Page 1

AN2349
Application note
Simple cost-effective PFC using Bipolar Transistors
for low-to-medium power HF Ballasts
Introduction
This note deals with the implementation of a Power Factor Correction (PFC) in a
Discontinuous-mode Boost Converter where a PFC stage is achieved with a power bipolar
transistor driven in self oscillating configuration. The new solution proposed exploits the
physical relation (t
(PWM) signal in a Boost Converter.
, IC) of any bipolar transistor to achieve the Pulse Width Modulation
S
June 2006 Rev 1 1/30
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2349
Contents
1 PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Application description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Feedback block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Selection of boost output inductor L1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1 Selection of boost output capacitor C4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4 PFC driving network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.1 Feed-Back block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5 T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1 220V design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.2 120V design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2/30
Page 3

AN2349 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. 40W Demoboard 220V bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 2. 40W Demoboard 120V bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 3. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3/30
Page 4

List of figures AN2349
List of figures
Figure 1. Valley Fill circuit schematic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. Valley Fll input current waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3. Active PFC with IC and MOSFET in boost topology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. Base schematic of Bipolar PFC in HF ballast voltage Fed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 5. Ts modulation in bipolar PFC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 6. Imain achieved using the basic Bipolar PFC shown in Figure 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 7. Detail of storage time value and Ic in t2 istant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 8. Detail of storage time value and Ic in t1 istant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 9. Complete electrical schematic of the Bipolar PFC in HF Ballast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 10. PFC stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 11. Feed-back block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 12. PFC waveforms with Feedback block working . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 13. Imain achieved by the proposed bipolar PFC solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 14. Detail of Storage time value in t2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 15. Detail of storage time value in t1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 16. Pre-heating @ 220V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 17. Current on the electrolytic capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 18. Inductor current with di/dt>0 and transformer voltage shape . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 19. Inductor current with di/dt=0 and transformer voltage shape . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 20. Inductor current with di/dt<0 and transformer voltage shape . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 21. Transformer Vout shape and base current shape . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 22. Collector current and base current shape. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 23. Detail of T1 total charge during Ton . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 24. 40W demoboard electrical schematic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 25. 40W demoboard PCB layout and mounting components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4/30
Page 5
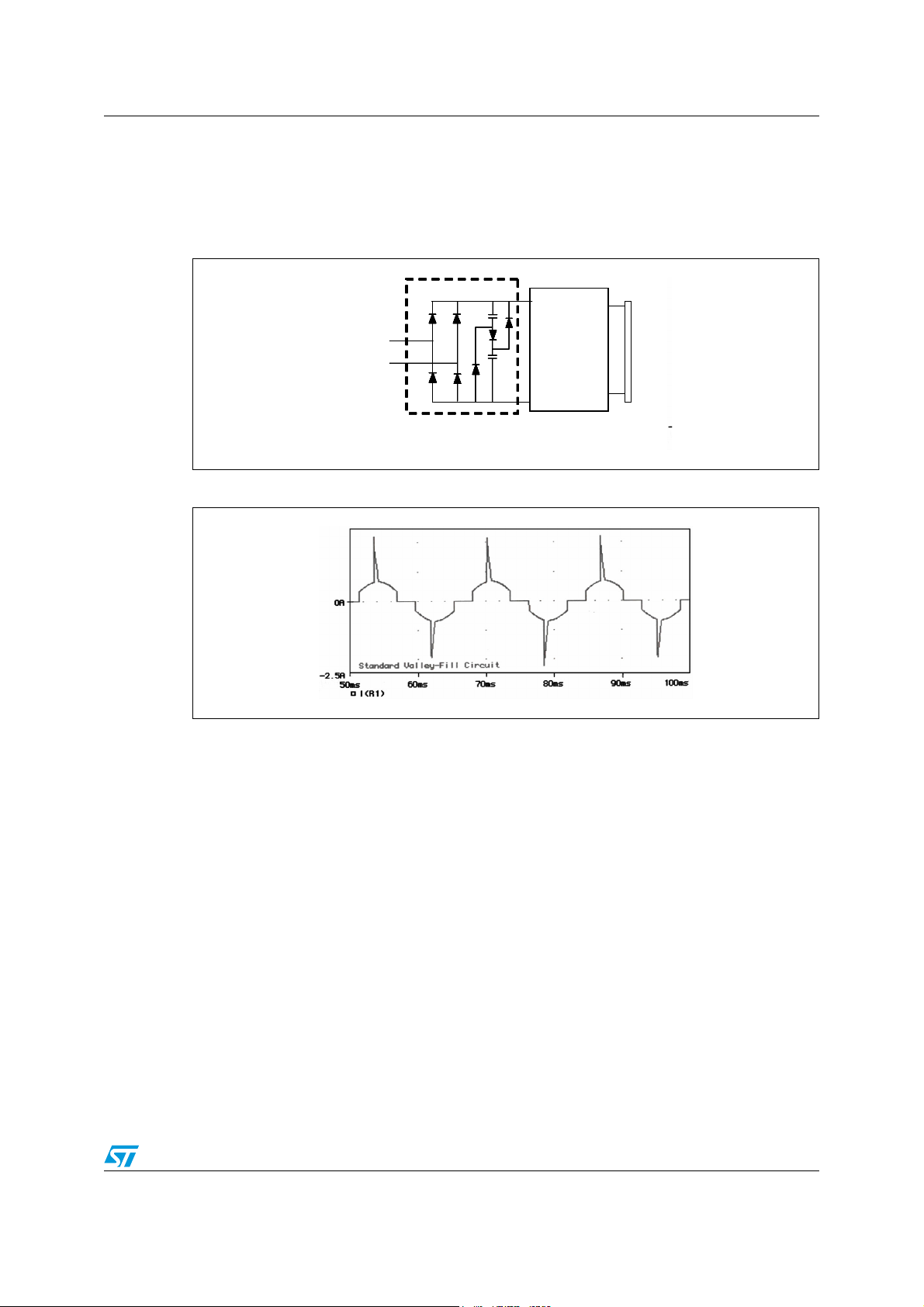
AN2349 PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts
1 PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts
The Valley Fill circuit is an example of a low-cost passive PFC available on the market.
Figure 1. Valley Fill circuit schematic diagram
DC-AC
DC-AC
DC-AC
DC-AC
CONVERTER/
CONVERTER/
CONVERTER/
AC
AC
AC
AC
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
RECTIFIER+PFC+DC
RECTIFIER+PFC+DC
RECTIFIER+PFC+DC
RECTIFIER+PFC+DC
FILTER BLOCK
FILTER BLOCK
FILTER BLOCK
FILTER BLOCK
Figure 2. Valley Fll input current waveform
CONVERTER/
BALLAST
BALLAST
BALLAST
BALLAST
LAMP
LAMP
LAMP
LAMP
The capacitors are charged in serie, and discharged, via the two diodes, in parallel. Current
is drawn from the line from 30° to 150°, and then from 210° to 330°. Discontinuities occur
from 150° to 210° and from 330° to 360°, and then the cycle repeats itself.
Disadvantages of this PFC solution are spikes on input current waveform and large zero
current gaps between the half sinusoidal wave and the next one (meaning a lower power
factor and high input current distortion), and high ripple in the DC output voltage that causes
poor performance in High Power Lamps. On the other hand, high performances can be
achieved by IC driver optimized for controlling PFC regulators in boost topology as shown in
Figure 3.
5/30
Page 6
PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts AN2349
Figure 3. Active PFC with IC and MOSFET in boost topology
The proposed Bipolar PFC solution targets the low-cost HF Ballast market up to 80 W as it
provides a simple cost-effective solution without sacrificing THD and PF levels. It does not
need any ICs to achieve the PWM signal since it uses just a power bipolar transistor and a
closed-loop feedback that performs the duty cycle modulation and a satisfactory output
power regulation.
1.1 Application description
The active PFC solution with Bipolar transistor adopts the Boost topology working in
Discontinuous Conduction mode. This is the most simple and cost-effective solution for
220V and 120V mains and low\medium power.
Figure 4. Base schematic of Bipolar PFC in HF ballast voltage Fed
No IC is used to generate a PWM signal, but the physical relation (t
, IC) of any power
S
bipolar transistor is exploited when the base current IB value is kept constant.
Figure 5 shows two different storage time values at two different input V
bipolar reaches a higher saturation level than in t
The overall switch on time is given by the sum of "I
therefore, if the "I
time" is constant, the duty cycle changes according to the ts
BON
modulation. This natural duty cycle variation generates an appropriate PWM signal to
6/30
, and this means tS1>tS2.
2
time" plus the storage time,
BON
AC
values: in t1 the
Page 7
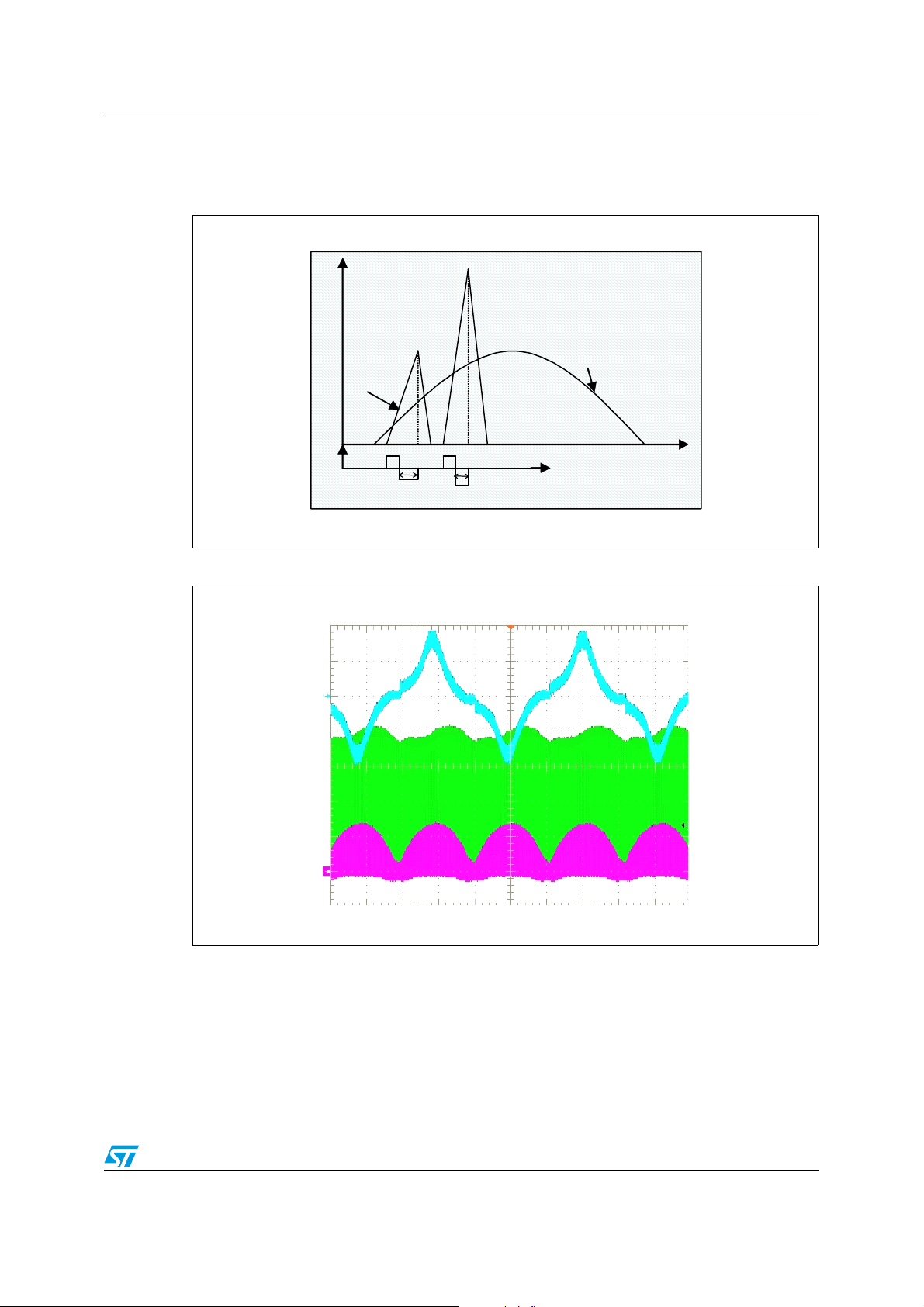
AN2349 PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts
AV
control the PFC stage and reduces the Imain distortion achieving a THD in the range of
about 30%, with a shape of the current drawn from the main as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 5. Ts modulation in bipolar PFC
I
IN
IIN
IL=I
c
t
I
B
s1
t
s2
t
t
Figure 6. Imain achieved using the basic Bipolar PFC shown in Figure 4
Imain
Vce
Ic
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show in a real situation, what has been explained before.
7/30
Page 8
PFC solutions for low-medium power HF Ballasts AN2349
Figure 7. Detail of storage time value and Ic
istant
in t
2
Injected charges
Injected charges
Storage time
Storage time
Ib
Ib
Vce
Vce
Ic
Ic
The PWM signal acts on T1 bipolar transistor base through an auxiliary winding T on the
transformer normally used in the ballast.
Figure 8. Detail of storage time value and Ic
in t1 istant
Injected charges
Injected charges
Storage time
Storage time
Ib
Ib
Vce
Vce
Ic
Ic
8/30
Page 9
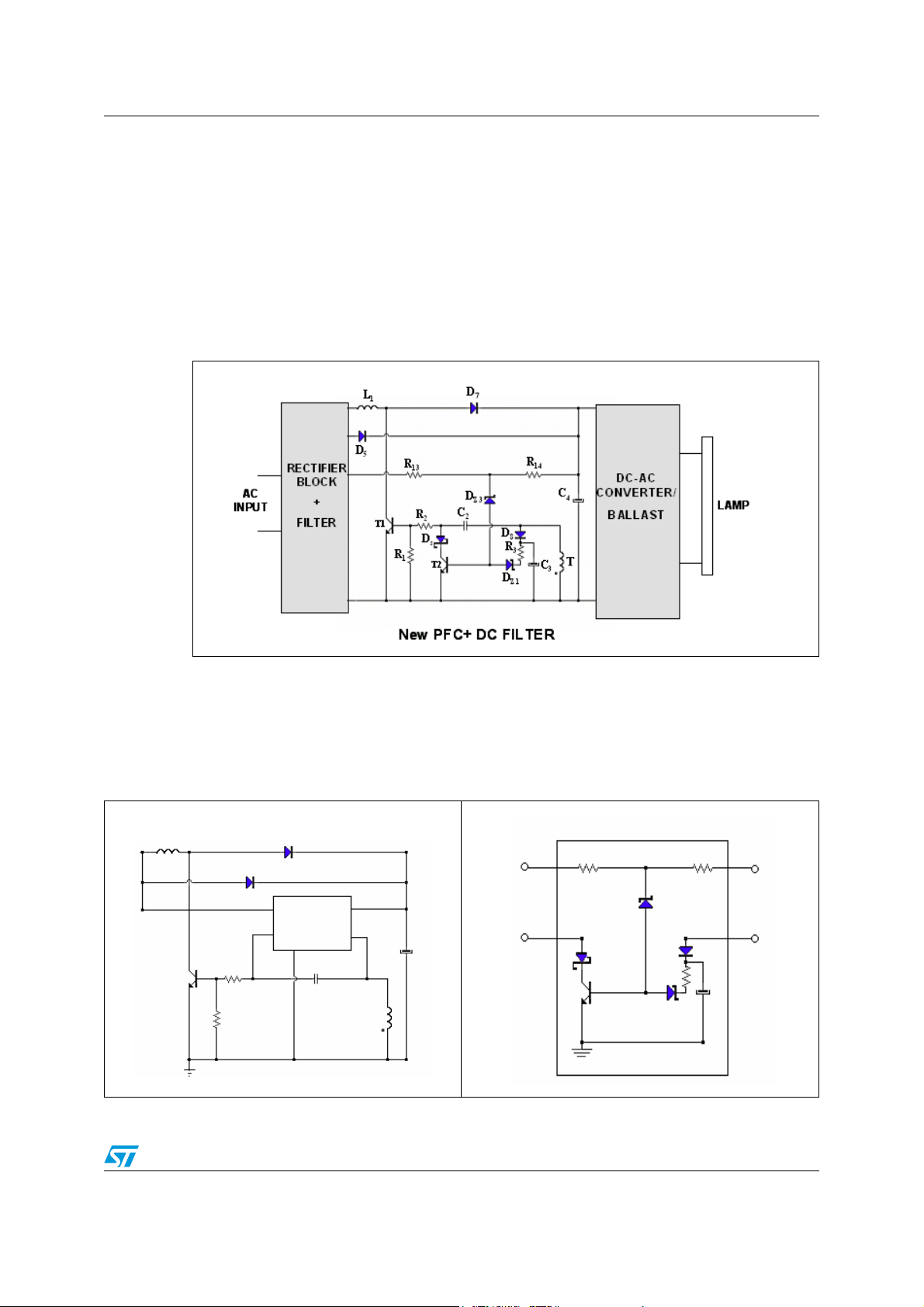
AN2349 Feedback block
2 Feedback block
The duty cycle modulation performed by the Basic Solution shown in Figure 4 is not enough
effective to achieve high THD values and no protection task can be implemented against
overoload or high VAC values.
A negative feedback network has been introduced to further control the duty cycle
modulation by modifying the total Q
Chapter Figure 9. on page 9 shows the complete solution of the proposed PFC stage.
Figure 9. Complete electrical schematic of the Bipolar PFC in HF Ballast
charge which is injected into the T1 base.
on
The feed-back block in Figure 11 changes the T
amplitude and duration through the intervention of the transistor T
proposed network by the T
duty cycle of the main switch (T
conduction reduces the base current permitting to reduce the
2
) performing a further THD correction and output power
1
charge by modifying both the I
1 QON
. In particular the
2
regulation.
Figure 10. PFC stage Figure 11. Feed-back block
D7
D5
D5
D7
Feed-Back
Feed-Back
Block
Block
C2
C2
Input 2
Input 2
Input 3
Input 3
T
T
C4
C4
Input 1
Input 1
Output
Output
R13
R13
Ds D8
Ds D8
T
T
2
2
Dz3
Dz3
Dz1
Dz1
L1
L1
Input 1
Input 1
Output
Output
T
T
1
1
R2
R2
R1
R1
R3
R3
R14
R14
C3
C3
Input 2
Input 2
Input 3
Input 3
BON
9/30
Page 10

Feedback block AN2349
The network D8, R3, DZ1, and C3 in Figure 11 ensures the switch protection during start-up
thanks to a smart combination of three input signals.
1. Input 1 comes from the Main Voltage and it'is used to limit the amount of the distortion
improving the THD.
2. Input 2 comes from PFC Vout : it'is used to further regulate the power factor and to
regulate the PFC Vout against supply voltage variations.
3. Input 3 signal is a voltage proportional to the pre-heating current during start up and it'
is used. to protect the power switch against over voltage . The Output signal is the base
current driving the T
The transistor T
during its On-state modifies the natural modulation imposed by the storage
2
time variation of the transistor T
● It reduces the time constant during the charge of the capacitor C
time length of the On base current of T
●
It shunts part of the same current to ground thus reducing its amplitude.
main switch.
1
since:
1
thus reducing the
2
1
The combination of the previous two effects implies a reduction of the duty cycle of the
transistor T
The schottky diode Ds in series with the collector of the transistor T
current on the transistor itself ensures a low voltage drop during T
helping to correct the THD and the power factor level .
1
by blocking any reverse
2
on state.
2
The steady state waveforms associated to the new proposed circuit are below reported in
Figure 16.
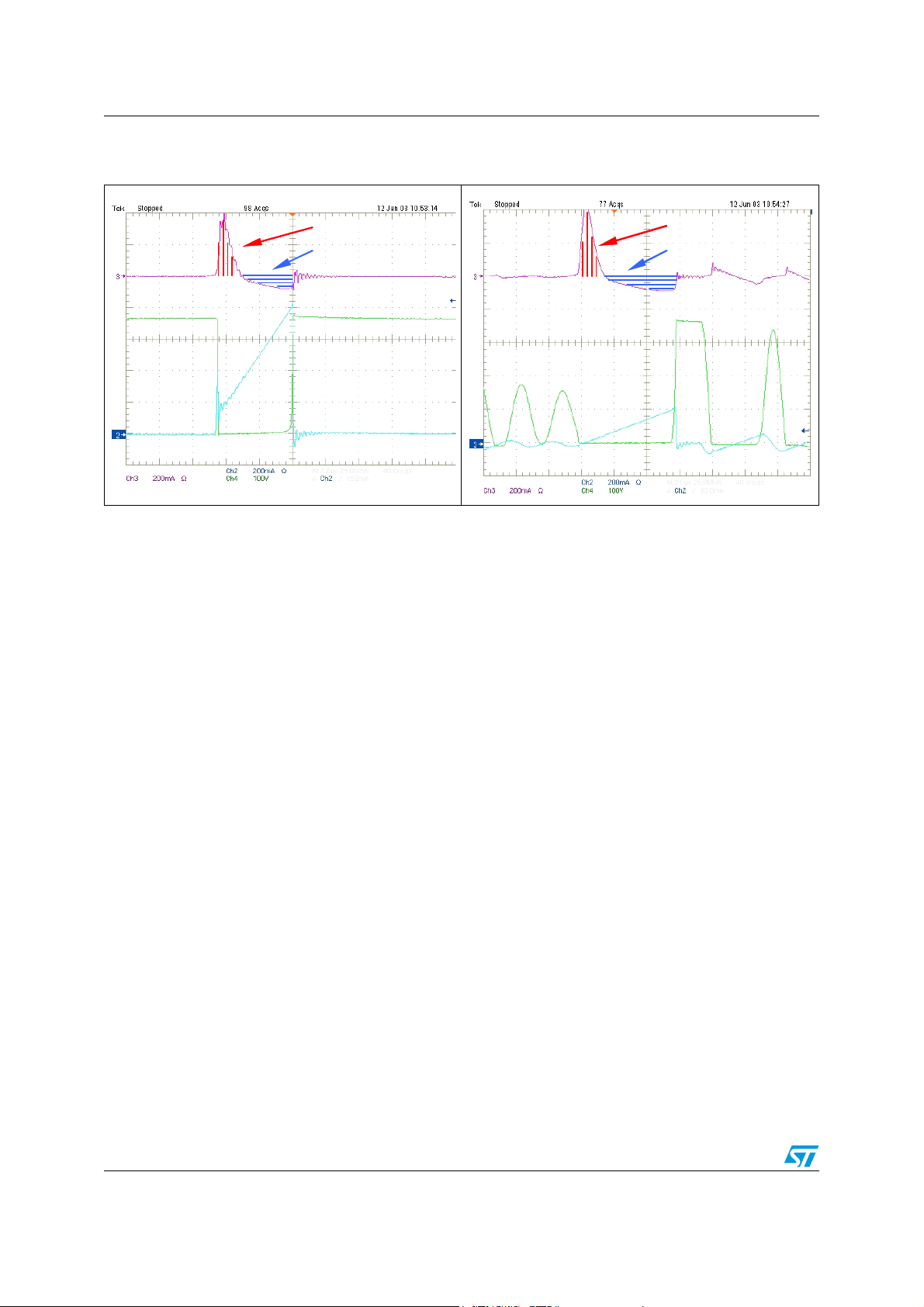
Figure 12. PFC waveforms with Feedback
block working
Figure 13. Imain achieved by the proposed
bipolar PFC solution
Imain
Imain
Vce
Vce
Ic
Ic
Components values of the Feedback block have been chosen to achieve a base current
modulation that allows obtaining a constant collector current in the range of V
sen ωt with
M
30° ≤ωt≤ 150°.
Waveforms reported in Figure 13 shows now a quasi-sinusoidal behavior of the current
drawn from the main, while the blue waveform in Figure 12 shows the T
1 IBON
modulation
performed by the negative feedback.
10/30
Page 11

AN2349 Feedback block
The overall storage time modulation achieved by the Bipolar PFC working with the negative
feedback network is evident in Figure 14 and Figure 15 showing real values of storage time
detected on the oscilloscope at t
Figure 14. Detail of Storage time value in t
Injected charges
Injected charges
Storage time
Storage time
and t2 instances.
1
Figure 15. Detail of storage time value in t1
2
Injected charges
Injected charges
Storage time
Storage time
Figure 16 shows the pre-heating and start-up phase waveforms.
Figure 16. Pre-heating @ 220V
VceIcVce
Ic
11/30
Page 12

Selection of boost output inductor L1 AN2349
3 Selection of boost output inductor L
The boost output inductor L1 is calculated in the peak of sinusoidal voltage at maximum
instantaneous input power in order to obtain the minimum I
discontinuous mode operation. This calculation is made considering a working operation at
constant current peak I
, due to the base current modulation, and fixing a working switching
P
frequency. Supposed a purely resistive load it is:
Equation 1
V
MIM
------------------------ -==
2
where V
PV
is the maximum input main voltage and IM is the maximum input main current.
M
•
effIeff
Then from Equation 1,
Equation 2
• 2P=
V
MIM
Now considered the total energy stored by the inductor in the period at the maximum input
main voltage:
Equation 3
2P
2PT
-------==
f
sw
where T is the period and f
E
TOT
is the working switching frequency.
SW
But the total energy stored by the inductor in the period is, also, the sum of two contributes,
the first LI
2
/2, due to the inductor L1 charge and the other one, VMIptB/2, due to the
P
discharge of the same via the main voltage, then equalizing the two terms we obtain:
value assuring the
P
•()
1
Equation 4
2P
---------
f
SW
where I
is the peak of the working switching current at maximum voltage VM and tB is the
P
inductor discharge time that is:
Equation 5
with V
Substituting t
imposed at 390V and it is the PFC output voltage.
out
in Equation 4:
B
Equation 6
2P
---------
f
SW
LI
-----------
2
2
P
•
V
MIP
------------------ -
2
calculated in the max point of the sinusoid, in general for 30°≤ ωt ≤150° it can be can
written:
12/30
2
V
LI
-----------
2
t
-------------------------=
B
V
•
MIp
P
----------------------- -+=
LI
P
–
outVM
LI
P
-------------------------
V
–
outVM
• t
2
B
2
LI
-----------
=+=
V
P
-------------------------
2
V
outVM
out
–
Page 13

AN2349 Selection of boost output inductor L1
tAt
Equation 7
2P t()
--------------
f
SW
LI
-----------
2
2
P
senωtIP•
V
M
---------------------------------- -
2
-----------------------------------------
•
V
outVM
where according to the working operation, LI
LI
P
senωt–
2
/2 is the constant term, while the other one
P
LI
-----------
2
2
P
•=+=
V
out
-----------------------------------------
V
outVM
senωt–
contains the sinusoidal modulation of the main current with 30°<ωt<150°.
In order to calculate I
, you consider the instantaneous Max Power in a 50 Hz period:
P
Equation 8
PMVMIM•=
is also the medium value of the peak of the working switching current in the period T
but I
M
corresponding to the max point of the Main Voltage V
.
M
Equation 9
+
B
--------------- -
•=
2T
is the L1 discharge time.
out-VM
where t
I
MIP
=LIP/VM is the L1 charge time and tB=LIP/V
A
Now from Equation 9:
Equation 10
2T
M
--------------- -
•=
t
+
AtB
IPI
Substituting Equation 10 in Equation 7 and resolving by L:
Equation 11
2
where t
t
+
P
AtB
--- -
L
/T is chosen equal to 0.70 in order to ensure that the circuit remains in the
A+tB
--------------- -
•
f
T
--------
•
I
V
1
-------------------------
•=
2
M
discontinuous mode leaving a dead-time of 0.3T.
3.1 Selection of boost output capacitor C
The PFC works to obtain a sinusoidal Main Current. Therefore the capacitor C4 will charge
with a rectified current at double half-wave shape, as shown in Figure 17. This current shape
will generate on the electrolytic capacitor an almost continuous voltage with a ripple value
depending on the same capacitor value. In order to calculate the capacitor C4, the current
flowing on the electrolytic capacitor can be asssumed as thoroughly the sum of two
contributions, one due to a continuous component and other one due to an alternate
component, as shown in Figure 17. The alternate component will have double frequency
respect to the main frequency.
–
outVM
V
out
4
13/30
Page 14

Selection of boost output inductor L1 AN2349
Figure 17. Current on the electrolytic capacitor
I
I
|IMsenωt|
|IMsenωt|
I
I
= 2*IM/π
= 2*IM/π
DC
DC
I
I
AC
AC
IM –2*IM/π
IM –2*IM/π
π
π
I
I
M
M
2π
2π
T
T
T
T
Thus for 0<ωt<Π:
Equation 12
IMωtsin I
+≅
DCIAC
where I
, the continuous component, is the mean value of IM sinωt :
DC
Equation 13
π
and I
I
M
I
DC
is the alternate component with double frequency and out of phase of π/2 respect to
AC
-----
=
∫
ωt • t
π
0
2I
-------- -=dsin
M
π
the main one that is:
Equation 14
I
I
AC
M
2I
-------- -–
M
sin=
π
π
2ωt–
-- -–
2
Now substituting Equation 13 and Equation 14 into Equation 12, we have:
Equation 15
I
ωtsin
M
V
The peak ripple voltage is:
M
RIPPLE
2I
M
-------- - I
π
2I
M
---------–
M
sin+≅
π
π
2ωt–
-- -–
2
Equation 16
V
PP
RIPPLE
V
M
RIPPLE
V
M
But is the alternate voltage on the capacitor due to the I
RIPPLE
----------------------- -=
2
AC
Equation 17
V
M
RIPPLE
14/30
2I
M
I
-------- -–
M
XC•=
π
Page 15

AN2349 Selection of boost output inductor L1
V
V
where from Equation 17, the IM-2IM/π is the max amplitude of the alternate current IAC on
the electrolytic capacitor, while X
electrolytic capacitor, with f
*
is the capacitive reactance XC=ωC
C
=2f
main(fmain
=50/60Hz).
=2πf* of the
OUT
Equalizing Equation 16 and Equation 17 you have
Equation 18
PP
RIPPLE
----------------------- -
2
=
2I
M
I
-------- -–
M
2πf• C
π
OUT
and resolving by C:
Equation 19
OUT
----------------------- -
4πf
C
where is the peak to peak ripple voltage and from Equation
2 I
V
=2*P/VM.
M
PP
RIPPLE
v
DC
MAXVDC
OUT
–=
out
MIN
PP
RIPPLE
1
-----
•=
I
M
15/30
Page 16

PFC driving network AN2349
4 PFC driving network
The network composed by the capacitor and resistor in series to the base of the power
bipolar transistor T1 are chosen in order to fix the duty-cycle at level less than 50% in the
max point of the main sinusoid and they determine the conduction time of the device, while
the base-emitter resistor has the function to regulate the capacitor discharge during the off
state of the device and to define the duty-cycle. The bipolar transistor used as switching is
driven in a self-oscillating configuration taking the signal in order to polarize its base through
an auxiliary winding on the transformer normally used in the ballast. This signal can assume
three different shapes depending on the signal shape on the ballast due to the di/dt
variation of the Ballast inductor current. The inductor current is the sum of the Transistor
Collector Current, Diode Current and Snubber Capacitor Current.
1. End collector current with di/dt>0
Figure 18. Inductor current with di/dt>0 and transformer voltage shape
I
I
CT1 I
CT1 I
I
I
D1
D1
+
+
A
A
V
V
A
A
di/dt
di/dt
B
B
+
+
D2
D2
I
I
CT2
CT2ICT2
I
I
T2
T2
I
I
L
L
I
I
T1
T1
V
V
B
B
T
T/2
T/2
T
2. End collector current with di/dt= 0
Figure 19. Inductor current with di/dt=0 and transformer voltage shape
I
I
D2
T/2
T/2
D2
I
I
CT2
CT2
I
I
T2
T2
I
I
L
L
I
I
T1
T1
T
T
I
I
CT1
CT1
di/dt
di/dt
I
I
D1
D1
A
A
+
+
V
V
A
A
= 0
= 0
B
B
V
V
B
B
16/30
Page 17

AN2349 PFC driving network
3. End collector current with di/dt < 0
Figure 20. Inductor current with di/dt<0 and transformer voltage shape
The first condition is considered for our reference design, di/dt > 0, and in particular the
slope on the point A has a di/dt value four times larger than the slope of the point B.
Figure 21 shows the output voltage of the transformer where the V
larger than the V
Figure 21. Transformer V
value.
B
shape and base current shape
out
value is four times
A
17/30
Page 18

PFC driving network AN2349
The output voltage VT of the transformer at the initial instant is:
Equation 20
V
V
V
V
T
C
0
2.5V= V
V
C
where is the initial capacitor voltage, is the resistor R
the T
0
BE voltage.
1
R
0
2
BEVA
R
2
=++=
voltage and VBE is
2
The shape of the transformer voltage in a half period T/2 is:
Equation 21
VAVB–()t•
VTt() V
After the initial instant, the capacitor begins to charge and, as soon as V
current I
B
considering this instant t
V
R
and are equal to zero and the storage time of the device is beginning, so
2
that is you have:
2
t
I
BON
---------------------------------–=
A
T
---
2
(t)=VT(t) the base
C
Equation 22
VTt2() V
where V
capacitor voltage, and vc(t
V
= 0.2V is base-emitter voltage when IB is equal to zero and taking in consideration that
BE
), voltage on the capacitor C2, is the sum of two terms , that is the initial
C(t2
) , that is the voltage variation due to the charge of the capacitor,
2
BEVCt2
() VBEV
vCt2()++=+=
C
0
V
C
0
there are charges stored into the base of the transistor.
Equalizing the two expressions 21 and 22 at this instant, you obtain:
Equation 23
VAVB–()t2•
by considering V
=4VB≅ 6V, VB=1.5V and t2=.
A
In order to calculate t
----------------------------------- -
V
A
t
I
= you have:
BON
2
T
---
2
V
t
I
BON
BEVC
vCt2()++=–
0
Equation 24
LI
p
tAt
calculated when the collector current I
base current I
is without modulation yet (as shown in Figure 22).
b
I
BON
(for ωt=30°) reaches its maximum value and the
C
t
ST
----------------------- -=+=
VMsenωt
18/30
Page 19

AN2349 PFC driving network
Figure 22. Collector current and base current shape
t
Since v
)=Q/C=Ib
c(t2
*t2 /2C having imposed that at the instant =tST=t
peak
I
BON
2
Equation 25
Ib
•
peakt2
C
---------------------------=
()•
2v
ct2
where it has been imposed Ib
V
Now from Equation 20 can be calculated:
R
2
=0.75*Ip=0.53mA.
peak
Equation 26
V
where V
Then, since , R
=1V is the base-emitter voltage of the device at the working current.
BE
V
Ib
R
2
•=
peakR2
VTV
R
2
is determined:
2
VBE––=
C
0
Equation 27
V
R
2
----------------=
R
2
Ib
peak
It has been said that the base-emitter resistor R
has the function to regulate the capacitor
1
discharge during the off state of the device and to define the duty-cycle.
I
The mean current on the R
R1Mean
resistor during the off state of the device:
1
Equation 28
VAVB+
-------------------- - 0.6 V
2
I
R1Mean
where it has been considered a mean value of .
--------------------------------------------------------------=
R
VC0.6 V
+
1R2
•+
C
0
•=
C
0
19/30
Page 20

PFC driving network AN2349
You consider the instant of the main sinusoidal in which the collector current IC (for ωt=30°)
reaches its maximum value and the base current Ib without modulation yet (see Figure 22).
Multiplying this value for T/2, the amount of charge on the capacitor C
during the off state of
2
the device can be calculated:
Equation 29
T
1
Mean
---
=
• Q
2
C2OFF
I
R
this value must be equal at the amount of charge on the same capacitor during the on state
of the device:
Equation 30
I
R1Mean
---
• Q
2
C2ONQTOT
Q
+==
T
T1
2
T
Substituting Equation 28 into Equation 30 you obtain:
Equation 31
VAVB+
-------------------- - 0.6 V
2
--------------------------------------------------------------
Q
where is the total amount of charge on T
collector of T
TOT
T1
.
2
R
In the following picture it has been indicated with Q
base during the turn-on of the device, while the Q
+
1R2
•+
C
0
T
---
• Q
TOT
2
and is the amount of charge on the
1
is the amount of charge during the
2
Q
Q
=+=
T
T1
Q
T
2
the amount of charge provided in the
1
C2ON
2
storage time, thus the total amount of charge is:
Figure 23. Detail of T1 total charge during Ton
where Q
=0.6Q1 due to the recombination of some charges, so substituting in (5.13) it
2
obtains:
Equation 32
Q
TOT
Q10.6Q10.4Q
T1
Equation 33
but
I
t
•
B
I
Peak
------------------------------=
Q
1
BON
2
Substituting Equation 33 into Equation 32 you obtain:
=–=
1
20/30
Page 21

AN2349 PFC driving network
Equation 34
Q
TOT
I
-------------------------------- -
0.4
T1
• 0.42µC==
B
Peak
tIbon•
2
Now, the amount of charge on the collector of T2 is:
Equation 35
I
t
Q
T
2
CT
•=
I
2
BON
with
Equation 36
I
I
CT
2
–=
BpeakIBmin
Now the I
at the instant where the main voltage reaches its max value, v(t)=VM=310V.
Bmin
We consider
Equation 37
di
vt() L
---- -
•=
dt
Equation 38
V
--- -
t
P
cond
L
Resolving Equation 38 by t
cond
II
==
:
Equation 39
IPL•
cond
t
I
BON
Q
TOT
--------------
T1
4.5µs==
V
0.4Q
= Q
1
TOT
T1
t
t
but t
I
=+tST and in this instant =tst=2.25µs
BON
cond
From Equation 32, we already know , where , such to keep
I
=0.7A, in this case is calculated when the base current reaches its minimum value, so
C=IP
knowing the h
h
= 19, we have:
FE
of the device to obtain the saturation at this current value IC, that is
FE
Equation 40
I
C
Q
TOT
Q
Now from , we obtain:
TOT
0.4Q
=
T1
1
---------
t
• 0.15µC≅=
T1
cond
h
FE
Equation 41
But
Equation 42
So
Q
TOT
--------------=
Q
1
0.4
I
•
BONtI
Q
----------------------------- -=
1
BON
2
21/30
Page 22

PFC driving network AN2349
Equation 43
2Q
•
I
BONIBMIN
1
---------------- -==
t
I
BON
From Equation 36, we can obtain
Equation 44
I
CT
Then the amount of charge on the T
I
BpeakIBmin
2
collector is:
2
180mA=–=
Equation 45
Q
I
t
CT
• 0.4µC==
I
2
BON
during the on state of the device is:
2
T
2
So, the total amount of charge on the capacitor C
Equation 46
Q
C2ONQTOT
Q
0.42 0.4 0.82µC=+=+=
T
T1
2
Substituting Equation 46 into Equation 31 and resolving by R
Equation 47
R
1
4.1 Feed-Back block
In order to calculate the two resistors R13 and R14 value in Figure 11 it has been imposed
V
=200V, supposing that this feed-back block acts from this voltage value.
z3
Two instants must be considered:
1. The zener diode doesn't yet conduct for ωt=30°;
2. The zener diode already conducts for ωt=90°.
Therefore the two equations to be considered are:
Equation 48
V
DCoutVZ3
----------------------------------
V
----------------------------------
–
DCoutVZ3
R
14
VAVB+
T
---
-------------------- - 0.6V
2
–
R
14
+
2
ωt30°=()V
V
in
-------------------------------------------------- -
ωt90°=()V
V
in
-------------------------------------------------- -
R
13
1
------------------- -
C
0
ON
Q
C
2
–
Z3
R
13
–
Z3
I
Z3IBONT2
==+
, it can be calculated:
1
R2–=
0=+
where I
current value (I
Equation 48 has to be solved by R
can be calculated knowing the the peak hFE of the T2 device at a minimum
BON T2
=50mA ) (hFE =170).
C
and R14.
13
22/30
Page 23

AN2349 T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications
5 T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications
5.1 220V design
The transformer T has to be choosen as following:
1. The core type is N87-EFD25/13/9 by Epcos
2. The wire gauge used to wind the transformer is 0.28 mm
3. The number of primary winding is 150 turns, the air gap lenght has been chosen in
order to obtain a saturation current of about 1.6A and an inductance value of 2.2mH ±
2.5%
4. The number of secondary winding is 2 turns for each of the two secondaries
The Boost inductor L1 has to be choosen as following:
1. The core type is N27-E20/6 (EF20) by Epcos
2. The number of primary winding is 150 turns, the air gap length has been chosen in
order to obtain a saturation current of about 1.7A and an inductance value of 1.8mH ±
2.5%
3. The wire gauge to wind the transformer is 0.22 mm
5.2 120V design
The transformer T has to be choosen as following:
1. The core type is N87-EFD25/13/9 by Epcos
2. The wire gauge used to wind the transformer is 0.28 mm
3. The number of primary winding is 150 turns, the air gap lenght has been chosen in
order to obtain a saturation current of about 1.7A and an inductance value of 2.1mH ±
2.5%
4. The number of secondary winding is 3 turns in the PFC stage and 2 turns in the
converter stage
The Boost inductor L1 has to be choosen as following:
1. The core type is N27-E20/6 (EF20) by Epcos
2. The number of primary winding is 150 turns, the air gap lenght has been chosen in
order to obtain a saturation current of about 1.7A and an inductance value of 1.5mH ±
2.5%
3. The wire gauge to wind the transformer is 0.22 mm
23/30
Page 24

T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications AN2349
Figure 24. 40W demoboard electrical schematic
24/30
Page 25

AN2349 T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications
Figure 25. 40W demoboard PCB layout and mounting components
Table 1. 40W Demoboard 220V bill of materials
Item Qty Reference Part Description
1 5 D1…D5 1N4007 High Voltage Low frequency Diode
2 1 D6 1N5818 Power schotky diode
3 5 D17,D7, D9,D10,D11 BA159 High Voltage High Frquency diode
4 2 D8, D13 1N4148 Small signal diode
25/30
Page 26

T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications AN2349
Table 1. 40W Demoboard 220V bill of materials (continued)
Item Qty Reference Part Description
5 1 Dz2, 47V Glass zener diode
6 1 Dz1 5.6V Glass zener diode
7 1 L1 1.8mH
8 1 L2 100µH Axial inductor 0.25W
9 1 C1 220nF 400V Medium voltage ceramic capacitor
10 1 C2 470nF 100V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
Mounting type: Through hole.
Size: 14mm x 22mm. Height: < 18mm
11 1 C3 1µF 63V
Low voltage Radial Electrolytic
capacitor
12 1 C4 22uF 450V High Voltage Electrolytic capacitor
13 1 C5 47nF 63V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
14 2 C6, C7 220nF 100V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
15 1 C8 1.5nF 630V High Voltage ceramic capacitor
16 1 C9 1nF/16V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
17 1 C10 10µF/35V Radial Electrolytic capacitor
18 1 C11 47nF/400V Medium Voltage ceramic capacitor
19` 1 C12 6.8nF/1000V High Voltage ceramic capacitor
20 2 C13, C14,C15 100nF/400V Medium Voltage ceramic capacitor
22 1 R1 82Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
23 1 R2 4.7Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
24 1 R3 220Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
25 2 R5, R7 330KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
26 1 R6 220Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
27 1 R8 1KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
28 1 R9 22KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
29 1 R10 680KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
30 1 R11 56KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
31 1 R12 39Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
32 2 R13, R14 180KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
33 1 Rfuse 1Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
34 1 D16 200V Zener Diode
35 1 D15 100V Zener Diode
36 1 L3 1mH Axial inductor 1W
37 1 SCR X0203NA/X0202NA
38 1 PTC R(25°C)=600Ω Type C884 PTC thermistor, 600Ω
26/30
TO92, V
I
=1.25A
TRMS
DRM/VRMM
=800V;IGT=200 uA,
Page 27

AN2349 T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications
Table 1. 40W Demoboard 220V bill of materials (continued)
Item Qty Reference Part Description
39 1 T
Lp=2.3mH,
Ns=2(PFC),
Ns=2(Half Bridge)
Mounting type: Through hole.
Size: Approx. 25mm x 25mm
Height: 12 mm
40 1 D14 Short circuit
Table 2. 40W Demoboard 120V bill of materials
Item Qty Reference Part Description
1 5 D1…D5 1N4007 High Voltage Low frequency Diode
2 1 D6 1N5818 Power schotky diode
3 5 D7,D9,D10,D11,D14 BA159 High Voltage High Frquency diode
4 2 D8, D13 1N4148 Small signal diode
5 1 Dz2 47V Glass zener diode
6 1 Dz1 7.5V Glass zener diode
7 1 L1 1.5mH
Mounting type: Through hole.
Size: 14mm x 22mm. Height: < 18mm
81L2 120µH Axial inductor 0.25W
9 1 C1 680nF, 250V Medium voltage ceramic capacitor
10 1 C2 680nF 100V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
11 1 C3 1µuF 63V
Low Voltage Radial Electrolytic
capacitor
12 1 C4 22µuF 400V
High Voltage Radial Electrolytic
capacitor
13 1 C5 56nF 63V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
14 2 C6, C7 220nF 100V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
15 1 C8 2.2nF ,630V High Voltage ceramic capacitor
16 1 C9 1nF/16V Low voltage ceramic capacitor
17 1 C10 10uF/35V
Low Voltage Radial Electrolytic
capacitor
18 1 C11 47nF/400V Medium Voltage ceramic capacitor
19` 1 C12 6.8nF/1000V High Voltage ceramic capacitor
20 2 C13, C14 100nF/400V Mediun Voltage ceramic capacitor
21 1 C15 220nF/250V Medium Voltage ceramic capacitor
22 1 R1 22Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
23 1 R2 6.8Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
24 1 R3 100Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
25 1 R4 8.2Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
26 2 R5, R7 330KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
27/30
Page 28

T Transformer and L1 inductor specifications AN2349
Table 2. 40W Demoboard 120V bill of materials (continued)
Item Qty Reference Part Description
27 1 R6 220Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
28 1 R8 1KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
29 1 R9 22KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
30 1 R10 680KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
31 1 R11 56KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
32 1 R12 39Ω 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
33 1 R13 220KΩ 0.25W 10% Axial Resistor
34 1 R14 68KΩ 0.25 W 10% Axial Resistor
35 1 L ( in place of Rfuse ) 1mH Axial inductor 1W 10%
36 1 D16 130V Zener Diode
37 1 D15 180V Zener Diode
38 1 L3 1mH Axial inductor 1W
39 1 SCR X0203NA/X0202NA
TO92, V
I
=1.25A
TRMS
DRM/VRMM
=800V;IGT=200 uA,
40 1 PTC R(25°C)=600Ω Type C884 PTC thermistor, 600Ω
41 1 T
Lp=2.1mH,
Ns=3(PFC),
Ns=2(Half Bridge)
Mounting type: Through hole.
Size: Approx. 25mm x 25mm
Height: 12mm
42 1 D17 Short circuit
28/30
Page 29

AN2349 Revision history
6 Revision history
Table 3. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
06-Jun-2006 1 Initial release
29/30
Page 30

AN2349
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZE REPRESENTATIVE OF ST, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED,
AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS,
NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS, WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY, DEATH, OR
SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2006 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
30/30
 Loading...
Loading...