4 A continuous (more than 5 A pulsed) step-down switching
regulator with synchronous rectification
Features
■ 4 A output current (more than 5 pulsed)
■ Operating input voltage from 2.9 V to 18 V
■ External 1.8 V ± 2% reference voltage
■ Output voltage from 0.6 to input voltage
■ MLCC compatible
■ 200 ns T
■
Programmable UVLO matches 3.3 V, 5 V and
12 V bus
■ F
SW
■ Voltage feed-forward
■ Zero-load current operation
■ Programmable current limit on both switches
■ Programmable sink current capability
■ Pre-bias start up capability
■ Thermal shutdown
ON
programmable up to 1 MHz
L5988D
HTSSOP 16
Applications
■ Consumer: STB, DVD, LCD TV, VCR, car
radio, LCD monitors
■ Networking: XDSL, modems, routers and
switches
■ Computer and peripherals: printers, audio /
graphic cards, optical storage, hard disk drive
■ Industrial: DC-DC modules, factory automation
■ HC LED driving
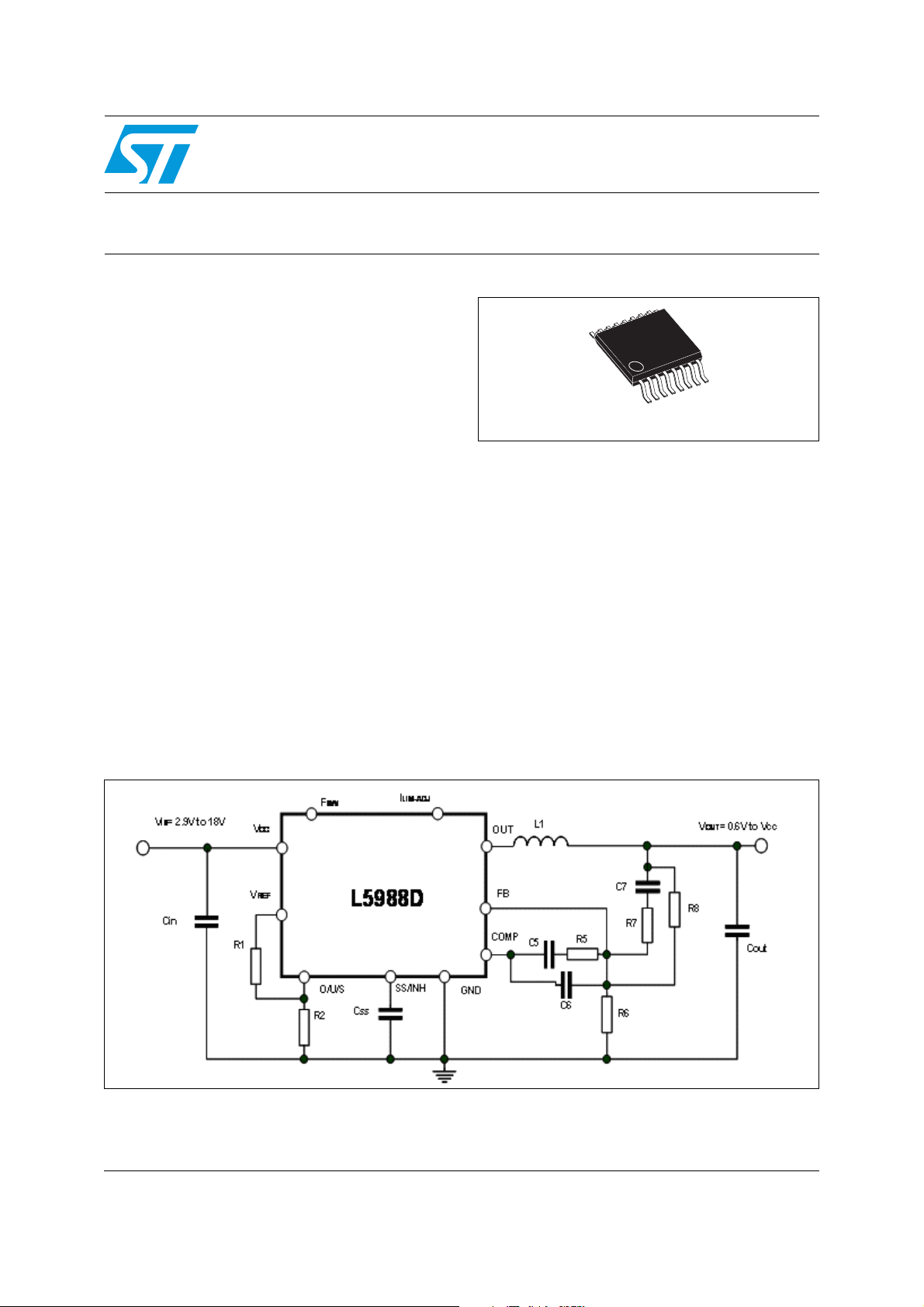
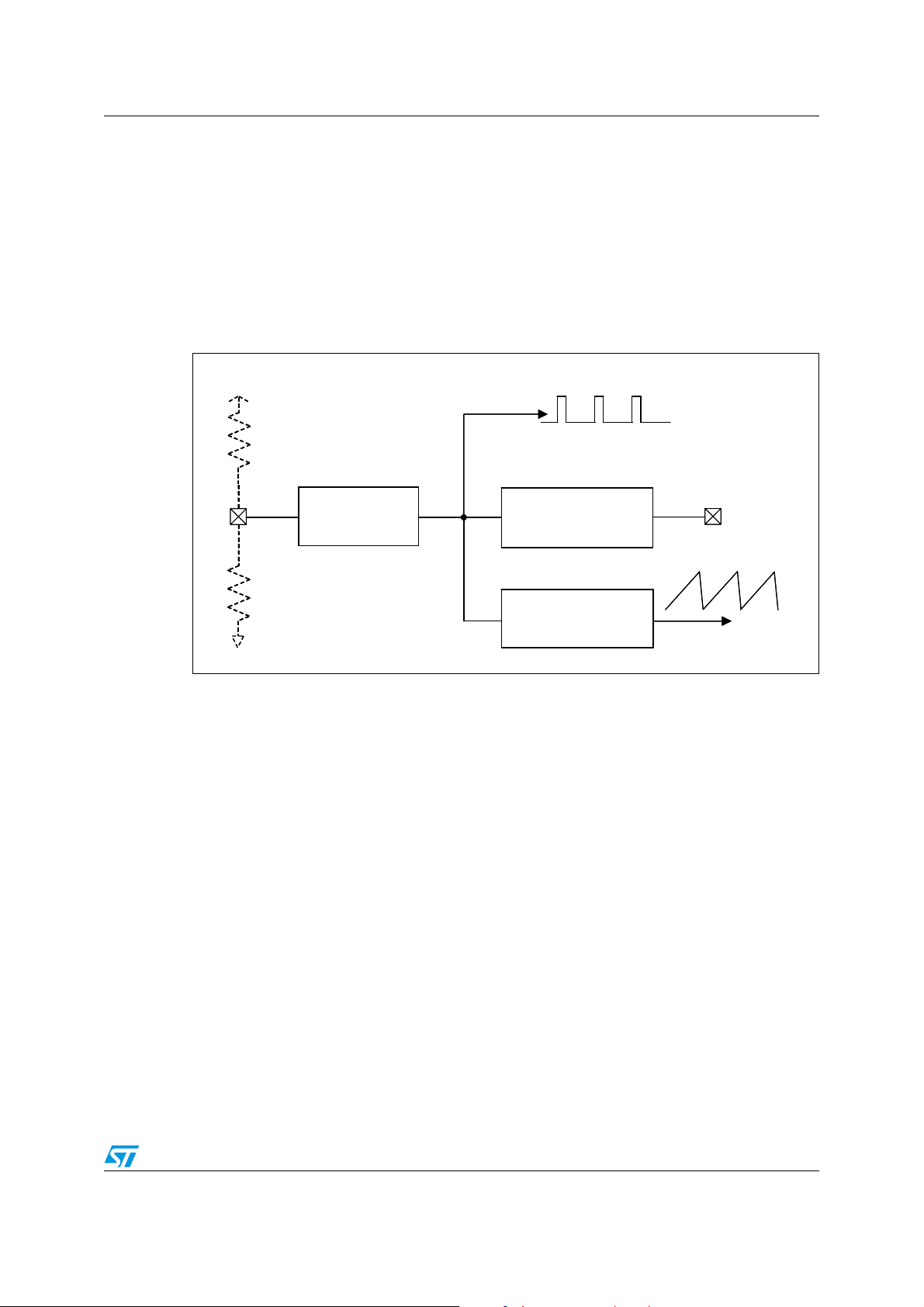
Figure 1. Test application circuit
January 2010 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 1/52
www.st.com
52

Contents L5988D
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Pin function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
5 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1 Multifunction pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.2 Oscillator and synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3 External voltage reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.4 Soft-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5 Monitoring and protections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5.1 Overvoltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5.2 Current limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.5.3 UVLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.5.4 Thermal shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.6 Minimum on time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.7 Error amplifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.1 Input capacitor selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.2 Inductor selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.3 Output capacitor selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.4 Compensation network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.4.1 Type III compensation network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.4.2 Type II compensation network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.5 R.M.S. current of the embedded power MOSFETs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.6 Thermal considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.7 Layout considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.8 Application circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Contents
7 Typical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
9 Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
10 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 3/52

List of table L5988D
List of table
Table 1. Pinout description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 3. Thermal data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4. Electrical characteristic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 5. A/D voltage windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 6. UOS voltage biasing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 7. FSW resistor examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 8. ILIM-ADJ resistor examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. Input capacitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 11. Inductors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 12. Output capacitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 13. Component list application circuit (fSW = 400 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 14. Component list application circuit (fSW = 600 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 15. HTSSOP16 mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 16. Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 17. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
4/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Test application circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. Pin connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3. Voltage mode control loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 4. Internal block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 5. Oscillator circuit block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 6. Sawtooth: voltage feed forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 7. Sawtooth: synchronization and frequency adjust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 8. Input RMS current of two synchronized regulators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 9. OVP not latched . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 10. OVP latched . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 11. constant current protection at extreme duty cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 12. minimum TON. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 13. Type III compensation network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 14. Open loop gain: module bode diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 15. Open loop gain bode diagram with ceramic output capacitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 16. Type II compensation network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 17. Open loop gain: module bode diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 18. Open loop gain bode diagram with high ESR output capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 19. Maximum continuos output current vs. duty cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 20. Switching losses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 21. Estimation of the internal power losses (V
Figure 22. Estimation of the internal power losses (V
Figure 23. Measurement of the thermal impedance of the evaluation board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 24. Top board layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 25. Bottom board layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 26. Demonstration board application circuit (fSW = 400 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 27. Demonstration board application circuit (fSW = 600 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 28. Junction temperature vs. fSW at VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 29. Junction temperature vs. fSW at VIN = 5 V, VOUT = 3.3 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 30. Junction temperature vs. fSW at VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 31. Junction temperature vs. VOUT at VIN = 12 V, fSW = 400 kHz. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 32. Junction temperature vs. VOUT at VIN = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 33. Junction temperature vs. VOUT at VIN = 3.3 V, fSW = 400 kHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 34. Efficiency vs. output current at VIN = 3.3 V, fSW = 400 kHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 35. Efficiency vs. output current at VIN = 5 V, fSW = 250 kHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 36. Efficiency vs. output current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 37. Load regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 38. Line regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 39. Load transient from 0 to 3 A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 40. Soft-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 41. HTSSOP16 mechanical drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
= 12 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, fSW = 400 kHz) . . . . 38
IN
= 5 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, fSW = 400 kHz) . . . . . 39
IN
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 5/52

Description L5988D
1 Description
The L5988D is a monolithic step down power switching regulator able to deliver a continuos
output current of 4 A to the load in most of the application conditions limited only by the
thermal performance (see Chapter 6.5 for details). The device is able to deliver more than
5 A to the load for a maximum time which is dependent on the thermal impedance of the
system and the specific operating conditions (see Chapter 6.6).
The input voltage can range from 2.9 V to 18 V. The device is capable of 100% duty cycle
operation thanks to the embedded high side PMOS switch which doesn’t need external
bootstrap capacitor to be driven.
The internal switching frequency is adjustable by external resistor and can be set
continuously from 100 kHz to 1 MHz. The L5988D can also be synchronized to an external
frequency signal driven to the SYNCH pin I/O pin.
The multifunction UOS pin allows to set-up properly the additional embedded features
depending on the value of the voltage level.
● U (UVLO): two UVLO thresholds can be selected to match the 3.3 V and 5 V or 12 V
input buses
● O (OVP): latched or not latched OVP protection selectable. In latched mode the
switching activity is interrupted until an UVLO or INH event happens
● S (SINK): the sink capability is always disabled during soft-start time to support pre-
biased output voltage. Afterwards the sink capability can be enabled or not depending
on the voltage set on the multifunction pin.
During soft-start phase a constant current protection is active to deliver extra current
necessary to load the output capacitor. The current limit protection is achieved by sensing
the current flowing in both embedded switches to assure an effective protection even at
extreme duty cycle operations. Finished the soft-start phase the current protection feature
triggers the “HICCUP” mode forcing the soft-start capacitor to be discharged and recharged.
The current thresholds of both switches can be adjusted in tracking by using an external
resistor to dimension the current protection accordingly to the local application.
The soft-start time is based on a constant current charge of an external capacitor. As a
consequence the time can be set accordingly to the value of the output capacitor.
The latest smart power technology BCD6 (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS version 6) features a low
resistance of the embedded switches (35 mΩ typical for a NMOS, 50 mΩ typical for a
PMOS), achieving high efficiency levels.
The HTSSOP16 package with exposed pad accomplishes low R
(40 °C/W), useful in
thJA
dissipating power internally generated during high output current / high frequency
operations.
6/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
L5988D Pin function
2 Pin function
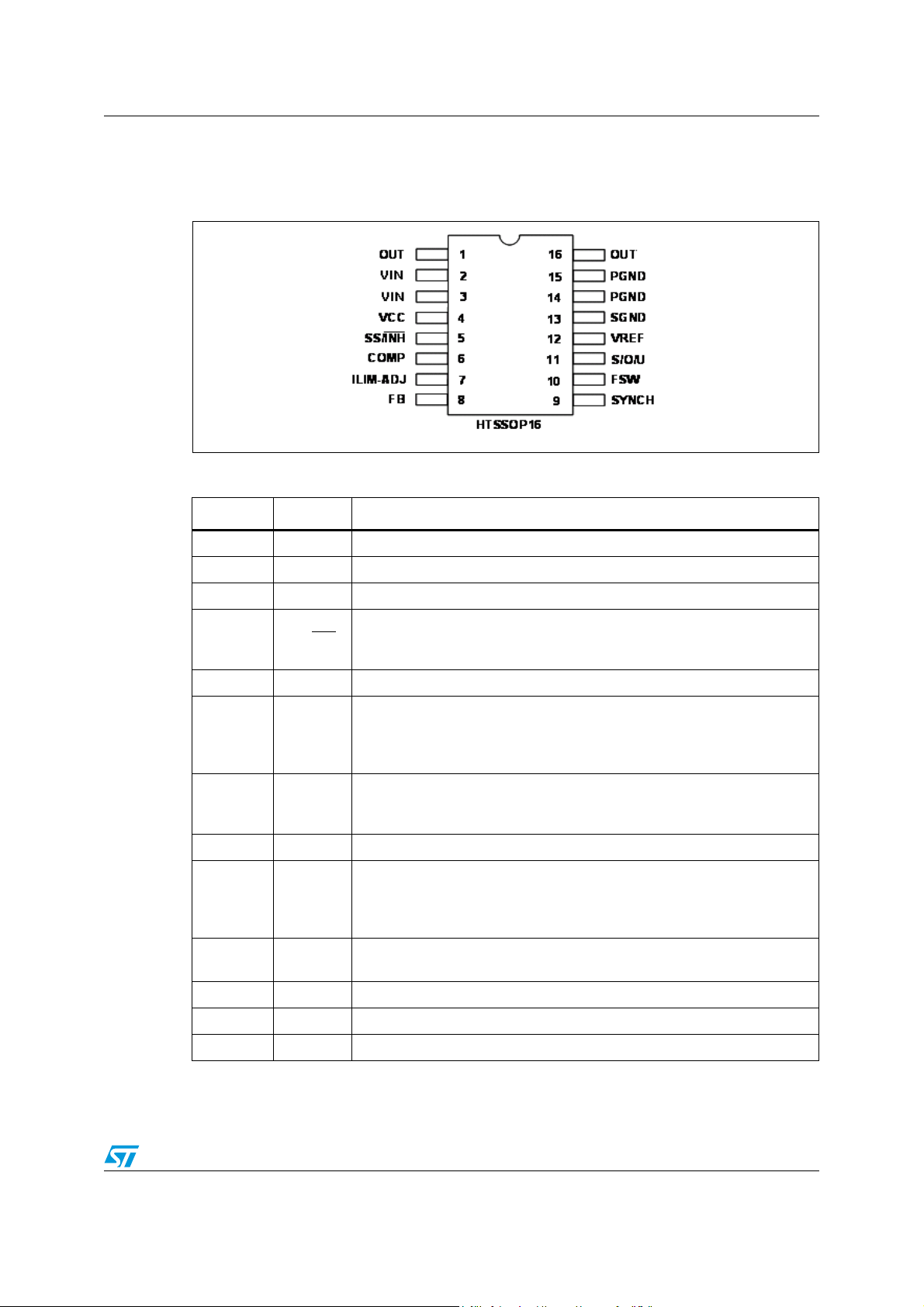
Figure 2. Pin connection
Table 1. Pinout description
N. Name Description
1, 16 OUT Regulator output
2, 3 VIN Unregulated DC input voltage
4 VCC Unregulated DC signal input voltage
An external logic signal (active LOW) disables the device. In case the pin is
5 SS/INH
6 COMP Error amplifier output for frequency compensation
7 ILIM-ADJ
8FB
9 SYNCH Master/slave synchronization
10 FSW
11 U/O/S
12 VREF 1.8 V voltage reference
13 SGND Signal ground
14, 15 PGND Power ground
floating the device deliver a constant current (22 μA typ.) to charge the
soft-start capacitor (see 5.4)
Connecting a pull-up resistor to VREF or a pull-down resistor to GND the
internal current limit thresholds can be tuned to match the local application.
In case the pin is left floating no changes are applied to the default current
limit thresholds
Feedback input. Connecting the output voltage directly to this pin results in
a regulation voltage of 600 mV. An external resistive divider is required for
higher output voltages
Connecting a pull-up resistor to VREF or a pull-down resistor to GND the
internal oscillator frequency will be increased or decreased respectively. In
case the pin is left floating the predefined oscillator frequency
(400 kHz ± 10%) is active
Multifunction pin used to program additional features: UVLO thresholds,
OVP latched/not latched, SINK enabled/disabled
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 7/52
Maximum ratings L5988D
3 Maximum ratings
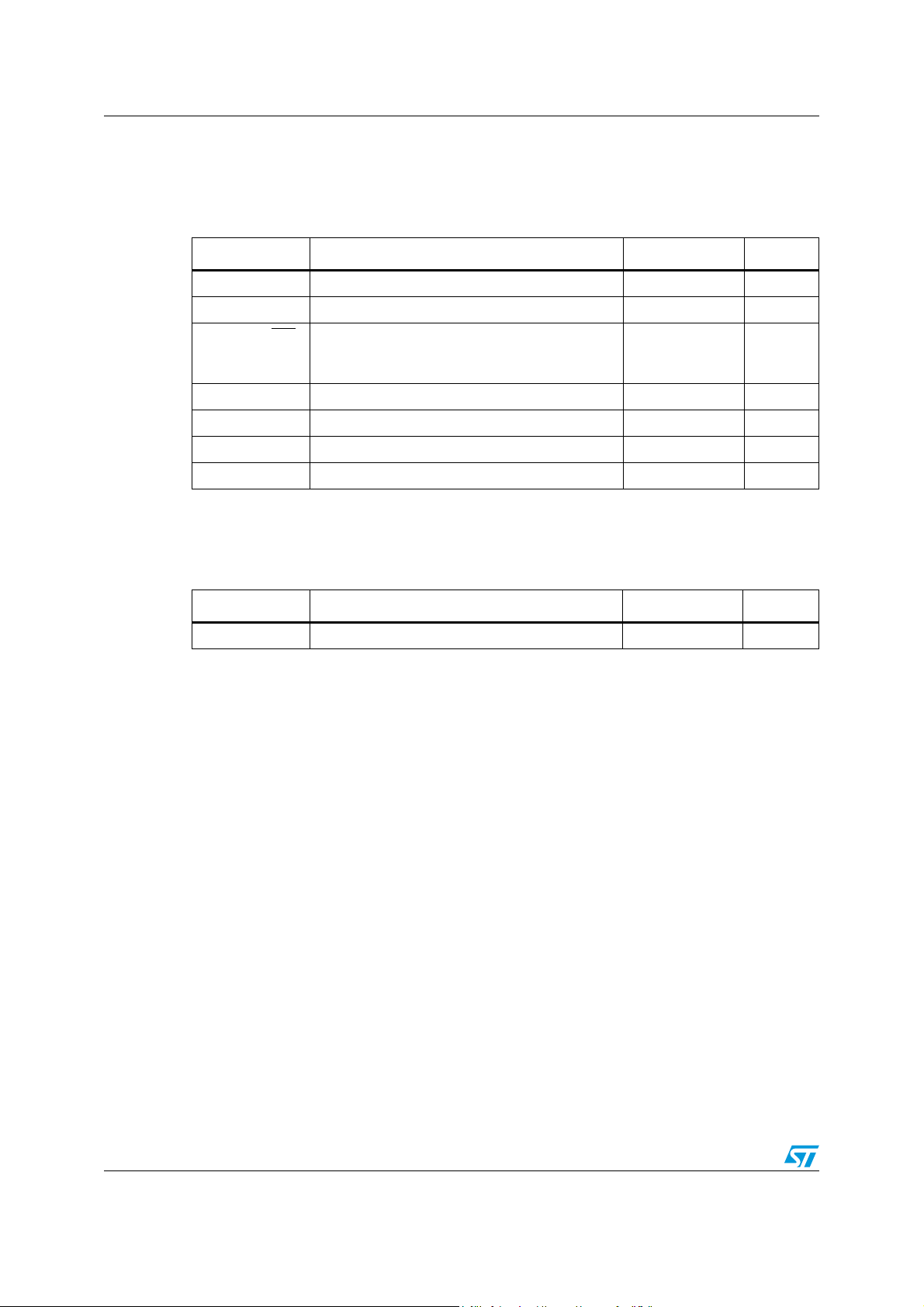
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
VCC Input voltage 20 V
VOUT Output DC voltage -0.3
U/O/S, SS/INH
COMP, SYNCH,
,
Analog pins -0.3 to 4 V
Fsw, ILIM-ADJ
FB Feedback voltage 1.5 V
(1)
to VCC
V
P
tot
T
J
T
STG
1. During the switching activity the negative peak voltage could reach -1.5 V without any damage for the
device
Power dissipation at TA < 60 °C 2.25 W
Junction temperature range -40 to 150 °C
Storage temperature range -55 to 150 °C
Table 3. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
thJA
1. HTSSOP16 package mounted on ST demonstration board
Thermal resistance junction to ambient max 40
(1)
°C/W
8/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
L5988D Electrical characteristics
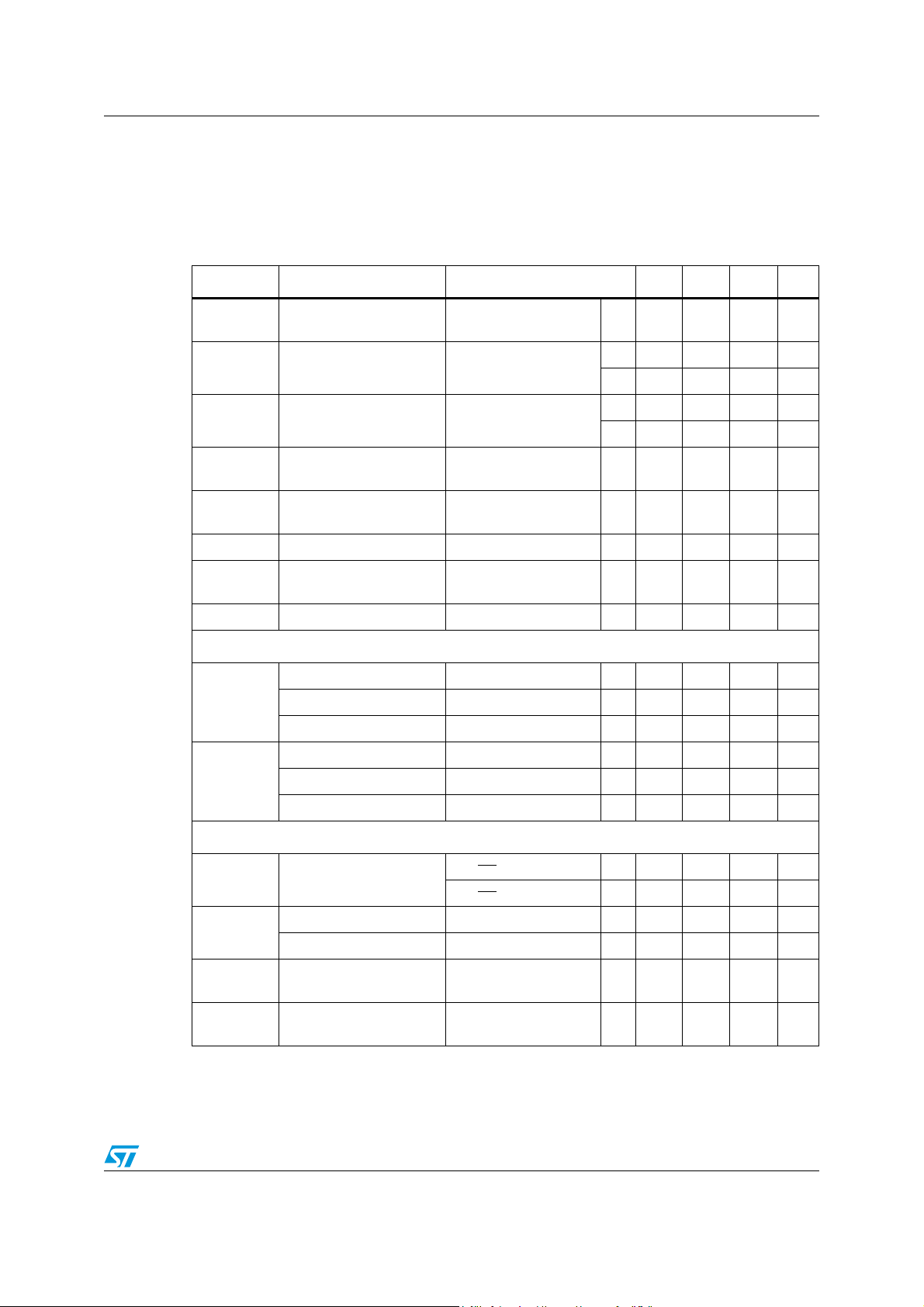
4 Electrical characteristics
VCC = 12 V, TJ = 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
Table 4. Electrical characteristic
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
V
CC
R
DS(on)
R
DS(on)
I
L HIGH SIDE
I
L LOW SIDE
f
SW
f
SW ADJ
Operating input voltage
range
High side MOSFET on
HS
resistance
Low side MOSFET on
LS
resistance
Maximum peak limiting
current
Maximum valley limiting
current
Vout = 0.6 V; Iout=3 A 2.9 18 V
75 85 95 mΩ
Iout=1.0 A
(1)
111 120 132 mΩ
62 67 72 mΩ
Iout=1.0 A
I
I
= float 3.6 4 4.4 A
LIM-ADJ
= float 4.14 4.6 5.06 A
LIM-ADJ
(1)
92 100 106 mΩ
Switching frequency FSW = floating 360 400 440 kHz
adjusted switching
frequency
R
FSW PULL DWN
= 27 kΩ 1000 kHz
D Duty cycle 0 100 %
Selectable under voltage lock-out (UVLO)
Turn ON Vcc threshold 2.7 2.8 V
3.3 V BUS
Turn OFF Vcc threshold 2.4 2.5 V
Hysteresis 200 mV
Turn ON Vcc threshold 8 8.6 V
12 V BUS
Turn OFF Vcc threshold 6.8 7 V
Hysteresis 1 V
DC characteristic
I
SS
Soft-start current
Device ON level 0.8 V
INH
Device OFF level 0.3 V
I
I
q st-by
q
Quiescent current
Total stand-by quiescent
current
V
V
Duty Cycle = 0;
V
= 2 V 22 μA
SS/INH
= 0 5 μA
SS/INH
= 1 V
FB
3mA
35 μA
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 9/52
Electrical characteristics L5988D
Table 4. Electrical characteristic (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
Dynamic characteristic (see figure 1)
VFB
Error amplifier
V
OH
V
OL
I
O SOURCE
I
O SRCE LIM
I
O SINK
A
V0
Sync function
Voltage feedback in
regulation
2.9 V < VCC < 18 V
0.595 0.6 0.605
(1)
0.592 0.6 0.609
High level output voltage VFB = 0.2 V; SS floating 3.1 V
Low level output voltage VFB = 1.0 V 0.1 V
Source output current VFB = 0.2 V
Source current limitation VFB = 0.2 V, V
Sink output current VFB = 1.0 V, V
DC open loop gain
COMP
COMP
(2)
25 mA
= 3 V 2 mA
= 0.5 V 30 mA
(2)
100 dB
High input voltage 2.9 4.0 V
Low input voltage 0.74 V
V
= 3.3 V;
Slave sink current
Master output amplitude I
SYNC
FSW = float
SOURCE
= 5 mA 2.9 V
1mA
Output pulse width SYNCH = floating 100 ns
Input pulse width 70 ns
V
Reference section
V
REF
Reference voltage Vcc = 2.9 V to 18 V
Line regulation
Load regulation I
Short circuit current 12 18 24 mA
Protections
V
FB_OVP
Overvoltage trip
(V
FB_OVP
Bus thresholds
- UVLO 3.3 V bus
TH1
- OVP not latched
- No sink
- UVLO 3.3 V bus
TH2
- OVP not latched
- Sink
- VFB) / V
FB
1.756 1.8 1.837 V
(1)
1.754 1.8 1.852 V
Vcc = 2.9 V to 18 V
I
= 0 mA
REF
= 0 to 5 mA 7.5 15 mV
REF
V
rising 15 20 24
FB
(3)
00.2V
(3)
0.26 0.425 V
612mV
%
V
FB
10/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
L5988D Electrical characteristics
Table 4. Electrical characteristic (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
- UVLO 3.3 V bus
(3)
TH3
- OVP latched
0.48 0.65 V
- No sink
- UVLO 3.3 V bus
TH4
- OVP latched
(3)
0.71 0.875 V
- Sink
- UVLO 12 V bus
TH5
- OVP not latched
(3)
0.93 1.085 V
- No sink
- UVLO 12 V bus
TH6
- OVP not latched
(3)
1.16 1.31 V
- Sink
- UVLO 12 V bus
TH7
- OVP latched
(3)
1.385 1.525 V
- No sink
- UVLO 12 V bus
TH8
- OVP latched
(3)
1.615 VREF V
- Sink
1. Specification over the junction temperature range (TJ) of -40 to +125 °C are guaranteed by design,
characterization and statistical correlation
2. Guaranteed by design
= 4 V
3. V
CC
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 11/52
Functional description L5988D
5 Functional description
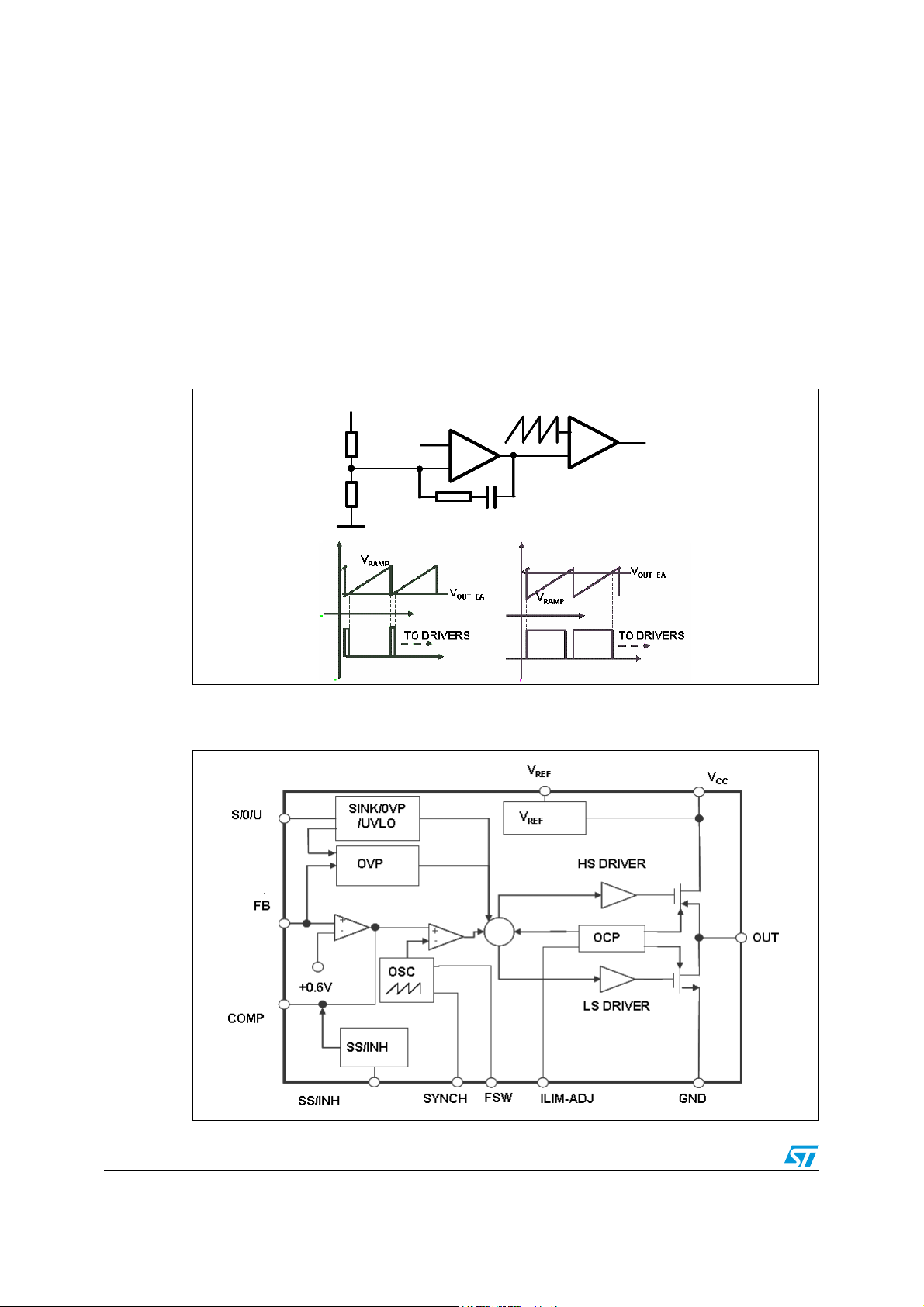
The L5988D is based on a voltage mode control loop. Therefore the duty ratio of the internal
switch is obtained through a comparison between a saw-tooth waveform (generated by an
oscillator) and the output voltage of the error amplifier as shown in Figure 3. The advantage
of this technique is the very short conduction time of the power elements thanks to the
proper operation of the control loop without a precise current sense, which instead is
required in current mode regulators. Thanks to this architecture the L5988D supports
extremely low conversion ratio (D = V
OUT/VIN
(up to 1 MHz).
Figure 3. Voltage mode control loop
V
V
V
V
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
V
V
V
V
REF
REF
REF
REF
) even at very high switching frequency
OSCILLATOR RAM P
OSCILLATOR RAM P
OSCILLATOR RAM P
OSCILLATOR RAM P
-
-
-
+
+
+
+
E/A
E/A
E/A
E/A
-
-
-
-
-
PWM
PWM
PWM
PWM
+
+
+
+
The main internal blocks are represented in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Internal block diagram
12/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Functional description
Below follows a brief description of the main blocks:
● A voltage pre-regulator supplies the internal circuitry. The external 1.8 V voltage
reference is supplied by this regulator.
● A voltage monitor circuit that checks the input and internal voltages
● A fully integrated sawtooth oscillator whose frequency is 400 kHz ± 10% when the Fsw
pin is floating. Its frequency can be increased/decreased connecting a proper resistor
to GND or VREF
● The internal current limitation circuitry monitors the current flowing in both embedded
switches to guarantee an effective protection even in extreme duty cycle conditions
● The over voltage protection (OVP) monitors the feedback voltage. If the voltage of this
pin overcomes the 20% of the internal reference value (600 mV ± 1%) it will force the
conduction of the low side switch until the overshoot is present
● A voltage mode amplifier. The inverting input and the output are externally available for
compensation
● A pulse width modulator (PWM) comparator and the relative logic to drive the
embedded switches
● The soft-start circuit charges an external capacitor with a constant current equal to
20 µA (typ.). The soft-start feature is realized clamping the output of the error amplifier
until the voltage across the capacitor is below 2.7 V
● The circuitry acting on the SYNCH pin provides external signal reference to slave
devices when the regulator works as a master or accept the synchronization from an
external reference source
● The circuitry related to the UOS multifunction pin is composed of a 3 bit A/D converter
and the decoding logic. It recognizes eight different voltage windows of a VREF voltage
magnitude for selecting additional features.
● An inhibit block for stand-by operation
● A circuit to realize the thermal protection function
5.1 Multifunction pin
The UOS pin is used to configure the device additional features accordingly to the voltage
bias imposed through VREF voltage partitioning.
The selectable options are:
● UVLO level: two pre-defined the under voltage lock out thresholds can be selected to
match the 3.3 V and 5 V or 12 V power bus
● SINK capability: this feature is always disabled during the soft-start period to be
compatible with pre-biased output voltages. After the soft-start phase, the synchronous
rectification can be enabled or not depending on the status of the UOS pin. Anyway, in
case an overvoltage is detected, the sink capability is always enabled to bring the FB
back to regulation as fast as possible
● OVP management: in case the latched mode is selected and an overvoltage event
recurs, the switching activity will be suspended until VCC is reapplied or the SS/INH
is toggled. Otherwise when the overvoltage transient is ended the regulator will work
accordingly to the load request without regulation discontinuity
The circuitry related to the UOS multifunction pin is composed of a 3 bit A/D converter and
the decoding logic. Table 5 shows the internal thresholds of each voltage window
pin
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 13/52
Functional description L5988D
composing the VREF magnitude. The voltage biasing of the multifunction can be set
accordingly to table Table 6 .
Table 5. A/D voltage windows
UVLO OVP SINK
1.8 V
1.575 V
1.35 V
1.125 V
0.9 V
0.675 V
0.45 V
0.225 V
0 V
12 V BUS LATCH SINK
12 V BUS LATCH NO SINK
12 V BUS NO LATCH SINK
12 V BUS NO LATCH NO SINK
3.3 V BUS LATCH SINK
3.3 V BUS LATCH NO SINK
3.3 V BUS NO LATCH SINK
3.3 V BUS NO LATCH NO SINK
Table 6. UOS voltage biasing
R1 (kΩ)R2 (kΩ)V
0 N.C. 1.8 12 V BUS LATCH SINK
0.68 2.7 1.438 12 V BUS LATCH NO SINK
1.2 2.7 1.246 12 V BUS NO LATCH SINK
2 2.7 1.034 12 V BUS NO LATCH NO SINK
(V) UVLO OVP SINK
OUS
3.3 2.7 0.810 3.3 V BUS LATCH SINK
6.2 2.7 0.546 3.3 V BUS LATCH NO SINK
11 2.7 0.355 3.3 V BUS NO LATCH SINK
N.C. 0 0 3.3 V BUS NO LATCH NO SINK
14/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
L5988D Functional description
5.2 Oscillator and synchronization
The generation of the internal saw-tooth waveform is based on the constant current charge /
discharge of an internal capacitor. The current generator is designed to get a switching
frequency of 400 kHz ± 10% in case the FSW pin is left floating.
The current mirror connected to FSW (see Figure 5.) pin acts increasing / decreasing the
value of the internal charging current to adjust the oscillator frequency. Since the internal
circuitry forces the FSW voltage bias at 1.235 V, the user can easily source / sink current in
this pin connecting a pull up resistor to VREF or a pull down to GND respectively.
Figure 5. Oscillator circuit block diagram
VREF
VREF
Clock
ClockClock
Clock
Clock
Generator
Generator
Synchronization
Synchronization
SYNCH
SYNCH
Ramp
Ramp
Sawtooth
Generator
Generator
Sawtooth
The value of the pull up resistor versus VREF to decrease the oscillator frequency follows
the formula:
8.5 103⋅
R1KΩ()
-------------------------------------------- - 0.95+=
400 F
SW
KHz()–
In the same way to increase the switching frequency the pull down resistor is selected using
the formula:
R
2
KΩ()
18 103⋅
-------------------------------------------- - 2.1–=
F
KHz()400–
SW
Ta bl e 1 0 shows some resistor values to adjust the oscillator frequency
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 15/52
Functional description L5988D
Table 7. FSW resistor examples
R1 (kΩ)f
43 198 360 450
47 215 180 499
56 245 120 548
62 261 91 594
82 295 56 711
110 322 43 801
150 343 33 915
220 361 27 1022
(kHz) R2 (kΩ)f
SW
SW
(kHz)
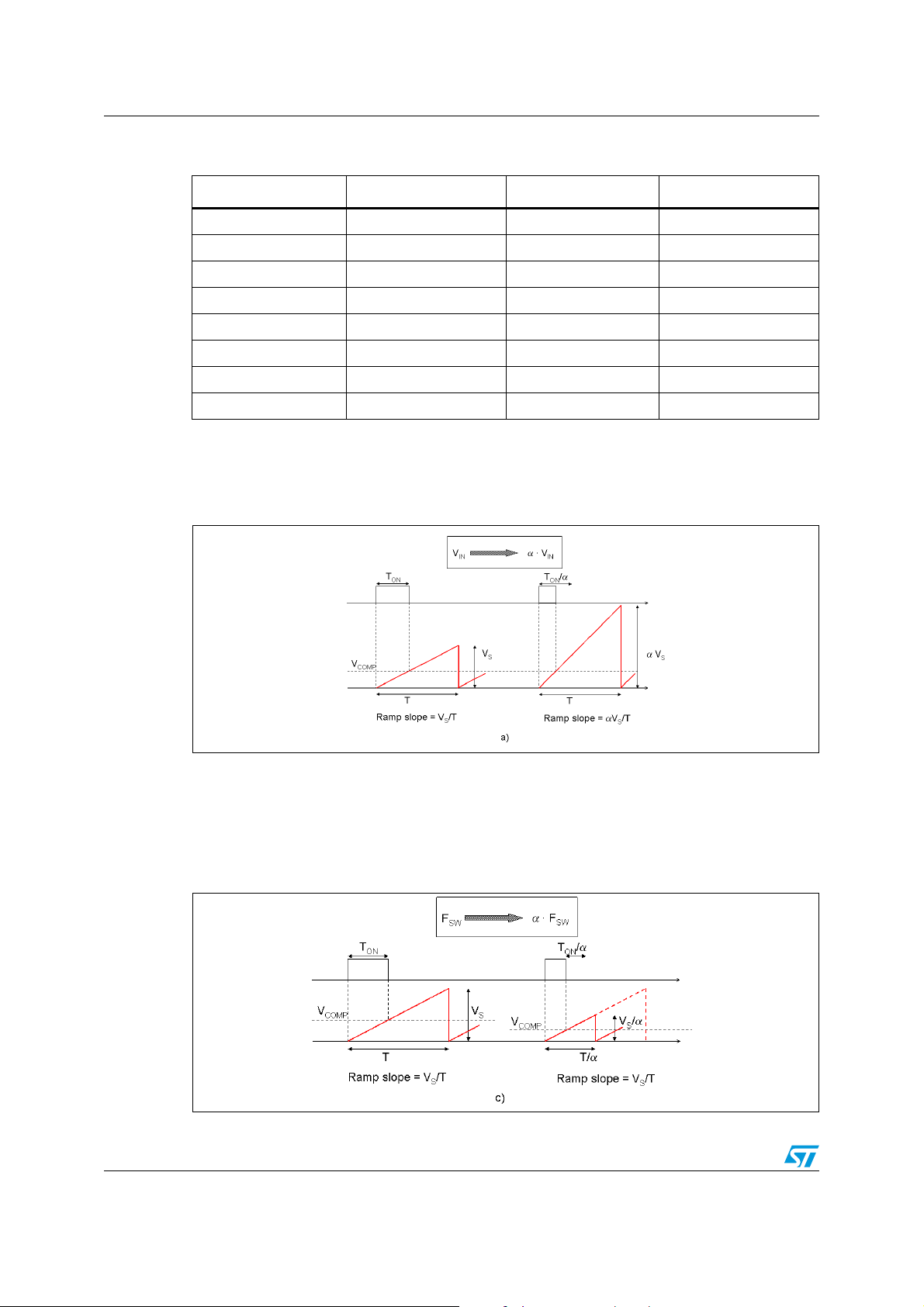
To improve the line transient performance, the voltage feed forward is implemented by
changing the slope of the sawtooth according to the input voltage change (see Figure 6 a).
Figure 6. Sawtooth: voltage feed forward
The slope of the sawtooth does not change if the oscillator frequency is increased by an
external signal or adjusted by the external resistor (see Figure 7). As a consequence the
gain of the PWM stage is a function of the switching frequency and its contribution must be
taken in account when performing the calculations of the compensation network (see
Chapter 6.4.1 and Chapter 6.4.2).
Figure 7. Sawtooth: synchronization and frequency adjust
16/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Functional description
Beating frequency noise is an issue when more than one voltage rail is on the same board.
A simple way to avoid this problem is to operate all the regulators at the same switching
frequency. The synchronization feature of a set of L5988D is simply get connecting together
their SYNCH pin. The device with highest switching frequency will be the MASTER and
provides the synchronization signal to the others. Therefore the SYNCH is a I/O pin to
deliver or recognize a frequency signal.
In order to minimize the RMS current flowing through the input filter, the L5988D provides a
phase shift of 180° between the master and the SLAVES. In cases where more than two
devices are synchronized, all slaves will have a common 180° phase shift with respect to the
master.
In case the synchronized set shares a switching frequency different to the nominal 400 kHz,
it is suggested to provide the proper FSW resistor to each device. In this way all the devices
will have a common peak amplitude of the internal sawtooth signal so the same oscillator
gain in the open loop gain transfer function. In this way the same compensation network is
valid for all the devices.
Taking in account the case of two synchronized L5988D regulating the same output voltage,
the RMS current in the input filter will be optimized and will observe the following formula:
⎧
I
OUT
⎪
I
RMS
----------- -
⎪
=
⎨
I
⎪
----------- -
⎪
⎩
2
OUT
2
2D 1 2D–()⋅ if D < 0.5⋅
2D 1–()22D–()⋅ if D > 0.5⋅
Multiple regulators can be also synchronized to an external frequency signal fed to the
SYNCH pin. In this case the set is phased to the reference and all the devices will work with
0° phase shift.
The graphical representation of the input RMS current of the input filter in the case of two
devices with 0° phase shift (synchronized to an external signal) or 180° phase shift
(synchronized connecting their SYNCH pins) regulating the same output voltage is provided
in Figure 8. To dimension the proper input capacitor please refer to Chapter 6.1
Figure 8. Input RMS current of two synchronized regulators
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 17/52

Functional description L5988D
5.3 External voltage reference
An external 1.8 V regulated voltage is provided. This reference is useful to set the voltage at
the multifunction pin (see 5.1) or to source current to ILIM-ADJ and FSW pins (see and
5.5.2). The typical current capability is 4 mA.
5.4 Soft-start
When VCC is above the selected UVLO threshold the start-up phase takes place. At startup, a voltage ramp is generated charging the external capacitor C
generator. The device is in inhibit mode as long as SS/
INH pin is below the INH threshold.
The L5988D implements the soft-start phase by clamping the output of the error amplifier
and, being based on a voltage mode control, the duty cycle. In fact the comparison between
the output of the error amplifier and the internal saw tooth waveform generates the duty
cycle needed to keep the output voltage in regulation.
Two different current sources charge the external capacitor depending on the pin voltage in
order to reduce the power consumption in INH mode.
with an internal current
SS
I
⎧
I
=
⎨
SS
⎩
5= μA 0 V
SS1
2= 2μA 1 V
I
SS2
SS/INH
SS/INH
1<<
2.9<<
The equation for the soft-start time is:
C
SS
---------- -
I
SS2
2.9 1–()×+==
Considering I
SS2/ISS1
C
SS
SS
T1Δ T2Δ+
T
---------- -
I
10–()×
SS1
= 22/5 = 4.4, the proper soft-start capacitor is simply calculated as
follows:
CnF() Tss mS()3.5×=
During the soft-start phase (V
● the sink capability is always disabled (independently from the multifunction pin settings)
< 2.9 V):
SS
to be compatible with pre-biased output voltage
● in case the overcurrent limit is detected, a constant current protection is provided in
order to deliver extra current for charging the output capacitor (see 5.5.2 for description
of current protection management).
18/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Functional description
During normal operation the C
● HICCUP mode is triggered (see 5.5.2)
● the input voltage goes below the UVLO threshold (see 5.5.3)
● the internal temperature is over 150°C (see 5.5.4)
A new SS cycle will start when the V
is discharged with a constant current of 22 μA (typ.) only if:
SS
drops below the INH threshold.
SS
New high performance ICs often require more than one supply voltage. Most of these
applications require well defined start-up sequencing, in order to avoid potential damage
and latch-up of the processing core. Sharing the same soft-start capacitor for a set of
regulators, the output voltages increase with the same slew rate implementing a
“simultaneous start-up” sequencing method.
5.5 Monitoring and protections
5.5.1 Overvoltage
The device provides the overvoltage protection monitoring the output voltage through the FB
pin. If the voltage sensed on FB pin reaches a value 20% (typ.) greater than the reference of
the error amplifier, the low-side MOSFET is turned on to discharge as fast as possible the
output capacitor. It is possible to set two different behaviors in case of OVP:
● In case the OVP latched mode is active (see 5.1), the internal oscillator is suspended
and the low side switch will be kept on until the input voltage goes below the selected
UVLO threshold or the SS/
● In case of NOT latched OVP mode is active, the low side MOS is forced ON until the
feedback voltage is higher than the OVP threshold (20% greater than the reference of
the error amplifier).
INH pin is forced below the INH threshold.
Figure 9. OVP not latched
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 19/52

Functional description L5988D
Figure 10. OVP latched
20/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Functional description
5.5.2 Current limiting
The current limiting feature acts in different ways depending on the operative conditions.
● In case an overcurrent detection happens after the soft-start phase, the internal logic
will trigger the “HICCUP” mode. Both switches are turned off and the soft-start
capacitor is discharged with a constant current of 22
voltage drops below the INH threshold a new SS cycle will start.
● During the soft-start phase the overcurrent information is used to provide a constant
current protection. In this way additional current is available to charge the output
capacitor during power up.
The most common way is to sense the current flowing through the power MOSFETs.
However, due to the noise created by the switching activity of the power MOSFETs, the
current sense is disabled during the initial phase of the conduction time. This avoids an
erroneous detection of a fault condition. This interval is generally known as “masking time”
or “blanking time”. For this reason, the current cannot be sensed through the high-side
MOSFET in the case of extremely low duty cycles, nor through the low-side MOSFET in the
case of very high duty cycles.
The L5988D assures the effective protection sensing the current flowing in both embedded
switches. The protection achieved by sensing the current in the high-side MOSFET is called
“peak overcurrent protection”, while the protection achieved by sensing the current in the
low-side MOSFET is called “valley overcurrent protection”. When the current limit is reached
during normal operation, the so called HICCUP mode is triggered, and the soft-start cap is
discharged and recharged. However, during the start-up phase, additional current is
required to charge the output capacitor. This could continuously trigger the HICCUP
intervention preventing the system from reaching a steady working condition. For this
reason the HICCUP feature is disabled during the start-up phase and a constant current
mode is active to charge the output capacitor. In this case, when the peak current limit is
triggered after a conduction time equal to the “masking time”, the high-side MOSFET is
turned off and the low side MOSFET is kept on until the flowing current goes below the
“valley” current limit. If necessary, some switching pulses are skipped, as illustrated in
Figure 11. Thus, the combination of the “peak” and “valley” current limits assure the
effectiveness of the overcurrent protection even in extreme duty cycle conditions. The
current threshold of the low side is designed higher than the high side one to guarantee the
proper protection.
μA (typ.). When the SS/INH
The constant current mode during the soft-start phase limits the maximum current up to:
I
MAXIVALLEY_TH
----------------------------- -
L
⋅+=
T
MASK
VINV
–
OUT
The overcurrent limit protection is adjustable (higher or lower than the nominal value)
through an external resistor. To guarantee effective protection, both thresholds (valley and
peak) are in tracking.
The typical active thresholds in case of ILIM-ADJ pin left floating are I
I
VALLEY_TH
= 4.7 A. The dimensioning of the pull up resistor versus VREF to decrease the
PEAK_TH
= 4.0 A,
peak (and valley) thresholds follows the formula:
In the same way the pull down resistor is selected using the following formula to increase the
maximum current thresholds:
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 21/52

Functional description L5988D
5
1.2·10
R9Ω()
------------------------------------ -=
–
4.0 I
⋅
PEAK_TH
R3Ω()
2.706·105⋅
------------------------------------ -=
I
PEAK_TH
4.0–
Figure 11. constant current protection at extreme duty cycles
ZOOM
Constant current pr otecti on
Constant current pr otecti on
during soft st art time
during soft st art time
soft star t time
soft star t time
HICCUP pr otecti on
HICCUP pr otecti on
Is triggered at the
Is triggered at the
end of the SS time
end of the SS time
ZOOM
skipped switchi ng pulses
skipped switchi ng pulses
Ta bl e 8 shows some resistor values to adjust the current limits
Table 8. ILIM-ADJ resistor examples
R9(kΩ)I
LIM PEAK
43 1.24 1.62 1500 4.2 4.75
47 1.47 1.87 750 4.38 4.95
(A) I
LIM VALLEY
(A) R3(kΩ)I
LIM PEAK
(A) I
Valley curr ent limit
Valley curr ent limit
LIM VALLEY
(A)
56 1.88 2.31 470 4.6 5.18
68 2.26 2.71 330 4.8 5.42
91 2.71 3.18 270 5.0 5.62
120 3.03 3.52 220 5.20 5.82
200 3.43 3.94 180 5.50 6.12
560 3.81 4.35 160 5.70 6.30
5.5.3 UVLO
The under-voltage-lock-out (UVLO) is adjustable by the multifunction pin (see 5.1). It is
possible to set two different thresholds:
● 2.9 V for 3.3 V BUS
● 8 V for 12 V BUS
22/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Functional description
5.5.4 Thermal shutdown
When the junction temperature reaches 150 °C the device enters in thermal shutdown. Both
MOSFETs are turned off and the soft-start capacitor is discharged with a current of 22 µA.
The device doesn’t restart until the junction temperature goes down to 120 °C.
5.6 Minimum on time
The L5988D is based on a voltage mode control loop. The advantage of this technique is the
very short conduction time of the power elements thanks to the proper functioning of the
control loop without a current sense (that is challenging with low conduction times), which
instead is required in current mode regulators. The optimized architecture, the design
solutions and the high performance fabrication technique allow power elements to achieve
extremely short conduction times. This allows very high switching frequency operation even
in very low duty cycle applications. Figure 12 shows how the L5988D can easily manage a
minimum conduction time of 200ns. Moreover, thanks to the embedded P-MOS used for the
high-side, no bootstrap capacitor is required. This means that the device is able to manage
a duty cycle of 100%.
Figure 12. minimum T
ON
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 23/52

Functional description L5988D
5.7 Error amplifier
The error amplifier (E/A) provides the error signal to be compared with the sawtooth to
perform the pulse width modulation. Its non-inverting input is internally connected to a 0.6 V
voltage reference, while its inverting input (FB) and output (COMP) are externally available
for feedback and frequency compensation. In this device the error amplifier is a voltage
mode operational amplifier so with high DC gain and low output impedance.
The uncompensated error amplifier characteristics are the following:
Table 9. Uncompensated error amplifier
Low frequency gain 100 dB
GBWP 4.5 MHz
Slew rate 7 V/μs
Output voltage swing 0 to 3.3 V
Maximum source/sink current 25 mA / 40 mA
In continuos conduction mode (CCM), the transfer function of the power section has two
poles due to the LC filter and one zero due to the ESR of the output capacitor. Different
kinds of compensation networks can be used depending on the ESR value of the output
capacitor. In case the zero introduced by the output capacitor helps to compensate the
double pole of the LC filter a type II compensation network can be used. Otherwise, a type
III compensation network has to be used (see Chapter 6.4 for details about the
compensation network selection).
Anyway the methodology to compensate the loop is to introduce zeros to obtain a safe
phase margin.
24/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
6 Application information
6.1 Input capacitor selection
The capacitor connected to the input has to be capable to support the maximum input
operating voltage and the maximum RMS input current required by the device. The input
capacitor is subject to a pulsed current, the RMS value of which is dissipated over its ESR,
affecting the overall system efficiency.
So the input capacitor must have a RMS current rating higher than the maximum RMS input
current and an ESR value compliant with the expected efficiency.
The maximum RMS input current flowing through the capacitor can be calculated as:
I
RMSIO
2D2⋅
D
-------------- -–
η
2
D
------ -+⋅=
2
η
Where Io is the maximum DC output current, D is the duty cycles, η is the efficiency. This
function has a maximum at D = 0.5 and, considering η = 1, it is equal to Io/2.
In a specific application the range of possible duty cycles has to be considered in order to
find out the maximum RMS input current. The maximum and minimum duty cycles can be
calculated as:
D
MAX
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
V
INMIN
V
OUT
ΔV
LOW_SIDE
ΔV
+
LOW_SIDE
ΔV
–+
HIGH_SIDE
and
Where
ΔV
HIGH_SIDE
D
and ΔV
MIN
LOW_SIDE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
V
V
INMAX
are the voltage drops across the embedded switches.
OUT
ΔV
LOW_SIDE
ΔV
+
LOW_SIDE
ΔV
–+
HIGH_SIDE
The peak to peak voltage across the input filter can be calculated as:
I
PP
-----------------------
CINfSW⋅
V
O
D
⎛⎞
1
--- -–
⎝⎠
η
D
--- -
D⋅
1D–()⋅+ ESR IO⋅+⋅=
η
Given a physical dimension, ceramic capacitors can met well the requirements of the input
filter substaining an higher input current than electrolytic / tantalum types. In this case the
equation of C
as a function of the target VPP can be written as follows:
IN
C
IN
I
O
------------------------ -
VPPfSW⋅
D
⎛⎞
1
--- -–
⎝⎠
η
D
--- -
D⋅
1D–()⋅+⋅=
η
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 25/52

Application information L5988D
Considering η=1 this function has its maximum in D = 0.5:
I
C
IN_MIN
--------------------------------------------- -=
2V⋅
O
PP_MAXfSW
⋅
Typically C
in the order of 1% V
is dimensioned to keep the maximum peak-peak voltage across the input filter
IN
IN_MAX
Table 10. Input capacitors
Manufacture Series Cap value (μF) Rated voltage (V)
MURATA
TDK C3225 10 25
6.2 Inductor selection
The inductance value fixes the current ripple flowing through the output capacitor. So the
minimum inductance value in order to have the expected current ripple has to be selected.
The rule to fix the current ripple value is to have a ripple at 20%-40% of the output current.
The inductance value can be calculated by the following equation:
Where T
current ripple, at fixed Vout, is obtained at maximum T
previous section to calculate minimum duty). So fixing ΔI
output current, the minimum inductance value can be calculated:
ON
and T
are the on and off time of the internal power switch. The maximum
OFF
GRM31 10 25
GRM55 10 25
VINV
ΔI
L
–
OUT
----------------------------- -
L
⋅
T
ON
V
OUT
--------------
⋅==
T
OFF
L
that is at minimum duty cycle (see
OFF
= 20% to 40% of the maximum
L
V
+
OUTVF
--------------------------- -
MIN
IN
ΔI
MAX
= 12 V, IO = 4 A and F
where F
For example for V
is the switching frequency 1/(TON + T
SW
= 3.3 V, V
OUT
inductance value to have ΔI
L
= 30% of IO is about 4.7 µH.
L
The peak current through the inductor is given by:
I
LPK,
I
O
So if the inductor value decreases, the peak current (that has to be lower than the current
limit of the device) increases. The higher is the inductor value, the higher is the average
output current that can be delivered, without reaching the current limit.
26/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
1D
---------------------- -
⋅=
).
OFF
ΔI
L
--------+=
2
–
MIN
F
SW
= 400 kHz the minimum
SW

L5988D Application information
In the table below some inductor part numbers are listed.
Table 11. Inductors
Manufacturer Series Inductor value (μH) Saturation current (A)
XPL7030 2.2 to 4.7 6.8 to 10.5
Coilcraft
Wurth
Coiltronics
BI HM78-60 4.7 to 10 5.4 to 6.8
SUMIDA HM78-60 4.7 to 10 5.4 to 6.8
MSS1048 2.2 to 6.8 4.14 to 6.62
MSS1260 10 5.5
WE-HC/HCA 3.3 to 4.7 7 to 11
WE-TPC type XLH 3.6 to 6.2 4.5 to 6.4
WE-PD type L 10 5.6
DR74 3.3 to 4.7 4.3 to 5.4
DR125 10 5.3
6.3 Output capacitor selection
The current in the capacitor has a triangular waveform (with zero average value) which
generates a voltage ripple across it. This ripple is due to the capacitive component and the
resistive component (ESR). So the output capacitor has to be selected in order to have a
voltage ripple compliant with the application requirements.
The amount of the voltage ripple can be calculated starting from the current ripple obtained
by the inductor selection.
ΔV
Usually the resistive component of the ripple is much higher than the capacitive one, if the
output capacitor adopted is not a multi layer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) with very low ESR
value.
The output capacitor is important also for loop stability: it fixes the double LC filter pole and
the zero due to its ESR. In Chapter 6.4, it will be illustrated how to consider its effect in the
system stability.
For example with V
order to have a ΔV
OUT
OUT
= 3.3 V, V
= 0.01·V
needed and the ESR effect on the output voltage ripple can be neglected. In case of not
negligible ESR (electrolytic or tantalum capacitors), the capacitor is chosen taking into
account its ESR value. So 100 µF with ESR = 40 mΩ is compliant with the requested output
voltage ripple.
ESR ΔI
OUT
= 12 V, ΔIL = 0.6 A (resulting by the inductor value), in
IN
, if the multi layer capacitor are adopted, 10 µF are
OUT
MAX
------------------------------------ -+=
8C
⋅⋅
OUTfSW
⋅
ΔI
MAX
The output capacitor is also important to sustain the output voltage when a load transient
with high slew rate is required by the load. When the load transient slew rate exceeds the
system bandwidth the output capacitor provides the current to the load. So if the high slew
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 27/52

Application information L5988D
rate load transient is required by the application the output capacitor and system bandwidth
have to be chosen in order to sustain load transient and to have a fast response to the
transient.
In the table below some capacitor series are listed.
Table 12. Output capacitors
Manufacturer Series Cap value (μF) Rated voltage (V) ESR (mΩ)
MURATA
PANASONIC
SANYO TPA/B/C 100 to 470 4 to 16 40 to 80
TDK C3225 22 to 100 6.3 < 5
GRM32 22 to 100 6.3 to 25 < 5
GRM31 10 to 47 6.3 to 25 < 5
ECJ 10 to 22 6.3 < 5
EEFCD 10 to 68 6.3 15 to 55
6.4 Compensation network
The compensation network has to assure stability and good dynamic performance. The loop
of the L5988D is based on the voltage mode control. The error amplifier is a voltage
operational amplifier with high bandwidth. So selecting the compensation network the E/A
will be considered as ideal, that is, its bandwidth is much larger than the system one.
The transfer functions of PWM modulator and the output LC filter are studied. The transfer
function PWM modulator, from the error amplifier output (COMP pin) to the OUT pin, results:
G
where V
As seen in Chapter 5.2, the voltage feed forward generates a sawtooth amplitude directly
proportional to the input voltage, that is:
is the sawtooth amplitude and H represent its reliance on the switching frequency.
S
()
PW0fSW0
V
-------- -
V
IN
Hf
()⋅=
SW0
s
V
()KVINHf
SfSW0
The internal saw tooth is designed in order to have the maximum amplitude at the natural
switching frequency of the device.
At f
= 400 kHz the PWM modulator can be written as:
SW0
G
400 kHz()
PW0
1
--- -
K
The synchronization of the device with an external clock fed into the SYNCH pin and the
adjustment of the switching frequency through the FSW pin modify the gain of the internal
saw tooth (see Chapter 5.2).
28/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
()⋅⋅=
SW0
V
IN
---------------------------------- 9== =
VS400 kHz()

L5988D Application information
The PWM modulator gain is a function of the switching frequency:
G
PW0fSW
()G
400 kHz()
PW0
kHz()
f
SW
------------------------- -
⋅ 9
400
fSWkHz()
------------------------- -
⋅==
400
The transfer function on the LC filter is given by:
s
------------------------- -+
1
⋅
2π f
G
s()
LC
------------------------------------------------------------------------ -=
1
----------------------------
++
2π Qf⋅
⋅
zESR
s
⎛⎞
-------------------
⎝⎠
2π f
LC
2
s
⋅
LC
where:
f
----------------------------------------------------------------------- -= f
LC
2π LC
R
OUT
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q
LC
1
⋅ 1
OUT
LC
OUTROUT
OUTROUT
ESR
-------------- -+⋅⋅
R
OUT
ESR⋅⋅+
zESR
------------------------------------------- -=,
2π ESR C
ESR+()⋅⋅ ⋅
1
⋅⋅
OUT
V
--------------=,=
I
OUT
R
OUT
OUT
Two different kind of networks can compensate the loop depending on the output capacitor.
Type II network is used to compensate the loop with high ESR output capacitors, type III
with low ESR output capacitors (MLCC). In the two following paragraph the guidelines to
select the Type II and Type III compensation network are illustrated.
6.4.1 Type III compensation network
The methodology to stabilize the loop consists of placing two zeros to compensate the effect
of the LC double pole, so increasing phase margin; then to place one pole in the origin to
minimize the dc error on regulated output voltage; finally to place other poles far away the
zero dB frequency.
In Figure 13 the type III compensation network is shown. This network introduces two zeros
(f
, fZ2) and three poles (fP0, fP1, fP2). They expression are:
Z1
f
------------------------------------------------= f
Z1
2π C7R8R7+()⋅⋅
fP00= f
1
----------------------------- -= f
P1
2π R
1
⋅⋅
7C7
Z2
P2
1
----------------------------- -=,
2π R5C
⋅⋅
------------------------------------------- -=,,
2π R
1
⋅⋅
5
5
C5C6⋅
--------------------
C
+
5C6
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 29/52

Application information L5988D
Figure 13. Type III compensation network
In Figure 14 the Bode diagram of the PWM and LC filter transfer function (G
and the open loop gain (G
LOOP
(f) = G
· GLC(f) · G
PW0
(f)) are drawn.
TYPEIII
PW0
· GLC(f))
Figure 14. Open loop gain: module bode diagram
The guidelines for positioning the poles and the zeroes and for calculating the component
values can be summarized as follow:
30/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
1. Choose a value for R1, usually between 1 kΩ and 5 kΩ.
2. Choose a gain (R
) in order to have the required bandwidth (BW), that means:
5/R8
BW
1
--------- -
R
5
--- -
⋅⋅=
R
f
LC
8
K
where K is the feed forward constant and 1/K is equals to 18.
3. Calculate C
by placing the zero at 50% of the output filter double pole frequency (fLC):
5
1
---------------------------=
C
5
⋅⋅
π R
5fLC
4. Calculate C
by placing the second pole at four times the system bandwidth (BW):
6
C
C
------------------------------------------------------------- -=
6
2π R5C54BW⋅ 1–⋅⋅⋅
5
5. Set also the fist pole at four times the system bandwidth and also the second zero at
the output filter double pole:
R
8
-------------------------- -= C
R
7
4BW⋅
----------------- 1–
f
LC
7
1
---------------------------------------- -=,
2π R74BW⋅⋅⋅
The suggested maximum system bandwidth is equals to the switching frequency divided by
3.5 (F
For example with V
/3.5), anyway lower than 120kHz if the FSW is set higher than 500kHz.
SW
OUT
= 1.2 V, V
= 12 V, IO = 4 A, L = 4.7 μH, C
IN
= 47 μF, the type III
OUT
compensation network is:
R
4.7kΩ= R64.7kΩ= R756Ω= R51.2KΩ= C710nF= C522nF= C61nF=,,,,,,
8
In Figure 15 is shown the module and phase of the open loop gain. The bandwidth is about
68 kHz and the phase margin is 50°.
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 31/52

Application information L5988D
Figure 15. Open loop gain bode diagram with ceramic output capacitor
32/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
6.4.2 Type II compensation network
In Figure 16 the type II network is shown.
Figure 16. Type II compensation network
The singularities of the network are:
----------------------------- -= f
f
Z1
⋅⋅
2π R
1
5C5
P0
0= f
P1
------------------------------------------- -=,,
2π R
1
C5C6⋅
--------------------
⋅⋅
5
C
+
5C6
In Figure 17 the bode diagram of the PWM and LC filter transfer function (G
and the open loop gain (G
LOOP
(f) = G
· GLC(f) · G
PW0
(f)) are drawn.
TYPEII
Figure 17. Open loop gain: module bode diagram
PW0
· GLC(f))
The guidelines for positioning the poles and the zeroes and for calculating the component
values can be summarized as follow:
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 33/52

Application information L5988D
1. Choose a value for R8, usually between 1k and 5k, in order to have values of C5 and
C6 not comparable with parasitic capacitance of the board.
2. Choose a gain (R
) in order to have the required bandwidth (BW), that means:
5/R8
Where f
is the ESR zero:
ESR
R
5
f
f
ESR
⎛⎞
----------- -
⎝⎠
f
LC
ESR
2
⋅⋅⋅=
------------------------------------------- -=
⋅⋅
2π ESR C
BW
----------- -
f
ESR
V
S
-------- -
R
8
V
IN
1
OUT
and Vs is the saw-tooth amplitude. The voltage feed forward keeps the ratio Vs/Vin constant.
3. Calculate C
4. Then calculate C
by placing the zero one decade below the output filter double pole:
5
------------------------------ -=
⋅⋅
2π R
10
5fLC
C
5
in order to place the second pole at four times the system bandwidth
7
(BW):
C
5
= 330 μF,
OUT
For example with V
OUT
= 1.2V, V
C
------------------------------------------------------------- -=
7
2π R5C54BW⋅ 1–⋅⋅⋅
= 12 V, IO = 4 A, L = 4.7 μH, C
IN
ESR = 35 mΩ, the type II compensation network is:
4.7kΩ= R64.7KΩ= R522kΩ= C52.2nF= C633p F=,,,,
R
8
In Figure 18 is shown the module and phase of the open loop gain. The bandwidth is about
42 kHz and the phase margin is 56°.
34/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
Figure 18. Open loop gain bode diagram with high ESR output capacitor
The response of the system to a load transition in terms of output voltage regulation is
affected not only by the designed compensation network but it also rely on the selection of
the power components (the inductor value, for example, limits the slew rate of the current).
Some measurements of the output regulation during load transient for the examples
provided in Chapter 6.8 are provided at the end of this document.
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 35/52

Application information L5988D
6.5 R.M.S. current of the embedded power MOSFETs
The L5988D integrates both the power elements (high side and low side) and so the power
dissipation is often the bottleneck for the output current capability (refer to Chapter 6.6 for
the estimation of the operating temperature).
Nevertheless, as mentioned in Description on page 6 the device can manage a continuos
output current of 4 A in most of the application conditions.
However the rated continuos current is 5 A and the rated RMS current of the power
elements is 4.5 A, where:
I
RMS HSILOAD
I
RMS LSILOAD
D⋅=
1D–⋅=
and the duty cycle D:
Fixing the limit of 4.5 A for I
V
OUTRDS ON LS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
D
V
INRDS ON LSRDS ON HS
RMS HS
and I
RMS LS
DCR+()I
⋅+
LOAD
–()I
⋅+
LOAD
the maximum output current can be derived,
as illustrated in Figure 19..
Figure 19. Maximum continuos output current vs. duty cycle
36/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
6.6 Thermal considerations
The thermal design is important to prevent the thermal shutdown of the device if the junction
temperature goes above 150 °C. The three different sources of losses within the device are:
a) conduction losses due to the not negligible R
equal to:
of the power switch; these are
DSON
P
ON
R
DSON_HSIOUT
()2DR
DSON_LSIOUT
()21D–()⋅⋅+⋅⋅=
Where D is the duty cycle of the application. Note that the duty cycle is theoretically given by
the ratio between V
an VIN, but actually it is quite higher to compensate the losses of the
OUT
regulator. So the conduction losses increases compared with the ideal case.
b) switching losses due to power MOSFET turn ON and OFF; these can be
calculated as:
T
+()
RISETFALL
------------------------------------------ -
OUT
2
Where T
RISE
P
SW
and T
VINI
represent the switching times of the power element that cause the
FAL L
switching losses when driving an inductive load (see Figure 20). T
Fsw⋅⋅ ⋅ V
⋅⋅⋅==
INIOUTTSWFSW
is the equivalent
SW
switching time.
Figure 20. Switching losses
c) Quiescent current losses, calculated as:
where I
is the quiescent current.
Q
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 37/52
PQVINIQ⋅=

Application information L5988D
The junction temperature TJ can be calculated as:
TJTARthJAP
Where T
R
thJA
is the ambient temperature and P
A
TOT
is the equivalent static thermal resistance junction to ambient of the device; it can be
⋅+=
TOT
is the sum of the power losses just seen.
calculated as the parallel of many paths of heat conduction from the junction to the ambient.
For this device the path through the exposed pad is the one conducting the largest amount
of heat. The static Rth
measured on the application is about 40 °/W.
JA
The thermal impedance of the system, considered as the device in HTSSOP16 package
soldered on the application board, takes on an important rule when the maximum output
power is limited by the static thermal performance and not by the electrical performance of
the device. Therefore the embedded power elements could manage an higher current but
the system is already taking away the maximum power generated by the internal losses.
In case the output power increases the thermal shutdown will be triggered because the
junction temperature triggers the designed thermal shutdown threshold.
The R
is a static parameter of the package: it sets the maximum power loss which can be
TH
generated from the system given the operation conditions.
If we suppose, as an example, T
before triggering the thermal shutdown and R
= 40 °C, 140 °C is the maximum operating temperature
A
= 40 °C/W so the maximum power loss
TH
achievable with the thermal performance of the system will be:
T
P
MAX DC
ΔT
---------- -
R
TH
–
J MAXTAMB
------------------------------------- -
R
TH
100
--------- - 2.5W== ==
40
The switching, conduction and quiescent losses in case of V
= 12 V, V
IN
OUT
= 1.2 V, f
SW
400 kHz are plotted in Figure 21. The calculations are performed considering the typical
R
R
Figure 21. Estimation of the internal power losses (V
of the power element for a junction temperature of 125 °C (R
DS(on)
DS_ON LS
= 83 mΩ; see Maximum ratings on page 8 for details).
f
= 400 kHz)
SW
= 12 V, V
IN
DS_ON HS
= 1.2 V,
OUT
= 120 mΩ,
=
38/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
The red trace represents the maximum power which can be taken away as calculated
above, whilst the purple trace is the total internal losses.
As a consequence, given these operating conditions, the system can manage a continuos
output current up to 4.2 A. The device could deliver a continuos output current up to 5 A to
the load (see Chapter 6.5), however the maximum power loss of 2.5 W is reached with an
output current of 4.2 A, so the maximum output power is derated.
The calculation of the internal power losses must be done for each specific operating
condition given by the final application.
For example, the result showed in Figure 21. is not valid in case the V
is equal to 5 V
IN
instead of 12 V: the lower contribution of the switching losses, which are proportional to the
input voltage, increases the maximum output current from 4.2 A to 4.5 A (see Figure 22.).
Figure 22. Estimation of the internal power losses (V
f
= 400 kHz)
SW
= 5 V, V
IN
OUT
= 1.2 V,
In applications where the current to the output is pulsed, the thermal impedance should be
considered instead of the thermal resistance. Also, in these conditions, the current
limitations described in Chapter 6.5 are no more valid since they are related to continuos
output current delivery.
The thermal impedance of the system could be much lower than the thermal resistance,
which is a static parameter. As a consequence the maximum power losses can be higher
than 2.5 W if a pulsed output power is requested from the load:
T
P
MAX
t()
ΔT
---------------- -
Z
TH
t()
–
J MAXTAMB
------------------------------------- -==
Z
t()
TH
So, depending on the pulse duration and its frequency, the maximum output current (even
more than 5 A) can be delivered to the load.
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 39/52

Application information L5988D
The characterization of the thermal impedance is strictly dependent on the layout of the
board. In Figure 23. the measurement of the thermal impedance of the evaluation board of
the L5988D is provided.
Figure 23. Measurement of the thermal impedance of the evaluation board
As it can be see, for example, for load pulses with duration of 1 second, the actual thermal
impedance is lower than 20 °C/W. This means that, for short pulses, a current higher that 5A
(provided the current limitation is set correctly) can be managed.
6.7 Layout considerations
The PC board layout of switching DC/DC regulator is very important to minimize the noise
injected in high impedance nodes and interferences generated by the high switching current
loops. The L5988D is a monolithic device so most of the critical path are designed internally
minimizing the potential issues introduced by the board layout.
In the operation of a step down converter two high current loops become evident and
critical. The conduction of the high side switch highlight a current loop composed by the
input capacitor, the inductor and the output capacitor whilst during the conduction of the low
side switch the current flows from the power ground to the inductor and again the output
capacitor.
The first consideration is to keep the trace of the switching node as short as possible to
reduce radiated emission.
The bandwidth of the external power supply is limited if compared to the switching frequency
of the device so the power supply delivers a certain RMS current in the switching period. As
a consequence the input filter substains the input voltage during the conduction time of the
40/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
HS switch delivering an impulsive extra current equal to I
LOAD
+ I
RIPPLE
- I
IN RMS
and it is
recharged during the conduction time of the low side by the external power supply.
The golden rule is to reduce as much as possible the stray inductance of the path related to
the capacitor and V
to reduce injected noise: the suggested layout (see Figure 24 and
IN
Figure 25) solves this matter placing the input filter just above the package of the device to
minimize noise. This placement offers the best filtering for the device and minimize the noise
injected by the pulsing current path. The additional stray inductance introduced in the path
from the switching node and the external inductor is not critical for the operation of the
device.
The pin 4 of the L5988D supplies most of the analog circuitry and MOSFET drivers so an
RMS current of few mA flows in its trace. A decoupling path between the power and signal
input reduces the issues induced by the switching noise: an RC network is helpful to filter
the signal supply from the noise generated by the switching activity and it becomes effective
when its time constant is bigger than two or three switching cycles. The pin 4 supplies the
drivers of the embedded MOSFET so the R value has to be kept limited to avoid voltage
spikes during the operation of the embedded driver (the maximum value is in the order of
few ohms).
The inductor current flows from power GND to the output capacitor during the conduction
time of the LS switch: the power ground plane and the signal ground are kept partitioned in
the PCB layout to minimize the injected noise on the signal ground. They are connected
together below the ground of the output capacitor which is the less noisy power component.
The connection of the external resistor divider to the feedback pin (FB) is an high
impedance node, so the interferences can be minimized placing the routing of feedback
node as far as possible from the high current paths. To reduce the pick up noise the resistor
divider has to be placed very close to the device.
Thanks to the exposed pad of the device, the ground plane helps to reduce the thermal
resistance junction to ambient; so a large ground plane enhances the thermal performance
of the converter allowing high power conversion.
Figure 24. Top board layout
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 41/52

Application information L5988D
Figure 25. Bottom board layout
6.8 Application circuit
In Figure 26 is shown the demonstration board application circuit working.
The operating switching frequency is 400 kHz. The designed system bandwidth is 68 kHz
with a the phase margin of 50°. The peak current limitation is set 5.2 A, the valley current
limitation 5.8 A in order to deliver up to 4 A DC to the load.
Figure 26. Demonstration board application circuit (f
= 400 kHz)
SW
42/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Application information
Table 13. Component list application circuit (f
Reference Part number Description Manufacturer
C1 GRM32ER61E226KE15 Chip capacitor 22 µF 25 V Murata
C10 GRM188R71E105KA12 Chip capacitor 1µF 25 V Murata
C2A GRM32ER61C476KE15 Chip capacitor 47 µF 16 V
C8 Chip capacitor 1 µF
C3 Chip capacitor 330 nF
C5 Chip capacitor 22 nF
C6 Chip capacitor 1 nF
C7 Chip capacitor 10 nF
L1 744 311 470 Inductor 4.7 µH Wurth elektronik
R1 Chip resistor 12 kΩ ± 1%
R2 Chip resistor 3.3 kΩ ± 1%
R3 Chip resistor 220 kΩ ± 1%
R5 Chip resistor 1.2 kΩ ± 1%
R6 Chip resistor 4.7 kΩ ± 1%
R7 Chip resistor 56 Ω ± 1%
R8 Chip resistor 4.7 kΩ ± 1%
= 400 kHz)
SW
R12 Chip resistor 5.6 R ± 1%
U1 I.C. L5988D STMicroelectronics
In Figure 27. is shown an additional application example where the L5988D operates at a
switching of 600 kHz. The designed system bandwidth is 73 kHz with a the phase margin of
51°. The peak current limitation is set 5.2 A, the valley current limitation 5.8 A in order to
deliver up to 4 A DC to the load.
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 43/52

Application information L5988D
Figure 27. Demonstration board application circuit (fSW = 600 kHz)
Table 14. Component list application circuit (f
Reference Part number Description Manufacturer
C1 GRM32ER61E226KE15 Chip capacitor 22 µF 25 V Murata
C10 GRM188R71E105KA12 Chip capacitor 1 µF 25 V Murata
C2A GRM32ER61C476KE15 Chip capacitor 47 µF 16 V
C8 Chip capacitor 2.2 µF
C3 Chip capacitor 330 nF
C5 Chip capacitor 22 nF
C6 Chip capacitor 1 nF
C7 Chip capacitor 10 nF
L1 744 311 330 Inductor 3.3 µH Wurth elektronik
R1 Chip resistor 12 kΩ ±1%
R2 Chip resistor 3.3 kΩ ±1%
R3 Chip resistor 220 kΩ ±1%
R4 Chip resistor 82 kΩ ±1%
R5 Chip resistor 560 Ω ±1%
R6 Chip resistor 1.1 kΩ±1%
R7 Chip resistor 68 Ω ± 1%
R8 Chip resistor 4.99 kΩ ±1%
= 600 kHz)
SW
R12 Chip resistor 5.6 Ω ±1%
U1 I.C. L5988D STMicroelectronics
44/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Typical characteristics
7 Typical characteristics
Figure 28. Junction temperature vs. f
at VIN = 12 V, V
OUT
= 3.3 V
Figure 30. Junction temperature vs. f
at VIN = 3.3 V, V
OUT
= 1.2 V
SW
SW
Figure 29. Junction temperature vs. f
at VIN = 5 V, V
OUT
= 3.3 V
Figure 31. Junction temperature vs. V
at VIN = 12 V, fSW = 400 kHz
SW
OUT
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 45/52

Typical characteristics L5988D
Figure 32. Junction temperature vs. V
at VIN = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz
OUT
Figure 34. Efficiency vs. output current
at V
= 3.3 V, fSW = 400 kHz
98.00
93.00
88.00
83.00
(%)
¬
78.00
73.00
68.00
63.00
0.2 0.6 1.0 1.4 1.8 2.2 2.6 3.0 3.4 3.8
IN
VIN = 3.3v fSW = 400 kHz
VIN=3.3 VOUT=1.2 250 kHz
VIN=3.3 VOUT=1.5 250 kHz
VIN=3.3 VOUT=1.8 250 kHz
VIN=3.3 VOUT=2.5 250 kHz
I
(A)
LOAD
Figure 33. Junction temperature vs. V
at VIN = 3.3 V, fSW = 400 kHz
Figure 35. Efficiency vs. output current
at VIN = 5 V, fSW = 250 kHz
95.00
90.00
85.00
(%)
¬
80.00
75.00
70.00
65.00
0.2 0.6 1.0 1.4 1 .8 2.2 2.6 3.0 3.4 3.8
VIN = 5v fSW = 250 kHz
VIN=5 VOUT=1.2 250 kHz
VIN=5 VOUT=1.5 250 kHz
VIN=5 VOUT=1.8 250 kHz
VIN=5 VOUT=2.5 250 kHz
VIN=5 VOUT=3.3 250 kHz
I
(A)
LOAD
OUT
46/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Typical characteristics
Figure 36. Efficiency vs. output current Figure 37. Load regulation
95.00
90.00
85.00
80.00
(%)
¬
75.00
70.00
65.00
60.00
0.2 0.6 1.0 1.4 1.8 2.2 2.6 3.0 3.4 3.8
Figure 38. Line regulation Figure 39. Load transient from 0 to 3 A
VIN = 12v fSW = 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=1.2 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=1.5 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=1.8 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=2.5 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=3.3 250 kHz
VIN=12 VOUT=5.0 250 kHz
η(%)
I
(A)
LOAD
L5988D LOAD REGULATI ON (VIN 12V - L = 4.7μH)
3.36
3.355
3.35
3.345
3.34
3.335
3.33
3.325
3.32
3.315
3.31
3.305
3.3
0 0 .5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3 .5 4
L5988D_3.3v_400k_AFP]
I
(A)
LOAD
3.36
3.355
3.35
3.345
3.34
3.335
3.33
η(%)
3.325
3.32
3.315
3.31
3.305
3.3
Figure 40. Soft-start
L5988D LI NE REGULATION (L = 4.7μH)
L5988D_3.3v_400k
3.5 5.5 7.5 9.5 11.5 13.5 15.5 17.5
(A)
I
LOAD
fsw=400 kHz
100mV/div
fsw=600 kHz
Cout=47uF
SR = 2.5A/us
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 47/52

Package mechanical data L5988D
8 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
Table 15. HTSSOP16 mechanical data
(mm)
Dim.
Min. Typ. Max.
A 1.20
A1 0.15
A2 0.80 1.00 1.05
b 0.19 0.30
c 0.09 0.20
D 4.90 5.00 5.10
D1 2.8 3 3.2
E 6.20 6.40 6.60
E1 4.30 4.40 4.50
E2 2.8 3 3.2
e 0.65
L 0.45 0.60 0.75
L1 1.00
k 0.00 8.00
aaa 0.10
48/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Package mechanical data
Figure 41. HTSSOP16 mechanical drawing
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 49/52

Order codes L5988D
9 Order codes
Table 16. Order codes
Order codes Package Packaging
L5988D
VFQFPN8
L5988DTR tape and reel
Tube
50/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3

L5988D Revision history
10 Revision history
Table 17. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
20-Jan-2009 1 Initial release
24-Sep-2009 2 Updated: coverpage, Table 4 on page 9
18-Jan-2010 3
Updated: Section 5.2 on page 15, Section 6.4 on page 28 and
Table 13 on page 43
Doc ID 15324 Rev 3 51/52

L5988D
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2010 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
52/52 Doc ID 15324 Rev 3
 Loading...
Loading...