Page 1

AN2475
Application note
STR91xFAxxx in-application programming using UART
Introduction
An important requirement for most Flash-based systems is the ability to update firmware
while the system is installed in the end product. This is referred to as In-Application
Programming (IAP).
STR9 MCUs have the capability of running user-specific firmware to perform In Application
Programming of the MCU embedded Flash memory. This feature allows the use of any type
of communication protocol for the reprogramming process (for example, CAN, UART, USB).
In this application note, UART is used as an example.
This application note outlines general guidelines for creating an IAP application using two
different methods: the first one is based on the Ymodem protocol and the second one is
based on a customized UART protocol using the free Flash Loader utility provided by ST.
The STR91x evaluation boards have been used to validate the IAP driver.
The IAP Firmware is available on www.st.com.
September 2008 Rev 2 1/37
www.st.com
Page 2

Table of contents AN2475
Table of contents
1 IAP overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Principle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 Triggering execution of the IAP driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 IAP using the Ymodem protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1 Driver description and code sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.2 Running the IAP driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2.1 HyperTerminal configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2.2 IAP driver menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2.3 Download image to internal Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2.4 Execute the new program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 IAP using the ST Flash loader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1 IAP code sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.2 Command set description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2.1 Get command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2.2 Get ID command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.2.3 Go command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.2.4 Write command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2.5 Read command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2.6 Erase command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.2.7 Write Unprotect command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.3 Running the IAP driver firmware using the Flash loader . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3.3.1 Serial communication set-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3.2 STR91x FA target device selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.3.3 Download image to internal Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4 How to use the IAP drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
5 Software remapping and user application interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6 STR9 IAP implementation summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2/37
Page 3

AN2475 IAP overview
1 IAP overview
1.1 Principle
The IAP driver must be programmed by the user in the Flash Bank1 after being remapped in
hardware to address 0x00 (Bank0 is hardware remapped at address 0x80000 for
256 or 512 Kbytes devices and at address 0x200000 for 1 or 2 Mbytes devices).
Note: For 256K, Bank 0 must be at a 256K boundary (Bank 0 base addresses can be: 0x00,
ox40000, ox80000, etc.).
For 512K, Bank 0 must be at a 512K boundary (Bank 0 base addresses can be: 0x00,
ox80000, ox100000, etc.).
For 1M, Bank 0 must be at a 1M boundary (Bank 0 base addresses can be: 0x00,
0x100000, 0x200000, etc.).
For 2M, Bank 0 must be at a 2M boundary (Bank 0 base addresses can be: 0x00,
0x200000, 0x400000, etc.).
Programming is performed via JTAG using a Flasher toolset.
1.2 Triggering execution of the IAP driver
In this application note, the pin 4 of port 7 connected to the push button (PB3) on the
STR91xFA evaluation board is used as an example. This configuration allows the execution
of the IAP driver. By pressing the push button at reset, the user is able to run the IAP driver
to reprogram the STR91x internal Flash.
It is not mandatory to use the push button; the user can simply enter a signal on this pin with
respect to its corresponding active level.
3/37
Page 4

IAP using the Ymodem protocol AN2475
2 IAP using the Ymodem protocol
Using the UART, the IAP driver loads a binary file from HyperTerminal to the STR91xFA
internal Flash bank0, and then jumps to execute it.
2.1 Driver description and code sequence
The IAP driver code size is 7.5K approximately.
It contains a set of source files:
● main.c: where the UART initialization and PLL configuration are set. Then, a main
menu is executed from the common.c file.
● common.c: contains display functions and the main menu routine. The main menu
gives the choice between loading a new binary file and executing the binary file already
loaded.
● ymodem.c and download.c: they allow all data to be received from the HyperTerminal
(using the YMODEM protocol (see note 1 below) then loaded into STR9 internal RAM.
In the event of a failure in data reception, the error message ‘Failed to receive the file’ is
displayed in the HyperTerminal window. Otherwise, after successful reception, the data
is then programmed into internal Flash at the appropriate address. A comparison
between internal RAM and internal Flash contents is performed to check the data
integrity. If there is a mismatch, the error message ‘Verification failed’ is displayed in the
HyperTerminal window. Other error messages are also displayed when the image size
is higher than the allowed memory space and when there is an abort by the user.
Note: The Ymodem protocol sends data in 1024-byte blocks. Error detection is applied to data
blocks transmitted to the STR91xFA internal RAM. This is done through a comparison
between the transmitted and received data. Blocks received unsuccessfully are
acknowledged with a NAK (Negative Acknowledgement). For more details about the
Ymodem protocol, please refer to the existing literature.
● Some STR91xFA firmware library source files and header files
– 91x_fmi.c and 91x_fmi.h
– 91x_gpio.c and 91x_gpio.h
– 91x_scu.c and 91x_scu.h
– 91x_uart.c and 91x_uart.h
– 91x_lib.h
– 91x_map.h
– 91x_type.h
– 91x_it.c
– 91x_it.h
A pin connected to a push button is used to select between jumping to the user application
and executing the IAP for reprogramming purposes:
● At reset, the push button is pressed: the IAP main menu is displayed
● At reset, the push button is not pressed: Jump to the user application.
Figure 1 shows the IAP flowchart.
4/37
Page 5
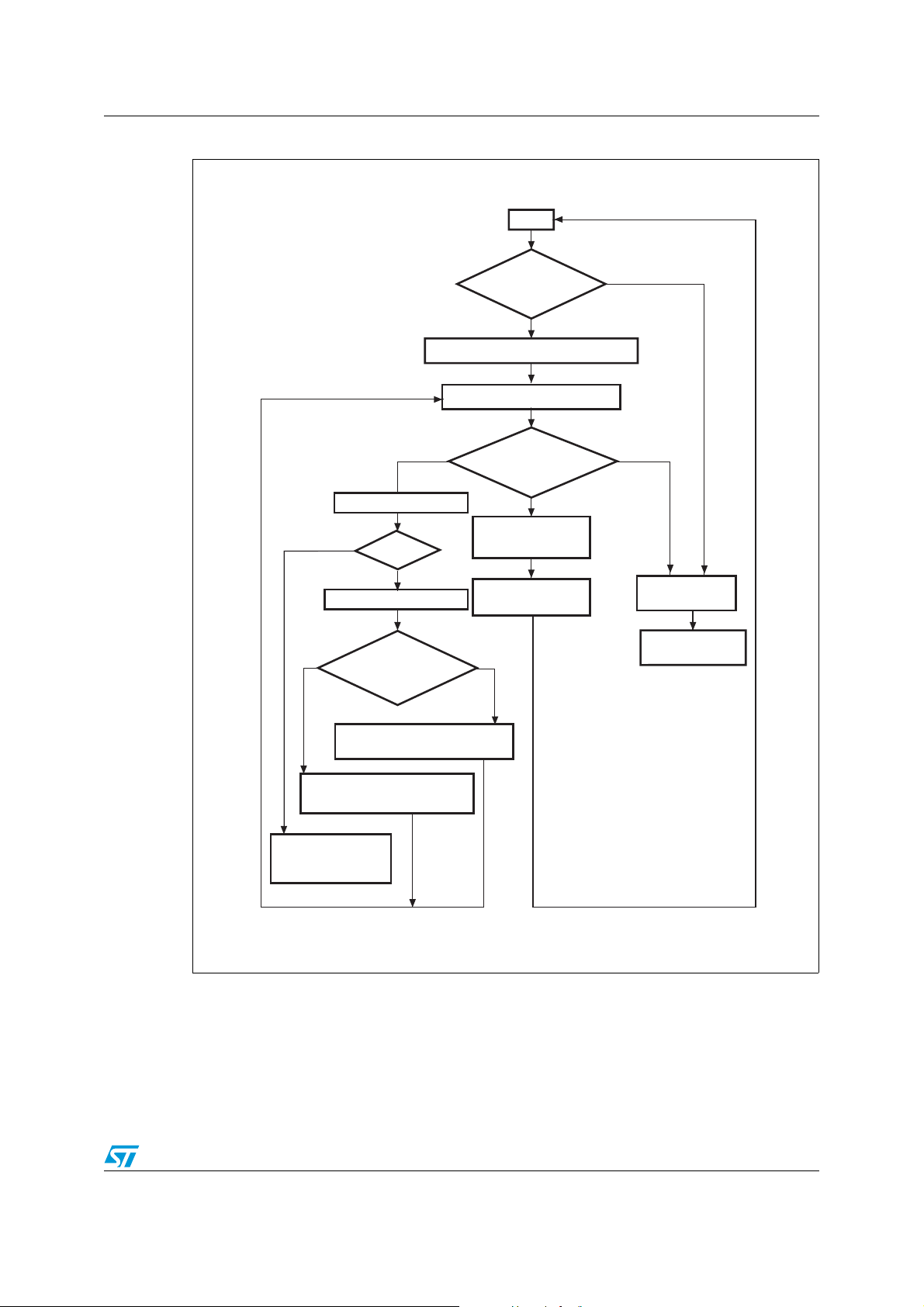
AN2475 IAP using the Ymodem protocol
Figure 1. Flowchart of the IAP using the Ymodem protocol driver
Start
Download
Receive a binary file
No
Success
Ye s
Program the internal Flash
No
All data programmed
successfully?
Push button
pressed
Ye s
Initialize the STR9 UART & PLL
Display the IAP main menu
Download or
jump ?
Disable the write-
protection
System reset
generation
Ye s
No
Jump to user
program
Jump to user
program
User application
firmware
Display the name and size of
received file
Display the error message
"Verification failed"
Display the error
message "Failed to
receive the file"
2.2 Running the IAP driver
On STR91xFA devices, the IAP driver is programmed in Bank1 which is remapped in
hardware to address 0x00.
ai15300
5/37
Page 6
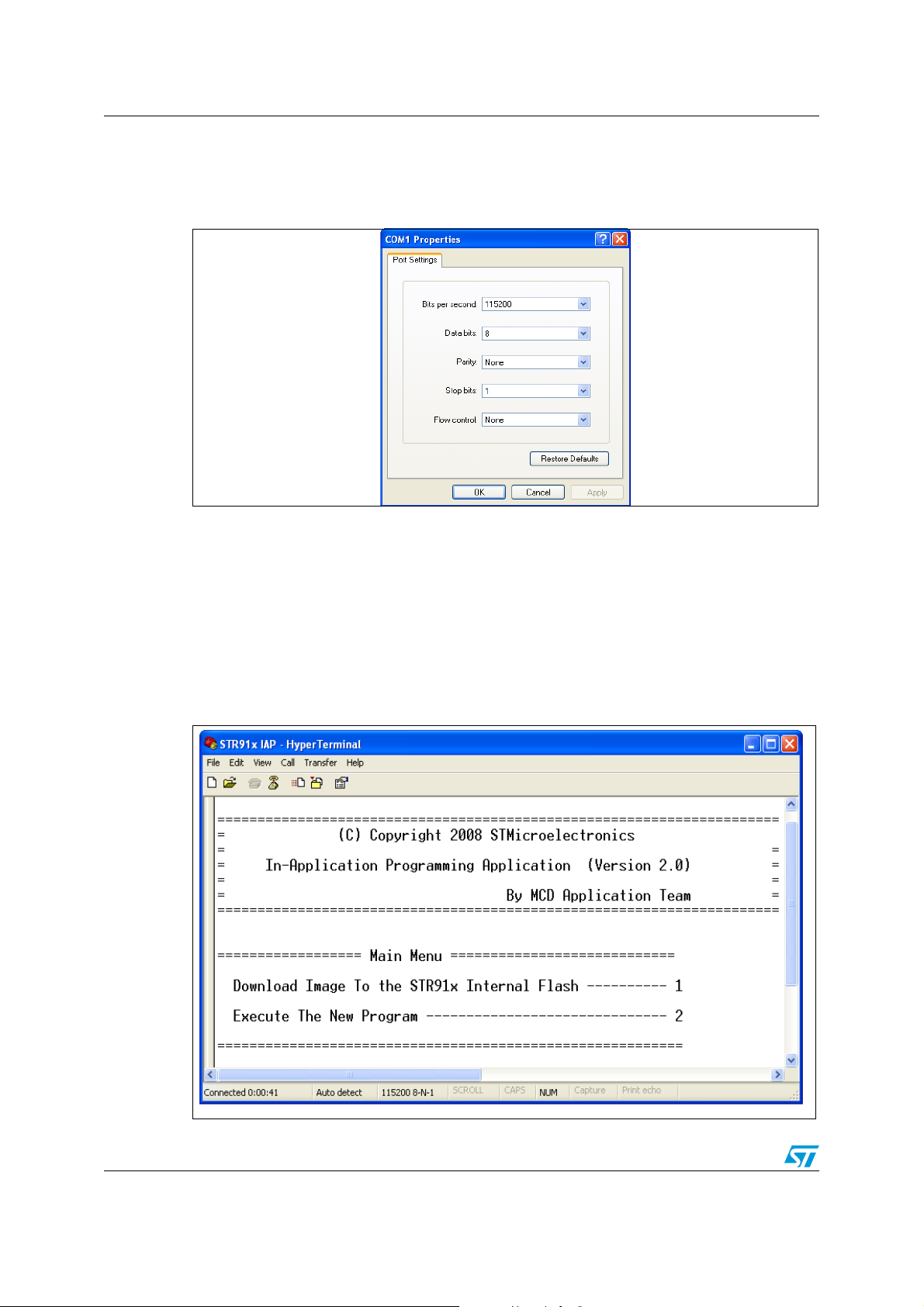
IAP using the Ymodem protocol AN2475
2.2.1 HyperTerminal configuration
The IAP requires a PC running HyperTerminal with the following settings:
Figure 2. COM Port Properties
Note: A baud rate value of 115200 bps is used as an example.
Care should be taken when selecting the system clock frequency. Ensure that with the
system clock frequency used in the application, a baud rate equal to 115200 bps can be
generated in order to guarantee successful communication via UART.
2.2.2 IAP driver menu
The execution of the IAP firmware results in the following menu displayed in the
HyperTerminal window.
Figure 3. IAP driver menu
6/37
Page 7

AN2475 IAP using the Ymodem protocol
2.2.3 Download image to internal Flash
To download a binary file via HyperTerminal to the STR91xFA internal Flash, follow the
procedure below:
● Press “1” on the keyboard to choose the menu “Download image to internal Flash”
Then, in the Transfer menu, select “Send file”:
● In the filename field, type the name and the path of the binary file to be sent.
● In the protocol list, choose the Ymodem protocol,
● Click the “Send” button.
Following these steps, the IAP driver loads the binary file into the STR91xFA internal Flash
from Bank0 sector0 base address and displays the binary file name and file size in the
HyperTerminal window.
2.2.4 Execute the new program
After loading the new program from HyperTerminal by selecting the “Download image to
internal Flash” menu, the code can be executed by selecting the “Execute the new
program” menu by pressing “2” from the keyboard.
7/37
Page 8

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
3 IAP using the ST Flash loader
ST provides a free Flash loader utility allowing the program of the STR91xFA internal Flash
Bank0 using an IAP driver to be loaded in the Flash Bank1.
3.1 IAP code sequence
The IAP driver code size is approximately 6 Kbytes.
It contains a set of source files:
● main.c
●
iap.c
● Some STR91xFA firmware library source files and header files
– 91x_fmi.c and 91x_fmi.h
– 91x_gpio.c and 91x_gpio.h
– 91x_scu.c and 91x_scu.h
– 91x_uart.c and 91x_uart.h
– 91x_lib.h
– 91x_map.h
– 91x_type.h
– 91x_it.c and 91x_it.h
A pin connected to a push button is used to select between jumping to the user application
and executing the IAP for reprogramming purposes:
● At reset, the push button is pressed: connection to the ST Flash Loader.
● At reset, the push button is not pressed: Jump to the user application.
8/37
Page 9
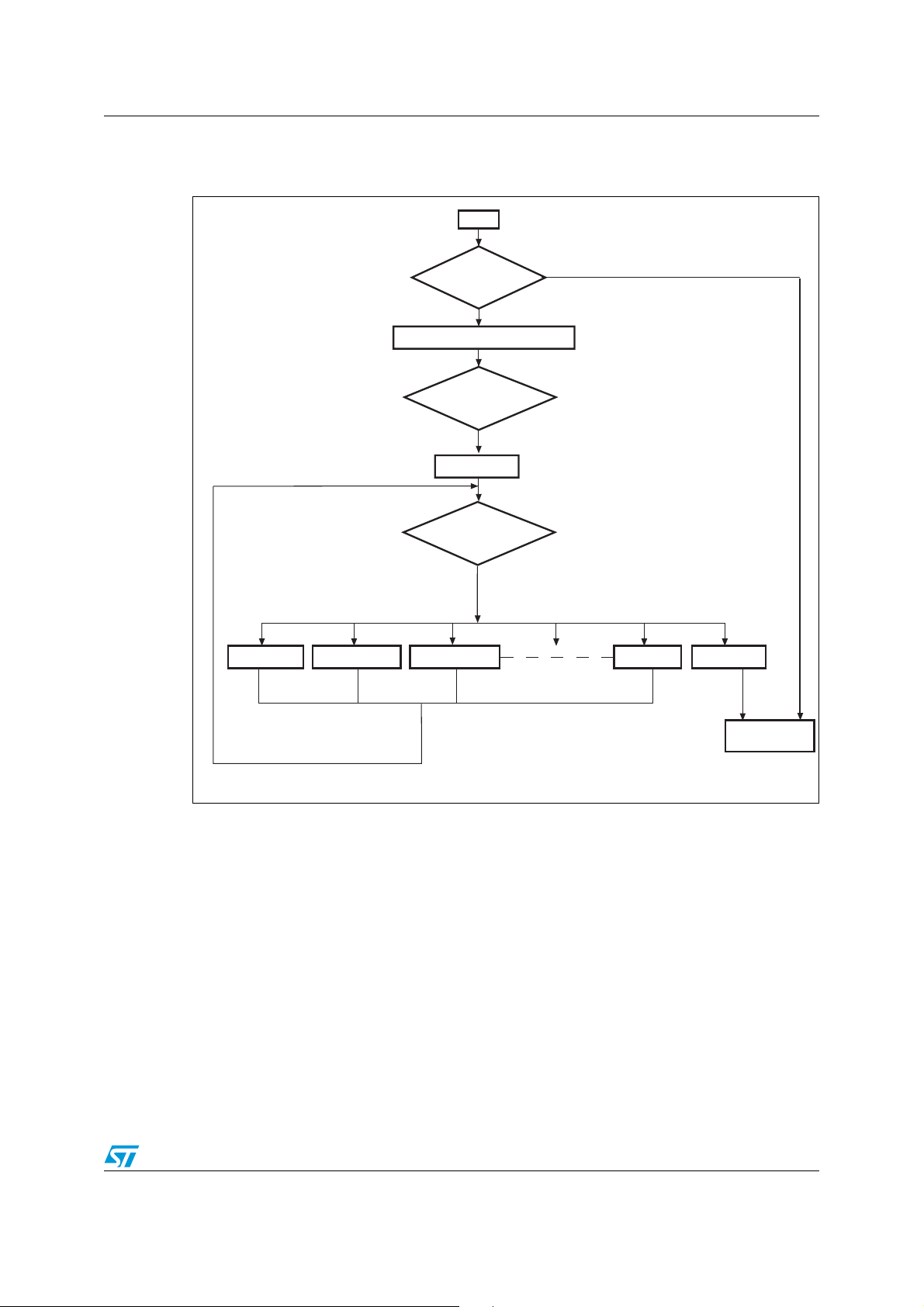
AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Send ACK byte
No
Ye s
Wait for 0x7F from
the host
Jump to user
program
Initialize the STR9 UART & PLL
Start
ai15301
Wait for a command
GET command GET ID command WRITE command
GO command
Push button
pressed
The figure below shows the IAP flowchart.
Figure 4. Flowchart of the IAP using the bootloader protocol driver
Once the push button is pressed, the IAP code begins to scan the UART0_RX line, waiting
to receive 0x7F data from the host: one start bit, 0x7F data bits, even parity bit and one stop
bit.
Next, the code initializes the serial interface (115200 bps, Even Parity, One Stop bit). Then,
the STR91xFA returns an acknowledge byte (0x79) to the host, signaling that it received the
0x7F byte and it is ready to receive user commands.
9/37
Page 10
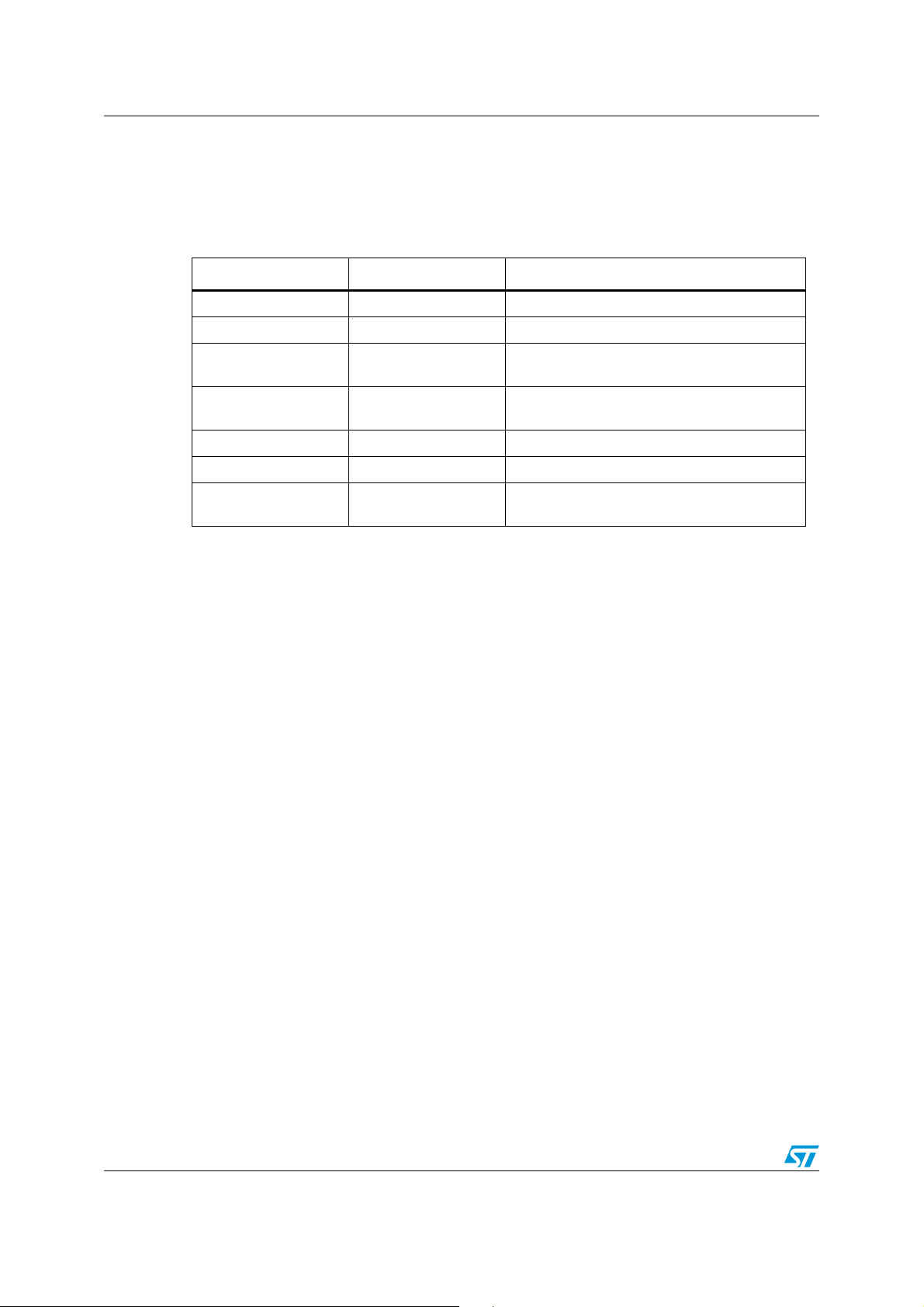
IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
3.2 Command set description
The supported commands are listed in the table below. Each command is further described
in this section.
Table 1. Command list
Command Command code Command description
GET 0x00 Get the version and the allowed commands.
GET ID 0x02 Get the Chip ID.
WRITE 0x31
Write maximum 256 bytes to the Flash Bank0
starting from an address specified by the user.
READ 0x11
ERASE 0x43 Erase from one to all the Bank0 sectors.
WRITE UNPROTECT 0x71 Write Unprotect all Bank0 sectors.
GO 0x21
Communication safety
All communication from the programming tool (PC) to the device is verified in the following
ways:
1. Checksum: all received bytes are XORed. A byte containing the computed XOR of all
previous bytes is added at the end of each communication (Checksum byte). By
XORing all received bytes (data + Checksum), the result, at the end of the packet, must
be 0x00.
2. For each command, the host sends a byte and its complement (XOR = 0x00).
3. UART: a parity check is active (even parity).
Each packet is either accepted (ACK answer) or discarded (NACK answer).
● ACK = 0x79
● NACK = 0x1F
Read up to 256 bytes of Flash Bank0 starting
from an address specified by the user.
Jump to Bank0 base address specified by the
user to execute a loaded code.
3.2.1 Get command
The Get command allows the user to get the version of the IAP and the supported
commands. When the STR91xFA receives the Get command, it transmits the version and
the supported command codes to the host, as described in Figure 5.
10/37
Page 11
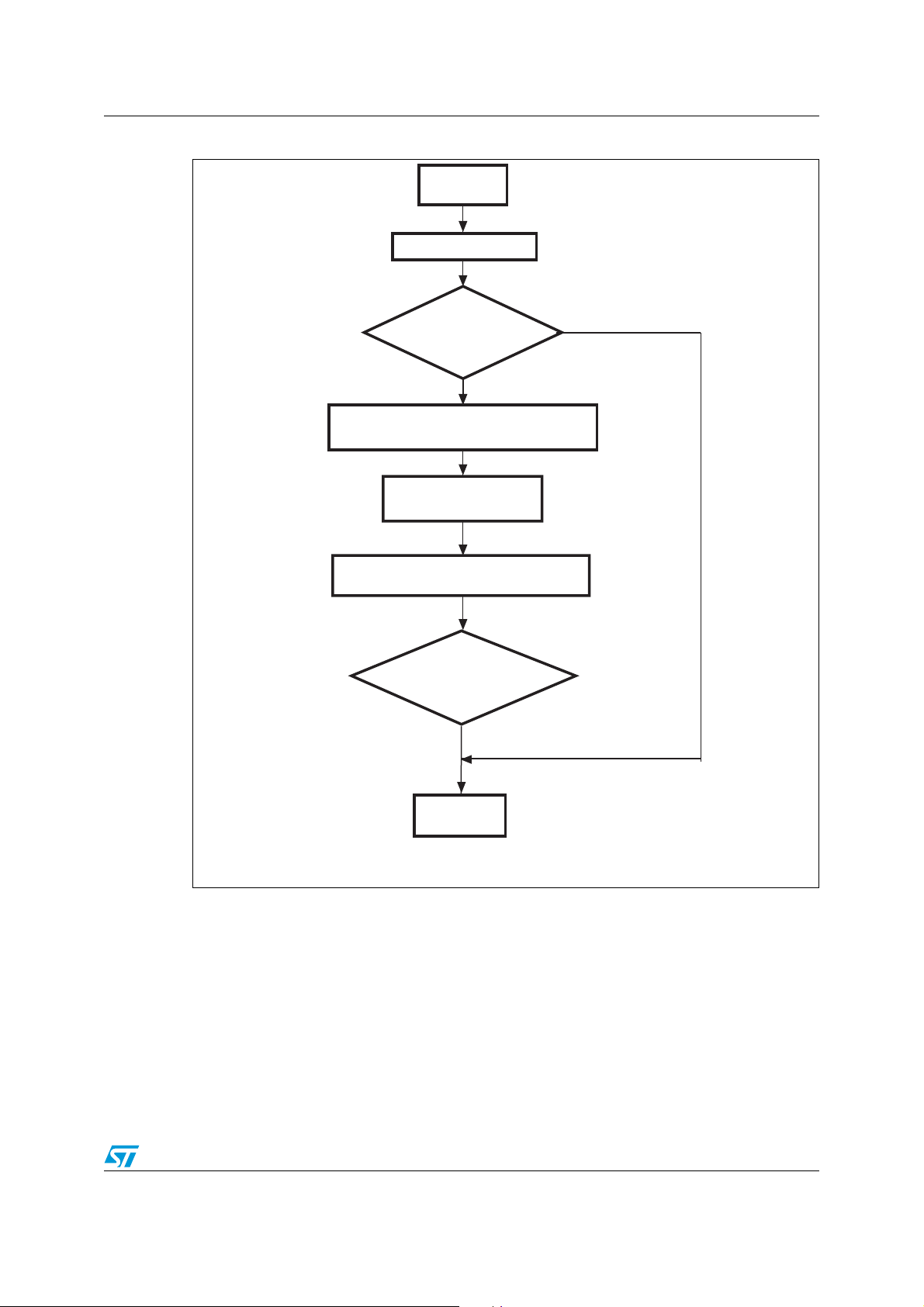
AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Receive the supported commands
NACK
ACK
Receive the version
Receive the number of bytes
Wait for
ACK or NACK
Send 0x00 + 0xFF
ai15302
Wait for ACK or NACK
Start Get
(version + commands)
End Get
Figure 5. Get command host side
11/37
Page 12
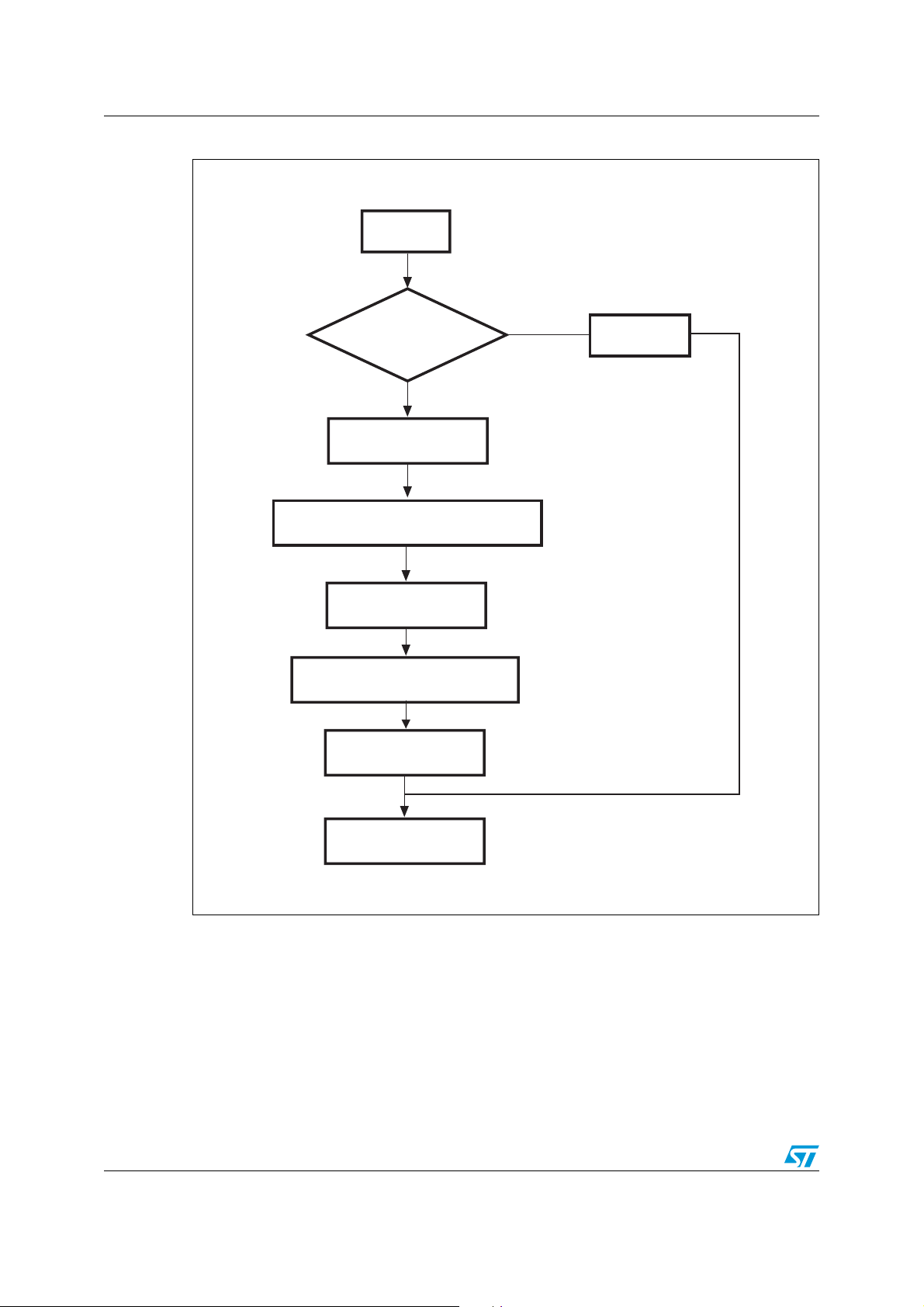
IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Start Get
Is 0x00 + 0xFF
received ?
Send the ACK byte
Send the number of bytes -1
(version + commands)
Send the version
Send the supported commands
Send the ACK byte
End Get
Send NACK
No
ai15303
Figure 6. Get command STR91xFA side
12/37
Page 13

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
The STR91xFA sends the bytes as follows:
● Byte 1: ACK
● Byte 2: N = 7 = the number of bytes to follow – 1 except current and ACKs.
● Byte 3: Version (0 < Version ≤ 255): 10 = Version 1.0
● Byte 4: 0x00 – Get command
● Byte 5: 0x02 – Get ID
● Byte 6: 0x11 – Read Memory command
● Byte 7: 0x21 – Go command
● Byte 8: 0x31 – Write Memory command
● Byte 9: 0x43 – Erase command
● Byte 10: 0x71 – Write Unprotect command
● Last byte (11) – ACK
13/37
Page 14

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Start Get ID
Send 0x02 + 0xFD
Wait for ACK or NACK
NACK
ACK
Receive N = number of bytes -1
Receive PID
Wait for ACK or NACK
End Get ID
ai15304
3.2.2 Get ID command
This command allows the user to get the Chip ID. When the STR91xFA receives the Get ID
command, it transmits to the host the Product ID.
Figure 7. Get ID command host side
14/37
Page 15

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Start Get ID
Is 0x02 + 0xFD
received ?
Send N = number of bytes -1
Send the Product ID
End Get ID
ai15305
Send the ACK byte
Send the ACK byte
Send NACK
No
Figure 8. Get ID command STR91xFA side
The STR91xFA sends the bytes as follows:
● Byte 1: ACK
● Byte 2: N = the number of bytes – 1 (N = 3), except for current byte and ACKs.
Note: PID is the product ID. For STR91xFA products, it is the same as the JTAG ID.
● Bytes 3-6 (corresponding to the PID): byte 3 = 25, byte 4 = 96, byte 5 = 60, byte 6 = 41
15/37
Page 16
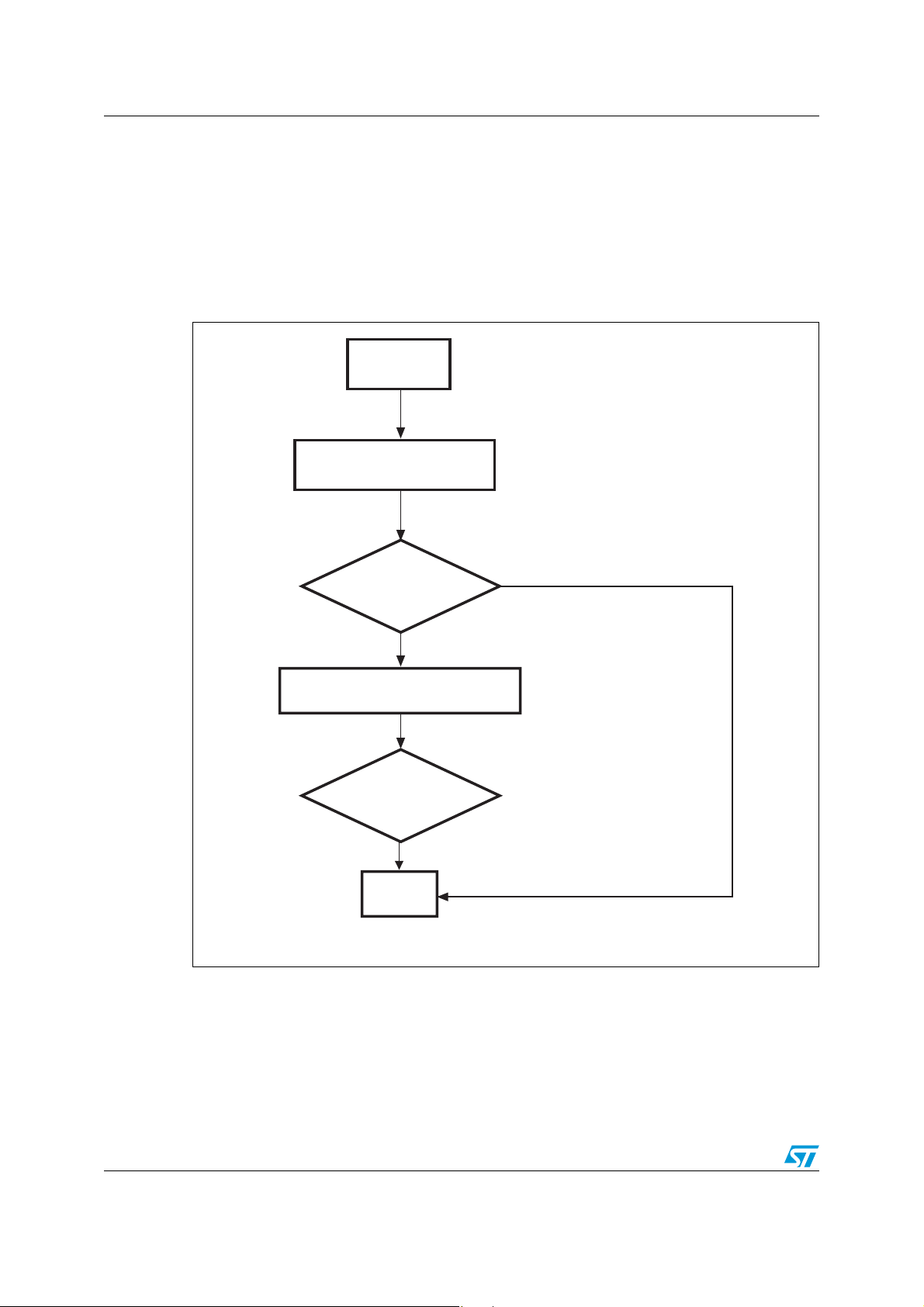
IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Send 0x21 + 0xDE
ai15306
NACK
Start GO
Wait for ACK or NACK
ACK
Send the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum
Wait for ACK or NACK
End Go
3.2.3 Go command
This command allows the user to execute the downloaded code or any other code in Bank0
after being remapped to address 0x00. This address is checked: if the address is valid and
checksum is OK, the STR91xFA transmits an ACK byte, otherwise it transmits a NACK byte
and exits from the command. When the address is valid and checksum is OK, a software
remapping is performed and the program counter of the CPU jumps automatically to
address 0x00.
Figure 9. GO command host side
16/37
Page 17

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Is 0x21 + 0xDE
received ?
ai15307
No
Start GO
Receive the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum
Address valid
and checksum OK?
Jump to address
Ye s
Send the ACK byte
Ye s
Send the ACK byte
No
End GO
Send NACK
Figure 10. GO command STR91xFA side
The host sends the bytes to the STR91xFA as follows:
● Byte 1: 0x21
● Byte 2: 0xDE
● Wait for ACK
● Byte 3 to Byte 6: start address (byte 3: MSB and byte 6: LSB)
● Byte 7: checksum: XOR (byte 3, byte 4, byte 5, byte 6)
17/37
Page 18

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
3.2.4 Write command
This command allows the user to write a data to any address in Flash Bank0. When the
STR91xFA receives the Write Memory command, it transmits the ACK byte to the user.
Once the ACK byte is transmitted, the STR91xFA waits for an address (4 bytes, byte 1 is the
MSB and byte 4 is LSB of the address) and a checksum byte. This address is checked: if it
is valid and checksum is OK, the STR91xFA transmits an ACK byte, otherwise it transmits a
NACK byte and exits from the command. When the address is valid and checksum is OK,
the STR91xFA:
● Gets a byte, N - 1, where N = the number of data bytes to be received,
● Receives the user data (N bytes) and the Checksum (XOR of the first byte (N-1) and of
all data bytes which follow).
● If checksum is correct, the user data are programmed to Flash Bank0 starting from the
received address which is 0x80000 for 256/512Kbytes devices or 0x200000 for
1/2Mbytes devices.
Finally, at the end of the command, the STR9 transmits the ACK byte if the write operation is
completed successfully, otherwise a NACK byte is transmitted to the user and the command
is exited.
Note: The maximum length of the block to be written is 256. If N is higher than the maximum
length, the command will be NACKed.
18/37
Page 19
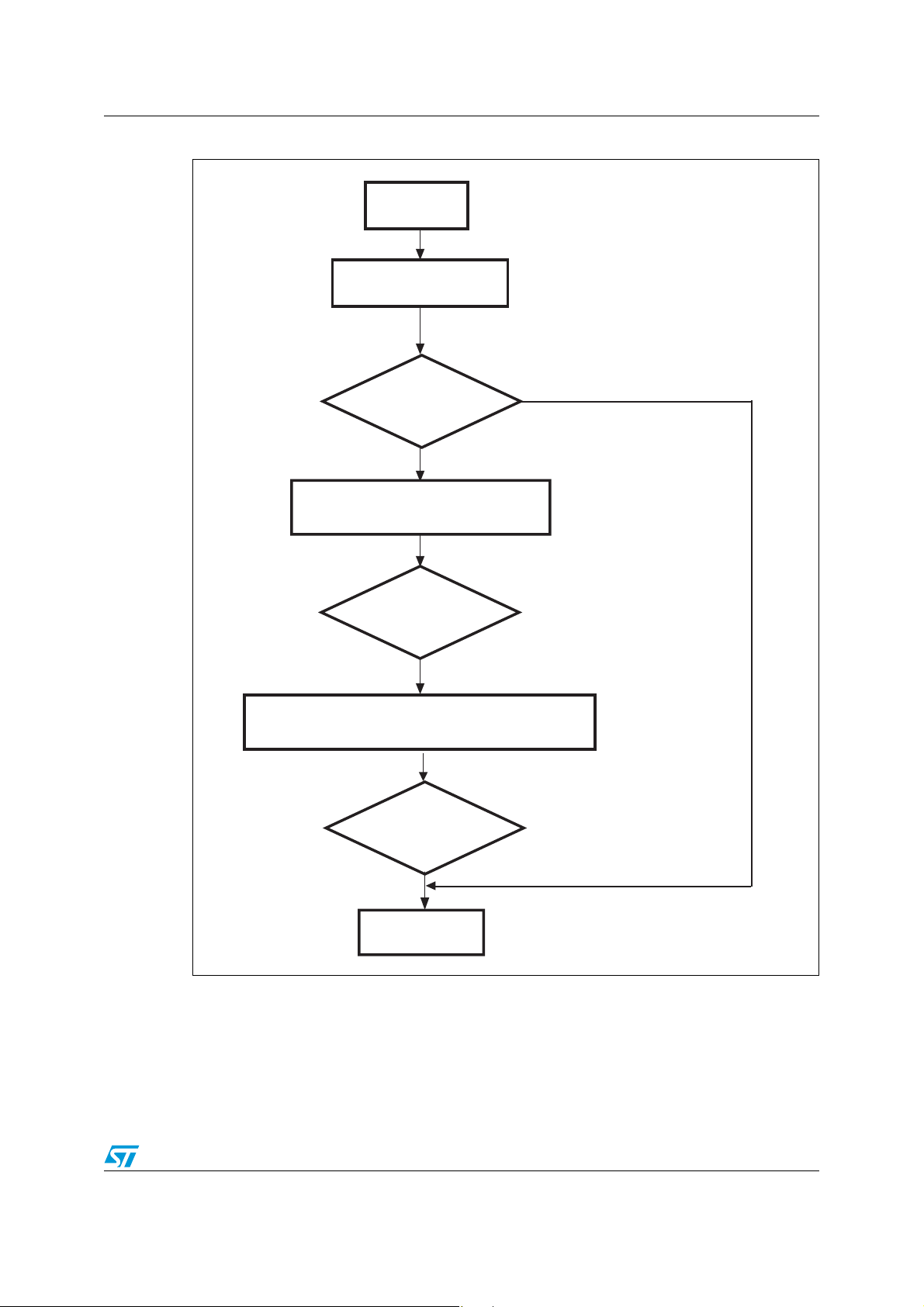
AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Wait for ACK or NACK
ai15308
Start Write
ACK
Ye s
End Write
Send 0x31 + 0xCE
NACK
Send the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum (see note below)
Wait for ACK or NACK
Send the number of bytes to be written -1,
the data to be written + checksum
Wait for ACK or NACK
Figure 11. Write command host side
Note: The Start address to be sent by the user is the Flash Bank0 base address i.e. 0x80000 for
256/512Kbytes devices and 0x200000 for 1/2 Mbytes devices.
19/37
Page 20

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
ai15309
Start Write
End Write
No
Receive the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum
Valid address
& checksum OK?
Receive the number of bytes to be written -1,
the data to be written and the checksum
Checksum OK?
Send NACK
Is 0x31 + 0xCE
received?
Send the ACK byte
Ye s
Send the ACK byte
No
Ye s
Write the data
Send the ACK byte
No
Figure 12. Write command STR91x side
20/37
Page 21

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
The host sends the bytes to the STR91xFA as follows:
● Byte 1: 0x31
● Byte 2: 0xCE
● Wait for ACK
● Byte 3 to byte 6: start address
● Byte 3: MSB and byte 6: LSB
● Byte 7: Checksum: XOR (byte 3, byte 4, byte 5, byte 6)
● Wait for ACK
● Byte 8: Number of bytes to be received (0 < N ≤ 255)
● N +1 data bytes: (max. 256 bytes)
● Checksum byte: XOR (N, N+1 data bytes)
● Wait for ACK
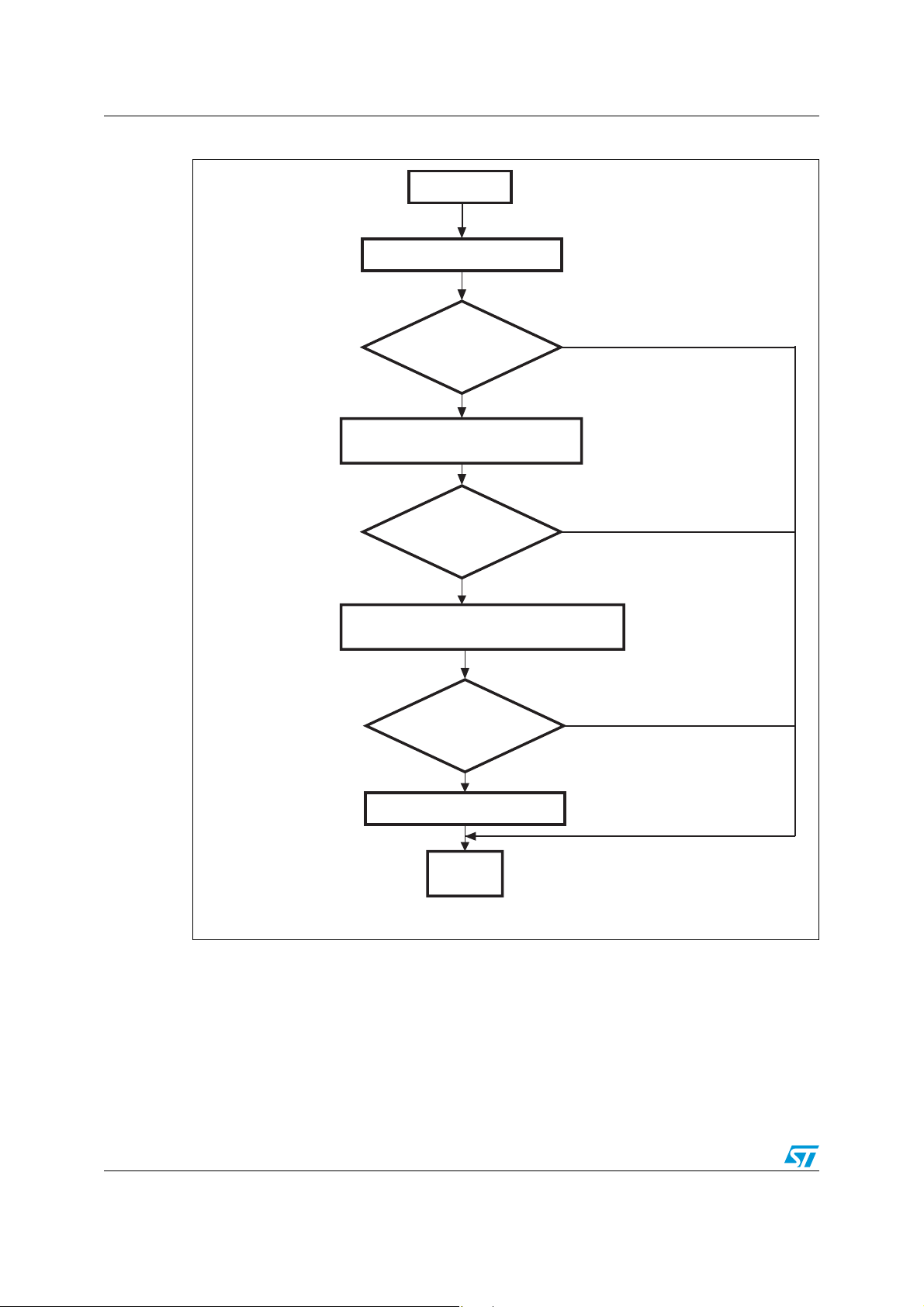
3.2.5 Read command
This command allows the host to read the Flash Bank0 locations. When the STR91xFA
receives the Read Memory command, it transmits the ACK byte to the host. After the
transmission of the ACK byte, the STR91xFA waits for an address (4 bytes: byte 1 is the
MSB and byte 4 is LSB of the address) and for a checksum byte. This address is checked: if
the address is valid and checksum is OK, it transmits an ACK byte, otherwise it transmits a
NACK byte and exits from the command. When the address is valid and checksum is
correct, the STR91xFA sends an ACK byte and waits for the information on the number of
bytes to be transmitted (N-1 value) and for its complement (checksum). If the checksum is
correct then it transmits to the user the needed data (N bytes) starting from the received
address, otherwise it sends a NACK before exiting from the command.
21/37
Page 22
IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Send 0x11 + 0xEE
ai15311
NACK
Start Read
Wait for ACK or NACK
ACK
Send the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum (see note below)
Wait for ACK or NACK
End Read
Send the number of bytes to be read -1
+ checksum
Wait for ACK or NACK
Receive the read data
NACK
NACK
Figure 13. Read command host side
22/37
Page 23
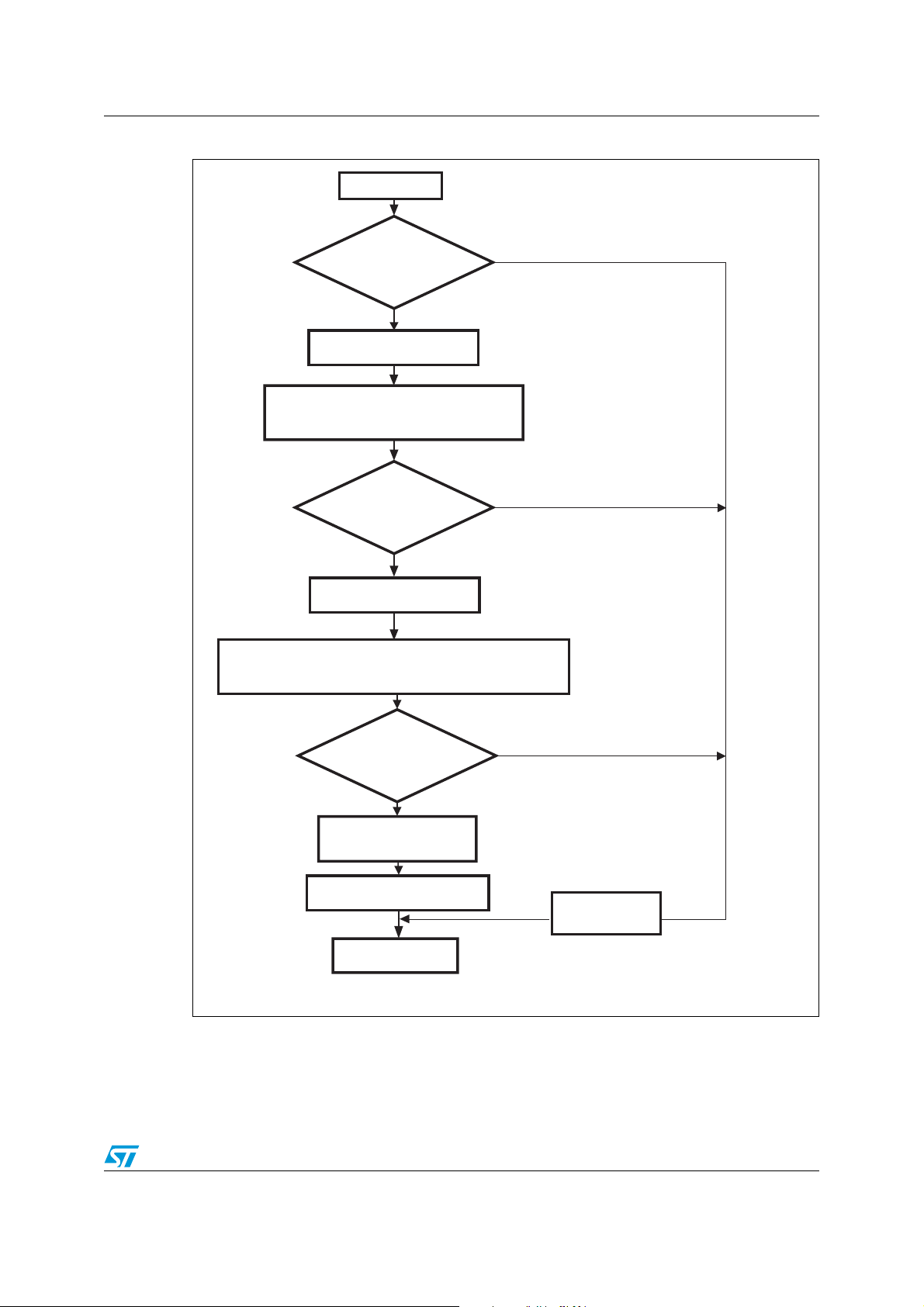
AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
ai15312
Start Read
End Read
No
Receive the Start address (4 bytes)
+ checksum
Valid address
& checksum OK?
Receive the number of bytes to be read -1
and the checksum
Checksum OK?
Send NACK
Is 0x11 + 0xEE
received?
Send the ACK byte
Ye s
Send the ACK byte
No
Ye s
No
Send the ACK byte
Send data to the host
Figure 14. Read command STR91xFA side
23/37
Page 24

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
The host sends the bytes to the STR91xFA as follows:
● Bytes 1-2: 0x11+ 0xEE
● Wait for ACK
● Bytes 3 to 6: start address (byte 3: MSB and byte 6: LSB)
● Byte 7: Checksum: XOR (byte 3, byte 4, byte 5, byte 6)
● Wait for ACK
● Byte 8: The number of bytes to be read – 1 (0 < N ≤255);
● Byte 9: Checksum: XOR byte 8 (complement of byte 8)
3.2.6 Erase command
This command allows the host to erase the sectors of the Flash Bank0. When the
STR91xFA receives the Erase command, it transmits the ACK byte to the host. Once the
ACK byte is transmitted, the STR91xFA receives the number of bytes to be received - 1
(number of sectors to be erased - 1), the Bank0 sector codes and a checksum byte. If the
checksum is correct, then the erase operation is performed, an ACK byte is sent to the host,
otherwise a NACK byte is sent to the host and the command is exited. The Erase command
proceeds as follows:
1. Receive one byte, N-1 (where N = number of sectors to be erased). The value 0xFF is
reserved for global erase request.
2. Receive N bytes, each byte containing a sector code.
24/37
Page 25
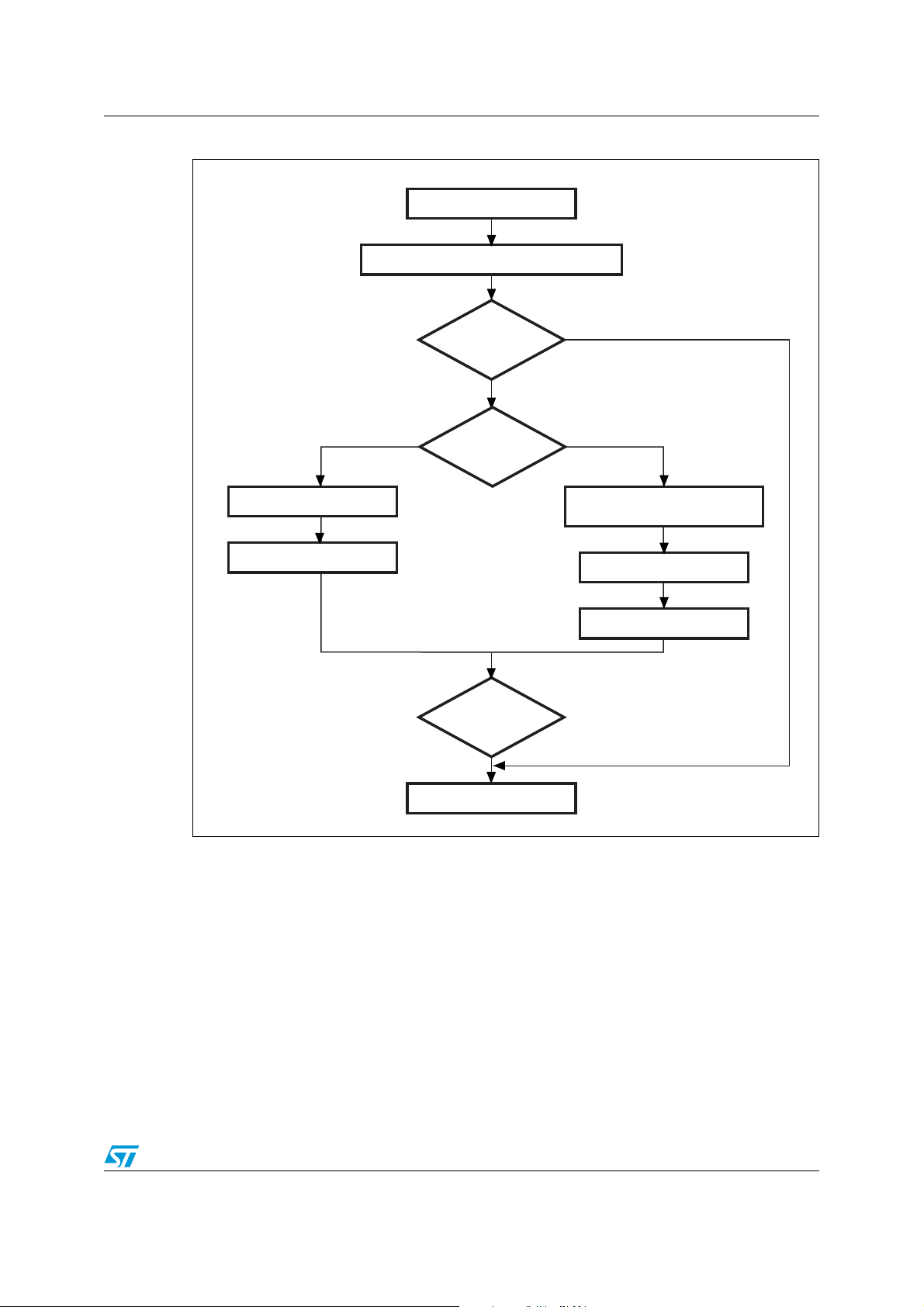
AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Wait for ACK
or NACK
Wait for ACK
or NACK
End Erase
NACK
ACK
ai15322
Send 0x43+0xBC
Start Erase
Global
Erase?
NoYe s
Send 0xFF
Send 0x00
Send the number of sectors
to be erased -1
Send the sector codes
Send checksum
Figure 15. Erase command host side
25/37
Page 26

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Figure 16. Erase command STR91xFA side
Start Erase
0x00 received ?
Ye s
Global Erase
Is 0x43 + 0xBC
received?
Ye s
Send the ACK byte
Ye s
Receive the number of sectors to be erased - 1
No
0xFF received ?
No
Receive the sector codes
Receive the checksum
Checksum OK?
No
No
Erase the corresponding sectors
26/37
Erase OK ?
Send the ACK byte
End Erase
Ye s
No
Ye s
Send NACK
ai15313
Page 27

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
Start WU
Send 0x71 + 0x8E
Wait for ACK or NACK
NACK
ACK
Wait for ACK or NACK
End WU
ai15314
The host sends the bytes to the STR91xFA as follows:
● Byte 1: 0x43
● Byte 2: 0xBC
● Wait for ACK
● Byte 3: 0xFF or number of sectors to be erased - 1 (N = number of sectors)
● Byte 0x00 or (N + 1 bytes (sector codes) and then the checksum for byte 3 and the
following bytes)
3.2.7 Write Unprotect command
This command allows the user to disable the write protection for all Bank0 sectors. When
the STR91xFA receives the write unprotect command, it transmits the ACK byte to the host.
Once the ACK byte is transmitted, the write protection for all Bank0 sectors is disabled.
Finally, at the end of the command, the STR91xFA transmits the ACK byte if the
unprotection is completed successfully, otherwise a NACK byte is transmitted to the host.
Figure 17. Write Unprotect command host side
27/37
Page 28

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
Start WU
Is 0x71 + 0x8E
received ?
No
End WU
ai15315
Send the ACK byte
Send the ACK byte
Remove write protection
Successful or not ?
Ye s
Send NACK
No
Figure 18. Write Unprotect command STR91xFA side
3.3 Running the IAP driver firmware using the Flash loader
The IAP driver is programmed in Bank1 which is remapped in hardware at address 0x00.
ST provides a free tool (Flash loader) that performs the IAP commands previously listed in
Section 3.2: Command set description.
For more details, please refer to next sections and to the Flash loader user manual.
28/37
Page 29

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
3.3.1 Serial communication set-up
When launching the Flash Loader, the following figure appears:
Figure 19. Communication port selection and set-up
● Configure the serial communication as shown in the figure above.
● Click Next
29/37
Page 30

IAP using the ST Flash loader AN2475
3.3.2 STR91x FA target device selection
The following figure appears:
Figure 20. Device selection
● Select the STR91xFA target device to be used
● Click Next
30/37
Page 31

AN2475 IAP using the ST Flash loader
3.3.3 Download image to internal Flash
The following figure appears:
Figure 21. Download image
You can perform any other operation: erase all the Flash, erase some sectors, read the
Flash content...
31/37
Page 32

How to use the IAP drivers AN2475
ai15316
Current directory
FWLib
inc
src
Examples
IAP_AN
Example 1
Example 2
include
Project
source
include
Project
source
4 How to use the IAP drivers
The IAP package consists of an archived file containing 3 subfolders:
● IAP_AN: This contains two subfolders:
– Example 1: shows IAP based on the Ymodem protocol.
– Example 2: shows IAP based on the customized UART protocol using the Flash
Loader utility.
● FWLib: This contains the STR91xFA standard library files.
● Examples: The compiled examples are provided to show the project settings of a user
program to be loaded in the STR91xFA internal Flash.
The file structure is described in the following figure:
Figure 22. IAP driver directory structure
32/37
To use the IAP drivers properly, please follow the different steps below:
● Remap the Bank0 to address 0x80000 or 0x200000 (depending on the STR91xFA
device being used) and remap Bank1 to address 0x00.
Page 33

AN2475 How to use the IAP drivers
The drivers delivered with the application note support the STR91xFA with 512Kbytes. In
order to adapt them to another target device (256 Kbytes or 1 Mbyte or 2 Mbytes), just:
● in 91x_init.s start-up file, uncomment "#define Flash_256KB_Bank1_Boot" or "#define
Flash_512KB_Bank1_Boot" or "#define Flash_2MB_Bank1_Boot" or "#define
Flash_1MB_Bank1_Boot".
● in 91x_conf.h, uncomment "#define Flash_512KB_256KB" or "#define
Flash_2MB_1MB" (and "#define Flash_512KB" or "#define Flash_256KB" or "#define
Flash_1MB" or "#define Flash_2MB" in common.h for IAP based on the Ymodem
protocol only)
● Download the IAP driver to the STR91xFA internal Flash via JTAG using a Flasher
toolset (see note below).
Note: Be careful when re-downloading IAP in Bank1 using the toolset: when the user application
(loaded using IAP) is being executed (Bank0 at 0x00) and you try to re-download the IAP,
the user application will be erased. To avoid this, make sure you are in IAP mode (that is,
push button pressed at reset) when downloading the IAP in Bank1.
When using IAP with the ST Flash loader:
● Keep the push button pressed at reset.
● Connect to the Flash loader using the settings already defined in Section 3.3.1: Serial
communication set-up
● Launch any operation you want: download an application, upload the Flash content
etc... (for more details, please refer to the ST Flash Loader user manual).
When using IAP based on the Ymodem protocol:
● Open a HyperTerminal window with the settings already defined in Section 2.2.1:
HyperTerminal configuration
● To run the IAP driver, keep the push button pressed at reset. The IAP main menu will
be displayed on the HyperTerminal window.
● To download an application, press 1 and use the YMODEM protocol as described in
Section 2.2.3: Download image to internal Flash.
33/37
Page 34

Software remapping and user application interrupts AN2475
5 Software remapping and user application interrupts
A software remapping, of Bank0 at 0x00 and Bank1 at 0x80000 (or 0x200000) is performed
before jumping to the user application at address 0x00. The user application containing
interrupts (IRQ, FIQ etc…) is then executed without constraints.
In case the STR91x revision is different from revision H, a system reset does not execute
the IAP nor the user application (please refer to the STR91xFA erratasheet, section 2.3
Flash memory remapping). In this case, a jump to the user application mapped at 0x80000
or at 0x200000 (depending on the device) should be performed instead.
If no software remapping is performed, to execute interrupts, please consider the following
points:
● In the 91x_vect.s start-up file,
‘
LDR PC, Undefined_Addr
LDR PC, SWI_Addr
LDR PC, Prefetch_Addr
LDR PC, Abort_Addr
NOP ; Reserved vector
LDR PC, IRQ_Addr
‘
is replaced by
‘
LDR PC, =0x80004 (or 0x200004)
LDR PC, =0x80008 (or 0x200008)
LDR PC, =0x8000C (or 0x20000C)
LDR PC, =0x80010 (or 0x200010)
NOP ; Reserved vector
LDR PC, IRQ_Addr
LDR PC, =0x8001C (or 0x20001C)
‘
In this case, for the interrupt request (IRQ), there is no problem in the IAP (the IAP provided
by ST does not contain interrupts) or in the user application. FIQ, SWI etc… in the user
application are executed properly but if the IAP application requires SWI or FIQ, they will not
be executed.
● If the IAP is using the ST FWLib v2.0 and the user application is using the ST FWLib
v1.x, then the IRQ interrupts will not be managed properly.
34/37
Page 35
AN2475 STR9 IAP implementation summary
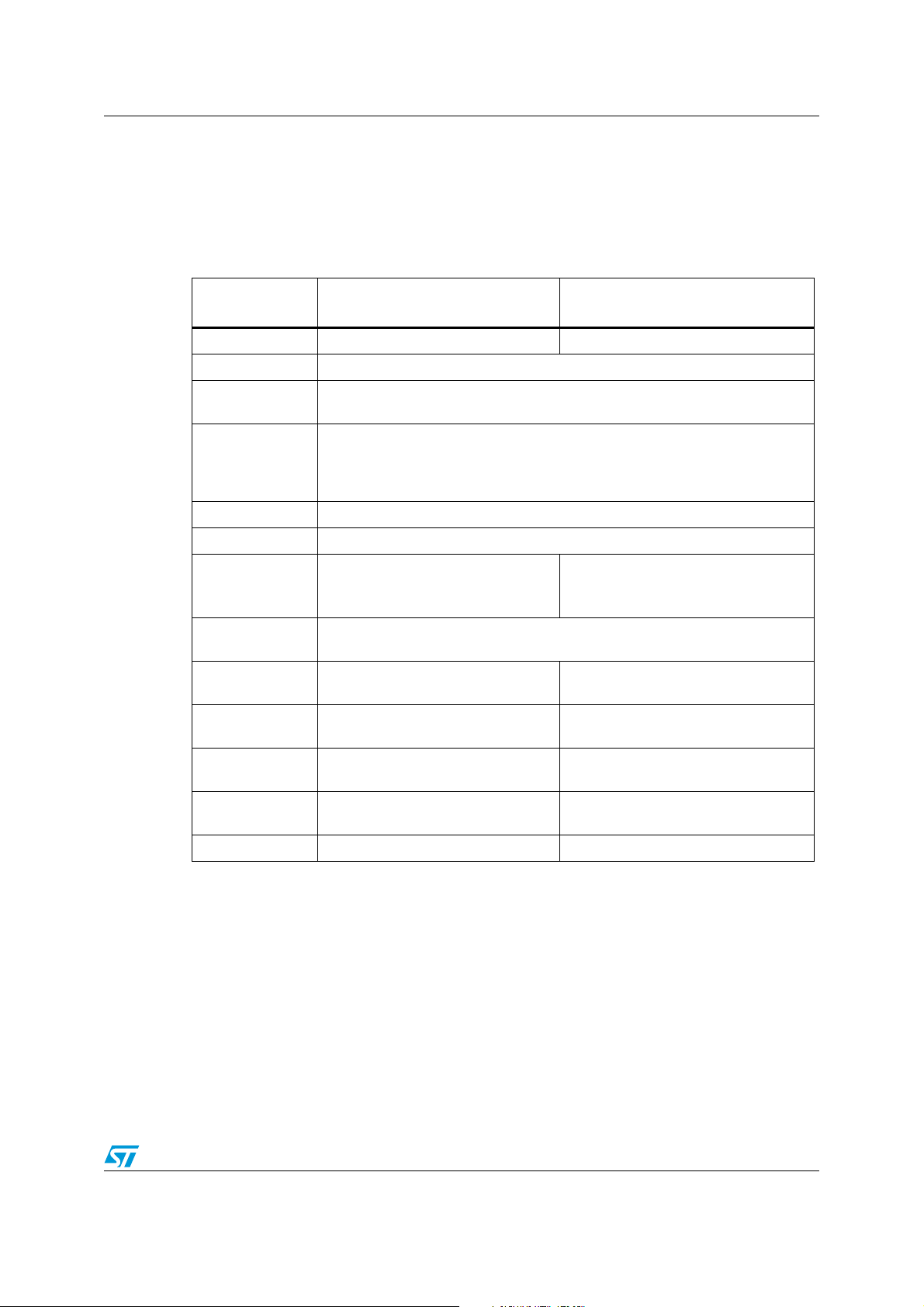
6 STR9 IAP implementation summary
A summary of the STR91x IAP implementation using both methods is described in the table
below:
Table 2. IAP implementation
IAP parameters
IAP based on the Ymodem
protocol
IAP using the ST Flash Loader
IAP code size 7.5K 6K
IAP driver location Bank 1
User application
location
Bank 0
By default, Bank0 is mapped at address 0x00. If the IAP driver must be located
Flash remapping
in Bank1 and the user application is located in Bank0, you must remap the
banks (remap Bank1 to address 0x00 and Bank0 to address 0x80000 for 512
Kbytes and 256 Kbytes and address 0x200000 for 1 Mbyte and 2 Mbytes).
Flash routines All Flash routines are executed from internal SRAM.
Push button P7 (pin 4): Push button
UART used and
communication
115200 bps, 8-Bit data, No parity,
settings
Maximum loaded
image size
The maximum size of the image to be loaded in the STR91xFA Internal Flash is
limited by the size of Bank0, i.e. 256 Kbytes, 512 Kbytes, 1 Mbyte or 2 Mbytes.
Downloading time
of an image 256K
Downloading time
of an image 512K
Downloading time
of an image 1M
Downloading time
of an image 2M
Speed (bit/s)
1. The speed is calculated by dividing the size by the downloading time.
Example of 256K: Speed = 256 x 1024 x 8/33 = 63550 bits/s (with downloading time = erasing time +
verifying time)
(1)
UART0
115200 bps, 8-Bit data, Even parity,
1 Stop bit
33 s 62 s
64 s 121 s
124 s 238 s
247 s 469 s
65325 34461
UART0
1 Stop bit
35/37
Page 36
Revision history AN2475
7 Revision history
Table 3. Revision history
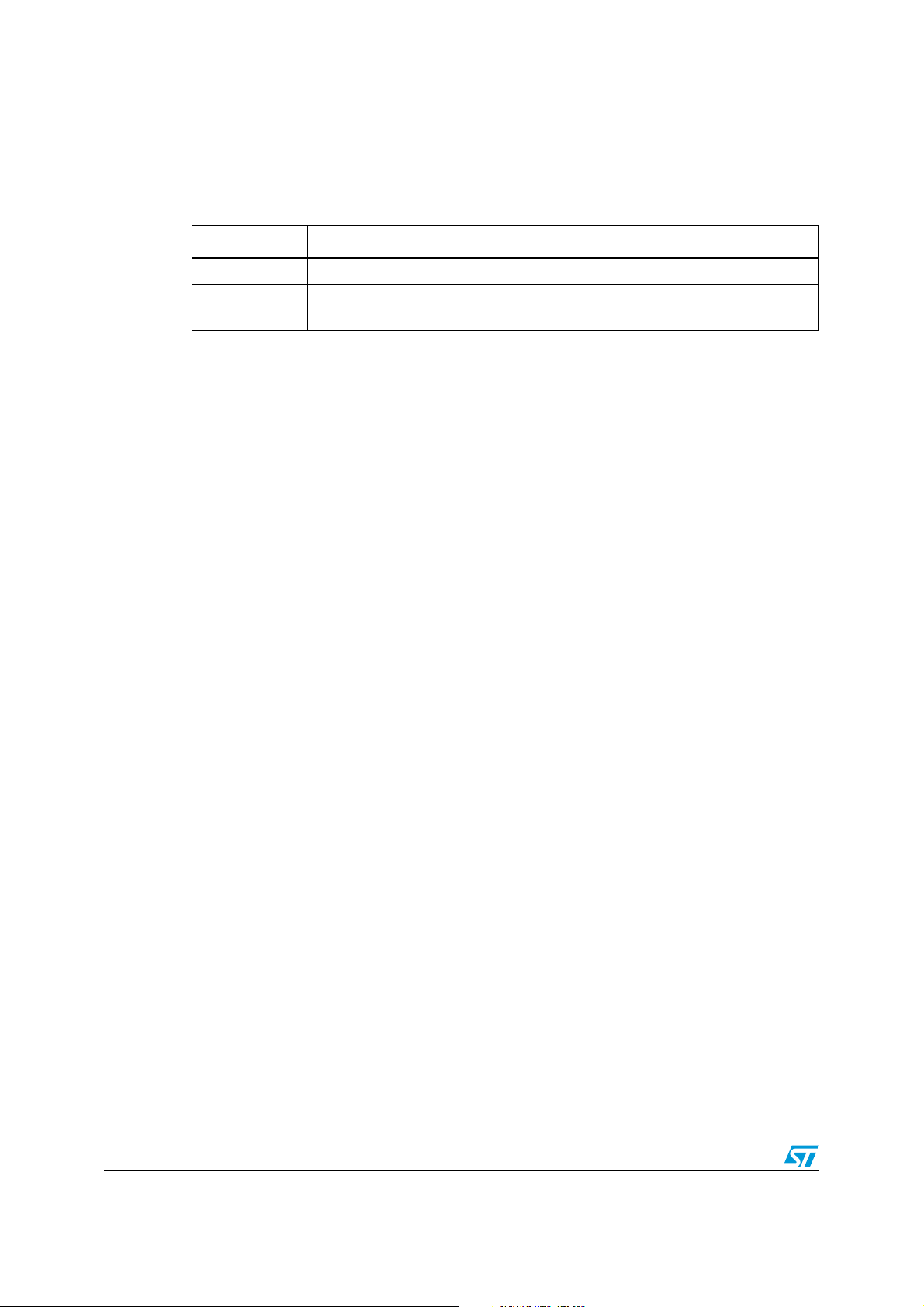
Date Revision Description of changes
12-Jan-2007 1 Initial release.
01-Sep-2008 2
Updated for 256 Kbyte, 1 and 2 MByte Flash sizes.
A second method of IAP added.
36/37
Page 37

AN2475 Revision history
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2008 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
37/37
 Loading...
Loading...