Page 1
AN2208
APPLICATION NOTE
Designing Industrial Applications with
VN808/VN340SP High-side Drivers
Introduction
This application note describes the functions of VN808/VN340SP high-side drivers in industrial
applications. The VN340SP and VN808 are monolithic devices based on VIPower technology. With
primary application requirements being safety and reliability , this application note co v ers the v arious tests
used to ensure compliance with international electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) specifications as well
as other requirements.
VN808/VN340SP high-side drivers are teste d mounted on their respecti ve ref eren ce design board (RDB).
Note: Additional information concerning the L5970D DC/DC converter, based on BCD technology, is
included in Section Appendix C: L5970D DC/DC converter on page 46.
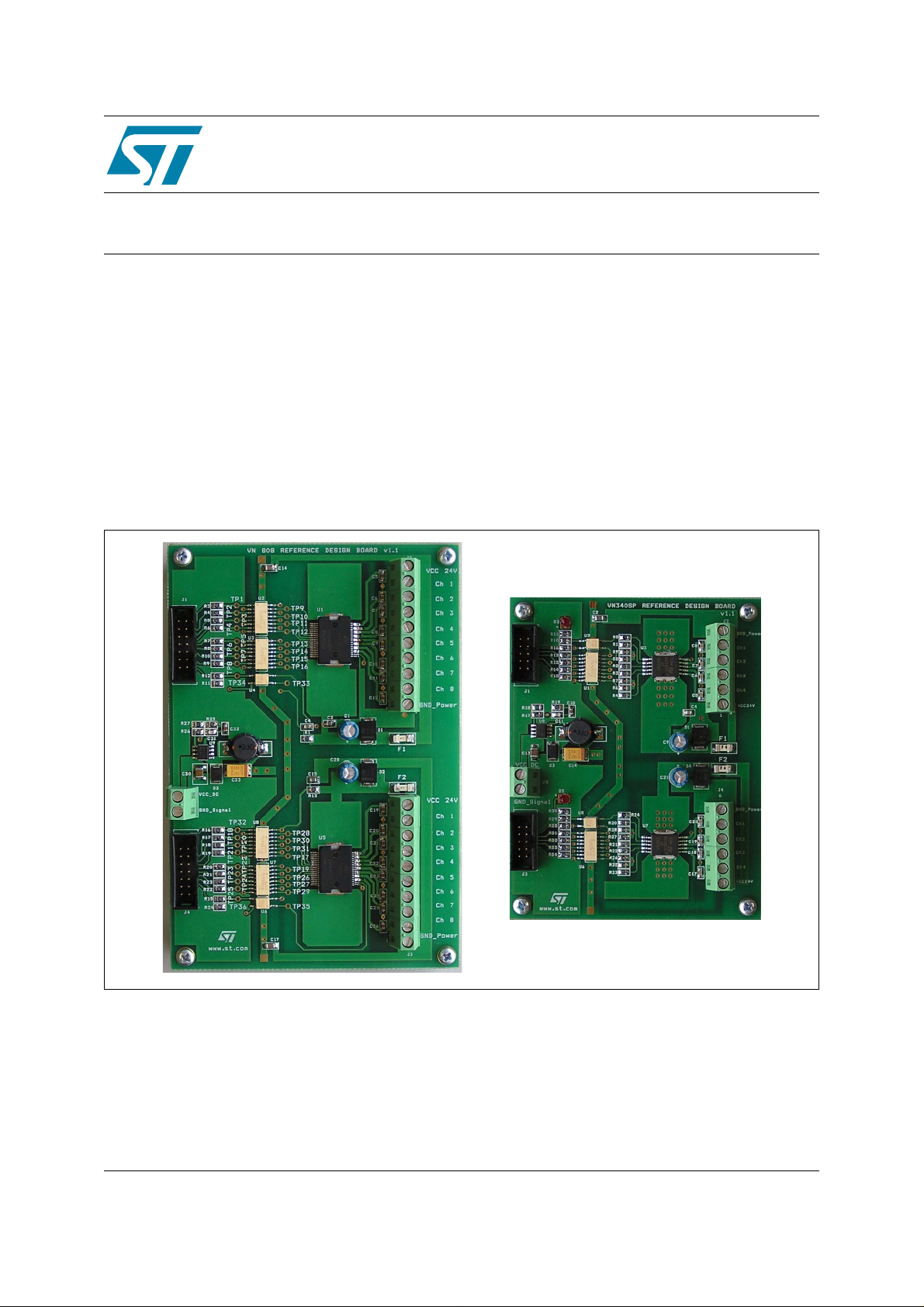
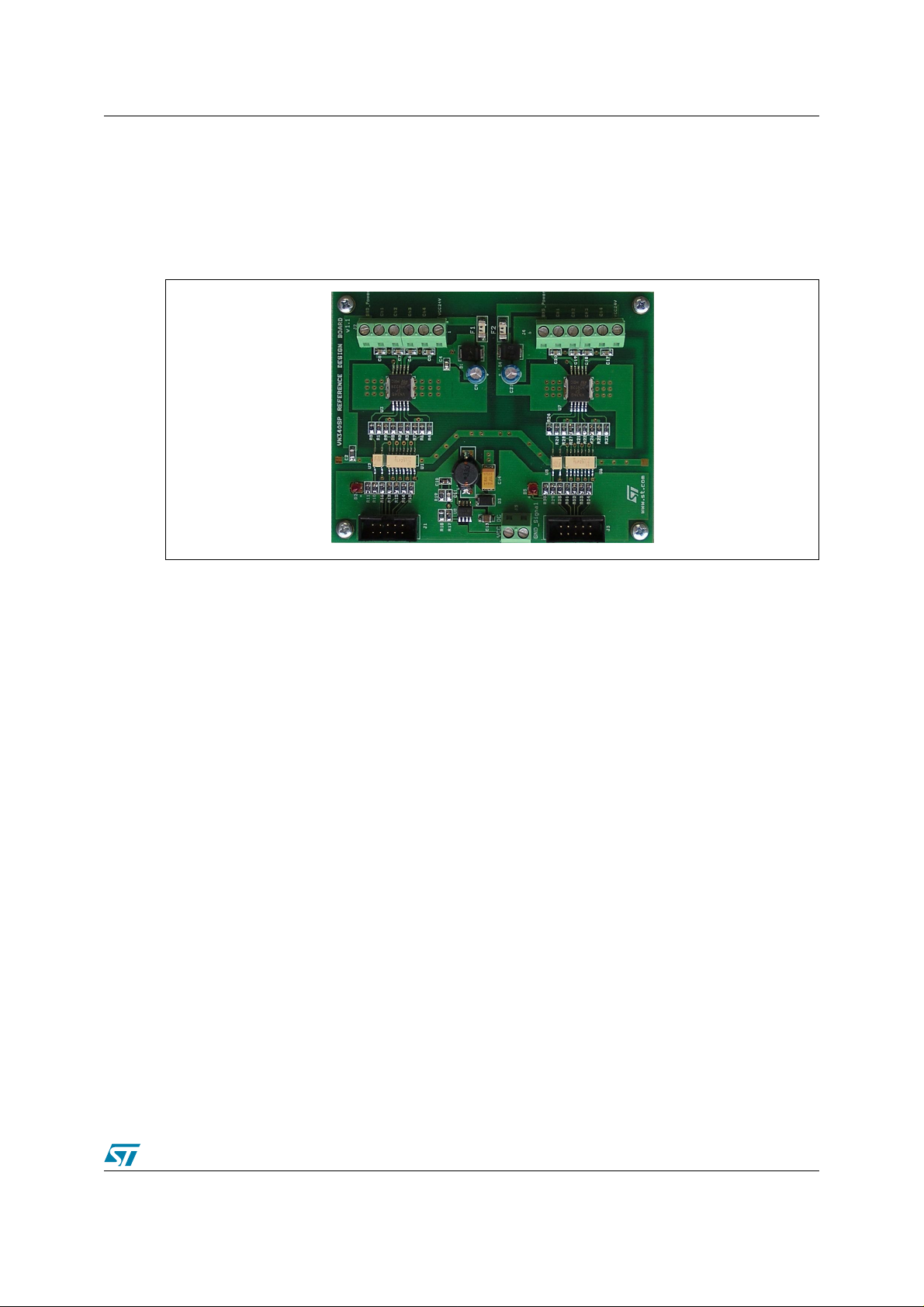
Figure 1. VN808 and VN340SP reference design boards
Rev. 1
September 2005 1/51
http:/www.st.com
1
Page 2

AN2208
Contents
1 High-side driver description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 VN808 reference design board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.1 Circuit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2 Surge suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 Isolation recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.4 Heatsink recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.5 Schematic diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3 VN340SP reference design board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1 Circuit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2 Schematic diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4 Load switching tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5 Thermal stress tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.1 Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.2 List of EMC test equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.3 Requested test levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.3.1 IEC 61000-4-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.3.2 IEC 61000-4-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.3.3 IEC 61000-4-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.4 IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.4.1 Power supply tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.4.2 Input port tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.4.3 Output port tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.5 IEC 61000-4-5 surge test setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.5.1 Power supply tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.5.2 Output port tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.6 IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.6.1 Power supply tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2/51
Page 3

AN2208
6.6.2 Input port tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.6.3 Output port tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7 Test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
7.1 VN808 HSD test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
7.1.1 Load switching test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
7.1.2 Thermal stress test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
7.1.3 EMC test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.2 VN340SP HSD test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.2.1 Load switching test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.2.2 Thermal stress test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.2.3 EMC test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Appendix A VN808 reference design board (RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
A.1 VN808 RDB bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
A.2 Recommended VN808 PCB Layout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Appendix B VN340SP reference design board (RDB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
B.1 VN340SP RDB bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
B.2 Recommended VN340SP RDB PCB layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Appendix C L5970D DC/DC converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
C.1 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
C.2 L5970D layout recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
C.3 L5970D DC/DC converter load test results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3/51
Page 4

AN2208
List of figures
Figure 1. VN808 and VN340SP reference design boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. VN808 block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 3. VN340SP block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 4. VN808 reference design board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 5. Surge Suppression Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 6. Typical input/status isolation by optocouplers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 7. Burst pulse affecting one input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 8. Recommended layout for High Power Dissipation capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 9. DC/DC part of the application circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 10. Current and voltage conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 11. Complete application circuit with VN808 and L5970D devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 12. Switching part of the application circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 13. VN340SP reference design board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 14. Switching part of the application circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 15. Complete application circuit with VN340SP and L5970D devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 16. Description of the switching inductor loads. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 17. IPS simplified structure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 18. Simplified thermal models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 19. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-4). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 20. Switch diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 21. Test on input ports (IEC 61000-4-4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 22. Output port tests (IEC 61000-4-4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 23. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-5). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 24. Test on Output Ports (IEC 61000-4-5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 25. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-6). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 26. Input port tests (IEC 61000-4-6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 27. Output port tests (IEC 61000-4-6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 28. VN808 Waveforms (Part 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 29. VN808 Waveforms (Part 2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 30. GND_Power disconnection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 31. Switching lamps: VCC = 24V, f = 0.5 Hz, Wave1 = VINOPT,
Wave2 = VOUT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 32. Waveform tOFF inductor load: VCC = 24V, L = 130mH, RLOAD = 63W,
tOFF = 1.2101 ms, Wave2 = VOUT, Wave1 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 33. Waveform switching inductive load: VCC = 24V, L = 130mH, RLOAD = 48W,
f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = VOUT, Wave1 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 34. Switching with short circuit: VCC = 24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = VSTATUSOPT,
Wave1 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 35. Time delay between VINOPT and VOUT: VCC = 24V, Load = Lamp,
Wave2 = VOUT, Wave3 = VINOPT, Dt = 58.462 µs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 36. GND_Power disconnection for VN808: VCC = 25V, Load = Lamp,
Wave1 = VCC, Wave2 = VOUT, Wave3 = GND of power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 37. Waveform ITOT and VINOPT during the test with short circuit VCC = 28V,
TA = 85°C, Wave4 = ITOT, Wave1 = VINOPT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 38. Waveform on ITOT and VINOPT during the test with short circuit VCC = 28V,
TA = –25°C, Wave4 = ITOT, Wave1 = VINOPT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 39. Case temperature dependency vs. current ITOT (TA = 25°C and VCC = 24 V) . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 40. Burst applied on the power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4/51
Page 5

AN2208
Figure 41. Burst applied on the output channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 42. Positive surge applied on power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 43. Negative surge applied on power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 44. Switching lamps: Vcc = 24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave3 = VINOPT,
Wave2 = VOUT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 45. Waveform tOFF inductor load: Vcc = 24V, L = 130mH, RLOAD = 60W,
tOFF = 1.2276ms, Wave2 = VOUT, Wave3 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT. . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 46. Time delay between VINOPT and VOUT: Vcc = 24V, Load = Lamp,
Wave2 = VOUT, Wave3 = VINOPT, Dt = 139µs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 47. Switching with short circuit: Vcc = 24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = VSTATUSOPT,
Wave3 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 48. Waveform switching inductive load: Vcc = 24V, L = 130mH, RLOAD = 48W,
f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = VOUT, Wave3 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 49. Switching with short circuit: Vcc = 24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = VSTATUSOPT,
Wave3 = VINOPT, Wave4 = ICH1OUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 50. Waveform ITOT and VSTATUSOPT during the test with short circuit:
Vcc = 28V, TA = 85°C, Wave4 = ITOT, Wave1 = VSTATUSOPT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 51. Waveform on ITOT and VSTATUSOPT during the test with short circuit:
Vcc = 28V, TA = –25°C, Wave4 = ITOT, Wave1 = VSTATUSOPT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 52. VN808 RDB PCB layout (top and bottom) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 53. VN808 RDB PCB layout (component side) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 54. VN340SP RDB PCB layout (Top side) and (Bottom side) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 55. VN340SP RDB PCB layout (component side) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 56. L5970D block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 57. L5970 DC/DC converter layout example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 58. Efficiency vs. output current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 59. Output voltage stability of L5970D, Vss = 24 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 60. Voltage ripple on capacitor C30, IOUTDC = 0.4A, Vss = 24V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 61. Waveform on coil L1, IOUTDC = 0.4A, Vss = 24V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 62. Voltage ripple on capacitor C33, Vss = 24V, IOUTDC = 0.4 A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 63. Waveform on coil L1, without load, Vss = 24V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
5/51
Page 6

AN2208
List of tables
Table 1. VN808 and VN340SP main characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. EMC industrial compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 3. Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 4. Equipment list for EMC tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 5. Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 6. EMC test IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test results (VN808 RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 7. EMC test IEC61000-4-5 surge test results (VN808 RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 8. EMC test IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test results (VN808 RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 9. EMC test IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test results (VN340SP RDB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 10. EMC test IEC61000-4-5 surge test results (VN340SP RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 11. EMC test IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test results (VN340SP RDB) . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 12. VN808 RDB bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 13. VN340SP RDB bill of materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
6/51
Page 7
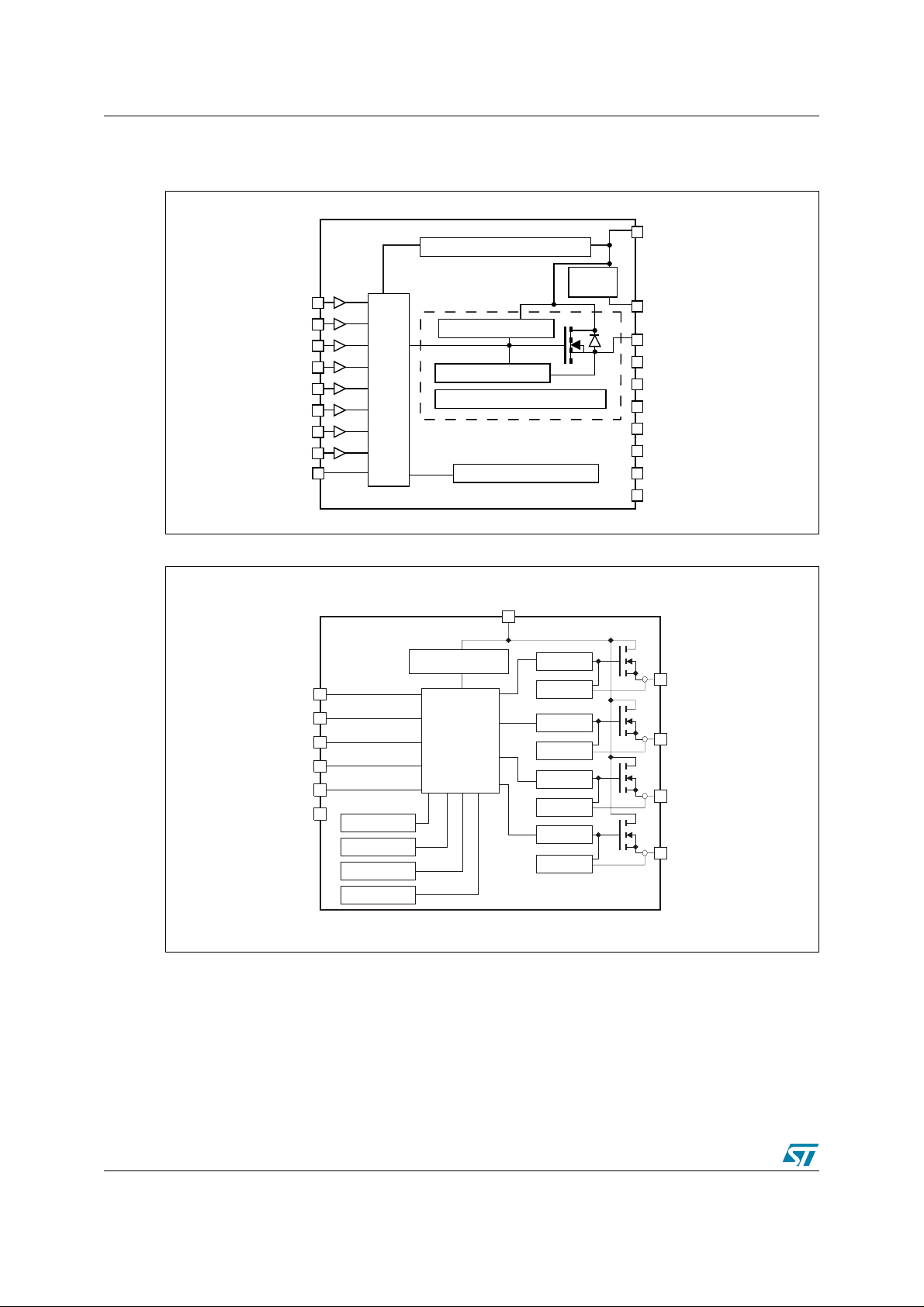
AN2208 1 High-side driver description
1 High-side driver description
The VN808 (Figure 2) is a high-side driver (HSD) us ed to driv e eight ind epend ent l oads . Act ive
current limitation combined with thermal shutdown and automatic restart functions protect the
device against ov erload. A thermal case substrat e protection is implemented to prot ect the FRx
substrate under short circuit and worst case ambient conditions in terms of reliability. The
device automatically turns off when the ground pin is disconnected. The VN340SP and VN808
are especially suitable for use with programmable logic controllers (PLC) in industrial
applications.
The VN340SP (Figure 3) is used to drive four independent resistive, capacitive and inductive
loads in high-side configurations. Active current limitation prevents the system power supply
from dropping in the event of a short load. A built-in thermal shutdown circuit protects the chip
from high temperatures and short circuits. Each I/O is pulled down when an over-temperature
condition of the relative channel is detected and restarts after reaching the lower thermal
threshold. The system oscillates depending on the thermal impedance of the application.
Table 1. VN808 and VN340SP main characteristics
VN340SP HSD VN808 HSD
Output current per channel 0.5A at 24V
Built-in current limiter
Short-load and overtemperature (Junction)
protection
Under-voltage shutdown
Open-drain diagnostic output Status output current 2 to 4 mA
DC supply voltage 36V DC supply voltage 45V
V e ry low stand-by current
Short-load and overtemperature (Junction and
Case) protection
7/51
Page 8
1 High-side driver description AN2208
Figure 2. VN808 block diagram
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
INPUT 3
INPUT 4
INPUT 5
INPUT 6
INPUT 7
LOGIC CONTROL
INPUT 8
STATUS
Figure 3. VN340SP block diagram
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
DIAG
GROUND
Overtemp 1
Overtemp 2
Overtemp 3
Overtemp 4
UNDERVOLTAGE DETECTION
CLAMP POWER
CURRENT LIMITER
JUNCTION TEMP. DETECTION
Same struct ure f or al l channels
CASE TEMP. DETECTION
V
CC
Undervoltage
Control
Logic
Driver 1
I Limit 1
Driver 2
I Limit 2
Driver 3
I Limit 3
Driver 4
I Limit 4
V
CC
CLAMP
VCC
GND
OUTPUT 1
OUTPUT 2
OUTPUT 3
OUTPUT 4
OUTPUT 5
OUTPUT 6
OUTPUT 7
OUTPUT 8
Ai11606
OUTPUT 1
OUTPUT 2
OUTPUT 3
OUTPUT 4
8/51
SC07950
Page 9
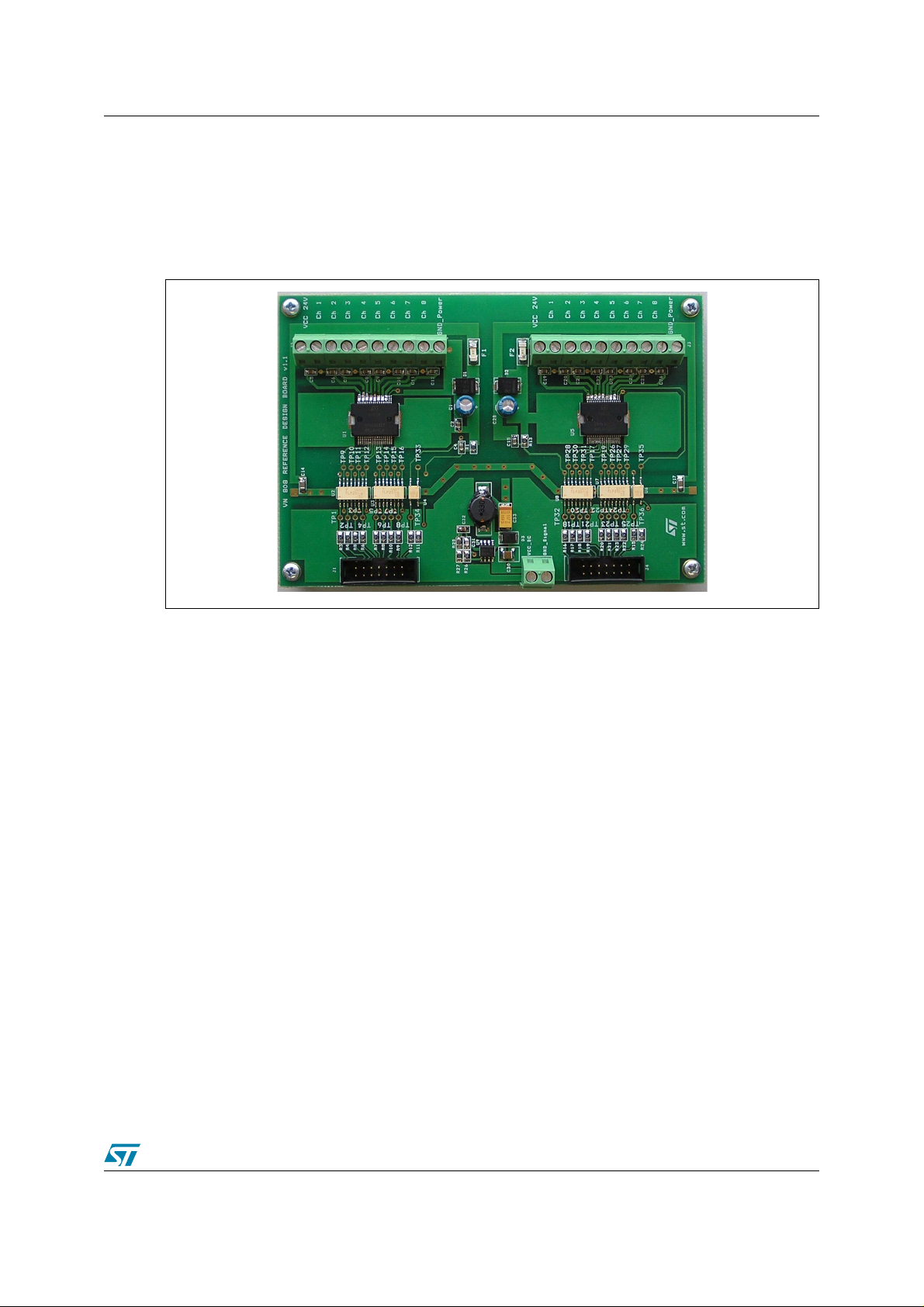
AN2208 2 VN808 reference design board
2 VN808 reference design board
This is a practical example how the VN808 high-side driver (HSD) can be used in applications
for an industrial environment.
Figure 4. VN808 reference design board
2.1 Circuit description
In order to protect the high-side driver (HSD) from the harsh industrial conditions of power
supply lines, usually optocouplers and Transil diodes are used to separate the ap plic at ion
control circuits from the power supply. Figure 11 shows a complete schematic diagram of the
VN808 reference design board.
The VN808 reference design board uses multi-channel TLP281-4 and TLP181 optocouplers.
The TLP281-4 and TLP181 are small and thin couplers, suitable for surfa ce-mounted
assemblies that consist of a photo transistor optically coupled to a gallium-arsenide infrared
emitting diode. The isolation voltage for this type of optocoupler is 2500 V
The clamping function of Transil diodes protect the HSD against transient overvoltages. The
reference design board is assembled with uni-directional SM15TXXA Transil diodes because
they protect the HSD against both positi ve and negative surge pulses. For more information
about SM15TXXA Transil diodes from STMicroelectronics, please refer to the SM15T36A
Datasheet av ailable at www.st.com.
Refer to Section A.2: Recommended VN808 PCB Layout on page 43 for more information
about designing boards to improve EMC immunity and performance in industrial environments.
2.2 Surge suppression
When designing your application, VCC and ground lines should lay on top of ea ch other,
minimizing the closed loop area and increasing the ability of the application to reject
RMS
.
9/51
Page 10
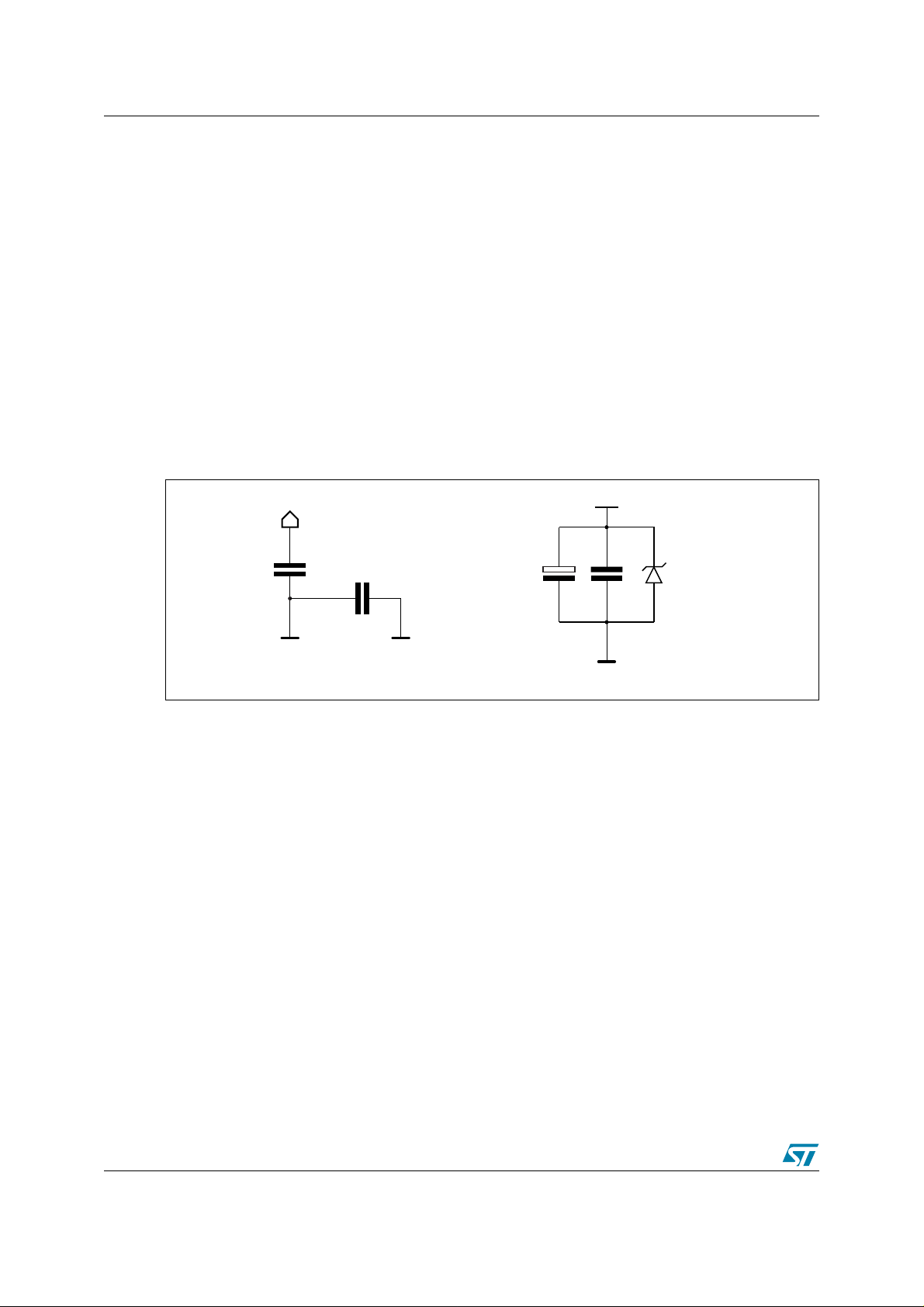
2 VN808 reference design board AN2208
environmental noise. Figure 5 shows a surge suppression block using a un i-directional
SM15T36A Transil diode.
The Transil diode provides overvoltage protection for the HSD. The SM15T36A has a peak
pulse power dissipation of 1500 W, stand-off voltage of 36 V and breakdown voltage of 37.8 V.
Depending on the application, a Transil diode with a different v a lue (for example, betw een 2 8 V
and 40 V) may be used.
An electrolytic capacitor (C1) must be placed immedi a tely afte r th e sur g e sup p re ssio n block.
The size of the electrolytic capacitor is selected based on the slope of the output current, the
impedance of the complex power supply cables, as well as the maximum allowed voltage drop
across the device . The C1 v a lue is ge ner ally 25 µF per chip. For more inf ormation about th e C1
value, please refer to Application Note AN1351: VIPower and BCDMultipower: Making life
easier with ST's high-side drivers.
A low ESR SMD capacitor (C2) must be placed as close as possib le to the HSD in order to f ilter
the power supply line for electromagnetic compatibility concerns. The suggested C2 value is
100 nF.
Figure 5. Surge Suppression Block
24V DC Input
C14
4.7 nF
GND_EARTH GND_POWER
C13
4.7 nF
2.3 Isolation recommendations
Industrial environments require good isolation between digital and power supply parts.
Optocouplers are widely used and multi-channel optocouplers represent a very attractive
solution. Figure 6 shows a schematic diagram with optocouplers connected to ground.
Although optocouplers are good isolators, they may lower the category of the Electrical Fast
Transients (EFT) immunity tests as the primary and secondary sides of the optocouplers may
still have parasitic capacitance “bonding” to each other, even though they are isolated. This
parasitic capacitance may inject a current through the base emitter junction of the
phototransistor when one half of the optocoupler is “tight” due to fast voltage transients with
respect to the other side as shown in Figure 7.
C1
22 µF
50V
VCC 24V
+
C2
100 nF
GND_POWER
D1
SM15T36A
Ai11615
If an optocoupler is used in an emitter-follower configuration, as in most industrial applications,
a high emitter voltage sig nal ma y b e induced b y applying EFTs e ven after opening the collector
termination. An efficient way to prevent this high emitter voltage signal is to provide a
conducting plane connected to gro und on both the top and bo ttom la y ers of th e PCB (under the
optocouplers) as shown in Figure 52: VN808 RDB PCB layout (top and bottom).
10/51
Page 11
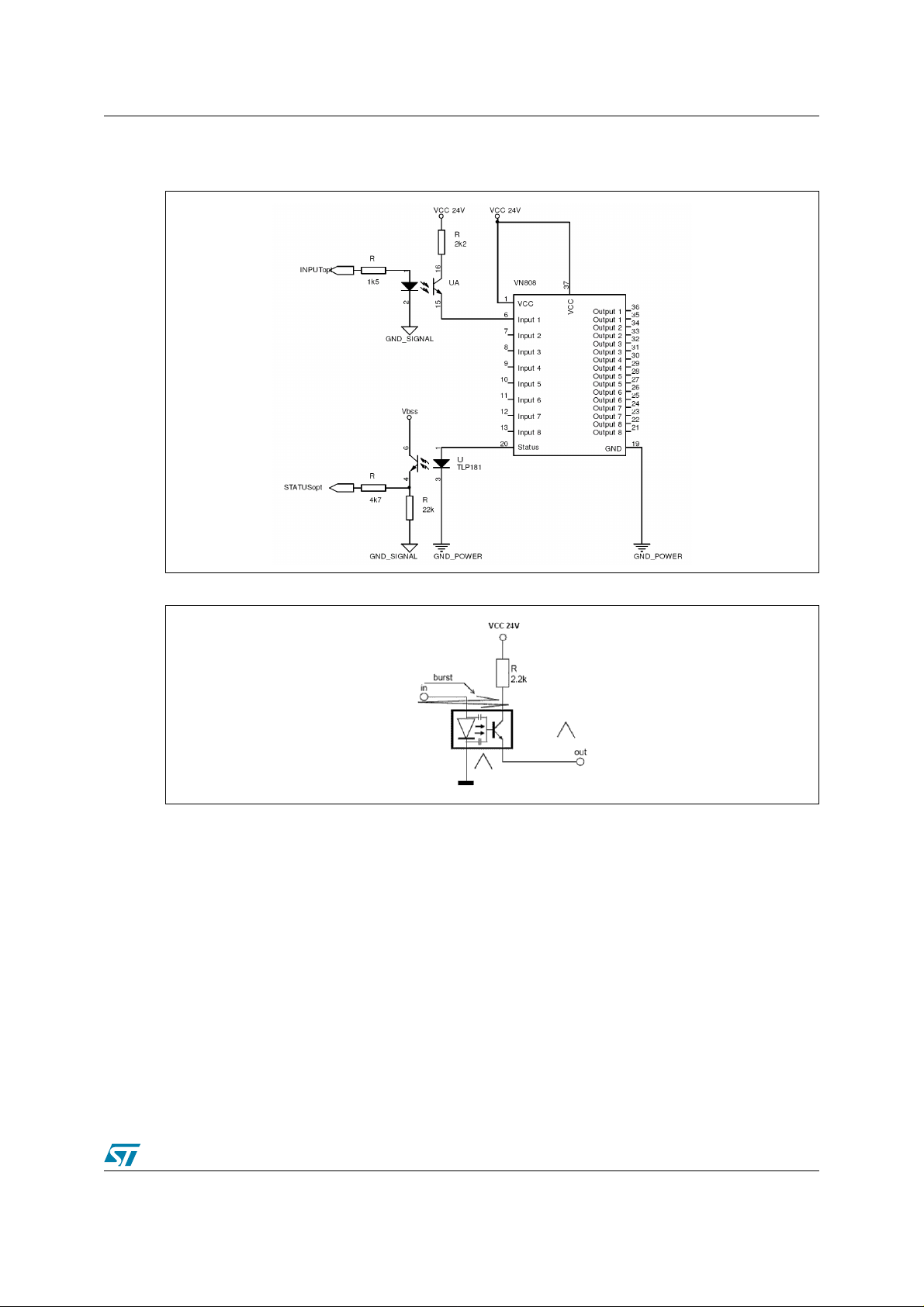
AN2208 2 VN808 reference design board
Figure 6. Typical input/status isolation by optocouplers
Figure 7. Burst pulse affecting one input
2.4 Heatsink recommendations
Depending on ambient thermal conditions, HSD’s with a PowerSO10/SO36 package require
external cooling as the copper bott om p lat e of t he PSO-Package, u sed to maint ain t he ju nctio n
temperature during inductive switching, acts as a thermal capacitor.
11/51
Page 12
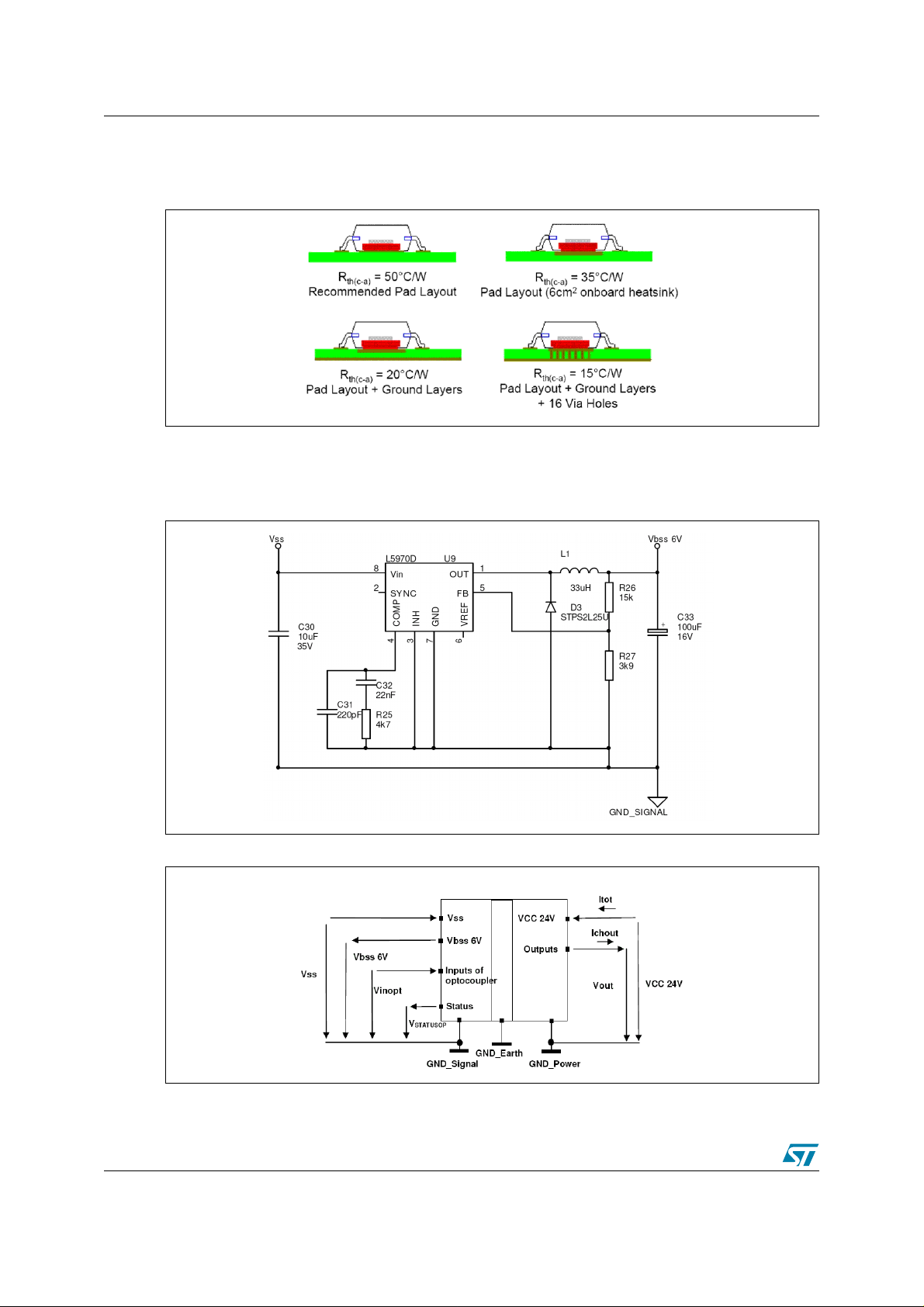
2 VN808 reference design board AN2208
The VN808 reference board is designed with an onboard heatsink capability (minimum heat
sink area is 6 cm²). The recommended layout for Power SO packages is shown in Fig ure 8.
Figure 8. Recommended layout for High Power Dissipation capability
2.5 Schematic diagrams
Figure 9. DC/DC part of the application circuit
Figure 10. Current and voltage conventions
12/51
Page 13
AN2208 2 VN808 reference design board
Figure 11. Complete application circuit with VN808 and L5970D devices
13/51
Page 14
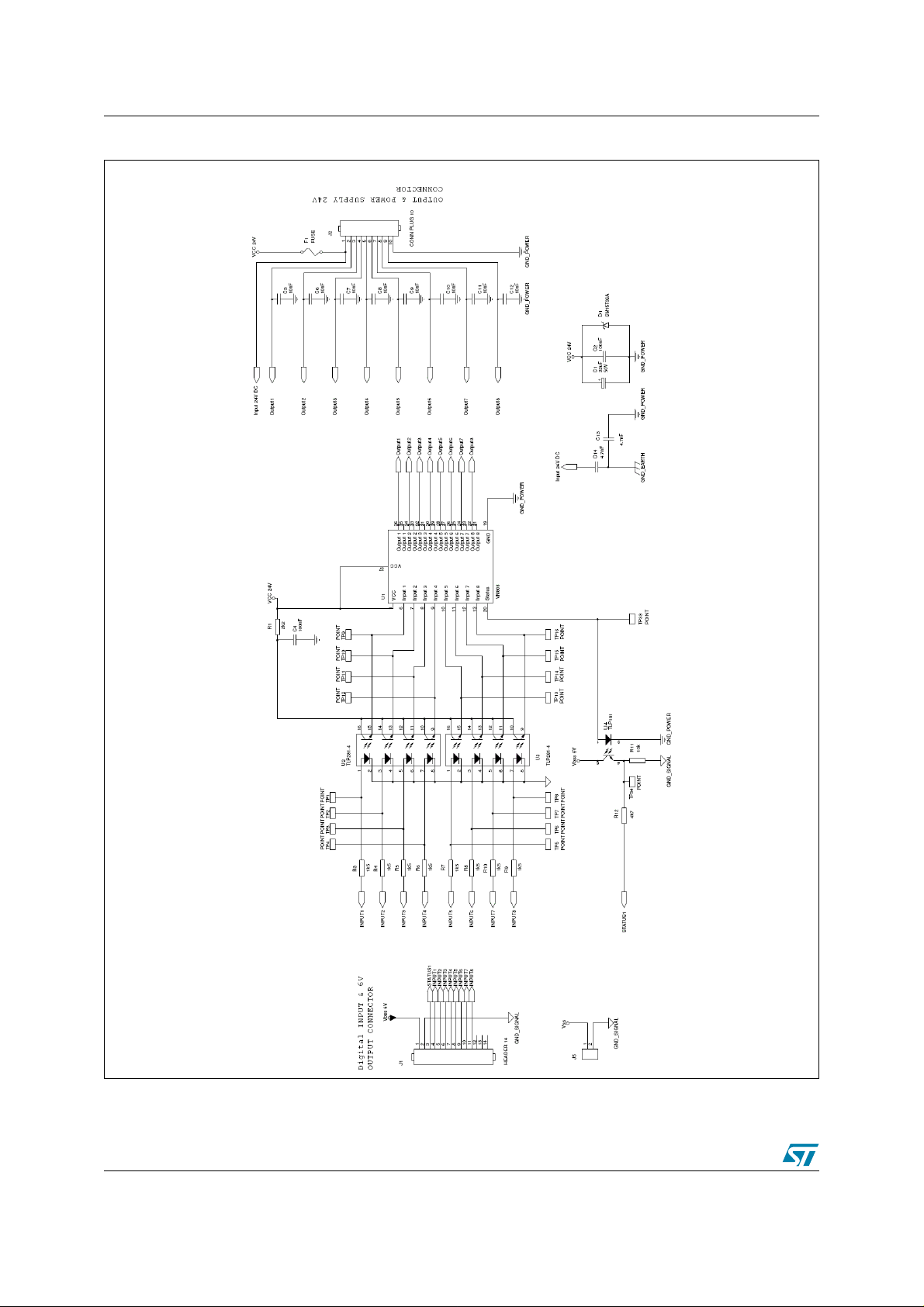
2 VN808 reference design board AN2208
Figure 12. Switching part of the application circuit
14/51
Page 15
AN2208 3 VN340SP reference design board
3 VN340SP reference design board
This is a practical example how the VN340SP high-side driver (HSD) can be used in
applications for an industrial environment.
Figure 13. VN340SP reference design board
3.1 Circuit description
The application described below is very similar to that of the VN808 reference design board;
only the type of HSD and the optocoupler inter-co nn e ctio n is different. Figure 15 shows a
complete schematic diagram of the VN340SP reference design board. The optocouplers and
Transil diodes are the same as those used in the VN808 reference design board.
15/51
Page 16
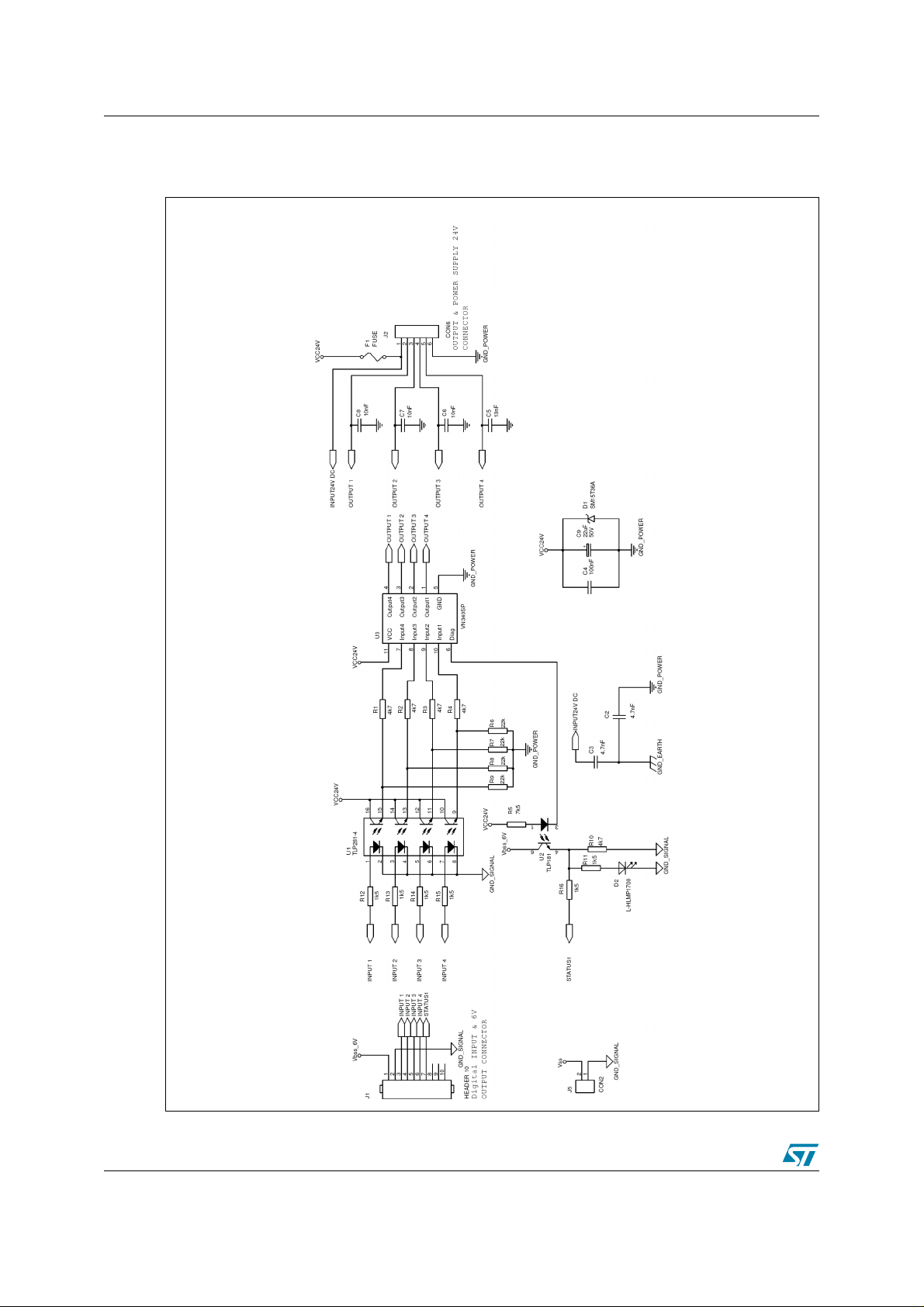
3 VN340SP reference design board AN2208
3.2 Schematic diagrams
Figure 14. Switching part of the application circuit
16/51
Page 17

AN2208 3 VN340SP reference design board
Figure 15. Complete application circuit with VN340SP and L5970D devices
17/51
Page 18

4 Load switching tests AN2208
4 Load switching tests
Many differen t types of loads can be found in an industrial environment. Typical loads have
inductive or resistive characteristics. Applications compliant with UL 508 (48Ω and 1.15H)
specifications are generally considered as the worst case.
A basic description of typical switching inductor loads is given in Figure 16. The supply voltage
is nominally 24V but can rise up to 30.5V. In this application, 24V filament lamps are used with
130mH/48Ω inductors as the loads. The V
The V
switch off the circuit, the bigger | V
voltage value decides the t
CLAMP
CLAMP
Figure 16. Description of the switching inductor loads
supply condition is between 18.5V and 28. 5V DC .
CC
demagnetization duration: the faster you want to
OFF
| compared with | VCC| has to be.
Note: Typical V
STMicroelectronics’ Intelligent Powe r Switches (IPSs) provide a “fast demagnetization” output
structure, an integrated solution for fast switch-off of inductive loads.
IPSs are basically a Zener diode with a 52V breakdown (approx.) and high power dissipation
capability connected between an output and V
the output voltage is then clamped at V
supply voltage.
The integrated clamping structure saves on components and space. Internal demagnetization
can be used only if thermal behavior and load conditions are well known to designers.
Therefore a detailed analysis of thermal behavior related to inductive load switching is
mandatory to prevent improper utilization of the IPSs.
VINx Load x
VINx Load x
VINx Load x
VN808
VINx
L
V
OUT
R
value for VN808 is 52V.
CLAMP
V
IN
V
V
OUT
V
I
OUT
= VCC - 52, and is therefore dependent on the
OUT
I
OUT
as shown in Figure 17. In most applications,
CC
t
OFF
I
O
CC
CLAMP
Ai11608
18/51
Page 19

AN2208 4 Load switching tests
Figure 17. IPS simplified structure
VCC
ZD1
50V
High Side Switch
S1
GND
The parameters are given by the following formulas:
E
OFF
t
OFF
V
CLAMP
---------------------
R
LOAD
L
----------------- -
R
LOAD
•=
-------------------------------------- -+
ln•=
1
V
CLAMPVCC
LV
•
CC
-------------------- V
R
LOAD
P
t
OFF
CLAMPVCC
E
OFF
------------- -=
t
OFF
For example for VN808:
Where, I
V
CLAMP
t
= 1.6 ms
OFF
E
= 21 mJ per channel
OFF
= 0.5 A, L = 130 mH, f = 0.5 Hz, VCC = 24 V and V
OUT
- VCC = 28 V and R
LOAD
P
= 48 Ω
t
OFF
4
21mJ
---------------- -
• 52.5W==
1.6ms
OUT
V
CC
–
–()t
Ai11609
•()–
OFF
CLAMP
= 52 V
Note: For more information about switching inductor loads, see Application Note AN1351.
19/51
Page 20

5 Thermal stress tests AN2208
5 Thermal stress tests
The thermal model of a generic Intelligent Power Switch (IPS) can be exemplified as shown in
Figure 18. R
resistance, whereas C
package itself.
Figure 18. Simplified thermal models
thJC
and R
represent the junction-to-case and the case-to-ambient thermal
thCA
is the predominant thermal capacitance and is basically related to the
thC
VN340 (4-channel IPS)
R
= 1.33˚ C/W R
th1
T
J1
T
J2
T
J3
T
J4
= 1.67˚ C/W
th2
C
thC
T
C
VN808 (8-channel IPS)
R
= 1.9˚ C/W R
th1
T
J1
T
J2
T
J3
T
J8
= 1.1˚ C/W
th2
C
thC
T
Note: Case thermal time co n st an t of 48 ms with out exter n al co olin g.
R
= R
thJC
th2+Rth1
If Nb = 8, R
If Nb = 4, R
/Nb of channels
= 1.34°C/W
thJC
= 2°C/W
thJC
The aim of the designer will be to provide the lowest possible junction–ambient thermal
impedance, in order to minimize the chip temperature jump-up.
16 mJ/K
C
36 mJ/K
R
thCA
T
A
R
thCA
T
A
Ai11610
Example VN808:
I = 0.5 A, L = 130 mH, f = 0.5 Hz, T
= 60°C, Duty cycle = 0.5, VCC = 24 V,
A
8 channels active, 4 chann els working at the same time.
Conduction losses:
Losses due to I
(supply current): 24V* 12mA(max.) = 288 mW
SON
PowerMOS losses at ON State: 280 mΩ(max.)*(0.5)^2*0.5*8 = 280 mW
Switching losses:
Switching losses are due to inductance discharge:
P
DOFF
= 8* E
*F = 8* 21mJ * 0.5 = 84 mW
OFF
Total losses and Junction temperature:
Total power losses = 652 mW (0.652 W)
20/51
Page 21

AN2208 5 Thermal stress tests
If the PSO36 is on FR4, R
t
= 1.6 ms << 48 ms (constant time of the PSO36)
OFF
T
= TA + Pmean* R
C
thCA
= 50°C/W
thCA
TC = 60°C +34 °C = 94°C
T
JMax
during t
= 94 + (1.1 + (1.9/4))*52 = 175°C
OFF
21/51
Page 22

6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests AN2208
6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests
The VN808 and VN340SP reference design boards pass t he f ollo wing indu strial tests. (Re f er to
specific product datasheet for electrostatic discharge (ESD) characteristics).
Table 2. EMC industrial compliance
IEC Specification Description
61000-4-4 Electric Fast Transients (EFT)
61000-4-5 Surge protection
61000-4-6 Immunity to conducted disturbances
6.1 Terminology
Table 3. Abbreviations
Abbreviations
CC Current Clamp
CCC Capacitive Coupling Clamp
CDN Coupling/Decoupling Network
DN Decoupling Network
EFT Electric Fast Transients
EFT Generator Generator with CDN according IEC 61000-4-4
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
EUT Equipment Under Test
HSD High-side Driver
IPS Intelligent Power Switch
PE Protected Earth (metal plane)
Signal Generator Wave generator with power amplifier according IEC 61000-4-6
Surge Generator Generator with CDN according IEC 61000-4-5
Description
22/51
Page 23

AN2208 6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests
6.2 List of EMC test equipment
Table 4. Equipment list for EMC tests
Equipment Description
Surge Generator EM Test Surge generator VCS 500 with CDN
EFT Generator EM Test EFT 800 EFT/burst generator with CDN
CC EMC Partner CN-EFT 1000 Capacitive coupling clamp
Pow er Supply
Decoupling network Trennstelltrafo LTS 606 for separation from the mains
Loads
Signal Generator
CDN
Attenuator EM TEST ATT6/75
Multimeter FLUKE 189
Oscilloscope LECROY LT 374M
Current Probe LECROY AP015
Wood table 1-meter high
Metal plane Size in proportion to wood table and test setup
Wood isolation 0.1-meter thick
PCE A1200 40 30 DC power supply 40V/30A
Toellner TOE 8733
Osram 8x lamps 24V/15W
8x Inductor 130mH/48Ω
Agilent 33220A
PMM 3000 according IEC 61000-4-6
EMC Partner CDN-1000 KIT for surge test
EMC Partner CN-EFT-1000
FCC-M3-16A for IEC 61000-4-6
FCC F-120-9A Current Injection Probe for IEC 61000-4-6
6.3 Requested test levels
6.3.1 IEC 61000-4-4
● Polarity: positive/negative
● Test voltage: Level 4 (4 kV)
● Burst duration: 15ms±20% at 5 kHz
● Burst period: 300 ms±20%
● Duration time: 60 seconds (min.)
● Applied to: Input/Output ports and Supply lines
6.3.2 IEC 61000-4-5
● Polarity: positive/negative
● Test voltage: Level 3 (2 kV)
● Number of Discharges: 5
● Repetition Rate: 1 per min.
● Applied to: Output ports and Supply lines (all combinations)
23/51
Page 24

6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests AN2208
6.3.3 IEC 61000-4-6
● Test voltage: Level 3 (10 V)
● Frequency range: 150 kHz to 80MHz
● Modulation: 80% dept h by AM 1 kHz
● Frequency step: 1%
● Dwell Time 100 ms
● Applied to: Input/Output ports and Supply lines
6.4 IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test setup
The reference design boards are tested on input/output ports and power supply lines. The test
voltage is applied from the EFT generator to the EUT via a capacitive coupling clamp. The test
setup and test voltage waveform comply with IEC 61000-4-4 specification s. The capacitive
coupling clamp is connected by a high-voltage coaxial cable to the generator as close as
possible to the EUT.
6.4.1 Power supply tests
Figure 19 illustrates the power supply test setup. A capacitive coupling clamp applies the test
voltage (max. 4 kV) to the power supply lines. A decoupling network (DN) protects the power
supply against the test voltage.
EUT test conditions:
Input port ON/OFF and f
Input port wave form: Square 0/5V; f = 1 Hz
Figure 19. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-4)
6.4.2 Input port tests
Figure 21 illustrates the input port test setup. The RDB input ports are tested by first switching
them to ground and then to the 5V supply using the battery-power ed s witch sho wn in Figure 20
to increase protection.
OPER
= 1 Hz
Maximum test voltage must not exceed 4 kV.
24/51
Page 25

AN2208 6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests
Figure 20. Switch diagram
V
PP
Input
OPT
Figure 21. Test on input ports (IEC 61000-4-4)
6.4.3 Output port tests
Figure 22 illustrates the output port test setup. The capacitive coupling clamp is the
recommended method for coupling the generator source voltage into the output ports. All
auxiliary devices are placed on the wood isolation board (0.1-meter thick). The test is
performed while the HSD output port is switched On/Off at 1 Hz.
GND
Ai11611
Maximum test voltage must not exceed 4 kV.
25/51
Page 26

6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests AN2208
Figure 22. Output port tests (IEC 61000-4-4)
6.5 IEC 61000-4-5 surge test setup
Section 5 of the IEC 61000-4 specification concerns the immunity requirements, test methods,
and range of recommended test levels for equipmen t to unidirectional surges caused by
overvoltages from switching and lightning transients. The reference design boards are tested
on the power supply lines and output port.
6.5.1 Power supply tests
Figure 23 illustrates the power supply test setup. The reference design boards are tested with
different coupling modes:
● Line-to-line coupling mode with source impedance 42Ω (meaning V
GND_Power on the board, both polarities)
● Line-to-PE coupling mode with sou rce i mpedan ce 42Ω (meaning V
GND_earth on the board, both polarities)
● Output to GND_Power with source impedance 42Ω
● Output to V
● Output to Protect Earth with source impedance 42Ω
24V with source impedance 42Ω
CC
24V and
CC
24V/GND_Pow er to
CC
26/51
Page 27

AN2208 6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests
The maximum surge voltage may not exceed 2kV for line-to-line coupling mode and 2kV for
line-to-PE coupling mode. The test is performed while the HSD output port is switched On/Off
at 1Hz. The maximum length of the cables between the EUT and CDN is 2 meters.
Figure 23. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-5)
6.5.2 Output port tests
Figure 24 illustrates the output port test setup. The maximum surge voltage and coupling mode
is same as with the power supply tests. The test is performed while the HSD output port is
switched On/Off with both polarities. The output lines are tested between V
Figure 24. Test on Output Ports (IEC 61000-4-5)
/GND and PE.
CC
6.6 IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity
The reference design boards are t ested on the Input/Output ports and P ow er supply lines with a
maximum voltage of 10 V
frequency swe eps from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz with a 80% amplitude modulation at 1 kHz of the
same signal. The EUT clearance from all metallic objects must be at least 0.5 meters.
. The test signal is basically a sinusoidal waveform, whose
RMS
27/51
Page 28

6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests AN2208
6.6.1 Power supply tests
Figure 25 illustrates the power supply test setup. The test voltage is applied by coupling
decoupling networks CDN. The maximum voltage is 10 V
EUT and CDN is 0.3 meters. All Auxiliary Units (AU) such as power supplies switching devices
must be placed on the wood isolation.
Figure 25. Power supply tests (IEC 61000-4-6)
. The maximum distance between
RMS
6.6.2 Input port tests
Figure 26 illustrates the input port test setup. The test voltage from the signal generator to the
EUT is applied by the current clamp. This device establishes inductive coupling to the cable
connected to the EUT. The maximum distance between the EUT and t he CC is 0.3 meters . The
test is performed while the HSD input port is switched On/Off at 1Hz .
Figure 26. Input port tests (IEC 61000-4-6)
6.6.3 Output port tests
Figure 27 illustrates the output port test setup. The power supply must be protected to
disturbance signal by a decoupling network. The current clamp is used as the coupling device
28/51
Page 29

AN2208 6 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests
for the signal generator. The test is performed while the HSD output port is switched On/Off at
1Hz.
Figure 27. Output port tests (IEC 61000-4-6)
29/51
Page 30

7 Test results AN2208
7 Test results
The following abbreviations are used in this section.
Table 5. Abbreviations
Symbol Parameter
V
V
V
T
A
T
T
T
TC
T
T
IN
OUT
STAT
JSD
R
CSD
CR
j
Input Voltage
Output Voltage
Voltage on STATUS pin
Ambient temperature
Junction shut-down temperature
Junction Reset temperature
Case shut-down temperature
Case operating temperature
Case reset temperature
Junction operating temperature
7.1 VN808 HSD test results
The typical behavior of the VN808 HSD according the datasheet is shown in Figure 28 and
Figure 29.
Figure 28. VN808 Waveforms (Part 1)
V
IN
V
OUT
V
STAT
V
CC
V
IN
V
OUT
V
USD
Normal Operation
Undervoltage
V
USDhyst
V
STAT
30/51
Undefined
Ai11622
Page 31

AN2208 7 Test results
Figure 29. VN808 Waveforms (Part 2)
Hard Short Circuit
> T
T
J
TSD
T
TSD
T
R
T
CSD
T
CR
V
V
T
V
IN1
OUT1
STAT
V
I
OUT2
T
IN2
J1
C
T
J1
T
C
V
IN1
V
OUT1
V
STAT
7.1.1 Load switching test results
Test conditions: T
Switching loads: Lamp 24V, 15W; Inductor L = 130 mH, R
In the event of GND_Pow er disconnection, the device turns off immediately. The test was
performed with different V
Test Results: The VN808 HSD worked properly during the test.
= 25° C, VCC = 24 V, f = 0.5 Hz
AMB
values.
CC
Overload Condition
> T
T
C
CSD
LOAD
= 48Ω
Ai11623
T
TSD
T
R
T
CSD
T
CR
31/51
Page 32

7 Test results AN2208
The waveform after GND_Power disconnection is shown in Figure 30 with the following
conditions: Power supply = 24V, Load = 24V /15W lamp, and HSD input = ON.
If the HSD input is OFF, then the output will still switch OFF after GND_Power disconnection.
Figure 30. GND_Power disconnection
V
CC24
Output 1
Load
V
OUT
Switch
Figure 31. Switching lamps: V
0.5 Hz, Wave1 = V
Wave2 = V
, Wave4 = I
OUT
= 24V, f =
CC
INOPT
,
CH1OUT
GND_Power
Figure 32. Waveform t
Ai11624
inductor load: VCC =
OFF
24V, L = 130mH, R
t
= 1.2101 ms, Wave2 = V
OFF
Wave1 = V
INOPT
LOAD
, Wave4 = I
= 63Ω,
OUT
CH1OUT
,
32/51
Page 33

AN2208 7 Test results
Figure 33. Waveform switching inductive load:
V
= 24V, L = 130mH, R
CC
f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = V
V
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
OUT
CH1OUT
Figure 35. Time delay between V
: VCC = 24V, Load = Lamp,
V
OUT
Wave2 = V
, Wave3 = V
OUT
INOPT
= 48Ω,
LOAD
, Wave1 =
and
, ∆t =
INOPT
58.462 µs
Figure 34. Switching with short circuit: VCC =
24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = V
Wave1 = V
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
STATUSOPT
CH1OUT
Figure 36. GND_Power dis connection for
VN808: V
Wave1 = V
= 25V, Load = Lamp,
CC
, Wave2 = V
CC
OUT
,
Wave3 = GND of power supply
,
7.1.2 Thermal stress test results
1. All channels shorted: f
2. All channels shorted: f
3. All channels shorted: f
Test Results: The case temperature with 8 channels shorted oscillates between 116 and
119°C with an ambient temperature of 25°C. The case temperature increases to between 116
and 121°C with an ambient temperature of 85°C.
SWITCH
SWITCH
SWITCH
Ground Disconnection
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 72 hours, TA = 25°C.
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 8 hours, TA = 85°C.
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 8 hours, TA = –25°C.
33/51
Page 34

7 Test results AN2208
Figure 37 and Figure 38 illustrate thermal behavior by showing the w aveform of I
HSD during the short circuit with different ambient temperature. The input is switched at 1 Hz.
The thermal shutdown is active and the output channel is switched off because it is shorted.
The maximum case temperature with maximum current I
(without short circuit) as shown in Figure 39.
Figure 37. Waveform I
the test with short circuit V
= 85°C, Wave4 = I
T
A
Wave1 = V
TOT
INOPT
and V
INOPT
TOT
during
,
CC
= 28V,
is 42°C during normal operation
TOT
Figure 38. Waveform on I
the test with short circuit V
= –25°C, Wave4 = I
T
A
Wave1 = V
INOPT
TOT
and V
TOT
current to
TOT
INOPT
CC
,
during
= 28V,
Figure 39. Case temperature dependency vs. current I
(TA = 25°C and VCC = 24 V)
TOT
Note: The temperature measured in thermal chamber using the FLUKE 189 multimeter and thermo-
coupler. No airflow present during the test.
34/51
Page 35

AN2208 7 Test results
7.1.3 EMC test results
IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test
The VN808 reference design board is tested according IEC 61000-4-4 for ±4kV level. Table 6
lists test results. Waveforms of bursts injected during the tests are shown in Figure 40 and
Figure 41.
The test lasted approximately 1 minute with ±4 kV and a repetition rate of 5 kHz. During the
tests, all channels were switched.
Test result: The VN808 HSD worked properly during the test.
Table 6. EMC test IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test results (VN808 RDB)
IEC 61000-4-4 Burst test Test Condition VN808 RDB 1/2 VN808 RDB 2/2
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Power supply
Output
Input
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Switch @ 1Hz ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Switch @ 1Hz ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Figure 40. Burst applied on the power supply Figure 41. Burst applied on the output channel
IEC 61000-4-5 surge test
A coupling decoupling network with a 42 Ω impedance was used when pe rforming the test. The
test was executed with ±2kV.
When testing power supply lines , a ll channels w ere switched. When testing the output channel,
only the tested channel was switched.
A 4.7nF 500V capacitor was placed between the power supply and the earth protection.
35/51
Page 36

7 Test results AN2208
Figure 42 and Figure 43 illustrate active Transil protection. The pulse from generator was
applied on the power supply an d the Transil diode limited the voltage fr om 2kV to appro ximate ly
50V. The test contained five positive and five negative discharges with each polarity. Repetition
rate was 1 discharge per minute.
Test result: The VN808 HSD worked properly during the test.
Table 7. EMC test IEC61000-4-5 surge test res u lts (VN808 RDB)
IEC 61000-4-5 Surge Test Test Condition VN808 RDB 1/2 VN808 RDB 2/2
Power supply V
to Earth
V
CC
GND to Earth
Output of the RDB to V
Output of the RDB to GND_Power
Output of the RDB to Earth
to GND_Power
CC
CC
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ± 2kV OK ± 2kV OK
Input OFF ± 2kV OK ± 2kV OK
Input ON ± 2kV OK ± 2kV OK
Input OFF ± 2kV OK ± 2kV OK
Figure 42. Positive surge applied on power
supply
IEC61000-4-6 conducted immunity
This is the most difficult test and requires the use of a coupling decoupling network for power
supply lines and special current clamp for output and data lines. The test was executed with
Level 3 (10V) compliance. Table 8 lists test results.
Figure 43. Negative surge applied on power
supply
36/51
Page 37

AN2208 7 Test results
If input lines are grounded, the optocoupler will switch on during the test because the inducted
voltage is too high. This is a normal reaction and when the test fin ish es, the optocoupler works
normally.
Test result: The VN808 HSD worked properly during the test.
Table 8. EMC test IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test results (VN808 RDB)
IEC 61000-4-6 Test Condition VN808 RDB 1/2 VN808 RDB 2/2
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Power supply
Output
Input
Note: B means a temporary degradation or loss of function or performance, with an automatic return
to normal operation.
Input OFF 10V OK 10V OK
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Input OFF 10V OK 10V OK
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Input OFF 10V OK B 10V OK B
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
7.2 VN340SP HSD test results
7.2.1 Load switching test results
Test conditions: T
Switching loads: Lamp = 24V, 15W; Inductor L = 130 mH, R
Test result: The VN340SP HSD worked properly during the test.
Figure 44 to Figure 49 show the waveforms during the load switching tests.
If input is ON, the output will switch off immediately if GND_Power is disconnected. If the input
is OFF, the output remains OFF.
7.2.2 Thermal stress test results
1. All channels shorted: f
2. All channels shorted: f
3. All channels shorted: f
Test result: The VN340SP HSD worked properly during the test.
The maximum temperature with 4 channels shorted is 156°C with an ambient temperature of
25°C and 159°C with an ambient temperature of 85°C. Figure 50 and Figure 51 show behavior
during the thermal stress tests.
= 25° C, VCC = 24 V, f = 0.5 Hz
AMB
SWITCH
SWITCH
SWITCH
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 72 hours, TA = 25°C.
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 8 hours, TA = 85°C.
= 0.5 Hz, VCC = 28V, duration 8 hours, TA = –25°C.
LOAD
= 48Ω
37/51
Page 38

7 Test results AN2208
The input was switched at 1 Hz. The thermal shutdown is shown in the figures below.
Figure 44. Switching lamps: V
0.5Hz, Wave3 = V
Wave2 = V
OUT
CC
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
Figure 46. Time delay between V
: VCC = 24V, Load = Lamp,
V
OUT
Wave2 = V
, Wave3 = V
OUT
139µs
= 24V, f =
,
CH1OUT
and
INOPT
, ∆t =
INOPT
Figure 45. Waveform t
inductor load: VCC =
OFF
24V, L = 130mH, R
= 1.2276ms, Wa ve2 = V
t
OFF
Wave3 = V
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
Figure 47. Switching with short circuit: V
24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = V
Wave3 = V
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
LOAD
= 60Ω,
OUT
CH1OUT
STATUSOPT
CH1OUT
,
CC
=
,
38/51
Page 39

AN2208 7 Test results
Figure 48. Waveform switching inductive load:
V
= 24V, L = 130mH, R
CC
f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = V
V
INOPT
, Wave4 = I
Figure 50. Waveform I
TOT
CH1OUT
and V
OUT
STATUSOPT
= 48Ω,
LOAD
, Wave3 =
during the test with shor t ci rcuit:
= 28V, TA = 85°C, Wave4 = I
V
CC
Wave1 = V
STATUSOPT
TOT
,
Figure 49. Switching with short circuit: V
24V, f = 0.5Hz, Wave2 = V
Wave3 = V
INOPT
Figure 51. Waveform on I
, Wave4 = I
and V
TOT
STATUSOPT
CH1OUT
STATUSOPT
during the test with short circuit:
= 28V, TA = –25°C, Wave4 = I
V
CC
Wave1 = V
STATUSOPT
CC
=
TOT
,
,
Note: The temperature measured in thermal chamber using a FLUKE 189 multimeter and thermo-
coupler.
7.2.3 EMC test results
IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test results
The VN340SP HSD is tested according IEC 61000-4-4 Level 4 (4kV). Power supply and input/
output ports are tested while all other channels are active. Table 9 lists test results.
39/51
Page 40

7 Test results AN2208
Test result: The VN340SP HSD worked properly during the test.
Table 9. EMC test IEC 61000-4-4 EFT test results (VN340SP RDB)
IEC 61000-4-4 Burst Test Test Condition RDB VN340SP 1/2 RDB VN340SP 2/2
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Power supply
Output
Input
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Switch @ 1Hz ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Switch @ 1Hz ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input ON ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
Input OFF ±4kV OK ±4kV OK
IEC 61000-4-5 surge test results
The board was tested with 42Ω coupling/decoupling network. All channels were active during
the test. Different combinations of channel activity were also tested. Table 10 lists test results.
A 4.7nF 500V capacitor was placed between the power supply and earth protection.
Test result: The VN340SP HSD worked properly during the test.
Table 10. EMC test IEC61000-4-5 surge test results (VN340SP RDB)
IEC 61000-4-5 Surge Test Test Condition VN340SP RDB 1/2 VN340SP RDB 2/2
Power supply V
GND:_Power
to Earth
V
CC
GND to Earth
Output of the RDB to V
Output of the RDB to
GND_Power
Output of the RDB to Earth
CC
to
CC
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input ON ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
Input OFF ±2kV OK ±2kV OK
IEC61000-4-6 conducted immunity test results
The test was executed according the standard with required levels. Table 11 lists test results.
Test results: Loss of function was observed during the test on output lines when HSD input
was OFF. Lamps shone little bit. (Normal behavior: Lamps switched OFF.)
40/51
Page 41

AN2208 7 Test results
Loss of function was observed during the test on input lines, but is considered as normal
behavior because the conducted voltage was too high and optocoupler input channels were
switched.
Table 11. EMC test IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test results (VN340SP RDB)
IEC 61000-4-6 Test Condition VN340SP RDB 1/2 VN340SP RDB 2/2
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Power supply
Output of the RDB
Input of the RDB
Note: B means a temporary degradation or loss of function or performance, with an automatic return
to normal operation.
Input OFF 10V OK 10V OK
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Input OFF 10V OK B 10V OK B
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
Input ON 10V OK 10V OK
Input OFF 10V OK B 10V OK B
Switch @ 1Hz 10V OK 10V OK
41/51
Page 42

7 Test results AN2208
Appendix A VN808 reference design board (RDB)
A.1 VN808 RDB bill of materials
The list of parts for the VN808 Reference Design Board is provided in Table 12.
Table 12. VN808 RDB bill of materials
Item Quantity Reference Value Note
1 16 C5, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12 10nF
C19, C20, C21, C22, C23, C24, C25, C26
2 4 C14, C13, C18, C17 4.7nF 500V SMD 1206
3 4 C2, C4, C15, C27 100nF 50V SMD 0805
4 2 C1, C28 22uF/50V
5 1 C30 10µF/35V ceramic
6 1 C33 100µF/16V tantalum
7 1 C31 220pF
8 1 C32 22nF
9 2 D1, D2 SM15T36A
10 1 D3 STPS2L25U
11 2 J1, J4 Headers 2line 14pin
12 2 J2, J3 Terminal bloc k 5,08 mm
13 1 L1 33µH/2A
14 2 R1, R13 2k2
15 16 R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10 1k5
R16, R17, R18, R19, R20, R21, R22,
R23
16 1 R26 15K
17 3 R12, R15, R25 4k7
18 1 R27 3k9
19 1 R11, R24 10k
20 1 J5 Terminal block 5.08mm
21 4 U2, U3, U7, U8 TLP281-4
22 2 U1, U5 VN808
23 2 U4, U6 TLP181
24 1 U9 L5970
25 2 F1, F2 7A
42/51
Page 43

AN2208 7 Test results
A.2 Recommended VN808 PCB Layout
The PCB layout is very important in order to operate the devices in the worst condition and
under EMC immunity.
Figure 52. VN808 RDB PCB layout (top and bottom)
Figure 53. VN808 RDB PCB layout (component side)
43/51
Page 44

7 Test results AN2208
Appendix B VN340SP reference design board (RDB)
B.1 VN340SP RDB bill of materials
The list of parts for the VN340SP Reference Design Boa rd is provided in Table 13.
Table 13. VN340SP RDB bill of materials
Item Quantity Reference Part Note
1 4 C2, C3, C12, C15 10nF
2 2 C4, C16 100nF 50V 0805
3 8 C5, C6, C7, C8, C17, C18, C19, C20 4n7 500V 1206
4 2 C9, C21 22µF
5 1 C10 22nF
6 1 C11 220pF
7 1 C13 10uF/35V Ceramic
8 1 C14 100uF/16V Tantalum
9 2 D1, D4 SM15T36A
10 1 D3 STPS2L25U
11 2 D2, D5 L-HLMP1700
12 1 J5 Terminal Block 5.08mm
13 2 J1, J3 HEADER 2 line 10 pin
14 2 J2, J4 Terminal Block 5.08mm
15 1 L1 33uH/2A
16 13
17 2 R5, R24 7k5
18 8 R6, R7, R8, R9, R25, R26, R27, R28, 22k
19 10
20 1 R17 15k
21 1 R18 3k9
22 2 F1, F2 Fuse 4A
23 2 U1, U6 TLP281-4
24 2 U2, U5 TLP181
25 2 U3, U7 VN340SP
26 1 U8 L5970D
R1, R2, R3, R4, R19, R10, R20, R21, R22, R23,
R29,
R11, R12, R13, R14, R15, R30, R31, R32, R33,
R34, R16, R35
4k7
1k5
44/51
Page 45

AN2208 7 Test results
B.2 Recommended VN340SP RDB PCB layout
Figure 54. VN340SP RDB PCB layout (Top side) and (Bottom side)
Figure 55. VN340SP RDB PCB layout (component side)
45/51
Page 46

7 Test results AN2208
Appendix C L5970D DC/DC converter
C.1 Functional description
The L5970D (Figure 56) is a step-down power regulator capable of delivering output voltages
from 1.235 to 35V (up to 1A). The operat ing input v oltage r anges from 4.4 to 36V. It is designed
in BCD5 technology and the power switching element is a P-Channel D-MOS power transistor.
An internal oscillator sets the switching frequency at 250 kHz, minimizing the LC output filter.
The L5970D is used for supplying optocouplers and other applications.
Figure 56. L5970D block diagram
VCC
+
-
VOLTAGE
MONITOR
PWM
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
SUPPLY
1.235V 3.5V
PEAK TO PEAK
CURRENT LIMIT
DCkQ
FREQUENCY
SHIFTER
DRIVER
V
REF
BUFFER
LPDMOS
POWER
OUTGND
V
Ai11607
REF
INH
COMP
SYNC
TRIMMING
INHIBIT
E/A
1.235V
-
+
OSCILLATOR
FB
The VN808 and VN340SP reference design boards use the L5970D DC/DC Converter for the
power supplies f or the data parts. With an output v olt age of 6V and ou tput cu rrent up to 1A, the
L5970D is an attractive and simp le solution.
The main internal blocks are shown in Figure 56 where is reported the device block diagram.
They are:
● A voltage regu lator that supp lies the internal circuitry. From this regulator a 3.3V reference
voltage is externally available.
● A voltage moni tor circuit that checks the input and internal voltages.
● A fully integrated sawtooth oscillator whose frequency is 250 kHz ±5%, including also the
voltage feed forward function and an input/output synchronization pin.
● Two embedded current limitations circuitries which control the current that flows through
the power switch. The Pulse by Pulse Current Limit forces the power switch OFF cycle by
cycle if the current reaches an internal threshold, while the Frequency Shifter reduces the
switching frequency in order to strongly reduce the duty cycle.
● A transconductance error amplifier.
● A pulse width modulator (PWM) comparator and the relative logic circuitry necessary to
drive the internal power.
● A high-side driver for the internal P-MOS switch.
● An inhibitor block for stand-by operation.
● A circuit to provide the thermal protection function.
46/51
Page 47

AN2208 7 Test results
The output voltage can be adjustab le b y v oltage divider. In Figure 9 can be seen voltage di vider
by resistors R26 and R27. The value of resistor R26 is equal to:
–
V
OUTVFB
R26 R27
=
------------------------------ -
V
FB
Note: V
= 1.235 V
FB
For more information and technical data about L5970D, refer to the L5970D datasheet.
C.2 L5970D layout recommendations
A optimized layout is on of the key f actors to operate the DC/DC converter. It redu ce noise an d
interference. P ower-ge nerating portions of the lay out are the main cause of n oise, theref ore, the
high switching current loop areas, should be kept as small as possible as well as lead lengths
has to be kept short as possible.
High impedance paths (in particular the feedbac k connections) are susceptible to interference
and so they should be as far as possible from the high current paths.
Below there is a layout example on Figure 57. The input and output loops ar e minimized to
avoid radiation and high frequency resonance problems. The feedback pin connections to the
external divider are ve ry close to the device to a v oid pic k up noise. Mo reov er the GND pin of the
device is connected to the ground plane directly with VIA on the bottom side of the PCB.
Figure 57. L5970 DC/DC converter layout example
47/51
Page 48

7 Test results AN2208
C.3 L5970D DC/DC converter load test results
Table 14. L5970D electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
SS
I
QOP
I
OUTDC
f
S
d Duty cycle 0 100 %
TA
P
TOTDC
The DC/DC converter was tested with a constant output current with resistive load.
The Waveform on coil L1 has to be clear without overshot (see Figure 61., Figure 63.).
Input/output voltage ripple depends on ESR capacitor values.
Operating input voltage 6.6 35 V
Total operating quiescent current 2.4 5 mA
Maximum limiting current 1.0 1.4 A
Switching frequency 243 250 kHz
Operating Temperature Range –25 to 85°C °C
Power dissipation at Tamb = 60°C 0.75 W
Only low ESR capacitors have been used on V
and V
SS
OUT
.
Test conditions
● Resistive load = 12Ω.
● Input voltages V
● Output volt age V
● Output current I
● Ambient Temperature (T
Test results: If output current is increase up to 1.4 A, then the current limiter will be active.
Output voltage ripple can be seen in Figure 62. The maximum value of ripple is 93 mV. The
efficiency measurement results are shown in Figure 58.
Figure 58. Efficie n cy vs. ou t pu t cur r e nt
= 8, 12, and 24V.
SS
= 5V
BSS
= 0.4A
OUTDC
) = 25°C
A
48/51
Page 49

AN2208 7 Test results
Figure 59. Output voltage stability of L5970D, VSS = 24 V
Figure 60. Voltage ripple on capacitor C30,
I
= 0.4A, VSS = 24V
OUTDC
Figure 62. Voltage ripple on capacitor C33,
V
= 24V, I
SS
OUTDC
= 0.4 A
Figure 61. Waveform on coil L1, I
0.4A, V
= 24V
SS
OUTDC
Figure 63. Waveform on coil L1, without
load, VSS = 24V
=
49/51
Page 50

8 Revision history AN2208
8 Revision history
Date Revision Changes
16-Sept-2005 1.0 Initial release.
50/51
Page 51

AN2208
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor fo r any infringement of p atents or other righ ts of third parties w hich may result from its use. No license is g ranted
by implication or otherwise under any pa tent or paten t right s of ST Microel ect ronics . Spec ifica tions me ntio ned i n this pu blicat ion are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critica l components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of t heir respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of compan ie s
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Ho ng Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
51/51
 Loading...
Loading...