Page 1

AN2385
Application note
Power dissipation and its linear derating factor, silicon
Limited Drain Current and pulsed drain current in MOSFETs
Introduction
Datasheets of the modern power MOSFET devices, either of low voltage or of high voltage,
show in the section entitled "Absolute Maximum Rating" the values of some important
parameters that regard the SOA (safe operating area). As it is well kwown in literature, SOA
is the area that includes all the I
conditions.
These important parameters are studied in this technical article. In particular, attention will
be focused on the Power Dissipation and its Linear Derating Factor, Silicon Limited Drain
Current and Pulsed Drain Current. This technical article will explain what these parameters
are and how they can be calculated. It will recall some basic and simple technical concepts
and can be a useful tool for customers to understand and facilitate reading of a power
MOSFET datasheet.
operating points where the device works in safety
D-VDS
June 2006 Rev 1 1/14
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2385
Contents
1 Determination of the SOA limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Silicon limited drain current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Determination of the power dissipation and its derating factor . . . . . . 9
4 Pulsed drain current (IDM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5 Conclusions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
6 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2/14
Page 3

AN2385 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Typical FBSOA of a Power MOSFET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. R
Figure 3. Typical RBSOA of a Power MOSFET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. Silicon limited drain current vs case temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 5. Power dissipation vs T . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 6. IDM determination considering the output characteristic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 7. Junction to case maximum effective transient thermal impedance for TO-220 package.. . 10
Figure 8. Determination of the maximum rectangular pulse duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
limit for MOSFET's FBSOA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
DSON
3/14
Page 4

List of tables AN2385
List of tables
Table 1. Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4/14
Page 5
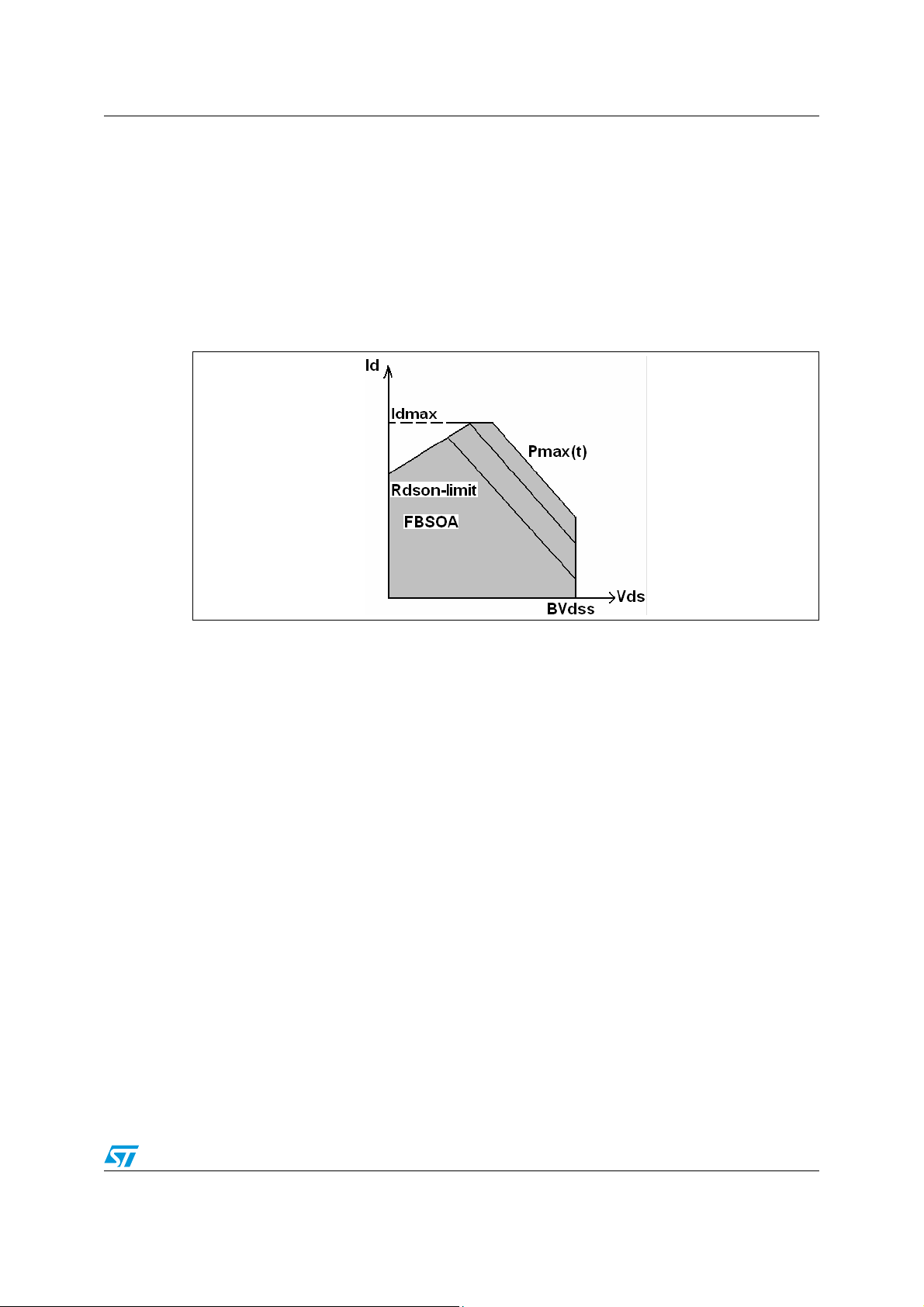
AN2385 Determination of the SOA limits
1 Determination of the SOA limits
SOA is the acronym of Safe Operating Area. It includes all the ID-VDS operating points
inside where the device works in safety conditions. There are two kinds of SOA. The first
one is named Forward Biased Safe Operating Area (FBSOA), while the second one is
named Reverse Biased Safe Operating Area (RBSOA). FBSOA is the SOA during the
device on state, while RBSOA is the SOA when the MOSFET switches off. Supposing that
the I
and VDS axis are in log scale, a typical FBSOA can be depicted as in Figure 1.
D
Figure 1. Typical FBSOA of a Power MOSFET
I
is the maximum drain current limit of the MOSFET. It is usually fixed by the wires that
Dmax
connect the drain and source pads to the package pins respectively. BVdss is the maximum
drain-source voltage that the device can sustain (breakdown voltage). P
max(t)
is the
maximum power that the device can dissipate. It depends on the junction temperature and
power pulse interval time and on the package used. In fact, if the junction temperature
overcomes typically 150'C or 175'C, as defined in the automotive devices, the MOSFET
could fail or, however, the device works out of the guaranteed temperature spec.
Furthermore, increasing the case temperature, the P
value decreases due to a lower
max(t)
energy, which is necessary to bring the junction temperature to the maximum guaranteed
value. P
is also a function of the power pulse interval time because, fixing the power
max
pulse, the energy dissipated in the MOSFET, as well as the junction temperature rises,
increasing the power interval time. In particular, when the power pulse interval time
increases, P
Another limit for FBSOA is established by R
decreases and the SOA area decreases too.
max(t)
of the device. In fact, when the device is in
DSON
on state without loads connected to the component, all the voltage feed is applied on the
drain-source terminals and, thus, the maximum drain current that can flow in the transistor is
fixed by V
DD
and R
DSON
(Figure 2.).
5/14
Page 6

Determination of the SOA limits AN2385
Figure 2. R
In RBSOA the limits are fixed by the I
limit for MOSFET's FBSOA
DSON
DMAX
and BV
Figure 3. Typical RBSOA of a Power MOSFET
(Figure 3.).
DSS
6/14
Page 7

AN2385 Silicon limited drain current
2 Silicon limited drain current
Usually, in every Power MOSFET datasheet the drain current limit is fixed by the package
limit. It depends on the kind, number and the size of the wires that connect the drain and the
source pads to the respective package pins. However, another important parameter defined
in the Power MOSFET datasheets is the Silicon Limited Drain Current. The Silicon Limited
Drain Current is the maximum drain current that can flow in the device excluding the
package limitation and considering as thermal impedance the junction to case thermal
resistance value (R
calculated considering the device in "on state" with a case temperature equal to 25°C and
supposing that it works at the maximum junction temperature. Considering this last
operating condition, R
around two times higher at the ambient temperature (25°C). In thermal equilibrium
conditions, the following expression can be written as shown below:
Equation 1
P
is the maximum power that the device can dissipate at the maximum junction
MAX
temperature. P
MAX
). Furthermore, the Silicon Limited Drain Current is typically
THJC
must be considered at the maximum junction temperature. It is
DSON
T
JMAX
25° CR
THJCPMAX
•=–
can be written as:
Equation 2
JMAX
2
I
•=
DSL
I
is the Silicon Limited Drain Current. I
DSL
P
MAX
R
DSON T
()
can be written as:
DSL
Equation 3
I
DSL
-----------------------------------------------------------=
R
DSON T
T
25° C–
JMAX
•
()RTHJC
JMAX
Sometimes, in the Power MOSFET datasheets, the Silicon Limited Drain Current is shown
at different case temperature conditions. In this case, the expression of I
becomes:
DSL
Equation 4
I
DSL
T()
-----------------------------------------------------------=
R
DSON T
T
()RTHJC
JMAX
JMAX
T–
•
The Limited Drain Current versus case temperature is also shown in the Figure 4. This is
considering an example where the junction to case thermal resistance equals 0.5°C/W, the
maximum junction temperature is 175°C and the R
DSON(TJMAX)
equals 16mOhm. In the
graph, the Package limited Drain Current is also highlighted (75A).
7/14
Page 8

Silicon limited drain current AN2385
Figure 4. Silicon limited drain current vs case temperature
For Case Temperatures that are lower of around 110°C, the Package Limited Current is
lower than the silicon one and thus, the device Limited Current is fixed at 75A. When the
case temperature overcomes 110°C, the device Limited Current equals the Limited Silicon
Current.
8/14
Page 9

AN2385 Determination of the power dissipation and its derating factor
3 Determination of the power dissipation and its
derating factor
The Power Dissipation value is the maximum power that the device can dissipate in
continuous operating mode when the device works in "on state" and the thermal impedance
is only due to R
Power MOSFET datasheets, it is reported at ambient temperature (25°C). In order to
calculate the power dissipation value the consider R
maximum junction temperature. It is possible to demonstrate that such value is around two
times the values of R
Dissipation can be written as:
Equation 5
Furthermore, P
considering that the guaranteed maximum junction temperature is 150°C or 175°C (see
Figure 5.).
Figure 5. Power dissipation vs T
. The power dissipation depends on the case temperature. Typically, in
THJC
value must be considered at the
DSON
at ambient temperature considering the data measured. Power
DSON
T
P
D
T25° C=()
can be established for any other fixed operation case temperature
D
R
DSON T
()
JMAX I
()
DSL
2
I
•
DSL
JMAX 25° C–
---------------------------------==
R
THJC
The Linear Derating Factor of Power Dissipation factor is defined as the angular coefficient
of the line shown in Figure 5. It can be calculated as:
Equation 6
D
---------------------------------
T
P
D
T25° C=()
JMAX 25° C–
--------------------==
R
THLJC
1
9/14
∂P
----------
∂T
Page 10

Pulsed drain current (IDM) AN2385
4 Pulsed drain current (IDM)
The Pulsed Drain Current (IDM) is the maximum current that the device can bring, excluding
the package limitation and considering a very short power pulsed interval time. It depends
on the guaranteed maximum gate-source voltage and on the device trans-conductance at
the specific I
gate voltage equal to the guaranteed maximum permissible gate-source value when the
transistor works in switching mode and not in the linear zone (see Figure 6.).
. In particular, IDM is the current that the device can bring with an applied
DM
Figure 6. I
determination considering the output characteristic
DM
In order to establish the Pulsed Drain Current interval time, avoiding that the junction
temperature overcomes the maximum guaranteed value, the Junction to Case Maximum
Effective Transient Thermal Impedance must be considered (see Figure 7.).
Figure 7. Junction to case maximum effective transient thermal impedance for TO-
220 package.
Considering that the Dissipated Power is equal to:
Equation 7
PDR
10/14
2
I
DSON 175° CIDM,()()
•=
DM
Page 11

AN2385 Pulsed drain current (IDM)
where R
DSON(175°C@IDM)
is the on resistance of the device at the guaranteed maximum
junction temperature and at the Pulsed Drain Current value, and that:
Equation 8
PDZ
where Z
is the junction to case thermal impedance at the specific operation conditions,
THJC
the maximum acceptable Z
• TT
THJC
value can be achieved as:
THJC
JMAX
25° C–=∆=
Equation 9
Z
THJC
T
----------------------------------------------- -=
R
DSON175° CI
JMAX
25° C–
2
,()
DM
Thus, considering a specific Power Pulse with a fixed duty cycle, the maximum Rectangular
Pulse Duration can be achieved.
As example, Figure 8. shows the determination of the maximum Rectangular Pulse Duration
considering a Pulsed Drain Current equal to 600A, T
25°C, duty cycle of 0.02 and R
DSON(175°C, IDM)
equal to 20mOhm. Z
of 175°C, case temperature of
JMAX
can be calculated
THJC
as:
Equation 10
Z
THJC
175° C25° C–
---------------------------------------------- -
20 10
3–
•
600•
2
0.021
° C
-------
•==
W
Figure 8. Determination of the maximum rectangular pulse duration
In this example, the maximum Rectangular Pulse Duration equals 30usec. For power pulse
of higher duration the junction temperature overcomes 175°C and the device could fail.
It is important to highlight that the measured on resistance must be performed at the
maximum junction temperature and also at the specific Pulsed Drain Current. In fact,
increasing the drain current also R
increases and thus, of course, this effect must be
DSON
taken into account.
11/14
Page 12

Conclusions AN2385
5 Conclusions
This technical article has explained what the Power Dissipation and its Linear Derating
Factor, Silicon Limited Drain Current and Pulsed Drain Current (I
are and how they can be calculated. Furthermore, attention has also been placed on the
definition of the MOSFETs SOA (FBSOA and RBSOA) and on the Junction to Case
Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance.
) in MOSFET datasheets
DM
12/14
Page 13

AN2385 Revision history
6 Revision history
Table 1. Revision history
Date Revision Changes
13-Jun-2006 1 Initial release
13/14
Page 14

AN2385
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZE REPRESENTATIVE OF ST, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED,
AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS,
NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS, WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY, DEATH, OR
SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2006 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
14/14
 Loading...
Loading...