Page 1

1725-86984-000 Rev: P
September 2016
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone
Administration Guide
Page 2

Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 2
Copyright Notice
© 2012-2016 Spectralink Corporation All rights reserved. SpectralinkTM, the Spectralink logo and
the names and marks associated with Spectralink’s products are trademarks and/or service
marks of Spectralink Corporation and are common law marks in the United States and various
other countries. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners. No portion hereof
may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, for any purpose other than the
recipient’s personal use, without the express written permission of Spectralink.
All rights reserved under the International and pan-American Copyright Conventions. No part of
this manual, or the software described herein, may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or
by any means, or translated into another language or format, in whole or in part, without the
express written permission of Spectralink Corporation.
Do not remove (or allow any third party to remove) any product identification, copyright or other
notices.
Notice
Spectralink Corporation has prepared this document for use by Spectralink personnel and
customers. The drawings and specifications contained herein are the property of Spectralink and
shall be neither reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written approval of Spectralink,
nor be implied to grant any license to make, use, or sell equipment manufactured in accordance
herewith.
Spectralink reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained
in this document without prior notice, and the reader should in all cases consult Spectralink to
determine whether any such changes have been made.
NO REPRESENTATION OR OTHER AFFIRMATION OF FACT CONTAINED IN THIS
DOCUMENT INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO STATEMENTS REGARDING CAPACITY,
RESPONSE-TIME PERFORMANCE, SUITABILITY FOR USE, OR PERFORMANCE OF
PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN SHALL BE DEEMED TO BE A WARRANTY BY
SPECTRALINK FOR ANY PURPOSE, OR GIVE RISE TO ANY LIABILITY OF SPECTRALINK
WHATSOEVER.
Warranty
The Product Warranty and Software License and Warranty and other support documents are
available at +http://support.spectralink.com.
Contact Information
US Location Denmark Location UK Location
+1 800-775-5330 +45 7560 2850 +44 (0) 20 3769 9800
Spectralink Corporation Spectralink Europe ApS Spectralink Europe UK
2560 55th Street Bygholm Soepark 21 E Stuen 329 Bracknell, Doncastle Road
Boulder, CO 80301 8700 Horsens Bracknell, Berkshire, RG12 8PE
USA Denmark United Kingdom
info@spectralink.com infoemea@spectralink.com infoemea@spectralink.com
Page 3

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 3
Contents
About This Guide .............................................................. 11
Who Should Read This Guide? .......................................................................................11
What’s New in This Guide ...............................................................................................11
Recommended Software Tools .......................................................................................12
Reading the Feature Parameter Tables ..........................................................................12
Product Support ..............................................................................................................12
Spectralink References ...................................................................................................13
Specific Documents ....................................................................................................13
Conventions Used In This Document .............................................................................15
Icons ...........................................................................................................................15
Writing Conventions ....................................................................................................16
Part I: Getting Started ...................................... 17
Chapter 1: Welcome to the Spectralink 84-Series Handsets ......... 18
Key Features of your Spectralink Handsets ..................................................................20
Chapter 2: System Overview ................................................ 21
What is SIP? .....................................................................................................................21
Network Requirements ....................................................................................................21
Network Configuration ....................................................................................................22
Understanding Spectralink Phone Software Architecture ............................................23
What is the Updater? ..................................................................................................23
What is the Spectralink Software? ...............................................................................24
What are the configuration files? .................................................................................24
What are the resource files? .......................................................................................25
Part II: Setting Up Your Environment ................... 26
Chapter 3: Setting Up Your Device Network ............................. 27
Wireless Device Settings .................................................................................................27
IP Communication Settings ............................................................................................27
Provisioning Server Discovery .......................................................................................28
Supported provisioning protocols ................................................................................29
Network Configuration Menus ........................................................................................30
Network configuration menu ........................................................................................31
Provisioning server menu ............................................................................................32
Network Interfaces Menu ............................................................................................34
Page 4

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 4
Syslog Menu ...............................................................................................................39
Login Credentials Menu .............................................................................................. 40
TLS Security Menu ...........................................................................................................41
TLS Profile Menu ........................................................................................................41
TLS Applications Menu ...............................................................................................41
Chapter 4: Setting Up the Provisioning Server.......................... 43
Why Use a Provisioning Server? ................................ ....................................................43
Provisioning Server Redundancy ................................................................................43
Provisioning Server Security Notes ...............................................................................44
Setting up an FTP Server as Your Provisioning Server ................................................44
Downloading Spectralink Software Files to the Provisioning Server ..........................46
Microsoft® Skype for Business compatibility ................................................................46
Spectralink 84-Series Hardware IDs ............................................................................47
Deploying and Updating Spectralink Handsets with a Provisioning Server ................48
Shortcut Method to Deploy Spectralink Handsets with a Provisioning Server ..............49
Upgrading Spectralink Software ..................................................................................51
Chapter 5: Understanding the Files Written by the Handsets ........ 52
Log Files ...........................................................................................................................53
Overrides ..........................................................................................................................53
Deleting the override file ..............................................................................................54
Contacts ...........................................................................................................................54
Call List .............................................................................................................................55
Part III: Configuring Features ............................. 58
Chapter 6: Features that Cannot be Configured ........................ 59
Audio Processing Features .............................................................................................59
Automatic Gain Control ...............................................................................................59
Background Noise Suppression ..................................................................................59
Comfort Noise Fill ........................................................................................................59
Dynamic Noise Reduction ...........................................................................................59
Jitter Buffer and Packet Error Concealment ................................................................59
Low-Delay Audio Packet Transmission .......................................................................60
Call Timer .........................................................................................................................60
Called Party Identification ...............................................................................................60
Connected Party Identification .......................................................................................60
Microphone Mute .............................................................................................................60
Synthesized Call Progress Tones ...................................................................................61
Page 5

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 5
Chapter 7: Configurable Features on the User Menus ................ 62
Call Forwarding ................................................................................................................62
Keypad Lock ....................................................................................................................66
Multi Key Answer .............................................................................................................67
Notification Profiles .........................................................................................................67
Time and Date Display .....................................................................................................77
Synchronizing with SNTP ............................................................................................79
User Preferences Parameters .........................................................................................80
Chapter 8: Features Configured by the Administrator ................ 82
AutoComplete List ...........................................................................................................82
Audio Settings .................................................................................................................83
Context Sensitive Volume Control ...............................................................................83
<voice.volume/> ..........................................................................................................83
<voice/> ......................................................................................................................84
<rxQoS/>.....................................................................................................................84
Automatic Off-Hook Call Placement ...............................................................................85
Background Images .........................................................................................................86
Configuring Background Images .................................................................................86
Backlight Off while Phone is Charging ..........................................................................87
Battery End-of-life Alert ...................................................................................................87
Feature and Basic Settings Menu Password .................................................................88
Call Hold ...........................................................................................................................89
Call Handling Features ....................................................................................................91
Call Park and Retrieve ................................................................................................92
Call Waiting Alerts .......................................................................................................92
Calling Party Identification ...........................................................................................92
Missed Call Notification ...............................................................................................93
Call Transfer ...............................................................................................................93
Call Lists ................................ ................................................................ .....................95
Miscellaneous Call Handling Parameters ....................................................................95
CMS 2.0 .............................................................................................................................97
Conference Calls .............................................................................................................97
Corporate Directory .........................................................................................................98
Default Ring Tones and Alert Tones............................................................................. 101
Call Progress Patterns .............................................................................................. 104
Do Not Disturb ............................................................................................................... 106
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) Tones ................................................................... 106
DTMF Event RTP Payload ........................................................................................ 107
Emergency Calls ............................................................................................................ 108
Emergency Dial via Authorized Call menu................................................................. 108
Emergency Dial via Duress Button ............................................................................ 109
Enhanced Feature Keys ................................................................................................ 111
Page 6

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 6
Guidelines for Configuring Enhanced Feature Keys .................................................. 112
Understanding Macro Definitions .............................................................................. 115
Macro Action ............................................................................................................. 115
Prompt Macro Substitution ........................................................................................ 117
Expanded Macros ..................................................................................................... 118
Special Characters .................................................................................................... 118
Features Softkey Menu Options Customization .......................................................... 120
Example Softkey Configurations ............................................................................... 122
Handsfree Settings ........................................................................................................ 125
Bluetooth Headset Support ....................................................................................... 126
Language Support ......................................................................................................... 126
Local Contact Directory................................................................................................. 129
Provisioning the Seed Directory ................................................................................ 130
Configuring the Contact Directory ............................................................................. 132
Editing the Users’ MACaddress-directory.xml File ..................................................... 133
Specialized Caller Treatments ................................................................................... 133
Location Services (Ekahau) .......................................................................................... 135
Microsoft Exchange Calendar Integration.................................................................... 136
Open Application Interface ........................................................................................... 138
Passwords – User and Administrator ................................................................ ........... 139
Personal Alarms ............................................................................................................ 141
Administrator Configurable Options ........................................................................... 142
User Experience........................................................................................................ 144
Integration with Third Party Applications ................................................................... 147
XML API Detail .......................................................................................................... 151
Viewing an Alarm Event ............................................................................................ 151
Configuration Template ............................................................................................. 152
Phone Lock .................................................................................................................... 153
Provisional Polling of Spectralink Handsets ............................................................... 155
Push-to-talk and Group Paging .................................................................................... 156
Push-to-talk ............................................................................................................... 157
Group Paging ............................................................................................................ 159
Quick Barcode Connector Application ......................................................................... 161
Registrations .................................................................................................................. 161
Multiple Registrations ................................................................................................ 164
Multiple Concurrent Calls .......................................................................................... 165
Flexible Call Appearances ......................................................................................... 167
User Profiles................................................................................................................... 167
Placing Authorized (Emergency) Calls without Logging In ......................................... 169
Voicemail Integration ..................................................................................................... 170
<voIpProt/> ................................................................ ..................................................... 172
Web Browser .................................................................................................................. 178
<mb/> ........................................................................................................................ 181
<oai/> ........................................................................................................................ 182
Page 7

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 7
Chapter 9: Web Application Parameters................................ 183
Application menu configuration <apps.> ..................................................................... 183
Web browser parameters <mb.> ................................................................................... 184
State Polling Parameters <apps.statePolling.> ........................................................... 185
Push Request Parameters <apps.push.> ..................................................................... 185
Telephony Notification Parameters (apps.telNotification.> ........................................ 187
Open Application Interface parameters <oai.> ............................................................ 189
Sample Configurations .................................................................................................. 189
Push .......................................................................................................................... 189
Telephony Notifications ............................................................................................. 190
State Polling .............................................................................................................. 190
Personal Alarms ........................................................................................................ 191
Chapter 10: System-Level Parameters .................................. 192
Configuration File Encryption ....................................................................................... 192
Understanding Digital Certificates ............................................................................... 193
About Digital Certificates ........................................................................................... 195
Types of certificates .................................................................................................. 195
Configuring certificates .............................................................................................. 196
Generating a Certificate Signing Request ................................................................. 207
Downloading Certificates to a Spectralink Phone ...................................................... 208
DNS SIP Server Name Resolution ................................................................................ 208
Behavior When the Primary Server Connection Fails ................................................ 209
Incoming Signaling Validation ...................................................................................... 211
Instant Messaging.......................................................................................................... 212
IP Type-of-Service.......................................................................................................... 215
<qos/> ....................................................................................................................... 215
Logging Parameters ...................................................................................................... 216
<level/> <change/>and<render/> .............................................................................. 217
<sched/> ................................................................................................................... 218
Microsoft Skype for Business Integration.................................................................... 219
Network Address Translation (NAT) ............................................................................. 219
Provisioning Server System Settings ........................................................................... 220
<request/> ...................................................................................................................... 221
Security <sec/> .............................................................................................................. 221
<srtp/> ................................ ....................................................................................... 221
<dot1x><eapollogoff/>............................................................................................... 222
Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol .......................................................................... 222
Server Redundancy ....................................................................................................... 225
Terminology .............................................................................................................. 225
About the Optional Failover Behaviors ...................................................................... 226
Fallback Deployments ............................................................................................... 229
Failover Deployments ............................................................................................... 230
Page 8

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 8
DNS Server Unavailability ......................................................................................... 230
Redundancy Parameters ........................................................................................... 230
Supporting 802.1X Authentication ................................................................................ 233
<tcpIpApp/> .................................................................................................................... 235
<dhcp/> ..................................................................................................................... 235
<dns/> ....................................................................................................................... 235
<ice/> ........................................................................................................................ 235
<keepalive/> .............................................................................................................. 236
Tones <tones/> .............................................................................................................. 237
<chord/> .................................................................................................................... 237
Web Configuration Utility .............................................................................................. 238
<httpd/> ..................................................................................................................... 238
Chapter 11: Special Use Cases ........................................... 239
Acoustic Echo Cancellation .......................................................................................... 239
Audio Codecs ................................................................................................................. 239
Band Steering ................................................................................................................ 240
Bridged Line Appearance .............................................................................................. 242
Local Digit Map .............................................................................................................. 243
Understanding Digit Map Rules ................................................................................. 244
Location Values for E.911 Services .............................................................................. 249
Real-Time Transport Protocol Ports ............................................................................. 250
Shared Line Appearances ............................................................................................. 251
Shared Call Appearance Signaling ............................................................................ 252
Static DNS Cache ........................................................................................................... 253
Using Static DNS Cache for Redundancy ................................................................. 258
DNS Cache <dns/> ................................ ................................................................ ......... 259
NAPTR <NAPTR/> .................................................................................................... 259
SRV <SRV/> ............................................................................................................. 260
A <A/> ....................................................................................................................... 260
Voice Activity Detection ................................................................................................ 264
Part IV: Troubleshooting and Maintaining your
Deployment ................................................. 265
Chapter 12: Troubleshooting Your Spectralink Handsets .......... 266
Troubleshooting Flow Diagram .................................................................................... 267
Understanding Error Message Types ........................................................................... 268
Updater Error Messages ........................................................................................... 268
Spectralink Software Error Messages ....................................................................... 270
Status Menu ................................ ................................................................ ................... 275
Log Files ......................................................................................................................... 276
Page 9

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 9
Logging Modules ....................................................................................................... 278
Major categories of WLAN entries ............................................................................. 278
Managing the Phone’s Memory Resources ................................................................. 280
Identifying Symptoms ................................................................................................ 280
Checking the Phone’s Available Memory .................................................................. 281
Managing the Phone Features .................................................................................. 282
Testing Phone Hardware ............................................................................................... 283
Uploading a Phone’s Configuration ............................................................................. 284
Network Diagnostics ..................................................................................................... 284
Network Protocols and Ports Used on Spectralink Handsets .................................... 285
Power and Startup Issues ............................................................................................. 286
Key Pad Issues .............................................................................................................. 286
Screen and System Access Issues .............................................................................. 287
Calling Issues ................................................................................................................. 287
Display Issues ................................................................................................................ 288
Audio Issues .................................................................................................................. 288
Upgrading Issues ........................................................................................................... 289
Chapter 13: Miscellaneous Maintenance Tasks ....................... 291
Encrypting Configuration Files ..................................................................................... 291
Comparing encrypted and unencrypted files ............................................................. 295
Decrypting existing configuration files ....................................................................... 295
Changing an existing key .......................................................................................... 296
Log messages ........................................................................................................... 296
Multiple Key Combinations ........................................................................................... 297
Rebooting the Phone ................................................................................................ 297
Resetting to factory defaults ...................................................................................... 298
Updating log files ....................................................................................................... 298
Setting base profile ................................................................................................... 298
Default Feature Key Layouts ......................................................................................... 299
Parsing Vendor ID Information ..................................................................................... 300
Product Model Number and Hardware ID Mapping ..................................................... 301
Capturing the Phone’s Current Screen ........................................................................ 302
Part V: Appendices ........................................ 303
Appendix A: Ringtone Pattern Names and Sound Effects Parameters
.................................................................................. 304
Ringer Patterns .............................................................................................................. 304
Ring Tones <rt/> ............................................................................................................ 305
Page 10

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 10
Appendix B: Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Information ......... 307
RFC and Internet Draft Support .................................................................................... 307
Request Support ....................................................................................................... 309
Header Support ......................................................................................................... 309
Response Support .................................................................................................... 312
Hold Implementation ................................................................................................. 314
Reliability of Provisional Responses .......................................................................... 315
Transfer .................................................................................................................... 315
Third party call control ............................................................................................... 315
SIP for Instant Messaging and Presence .................................................................. 315
Appendix C: Open Source Information ................................. 316
OFFER for Source for GPL and LGPL Software .......................................................... 316
Contact Information for Requesting Source Code ..................................................... 316
Appendix D: Library of <device/> Settings ............................. 317
Appendix E: Trusted Certificate Authority List........................ 324
Appendix F: Spectralink Certificates ................................... 335
Page 11

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 11
About This Guide
This Spectralink 84-Series Administration Guide provides advanced instructions for installing,
provisioning, and administering Spectralink handsets. It is a companion to the Spectralink
84-Series Deployment Guide which is your essential reference for understanding how to
provision and deploy Spectralink 84-Series handsets in any environment. This guide expands
upon the information provided in the Deployment Guide and provides additional data about how
the software works and provides descriptions of all applicable parameters. Specifically, this
Administration Guide will help you perform the following tasks:
Install and configure your handset on a network server or Web server
Configure your handset’s features and functions
Configure your handset’s user settings
Troubleshoot common handset issues
Who Should Read This Guide?
System administrators and network engineers should read this guide for advanced information
on configuring and understanding Spectralink 84-Series handsets. This guide describes
administration-level tasks and is not intended for end users.
Before reading this guide, you should be familiar with the following:
The information in the Spectralink 84-Series Deployment Guide is not duplicated in this
document. This document expands upon the basic configuration settings in the
Deployment Guide and this document assumes you are familiar with Deployment Guide
information.
Computer networking and driver administration for your operating system
An XML editor
The XML-based configuration file format that the Spectralink Software and its supported
handsets use.
What’s New in This Guide
The content in this guide has been significantly revised from the Polycom UCS version for use
with the Spectralink 84-Series handsets. It is designed for clarity and to provide more
information to system administrators who are already familiar with deploying Spectralink
84-Series handsets.
Page 12

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 12
Recommended Software Tools
Spectralink recommends that you use an XML editor – such as XML Notepad – to create and
edit configuration files. In this way, all configuration files that you create will be valid XML files.
If the configuration files are not valid XML, they will not load on the handset and an error
message will be logged to the provisioning server.
See the Spectralink 84-Series Deployment Guide for a discussion on XML editor options,
usefulness and limitations.
Reading the Feature Parameter Tables
Each of the feature descriptions discussed in Part III: Configuring Features includes a table of
parameters that you configure to make the features work. Although there are three provisioning
methods you can use to configure a feature: a centralized provisioning server, the Web
Configuration Utility, or the local handset user interface, this document emphasizes the central
provisioning server method. It is the preferred method for deploying advanced configurations
such as those covered in this document as it is the only method that is available for every
feature. The Web Configuration Utility and the local handset user interface do not provide
access to all features.
The central provisioning server method requires you to configure parameters located in
template configuration files that Spectralink provides in XML format.
We recommend using the search feature of your XML editor to locate the parameters you need
to find.
Product Support
Spectralink wants you to have a successful installation. If you have questions please contact the
Customer Support Hotline at 1-800-775-5330.
The hotline is open Monday through Friday, 6 a.m. to 6 p.m. Mountain time.
For Technical Support: mailto:technicalsupport@spectralink.com
For Knowledge Base: http://support.spectralink.com
For Return Material Authorization: mailto:nalarma@spectralink.com
Page 13
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 13
Spectralink References
All Spectralink documents are available at http://support.spectralink.com.
To go to a specific product page:
Select the Product Category and Product Type from the dropdown lists and then select the
product from the next page. All resources for that particular product are displayed by default
under the All tab. Documents, downloads and other resources are sorted by the date they were
created so the most recently created resource is at the top of the list. You can further sort the
list by the tabs across the top of the list to find exactly what you are looking for. Click the title to
open the link.
Specific Documents
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide This document introduces
deployment concepts and the methods of provisioning the 84-Series handsets in any type of
facility. It is the fundamental text and a prerequisite to this Administration Guide, especially for
administrators who are new to the Spectralink 84-Series handsets or who may wish a refresher
course.
Page 14
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 14
Spectralink Deploying Enterprise-Grade Wi-Fi Telephony This document covers the security,
coverage, capacity and QoS considerations necessary for ensuring excellent voice quality within
enterprise Wi-Fi networks.
Best Practices Guide to Network Design Considerations for Spectralink Wireless Telephones
This document provides recommendations for ensuring that a network environment is
adequately optimized for use with Spectralink Wireless Telephones. It provides detailed
information on wireless LAN layout, network infrastructure, QoS, security and subnets and
identifies issues and solutions based on Spectralink’s extensive experience in enterprise-class
Wi-Fi telephony. This document has a brief discussion about wireless security.
Understanding Wireless Security on Your Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Phones
Provides more information and assistance in determining which security method to use.
Barcode Administration Guide Provides information about barcode symbologies and how to
configure and implement the barcode feature on the handset. The Spectralink 84-Series User
Guide also contains information about using the barcode feature.
Quick Barcode Connector Administration Guide Provides instruction for implementation of the
barcode application. The Spectralink 84-Series User Guide also contains information about
deploying the barcode feature.
The Spectralink 84-Series User Guide offers comprehensive instructions on using each of the
features deployed on the handsets.
For information on IP PBX and softswitch vendors, see the Spectralink 84-Series Call Server
Interoperability Guide.
For information about combining Polycom desksets and Spectralink 84-Series handsets in the
same facility, see the Interoperability Guide: Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephones and
Polycom Desksets.
AP Configuration Guides explain how to correctly configure access points and WLAN controllers
(if applicable) and identify the optimal settings that support Spectralink 84-Series handsets.
Technical Bulletins and Feature Descriptions explain workarounds to existing issues and
provides expanded descriptions and examples.
Release Notes describe the new and changed features, and resolved issues in the latest
version of the software. Find them in the Downloads section of the support site.
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephones Web Developer’s Guide assists with the
development of applications that run on the browser on the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless
Handsets.
Spectralink 8000 Open Applications Interface (OAI) Gateway Administration Guide provides
information about deploying third party applications through the OAI gateway interface.
For other references, look for the Web Info icon throughout this Administration Guide.
Page 15

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 15
Conventions Used In This Document
Icons
Icons indicate extra information about nearby text.
Warning
The Warning icon highlights an action you must perform (or avoid) to avoid
exposing yourself or others to hazardous conditions.
Caution
The Caution icon highlights information you need to know to avoid a hazard that
could potentially impact device performance, application functionality, successful
feature configuration and/or affect handset or network performance.
Note
The Note icon highlights information of interest or important information that will
help you be successful in accomplishing a procedure or understanding a concept.
Tip
The Tip icon highlights information that may be valuable or helpful for users to
know, such as special techniques, shortcut methods, or information that will make
user tasks easier to perform.
Web
The Web Info icon highlights supplementary information available online such as
documents or downloads on support.spectralink.com or other locations.
Timesaver
A time-saving tip is typically used to mention or highlight a faster or alternative
method for users who may already be familiar with the operation or method being
discussed.
Admin Tip
This tip advises the administrator of a smarter, more productive or alternative
method of performing an administrator-level task or procedure.
Page 16
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 16
Power User
A Power User Tip is typically reserved for information directed specifically at highlevel users who are familiar with the information or procedure being discussed and
are looking for better or more efficient ways of performing the task. For example,
this might highlight customization of a feature for a specific purpose.
Troubleshooting
This element can be used in any type of document and is typically used to highlight
information to help you solve a relevant problem you may encounter, or to point to
other relevant troubleshooting reference information.
Settings
The Settings icon highlights information to help you zero in on settings you need to
choose for a specific behavior, to enable a specific feature, or access
customization options.
Writing Conventions
Convention
Description
<MACaddress>
Indicates that you must enter information specific to your installation, phone, or
network. For example, when you see <MACaddress>, enter your phone’s 12-digit
MAC address. If you see <installed-directory>, enter the path to your installation
directory.
>
Indicates menu navigation. For example, Settings> Basic indicates that you need
to select Basic from the Settings menu.
parameter.*
Used for configuration parameters. If you see a parameter name in the form
parameter.* , the text is referring to all parameters beginning with parameter.
Page 17

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 17
Part I: Getting Started
Part I gives you an overview of the Spectralink 84-Series handsets and of the Spectralink
Software.
Page 18

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 18
Chapter 1: Welcome to the Spectralink
84-Series Handsets
This chapter introduces Spectralink 84-Series handsets used with Spectralink Software version
4.2.0 and above.
The Spectralink family of handsets provides a powerful, yet flexible wireless IP communications
solution for Ethernet TCP/IP networks. Not only do the handsets deliver excellent voice quality,
but also come with a high-resolution graphic display screen for call information, multiple
languages, directory access, and system status. The handsets can also support advanced
functionality, including multiple call and flexible line appearances, HTTPS secure provisioning,
presence, custom ringtones, and local conferencing.
Note: Indoor use only
This device is intended for indoor use only.
Caution: Product compatibility/safety
Spectralink 84-Series handsets are intended for operation only with Spectralink 84Series battery packs and Spectralink 84-Series chargers. These Spectralink
components are critical to product safety certification and may not be substituted.
Representative samples of the Spectralink 84-Series handsets, battery packs and
chargers have been tested as a complete system by an independent testing
organization and have been certified by that organization to meet applicable safety
standards. Use or operation of the Spectralink 84-Series handsets with batteries or
chargers other than those authorized by Spectralink has not been tested or safety
certified. Spectralink 84-Series handsets, battery packs or chargers used or
operated with products not authorized by Spectralink are not covered by the
Spectralink Limited Product Warranty.
Caution: Use authorized components only
Only Spectralink 84-Series battery packs and Spectralink 84-Series chargers are
authorized for use or operation with Spectralink 84-Series handsets.
Only Spectralink 84-Series battery packs are authorized for use or operation with a
Spectralink 84-Series charger and are not authorized to be used or operated in any
other charger.
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephones were originally developed in conjunction with
Polycom Inc. In September 2012 the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone software code
and Polycom UCS deskset software code were split into two separate streams. The same code
no longer serves both Spectralink Wireless Telephones and Polycom wired desksets.
Page 19

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 19
Using Spectralink Handsets and Polycom Desksets in a combined
environment
Special configuration steps need to be taken in environments where both
Spectralink and Polycom phones are deployed. For more information on using
Spectralink 84-Series handsets and Polycom wired desksets in a facility see the
Interoperability Guide: Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephones and Polycom
Desksets.
From an administrator’s perspective, the handsets are endpoints in an overall network topology
designed to interoperate with other compatible equipment including application servers, media
servers, internet-working gateways, voice bridges, and other end points.
If you want to begin setting up your Spectralink handsets on the network, go to Setting Up Your
Device Network.
If you want to begin configuring the features available for your Spectralink handsets, go to Part
III: Configuring Features.
Support for Spectralink Handsets
You can find all documentation for all Spectralink handsets on Spectralink Support
Website. For more information, contact your Spectralink distributer.
Spectralink 8440/8441
Spectralink 8450/8452/8453
Page 20

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 20
Key Features of your Spectralink Handsets
Spectralink handsets running Spectralink Software include the following key features:
Award winning sound quality with a full-duplex speakerphone
○ Permits natural, high-quality, two-way conversations
○ Supports HDVoice
Easy-to-use
○ An easy transition from traditional PBX systems into the world of IP Communications
○ Four context-sensitive softkeys for further menu-driven activities
Platform independent
○ Supports multiple protocols and platforms enabling standardization of one handset
for multiple locations, systems, and vendors
Faster Boot Time
○ The time between handset reboot and obtaining a dial tone has been noticeably
reduced.
Field upgradeable
○ Upgrade handsets as standards develop and protocols evolve
○ Extends the life of the handset to protect your investment
○ Application flexibility for call management and new telephony applications
Large LCD
○ Easy-to-use, easily readable, and intuitive interface
○ Support of rich application content, including multiple call appearances, presence
and instant messaging, and XML services
○ 240 x 320 pixel graphical color LCD
Multiple language support
○ Set on-screen language to your preference. Select from Chinese (Simplified and
Traditional), Danish, Dutch, English (Canada, United Kingdom, and United States),
French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese
(Brazilian), Russian, Slovenian, Spanish (International), and Swedish.
Web Browser
○ Supports a subset of XHTML constructs that run like any other Web browser
XML status/control API
○ Ability to poll handsets for call status and device information
○ Ability to receive telephony notification events
Page 21
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 21
Chapter 2: System Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the Spectralink Software, providing an understanding of
how the handsets are deployed within the greater LAN and wireless LAN configuration. To
begin setting up your Spectralink handsets, refer to the Spectralink 84-Series Deployment
Guide and review the Infrastructure chapter.
The Spectralink handsets are deployed in an 802.1X wireless environment.
Deploying Spectralink Handsets in a Completely Wireless Environment
For more information on using these handsets in a completely wireless
environment, see the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment
Guide.
What is SIP?
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard for
multimedia communications over IP. It is an ASCII-based, application-layer control protocol
(defined in RFC 3261) that can be used to establish, maintain, and terminate calls between two
or more endpoints. Like other voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, SIP is designed to address the
functions of signaling and session management within a packet telephony network. Signaling
allows call information to be carried across network boundaries. Session management provides
the ability to control the attributes of an end-to-end call.
Network Requirements
For Spectralink handsets to successfully operate as a SIP endpoint in your network, you will
require:
A working IP network
Routers configured for VoIP
VoIP gateways configured for SIP
The latest (or a compatible version) Spectralink Software image
An active, configured call server to receive and send SIP messages
For information on IP PBX and softswitch vendors, see the Spectralink 84-Series Call
Server Interoperability Guide.
Page 22
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 22
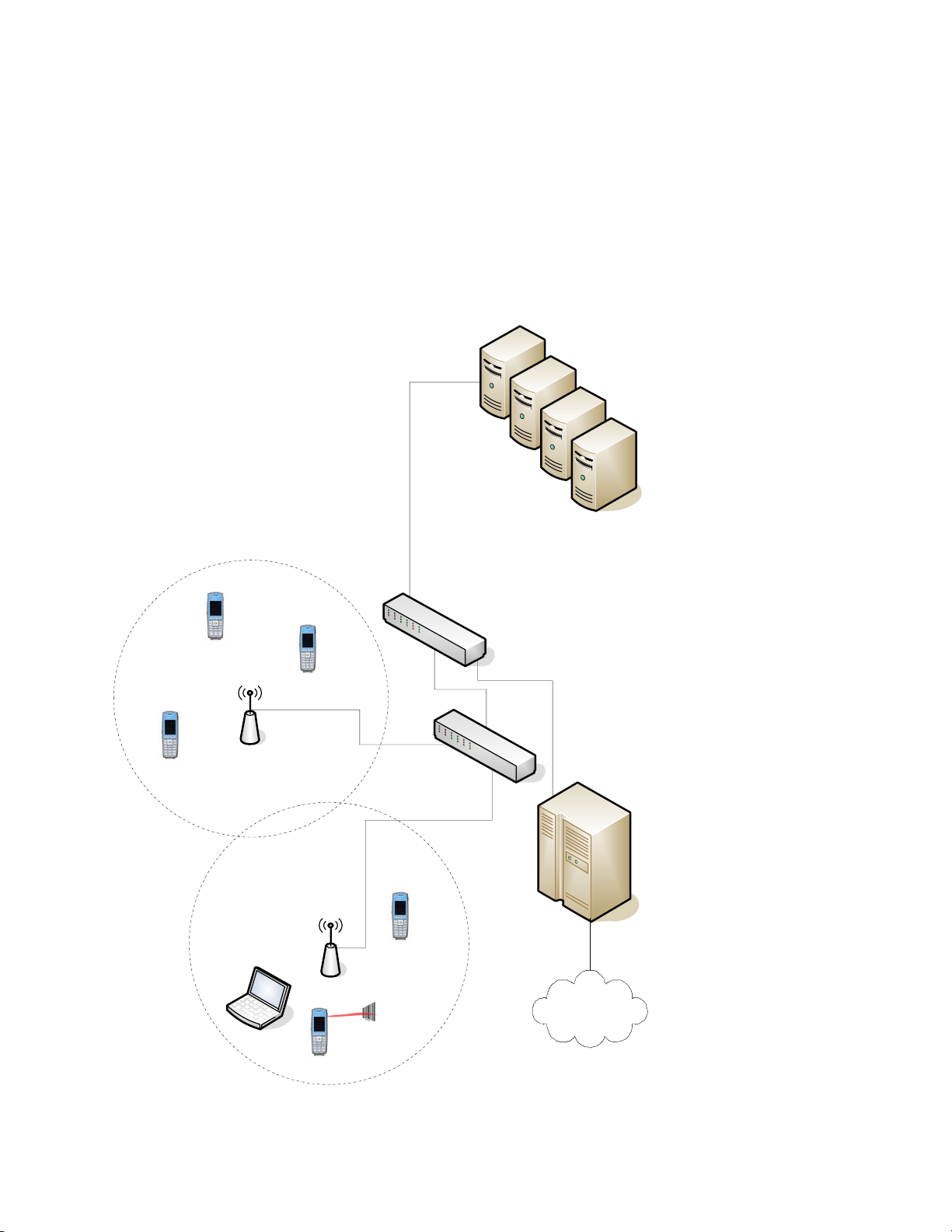
Network Configuration
Many desktop phones connect physically through a Category 5 (Cat-5) cable to a standard
office twisted-pair (IEEE 802.3) 10/100/1000 megabits per second Ethernet LAN. Spectralink
wireless handsets, however, connect to a WLAN to send and receive all data using
802.11a/b/g/n technology to access telephony resources on the wired LAN.
There are many ways to set up a phone network using Spectralink wireless handsets and the
diagram shown next is just one example of a network setup.
SIP Call Server
Ethernet switch
Wi-Fi AP
WLAN Controller
Wi-Fi AP
PSTN
Access point
area
Servers:
Time Server
LDAP Server
Radius Server
DHCP Server
Exchange Server
Application Server
OCS or Lync Server
Provisioning Server
8450/8452
QBC-enabled
computer
Page 23

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 23
Understanding Spectralink Phone Software Architecture
The Spectralink handset software is made of four basic components:
Updater The software that loads & runs first when the handset is powered on
Spectralink Software The software that implements the handset functions and
features
Configuration files The files that contain the handset’s parameter settings
Resource files Optional files that contain settings for advanced features
Figure 2-2: Spectralink phone software
What is the Updater?
The Updater is a small application that resides in the flash memory on the handset. The Updater
is installed at the factory and is already installed on your new Spectralink handsets.
When you start/boot/reboot the handset, the Updater performs the following tasks:
1 Enables you to open the setup menu so you can set various network and provisioning
options.
The Updater requests IP settings and accesses the provisioning server (also called the
boot server) to look for any changes to the Updater software.
If updates are found, they are downloaded and saved to flash memory, which overwrites
itself after verifying the integrity of the download.
2 If new updates are downloaded, the Updater formats the file system, removes any
application software and configuration files that were present.
3 Downloads the master configuration file.
The Updater and the application use this file to acquire a list of other files that the
handset needs.
Page 24

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 24
4 Examines the master configuration file for the name of the application file, and then
looks for this file on the provisioning server.
If the copy on the provisioning server is different than the one stored in device settings,
or there is no file stored in flash memory, the application file is downloaded.
5 Extracts the Spectralink Software from flash memory.
6 Installs the application into RAM, then uploads an event log file from the boot cycle.
The Updater will then terminate, and the Spectralink Software will take over.
What is the Spectralink Software?
The Spectralink Software manages the protocol stack, the digital signal processor (DSP), the
user interface, and the network interaction. The Spectralink Software implements the following
functions and features on the handsets:
VoIP signaling for a wide range of voice telephony functions using SIP signaling for call
setup and control
Industry standard security techniques for ensuring that all provisioning, signaling, and
media transactions are robustly authenticated and encrypted across the WLAN
Advanced audio signal processing for handset, headset, and speakerphone
communications using a wide range of audio codecs
Flexible provisioning methods to support single handset, small business, and large multi-
site enterprise deployments
The software is a binary file image and contains a digital signature that prevents tampering or
the loading of rogue software images.
Each release of software includes a new image file.
Both the Updater and Spectralink Software run on all 84-Series handset models that Spectralink
currently supports.
What are the configuration files?
The Spectralink Software that you download contains configuration file templates, valid XML
files that you can edit using an XML editor. These files contain all the parameters explained in
this document that provision the handsets with features and settings. The configuration files are
very flexible: you can rearrange the parameters within the file, move parameters to new files, or
create your own configuration files with only those parameters you want. This flexibility is useful
when you want to apply the same features and settings to a large number of handsets. Use of
the configuration files to provision the handsets with features and settings is called the
centralized provision method – the configuration files enable you to store a single set of
configuration files on a central provisioning server and configure all of your handsets to read the
same set of files. You can also configure a subset of handsets to use only specific files, thereby
deploying different handsets with different sets of features.
Page 25

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 25
Spectralink recommends that you configure handsets using the centralized provisioning method.
However, you can also configure individual handsets using the handset’s menu system,
accessible through the local user keypad interface, or you can configure select parameters by
using the Web Configuration Utility.
You will need to keep in mind that there is a hierarchy among the configuration methods and
settings. Using a higher-priority method will override settings you make using a lower-priority
method. The following lists all of the available ways to set features and settings for the
handsets. Spectralink strongly recommends becoming familiar with each of the configuration
methods.
Override files are maintained on the central provisioning server. See Understanding the Files
Written by the Handsets for additional information on how precedence is used by the handsets.
Configuration Methods
You can make changes to the handset’s configuration using any of the following configuration methods. Take note
that there is a precedence order among the configuration methods: changes made to settings using a higherpriority method override settings made using a lower-priority method. Configuration changes are uploaded to the
handset as override files that remain active until you remove them or reset to default.
The precedence order for configuration parameter changes is as follows (highest to lowest priority):
Local handset user interface
Web Configuration Utility
Central Provisioning Server
Default values (if Null then the value will be obtained from a higher priority method.)
Each of these configuration methods is detailed in Part III: Configuring Features.
What are the resource files?
In addition to the software and configuration files, the handsets may require resource files in
order to use some of the advanced features.
Examples of resource files include:
Language dictionaries
Ringtones
Contact directories
Custom backgrounds
If you need to remove resource files from a handset at a later date - for example, if you are
giving the handset to a new user - you will have to apply factory default settings to that handset.
For instructions on how to reset your handset to factory default settings, see the Spectralink
84-Series Deployment Guide.
Page 26

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 26
Part II: Setting Up Your Environment
Part II provides you with essential information on how to set up your handset network and
provisioning server, and on the configuration methods you can use to set up handset features.
You will find basic and advanced instructions on how to set up a provisioning server, how to
deploy the Spectralink handsets from the provisioning server, and how to upgrade the software.
Part II consists of the following chapters:
Chapter 3: Setting Up Your Device Network
Chapter 4: Setting Up the Provisioning Server
Chapter 5: Understanding the Files Written by the Handsets
Page 27
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 27
Chapter 3: Setting Up Your Device
Network
The Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Handsets operate on a Wi-Fi LAN (WLAN). Local area
network design varies by organization and Spectralink handsets can be configured to
accommodate a number of network designs. This chapter shows you several automated and
manual ways to configure Spectralink handsets to operate in a LAN.
See the Spectralink 84-Series Deployment Guide for detailed information about how the
handset authenticates and associates with the WLAN.
Once the provisioning server discovery is complete the handset will initiate the provisioning
process described in Chapter 4: Setting Up the Provisioning Server.
Wireless Device Settings
You must configure wireless devices before they can establish a connection to a wireless
network. You can configure wireless devices manually, but it is more common to configure them
prior to deployment using the USB interface (USBNet) to the device (and the device.set
parameters in the configuration file). See the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone
Deployment Guide for full information about using the USB interface and basic wireless settings.
More advanced wireless settings that may need to be set up to connect your device to the
Wireless LAN (WLAN) are located in the Wi-Fi Menu section.
IP Communication Settings
When the handset has established network connectivity it needs to acquire several IP network
settings to proceed with provisioning. These settings are typically obtained automatically from a
DHCP server.
Tip: Novice administrator?
Read this section if you are new to this process or have never set up a provisioning
server before.
You have the option to set the IP communication settings manually from the handset UI, or to
pre-provision using a device.set capability.
When making the DHCP request the handset will include information in Option 60 that can
assist the DHCP server in delivering the appropriate settings to the device.
Page 28
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 28
Timesaver: Reducing repetitive data entry
Spectralink recommends using DHCP where possible to eliminate repetitive
manual data entry.
The following table details the settings that are supported through the DHCP menu:
Option
SIP Parameter
Meaning
1
NA
Subnet mask
3
NA
Default gateway
6
DNSSRVR
DNS server
7
LOGSRVR
Syslog server logging
15
DOMAIN
Domain name
42
SNTPSRVR
NTP Server
43
sec.TLS.customCaCert.x
Auto discovery of the root CA certificate. If this setting is unavailable,
set the parameter per this guide.
66
TFTPSRVR
TFTP server
Web Info: RFC information on DHCP options
For more information on DHCP options, see RFC 2131 and RFC 2132.
Settings: Overriding the SNTP values set by DHCP
The configuration file value for SNTP server address and SNTP GMT offset can
be configured to override the DHCP value. See
tcpIpApp.sntp.address.overrideDHCP.
If you do not have control of your DHCP server or do not have the ability to set the DHCP
options, you will need to enable the handset to automatically discover the provisioning server
address. One way is to connect to a secondary DHCP server that responds to DHCP INFORM
queries with a requested provisioning server value. For more information, see RFC 3361 and
RFC 3925.
Provisioning Server Discovery
After the handset has established network connectivity it proceeds to the Configuration stage. In
this stage the following steps are carried out:
Software Update
Application of configuration settings relevant to a customer network
Page 29
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 29
Tip: Novice Administrator?
Read this section if you are new to this process or have never set up a provisioning
server before.
In many deployments a centralized provisioning server is used for the software update and
configuration functions. The handset supports several methods to ‘discover’ this provisioning
server:
Static You can manually configure the server address from the handset's user
interface or the Web Configuration Utility, or you can pre-provision the handset with an
initial provisioning server. The parameters are:
device.prov.serverName.set="1" and device.prov.serverName="" in a
configuration file.
DHCP DHCP option 66 is used to provide the address or URL of the provisioning
server.
DHCP INFORM The handset makes an explicit request for a DHCP option (which can
be answered by a server that is not the primary DHCP server). For more information,
see RFC 3361 and RFC 3925.
To change these parameters, go to Provisioning Server Menu.
Supported provisioning protocols
The Updater performs the provisioning functions of uploading log files, master configuration
files, software updates, and device setting menu changes.
By default, handsets are shipped with FTP enabled as the provisioning protocol. You can
change the provisioning protocol by updating the Server Type option. Or, you can specify a
transfer protocol in the Server Address, for example, http://usr:pwd@server (see Provisioning
Server Menu). The Server Address can be an IP address, domain string name, or URL. It can
be obtained through DHCP.
Supported protocols include: ftp, ftps, tftp, http and https.
In some cases a config file might need to be secured. You can use unique credentials to
connect to a server and include the transfer protocol in the configuration file name. For example,
https://usr:pwd@server/dir/file.cfg.
If a user name and password are specified as part of the server address or file name, they will
be used only if the server supports them. If a user name and password are required but not
specified, the device settings are sent to the server.
Settings: Choosing a valid URL
A URL should contain forward slashes (not back slashes) and should not contain
spaces. Escape characters are not supported. If a user name and password are
Page 30
Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 30
not specified, the Server User and Server Password from device settings will be
used (see Provisioning Server Menu).
Note: Active and passive FTP methods
There are two types of FTP methods - active and passive. Spectralink Software is
not compatible with active FTP.
To guarantee software integrity, the Updater will download only cryptographically signed
Updater or Spectralink Software images. For HTTPS, widely recognized certificate authorities
are trusted by the handset and custom certificates can be added to the handset.
Web Info: Viewing trusted certificate authorities
For more information, see Appendix E: Trusted Certificate Authority List and
Technical Bulletin CS-13-06: Using custom certificates with Spectralink 8400
handsets.
Digest Authentication for Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS)
If you want to use digest authentication against the Microsoft Internet Information Services server:
Use Microsoft Internet Information Server 6.0 or later.
Digest authentication needs the user name and password to be saved in reversible encryption.
The user account on the server must have administrative privileges.
The wildcard must be set as MIME type; otherwise, the handset will not download *.cfg, *.ld and other
required files. This is because the Microsoft Internet Information Server cannot recognize these extensions
and will return a “File not found” error. To configure wildcard for MIME type, see
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/326965.
For more information, see
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/WindowsServer2003/Library/IIS/809552a3-3473-48a79683-c6df0cdfda21.mspx?mfr=true.
Network Configuration Menus
You can update the network configuration parameters in two ways:
During the Updater Phase. The setup menu is accessible during the auto-boot
countdown of the Updater phase of operation. While your handset boots up, press the
Cancel softkey, and press the Setup softkey to launch the setup menu. To access the
setup menu, you will have to enter the administrator’s password.
After your handset starts and is running Spectralink Software. The network
configuration menu is accessible from the handset’s main menu. Select Settings>
Advanced Settings> [enter password]> Administration Settings> Network
Configuration. To access the Advanced Settings menu, you will have to enter the
administrator’s password which is 456 by default.
Page 31

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 31
Admin: Changing the default administrator password
Spectralink recommends that you change the default administrative password. See
Passwords – User and Administrator.
You have the option of modifying the handset network configuration parameters in the following
menus and sub-menus:
Main Menu
Provisioning Server Menu
Network Interfaces Menu (Ethernet Menu)
TLS Menu
Syslog Menu
Use the softkeys, the arrow keys, and the Select and Delete keys to make changes.
Certain parameters are read-only due to the value of other parameters. For example, if the
DHCP client parameter is enabled, the Phone IP Address and Subnet Mask parameters are
grayed out or not visible since the DHCP server automatically supplies these parameters and
the statically assigned IP address and subnet mask will never be used in this configuration.
Settings: Resetting network configurations
The basic network configuration referred to in the subsequent sections can be reset
to factory default settings using the handset’s main menu: Select Settings>
Advanced Settings> [enter password]> Administration Settings> Reset to
Defaults> Reset Device Settings. Or use a multiple key combination, as
described in Multiple Key Combinations.
Network configuration menu
You can modify the following configuration parameters from the setup menu while the handset
boots, or from the Administrative Settings menu from a handset running Spectralink Software:
Name
Possible Values
Provisioning server menu
See Provisioning Server Menu.
Network interfaces menu or Ethernet menu
See Network Interfaces Menu (Ethernet Menu).
SNTP address
Dotted-decimal IP address OR Domain name string
The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server the handset obtains the current time from.
GMT offset
-13 through +12
The offset of the local time zone from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) in half hour increments.
Page 32

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 32
Name
Possible Values
DNS server
Dotted-decimal IP address
The primary server the handset directs Domain Name System (DNS) queries to.
DNS INFORM server
Dotted-decimal IP address
The secondary server to which the handset directs DNS queries.
DNS domain
Domain name string
The handset’s DNS domain.
Hostname
hostname
The DHCP client hostname.
Syslog menu
See Syslog Menu.
Base profile
Generic, Lync*
* Select Lync if using Microsoft Server 2010 or 2013 or Skype for Business.
Provisioning server menu
The following configuration parameters can be modified on the Provisioning Server Menu.
Settings> Advanced Settings> [enter password]> Administration Settings> Network
Configuration> Provisioning Server:
Name
Possible Values
DHCP menu
See DHCP Menu. Note: This menu is disabled when the DHCP client is disabled.
Server type
0=FTP, 1=TFTP, 2=HTTP, 3=HTTPS, 4=FTPS
The protocol that the handset will use to obtain configuration and handset application files from the provisioning
server. See Supported Provisioning Protocols.
Note: Active FTP is not supported for BootROM version 3.0 or later. Passive FTP is supported. Only implicit FTPS
is supported.
Server address
Dotted-decimal IP address OR URL
Domain name string or a URL. All addresses can be followed by an optional directory. The address can also be
followed by the file name of a .cfg master configuration file, which the handset will use instead of the default
<MACaddress>.cfg file.
The provisioning server to use if the DHCP client is disabled, if the DHCP server does not send a boot server
option, or if the Boot Server parameter is set to Static.
The handset can contact multiple IP addresses per DNS name. These redundant provisioning servers must all use
the same protocol.
If a URL is used, it can include a user name and password. See Supported Provisioning Protocols. For information
on how to specify a directory and use the master configuration file, see Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone
Deployment Guide.
Note: ":", "@", or "/" can be used in the user name or password if they are correctly escaped using the method
specified in RFC 1738.
Server user
String
The user name requested when the handset logs into the server (if required) for the selected Server type.
Note: If the Server address is a URL with a user name, this will be ignored.
Page 33

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 33
Name
Possible Values
Server password
String
The default password is 456.
File Transmit Tries
1 to 10 Default 3
The maximum number of attempts to transfer a file. (An attempt is defined as trying to download the file from all IP
addresses that map to a particular domain name.)
Retry Wait
0 to 300 seconds Default 1
The minimum amount of time that must elapse before retrying a file transfer. The time is measured from the start
of a transfer attempt, which is defined as the set of upload/download transactions made with the IP addresses that
map to a given provisioning server’s DNS. If the set of transactions in an attempt is equal to or greater than the
Retry Wait value, then there will be no further delay before the next attempt is started.
Tag SN to UA
Disabled, Enabled
If enabled, the handset’s serial number (MAC address) is included in the User-Agent header of HTTP/HTTPS
transfers and communications to the browser.
The default value is Disabled.
Upgrade Server
Non-editable string (auto-populated by the Web
Configuration Utility)
The Upgrade server is an alternate way of getting software updates into the handset through the Web
Configuration Utility. It is a completely different process than using a provisioning server method.
When a value is displayed in this field, it is the address/URL that has been accessed for software updates through
the Web Configuration Utility. This value is also stored in the handset’s override file on the provisioning server.
If this field in the handset menu is populated then you cannot get code onto the phone from any other method than
using the WebUI upgrade method because handset settings have highest precedence and this setting is basically
a mirror of the override file. If you want to download code into a particular handset using a provisioning server,
clear the value set by the WebUI, or edit the override file parameter to “” which will also delete the setting in the
handset.
Changing the Default Passwords
The Server User and Server Password parameters should be changed from the
default values.
DHCP Menu
The DHCP menu is accessible only when the DHCP client is enabled. You can update the
following DHCP configuration parameters from the DHCP menu:
Name
Possible Values
Boot Server
0=Option 66, 1=Custom, 2=Static, 3=Custom+Option 66
Option 66: The handset will look for option number 66 (string type) in the response received from the DHCP
server. The DHCP server should send address information in option 66 that matches one of the formats described
for Server Address in Provisioning Server Menu.
Custom: The handset will look for the option number specified by the Boot Server Option parameter (below), and
the type specified by the Boot Server Option Type parameter (below) in the response received from the DHCP
server.
Static: The handset will use the boot server configured through the Server Menu. For more information, see
Provisioning Server Menu.
Custom + Option 66: The handset will use the custom option first or use Option 66 if the custom option is not
present.
Note: If the DHCP server sends nothing, the following scenarios are possible:
Page 34

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 34
Name
Possible Values
If a boot server value is stored in flash memory and the value is not 0.0.0.0, then the value stored in
flash is used.
Otherwise the handset sends out a DHCP INFORM query.
○ If a single DHCP INFORM server responds, this is functionally equivalent to the scenario where the
primary DHCP server responds with a valid boot server value.
○ If no DHCP INFORM server responds, the INFORM query process will retry and eventually time out.
Boot Server Option
128 through 254 (Cannot be the same as VLAN ID Option)
When the Boot Server parameter is set to Custom, this parameter specifies the DHCP option number in which the
handset will look for its boot server.
Boot Server Option Type
0=IP Address, 1=String
When the Boot Server parameter is set to Custom, this parameter specifies the type of DHCP option in which the
handset will look for its provisioning server. The IP Address provided must specify the format of the provisioning
server. The String provided must match one of the formats described for Server Address in Provisioning Server
Menu.
Option 60 Format
0=RFC 3925 Binary, 1=ASCII String
RFC 3925 Binary: Vendor-identifying information in the format defined in RFC 3925.
ASCII String: Vendor-identifying information in ASCII.
For more information, see Technical Bulletin Using DHCP Vendor Identifying Options with Spectralink Handsets.
Note: DHCP option 125 containing the RFC 3295 formatted data will be sent whenever option 60 is sent. DHCP
option 43 data is ignored.
Multiple DHCP INFORM Servers
If multiple DHCP INFORM servers respond, the handset should gather the
responses from these DHCP INFORM servers. If configured for Custom+Option66,
the handset will select the first response that contains a valid custom option value.
If none of the responses contain a custom option value, the handset will select the
first response that contains a valid option66 value.
Network Interfaces Menu
You can select the following items in the Network Interfaces menu:
Wi-Fi Menu
USBNet Menu
Wi-Fi Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the Wi-Fi menu:
Table 3-10: Wi-Fi Menu
Name
Possible Values
Enabled
Yes, No
A flag to determine if the wireless interface is enabled or not.
Page 35

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 35
Name
Possible Values
DHCP
Enabled, Disabled
If enabled, DHCP will be used to obtain the parameters discussed in DHCP or Manual TCP/IP Setup.
DHCP Boot Server
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine if the DHCP server is accessible.
IP Address
Dotted-decimal IP address
The handset’s IP address.
Note: This option is not available when the DHCP parameter is Enabled.
Subnet Mask
Dotted-decimal subnet mask
The handset’s subnet mask.
Note: This option is not available when the DHCP parameter is Enabled.
IP Gateway
Dotted-decimal IP address
The handset’s default router.
AC Required
Yes, No
A flag to determine if handsets will connect only to APs (access points) that enforce access control (Wi-Fi
Multimedia Admission Control [WMM-AC]). (See Caution note below.)
SSID
string
The Service Set Identifier (SSID) of the wireless network.
Security
0=No security, 1=WEP, 2=WPA-PSK, 3=WPA2-PSK, 4=WPA2Enterprise
The wireless security mode.
WEP
See WEP Menu.
WPA(2)-PSK
See WPA (2) PSK Menu.
WPA2-Enterprise
See WPA2-Enterprise Menu.
Radio
See Radio Menu.
Caution: WMM-AC not supported by 87-Series handsets
When deploying both 84-Series and 87-Series handsets in the same facility using
the same Wireless LAN, Wi-Fi Multimedia Admission Control (aka access control,
AC or WMM-AC) must be disabled in any handset parameters and APs as it is not
supported by 87-Series handsets. Any parameter that requires or enforces AC
must be disabled.
Page 36

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 36
WEP Menu
You can modify the following Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) configuration parameters on the
WEP menu:
Table 3-11: WEP Menu
Name
Possible Values
Authentication
0=Open System (default), 1=Shared Key
The WEP authentication method.
Key Length
0=40 bits (default), 1=104 bits
The authentication key length.
Default Key
1 to 4
The default key. The default key is 1.
Encryption
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine if wireless data is encrypted.
Key1, Key2, Key3, Key4
Hexadecimal value
The authentication keys. There are four possible keys. The key length is determined by the Key Length
parameter.
WPA (2) PSK Menu
You can modify the following Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)/WPA2 Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
configuration parameters on the WPA(2)-PSK menu:
Table 3-22: WPA (2) PSK Menu
Name
Possible Values
PSK Type
0=Passphrase (default), 1=Hexadecimal key
The pre-shared key type.
Passphrase
8 to 63 character ASCII string
The authentication passphrase.
Note: This parameter is unavailable when PSK Type is 1.
Key
256 bit hexadecimal string
The authentication key.
Note: This parameter is unavailable when PSK Type is 0.
WPA2-Enterprise Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the WPA2-Enterprise menu:
Page 37

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 37
Table 3-3: WPA2-Enterprise Menu
Name
Possible Values
Fast Roaming Method
0=Opportunistic Key Caching (OKC) , 1= Cisco
Centralized Key Management (CCKM)
The fast roaming method. These fast roaming methods allow for the part of the key derived from the server to be
cached in the wireless network, thereby, shortening the time to renegotiate a secure handoff.
EAP Method
1=EAP-TLS, 2=EAP-PEAPv0/MSCHAPv2 (default),
6=EAP-FAST
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
User ID
String
The authentication user name.
Password
String
The authentication password.
PAC File Info
See PAC File Information.
EAP-FAST Inband Provisioning
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine whether or not EAP-FAST Inband Provisioning is enabled. Note: This parameter is unavailable
when EAP Method is 2.
Table 3-8: 802.1X Menu
Name
Possible Values
EAP Method
0 = None, 1=EAP-TLS, 2=EAP-PEAPv0/MSCHAPv2, 3=EAP-PEAPv0/GTC, 4=EAPTTLS/EAP-MSCHAPv2, 5=EAP-TTLS/EAP-GTC, 6=EAP-FAST, 7=EAP-MD5
The selected EAP type to be used for authentication. For more information, see Supporting 802.1X Authentication.
User ID
UTF-8 encoded string
The identity (or user name) required for 802.1X authentication.
Password
UTF-8 encoded string
The password required for 802.1X authentication. The minimum length is 6 characters.
PAC File Info
See PAC File Information.
EAP-FAST Inband
Provisioning
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine whether EAP-FAST Inband Provisioning is enabled. This parameter is used only if EAP
Method is EAP-FAST.
PAC File Information
You can modify Protected Access Credential (PAC) File Information from the PAC File
Information menu:
Page 38

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 38
Table 3-9: PAC File Information Menu
Name
Possible Values
Description
PAC File Password
UTF-8 encoded string
The password required to decrypt the PAC file.
PAC File Name
UTF-8 encoded string
The path or URL of the PAC file for download.
Remove PAC File
UTF-8 encoded string
A flag to determine whether or not to delete the PAC file from
the handset.
Radio Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the Radio menu:
Table 3-44: Radio Menu
Name
Possible Values
Regulatory Domain
0, 1, 2 or 10
Available values specify the regulatory domain. The supported values are 1 (North America), 2 (Europe) and 10
(Australia). If 0, no regulatory domain is selected. You must set the regulatory domain before the handsets can be
used. There is no default setting for this option and the handsets will not associate with an access point (AP) until
you specify a value.
5 GHz
See 5 GHz Menu.
2.4 GHz
See 2.4 GHz Menu.
5 GHz Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the 5 GHz menu:
Table 3-55: 5 GHz Menu
Name
Possible Values
5 GHz Enable
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine if the 5 GHz band is enabled.
Sub-bandx Enable
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine if the 5 GHz sub-band is enabled. There are four sub-bands (x=1 to 4).
Sub-bandx Transmit Power
1 to 7
The maximum power that the handset uses to transmit in the 5 GHz sub-band. The “7” setting is also called Auto
in some menus and is the maximum allowable power for that channel and data rate. If no maximum is set, the
handset uses the P5 settings for each channel activated. For more information, see the
device.wifi.radio.band5GHz.subBandx.txPower set of parameters in Appendix D.
Page 39

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 39
2.4 GHz Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the 2.4 GHz menu:
Table 3-6: 2.4 GHz Menu
Name
Possible Values
2.4 GHz Enable
Enabled, Disabled
A flag to determine if the 2.4 GHz band is enabled.
2.4 GHz Transmit Power
1 to 7
The maximum power that the handset uses to transmit in the 2.4 GHz sub-band. The “7” setting is also called Auto
in some menus. If no maximum is set, the handset uses the P5 settings for each channel activated. Note that ESTI
regulations limit the maximum setting in Europe. If P4 or above is selected for domain 2, the handset will
broadcast at the maximum allowable power which is 12 mW.. For more information, see the
device.wifi.radio.band2.4GHz.subBandx.txPower set of parameters in Appendix D.
USBNet Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the USBNet menu:
Table 3-77: USBNet Menu
Name
Possible Values
Enabled
1=Yes, 2=No
A flag to determine if USB networking is supported. USBnet is used by SLIC and USB Setup for initial provisioning.
SLIC disables it when the files are produced. Parameter: device.usbnet.enabled
IP Address
Dotted-decimal IP address
The handset’s dotted-decimal IP address on the USBNet interface. For Spectralink handsets, the default value is
169.254.1.2 .
Subnet Mask
Dotted-decimal subnet mask
The handset’s subnet mask. For Spectralink handsets, the default value is 255.255.0.0 .
IP Gateway
Dotted-decimal IP address
The handset’s default router. For Spectralink handsets, the default value is 169.254.1.1 .
DHCP
Enabled, Disabled
If enabled, DHCP will be used to obtain the parameters discussed in DHCP or Manual TCP/IP Setup.
Syslog Menu
Syslog is a standard for forwarding log messages in an IP network. The term ‘syslog’ is often
used for both the actual syslog protocol, as well as the application or library sending syslog
messages.
The syslog protocol is a simple protocol: the syslog sender sends a small textual message (less
than 1024 bytes) to the syslog receiver. The receiver is commonly called ‘syslogd’, ‘syslog
daemon’ or ‘syslog server’. Syslog messages can be sent through UDP, TCP, or TLS. The data
is sent in cleartext.
Page 40

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 40
Because syslog is supported by a wide variety of devices and receivers, syslog can be used to
integrate log data from many different types of systems into a central repository.
Web Info: Information on Syslog
For more information on the syslog protocol, see RFC 3164.
You can modify the following parameters from the Syslog Menu:
Table 3-83: Syslog Menu
Name
Possible Values
Server Address
Dotted-decimal IP address OR Domain name string
The syslog server IP address. The default value is Null.
Server Type
None=0, UDP=1, TCP=2, TLS=3
The protocol that the handset will use to write to the syslog server. If set to None (or 0), transmission is turned off,
but the server address is preserved.
Facility
0 to 23
A description of what generated the log message. For more information, see section 4.1.1 of RFC 3164.
The default value is 16, which maps to ‘local 0’.
Render Level
0 to 6
Specifies the lowest class of event that will be rendered to syslog. It is based on device.syslog.renderLevel
and can be a lower value. See Appendix D for device parameters.
Note: Use left and right arrow keys to change values when using the Admin menu on the handset.
Prepend MAC Address
Enabled, Disabled
If enabled, the handset’s MAC address is prepended to the log message sent to the syslog server. Spectralink
recommends enabling this parameter.
Login Credentials Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the Login Credentials menu:
Table 3-9: Login Credentials Menu
Name
Possible Values
Domain
UTF-8 encoded string
The domain name used by a server.
User
UTF-8 encoded string
The user name used to authenticate to a server.
Password
UTF-8 encoded string
The password used to authenticate to a server.
Page 41

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 41
TLS Security Menu
This section refers to the TLS Menu available in the Updater, not Spectralink Software. There is
another menu, called TLS Security, available in the Admin menu. Navigate to Advanced
Settings> [password] Administration Settings> TLS Security. You can modify the following
parameters from the TLS Menu:
Table 3-10: TLS Menu
Name
Possible Values
View or install a custom CA cert
URL
A CA certificate that is installed on the handset to be used for TLS authentication.
View or clear a custom device credentials
Yes, No
A flag to determine whether or not the device certificate can be removed from the handset.
Configure TLS Profiles
There are two TLS Platform Profiles and six TLS Application Profiles. See TLS Profile Menu.
Configure TLS Applications
See Applications Menu.
TLS Profile Menu
You can modify the following parameters from the TLS Profile Menu:
Table 3-11: TLS Profile
Name
Possible Values
SSL Cipher Suite
String
The global cipher suite.
Custom SSL Cipher Suite
String
A custom cipher suite.
CA Cert List
String
The CA certificate sources that are valid for this profile.
Device Cert List
String
The device certificate sources that are valid for this profile.
TLS Applications Menu
You can modify which platform profile is used for applications from the Applications Menu.
Although not listed here, SIP, browser and LDAP are similarly available:
Page 42

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 42
Table 3-12: Applications Menu
Name
Possible Values
802.1X
1 or 2
The TLS Profile to use for 802.1X authentication.
Provisioning
1 or 2
The TLS Profile to use for provisioning authentication.
Syslog
1 or 2
The TLS Profile to use for syslog authentication.
Page 43

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 43
Chapter 4: Setting Up the Provisioning
Server
This chapter provides instructions for setting up your Spectralink handsets with a central
provisioning server. If you are new to this process, it is important to read every section in this
chapter. Please also refer to the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide
for basic information.
Because of the large number of optional installations and configurations that are available, this
chapter focuses on one particular way that the Spectralink Software and the required external
systems might initially be installed and configured in your network.
If you want to begin setting up handset features, go to Part III: Configuring Features.
Why Use a Provisioning Server?
Spectralink strongly recommends that you use a central provisioning server to install and
maintain your Spectralink handsets. You can set up a provisioning server on the local LAN or
anywhere on the Internet. A provisioning server maximizes the flexibility you have when
installing, configuring, upgrading, and maintaining the handsets, and enables you to store
configuration, log, directory, and override files on the server. If you allow the handset write
access to your provisioning server, the handset can use the server to upload all of the file types
and store administrator and user settings. The handset is designed such that if it cannot locate a
provisioning server when it boots up, it will operate with internally saved parameters. This is
useful when the provisioning server is not available.
The default number of provisioning servers is one and the maximum number is eight. For more
information on the protocol used, see Supported Provisioning Protocols.
Provisioning Server Redundancy
You can configure multiple (redundant) provisioning servers—one logical server with multiple
addresses—by mapping the provisioning server DNS name to multiple IP addresses. See
Server Redundancy for more information.
If you set up multiple provisioning servers, you must be able to reach all of the provisioning
servers with the same protocol and the contents on each provisioning server must be identical.
The parameters described in Provisioning Server Menu can be used to configure the number of
times each server will be tried for a file transfer and also how long to wait between each
attempt. You can configure the maximum number of servers to be tried. For more information,
contact your Certified Spectralink Reseller.
Page 44

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 44
Provisioning Server Security Notes
For organizational purposes, Spectralink recommends configuring a separate log file directory,
an override directory, and a contact directory. Each directory can have different access
permissions. Normally, LOG, CONTACTS, and OVERRIDES have full read and write access.
See Understanding the Files Written by the Handsets for complete information.
Ensure that the file permissions you create provide the minimum required access and that the
account has no other rights on the server.
Tip: Allowing File Uploads to Your Provisioning Server
Spectralink recommends that you allow file uploads to the provisioning server
where the security environment permits. File uploads allow event log files to be
uploaded to the provisioning server. File uploads provide backup copies (override
configuration files) of changes users make to the handset’s configuration settings
through the Web server and/or local user interface. These override and log files
help service providers and Spectralink provide customer support when diagnosing
issues that may occur with the handset operation.
The handset’s server account needs to be able to add files that it can write to in the log file
directory and the provisioning directory. It must also be able to access files in all directories
mentioned in the <MAC-address>.cfg file. All other files that the handset needs to read, such
as the application executable and the standard configuration files, should be made read-only
using file server file permissions.
Tip: Use RFC-Compliant Servers
Spectralink recommends that you use RFC-compliant servers.
Each handset may open multiple connections to the server.
The handset will attempt to upload log files, a configuration override file, and a directory file to
the server if changed. This requires that the handset’s account has delete, write, and read
permissions. The handset will still function without these permissions, but will not be able to
upload or save files.
If you know the handset is going to download a file from the server, you should mark the file as
read-only.
Setting up an FTP Server as Your Provisioning Server
A basic provisioning configuration uses File Transfer Protocol or FTP. FTP servers are free,
require installation, and use logins and passwords. A free and popular server, FileZilla Server, is
available for Windows. FileZilla Server (version 0.9.xx) has been tested with the Spectralink
Software.
Page 45

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 45
Tip: Choosing a Provisioning Protocol
By default, Spectralink sets FTP as the provisioning protocol on all Spectralink
handsets. This guide focuses on the FTP provisioning protocol. Other supported
protocols include FTPS, TFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS.
See the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide for a full
explanation of setting up FTP directories for both initial and central provisioning.
To set up an FTP server using FileZilla Server:
1 Download and install the latest version of FileZilla Server.
2 After installation, a Connect to Server pop-up displays on your computer. Select OK to
open the administrative user interface.
3 To configure a user, select Edit> Users in the status bar.
4 Select Add.
5 Enter the user name for the handset and select OK.
For example, bill123.
6 Select the Password checkbox and enter a password.
For example, 1234. The handset will use this password to log in.
Settings: FTP username and password
When you set up the initial provisioning server as an FTP server, use
administrator for the username and admin123 for the password. Ensure all
checkboxes are checked.
7 Select Page> Shared folders to specify the server-side directory where the provisioning
files will be located (and the log files uploaded).
8 Select Add and pick the directory.
9 To allow the handset to upload logs onto the provisioning server, select the Shared
Folders> Files> select Write and Delete checkboxes, and then select OK.
10 Determine the IP address of the FTP server by entering cmd in the Run dialog on your
Start menu, and ipconfig in the command prompt.
IP addresses of your network cards are displayed. One of them (if there are more than
one) will be your FTP server.
Page 46

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 46
Downloading Spectralink Software Files to the Provisioning Server
This section explains how to download the Spectralink Software to the provisioning server.
Admin Tip: Upgrading Software
If you need to upgrade software on your handsets, please see Appendix B in the
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide.
Microsoft® Skype for Business compatibility
Note: What is Skype for Business?
Microsoft has re-branded its software products formerly sold under the Lync name
to Skype for Business. In this document, when Skype for Business is referenced,
former Lync products are included.
Spectralink software is available in two variants – Skype for Business and non-Skype for
Business (or open SIP/Generic). Starting with Spectralink software 4.3/4.4, even numbered
releases support both Skype for Business and open SIP and odd numbered releases support
open SIP only. Release 4.7 and above differentiate Skype for Business and open SIP releases
by the build number. The last four digits of the build number denotes the build ID. For
Lync/Skype for Business releases the first digit is set to 1. For non-Lync/SIP/Generic releases,
the first digit is set to 2. For example:
Skype for Business – 5.0.0.1077
SIP/Generic – 5.0.0.2077
Handsets purchased without Skype for Business capability will not run Skype for Business
software releases, e.g. 5.0.0.1xxx. Handsets with Lync/Skype for Business compatibility will run
BOTH Skype for Business and SIP/Generic software releases.
All legacy phones manufactured prior to June 2013 support Skype for Business.
Manufacturing date
Support Skype for Business?
Prior to June 2013
Yes
June 2013 and later
Two handset variations:
1. Skype for Business-enabled: supports Skype for Business and SIP/Generic
2. SIP/Generic: does not support Skype for Business
All handsets have product ID’s that identify them as Skype for Business (WITH LYNC) or nonSkype for Business (WITHOUT LYNC) compatible.
Page 47

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 47
84-Series Product IDs with Microsoft Skype for Business Support Label example
Model
Skype for Business SKUs
8440:
2200-37149-001, 2200-37150-001
2200-37174-101, 2200-37175-101
8441:
2200-37290-001, 2200-37290-101
8452:
2200-37172-001, 2200-37173-001
2200-37198-101, 2200-37199-101
8453:
2200-37294-001, 2200-37294-101
84-Series Product IDs without Microsoft Skype for Business Support Label example
Model
Open SIP SKUs
8440:
2200-37147-001, 2200-37148-001
2200-37165-101, 2200-37164-101
8441:
2200-37288-001, 2200-37288-101
8450:
Legacy 8450 models support Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010
8452:
2200-37163-001, 2200-37162-001
2200-37161-101, 2200-37160-101
8453:
2200-37292-001, 2200-37292-101
Admin Tip
Handsets manufactured prior to June 2013 are not differentiated on the label as to
Lync or Lync. All handsets manufactured before June 2013 are Microsoft Lync
Server 2013/2010 compatible. Please consult the label date to determine Lync
compatibility.
To help understand if your 84-Series handset supports Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010, look at the manufacturing date on the label in the battery compartment.
ALL 84-Series handsets produced before June 2013 support Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or
2010. For handsets built during or after June 2013, check the label text. The product ID and the
“with Lync” or “without Lync” text on the label will confirm whether or not the handset is enabled
for Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or 2010.
Spectralink 84-Series Hardware IDs
Each Spectralink 84-Series model has a unique hardware ID. You can find this number printed
on the handset’s label inside the battery compartment. This number enables the handset model
to identify itself and provides flexibility to the administrator, permitting different models to load
Page 48

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 48
different code versions. See Product Model Number and Hardware ID Mapping for more
information about how hardware IDs are used.
Model Name
Hardware ID
SL8440
SL8450
SL8452
SL8441
SL8453
3111-36150-001
3111-36152-001
3111-36154-001
3111-67360-001
3111-67361-001
Go to the Spectralink Support Website to download current and past releases and access
supporting documentation.
Spectralink provides the Spectralink Software download in ZIP file format.
To download the Spectralink Software :
1 Access Spectralink Software from the Spectralink Support Website.
2 Acknowledge that you read the notices, accept the agreement, and choose Submit.
3 Save the Spectralink Software ZIP file download.
4 Extract (uncompress) the ZIP file.
Copy all files from the distribution ZIP file to working directory on the provisioning server,
maintaining the same folder hierarchy. To simplify provisioning, Spectralink
recommends, as a best practice, to start creating new configuration files from unedited
template files containing the default values. Rename the template file to your specific file
name as you configure and add specific parameter values for your site.
You will see one sip.ld file that includes all handset models. Accompanying folders
contain the configuration file templates and localization files.
See the Release Notes for a Description of all Parameters for a Spectralink
Software Release
For a description of each file in a Spectralink Software distribution, see the
Spectralink Software Release Notes for a particular Spectralink Software release
on the Spectralink Software Support Center.
Deploying and Updating Spectralink Handsets with a Provisioning Server
This section explains how to deploy and update Spectralink handsets from a provisioning
server. If you are provisioning the handsets using a provisioning server for the first time, follow
the provisioning process described in the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone
Deployment Guide.
Page 49

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 49
You can create as many configuration files as you want and your configuration files can contain
any combination of parameters you put in them. You can put all parameters into one file or, for
example, you can put SIP server parameters in one file and handset features parameters in
another file. Configuration file variances are explained in the Spectralink 84-Series Wireless
Telephone Deployment Guide.
For large-scale deployments, the centralized provisioning method using configuration files is
strongly recommended. For smaller scale deployments, the Web Configuration Utility or local
interface may be used, but administrators need to be aware that settings made using these
methods will override settings made using configuration files.
For instructions on how to encrypt your configuration files, see Encrypting Configuration Files.
Shortcut Method to Deploy Spectralink Handsets with a Provisioning Server
The following steps are a shortcut method for provisioning procedure. Please use the
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide for detailed instructions for each
of these steps.
To deploy handsets with a provisioning server using a shortcut method:
1 Obtain a list of MAC addresses for the handsets you want to deploy.
The MAC address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number on a label on the back of the
handset and on the outside of the shipping box. It is also available on the Status menu.
2 Create a per-handset <MACaddress>-ext.cfg file.
Do NOT use these names for a per-handset configuration file
Do NOT use the following file names as your per-handset file name:
<MACaddress>-phone.cfg,
<MACaddress>-Web.cfg,
<MACaddress>-app.log,
<MACaddress>-boot.log, or
<MACaddress>-license.cfg.
These file names are used by the handset itself to store user preferences
(overrides) and logging information.
Add handset registration parameters to the file, for example reg.1.address,
reg.1.label, and reg.1.type.
3 Create a per-site site<location>.cfg file.
For example, add the SIP server or feature parameters like
voIpProt.server.1.address and feature.corporateDirectory.enabled.
Settings: Configuring Your Phone for Local Conditions
Page 50

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 50
Some of the default settings are typically adequate; however, if SNTP settings are
not available through DHCP, you will need to edit the SNTP GMT offset, and
(possibly) the SNTP server address for the correct local conditions. Changing the
default daylight savings parameters will likely be necessary outside of North
America. Disable the local Web (HTTP) server or change its signaling port if the
local security policy dictates (see <httpd/>). Change the default location settings for
user interface language and time and date format (see Time and Date Display).
Modify any settings to match your WLAN and network as needed.
4 Create a master configuration file by performing the following steps:
a Enter the name of each per-handset and per-site configuration files created in steps
2 and 3 in the CONFIG_FILES attribute of the master configuration file
(000000000000.cfg).
b Optional) Edit the LOG_FILE_DIRECTORY attribute of master configuration file so
that it points to the log file directory.
c (Optional) Edit the CONTACT_DIRECTORY attribute of master configuration file so
that it points to the organization’s contact directory.
d (Optional) Edit the USER_PROFILES_DIRECTORY attribute of master configuration
file, if you intend to enable the User Login feature, so that it points to the directory
where user profile files are stored.
e (Optional) Edit the CALL_LISTS_DIRECTORY attribute of master configuration file
so that it points to the user call lists.
5 Perform the following steps to configure the handset to point to the IP address of the
provisioning server and set up the user:
6 On the handset’s Home screen or idle display, select Settings> Advanced Settings>
[enter password]> Administration Settings> Network Configuration> Provisioning
Server> DHCP Menu.
When prompted for the administrative password, enter 456.
a Open the DHCP Server menu by pressing the Select softkey. Set Boot Server to
Static and press to return to the Provisioning Server menu.
b Scroll down to Server Type and ensure that it is set to FTP.
c Scroll down to Server Address and enter the IP address of your provisioning server.
d Press the Edit softkey to edit the value and the OK softkey to save your changes.
e Scroll down to Server User and Server Password and enter the user name and
password of the profile you created on your provisioning server.
In Setting up an FTP Server as Your Provisioning Server the example user given
was bill1234 and the example password was 1234.
f Press the Back softkey twice.
Page 51

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 51
g Scroll down to Save & Reboot, and then press the Select softkey.
The handset reboots.
After this step, if the file does not exist, the Spectralink Software will try the
unmodified APPLICATION APP_FILE_PATH attribute (sip.ld).
For more information, see Parsing Vendor ID Information.
7 Ensure that the configuration process completed correctly.
On the handset, press the arrow key, and then select Settings> Status> Platform>
Application> Main> OK to see the Spectralink Software version and Settings> Status>
Platform> Configuration> OK to see the configuration files downloaded to the handset.
Monitor the provisioning server event log and the uploaded event log files (if permitted).
All configuration files used by the provisioning server are logged.
The handset will upload two logs files to the LOG_DIRECTORY directory:
<MACaddress>-app.log and <MACaddress>-boot.log.
You can now test your deployment by making calls and testing features.
Upgrading Spectralink Software
You can upgrade the software that is running on the Spectralink handsets in your organization.
The upgrade process varies with the version of Spectralink Software that is currently running on
your handsets and with the version that you want to upgrade to. The Updater, Spectralink
Software executable, and configuration files can all be updated using centralized provisioning.
Updating Spectralink Software on a Single Phone
Starting with Spectralink Software 4.3.x, you can use the Software Upgrade tool in
the Web Configuration Utility to update the Spectralink Software version running on
a single handset. Note that configuration changes made to individual handsets
using the Web Configuration Utility will override configuration settings made using
central provisioning. For instructions on how to update Spectralink Software, see
Technical Bulletin Using the Software Upgrade Tool in the Web Configuration
Utility.
To continue setting up a provisioning server, use the instructions in the Spectralink 84-Series
Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide.
Page 52

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 52
Chapter 5: Understanding the Files
Written by the Handsets
The Spectralink 84-Series handsets can write several types of information into directories set up
on the central provisioning server. These directories serve as repositories for the different types
of files written by the handsets and allow an administrator to easily find needed information. If
separate directories are not provisioned, and if the handset has write privileges, all files will be
written to the root directory.
The Spectralink 84-Series Deployment Guide explains how to set up directories on the central
provisioning server (or elsewhere) so that the files written by the handset can be sorted and
viewed efficiently. These directories must have full read and write access. The “Directory
element” in the table below is referring to the directories that are provisioned in the master
configuration file. The Directory names tell the handset where to write the files it produces. For
example:
Filenames for the files produced by the handset start with the MACaddress and use an
extension to signify the type of information in it. E.g. 00907a0cd989-phone.cfg is the filename of
an override file created when the user changed a parameter in the handset keypad menus.
If User Profiles are deployed, files start with the login name instead of the MACaddress. E.g.
lgates-phone.cfg.
Log files are written and stored as text files. All other files are written and stored as .xml files.
Type of file
Directory element
Contents
Extension
Log
LOG_FILE_DIRECTORY
This is the directory where the
handset will write its log files.
-boot.log
-app.log
Override
OVERRIDES_DIRECTORY
Parameters set in the .cfg files can
be overridden when changed in the
Web Configuration Utility or in the
handset menus using its keypad.
This directory stores these
overrides by MACaddress so that
they are available when the handset
restarts.
-phone.cfg
-web.cfg
Contacts
CONTACTS_DIRECTORY
Contacts are stored by
MACaddress in this directory as a
backup so that they can be
reloaded when the handset reboots.
-directory.xml
Calls
CALL_LISTS_DIRECTORY
Call lists are stored by handset or
by User Profile.
-calls.xml
Page 53

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 53
Log Files
Log files are discussed in detail in the Troubleshooting section.
Overrides
Certain configuration methods take precedence over other methods and produce override files
on the central provisioning server. The handset reads these files when it checks in with the
central provisioning server and uses the information stored in them for operational information
and parameter configuration.
The precedence order for configuration methods follows this sequence (highest to lowest
priority):
1 Local handset user interface
2 Web Configuration Utility
3 Central Provisioning Server
4 Default values
If you set a parameter in the central provisioning server and the user later changes it in the
handset menus, the setting made by the user will take precedence and override the setting in
the central provisioning server. This action updates an overrides file that is stored in the
Overrides directory, if specified.
Note that although certain parameters take precedence and overrule other parameters, this type
of behavior does NOT produce an override file. This behavior is fully explained in the given
parameter description. We use the term “overrule” to describe parameter precedence. We use
the term “override” to describe configuration method precedence.
Example:
Page 54

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 54
This example shows an overrides file for one handset that shows what the user has done to
change from the default or configured settings:
set the normal notification profile (np) to a silent ring, etc.
set the selected notification profile to silent,
has forwarded a call to extension 0567,
changed various PTT channel settings.
Deleting the override file
The administrator might want to delete all overrides. This can be done both remotely and if you
have access to the phone.
With phone access
1 Power off the phone.
2 Modify the override files to have empty <PHONE_CONFIG> tags. Open the override file
and remove all tags. The file should only have these active parameters:
<PHONE_CONFIG>
</PHONE_CONFIG>
3 Power the phone back on.
Remotely
The remote method could work in conjunction with a shift change where the likelihood of the
phones power cycling is high. It is also possible to automate this process with scripts.
1 Modify the override files to have empty <PHONE_CONFIG> tags. Open the override file
and remove all tags. The file should only have these active parameters:
<PHONE_CONFIG>
</PHONE_CONFIG>
2 Make the override file read-only. This can be done at the individual file level, or (if a
specific Override directory is specified in the configuration files) by making the entire
directory read-only.
3 Wait for the phone to power cycle at least once.
4 Allow the override file to be writable, if desired.
Contacts
Each handset can store up to 9999 contacts in its local Contact Directory. The Contact Directory
can be viewed on the handset by navigating to Home> Contacts / Call Lists> Contact
Directory. This contact list is also written to the central provisioning server and stored in a
Contacts Directory whenever any information is changed. Contact information is also stored
Page 55

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 55
locally in the handset so the file on the central provisioning server serves as a backup in case
the handset loses its memory.
Call List
The 84-Series handset records missed, received and placed calls in a call list that can be
viewed on the handset by navigating to Home> Contacts / Call Lists> Call Lists. Call history
is stored locally on the handset and will survive a restart or reboot unless the list has been
cleared. The user can use the call list to redial previous outgoing calls, return incoming calls,
and save contact information from call list entries to the contact directory.
Such calls are logged in the Call List directory that resides on the central provisioning server.
These call logs contain call information such as remote party identification, time and date of the
call, and call duration. All call logs are enabled by default but can be disabled by turning off the
unwanted parameter.
The Call List directory on the central provisioning server is a real-time file. When a new call is
made, the call is logged. When the lists are cleared on the handset, the calls in the cleared list
are also cleared out of the Call List directory on the central provisioning server.
Table 6-1: Configuring the Call Lists
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
feature.callList.enabled
All locally controlled call lists.
0 or 1
1
feature.callListMissed.enabled1
The missed calls list.
0 or 1
1
feature.callListPlaced.enabled1
The placed calls list.
0 or 1
1
feature.callListReceived.enabled1
The received calls list.
0 or 1
1
If 0, the call list is disabled. If 1, the call list is enabled. To enable the Missed, Placed, or Received call lists,
feature.callList.enabled must be enabled.
Call log example
A logged call from the call list looks like this:
Page 56

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 56
The next table describes each element and attribute that displays in the call log
Table 6-2: Call Log Elements and Attributes
Element
Permitted Values
direction
In, Out
Call direction with respect to the user.
disposition
Busy, Forwarded, Normal, Partial, Preempted,
Rejected, RemotelyHandled, Transferred
What happened to the call. When a call entry is first created, the disposition is set to Partial.
line
Positive integer
The line (or registration) index.
protocol
SIP
The line protocol.
startTime
String
The start time of the call. For example: 2010-01-05T12:38:05 in local time.
duration
String
The duration of the call, beginning when it is connected and ending when the call is terminated.
For example: PT1H10M59S.
count
Positive Integer
The number of consecutive missed and abandoned calls from a call destination.
destination
Address
The original destination of the call.
For outgoing calls, this parameter designates the outgoing call destination; the name is initially supplied by the
local handset (from the name field of a local contact entry) but may later be updated via call signaling. This field
should be used for basic redial scenarios.
For incoming calls, the called destination identifies the requested party, which may be different than any of the
parties that are eventually connected (the destination may indicate a SIP URI which is different from any SIP URI
assigned to any lines on the handset).
Page 57

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 57
Element
Permitted Values
source
Address
The source of the call (caller ID from the call recipient’s perspective).
Connection
Address
An array of connected parties in chronological order.
As a call progresses, the connected party at the far end may change, for example, if the far end transfers the call
to someone else. The connected element allows the progression of connected parties, when known, to be saved
for later use. All calls that contain a connected state must have at least one connection element created.
finalDestination
Address
The final connected party of a call that has been forwarded or transferred to a third party.
Page 58

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 58
Part III: Configuring Features
Part III provides you with an in-depth look at advanced features and parameters. The
Spectralink 84-Series Wireless Telephone Deployment Guide covers parameters that are used
by 80% of all installations. However, since requirements vary, Part III covers the entire range of
configurable parameters for every type of feature and functional requirement.
Part III is arranged by types of features and settings that you might need to deploy to further
customize your installation. This Part is divided into four Chapters that cover:
An explanation of inherent features that are not configurable,
User settings that can be set by the administrator but the user can freely alter through
the user menus. Some of these options can be locked or made unavailable by the
administrator.
Feature settings that are configured by the administrator. These settings are optional
and only available if configured by an administrator. In some cases once the feature is
configured, user menus contain options that the user can configure to customize the
feature for individual use and preferences.
System settings that the administrator configures to adjust the way the handset interacts
with the greater infrastructure.
Configuration parameters are named for the function they provide but frequently several types
of parameters must be configured to provision a feature or function. Therefore this section is
arranged by feature and function, not by parameter name.
The parameters listed in this section are available in the Config folder that is downloaded with
the software. For any parameters not available in the scenario templates, look in the
Troubleshooting folder for the “everything.cfg” file. You will find an alphabetical folder hierarchy
of all the parameters detailed in this document. To find the exact parameters you want to use,
open the file and use your search tools.
The easiest way to provision any parameter is to simply drag and drop or copy/paste it from the
source template into the .cfg file you will use to deploy the handsets. Edit it in your final .cfg file
per the instructions in the parameter list.
Page 59

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 59
Chapter 6: Features that Cannot be
Configured
Audio Processing Features
The Spectralink 84-Series handsets have these built-in audio processing features: automatic
gain control, background noise suppression, comfort noise fill, dynamic noise reduction, jitter
buffer and packet error concealment, and low delay audio packet transmission. These features
work automatically, without configuration changes.
Automatic Gain Control
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) is applicable to handsfree operation and is used to boost the
transmit gain of the local talker in certain circumstances. This increases the effective userhandset radius and helps with the intelligibility of soft-talkers.
Background Noise Suppression
Background noise suppression (BNS) is designed primarily for handsfree operation and reduces
background noise to enhance communication in noisy environments.
Comfort Noise Fill
Comfort noise fill is designed to help provide a consistent noise level to the remote user of a
handsfree call. Fluctuations in perceived background noise levels are an undesirable side effect
of the non-linear component of most acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) systems. This feature
uses noise synthesis techniques to smooth out the noise level in the direction toward the remote
user, providing a more natural call experience. This feature is different from Voice Activity
Detection.
Dynamic Noise Reduction
Dynamic noise reduction (DNR) provides maximum microphone sensitivity, while automatically
reducing background noise— from fans, projectors, heating and air conditioning—for clearer
sound and more efficient conferencing.
Jitter Buffer and Packet Error Concealment
The handset employs a high-performance jitter buffer and packet error concealment system
designed to mitigate packet inter-arrival jitter and out-of-order, or lost or delayed (by the
network) packets. The jitter buffer is adaptive and configurable for different network
Page 60

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 60
environments. When packets are lost, a concealment algorithm minimizes the resulting negative
audio consequences.
Low-Delay Audio Packet Transmission
The handset is designed to minimize latency for audio packet transmission.
Call Timer
A call timer displays on the handset’s screen. A separate call duration timer displays the hours,
minutes, and seconds of each call in progress.
There are no related configuration changes.
Called Party Identification
By default, the handset displays and logs the identity of parties called from the handset. The
handset obtains called party identity from the network signaling. Because Called Party
Identification is a default state, the handset will display caller IDs matched to the call server and
does not match IDs to entries in the Local Contact Directory or Corporate Directory.
There are no related configuration changes.
Connected Party Identification
By default, the handset displays and logs the identity of remote parties you connect to if the call
server can derive the name and ID from the network signaling. Note that in cases where remote
parties have set up certain call features, the remote party you connect to—and the caller ID that
displays on the handset—may be different than the intended party. For example, Bob places a
call to Alice, but Alice has call diversion configured to divert Bob’s incoming calls to Fred. In this
case, the handset will log and display the connection between Bob and Fred. Note that the
handset does not match party IDs to entries in the contact directory or the corporate directory.
Microphone Mute
The handsets have a microphone mute softkey. When you activate microphone mute, a mute
icon will display on the status bar.
No configuration changes can be made to the microphone mute feature.
Page 61

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 61
Synthesized Call Progress Tones
Spectralink handsets play call signals and alerts, called call progress tones, such as busy
signals, ringback sounds, and call waiting tones. The built-in call progress tones on your
handset match standard North American tones.
Page 62

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 62
Chapter 7: Configurable Features on the
User Menus
Features that are available on the User menus, such as ring tones, can be configured by the
administrator in the central provisioning server but may be changed by the user, creating
override files stored on the central provisioning server. Some user-level parameters that are
made available to users by default can be disabled by the administrator if certain usability
factors need to be enforced. This chapter covers features that are available on the User menus
that have user-level parameters that can be configured on the central provisioning server.
Some features, such as Push-to-talk, are set up by the administrator and are designed to be
customized by the user, like subscribing to certain channels that have been enabled by the
administrator. These features are covered in the next chapter.
Features that are not on the User menus but can be set through the Web Configuration Utility
are covered in the next chapter.
Call Forwarding
The handset provides a flexible call forwarding feature that enables you to forward incoming
calls to another destination. To enable and set call forwarding from the handset, navigate to
Home> Settings> Feature Settings> Forward. From this menu you can apply call forwarding
in the following ways:
To all calls
When your handset is busy
(Since the 84-Series handsets support 24 incoming calls by default [call.callsPerLineKey]
they won’t offer a busy signal to the PBX unless it’s handling 24 calls to any given
handset, an unlikely event. In order to forward on busy, the callsPerLineKey must be set
to 1 or 2 instead of 24.)
When the handset has not been answered within a specified number of rings
Call forwarding is also available as a divert function in the Contacts Directory:
To incoming calls from a specific caller or extension
You can have incoming calls forwarded automatically to a predefined destination you
choose or you can manually forward calls to a destination.
To enable server-based call forwarding, see your PBX manual and the Interop Guide relating to
that server.
Page 63

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 63
Troubleshooting: If Call Forwarding Does Not Work
The server-based and local call forwarding features do not work with the Shared
Call Appearance (SCA) and Bridged Line Appearance (BLA) features. If you have
SCA or BLA enabled on your handset, you will need to disable the feature before
you can use call forwarding.
The call server uses the Diversion field with a SIP header to inform the handset of a call’s
history. For example, when you enable call forwarding, the Diversion header allows the
receiving handset to indicate who the call was from, and the handset number it was forwarded
from.
Summary
Parameter
Used to:
voIpProt.SIP.serverFeatureControl.cf
Enable or disable server-based call forwarding
voIpProt.SIP.serverFeatureControl.localProcessing.cf
Enable or disable local call forwarding behavior when
server-based call forwarding is enabled
voIpProt.SIP.header.diversion.*
Enable or disable the display of the Diversion header and
the order in which to display the caller ID and number
divert.*
Set all call diversion settings including a global forward-to
contact and individual settings for call forward all, call
forward busy, call forward no-answer.
reg.x.fwd.*
Enable or disable server-based call forwarding as a perregistration feature
Table 7-1: Configuring Call Forwarding
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voIpProt.SIP.serverFeatureControl.cf1
0 or 1
0
If set to 1, server-based call forwarding is enabled. The call server has control of call forwarding.
If set to 0, server-based call forwarding is not enabled.
voIpProt.SIP.serverFeatureControl.localProcessing.cf
0 or 1
1
If set to 0 and voIpProt.SIP.serverFeatureControl.cf is set to 1, the handset will not perform local Call
Forward behavior.
If set to 1, the handset will perform local Call Forward behavior on all calls received.
voIpProt.SIP.header.diversion.enable1
0 or 1
0
If set to 1, the diversion header is displayed if received. If set to 0, the diversion header is not displayed.
voIpProt.SIP.header.diversion.list.useFirst1
0 or 1
1
If set to 1, the first diversion header is displayed. If set to 0, the last diversion header is displayed.
reg.x.fwdcontact
string
Null
The forward-to contact for calls when always is specified. If Null, calls are not forwarded.
reg.x.fwd.noanswer.status
0 or 1
0
If 0, calls are not forwarded if there is no answer. If 1, calls are forwarded to the contact specified by
reg.x.noanswer.contact after ringing for the length of time specified by reg.x.fwd.noanswer.ringCount.
Page 64

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 64
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
reg.x.fwd.noanswer.contact
string
Null
The forward-to contact used for calls forwarded due to no answer. If Null, the contact specified by
divert.x.contact will be used.
reg.x.fwd.noanswer.ringCount
0 to 65535
0
The number of seconds the handset should ring for before the call is forwarded because of no answer. Note: The
maximum value accepted by some call servers is 20.
reg.x.fwd.busy.status
0 or 1
0
If 0, incoming calls that receive a busy signal will not be forwarded. If 1, busy calls are forwarded to the contact
specified by reg.x.fwd.busy.contact.
reg.x.fwd.busy.contact
string
Null
The forward-to contact for calls forwarded due to busy status. If Null, the contact specified by divert.x.contact
will be used.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Example Call Forwarding Configuration
In the example configuration shown next, the call forwarding parameters for registration 1 have
been changed from the default values.
The forward-always contact for registration 1 is 5557 and this number will be used if the
parameters divert.busy, divert.dnd, or divert.noanswer are not set.
Parameters you set in those fields will overrule divert.1.contact.
To enable these three divert options for each registration, you will need to enable the
divert.fwd.x.enabled parameter and the .enabled parameter for each of the
three forwarding options you want to enable.
In this example, divert.fwd.1.enabled has been disabled; all calls to registration 1
will be diverted to 5557 and you do not have the option of enabling any of the three
forwarding options on the handset.
The three divert options are enabled for registration 2 in the divert.fwd.2.enabled
parameter, giving you the option to enable or disable any one of the three forwarding
options on the handset.
When do not disturb (DND) is turned on, you can set calls to registration 2 to be diverted
to 6135559874 instead of 5557.
The parameter divert.noanswer.2.enabled is enabled so that, on the handset,
you can set calls to registration 2 that ring for more than 15 seconds, specified in
divert.noanswer.2.timeout, to be diverted to 2987, as set in
divert.noanswer.2.contact.
Page 65

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 65
The handset has a flexible call forward/diversion feature for each registration. In all cases, a call
will only be diverted if a non-Null contact has been configured.
In the following table, x is the registration number. SL8400: x=1-6.
Table 7-2: Call Diversion (Call Forwarding) Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
divert.x.contact1
contact address: ASCII encoded string containing digits
(the user part of a SIP URL) or a string that constitutes a
valid SIP URL (6416 or 6416@Spectralink.com)
Null
The forward-to contact used for all automatic call diversion features. All automatically forwarded calls will be
directed to this contact. The contact can be overridden by a busy contact, DND contact, or no-answer contact as
specified by the busy, dnd, and noAnswer parameters that follow.
divert.x.sharedDisabled1
0 or 1
1
If 0, call diversion features can be used on shared lines. If 1, call diversion features are disabled on shared lines.
Page 66

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 66
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
divert.x.autoOnSpecificCaller2
0 or 1
1
If 0, the Auto Divert feature of the contact directory is disabled for registration x. If 1, calls on registration x may be
diverted using Auto Divert, you may specify to divert individual calls or divert all calls.
divert.busy.x.enabled2
divert.busy.x.contact1
0 or 1
contact address
1
Null
Divert incoming calls that reach a busy signal. If enabled is set to 1, calls will be diverted when registration x is
busy. Calls will be sent to the busy contact’s address if it is specified; otherwise calls will be sent to the default
contact specified by divert.x.contact. If enabled is set to 0, calls will not be diverted if the line is busy.
divert.dnd.x.enabled2
divert.dnd.x.contact1
0 or 1
contact address
0
Null
Divert calls when Do Not Disturb is enabled. If enabled is set to 1, calls will be diverted when DND is enabled on
registration x. Calls will be sent to the DND contact’s address if it is specified; otherwise calls will be sent to the
default contact specified by divert.x.contact.
divert.fwd.x.enabled2
0 or 1
1
If 0, the user cannot enable universal call forwarding (automatic forwarding for all calls on registration x). If 1, a
Forward softkey will display on the flyout menu when you press the Features softkey.
divert.noanswer.x.enabled2
divert.noanswer.x.contact1
divert.noanswer.x.timeout1
0 or 1
contact address
positive integer
1
Null
55
If no-answer call diversion is enabled, calls that are not answered after the number of seconds specified by
timeout will be sent to the no-answer contact. If the no-answer contact is set to Null, the call will be sent to the
default contact specified by divert.x.contact. If enabled is set to 0, calls will not be diverted if they are not
answered.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
2
Change causes handset to restart or reboot. If server-based call forwarding is enabled, this parameter is disabled.
Keypad Lock
Keypad Lock is enabled by default. This feature locks the keypad to prevent inadvertent dialing
while the phone is idle and/or while in a call. The feature adds a Keypad Lock and/or an In-call
Keypad Lock option on the Features softkey menu. Once the handset is locked for idle, an
Unlock softkey appears. When pressed it will unlock the keypad. No password is required. The
in-call keypad lock will expire when the phone call is ended.
If your deployment requires additional handset security, please see the Phone Lock section.
Table 7-3: Keypad Lock
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
keypadLock.enabled1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the keypad lock feature is disabled. If 1, the feature is enabled.
keypadLock.idleTimeout1
0 to 65535
0
The maximum time (in seconds) the handset can be idle before the keypad will lock.
Page 67

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 67
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
inCall.keypadLock.enabled
0 or 1
0
If enabled the In-call Keypad Lock item will appear on the Profile soft key when a call is connected. Note that if
more than one call connected at the same time, this item will not show up as the space on the flyout is used by
other items.
inCall.keypadLock.autoLockTime
0 to 30
0
If 0, auto-lock is not enabled.
If not zero then the In-call Keypad Lock will be engaged nn seconds after a call is fully connected.
Only 1 call can engage the lock. If a second call is started during the timeout period for the first call, the auto-lock
for the second call will be ignored. The In-call Keypad Lock item on the Profile soft key flyout can still be used even
if auto-lock is configured.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Multi Key Answer
Multikey Answer enables you to answer incoming calls by pressing any key on the handset’s
keypad. Multikey Answer is disabled by default but may be enabled by the administrator. You
cannot use the Multi Key Answer feature for Open Application Interface (OAI) calls, Group
Paging, or Push-to-talk (PTT) calls. Navigate to the option by going to Settings> Basic
Settings> Preferences> Multi Key Answer.
Table 7-4: Enabling Multi Key Answer
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
up.multiKeyAnswerEnabled
0 or 1
0
If 1, incoming calls can be answered by pressing any key. If 0, incoming calls can only be answered using the Talk
button or the Start key.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Notification Profiles
The Spectralink handsets support four profiles for notification alerts: Normal, Silent, Meeting,
and Custom1. You can customize each profile with a unique name, unique ringtones, alerts,
and vibrations for specific situations. For example, you can customize barcode scan alerts or
when you receive an instant message.
Notification Profiles are selectable on the handset by selecting a profile from the standby mode
Profile softkey or by navigating to Settings> Basic Settings> Notification Profiles where
profiles can be modified by the user.
By default, the ringing and alert volumes are at the same level. You can configure the ringer
volume for ringing only and set a distinct alert volume for each alert type. By default, the
handset will maintain changes you make to the ringer volume when the handset reboots or
restarts.
Page 68

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 68
This section shows you how to choose a default notification profile from four available types Normal, Silent, Meeting, Custom1 - and shows you the parameters you can set for each type.
Each profile is defined by an alert type and a ring type; there are 15 alert types and three ringing
types.
For each alert type:
You can select a tone pattern from the patterns defined in se.pat.misc. These patterns
include: custom1 to custom10, instantMessaging, localHoldNotification,
messageWaiting, misc1 to misc9, negativeConfirm, positiveConfirm,
remoteHoldNotification, silent, and welcome. For information on customizing these
parameters, refer to se.pat.misc.
You can determine if the handset should vibrate for the alert. Set the vibrate parameter
to 0 to disable vibration or 1 to enable vibration.
For each ringer type:
You can choose a tone pattern from the patterns defined in se.pat.ringer. These
patterns include: default, ringer1 to ringer 24, and 1 to 22.
You can also set the vibration type for the ringer. You can select off, continuous,
shortPulse, or longPulse.
Configure the default notification profile by setting the parameter shown in the following table:
Table 7-5: Notification Profile Selection Parameter
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.selected
Normal, Silent, Meeting, Custom1
Normal
The initial profile that is selected when the handset powers on and active during operation. The user can override
this default profile to set a new default profile that will be selected when the handset powers on the next time.
Table 7-6: Normal Profile Alert Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.normal.label
String
Normal
The name of the profile type.
np.normal.alert.barcodeBeep.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.barcodeBeep.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc2
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when a barcode is scanned.
np.normal.alert.docked.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.docked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
positiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset is docked.
np.normal.alert.undocked.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.undocked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset is undocked.
Page 69

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 69
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.normal.alert.instantMessaging.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.instantMessaging.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
instantMessage
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the instant message alert.
np.normal.alert.localHoldNotification.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.localHoldNotification.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
localHoldNotification
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the local hold notification alert.
np.normal.alert.lossOfNetwork.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.lossOfNetwork.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the network is lost.
np.normal.alert.lowBattery.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.lowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is low.
np.normal.alert.veryLowBattery.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.veryLowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is very low.
np.normal.alert.messageWaiting.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.messageWaiting.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
messageWaiting
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if there is a message waiting.
np.normal.alert.negativeConfirm.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.negativeConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the negative confirmation alert.
np.normal.alert.positiveConfirm.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.positiveConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
positiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the positive confirmation alert.
np.normal.alert.pttTransmit.tonePatterna
np.normal.alert.pttTransmit.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc3
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if sending a push-to-talk page.
np.normal.alert.pttWait.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.pttWait.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc4
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the push-to-talk wait alert.
np.normal.alert.welcome.tonePattern
np.normal.alert.welcome.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
Welcome
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset turns on.
np.normal.ringing.calls.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
default
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.normal.ringing.calls.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.normal.ringing.oai1.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer2
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
Page 70

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 70
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.normal.ringing.oai1.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.normal.ringing.oai2.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer2
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2
communications.
np.normal.ringing.oai2.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2 communications.
np.normal.ringing.privateLine.tonePattern
default, ringer1 to ringer24
default
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010.
np.normal.ringing.privateLine.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
shortPulse
The vibration pattern for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or
2010.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.handset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Handset and Normal profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.headset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Normal profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.chassis
-1000 to 1000
0
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Chassis and Normal profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.dock
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when handset is at the speakerphone dock and Normal profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.bluetoothHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Bluetooth Headset and Normal profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.reserved
-1000 to 1000
-21
Not currently used. Reserved for future use.
np.normal.ringing.toneVolume.usbHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is a USB headset and Normal profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
Table 7-7: Silent Profile Alert Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.silent.label
String
silent
The name of the profile type.
Page 71

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 71
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.silent.alert.barcodeBeep.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.barcodeBeep.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when a barcode is scanned.
np.silent.alert.docked.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.docked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is docked.
np.silent.alert.undocked.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.undocked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is undocked.
np.silent.alert.instantMessaging.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.instantMessaging.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the instant message alert.
np.silent.alert.localHoldNotification.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.localHoldNotification.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the local hold notification alert.
np.silent.alert.lossOfNetwork.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.lossOfNetwork.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the network is lost.
np.silent.alert.lowBattery.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.lowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is low.
np.silent.alert.veryLowBattery.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.veryLowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is very low.
np.silent.alert.messageWaiting.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.messageWaiting.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if there is a message waiting.
np.silent.alert.negativeConfirm.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.negativeConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the negative confirmation alert.
np.silent.alert.positiveConfirm.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.positiveConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the positive confirmation alert.
np.silent.alert.pttTransmit.tonePatterna
np.silent.alert.pttTransmit.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if sending a push-to-talk page.
np.silent.alert.pttWait.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.pttWait.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the push-to-talk wait alert.
np.silent.alert.welcome.tonePattern
np.silent.alert.welcome.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
silent
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset turns on.
Page 72

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 72
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.silent.ringing.calls.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.silent.ringing.calls.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.silent.ringing.oai1.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.silent.ringing.oai1.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.silent.ringing.oai2.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2
communications.
np.silent.ringing.oai2.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
off
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2 communications.
np.silent.ringing.privateLine.tonePattern
default, ringer1 to ringer24
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010.
np.silent.ringing.privateLine.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
shortPulse
The vibration pattern for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or
2010.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.handset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Handset and Silent profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.headset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Silent profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.chassis
-1000 to 1000
0
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Chassis and Silent profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.dock
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when handset is at the speakerphone dock and Silent profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.bluetoothHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Bluetooth Headset and Silent profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.reserved
-1000 to 1000
-21
Not currently used. Reserved for future use.
Page 73

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 73
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.silent.ringing.toneVolume.usbHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is a USB headset and Silent profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
Table 7-8: Meeting Profile Alert Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.meeting.label
String
Meeting
The name of the profile type.
np.meeting.alert.barcodeBeep.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.barcodeBeep.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc2
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when a barcode is scanned.
np.meeting.alert.docked.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.docked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
postiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is docked.
np.meeting.alert.undocked.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.undocked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is undocked.
np.meeting.alert.instantMessaging.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.instantMessaging.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
instantMessage
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the instant message alert.
np.meeting.alert.localHoldNotification.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.localHoldNotification.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
localHoldNotification
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the local hold notification alert.
np.meeting.alert.lossOfNetwork.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.lossOfNetwork.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the network is lost.
np.meeting.alert.lowBattery.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.lowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is low.
np.meeting.alert.veryLowBattery.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.veryLowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is very low.
np.meeting.alert.messageWaiting.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.messageWaiting.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
messageWaiting
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if there is a message waiting.
np.meeting.alert.negativeConfirm.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.negativeConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the negative confirmation alert.
np.meeting.alert.positiveConfirm.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.positiveConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
positiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the positive confirmation alert.
Page 74

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 74
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.meeting.alert.pttTransmit.tonePatterna
np.meeting.alert.pttTransmit.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc3
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if sending a push-to-talk page.
np.meeting.alert.pttWait.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.pttWait.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc4
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the push-to-talk wait alert.
np.meeting.alert.welcome.tonePattern
np.meeting.alert.welcome.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
Welcome
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset turns on.
np.meeting.ringing.calls.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.meeting.ringing.calls.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.meeting.ringing.oai1.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.meeting.ringing.oai1.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.meeting.ringing.oai2.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer1
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2
communications.
np.meeting.ringing.oai2.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2 communications.
np.meeting.ringing.privateLine.tonePattern
default, ringer1 to ringer24
ringer9
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010.
np.meeting.ringing.privateLine.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
shortPulse
The vibration pattern for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or
2010.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.handset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Meeting profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.headset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Meeting profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.chassis
-1000 to 1000
0
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Chassis and Meeting profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
Page 75

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 75
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.dock
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when handset is at the speakerphone dock and Meeting profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.bluetoothHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Bluetooth Headset and Meeting profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.reserved
-1000 to 1000
-21
Not currently used. Reserved for future use.
np.meeting.ringing.toneVolume.usbHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is a USB headset and Meeting profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
Table 7-9: Custom1 Profile Alert Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.custom1.label
String
Custom1
The name of the profile type.
np.custom1.alert.barcodeBeep.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.barcodeBeep.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc2
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when a barcode is scanned.
np.custom1.alert.docked.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.docked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
postiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is docked.
np.custom1.alert.undocked.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.undocked.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the handset is undocked.
np.custom1.alert.instantMessaging.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.instantMessaging.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
instantMessage
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the instant message alert.
np.custom1.alert.localHoldNotification.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.localHoldNotification.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
localHoldNotification
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the local hold notification alert.
np.custom1.alert.lossOfNetwork.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.lossOfNetwork.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the network is lost.
np.custom1.alert.lowBattery.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.lowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is low.
np.custom1.alert.veryLowBattery.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.veryLowBattery.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc1
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if the battery is very low.
Page 76

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 76
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.custom1.alert.messageWaiting.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.messageWaiting.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
messageWaiting
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if there is a message waiting.
np.custom1.alert.negativeConfirm.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.negativeConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
negativeConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the negative confirmation alert.
np.custom1.alert.positiveConfirm.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.positiveConfirm.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
positiveConfirm
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the positive confirmation alert.
np.custom1.alert.pttTransmit.tonePatterna
np.custom1.alert.pttTransmit.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc3
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played if sending a push-to-talk page.
np.custom1.alert.pttWait.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.pttWait.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
misc4
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the push-to-talk wait alert.
np.custom1.alert.welcome.tonePattern
np.custom1.alert.welcome.vibration
Any tone (see se.pat.misc)
0 or 1
Welcome
0
The tone pattern and vibration (1 to enable) for the alert played when the handset turns on.
np.custom1.ringing.calls.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer2
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.custom1.ringing.calls.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for normal calls.
np.custom1.ringing.oai1.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer2
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.custom1.ringing.oai1.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) communications.
np.custom1.ringing.oai2.tonePattern
A ringer (see se.pat.ringer)
ringer2
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) and vibration (1 to enable) for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2
communications.
np.custom1.ringing.oai2.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
continuous
The vibration pattern for Open Application Interface (OAI) version 2.2 communications.
np.custom1.ringing.privateLine.tonePattern
default, ringer1 to ringer24
ringer9
The ringtone (see se.pat.ringer) for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync
Server 2013 or 2010.
np.custom1.ringing.privateLine.vibration
off, continuous, shortPulse,
longPulse
shortPulse
The vibration pattern for a private line registered to Microsoft Skype for Business or Microsoft Lync Server 2013 or
2010.
Page 77

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 77
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.handset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Custom1 profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.headset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Headset and Custom1 profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.chassis
-1000 to 1000
0
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Chassis and Custom1 profile is active.
Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.dock
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when handset is at the speakerphone dock and Custom1 profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.bluetoothHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is Bluetooth Headset and Custom1 profile
is active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.reserved
-1000 to 1000
-21
Not currently used. Reserved for future use.
np.custom1.ringing.toneVolume.usbHeadset
-1000 to 1000
-21
The attribute is set (on adjusting ring volume) when ringing termination is a USB headset and Custom1 profile is
active. Although the permitted values are -1000 to 1000, the practical limits used by the handset are -50 to 10.
Time and Date Display
A clock and calendar are enabled by default. View/edit by navigating to Home> Settings>
Basic Settings> Preferences> Time & Date. You can display the time and date for your time
zone in several formats, or you can turn it off altogether. You can also set the time and date
format to display differently when the handset is in certain modes. For example, the display
format can change when the handset goes from idle mode to an active call.
There are multiple formats to this parameter and as a result there is a hierarchy of precedence.
Example: the device.sntp parameter would be considered a base level parameter whereas the
tcpipApp.sntp.address parameter takes precedence over the device.sntp parameter. Further still
DHCP can override both and take precedence. However, tcpipApp.sntp.address.overrideDHCP
can be configured to override DHCP.
The templates contain the parameter device.sntp in the wireless.cfg file. No other template file
contains any of these sntp base parameters. They are available in the everything.cfg.
In order to display the time and date accurately, you will have to synchronize the handset to the
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) time server. Until a successful SNTP response is
received, the handset will continuously flash a time and date to indicate that they are not
accurate.
Page 78

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 78
Caution: Some language parameters may overrule lcl.dateline parameters.
Certain languages use date and time settings that overrule lcl.dateline parameters.
See the Languages section for details.
Table 7-10: Setting the Time and Date Display
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
up.localClockEnabled
0 or 1
1
If 0, the date and time are not shown on the idle display. If 1, the date and time and shown on the idle display.
lcl.datetime.date.format
string which includes ‘D’, ‘d’ and
‘M’ and two optional commas
D,Md
Controls format of date string. D = day of week, d = day, M = month.
Up to two commas may be included.
For example: D,dM = Thursday, 3 July or Md,D = July 3, Thursday
The field may contain 0, 1 or 2 commas which can occur only between characters and only one at a time. For
example: “D,,dM” is illegal.
lcl.datetime.date.longFormat
0 or 1
1
If set to 1, display the day and month in long format (Friday/November), otherwise, use abbreviations (Fri/Nov).
lcl.datetime.time.24HourClock
0 or 1
0
If set to 1, display time in 24-hour clock mode rather than a.m./p.m.
Table 7-11: Date Formats
lcl.datetime.date.format
lcl.datetime.date.longformat
Date Displayed on Phone
dM,D
0
19 Aug, Fri
dM,D
1
19 August, Friday
Md,D
0
Aug 19, Fri
Md,D
1
August 19, Friday
D,dM
0
Fri, 19 Aug
D,dM
1
Friday, 19 August
D,Md
0
Fri, Aug 19
D,Md
1
Friday, August 19
DD/MM/YY
n/a
19/08/11
DD/MM/YYYY
n/a
19/08/2011
MM/DD/YY
n/a
08/19/11
MM/DD/YYYY
n/a
08/19/2011
YY/MM/DD
n/a
11/08/19
YYYY/MM/DD
n/a
2011/08/19
Page 79

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 79
Synchronizing with SNTP
The following table describes the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) parameters used to set
up time synchronization and daylight savings time. The default values will enable and configure
daylights savings time (DST) for North America.
Daylight savings time defaults:
Do not use fixed day, use first or last day of week in the month.
Start DST on the second Sunday in March at 2am.
Stop DST on the first Sunday in November at 2am.
Table 7-12: Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
tcpIpApp.sntp.address
Valid hostname or IP
address
Null
The address of the SNTP server.
tcpIpApp.sntp.address.overrideDHCP
0 or 1
0
If 0, the DHCP values for the SNTP server address will be used. If 1, the SNTP parameters will overrule the DHCP
values.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.enable
0 or 1
1
If 0, daylight savings time rules are not applied to the displayed time. If 1, the daylight savings rules apply.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.fixedDayEnable
0 or 1
0
If 0, month, date, and dayOfWeek are used in the DST calculation. If 1, only month and date are used.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.start.date
1 to 31
8
The start date for daylight savings time. If fixedDayEnable is set to 1, the value of this parameter is the day of
the month to start DST. If fixedDayEnable is set to 0, this value specifies the occurrence of dayOfWeek when
DST should start. Set 1 for the first occurrence in the month, set 8 for the second occurrence, 15 for the third
occurrence, or 22 for the fourth occurrence. For example, if set to 15, DST starts on the third dayOfWeek of the
month.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.start.dayOfWeek
1 to 7
1
The day of the week to start DST. 1=Sunday, 2=Monday, … 7=Saturday. Note: this parameter is not used if
fixedDayEnable is set to 1.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.start.dayOfWeek.lastInMonth
0 or 1
0
If 1, DST starts on the last dayOfWeek of the month and the start.date is ignored. Note: this parameter is not
used if fixedDayEnable is set to 1.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.start.month
1 to 12
3 (March)
The month to start DST. 1=January, 2=February… 12=December.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.start.time
0 to 23
2
The time of day to start DST – in 24 hour clock format. 0= 12am, 1= 1am,… 12= 12pm, 13= 1pm, … 23= 11pm.
Page 80

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 80
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.stop.date
1 to 31
1
The stop date for daylight savings time. If fixedDayEnable is set to 1, the value of this parameter is the day of
the month to stop DST. If fixedDayEnable is set to 0, this value specifies the occurrence of dayOfWeek when
DST should stop. Set 1 for the first occurrence in the month, set 8 for the second occurrence, 15 for the third
occurrence, or 22 for the fourth occurrence. For example, if set to 22, DST stops on the fourth dayOfWeek of the
month.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.stop.dayOfWeek
1 to 7
1
The day of the week to stop DST. 1=Sunday, 2=Monday, … 7=Saturday. Note: this parameter is not used if
fixedDayEnable is set to 1.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.stop.dayOfWeek.lastInMonth
0 or 1
0
If 1, DST stops on the last dayOfWeek of the month and the stop.date is ignored. Note: this parameter is not
used if fixedDayEnable is set to 1.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.stop.month
1 to 12
11
The month to stop DST. 1=January, 2=February… 12=December.
tcpIpApp.sntp.daylightSavings.stop.time
0 to 23
2
The time of day to stop DST – in 24 hour clock format. 0= 12am, 1= 1am,… 12= 12pm, 13= 1pm, … 23= 11pm.
tcpIpApp.sntp.gmtOffset
positive or negative
integer
0
The offset in seconds of the local time zone from GMT.3600 seconds = 1 hour, -3600 seconds = -1 hour.
tcpIpApp.sntp.gmtOffset.overrideDHCP
0 or 1
0
If 0, the DHCP values for the GMT offset will be used. If 1, the SNTP values for the GMT offset will be used.
tcpIpApp.sntp.resyncPeriod
positive integer
86400
The period of time (in seconds) that passes before the handset resynchronizes with the SNTP server. Note: 86400
seconds is 24 hours.
User Preferences Parameters
Options on various user menus can be pre-configured by the administrator.
Table 7-13: User Preferences Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
up.backlight.idleIntensity
0, 1, 2, or 3
0
The brightness of the LCD backlight when the handset is idle. 0 – off, 1 – low, 2 – medium, 3 – high. Note: If this is
higher than the active backlight brightness (onIntensity), the active backlight brightness is used. When the
phone is in the charger, this parameter does not take effect, the backlight is always on.
up.backlight.onIntensity
0, 1, 2, or 3
3
The brightness of the LCD backlight when the handset is active (in use). 0: off, 1 – low, 2 – medium, 3 – high
up.backlight.timeout
5 to 60
10
The number of seconds to wait before the backlight dims from the active intensity to the idle intensity.
Page 81

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 81
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
up.hearingAidCompatibility.enabled
0 or 1
0
If set to 1, the handset audio Rx (receive) equalization is disabled for hearing aid compatibility. If 0, audio Rx
equalization is enabled.
up.idleTimeout1
0 to 65535, seconds
40
The number of seconds that the handset can be idle before automatically leaving a menu and showing the idle
display. If 0, there is no timeout and the handset does not automatically exit to the idle display.
up.numberFirstCID1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the caller ID display will show the caller’s name first. If 1, the caller’s handset number will be shown first.
up.onHookDialingEnabled
0 or 1
1
If 0, on hook dialing is disabled. If 1, on-hook dialing is enabled.
up.screenCapture.enabled1
0 or 1
0
If 0, screen captures are disabled. If 1, the user can enable screen captures from the Screen Capture menu on the
handset. Note: when the handset reboots, screen captures are disabled from the Screen Capture menu on the
handset.
up.simplifiedSipCallInfo
0 or 1
0
If 1, the displayed host name is trimmed for both incoming and outgoing calls and the protocol tag/information is
not displayed for incoming and outgoing calls.
up.warningLevel1
0 to 2
0
If 0, the handset’s warning icon and a pop-up message display on the handset for all warnings. If 1, the warning
icon and pop-up messages are only shown for critical warnings. If 2, no warnings are displayed. Note: All warnings
are listed in the Warnings menu (navigate to Menu> Status> Diagnostics> Warnings on the handset).
up.welcomeSoundEnabled1
0 or 1
1
If 0, the welcome sound is disabled. If 1, the welcome sound is enabled and played each time the handset reboots.
up.welcomeSoundOnWarmBootEnabled1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the welcome sound is played when the handset powers up (cold boot), but not after it restarts or reboots
(warm boot). If 1, the welcome sound plays each time the handset powers up, reboots, or restarts.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Page 82

1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 82
Chapter 8: Features Configured by the
Administrator
Certain features are entirely set by the administrator and for the most part the user cannot
change them. However, some have user-configurable options available on the user menus.
Features of this type are covered in this chapter.
Finding the Parameters in the Config files
The parameters detailed in this chapter are mostly found in the “everything.cfg” file
located in the troubleshooting folder in the Config folder that you download with the
software starting with Spectralink software version 4.2.x.
AutoComplete List
The autocomplete list displays when the user goes off hook and when transferring a call. It is
composed of your Call List and Contact Directory entries, sorted alphabetically.
When the autocomplete list is presented, the user can type in numbers or letters (using the Dial
mode softkey to switch between modes) to get a list of matches.
The default method of finding matches is to match the entered characters to the starting
characters in the fields checked following this logic:
For the Call List entries, the handset checks for matches within the name and the
contact fields.
For the Contact Directory items, the handset checks for matches within the first name,
last name, and contact fields.
The search is always case insensitive.
The administrator can configure the handset to have the search find matches that “contain” the
entered characters.
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
autoComplete.useContainsSearch
0 or 1
0
When set to 0, the search will compare the entered characters against the starting characters of each field
searched. This is the default behavior. When set to 1, the search will look for the entered characters anywhere
inside each field searched.
Note that the handset limits the search to a certain period of time (because otherwise it can
interfere with entering letters in the search field) so not all possible matches may be shown in
the list after the user enters a single letter or number. This is especially true when using a
“contains” search. The user might need to enter 2 or 3 characters to narrow down the search
Page 83

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 83
enough for the handset to show all the possible matches. This should only be necessary when
very large lists are present.
Audio Settings
Context Sensitive Volume Control
The parameters shown below enable you to adjust the volume of handset sound effects — such
as the ringer and the volume of receiving call audio — separately for the speakerphone,
handset, and headset. While transmit levels are fixed according to the TIA/EIA-810-A standard,
you can adjust the receive volume.
In some countries, regulations state that a handset’s receiver volume must be reset to a nominal
level for each new call. This is the handset’s default behavior. Using this parameter, you can set
the receiver volume to persist across calls each time a user makes changes to the default
volume level.
<voice.volume/>
Table 8-1: Context Sensitive Volume Control
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voice.volume.persist.bluetooth.headset1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the Bluetooth headset receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If
1, the volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
voice.volume.persist.handset1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the handset receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If 1, the
volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
voice.volume.persist.headset1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the headset receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If 1, the
volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
voice.volume.persist.handsfree1
0 or 1
1
If 0, the speakerphone receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If 1,
the volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
voice.volume.persist.usb.handsfree1
0 or 1
1
If 0, the USB headset receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If 1, the
volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
voice.volume.persist.usbHeadset1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the USB headset receive volume will automatically reset to a nominal level after each call. If 1, the
volume for each call will be the same as the previous call.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Page 84

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 84
<voice/>
The <voice/> parameter controls the settings related to the audio on the handset.
Table 8-2: Voice Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voice.txPacketDelay1
low, normal, Null
Null
If set to normal or Null, no audio parameters are changed.
If set to low and there are no precedence conflicts, the following changes are made:
• voice.codecPref.G722="1"
• voice.codecPref.G711_Mu="2"
• voice.codecPref.G711_A="3"
• voice.codecPref.<OtherCodecs>=""
• voice.audioProfile.G722.payloadSize="10"
• voice.audioProfile.G711Mu.payloadSize= "10"
• voice.audioProfile. G711A.payloadSize= "10"
• voice.aec.hs.enable="0"
• voice.ns.hs.enable="0"
voice.txPacketFilter1
0 or 1
0
If 0, no Tx filtering is performed. If 1, narrowband Tx high pass filter is enabled.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
<rxQoS/>
The following table lists the jitter buffer parameters for wired network interface voice traffic,
wireless network interface voice traffic, and push-to-talk interface voice traffic.
Caution: Do not change these settings.
Changing any rxQoS settings can impair system operation. Do not change any
rxQoS parameters without prior consultation with Spectralink Technical Support.
Table 8-3: Voice Jitter Buffer Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voice.rxQoS.avgJitter1
voice.rxQoS.maxJitter1
0 to 80
0 to 200
20
160
The average and maximum jitter in milliseconds for wired network interface voice traffic.
avgJitter – The wired interface minimum depth will be automatically configured to adaptively handle this level of
continuous jitter without packet loss.
maxJitter – The wired interface jitter buffer maximum depth will be automatically configured to handle this level
of intermittent jitter without packet loss.
Actual jitter above the average but below the maximum may result in delayed audio play out while the jitter buffer
adapts, but no packets will be lost. Actual jitter above the maximum value will always result in packet loss. Note
that if legacy voice.audioProfile.x.jitterBuffer.* parameters are explicitly specified, they will be used
to configure the jitter buffer and these voice.rxQoS parameters will be ignored.
Page 85

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 85
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voice.rxQoS.wireless.avgJitter1
voice.rxQoS.wireless.maxJitter1
0 to 200
20 to 500
70
300
The average and maximum jitter in milliseconds for wireless network interface voice traffic.
avgJitter – The wireless interface minimum depth will be automatically configured to adaptively handle this
level of continuous jitter without packet loss.
maxJitter – The wireless interface jitter buffer maximum depth will be automatically configured to handle this
level of intermittent jitter without packet loss.
Actual jitter above the average but below the maximum may result in delayed audio play out while the jitter buffer
adapts, but no packets will be lost. Actual jitter above the maximum value will always result in packet loss.
Note: if legacy voice.audioProfile.x.jitterBuffer.* parameters are explicitly specified, they will be
used to configure the jitter buffer and these voice.rxQoS parameters will be ignored for wireless interfaces.
voice.rxQoS.ptt.avgJitter1
voice.rxQoS.ptt.maxJitter1
0 to 200
20 to 500
150
480
The average and maximum jitter in milliseconds for IP multicast voice traffic (wired or wireless).
avgJitter – The PTT/Paging interface minimum depth will be automatically configured to adaptively handle this
level of continuous jitter without packet loss.
maxJitter – The PTT/Paging interface jitter buffer maximum depth will be automatically configured to handle this
level of intermittent jitter without packet loss.
Actual jitter above the average but below the maximum may result in delayed audio play out while the jitter buffer
adapts, but no packets will be lost. Actual jitter above the maximum value will always result in packet loss.
Note: if legacy voice.audioProfile.x.jitterBuffer.* parameters are explicitly specified, they will be
used to configure the jitter buffer and these voice.rxQoS parameters will be ignored for PTT/Paging interface
interfaces.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Automatic Off-Hook Call Placement
You can configure the handset to automatically place a call to a specified number when you go
off-hook. This feature is sometimes referred to as Hot Dialing. The handset goes off-hook when
you lift the handset, press the New Call softkey, or press the headset or speakerphone buttons
on the handset. You can specify an off-hook call contact and enable or disable the feature for
specific line registrations.
Table 8-4: Enabling Automatic Off-Hook Call Placement
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.autoOffHook.x.enabled1
0 or 1
0
Enable or disable the feature
If enabled is set to 0, no call is placed automatically when the handset goes off hook, and the other parameters are
ignored. If enabled is set to 1, a call is automatically placed to the contact.
call.autoOffHook.x.contact1
a SIP URL
Null
The contact address to where the call is placed
The contact must be an ASCII-encoded string containing digits, either the user part of a SIP URL (for example,
6416), or a full SIP URL (for example, 6416@Spectralink.com).
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Page 86

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 86
Background Images
The Spectralink 84-Series wireless handsets include a feature that enables you to add a custom
background using a digital image. Using a digital image enables you to display a company logo
or product brand as the background on your handset. Supported graphics files are PNG, JPEG,
or BMP images. The maximum supported is size is 240x270 pixels. Progressive or multiscan
JPEG images are not supported.
After one or more backgrounds have been provisioned, the user can select one of them by
navigating to Menu> Settings> Basic> Preferences> Background.
Choosing a Graphic Display Background
Depending on the image you use, the graphic display background may affect the
visibility of text and numbers on the handset screen. As a general rule,
backgrounds should be light in shading for better handset and feature usability.
Configuring Background Images
You may want to define a set of images that the user can select from and set one of them as the
default. This feature is commonly used to set the company logo as a background or to
distinguish handsets that are provisioned for specific purposes or in specific groups. Limit the
configurable options by limiting the number of images available.
Table 8-5: Background Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
bg.color.selection
w,x
1,1
Set the background. Specify which type of background (w) and index (x) for that type is selected on reboot. The
default selection is 1,1 the first solid background.
Use w=1 and x=1 (1,1) to select the built-in image.
Use w=3 and x= 1 to 6 to select one of the six background bm images
bg.color.bm.x.name
Phone screen background image file
URL or file path of a BMP or JPEG
image
null
The name of the image file (including extension).
Example configuration
In this example, four of the graphic images are located in the root directory of the central
provisioning server. The fifth image, Jellyfish.jpg, is located in a subdirectory. Each of these
images will appear on the Background menu and is user-selectable.
Page 87

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 87
The figure shown next is an example of a digital image background on a Spectralink 84-Series
handset.
Backlight Off while Phone is Charging
The administrator can configure the phone so that the backlight turns off when the phone is in
the desktop charger. This configuration parameter is available in the everything.cfg file.
Parameter
Modification
Default
up.backlight.onAcCharger.enabled
Added
1
If 1 after an idle timeout display backlight is always ON to low intensity.
If 0 after an idle timeout display backlight will be OFF.
Battery End-of-life Alert
When a battery degrades through normal use, it will eventually not last as long between
charges. When a worn out battery is detected a warning message will appear on the display
which the user can clear. A warning alert icon will remain in the status bar until the battery is
replaced.
Page 88

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 88
These configuration parameters are available in the everything.cfg file.
Parameter
Modification
Min
Max
Default
battery.check.fullCapacity1100Min
battery.check.fullCapacity1750Min
Added
Added
0 0 9999
9999 0 0
If the customer decides to screen batteries, these are the recommended settings:
For 1100 (standard batteries) the recommended value is 1010.
For 1750 (extended batteries) the recommended value is 1600.
If set above the recommended value, perfectly functional batteries might be detected as worn out. If set below the
recommended setting, worn out batteries might not be detected at all.
The default of 0 ensures that batteries will not be screened at all.
When a worn out battery is detected a warning message will appear on the display and a warning alert icon will
remain in the status bar until the battery is replaced.
Feature and Basic Settings Menu Password
Certain installations need to restrict access to options on the Settings menu. The Advanced
Settings option is already behind an admin password. These parameters allow you to require a
password to access Basic Settings and Feature Settings.
Parameter
Permitted values
Defaul
settingsLock.basicSettingsPassword
String (1-32 characters)
null
If set, the indicated password is required to enter the Basic Settings menu. Also causes Edit item to be removed
from the Profiles softkey flyout menu. This allows user to change which profile is current, but not modify the
settings for each profile. Defaults to Null which means no password required.
settingsLock.featureSettingsPassword
String (1-32 characters)
Null
If set, the indicated password is required to enter the Feature Settings menu. Also causes the Forward item to be
removed from the Features softkey flyout menu. Defaults to Null which means no password required. Note that the
Feature Settings menu has DND, Forward and also the Microsoft Skype for Business Signin/Signout menus.
However, the Skype for Business Signin/Signout items can be configured to be on the Features softkey flyout
menu so one can always signin and signout.
Page 89

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 89
Parameter
Permitted values
Defaul
settingsLock.disallowProfileSoftkey
0 or 1
0
If 1, the Profile softkey will not be shown at all. Default is 0 which is current behavior.
Call Hold
The 84-Series handset has local hold functionality. Rarely, a server may not recognize this
functionality and the call can be lost. If this situation occurs, a server-based call hold feature
may be required and the parameters described in this section can be used.
The purpose of call hold is to pause activity on one call so that you can use the handset for
another task, for example, to place or receive another call or to search your handset’s menu for
information. When you place an active call on hold, a message will inform the held party that
they are on hold. You can also configure a call hold alert to remind you after a period of time
that a call is still on hold.
Table 8-6: Enabling Call Hold
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
voIpProt.SIP.useRFC2543hold
0 or 1
0
If set to 0, use SDP media direction parameters (such as a=sendonly) per RFC 3264 when initiating a call.
Otherwise use the obsolete c=0.0.0.0 RFC2543 technique. In either case, the handset processes incoming hold
signaling in either format.
Note: voIpProt.SIP.useRFC2543hold is effective only when the call is initiated.
voIpProt.SIP.useSendonlyHold
0 or 1
1
If set to 1, the handset will send a reinvite with a stream mode parameter of “sendonly” when a call is put on hold.
This is the same as the previous behavior.
If set to 0, the handset will send a reinvite with a stream mode parameter of “inactive” when a call is put on hold.
NOTE: The handset will ignore the value of this parameter if set to 1 when the parameter
voIpProt.SIP.useRFC2543hold is also set to 1 (default is 0).
call.hold.localReminder.enabled1
0 or 1
0
If 1, users are reminded of calls that have been on hold for an extended period of time. If 0, there is no hold
reminder.
call.hold.localReminder.period1
non-negative integer
60
Specify the time in seconds between subsequent hold reminders.
call.hold.localReminder.startDelay1
non-negative integer
90
Specify a time in seconds to wait before the initial hold reminder.
voIpProt.SIP.musicOnHold.uri
a SIP URI
Null
A URI that provides the media stream to play for the remote party on hold. This parameter is used if
reg.x.musicOnHold.uri is Null.
Note: The SIP URI parameter transport is supported when configured with the values of UDP, TCP, or TLS.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Page 90

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 90
Example Call Hold Configuration
The following two illustrations show a sample configuration for the call hold feature. In the first
illustration, the three localReminder.* parameters have been configured to play a tone to
remind you of a party on hold, that the tone will begin to play 45 seconds after you put a party
on hold, and that the tone will repeat every 30 seconds.
Page 91

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 91
In the second illustration, the musicOnHold.uri parameter has been configured so the party
on hold will hear music played from SIP URI moh@example.com.
Call Handling Features
The call handling features described in this section require support from a SIP server and setup
of these features depend on the SIP server. For example, while some SIP servers implement
Page 92

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 92
group call pick-up using a particular star-code sequence, others implement the feature using
network signaling.
The Spectralink 84-Series handsets can bypass some SIP server requirements and implement
various call handling features using Enhanced Feature Keys (EFK) instead. Please refer to the
EFK section for more information.
Call Park and Retrieve
You can park an active call and retrieve parked calls from any handset. Whereas call hold
keeps the held call on the same line, call park moves the call to a separate address where the
call can be retrieved by any handset.
Table 8-7: Configuring Call Park and Retrieve
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
feature.callPark.enabled1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the call park and call retrieve features are disabled. If 1, the features are enabled.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Call Waiting Alerts
By default, the handset will alert you to incoming calls while you are in an active call.
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.callWaiting.enable
0 or 1
1
If 1, the handset alerts you to an incoming call while you are in an active call. If 0, you are not alerted to incoming
calls while in an active call and the incoming call is treated as if you did not answer it. If 1, and you end the active
call during a second incoming call, you are alerted to the second incoming call.
call.callWaiting.ring1
beep, ring, silent
beep
Specifies the ringtone of incoming calls when another call is active. If set to Null, the default value is beep.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Calling Party Identification
By default, the handset displays the identity of incoming callers if available to the handset
through the network signal. If the caller is in the contact directory, you can choose to display that
name instead. Note that the handset cannot match the identity of calling parties to entries in the
Corporate Directory.
Table 8-8: Configuring Calling Party Identification
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
up.useDirectoryNames1
0 or 1
1
If 0, names provided through network signaling are used for caller ID. If 1, the name field in the local contact
directory will be used as the caller ID for incoming calls from contacts in the local directory. Note: Outgoing calls and
corporate directory entries are not matched.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Page 93

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 93
Missed Call Notification
By default, the missed call notification displays on the 84-Series handset’s status bar. A counter
shows the number of missed calls. The counter is reset by viewing the Missed Calls list on the
handset.
The Missed Call Notification can be disabled for each registered line on a handset.
Table 8-9: Disabling Missed Call Notification
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.missedCallTracking.x.enabled1
0 or 1
1
If set to 1, missed call tracking is enabled.
If call.missedCallTracking.x.enabled is set to 0, then missedCall counter is not updated regardless of
what call.serverMissedCalls.x.enabled is set to (and regardless of how the server is configured). There is
no Missed Call List provided under Menu> Features of the handset.
If call.missedCallTracking.x.enabled is set to 1 and call.serverMissedCalls.x.enabled is set to 0, then the
number of missedCall counter is incremented regardless of how the server is configured.
If call.missedCallTracking.x.enabled is set to 1 and call.serverMissedCalls.x.enabled is set to
1, then the handling of missedCalls depends on how the server is configured.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Example Missed Call Notification Configuration
In the following example, the missed call counter is enabled by default for registered lines 1 and
2, and only server-generated missed calls will be displayed on line 1.
Call Transfer
Two types of call transfer behavior is available on the 84-Series handsets. When Party A is
talking to Party B and wishes to transfer the call to Party C:
Page 94

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 94
Blind Transfer Party A calls Party C and presses the Transfer softkey while the call is
ringing. The call between Party A and Party B is ended when the Transfer softkey is
pressed.
Consultative Transfer Party A calls Party C while Party B is on hold. The call between
Party A and Party B is ended when Party A presses the Transfer softkey.
By default, the Transfer softkey uses the consultative transfer functionality and the blind transfer
is available on the Features softkey menu. This parameter allows you to change the Transfer
softkey to use the blind transfer functionality.
Table 8-10: Using Call Transfer
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.transfer.blindPreferred
0 to 1
0
If set to 1, the default softkey will be for blind transfer.
If set to 0, the default softkey will be for consultative transfer.
The other method is always available on the Features softkey menu when the handset is in call.
Example Call Transfer Configuration
In the following example configuration, the parameter allowTransferOnProceeding has
been disabled so that the Transfer softkey will not display while the third-party handset is
ringing, the proceeding state. Once you have connected to the third-party, the Transfer softkey
will display. If the third-party does not answer, you can press the Cancel softkey to return to the
active call.
Page 95

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 95
Call Lists
Table 8-11: Call List (Call Log) Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
feature.callList.enabled1
All locally controlled call lists.
feature.callListMissed.enabled1
The missed calls list.
feature.callListPlaced.enabled1
The placed calls list.
feature.callListReceived.enabled
1
The received calls list.
0 or 1
0 or 1
0 or 1
0 or 1
1
1
1
1
If 0, the call list is disabled. If 1, the call list is enabled. To enable the Missed, Placed, or Received call lists,
feature.callList.enabled must be enabled.
callLists.grouping
Unified, InOut,
InOutMissed
Unified
Used by callLists.collapseDuplicates and callLists.size.
Unified - apply the limit in callLists.size to the total number of call list entries, regardless of their type.
InOut - apply the limit to incoming (Received + Missed) calls, and apply it separately to outgoing (Placed) calls.
Thus, the total number of call list entries is actually twice that specified in callLists.size.
InOutMissed - apply the limit to Missed calls, and then separately to Placed Calls, and then separately again to
Received calls. Thus, the total number of allowed call list entries is three times that specified in callLists.size.
callLists.collapseDuplicates
0 or 1
1
If 0, all calls are archived and presented in the call lists. If 1, consecutive incomplete calls between the same party
in the same direction (outgoing/incoming) are collapsed into one record with the most recent call displaying.
callLists.logConsultationCalls
0 or 1
0
If 1, all consultation calls are logged. (Calls made to a third party—while the original party is on hold—when
settings up a conference call are called consultation calls.)
If 0, consultation calls are not logged.
callLists.size
10 to 99
99
The maximum number of retained records of each type (incoming, outgoing, and missed). When the maximum
number is reached, new records will overwrite existing records. You can clear the list using the handset’s menu
system. If you want to prevent the records from uploading to the provisioning server, enter a false URL in the
CALL_LISTS_DIRECTORY field in the master configuration file.
callLists.writeDelay.journal
1 to 600
5
The delay (in seconds) before changes due to an in-progress call are flushed to the file system as a journal.
callLists.writeDelay.terminated
10 to 600
60
The minimum period between writing out the complete XML file to the local file system and, optionally, to the
provisioning server.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Miscellaneous Call Handling Parameters
The handset supports an optional per-registration feature that enables automatic call placement
when the handset is off-hook.
Page 96

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 96
The handset supports a per-registration configuration that determines which events will cause
the missed-calls counter to increment.
You can enable/disable missed call tracking on a per-line basis.
Note: Reading the Call Parameter Table
In the following table, x is the registration number. For the Spectralink 84-Series
handsets, x=6.
This per-site and per-handset configuration parameters are defined as follows:
Table 8-12: Call Parameters
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
feature.ringDownload.enabled1
0 or 1
1
If 0, the handset will not download ringtones when it starts up. If 1, the handset will download ringtones when it
starts up.
feature.nonVolatileRingerVolume.enabled
0 or 1
1
If 0, user changes to the ringer volume are reset to default when the handset reboots. If 1, user changes to the
ringer volume are saved and maintained when the handset reboots.
call.autoAnswer.micMute
0 or 1
1
If 0, the microphone is active immediately after a call is auto-answered. If 1, the microphone is initially muted after
a call is auto-answered.
call.autoAnswer.ringClass
see the list of ring classes.
ringAutoAnswer
The ring class to use when a call is to be automatically answered using the auto-answer feature. If set to a ring
class with a type other than answer or ring-answer, the setting will be overridden such that a ringtone of
visual (no ringer) applies.
call.dialtoneTimeOut1
positive integer
60
The time is seconds that a dial tone will play before a call is dropped. If set to 0, the call is not dropped.
call.enableOnNotRegistered1
0 or 1
1
If 1, users can make calls when the handset is not registered. If 0, calls are not permitted without registration.
call.offeringTimeOut1
positive integer
60
Specify a time in seconds that an incoming call will ring before the call is dropped, 0=infinite.
Note: The call diversion, no answer feature will overrule this feature if enabled.
call.ringBackTimeOut1
positive integer
60
Specify a time in seconds to allow an outgoing call to remain in the ringback state before dropping the call,
0=infinite.
call.stickyAutoLineSeize1
0 or 1
0
If set to 1, the handset uses sticky line seize behavior. This will help with features that need a second call object to
work with. The handset will attempt to initiate a new outgoing call on the same SIP line that is currently in focus on
the LCD (this was the behavior in SIP 1.6.5). Dialing through the call list when there is no active call will use the
line index for the previous call. Dialing through the call list when there is an active call will use the current active
call line index. Dialing through the contact directory will use the current active call line index.
If set to 0, the feature is disabled (this was the behavior in SIP 1.6.6). Dialing through the call list will use the line
index for the previous call. Dialing through the contact directory will use a random line index.
Note: This may fail due to glare issues in which case the handset may select a different available line for the call.
Page 97

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 97
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.stickyAutoLineSeize.onHookDialing1
0 or 1
0
If call.stickyAutoLineSeize is set to 1, this parameter has no effect. The regular stickyAutoLineSeize
behavior is followed.
If call.stickyAutoLineSeize is set to 0 and this parameter is set to 1, this overrules the stickyAutoLineSeize
behavior for hot dial only. (Any new call scenario seizes the next available line.)
If call.stickyAutoLineSeize is set to 0 and this parameter is set to 0, there is no difference between hot
dial and new call scenarios.
Note: A hot dial occurs on the line which is currently in the call appearance. Any new call scenario seizes the next
available line.
call.suppressFullUrlDisplay.enabled1
0 or 1
0
This parameter affects the display on the connected in-call screen.
If 0, the handset displays the full SIP URL of an incoming call when the call is from a server the phone is not
registered to.
If 1, the handset displays only the number of an incoming call when the call is from a server the phone is not
registered to.
call.suppressIgnoreSoftkey1
0 or 1
0
If this is 1, the "Ignore" softkey will not show up on the incoming call screen. Instead, the softkey will be blank.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
CMS 2.0
Configuration Management Software is a UI administrative tool to accelerate configuration of
individual handsets and facilitate management of all handsets in a facility. It is a licensed
product accessible through an account key which must be present on every handset.
Two parameters ensure that the handset’s heartbeat can reach CMS and that CMS recognizes
the handset. Both of these parameters must set to a non-Null value for the CMS heartbeat to be
enabled.
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
cms.heartbeat.URL
A string of 0-256 characters
Null
This is the URL to which the phone sends the heartbeats. It must be HTTPS.
cms.heartbeat.accountKey
A string of 0-100 characters
Null
The unique id that identifies the customer. (Provided by Spectralink)
Conference Calls
Local conferences require a host handset, which processes the audio of all parties. All handsets
support three-party local conferencing.
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.localConferenceEnabled1
0 or 1
1
If set to 0, the Conference and Join softkeys do not display during an active call and you cannot establish
conferences on the handset.
If set to 1, the Conference and Join softkeys display during an active call and you can establish conferences on
the handset.
Page 98

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 98
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
call.transferOnConferenceEnd1
0 or 1
1
The behavior when the conference host exits a conference. If 0, all parties are disconnected when the conference
host exits the conference. If 1, the other parties are left connected when the host exits the conference.
call. localConferenceCallHold1
0 or 1
0
If set to 0, a hold will happen for all legs when conference is put on hold.
If set to 1, only the host is out of the conference, all other parties in conference continue to talk.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
Corporate Directory
You can connect your handset to a corporate directory server that supports the Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) version 3. The corporate directory is a flexible feature and
provides you with the parameters you can configure. Once set up on the handsets, the
corporate directory can be browsed or searched. The user can call numbers and save entries
retrieved from the LDAP server to the local contact directory on the handset.
Spectralink 84-Series handsets currently support the following LDAP servers:
Microsoft® Active Directory 2003 SP2
Sun ONE Directory Server 5.2 p6
Open LDAP Directory Server 2.4.12
Microsoft Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM) 1.0 SP1
Spectralink handsets support corporate directories that support server-side sorting and those
that do not. For handsets that do not support server-side sorting, sorting is performed on the
handset.
Tip: Better Performance With Server-Side Sorting
Spectralink recommends using corporate directories that have server-side sorting
for better performance. Consult your LDAP Administrator when making any
configuration changes for the corporate directory. For more information on LDAP
attributes, see RFC 4510 - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP):
Technical Specification Road Map.
Web Info: Supported LDAP Directories
Configuration of a corporate directory depends on the LDAP server you use. For
detailed explanations and examples of all currently supported LDAP directories,
see Technical Bulletin CS-14-19 Corporate Directory Best Practices.
A portion of the corporate directory is stored in flash memory on the handset. Spectralink
84-Series handsets have 256Mb of flash memory.
Page 99

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 99
Table 8-13: Using the Corporate Directory
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
feature.corporateDirectory.enabled
0 or 1
0
If 0, the corporate directory feature is disabled. If 1, the feature is enabled.
dir.corp.address1
dotted-decimal IP address or
hostname or FQDN
Null
The IP address or hostname of the LDAP server interface to the corporate directory. For example,
host.domain.com.
dir.corp.attribute.x.filter1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The filter string for this parameter, which is edited when searching.
dir.corp.attribute.x.label1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The label when data is displayed.
dir.corp.attribute.x.name1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The name of the parameter to match on the server. Each name must be unique; however, an LDAP entry can
have multiple parameters with the same name. Up to eight parameters can be configured (x = 1 to 8).
dir.corp.attribute.x.searchable1
0 or 1
0
If 0, quick search on parameter x (if x is 2 or more) is disabled. If 1, quick search on x (if x is 2 or more) is enabled.
dir.corp.attribute.x.sticky1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the filter criteria for attribute x is reset after a reboot. If 1, the filter criteria are retained through a reboot. If you
set an attribute to be sticky (set this parameter to 1), a ‘*’ will display before the label of the attribute on the
handset.
dir.corp.attribute.x.type1
first_name, last_name,
phone_number, SIP_address,
H323_address URL, other
last_name
Defines how parameter x is interpreted by the handset. Entries can have multiple parameters of the same type.
The value other is used for display purposes only.
If the user saves the entry to the local contact directory on the handset, first_name, last_name, and
phone_number are copied. The user can place a call to the phone_number and SIP_address from the
corporate directory.
dir.corp.autoQuerySubmitTimeout1
0 to 60 seconds
0
The timeout (in seconds) between when the user stops entering characters in the quick search and when the
search query is automatically submitted. If 0, there is no timeout (automatic submit is disabled).
dir.corp.backGroundSync1
0 or 1
0
If 0, background downloading from the LDAP server is disabled. If 1, background downloading is enabled.
dir.corp.backGroundSync.period1
3600 to 604800
86400
The corporate directory cache is refreshed after the corporate directory feature has not been used for this period of
time in seconds. The default period is 24 hours (86400 seconds). The minimum is 1 hour and the maximum is 7
days.
dir.corp.baseDN1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The base domain name. This is the starting point for making queries on the LDAP server.
dir.corp.bindOnInit1
0 or 1
1
If 0, do not use bind authentication on initialization. If 1, use bind authentication on initialization.
dir.corp.cacheSize1
8 to 256
128
The maximum number of entries that can be cached locally on the handset.
Page 100

Spectralink 84-Series Series Wireless Telephones Administration Guide
1725-86984-000_P.docx
September 2016 100
Parameter
Permitted Values
Default
dir.corp.filterPrefix1
UTF-8 encoded string
(objectclass=person)
The predefined filter string for search queries.
dir.corp.pageSize1
8 to 64
32
The maximum number of entries requested from the corporate directory server with each query.
dir.corp.password1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The password used to authenticate to the LDAP server.
dir.corp.port1
0, 1 to 65535
389 (TCP) 636 (TLS)
The port that connects to the server if a full URL is not provided. When the value is set to 0, the default value will
be used.
dir.corp.scope1
one, sub, base
sub
The type of search that is performed. If one, a search of one level below the base domain name (DN). If sub, a
recursive search of all levels below the base DN. If base, a search at the base DN level.
dir.corp.sortControl1
0 or 1
0
Controls how a client can make queries and sorts entries locally. If 0, leave sorting as negotiated between the
client and server. If 1, force sorting of queries (this causes excessive LDAP queries and should only be used to
diagnose LDAP servers with sorting problems).
dir.corp.transport1
TCP, TLS, Null
TCP
Specifies whether a TCP or TLS connection is made with the server, if a full URL is not provided.
dir.corp.useContainsSearch1
0 or 1
0
When set to 0, the search will compare the entered characters against the starting characters of each field
searched. This is the default behavior. When set to 1, the search will look for the entered characters anywhere
inside each corporate directory field.
dir.corp.user1
UTF-8 encoded string
Null
The user name used to authenticate to the LDAP server.
dir.corp.viewPersistence1
0 or 1
0
If 0, the corporate directory search filters and browsing position are reset each time the user accesses the
corporate directory. If 1, the search filters and browsing position from the previous session are displayed each time
the user accesses the corporate directory.
dir.corp.vlv.allow1
0 or 1
0
If 0, virtual view list (VLV) queries are disabled. If 1, VLV queries are enabled and can be made if the LDAP server
supports VLV.
dir.corp.vlv.sortOrder1
list of parameters
Null
The list of parameters —in exact order — for the LDAP server to use when indexing. For example: sn,
givenName, telephoneNumber.
1
Change causes handset to restart or reboot.
The following illustration points you to the minimum parameters you need to set. You will need
to enter a corporate directory address in dir.corp.address. You will need to specify where
on the corporate directory server you want to make queries in dir.corp.baseDN. In addition,
you will require a user name and password. The dir.corp.attribute.x.name must match
the attributes in the server.
 Loading...
Loading...