Page 1

AN4027
Application note
12 V - 150 W resonant converter with synchronous rectification
using the L6563H, L6699 and SRK2000
By Claudio Spini
Introduction
This application note describes the EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board features, a
12 V - 150 W converter tailored to a typical specification of an all-in-one (AIO) computer
power supply or a high power adapter.
The architecture is based on a two-stage approach: a front-end PFC pre-regulator based on
the L6563H TM PFC controller and a downstream LLC resonant half bridge converter using
the new L6699 resonant controller. The L6699 integrates some very innovative functions
such as self-adjusting adaptive deadtime, anti-capacitive mode protection and proprietary
“safe-start” procedure preventing hard switching at startup.
Thanks to the chipset used, the main features of this power supply are very high efficiency,
compliant with ENERGY STAR
external power supplies) and with the latest ENERGY STAR
computers (ENERGY STAR
efficiency at light load too, and compliance to the new EuP Lot 6 Tier 2 requirements. No
load input power consumption is very low as well, within the international regulation limits.
Figure 1. EVL6699-150W-SR: 150 W SMPS demonstration board
®
eligibility criteria for adapters (ENERGY STAR® rev. 2.0 for
®
ver. 6.0 for computers). The power supply also has very good
®
qualification criteria for
July 2012 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 1/38
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN4027
Contents
1 Main characteristics and circuit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Standby power saving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Startup sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3 L6563H brownout protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.4 L6563H fast voltage feed-forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.5 L6699 overload and short-circuit protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.6 L6699 anti-capacitive protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.7 Output voltage feedback loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.8 Open loop protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2 Efficiency measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1 ENERGY STAR® for external power supplies ver. 2.0 compliance verification
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
®
2.2 ENERGY STAR
2.3 Light load operation efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Measurement procedure: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
for computers ver. 6.0 compliance verification . . . . . . . 13
3 Harmonic content measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4 Functional check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.1 Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.2 Burst mode operation at light load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.3 Overcurrent and short-circuit protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.4 Anti-capacitive mode protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5 Thermal map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6 Conducted emission pre-compliance test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7 Bill of material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
8 PFC coil specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.1 General description and characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 3

AN4027 Contents
8.2 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.3 Electrical diagram and winding characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.4 Mechanical aspect and pin numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.5 Manufacturer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
9 Transformer specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
9.1 General description and characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
9.2 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
9.3 Electrical diagram and winding characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
9.4 Mechanical aspect and pin numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.5 Manufacturer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
10 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 3/38
Page 4

List of tables AN4027
List of tables
Table 1. Main characteristics and circuit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 2. Efficiency measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 3. ENERGY STAR
Table 4. ENERGY STAR
Table 5. Light load efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 6. Thermal maps reference points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 8. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: daughterboard bill of material . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 9. PFC coil winding data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 10. Transformer winding data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 11. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
®
for external power supplies ver. 2.0 compliance verification . . . . . . . . . 14
®
for computers ver. 6.0 compliance verification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 5

AN4027 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. EVL6699-150W-SR: 150 W SMPS demonstration board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. Burst-mode circuit block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 3. Electrical diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 4. Graph of efficiency measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 5. Light load efficiency diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 6. Compliance to EN61000-3-2 at 230 V
Figure 7. Compliance to JEITA-MITI at 100 V
Figure 8. Mains voltage and current waveforms at 230 V - 50 Hz - full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 9. Mains voltage and current waveforms at 100 V - 50 Hz - full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 10. Resonant stage waveforms at 115 V
Figure 11. SRK2000 key signals at 115 V
- 60 Hz - full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ac
Figure 12. HB transition at full load - rising edge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 13. HB transition at full load - falling edge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 14. HB transition at 0.25 A - rising edge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 15. HB transition at 0.25 A - falling edge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 16. L6699 pin signals-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 17. L6699 pin signals-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 18. Startup at 90 V
Figure 19. Startup at 265 V
Figure 20. Startup at 115 V
- full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
ac
- no load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
ac
- full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
ac
Figure 21. Startup at full load - detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 22. Pout = 250 mW operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 23. Pout = 250 mW operation - detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 24. Transition full load to no load at 115 V
Figure 25. Transition no load to full load at 115 V
Figure 26. Short-circuit at full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 27. Short-circuit at full load – detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 28. Short-circuit - hiccup mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 29. Thermal map at 115 V
Figure 30. Thermal map at 230 V
- 60 Hz - full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
ac
- 50 Hz - full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
ac
Figure 31. CE average measurement at 115 Vac - 60 Hz and full load. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 32. CE average measurement at 230 Vac - 50 Hz and full load. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 33. PFC coil electrical diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 34. PFC coil mechanical aspect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 35. Transformer electrical diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 36. Transformer overall drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
- 50 Hz, full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ac
- 50 Hz, full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ac
- 60 Hz - full load. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ac
- 60 Hz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ac
- 60 Hz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ac
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 5/38
Page 6
Main characteristics and circuit description AN4027
1 Main characteristics and circuit description
The SMPS main features are listed below:
Table 1. Main characteristics and circuit description
Parameter Value
Input mains range 90 - 264 V
Output voltage 12 V at 12.5 A continuous operation
Mains harmonics Meets EN61000-3-2 Class-D and JEITA-MITI Class-D
No load mains consumption
Avg. efficiency
Light load efficiency According to EuP Lot 6 Tier 2 requirements
EMI Within EN55022 Class-B limits
Safety Meets EN60950
Dimensions 65 x 154 mm, 28 mm component maximum height
PCB Double side, 70 µm, FR-4, mixed PTH/SMT
< 0.17 W at 230 V
for external power supplies
> 91% at 115
for external power supplies
- frequency 45 to 65 Hz
ac
, according to ENERGY STAR® 2.0
ac
V
, according to ENERGY STAR® 2.0
ac
The circuit is made up of two stages: a front-end PFC using the L6563H, an LLC resonant
converter based on the L6699, and the SRK2000, controlling the SR MOSFETs on the
secondary side. The SR driver and the rectifier MOSFETs are mounted on a daughterboard.
The L6563H is a current mode PFC controller operating in transition mode and implements
a high-voltage startup to power on the converter.
The L6699 integrates all the functions necessary to properly control the resonant converter
with a 50 % fixed duty cycle and working with variable frequency.
The output rectification is managed by the SRK2000, an SR driver dedicated to LLC
resonant topology.
The PFC stage works as pre-regulator and powers the resonant stage with a constant
voltage of 400 V. The downstream converter operates only if the PFC is on and regulating.
In this way, the resonant stage can be optimized for a narrow input voltage range.
The L6699 LINE pin (pin 7) is dedicated to this function. It is used to prevent the resonant
converter from working with too low input voltage that can cause incorrect Capacitive mode
operation. If the bulk voltage (PFC output) is below 380 V, the resonant startup is not
allowed. The L6699 LINE pin internal comparator has a current hysteresis allowing the turnon and turn-off voltage to be independently set. The turn-off threshold has been set to 300 V
to let the resonant stage operate in the case of mains sag and consequent PFC output dip.
The transformer uses the integrated magnetic approach, incorporating the resonant series
inductance. Therefore, no external, additional coil is needed for the resonance. The
transformer configuration chosen for the secondary winding is centre tap.
On the secondary side, the SRK2000 core function is to switch on each synchronous
rectifier MOSFET whenever the corresponding transformer half-winding starts conducting
6/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 7

AN4027 Main characteristics and circuit description
(i.e. when the MOSFET body diode starts conducting) and then to switch it off when the
flowing current approaches zero. For this purpose, the IC is provided with two pins (DVS1
and DVS2) sensing the MOSFETs drain voltage level.
The SRK2000 automatically detects light load operation and enters sleep mode, disabling
MOSFET driving and decreasing its own consumption. This function allows great power
saving at light load with respect to benchmark SR solutions.
In order to decrease the output capacitors size, aluminium solid capacitors with very low
ESR were preferred to standard electrolytic ones. Therefore, high frequency output voltage
ripple is limited and an output LC filter is not required. This choice allows the saving of
output inductor power dissipation which can be significant in the case of high output current
applications such as this.
1.1 Standby power saving
The board has a burst mode function implemented that allows power saving during light load
operation.
The L6699 STBY pin (pin 5) senses the optocoupler’s collector voltage (U3), which is
related to the feedback control. This signal is compared to an internal reference (1.24 V). If
the voltage on the pin is lower than the reference, the IC enters an idle state and its
quiescent current is reduced. As the voltage exceeds the reference by 30 mV, the controller
restarts the switching. The burst mode operation load threshold can be programmed by
properly choosing the resistor connecting the optocoupler to pin RFMIN (R34). Basically,
R34 sets the switching frequency at which the controller enters burst mode. Since the power
at which the converter enters burst mode operation heavily influences converter efficiency at
light load, it must be properly set. However, despite this threshold being well set, if its
tolerance is too wide, the light load efficiency of mass production converters has a
considerable spread.
The main factors affecting the burst mode threshold tolerance are the control circuitry
tolerances and, even more influential, the tolerances of the resonant inductance and
resonant capacitor. Slight changes of resonance frequency can affect the switching
frequency and, consequently, notably change the burst mode threshold. Typical production
spread of these parameters, which fits the requirements of many applications, are no longer
acceptable if very low power consumption in standby must be guaranteed.
As reducing production tolerance of the resonant components causes a rise in cost, a new
cost-effective solution is necessary.
The key point of the proposed solution is to directly sense the output load to set the burst
mode threshold. In this way the resonant elements parameters no longer affect this
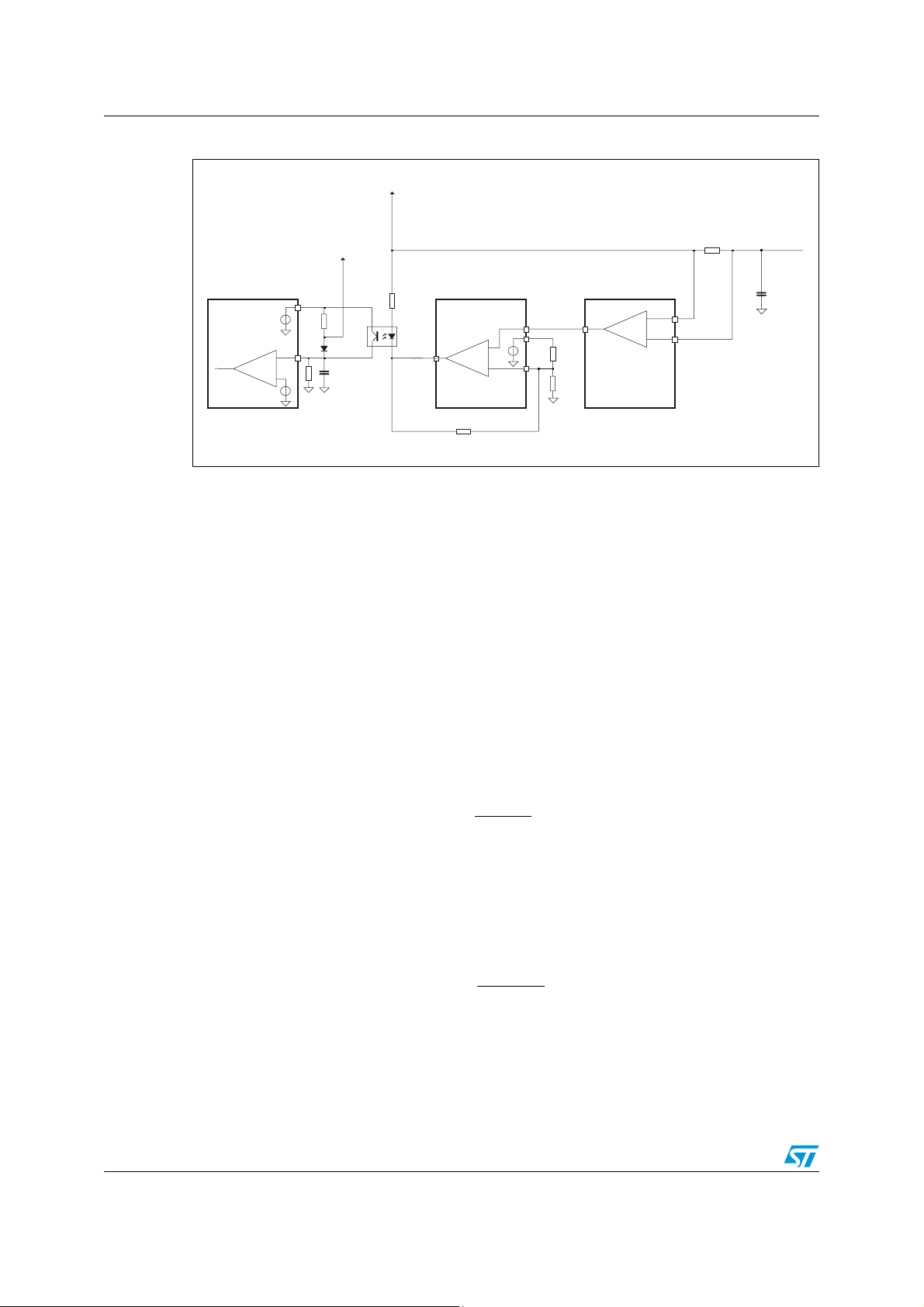
threshold. The implemented circuit block diagram is shown in
Figure 2
.
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 7/38
Page 8
Main characteristics and circuit description AN4027
Figure 2. Burst-mode circuit block diagram
TOP
OWERTRANSFORMER
2
#3
TO&"OPTOCOUPLER
TOLOAD
,! 43-
3TANDBY
#OMP
6
2&-).
6
2
&"
34"9
2"-2
"-
2
LIM
##?/54
#OMP
2
(TS
The output current is sensed by a resistor (R
## /54
6?2%&
6
##
); the voltage drop across this resistor is
CS
43#
60
%!
2
(
2
,
6-
!-6
amplified by the TSC101, a dedicated high-side current sense amplifier; its output is
compared to a set reference by the TSM1014; if the output load is high, the signal fed into
the CC- pin is above the reference voltage, CC_OUT stays down and the optocoupler
transistor pulls up the L6699 STBY pin to the RFMIN voltage (2 V), setting continuous
switching operation (no burst mode); if the load decreases, the voltage on CC- falls below
the set threshold, CC_OUT goes high opening the connection between RFMIN and STBY
and allowing burst mode operation by the L6699. R
is dimensioned considering two
CS
constraints. The first is the maximum power dissipation allowed, based on the efficiency
target. The second limitation is imposed by the need to feed a reasonable voltage signal into
the TSM1014A inverting input. In fact, signals which are too small would affect system
accuracy.
On this board, the maximum acceptable power dissipation has been set to P
mW. R
maximum value is calculated as follows:
CS
loss,MAX
= 500
Equation 1
P
=R
MAXCS,
MAXlo ss,
2
I
MA Xout,
The burst mode threshold is set at 5 W corresponding to I
12 V. Choosing V
good signal to noise ratio, the R
= 50 mV as minimum reference of the TSM1014A, which permits a
CC+min
minimum value is calculated as follows:
CS
Equation 2
=R
minCS,
The actual value of the mounted resistor is 2 mΩ, corresponding to P
losses at full load. The actual resistor value at the burst mode threshold current provides an
output voltage by the TSC101 of 83 mV. The reference voltage of TSM1014 V
8/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
•
3.2mΩ=
= 417 mA output current at
BM
V
min+CC
I 100
BM
1.2mΩ=
= 312 mW power
loss
must be
cc+
Page 9

AN4027 Main characteristics and circuit description
set at this level. The resistor divider setting the TSM1014 threshold RH and RL should be in
the range of kΩ to minimize dissipation. Selecting R
as follows:
Equation 3
= 22 KΩ, the right RH value is obtained
L
The value of the mounted resistor is 330 kΩ.
RHts sets a small debouncing hysteresis and is in the range of mega ohms. Rlim is in the
range of tens of kΩ and limits the current flowing through the optocoupler's diode. Both
L6699 and L6563H implement their own burst mode function but, in order to improve the
power supply overall efficiency, at light load the L6699 drives the L6563H via the
PFC_STOP pin and enables the PFC burst mode: as soon as the L6699 stops switching
due to load drops, its PFC_STOP pin pulls down the L6563H PFC_OK pin, disabling PFC
switching. Thanks to this simple circuit, the PFC is forced into idle state when the resonant
stage is not switching and rapidly wakes up when the downstream converter restarts
switching.
1.2 Startup sequence
The PFC acts as master and the resonant stage can operate only if the PFC output is
delivering the rated output voltage. Therefore, the PFC starts first and then the LLC
converter turns on. At the beginning, the L6563H is supplied by the integrated high-voltage
startup circuit; as soon as the PFC starts switching, a charge pump circuit connected to the
PFC inductor supplies both PFC and resonant controllers, therefore, the HV internal current
source is disabled. Once both stages have been activated, the controllers are supplied also
by the auxiliary winding of the resonant transformer, assuring correct supply voltage even
during standby operation. As the L6563H integrated HV startup circuit is turned off, it greatly
contributes to power consumption reduction when the power supply operates at light load.
R
H
()
=
V
BM
V1.25VR
−
BML
309kΩ
=
1.3 L6563H brownout protection
Brownout protection prevents the circuit from working with abnormal mains levels. It is easily
achieved using the RUN pin (pin 12) of the L6563H: this pin is connected through a resistor
divider to the VFF pin (pin 5), which provides the information of the mains voltage peak
value. An internal comparator enables the IC operations if the mains level is correct, within
the nominal limits. At startup, if the input voltage is below 90 V
inhibited.
1.4 L6563H fast voltage feed-forward
The voltage on the L6563H VFF pin (pin 5) is the peak value of the voltage on the MULT pin
(pin 3). The RC network (R15+R26, C12) connected to VFF completes a peak-holding
circuit. This signal is necessary to derive information from the RMS input voltage to
compensate the loop gain that is mains voltage dependent.
Generally speaking, if the time constant is too small, the voltage generated is affected by a
considerable amount of ripple at twice the mains frequency, therefore causing distortion of
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 9/38
(typ.), circuit operations are
ac
Page 10

Main characteristics and circuit description AN4027
the current reference (resulting in higher THD and lower PF). If the time constant is too
large, there is a considerable delay in setting the right amount of feed-forward, resulting in
excessive overshoot or undershoot of the pre-regulator's output voltage in response to large
line voltage changes.
To overcome this issue, the L6563H implements the fast voltage feed-forward function. As
soon as the voltage on the VFF pin decreases by a set threshold (40 mV typically), a mains
dip is assumed and an internal switch rapidly discharges the VFF capacitor via a 10 kΩ
resistor. Thanks to this feature, it is possible to set an RC circuit with a long time constant,
assuring a low THD, keeping a fast response to mains dip.
1.5 L6699 overload and short-circuit protection
The current into the primary winding is sensed by the lossless circuit R41, C27, R78, R79,
and C25 and it is fed into the ISEN pin (pin 6). In the case of overload, the voltage on the pin
surpasses an internal threshold (0.8 V) that triggers a protection sequence. An internal
switch is turned on for 5 µs and discharges the soft-start capacitor C18. This quickly
increases the oscillator frequency and thereby limits energy transfer. Under output shortcircuit conditions, this operation results in a peak primary current that periodically oscillates
below the maximum value allowed by the sense resistor R78.
The converter runs under this condition for a time set by the capacitor (C45) on pin DELAY
(pin 2). During this condition, C45 is charged by an internal 150 µA current generator and is
slowly discharged by the external resistor (R24). If the voltage on the pin reaches 2 V, the
soft-start capacitor is completely discharged so that the switching frequency is pushed to its
maximum value. As the voltage on the pin exceeds 3.5 V, the IC stops switching and the
internal generator is turned off, so that the voltage on the pin decays because of the external
resistor. The IC is soft-restarted as the voltage drops below 0.3 V. In this way, under shortcircuit conditions, the converter works intermittently with very low input average power.
This procedure allows the converter to handle an overload condition for a time lasting less
than a set value, avoiding IC shutdown in the case of short overload or peak power
transients. On the other hand, in the case of dead short, a second comparator referenced to
1.5 V immediately disables switching and activates a restart procedure.
1.6 L6699 anti-capacitive protection
The LLC resonant half bridge converter must operate with the resonant tank current lagging
behind the square-wave voltage applied by the half bridge leg. This is a necessary condition
in order to obtain correct soft switching by the half bridge MOSFETs. If the phase
relationship reverses, i.e. the resonant tank current leads the applied voltage, like in circuits
having a capacitive reactance, soft switching is lost. This condition is called capacitive mode
and must be avoided because of significant drawbacks coming from hard switching (refer to
the L6699 datasheet).
Resonant converters work in capacitive mode when their switching frequency falls below a
critical value that depends on the loading conditions and the input-to-output voltage ratio.
They are especially prone to run in capacitive mode when the input voltage is lower than the
minimum specified and/or the output is overloaded or short-circuited. Designing a converter
so that it never works in capacitive mode, even under abnormal operating conditions, is
certainly possible but this may pose unacceptable design constraints in some cases.
To prevent the severe drawbacks of capacitive mode operation, while enabling a design that
needs to ensure Inductive mode operation only in the specified operating range, neglecting
10/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 11

AN4027 Main characteristics and circuit description
abnormal operating conditions, the L6699 provides the capacitive mode detection function.
The IC monitors the phase relationship between the tank current circuit sensed on the ISEN
pin and the voltage applied to the tank circuit by the half bridge, checking that the former
lags behind the latter (Inductive mode operation). If the phase shift approaches zero, which
is indicative of impending capacitive mode operation, the monitoring circuit activates the
overload procedure described above so that the resulting frequency rise keeps the
converter away from that dangerous condition. Also in this case, the DELAY pin is activated,
so that the OLP function, if used, is eventually tripped after a time TSH causing intermittent
operation and reducing thermal stress.
If the phase relationship reverses abruptly (which may happen in the case of dead short at
the converter's output), the L6699 is stopped immediately, the soft-start capacitor C18 is
totally discharged and a new soft-start cycle is initiated after 50 µs idle time. During this idle
period the PFC_STOP pin is pulled low to stop the PFC stage as well.
1.7 Output voltage feedback loop
The feedback loop is implemented by means of a typical circuit using the dedicated
operational amplifier of the TSM1014A modulating the current in the optocoupler diode. The
second operational amplifier embedded in the TSM1014A, usually dedicated to constant
current regulation, is here utilized for burst mode as previously described.
On the primary side, R34 and D17 connect the RFMIN pin (pin 4) to the optocoupler's photo
transistor closing the feedback loop. R31, which connects the same pin to ground, sets the
minimum switching frequency. The RC series R44 and C18 sets both soft-start maximum
frequency and duration.
1.8 Open loop protection
Both circuit stages, PFC and resonant, are equipped with their own overvoltage protection.
The PFC controller L6563H monitors its output voltage via the resistor divider connected to
a dedicated pin (PFC_OK, pin 7) protecting the circuit in case of loop failures or
disconnection. If a fault condition is detected, the internal circuitry latches the L6563H
operations and, by means of the PWM_LATCH pin (pin 8), it latches the L6699 as well via
the DIS pin (pin 8). The converter is kept latched by the L6563H internal HV startup circuit
that supplies the IC by charging the V
operation, mains restart is necessary. The LLC open loop protection is realized by
monitoring the output voltage through sensing the V
D12 breakdown voltage, Q9 pulls down the L6563H INV pin latching the converter. Even in
this case, to resume converter operation, mains restart is necessary.
capacitor periodically. To resume converter
cc
voltage. If Vcc voltage overrides the
cc
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 11/38
Page 12
Main characteristics and circuit description AN4027
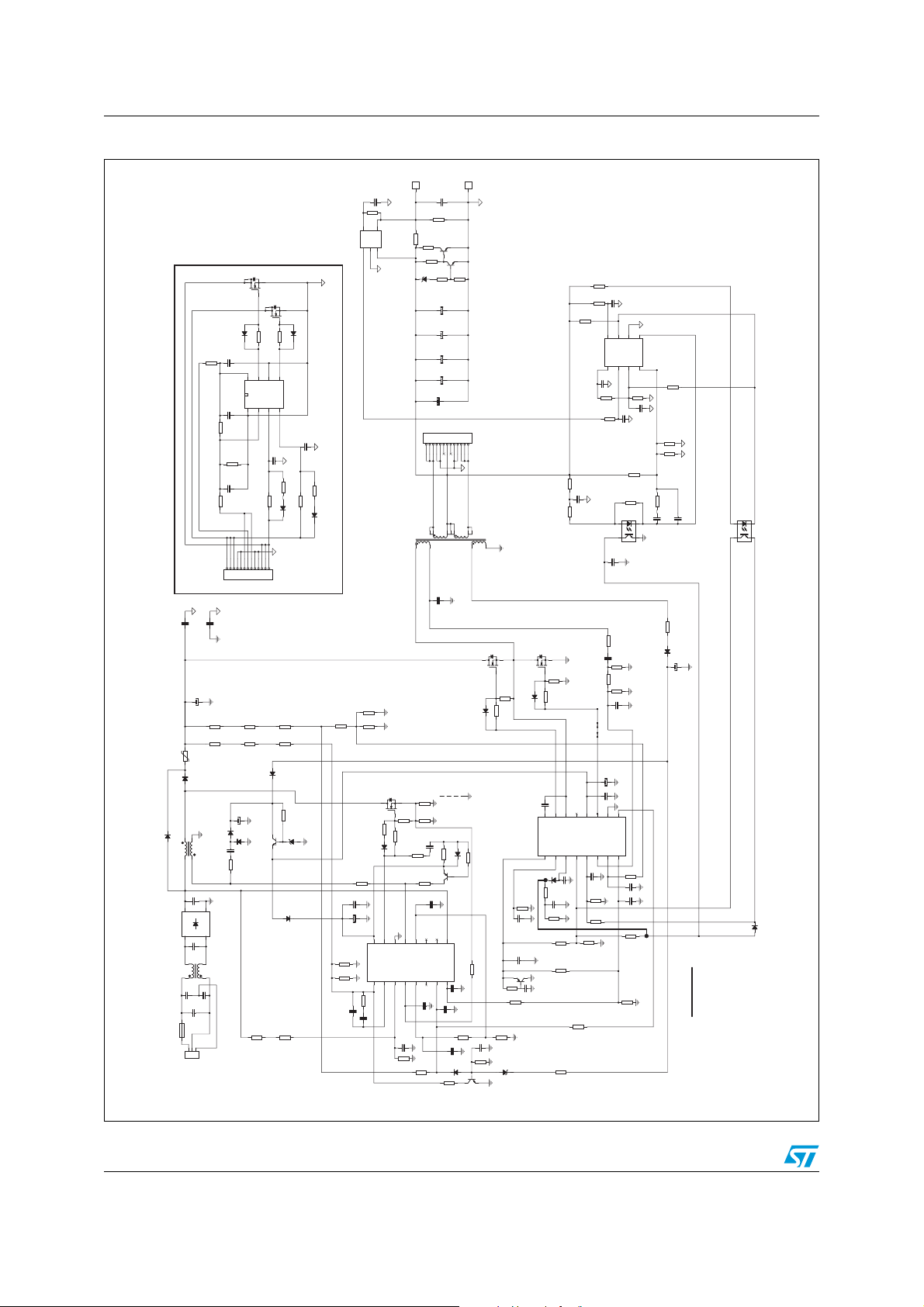
Figure 3. Electrical diagram
C16
RUN
R37
FASTON
R66
N.M.
R65
N.M.
D15
C29
1
4
R23
0R22
R23
R22
0R22
R22
C33
1N5
33R
R55
2K7
R55
2K7
2N2
2N2
11
PWM-STOP
C22
220K
C38
100N
R61
N.M.
R61
N.M.
Q6
N.M.
3
2
Q5
N.M.
1
3 2
1
2 1
N.M.
R56
C37
470uF-16V
470uF-16V
C50
470uF-16V
C49
C30
470uF-16V
470uF-16V
2
34567891011
10
11
9
C28
22NF
HS1
D6
R52
1K5
23
9
10
NC
HVS
8
220pF
C10
C10
D13
N.M.
R75
0R0
R75
0R0
N.M.
1N0
12
J2
FASTON
R68
STF8NM50N
100K
15
HVG
2K7
C6
N.M.
N.M.
R44
R33
5K6
C51
100N
R73
22R
R74
N.M.
7
6
5
8
VCC
GND
CV_OUT
CC_OUT
V_REF
CC+3CC-
U5
TSM1014AIST
1
2
C48
1N0
R70
R72
330K
R71
1K0
C32
470N
R49
91K
R49
R43
51R
R43
51R
C36
1uF - 50V
C36
1uF - 50V
R42
1K0
R42
1K0
56R
12
13
14
NC
VCC
OUT
C17
C17
330PF
330N
6K2
R31
R31
N.M.
R54
0R0
R77
1K0
91K
R47
N.M.
R47
N.M.
1 2
4 3
C41
N.M.
R41
100R
R78
33R
C27
220PF-630V
R79
270R
N.M.
R39
C25
1.5NF
JPX1JPX1
C26
10uF-50V
C40
100N
9
10
11
LVG
GND
PFC-STOP
DIS
8
7
R30
R30
C44
1.5NF
C44
1.5NF
C43
R36
1M8
R36
1M8
10N
C23
R32
47R
R32
47R
R34
8K2
20K
R60
10K
CV-
4
22K
C47
U3
SFH617A-2
10R
4N7
1N0
R51
R51
R50
R50
R48
47K
R48
47K
C34
100N
C34
100N
R40
0R68
D9
1 2
STPS2H100A
Rev 1.3
R64
10Meg
91K
91K
12K
12K
C35
N.M.
C35
N.M.
C24
220uF-50V
CONNECTION MADE BY REWORK
U4
12
43
SFH617A-2
D17
12
LL4148
AM11397v1
R62
N.M.
R62
12
13
12138
14
7
6
100K
D19
56R
R24
1M0
1M0
C45
220NF
220NF
4u7F
C18
C18
23
1
R67
N.M.
R29
1K0
R29
1K0
BZV55-C43
Q4
213
R59
R38
LL4148
1 2
C19
100N
16
VBOOT
CSS1DELAY2CF3RFMIN4STBY5ISEN6LINE
U2
L6699D
D16
N.M.
N.M.
12
R16
R4
N.M.
C46
213
Q3
STF8NM50N
R58
D18
LL4148
R25
1 2
HEAT-SINK
LL4148
R53
R53
2K2
1
Q2
BC857
R27
470R
Q7
N.M.
C31
N.M.
C31
R15
56K
R15
56K
R26
1M0
R26
1N0
C52
C12
1uF
D12
R76
33K
21
1
32
BC847C
Q9
J3
C42
100N
0R0
R63
5
U6
1
STL140N4LLF5
R501
10R
7
8
VCC
SRK2000
SGND1EN2DVS13DVS2
R506
2M2
R11
R3
2M2
C8
10uF-50V
D2
LL4148
6M8
R1
Q502
STL140N4LLF5
R502
D502
BAS316
10R
5
6
GD2
GD1
PGND
4
N.M.
C505
C504
N.M.
R508
N.M.
R509
N.M.
R507
330R
10
11
D21
Q8
330R
D505
N.M.
D503
N.M.
12
13
R12
2M2
R8
2M2
LL4148
1 2
R69
32
1
1
BC847C
D7
2
R2
5M6
24K
D20
D20
BZV55-B15
2
STPS140Z
STPS140Z
1
EVLSRK2000-L-40
R13
9K1
56K
R10
R10
R9
160K
C14
68N
68N
R19
C39
C39
C15
47uF-50V
U1
L6563H
Q501
D501
BAS316
R503
10R
C503
1uF
U501
C502
100NF
R504
150K
R505
33k
C501
4nF7
RX1
0R0
123456789
JP501JP501
2N2-Y1
C20
2N2-Y1
C21
C9
100uF - 450V
R17
2M2
R7
2M2
R6
NTC 2R5-S237
12
D4
STTH5L06
D3
1N4005
1N4005
12
F1
L2
1975.0004
D1
L1
2019.0002
FUSE T4A
J1
GBU8J
GBU8J
MKDS 1,5/ 3-5,08
5
9
11 3
4
+
+
~
~
2
124
C2
2N2-Y1
1
2
C4
C1
C1
3
C5
C5
470N-X2
470N-X2
_
_
3 1
C3
~
~
3
2N2-Y1C32N2-Y1
90-264Vac
12
D5
LL4148
1 2
C7
100N
R5
75R
470N - 520V
12V-12.5A
4
Vm
Vcc
R57
R002
TSC101
Out
GND2Vp
3
1860.0069
T1
2
R35
180K
R28
33K
Q1
STF21NM65M5
213
R46
100K
R46
R45
3R3
3R3
R21
22R
R20
D14
LL4148
LL4148
1 2
56K
56K
100N
14
15
16
13
12
GD
ZCD
VCC
GND
INV1COMP2MULT3CS4VFF5TBO6PFC-OK7PWM-LATCH
82K
R18
680N
C13
2N2
C11
R14
100K
12/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 13

AN4027 Efficiency measurements
85%
2 Efficiency measurements
Ta bl e 2
nominal mains voltages. At 115 V
shows the no load consumption and the overall efficiency measurements at the
the full load efficiency is 91.5%, and at 230 Vac it is
ac
93.2%, which are both high values for a double stage power supply and confirm the benefit
of implementing the synchronous rectification. The results are also shown in
Figure 5.
as a
graph.
Also at no load, the board performance is superior for a 150 W power supply: no load
consumption at nominal mains voltage is lower than 160 mW.
Table 2. Efficiency measurements
Input voltage
115 V-60 Hz
230 V-50 Hz
Load
condition
Vout [V] Iout [A] Pout [W] Pin [W] Efficiency (%)
no load 12.00 0.00 0.00 0.142 -
20% 11.99 2.50 29.98 35.58 84.2
25% 11.99 3.13 37.53 43.36 86.6
50% 11.97 6.25 74.81 82.53 90.6
75% 11.96 9.38 112.18 122.54 91.5
100% 11.94 12.50 149.25 163.12 91.5
No load 12.00 0.00 0.00 0.158 -
20% 11.99 2.50 29.98 35.35 84.8
25% 11.98 3.14 37.62 43.27 86.9
50% 11.97 6.25 74.81 81.56 91.7
75% 11.96 9.38 112.18 120.66 93.0
100% 11.94 12.50 149.25 160.22 93.2
Figure 4. Graph of efficiency measurements
95%
94%
93%
92%
91%
90%
89%
88%
87%
86%
Efficiency
84%
83%
82%
81%
80%
20%30% 40% 50% 60% 70%80% 90% 100%
Output load
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 13/38
Meas. eff. @230V
Meas. eff. @115V
AM11397v2
Page 14

Efficiency measurements AN4027
2.1 ENERGY STAR® for external power supplies ver. 2.0 compliance verification
In
Ta bl e 3
reported: note that the design overcomes the requirements with margin. The average
efficiency is measured at 25 %, 50 %, 75 %, 100 % load, the no load input power
consumption and the power factor at full load meet these regulation requirements for
adapters.
the comparison between the regulation requirements and the test results are
Table 3 . EN E RG Y STAR
®
for external power supplies ver. 2.0 compliance
verification
ENERGY STAR® requirements for
external power supplies ver. 2.0:
Average efficiency 25 %, 50 %, 75 %, 100
% load
No load input power [W] 0.142 0.158 < 0.5 W
Power factor 0.991 0.972 > 0.9
115 V
Test results
Limits Status
- 60 Hz 230 Vac - 50 Hz
ac
0.901 0.912 > 0.87
2.2 ENERGY STAR® for computers ver. 6.0 compliance verification
Because the EVL6699-150W-SR design is suitable to power even all-in-one computers,
having to meet the ENERGY STAR
compared with the latest ver. 6.0 requirements of this document. In the comparison
between the regulation requirements and the test results are reported: note that, in this case
the efficiency limit is not the average efficiency measured at different loads but there are
three different values of minimum efficiency to be met, at 20 %, 50 %, and 100 % load. Even
in this case, at full load the minimum power factor must be 0.9 minimum. In all load and line
conditions the EVL6699-150W-SR has efficiency and power factor much better than the
minimum required by the ENERGY STAR
®
regulation for computers, the test results have been
®
regulation.
Pass
Table 4 . EN E RG Y STAR® for computers ver. 6.0 compliance verification
ENERGY STAR® requirements for
computers ver. 6.0:
Efficiency @ 20 % load 0.842 0.848 > 0.82
Efficiency @ 50 % load 0.906 0.917 > 0.85
Efficiency @ 100 % load 0.915 0.932 > 0.82
Power factor 0.991 0.972 > 0.9
115
V
- 60 Hz 230 Vac - 50 Hz
ac
2.3 Light load operation efficiency
Computer power supplies must now meet higher efficiency limits than in the past even at
light load because, according to latest regulations such as the EuP Ecodesign requirements
14/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Test results
Limits Status
Pass
Page 15

AN4027 Efficiency measurements
for household and office equipment Lot 6 Tier 2, the maximum power consumption during
computer standby and off mode has decreased.
Measurement results are reported in
better than 50% even for very light loads such as 250 mW. This high efficiency at light load
allows the board to meet also the regulation of the low power status ENERGY STAR
program for computers ver. 5.0.
Measurement procedure:
1. Because the current flowing through the circuit under measurement is relatively small,
the current measurement circuit is connected to the demonstration board side and the
voltage measurement circuit is connected to the AC source side. In this way, the current
absorbed by the voltage circuit is not considered in the measured consumption
amount.
2. During any efficiency measurement, remove any oscilloscope probe from the board.
3. For any measurement load, apply a warm-up time of 20 minutes by each different load.
Loads have been applied increasing the output power from minimum to maximum.
4. Because of the input current shape during light load condition, the input power
measurement may be critical or unreliable using a power meter in the usual way. To
overcome this issue, all light measurements have been done by measuring the active
energy consumption of the demonstration board under test and then calculating the
power as the energy divided by the integration time. The integration time has been set
to 36 seconds, as a compromise between a reliable measurement and a reasonable
time measurement time. The energy is measured in mWh, the result in mW is then
simply calculated by dividing the instrument reading (in mWh) by 100. The instrument
used was the Yokogawa, WT210 power meter.
Ta bl e
and plotted in
Figure 5
. As seen, efficiency is
®
Table 5. Light load efficiency
230 V - 50 Hz 115 V - 60 Hz
Test
Vout [V] Iout [mA] Pout [W] Pin [W] Eff. [%] Vout [V] Iout [mA] Pout [W] Pin [W] Eff. [%]
0.25 W 12.00 10.40 0.125 0.319 39.1 12.00 10.40 0.125 0.310 40.3
0.5 W 12.00 20.90 0.251 0.473 53.0 12.00 20.90 0.251 0.471 53.2
1.0 W 12.00 41.68 0.500 0.768 65.1 12.00 41.68 0.500 0.785 63.7
1.5 W 12.00 83.50 1.002 1.358 73.8 12.00 83.50 1.002 1.415 70.8
2.0 W 12.00 125.03 1.500 1.940 77.3 12.00 125.03 1.500 2.045 73.4
2.5 W 12.00 167.09 2.005 2.525 79.4 12.00 166.84 2.002 2.651 75.5
3.0W 12.00 209.09 2.509 3.112 80.6 12.00 208.56 2.503 3.267 76.6
3.5 W 12.00 250.37 3.004 3.687 81.5 12.00 250.09 3.001 3.867 77.6
4.0 W 12.00 291.65 3.500 4.260 82.2 12.00 292.02 3.504 4.479 78.2
4.5 W 12.00 333.65 4.004 4.844 82.7 12.00 333.65 4.004 5.090 78.7
5.0 W 12.00 375.43 4.505 5.423 83.1 12.00 375.65 4.508 5.683 79.3
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 15/38
Page 16

Harmonic content measurement AN4027
FF
r
Figure 5. Light load efficiency diagram
ICIENCY;=
%
0OUT;7=
6(Z
6( Z
!-V
3 Harmonic content measurement
The board has been tested according to the European Standard EN61000-3-2 Class-D and
Japanese standard JEITA-MITI Class-D, at both the nominal input voltage mains. As
reported in the following figures, the circuit is able to reduce the harmonics well below the
limits of both regulations.
On the bottom side of the diagrams the total harmonic distortion and power factor have been
measured too. The values in all conditions give a clear idea about the correct functionality of
the PFC.
Figure 6. Compliance to EN61000-3-2 at
1
0.1
0.01
monic Current [A]
0.001
Ha
230 V
Measured value EN61000-3-2 Class-D limits
- 50 Hz, full load
ac
Figure 7. Compliance to JEITA-MITI at
100 Vac - 50 Hz, full load
Measured value
10
1
0.1
0.01
monic Current [A]
Har
0.001
JEITA-MITI Class-D limits
0.0001
13579111315171921232527293133353739
Harmonic Order [n]
THD: 18.2 % - PF = 0.972
AM11399v1
0.0001
13579111315171921232527293133353739
Harmonic Order [n]
THD: 7.5 % - PF = 0.933
AM11400v1
16/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 17

AN4027 Functional check
p
In
Figure 7
and
Figure 8
the input mains current is shown at both nominal mains input
voltages, European and Japanese. At European mains the waveforms show a slightly higher
THD value because, in order to increase the efficiency, the PFC switching frequency is
limited to a value around 125 kHz. However, all harmonics are within the limits specified by
both regulations.
Figure 8. Mains voltage and current
waveforms at 230 V - 50 Hz - full
load
Figure 9. Mains voltage and current
waveforms at 100 V - 50 Hz - full
load
CH1: Mains voltage
AM11401v1
4 Functional check
In
Figure 10
are reported. The selected switching frequency is about 120 kHz, in order to have a good
trade-off between transformer losses and dimensions. The converter operates slightly above
the resonance frequency.
MOSFET is switched on and off according to its drain-source voltage which, during
conduction time, is the voltage of the current flowing through the MOSFET.
Figure 10. Resonant stage waveforms at 115
V
- 60 Hz - full load
ac
some waveforms relevant to the resonant stage during steady-state operation
Figure 11
shows key signals of the SRK2000: each rectifier
CH1: Mains voltage
CH2: Mains current
Figure 11. SRK2000 key signals at 115 V
Hz - full load
AM11402v1
- 60
ac
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG pin voltage
CH3: HVG pin voltage CH4: ISEN pin voltage
AM11403v1
CH1: GD1 pin voltage CH2: DVS1 pin
CH3: GD2
in voltage CH4: DVS2 pin
AM11404v1
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 17/38
Page 18

Functional check AN4027
A peculiarity of the L6699 is the self-adaptive deadtime, modulated by the internal logic
according to the half bridge node transition time. This feature allows the maximization of the
transformer magnetizing inductance, therefore obtaining good light load efficiency and also
keeping correct operation by the HB.
Figure 12
and
Figure 13
show the waveforms during
full load operation. It is possible to note the measurement of the edges and the relevant
deadtime.
Figure 12. HB transition at full load - rising
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: HVG CH4: ISEN pin voltage
edge
In
Figure 14
and
Figure 15
AM11405v1
the same images are captured during light load operation: note
that because of the resonant tank parameters, the half bridge transitions have similar rise
and fall times because the switched current is almost the same value in both load
conditions. In this case, the L6699 does not appreciably change the deadtime. In all
conditions it can be noted that both MOSFETs are turned on while resonant current is
flowing through their body diodes and drain-source voltage is zero, therefore achieving the
MOSFETs ZVS operation at turn-on.
Figure 13. HB transition at full load - falling
edge
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: HVG CH4: ISEN pin voltage
AM11406v1
Figure 14. HB transition at 0.25 A - rising edge Figure 15. HB transition at 0.25 A - falling edge
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: HVG CH4: ISEN pin voltage
AM11407v1
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: HVG CH4: ISEN pin voltage
AM11408v1
18/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 19

AN4027 Functional check
Figure 16. L6699 pin signals-1 Figure 17. L6699 pin signals-2
CH1: DIS CH2: LINE
CH3: DELAY CH4: ISEN
In
Figure 16
CH1: RFmin CH2: STBY
AM11409v1
CH3: CSS CH4: CF
some signals at L6699 pins are measured. It can be seen that the signal on the
ISEN pin (#6) matches the instantaneous current flowing in the transformer primary side.
Contrary to the former resonant controllers such as the L6599A and others, requiring an
integration of current signal, the L6699 integrates the anti-capacitive mode protection,
therefore it needs to sense the instantaneous value of the current in order to check the
phase between the voltage and current. The LINE pin (#7) has been dimensioned to start up
the L6699 once the PFC output voltage has reached the rated value, in order to have correct
converter sequencing, with PFC starting first and LLC star ting later in order to optimize the
design of the LLC converter and prevent capacitive mode operation that may occur because
of operation at too low input voltage.
AM11410v1
The DELAY pin (#2) is zero, as it must be during normal operation, because it works during
the overcurrent protection operation. The DIS pin (#8) is used for open loop protection and
therefore, even in this case, its voltage is at ground level.
In
Figure 17
RFmin pin (#4) is a 2 V (typ.) reference voltage of the oscillator, the switching frequency is
proportional to the current flowing out from the pin. CSS pin (#1) voltage is the same value
as pin #4 because it is connected to the latter via a resistor (R44), determining the soft-start
frequency. A capacitor (C18) is also connected between the CSS pin and ground, to set the
soft-start time. At the beginning of L6699 operation the voltage on the CSS pin is at ground
level because C18 is discharged, then the CSS pin (#1) voltage increases according to the
time constant till the RFmin voltage level is reached. The STBY pin (#5) senses the
optocoupler voltage; once the voltage decreases to 1.25 V, both gate drivers stop switching
and the circuit works in burst mode. The CF pin (#3) is the controller oscillator; its ramp
speed is proportional to the current flowing out from the RFmin pin (#4). The CF signal must
be clean and undistorted to obtain correct symmetry by the half bridge current, and
therefore care must be taken in the layout of the PCB.
4.1 Startup
The waveforms relevant to the board startup at 90 Vac and full load have been captured in
Figure 18
after plug-in. The L6563H, HV PFC controller, has an embedded high-voltage startup
the pin voltages relevant to the control part of the L6699 are reported: the
. Note that the output voltage reaches the nominal value approximately 800 ms
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 19/38
Page 20

Functional check AN4027
charging the Vcc capacitor by a constant current, ensuring a constant wake-up time. This
can be seen by comparing
Figure 18
with
Figure 19
, relevant to a startup at 265 Vac and no
load, the output voltage rises at the nominal level in the same time. In both conditions the
output voltage has no overshoot or dips.
Figure 18. Startup at 90 V
CH1: C9 bulk voltage CH2: GD L6563H
CH3: +12 Vout CH4: VCC L6563H
In
Figure 20
reported. In
- full load Figure 19. Startup at 265 Vac - no load
ac
AM11411v1
the salient waveforms in the resonant tank during start up of the LLC are
Figure 21
the detail of waveforms at the beginning of operation shows that the
resonant circuit is working correctly in zero voltage switching operation from the initial
cycles. In the L6699 a new startup procedure, called “safe-start”, has been implemented in
order to prevent loss of soft-switching during the initial switching cycles which typically is not
guaranteed by the usual soft-start procedure. At startup, the voltage across the resonant
capacitor is often quite different from Vin/2, as during normal steady-state operation, so it
takes some time for its DC component to reach the steady-state value Vin/2. During this
transient, the transformer is not driven symmetrically and there is a significant V·s imbalance
in two consecutive half-cycles. If this imbalance is large, there is a significant difference in
the up and down slopes of the tank current and, in a typical controller working with fixed
50% duty cycle, as the duration of the two half-cycles is the same, the current may not
reverse in a switching half-cycle. Therefore, one MOSFET can be turned on while the body
diode of the other is conducting and this may happen for a few cycles. To prevent this, the
L6699 is provided with a proprietary circuit that modifies the normal operation of the
oscillator during the initial switching cycles, so that the initial V·s unbalance is almost
eliminated. Its operation is such that current reversal in every switching half-cycle and, then,
soft-switching, is ensured. In
Figure 21
it can be noted that at the beginning of operation the
duty cycle of the half bridge is initially considerably less than 50%, the tank current has
lower peak values and changes sign every half-cycle, while the DC voltage across the
resonant capacitor reaches the steady-state. The device goes to normal operation after
approximately 50 µs from the first switching cycle. This transition is almost seamless and
just a small perturbation of the tank current can be observed.
CH1: C9 bulk voltage CH2: GD L6563H
CH3: +12 Vout CH4: VCC L6563H
AM11412v1
20/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 21

AN4027 Functional check
Figure 20. Startup at 115 V
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: CSS CH4: ISEN
- full load Figure 21. Startup at full load - detail
ac
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
AM11413v1
CH3: CSS CH4: ISEN
4.2 Burst mode operation at light load
In
Figure 22
burst pulses are very narrow and their period is quite long, therefore the resulting equivalent
switching frequency is very low, ensuring high efficiency. The resulting output voltage ripple
during burst mode operation is about 200 mV peak-to-peak.
some burst mode pulses are captured during 250 mW load operation. The
AM11414v1
In
Figure 23
the detail of the burst is reported: the first initial pulse is shorter than the
following ones avoiding the typical high current peak at half bridge operation restarting, due
to the recharging or the resonant capacitor. The maximum operating frequency of the half
bridge, set by the resistor R34 in series to the optocoupler, is around 77 kHz.
Figure 22. Pout = 250 mW operation Figure 23. Pout = 250 mW operation - detail
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
CH3: STBY CH4: Vout (AC coupl.)
In
Figure 24
and
Figure 25
CH1: HB voltage CH2: LVG
AM11624v1
CH3: STBY CH4: Res. tank current
AM11625v1
the transitions from full load to no load and vice versa have been
checked. As seen in the images, both transitions are clean and there isn't any output voltage
dip.
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 21/38
Page 22

Functional check AN4027
Figure 24. Transition full load to no load at
CH1: LVG pin CH2: PFC gate
CH3: Output voltage CH4: Output current
115 V
- 60 Hz
ac
AM11626v1
Figure 25. Transition no load to full load at
115 Vac - 60 Hz
CH1: LVG pin CH2: PFC gate
CH3: Output voltage CH4: Output current
4.3 Overcurrent and short-circuit protection
The L6699 is equipped with a current sensing input (pin 6, ISEN) and a dedicated
overcurrent management system. The current flowing in the resonant tank is detected and
the signal is fed into the ISEN pin. It is internally connected to a first comparator, referenced
to 0.8 V, and to a second comparator referenced to 1.5 V. If the voltage externally applied to
the pin exceeds 0.8 V, the first comparator is tripped causing an internal switch to be turned
on and to discharge the soft-start capacitor CSS.
AM11627v1
Under output short-circuit, this operation results in a nearly constant peak primary current.
With the L6699, the board designer can externally program the maximum time that the
converter is allowed to run overloaded or under short-circuit conditions. Overloads or shortcircuits lasting less than the set time do not cause any other action, therefore providing the
system with immunity to short duration phenomena. If, instead, the overload condition keeps
going, a protection procedure is activated that shuts down the L6699 and, in the case of
continuous overload/short-circuit, results in continuous intermittent operation with a user
defined duty cycle. This function is realized with the DELAY pin (pin 2), by means of a
capacitor C45 and the parallel resistor R24 connected to ground. As the voltage on the
ISEN pin exceeds 0.8 V, the first OCP comparator, in addition to discharging CSS, turns on
an internal 150 µA current generator that, via the DELAY pin, charges C45. When the
voltage on C45 is 3.5 V, the L6699 stops switching and the PFC_STOP pin is pulled low.
Also the internal generator is turned off, so that C45 is now slowly discharged by R24. The
IC restarts when the voltage on C45 becomes lower than 0.3 V.
Additionally, if the voltage on the ISEN pin reaches 1.5 V for any reason (e.g. transformer
saturation), the second comparator is triggered, the L6699 shuts down and C45 is charged
to 3.5 V. Even in this case, the operation is resumed once the voltage on C45 drops below
0.3 V.
In
Figure 26
a dead short-circuit event has been captured. In this case the overcurrent
protection is triggered by the second comparator referenced at 1.5 V which immediately
stops switching by the L6699 and discharging of the soft-start capacitor; at the same time
the capacitor connected to the DELAY pin (#2) begins charging up to 3.5 V (typ.). Once the
voltage on the DELAY pin reaches 3.5 V, the L6699 stops charging the delay capacitor
22/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 23

AN4027 Functional check
(C45) and the L6699 operation is resumed once the DELAY pin (#2) voltage decays to 0.3 V
(typ.) by the parallel resistor (R24), via a soft-start cycle. If the short-circuit condition is
removed, the converter again starts operation, otherwise if the short is still there, the
converter operation results in an intermittent operation (Hiccup mode) with a narrow
operating duty cycle of the converter, in order to prevent overheating of power components,
as can be noted in
In
Figure 27
details of peak current with short-circuit occurring is shown. It is possible to see
Figure 28
.
the ZVS correct operation by the half bridge MOSFETs.
Figure 26. Short-circuit at full load Figure 27. Short-circuit at full load – detail
CH1: HB voltage CH2: DELAY
CH3: CSS CH4: ISEN
AM11628v1
CH1: HB voltage CH2: DELAY
CH3: CSS CH4: ISEN
.
Figure 28. Short-circuit - hiccup mode
CH1: HB voltage CH2: DELAY
CH3: CSS CH4: ISEN
AM11630v1
4.4 Anti-capacitive mode protection
AM11629v1
The EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board has been designed in such a way that the
system does not work in capacitive mode during normal operation or failure conditions. As
seen in
Figure 27
, even in dead short condition the LLC operates correctly in the inductive
region, the same correct operation happens during load or input voltage transients.
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 23/38
Page 24

Functional check AN4027
Normally, the resonant half bridge converter operates with the resonant tank current lagging
behind the square-wave voltage applied by the half bridge leg, like a circuit having a
reactance of an inductive nature. In this way the applied voltage and the resonant current
have the same sign at every transition of the half bridge, which is a necessary condition in
order for soft-switching to occur (zero-voltage switching, ZVS at turn-on for both MOSFETs).
Therefore, should the phase relationship reverse, i.e. the resonant tank current leads the
applied voltage, such as in circuits having a capacitive reactance, soft-switching would be
lost. This is termed capacitive mode operation and must be avoided because of its
significant drawbacks:
1. Both MOSFETs feature hard-switching at turn-on, like in conventional PWM-controlled
converters (see
Figure 14
). The associated capacitive losses may be considerably
higher than the total power normally dissipated under “soft-switching” conditions and
this may easily lead to their overheating, as heatsinking is not usually sized to handle
this abnormal condition.
2. The body diode of the MOSFET just switched off conducts current during the deadtime
and its voltage is abruptly reversed by the other MOSFET turned on (see
Figure 14
).
Therefore, the conducting body diode (which does not generally have great reverse
recovery characteristics) keeps its low impedance until it recovers, and so originating a
condition equivalent to a shoot-through of the half bridge leg. This is a potentially
destructive condition (see point 3) and causes additional power dissipation due to the
current and voltage of the conducting body diode simultaneously high during part of its
recovery.
3. There is an extremely high reverse dv/dt (many tens of V/ns!) experienced by the
conducting body diode at the end of its recovery with the other MOSFET turned on.
This dv/dt may exceed the rating of the MOSFET and lead to an immediate failure
because of the second breakdown of the parasitic BJT intrinsic in its structure. If a
MOSFET is hot, the turn-on threshold of its parasitic BJT is lower, this dv/dt-induced
failure is then far more likely.
4. When either MOSFET is turned on, the other one can be parasitically turned on too, if
the current injected through its Cgd and flowing through the gate driver's pull-down is
large enough to raise the gate voltage close to the turn-on threshold. This would be a
lethal shoot-through condition for the half bridge leg.
5. The recovery of the body diodes generates large and energetic negative voltage spikes
because of the unavoidable parasitic inductance of the PCB subject to its di/dt. These
are coupled to the OUT pin and may damage the L6699.
6. There is a large common-mode EMI generation that adversely affects EMC.
Resonant converters work in capacitive mode when their switching frequency falls below a
critical value that depends on the loading conditions and the input-to-output voltage ratio.
They are especially prone to run in capacitive mode when the input voltage is lower than the
minimum specified and/or the output is overloaded or short-circuited. Designing a converter
so that it never works in capacitive mode, even under abnormal operating conditions, is
certainly possible but this may pose unacceptable design constraints in some cases.
To prevent the severe drawbacks of capacitive mode operation, while enabling a design that
needs to ensure Inductive mode operation only in the specified operating range, neglecting
abnormal operating conditions, the L6699 provides the capacitive mode detection function.
The L6699 monitors the phase relationship between the tank current circuit sensed on the
ISEN pin and the voltage applied to the tank circuit by the half bridge, checking that the
former lags behind the latter (inductive mode operation). If the phase-shift approaches zero,
which is indicative of impending capacitive mode operation, the monitoring circuit activates
the anti-capacitive mode protection procedure so that the resulting frequency rise keeps the
24/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 25

AN4027 Thermal map
converter away from that dangerous condition. Also in this case, the DELAY pin is activated,
so that the OLP function, if used, is eventually tripped, causing intermittent operation and
reducing thermal stress.
If the phase relationship reverses abruptly (which may happen in the case of dead short at
the converter output), the L6699 is stopped immediately, the soft-start capacitor CSS is
totally discharged and a new soft-start cycle is initiated after 50 µs idle time. During this idle
period the PFC_STOP pin is pulled low to stop the PFC stage as well.
5 Thermal map
In order to check the design reliability, a thermal mapping by means of an IR camera was
done. Below, the thermal measurements of the board, component side, at nominal input
voltage are shown. Some pointers, visible on the images, have been placed across key
components or components showing high temperature. The ambient temperature during
both measurements was 26 °C.
Figure 29. Thermal map at 115 V
Figure 30. Thermal map at 230 V
- 60 Hz - full load
ac
- 50 Hz - full load
ac
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 25/38
Page 26

Conducted emission pre-compliance test AN4027
Table 6. Thermal maps reference points
Point Reference Description
A D1 Bridge rectifier
B L1 EMI filtering inductor
C L2 PFC inductor
D Q8 ICs supply regulator
E D4 PFC output diode
F R6 Inrush limiting NTC resistor
G Q4 Resonant low-side MOSFET
H T1 Resonant power transformer
I Q501 SR MOSFET
6 Conducted emission pre-compliance test
The following figures represent the average measurement of the conducted emission at full
load and nominal mains voltages. The EN55022 Class-B limit relevant to average
measurements is indicated in red on the diagrams. In all test conditions the measurements
are significantly below the limits.
Figure 31. CE average measurement at
115 V
- 60 Hz and full load
ac
AM11633v1
Figure 32. CE average measurement at
230 Vac - 50 Hz and full load
AM116
34v1
26/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 27

AN4027 Bill of material
7 Bill of material
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material
Part number / part
Des.
C1 470N-X2 X2 - film cap - B32922C3474K EPCOS 9.0 × 18.0 p15 mm
C2 2N2-Y1 Y1 safety cap. CD12-E2GA222MYGSA EPCOS p10 mm
C3 2N2-Y1 Y1 safety cap. CD12-E2GA222MYGSA EPCOS p10 mm
C4 470N-X2 X2 - film cap. B32922C3474K EPCOS 9.0 × 18.0 p15 mm
C5 470N - 520V 520 V - film cap. - B32673Z5474K EPCOS 7.0 x 26.5 p22.5mm
C6 330N 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C7 100N 100 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX PTH
C8 10 µF-50 V Aluminium Elcap - YXF series - 105 °C Rubycon Dia 5.0 x 11 mm
C9 100 µF - 450 V Aluminium Elcap - UPZ series - 105 °C Nichicon Dia 18 x 32 mm
C10 1N0 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C11 2N2 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C12 1µF 25 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
value
Description Supplier Case
C13 680N 25 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C14 68N 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C15 47 µF-50 V Aluminium Elcap - YXF series - 105 °C Rubycon Dia 6.3 x 11 mm
C16 2N2 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C17 330 pF 50 V - 5 % - C0G - CERCAP AVX SMD 0805
C18 4µF 25 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C19 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C20 2N2-Y1 Y1 safety cap. CD12-E2GA222MYGSA EPCOS p10mm
C21 2N2-Y1 Y1 safety cap. CD12-E2GA222MYGSA EPCOS p10mm
C22 220 pF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C23 10 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C24 220 µF-50 V Aluminium Elcap - YXF series - 105 °C Rubycon Dia 10 x 16 mm
C25 1.5 nF 50V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C26 10 µF-50 V Aluminium Elcap - YXF series - 105 °C Rubycon Dia 5.0 x 11 mm
C27 220 pF-630 V 630 V CERCAP - GRM31A7U2J220JW31 Murata SMD 1206
C28 22 nF 1K V - film cap. B32652A223K EPCOS 5.0 x 18.0 p 15 mm
C29 470 µF-16 V 16 V alluminium Elcap Sanyo dia 10 x 13 p 5 mm
C30 470 µF-16 V 16 V alluminium Elcap Sanyo dia 10 x 13 p 5 mm
C32 470 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C33 1.5 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 27/38
Page 28

Bill of material AN4027
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material (continued)
Part number / part
Des.
C34 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C36 1 µF - 50 V 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C37 470 µF-16 V 16 V alluminium Elcap Sanyo DIA 10 x 13 p5 mm
C38 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C39 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C40 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 1206
C42 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C43 4N7 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C44 1.5 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C45 220 nF 25 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C47 1N0 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C48 1N0 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C49 470 µF-16 V 16 V alluminium Elcap Sanyo DIA 10 x 13 p5 mm
C50 470 µF-16 V 16 V alluminium Elcap Sanyo DIA 10 x 13 p5 mm
value
Description Supplier Case
C51 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
C52 1N0 25 V CERCAP - general purpose AVX SMD 0805
D1 GBU8J Single-phase bridge rectifier Vishay STYLE GBU
D2 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D3 1N4005 General purpose rectifier Vishay DO-41
D4 STTH5L06 Ultrafast high-voltage rectifier ST DO-201
D5 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D6 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D7 STPS140Z Power Schottky rectifier ST SOD-123
D9 STPS2H100A Power Schottky diode ST SMB
D12 BZV55-C43 Zener diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D14 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D17 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D18 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D19 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D20 BZV55-B15 Zener diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
D21 LL4148 High speed signal diode Vishay Mini Melf SOD-80
F1 FUSE T4A Fuse 4 A - Time Lag - 3921400 Littlefuse 8.5x4 p.5.08 mm
HS1 HEAT-SINK Heatsink for D1, Q1, Q3, Q4 DWG
J1 MKDS 1,5/ 3-5,08 PCB term. block, screw conn., pitch 5 mm - 3 W
28/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Phoenix
Contact
DWG
Page 29

AN4027 Bill of material
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material (continued)
Part number / part
Des.
J2 FASTON FASTON - connector DWG
J3 FASTON FASTON - connector DWG
value
Description Supplier Case
JPX
1
L1 2019.0002 Common mode choke - EMI filter Magnetica DWG
L2 1975.0004 PFC inductor - 0.31 mH - PQ26/25 Magnetica DWG
Q1 STF21NM65M5 N-channel Power MOSFET ST TO-220FP
Q2 BC857C PNP small signal BJT Vishay SOT-23
Q3 STF8NM50N N-channel Power MOSFET ST TO-220FP
Q4 STF8NM50N N-channel Power MOSFET ST TO-220FP
Q8 BC847C NPN small signal BJT Vishay SOT-23
Q9 BC847C NPN small signal BJT Vishay SOT-23
R1 6M8 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R2 5M6 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R3 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R5 75R SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R6 NTC 2R5-S237 NTC resistor B57237S0259M000 EPCOS DWG
R7 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R8 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R9 160K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
JUMPER Bare copper wire jumper DWG
R10 56K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R11 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R12 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R13 9K1 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R14 100K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R15 56K SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R16 2K7 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R17 2M2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R18 82K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R19 56K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R20 33R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R21 22R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R22 0R22
R23 0R22
RSMF1TB - metal film res. - 1 W - 2 % 250 ppm/°C
RSMF1TB - metal film res. - 1 W - 2 % 250 ppm/°C
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 29/38
AKANEOHM PTH
AKANEOHM PTH
Page 30

Bill of material AN4027
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material (continued)
Part number / part
Des.
R24 1M0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R25 56R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R26 1M0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R27 470R SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R28 33K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R29 1K0 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R30 10R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R31 20K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R32 47R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R34 8K2 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R35 180K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R36 1M8 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R37 220K SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R38 56R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
value
Description Supplier Case
R40 R68 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R41 100R
R42 1K0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R43 51R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R44 6K2 SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R45 3R3 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R46 100K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R48 47K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R49 91K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R50 12K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R51 91K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R52 1K5 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R53 2K2 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R54 0R0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R55 2K7 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R57 R002 SMD current sense resistor - ERJM1WTF2M0U Panasonic SMD 2512
R58 100K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
SFR25 axial stand. Film res. - 0.4 W - 5 % 250 ppm/°C
Vishay PTH
R59 100K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R60 10K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R63 0R0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
30/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 31

AN4027 Bill of material
Table 7. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: motherboard bill of material (continued)
Part number / part
Des.
value
R64 10Meg SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5% - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R68 5K6 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R69 24K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R70 22K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R71 1K0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R72 330K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R73 22R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R75 0R0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R76 33K SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R77 1K0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R78 33R SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
R79 270R SMD STD film res. - 1/4 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 1206
T1 1860.0069 Resonant power transformer Magnetica ETD34
U1 L6563H High-voltage startup TM PFC controller ST SO-16
Description Supplier Case
U2 L6699D Improved HV resonant controller ST SO-16
Table 8. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: daughterboard bill of material
Des.
Part number
Part value
Description Supplier Case
C501 4.7 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose Vishay SMD 0805
C502 100 nF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose Vishay SMD 0805
C503 1 µF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose Vishay SMD 0805
C504 150 pF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose Vishay SMD 0805
C505 150 pF 50 V CERCAP - general purpose Vishay SMD 0805
D501 BAS316 Fast switching signal diode ST SOD-123
D502 BAS316 Fast switching signal diode ST SOD-123
JP501 HEADER 13 13 pin connector
Q501 STK32N4LLF5 N-channel Power MOSFET ST POLAR PAK
Q502 STK32N4LLF5 N-channel Power MOSFET ST POLAR PAK
R501 10R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R502 10R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R503 10R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R504 150k SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R505 33k SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 1 % - 100 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 31/38
Page 32

PFC coil specification AN4027
Table 8. EVL6699-150W-SR demonstration board: daughterboard bill of material (continued)
Des.
R506 330R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
R507 330R SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
RX1 0R0 SMD STD film res. - 1/8 W - 5 % - 250 ppm/°C Vishay SMD 0805
U501 SRK2000 SR smart driver for LLC resonant converter ST SO8
Part number
Part value
Description Supplier Case
8 PFC coil specification
8.1 General description and characteristics
● Application type: consumer, home appliance
● Transformer type: open
● Coil former: vertical type, 6+6 pins
● Max. temp. rise: 45 ºC
● Max. operating ambient temperature: 60 ºC
● Mains insulation: n.a.
● Unit finishing: varnished.
8.2 Electrical characteristics
● Converter topology: boost, transition mode
● Core type: PQ26/25-PC44 or equivalent
● Min. operating frequency: 40 kHz
● Typical operating frequency: 120 kHz
● Primary inductance: 310 µH±10% at 1 kHz-0.25 V
●
Peak current: 5.6 Apk.
a. Measured between pins #5 and #9.
(a)
32/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 33

AN4027 PFC coil specification
8.3 Electrical diagram and winding characteristics
Figure 33. PFC coil electrical diagram
5
9
Table 9. PFC coil winding data
Pins Windings RMS current Number of turns Wire type
11 - 3 AUX 0.05 A
5 - 9 Primary 2.3 A
RMS
RMS
11
3
5 φ 0.28 mm – G2
50 50xφ 0.1 mm – G1
8.4 Mechanical aspect and pin numbering
● Maximum height from PCB: 30 mm
● Coil former type: vertical, 6+6 pins (pins 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10, 12 are removed)
● Pin distance: 3.81 mm
● Row distance: 25.4 mm
● External copper shield: not insulated, wound around the ferrite core and including the
coil former. Height is 8 mm. Connected to pin #3 by a soldered solid wire.
AM11635v1
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 33/38
Page 34

Transformer specifications AN4027
Figure 34. PFC coil mechanical aspect
8.5 Manufacturer
● Magnetica - Italy
● Inductor P/N: 1975.0004.
9 Transformer specifications
9.1 General description and characteristics
● Application type: consumer, home appliance
● Transformer type: open
● Coil former: horizontal type, 7+7 pins, two slots
● Max. temp. rise: 45 ºC
● Max. operating ambient temperature: 60 ºC
● Mains insulation: acc. to EN60065.
AM11636v1
34/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 35

AN4027 Transformer specifications
9.2 Electrical characteristics
● Converter topology: half bridge, resonant
● Core Type: ETD34-PC44 or equivalent
● Min. operating frequency: 60 kHz
● Typical operating frequency: 100k Hz
● Primary inductance: 1000 µH ±10% at 1 kHz-0.25 V
●
Leakage inductance: 100 µH ±10% at 100 kHz-0.25 V
(b)
(c)
.
9.3 Electrical diagram and winding characteristics
Figure 35. Transformer electrical diagram
2
8
9
10
11
12
4
6
13
14
7
Table 10. Transformer winding data
Pins Winding RMS current Number of turns Wire type
2 - 4 Primary 1 A
8 - 11 SEC-1A
9 -10 SEC-1B
10 - 13 SEC-2A
12 - 14 SEC-2B
6 - 7 AUX
1. Secondary windings A and B are in parallel.
2. Aux winding is wound on top of primary winding.
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
8.5 A
8.5 A
8.5 A
8.5 A
0.05 A
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
34 30 x ∅ 0.1 mm – G1
290 x ∅ 0.1 mm – G1
290 x ∅ 0.1 mm – G1
290 x ∅ 0.1 mm – G1
290 x ∅ 0.1 mm – G1
3 ∅ 0.28 mm – G2
AM11637v1
b. Measured between pins 2-4.
c. Measured between pins 2-4 with only half secondary winding shorted at a time.
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 35/38
Page 36

Transformer specifications AN4027
9.4 Mechanical aspect and pin numbering
● Maximum height from PCB: 30 mm
● Coil former type: horizontal, 7+7 pins (pins #3 and #5 are removed)
● Pin distance: 5.08 mm
● Row distance: 25.4 mm.
Figure 36. Transformer overall drawing
9.5 Manufacturer
● Magnetica - Italy
● Transformer P/N: 1860.0069.
36/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
Page 37

AN4027 Revision history
10 Revision history
Table 11. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
19-Jul-2012 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 022604 Rev 1 37/38
Page 38

AN4027
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
38/38 Doc ID 022604 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...