend
/WP PIN for FAST PROGRAM and
store additional information
M29W320ET
M29W320EB
3V Supply Flash Memory
Figure 1. Packages
TSOP48 (N)
12 x 20mm
FBGA
TFBGA48 (ZE)
6 x 8mm
1/46March 2005

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES SUMMARY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 1. Packages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. Logic Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 1. Signal Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3. TSOP Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. TFBGA48 Connections (Top view through package) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 5. Block Addresses (x8). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6. Block Addresses (x16). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Address Inputs (A0-A20). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A–1).. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chip Enable (E
Output Enable (G
Write Enable (W
V
Write Protect (V
PP/
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP
Ready/Busy Output (RB
Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE
Supply Voltage (2.7V to 3.6V).. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
V
CC
V
Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
SS
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
WP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
PP/
).. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
BUS OPERATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Bus Read. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Bus Write. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Output Disable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Automatic Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Special Bus Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Electronic Signature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Block Protect and Chip Unprotect. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 2. Bus Operations, BYTE
Table 3. Bus Operations, BYTE
= VIL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
= VIH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
COMMAND INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Read/Reset Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Auto Select Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Read CFI Query Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Program Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Fast Program Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Quadruple Byte Program Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Double Word Program Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Unlock Bypass Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Unlock Bypass Program Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Unlock Bypass Reset Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Chip Erase Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Block Erase Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Erase Suspend Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Erase Resume Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Enter Extended Block Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Exit Extended Block Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Block Protect and Chip Unprotect Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 4. Commands, 16-bit mode, BYTE
Table 5. Commands, 8-bit mode, BYTE
Table 6. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
STATUS REGISTER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Data Polling Bit (DQ7). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Toggle Bit (DQ6).. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Error Bit (DQ5). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Erase Timer Bit (DQ3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2).. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 7. Status Register Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 7. Data Polling Flowchart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 8. Toggle Flowchart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
= VIH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
= VIL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MAXIMUM RATING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 8. Absolute Maximum Ratings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DC and AC PARAMETERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 9. Operating and AC Measurement Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 9. AC Measurement I/O Waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 10.AC Measurement Load Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. Device Capacitance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 11. DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 11.Read Mode AC Waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 12. Read AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Figure 12.Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 13. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 13.Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 14. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 14.Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Chip Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 15.Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Output Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 15. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits AC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 16.Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 16. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 17.Accelerated Program Timing Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
PACKAGE MECHANICAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 18.TSOP48 Lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12x20 mm, Bottom View Package Outline . . 29
Table 17. TSOP48 Lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12x20 mm, Package Mechanical Data . . . . . 29
Figure 19.TFBGA48 6x8mm - 6x8 Ball Array, 0.8mm Pitch, Bottom View Package Outline. . . . . . 30
Table 18. TFBGA48 6x8mm - 6x8 Ball Array, 0.8mm Pitch, Package Mechanical Data. . . . . . . . . 30
PART NUMBERING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 19. Ordering Information Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
APPENDIX A.BLOCK ADDRESSES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 20. Top Boot Block Addresses, M29W320ET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 21. Bottom Boot Block Addresses, M29W320EB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
APPENDIX B.COMMON FLASH INTERFACE (CFI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 22. Query Structure Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Table 23. CFI Query Identification String. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Table 24. CFI Query System Interface Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 25. Device Geometry Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Table 26. Primary Algorithm-Specific Extended Query Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 27. Security Code Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
APPENDIX C.EXTENDED MEMORY BLOCK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Factory Locked Extended Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Customer Lockable Extended Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 28. Extended Block Address and Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
APPENDIX D.BLOCK PROTECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Programmer Technique . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
In-System Technique . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 29. Programmer Technique Bus Operations, BYTE
= VIH or V
IL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 20.Programmer Equipment Group Protect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 21.Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 22.In-System Equipment Group Protect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 23.In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
REVISION HISTORY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 30. Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
4/46

SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W320E is a 32 Mbit (4Mb x8 or 2Mb x16)
non-volatile memory that can be read, erased and
reprogrammed. These operations can be performed using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V)
supply. On power-up the memory defaults to its
Read mode.
The device features an asymme trical block ar chitecture. The M29W320E has an array of 8 parameter and 63 main blocks. M29W320ET locates the
Parameter Blocks at the top of the memory address space while the M29W320EB locates the
Parameter Blocks starting from the bottom.
M29W320E has an extra 32 KWord (x16 mode) or
64 KByte (x8 mode) block, the Extended Block,
that can be accessed using a dedicated command. The Extended Block c an be protected and
so is useful fo r storing security in formation . However the protection is irreversible, o nce protected
the protection cannot be undone.
Each block can be eras ed independently so it is
possible to prese rve valid data while old data i s
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
erased. The blocks can be protected to prevent
accidental Program or Erase commands from
modifying the memory. Program and Erase com mands are written to the Command Interface of
the memory. An on-chip Program/Erase Controller
simplifies the proces s of programming or e rasing
the memory by taking care of all of the special operations that are required to upd ate the memory
contents. The end of a program or erase operation
can be detected an d any error conditions identified. The command set required to control the
memory is consistent with JEDEC standards.
Chip Enable, Output Enable and Write Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allow simple connection to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered i n TSOP48 (12x20mm), and
TFBGA48 (6x8mm, 0.8mm pitch) packages. The
memory is supplied with all the bits erased (set to
’1’).
Figure 2. Logic Diagram Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A20 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
VPP/WP
V
A0-A20
W
RP
CC
21
E
G
M29W320ET
M29W320EB
V
SS
15
DQ0-DQ14
DQ15A–1
BYTE
RB
AI09346
DQ8-DQ14 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1 Data Input/Output or Address Input
E
G
W
RP
RB
BYTE
V
CC
VPP/WP
V
SS
NC Not Connected Inter na lly
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Write Enable
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
Ready/Busy Output
Byte/Word Organization Select
Supply Voltage
VPP/Write Protect
Ground
5/46
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
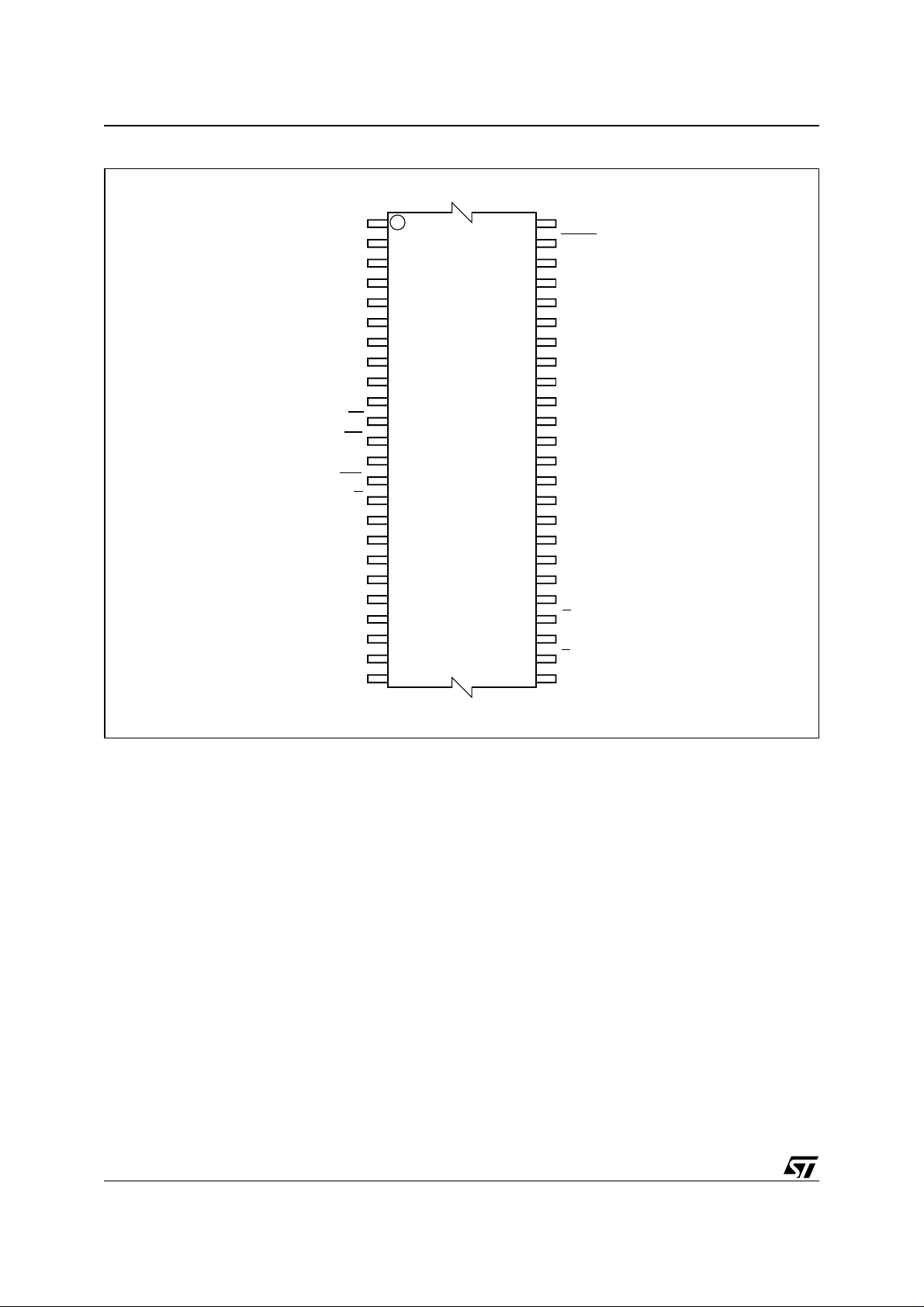
Figure 3. TSOP Connections
A15
1
48
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10 DQ14
A9
A8
A19
A20
M29W320ET
M29W320EB
W
RP
NC
12
13
37
36
VPP/WP
RB
A18
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
24 25
A16
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
G
V
SS
E
A0
AI09347
6/46
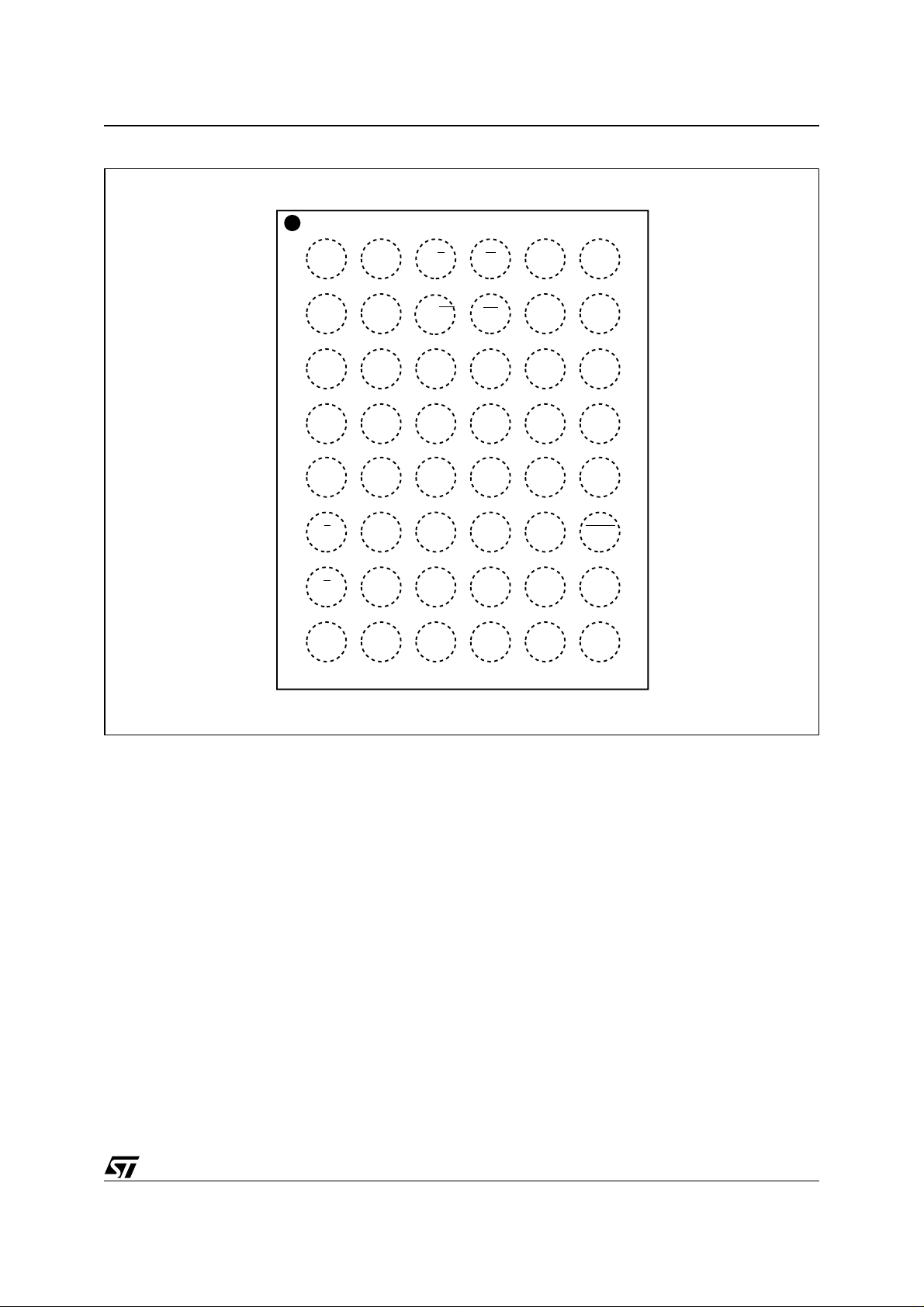
Figure 4. TFBGA48 Connections (Top view through package)
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
A3
A4
A2
A1
A0
E
G
V
SS
A7
A17
A6
A5 A20
DQ0
DQ8
DQ9
DQ1
RB
V
PP
A18
DQ2
DQ10
DQ11
DQ3
/
WP
W
RP
NC
A19
DQ5
DQ12
V
CC
DQ4
A9
A8
A10
A11
DQ7
DQ14
DQ13
DQ6
A13
A12
A14
A15
A16
BYTE
DQ15
A–1
V
SS
AI08084
7/46
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
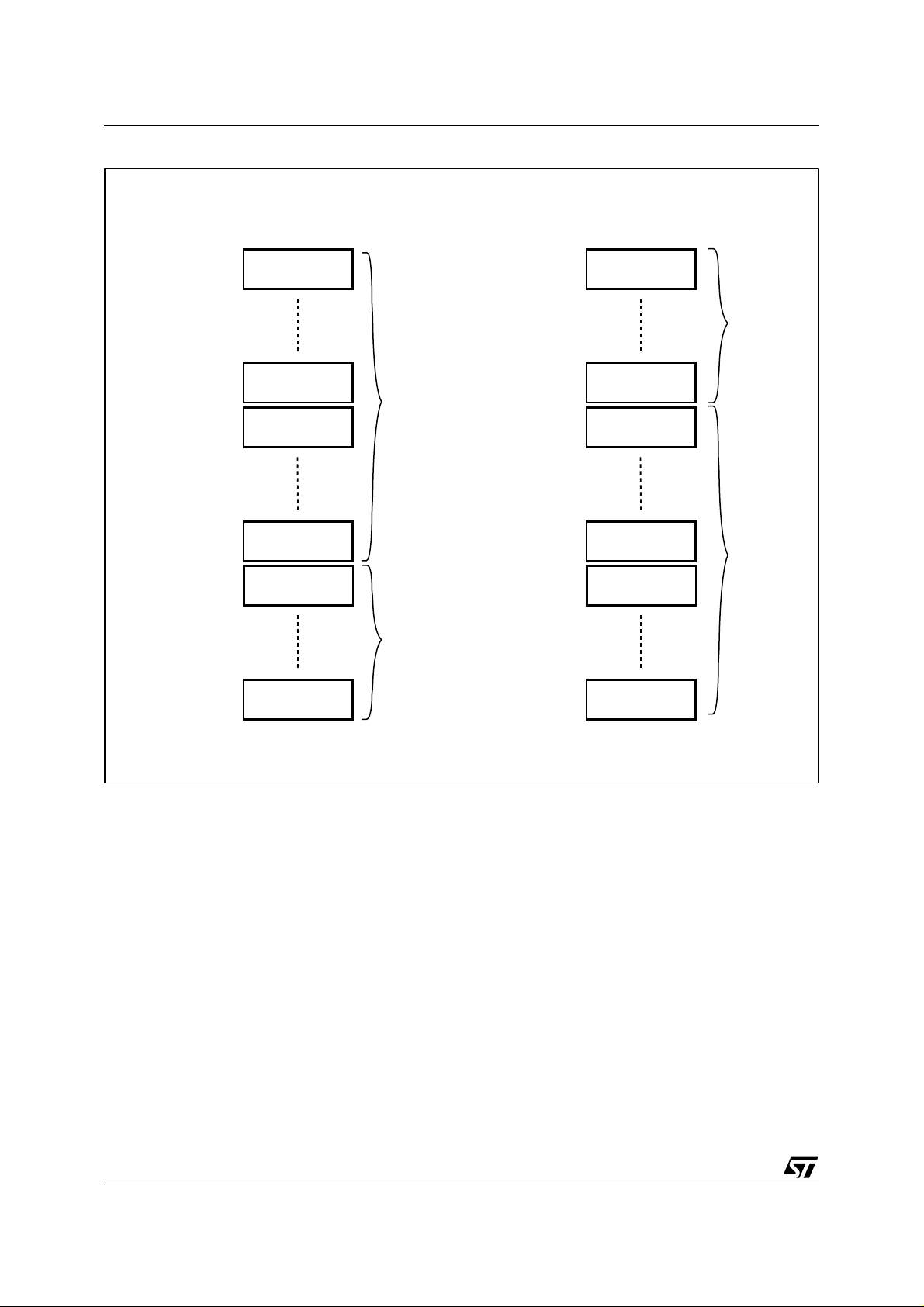
Figure 5. Block Addresses (x8)
Top Boot Block (x8)
Address lines A20-A0, DQ15A-1
000000h
00FFFFh
2F0000h
2FFFFFh
300000h
30FFFFh
3E0000h
3EFFFFh
3F0000h
3F1FFFh
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
8 KByte or
4 KWord
Total of 63
Main Blocks
Total of 8
Parameter
(1)
Blocks
Bottom Boot Block (x8)
Address lines A20-A0, DQ15A-1
000000h
001FFFh
00E000h
00FFFFh
010000h
01FFFFh
0F0000h
0FFFFFh
100000h
10FFFFh
8 KByte or
4 KWord
8 KByte or
4 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
Total of 8
Parameter
(1)
Blocks
Total of 63
Main Blocks
3FE000h
3FFFFFh
Note 1. Used as Extended Block Addresses in Extended Block mode.
Note: Also see APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21. for a full listing of the Block Addresses.
8 KByte or
4 KWord
3F0000h
3FFFFFh
64 KByte or
32 KWord
AI09348
8/46
Figure 6. Block Addresses (x16)
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
000000h
007FFFh
178000h
17FFFFh
180000h
187FFFh
1F0000h
1F7FFFh
1F8000h
1F8FFFh
Top Boot Block (x16)
Address lines A20-A0
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
8 KByte or
4 KWord
Total of 63
Main Blocks
Total of 8
Parameter
(1)
Blocks
000000h
000FFFh
007000h
007FFFh
008000h
00FFFFh
078000h
07FFFFh
080000h
087FFFh
Bottom Boot Block (x16)
Address lines A20-A0
8 KByte or
4 KWord
8 KByte or
4 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
64 KByte or
32 KWord
Total of 8
Parameter
(1)
Blocks
Total of 63
Main Blocks
1FF000h
1FFFFFh
Note 1. Used as Extended Block Addresses in Extended Block mode.
Note: Also see APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21. for a full listing of the Block Addresses.
8 KByte or
4 KWord
1F8000h
1FFFFFh
64 KByte or
32 KWord
AI09349
9/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 2., Logic Diagram, and Table
1., Signal Names, for a brief overview of the sig-
nals connected to this device. Address Inputs (A0-A20). The Address Inputs
select the cells in the memory array to access during Bus Read operations. During Bus Write operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the Program/Erase Controller.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). The Data I/O outputs the data stored at the selected address during a Bus Read operation. During Bus Write operations they repr esent the commands s ent to the Command Interface of the Program/Erase Controller.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14). The Data I/O outputs the data stored at the selected address during a Bus Read operati on wh en B YTE V
. When BYTE is Low, VIL, these pins are not
IH
used and are hig h impedance. During Bus W rite
operations the Command Regis ter does not use
these bits. When reading the Status Register
these bits should be ignored.
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A –1).
When BYTE
is High, VIH, this pin behaves as a
Data Input/Output pin (as DQ8-DQ14). When
BYTE
is Low, VIL, this pin behaves as an address
pin; DQ15A–1 Low will select the LSB of the addressed Word, DQ15A–1 High will select the MSB.
Throughout the text consider references to the
Data Input/Output to include this pin when BYTE
High and references to t he Address Inputs to include this pin when BYTE
is Low except when
stated explicitly otherwise.
Chip Enable (E
). The Chip Enable, E, activates
the memory, allowing Bus Read and Bus Write operations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, V
Output Enable (G
, all other pins are ignored.
IH
). The Output Enable, G, con-
trols the Bus Read operation of the memory.
Write Enable (W
). The Write Enabl e, W, controls
the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interface.
V
Write Protect (VPP/WP). The VPP/Write
PP/
Protect
pin provides two functions. T he VPP function allows the memory to use an external high
voltage power supply to reduc e the time required
for Program operations. This is achieved by bypassing the unlock cycles and/or using the Double
Word or Quadruple Byte Program commands.
The Write Protect function provides a hardware
method of protecting the two outermost boot
blocks. When V
/Write Protect is L ow, VIL, the
PP
memory protects the two outer most boot blocks;
Program and Erase operations in these blocks are
is High,
is
ignored while V
RP
is at VID.
When V
/Write Protect is High, VIH, the memory
PP
/Write Protect is Low, even when
PP
reverts to the previous protection status of the two
outermost boot blocks. Program and Erase operations ca n now mod ify th e data in these blocks unless the blocks are protected using Block
Protection.
When V
/Write Protect is raised to V
PP
the mem-
PP
ory automatically enters the Unlock Bypass mode.
When V
/Write Protect returns to VIH or VIL nor-
PP
mal operation resumes. During Unlock Bypass
Program operations th e memory draws I
PP
from
the pin to supply the programming circuits. See the
description of the Unl ock By pas s c omm and in the
Command Interface sec tion. The transitio ns from
V
to VPP and from VPP to VIH must be slower
IH
than t
Never raise V
, see Figure 17.
VHVPP
/Write Protect to VPP from any
PP
mode except Read mode, otherwise the memory
may be left in an indeterminate state.
The V
/Write Protect pin must not be left floating
PP
or unconnected or the device may become unreliable. A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between the V
/Write Protect pin and the V
PP
SS
Ground pin to decouple the current surges from
the power supply. The PCB track widths must be
sufficient to carry the currents required during
Unlock Bypass Program, I
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP
PP
.
). The
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be
used to apply a Hardware Reset to the memory or
to temporarily unprote ct all Bl oc ks t hat h av e be en
protected.
Note that if V
/WP is at VIL, then the two outer-
PP
most boot blocks will remain protected even if RP
is at V
ID
.
A Hardware Reset is achieved by holdi ng Reset/
Block Temporary Unp rotect Low, V
t
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
PLPX
goes High, V
, the memory will be ready f or Bus
IH
Read and Bus Write operations after t
, whichever occurs last. See the Ready/Busy
t
RHEL
, for at least
IL
PHEL
or
Output section, Tabl e 16. and Figure 16., Reset/
Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms, for
more details.
Holding RP
at VID will temporarily unprotect the
protected Blocks in the memory. Program and
Erase operations on all blocks will be possible.
The transition from V
PHPHH
.
t
Ready/Busy Output (RB
to VID must be slower than
IH
). The Ready/Busy pin
is an open-drain output that can be used to identify
when the device is performing a Program or Erase
operation. During Program or Erase operations
10/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Ready/Busy is Low, VOL. Ready/Busy is hig h-impedance during Read mode, Auto Select mode
and Erase Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and Bus Write
operations cannot begin until Ready/Busy becomes high-impedance. See Table 16. and Figure
16., Reset/Block Tem porary Unp rotect AC Waveforms.
The use of an open-drain output allows the Ready/
Busy pins from several memories to be connected
to a single pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate
that one, or more, of the memories is busy.
Byte/Word Organizatio n Select (BYTE
). The
Byte/Word Organization Select pin is used to
switch between the x8 and x16 Bus modes of the
memory. When Byte/ Word Organi zation Sel ect is
Low, V
High, V
, the memory is in x8 mode, when it is
IL
, the memory is in x16 mode.
IH
Supply Voltage (2.7V to 3.6V). VCC pro-
V
CC
vides the power su pply for all operations (Read,
Program and Erase).
The Command Interface is disabled when the V
CC
Supply Voltage is le ss than the Lockout Vo ltage,
V
. This prevents Bus Write operations from ac-
LKO
cidentally damaging the data during power up,
power down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is programming or erasing during
this time then the operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacito r should be connected between
the V
Supply Voltage pin and the VSS Ground
CC
pin to decouple the current surges from the power
supply. The PCB track widths must be sufficient to
carry the currents required during Program and
Erase operations, I
Ground. VSS is the referenc e for all voltage
V
SS
measurements. The d evic e fe atures tw o V
CC3
.
pins
SS
which must be both connected to the system
ground.
11/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
BUS OPERATIONS
There are five standard bus operations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Writ e, Output Disable, Standby and Automatic Standby.
See Table 2. and Table 3., Bus Operations, for a
summary. Typically glitches of less than 5ns on
Chip Enable or Write En able are ignored by the
memory and do not affect bus operations.
Bus Read. Bus Read operations read from the memory cells, or specific registers in the Command Interface. A valid Bus Read operation involves setting the desired address on the Address Inputs, applying a Low s ig nal, V and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable High, V
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will ou tpu t the
IH
value, see Figure 11., Read Mode AC Waveforms,
and Table 12., Read AC Characteristics, for details of when the output becomes valid.
Bus Write. Bus Write operations write to the Command Interface. A v alid Bus Write operati on begins by setting the desired address on the Address Inputs. The Ad dress Inputs are latched b y the Command Interface on the falling edge of Chip Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last. The Data Inputs/Outputs ar e latched by the Com mand Interface on the rising ed ge of Chip Enab le or Write Enable, whichever occurs first. Output Enable must remain High, V
IH
Write operation. See Figure 12. and Figure 13.,
Write AC Waveforms, and Table 13. and Table
14., Write AC Characteristics, for details of the tim-
ing requirements. Output Disable. The Data Inputs/Outpu ts are in
the high impedance state when Output Enable is
High, V
.
IH
Standby. When Chip Enable is High, V memory enters Standby mode and the Data Inputs/Outputs pins are placed in the high-impedance state. To reduce the Su pply Current to the Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
, to Chip Enable
IL
, during the whole Bus
, the
IH
, Chip Enable should
be held within V
± 0.2V. For the Standby current
CC
level see Table 11., DC Characteristics.
During program or eras e operations the memory
will continue to use the Program/Erase Supply
Current, I
, for Program or Erase operations un-
CC3
til the operation completes. Automatic Standby. If CMOS levels (V
± 0.2V)
CC
are used to drive the bus and the bus is inactive for
300ns or more the memory enters Automatic
Standby where the interna l Supply Current is reduced to the Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
. The
Data Inputs/Outputs will still output data if a Bus
Read operation is in progress.
Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to
read the Electronic Signature and also to apply
and remove Block Protection. These bus operations are intended for us e by progr ammin g equip ment and are not usually used in applications.
They require V
to be applied to some pins.
ID
Electronic Signature. The memory has two codes, the manufacturer code and the device code, that can be read to identify the memory. These codes can b e read b y apply ing the sig nals listed in Table 2. and Table 3., Bus Operati ons.
Block Protect and Chip Unprotect.
Groups of
blocks can be protected against accidental Program or Erase. The Prot ection Groups are sh own
in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21., Block
Addresses. The whole chip ca n be unp ro tec ted to
allow the data inside the blocks to be changed.
The V
the two outermost boot blocks. When V
Protect
/Write Protect pin can be used to protect
PP
is at V
the two outermost boot blocks are
IL
PP
/Write
protected and remain protected regardless of the
Block Protection Status or the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin status.
Block Protect an d Chip Unprotect ope rations are
described in APPENDIX D.
12/46
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 2. Bus Operations, BYTE = V
Operation E G W
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
Read Manufacturer
Code
Read Device Code
Extended Memory
Block Verify Code
Note: X = VIL or VIH.
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
IL
IL
IH
IL
IL
IL
IL
V
IH
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
Table 3. Bus Operations, BYTE = V
Operation E
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
Read Manufacturer
Code
Read Device Code
Extended Memory
Block Verify Code
Note: X = VIL or VIH.
V
V
V
V
V
V
G W
V
IL
IL
IH
IL
IL
IL
IL
V
IH
V
IH
XXX Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
IL
Address Inputs
DQ15A–1, A0-A2 0
V
Cell Address Hi-Z Data Output
IH
V
Command Address Hi-Z Data Input
IL
V
X Hi-Z Hi-Z
IH
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
V
IH
Others V
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIL,
V
IH
A9 = V
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIH, A6 = VIL,
V
IH
A9 = V
IH
or V
IL
IH
, Others VIL or V
ID
, Others VIL or V
ID
DQ14-DQ8 DQ7-DQ0
IH
IH
Address Inputs
A0-A20
V
Cell Address Data Output
IH
V
Command Address Data Input
IL
V
XHi-Z
IH
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
V
IH
Others VIL or V
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
V
IH
Others VIL or V
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIH, A6 = VIL,
V
IH
A9 = V
ID
IH
IH
, Others VIL or V
IH
Data Inputs /Ou tpu t s
Hi-Z 20h
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
56h (M29W320ET)
57h (M29W320EB)
81h (factory locked)
01h (not factory locked)
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1, DQ14-DQ0
0020h
2256h (M29W320ET)
2257h (M29W320EB)
81h (factory locked)
01h (not factory locked)
13/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations to the memory are interpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of Bus
Write operation s will result in the memory return ing to Read mode. The long command sequences
are imposed to maximize data security.
The address used for the commands changes depending on whether the memory is in 16-bit or 8bit mode. See either Table 4., or Table 5., depending on the configuration that is being used, for a
summary of the commands.
Read/Reset Command
The Read/Reset command returns the memory to
its Read mode. It also resets the errors in the Status Register. Either one or three Bus Wr i te ope ra tions can be used to issue the Read/Reset
command.
The Read/Reset command can be issued, between Bus Write cycles before the start of a program or erase operation, to return the device to
read mode. If the Read/Reset command is issu ed
during the time-out of a Block erase operation then
the memory will take up to 10µ s to abort. During
the abort period no valid data can be read from the
memory. The Read/Reset command will not abort
an Erase operation when issued while in Erase
Suspend.
Auto Select Command
The Auto Select command is used to read the
Manufacturer Code, th e Device Code, the Block
Protection Status and the Extended Memory Block
Verify Code. Three consecuti ve Bus Write ope rations are required t o issue the Auto Select command. The memory remai ns in Auto Sel ect mode
until a Read/Reset or CFI Query command is issued.
In Auto Select mode the M anufacturer Code can
be read using a Bus Read operation with A0 = V
and A1 = VIL. The other address bits may be set to
either V
The Device Code ca n be read using a Bu s Read
operation with A0 = V
address bits may be set to either V
The Block Protectio n Statu s of ea ch block c an be
read using a Bus Read ope ration with A0 = V
A1 = V
dress. The other address bits may be set to either
V
IL
or VIH.
IL
and A1 = VIL. The other
IH
and A12-A20 specifying the block ad-
IH
or VIH.
IL
IL
or VIH. If the addressed block is protected then
01h is output on Data Inputs/Ou tputs DQ0-DQ7,
otherwise 00h is output.
Read CFI Query Command
The Read CFI Query Comma nd is used to read
data from the Common Flash Interface (CFI)
Memory Area. This command is valid when the device is in the Read Array mode, or when the device
is in Auto Select mode.
One Bus Write cycle is required to issue the Read
CFI Query Command . Once the command is issued subsequent Bus Read operatio ns read from
the Common Flash Interface Memory Area.
The Read/Reset command must be issue d to return the device to the previous mode (the Read Array mode or Aut o Select mode ). A second R ead/
Reset command would be needed if the d evice i s
to be put in the Read Array mode from Auto Select
mode.
See APPENDIX B. , Tables 22, 23, 24, 25, 26 and
27 for details on the informati on contained in the
Common Flash Interface (CFI) memory area.
Program Command
The Program command can be used to program a
value to one address in the memory array at a
time. The command requires four Bus Write op er ations, the final write operation latches the address and data, and starts the Program/Erase
Controller.
If the address falls in a protect ed block then the
Program command is ignored, the data remain s
unchanged. The Status Register is never read and
no error condition is given.
During the program operation th e memory will ig nore all commands. It is no t possib le to is sue any
command to abort or pause the operation. After
programming has started, Bus Read operations
output the Status Re gister content. See the s ection on the STATUS REGISTER for more details.
IL
Typical program times are given in Table 6.
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs Bus
Read operations will continue to output the Status
Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued
to reset the error condition and return to Read
,
mode.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ back t o ’1’. One of the Erase Commands must be used to set all the bits in a block or
in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
14/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Fast Program Commands
There are two Fast P rogr am c omm and s av ail ab le
to improve the programming throughput, by writing
several adjacent words or bytes in parallel. The
Quadruple Byte Program command is available for
x8 operations, while the Double Word Program
command is available for x16 operations.
Fast Program commands should not be attempted
when V
because applying a 12V V
pin will temporarily unprotect any protected
WP
WP is not at VPP. Care must be taken
PP/
voltage to the VPP/
PP
block.
After programming h as started, Bus R ead opera-
tions output the Status Register content.
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs Bus
Read operations will continue to output the Status
Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued
to reset the error condition and return to Read
mode.
Note that the Fast Program commands cannot
change a bit set at ’0’ back to ’1’. One of the Erase
Commands must be us ed to set all the bits in a
block or in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Typical Program times are given in Table
6., Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase
Endurance Cycles
Quadruple Byte Program Command. The Quadruple Byte Program co mmand is used to wr ite a page of four adjacent Bytes in parallel. The four bytes must differ only for addresses A0, DQ15A-1. Five bus write cycles are necessary to issue the Quadruple Byte Program command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Quadruple Byte
Program Command.
■ The second bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the first byte to be written.
■ The third bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the second byte to be written.
■ The fourth bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the third byte to be written.
■ The fifth bus cycle latches the Address and the
Data of the fourth byte to be written and starts
the Program/Erase Controller.
Double Word Program Command. The Double Word Program com mand is used to write a page of two adjacent wor ds in parallel. The tw o words must differ only for the address A0.
Three bus write cy cles ar e ne ce ss ar y to i ss ue the
Double Word Program command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Double Word
Program Command.
■ The second bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the first word to be written.
■ The third bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the second word to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
Unlock Bypass Command
The Unlock Bypass com mand is used in conju nction with the Unlock Bypass Program command to
program the memory faster than with the standard
program commands. W hen the cycle time to the
device is long, considerable time saving can be
made by using these commands. Three Bus Write
operations are required to issue the Unlock Bypass command.
Once the Unlock Bypass c ommand has been issued the memory enters Unlock Bypass mode.
The Unlock Bypass Progr am command can then
be issued to program addresses or the Unlock Bypass Reset command can be issued to return to
Read mode. In Unlock Bypa ss mod e t he mem ory
can be read as if in Read mode.
When V
is applied to the VPP/Write Protect pin
PP
the memory automatica lly enters the Unlock Bypass mode and the Unlock Bypass Program command can be issued immediately. Care must be
taken because applying a 12V V
VPP/WP
pin will temporarily unprotect any protect-
voltage to the
PP
ed block.
Unlock Bypass Program Command
The Unlock Bypass Program command can be
used to program one address in the memory array
at a time. The command requires two Bus Write
operations, the final write operation latches the address and data, and starts the Program/Erase
Controller.
The Program operation us ing the Unlock Bypass
Program command behaves identically to the Program operation using the Program command. The
operation cannot be aborted, a Bus Read ope ration outputs the Status Register. See the Program
command for details on the behavior.
Unlock Bypass Reset Command
The Unlock Bypass Re se t co mm and ca n be used
to return to Read/Reset mode from Unlock Bypass
Mode. Two Bus Write operations are required to
issue the Unlock B ypass Reset command. Re ad/
Reset command does not exit from Unlock Bypass
Mode.
Chip Erase Command
The Chip Erase command c an be used to erase
the entire chip. Six B us Write operations are required to issue the Chip Erase Command and start
the Program/Erase Controller.
If any blocks are protected then these are ignored
and all the other blocks are erased. If all of the
blocks are protected the Chip Erase operation appears to start but will terminate within about 100µs,
15/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
leaving the data unc hanged . No er ror con dition is
given when protected blocks are ignored.
During the erase operation the memory will ignore
all commands, includin g the Er ase S usp end command. It is not po ssible to issue any co mmand to
abort the operation. Typ ical chip erase times ar e
given in Table 6.. All Bus Re ad opera tions du ring
the Chip Erase operation will output the Status
Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs. See the section on the Status Register for more details.
After the Chip Erase o per at ion has c om ple ted the
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Statu s Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read Mode.
The Chip Erase Command sets all of the bits in unprotected blocks of the memory to ’1’. All previous
data is lost.
Block Erase Command
The Block Erase command can be used to er ase
a list of one or more blocks. It sets all of the bits in
the unprotected selected blocks to ’1’. All previous
data in the selected blocks is lost.
Six Bus Write operations are required to select the
first block in the list. Each addit ional block in the
list can be selected by repeating the sixth Bus
Write operation using the address of the additional
block. The Block Er ase operation starts the Program/Erase Controller after a time-out period of
50µs after the last Bus Wr ite operation. O nce the
Program/Erase Control ler starts it is not possible
to select any more blocks. Each addition al block
must therefore be selec ted wi thin 50µ s o f the last
block. The 50µ s tim er rest arts when an additi onal
block is selected. After the s ixth Bus Write operation a Bus Read o peration will output the S tatus
Register. See the S tatus Register sec tion for details on how to identify if the P rogram/Er ase Controller has started the Block Erase operation.
If any selected blocks are protected then these are
ignored and all the other selected blocks are
erased. If all of the sel ected blocks are pr otected
the Block Erase operation appears to start but will
terminate within about 100µs, leaving the data unchanged. No error condition is given when protected blocks are ignored.
During the Block Eras e o perat ion the memory will
ignore all comman ds except the Erase Suspend
command and the Read/Reset command which is
only accepted during the 50µs time-out period.
Typical block erase times are given in Table 6.
After the Erase operation has started all Bus Read
operations will outpu t the Status Register on the
Data Inputs/Outputs. See the s ection on the Status Register for more details.
After the Block Erase operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs Bus
Read operations will continue to output the Status
Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued
to reset the error condition and return to Read
mode.
Erase Suspend Command
The Erase Suspend Command may be used to
temporarily suspe nd a Bl ock Er ase op eration a nd
return the memory to Read mode. The command
requires one Bus Write opera tio n.
The Program/Erase Control ler will sus pend with in
the Erase Suspend Latency time of the Erase Suspend Command being issued. Once the Program/
Erase Controller has st opped the memo ry will be
set to Read mode and the Erase will be susp ended. If the Erase Suspend command is issued d uring the period when the memo ry is waiting for an
additional block (bef ore the Program/Erase Controller starts) then the Erase is suspended immediately and will start immediately when the Erase
Resume Command is issu ed. It is not possible to
select any further b locks to erase a fter the Erase
Resume.
During Erase Suspend i t is possible to Read and
Program cells in blocks that are not being erased;
both Read and Program operations behave as
normal on these blocks. I f any atte mpt is made to
program in a protected bloc k or in the sus pended
block then the Program command is ign ored and
the data remains unchanged. The Status Register
is not read and no error c ondition is gi ven. Read ing from blocks tha t are being erased wil l output
the Status Register.
It is also possible t o issue the Auto Selec t, Read
CFI Query and Unlock Bypass com mands during
an Erase Suspend. The Read/Reset command
must be issued to return the device to Read Array
mode before the Resume command will be accepted.
During Erase Suspend a Bus Read operation to
the Extended Block will output the Extended Block
data.
Erase Resume Command
The Erase Resume command must be used to restart the Program/Er ase Controll er after an Er ase
Suspend. The device must be in Read Array mode
before the Resume command will be accepted. An
erase can be suspended and resume d more th an
once.
Enter Extended Block Command
The M29W320E has an extra 64KBy te block (Ex tended Block) that can only be accessed using the
Enter Extended Bloc k com mand. T hre e Bus write
cycles are requi red to issue the Ex tended Block
command. Once the comm and has been issued
16/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
the device enters Exte nded Bl ock mod e wh er e al l
Bus Read or Program operations to the Boot Block
addresses access the Extended Block. The Extended Block (with the same address as the boot
block) cannot be erased, and can be treated as
one-time programmable (OTP) memory. In Extended Block mode the Boot Blocks are not accessible.
To exit from the Extended Block mode the Exit Extended Block command must be issued.
The Extended Block can be protected, however
once protected the protection cannot be undone.
Exit Extended Block Command
The Exit Extended Block command is used to exit
from the Extended Bloc k m ode and re turn th e de vice to Read mode. Four Bus Write operations are
required to issue the command.
Block Protect and Chip Unprotect Commands
Groups of blocks c an be protected against acci -
dental Program or Erase. The Protection Groups
are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table
21., Block Addresses. The whol e chip can be un-
protected to allow the data ins id e the blo cks t o be
changed.
Block Protect an d Chip Unprotect ope rations are
described in APPENDIX D.
Table 4. Commands, 16-bit mode, BYTE
Command
Read/Reset
Auto Select 3 555 AA 2AA 55
Program 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 A0 PA PD
Double Word Program 3 555 50 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1
Unlock Bypass 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 555 AA 2AA 55 55 5 80 555 AA 2AA 55 555 10
Block Erase 6+ 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 BA B0
Erase Resume 1 BA 30
Read CFI Query 1 55 98
Enter Extended Block 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 88
Exit Extended Block 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 90 X 00
Note: X Don’t Care, PA Program A ddr ess, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block. All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
The Command Interface only uses A–1, A0-A10 and DQ0-DQ7 to verify the commands; A11-A20, DQ8-DQ14 and DQ15 are Don’t
Care. DQ15A–1 is A–1 when BYTE
1X F0
3555 AA2AA 55 X F0
2 X A0 PA PD
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
is VIL or DQ15 when BYTE is VIH.
= V
IH
Bus Write Operations
(BA)
555
90
17/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 5. Commands, 8-bit mode, BYTE = V
IL
Bus Write Operations
Command
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
1X F0
Read/Reset
3AAA AA 555 55 X F0
Auto Select 3 AAA AA 555 55
(BA)
AAA
90
Program 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA A0 PA PD
Quadruple Byte Program 5 AAA 55 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1 PA2 PD2 PA3 PD3
Unlock Bypass 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 20
Unlock Bypass Program 2 X A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 AAA AA 555 5 5 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 10
Block Erase 6+ AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 BA B0
Erase Resume 1 BA 30
Read CFI Query 1 AA 98
Enter Extended Block 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 88
Exit Extended Block 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 90 X 00
Note: X Don’t Care, PA Program A ddr ess, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block. All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
The Command Interface only uses A–1, A0-A10 and DQ0-DQ7 to verify the commands; A11-A20, DQ8-DQ14 and DQ15 are Don’t
Care. DQ15A–1 is A–1 when BYTE
is VIL or DQ15 when BYTE is VIH.
Table 6. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles
Parameter Min
Typ
(1, 2)
Chip Erase 40
Block Erase (64 KBytes) 0.8
Erase Suspend Latency Time
Program (Byte or Word) 10
Double Word Program (Byte or Word) 10
Chip Program (Byte by Byte) 40
Chip Program (Word by Word) 20
Chip Program (Quadruple Byte or Double Word) 10
Program/Erase Cycles (per Block) 100,000 cycles
Data Retention 20 years
Note: 1. Typical values measured at room temperature and nominal voltages.
2. Sampled, but not 100% tested.
3. Maximum value measured at worst case conditions for both temperature and V
4. Maximum value measured at worst case conditions for both temperature and V
after 100,00 program/erase cycles.
CC
.
CC
18/46
Max
200
6
50
200
200
200
100
100
(3)
(4)
(3)
(4)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(2)
Unit
µs
µs
µs
s
s
s
s
s

STATUS REGISTER
The M29W320E has one Status Re gister. It provides information on the current or previous Program or Erase operations. The various bits convey
information and errors on the operation. Bus Read
operations from any address, always read the Status Register during Program and Erase operations. It is also read durin g Erase Suspend when
an address within a block being erased is accessed.
The bits in the Status R egi st er are s umm ar iz ed in
Table 7., Status Register Bits.
Data Polling Bit (DQ7). T he Data P ollin g Bit can be used to identify whether the Program/Erase Controller has successfully completed its operation or if it has respond ed to an Erase Suspend. The Data Polling Bit is output on DQ7 whe n the Status Register is read.
During Program operations the Data Polling Bit
outputs the complement of the bit being programmed to DQ7. After successful completion of
the Program operation the memory returns to
Read mode and Bus Read operations from the address just programm ed output DQ7, not its complement.
During Erase operations the Data Polli ng Bit outputs ’0’, the complement of the erased state of
DQ7. After su ccess ful co mpl etion of t he Er ase o peration the memory returns to Read Mode.
In Erase Suspend mode the Data Polli ng Bit will
output a ’1’ during a Bus Rea d operation withi n a
block being erased. The Data Polling Bit will
change from a ’0’ to a ’1’ when the Program/Erase
Controller has suspended the Erase operation.
Figure 7., Data Polling Flowcha rt, gives a n exam -
ple of how to use the Data Po lli ng Bit . A Va li d Ad dress is the address being programmed or an
address within the block being erased.
Toggle Bit (DQ6). The Toggle Bit can be used to identify whether the Program/Erase Controller has successfully completed its operation or if it has responded to an Erase Suspend. The To ggle Bit is output on DQ6 when the Status Register is read.
During Program and Er ase oper ations the Togg le
Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1 ’ to ’0’, etc., with succes sive Bus Read operations at any address. After
successful completion of the operation the memory returns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend mode the Toggle Bit will
output when addressing a cell within a block being
erased. The Toggle Bit will stop toggling when the
Program/Erase Controller has suspended the
Erase operation.
Figure 8., Toggle Flowchart, gives an example of
how to use the Data Toggle Bit. Figure 14. and
Figure 15. describe Toggle Bit timing waveform.
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Error Bit (DQ5). The Error Bit can be used to
identify errors detected by the Program/Erase
Controller. The Error Bit is set to ’1’ when a Program, Block Erase or Chip Erase operation fails to
write the correct data to the memory. If the Error
Bit is set a Read/Reset command mus t be issu ed
before other comma nds are issued. The Error bit
is output on DQ5 when the Status Register is read.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set to ’0’ back to ’1’ and attempting to do so will
set DQ5 to ‘1’. A Bus Read ope ration to that address will show the bi t is st ill ‘0 ’. On e of the Er as e
commands must be used to set all the bits in a
block or in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Erase Timer Bi t (DQ3). The Erase Timer Bit can be used to identify the start of Program/Erase Controller operation during a Block Erase command. Once the Program/Erase Controller starts erasing the Erase Timer Bit is set to ’1’. Before the Program/Erase Cont roller starts the Erase Timer Bit is set to ’0’ and additiona l blocks t o be erased may be written to the Command Interface. The Erase Timer Bit is output on DQ3 when the Status Register is read.
Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2). The Alternative Toggle Bit can be u sed to monitor the Program/ Erase controller d uring Eras e operations. The Alternative Toggle Bit is output on DQ2 when the Status Register is read.
During Chip Erase and Block Erase operations the
Toggle Bit changes from ’0 ’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., wi th
successive Bus Rea d operations from ad dresses
within the blocks being eras ed. A protect ed block
is treated the sam e as a block no t being erased.
Once the operation completes the memory returns
to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend the Alternative Toggle Bit
changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc. with successive
Bus Read operations from addresses within the
blocks being erased . Bus Read operations to addresses within blocks not b ei ng e rase d wi ll output
the memory cell data as if in Read mode.
After an Erase o per at ion th at ca us es th e Er ror B it
to be set the Alternative Toggle Bit can be used to
identify which block or blocks have caused the error. The Alternative Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to
’1’ to ’0’, etc. with successive Bus Read Operations from addresses with in blocks that have not
erased correctly. Th e Alternative Toggle B it does
not change if the addressed block has erased correctly.
Figure 14. and Figure 15. describe Alternative
Toggle Bit timing waveform.
19/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 7. Status Register Bits
Operation Address DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ3 DQ2 RB
Program Any Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – –
0
Program During Erase
Suspend
Any Address DQ7
Program Error Any Address DQ7
Toggle 0 – –
Toggle 1 – – Hi-Z
Chip Erase Any Address 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Block Erase before
timeout
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 Toggle 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 No Toggle 0
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Block Erase
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 No Toggle
Erasing Block 1 No Toggle 0 – Toggle Hi-Z
Erase Suspend
Non-Erasing Block Data read as normal Hi-Z
Good Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 No Toggle Hi-Z
Erase Error
Faulty Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 Toggle H i-Z
Note: Unspecified data bits should be ignored.
Figure 7. Data Polling Flowchart Figure 8. Toggle Flowchart
START
READ DQ5 & DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
YES
=
DATA
NO
NO
DQ5
= 1
YES
READ DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
START
READ DQ6
ADDRESS = BA
READ
DQ5 & DQ6
ADDRESS = BA
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
YES
NO
DQ5
= 1
YES
READ DQ6
TWICE
ADDRESS = BA
NO
0
0
20/46
DQ7
YES
=
DATA
NO
FAIL PASS
AI90194
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
YES
FAIL
Note: BA = Address of Block being Programmed or Erased.
NO
PASS
AI08929b

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
MAXIMUM RATING
Stressing the device above the ra ting l isted in the
Absolute Maximum Ratin gs table ma y cause per manent damage to the device. Expos ure to Ab so lute Maximum Rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability. These are
stress ratings only and operation of th e device at
Table 8. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
T
BIAS
T
STG
T
LEAD
V
IO
V
CC
V
ID
(5)
V
PP
Note: 1. Compliant with the ECOPACK® 7191395 specification for Lead-free soldering processes.
2. Not exceeding 250°C for more than 30s, and peaking at 260°C.
3. Minimum voltage may undershoot to –2V during transition and for less than 20ns during transitions.
4. Maximum voltage may overshoot to V
5. V
PP
Temperature Under Bias –50 125 °C
Storage Temperature –65 150 °C
Lead Temperature during Soldering
Input or Output Voltage
(3,4)
Supply Voltage –0.6 4 V
Identification Voltage –0.6 13.5 V
Program Voltage –0.6 13.5 V
+2V during transition and for less t han 20ns during transitions.
must not remain at 12V for more than a tota l of 80hrs.
CC
these or any other conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is
not implied. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics
SURE Program and o ther relevant quality documents.
(1)
–0.6
(2)
260
V
+0.6
CC
°C
V
21/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
DC AND AC PARAMETERS
This section summ arizes the operating measurement conditions, and th e DC and AC c haracteris tics of the device. The parameters in the DC and
AC characteristics Tables that follow, are derived
from tests performed under the Measurement
Table 9. Operating and AC Measurement Conditions
Parameter
Min Max Min Max
V
Supply Voltage
CC
Ambient Operating Temperature –40 85 –40 85 °C
Load Capacitance (C
Input Rise and Fall Times 10 10 ns
Input Pulse Voltages
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages
)
L
Conditions summarized in Table 9., Operating and
AC Measurement Conditions. Designers should
check that the operating conditi ons in their circuit
match the operating conditions when relying on
the quoted parameters.
M29W320E
2.7 3.6 2.7 3.6 V
30 30 pF
0 to V
CC
V
/2 VCC/2
CC
0 to V
CC
Unit70 90
V
V
Figure 9. AC Measurement I/O Waveform Figure 10. AC Measurement Load Circuit
V
PP
V
CC
VCC/2
0V
AI05557
V
CC
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
0.1µF
0.1µF
CL includes JIG capacitance
V
CC
C
L
Table 10. Device Capacitance
Symbol Parame te r Test Condition Min Max Uni t
C
IN
C
OUT
Note: Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
V
V
OUT
IN
= 0V
= 0V
6pF
12 pF
25kΩ
25kΩ
AI05558
22/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 11. DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
I
I
LO
I
CC1
I
CC2
I
CC3
V
V
V
I
PP
V
V
V
V
LKO
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Leakage Current
LI
Output Leakage Current
(2)
Supply Current (Read)
Supply Current (Standby)
Supply Current (Program/
(1,2)
Erase)
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
IL
Input High Voltage
IH
PP
Voltage for V
Acceleration
Current for V
/WP Program
PP
/WP Program
PP
Acceleration
Output Low Voltage
OL
Output High Voltage
OH
Identification Voltage 11.5 12.5 V
ID
Program/Erase Lockout Supply
Voltage
2. In Dual operations the Supply Current will be the sum of
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
E = VIL, G = VIH,
f = 6MHz
E
= VCC ±0.2V,
RP = VCC ±0.2V
Program/Erase
Controller active
= 2.7V ±10%
V
CC
= 2.7V ±10%
V
CC
I
= 1.8mA
OL
= –100µA
I
OH
I
CC1
≤ V
IN
CC
≤ V
OUT
CC
V
PP
V
IL
V
/WP = V
PP
(read) and I
/WP =
or V
IH
PP
(program/erase).
CC3
±1
±1
10 mA
100
20 mA
20 mA
0.7V
CC
VCC +0.3
11.5 12.5 V
15 mA
0.45 V
V
–0.4
CC
1.8 2.3 V
µA
µA
µA
V
V
23/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 11. Read Mode AC Waveforms
A0-A20/
A–1
tAVQV tAXQX
E
tAVAV
VALID
tELQV
tELQX tEHQZ
G
tGLQX tGHQX
tGLQV
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
tBHQV
BYTE
tELBL/tELBH tBLQZ
Table 12. Read AC Characteristics
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition
E
t
AVAV
t
AVQV
(1)
t
ELQX
t
ELQV
(1)
t
GLQX
t
GLQV
(1)
t
EHQZ
(1)
t
GHQZ
t
EHQX
t
GHQX
t
AXQX
t
ELBL
t
ELBH
t
BLQZ
t
BHQV
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
RC
t
ACC
t
LZ
t
CE
t
OLZ
t
OE
t
HZ
t
DF
t
OH
t
ELFL
t
ELFH
t
FLQZ
t
FHQV
Address Valid to Next Address Valid
Address Valid to Output Valid
Chip Enable Low to Output Transition
Chip Enable Low to Output Valid
Output Enable Low to Output
Transition
Output Enable Low to Output Valid
Chip Enable High to Outpu t Hi-Z
Output Enable High to Output Hi-Z
Chip Enable, Output Enable or
Address Transition to Output Transition
Chip Enable to BYTE Low or High Max 5 5 ns
BYTE Low to Output Hi-Z Max 25 30 ns
BYTE High to Output Valid Max 30 40 ns
= VIL,
G = V
E
= VIL,
G
= V
G
= V
G
= V
= V
E
E
= V
G
= V
E
= V
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
tEHQX
tGHQZ
VALID
AI05559
M29W320E
Unit
70 90
Min 70 90 ns
Max 70 90 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Max 70 90 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Max 30 35 ns
Max 25 30 ns
Max 25 30 ns
Min 0 0 ns
24/46

Figure 12. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A20/
A–1
tAVWL
E
VALID
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
tWLAX
tWHEH
tELWL
G
tWLWHtGHWL
W
tDVWH
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tVCHEL
VALID
tWHRL
Table 13. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
ELWL
t
WLWH
t
DVWH
t
WHDX
t
WHEH
t
WHWL
t
AVWL
t
WLAX
t
GHWL
t
WHGL
(1)
t
WHRL
t
VCHEL
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
CS
t
WP
t
DS
t
DH
t
CH
t
WPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 70 90 ns
Chip Enable Low to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Write Enable High Min 45 50 ns
Input Valid to Write Enable High Min 45 50 ns
Write Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Chip Enable High Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 50 ns
Output Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 35 ns
VCC High to Chip Enable Low
tWHGL
tWHWL
tWHDX
AI05560
M29W320E
Unit
70 90
Min 50 50 µs
25/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 13. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A20/
A–1
tAVEL
W
VALID
tELAX
tEHWH
tWLEL
G
tELEHtGHEL
E
tDVEH
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tVCHWL
VALID
tEHRL
Table 14. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
WLEL
t
ELEH
t
DVEH
t
EHDX
t
EHWH
t
EHEL
t
AVEL
t
ELAX
t
GHEL
t
EHGL
(1)
t
EHRL
t
VCHWL
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
WS
t
CP
t
DS
t
DH
t
WH
t
CPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 70 90 ns
Write Enable Low to Chip Enab le Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Chip Enable High Min 45 50 ns
Input Valid to Chip Enable High Min 45 50 ns
Chip Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Write Enable High Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Chip Enable Low Min 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 50 ns
Output Enable High Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 35 ns
VCC High to Write Enable Low
tEHGL
tEHEL
tEHDX
AI05561
M29W320E
Unit
70 90
Min 50 50 µs
26/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 14. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Chip Enable Controlled
A0-A20
E
G
(1)
(2)
/DQ6
DQ2
Note: 1. The Toggle bit is output on DQ6.
2. The Alternative Toggle bit is output on DQ2.
VALID ADDRESS VALID ADDRESSVALID ADDRESS
tAXEL
tELQV
Data Data
Alternative Toggle/
Toggle Bit
tELQV
Alternative Toggle/
Toggle Bit
Figure 15. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Output Enable Controlled
A0-A20
G
VALID ADDRESS VALID ADDRESSVALID ADDRESS
tAXGL
AI09350
E
tGLQV
(1)
(2)
/DQ6
DQ2
Note: 1. The Toggle bit is output on DQ6.
2. The Alternative Toggle bit is output on DQ2.
Data Data
Alternative Toggle/
Toggle Bit
Table 15. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits AC Characteristics
Symbol Alt Parameter
Note: t
t
AXEL
t
AXGL
ELQV
and t
values are presented in Table 12., Read AC Characteristics.
GLQV
Address Transition to Chip Enab le Low Min 10 10 ns
Address Transition to Output En ab le Low Min 10 10 ns
tGLQV
Alternative Toggle/
Toggle Bit
70 90
AI09351
M29W320E
Unit
27/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 16. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms
E, G
W,
tPHWL, tPHEL, tPHGL
RB
RP
Table 16. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics
Symbol Alt Parameter
(1)
t
PHWL
t
PHEL
(1)
t
PHGL
(1)
t
RHWL
(1)
t
RHEL
(1)
t
RHGL
t
PLPX
t
PLYH
(1)
t
PHPHH
(1)
t
VHVPP
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
RH
t
RB
t
RP
t
READY
t
VIDR
tPLPX
tPLYH
RP High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable Low,
Output Enable Low
RB High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable Low,
Output Enable Low
RP Pulse Width Min 500 500 ns
RP Low to Read Mode Max 50 50 µs
RP Rise Time to V
ID
VPP Rise and Fall Time
tRHWL, tRHEL, tRHGL
tPHPHH
AI02931B
M29W320E
Unit
70 90
Min 50 50 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Min 500 500 ns
Min 250 250 ns
Figure 17. Accelerated Program Timing Waveforms
V
PP
VPP/WP
V
or V
IL
IH
28/46
tVHVPP
tVHVPP
AI05563

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
PACKAGE MECHANICAL
Figure 18. TSOP48 Lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12x20 mm, Bottom View Package Outline
1
48
e
D1
24
E1
B
25
A2
L1
A
E
DIE
LA1 α
C
CP
Note: Drawing not to scale.
TSOP-G
Table 17. TSOP48 Lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12x20 mm, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.100 0.050 0.150 0.0039 0.0020 0.0059
A2 1.000 0.950 1.050 0.0394 0.0374 0.0413
B 0.220 0.170 0.270 0.0087 0.0067 0.0106
C 0.100 0.210 0.0039 0.0083
CP 0.080 0.0031
D1 12.000 11.900 12.100 0.4724 0.4685 0.4764
E 20.000 19.800 20.200 0.7874 0.7795 0.7953
E1 18.400 18.300 18.500 0.7244 0.7205 0.7283
e 0.500 – – 0.0197 – –
L 0.600 0.500 0.700 0.0236 0.0197 0.0276
L1 0.800 0.0315
α 305305
millimeters inches
29/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 19. TFBGA48 6x8mm - 6x8 Ball Array, 0.8mm Pitch, Bottom View Package Outline
D
FD
FE
D1
SD
SE
BALL "A1"
E1E
ddd
e
eb
A
A2
A1
BGA-Z32
Note: Drawing not to scale.
Table 18. TFBGA48 6x8mm - 6x8 Ball Array, 0.8mm Pitch, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.260 0.0102
A2 0.900 0.0354
b 0.350 0.450 0.0138 0.0177
D 6.000 5.900 6.100 0.2362 0.2323 0.2402
D1 4.000 – – 0.1575 – –
ddd 0.100 0.0039
E 8.000 7.900 8.100 0.3150 0.3110 0.3189
E1 5.600 – – 0.2205 – –
e 0.800 – – 0.0315 – –
FD 1.000 – – 0.0394 – –
FE 1.200 – – 0.0472 – –
SD 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
SE 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
millimeters inches
30/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
PART NUMBERING
Table 19. Ordering Information Scheme
Example: M29W320EB 70 N 1 T
Device Type
M29
Operating Voltage
W = VCC = 2.7 to 3.6V
Device Function
320E = 32 Mbit (x8/x16), Boot Block
Array Matrix
T = Top Boot
B = Bottom Boot
Speed
70 = 70 ns
90 = 90 ns
Package
N = TSOP48: 12 x 20 mm
ZE = TFBGA48: 6 x 8mm, 0.8mm pitch
Temperature Range
1 = 0 to 70 °C
6 = –40 to 85 °C
Option
Blank = Standard Packing
T = Tape & Reel Packing
E = Lead-free Package, Standard Packing
F = Lead-free Package, Tape & Reel Packing
Note: This product is also available with the Extended Block factory locked. For further details and ordering
information contact your nearest ST sales office.
Devices are shipped from the factory with the memory content bits erased to ’1’.
For a list of available options (Speed, Package, etc.) or for further information on any aspect of this device,
please contact the ST Sales Office nearest to you.
31/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
APPENDIX A. BLOCK ADDRESSES
Table 20. Top Boot Block Addresses, M29W320ET
Block (Kbytes/Kwords) Protection Block Group (x8) (x16)
0 64/32
1 64/32 010000h–01FFFFh 008000h–0FFFFh
2 64/32 020000h–02FFFFh 010000h–17FFFh
3 64/32 030000h–03FFFFh 018000h–01FFFFh
4 64/32
5 64/32 050000h–05FFFFh 028000h–02FFFFh
6 64/32 060000h–06FFFFh 030000h–037FFFh
7 64/32 070000h–07FFFFh 038000h–03FFFFh
8 64/32
9 64/32 090000h–09FFFFh 048000h–04FFFFh
10 64/32 0A0000h–0AFFFFh 050000h–057FFFh
11 64/32 0B0000h–0BFFFFh 058000h–05FFFFh
12 64/32
13 64/32 0D0000h–0DFFFFh 068000h–06FFFFh
14 64/32 0E0000h–0EFFFFh 070000h–077FFFh
15 64/32 0F0000h–0FFFFFh 078000h–07FFFFh
16 64/32
17 64/32 110000h–11FFFFh 088000h–08FFFFh
18 64/32 120000h–12FFFFh 090000h–097FFFh
19 64/32 130000h–13FFFFh 098000h–09FFFFh
20 64/32
21 64/32 150000h–15FFFFh 0A8000h–0AFFFFh
22 64/32 160000h–16FFFFh 0B0000h–0B7FFFh
23 64/32 170000h–17FFFFh 0B8000h–0BFFFFh
24 64/32
25 64/32 190000h–19FFFFh 0C8000h–0CFFFFh
26 64/32 1A0000h–1AFFFFh 0D0000h–0D7FFFh
27 64/32 1B0000h–1BFFFFh 0D8000h–0DFFFFh
28 64/32
29 64/32 1D0000h–1DFFFFh 0E8000h–0EFFFFh
30 64/32 1E0000h–1EFFFFh 0F0000h–0F7FFFh
31 64/32 1F0000h–1FFFFFh 0F8000h–0FFFFFh
32 64/32
33 64/32 210000h–21FFFFh 108000h–10FFFFh
34 64/32 220000h–22FFFFh 110000h–117FFFh
35 64/32 230000h–23FFFFh 118000h–11FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
000000h–00FFFFh 000000h–07FFFh
040000h–04FFFFh 020000h–027FFFh
080000h–08FFFFh 040000h–047FFFh
0C0000h–0CFFFFh 060000h–067FFFh
100000h–10FFFFh 080000h–087FFFh
140000h–14FFFFh 0A0000h–0A7FFFh
180000h–18FFFFh 0C0000h–0C7FFFh
1C0000h–1CFFFFh 0E0000h–0E7FFFh
200000h–20FFFFh 100000h–107FFFh
32/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Block (Kbytes/Kwords) Protection Block Group (x8) (x16)
36 64/32
37 64/32 250000h–25FFFFh 128000h–12FFFFh
38 64/32 260000h–26FFFFh 130000h–137FFFh
Protection Group
39 64/32 270000h–27FFFFh 138000h–13FFFFh
40 64/32
41 64/32 290000h–29FFFFh 148000h–14FFFFh
Protection Group
42 64/32 2A0000h–2AFFFFh 150000h–157FFFh
43 64/32 2B0000h–2BFFFFh 158000h–15FFFFh
44 64/32
45 64/32 2D0000h–2DFFFFh 168000h–16FFFFh
46 64/32 2E0000h–2EFFFFh 170000h–177FFFh
Protection Group
47 64/32 2F0000h–2FFFFFh 178000h–17FFFFh
48 64/32
49 64/32 310000h–31FFFFh 188000h–18FFFFh
Protection Group
50 64/32 320000h–32FFFFh 190000h–197FFFh
51 64/32 330000h–33FFFFh 198000h–19FFFFh
52 64/32
53 64/32 350000h–35FFFFh 1A8000h–1AFFFFh
Protection Group
54 64/32 360000h–36FFFFh 1B0000h–1B7FFFh
55 64/32 370000h–37FFFFh 1B8000h–1BFFFFh
56 64/32
57 64/32 390000h–39FFFFh 1C8000h–1CFFFFh
58 64/32 3A0000h–3AFFFFh 1D0000h–1D7FFFh
Protection Group
59 64/32 3B0000h–3BFFFFh 1D8000h–1DFFFFh
60 64/32
61 64/32 3D0000h–3DFFFFh 1E8000h–1EFFFFh
Protection Group
62 64/32 3E0000h–3EFFFFh 1F0000h–1F7FFFh
63 8/4 Protection Group
64 8/4 Protection Group
65 8/4 Protection Group
66 8/4 Protection Group
67 8/4 Protection Group
68 8/4 Protection Group
69 8/4 Protection Group
70 8/4 Protection Group
Note: 1. Used as the Extended Block Addresses in Extended Block mode.
240000h–24FFFFh 120000h–127FFFh
280000h–28FFFFh 140000h–147FFFh
2C0000h–2CFFFFh 160000h–167FFFh
300000h–30FFFFh 180000h–187FFFh
340000h–34FFFFh 1A0000h–1A7FFFh
380000h–38FFFFh 1C0000h–1C7FFFh
3C0000h–3CFFFFh 1E0000h–1E7FFFh
3F0000h–3F1FFFh
3F2000h–3F3FFFh
3F4000h–3F5FFFh
3F6000h–3F7FFFh
3F8000h–3F9FFFh
3FA000h–3FBFFFh
3FC000h–3FDFFFh
3FE000h–3FFFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
1F8000h–1F8FFFh
1F9000h–1F9FFFh
1FA000h–1FAFFFh
1FB000h–1FBFFFh
1FC000h–1FCFFFh
1FD000h–1FDFFFh
1FE000h–1FEFFFh
1FF000h–1FFFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
33/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 21. Bottom Boot Block Addresses, M29W320EB
Block (Kbytes/Kwords) Protection Block Gr oup (x8) (x16)
0 8/4 Protection Group
1 8/4 Protection Group
2 8/4 Protection Group
3 8/4 Protection Group
4 8/4 Protection Group
5 8/4 Protection Group
6 8/4 Protection Group
7 8/4 Protection Group
8 64/32
9 64/32 020000h-02FFFFh 010000h–017FFFh
Protection Group
000000h-001FFFh
002000h-003FFFh
004000h-005FFFh
006000h-007FFFh
008000h-009FFFh
00A000h-00BFFFh
00C000h-00DFFFh
00E000h-00FFFFh
010000h-01FFFFh 008000h–00FFFFh
10 64/32 030000h-03FFFFh 018000h–01FFFFh
11 64/32
040000h-04FFFFh 020000h–027FFFh
12 64/32 050000h-05FFFFh 028000h–02FFFFh
Protection Group
13 64/32 060000h-06FFFFh 030000h–037FFFh
14 64/32 070000h-07FFFFh 038000h–03FFFFh
15 64/32
16 64/32 090000h-09FFFFh 048000h–04FFFFh
Protection Group
080000h-08FFFFh 040000h–047FFFh
17 64/32 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 050000h–057FFFh
18 64/32 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 058000h–05FFFFh
19 64/32
0C0000h-0CFFFFh 060000h–067FFFh
20 64/32 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 068000h–06FFFFh
21 64/32 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 070000h–077FFFh
Protection Group
22 64/32 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 078000h–07FFFFh
23 64/32
100000h-10FFFFh 080000h–087FFFh
24 64/32 110000h-11FFFFh 088000h–08FFFFh
Protection Group
25 64/32 120000h-12FFFFh 090000h–097FFFh
26 64/32 130000h-13FFFFh 098000h–09FFFFh
27 64/32
28 64/32 150000h-15FFFFh 0A8000h–0AFFFFh
Protection Group
140000h-14FFFFh 0A0000h–0A7FFFh
29 64/32 160000h-16FFFFh 0B0000h–0B7FFFh
30 64/32 170000h-17FFFFh 0B8000h–0BFFFFh
31 64/32
180000h-18FFFFh 0C0000h–0C7FFFh
32 64/32 190000h-19FFFFh 0C8000h–0CFFFFh
33 64/32 1A0000h-1AFFFFh 0D0000h–0D7FFFh
Protection Group
34 64/32 1B0000h-1BFFFFh 0D8000h–0DFFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
000000h–000FFFh
001000h–001FFFh
002000h–002FFFh
003000h–003FFFh
004000h–004FFFh
005000h–005FFFh
006000h–006FFFh
007000h–007FFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
34/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Block (Kbytes/Kwords) Protection Block Gr oup (x8) (x16)
35 64/32
36 64/32 1D0000h-1DFFFFh 0E8000h–0EFFFFh
37 64/32 1E0000h-1EFFFFh 0F0000h–0F7FFFh
38 64/32 1F0000h-1FFFFFh 0F8000h–0FFFFFh
39 64/32
40 64/32 210000h-21FFFFh 108000h–10FFFFh
41 64/32 220000h-22FFFFh 110000h–117FFFh
42 64/32 230000h-23FFFFh 118000h–11FFFFh
43 64/32
44 64/32 250000h-25FFFFh 128000h–12FFFFh
45 64/32 260000h-26FFFFh 130000h–137FFFh
46 64/32 270000h-27FFFFh 138000h–13FFFFh
47 64/32
48 64/32 290000h-29FFFFh 148000h–14FFFFh
49 64/32 2A0000h-2AFFFFh 150000h–157FFFh
50 64/32 2B0000h-2BFFFFh 158000h–15FFFFh
51 64/32
52 64/32 2D0000h-2DFFFFh 168000h–16FFFFh
53 64/32 2E0000h-2EFFFFh 170000h–177FFFh
54 64/32 2F0000h-2FFFFFh 178000h–17FFFFh
55 64/32
56 64/32 310000h-31FFFFh 188000h–18FFFFh
57 64/32 320000h-32FFFFh 190000h–197FFFh
58 64/32 330000h-33FFFFh 198000h–19FFFFh
59 64/32
60 64/32 350000h-35FFFFh 1A8000h–1AFFFFh
61 64/32 360000h-36FFFFh 1B0000h–1B7FFFh
62 64/32 370000h-37FFFFh 1B8000h–1BFFFFh
63 64/32
64 64/32 390000h-39FFFFh 1C8000h–1CFFFFh
65 64/32 3A0000h-3AFFFFh 1D0000h–1D7FFFh
66 64/32 3B0000h-3BFFFFh 1D8000h–1DFFFFh
67 64/32
68 64/32 3D0000h-3DFFFFh 1E8000h–1EFFFFh
69 64/32 3E0000h-3EFFFFh 1F0000h–1F7FFFh
70 64/32 3F0000h-3FFFFFh 1F8000h–1FFFFFh
Note: 1. Used as the Extended Block Addresses in Extended Block mode.
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
1C0000h-1CFFFFh 0E0000h–0E7FFFh
200000h-20FFFFh 100000h–107FFFh
240000h-24FFFFh 120000h–127FFFh
280000h-28FFFFh 140000h–147FFFh
2C0000h-2CFFFFh 160000h–167FFFh
300000h-30FFFFh 180000h–187FFFh
340000h-34FFFFh 1A0000h–1A7FFFh
380000h-38FFFFh 1C0000h–1C7FFFh
3C0000h-3CFFFFh 1E0000h–1E7FFFh
35/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
APPENDIX B. COMMON FLASH INTERFACE (CFI)
The Common Flash Interface is a JEDEC approved, standardized data structure that can be
read from the Flash memory device. It allows a
system software to query the de vice to determine
various electrical a nd timing parameters, density
information and functions su pported by the mem ory. The system can interface easily with the device, enabling the so ftwar e to u pgr ade it se lf wh en
necessary.
When the CFI Query Command is issued th e device enters CFI Query mode and the data structure
Table 22. Query Structure Overview
Address
x16 x8
10h 20h CFI Query Identification String Command set ID and algorithm data offset
1Bh 36h System Interface Information Device timing & voltage information
27h 4Eh Device Geometry Definition Flash device layout
40h 80h
61h C2h Security Code Area 64 bit unique device number
Note: Query data are always presented on the lowest order data outputs.
Primary Algorithm-specific Extended
Query table
Sub-section Name Description
is read from the memory. Tables 22, 23, 24, 25, 26
and 27 sho w the addresses used to retrieve the
data.
The CFI data structure also contains a security
area where a 64 bit unique security number is written (see Table 27., Security Code Area). This area
can be accessed onl y in Read mode by the final
user. It is imposs ible to chang e the secur ity num ber after it has been written by ST.
Additional information specific to the Primary
Algorithm (optional)
Table 23. CFI Query Identification String
Address
x16 x8
10h 20h 0051h “Q”
11h 22h 0052h Query Unique ASCII String "QRY" "R"
12h 24h 0059h "Y"
13h 26h 0002h
14h 28h 0000h
15h 2Ah 0040h
16h 2Ch 0000h
17h 2Eh 0000h
18h 30h 0000h
19h 32h 0000h
1Ah 34h 0000h
Note: Query data are always presented on the lowest order data outputs (DQ7-DQ0) only. DQ8-DQ15 are ‘0’.
Data Description Value
Primary Algorithm Command Set and Control Interface ID code 16 bit
ID code defining a specific algorithm
Address for Primary Algorithm extended Query table (see Table 26.)P = 40h
Alternate Vendor Command Set and Control Interface ID Code second
vendor - specified algorithm supported
Address for Alternate Algorithm extended Query table
AMD
Compatible
NA
NA
36/46

Table 24. CFI Query System Interface Information
Address
x16 x8
1Bh 36h 0027h
1Ch 38h 0036h
1Dh 3Ah 00B5h
1Eh 3Ch 00C5h
1Fh 3Eh 0004h
20h 40h 0000h
21h 42h 000Ah
22h 44h 0000h
23h 46h 0004h
24h 48h 0000h
25h 4Ah 0003h
26h 4Ch 0000h
Data Description Value
V
Logic Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
CC
bit 7 to 4BCD value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100 mV
V
Logic Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
CC
bit 7 to 4BCD value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100 mV
[Programming] Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
V
PP
bit 7 to 4HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100 mV
V
[Programming] Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
PP
bit 7 to 4HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100 mV
Typical timeout per single byte/word program = 2
Typical timeout for minimum size write buffer program = 2
Typical timeout per individual block erase = 2
Typical timeout for full Chip Erase = 2
Maximum timeout for byte/word program = 2
Maximum timeout for write buffer program = 2
Maximum timeout per individual block erase = 2
Maximum timeout for Chip Erase = 2
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
n
ms
n
ms
n
times typical
n
times typical
n
times typical
n
µs
n
n
times typical
µs
2.7V
3.6V
11.5V
12.5V
16µs
NA
1s
NA
256 µs
NA
8s
NA
Table 25. Device Geometry Definition
Address
x16 x8
27h 4Eh 0016h
28h
29h
2Ah
2Bh
50h
52h
54h
56h
2Ch 58h 0002h
2Dh
2Eh
2Fh
30h
31h
32h
33h
34h
Note: For the M29W320EB, Region 1 corresponds to a ddresses 00 0000h to 007FFFh and Region 2 t o address es 008000h t o 1FFFFFh. For
the M29W320ET, Region 1 corresponds to addresses 1F8000h to 1FFFFFh and Region 2 to addresses 000000h to 1F7FFFh.
5Ah
5Ch
5Eh
60h
62h
64h
66h
68h
Data Description Value
0002h
0000h
0000h
0000h
Device Size = 2
n
in number of bytes
Flash Device Interface Code description
Maximum number of bytes in multi-byte program or page = 2
4 MByte
x8, x16
Async.
n
NA
Number of Erase Block Regions. It speci fies the number of
regions containing contiguous Erase Blocks of the same size.
0007h
0000h
0020h
0000h
003Eh
0000h
0000h
0001h
Region 1 Information
Number of Erase Blocks of identical size = 0007h+1
Region 1 Information
Block size in Region 1 = 0020h * 256 byte
Region 2 Information
Number of Erase Blocks of identical size = 003Eh+1
Region 2 Information
Block size in Region 2 = 0100h * 256 byte
8Kbyte
63
64Kbyte
2
8
37/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Table 26. Primary Algorithm-Specific Extended Query Table
Address
x16 x8
40h 80h 0050h
41h 82h 0052h "R"
42h 84h 0049h "I"
43h 86h 0031h Major version number, ASCII "1"
44h 88h 0030h Minor version number, ASCII "0"
45h 8Ah 0000h Address Sensitive Unlock (bits 1 to 0)
46h 8Ch 0002h Erase Suspend
47h 8Eh 0001h Block Protection
48h 90h 0001h Temporary Block Unprotect
49h 92h 0004h Block Protect /Unprotect
4Ah 94h 0000h
Data Description Value
Primary Algorithm extended Query table unique ASCII string “PRI”
00 = required, 01= not required
Silicon Revision Number (bits 7 to 2)
00 = not supported, 01 = Read only, 02 = Read and Write
00 = not supported, x = number of blocks in per group
00 = not supported, 01 = supported
04 = M29W320E
Simultaneous Operations, 00 = not supported
"P"
Yes
2
1
Yes
04
No
4Bh 96h 0000h Burst Mode, 00 = not supported, 01 = supported No
4Ch 98h 0000h Page Mode, 00 = not supported, 01 = 4 page word, 02 = 8 page word No
4Dh 9Ah 00B5h V
4Eh 9Ch 00C5h V
4Fh 9Eh 000xh Top/Bottom Boot Block Flag
Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
PP
bit 7 to 4 HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0 BCD value in 100 mV
Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
PP
bit 7 to 4 HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0 BCD value in 100 mV
02h = Bottom Boot device, 03h = Top Boot device
Table 27. Security Code Area
Address
x16 x8
61h C3h, C2h XXXX
62h C5h, C4h XXXX
63h C7h, C6h XXXX
64h C9h, C8h XXXX
Data Description
64 bit: unique device number
11.5V
12.5V
–
38/46

APPENDIX C. EXTENDED MEMORY BLOCK
The M29W320E has an extra block, the Extended
Block, that can be accessed using a dedicated
command.
This Extended Block is 32 KWords in x16 mode
and 64 KBytes in x8 mode. It is used as a security
block (to provide a permanent security ident ification number) or to store additional information.
The Extended Block is either Factory Locked or
Customer Lockable, i ts status is indicated by bit
DQ7. This bit is perma nen tly set to either ‘1’ or ‘0’
at the factory and cannot be changed. When set to
‘1’, it indicates that the device is factory locked and
the Extended Block is protected. When set to ‘0’, it
indicates that the device is customer lockable and
the Extended Block is unprotected . Bit DQ7 bei ng
permanently locked to either ‘1’ or ‘0’ is another
security feature which ensures that a customer
lockable device cannot be used instead of a factory locked one.
Bit DQ7 is the most signifi cant bi t i n the Ex tend ed
Block Verify Code a nd a specific pr ocedure must
be followed to read it. See “Extended Memory
Block Verify Code
Operations, BYTE = V
BYTE = V
, respectively, for details of how to read
IH
” in Table 2. and Table 3., Bus
and Bus Operations,
IL
bit DQ7.
The Extended Block ca n only be accessed when
the device is in Extended Bl ock mo de. For deta ils
of how the Extended Block mod e is entered and
exited, refer to the Enter Extended Block Com-
mand and Exit Extended Block Command para-
graphs, and to Table 4. and Table 5., “Commands,
16-bit mode, BYTE = V
mode, BYTE = V
”, respectively.
IL
” and “Commands, 8-bit
IH
Factory Locked Extended Block
In devices where the Extended Block is factory
locked, the Security Identific ation Number is written to the Extended Block address space (see Ta-
ble 28., Extended Block Add ress an d Data) i n t he
factory. The DQ7 bit is set to ‘1’ and the Extended
Block cannot be unprotected.
Customer Lockable Extended Block
A device where the Extended Block is customer
lockable is delivered with the DQ7 bit set to ‘0’ and
the Extended Block unprotected. It is up to the
customer to program and protect the Extended
Block but care must be taken because the protection of the Extended Block is not reversi ble .
There are two ways of protecting the Extended
Block:
■ Issue the Enter Extended Block command to
■ Issue the Enter Extended Block command to
Once the Extended Block is programmed and protected, the Exit Extended Block command must be
issued to exit the Extended Block mode and return
the device to Read mode.
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
place the device in Extended Block mode,
then use the In-System Technique with RP
either at V
or at V
IH
(refer to APPENDIX D.,
ID
In-System Technique and to the
corresponding flowcharts, Figure 22. and
Figure 23., for a detailed explanation of the
technique).
place the device in Extended Block mode,
then use the Programmer Technique (refer to
APPENDIX D., Programmer Technique and to
the corresponding flowcharts, Figure 20. and
Figure 21., for a detailed explanation of the
technique).
Table 28. Extended Block Address and Data
Device
x8 x16 Factory Locked Customer Lockable
3F0000h-3F000Fh 1F8000h-1F8007h
M29W320ET
3F0010h-3FFFFFh 1F8008h-1FFFFFh Unavailable
000000h-00000Fh 000000h-000007h
M29W320EB
000010h-00FFFFh 000008h-007FFFh Unavailable
Note: 1. S ee Table 20. and Table 21. , Top and Bottom Boot Block Addresses.
Address
(1)
Security Identification
Number
Security Identification
Number
Data
Determined by
Customer
Determined by
Customer
39/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
APPENDIX D. BLOCK PROTECTION
Block protection can be used to prevent any operation from modifying the data stored in the memory. The blocks are protected in groups, refer to
APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21. for details
of the Protection Groups. Once protected, Program and Erase operations within the protected
group fail to change the data.
There are three techniques that can be used to
control Block Pro tection, these are the Programmer technique, the In-System technique and Temporary Unprotection. Temporary Unprotection is
controlled by the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotection pin, RP
scriptions section.
Programmer Technique
The Programmer techniqu e uses high (V
age levels on some of the bus pins. These cannot
be achieved using a standard microprocessor bus,
therefore the technique is re commended only for
use in Programming Equipment.
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in
Figure 20., Program mer Eq uipmen t Blo ck Pr otect
Flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is necessary to protect all of the groups first, then all
groups can be unpr otected at the same time . To
unprotect the chip fo llow Figure 21., Pr ogrammer
Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart. Table
29., Programmer Technique Bus Operations,
BYTE = V
ation.
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care
should be taken to ensure th at, where a paus e is
; this is described in the Si gna l De -
) volt-
ID
or VIL, gives a summary of each oper-
IH
specified, it is followe d as closely as possible. Do
not abort the procedure befor e reaching the end.
Chip Unprotect can take several seconds and a
user message should be provided to show that the
operation is progressing.
In-System Technique
The In-System technique r equires a high voltage
level on the Reset/Blocks Temporary Unprotect
pin, RP
(1)
. This can be achie ved without viol ating
the maximum ratings of the components on the microprocessor bu s, ther efore this tec hnique is s uitable for use after the mem ory has been fitted to
the system.
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in
Figure 22., In-System Equipment Group Protect
Flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is neces-
sary to protect all of the groups first, then all the
groups can be un protected at the same time . To
unprotect the chip follow Figure 23., In-System
Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart.
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care
should be taken to ensure th at, where a paus e is
specified, it is followe d as closely as possible. Do
not allow the microproce ssor to servi ce interrupts
that will upset the timing and do not abort the procedure before reaching the end. Chip Unprotect
can take several seconds and a user message
should be provided to show that the operation is
progressing.
Note: 1. RP can be either at V
tem Technique to protect the Extended Block.
IH
or at V
when using the In-Sys-
ID
Table 29. Programmer Technique Bus Operations, BYTE = VIH or V
Operation E G W
Block (Group)
(1)
Protect
Chip Unprotect
Block (Group)
Protection Verify
Block (Group)
Unprotection Verify
Note: 1. Block Protection Groups are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21.
40/46
VILVIDVIL Pulse
V
VIDVIL Pulse
ID
V
V
IL
V
V
IL
V
IL
IL
IH
V
IH
A9 = V
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = VIL, A9 = VID,
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = VIH, A9 = VID,
Address Inputs
A0-A20
, A12-A20 Block Address
ID
Others = X
A9 = V
, A12 = VIH, A15 = VIH
ID
Others = X
A12-A20 Block Address
Others = X
A12-A20 Block Address
Others = X
IL
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1, DQ14-DQ0
X
X
Pass = XX01h
Retry = XX00h
Retry = XX01h
Pass = XX00h

Figure 20. Programmer Equipment Group Protect Flowchart
START
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
W = V
IH
n = 0
G, A9 = VID,
E = V
IL
Wait 4µs
W = V
IL
Wait 100µs
W = V
IH
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Verify Protect Set-upEnd
E, G = VIH,
A0, A6 = VIL,
A1 = V
IH
E = V
IL
Wait 4µs
G = V
IL
Wait 60ns
Read DATA
DATA
=
01h
YES
A9 = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
PASS
NO
++n
= 25
A9 = V
E, G = V
NO
YES
IH
IH
Note: Block Protection Groups are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Ta ble 21.
FAIL
AI05574
41/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 21. Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart
START
PROTECT ALL GROUPS
CURRENT GROUP = 0
ADDRESS = CURRENT GROUP ADDRESS
A0 = VIL, A1, A6 = V
n = 0
A6, A12, A15 = V
E, G, A9 = V
Wait 4µs
W = V
IL
Wait 10ms
W = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
E = V
IL
Wait 4µs
(1)
IH
ID
IH
G = V
IL
Wait 60ns
Verify Unprotect Set-upEnd
++n
NO
= 1000
YES
A9 = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
FAIL PASS
Note: Block Protection Groups are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Ta ble 21.
Read DATA
DATA
=
00h
YESNO
42/46
INCREMENT
CURRENT GROUP
LAST
GROUP
YES
A9 = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
NO
AI05575

Figure 22. In-System Equipment Group Protect Flowchart
START
n = 0
RP = V
ID
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Verify Protect Set-upEnd
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
WRITE 60h
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
WRITE 60h
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
Wait 100µs
WRITE 40h
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
Wait 4µs
READ DATA
DATA
RP = V
=
01h
NO
YES
IH
IL
IL
IL
IL
++n
= 25
NO
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
PASS
Note: 1. Block Protection Groups are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Table 21.
2. RP
can be either at V
IH
or at V
when using the In-System Technique to protect the Extended Block.
ID
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
RP = V
FAIL
YES
IH
AI05576
43/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Figure 23. In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart
START
PROTECT ALL GROUPS
Verify Unprotect Set-upEnd
CURRENT GROUP = 0
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
ADDRESS = CURRENT GROUP ADDRESS
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
ADDRESS = CURRENT GROUP ADDRESS
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A6 = V
n = 0
RP = V
ID
WRITE 60h
ANY ADDRESS WITH
WRITE 60h
ANY ADDRESS WITH
Wait 10ms
WRITE 40h
Wait 4µs
READ DATA
IH
IH
IH
IH
INCREMENT
CURRENT GROUP
DATA
++n
NO
= 1000
YES
RP = V
IH
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
FAIL
Note: Block Protection Groups are shown in APPENDIX A., Table 20. and Ta ble 21.
00h
YESNO
=
44/46
LAST
GROUP
RP = V
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
PASS
NO
YES
IH
AI05577

REVISION HISTORY
Table 30. Document Revision History
Date Version Revision Details
15-Apr-2004 1.0 First Issue.
Protection Group for Blocks 0 to 3 and and Blocks 67 to 70 modifed in Table 20., Top
18-Nov-2004 2.0
14-Mar-2005 3.0
Boot Block Addresses, M29W320ET and Table 21., Bottom Bo ot Block Addresses,
M29W320EB, res pe ctiv ely.
TFBGA48 Commercial Code changed from ZA to ZE.
updated in Table 7., Status Register Bits.
RB
Fast Program Commands restructured and updated.
Unlock Bypass Command updated.
M29W320ET, M29W320EB
45/46

M29W320ET, M29W320EB
Information furnished is be lieved to be a ccur ate and reli able. Howe ver, STMicroele ctronic s assu mes no r esponsib ilit y for th e consequences
of use of such information nor for any infrin gement of patent s or other rights of third parties which ma y result from it s use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwi se under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. S pecifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without not ice. This pub licat ion su persed es and repl aces all in format ion previou sly su pplie d. STMicroele c tronic s prod ucts ar e no t
authorized for use as critical compone nts in life support devices or systems witho ut express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - It aly - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
46/46
 Loading...
Loading...