Page 1

AN2452
Application note
STW8110x evaluation board and graphical user interface
Application and scope
This application note describes the evaluation board (EVB) and the graphical user interface
(GUI) of the STW81101, STW81102 and STW81103 multi-band RF frequency synthesizers
(with integrated VCOs).
The STW8110x GUI software allows the STW81101, STW81102 and STW81103
synthesizers to be programmed via an I
Three evaluation boards are available depending on the output matching network optimal
frequency range:
■ EVB1G (single output - 1 GHz - output divider by 4)
■ EVB2G (single output - 2 GHz - output divider by 2)
■ EVB4G (single output - 4 GHz - direct output)
2
C/SPI control interface.
February 2008 Rev 3 1/21
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2452
Contents
1 Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 Main form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.3 Tutorial operation mode form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.4 Waveform viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Evaluation board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1 Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2.1 Top view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2.2 Bottom view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.3 Schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.4 Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.5 Bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2/21
Page 3

AN2452 Software
1 Software
1.1 Installation
The STW8110x GUI software is built on the Microsoft (R) .NET Framework (see
http://www.microsoft.com/net/default.mspx
(R) .NET Framework version 2.0, which may require the installation of Windows Installer 3.0
(see
http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/en-
us/msi/setup/windows_installer_start_page.asp
install Microsoft (R) .NET Framework and Windows Installer.
Follow these steps to install the STW8110x GUI:
1. If an old version of the GUI is already installed, uninstall it.
2. Run
setup.exe
(datasheets, programming configuration files and desktop/quick launch
shortcuts are optional components installed by default).
3. Run
STW8110xGUI.exe
4. The default starting operation mode is Tutorial. The starting operation mode can be
modified by means of the radio buttons in the tutorial form:
a) Tutorial: a brief tutorial on the features of the GUI.
b) Basic: only the main options are enabled.
c) Advanced: all the available options are enabled.
). It may require the installation of the Microsoft
). Administrator privileges are required to
1.2 Main form
This section details the items on the main form. See
1. Pressing this button shows the About STW8110xGUI screen.
2. Pressing this button opens the datasheet of the selected device.
3. Help
4. Device selection (STW81101/2/3).
5. GUI operation modes:
Tutorial: A brief tutorial on the basic features of the GUI. An inner default configuration
is loaded.
Basic: only the main options are enabled. Frequency values must be set in the
following order:
a) Input reference frequency F
b) Output frequency step F
c) Output frequency F
The calibrator is always ON. VCO and output divider are set automatically.
Advanced: all the available options are enabled. Any F
message will warn if the inserted values are beyond the frequency limits of the VCOs.
Frequency values must be set in the following order:
a) Input reference frequency F
b) Output frequency step F
c) Output frequency F
Waveform Viewer: a form is opened displaying the bit sequence sent to the device.
out
out
step
.
step
or F
ref
.
ref
or F
vco
Figure 1: Main form
on page 4.
.
vco
or F
are allowed. A
out
.
.
pfd
.
3/21
Page 4

Software AN2452
Figure 1. Main form
1
5
17
6. Swallow counter A: 5-bit counter.
7. VCO calibrator:
– Last calibration F
: contains the last calibration data (VCO and frequency of
vco
calibration).
– Calibrator ON/OFF.
– The maximum allowed F
pfd
is programmed in two steps:
a) Device is programmed forcing calibration with the maximum F
(F
= F
pfd
/ R ≤ 1 MHz ==> R ≥ F
ref
b) Device is programmed with the desired F
Example with F
= 76.8 MHz:
ref
Desired values:
- F
= 1200 kHz
pfd
- R = F
ref
/ F
pfd
= 64
Forced values:
- R' = ⎡F
- F'
pfd
/ 106⎤ = ⎡76.8⎤ = 77
ref
= F
/ R' = 997.403 kHz
ref
Device programming in two steps:
a) Device is programmed with F
b) Device is programmed with F
2
6
10
14
18
78
during calibration is 1 MHz. If F
/ 106).
ref
.
pfd
= 997.403 kHz and Calibrator ON.
pfd
= 1200 kHz and Calibrator OFF.
pfd
3
11
15
19
> 1 MHz, the device
pfd
≤ 1MHz
pfd
4
9
12
13
16
20
21
4/21
Page 5

AN2452 Software
8. Output divider:
– Direct output.
– Divider by 2.
– Divider by 4.
9. Configurations:
– Load/Save: load/save a configuration file.
– Load default/Save default: load/save a default configuration.
10. Program counter B: 12-bit counter.
11. VCO. VCO settings:
– Output frequency range/VCOs frequency range: press this button to show
information on the limits of F
out/Fvco
(only for the embedded VCOs).
– VCO selection (enabled only in Advanced mode):
- EXT: external VCO. The external VCO buffer is able to manage a signal coming
from an external VCO in order to build a synthesizer using the STW8110x only as
PLL IC. The external VCO signal can range from 625 MHz up to 5 GHz. Its
minimum power level must be -10 dBm.
- VCO A/VCO B: embedded VCOs.
12. Parallel port address. Hex value of the parallel port base address:
– 278: normally assigned to LPT2.
– 378: normally assigned to LPT1.
–3BC
– FILE: output is saved to a text file.
13. Prescaler modulus:
–P=16
–P=19
14. Reference divider. The 10-bit programmable reference counter allows the input
reference frequency to be divided to produce the input clock to the phase frequency
detector (PFD):
F
= F
ref
/ R
pfd
where
–F
–F
: PFD input frequency
pfd
: input reference frequency
ref
Limits: 2 ≤ R ≤ 1023
15. Frequency settings:
–F
–F
– -/+: finds a lower/higher rational value for F
–F
: input reference frequency (MHz)
ref
- Limits: 10 MHz ≤ F
: phase frequency detector (PFD) input frequency (kHz)
pfd
F
= F
pfd
vco
F
vco
/ R, where R is the reference divider factor.
ref
: VCO oscillating frequency (MHz)
= N · F
pfd
.
≤ 200 MHz
ref
pfd
.
– N: PLL division ratio
N = B
· P + A.
5/21
Page 6

Software AN2452
16. Output frequency settings:
–F
–F
– -/+: finds a lower/higher rational value for F
: output frequency (MHz)
out
F
= F
/ DIV, where DIV is the output division ratio.
vco
: output frequency step (kHz)
= F
/ DIV, where DIV is the output division ratio.
pfd
F
out
step
step
step
.
17. Charge pump current. The nominal value of the output current is controlled by an
external resistor (R
) and can be varied over 8 levels by means of 3 dedicated
ext
programming bits:
– CPSEL[2:0]: bits controlling the charge pump current
–R
–I
: the minimum value of the current is:
ext
I
= 2 Vbg / R
min
: charge pump current (mA)
cp
I
= (CPSEL + 1) · I
cp
where Vbg = 1.17 V.
ext
min
18. VCO voltage amplitude. The voltage swing of the VCOs can be adjusted over 4 levels
by means of two dedicated programming bits:
– PLL_A[1:0]: bits controlling the voltage swing of the VCO.
This setting trades current consumption with the VCO’s phase noise
performances. Higher amplitudes provide better phase noise, whereas lower
amplitudes save power.
19. Two digital interfaces are available:
2
–I
C
- ACK: if checked and the acknowledge is not received, read and write operations
fail. Uncheck this if the board is not enabled to read.
- Read: read the read-only register.
- Write: write the 6 write-only registers.
- A[2:0]: the device address (1100A
2A1A0
) must be set.
–SPI
Show sent data: the programming sequence is shown on the message list.
20. Device programming:
– Device programming modes:
- Device ON: device on with output buffer control disabled.
- Out Buffer CTRL: device on with output buffer control enabled. This control mode
allows to enable/disable the output stage by a hardware control pin (EXT_PD, pin
23) while the PLL stays locked at the desired frequency; in such a way a very fast
switching time is achieved. This feature can be useful in designing a ping-pong
architecture saving the cost of an external RF switch.
- Power Down: 'Power Down' mode enabled (device off).
– SEND: press this button to program the device.
6/21
Page 7

AN2452 Software
21. Message list: displays information, warnings and errors:
– CLEAR: press this button to delete all the messages.
Clicking the right mouse button on the message list shows a menu:
– Copy: copy the selected messages to the clipboard.
– Copy to File: copy the selected messages to a file.
– Append Mode: file is opened in append mode when 'Copy to File' is used.
– Select All: all messages are selected (double-clicking the left mouse button has
the same effect).
– Deselect All: no message is selected.
– Clear after Send: clears the message list after pressing the Send button.
7/21
Page 8

Software AN2452
1.3 Tutorial operation mode form
Figure 2. Tutorial operation mode form
1
3
2
4
1. Help for the current GUI operation mode.
2. Start next session with: select the operation mode for the next session.
3. Always on top:
– Red: enabled
– Gray: disabled
4. The tutorial form shows a description of the evaluation board.
8/21
Page 9

AN2452 Software
1.4 Waveform viewer
Figure 3. Waveform viewer
1
3
2
1
The digital signals used to program the device can be displayed on a waveform viewer:
2
● I
C - the following are shown:
– SCL (clock) signals sent to the device
– SDA (data) signals sent to the device
– ACK signals sent from the device
● SPI - the following signals are shown:
–Clock
–Data
– Load
1. Traces can be arranged by means of the vertical sliders, or in two default positions
(separated or superimposed traces) by means of a button.
2. The checkboxes allow you to display or hide the traces and bit descriptions that
become visible when zooming in.
3. The mouse buttons have the following functions on the waveform display:
– Left: zoom in
– Right: zoom out
– Middle: pan
9/21
Page 10

Evaluation board AN2452
2 Evaluation board
2.1 Setup
1. Connect the evaluation board to the PC parallel port via the cable included in the kit.
2. Choose which digital bus is used: the SPI or I
3. If the I
4. Connect a signal generator to the REF_CLK connector (external reference clock).
5. Connect the RF OUT connector to a spectrum analyzer.
6. Make sure that the device is not in hardware power-down (that is, ensure the switch is
The lock detector LED is turned on when the device is locked.
The nominal value of the charge pump output current is controlled by the external resistor
R15 (4.7 kΩ on the evaluation board).
The loop filter components are: C28, R17, R18, R18, C25, C30.
2
C is set, the device address must be chosen by connecting ADD [2:0] to VCC
(1) or GND (0). The default is 000.
Set the frequency as desired (13 MHz, 19.2 MHz, 76.8 MHz,…) and set the level to
10 dBm.
not in the off position).
2
C.
The output matching network can be adjusted, depending on the application.
10/21
Page 11

AN2452 Evaluation board
2.2 Description
2.2.1 Top view
Figure 4. STW8110x EVB (1G/2G/4G): top view
2
9
53mm
1
3
4
7
8
6
5
10
11
12
57mm
1. Digital interface connector: connect to the PC parallel port through the supplied cable.
2. Power supply (5 V).
3. Hardware power down: turn on/off the device.
4. Digital interface selection between I
2
5. I
C device address (default: 000).
6. Identification label. Two ID labels are present on the board network (see also
2
C and SPI.
2.2.2
- 1):
single output EVB top: STW8110x-EVBy,
bottom: aaaaaaaaxyzzz, where:
aaaaaaaa = internal ST code
x = 1,2,3 depending on the device (STW81101/2/3)
y = 1,2,4 depending on the board (EVB1G/2G/4G)
zzz = progressive board number
7. RF output.
8. Single output EVB: RF output matching network (see also
2.2.2
- 3 and
Figure 6
).
Differential output EVB: RF output de-coupling capacitors (C46 and C47).
9. Reference clock input.
10. STW8110x.
11. Loop filter and external resistor controlling the charge pump current (R15).
12. Lock detector LED.
11/21
Page 12

Evaluation board AN2452
2.2.2 Bottom view
Figure 5. STW8110x evaluation board bottom view
1
2
3
The bottom view (with the exception of the SMA connectors) is common to both the single
and the differential output evaluation boards.
1. Identification label (see
2. The R5 short enables the I
3. RF output matching network (L1, R13, L2, R12) - (see
2.2.1
- 6).
2
C read mode.
2.2.1
- 8 and
Figure 6
).
Figure 6. Output matching network (single output top and bottom views)
Single output top Bottom
12/21
Page 13

AN2452 Evaluation board
2.3 Schematics
Figure 7. Main schematic
13/21
Page 14
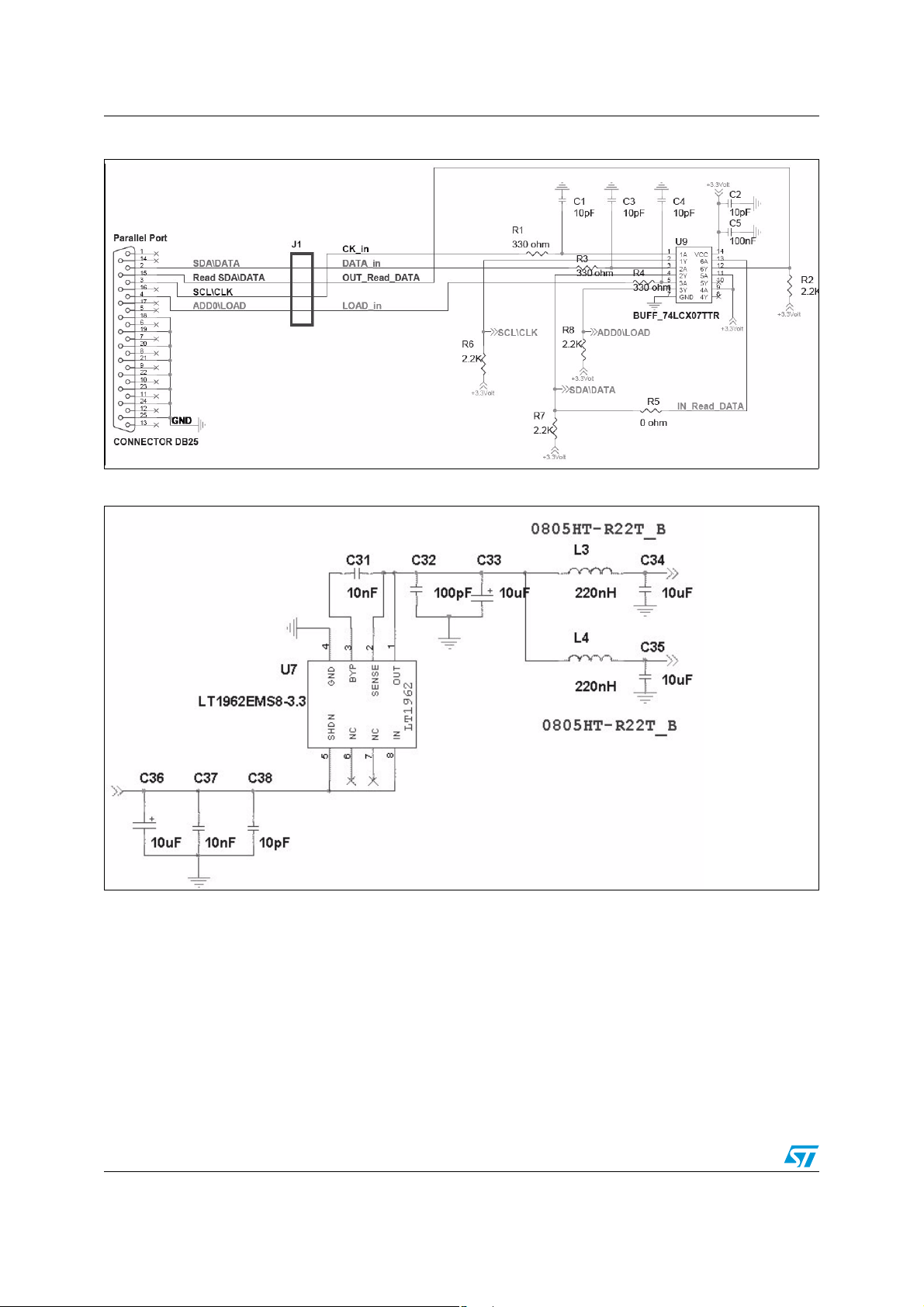
Evaluation board AN2452
Figure 8. Digital interface
Figure 9. Low noise voltage regulator
+3.3 V low noise
+3.3 V low noise
14/21
Page 15

AN2452 Evaluation board
Figure 10. Voltage regulator
+5 V
+5 V
+3.3 V
15/21
Page 16

Evaluation board AN2452
2.4 Layout
Figure 11. Top layer Figure 12. Bottom layer
Figure 13. Ground layer Figure 14. Power layer
2.5 Bill of materials
Table 1. Bill of materials common to all the EVBs (EVB1G/2G/4G)
Quantity Reference Part Part number - manufacturer
3 R1, R3, R4 330 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
5 R2, R6, R7, R8, R17 2.2 kΩ 0603 - PHICOMP
1R5 0 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
3 R9, R10, R11 100 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
1 R14 51 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
1 R15 4.7 kΩ 0603 - PHICOMP
16/21
Page 17

AN2452 Evaluation board
Table 1. Bill of materials common to all the EVBs (EVB1G/2G/4G) (continued)
Quantity Reference Part Part number - manufacturer
1 R16 270 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
1 R18 8.2 kΩ 0603 - PHICOMP
1R19 10 kΩ 0603 - PHICOMP
1 R20 4 kΩ 0603 - PHICOMP
C8, C13, C22, C25, C33, C34,
9
C35, C36, C40, C35, C36, C40
5 C1, C2, C3, C4, C38 10 pF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
3 C6, C7, C11 15 pF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
3 C5, C26, C39 100 nF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
5 C10, C18, C20, C23, C45 22 pF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
6 C9, C12, C14, C21, C24, C44 1 nF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
1 C19 1.8 nF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
1 C28 270 pF GRM188-COG - 0603 - Murata
1 C30 68 pF GRM188-COG - 0603 - Murata
1 C29 2.7 nF GRM188-COG - 0603 - Murata
10 F GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
1 C27 47 F 1210 - AVX TPS Series III
3 C31, C37, C42 10 nF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
1 C32 100 pF GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
2 C41, C43 1 F GRM188 - 0603 - Murata
2 L3,L4 220 nH 0805HT- R22T B - Coilcraft
3 U2, U3, U4 0 Ω 0603 - PHICOMP
1D1 LED
1Q1 BC847C ST
1 U6 STW8110x ST
1 U7 LT1962EMS8-3.3 Linear Technology
1 U8 LK112M33TR ST
1 U9 74LCX07TTR ST
1 SMA (1.6mm) SMA REF Freq
1 SMA (1.6mm) SMA Band 2
1 J1 10 pole connector
1J2 +5VOLT
1J3 GND
3 S1, S2, S3 Switch
17/21
Page 18

Evaluation board AN2452
Table 2. EVB1G output matching network
Quantity Reference Part Part number - manufacturer
1 Cs2 0.5 pF GRM1555C1HR50C - MURATA
1 XS1 2.1 nH 0403HQ-2N1XJL - COILCRAFT
Cs3 NC
Cs1 NC
Cs4 NC
Cs5 NC
1 C16 22 pF GRM1555C1H220J - MURATA
1 U5 0900BL15 0900BL15C050 - JOHANSON
2 C15, C17 8.2 pF GRM1555C1H8R2D - MURATA
2 R12, R13 24.9 Ω
2 L1, L2 18 nH 0403HQ-18NXJL- COILCRAFT
Table 3. EVB2G output matching network
Quantity Reference Part Part number - manufacturer
Cs2 NC
1 XS1 1.9 nH 0402PA-1N9X B - COILCRAFT
1 Cs3 1.2 pF GRM1555C1H1R2C - MURATA
Cs1 NC
Cs4 NC
Cs5 NC
1 C16 22 pF GRM1555C1H220J - MURATA
1 U5 1600BL15 1600BL15B100 - JOHANSON
2 C15, C17 22 pF GRM1555C1H220J - MURATA
2R12, R13 51 Ω
2 L1, L2 5.5 nH 0403HQ-5N5XJL - COILCRAFT
18/21
Page 19

AN2452 Evaluation board
Table 4. EVB4G output matching network
Quantity Reference Part Part number - manufacturer
1 Cs2 1.2 pF GRM1555C1H1R2C - MURATA
1 XS1 4.7 pF GRM1555C1H4R7C - MURATA
1 Cs3 1.2 pF GRM1555C1H1R2C - MURATA
Cs1 NC
1 Cs4 1 pF GRM1555C1H1R0C - MURATA
1 Cs5 1 pF GRM1555C1H1R0C - MURATA
1 C16 12 pF GRM1555C1H120J - MURATA
1 U5 3700BL15 3700BL15B100 - JOHANSON
2 C15, C17 12 pF GRM1555C1H120J - MURATA
2 R12, R13 51 Ω
1 L1, L2 5.5 nH 0403HQ-5N5XJL - COILCRAFT
19/21
Page 20

Revision history AN2452
3 Revision history
Table 5. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
17-Jul-2007 1 Initial release.
13-Aug-2007 2 Updated item 6 in
15-Feb-2008 3
Modified
mode form
Added
Section 1.2: Main form
.
Section 1.4: Waveform viewer
Section 2.2.1: Top view
and
Section 1.3: Tutorial operation
.
.
20/21
Page 21

AN2452
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2008 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
21/21
 Loading...
Loading...