AN3352
Application note
Dual LNB power supply based on the LNBH24L
supply and control IC with step-up and I²C interface
Introduction
This application note is intended to provide additional information and suggestions for the
correct use of the LNBH24L device. All waveforms shown are based on the demonstration
board order code STEVAL-CBL008V1 described in Section 3.
The LNBH24L is an integrated solution for supplying/interfacing two independent LNB
down-converters in antenna dishes and/or multi-switch box. It gives good performance in a
simple and cheap way, with minimum external components necessary. It includes all
functions needed for LNB supplying and interfacing, in accordance with international
standards. Moreover, it includes an I²C bus interface and, thanks to a fully integrated step-up
DC-DC converter, it functions with a single input voltage supply ranging from 8 V to 15 V.
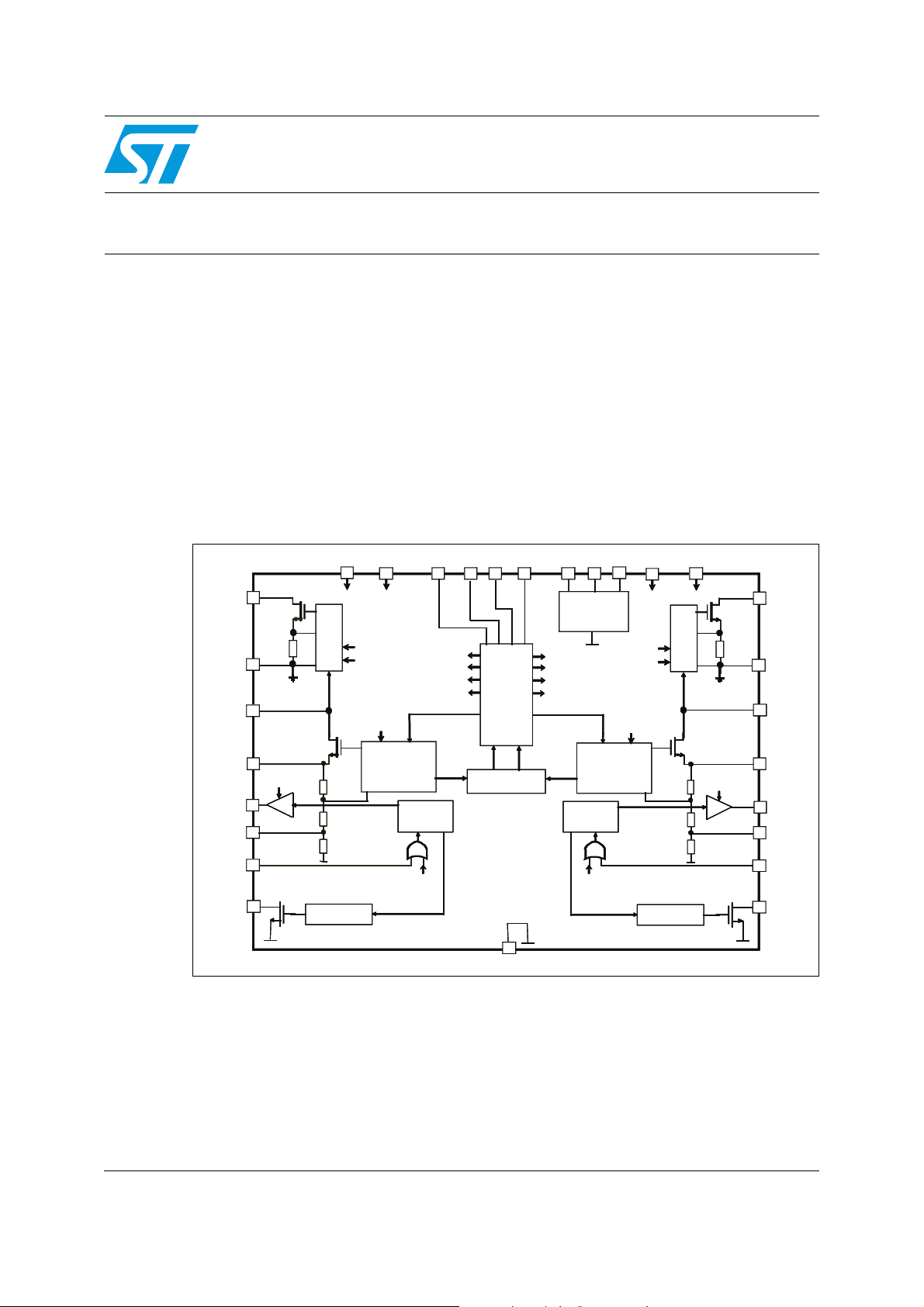
Figure 1. LNBH24L internal block diagram
TTX-
ADDR-
ISEL-
A
A
-
A
SDA SCL
ADDR -
- -- - -
BypVcc
B
Vcc-
L
ISEL-
TTX-
B
B
LX -
-
A
Rsense
P-GND-
- -
A
Vup-
-
A
VoRX-
-
A
A
TTX-
VoTX-
-
A
EXTM-
-
A
DSQIN -
-
A
-
PDC
A
PWM
Controller
Pull Down
Controller
A
EN-
A
VSEL-
A
ISEL-
Linear Post-reg
+Protections
+Diagnostics
FB
FBFBFB
TEN-
EN-
VSEL-
TTX-
VOUT-AControl
-
-
22 kHz
Oscillato r
A
TEN-
A
-
A
-
A
-
A
-
I²C Di agnostics
²
LNBH24L
A-GND
C interface
²
I
I
-
Preregul ator
+U.V.lockout
+P.ON reset
B
B
TEN-
B
EN-
-
B
-
VSEL-
B
TTX-
-
VOUT-BControl
-
Linear Post-reg
+Protections
+Diagnostics
22 kHz
Oscillato r
TEN-
TEN-
PWM
Rsense
B
EN-
B
VSEL-
B
ISEL-
-
FB
FB
B
B
Pull Down
Controller
Rsense
Controller
B
TTX-
AM09362v1
LX -B
-
P-GND-
Vup-
-
B
VoRX-
VoTX-B
EXTM-B
DSQIN -
-
-
PDC
B
-
B
-
-
-
B
B
November 2011 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 1/26
www.st.com

Contents AN3352
Contents
1 Block diagram and pin function description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Step-up controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Pre-regulator block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3 I²C interface and diagnostic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.4 DiSEqC™ 1.X implementation through EXTM pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.5 DiSEqC 1.X implementation through VoTX and EXTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.6 PDC optional circuit for DiSEqC 1.X applications using VoTX signal
on to EXTM pin and 22 kHz tone controlled by DSQIN pin . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.7 22 kHz oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.8 DiSEqC communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.9 Linear post-regulator, modulator and protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.10 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 Component selection guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1 DC-DC converter inductor (L1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2 Output current limit selection (R2-RSEL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.3 DC-DC converter Schottky diode (D1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.4 TVS diode (D6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.5 DC-DC output capacitors (C3, C4, C6) and ferrite bead . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.6 Input capacitors (C1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.7 PDC optional external circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.8 EXTM-VOTX resistor (R9) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.9 Undervoltage protection diode (D2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3 Layout guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.1 PCB layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2 PCB Thermal managing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4 Startup procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. LNBH24L I²C addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 2. Output load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 3. LNBH24L pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 4. LNBH24L demo-board BOM list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 5. Recommended Inductors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6. Recommended Schottky diode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 7. Recommended LNBTVS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 8. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 3/26

List of figures AN3352
List of figures
Figure 1. LNBH24L internal block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. EXTM example of use with 22 kHz IC controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 3. DiSEqC 1.X tone burst with 22 kHz IC controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 4. DiSEqC timing control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 5. LNBH24L pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 6. LNBH24L typical application circuit with internal tone generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 7. Typical output current limiting vs. RSEL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 8. Example of LNBTVS diode connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 9. DC-DC converter output stage with ferrite bead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 10. Application circuit with PDC optional solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 11. PDC optional circuit load calculation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 12. PDC circuit waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 13. Tone amplitude vs. R9 value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 14. PBC top layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 15. PBC bottom layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 16. PCB components layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 17. PCB connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Block diagram and pin function description
1 Block diagram and pin function description
Here below a description of the LNBH24L internal blocks that includes two completely
independent sections. Except for the V
controlled and contain independent external components. All the specifications below must
be considered equal for both sections (A/B).
1.1 Step-up controller
The LNBH24L features a built-in step-up DC-DC converter that, from a single supply source
ranging from 8 V to 15 V, generates the voltages that allow the linear post-regulator to work
with minimum power dissipation. The external components of the DC-DC converter are
connected to the LX and V
UP
1.2 Pre-regulator block
This block includes a voltage reference connected to the BYP pin, an undervoltage lockout
circuit, intended to disable the whole circuit when the supplied V
threshold (6.7 V typ), and a power-on reset that sets all the I²C registers to zero when the
V
is turned on and rises from zero above the “ON” threshold (7.3 V typ).
CC
pins (see Figure 6). No external power MOSFET is needed.
and I²C inputs, each circuit can be separately
CC
drops below a fixed
CC
1.3 I²C interface and diagnostic
The main functions of the device are controlled via the I²C bus by writing 5 bits on the
system register (SR bits in write mode). In the same register there are 5 bits that can be
read back (SR bits in read mode) and provide 2 diagnostic functions, whereas the other 3
bits are for internal use (TEST1, TEST2, and TEST3).
Two bits report the diagnostic status of the two internal monitoring functions:
– OTF: overtemperature flag. If an overheating occurs (junction temperature exceeds
150 °C), the OTF I²C bit is set to “1”.
– OLF: overload flag. If the output current required exceeds the current limit threshold
or a short-circuit occurs, the OLF I²C bit is set to “1”.
Moreover, three bits report the last output voltage register status (EN, VSEL, LLC) received
by the I²C. The LNBH24L I²C interface address can be selected from two different
addresses for each section A/B by setting the voltage level of the relevant ADDR pin
according to Ta bl e 1 :
Table 1. LNBH24L I²C addresses
Section Pin Set-up Write (HEX) Read (HEX)
A
B
ADDR-A=low or floating 10 11
ADDR-A=high 12 13
ADDR-B=low or floating 14 15
ADDR-B=high 16 16
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 5/26

Block diagram and pin function description AN3352
1.4 DiSEqC™ 1.X implementation through EXTM pin
The EXTM pin is an analog input to generate the 22 kHz tone superimposed to the V
output voltage. If the EXTM pin is used, the internal 22 kHz generator must be kept OFF
(TTX pin or TTX bit set LOW). A cheaper circuit must be used to couple the modulating
signal source to the EXTM pin (see Figure 2).
The EXTM pin modulates the V
V
(AC) = V
oRX
where:
–V
oRX
and EXTM pin
–G
EXTM
In order to avoid the 22 kHz tone distortion, a dummy output load may be necessary, strictly
dependent on the output bus capacitance.
Table 2. Output load
Output bus capacitance Output load
< 50 nF 10 mA
250 nF (EUTELSAT spec.) 30 mA
750 nF (DIRECT TV spec.) 80 mA
voltage through the series decoupling capacitor, so that:
oRX
(AC) x G
EXTM
(AC) and V
EXTM
(AC) are, respectively, the peak-to-peak voltage on the V
EXTM
is the voltage gain from EXTM to V
oRX
DC
oRX
oRX
.
For the correct DiSEqC implementation, during tone transmission, it is most important that
the DiSEqC_out pin of the 22 kHz IC controller, is set in low impedance and vice versa,
during no-tone transmission, it must be set in high impedance.
Figure 2 shows an example circuit as an appropriate solution with a 22 kHz IC controller to
drive the EXTM pin for the DiSEqC implementation.
Figure 2. EXTM example of use with 22 kHz IC controller
VDD 3V3
22 KHz IC
controller
DISEQC_OUT
PD
R
Vtone signal
R2
R3
15 K
R1
C1
1µF
LNBH24L
EXTM pin
EXTM
Z
VoRX
VoRx OUTPUT
AM09363v1
6/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3
AN3352 Block diagram and pin function description
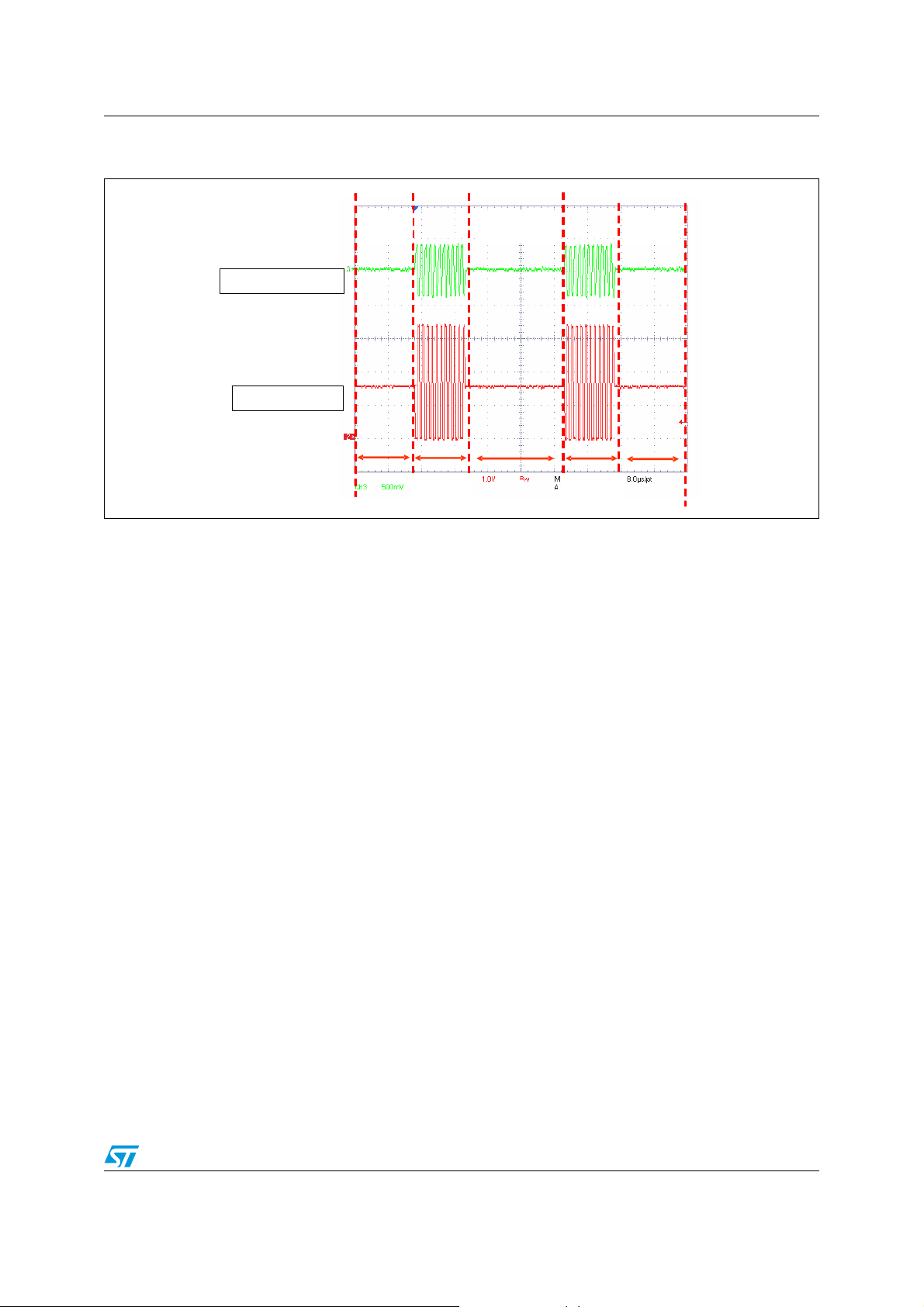
Figure 3. DiSEqC 1.X tone burst with 22 kHz IC controller
High-Z
VoRx OUTPUT
VoRx OUTPUT
Vtone signal
Vtone signal
High-Z
STATE
STATE
Push -pull
Push -pull
Action
Action
High-Z
High-Z
STATE
STATE
Push -pull
Push -pull
1.5 DiSEqC 1.X implementation through V
If an external 22 kHz tone source is not available, it is possible to use the internal 22 kHz
tone generator signal available through the V
V
22 kHz signal is superimposed to the V
oTX
kHz tone (see Figure 6). The internal 22 kHz tone generator, available through the V
must be activated during the 22 kHz transmission by the DSQIN pin or by the TEN bit. The
DSQIN internal circuit activates the 22 kHz tone on the V
delay from the TTL signal present on the DSQIN pin, and it stops with 1 cycle ± 25 µs delay
after the TTL signal has expired. The V
oTX
the TTX function. This can be controlled both through the TTX pin and the I²C bit. As soon
as the tone transmission has expired, the V
The 13/18 V power supply is always provided to the LNB from the V
pin to drive the EXTM pin. In this way the
oTX
DC voltage to generate the LNB output 22
oRX
pin internal circuit must be preventively set ON by
must be disabled by setting the TTX to LOW.
oTX
High-Z
High-Z
STATE
STATE
Action
Action
and EXTM
oTX
output with 0.5 cycles ± 25 µs
oTX
pin.
oRX
oTX
pin,
1.6 PDC optional circuit for DiSEqC 1.X applications using V
signal on to EXTM pin and 22 kHz tone controlled by DSQIN
pin
In some applications, at light output current (< 50 mA), having a heavy LNB output
capacitive load, the 22 kHz tone can be distorted. In this case it is possible to add the
“Optional” external components described on Section 2.7.
1.7 22 kHz oscillator
The internal 22 kHz tone generator is factory-trimmed in accordance with current standards
and can be selected by the I²C interface TTX bit (or TTX pin) and controlled by the DSQIN
pin (TTL compatible), which allows immediate DiSEqC data encoding. If the 22 kHz tone
presence is requested in continuous mode, the internal oscillator can be activated by the I²C
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 7/26
oTX

Block diagram and pin function description AN3352
interface TEN bit. The rise and fall edges are controlled to be in the 5 µs to 15 µs range, 8 µs
typ for 22 kHz. The duty cycle is 50% typ., it modulates the DC output with a 0.650 V
PP
(typ.)
amplitude as well as the DSQIN pin.
1.8 DiSEqC communication
The following steps must be taken to ensure the correct implementation of the DiSEqC
communication:
Figure 4. DiSEqC timing control
LNBout
LNBout
DSQIN
DSQIN
> 500µs
> 500µs
µ
µ
> 200 µs
> 200 µs
TTX
TTX
2
1
1
T
0
0
T
T
● T0: before starting the DiSEqC transmission. The TTX function must be activated
T
DiSEqC Transmit Mode
DiSEqC Transmit Mode
2
3
3
T
T
T
T
DiSEqC Receive Mode
DiSEqC Receive Mode
(through the TTX pin or TTX I²C bit)
● T1: after 500 µs minimum, the IC is ready to receive the DiSEqC code through the
DSQIN pin (or, alternatively, the TEN I²C bit can be set to HIGH to activate the 22 kHz
burst)
● T2: when the transmission has elapsed, the TTX function is set to LOW (through the
TTX pin or TTX I²C bit) not earlier than 200 µsec after the last falling edge of the
DiSEqC code.
1.9 Linear post-regulator, modulator and protection
The output voltage selection and the current selection commands join this block, which
manages the LNB output function. This block gives feedback to the I²C interface from the
diagnostic block, regarding the status of the thermal protection, overcurrent protection, and
output settings.
1.10 Pin description
The LNBH24L is available in an exposed pad QFN-32 package for surface mount assembly.
Figure 5 shows the device pinout and Tab le 3 briefly summarizes the pin function.
8/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Block diagram and pin function description
Figure 5. LNBH24L pin configuration
Table 3. LNBH24L pin description
QFN 5x5
pin n°
21 V
20 V
5/2
16/25
18/23
17/24
Symbol Name Pin function
CC
CC
LX-A /
LX-B
V
UP
V
UP
V
oRX
V
oRX
V
oTX
V
oTX
-A/
-B
-A/
-B
-A/
-B
Supply input 8 to 15 V IC DC-DC power supply
Supply input 8 to 15 V analog power supply
NMos drain Integrated N-channel power MOSFET drain
Input of the linear post-regulator. The voltage on this pin is monitored
Step-up voltage
by the internal step-up controller to keep a minimum dropout across
the linear pass transistor.
LDO output port Output of the linear post-regulator
Output port during
22 kHz tone TX
TX output to the LNB
6 SDA Serial data Bi-directional data from/to the I²C bus
7 SCL Serial clock Clock from the I²C bus
This pin accepts the DiSEqC code from the main microcontroller. The
LNBH24L uses this code to modulate the internally-generated 22 kHz
carrier. Set this pin to ground if not used.
10/31
DSQIN-A/
DSQIN-B
DiSEqC input
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 9/26

Block diagram and pin function description AN3352
Table 3. LNBH24L pin description (continued)
12/29
TTX-A/
TTX-B
TTX enable
11/30 Reserved Reserved To be connected to GND
This pin, as well as the TTX I²C bit of the system register, is used to
control the TTX function enable before starting the 22 kHz tone
transmission. Set this pin floating or to GND if not used.
9/32
13/28
PDC-A/
PDC-B
EXTM-A/
EXTM-B
Pull-down control
External modulation
4/3 P-GND Power ground
ePad ePad ePad
To be connected to the external NPN transistor base to reduce the 22
kHz tone distortion in case of heavy capacitive load at light output
current. If not used it can be left floating.
External Modulation Input acts on V
linear regulator output to
ORX
superimpose an external 22 kHz signal. Needs DC decoupling to the
AC source. If not used it can be left floating.
DC-DC converter power ground to be connected directly below the
ePad of the PCB top GND layer
On the bottom side of the QFN-32 package. It must be connected with
power ground and to the ground layer through vias to dissipate heat.
22 A-GND Analog ground Analog circuits ground
Needed for internal pre-regulator filtering. The BYP pin is intended
19 BYP Bypass capacitor
only to connect an external ceramic capacitor. Any connection of this
pin to an external current or voltage sources may cause permanent
damage to the device.
8/1
15/26
ADDR-A/
ADDR-B
ISEL-A/
ISEL-B
Address setting Two I²C bus addresses available by setting the ADDR pin voltage level
connected between I
SEL
SEL
Current selection
The resistor R
linear regulator current limit threshold by the equation: I
10000 / R
SEL
14/27 Reserved Reserved To be left floating. Do not connect to GND.
and GND defines the
(typ.) =
max
10/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Component selection guidelines
V
V
V
V
2 Component selection guidelines
The LNBH24L application schematic in Figure 6 shows the typical configuration for a single
LNB power supply.
Figure 6. LNBH24L typical application circuit with internal tone generator
Vup
Vup
Vup
Vup
C3
C3
C3
C3C3
C3C3
in
in
in
in
12V
12V
12V
12V
C1
C1
C1
C1
C3C3C3C3C3
D1
D1D1
D1
D1D1
L1
L1
L1
L1
Tone Enabl e control
Tone Enabl e control
Tone Enabl e control
TTL
TTL
TTL
C8
C8
C8
C8
C8
C8
220nF
220nF
220nF C8220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF C8220nF
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
2.2µF
2.2µF
2.2µF
I2C Bus
I2C Bus
I2C Bus
LX
LX
LX
LX
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
SDA
SDA
SDA
{
{
{
SCL
SCL
SCL
ADDR
ADDR
ADDR
TTX
TTX
TTX
DSQIN
DSQIN
DSQIN
D3
D3D3
D3
D3D3
LNBH24L
LNBH24L
(sections A/B)
(sections A/B)
P-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GNDP-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GNDP-GND A-GND
VoTX
VoTX
EXTM
EXTM
EXTM
EXTM
VoRX
VoRX
VoRX
VoRX
PDC
PDC
PDC
PDC
EXTM
EXTM
ISEL
ISEL
Byp
Byp
R9
R9R9
R9
R9R9
2KOhm
2KOhm
C10
C10
C10
C10
C10
C10
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
C11
C11
220nF
220nF
C15
C15
C15
C15
47 nF
47 nF
47 nF
47 nF
D4
D4D4
D2D2D2
D2D2D2D2D2D2
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
15kOhm
15kOhm
to LNB
to LNB
to LNB
to LNB
500mA max
500mA max
500mA max
500mA max
Note: TVS D6 diode to be used if surge protection is required (see Section 2.4).
Table 4. LNBH24L demonstration board BOM list
Index Quantity Reference Value / generic part number Package
1 2 RSELA, RSELB 15 kΩ 1/8 W (see Section 2.2) 1206
2 2 R5A, R5B 2.2 kΩ 1/8 W (see Section 2.7) 1206
3 2 R7A, R7B 22 Ω 1/2 W (see Section 2.7) 1206
4 2 R8A, R8B 150 Ω 1/2 W (see Section 2.7) 1206
5 2 R9A, R9B 1.5 kΩ 1/8 W (see Section 2.8) 1206
6 4 C8, C10A, C10B, C11 0.22 µF 1206
7 2 C15A, C15B 47 nF 1206
8 2 C14A, C15B 1 nF 1206
9 2 C4A, C4B, C6A, C6B 0.47 µF (see Section 2.5) 1206
10 1 C1
100 µF > 25 V ESR = 150 mΩ − 350 mΩ higher
value is suitable (see Section 2.6)
El.Al. Radial
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 11/26

Component selection guidelines AN3352
Table 4. LNBH24L demonstration board BOM list (continued)
Index Quantity Reference Value / generic part number Package
11 2 C3A, C3B
12 2 L1A, L1B 22 µH inductor with I
220 µF > 25 V ESR = 50 mΩ − 350 mΩ (see
Section 2.5)
SAT
> I
(see Section 2.1)Radial
PEAK
El.Al. Radial
13 2 D1A, D2B STPS130A (see Section 2.3)SMB
14 2 D2A, D2B STPS130A (see Section 2.9)SMB
15 2 D3A, D3B S1A or equivalent SMB
16 2 D4A, D4B
BAT54, STPS130A, BAT43, 1N5818, or similar
Schottky diode with V
RRM
> 20 V.
SOD123
17 1 IC1 To be placed as close as possible to EXTM pin QFN32
18 2 TR1A, TR1B BC817 SOT23-3L
19 2 D8A, D8B LL4148 MINIMELF
20 3 CN3, CN6, CN7 Strip 4p M HDR1X4
CN1, CN4, CN5,
21 9
JP1-A, JP1-B, JP2-A,
JP2-B, LNBOUT-A,
Strip 2p M HDR1X2
LNBOUT-B
2.1 DC-DC converter inductor (L1)
The LNBH24L operates with a standard 22 µH inductor for the entire range of supply
voltages and load current. The inductor saturation current rating (where inductance is
approximately 70% of zero current inductance) must be greater than the switch peak current
(I
> I
SAT
– maximum load (I
– minimum input voltage (V
– maximum DC-DC output voltage (V
In this condition the switch peak current is calculated using the formula in Equation 1:
) calculated at:
PEAK
OUTmax
)
INmin
)
UPmax
= V
OUTmax
+ 0.75 V typ.)
Equation 1
maxmax*
Ipeak
IO UTVUP
min*
VINEff
where:
– Eff is the efficiency of the DC-DC converter (93% typ. at highest load)
– L is the inductance (22 µH typ.)
– F is the PWM frequency (220 kHz typ.)
Example:
Application conditions:
V
OUTmax
V
INmin
12/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3
= 19.2 V (supposing EN=VSEL=1, LLC=0)
= 11 V
VIN
min
⎛
−+=
1
⎜
2
LF
⎝
VIN
VUP
min
max
⎞
⎟
⎠

AN3352 Component selection guidelines
V
I
UPmax
OUTmax
= V
OUTmax
= 500 mA
+ V
DROP
Eff = 90% (worst-case in these conditions)
Based on Equation 1 and the preceding application conditions, I
Equation 2
Ipeak
=
Then, in this example, an inductor with saturation current > 1.52 A should be recommended.
Several inductors suitable for the LNBH24L are listed in Ta bl e 5 , although there are many
other manufacturers and devices that can be used. Consult each manufacturer for more
detailed information and for their entire selection of related parts, as many different shapes
and sizes are available. Ferrite core inductors should be used to obtain the best efficiency.
Choose an inductor that can handle at least the I
that the inductor has a low DCR (copper wire resistance) to minimize power losses and,
consequently, to maximize the total efficiency.
Table 5. Recommended Inductors
= 19.2 V + 0.75 V = 19.95 V
−
11
current without saturating, and ensure
PEAK
5.095.19
∗
119.0
∗
is:
PEAK
11
⎛
1
−+
⎜
36
10*220*10*22*2
⎝
⎞
⎟
95.19
⎠
A52.1
=
Vendor Part number I
Sumida
To ko
Panasonic
Coilcraft
CD104-220MC
RHC110-220M
822LY-220K
824LY-220K
A671HN-220L
A814LY-220M
ELC08D220E
ELC10D220E
DC1012-223
PVC-0-223-03
DO3316P-223
(A) DRC (m?) Mounting type
SAT
1.6
2.4
1.3
1.72
2.44
2.0
1.8
3.2
2.5
3
2.6
67
88
70
76
21
75
51
40
46
35
85
2.2 Output current limit selection (R2-RSEL)
The linear regulator current limit threshold can be set through an external resistor connected
to the I
equation:
Equation 3
pin. The resistor value defines the typical output current threshold limit by the
SEL
10000
Aax
)(Im =
Rsel
SMD
Through-hole
Through-hole
Through-hole
Through-hole
SMD
Through-hole
Through-hole
Through-hole
Through-hole
SMD
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 13/26

Component selection guidelines AN3352
=+=
=−=
=+=
where R
limit threshold is 0.650 A typ. with R
is the resistor connected between I
SEL
SEL
= 15 kΩ.
and GND. The highest selectable current
SEL
To set the current limitation, ±15% tolerance, referred to the typical I
be considered. At this tolerance, the tolerance of the R
resistor must be added.
SEL
For example:
resistor = 15 kΩ ± 1%
R
SEL
10000
To calculate the I
max(min.)
and I
max(max.)
)typ(axIm ==
15000
values:
mA666
%16%1%15ceTotToleran
where:
– 15% is the LNBH24L tolerance
– 1% is the R
tolerance
SEL
and then:
mA559%16mA666(min)axIm
current value, must
max
Figure 7. Typical output current limiting vs. R
1.4
1.4
1.2
1.2
0.8
0.8
[mA]
[mA]
0.6
0.6
MAX
MAX
I
I
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
VCC=12V
VCC=12V
1
1
0
0
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
The formula below allows correct dimensioning of the R
R
R
SEL
SEL
SEL
[K ]
[K ]
mA772%16mA666(min)axIm
total power dissipation:
SEL
14/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Component selection guidelines
)I(RselΩ=
V1
)(Rsel
supposing:
R
resistor = 15 kΩ
SEL
V1
Ω
)(15000
W
RSEL
= R
SEL(I)
2
x R
)I(Rsel μ=
=
= (66 µA) 2 x 15000 = 65 µW
SEL
2.3 DC-DC converter Schottky diode (D1)
In typical application conditions it is beneficial to use a 1 A Schottky diode which is suitable
for the LNBH24L DC-DC converter. Taking into account that the DC-DC converter Schottky
diode must be selected depending on the application conditions (V
Schottky diode such as the STPS130A is suitable.
The average current flowing through the Schottky diode is lower than I
calculated by
output current, a Schottky diode capable of supporting the I
can be calculated using
Equation 4. In worst-case conditions, such as low input voltage and higher
Equation 1.
A66
> 25 V), in general a
RRM
PEAK
should be selected. I
PEAK
and can be
PEAK
Equation 4
Table 6. Recommended Schottky diode
STMicroelectronics
Vendor Part number IF (av) VF (max.)
1N5818 1 A 0.50 V
1N5819 1 A 0.55 V
STPS130A 1 A 0.46 V
STPS1L30A 1 A 0.30 V
STPS2L30A 2 A 0.45 V
1N5822 3 A 0.52 V
STPS340 3 A 0.63 V
STPS3L40A 3 A 0.5 V
2.4 TVS diode (D6)
The LNBH24L device is directly connected to the antenna cable in a set-top box.
Atmospheric phenomenon can cause high voltage discharges on the antenna cable causing
Vout
IoutId ×=
Vin
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 15/26

Component selection guidelines AN3352
damage to the attached devices. In applications where it is required to protect against
lightning surges, transient voltage suppressor (TVS) devices like the LNBTVSx-22xx can be
used to protect the LNBH24L and the other devices electrically connected to the antenna
cable.The LNBTVSx-22xx diodes, developed by STMicroelectronics, are dedicated to
lightning and electrical overstress surge protection for LNBHxx voltage regulators. These
protection diodes were designed to comply with the stringent IEC61000-4-5 standard with
surges up to 500 A in a whole range of products.
Note: TVS diodes have intrinsic capacitance that attenuates the RF signal. For this reason, the
LNBTVSx-22xx cannot be directly connected to the I
(RX/TX) cable connector that carries
F
the RF signals coming from the LNB. To suppress effects of the intrinsic capacitance, an
inductance must be placed in series with the TVS diode (see Figure 6 example). The goal of
the L series inductance added to the CLNBTVS is to be transparent at 22 kHz and to reject
frequencies higher than 900 MHz.The value of the series inductance is usually >13 nH, with
a current capability higher than the I
Figure 8. Example of LNBTVS diode connection
D3
1N4007
(peak pulse current) expected during the surge.
PP
LNBH24L
The selection of the TVS diode must be based on the maximum peak power dissipation that
the diode is capable of supporting.
Table 7. Recommended LNBTVS
Vendor Part number VBR
STMicroelectronics
VoTX
EXTM
VoRX
C10
C10
R9
R9
C15
D2
D2
IF Connector
Lseries >13nH
D6
LNBTVSx -22xx
(V) Ipp (A) 8/20 µs
TYP
LNBTVS4-220S 23.1 334
LNBTVS4-221S 23.1 334
LNBTVS4-222S 23.1 334
LNBTVS6-221S 23.1 500
Select the TVS diode which is capable of supporting the required Ipp (A) value indicated in
Ta bl e 7 .
16/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Component selection guidelines
2.5 DC-DC output capacitors (C3, C4, C6) and ferrite bead
An electrolytic low cost capacitor is needed on the DC-DC converter output stage (C3 in
Figure 6). Moreover, two ceramic capacitors are recommended to reduce the high
frequency switching noise. The switching noise is due to the voltage spikes of the fast
switching action of the output switch, and to the parasitic inductance of the output
capacitors. To minimize these voltage spikes, special low-inductance ceramic capacitors
can be used, and their lead lengths must be kept short and as close as possible to the IC
pins (C4 and C6 in
the C6 capacitor up to 4.7 µF, 2.2 µF is a good compromise to reduce the switching noise.
Figure 9. DC-DC converter output stage with ferrite bead
Figure 9). In the case of high switching noise, it is possible to increase
The most important parameter for the DC-DC output electrolytic capacitors is the effective
series resistance (ESR). The DC-DC converter control loop circuit has been designed to
work properly with low-cost electrolytic capacitors which have ESR in the range of 200 mΩ.
A 220 µF with ESR between 100 mΩ and 350 mΩ is a good choice in most application
conditions. If it is requested to further reduce the switching noise, a ferrite bead with a
current rating of at least 2 A and impedance higher than 60 Ω at 100 MHz may be used.
In this case, it is recommended to use two electrolytic capacitors of 100 µF (see C3 and C3A
in
Figure 9) with ESR between 150 mΩ and 350 mΩ adding the ferrite bead in accordance
Figure 9.
to
The DC-DC capacitor's voltage rating must be at least 25 V, but higher voltage capacitors
are recommended.
2.6 Input capacitors (C1)
An electrolytic bypass capacitor (C1 in Figure 6) between 100 µF and 470 µF, located close
to the LNBH24L, is needed for stable operation. In any case, a ceramic capacitor (C2 in
Figure 6) between 100 nF and 470 nF is recommended to reduce the switching noise at the
input voltage V
CC
pins.
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 17/26

Component selection guidelines AN3352
V
V
V
V
2.7 PDC optional external circuit
This optional circuit, internally controlled by the PDC output pin, acts as an active pull-down
discharging the output capacitance only when the internal 22 kHz tone is activated
(TEN=TTX=1 or DSQIN=1).
This optional circuit is not needed in standard applications having I
capacitive load up to 250 nF where the PDC pin can be left floating.
Figure 10. Application circuit with PDC optional solution
D3
D3D3
D3
D3D3
Vup
Vup
Vup
Vup
C3
C3
C3
C3C3
C3C3
in
in
in
in
12V
12V
12V
12V
C1
C1
C1
C1
C3C3C3C3C3
D1
D1D1
D1
D1D1
L1
L1
L1
L1
Tone Enable control
Tone Enable control
Tone Enable control
TTL
TTL
TTL
C8
C8
C8
C8
C8
C8
220nF
220nF
220nF C8220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF C8220nF
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
2.2µF
2.2µF
2.2µF
I2C Bus
I2C Bus
I2C Bus
EXTM
EXTM
EXTM
LNBH24L
LNBH24L
(sections A/B)
(sections A/B)
LX
LX
LX
LX
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
Vcc-L
SDA
SDA
SDA
{
{
{
SCL
SCL
SCL
ADDR
ADDR
ADDR
TTX
TTX
TTX
DSQIN
DSQIN
DSQIN
P-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GNDP-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GND
P-GND A-GNDP-GND A-GND
EXTM
VoRX
VoRX
VoRX
VoRX
VoTX
VoTX
VoTX
VoTX
PDC
PDC
PDC
PDC
ISEL
ISEL
ISEL
ISEL
ISEL
ISEL
Byp
Byp
Byp
Byp
Byp
Byp
Byp
Byp
R9
R9R9
R9
R9R9
2KOhm
2KOhm
C15
C15
C15
C15
47 nF
47 nF
47 nF
47 nF
D4
D4D4
C10
C10
C10
C10
C10
C10
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
*R5
*R5
*R5
*R5
2.2K Ohm
2.2K Ohm
2.2K Ohm
2.2K Ohm
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
C11
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
220nF
3.3V
3.3V
3.3V
3.3V
> 50 mA and
OUT
D2
D2D2
D2
D2D2
D8
D8
1N4148
1N4148
*C14
*C14
*C14
*C14
1nF
1nF
1nF
1nF
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
R2 (RSEL)
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
15kOhm
to LNB
to LNB
to LNB
to LNB
500mA max
500mA max
500mA max
500mA max
*R8
*R8
*R8
*R8
150 Ohm
150 Ohm
150 Ohm
150 Ohm
*TR1
*TR1
*TR1
*TR1
*R7
*R7
*R7
*R7
22 Ohm
22 Ohm
22 Ohm
22 Ohm
(*)OPTIONAL components.
(*)OPTIONAL components.
(*)OPTIONAL components.
(*)OPTIONAL components.
(*)OPTIONAL components.
(*)OPTIONAL components.
To be used only in case
To be used only in case
To be used only in case
To be used only in case
To be used only in case
To be used only in case
of heavy capacitive load
of heavy capacitive load
of heavy capacitive load
of heavy capacitive load
of heavy capacitive load
of heavy capacitive load
The formula to calculate the transistor IC current with PDC circuit is:
Equation 5
--
--
V
BYP
BYP
R
R
+
+
7
7
V
V
V
D
D
R
R
5
5
TR1hfe
TR1hfe
BE
BE
V
V
=
=
I
I
C
C
The current flows through R8, TR1, and R7 during fall time of 22 kHz tone and the power
dissipated by these passive components is 1/3 because the D.C. is 30% (see
18/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3
Figure 11).

AN3352 Component selection guidelines
Figure 11. PDC optional circuit load calculation
Figure 12. PDC circuit waveform
2.8 EXTM-V
resistor (R9)
OTX
The LNBH24L device offers the possibility to customize the output tone amplitude through
the R9 resistor variation. According to the graph in
modified to change the output tone amplitude when the internal 22 kHz tone generator is
used. Values between 1 kΩ and 2.7 kΩ are recommended.
Figure 13, the R9 resistor can be slightly
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 19/26

Component selection guidelines AN3352
Figure 13. Tone amplitude vs. R9 value
0.9
0.85
0.8
0.75
0.7
0.65
0.6
0.55
0.5
0.45
0.4
Tone Amplitude (Vpp)
0.35
0.3
0.511.522.533.544.5
R9 value (kohm)
2.9 Undervoltage protection diode (D2)
During a short-circuit event on the LNB output, negative voltage spikes may occur on the
pin. To prevent reliability problems, a low-cost Schottky diode with low VF clamping
V
oRX
voltage is used between this pin and GND (see D2 in
the protection diode cathode as close as possible to the V
Figure 6). It is recommended to place
pin.
oRX
20/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Layout guidelines
3 Layout guidelines
Due to high current levels and fast switching waveforms, which radiate noise, a proper
printed circuit board (PCB) layout is essential. Sensitive analog grounds can be protected by
using a star ground configuration. Also, lead lengths should be minimized to reduce stray
capacitance, trace resistance, and radiated noise. Ground noise can be minimized by
connecting GND, the input bypass capacitor ground lead, and the output filter capacitor
ground lead to a single point (star ground configuration). Place input bypass capacitors (C1,
C2, and C8) as close as possible to V
and C6) as close as possible to V
undervoltage protection circuitry, resetting the I²C internal registers. If this occurs, the
registers are set to zero and the LNBH24L is put into shutdown mode.
An LNB power supply demonstration board is available.
3.1 PCB layout
Any switch-mode power supply requires a good PCB layout in order to achieve maximum
performance. Component placement and GND trace routing and width, are the major
issues. Basic rules commonly used for DC-DC converters for good PCB layout should be
followed. All traces carrying current should be drawn on the PCB as short and as thick as
possible. This should be done to minimize resistive and inductive parasitic effects, and
increase system efficiency. White arrows indicate the suggested PCB (ring) ground plane to
avoid spikes on the output voltage (this is related to the switching side of the LNBH24L).
Good soldering of the ePad helps on this issue.
UP
and GND, and the DC-DC output capacitors (C3
CC
. Excessive noise at the VCC input may falsely trigger the
Figure 14. PBC top layer
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 21/26

Layout guidelines AN3352
Figure 15. PBC bottom layer
Figure 16. PCB component layout
22/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Layout guidelines
3.2 PCB thermal management
The LNBH24L power dissipation inside the IC is mainly due to the DC-DC integrated
MOSFET power loss plus the linear regulator power dissipation. The total power dissipation
calculated, considering both the DC-DC and linear regulator power loss at the maximum
output current (500 mA for each output) with 18 V for LNB output and V
W. The heat generated due to this power dissipation level requires a suitable heatsink to
keep the junction temperature below the overtemperature protection threshold at the rated
ambient temperature inside the set-top box.
The best thermal and electrical performance can be achieved when an array of copper vias
barrel plating is incorporated in the land pattern at 1.2 mm grid. It is also recommended that
the via diameter should be 0.30 mm to 0.33 mm with 1 oz copper via barrel plating.
If the copper plating does not plug the vias, a solder mask material must be used to cap the
vias with a dimension equal to the via diameter + 0.1 mm minimum. This prevents the solder
from not being well spread through the thermal via and potentially creating a solder void
between the package bottom and the ground plane of the PCB.
Taking into account that the solder mask diameter should be at least 0.1 mm larger than the
via diameter.
However, different layouts are also possible. Basic principles suggest keeping the IC and its
ground exposed pad approximately in the middle of the dissipating area; to provide as many
vias as possible; to design a dissipating area having a shape as square as possible and not
interrupted by other copper traces.
= 11 V, is around 2
IN
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 23/26

Startup procedure AN3352
4 Startup procedure
Testing the demonstration board requires a PC with a parallel port (ECP printer port), an I²C
bus interface, software (LNBxx control suite), a dual-output power supply (3 A clamp current
or higher), and an electronic load.
– Step 1: Install the LNBxx control suite software (Software installation)
– Step 2: Plug the I²C connector on CN3
– Step 3: Supply the demo-board through CN2
– Step 4: Manage the demo-board through LNBxx control suite software
Figure 17. PCB connector
24/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3

AN3352 Revision history
5 Revision history
Table 8. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
29-Apr-2011 1 Initial release
16-Sep-2011 2
– Removed watermark from document pages
– Minor text changes
25-Nov-2011 3
Updated Table 1 on page 5, removed paragraph 1.3.1
Doc ID 018526 Rev 3 25/26

AN3352
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2011 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
26/26 Doc ID 018526 Rev 3
 Loading...
Loading...