Page 1

SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Troubleshooting Manual
C905
1222-9526 rev. 1
APPENDIXCOMPONENT OVERVIEW FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEWABOUTABOUT TROUBLESHOOTING MEASUREME NT POINTS
1 (124)
Page 2

ABOUT
Con tents
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
ABOUT
General information
The purpose of this document is to provide enhanced technic al information for Sony Ericsson
repair technicians in order to assist during service, repair and troubleshooting operations on Sony
Ericsson mobile phones. It should be used as a c omplement to other repair instructions and tools
as notifi ed by the local Sony Ericsson representative.
To search for components throughout the entire document use the “search” function in Adobe
Acrobat Reader 7.0 (or later version) and enter the component name or other word. Use zoom to
enlarge.
For easier navigation of the document you can use the bookmarks that appear in the Bookmarks
tab on the left side of the Adobe Acrobat Reader window. Each bookmark jumps to a page in the
document.
Disclaimer
This document is Sony Ericsson confi dential and should be treated as confi dential in accordance
with the agreement with Sony Ericsson. This document is intended for use by authorized ser vice
technicians only. Sony Ericsson is not to be held responsible for any damages or losses caused
intentionally or unintentionally due to unauthorise d use of the information in this document.
Revision History
Rev. Date Changes / Comments
112/05/2008Initital revision.
ABOUT 2
Contents 2
Equipme nt L ist 3
TROUBLESHOOTING 8
Power On/Off Problems 8
USB and Software Flash Problems 8
Dead Phone Problems 9
Display Problems 10
Display Illumination Problems 11
Opto Sensor Problems 11
On- Off Key Problem s 12
Numeric Keypad &
Camera Snap But to n Pr ob le ms 12
Navigation Keypad & Game B utton Problems 13
Vol um e Button Prob le ms 13
Camera Play and Mode But to n Pr ob le ms 14
Numeric Keypad LED Proble ms 14
Navigation Keypad LED Problem s 15
Auto Focus LED Problems 15
Back Side LED Problems 16
Tally LED Problems 16
Camera Snap But to n LED Pro b le ms 17
Camera Navigation LED Problems 17
Trickle Charge LED Problems 18
Xenon Flash Problems 18
Multimedia Comb o Chip Pro bl em s 19
Camera Problems 19
Camera Cover Detec t Pro b le m s 20
TV Out Pro b le m s 20
Charging Problems 21
USB/VBUS Charging Problems 21
SIM Problems 22
Memor y S t i c k Pr o bl em s 22
Primary & Se condary M i c Pro b lem s 23
Ear Speaker Problems 23
Loudspeaker Problems 24
Handsfree (PHF) Problems 24
FM Radio Problems 25
FM Radio Antenna Problems 25
Bluetooth Problems 26
WLAN Problems 26
GSM Problems 27
WCDMA I, II and V Pro bl em s 27
WCDMA VIII Problems 28
A-GPS Problems 28
Accelerometer Problems 29
Vibrator Problems 29
Real Time Clock Probl em s 30
Slide Sensor Problems 30
System Connector Protection Test 31
Current Consumption Test 31
Backup Capacitor Test 33
Charging Test 33
ASIC Revision Test 34
Measurement Points Pictures 35
MEASUREMENT POINTS 52
Front S ide 52
Back Side 53
Top Schematic 54
Audio Top 55
Audio Analog 56
Audio Digital 57
Audio FM Radio 58
Applicatio n & S ystem Performance Top 59
System Top 60
System Control - Clo c ks & Re s ets 61
System Memories 62
System PoP IF 63
Power Top 64
Power Regulators & Charging 65
Power Imaging 66
Power ASICs 67
Power WL AN 68
Connectivity Top 69
Connectivity I2C & ADC 70
Connectivity Cards 71
Connectivity 72
Connectivity Keypad 73
Connectivity Video Compani on Chip 74
Imaging Top 75
Imaging Display 76
Imaging Camera 7 7
Imaging LMU & Flash 78
Access Top 79
Access GS M & UMTS 80
Access Blueto ot h 81
Access AGPS 82
Access WLAN 83
Test 84
COMPONENT OVERVIEW 85
Front S ide 85
Back Side 86
FUNCTIONAL OVERIEW 87
Technical Description 87
Platform Block Diagram 99
Block Diagram Power Distribution 100
Block Diagram Cloc k in g C oncept 101
APPENDIX 102
Replaceable Parts 102
Components - L2200, L4201-04 103
Components - L2406, L420 0 103
Components - N1210, N1211 104
Components - N1510, N2200 104
Components - N1300, N22 06 105
Components - N2212, N2213 105
Components - N2300, N2410, N2411 106
Components - N2420, N2421, N2422 107
Components - N 2500, N2700, N 3100 108
Components - N3101, N4400, S2415 109
Components - V2200, V2202 109
Components - V2412, V2417 109
Components - V2414-16, V2470, V4201 110
Components - V4203, X1200, X1210-11 110
Components - X1540, X22 01 111
Components - X2401, X2402 111
Components - X2410, X4200, X43 00 112
Components - X4311-15, X4400 112
Components - X4410, Z240 0, Z4200-02 113
Keyboa rd FPC S chema tics 114
Troubleshooting Software Document at i o n 115
Troubleshooting Fixture Setup Instructions 122
ABOUT
1222-9526 rev. 1
2 (124)
Page 3

TROUBLESHOOTING
f
Equip ment List
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
C905 Equipment List
Note! Additional information about the equipment used for TRS can be found in the following
locations:
Location 1: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Additional Soldering Process – C905, C905a or C905c –
Equipment List.
Location 2: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pd
or matris.xls – C Model Tab.
Troubleshooting Fixture
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Additional Soldering Process – C905, C905a or C905c –
Equipment List.
Part number: 1218-4986
Note! Additional information about the TRS Fixture Kit can be found in the Trouble Shooting
Fixtures Setup Instructions document which is included in the appendix of this manual.
Dummy Battery
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Additional Soldering Process – C905, C905a or C905c –
Equipment List.
Part number: 1208-5627
Power Supply Channel 2 (DCIO/SEPI)
Agilent 6632B or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Instrument Settings:
Voltage: 5.0 Volt
Limiter: 2.0 A
Oscilloscope
Agilent DSO7052A or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Digital Multimeter (DMM)
Fluke 83 or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Note! The 0, 64 mm Test Probes is recommended by Sony Ericsson when DMM is in use
see Picture 1.
Picture 1
Spectrum Analyzer
R&S FSL 9 kHz – 3 GHz or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
RF probe
HP 85024A or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Mobile Phone Tester
Yokogawa VC200 or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
FM Signal Generator
R&S SMC100A or similar
Location: -
TROUBLESHOOTING
Note! The resistance between GND and BDATA should be approximately 27K Ohm.
Instruments
Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Agilent 6632B or similar
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Instrument Settings:
Voltage: 3.8 Volt
Limiter: 2.0 A
Note! Maximal cable length between the Power Supply Channel 1 VBATT and the dummy battery
cannot be more than 1 meter. The cable must be able to handle at least 16A.
1222-9526 rev. 1
3 (124)
Page 4
TROUBLESHOOTING
Equipment List
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
RF Adaptor
Adaptor 33 N-BNC-50-1
Adaptor to Signal Generator RF Output
See Picture 2
Location: -
Picture 2
PC Package & PC Software
PC Package (Computer)
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Urquell Fault Trace SW with project file
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions - Electrical – C905, C905a or C905c – Trouble Shooting
Application
Project File: C905, C905a, C905c Project_R1A
Cables
USB Computer Cable
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – Re
See Picture 4.
Picture 4
DSU-60/USB Cable
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – Re
Part number: KRY 101 1413
RF Test Cable Flexible
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – Re
Part number: RPM 119 885
See Picture 5.
Picture 5
TROUBLESHOOTING
Drivers
SEPI BOX Drivers
Location: http://emma.extranet.sonyericsson.com
SE Communication Interface SEPI BOX
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Part number: LTN 214 1484
See Picture 3.
Picture 3
– Drivers – DSS / SEPI / SEMUTS
SEPI Interface Cable – A1
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – Re
Part number: KRY 101 1119/1
See Picture 6.
Picture 6
1222-9526 rev. 1
4 (124)
Page 5

TROUBLESHOOTING
Equipment List
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Power Cable RED to Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Maximum Length: 1m
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Power Cable BLACK to Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Maximum Length: 1m
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Customized Power Supply Channel 2 Cable (DCIO/SEPI)
Customize the cable according to following instructions below:
(Step 1, Step 2, Step 3 and Step 4)
Step 1:
Take the CST-75 battery charger and cut of the charger according to Picture 7.
Picture 7
Step 3:
Cut off insulating material from the inside of the charger plug according to Picture 9.
Picture 9
TROUBLESHOOTING
Step 4:
Connect DCIO Cable and SEPI Interface Cable – A1 according to Picture 10.
Picture 10
Note! The Cable length must be exactly 1.3 meters.
Step 2:
Connect the CST-75 charger Red or White wire to the Plus Output and the Black wire to the Minus
(GND) Output at backside of the Power Supply Channel 2 (DCIO/SEPI) according to Picture 8.
Picture 8
Picture 11
Note! The setup example presented in the Picture 11 is wrong!
1222-9526 rev. 1
5 (124)
Page 6
TROUBLESHOOTING
Equipment List
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Connection Instructions for the Dummy Battery
This is the correct setup when using the Dummy Battery.
See Pictures 12 and 13.
Picture 12
Picture 13
Step 2:
Cut the Red Lab Plug connector according to Picture 15.
Picture 15
TROUBLESHOOTING
Step 3:
Use any Hands-Free (PHF) Cable and cut it according to Picture 16.
Picture 16
Customized FM Radio Cable
Step 1:
Use the Test lead BNC-4mm 1,5m Cable, see Picture 14.
Picture 14
Product Name: Test lead BNC-4mm 1,5m
Product Description: Test lead with 4 mm lab plugs at one end and a BNC plug at the other.
Manufacturer: PMK Germany
Location: http://www.elfa.se/en/
or other supplier.
Part number: 46-310-40
Note! This is the ELFA part number.
Note! Cable length should be at least 40 cm.
Step 4:
Only use the Wire that is connected to PIN2 and cut out all others according to Picture 17.
Picture 17
Note! Use DMM instrument to ensure which of the wires are connected to PIN2 at Hands-Free
(PHF) system connector plug.
1222-9526 rev. 1
6 (124)
Page 7

TROUBLESHOOTING
Equipment ListEquipment ListEquipment List
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Step 5:
Connect the Cable from the Picture 15 and Cable from the Picture 17 according to Picture 18.
Note! Use a soldering iron for this action and then use insulating material to protect the contact
point.
Picture 18
Test Cards
Local SIM
Any functional Local SIM Card
See Picture 19.
Picture 19
Sony Memory Stick M2
Any functional Memory Stick Micro M2 Card
See Picture 21.
Picture 21
TROUBLESHOOTING
SMK RF Probe
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – Re
Part number: SXA 109 6356
See Picture 22.
Picture 22
Test SIM GSM/UMTS
One Test SIM GSM/UMTS is needed to perform Current Consumption Test, see Picture 20.
Location: CSPN – Repair Instructions – Mechanical – Tool Catalogue – RepairToolsCatalogue.pdf
Note! To buy a Test SIM GSM/UMTS, please contact your supplier of test equipment.
Picture 20
1222-9526 rev. 1
7 (124)
Page 8
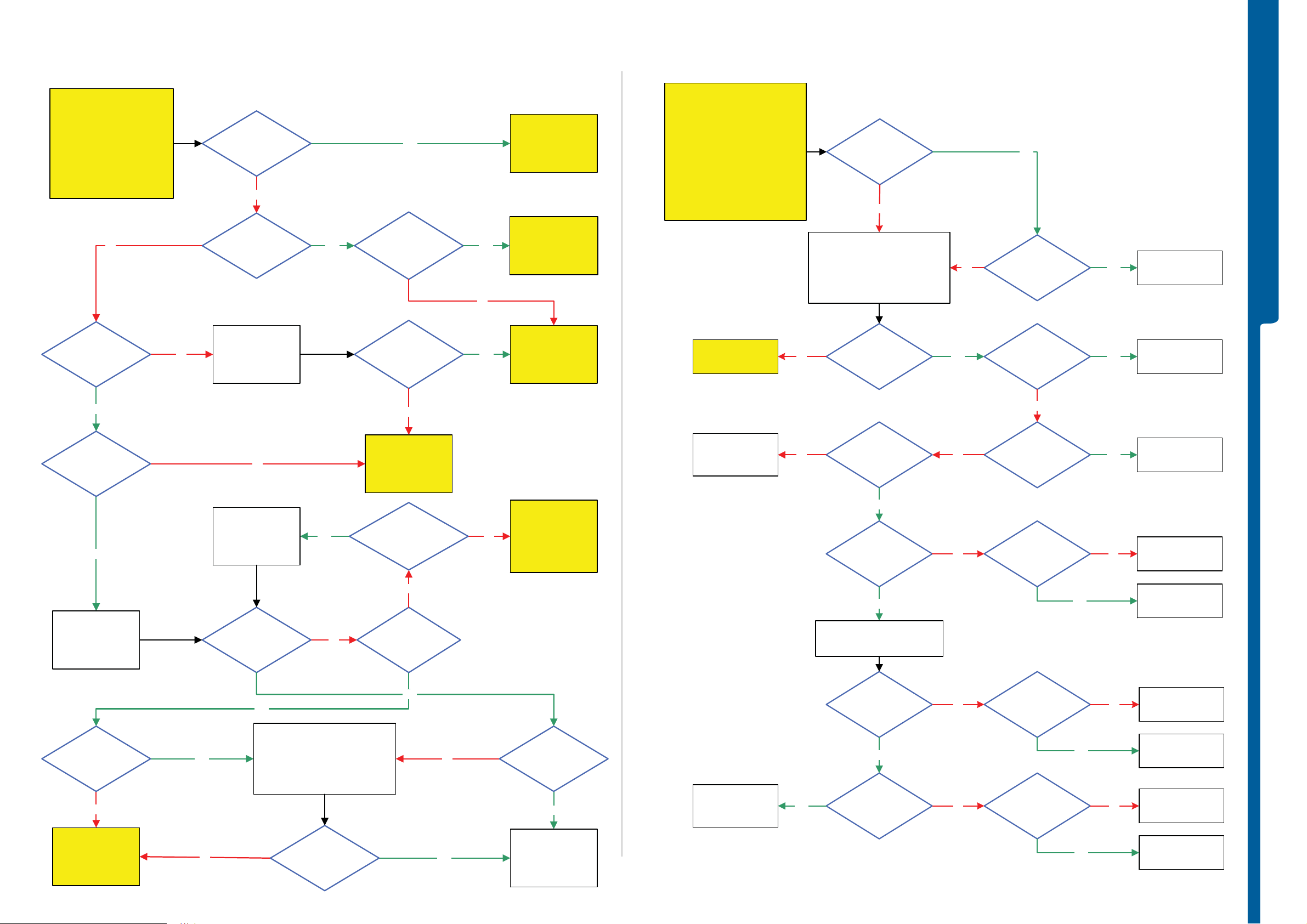
TROUBLESHOOTING
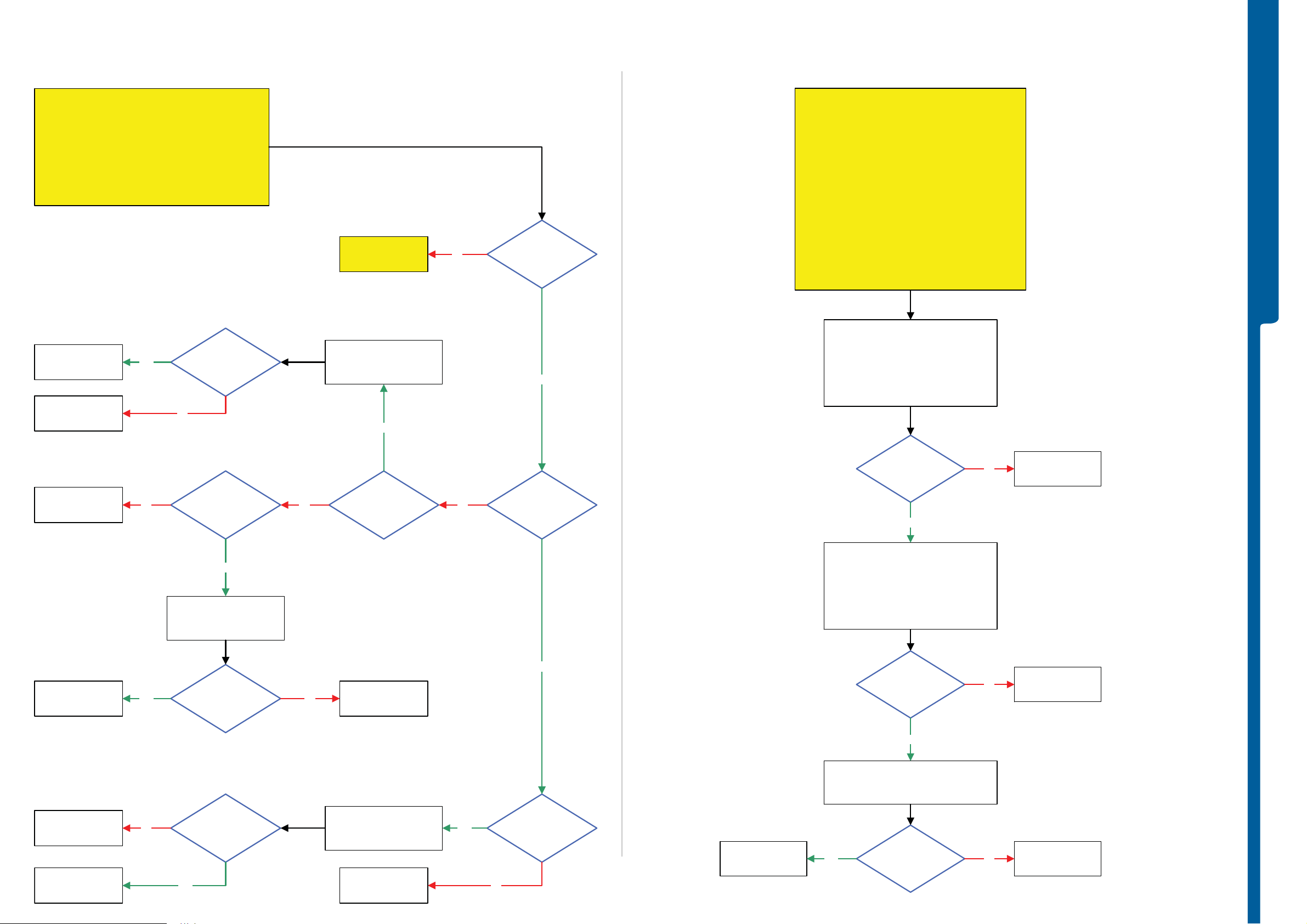
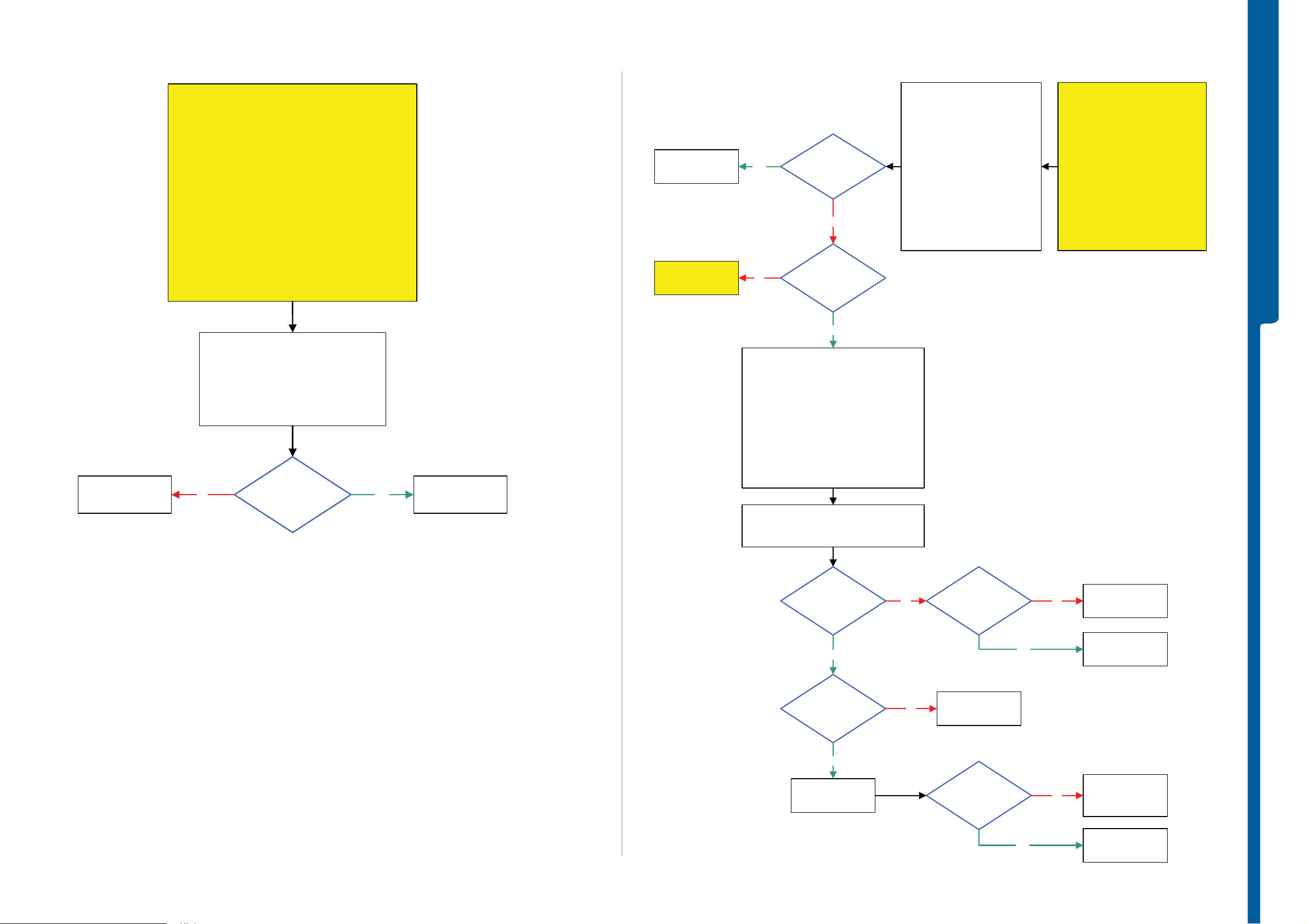
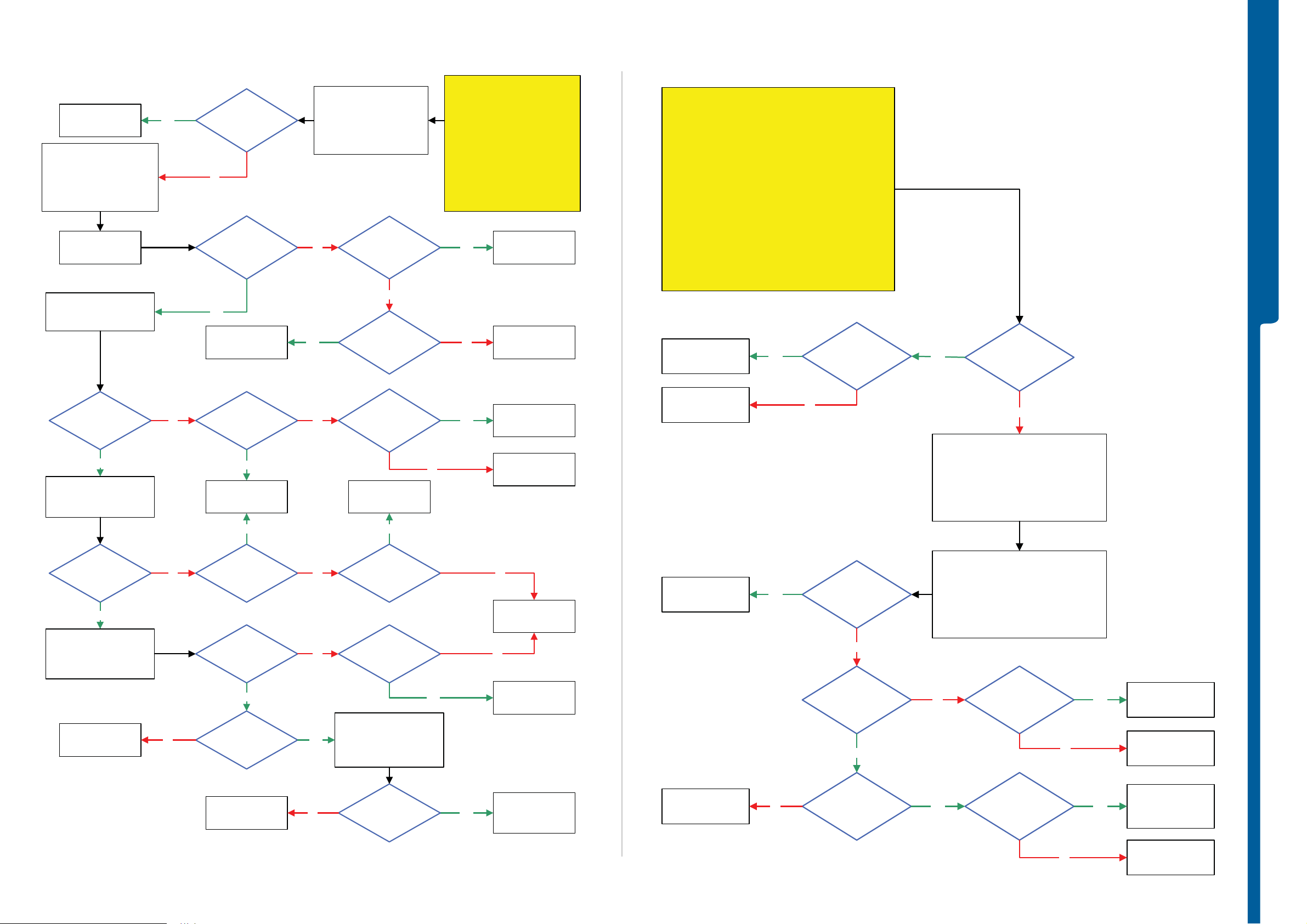
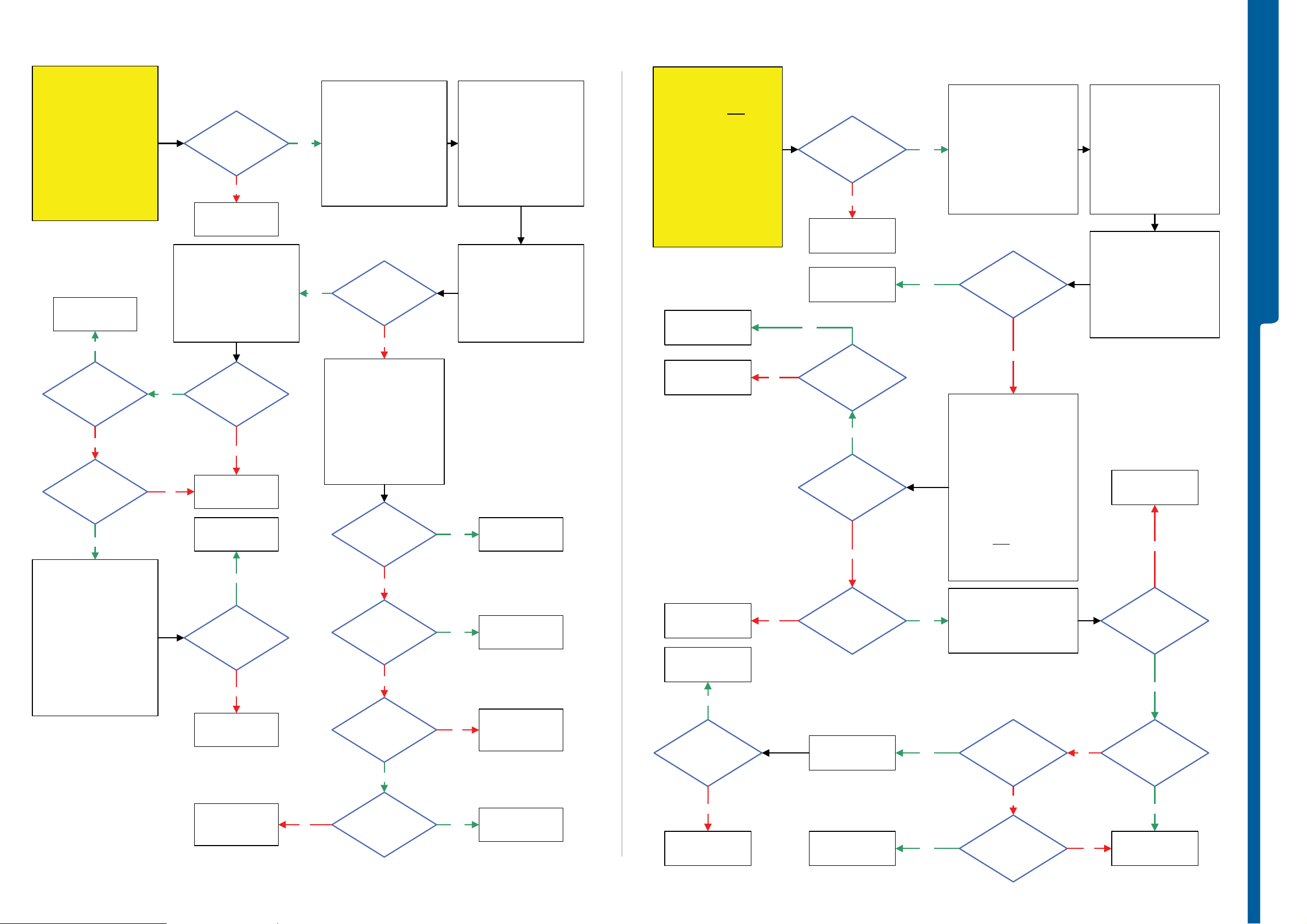
Power On/Off Problems - US B a nd S o ftware Flash Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Use
Dummy Battery
Connected to
Power Supply Channel 1
(VBATT)
No
Is the
phone consuming
any current when
powering on the
phone
Power On/Off Problems
Is the phone
consuming more than
1mA when the phone
is powered off
No
Is it possible to
power on the phone
Connect a chargerNo
Yes
Yes
Is it possible to power
off the phone
Is the phones
behavior as normal
Optimized
charging
Yes
No
Yes
Go to
Dead phone
Problems part 1
TRS guide
Go to
Current
Consumption Test
After this go to
Charging Test
Go to
On-Off Key Problems
TRS guide
START
Step 1:
Perform
System Connector Protectio n Test
If successful go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Go to
USB/VBUS
Charging Problems
USB and Software Flash Problems
Does the
Flash process
Start-up when using
EMMA SW
No
Use TRS Fixture
1: Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
2: Remove: DCIO/SEPI
3: Connect: USB Cable from the PC
Does
the Phone
Indicate charging
on the display
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
Is the
No
YesNo
ITP SW Flash
Successful
Is
MP X2405_Pin 10
Short circuit to the
PBA GND
(Shield
Can Fence)
Yes
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
V2415
Yes
Is the current
consumption between
10mA to 70mA
Yes
Flash
the phone with
correct CDA
software
No
Flash
the phone with
correct CDA
software
CDA Software
Flash
Successful
Yes
Yes
No
No
Go to
Dead Phone
Problems part 1
TRS guide
Press ”C”
Connect USB from PC
Run SEMC BOOT
if necessary
Run SUCR SW
Is Phone Flash
OK
No
Is the
Flash process
started
Yes
System Connector
Protection Test
No
After this go to
USB and Software
Flash Problems TRS
Go to
guide
SL 4 Replace
N2420
SL 5 Replace
R2442
No
5 Volt DC at
MP 6 (C2433)
Yes
2.7V – 3.3V DC
at MP 9 (C2436) and
1.8V DC at MP 7
(C2435)
Yes
Disconnect:
VBATT and USB Cable
Max
2 Ohm between
MP X2405_Pin 11 and
MP 10 (Z2400_Pin 3)
No
No
No
No
Is the
MP X2405_Pin 11
Short circuit to the PBA
GND (Shield
Can Fence)
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 8 (R2431)
Max
0.5 Ohm between
MP X2405_Pin 11 and
MP 13 (Z2400_Pin 2)
Yes
Yes
No
No
Replace
V2416
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2420
Replace
X2405
Flash
The phone with
ITP software.
Is the ITP Flash
Successful
No
Go to
USB and Software
Flash Problems
TRS guide
No
1. Customize the phone into DPY/Z
2. Startup the phone and wait for
the configuration to take place
(takes less than a minute)
3. Customize with correct CDA
4. Activate the phone
Is the Problem
solved
NoYes
Yes
Is the Problem
solved
Yes
Claim for a
SW Upgrade
SL 4 Replace
N2420
SL 5 Replace
N2010
Yes
Yes
Max
2 Ohm between
MP X2405_Pin 10 and
MP 12 (Z2400_Pin 4)
No
Max
0.5 Ohm between
MP X2405_Pin 10 and
MP 11 (Z2400_Pin 1)
Yes
No
Yes
1222-9526 rev. 1
Replace
Z2400
Replace
X2405
Replace
Z2400
8 (124)
Page 9
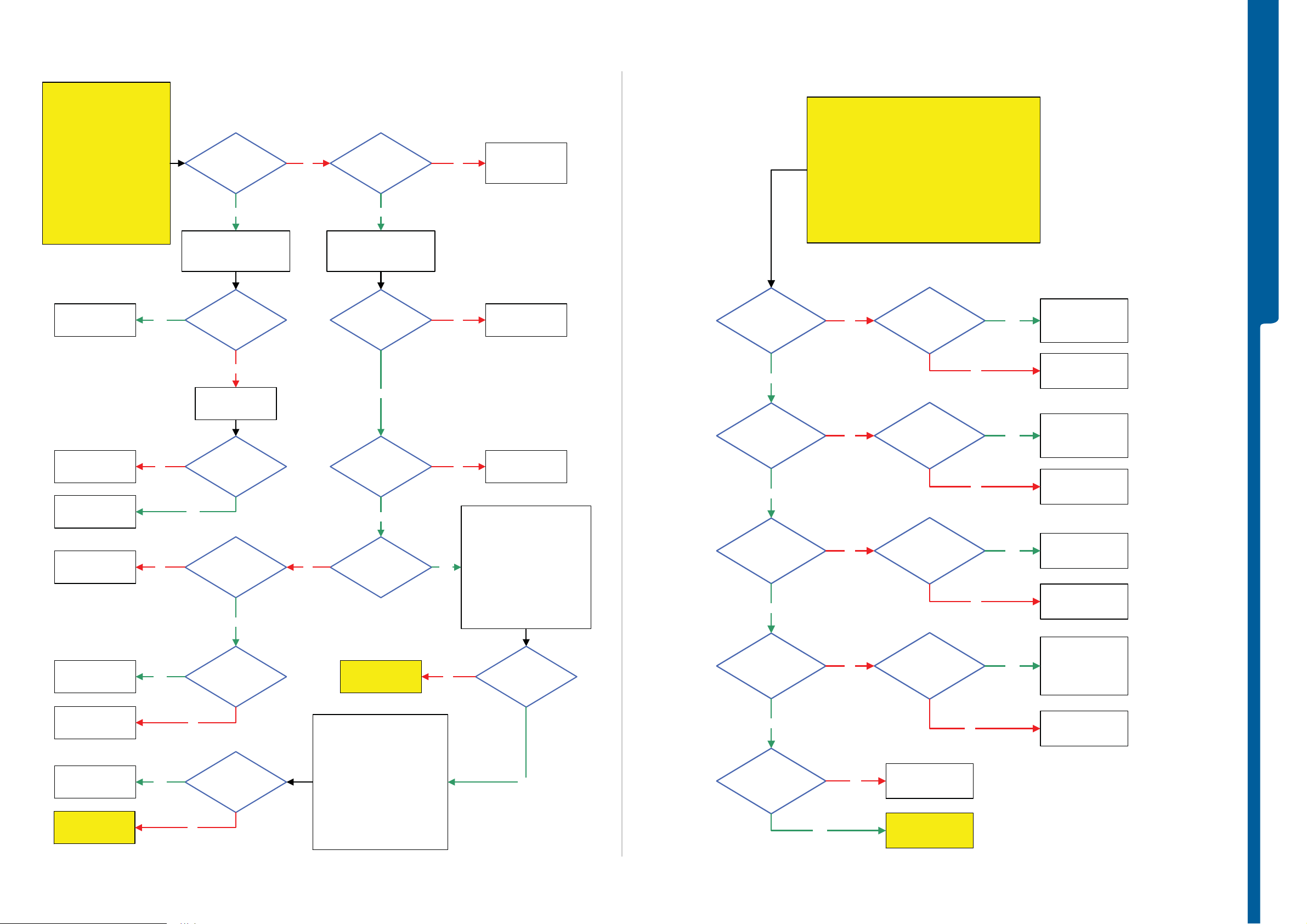
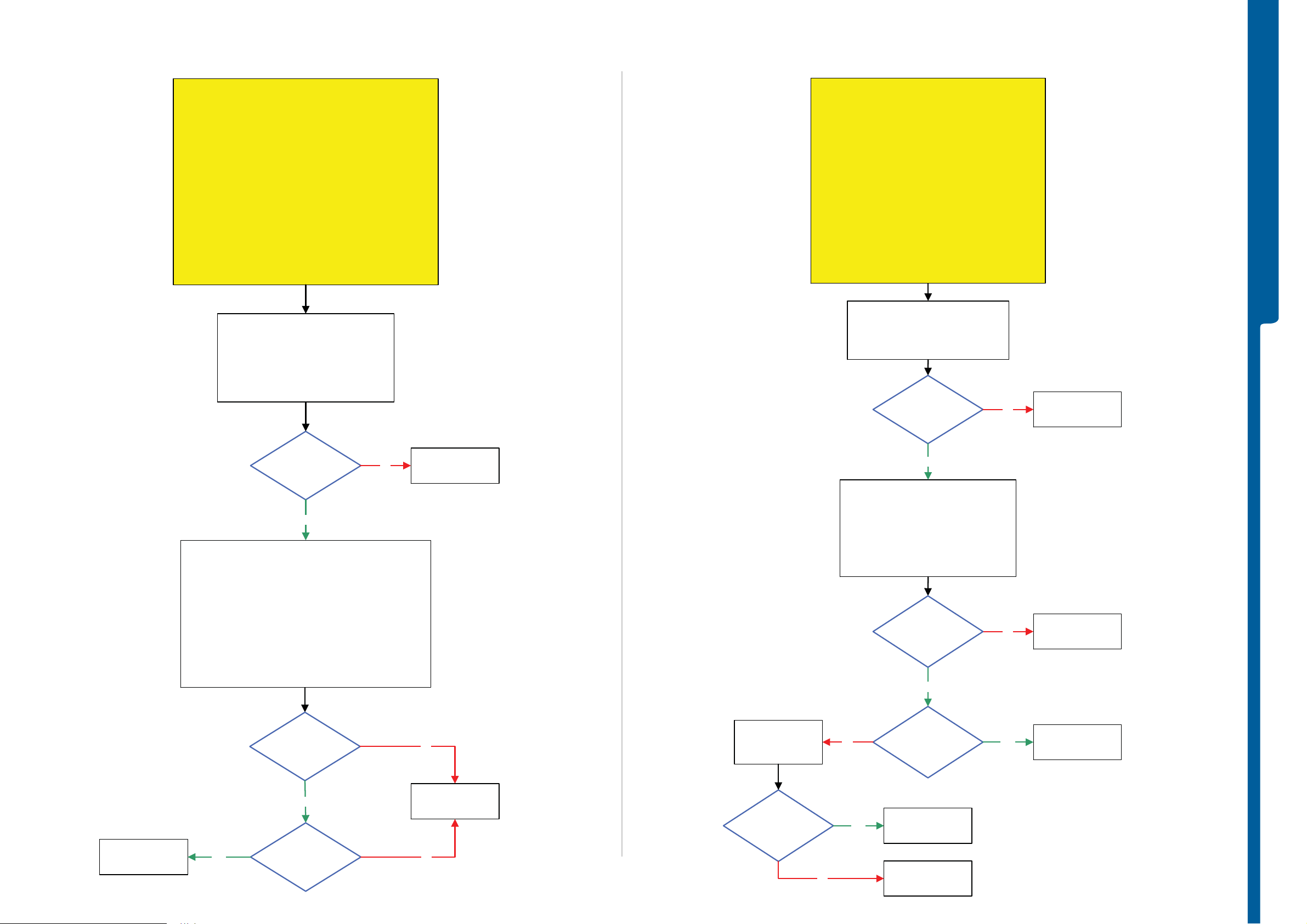
TROUBLESHOOTING
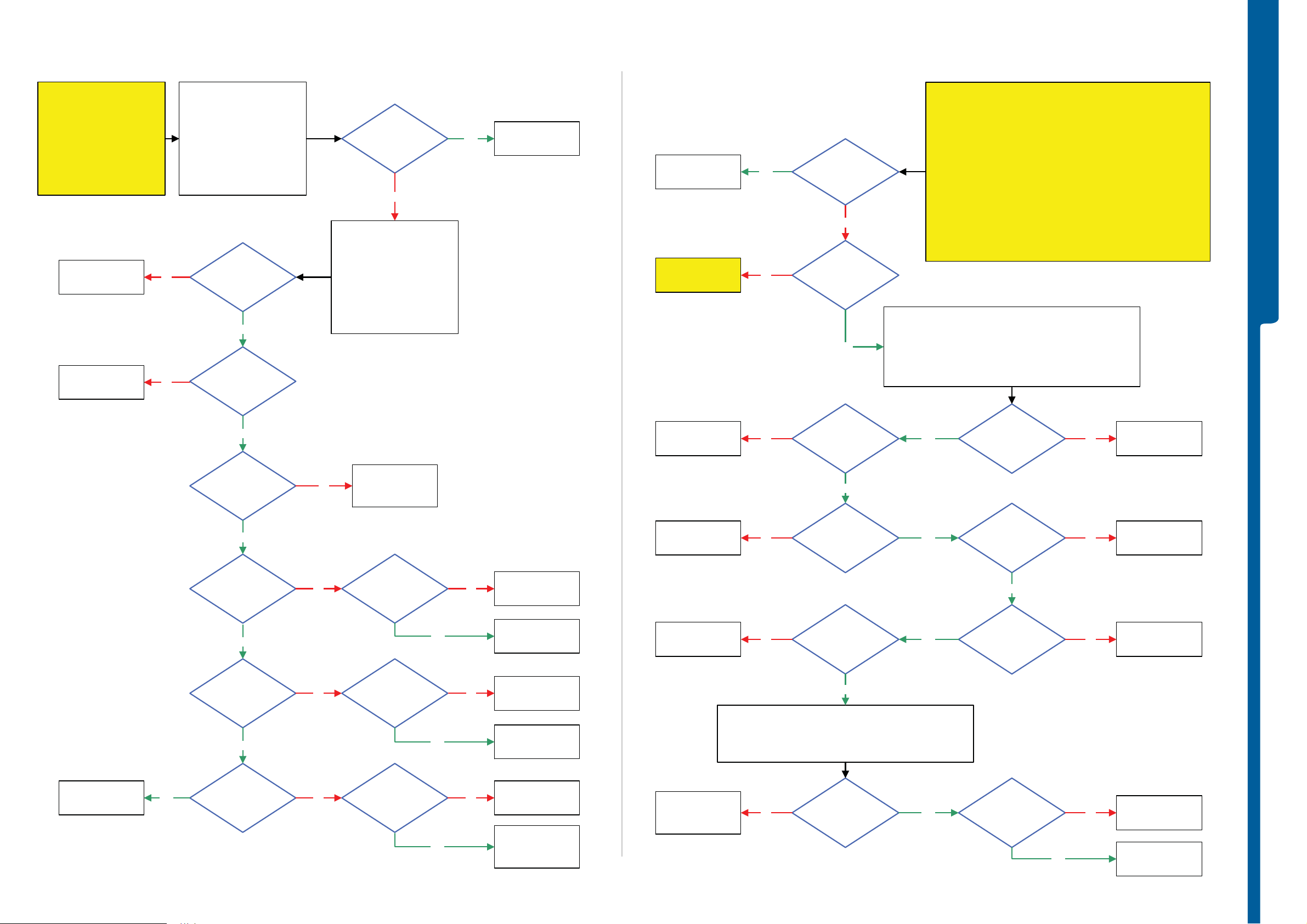
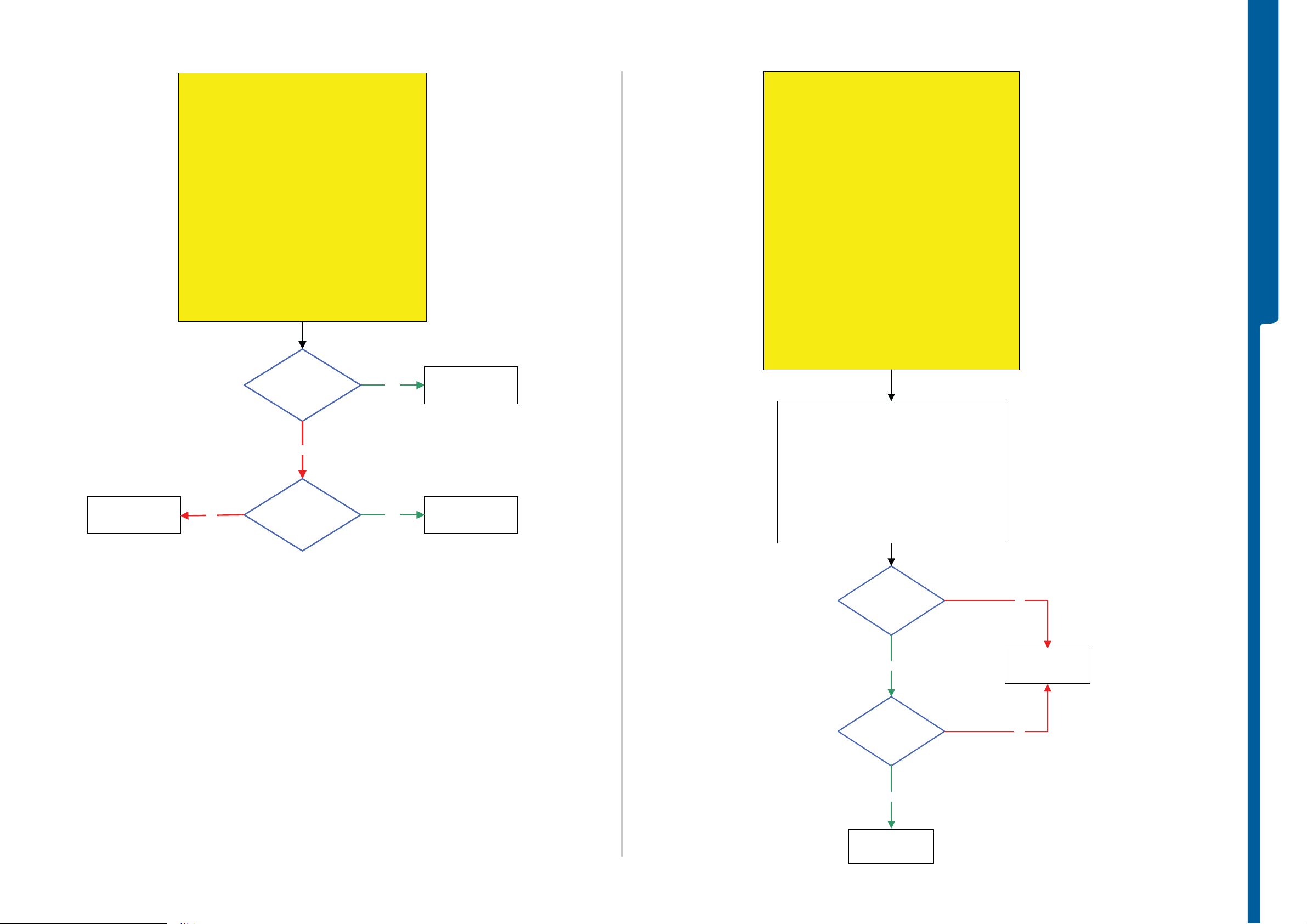
Dead Phone Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Try to recover the phone by using
Run SEMC BOOT if necessary
If successful claim SW Flash
If not continue with the step 2.
Try to trace Faulty
Component by using
Step 1:
EMMA SW
Press ”C”
Connect USB from PC
Run SUCR SW
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect Only: VBATT
Replace
N1200
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Freezing Spray
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
No
Dead Phone Problems part 1
Is the
current consumption
more than 1mA
Yes
Try to trace
Faulty Component
by using Freezing Spray
Is the
Radio Module
N1200 (Tiger)
getting hot
No
SL 5 Remove
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Is the
current consumption
still more than
1mA
Yes
1.8V DC
At MP 164
(ST2203 VDDE18) and 2.8V
DC at MP 163 (C1218
LDOA_OUT)
Yes
No
NoNo
Is the
connection between
MP 137 (X2201_Pin 3)
and PBA GND (Shield
Can Fence)
Ok
Yes
Connect:
DCIO/SEPI to the Phone
32 kHz at
MP 136 (C2100) and
MP 138 (C2101)
Yes
32 kHz
RTCCLK at
MP 135 (ST2104)
Yes
26 MHz
MCLK at
MP 38 (R2102)
SL 4 Replace
No
No
No
2.6V MP 125 (ST2201 VAUDIO26)
2.5V MP 165 (ST2202 VANA25)
Yes
2.7V MP 127 (ST2204 VBT27)
2.7V MP 126 (ST2205 VDIG)
2.6V MP 124 (ST2206 VBEAR26)
1.2V MP 116 (ST2209 VCORE12)
1.8V MP 40 (ST2225 VCORE18
X2201
SL 5 Replace
R2200
Replace
B2100
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Check the following
Voltages:
and VMEM18)
Is the
VAUDIO26
Voltage
Ok
Yes
Is the
VANA25
Voltage
Ok
Yes
Is the
VBT27
Voltage
Ok
Yes
Dead Phone Problems part 2
START
Before following this guide the
Dead Phone Problems part 1 TRS guide
No
No Yes
No
NOTE !
must be finishe d
Is any of
N2422 or N3103
getting hot
Is any of
N2200 or N2010
getting hot
Is N1300
getting hot
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
TROUBLESHOOTING
SL 4 Replace
N2422
SL 5 Replace
N3103
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
N2200
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N1300
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N1200
Replace
N1211
SL 5 Replace
N2020
SL 4 Escalate
Go to USB and
Software Flash
Problems TRS guide
Yes
Yes
at MP 65 (C1207)
(If C905c skip this
No
ITP SW Flash
No
2.8V DC
and replace
N1200)
Is the
Successful
Go to
Dead Phone
Problems part 2
Step 1:
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Step 2:
Connect:
Key Flex Assy and Slider FPC Assy
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT Only
Step 3:
Use EMMA SW
Press the ”C” key and Connect
USB Cable from the PC to the PBA
Flash the Phone with ITP SW
No
Is the
all Voltages
Ok
Yes
Is the
VDIG
Voltage
Ok
Yes
Is the
VBEAR26
Voltage
Ok
Yes
No
No
Is any of
N2411, N1300
N1500 or N1510 getting
hot. (Note: The N1500
is missing on
C905c)
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Go to
Dead Phone
Problems part 3
No
Yes
SL 4 Replace
N2411, N1300
or N1510
SL 5 Replace
N1500
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
9 (124)
Page 10
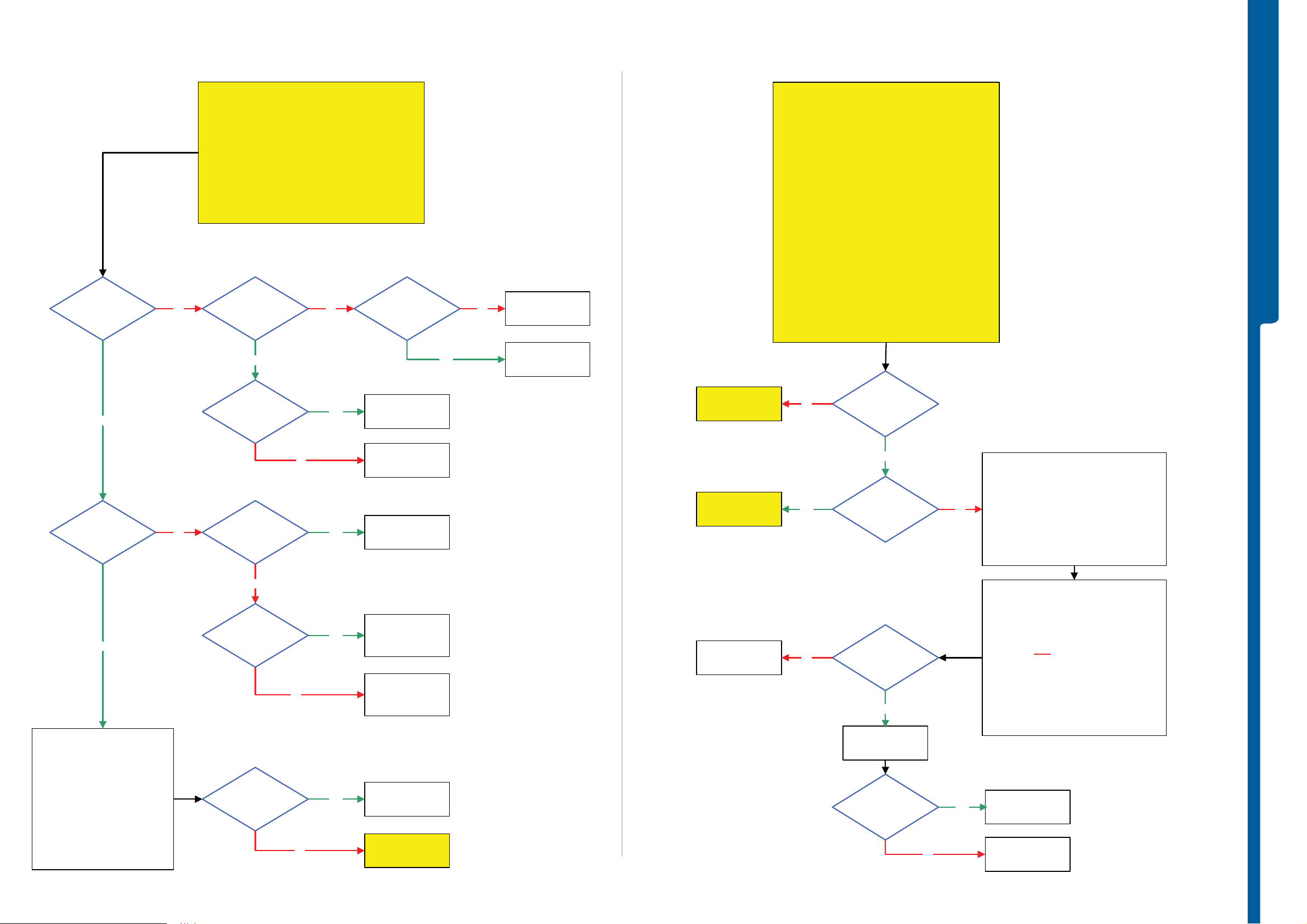
TROUBLESHOOTING
Dead Phone Problems - Display Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Is the
VCORE12
Voltage
Ok
No
Dead Phone Problems part 3
START
Before following this guide the
Dead Phone Problems part 2 TRS guide
1.1V – 1.2V DC
at MP 115
(V2201_Cathode)
Yes
NOTE !
must be finished
No
3.8 Volt DC at
MP 114 (L2201)
Yes
No
Replace
L2201
SL 5 Replace
V2201 or N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Display Problems
START
Step 1:
Flash the Phone with EMMA SUCR SW
If successful claim SW Flash
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
PBA Key Flex Flip, Slider FPC Assy and Display
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Display Pattern
Activate:
TV Test Pattern
If Display is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace
Display, PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If not then continue with
Display illumination Problems TRS guide
TROUBLESHOOTING
Yes
Is the
VCORE18/VMEM18
Voltage
Ok
Yes
Step 1:
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Step 2:
Connect:
Key Flex Assy and Slider FPC Assy
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT Only
Step 3:
Use EMMA SW
Press the ”C” key and Connect
USB Cable from the PC to the PBA
Flash the Phone with ITP SW
No
Is
MP 116 (ST2209)
Short circuit to the
PBA GND (Shield
Can Fence)
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 40 (ST2225)
No
Is
MP 40 (ST2225)
Short circuit to the
PBA GND
ITP SW Flash
(Shield
Can Fence)
Is the
Successful
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2000 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
L2200
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
N2200
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Replace
N2200
SL 5 Replace
L2202
SL 5 Replace
N2020
SL 4 Escalate
Go to USB and
Software Flash
Problems TRS guide
Go to
Dispaly illumination
Problems TRS guide
Go to
Opto Sensor
Problems TRS guide
Replace
Z4200, Z4201 or
Z4202
No
Yes
No
Is the
Display Backlights
Ok
Yes
Is the picture
too dark or
too light
Are all
Display Filters
Ok
Yes
Replace
X4200
Is the Display
Problem solved
No
Disconnect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI and
Remove PBA from the TRS Fixture
Use Digital Multimeter instrument (DMM)
No
Be very careful when you're cutting the
Shield Can Fence to avoid component damage
It is recommended to use microscope for these
Max 2 Ohm between the following pins:
Test 1 and 2 must be made on all filters
Yes
Claim Component
X4200
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
and perform:
Z4200, Z4201 and Z4202
Display Filter Test 1 and 2
NOTE !
measurements
Z4200, Z4201 and Z4202
Display Filter Test
Check if Pins: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
are NOT
Test 1:
short circuit to GND
Test 2:
Pin 1 and 5
Pin 2 and 6
Pin 3 and 7
Pin 4 and 8
NOTE !
1222-9526 rev. 1
10 (124)
Page 11
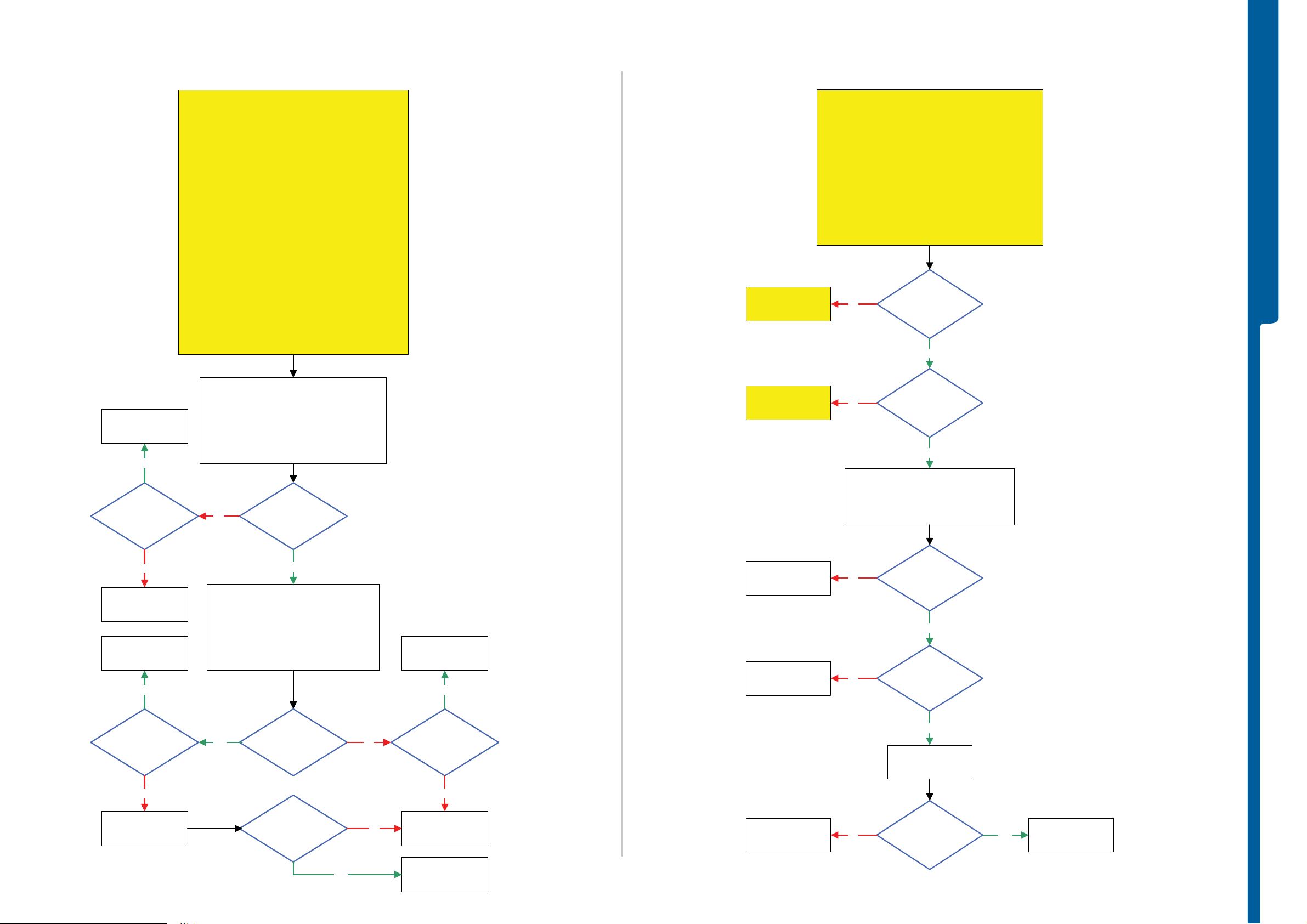
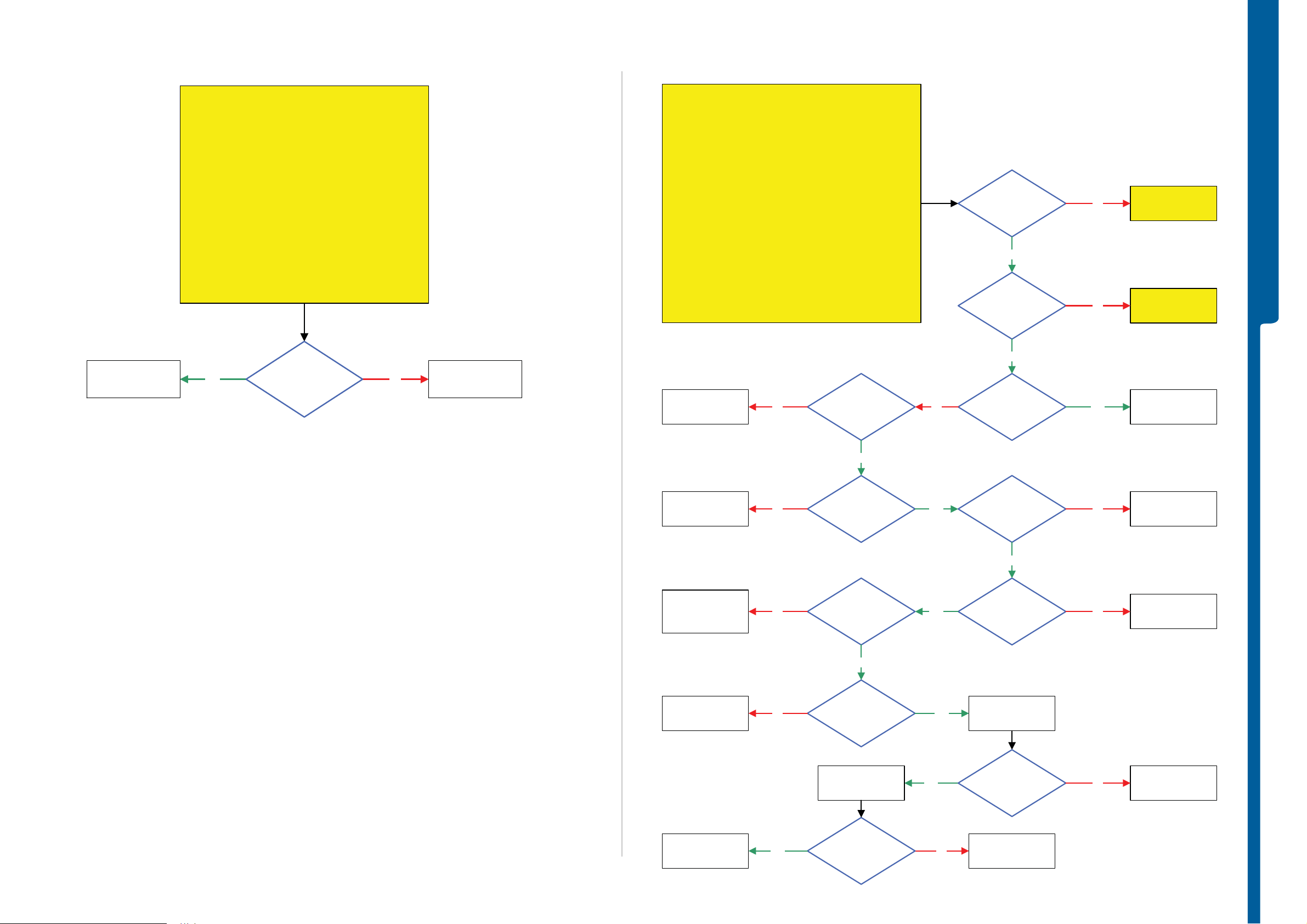
TROUBLESHOOTING Display Illumination Problems
- Opto Sensor Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Replace
V4201
Yes
Display Illumination Problems
START
Step 1:
Flash the Phone with EMMA SUCR SW
If successful claim SW Flash
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
PBA Key Flex Flip, Slider FPC Assy and Display
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Display Backlight
If Display Backlight is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace
Display, PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If not then continue with the
Display ilumination Problems TRS guide
1: Ues Fault trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Deactivate:
Display Backlight
2: Disconnect Slider FPC Assy from the PBA
Go to
Dispaly illumination
Problems TRS guide
Go to
Display Problems
TRS guide
Opto Sensor Problems
START
Replace PBA Key Flex Flip
If successful claim PBA Key Flex Flip
Replace Slider FPC Assy
If successful claim Slider FPC Assy
Opto Sensor Problems TRS guide
No
No
Step 1:
and retest the Phone
if not go to step 2.
Step 2:
and retest the Phone
if not continue with the
Is the
Display
Illumination (LEDs)
Ok
Yes
Can you see
any picture on
Display
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
3.7V - 3.8V DC
at MP 119
(V4201_Anode)
No
Replace
L4200
Replace
X4200
Yes
0 Volt DC at
MP 52 (TP4201)
No
No
Yes
3.7V - 3.8V DC
at MP 51 (TP4200)
Yes
Fault trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Display Backlight
17V - 20V DC at
MP 51 (TP4200)
No
Replace
V4200
Yes
More than
4 Volt DC
Pk-Pk Pulses
at MP 117
(V4200_Pin 3)
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2201
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 73 (R2217
No
No
OPTO_EN)
Shortly after phone
Power On
Yes
3 Volt
Pk-Pk Pulses at
MP 59 (TP2203
VOPTO30) Shortly after
phone Power On
Yes
Replace
X4200
Replace
V4203
Is the
Display illumination
Problem solved
Yes
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Claim Component
V4203
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No Yes
Is the
Opto Sensor Problem
solved
Claim Component
X4200
1222-9526 rev. 1
11 (124)
Page 12
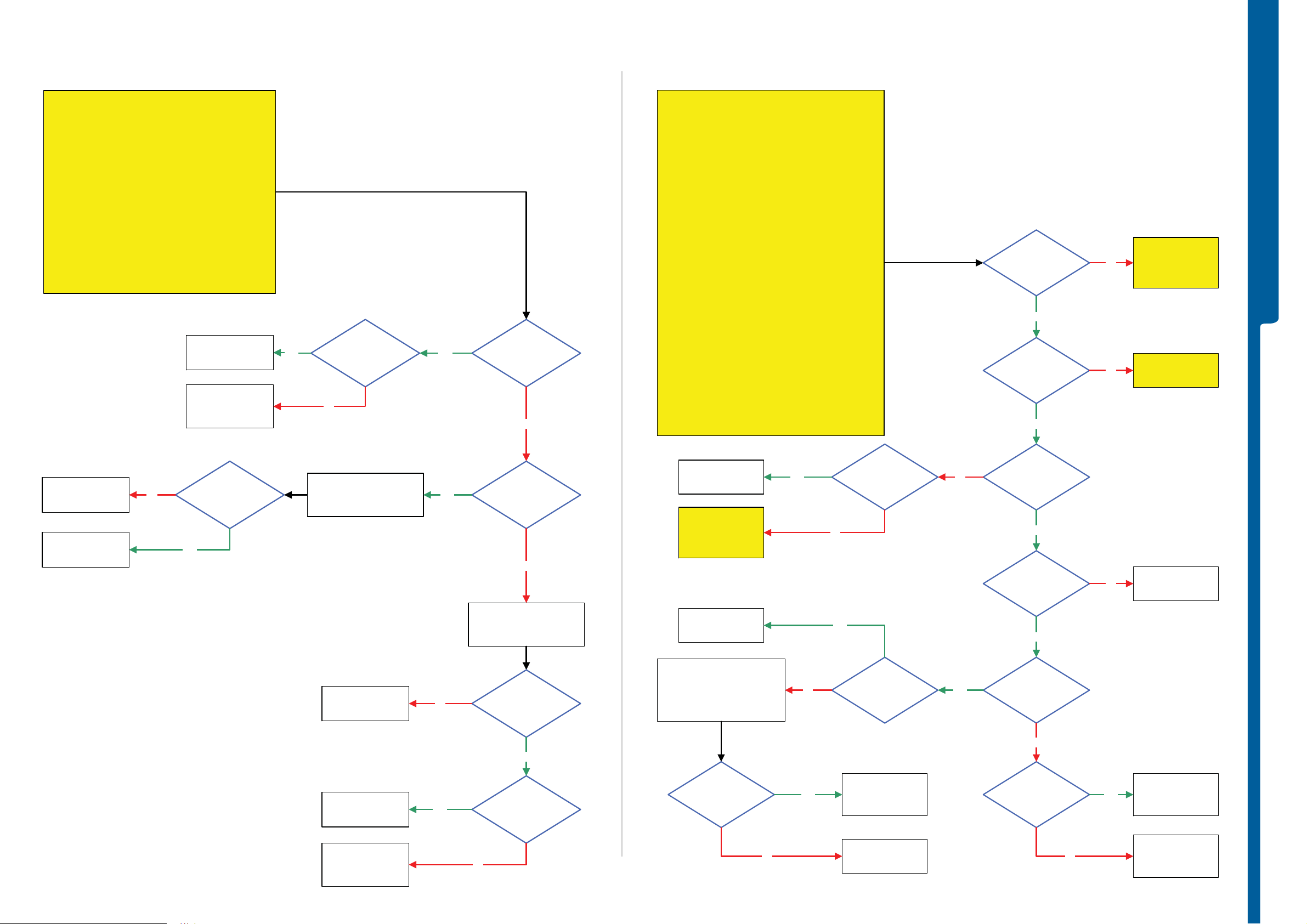
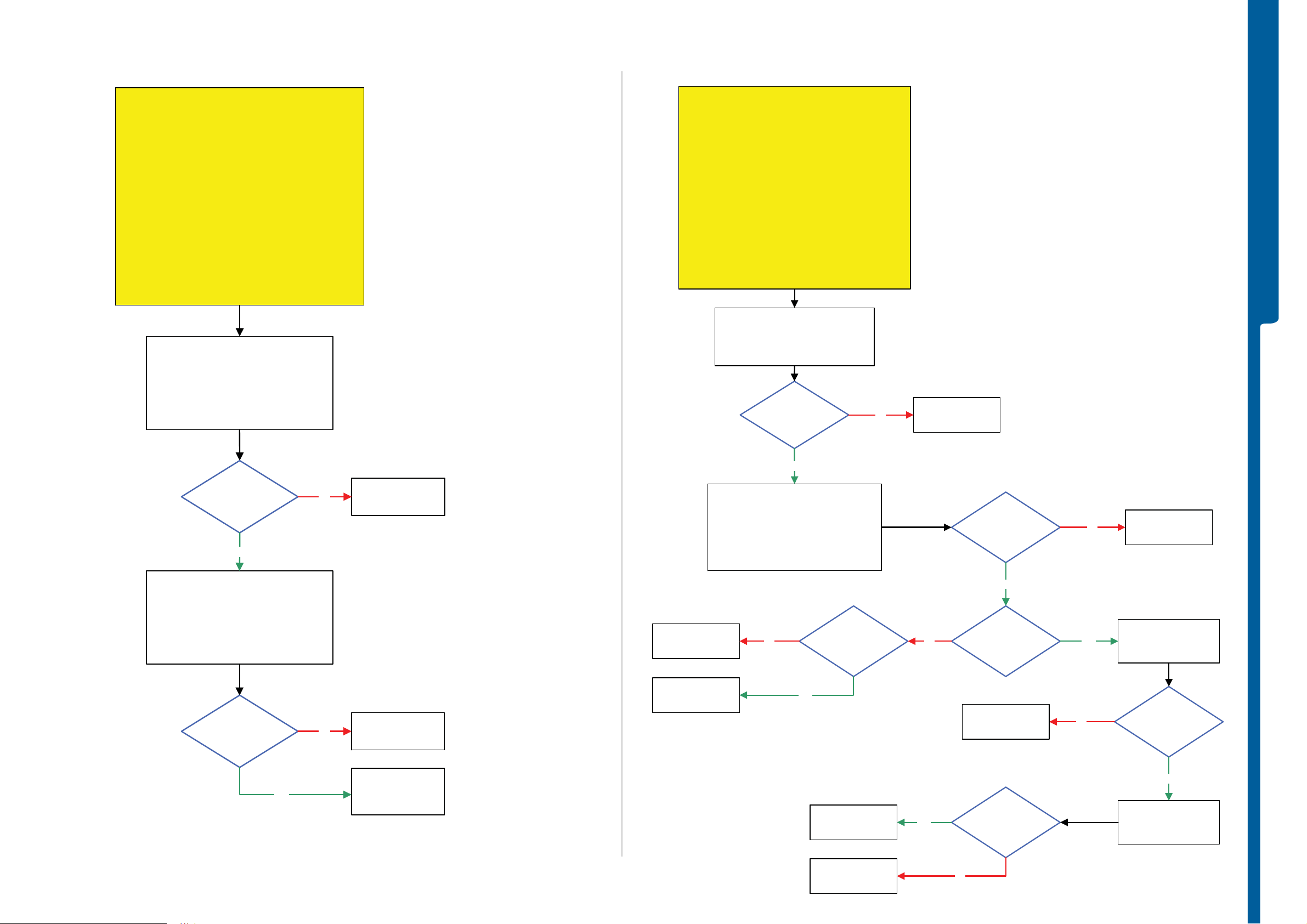
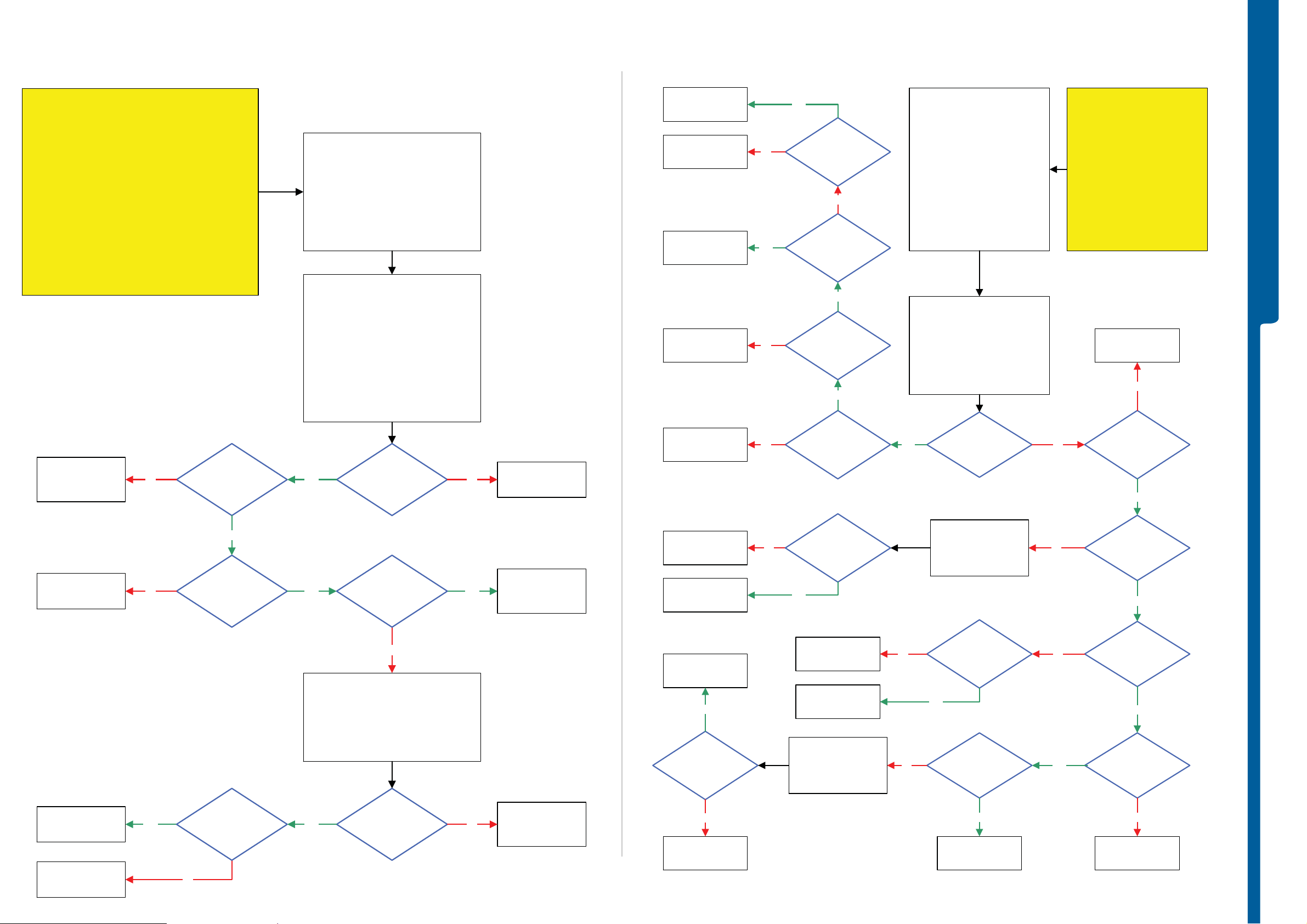
TROUBLESHOOTING On-O ff Key -
Numeric Keypad & Camera S n ap B u tt on Proble m s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Step 1:
Replace PBA Key Flex Flip and retest the Phone
If successful claim PBA Key Flex Flip
if not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Replace Slider FPC Assy and retest the Phone
If successful claim Slider FPC Assy
if not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Replace
V2470
SL 5 Replace
R2470, V2480 or
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
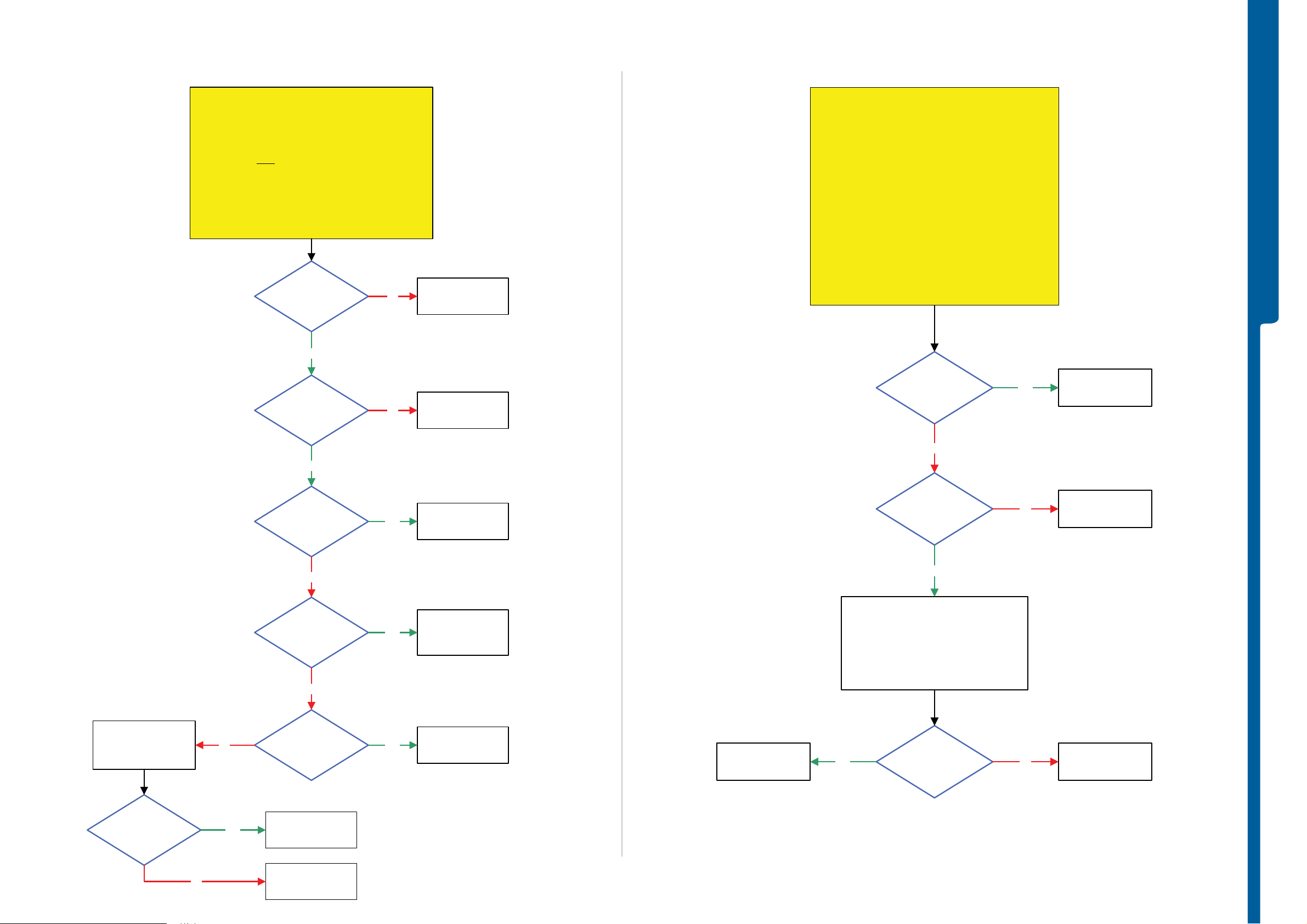
On-Off Key Problems
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 5 (R2470)
No
Yes
Is the
Problem with
Power Off
No
Numeric Keypad and Camera Snap Button Problems
START
Step 1:
If Problem with both Numeric and Navigation Keypads
go to step 3, if not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
Numeric Key Foil to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Activate
Keypad Scan Test
Perform Keypad Scan Test by pressing all
Keypads and Camera Snap Button on Numeric Key Foil
If successful then
Replace
Numeric Key Foil
If not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
Numeric Key Foil to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
and continue with the
Numeric Keypad and Camera Snap Button Problems
TRS guide
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 82 (S2415_Pin A) and
MP 88 (S2424_Pin A)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 96 (S2453_Pin A) and
MP 94 (S2454_Pin A)
Yes
Play and Mode (REC)
No
No
Button Problems
Up and Down Button
Problems TRS guide
TROUBLESHOOTING
Go to Camera
TRS guide
Go to Volume
Replace
X4200
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
0 Volt DC at
MP 60 (C2472)
Yes
Press the
On/Off Key
SL 5 Replace
R2470 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
Yes
3.7 Volt DC at
MP 60 (C2472)
No
Disconnect:
Slider FPC Assy
from the PBA
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 5 (R2470)
Yes
Replace
X2410 or X2411
Go to
Navigation Keypad
and Game A and B
Button Problems
TRS guide
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
1: Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
2: Disconnect:
Numeric Key Foil
from the PBA
Yes
No
Is the
problem with
Numeric Keypad and
Camera Snap
Button
No
Yes
0 Volt DC
when pressing
Key ”3" at MP 5 (R2470)
Key ”6" at MP 4 (R2471)
and Key ”1" at
MP 39 (R2472)
No
Yes
Is the
Problem with
both Numeric and
Navigation
Keypads
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 76
(V2481_Cathode)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 5 (R2470), MP 4
(R2471) and MP 39
(R2472)
No
No
SL 5 Replace
V2481
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
X4200
SL 4 Replace
V2470
SL 5 Replace
N2000
Yes
No
3.7 Volt DC at
MP 60 (C2472)
Is
MP 157 (C2461),
MP 158 (C2462), MP 159
(C2464) Short Circuit to GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
No
Yes
SL 5 Replace
V2486,
V2487 or V2484
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Is
MP 5 (R2470)
MP 4 (R2471), MP 39 (R2472)
Short Circuit to GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
No
SL 5 Replace
Yes
V2480,
V2473 or V2479
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
R2470, R2471 or
R2472
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
12 (124)
Page 13
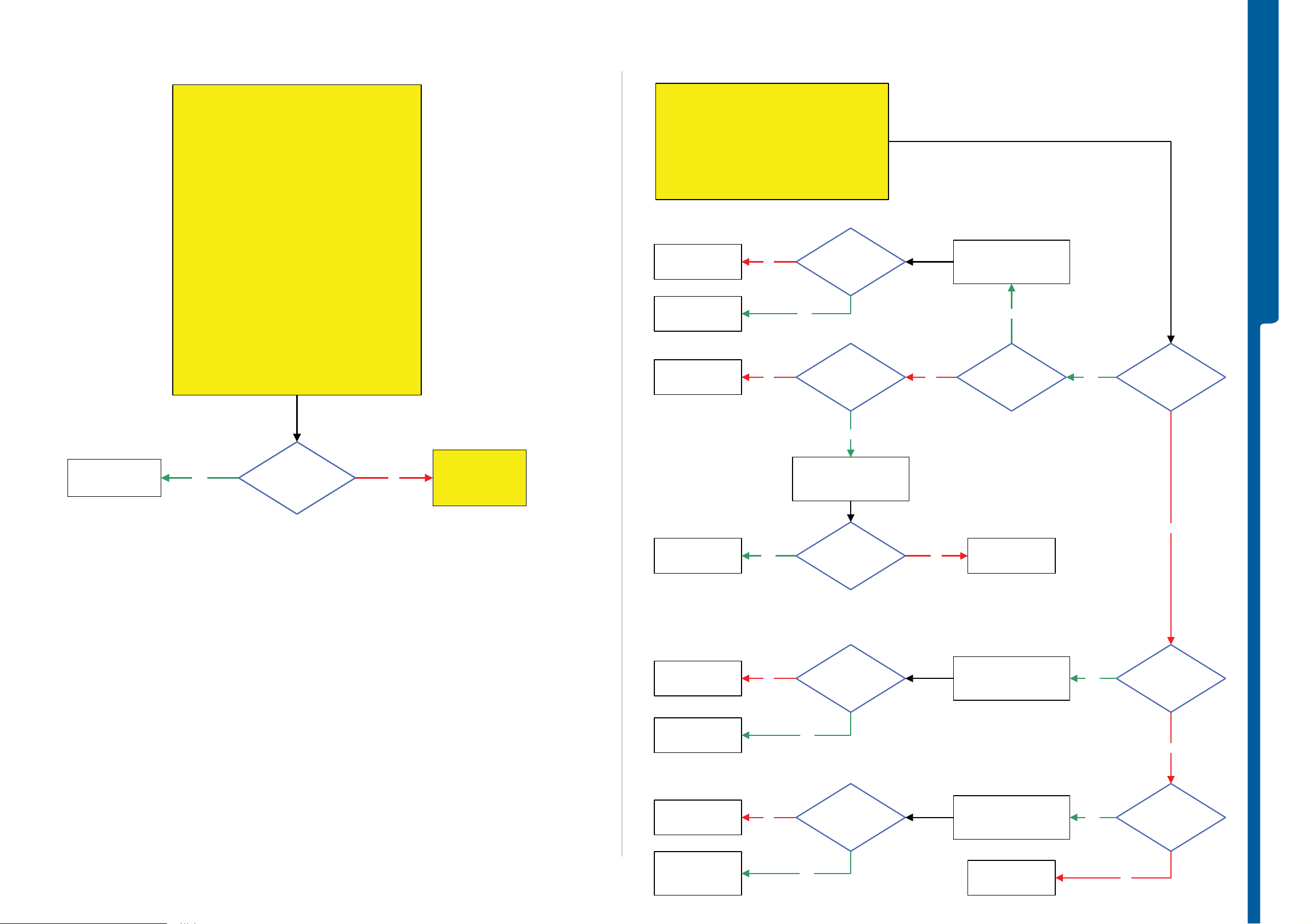
TROUBLESHOOTING
N avigat io n Keypad & Game B ut to n - Volume Butto n Proble m s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Navigation Keypad and Game A and B Button Problems
START
Step 1:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Activate
Keypad Scan Test
Perform Keypad Scan Test by pressing all Keypads and
Game A and B Buttons on Key Flex Flip Assy
If successful then
Replace
PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Continue with the
Navigation Keypad and Game A and B Button Problems
TRS guide
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Replace
S2453
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
R2473 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Volume Up and Down Button Problems
START
Use TRS Fixture
No
No No
0 Volt DC at
MP S2453_Pin A and
MP S2453_Pin B
Yes
Are
MP 96 (S2453_Pin A)
and MP 97 (S2453_Pin B)
short circuit to the PBA GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
Press the
S2453 Volume Up
Button
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 96 (S2453_Pin A) and
MP 97 (S2453_Pin B)
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
Is
the problem with
S2453 Volume Up
Button
Replace
X4200
Is the
Numeric Keypad
and Camera Snap
Button
Ok
Yes
Go to
NoYes
Numeric Keypad and
Camera Snap Button
Problems TRS guide
Remove the
S2453 Volume Up
Button
No
Are
SL 5 Replace
V2474 or V2478
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
S2454
Yes
No
MP 96 (S2453_Pin A)
and MP 97 (S2453_Pin B) still
short circuit to the PBA GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
0 Volt DC at
MP 94 (S2454_Pin A) and
MP 95 (S2454_Pin B)
No
Replace
S2453
Press the
S2454 Volume Down
Button
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 94 (S2454_Pin A) and
MP 95 (S2454_Pin B)
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
No
Replace
S2454 and S2424
SL 5 Replace
V2477,V2476
or V2472
SL 4 Escalate
No
Are
MP 94 (S2454_Pin A)
and MP 95 (S2454_Pin B) still
short circuit to the PBA GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
Yes
Remove the
S2454 Volume Down and
S2424 Camera Play
Buttons
SL 5 Replace
R2474 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
and MP 95 (S2454_Pin B)
short circuit to the PBA GND
No
1222-9526 rev. 1
Are
MP 94 (S2454_Pin A)
(Shield Can
Fence)
13 (124)
Page 14
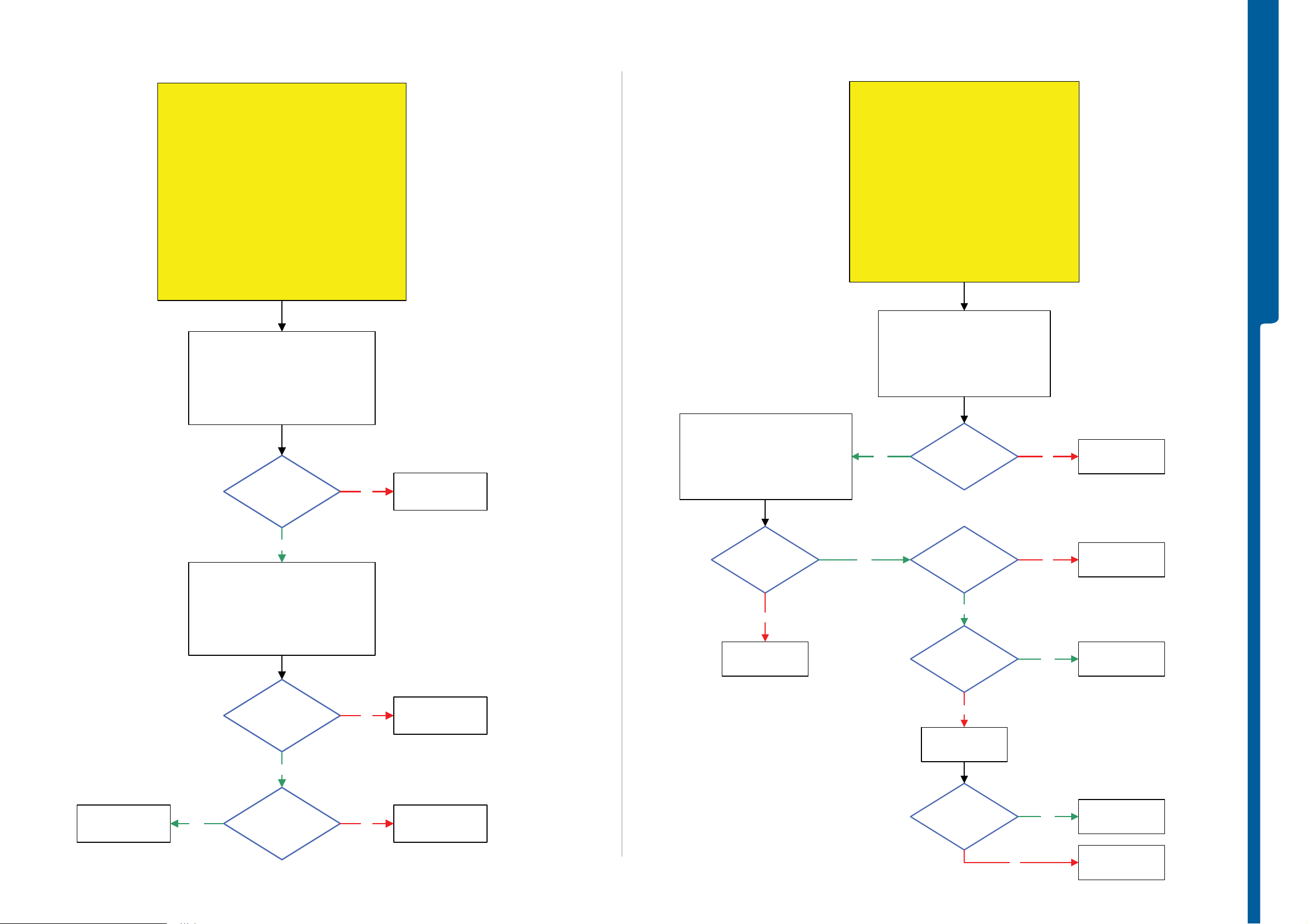
TROUBLESHOOTING Camera Play and Mode Button
- Numeric Keypad LED Proble ms
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
START
Use TRS Fixture
Yes
Camera Play and Mode (REC) Button Problems
Go to Volume
Up and Down Button
Problems TRS guide
0 Volt DC at
MP 82 (S2415_Pin A)
and MP 84
(S2415_Pin B)
S2415 Camera Mode (REC)
Press the
Button
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 96 (S2453_Pin A)
and MP 94
(S2454_Pin A)
Yes
Numeric Keypad LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Numeric Key Foil to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Keypad LED
If Keypad LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace Numeric Key Foil
If not then continue with the
Numeric Keypad LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Disconnect:
Numeric Key Foil
TROUBLESHOOTING
Replace
S2415
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
V2475 or V2471
SL 4 Escalate
No
Yes
No
Is the
MP 82
(S2415_Pin A)
and MP 84 (S2415_Pin B)
Short circuit to GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
Yes
Remove the
S2415 Camera Mode (REC)
Button
Is the
MP 82
(S2415_Pin A)
and MP 84 (S2415_Pin B)
still Short circuit to GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
No
No
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 82 (S2415_Pin A)
and MP 84
(S2415_Pin B)
Replace
S2415
No
Is there
a problem with
S2424 Camera Play
Button
Yes
Max 1 Ohm
between MP 74
(R4401) and MP 72
(C4401)
Yes
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Keypad LED
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400)
Yes
No
No
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N4400
Replace
S2424
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
0 Volt DC at
MP 88 (S2424_Pin A)
and MP 90
(S2424_Pin B)
Yes
Press the
S2424 Camera Play
Button
SL 5 Replace
V2482
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 88 (S2424_Pin A)
and MP 90
(S2424_Pin B)
No
Replace
X2410
Yes
Fault Trace SW
Deactivate:
Keypad LED
3.8 Volt DC
at MP 160 (C2473)
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
14 (124)
Page 15
TROUBLESHOOTING Navigation Keypad LED Problems
- Auto Focus LED Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Navigation Keypad LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Keypad LED
If Navigation Keypad LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace
PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If not then continue with the
Navigation Keypad LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Remove the PBA from the TRS Fixture
Auto Focus LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Flash Complete to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Auto Focus LED
If Auto Focus LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace Flash Complete
If not then continue with the
Auto Focus LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
TROUBLESHOOTING
Max 1 Ohm
between MP 74
(R4401) and MP 72
(C4401)
Yes
1: Cut the Shield Can Fence around the N4000, be very careful
to avoid component damage.
2: Use TRS Fixture
Connect: PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
3: Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Keypad LED
No
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
Max 1 Ohm
between MP 74
(R4401) and
MP 72 (C4401)
Yes
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Connect: Flash Complete to the PBA
Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Auto Focus LED
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400) when
Auto Focus LED is
Activated
Yes
No
No
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N4400
Replace
X4200
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400)
Yes
1.7V – 3V DC at
MP 78 (R4403), MP 77
(R4404), MP 75 (R4405)
and MP 79 (R4406)
No
NoYes
Replace
N4400
SL 4 Replace
N4400
SL 5 Replace
L4401
Is the
Problem solved
No
Yes
1.4V - 1.5V DC
at MP 93 (TP4401)
when Auto Focus LED
is Activated
Claim Component
N4400
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
YesNo
Replace
X4400
1222-9526 rev. 1
15 (124)
Page 16
TROUBLESHOOTING Back Side LED Problems
- Tally LED Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Back-Side LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Flash Complete to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Back-Side LED
If the Back-Side LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace Flash Complete
If not then continue with the
Back-Side LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Disconnect:
Flash Complete from the PBA
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Flash Complete to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Tally LED
If Tally LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace Flash Complete
If not continue with the
Tally LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Max 1 Ohm
between
MP 74 (R4401) and
MP 72 (C4401)
Tally LED Problems
SL 5 Replace
No
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
TROUBLESHOOTING
Max
1 Ohm between
MP 74 (R4401) and
MP 72 (C4401)
Yes
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Restart Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Back-Side LED
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400) when
Back-Side LED
is Activated
Yes
No
No
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N4400
SL 4 Replace
X4400
SL 5 Replace
N2000
Replace
N2410
SL 5 Replace
V4400
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Tally LED
No
and MP 148 (V4400_Pin 3)
Yes
Is
any of
MP 134 (V4400_Pin 1)
Short circuit to
PBA GND (Shield
Can Fence)
Replace
X4400
Yes
No
5 Volt DC
at MP 56 (TP4400)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 134
(V4400_Pin 1)
SL 5 Replace
V4400
SL 4 Escalate
0 Volt DC
at MP 148
(V4400_Pin 3)
No
Yes
No
Replace
N4400
Fault Trace SW:
Deactivate
Tally LED
2V – 2.5 Volt DC
at MP 148
(V4400_Pin 3)
Yes
Fault Trace SW:
Activate
Tally LED
SL 5 Replace
V4400
SL 4 Escalate
No
1222-9526 rev. 1
16 (124)
Page 17
TROUBLESHOOTING Camera Snap Button LED
- Camera Navigation LE D Proble m s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Camera Snap Button LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Numeric Key Foil to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Camera LED
If Camera Snap Button LED is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace Numeric Key Foil
If not then continue with the
Camera Snap Button LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Disconnect:
Numeric Key Foil
Camera Navigation LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy
to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Camera LED
If Camera Navigation LEDs is working on the TRS Fixture
then Replace
PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If not then continue with
Camera Navigation LED Problems TRS guide
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Disconnect:
PBA Key Flex Flip and Slider FPC Assy
from the PBA
TROUBLESHOOTING
Max
1 Ohm
between
MP 74 (R4401) and
MP 72 (C4401)
Yes
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Camera LED
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400) when
the Camera LED is
Activated
Yes
No
No
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N4400
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Restart the Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Camera LED
5 Volt DC at
MP 56 (TP4400) when
Camera LED is
Activated
No
Replace
N4400
Yes
Max 1 Ohm
between
MP 74 (R4401) and
MP 72 (C4401)
0 Volt DC
at MP 92 (C4215) and
MP 86 (C4217) when
Camera LED is
Activated
Yes
0 Volt DC
at MP 89 (C4218)
when Camera LED is
Activated
No
SL 5 Replace
V4208
SL 4 Escalate
NoYes
No
Yes
SL 5 Replace
L4400
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
X4200
Replace
X2410
Yes
0 Volt DC
at MP 161 (C2474)
when the Camera LED
is Activated
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Is
the Camera
Navigation LED
Problem solved
No
Yes
Claim Component
V4208
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
17 (124)
Page 18
TROUBLESHOOTING Trickle Charge LED Problems
- Xenon Flash Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Trickle Charge LED Problems
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Trickle Charge LED Problems TRS guide
No Yes
Use TRS Fixture
Use Fault Trace SW
Continue with the
Fault Trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Charge LED
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 118
(V4206_Anode)
Replace
V4206
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
Go to Camera
Problems TRS guide
Xenon Flash Problems
Is the
Yes
No
Flash Complete and Camera 8MP to the PBA
Xenon Flash Test
Ok
No
Is the
Camera working
properly
Yes
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Fault Trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Xenon Flash Test
Disconnect:
Flash Complete
Fault Trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Led and Backlight
Activate:
Xenon Flash Test
START
Step 1:
Replace Flash Complete
and retest the Phone
If successful claim
Flash Complete
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use Dummy Battery connected to the
Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Connect: DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
TROUBLESHOOTING
1.8V – 2V DC
at MP 149 (R4304)
Yes
Is
MP 133 (X4410)
connected to the PBA
(Shield Can
GND
Fence)
Yes
Replace
X4400
No
No
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 87 (R4303)
Replace
X4410
Is the
Xenon Flash
Problem solved
Yes
Yes
No
No
Replace
N2410
SL 5 Replace
N4300
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
N2410
SL 5 Replace
N2010
Claim Component
X4400
1222-9526 rev. 1
18 (124)
Page 19
TROUBLESHOOTING Multimedia Combo Chip Problems
- Camera Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use Dummy Battery connected
to Power Supply Channel 1
(VBATT)
Connect: DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2500
No
No
Multimedia Combo Chip Problems
Fault Trace SW
General
Selftest
Run N2500 Selftest
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 68 (R2502
VIDCC_RESn)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 71 (SP2505
VIDCC_L1DET)
2: Use Fault trace SW and go to:
N2500 Selftest
1: Use TRS Fixture
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Init Screen Testing
Multimedia Chip
Is the
Test result
0x0
No
Connect:
MMI
Misc
Activate:
Flash the Phone with
Yes
EMMA SUCR SW
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
Go to Multimedia
Combo Chip
Problems TRS guide
Yes
No
Is the
Camera working
Properly
No
Is the
Multimedia Combo
Chip Problems TRS
guide done
Yes
Camera Problems
START
Step 1:
Replace Camera 8MP and retest the Phone
If successful claim Camera 8MP
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use Dummy Battery connected to the Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Connect: DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Activate:
Camera Test
1: Use TRS Fixture
Connect: Camera 8MP to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
2: Use Fault trace SW and go to:
MMI, Misc, Init Screen Testing and Activate: Camera Test
TROUBLESHOOTING
Yes
26 MHZ
at MP 20 (ST2109
VIDCC_CLK)
Yes
1.2 Volt DC
at MP 69 (ST2226
VDD_L1)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 42 (ST2229
VSDR18)
Yes
No
No
No
SL 4 Replace
N2500
SL 5 Replace
N2102
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 70 (R2215
VIDCC_L1_EN)
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 67 (R2223
VIDCC_SDR_EN)
Yes
Yes
No
No
Replace
N2500
SL 5 Replace
N2210
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2500
SL 5 Replace
N2214
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2205
Replace
N2206
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
No
No
Deactivate Camera Test and go to:
General, Selftest and Run N2500 Selftest
2.8 Volt DC
at MP 131 (TP2210
VCAMAF28)
Yes
1.8V DC at
MP 130 (TP2208
VCAMSD18) and
2.8V DC at MP 128 (TP2209
VCAMSA28)
13 MHz at
MP 37 (ST2110
CAMSYSCLK)
Yes
Fault Trace SW
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 64 (R2210) and
MP 129 (N2206_Pin 6)
1.8 Volt DC at
Yes No
Yes
MP 54 (TP2206
VCAMIO18)
Yes
1.2 Volt DC
at MP 132 (TP2207
VCAML12)
NoYes
No
Replace
N2500
SL 5 Replace
V2212
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N2213
SL 5 Replace
N2010 or N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
1.2 Volt DC
at MP 66 (ST2228
VDD_L0)
No
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 36 (C2104
PWRRSTn)
Yes
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
N2212
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Replace
N2500
SL 5 Replace
N2010
Is the
No Yes
N2500 Selftest
Test result
0x0
Is the any of
X4311, X4312, X4313,
X4314 or X4315
damaged
Yes
No
Faulty Component
1222-9526 rev. 1
Replace
X4300
Replace
19 (124)
Page 20
TROUBLESHOOTING Camera Cover Detect Problems
- TV Out Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Camera Cover Detect Problems
START
Step 1:
Replace Flash Complete
and retest the Phone
If successful claim Flash Complete
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect Flash Complete to the PBA
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Continue with the
Camera Cover Detect Problems TRS guide
NOTE !
Camera Cover Detect Switch is mounted on
Flash Complete
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 41 (R4410)
when Camera Cover
Detect Switch is
Pressed-On
TV OUT Problems
START
Be very careful when you cut the Shield Can Fence
around the N2700 component to avoid component damage
Flash the Phone with EMMA SUCR SW
If successful claim SW Flash
Load ITP SW into the Phone
PBA Key Flex Flip, Slider FPC Assy and Display to the PBA
NoYes
Replace
X4400
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
NOTE !
Step 1:
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Display Pattern
Activate:
TV Test Pattern
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 61 (R2228)
No
Is the
Display Backlights
Ok
Yes
Is the
Display
Ok
Yes
Is the
MP X2405_Pin 7
Short circuit to the
PBA GND
(Shield
Can Fence)
No
No
Yes
Go to
Dispaly illumination
Problems TRS guide
Go to
Display Problems
TRS guide
Replace
V2414
TROUBLESHOOTING
Replace
N2209
SL 4 Replace
N2410
SL 5 Replace
N2102
Replace
N2700
No
No
No
Yes
1.5 Volt DC at
MP 18 (ST2232
VTV15)
26 MHz at
MP 19 (ST2108
TV_CLK)
Yes
0.9V – 1V
Pk-Pk Pulses at
MP 14 (L2405)
Replace
X2405
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 17 (R2214
VTV30_EN)
Yes
3 Volt DC at
MP 15 (ST2233
VTV30)
Disconnect:
VBATT and
DCIO/SEPI
Is
R2443 = Max 0.5 Ohm
No
No
No
Replace
N2700
Replace
N2208
Replace
R2443
Claim Component
X2405
Yes
Is the
TV OUT
Problem solved
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
20 (124)
Page 21
TROUBLESHOOTING Charging Problems
- USB/ V BUS Cha rg in g Proble ms
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Charging Problems
START
Step 1:
Perform Charging Test
successful go to step 2.
If NOT
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
3.8 Volt DC at
MP 33 (TP2201)
Yes
Is the
connection
between MP 139
(ST2211) and MP 141
(ST2212)
Ok
Yes
No
No
Replace
X2201
SL 5 Replace
R2200
SL 4 Escalate
USB/VBUS Charging Problems
START
Perform System Connector Protection Test
If successful go to step 2.
Use Phone with Normal SW (SSW)
Use TRS Fixture and connect: VBATT
Connect: USB Cable from the PC to the Phone
Step 1:
Step 2:
5V – 5.2V DC at
MP 16 (ST2213)
No
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
No
Is
MP 31 (TP2202)
Short circuit to PBA
GND (Shield
Can Fence)
No
5 Volt DC at
MP 113
(V2412_Cathode)
No
Is MP 113
(V2412_Cathode)
Short circuit to PBA
GND (Shield
Can Fence)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Replace
V2200
SL 4 Replace
V2202
SL 5 Replace
N2000
Replace
V2412
Replace
N2421
Yes
5V – 5.2V DC at
MP X2405_Pin 1
Yes
Disconnect:
VBATT and USB Cable
Is
L2407 = Max 1 Ohm
No
No
Replace
X2405
Replace
L2407
L2449 = Max 1 Ohm
Is
No
Yes
Replace
X2405
SL 5 Replace
L2449
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
21 (124)
Page 22
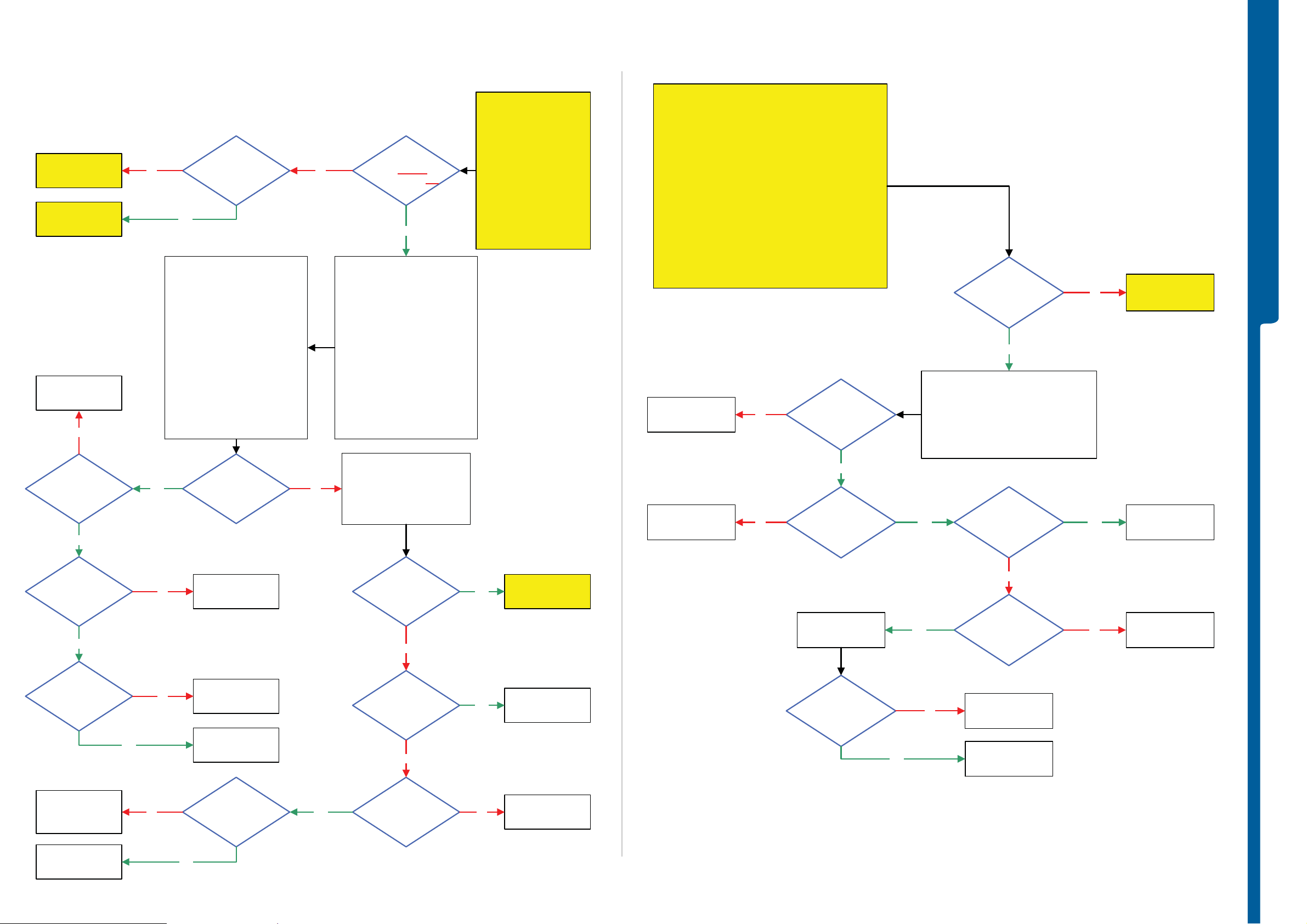
TROUBLESHOOTING SIM Problems
- Memory Stick Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
Remove Test SIM
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
Logic
SIM Card control
Activate:
SIMVCC
SIMVCC On
Activate:
SIMCONRST
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 153 (X2402_Pin 2)
Yes
No
SIM Problems
Is the
Sim Com Test
Passed
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 155 (X2402_Pin 1)
Yes
SL 5 Replace
C2414 or C2420
SL 4 Escalate
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 152 (C2419)
Yes
No
No
Fault Trace SW
Logic
SIM Card control
Activate:
SIM Com Test
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 156 (C2420)
No
Is any of
C2414 or C2420
Short circuit
Is C2419
Short circuit
START
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Dummy Battery connected to
Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Yes
No
Yes
Step 1:
Step 2:
Insert Test SIM
Connect:
and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Replace
X2402
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
C2419
SL 4 Escalate
START
NOTE !
SL 4 may only Repair X2401 on the C905c Phones
If there is a problem with X2401
on C905 or C905a Phones
SL 4 Escalate to SL 5
Replace
X2401
SL 5 Replace
X2401
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
No
Is this a
C905c phone
Memory Stick Problems
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
Is X2401
damaged
No
Yes
SIMVCC On
SIMCONRST On
Activate:
SIMCONCLK
0.9V-1V DC at
MP 151 (X2402_Pin 3)
Yes
SIMVCC On
SIMCONRST On
SIMCONCLK On
Activate:
SIMCONDAT
Replace
X2402
No
No
Yes
Replace
X2402
Yes
1MHz and
1.8 Volt Pk-Pk at
MP 107 (ST2410)
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 105 (ST2411)
Yes
Is
MP 154 (X2402_Pin 5)
Connected to
PBA GND
No
No
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
1MHz and
1.8V-2.2V Pk-Pk at
MP 34 (SP2410)
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 106 (C2413)
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
No
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2000 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
Yes
Is the
Memory Stick Test
Passed
No
0 Volt DC at
MP35 (R2422
MSDETECT)
Yes
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Insert Memory M2 Card
Use TRS Fixture
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Fault trace SW
SIM Card control
Memory Stick Test
No
C905c phone
Connect:
Logic
Activate:
Is this a
No
Yes
Replace
X2401
SL 5 Replace
X2401
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
R2416
SL 4 Escalate
No
8 Kohm
between
MP 155 (X2402_Pin 1)
(Red Probe) and
MP 150 (X2402_Pin 7)
(Black Probe)
Yes
SL 4 Replace
X2402
SL 5 Replace
N2000 or N2010
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 162 (ST2200
VMC18)
Yes
Is this a
C905c phone
No
SL 4 Replace
Yes
SL 5 Replace
SL 5 Replace
X2401 or N2010
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
X2401
N2010
22 (124)
Page 23
Primary and Secondary Mic Problems
TROUBLESHOOTING Primary & Second ary Mic Problem s
Ear Speaker Problems
- Ear Speaker Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Replace
X4400
START
Step 1:
Replace PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If successful claim PBA Key Flex Flip or Slider FPC Assy
If Secondary Mic problems replace Flash Complete and
Primary and Secondary Mic Problems TRS guide
No
If Primary Mic problem
and retest the Phone
If not go to step 3.
Step 2:
retest the phone
If successful claim Flash Complete
If not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Continue with the
Is the
problem with
both Primary and
Secondary
Mic
No
Is the
problem with
Primary Mic
Yes
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
X4200
START
Step 1:
Replace Ear Speaker
and retest the Phone
If successful claim Ear Speaker
If not then go to step 2.
Step 2:
Replace PBA Key Flex Flip
If successful claim PBA Key Flex Flip
If not then go to step 3.
Step 3:
Replace Slider FPC Assy
If successful claim Slider FPC Assy
If not then go to step 4.
Step 4:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Use Hands-Free (PHF) and
continue with the
Ear Speaker Problems TRS guide
1: Fault Trace SW
Audio and FM Radio
Audio Loop Test
Audio Input: AUX1
Loop Mode: Analog
Audio Output:
Ear Speaker
Apply Audio Loop
2: Remove the DCIO/SEPI Cable from the PBA
and Insert the Hands-Free (PHF) set to the PBA
TROUBLESHOOTING
2.6 Volt DC
at MP 125 (ST2201)
and MP 124 (ST2206)
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-Pk
at MP 58 (C3159_Side A) and
MP 57 (C3159_Side B)
when blowing into
PHF mic
Yes
Replace
X4200
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
1222-9526 rev. 1
23 (124)
Page 24
TROUBLESHOOTING Loudspeaker Problems
- Handsfree (PHF) Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Step 1:
Replace Loudspeaker Assembly
and retest the Phone
If successful claim Loudspeaker Assembly
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Signal Generator Instrument
Use Fault Trace SW and continue with the
Loudspeaker Problems TRS guide
Loudspeaker Problems
Fault trace SW
Audio and FM Radio
Audio Output: Loudspeaker
Frequency: 103 MHz
Set FM Radio
Remove: DCIO/SEPI Cable
Connect: Customized FM Radio Cable
Black Lab Plug to TRS Fixture GND Input
and PHF Connector to the
Phone System Connector
Signal Generator
Instrument Settings:
Frequency: 103 MHz
Amplitude/Level: 50μV
FM Dev: +/-22.5 kHz
FM Rate: 1kHz
FM Radio
Replace
N2422
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
SL 5 Replace
R2478
SL 4 Escalate
No
Yes
No
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 3 (SP2432)
No
2.6 Volt DC
at MP 110 (R2434)
Yes
0 Volt DC
at MP 111 (R2478)
Yes
Hands-Free (PHF) Problems
Fault trace SW
1: Logic
GPIO Manager
Application
GPIO_Low
GPIO_17
(Set GPIO_17 to Low)
2: Audio and FM Radio
Audio Loop Test
Audio Input: AUX1
Loop Mode: Analog
Audio Output:
AUX Earphone
Apply Audio Loop
Remove the DCIO/SEPI cabel
and Insert Hands-Free (PHF) set
Blow into the
Hands-Free (PHF) Mic
START
Step 1:
Perform
System Connector Protection Test
If successful go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
TROUBLESHOOTING
SL 4 Replace
N3100
SL 5 Replace
N2000
Replace
N3100 or N2410
No
More than
40 mV AC Pk-PK
1 KHz signal at MP 1
(C3137) and MP 30
Yes
2.6 Volt DC
at MP 125 (ST2201)
and MP 124 (ST2206)
No
(C3148)
Yes
Is any of
No Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 80 (R3153)
Yes
MP 147 (V3101_Pin 1)
and MP 146 (V3101_Pin 2)
Short circuit to the PBA
GND (Shield Can
Fence)
No
1: Disconnect:
Customized FM Radio Cable and VBATT
2: Remove the PBA from the TRS Fixture
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
V3101 or N3100
SL 5 Replace
C3107 or C3108
Replace
R2448 or V2417
Replace
L2401 or L2402
Replace
X2405 or N3101
Replace
X2405 or N3101
Yes
Is
L2403 = Max 2 Ohm
L2404 = Max 2 Ohm
L2406 = Max 1 Ohm
No
(V2417_Cathode)
No
L2401 = Max 2 Ohm
L2402 = Max 2 Ohm
Yes
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
0 Volt DC
at MP 112
Is
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N3103
SL 4 Escalate
Disconnect:
No
Yes
No
Can you
hear anything at
PHF earphone when
blowing into the
PHF Mic
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
0 Volt DC
at MP 120 (R3149)
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-Pk at
MP 108 (L2403) and
MP 109 (L2404)
when blowing into
the PHF mic
No
No
No
Yes
2V – 2.2V DC at
MP 104 (R3156)
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-Pk
at MP 102 (C3124), MP 99
(C3125) MP 121 (C3155),
MP 98 (C3156) when blowing
into the PHF mic
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-Pk at
MP 123 (R3151)
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-Pk at
MP 101 (L3125) and
MP 100 (L3126)
when blowing into
the PHF mic
Replace
X3102 or X3103
Replace
N3100
Yes
Is any of
X3102 or X3103
damaged
No
Is
L3108, L3109
L3110 and L3111
=Max 1 Ohm
SL 5 Replace
NoYes
L3108, L3109
L3110 or L3111
SL 4 Escalate
No
Replace
L2403, L2404 or
L2406
Yes
Replace
X2405
No
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
24 (124)
Page 25
TROUBLESHOOTING FM Radio Problems -
FM Radio Antenna Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Go to
Loudspeaker
Problems TRS guide
Go to
Hands-Free (PHF)
Problems TRS guide
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
No
Yes
1: Remove the DCIO/SEPI Cable
Customized FM Radio Cable
TRS Fixture GND Input and
Phone System Connector
Frequency: 103 MHz
Amplitude/Level: 50 μV
FM Dev: +/-22.5 kHz
FM Rate: 1 kHz
Is the
Loudspeaker
Ok
2: Connect:
Black Lab Plug to
PHF Connector to the
Signal Generator
Instrument Settings:
FM Radio Problems
No
1: Load ITP SW into the Phone
Audio Output: Loudspeaker
FM Radio
Is not
working neither
Loudspeaker nor
PHF set
2: Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
3: Use Fault Trace SW
and go to:
Audio and FM Radio
FM Radio
Freqvency: 103 MHz
Set FM Radio
with
Yes
START
NOTE !
Be very careful when you
cut the Shield Can Fence to
avoid component damage
START
Perform System Connector Protection Test
If successful continue with the
FM Radio Antenna Problems TRS guide
Replace
L2408
No
L2408 = Max 1 Ohm
FM Radio Antenna Problems
FM Radio Problems
Is
Digital Multimeter Instrument (DMM)
for these measurements
Is the
TRS guide
done?
Yes
Use
No
TROUBLESHOOTING
Go to
FM Radio Problems
TRS guide
2.6 Volt DC
at MP 125 (ST2201)
and MP 124
(ST2206)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 120 (R3149)
Yes
More than
40 mV AC Pk-PK
1 KHz signal at
MP 123 (R3151)
Yes
Yes
No
No
More than
40 mV AC Pk-PK
1 KHz signal at MP 122
(C3145) and MP 103
(C3146)
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N3103
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
Signal Generator
Instrument Settings:
Change Amplitude/Level to:
800 μV
Is that
any signal on
MP 122 (C3145) and
MP 103 (C3146)
No
Is the any of
C3145 or C3146
Short circuit
No
Yes
Yes
Go to
FM Radio Antenna
Problems TRS guide
SL 5 Replace
C3145 or C3146
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
L3300
SL 4 Escalate
No
Yes
Is
L3300 = Max 1.5 Ohm
Replace
N1300
Is the
Signal
Ok
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Is
C3306
Short Circuit
No
Is
MP X2405_Pin 2
Connected to the PBA
(Shield Can
GND
Fence)
SL 5 Replace
V2413
SL 4 Escalate
Claim Component
N1300
Yes
No
SL 5 Replace
C3306
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
X2405
SL 4 Replace
N1300
SL 5 Replace
N2100
Replace
N1300
26 MHz BT_CLK
at MP 22 (ST2106)
Yes
YesNo
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 25 (R3302
FM_INT)
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
25 (124)
Page 26
TROUBLESHOOTING Bluetooth Problems
- WLAN Problem s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Step 1:
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
and retest the Phone
If successful
claim SUCR SW Flash
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Continue with the
Bluetooth Problems TRS guide
Replace
X1530
Yes
Is MP 21
(X1530_Pin 1)
Short circuit to the PBA
GND (Shield
Can Fence)
No
Is
MOD 1 Freq.
minimum 230 KHz
higher than
MOD 0 Freq.
Yes
Change the
Bluetooth channels
from ch 0 to ch 78 by using the
Fault Trace SW and test
TX Output Power
Use:
Spectrum Analyzer
Span 170 MHz
BW: Auto
Amplitude: 10 dBm
Connect SMK RF Probe to
X1500 RF Connector on PBA
NOTE! Use Peak Search when
changing the channel to get
correct TX Power value
NOTE! 1 MHz channel spacing
Max
0.5 Ohm between
MP 29 (X1500_Pin 1) and
MP 23 (X1500_Pin 2)
No
Replace
X1500
Fault trace SW Settings:
TX and RX
Bluetooth
Channel 0
(This must be done before next
NOTE! Remember the Frequency
Yes
No
Turn Off
step)
Set MaxPwr MOD 1
Is the
Blt MaxPwr MOD 1
0 dBm
(±2 dBm)
No
Replace
N1300
Replace
WLAN/BT_Antenna
or X1530
Yes
Is the
TX Output Power
for all channels
0 dBm
(±2 dBm)
No
Replace
N1300
Bluetooth Problems
1: Load ITP SW into the Phone
2: Disconnect: WLAN/BT
Antenna from the X1530
3: Use TRS Fixture
Yes
Yes
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
4: Connect RF Cable Flexible
with SMK RF Probe to
Spectrum Analyzer instrument
5: Use Fault Trace SW
Blt MaxPwr MOD 0
and connect RF Probe to
Spectrum Analyzer instrument
NOTE! Do not use 10:1 Divider
Frequency: 2402 MHz
Amplitude: 10 dBm
NOTE! Use Peak Search (MKR)
to get correct TX Power value
MP 28 (W1300_Pin 3)
and MP 27 (W1300_Pin 4)
Connect:
Is the
0 dBm
(±2 dBm)
No
Disconnect
SMK RF Probe
Span: 10 MHz
0 dBm at
MP 48 (C1502
BT_ANT)
(±2 dBm)
No
0 dBm at
(±2 dBm)
No
2.7 Volt DC at
MP 26 (ST1302
VBT27)
Yes
Spectrum Analyzer
Instrument Settings:
Frequency: 2402 MHz
Span: 10 MHz
Amplitude: 10 dBm
Use Peak Search (MKR)
Connect SMK RF Probe to
X1500 RF Connector on PBA
Fault trace SW Settings:
TX and RX
Bluetooth
Channel 0
Set MaxPwr MOD 0
NOTE! Remember the Frequency
Yes
Yes
No
Replace
N1510
SL 5 Replace
W1300
SL 4 Escalate
SL 4 Replace
N1300
SL 5 Replace
N2000
START
This TRS guide is NOT
NOTE !
C905c Phones
Step 1:
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
and retest the Phone
If successful
claim SW Flashing
If not then go to Step 2.
Step 2:
Continue with the
WLAN Problems TRS guide
Replace
N1510
Replace
N2300
Replace
N2410
Claim Componenet
N2100
Yes
Is the
WLAN
Problem solved
valid for
WLAN Problems
Max
0.5 Ohm between
MP 29 (X1500_Pin 1) and
MP 23
(X1500_Pin 2)
No
Replace
X1500
Replace
WLAN/BT_Antenna
or X1530
Yes
3.3V – 3.5V DC
No
At MP 46 (ST2310
WLAN_VO33)
Yes
Is there
any signal
at MP 47 (N1500)
No
1.8 Volt DC at
No Yes
MP 85 (R2313
WLAN_PDn)
SL 5 Replace
N2100
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Yes
Yes
1: Load ITP SW into the Phone
2: Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
3: Connect RF Cable Flexible
with SMK RF Probe to
Spectrum Analyzer instrument
4: Use Fault Trace SW
NOTE! The WLAN/BT_Antenna
must be connected to X1530
Is WLAN
TX Output Power
13 dBm
(±5 dBm)
No
1: Disconnect:
SMK RF Probe from the PBA
and from the Spectrum Analyzer
instrument
2: Connect: RF Probe to the
Spectrum Analyzer instrument
NOTE! Do not use 10:1 Divider
Use Peak Search (MKR) and
Measure
WLAN TX Output Power
on top of the N1500 component
NOTE! Do NOT
touch the N1500
component with the RF Probe
to avoid component damaging
Check the Following Voltages:
1.9V DC at MP 45 (ST2311)
1.8V DC at MP 44 (ST2312)
3.0V DC at MP 43 (ST2313)
1.8V – 2V DC at
MP 50 (V2100_Pin 1
WLAN_CLKREQ)
Spectrum Analyzer
Instrument Settings:
Frequency: 2442 MHz
Span: 10 MHz
Amplitude: 20 dBm
Use Peak Search (MKR)
Connect
SMK RF Probe to
X1500 RF Connector on PBA
Fault trace SW Settings:
TX and RX
WLAN
Wlan Settings
WLAN Turn On
Replace
N2300
No
Are the
voltages
Ok
Yes
26 MHz Signal
No
At MP 24 (ST2105
WLAN_CLK)
TROUBLESHOOTING
SL 4 Replace
N1300
SL 5 Replace
N2100
No
26 MHz Signal
At MP 22 (ST2106
BT_CLK)
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
V2100
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
No
Is
MP 49 (V2100_Pin 3)
Short circuit to the PBA
GND (Shield
Can Fence)
No
SL 5 Replace
SL 4 Escalate
1222-9526 rev. 1
Yes
N1500
26 (124)
Page 27
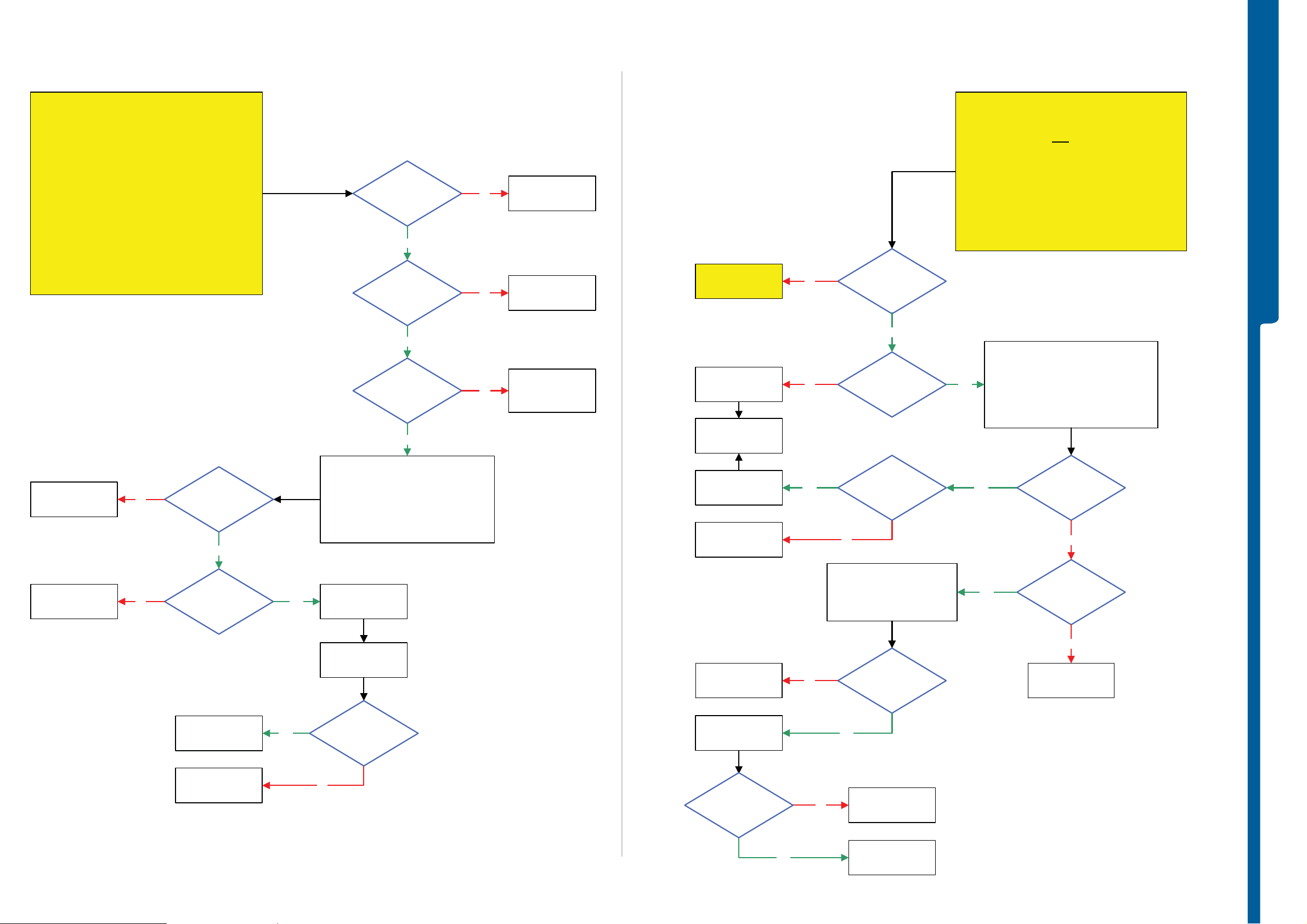
TROUBLESHOOTING GSM Problems
- WCDMA I, II and V Problem s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Step 1:
Replace Loudspeaker Assembly and retest the Phone
If successful claim Loudspeaker Assembly
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Perform SERP Calibration and retest the Phone
If successful claim SERP Calibration
If not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Disassembly the Phone and continue with the
GSM Network Problems TRS guide
GSM Network Problems
MP 62 (X1200_Pin 1) and
Max 0.5
Ohm between
MP 63 (X1200_Pin 2)
Yes
Is
MP 167 (X1210)
and MP 168 (X1211)
connected to GND
(Shield Can
Fence)
Yes
Max
1 Ohm between
MP 166 (Z1200_Pin
IN) and MP 167
(X1210)
Yes
No
No
No
Replace
X1200
Replace
X1210 or X1211
SL 5 Replace
Z1200, R1202 or
L1202
SL 4 Escalate
Go to
GSM Network
Problems TRS guide
Replace
N1200
Go to
SERP Calibration
WCDMA BAND I,II,V Network Problems
This TRS guide is NOT
Perform SERP Calibration and retest the Phone
No
No
Is the
GSM Network
Ok
Yes
Is there
problems with
WCDMA TX
Yes
START
NOTE !
valid for C905c Phones
Step 1:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
If successful claim SERP Calibration
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Fault Trace SW
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND I
Fast select channels:
Set Low Channel
Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
TROUBLESHOOTING
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N1211
No
No
2.8 Volt DC at
MP 163 (C1218
LDOA_OUT)
Yes
2.8V DC
at MP 65 (C1207)
(If C905c Skip This
and Replace
N1200)
Claim Component
N1200
SL 5 Replace
N2010 or N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Yes
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Replace
N1200
Go to
SERP Calibration
Is the
GSM Network
Problem
solved
No
Use TRS Fixture
Connect:
Replace
N1200
Replace
N1210
SL 5 Replace
L1200
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N1210
Is the
WCDMA TX
Problem solved
Yes
No
No
2.5V – 3V DC at
MP 143 (C1215
WPA_A_EN)
No
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Is
L1200 = Max 0.5 Ohm
Yes
SL 5 Replace
N2010 or N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Yes
3V – 3.8V DC at
MP 145 (ST1201
VCC_WPA)
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 144 (R1210
WPA0_EN)
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Claim Component
N1210
1222-9526 rev. 1
27 (124)
Page 28
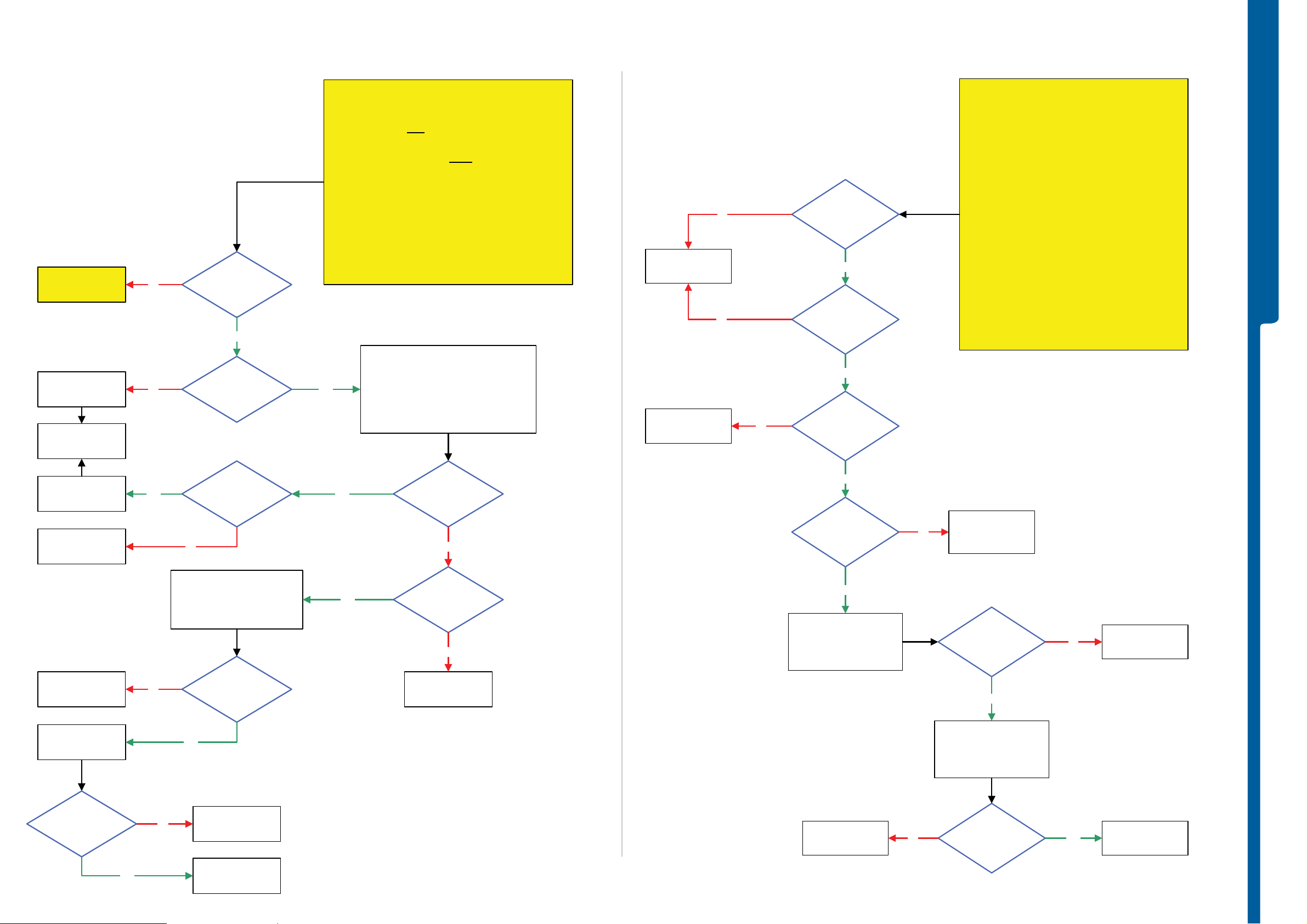
WCDMA BAND VIII Network Problems
TROUBLESHOOTING WCDMA VIII Problems
- A- G PS Proble ms
A-GPS Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Go to
GSM Network
Problems TRS guide
Replace
N1200
Go to
SERP Calibration
No
No
Is the
GSM Network
Ok
Yes
Is there
problems with
WCDMA TX
This TRS guide is NOT
This TRS guide is valid ONLY
if the WCDMA BAND VIII is supported
Perform SERP Calibration and retest the Phone
If successful claim SERP Calibration
Yes
START
NOTE !
valid for C905a and C905c Phones
NOTE !
for C905 Phones
Step 1:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Fault Trace SW
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND VIII
Fast select channels:
Set Low Channel
Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
Replace
N2410
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
No
No
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 91 (R1404
AGPS_LDO_EN)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 81 (R1401
AGPS_PWRON)
Yes
1.8 Volt DC
at MP 53 (R2116
AGPS_CLK_EN)
START
Step 1:
Got to Service Tests Menu and perform the GPS Test
If successful
Flash the Phone with EMMA SUCR SW
if not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Replace PBA Key Flex Flip
and retest the Phone
If successful claim PBA Key Flex Flip
if not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Replace Slider FPC Assy
and retest the Phone
If successful claim Slider FPC Assy
if not go to step 4.
Step 4:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
TROUBLESHOOTING
Replace
N1200
Replace
N1210
SL 5 Replace
L1200
SL 4 Escalate
Replace
N1210
Yes
No
2.8V - 3V DC at
MP 142 (C1214
WPA_C_EN)
No
Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Is the
L1200 = Max 0.5 Ohm
Yes
Yes
Yes
3V – 3.8V DC at
MP 145 (ST1201
VCC_WPA)
No
1.8 Volt DC at
MP 140 (R1209
WPA2_EN)
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
26 MHz at
MP 55 (ST2107
AGPS_CLK)
Yes
1: Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
2: Connect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
SL 4 Replace
No
SL 5 Replace
1.8V Pk-Pk Pulses
at MP 2 (ST1404)
shortly after phone
1: Disconnect:
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
N2410
N2102
More than
Power On
Yes
2: Connect:
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
Is the
WCDMA TX
Problem solved
Yes
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010 or N2000
SL 4 Escalate
Claim Component
N1210
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
More than
1.8V Pk-Pk Pulses
at MP 32 (ST1403)
shortly after phone
Power On
Yes
Replace
X4200
1222-9526 rev. 1
28 (124)
Page 29
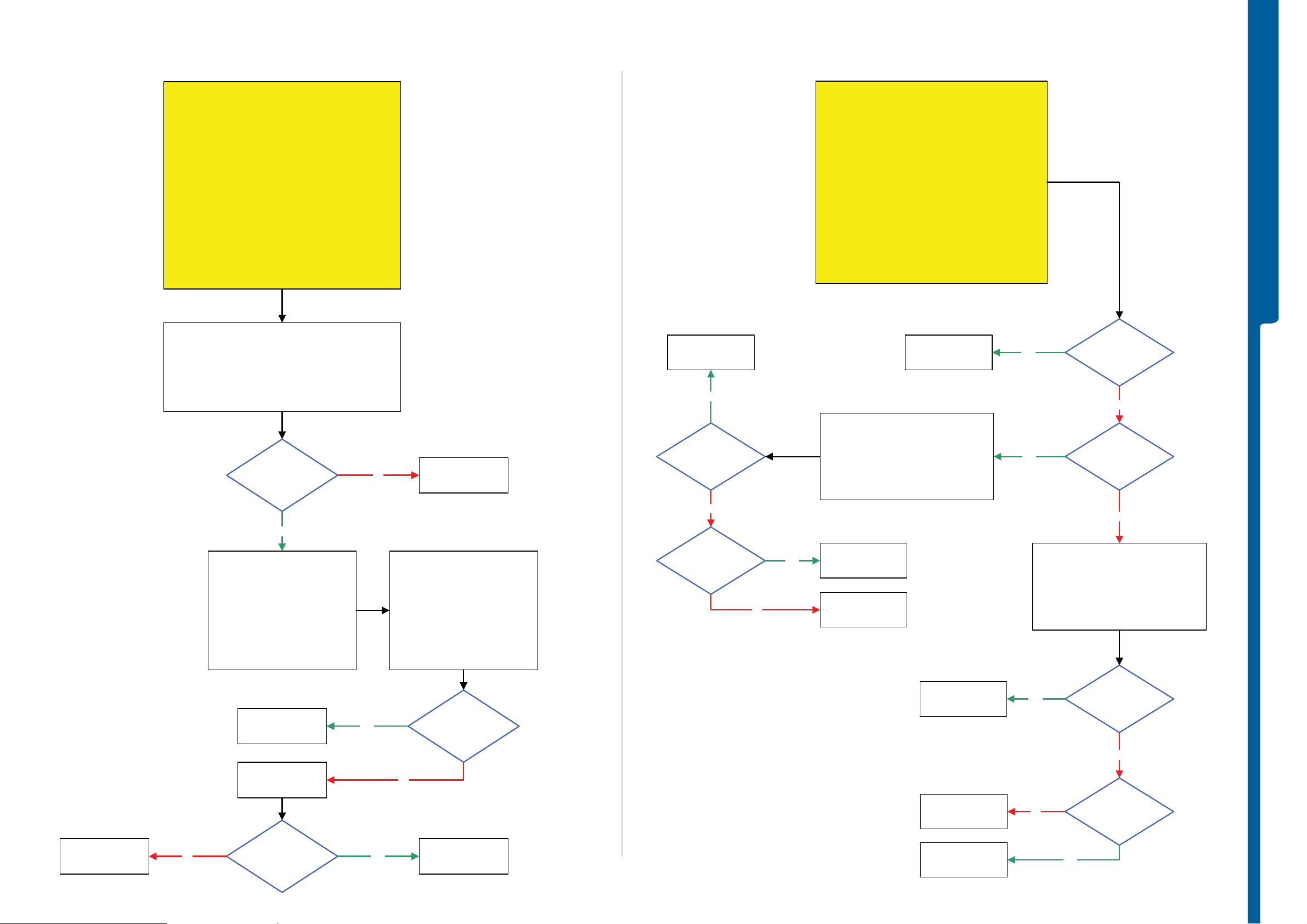
TROUBLESHOOTING Accelerometer Problems
- Vibrator Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Accelerometer Problems
START
Step 1:
Got to Service Tests Menu and perform
the Accelerometer Test
If successful
Flash the Phone with EMMA SUCR SW
if not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Use Dummy Battery connected to
Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Connect: DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW
Fault Trace SW
General
Asic Revisions
Read All
Clean
X4201 and X4202
Yes
Vibrator Problems
START
Step 1:
Load ITP SW into the Phone
Step 2:
Use TRS Fixture
Connect: VBATT and DCIO/SEPI
Use Fault Trace SW and go to:
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Activate:
Vibrator Test
Replace the
Vibrator
Yes
TROUBLESHOOTING
Is the
Vibrator working on
TRS Fixture
No
Is
Accelerometer
(N2411)
Asic Revision
0x3b
Yes
Fault Trace SW
MMI
Misc
Init Screen Testing
Activate:
Accelerometer Test
NOTE! Read X, Y, Z information in
the Info Box.
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
No
Activate Accelerometer Test again
NOTE! Read X, Y and Z information
NOTE! Repeat this Test Sequence
Yes
Replace
N2411
Move the Phone
and
in the Info Box.
10 Times
Can
you see
that X, Y and Z
information are
changing in the
info box
Is the
connection between
X4202 and
PBA GND (Shield
Can Fence)
Ok
No
L4202 = Max 1.5 Ohm
Is
No
Yes
Remove the PBA
from the TRS Fixture
Scrap the
PBA
SL 5 Replace
L4202
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
C4208
SL 4 Escalate
Yes
Yes
2.7V – 3.5V
Pk-Pk Pulses at
MP VIB + on
TRS Fixture
No
Remove the PBA
from the TRS Fixture
Is C4208
Short circuit
No
SL 5 Replace
N2010
SL 4 Escalate
No
Replace
N2411
Is the
Accelerometer
Problem solved
Yes
No
Claim Component
N2411
SL 5 Replace
L4201
SL 4 Escalate
SL 5 Replace
N2000
SL 4 Escalate
No
L4201 = Max 1.5 Ohm
Is
Yes
1222-9526 rev. 1
29 (124)
Page 30
TROUBLESHOOTING Real Time Clock Problems
- Slide Sensor Problems
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
START
Does
the Phone
Gain or Lose
Time
Real Time Clock Problems
Yes
Perform:
SERP Calibration
Slide Sensor Problems
START
Step 1:
Replace Numeric Key Foli and retest the Phone
If successful claim Numeric Key Foil
If not go to step 2.
Step 2:
Replace Cover Rear Assembly and retest the Phone
If successful claim Cover Rear Assembly
If not go to step 3.
Step 3:
Continue with the
Slide Sensor Problems TRS guide
SL 4 Replace
X2410
SL 5 Replace
N2010
TROUBLESHOOTING
No
Perform:
Backup Capacitor
Test
Is the
Test Passed
No
Yes
Is there
still problems with
Gaining or Losing
Time
Flash the Phone with
EMMA SUCR SW
SL 4 Replace
C2214
SL 5 Replace
N2000
Yes
No
Claim
SERP Calibration
Replace
B2100
1222-9526 rev. 1
30 (124)
Page 31

TROUBLESHOOTING
System Connector Protect io n Test - Current Cons um pt io n Test
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
System Connector Protection Test
Perform Diode and Ohm measurements, use the DMM instrument.
Note!
System Conn.
X2405
(PIN Position)
1 0L 1M - 0L
2 00
3 2.6 – 2.8 12K
4 0.7 - 1.2 1.0K – 1.1K
5 1.8 – 2.0 2.0K – 2.2K
6 1.8 – 2.0 2.0K – 2.2K
7 075
8 2.0 - 2.6 500K – 700K
The Battery must be removed from the Phone during this test.
Note! Connect the Black probe to X2405_PIN 9 (GND).
PIN_1 PIN_9 GND PIN_12
Diode
Measurements
(Volt)
Ohm
Measurements
(Ohm)
SL 4
(Repair Action)
X2405
L2407
N2421 if lower
X2405 if higher
L2406 if higher
X2405 if higher
L2401 if higher
N3101 if lower or higher
L2402 if higher
N3101 if lower or higher
X2405 if higher
X2405 if higher
L2403 if higher
N3101 if lower or higher
X2405 if higher
L2404 if higher
N3101 if lower or higher
X2405 if higher
V2414 if lower
R2443 if higher
N2700 if lower or higher
X2405 if higher
R2448 if higher
V2417 if lower
N2422 if lower or higher
SL 5
(Repair Action)
C2439 if lower
No Action
C2443 if lower
C2442 if lower
C2448 if lower
C2447 if lower
C2445 if lower
L2405 if higher
C2444 if lower
R2453 if higher
R2478 if higher
R2434 if higher
Current Consumption Test
Step 1:
Insert a Local SIM Card and use the phone with the Normal SW (SSW).
Use Dummy Battery connected to Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT).
Instrument settings: Voltage: 3.8 Volt, Limiter 3A.
Note: (Dummy Battery)
The resistance between GND and BDATA should be approximately 27KOhm.
Measure the current consumption when Phone is turned off.
Take a note of the current consumption at Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT).
The Current consumption in off mode should be less than 1mA.
If more than 1mA go to Dead Phone Problems part 1 TRS guide.
Step 2:
Turn the Phone On:
Measure the deep sleep current max 6mA typical between 0-3mA. Make sure that the
operator is running with deep sleep mode.
Note: This operation can be switched off by operator if network is busy or heavily-loaded.
If phone using more than 6mA, then go to EMMA and run Software Update Contents
Refresh (SUCR SW).
Step 3 with Fault Trace SW application:
- Flash the phone with ITP SW
- Use Dummy Battery connected to the Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
- Use Fault Trace SW
Connect the:
- Dummy Battery connected to the Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT):
Instrument settings: Voltage: 3.8 Volt, Limiter 3 A
- Connect DCIO/SEPI to the phone:
Instrument settings: Voltage: 5 Volt, Limiter 2 A
Perform the following tests:
- Max TX Power GSM 850 MHz
TROUBLESHOOTING
9GNDGNDX2405 if higher L2449 if higher
X2405
10 0.7 – 0L 50K – 0L
11 0.7 – 0L 50K – 360K
N2420 if lower or higher
12 0L 75K – 0L
Z2400
V2415 if lower
N2420 if lower
X2405 if higher
Z2400 if higher
V2416 if lower
V2412 if lower
V2202 if lower
R2445
R2446 if higher
C2440 if lower
C2441 if lower
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX GSM
GSM Mode Settings:
TX Switched
GSM Radio Settings:
Select Band: GSM 850
Channel: 128
Power Level: 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
31 (124)
Page 32

TROUBLESHOOTING
Current Consum pt io n Test
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Limits GSM 850 MHz
- Transmitter current: 325mA
- Tolerance: ±30%
- Max TX Power GSM 900 MHz
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX GSM
GSM Mode Settings:
TX Switched
GSM Radio Settings:
Select Band: GSM 900
Channel: 1
Power Level: 5
Limits GSM 900 MHz
- Transmitter current: 250mA
- Tolerance: ±30%
- Max TX Power DCS 1800 MHz
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX GSM
GSM Mode Settings:
TX Switched
GSM Radio Settings:
Select Band: DCS 1800
Channel: 512
Power Level: 0
Limits DCS 1800 MHz
- Transmitter current: 220mA
- Tolerance: ±30%
- Max TX Power PCS 1900 MHz
Limits WCDMA BAND I
- Transmitter current: 550mA
- Tolerance: ±25%
- Max TX Power WCDMA BAND II
(Note: Valid only for C905a)
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND I
Fast Select Channels: Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
Limits WCDMA BAND I
- Transmitter current: 470mA
- Tolerance: ±20%
- Max TX Power WCDMA BAND V
(Note: Valid only for C905a)
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND I
Fast Select Channels: Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
Limits WCDMA BAND I
- Transmitter current: 590mA
- Tolerance: ±10%
- Max TX Power WCDMA BAND VIII
(Note: Valid only for C905 if WCDMA BAND VIII is supported)
TROUBLESHOOTING
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX GSM
GSM Mode Settings:
TX Switched
GSM Radio Settings:
Select Band: PCS 1900
Channel: 512
Power Level: 0
Limits PCS 1900 MHz
- Transmitter current: 180mA
- Tolerance: ±30%
- Max TX Power WCDMA BAND I
(Note: Valid only for C905 and C905a)
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND I
Fast Select Channels: Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
Fault Trace SW settings:
TX and RX WCDMA
Radio Settings:
Select Band: BAND I
Fast Select Channels: Ch LOW
Modes: Max Pwr 23dBm
Limits WCDMA BAND I
- Transmitter current: 700mA
- Tolerance: ±10%
If current consumption is out of the test limits, try to solve the problem by running SERP
Calibration. If still problem with current consumption then go to:
GSM and WCDMA Network problems TRS guides.
If the current consumption is equal to the test limits then go to:
Charging Test.
1222-9526 rev. 1
32 (124)
Page 33

TROUBLESHOOTING Backup Capacitor Test
- Charging Test
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Backup Capacitor Test
To perform this test use:
- Phone with ITP SW
- Power Supply Channel 1 VBATT: Instrument settings: Voltage: 3.8V, Limiter: 2A
- Power Supply Channel 2 DCIO/SEPI: Instrument settings Voltage: 5V, Limiter: 2A
This test should be performed in 3 steps:
Step1:
Measure the voltage at the Backup capacitor by using Fault Trace SW- Logic - ADC
Values – Read ADC Value (Reading 1).
Step2:
This step should be done 30 seconds after Step 1. Measure the voltage at the
Backup capacitor by using Fault Trace SW - Logic – ADC Values - ADC Channels
– Read ADC Value (Reading 2).
Step3:
Compare the difference between Reading 1 and Reading 2 with the reference table
below. If the Reading 1 value is between 50 and 680 go to Interval 1, if between 681
and 800 go to Interval 2, if between 801 and 880 go to Interval 3 and compare with
the Reading 2 – Reading 1 Min and Max Limits.
Reference Table:
Min Max Unit
Charging Test
To perform this test use:
- Phone with the Normal SW (SSW)
- Dummy Battery connected to Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT)
Note! The Dummy Battery should have approximately 27 KOhm resistance
between GND and BDATA.
- Power Supply Chann e l 1 (V BATT)
Instrument settings:
Voltage: from 3.0 Volt to 4.2 Volt, according to VBATT row in the Reference Table.
Limiter: 2A
- Power Supply Channel 2 (DCIO/SEPI)
Instrument settings:
Voltage: 5V
Limiter: 2A
Test instructions:
- Disconnect the DCIO/SEPI Cable between each measurement and wait for the
phone to shut down when changing VBATT voltage.
- Take a note of Current measurements at Power Supply Channel 2 DCIO/SEPI and
Display charging indicator X seconds after DCIO/SEPI cable has been inserted
according to Test Time row in the reference table below.
- Compare test results with reference table below, tolerance +/-20%.
Reference Table
VBATT x Volt 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4.0 4.1 4.2
Test Time x sec. 15s 15s 15s 25s 25s 25s 25s 30s 30s 30s 30s 30s 45s
DCIO/SEPI
Current mA
Display indicate
charging
250 250
Nothing Nothing
250-
500
Yes or
Nothing
800-
500
500 500 500
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
1000
800-
1000
8001000
800-
1000
500-
750
0
Fully
Charged
TROUBLESHOOTING
Absolute readout
50 880 Dec
Reading 1
Reading 1 (Dec) Reading 2 – Reading 1 (Dec)
Min Max
Interval 1 (50 – 680) 20 210
Interval 2 (681 – 800) 530
Interval 3 (801 – 880) 010
Note: The upper table contains the absolute limits for the readouts. The lower table
contains the allowed delta between the first and the second readout, separated in
time with 30 seconds.
If the readings are out of limits replace C2214 Backup capacitor.
Note! The Power Supply Channel 1 (VBATT) must allow reverse current.
If the charging current is NOT
Charging Problems TRS Guide.
If the charging current is equal to the reference table value then insert the normal battery
and test the charging current to verify that the phone battery is working properly.
Measure the voltage at the battery to define the current level.
If the battery is receiving the right current, then the phone and the battery are working
properly.
equal to the reference table then go to:
If the problem is not solved then SL 5 Replace N2000 SL 4 Escalate.
1222-9526 rev. 1
33 (124)
Page 34

ASIC Revision Test
Note:
The Keypad Scan Test may not be activated when performing this test.
Purpose:
TROUBLESHOOTING ASIC Revision Te st
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
- To verify that the ASIC is correctly mounted, that the communication works
and that the revision is correct.
The tested ASICs are:
- D2010 (Kajsa)
- N2000 (Vera)
- N1300 (Bluetooth and FM Radio ASIC)
- N2411 (Accelerometer)
- N1400 (A-GPS Module)
To perform this test use:
- Phone with ITP SW
- TRS Fixture
- Power Supply Channel 1 VBATT (Voltage: 3.8V, Limiter: 2A)
- Power supply Channel 2 DCIO/SEPI (Voltage: 5V, Limiter: 2A)
- Fault Trace SW, go to: General – Asic Revisions – Read All
Reference Table:
ASIC
Part
number
Description Return value (hex)
TROUBLESHOOTING
N2010 1208-3871 CPU (Kajsa) 0xE8
N2000 1202-0639
N1300 1200-6182
N2411 1202-1676 Accelerometer 0x3b
N1400 1200-0700
Power Management
(Vera)
Bluetooth
Firmware Revision Ox5,0x3
Chip ID 0x0,0x0,0x0,0x0
0xC8
Will always return 0 on STLC because
Chip ID is not supported.
A-GPS Module 254,0,253,192,0,242,113,9,16,252
NOTE! The Key Flip Flex Assy must be
connected to the PBA during this test.
N1300 1200-6182 FM Radio
When FM Radio is On: Ox1253
When FM Radio is Off: Ox1200
1222-9526 rev. 1
34 (124)
Page 35

TROUBLESHOOTING Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 1, MP 30 (C3137 and C3148)
MP 2 (ST1404) Shortly after the phone is powered on
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
1222-9526 rev. 1
35 (124)
Page 36

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 14 (L2405 TV_OUT)
MP 19 (ST2108 TV_CLK)
1222-9526 rev. 1
36 (124)
Page 37

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 20 (ST2109 VIDCC_CLK)
MP 22 (ST2106 BT_CLK)
1222-9526 rev. 1
37 (124)
Page 38

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 24 (ST2105 WLAN_CLK)
MP 27 (W1300_Pin 4)
1222-9526 rev. 1
38 (124)
Page 39

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 28 (W1300_Pin 3)
MP 32 (ST1403) Shortly after the phone is powered on
1222-9526 rev. 1
39 (124)
Page 40

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 34 (SP2410)
MP 37 (ST2110 CAMSYSCLK)
1222-9526 rev. 1
40 (124)
Page 41

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 38 (R2102_MCLK)
MP 47 (N1500)
1222-9526 rev. 1
41 (124)
Page 42

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 55 (ST2107 AGPS_CLK)MP 48 (C1502 BT_ANT)
1222-9526 rev. 1
42 (124)
Page 43

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 59 (TP2203 VOPTO30)
MP 100, MP 101 (L3126, L3125)
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
1222-9526 rev. 1
43 (124)
Page 44

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 99, MP 102 (C3125, C3124)
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
MP 103 (C3146)
1222-9526 rev. 1
44 (124)
Page 45

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 107 (ST2410)
MP 108, MP 109 (L2403, L2404)
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
1222-9526 rev. 1
45 (124)
Page 46

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 117 (V4200_Pin 3)
MP 98, MP 121 (C3156, C3155)
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
1222-9526 rev. 1
46 (124)
Page 47

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 123 (R3151 1 kHz)MP 122 (C3145)
1222-9526 rev. 1
47 (124)
Page 48

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
Note: This is an example! The shape of the signal can be different.
MP 135 (ST2104 RTCCLK)MP 123 (R3151) Handsfree (PHF) Problems TRS-Guide
1222-9526 rev. 1
48 (124)
Page 49

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
MP 138 (C2101 32 kHz)MP 136 (C2100 32 kHz)
1222-9526 rev. 1
49 (124)
Page 50

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
WLAN TX Output PowerMP Vibrator + on TRS Fixture
1222-9526 rev. 1
50 (124)
Page 51

TROUBLESHOOTING
Measurement Points Pictures
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TROUBLESHOOTING
Blt MaxPwr MOD 1Blt MacPwr MOD 0
1222-9526 rev. 1
51 (124)
Page 52

MEASUREMENT POINTS Front Side
12 1234567891011
MP X2405 Pin 1-12
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
OUT
MP Z4202 Pin 1-8
5
C905
MP 30
MP 31
MP 32
MP 33
MP 34
MP 35
MP 36
MP 37
MP 38
MP 39
MP 40
MP 41
MP 4 MP 11MP 10MP 9MP 8MP 7MP 6MP 5 MP 15MP 14MP 13MP 12 MP 16 MP 23MP 22MP 21MP 20MP 19MP 18MP 17 MP 27MP 26MP 25MP 24 MP 28 MP 29
MP 3MP 2MP 1
X2405
V2414
V2415
R2443
C2446
C2445
R2453
L2405
C2444
ST2233
R2441
SP2423 SP2424
C2282
SP2425
SP2426
SP2427
SP2428SP2420
SP2429
R2451
C2432
R2452
ST2421
C2346
SP5110
C2347
V2482
SP3208
SP3214
SP5101
C2469
SP3209
R3203
R3204
ST2228
C2278
C2252
N2212
C2266
C2262
C2277
C2256
L2213
C2468
V2481
C2258
C2257
C2260
ST4401
SP2505
C4401
R2502
L4400
ST2213
R2444
N2421
R2447
R2214
ST2230
R4216
R2213
C2279
R4215
N2700
C2281
C2280
ST2232
R2125
ST2108
ST2109
SP1303
R5100
R4205
C2321
C2313
R2113
R4220
C2331
R4219
R2101
R2112
R2407
R2108
C2312
ST2106
C2460
N2100
R2103
C2311
V2101
C2310
R2111
R2104
C2330
C2105
N2102
R2116
R2117
C2403
ST2107
R1404
ST2102
ST2103
ST2101
C2288
R3153
C2289
R2217
N2201
C4405
ST4403
C4403
C4402
C4404
R4401
R4405
ST2231
C4300
S4300
R4300
ST2105
N2410
N4400
L4401
L2407
V4203
IN IN
IN
C3139
C3140
ST2400
R1526
C4406
C4400
R4404
C2439
SP4203
SP4202
SP4201
R4301
V2470
C2284
N2208
C2283
C2285
N2209
C2286
R2408
R2313
L1400
R4402
Z4202
Z4201
Z4200
ST3105
ST3106
R1407
C1400
C4407
R4400
R4403
R2474
R4303
R1408
R4406
OUT
OUT
OUT
X1530
R3100
ST3103
C4210
C4211
R4222
R4221
SP4200
ST4201
C4213
C4214
C4410
R4218
R4217
C3159
C2472
C4215
V4208
C4218
C4216
C4217
C4229
R1402
R1403
ST1406
ST1402
R1406
ST1400
R1401
C1512
C1530
C3110
C1511
OUT
X1500
IN
ST3304
C3305
R3302
C3304
SP1300
ST1302
C1302
N1300
W1300
C1510
SP5125
R1534
R1533
R1532
N1510
SP2102
C1502
SP1305
L1503
R1514
ST1520
R1512
R1511
C1506
C1507
C1508
0.8mm
X4200
C4412
C4413
C4414
C4415
C4219
C4220
A1
B1
A
BA
S2415
V2475 V2476
DC
L3300
C3306
ST1303
C1303
E1003
ST1301
C1301
ST1300
C1300
C1509
C1513
TP4200
TP4201 TP2206
TP4400
TP2203
TP4401
C2214
S2424
C2376
L2313
C2371
L2310
ST2313
SP1502
ST2312
C1505
C1518
R1502
C1523
C1520
C1519
C1521
C1522
N1500
L1501
L1502
L1500
C1503
C1516
C1515
C1514
C1517
C2377
N2300
C2372
C2373
C2379
C1524
R1505
R1506
L2311
R1515
R1508
R1507
R1509
R1510
C1504
ST2311
ST2310
C1526
C2374
SP1500
C1528
SP1503
C1527
R1525
ST1517
ST1518
SP1507
SP1501
ST1519
C1525
SP1504
R1518
V2100
R1522
R1517
R1521
R1519
X4311
LABEL
X4315
B
DC
C3118
L3110
C3101 C3117
L3111
V2416
Z2400
SP5104
SP5103
SP5107
SP5102
SP5105
SP5106
SP2200
TP2204
TP2202
TP2201
C3105
C3107
C3104
C3108
N3100
R3128
C3106
ST3100
R3127
R3106
R3102
C3137
C3148
SP1302
R5102
ST1403
ST1407
C2348
R1102
R1101
SP2410
C2324
C2305
R1103
C2337
C2325
C2343
C2342
C2341
R2422
C2353
SP2104
C2354
C2104
C2340
R2115
C2339
R2122
C2338
C2336
C2326
C2320
ST2300
C2307
R2123
ST2110
C2103
R2102
R2472
C2327
C2349
SP2411
C2352
SP2103
C2345
C2404
C1217
ST2225
C2406
ST2402
ST4200
N2214
R1211
N1211
SP2401 SP2400
N2411
ST2401
C2405
C2251
IN
X1200
C2431
ST2422
R1527
SP2432
SP1304
SP1301
R5101
ST1404
ST1405
C2323
C2303
C2344
C2304
R2473
R4410
C2314
C2351
C2308
C2306
SP2105
C2268
ST2229
SP2504
C2263
C2267
C2265
C1221
C2254
R2210
C1207
R2445
C2437
SP5124
R2430
R2431
SP5116
C2436
C2433
SP2421
SP5123
R2442
C2434
C2435
R2470
R2475
R2471
C2322
C2301
N2010
N2020
E1001
R2228
C2328
C2309
C2350
SP2500
SP2501
C2261
C2269
C2255
C2264
N2500
R2503
C2259
C2270
C2253
SP2503
R2446
N2420
SP2435
SP2430
R2440
C2302
C2329
R3202
R3201
R2223
R2501
C2271
R2215
ST2226
SP2422
N2210
C2274
OUT
Z4200Z4201Z4202
X4300
B1
A1
8
7
6
OUT
MP Z4201 Pin 1-8
5
8
MP Z4200 Pin 1-8
7
6
OUT
5
C4324
C4303
R4324
C4332
R4323
C4331
ST4402
C4339
C4337
C4335
C4333
C4308
C4302
C4325
4
3
IN IN
2
1
4
3
IN
2
1
C4323
C4304
C4322
C4301
C4340
C4338
C4336
C4334
C4320
C4321
C4330
R4321
Cutout
Cutout
E1000
X4312
X4313
X4314
AB
B
V2477
DC
V2474
A
S2453S2454
CD
MP 43
MP 44
MP 45
MP 46
MP 47
MP 48
MP 49
MP 50
MP 51
MP 52
MP 53
MP 54
MP 55
MP 56
MP 57
MP 58
MP 59
MP 60
MEASUREMENT POINTS
MP 42
MP 64 MP 71MP 70MP 69MP 68MP 67MP 66MP 65 MP 75MP 74MP 73MP 72 MP 76 MP 83MP 82MP 81MP 80MP 79MP 78MP 77 MP 87MP 86MP 85MP 84 MP 88 MP 95MP 94MP 93MP 92MP 91MP 90MP 89 MP 97MP 96
MP 63MP 62MP 61
1222-9526 rev. 1
52 (124)
Page 53

MEASUREMENT POINTS
Back Side
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
X4202
L4202
V2413
L2401
L2408
C2443
L2406
C2449
SP2434
C3158
R2201
C3153
R2416
ST2411
V2400
R2415
ST2410
C2412
C2413
C3136
C3151
C3152
ST3102
C3102
C3100
C3124
C3126
C3127
R3112
C3133
C3125
C3155
C3146
C2212
C3135
ST2206
R3150
C3166
ST2205
ST2204
X2410
C2462
MP 107MP 106MP 105 MP 108 MP 116MP 115MP 114MP 113MP 112MP 111MP 110MP 109 MP 119MP 117 MP 118MP 103 MP 104
MP 135
MP 136
R2448
C2448
N2422
C2414
C2473
L2404
C2207
SP3213
SP3205
C2447
V2202
ST2201
C1218
L2449
C2438
R2434
C2440
R2478
C2441
V2417
C2215
L2201
C2217
SP3204
C2221
C2223
SP3206
C2224
N2000
C2225
C3154
C1208
R3154
C3138
C2204
SP2106
SP2107
N1200
C2470
V2471
V2472
C2466
V2473
C2471
C2209
V2412
C2216
ST2203
C2208
ST2202
R2476
C2474
V2486
V2487
L2200
C4206
R4203
C4204
C4205
E1002
R4204
R2402
R2403
R2404
C2402
ST2104
C2227
ST2240
C2226
R2203
C4209
C2205
C2213
R2204
ST2207
V2484
V2201
R4200
R4202
C2100
ST2100
C2101
R2406
R2405
C2218
C2219
C2220
ST2209
L4200
C4201
R4201
V4200
B2100
X2411
C4200
C1216
R1203
C1214
C1215
R1210
ST2210
V4201
C4203
V4206
MP138
C2231
C2230
L2202
C2232
R2207
R2208
ST4202
C2228
C4202
ST4203
R1209
C1213
C1201
N1210
C1206
ST1201
ST1200
V2200
C1204
N2200
ST2214
C2201
C2200
ST2211
ST2212
L1200
R2231
C2233
C2229
R2200
C2202
C2203
C1203
C1205
C1220
C1219
L3108
C2400
R2400
3
2
1
V3101
L3109
X2201
MP 139
MP 140
MP 141
MP 142
MP 143
MP 144
MP 145
MP 146
MEASUREMENT POINTS
MP 147
C1209
MP 137
X1211
C1200
R1201
Z1200
X1210
C1211
L1202
X3103
X3102
R1202
L2403
L2402
SP2433
C2442
R2450
C2430
C2222
SP3207
C2210
C2211
ST2200
C2206
C2464
MP 99MP 98 MP 102MP 100 MP 101
MP 120
MP 121
MP 122
X1540
MP 123
R2417
R2419
MP 124
R2418
X2401
R2420
X4201
MP 125
MP 126
C2411
R2421
SP2412
C2421
C2410
C2422
Cutout
V4202
L4201
C4208
C4207
X4410
MP 127
MP 128
MP 129
MP 130
MP 131
MP132
MP 133
MP 134
ST2221
C2243
R2211
N2206
C2245 ST2222
ST2220
C2292
C2290
R2226
E1004
R4302
R2220
V2212
L2212
ST2224
C2249
SP4401
C4411
SP4400
SP4404
R2221
C2241
N2205
N4300
N2213
C2248
A1
B1
SP4402
C2242 C2244
C2240
C2250
C2272
ST2223
C2417
7
5
X2402
ST4400
C4416
C2416
C2419
SP4403
C2418
123
C2287
TP2209
R2212
TP2208
TP2210
TP2207
R4409 R4413
R4414
V4400
ST3104 C3144
R3118
X4400
R4304
R4411
C2420
C3115 C3116
C3114
N3101
C3157
L3126
L3125
R3148
R3147
R3156
C3150
C3149
C3112
C3167
R3149
C3156
N3103
C3145
ST3101
C3131
R3151
C3121
R3155
C3165
R3160
C2465
C2415
V2480
V2479
V2478
B1
C2467
A1
C2461 C2463
MP 156
MP 155MP 154MP 153MP 152MP 151MP 150MP 149MP 148
MP 158MP 157 MP 166MP 165MP 164MP 163MP 162MP 161 MP 167 MP 168MP 159 MP 160
1222-9526 rev. 1
53 (124)
Page 54

E1000
Clamp
1
GND
Will be connected
to GND in PCB
SHIELD_CAN_SHIHO_CAMERA
1205-1771
E1001
Clamp
1
GND
Will be connected
to GND in PCB
SHIELD_CAN_SHIHO_KAJSA
1205-1773 2
E1002
Clamp
1
GND
Will be connected
to GND in PCB
SHIELD_CAN_SHIHO_VERA
1205-1776
STEPUP50
E1003
Clamp
1
GND
Will be connected
to GND in PCB
SHIELD_CAN_SHIHO_WLAN
1205-1779
Pages B1-B16
STEPUP50
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
OPTOSENSE
OPTOTEMP
MCLK
CHARGE_LED
TX_ADSTR
OPTO_EN
TESTOUT
CAMSYSCLK
CAM_LDO_EN
WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
WLAN_SCLK
RF_ID
AGPS_RSTn
VAD
SPL
MICN/AUXinR
SPR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
Application& Sys.PerformanceApplication& Sys.Performance
E1004
Clamp
1
GND
Will be connected
to GND in PCB
SHIELD_CAN_SHIHO_REGULATOR
1205-1781
VBAT
VDDE18
VDIG
VBT27
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VOPTO30
CAMRESn
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
WLAN_CLK
AGPS_CLK
MCLKREQ
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
PWRRSTn
VBAT
VDDE18
MEASUREMENT POINTS Top Schematic
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
LED_CAM1
LED_KEYPAD
WLAN_VO33
VBAT
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
RTCCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
PWRRSTn
FM_ANTENNA
Audio
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_LDO18A
Pages A1-A4
RF_ID
WLAN_SCLK
MCLKSEC
BT_CLKREQn
WLAN_CLKREQ
TESTOUT
OPTO_EN
TX_ADSTR
MCLK
VDDE18
VOPTO30
VDDE18
VOPTO30
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VDIG
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_VO18
VDIG
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VAD
SPL
SPR
Page T1
Page T1
VBT27
VDDE18
VBAT
VBAT
VDDE18
VBT27
VDIG
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_CLK
AGPS_CLK
MCLKREQ
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
Access
Access
Pages R1-R5
VCAMIO18
XEFL_SPDA
TX_ADSTR
OPTO_EN
TESTOUT
WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
WLAN_SCLK
VDDE18
MCLK
RF_ID
VBAT
XEFL_SP DA
VBAT
VDDE18
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28
VCAMSA28
VCAML12
VOPTO30
VDIG
CAMRESn
CHARGE_LED
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
CAMSYSCLK
CAM_LDO_EN
XEFL_SP DA
Imaging
Imaging
Pages I1-I4
STEPUP50
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
OPTOSENSE
OPTOTEMP
STEPUP50
VCAMSD18
VCAMSA28
VDIG
VBT27
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28
VBEAR26
RTCCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
PWRRSTn
FM_ANTENNA
SPR
SPL
VAD
VCAML12
VAUDIO26
VCAMSA28
CAMRESn
CHARGE_LED
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
CAMSYSCLK
CAM_LDO_EN
WLAN_CLK
AGPS_CLK
MCLKREQ
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
VDDE18
VCAMIO18
WLAN_VO18
VBAT
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Access side GPIO mapping
AccGPIO00
USB_HSSTP
USB_HSDIR
AccGPIO01
AccGPIO02
CTMS B14
AccGPIO03
CFMS
USB_HSINCLK
AccGPIO04
USB_HSNXT
AccGPIO05
AccGPIO06
AccGPIO07
USB_HSDATA5 B14
AccGPIO08
USB_HSDATA6 B14
AccGPIO09
USB_HSDATA7
AccGPIO10
UART3_RX R04
AccGPIO11
UART3_TX
AccGPIO12
AccGPIO13
UART3_RTS
AccGPIO14
CH_DET_DP
AccGPIO15
CH_DET_DM
AccGPIO16
USB_HSCHIP_SEL B14
AccGPIO17
AccGPIO18
USB_HSDATA3
AccGPIO19
AccGPIO20
ACC_SPI_DI
AccGPIO21
ACC_SPI_DO
AccGPIO22
ACC_SPI_CLK
AccGPIO23
OVP_FLAG B14
not used
AccGPIO24
AccGPIO25
WLAN_SPI_IRQ R05
BT-chip GPIO mapping
BTGPIO0
WLAN_CONFIRMn R03
BTGPIO8
WLAN_BT_STATE R03
BTGPIO9
not used R03
BTGPIO10
BTGPIO11
not used R03
BTGPIO16
Application s ide GPIO mapping
Port Usage Pag e
AppGPIO00
FM_INT A04
AppGPIO01
APP_LOG B14
AppGPIO02
AppGPIO03
AppGPIO04
SLIDE_SENSE B15
AppGPIO05
VIDCC_SPI_CS B16
AppGPIO06
AppGPIO07
AppGPIO08
VIDCC_SPI_DO B16
AppGPIO09
AppGPIO10
AppGPIO11
AppGPIO12
MSDETECT B13
AppGPIO13
AFLED_EN
AppGPIO14
TV_CS
AppGPIO15
DCON xxx
AppGPIO16
VIDCC_INT
AppGPIO17
AppGPIO18
TV_RESn I02
AppGPIO19
MP202 GPO mappi ng
Port Usage Page
GPO_P0
not used
GPO_P1
not used
GPO_P2
not used
GPO_P3
not used
PO0
CAM_LDO_EN B16
not used B16
PO1
VCAMSD_EN
PO2
CAMRESn
PO3
PO4
PO5
VIDCC_L1_EN B16
PO6
VIDCC_SDR_EN B16
PO7
VIDCC_CLKREQn B16
GPIO expander mappi ng
not used T01
GPIO_O0
GPIO_O1
GPIO_O6
GPIO_O7
LED_TALLY I04
GPIO_O8
WLAN_RSTn_PDn R05
GPIO_O9
WLAN_PDn B10
GPIO_O10
GPIO_O11
GPIO_O12
GPIO_O13
GPIO_O14
XEFL_SP D1 I04
GPIO_O15
GPIO_P2
GPIO_P3
GPIO_P4
GPIO_P5
PageUsagePort
B14
B14
B14
B14
B14
B14USB_HSDATA4
B14
R04
R04UART3_CTS
R04
B14
B14
R04AGPS_SYNC
B14
R05WLAN_SPI_CSn
R03
R03
R03
T01
R03BT_SPI_CSnAccGPIO26
R03BT_SPI_INTAccGPIO27
PageUsagePort
R03not used
R03WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
I03CAMIRQ
I03COVER_OPEN
B08VTV15_EN
B16VIDCC_SPI_DI
B16VIDCC_SPI_CLK
B03AGPS_CLK_EN
I04X_CHARGE_RDY
I04
I02
B16
A02FM_SELECT
B16VIDCC_RESn
B16
B16
B16
B16
B16
B16
B16VIDCC_L1DET
PageUsagePort
R04AGPS_LDO_EN
A02AMPCTRL
R04AGPS_PWRON
I03XEFL_CHARGE_EN
I04XEFL_FC D
I04XEFL_SB
I04XEFL_SP D0
B03AGPS_CLKREQn
B03TV_CLKREQn
T01not used
T01not used
MEASUREMENT POINTS
Made for
Test
Top Schematic
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page 1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
54 (124)
Page 55

MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
MEASUREMENT POINTS Audio Top
VBATVAUDIO26VBEAR26
Page 2Page 2
VBAT
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL VAD
VBATVDDE18
VBAT
VDDE18
Page 4
Page 4
FMR
FML
FMR
FML
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FMR
FML
VAD
SPL
SPR
SPL
SPR
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
VAD
SPL
SPR
FM_ANTENNA
PWRRSTn
RTCCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
FM_ANTENNA
PWRRSTn
RTCCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
FM_ANTENNA
PWRRSTn
RTCCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
FM Radio
FM Radio
Audio Digital
Audio Digital
Page 3
Page 3
Audio Analog
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VBAT
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
VBAT VDDE18 VAUDIO26 VBEAR26
Made for
Audio
Audio Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page A1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
55 (124)
Page 56

Primary MIC
Secondary MIC
VBAT
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
X4200
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
1204-5252 2 (#5/6)
100-pin
X4400
XE-FLASH MODULE
CONNECTOR
1201-5197
24-pin
FMR
FML
MICP/AUXinL
MICN/AUXinR
VBAT
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
6
4
8
B10
B11
B12
(#2/2)
N2010
APPLICATIONGPIO_17
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VAUDIO26 VBEAR26
GPIO_O6_OUTPUT
R22
C3114
33pF
<NM>
MP 80
7
C3110
33pF
<NM>
C3144
33pF
<NM>
R3153
100Kohms
R3100
0ohms
ST3103
21
R3118
0ohms
ST3104
21
R3160
0ohms
Shield with GND
C3115
33pF
<NM>
C3116
33pF
<NM>
AMPCTRL
MP 103
MP 122
C3146
220nF
C3145
220nF
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
FBMH1608HL331
FBMH1608HL331
V3101
1001-0730
UESD6.0DT5G
Radio Components
L3108
L3109
BEARP
BEARN
L3110
FBMH1608HL601
C3101
33pF
L3111
FBMH1608HL601
C3117
C3118
33pF
33pF
<NM>
<NM>
X4200
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
58
60
1204-5252 2 (#6/6)
100-pin
SPEAKER_P
SPEAKER_N
SPEAKER
X3102
1
X3103
1
C905
MEASUREMENT POINTS
R3155
2.2Kohms
C3165
C3166
33pF
10uF
C3131
220nF
ST3101
21
220nFC3100
12
ST3102
R3150
100ohms
MEASUREMENT POINTS Audio Analog
VBAT
12
ST3100
R3106
4.7Kohms
C3153
33pF
<NM>
C3104
470nF
N3100
AUDIO_PA
A1
INM
INP
C1
Bypass
C3
SHDN
NCP2990
1200-9978
OUTA
OUTB
VM_P
B3
VP
2A3A
C2
B1
B2
VM
C3106
10uF
C3139
33pF
<NM>
C3105
33pF
<NM>
C3107
56pF
ST3105
12
ST3106
12
C3140
33pF
<NM>
2.2KohmsR3102
2.2KohmsR3127
0ohmsR3128
<NM>
CCO_INTMIC
C3148
C3137
470nF
470nF
MP 1
AUXO1
AUXO2
R3154
24Kohms
C3138
47nF
<NM>
MP 30
C3102
33pF
<NM>
C3154
3.3nF
VBEAR26
LINEIN1
LINEIN2
C3151
1uF
VAUDIO26
C3135
100nF
C3133
220nF
C3126
220nFC3121
MIC1P
MIC1N
220nFC3112
MIC3P
MIC3N
33pF
<NM>
C3127
33pF
<NM>
PHFMICP
PHFMICN
C3136
33pF
C3152
100nF
N10
M10
N9
P9
N8
P8
N11
P10
P12
P11
P7
P13
P6
P3
N2000
MIC1P
MIC1N
MIC2P
MIC2N
MIC3P
MIC3N
MIC4P
MIC4N
LINEIN1
LINEIN2
VDD_SPKR
VDD_AUDIO
VDD_BEAR
VDD_AUXO
AB3100
1202-0639
Ericsson AB 3100
MMI
AUDIO IF
SPKRP_OUT
SPKRN_OUT
BEARP_OUT
BEARN_OUT
AUXO1_OUT
AUXO2_OUT
MIDR_OUT
PLL_DEC3
PLL_DEC4
VSS_SPKR
VSS_BEAR
2
CCO1
CCO2
N13
P14
N7
N6
P5
M5
M4
P4
N4
NC
H14
J12
M7
N5
C3108
56pF
MP 58
MP 57
C3159
33pF
<NM>
MP 146
MP 147
2
C2
A
1
C1
3
MP 123
R3151
0ohms
VAD
SPR
SPL
FM_SELECT
<NM>
FM_R
FM_L
R3112
R3156
C3157
33pF
MP 101
MP 100
C3158
10uF
100ohms
MP 104
N3101
TJATTE3
A5
V_MIC
NC
B3
INTMICint
NC
B5
INTMIC
NC
MICP
MICN
SPL
SPR
1000-0198
SP_ref
MICP_int
MICN_int
SPL_int
SPR_int
LeadfreeTJATTE3
B2
COO
D1
NC
1A2D
2A3D
100nHL3125
3A4D
100nHL3126
4A5D
B1
VAD
C1
GND
C2
GND
C3
GND
C4
GND
C5
GND
B4
GND
100Kohms
<NM>
C3124
100nF
MP 102 MP 99 MP 98 MP 121
C3125
100nF
C3156
470nF
C3155
470nF
N3103
SPDT Analog switch or
Mux/Demux bus switch
B1
GND
3
B0
FSA3157BL6X_F113
1213-5382
R3147
2.2Kohms
VAUDIO26
MP 120
61
S
52
VCC
4
A
R3148
2.2Kohms
R3149
100Kohms
C3167
100nF
150uFC3150
C3149
150uF
VAD
SPR
SPL
Made for
Audio
Audio Analog
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page A2 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
56 (124)
Page 57

MEASUREMENT POINTS Audio Digital
SP3213
APP_I2S0_DATA_B
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_APP
I2S_PCM_A_10_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_APP_I2S_PCM
KAJSA_BOTTOM_AUDIO
T23
I2S0ULD/PCM0ULD
U23
I2S1ULD/PCM1ULD
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
I2S0CLK/PCM0CLK
I2S0WS/PCM0SYN
I2S0DLD/PCM0DLD
I2S1CLK/PCM1CLK
I2S1WS/PCM1SYN
I2S1DLD/PCM1DLD
T24
U15
T22
V22
V23
W24
R3201
100Kohms
<NM>
SP3207
R3202
100Kohms
<NM>
R3203
100Kohms
<NM>
APP_I2S1_WS_1
APP_I2S1_CLK_1
APP_I2S1_DATA_B_1
R3204
100Kohms
M4
P4
N4
N3
N2500
PM1_SEN
PM1_CLK
PM1_SO
PM1_SI
MP202
1200-1414
APP_I2S0_CLK
APP_I2S0_WS
APP_I2S0_DATA_A
APP_I2S1_DATA_A
MP202_I2SIF
PM0_SEN
PM0_CLK
PM0_SO
PM0_SI
L3
L1
L2
M2
APP_I2S1_WS
APP_I2S1_CLK
NC
APP_I2S1_DATA_B
SP3206
SP3214
SP3204 SP3205
SP3208SP3209
K3
J3
J1
L3
K1
K4
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
SCK1
WS1
SDI1
SCK2
WS2
SDI2
AB3100
1202-0639
MMI
CODEC IF
2
SDO1
SDO2
MEASUREMENT POINTS
K2
L2
Made for
Audio
Audio Digital
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page A3 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
57 (124)
Page 58

FM_ANTENNA
PWRRSTn
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
RTCCLK
MEASUREMENT POINTS Audio FM Radio
VDDE18
N1300
L3300
270nH
C3306
220pF
PWRRSTn
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
RTCCLK
ST3304
VDDE18VBAT
21
C3304
C3305
22nF
100nF
B8
C9
D9
E9
D8
D7
A7
A6
A5
A4
B3
D6
FM_FMIP
FM_RFGND
FM_RST
FM_SENB
FM_SCL
FM_SDA
FM_RTCCLK
FM_GPIO1
FM_GPIO2
FM_GPIO3
FM_VA
FM_VD
FM_VIO
STLC2593
1200-9840
BLUETOOTH-FM_FM
FM_RADIO_IO
FM_PWR_GND
FM_ROUT
FM_LOUT
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
FM_GND
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
C5
5B8C
D4
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
F7
NC
F8
NC
L4
NC
L5
NC
L6
NC
A3
B4
B6
B7
C4
C6
C7
D5
FMR
FML
FMR
FML
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VBAT
VDDE18
VBAT
VDDE18
FM_INT
R3302
3.3Kohms
MP 25
N2010
R17
APPLICATION GPIO_00
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
Made for
Audio FM Radio
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page A4 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
58 (124)
Page 59

MCLK
MCLKSEC
BT_CLKREQn
WLAN_CLKREQ
MEASUREMENT POINTS Application & System Perfor ma nce Top
RTCCLK
USB_HS_CLK
DCON
VIDCC_CLK
VDDE18
Pages 2-5
MCLK
MCLKSEC
BT_CLKREQn
WLAN_CLKREQ
Pages 11-16
Pages 11-16
VBACKUPVBATVDIGVDDE18VMC18VAUDIO26
STEPUP50
VIDCC_CLK
DCON
USB_HS_CLK
RTCCLK
VBAT
VDIG
VDDE18
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VIDCC_CLKREQn
SERVICEnSTEPUP50
ONSWAnVBACKUP
VIDCC_CLKREQn
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
VDDE18
MCLK
MCLKSEC
BT_CLKREQn
WLAN_CLKREQ
VIDCC_CLKREQn
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
System Control
System Control
VIDCC_CLK
DCON
USB_HS_CLK
RTCCLK
BT_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
MCLKREQ
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLK
PWRRSTn
RTCCLK
BT_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
MCLKREQ
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLK
PWRRSTn
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
RTCCLK
BT_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
MCLKREQ
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLK
PWRRSTn
MEASUREMENT POINTS
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
TX_ADSTR
RF_ID
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
STEPUP50
WLAN_SCLK
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
VAD
SPL
SPR
STEPUP50
VAD
TX_ADSTR
RF_ID
SPL
SPR
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
WLAN_SCLK
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
VAD
TX_ADSTR
RF_ID
SPL
SPR
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
Connectivity
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
VBUS
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VCAMSD_EN
DCIO
VDDE18
VDIG
PWRRSTn
WLAN_CLKREQ
VBUS
DCIO
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
PWRRSTn
WLAN_CLKREQ
VBUS
DCIO
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
WLAN_SCLK
Pages 6-10
VBACKUP
VMC18
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VBT27
VOPTO30
VBAT
VMC18
VBAT
VBACKUP
VDIG
VAUDIO26
VBAT
VDDE18
VDIG
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VBT27
VOPTO30
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
VBAT
VDDE18
VDIG
VAUDIO26
VBEAR26
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VBT27
VOPTO30
OPTO_EN
OPTO_EN
OPTO_EN
Power
Power
CHARGE_LED
CHARGE_LED
CHARGE_LED
Made for
Application & System Performance Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
59 (124)
Page 60

WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
VIDCC_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
MCLK
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
MEASUREMENT POINTS System Top
VDDE18
Page 3
VDDE18
VIDCC_CLK
BT_CLK
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
VIDCC_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
MCLK
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
VIDCC_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
MCLK
SERVICEn
Clocks & Resets
Clocks & Resets
WLAN_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
RTCCLK
MCLKREQ
DCON
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
USB_HS_CLKONSWAn
PWRRSTn
MEMRESn
MEMRESn
VIDCC_CLK
BT_CLK
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
RTCCLK
MCLKREQ
DCON
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
USB_HS_CLK
PWRRSTn
VIDCC_CLK
BT_CLK
AGPS_CLK
WLAN_CLK
CAMSYSCLK
RTCCLK
MCLKREQ
DCON
BTRESn
AGPS_RSTn
USB_HS_CLK
PWRRSTn
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VDDE18
VDDE18
Page 4
MEMRESn
VDDE18
System Memories
VDDE18
Made for
Application & System Performance
System Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B2 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
60 (124)
Page 61

MEASUREMENT POINTS
System Control - Clocks & Re set s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
BT_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
MCLK
VIDCC_CLKREQn
AGPS_CLKREQn
TV_CLKREQn
WLAN_CLKREQ
SERVICEn
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2010
APPLICATION GPIO_10
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VIDCC_CLKREQn
GPIO_P2_BIDIR
GPIO_P3_BIDIR
WLAN_CLKREQ
K12
ST2101
ST2102
12
3
ST2103
12
4
21
MP 50
MP 53
1
VDDE18
R2116
100Kohms
R2104
100Kohms
MP 49
3
V2100
RN1108
1000-8463
2
R2103
100Kohms
<NM>
MP 38
R2102
100Kohms
<NM>
VDDE18
R2101
100Kohms
SP2104
SP2105
V2101
1000-0391
Leadfree
BT_CLKREQn
MCLKSEC
AGPS_CLK_EN
MCLK
RTCCLK
SYSCLKREQn
PWRRSTn
SERVICEn
MP 36
C2104
1nF
<NM>
VDDE18
N2102
B1
1A
C1
2Y
A1
1OE
GND
SN74LVC2G241YZPR
1204-8667
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM
SYSTEM_CONTROL_A_23_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SYSTEM_LEVEL
MCLK
V14
RTCCLKIN
V16
SYSCLKREQn
AA24
MSACCIRQn
V17
MSAPPIRQn
PWRRSTn
AD23
SERVICEn
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
CLOCKS
INTERRUPTS
RESETS
POWER CONTROL
R2111
10ohms
C2105
4.7uF
2A
1Y
2OE
VCC
MCLKREQ
SYSCLK0
SYSCLK1
SYSCLK2
RESOUT0n
RESOUT1n
RESOUT2n
ACCSLEEP
APPSLEEP
DCON
D2
C2
B2
AD20AE23
AD22
AB20
AC21
AC22AB19
AB18
AB23
AB17
AD21
Y22
N2100
1
OE
2
A
53
VCC
SN74LVC1G125YZPR
1200-0425
2A1D
MP 37
21
ST2110
22ohmsR2123
R2122
22ohms
Y
GND
R2125
100Kohms
ST2105
21
4
ST2106
C2103
33pF
<NM>
MP 24
MP 22
ST2107
MP 55
MP 19
ST2108
ST2109
MP 20
WLAN_CLK
21
R2108
100Kohms
21
R2117
100Kohms
21
21
1KohmsR2115
BT_CLK
AGPS_CLK
TV_CLK
VIDCC_CLK
RTCCLK
MCLKREQ
CAMSYSCLK
USB_HS_CLK
MEMRESn
AGPS_RSTn
BTRESn
SP2103
SP2102
N2700
S1D13771_CLOCK
H7
CLKI
S1D13771
1200-0362
WLAN_CLK
BT_CLK
AGPS_CLK
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VIDCC_CLK
RTCCLK
MCLKREQ
CAMSYSCLK
USB_HS_CLK
MEMRESn
AGPS_RSTn
BTRESn
DCON
PWRRSTn
ONSWAn
VDDE18
VDDE18
ST2104
MP 36
B2100
ONSWAn
C2100
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
SYSTEM CONTROL
SYSTEM POR
E13
E14
IRQB_N
PWRRST_N
21
XTAL_OUT
AB3100
1202-0639 2
RTC
CLOCK
ONSWA_NIRQA_N
ONSWB_N
ONSWC
XTAL1
XTAL2
SLEEP_A
SLEEP_B
MCLK
F13
F12
11F21E
A10B11
D11
E11
D14
H13
18pF
NC
ST2100
12
XTAL1
C2 C1
32.768kHz
1000-0036
DCON
PWRREQn
MCLK_VERA
XTAL2
C2101
18pF
MP 138MP 136
SP2107SP2106
Made for
Application & System Performance
System Control - Clocks & Resets
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B3 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
61 (124)
Page 62

MEASUREMENT POINTS System Memories
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SH_EMIF_A_8_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SYSTEM_LEVEL
KAJSA_BOTTOM
SHARED_MEMORY_IF(EMIF1)
E4
SH_D00
NC
F4
SH_D01
NC
G4
SH_D02
NC
G5
SH_D03
NC
H5
SH_D04
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
K5
SH_D05
J4
SH_D06
J5
SH_D07
F5
SH_D08
L4
SH_D09
K4
SH_D10
L9
SH_D11
L5
SH_D12
K9
SH_D13
M5
SH_D14
N5
SH_D15
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
MEMRESn
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM
DIRECT_MEMORY_A_22_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SYSTEM_LEVEL
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
MEMRESn
NAND_WPN
SDTEMP
J16
J17
NC
SH_A01
SH_A02
SH_A03
SH_A04
SH_A05
SH_A06
SH_A07
SH_A08
SH_A09
SH_A10
SH_A11
SH_A12
SH_A13/SH_SDBS0
SH_A14/SH_SDBS01
SH_A15/SH_SDBS1
SH_SDCSn
SH_SDCASn
SH_WEn
SH_SDCLK
SH_SDCKE
SH_SDRASn
SH_BE0n
SH_BE1n
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_APP_EMIF_A_9_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SYSTEM_LEVEL
KAJSA_BOTTOM_APPLICATION
MEMORY_IF(EMIF2)
E14
AP_D00
NC
E13
AP_D01
J14
AP_D02
NC
J15
AP_D03
NC
E15
AP_D04
NC
D15
AP_D05
NC
E16
AP_D06
NC
D17
AP_D07
NC
E17
AP_D08
NC
D18
AP_D09
NC
E18
AP_D10
R2112
100Kohms
<NM>
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
R2113
2.2Kohms
D19
AP_D11
E21
AP_D12
E19
AP_D13
D20
AP_D14
E20
AP_D15
D10
AP_NFIF_READY
AP_WAITn
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
AP_A13/AP_SDBS0
AP_A14/AP_SDBS01
AP_A15/AP_SDBS1
AP_OEn/RE/AP_SDCAS
F3
NC
H3
NC
J3
NC
J2
NC
G3
NC
K2
NC
K3
NC
L2
NC
L3
NC
M3
NC
M4
NC
N4
NC
P3
NC
N3
NC
P4
NC
C5
NC
C4
NC
D4
NC
H4
NC
C3
NC
D3
NC
E3
NC
E2
NC
VDDE18
AP_A01
AP_A02
AP_A03
AP_A04
AP_A05
AP_A06
AP_A07
AP_A08
AP_A09
AP_A10
AP_A11
AP_A12
AP_A16
AP_A17/AP_CLE
AP_A18/AP_ALE
AP_A19
AP_A20
AP_A21
AP_A22
AP_A23
AP_A24
AP_A25
AP_A26/AP_CRE
AP_CLK
AP_SDCLK
AP_FBCLK
AP_SDCKEN0
AP_SDCKEN1
ADVn/AP_SDRAS
AP_CS0n
AP_CS1n
AP_CS2n
AP_CS3n
AP_BE0n
AP_BE1n
AP_WEn
C13
NC
J12
NCNC
C14
NC
C15
NC
D16
NC
B15
NC
C16
NC
B17
NC
C17
NC
B18
NC
C18
NC
C19
NC
B20
NC
C20
NC
C21
NC
C22
NC
C23
NC
D21
NC
D23
NC
D22
NC
E23
NC
C24
NC
D24
NC
C25
NC
E24
NC
D25
NC
E12
NC
D11
D12
D14
NC
E5
NC
C12
NC
B11
NC
J10
NC
C10
NC
E11
NC
D7
NC
D13
NC
J11
NC
21B11C
NC
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VDDE18
VDDE18
Kajsa PoP MCP Memory
N2020
POP Symbol
KAL00900MX-AJ55_POP
1205-5912
POP_symbol
This symbol is placed here to include MCP memory in BOM
1
Electrical inferface can be seen on pageB05
NC
Made for
Application & System Performance
System Memories
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B4 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
62 (124)
Page 63

TOP_SH_D00
TOP_SH_D01
TOP_SH_D02
TOP_SH_D03
TOP_SH_D04
TOP_SH_D05
TOP_SH_D06
TOP_SH_D07
TOP_SH_D08
TOP_SH_D09
TOP_SH_D10
TOP_SH_D11
TOP_SH_D12
TOP_SH_D13
TOP_SH_D14
TOP_SH_D15
TOP_VDD_MEM_00
TOP_VDD_MEM_01
TOP_VDD_MEM_02
TOP_VDD_MEM_03
TOP_VDD_MEM_04
TOP_VDD_MEM_05
TOP_VDD_MEM_06
TOP_VDD_MEM_07
TOP_VDD_MEM_08
TOP_VDD_MEM_09
TOP_VDD_MEM_10
TOP_VDD_MEM_11
TOP_VDD_MEM_12
TOP_VDD_MEM_13
TOP_VDD_MEM_14
TOP_VDD_MEM_15
TOP_VDD_MEM_16
TOP_VDD_MEM_17
N2010
KAJSA_TOP_SH_EMIF_B_1_5
Kajsa-PoP_top-SYSTEM-LEVEL
KAJSA_SHARED_MEMORY_IF(EMIF1)
T_B7
SH_D00
T_A6
SH_D01
T_B6
SH_D02
T_A5
SH_D03
T_B5
SH_D04
T_B4
SH_D05
T_A4
SH_D06
T_A3
SH_D07
T_C1
SH_D08
T_F2
SH_D09
T_F1
SH_D10
T_G2
SH_D11
T_H1
SH_D12
T_J2
SH_D13
T_J1
SH_D14
T_K2
SH_D15
KAJSA_POP_TOP
1208-3871_TOP
T_A7
T_A10
T_A20
T_B1
T_B2
T_B3
T_B19
T_H2
T_L1
T_L2
T_N2
T_P21
T_W2
T_Y13
T_Y19
T_AA2
T_AA8
T_AA20
N2010
VDD_Q
VDD_Q
F_VDD
F_VDD
F_VDD
VDD_Q
VCC_N
VDD_Q
VDD_Q
F_VDD
VDD_Q
F_VDD
F_VDD
F_VDD
F_VDD
F_VDD
VCC_N
F_VDD
KAJSA_POP_TOP
1208-3871_TOP
N2010
KAJSA_POP_TOP
1208-3871_TOP
SH_A14/SH_SDBS01
SH_A15/SH_SDBS1
KAJSA_TOP_POWER_B_4_5
Kajsa-PoP_top-POWER
POWER
KAJSA_TOP_UNUSED_B_5_5
Kajsa-PoP_top-NOT_USED
UNUSED
SH_A01
SH_A02
SH_A03
SH_A04
SH_A05
SH_A06
SH_A07
SH_A08
SH_A09
SH_A10
SH_A11
SH_A12
SH_A13
SH_SDCSn
SH_SDCASn
SH_WEn
SH_SDCLK
SH_SDCKE
SH_SDRASn
SH_BE0n
SH_BE1n
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
GND_MEM
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
MEASUREMENT POINTS System PoP IF
TOP_SH_DATA_BUS TOP_APPLICATION_DATA_BUS
N2020
T_T20
T_U21
T_U20
T_V21
T_V20
T_W21
T_Y18
T_AA19
T_Y17
T_AA18
T_Y16
T_AA17
T_Y15
T_N21
T_R21
T_R20
T_T21
T_M21
T_P20
T_A2
T_A9
T_B21
T_C2
T_C20
T_G1
T_K1
T_N1
T_W1
T_W20
T_Y1
T_Y2
T_Y3
T_Y8
T_Y10
T_Y14
T_Y20
T_Y21
T_A1
T_A21
T_M1
T_AA1
T_AA4
T_AA21
T_AA16
T_AA5
T_D1
T_E1
T_D2
T_E2
TOP_VDD
TOP_GND_MEM_00
TOP_GND_MEM_01
TOP_GND_MEM_02
TOP_GND_MEM_03
TOP_GND_MEM_04
TOP_GND_MEM_05
TOP_GND_MEM_06
TOP_GND_MEM_07
TOP_GND_MEM_08
TOP_GND_MEM_09
TOP_GND_MEM_10
TOP_GND_MEM_11
TOP_GND_MEM_12
TOP_GND_MEM_13
TOP_GND_MEM_14
TOP_GND_MEM_15
TOP_GND_MEM_16
TOP_GND_MEM_17
TOP_NC_1
TOP_NC_2
TOP_NC_3
TOP_NC_4
TOP_NC_5
TOP_NC_6
TOP_NC_7
TOP_NC_8
TOP_SH_A01
TOP_SH_A02
TOP_SH_A03
TOP_SH_A04
TOP_SH_A05
TOP_SH_A06
TOP_SH_A07
TOP_SH_A08
TOP_SH_A09
TOP_SH_A10
TOP_SH_A11
TOP_SH_A12
TOP_SH_A13
TOP_SH_BA0
TOP_SH_BA1
TOP_SDRAM_CS_N
TOP_SDRAM_CAS_N
TOP_SDRAM_WE_N
TOP_SDRAM_CLK
TOP_SDRAM_CKE
TOP_SDRAM_RAS_N
TOP_SDRAM_BE0_N
TOP_SDRAM_BE1_N
KAL00900MX-AJ55_MCP_POP_SDRAM_EMIF1
2GbitNANDx8+128Mbitx16+512MbitSDRAMx16
T20
U21
U20
V21
V20
W21
Y18
AA19
Y17
AA18
Y16
AA17
Y15
D1
E1
N21
R21
R20
T21
M21
P20
D2
E2
A2
A9
B21
C2
C20
G1
K1
N1
W1
W20
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y8
Y10
Y14
Y20
Y21
N2020
KAL00900MX-AJ55_MCP_POP_UNUSED
2GbitNANDx8+128Mbitx16+512MbitSDRAMx16
A1
NC_13
A21
NC_14
M1
NC_15
AA1
NC_16
AA4
NC_17
AA21
NC_18
AA16
NC_19
AA5
NC_20
KAL00900MX-AJ55
1205-5912_POP
SHAREDMEMORYIF(EMIF1)
SDRAM_128_A0
SDRAM_128_A1
SDRAM_128_A2
SDRAM_128_A3
SDRAM_128_A4
SDRAM_128_A5
SDRAM_128_A6
SDRAM_128_A7
SDRAM_128_A8
SDRAM_128_A9
SDRAM_128_A10
SDRAM_128_A11
NC_1
SDRAM_128_BA0
SDRAM_128_BA1
SDRAM_128_CSn
SDRAM_128_CASn
SDRAM_128_WEn
SDRAM_128_CLK
SDRAM_128_CKE
SDRAM_128_RASn
SDRAM_128_LDQM
SDRAM_128_UDQM
KAL00900MX-AJ55
1205-5912_POP
N2020
KAL00900MX-AJ55_MCP_POP_VMEM_POWER
2GbitNANDx8+128MbitSDRAMx16+512MbitSDRAMx16
VSS_1
VSSQ_1
VSS_2
VSSQ_2
VSS_N_1
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_N_2
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
KAL00900MX-AJ55
1205-5912_POP
-
VDDMEMORIES
UNUSED
SDRAM_128_DQ0
SDRAM_128_DQ1
SDRAM_128_DQ2
SDRAM_128_DQ3
SDRAM_128_DQ4
SDRAM_128_DQ5
SDRAM_128_DQ6
SDRAM_128_DQ7
SDRAM_128_DQ8
SDRAM_128_DQ9
SDRAM_128_DQ10
SDRAM_128_DQ11
SDRAM_128_DQ12
SDRAM_128_DQ13
SDRAM_128_DQ14
SDRAM_128_DQ15
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VCC_N_1
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VCC_N_2
VDD_10
TOP_SH_D00
B7
TOP_SH_D01
A6
TOP_SH_D02
B6
TOP_SH_D03
A5
TOP_SH_D04
B5
TOP_SH_D05
B4
TOP_SH_D06
A4
TOP_SH_D07
A3
TOP_SH_D08
C1
TOP_SH_D09
F2
TOP_SH_D10
F1
TOP_SH_D11
G2
TOP_SH_D12
H1
TOP_SH_D13
J2
TOP_SH_D14
J1
TOP_SH_D15
K2
A7
TOP_VDD_MEM_00
A10
TOP_VDD_MEM_01
A20
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
N2010
KAJSA_POP_TOP
1208-3871_TOP
TOP_VDD_MEM_02
B1
TOP_VDD_MEM_03
B2
TOP_VDD_MEM_04
B3
TOP_VDD_MEM_05
B19
TOP_VDD_MEM_06
H2
TOP_VDD_MEM_07
L1
TOP_VDD_MEM_08
L2
TOP_VDD_MEM_09
N2
TOP_VDD_MEM_10
P21
TOP_VDD_MEM_11
W2
TOP_VDD_MEM_12
Y13
TOP_VDD_MEM_13
Y19
TOP_VDD_MEM_14
AA2
TOP_VDD_MEM_15
AA8
TOP_VDD_MEM_16
AA20
TOP_VDD_MEM_17
KAJSA_TOP_DIRECT_MEMORY_S IGNALS_B_3_5
Kajsa-PoP_top-SYSTEM-LEVEL
DIRECT_MEMORY_SIGNALS
NC_12
NC_13
NC_14
NAND_WPn
SDTEMP
T_A8
T_B9
T_B10
T_B8
T_B20
TOP_AP_D00
TOP_AP_D01
TOP_AP_D02
TOP_AP_D03
TOP_AP_D04
TOP_AP_D05
TOP_AP_D06
TOP_AP_D07
TOP_AP_D08
TOP_AP_D09
TOP_AP_D10
TOP_AP_D11
TOP_AP_D12
TOP_AP_D13
TOP_AP_D14
TOP_AP_D15
TOP_DMS_1
TOP_DMS_2
TOP_DMS_3
TOP_NAND_WP_N
TOP_DMS_5
N2010
KAJSA_TOP_AP_EMIF_B_2_5
Kajsa-PoP_top-SYSTEM-LEV EL
KAJSA_APPLICATION_MEMORY_IF(EMIF2)
T_P1
AP_D00
T_P2
AP_D01
T_R1
AP_D02
T_R2
AP_D03
T_T1
AP_D04
T_T2
AP_D05
T_U1
AP_D06
T_U2
AP_D07
T_Y5
AP_D08
T_AA6
AP_D09
T_Y6
AP_D10
T_AA7
AP_D11
T_Y7
AP_D12
T_AA9
AP_D13
T_Y9
AP_D14
T_AA10
AP_D15
T_B14
AP_NFIF_READY
KAJSA_POP_TOP
1208-3871_TOP
N2020
MCP_POP_DIRECT_MEMORY_SIGNALS
2GbitNANDx8+128Mbitx16+512MbitSDRAMx16
A8
NC_21
B9
NC_22
B10
NC_23
B8
NAND_WPn
B20
NC_24
KAL00900MX-AJ55
1205-5912_POP
AP_A14/AP_SDBS01
AP_A15/AP_SDBS1
AP_SDCAS/AP_RE/AP_OEn
KAL00900MX-AJ55
DirectMemorySignals
AP_A01
AP_A02
AP_A03
AP_A04
AP_A05
AP_A06
AP_A07
AP_A08
AP_A09
AP_A10
AP_A11
AP_A12
AP_A13
NC_1
NC_2
AP_A18/AP_ALE
AP_A17/AP_CLE
NC_3
NC_4
AP_A16
AP_A19
AP_A20
AP_A21
AP_A22
AP_A23
AP_A24
AP_A25
AP_A26/AP_CRE
NC_5
AP_SDCLK
AP_SDCKE0
AP_SDRAS/ADVn
NC_6
NC_7
NC_8
AP_CS0n
NC_9
AP_CS2n
AP_BE0n
AP_BE1n
NC_10
AP_WEn
NC_11
AP_WAITn
T_A14
T_B15
T_A15
T_B16
T_A16
T_B17
T_A17
T_B18
T_A18
T_A19
T_C21
T_D20
T_D21
T_E20
T_L21
T_E21
T_L20
T_F20
T_A12
T_F21
T_B12
T_G20
T_G21
T_H20
T_H21
T_J20
T_J21
T_K20
T_K21
T_M20
T_B13
T_M2
T_V2
T_AA14
T_Y11
T_A11
T_Y12
T_AA15
T_AA12
T_AA11
T_N20
T_Y4
T_AA3
T_A13
T_V1
T_B11
T_AA13
TOP_AP_A01
TOP_AP_A02
TOP_AP_A03
TOP_AP_A04
TOP_AP_A05
TOP_AP_A06
TOP_AP_A07
TOP_AP_A08
TOP_AP_A09
TOP_AP_A10
TOP_AP_A11
TOP_AP_A12
TOP_AP_A13
TOP_AP_A14
TOP_AP_A15
TOP_AP_A16
TOP_AP_A17
TOP_NAND_ALE
TOP_NAND_CLE
TOP_AP_A18
TOP_AP_A19
TOP_NAND_IO0
TOP_NAND_IO1
TOP_NAND_IO2
TOP_NAND_IO3
TOP_NAND_IO4
TOP_NAND_IO5
TOP_NAND_IO6
TOP_NAND_IO7
TOP_NAND_RE_N
TOP_AP_CLK
TOP_AP_SDCLK
TOP_AP_SDCKE
TOP_SDRAS_N_1
TOP_SDRAS_N_2
TOP_SDCAS_N_1
TOP_SDCAS_N_2
TOP_SDCAS_N_3
TOP_NAND_CE_N
TOP_AP_CS1_N
TOP_AP_CS2_N
TOP_AP_BE0_N
TOP_AP_BE1_N
TOP_AP_WE_N
TOP_AP_WE2_N
TOP_DMS_4
TOP_NAND_WE_N
TOP_NAND_Ry_By_N
N2020
KAL00900MX-AJ55_MCP_POP_NAND_EMIF2
2GbitNANDx8+128Mbitx16+512MbitSDRAMx16
APPLICATIONMEMORYIF(EMIF2)
A14
SDRAM_512_A0d
B15
SDRAM_512_A1d
A15
SDRAM_512_A2d
B16
SDRAM_512_A3d
A16
SDRAM_512_A4d
B17
SDRAM_512_A5d
A17
SDRAM_512_A6d
B18
SDRAM_512_A7d
A18
SDRAM_512_A8d
A19
SDRAM_512_A9d
C21
SDRAM_512_A10d
D20
SDRAM_512_A11d
D21
SDRAM_512_A12d
E20
NC_2
L21
BA0d
E21
NC_3
L20
BA1d
F20
NAND_ALE
A12
NAND_CLE
F21
NC_4
B12
NC_5
G20
NAND_IO0
G21
NAND_IO1
H20
NAND_IO2
H21
NAND_IO3
J20
NAND_IO4
J21
NAND_IO5
K20
NAND_IO6
K21
NAND_IO7
M20
NAND_REn
B13
NC_6
M2
SDRAM_512_CLK
V2
SDRAM_512_CKE
AA14
SDRAM_512_RASn
Y11
NC_7
A11
NC_8
Y12
NC_9
AA15
SDRAM_512_CASn
AA12
NAND_CEn
AA11
NC_10
N20
SDRAM_512_CSn
Y4
SDRAM_512_LDQM
AA3
SDRAM_512_UDQM
A13
NC_11
V1
SDRAM_512_WEn
B11
NC_12
AA13
NAND_WEn
KAL00900MX-AJ55
1205-5912_POP
Made for
Application & System Performance
System PoP IF
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B5 5
SDRAM_512_DQ0
SDRAM_512_DQ1
SDRAM_512_DQ2
SDRAM_512_DQ3
SDRAM_512_DQ4
SDRAM_512_DQ5
SDRAM_512_DQ6
SDRAM_512_DQ7
SDRAM_512_DQ8
SDRAM_512_DQ9
SDRAM_512_DQ10
SDRAM_512_DQ11
SDRAM_512_DQ12
SDRAM_512_DQ13
SDRAM_512_DQ14
SDRAM_512_DQ15
NAND_Ry/By_N
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TOP_AP_D00
P1
TOP_AP_D01
P2
TOP_AP_D02
R1
TOP_AP_D03
R2
TOP_AP_D04
T1
TOP_AP_D05
T2
TOP_AP_D06
U1
TOP_AP_D07
U2
TOP_AP_D08
Y5
TOP_AP_D09
AA6
TOP_AP_D10
Y6
TOP_AP_D11
AA7
TOP_AP_D12
Y7
TOP_AP_D13
AA9
TOP_AP_D14
Y9
TOP_AP_D15
AA10
B14
MEASUREMENT POINTS
1222-9526 rev. 1
63 (124)
Page 64

WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
MEASUREMENT POINTS Power Top
VBAT
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
Power WLAN
Page 10
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
OPTO_EN
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
PWRRSTn
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
VBUS
DCIO
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
PWRRSTn
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
VBUS
DCIO
VBUS
DCIO
Page 7
VBAT
VDDE18
VCORE18
VANA25
VCORE12
VMEM18
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VBT27
VDIG
VBEAR26
VBACKUP
VBAT
VCORE18
VANA25
VCORE12
VBAT
VCORE18
VDDE18
VANA25
VCORE12
VMEM18
VBAT
VDDE18
VCORE18
OPTO_EN
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
PWRRSTn
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
Power Imaging
VDDE18
VANA25
VCORE12
VMEM18
Power Asics
VBAT
VDDE18VDDE18
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VBT27
VDIG
VBEAR26
VBACKUP
Page 9
Page 8Page 8
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAML12
VOPTO30
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28VDDE18
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAML12
VOPTO30OPTO_EN
VCAMSD18
VCAMAF28
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAML12
VOPTO30
VBAT
VDDE18
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VBT27
VDIG
VBEAR26
VBACKUP
MEASUREMENT POINTS
CHARGE_LED
Regulators & ChargingRegulators & Charging
CHARGE_LED
CHARGE_LED
Made for
Application & System Performance
Power Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B6 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
64 (124)
Page 65

MEASUREMENT POINTS Power - Regulators & Charging
VDDE18
VANA25
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
SP2200
VBUS
21
ST2200
ST2201
12
ST2202
12
ST2203
ST2204
ST2205
ST2206
C2212
2.2uF
C2219
10uF
CHARGE_LED
VANA25 VCORE18
X2201
BATTERY
CONNECTOR
MP 137
MP 33
TP2201 TP2204
1
2
3
21201-0774
C2200
33pF
<NM>
R2200
25mohms
TP2202
MP 31
V2200
DF2S6.8FS
21
AC
BDATA
C2201
100nF
<NM>
C2202
22pF
C2203
3.3pF
VBAT
C2204
10uF
MP 139
ST2211
12
ST2212
12
C2226
1uF
MP 141
VDDE18
C2227
100nF
ST2240
21
R2203
100Kohms
A12
B10
A2
D12
A13
A14
R2201
MP 16
ST2213
100mohms
21
C2221
100nF
16V
<NM>
DCIO
V2202
D
D
4
3GS
8
1200-0145
FDMA1027P
5
V2202
D
D
1
6S
7
1200-0145
FDMA1027P
2
G
DCIO
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
VDD_IO
SPARE1
SPARE2
TEST
VREF
IREF
AB3100
1202-0639 2
POWER
IO LEVELS
TEST
REF
FGSENSEP
FGSENSEN
VBUS_VERA
C2222
1uF
25V
C2223
100nF
C2205
10uF
C2225
47pF
16V
C2224
1uF
K14
F14
M13
N14
B12
N2000
VBAT_B
VBAT_E
VBAT_F
VBAT_G
MOD1
Buck
0.9 - 1.8V
AB3100
1202-0639 2
N2000
A11
J14
J13
H2
H1
H3
J2
F1
E2
F3
G1
AB3100
1202-0639 2
Ericsson AB 3100
POWER
LDO REGULATORS
LDOG
1.5 - 2.85V
LDOD
2.65V
LDOF
1.05 - 2.5V
LDOE
0.9 - 2.8V
LDOH
1.2 - 2.75V
LDOK
1.8 - 2.75V
LDOC
2.65V
LPREG
2V
BUCK REGULATOR
5%
Ericsson AB 3100
POWER
BATTERY UART
BDATA
FUEL GAUGE
FGSENSEP
FGSENSEN
CHARGER CONTROL
VBAT_D
CHSENSEN
CHSENSEP
CHREG
DCIO_INT
DCIO
VBUS
VBAT_H
VDD_REF
LDOG_OUT
LDOD_OUT
LDOF_OUT
LDOE_OUT
LDOH_OUT
LDOK_OUT
LDOC_OUT
LDOLP_OUT
BUCK_FB
VBAT_C
VSS_BUCK
TRICKLE
VBUCK
L13
L12
G13
G14
L14
M14
N12
D13
E1
D1
C1
B1
F2G2
C2216
100nF
C2206
4.7uF
C2217
10uF
C2207
2.2uF
MP 115
C2208
1uF
V2201
1000-0087
Leadfree
C2229
2.2uF
<NM>
C2209
2.2uF
L2200
C2210
2.2uF
C2211
2.2uF
4.7uH
C2218
10uF
VBAT
1
ST2214
2
C2228
10uF
21
21
21
21
L2201
BLM18PG121SN1
1000-0118
C2220
100nF
N2200
DC-DC CONVERTER
VIN SW
4
EN
MODE FB
GND
TPS62290DRV
1204-4655
MP 162
MP 125
MP 165
MP 164
MP 127
MP 126
MP 124
C2213
1uF
MP 114
SLUG
4.7Kohms
VBAT
0402 Size
MP 116
15
32
76
R2204
ST2209
C2215
100nF
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VANA25
VDDE18
VBT27
VDIG
VBEAR26
21
R2231
100ohms
<NM>
C2233
150pF
<NM>
+
C2214
7uAh
1000-0335
2.2uHL2202
VCORE12
R2207
549Kohms
1%
R2208
270Kohms
1%
C2232
22pF
ST2207
1
2
C2231
10uF
21
1
ST2210
MP 40
ST2225
VMEM18
2
C2230
1nF
<NM>
VMC18
VAUDIO26
VANA25
VDDE18
VBT27
VDIG
VBEAR26
VBACKUP
VCORE12
CHARGE_LED
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VBAT
VCORE18
VMEM18
VBAT
VCORE18
VMEM18
Made for
Application & System Performance
Power - Regulators & Charging
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B7 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
65 (124)
Page 66

MEASUREMENT POINTS Power - Imaging
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
VCAMSD_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
Camera Power
VCAMSD_EN
R2212
100Kohms
MP 64
CAM_LDO_EN
R2210
100Kohms
C2279
100nF
C2280
100nF
C2282
100nF
VBAT
C2283
2.2uF
C2285
2.2uF
N2700
S1D13771_POWER
CORE_SUPPLY
G5
COREVDD
E7
COREVDD
E1
COREVDD
D8
COREVDD
A4
COREVDD
G6
IOVDD
G4
IOVDD
D7
IOVDD
D3
IOVDD
C6
IOVDD
B5
IOVDD
F2
DACVCC
F1
DACVCC
S1D13771
1200-0362
H6
VSS
G7
VSS
F6
VSS
F4
VSS
E8
VSS
IO_SUPPLY
E3
VSS
D1
VSS
C4
VSS
B6
VSS
B2
VSS
PLL_SUPPLY
DAC_SUPPLY
2
3
2
14
3
PLLVSSPLLVDD
DACVEE
DACVEE
DACVEE
N2208
CE
3V
IN
GND
R1115Z301D
1000-8623
N2209
CE
1.5V
IN
GND
R1115Z151D
1001-0062
7F8F
G2
G1
F3
VTV30
41
OUT
OUT
MEASUREMENT POINTS
C2284
2.2uF
51VTVTABV
C2286
2.2uF
12
12
C2
A2
C1
B8
G8H5
H1
H8
MP 18
ST2232
ST2233
MP 15
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
VTV15
VDDE18
MP 61
R2213
100Kohms
ST2230
21
ST2231
12
C2281
100nF
MP 17
VTV30_EN
R2214
100Kohms
VTV15_EN
R2228
100Kohms
TV_Out Power
VBAT
N2205
15KohmsR2226
C2290
220nF
C2240
2.2uF
EN
VIN
GND
7
SLUG
MIC5319-2.8YML
1001-5573
MIC5319
VOUT
61
BYP
43
52
NC
NC
C2241
C2292
2.2uF
100nF
VBAT
MP 129
C2242
2.2uF
4.7KohmsR2211
G
2
V2212
NTLJD3119C
1204-1592
C2287
33nF
7
6
SD1D2
1
VCORE18
D
3
4
S
R2221
100Kohms
2.2KohmsR2220
VBAT
C2248
2.2uF
C2250
2.2uF
N2213
6
2
5
4
MAX8640ZELT12
1208-4678
GND2
GND5
SHDN
V2212
NTLJD3119C
1204-1592
5
G
MAX8640
IN
LX
OUT
ST2220
8
D
1
3
MP 131
TP2210
21
N2206
2
6
5
R5323K022B-TR-FD
1201-6517
ST2223
1
C2272
33nF
1uH
L2212
VCAMAF28
VDD
GND_SLUG
MP 54
TP2206
2
VOUT2CE2
VOUT1CE1
C2249
2.2uF
GND
VCAMIO18
ST2224
1
3
47
MP 132
TP2207
21
MP 130 MP 128
12
ST2222
C2244
2.2uF
VCAML12
TP2208 TP2209
21
ST2221
C2243
2.2uF
VCAMSA28 VCAMSD18
C2245
33pF
<NM>
E2
NC
D2
NC
B1
NC
H4
NC
NC
E6
NC
A1
NC
A8
NC
N2010
APPLICATIONGPIO_06
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2700
S1D13771
MISCELLANEOUS
GPIO0
GPIO1
TESTEN PWRSVE
TEST0
TEST1
RESERVED
NC
NC
S1D13771
1200-0362
GPIO2
GPIO3
SCANEN
VTV15VTV30
VCP
NC
NC
N17
VBAT
VDDE18
VCORE18
VBAT
VDDE18
VCORE18
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
PWRRSTn
MP202 Power
MP 70
VIDCC_L1_EN
MP 67
VIDCC_SDR_EN
R2223
100Kohms
PWRRSTn
R2215
100Kohms
VCORE18
C2251
2.2uF
VCORE18
VBAT
N2210
2
CE
1.2
IN
3
GND
C2271
2.2uF
RP102Z121D-TR-F
1201-9681
N2214
LOAD SWITCH
VOUT
VIN
B2
ON
GND
TPS22902BYFPR
1212-7867
N2212
2
CE
14
IN
3
GND
C2277
2.2uF
R1183Z121D-TR-FD
1200-1974
VDD_L0
VDD_L1
C2252
100nF
C2253
C2254
100nF
C2255
100nF
C2260
100nF
C2263
100nF
C2266
100nF
C2269
100nF
100nF
C2256
100nF
C2261
100nF
C2264
100nF
C2267
100nF
C2270
100nF
VDD_L1
1
ST2226
MP 69
2
41
OUT
C2274
1uF
VSDR18
MP 42
ST2229
12
A1A2
B1
VDD_L0
ST2228
MP 66
OUT
21
C2278
2.2uF
VDD_L1
L2213
BLM15HD182SN
1200-0317
C2257
1uF
C2258
100nF
VDDE18
VSDR18
C2259
100nF
C2262
100nF
C2265
100nF
C2268
100nF
D11
C10
E11
E12
F13
K11
K12
M10
A10
B10
E13
E14
K13
K14
N10
P10
L4
C5
E3
K3
M5
G2
H2
A5
B5
E1
E2
K1
K2
N5
P5
C6
C9
D6
D9
F4
F11
J4
J11
L5
L6
L9
L10
M9
N2500
L0VDD
L0VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
L1VDD
PLLVDD
PLLVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
SDRVDD
MP202
1200-1414
MP202_POWER
L0_CORE_SUPPLY
L1_CORE_SUPPLY
PLL_SUPPLY
IO_SUPPLY
SDRAM_SUPPLY
OPTO_EN
OPTO_EN
MP 73
R2217
100Kohms
N2201
2
CE
3V
14
OUT
IN
3
GND
C2288
R1115Z301D
2.2uF
1000-8623
03OTPOVTABV
MP 59
TP2203
C2289
2.2uF
VCAMSD18 VCAMIO18
VOPTO30
VCAMSA28
VCAML12
VCAMAF28
Made for
Application & System Performance
Power - Imaging
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B8 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
66 (124)
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMIO18
VCAMSA28
VCAMSD18
VOPTO30
Page 67

VCORE12
100nF C2302
1uF C2301
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_PLL_A_15_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_PLL
PLL_FILTER
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
C2304
C2306
100nF
100nF
C2303
100nF
PLL_PG_416_VCONT
PLL_PG_416_FILTVDD
C2307
100nF C2305
100nF
PLL_26_VCONT
PLL_26_FILTVDD
C2308
100nF
AE17
AE18
AE20
AE19
C2309
100nF
C2310
100nF
C2311
100nF
C2353
C2354
C2312
100nF
C2313
100nF
C2314
100nF
33nF
33nF
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_1_2V
POWER_A_1_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_POWER
AC20
H2
M2
T2
AB2
AE5
AE9
AE22
AA25
Y25
T25
M25
B23
B21
B19
B16
B14
B7
K25
W25
VDDCORE(logic)
VDD_1v2
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_VDD_IO_POWER_A_4_24
KAJSA_POWER
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD_DIG_PLL
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VDD_IO
_
VANA25
GND_DIG_PLL
C2336
1uF
MEASUREMENT POINTS Power - ASICs
VDDE18
ST2300
12
E6
GND
F22
GND
AB21
GND
AB6
GND
J9
GND
K10
GND
P9
GND
V9
GND
P10
GND
L11
GND
P11
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
C2337
100nF
100nF C2338
R11
T11
L12
T12
J13
K13
L13
T13
U13
V13
L14
T14
L15
T15
L16
U10
100nF C2339
100nF C2340
100nF C2341
100nF C2342
C2343
100nF
VCORE12
C2344
100nF
100nF C2321
C2320
1uF
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_ANALOG
POWER_A_3_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_2.5V_POWER
AB7
VDDIO_2v5
AD19
VDDIO_2v5_PLL
AC19
VDDCO_PLL_1_2
AC18
VDDCO_PLL_3_4
AE16
VCC_AD1
AE14
VCC_AD2
AB15
VDDAD
AC11
VCCDA
AC12
VCCGPAD
R2
VDDCO_AF
AE12
VDD_ANA
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
C2323
100nF
C2322
100nF
VDDIO
VDD_ANALOG
C2325
100nF
C2326
100nF C2324
100nF
VSSCO_PLL_1_2
VSSCO_PLL_3_4
VSS_AD1
VSS_AD2
VSSDA
GNDAD
VSSGPAD
VSSCOMMON
GNDE_ANA
C2327
100nF
C2328
100nF
AD18
AD17
AD16
AE15
AB10
AB14
AB12
AE13
AC17
C2329
100nF
C2330
100nF
C2331
100nF
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_1_8V_POWER_A_2_24
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
VDD_1v8
KAJSA_POWER
VDD_1V8
B2
B4
N2
P2
AA2
AE4
AE10
AE21
AB25
R25
N25
J25
G25
B22
B13
B10
W2
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
GNDE
VMEM18
2.2uF C2345
M16
N16
R16
U17
P16
T16
K17
P17
J18
P18
V18
100nF C2346
100nF C2347
100nF C2348
100nF C2349
100nF C2350
100nF C2351
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM
VMEM_POWER_A_24_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_VMEM_POWER
D2
C2
F2
G2
E25
B25
AD2
AE2
AE3
AD25
V25
U25
P24
P25
U24
V24
MEMORY POWER
VDDQ
VDDQ
VDDQ
VDDQ
VDDQ
VDDQ
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
FVDD
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VCCN
VCCN
AE24
AE25
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
POWER
D4
D5
D6
D7
D9
D10
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
E9
E10
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
G3
G4
G5
G6
G7
G8
G9
G10
G11
G12
H4
H5
H6
H7
GROUND
VSS1
VSS2
VSS3
VSS4
VSS5 VSS39
VSS6
VSS7
VSS8
VSS9
VSS11
VSS12
VSS13
VSS14
VSS16
VSS17
VSS18
VSS19
VSS21
VSS22
VSS23
VSS24
VSS26
VSS27
VSS28
VSS29
VSS31
VSS32
VSS33
VSS34
AB3100
21202-0639
C2352
100nF
VSS35
VSS36
VSS37
VSS38
VSS40
VSS41
VSS42
VSS43
VSS44VSS10
VSS45
VSS46
VSS47
VSS48
VSS49VSS15
VSS50
VSS51
VSS52
VSS53
VSS54VSS20
VSS55
VSS56
VSS57
VSS58
VSS59VSS25
VSS60
VSS61
VSS62
VSS63
VSS64VSS30
VSS65
VSS66
VSS67
H8
H9
H10
H11
H12
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
K5
K6
K7
K8
K9
K10
K11
L4
L5
L6
L7
L8
L9
L10
L11
M6
M8
M9
M11
M12
C905
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VDDE18
VANA25
VCORE12
VMEM18
VDDE18 VANA25 VCORE12
VMEM18
Made for
Application & System Performance
Power ASICs
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B9 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
67 (124)
Page 68

MEASUREMENT POINTS Power - WLAN
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
WLAN_CLKREQ
WLAN_SCLK
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
GPIO_O10_OUTPUT
WLAN_CLKREQ
WLAN_PDn
12
WLAN_SCLK
MP 85
R2313
100Kohms
L2310
BLM18PG121SN1
1000-0118
VBAT
C2371
10uF
C2372
10uF
C2373
100nF
N2300
MARVELL_88PW886_2
16
SVIN
20
PVIN
6
PVIN
10
SLEEPn
11
PDn
13
SDI
8
GND
88PW886
1203-2790 2
SW3
VO3
PGND
SW1
VO1
PGND
SW2
PGND
VO2
VL2X
VL2Y
FB2
VL3
MP 46
ST2310
L2311
4.7uH
3
7
4
2
NC
5
1
L2313
2.2uH
19
15
18
14
9
12
NC
17
C2377
10uF
C2374
10uF
C2376
10uF
C2379
10uF
MP 45
ST2311
MP 44
ST2312
MP 43
ST2313
21
21
21
21
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VBAT
VBAT
Made for
Application & System Performance
Power - WLAN
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B10 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
68 (124)
Page 69

MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivity Top
VDDE18
STEPUP50
Page 15
VDDE18
STEPUP50
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
TX_ADSTR
VBACKUP
RF_ID
DCON
USB_HS_CLK
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
VDDE18
VDIG
AID_AD
VBAT
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
DCON
SPL
SPR
USB_HS_CLK
Connectivity
Connectivity
VAUDIO26
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
VAD
SPL
SPR
VAD
TX_ADSTR
VBACKUP
RF_ID
DCON
SPL
SPR
USB_HS_CLK
VDDE18
VAUDIO26 VBAT
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
KeypadKeypad
VDIG
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
TESTOUT
VAD
TX_ADSTR
VBACKUP
RF_ID
AID_AD
ADC & DAC
Page 12
Page 12
Page 14
ONSWAn
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
AID_AD
DCIO
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
VBUS
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
DCIO
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
VBUS
SERVICEn
ONSWAn
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
DCIO
MICN/AUXinR
MICP/AUXinL
FM_ANTENNA
VBUS
SERVICEn
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VIDCC_CLK
RTCCLK
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VMC18
STEPUP50
VDIG
VBAT
VDIG VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VMC18
VBAT
STEPUP50
VIDCC_CLK
RTCCLK
VDDE18
VDDE18
VMC18
VBAT
Page 16
Page 16
VIDCC_CLK
RTCCLK
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VIDCC_CLKREQn
Video Companion Chip
Page 13
Page 13
VBAT
VMC18
VDDE18
Cards
Cards
CAM_LDO_ENVDDE18
VCAMSD_EN
CAMRESn
VIDCC_L1_EN
CAM_LDO_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAMRESn
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VIDCC_CLKREQn
CAM_LDO_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAMRESn
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VIDCC_CLKREQn
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B11 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
69 (124)
Page 70

MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivity - I2C & ADC
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
TX_ADSTR
AID_AD
VAD
RF_ID
TESTOUT
OPTOTEMP
VBACKUP
OPTOSENSE
R2400
4.7Kohms
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_APP_I2C_A_7_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
APPLICATION_I2C_IF(APP#1)
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
I2CSDA2
I2CSCL2
W23
T17
R2407
3.3Kohms
C2400
33pF
<NM>
VDDE18
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SH_I2C_A_6_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
SHARED_I2C_IF(ACC+APP#0)
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
R2408
3.3Kohms
I2CSDA
I2CSCL
VDDE18
ST2400
TX_ADSTR
AID_AD
VAD
RF_ID
TESTOUT
RTEMP
OPTOTEMP
VBACKUP
OPTOSENSE
VDDE18
R2405
3.3Kohms
Y23
U18
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
GPIO expander main
2
1
C2403
100nF
N2410
MAX7327_MAIN
21
V+
19
SCL
20
SDA
23
RST
22
NC
INT
MAX7327
1200-1951
HEATSLUG
R2406
3.3Kohms
AD0
AD2
GND
R2402
4.7Kohms
1%
R2403
4.7Kohms
1%
VAUDIO26
R2404
4.7Kohms
1%
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
OP AND SERVICES
GPADC AND AUTOADC
A5
TXON
A9
GPA0
B9
GPA1
C9
GPA2
B8
GPA3
A8
GPA4
C8
GPA5
D8
GPA6
B7
GPA7
C7
GPA12
C10
VDD_ADC
AB3100
1202-0639
2
LDOD
ADC
10bit
AUTO
CTL
AD_OUT
C11
MEASUREMENT POINTS
C2402
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
OP AND SERVICES
I2CDAT0
I2CCLK0
18
24
9
25
B13
C13
SDA
SCL
AB3100
1202-0639
I2C IF
2
100nF
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VDIG
VDDE18
VAUDIO26
VDIG
21
ST2401
C2404
10uF
SP2400
SP2401
C2405
100nF
81EDDVGIDV
ST2402
12
AX_INT1
AX_INT2
C2406
100nF
Accelerometer
N2411
ACCELEROMETER
8
CS
11
INT_1
SDA/SDI/SDO
9
INT_2
1
VDD_IO
14
VDD
2
NC
NC
3
N.C
LIS331DL
1202-1676
GND_RES
VDD_RES
SDO
SCL/SPC
GND
GND
GND
GND
7
NC
6
4
5
12
13
16
10
15
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity - I2C & ADC
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B12 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
70 (124)
Page 71

MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivit y - Ca rd s
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
M2 IF
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM
MEMORY_CARD_A_19_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
MMC/SD/MSPRO_IF
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
MCCLK
MCCMD
MCDAT0
MCDAT1
MCDAT2
MCDAT3
MCCMDDIR
MCDATADIR
APPLICATION GPIO_12
AA23
AB24
AA22
AC24
AD24
AC23
AC25
AB22
U16
NC
VDDE18
MP 35
SP2411
R2422
470Kohms
SP2412
R2417
100Kohms
R2418
100Kohms
R2419
100Kohms
R2420
100Kohms
R2421
100Kohms
C2422
2.2uF
VMC18
C2410
2.2uF
C2421
100nF
MCCLK
MCCMD
MCDAT0
MCDAT1
MCDAT2
MCDAT3
MSDETECT
C2411
33pF
<NM>
X2401
M2
CONNECTOR
8
7
1
3
2
4
6
5
NC
NC
10
11
9
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
21200-9764
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VMC18
VDDE18
VBAT
VMC18
VDDE18
VBAT
SIM IF
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_SIM_A_20_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
SIM_INTERFACE
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
SDAT
SCLK
SRSTn
AE7
V11
V12
MP 34
SP2410
VDDE18
R2415
10Kohms
C2412
100nF
VBAT
MP 106
C2413
100pF
MP 156MP 152
N2000
ERICSSON AB 3100
OP AND SERVICES
VBAT_I
SIMOFF_N
SDAT
SCLK
SRST_N
AB3100
SIM IF
SIMLDO_OUT
21202-0639
SIMDAT
SIMCLK
SIMRST_N
C2414
1L2P
P1
N2
1N2M
1uF
M3
NC
N3
M1
R2416
10Kohms
V2400
<NM>
ST2410
MP 107
ST2411
MP 105
21
21
C2415
33pF
<NM>
C2416
33pF
<NM>
C2417
33pF
<NM>
C2418
33pF
<NM>
C2419
10nF
SIMVCC
SIMRSTn
SIMCLK
SIMDAT
C2420
1uF
MP 155
MP 153
MP 151
MP 154
NC
MP 150
X2402
1
SIMVCC
2
SIMCONRST
3
SIMCONCLK
5
GND
6
NC
7
SIMCONDAT
SIMHOLDER-SHIHO
1202-0528
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity - Cards
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B13 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
71 (124)
Page 72

N2010
APPLICATION GPIO_01
ACCESS GPIO_03
ACCESS GPIO_02
ACCESS GPIO_16
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
DCON
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_04
ACCESS GPIO_01
ACCESS GPIO_00
ACCESS GPIO_05
ACCESS GPIO_14
ACCESS GPIO_15
KAJSA_BOTTOM_USB_A_21_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
USB TRANSCEIVER IF
USB_HS_CLK
VAUDIO26
USB_SE0_VM
USB_DAT_VP
ACCESS GPIO_18
ACCESS GPIO_06
ACCESS GPIO_07
ACCESS GPIO_08
ACCESS GPIO_09
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
SPR
SPL
N2700
S1D13771_TVIF
S1D13771
1200-0362
VBAT
VDDE18
USB_OE
AOUT
VREF
VADJ
N22
R4
U3
V10
DCON
V2
T9
R9
U12
W4
Y3
M9
N9
U9
AC6
V3
U5
T4
U4
H2
G3
NC
H3
VBAT VDDE18
R2430
0ohms
<NM>
USB_HSINCLK
USB_HSDIR
USB_HSSTP
USB_HSNXT
Chinese Charger
Detect
USB_HSDATA0
USB_HSDATA1
USB_HSDATA2
USB_HSDATA3
USB_HSDATA4
USB_HSDATA5
USB_HSDATA6
USB_HSDATA7
R2451
560ohms
1%
R2452
1.5Kohms
1%
VAUDIO26
MP 8
USB_HSCHIP_SEL
R2431
100Kohms
SP2420 SP2422
SP2435
SP2423 SP2424 SP2425
SP2426
SP2427
SP2428
SP2429
SP2430
R2453
75ohms
SP2421
C2444
100pF
C2446
L2405
33pF
1.8uH
MP 14
APP_LOG
CFMS
CTMS
VDDE18 VBAT
ST2421
21
C2432
100nF
MP 6
C2433
1uF
C2445
270pF
MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivity
C2431
10uF
R2442
470ohms
R2444
100Kohms
MP 3
SP2432
ST2422
21
B2
B5
F4
C4
E1
B4
B3
C3
A4
E5
D6
D5
B1
A1
A2
A3
A5
A6
B6
C6
F5
F6
NC
C2
R2441
12Kohms
1%
N2420
USB_OTG_TRANSIVER
VCC
VCCIO_1
VCCIO_2
VBUS
TEST
CFG0
CFG1
CFG2
CHIP_SEL
CLOCK
DIR
STP
NXT
DATA0
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
XTAL1
XTAL2
RREF
ISP1508
1200-1694
VDDE18
REG3V3
REG1V8
NC_1
NC_2
PSW_N
FAULT
GND_1
GND_2
GND_3
R2450
100Kohms
DP
DM
ID
3E3F
E6
F1
F2
D1
C1
R2440
100Kohms
<NM>
D3
D4
E2
E4
C5
D2
TVOUT
SPR
SPL
VBUS
MP 7
NC
NC
VDDE18
NC
VAUDIO26
C2430
100nF
C2449
REG3_3V
REG1_8V
C2435
C2434
100nF
4.7uF
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_23
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
100nF
VDDE18
NC
MP 9
R2445
120Kohms
R2446
360Kohms
V2415
1201-8440
V2416
1201-8440
DMext/DFMS
DPext/DTMS
C2436
100nF
C2447
2.2nF
R23
A3
D3
A1
B1
C1
D1
D2
A2
12
CA
12
CA
N2422
VDD
VDIG
APP_LOG
CFMS/ID_SOURCE
CTMS
SERVICE_N
SERVICE
ADC
IP4826CX12/LF
1201-4120
2
C2437
4.7uF
C2448
2.2nF
OVP_FLAG
ELINA
ACB/RID
MP 10
MP 12
GND
GND
RID_OUT
ACB/RID_IN
Z2400
4
TCM1210-900-2P-T
1201-6833
N2421
4
OUT
5
OUT
6
FLAG GND
NCP360
1200-6309
VDDE18
R2447
100Kohms
B2
C2
C3
B3
V2417
BZX585C15
1000-0272
NCP360
GND_SLUG
MP 110
MP 111
P2P3
IN
EN
R2434
1Kohms 1%
R2478
100ohms
P1P4
3
1
7
2
12
MP 13
23
1
MP 11
CA
AID_AD
SERVICEn
MP 112
C2438
33pF
<NM>
L2407
BLM15EG121SN1
C2439
1uF
25V
MP 109
MP 108
SP2434 SP2433
0ohmsR2448
0ohmsR2443
L2404
L2403
L2402
L2401
V2414
12
CA
ESD9L5.0ST5Gw
1201-8440
100MHz
100MHz
100MHz
100MHz
BLM03BB470SN1
V2413
1201-2253
FM_ANTENNA
MICP/AUXinL
MICN/AUXinR
L2408
MP 113
2A1A
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
AID_AD
SERVICEn
VBUS
DCIO
C2440
C2441
1uF
10nF
25V
25V
CA
V2412
BZX585C15
1000-0272
21
X2405
SYSTEM CONNECTOR
12
DCIO
11
D-/DFMS
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Z1
Z2
1202-1195
C2442
10nF
D+/DTMS
GND
AID/ACB/RID
VIDEO
MP X2405_Pins 1-12
SPR
SPL
Mic-/AUXinR
Mic+/AUXinL
SPREF
VBUS
C2443
10nF
FM_ANTENNA
MICP/AUXinL
MICN/AUXinR
0ohmsL2449
L2406
BLM18BD102SN1
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B14 5
C905
MEASUREMENT POINTS
1222-9526 rev. 1
72 (124)
Page 73

MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivity - Keypad
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
VDDE18
STEPUP50
VDDE18
R2470
10Kohms
LED_CAM1
LED_KEYPAD
R2471
10Kohms
STEPUP50
VDDE18
R2472
10Kohms
MP 39MP 4MP 5
R2473
10Kohms
R2474
10Kohms
R2475
10Kohms
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM
KEYPAD_IF_A_18_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CONNECTIVITY
KEYPAD_INTERFACE
L10
KEYIN0
M10
KEYIN1
V15
KEYIN2
U14
KEYIN3
U22
KEYIN4
N10
KEYIN5
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
KEYOUT0
KEYOUT1
KEYOUT2
KEYOUT3
KEYOUT4
MP 60
ONSWAn
C2472
V2470
1000-0391
Leadfree
33pF
<NM>
ONSWAn
KEYIN0
KEYIN1
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
KEYIN3_1
KEYIN4
KEYIN5
KEYOUT4
KEYOUT3
KEYOUT2
KEYOUT1
KEYOUT0
X4200
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
73
71
69
67
65
32
63
61
64
66
68
70
72
1204-5252 2 (#2/6)
100-pin
Navigation Keypad
X2410
KEYFLEX
CONNECTOR
A6
A5
A4
A3
AC
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
B6
B5
B3
B2
B4
A2
B8
A9
A10
A8
Z1
Z2
1208-3264
24-pin
Numeric Keypad
N2010
SLIDE_SENSE
B9
A1
A7
A11
A12
B1
B7
B10
B11
B12
N24
APPLICATIONGPIO_04
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
C2462
33pF
<NM>
C2467
33pF
<NM>
C2463
33pF
<NM>
C2468
33pF
<NM>
MP 159MP 158
C2464
33pF
<NM>
C2469
33pF
<NM>
C2470
33pF
<NM>
12
V2474
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
21
AC
S2453
V2477
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
AC
S2454
MP 97 MP 95
d
b
a
NC
SKSCLAE010
1204-1127
b
a
c
SKSCLAE010
MP 94MP 96
1204-1127
Volume + Volume -
KEYOUT0 KEYOUT0
KEYOUT2 KEYOUT2
KEYOUT3 KEYOUT3
KEYOUT4
V2486
d
c
V2482 1000-0087
V2481 1000-0087
MP 76
MP 84
MP 82
S2415
SKSCLAE010
1204-1127
12
V2475
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
AC
NC NCNC NC
b
a
12
V2476
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
AC
S2424
V2471
MP 90
d
b
a
NC
SKSCLAE010
1204-1127
d
c
NCNC
c
MP 88
12
21
AC
AC
V2478
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
12
AC
V2472
V2479
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
ESD protection for keypad
STEPUP50
KEYIN4
KEYIN3
Cam PlayCam Rec
C2471
33pF
<NM>
LED_CAM1
LED_KEYPAD
12
AC
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
12
AC
V2473
12
AC
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
MP 160
KEYOUT1KEYOUT1
12
AC
V2487
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
KEYIN5KEYIN5
KEYIN4_1
KEYIN3_1
KEYIN2KEYIN2
KEYIN1KEYIN1
KEYIN0KEYIN0
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
12
AC
V2480
22ohmsR2476
MP 161
C2473
33pF
<NM>
12
V2484
ESDALC6V1-1BM2
1207-3081
VDDE18
C2474
33pF
<NM>
Y24
MP 157
W22
M11
K11
N11
C2460
C2461
33pF
33pF
<NM>
<NM>
C2466
C2465
33pF
33pF
<NM>
<NM>
MEASUREMENT POINTS
KEYOUT0
KEYOUT1
KEYOUT2
KEYOUT3
KEYOUT4
GND
KEYIN5KEYIN4KEYIN3KEYIN2KEYIN1KEYIN0
163
NumNumNum
Green
20 5 9
Num
Active
Menu
Nav
Rock
Down
Red
On/Off
Nav
Game
B
Upper
Num
Rock
Left
Soft
Left
Nav
NumNum
Rock
Up
Cam
AF
Num
CLR
-
NavNav
Num
Cam
Snap
Num
Rock
Push
-
Num
Cam
Play
Main
Rock
Right
NavNavNavNavNav
Vol-Vol+
MainMain
Game
-
8
#74
Upper
Cam
Rec
Main
Num
NumNum
Soft
Right
Nav
A
*
*
--
Game
B
Rock
Soft
Up
Left
Rock
Rock
Green
Active
Menu
Rock
Left
Push
Right
Rock
Down
123
456
789
0#
*
Clip
Camera
X2411
Switch Pad
1
Game
A
Vol+
Vol-
Soft
Right
Red
On/Off
CLR
Cam
Play
Cam
Rec
Cam
AF/Snap
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity - Keypad
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B15 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
73 (124)
Page 74

MEASUREMENT POINTS Connectivit y - V id eo C om pa nio n Chip
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
VDDE18
NC
NC
NC
NC
RTCCLK
VIDCC_CLK
N2500
J14
J13
H14
H13
MP202
1200-1414
VDDE18
N2010
APPLICATION GPIO_18
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
MP202_GPIO
GIO_P0
GIO_P1
GIO_P2
GIO_P3
PO0
PO1
PO2
PO3
PO4
PO5
PO6
PO7
K15
D14
D13
N11
P11
D3
D2
B4
A4
RTCCLK
VIDCC_CLK
VIDCC_RESn
NC
MP 68
R2502
470Kohms
VIDCC_L1DET
SP2500 SP2501 SP2503
R2503
100Kohms
<NM>
R2501
100Kohms
B6
B7
A6
A7
A11
N2500
MP202_HOSTIF_SPI
SPI0_SO
SPI0_SI
SPI0_SK
SPI0_CSZ
INT_B
MP202
1200-1414
SPI1_SO
SPI1_SI
SPI1_SK
SPI1_CSZ
B8
NC
B9
NC
A8
NC
A9
NC
MP 71
SP2505
D1
G1
H1
B11
B3
C3
C2
N2500
CK32KI
CKI
CKO
PLLMODE
L0_DET
L1_DET
RESETZ
MP202
1200-1414
MP202_SYSTEM
TCLKO
N2010
L25
APPLICATION GPIO_07
APPLICATION GPIO_08
J2
NC
APPLICATION GPIO_09
APPLICATION GPIO_05
APPLICATION GPIO_16
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VIDCC_SPI_DI
VIDCC_SPI_DO
M24
M23
VIDCC_SPI_CLK
N23
VIDCC_SPI_CS
P22
VIDCC_INT
MEASUREMENT POINTS
CAM_LDO_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAMRESn
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VIDCC_CLKREQn
N2500
N2500
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
MP202
1200-1414
MP202_IC
G3
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
IC
G12
H12
M11
M12
M13
N12
J10
J12
K10
L11
L12
NC
NC
H3
NC
NC
J3
NC
J5
NC
NC
NC
K4
NC
K5
NC
K6
NC
K9
NC
NC
NC
NC
M3
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
B12
NC
C4
NC
C7
NC
C8
NC
C11
NC
C12
NC
C13
NC
D4
NC
D5
NC
D10
NC
D12
NC
E4
NC
E5
NC
E6
NC
E9
NC
E10
NC
F3
NC
F5
NC
F6
NC
F10
NC
F12
NC
A1
A2
A3
A12
A13
A14
B1
B2
B13
B14
C1
C14
D7
D8
E7
E8
F1
F2
F14
G4
G5
G10
G11
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
MP202
1200-1414
MP202_GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
G13
G14
H10
H11
M14
N13
N14
P12
P13
P14
H4
H5
J1
K7
K8
L7
L8
M1
N1
N2
P1
P2
P3
SP2504
N2500
U70_SRIN
U70_SOUT
MP202
1200-1414
MP202_UART
L13
NC
L14
CAM_LDO_EN
VCAMSD_EN
CAMRESn
VIDCC_L1_EN
VIDCC_SDR_EN
VIDCC_CLKREQn
VDDE18
Made for
Application & System Performance
Connectivity - Video Companion Chip
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page B16 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
74 (124)
Page 75

MEASUREMENT POINTS Imaging Top
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
CAMSYSCLK
XEFL_SPDA
VDDE18
VCAMSD18 VCAMIO18 VCAMSA28 VCAMAF28
VCAML12
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
CAMSYSCLK
VCAMAF28
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VCAML12
VDDE18
CAMRESn
CAM_LDO_EN
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
CAMSYSCLK
Camera
Camera
Page 3
XEFL_TRIG
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
VBATVDDE18
XEFL_TRIG
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
XEFL_SPDA
LED_BACK
Page 4
VBAT
VDDE18
XEFL_TRIG
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
I2CCLK1
I2CDAT1
XEFL_SPDA
LED_BACK
LMU
LMU
MEASUREMENT POINTS
STEPUP50
STEPUP50
CHARGE_LED
VBAT
VDDE18
VOPTO30
VCAMSA28
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMIO18
VCAMSD18
VDIG
VBAT VDDE18 VOPTO30 VCAMSA28 VCAMAF28
VCAML12 VCAMIO18 VCAMSD18
VDIG
VOPTO30
VDIG
VBATVDDE18
VBAT
VDDE18
VDIG
CHARGE_LED OPTOSENSE
Display
Display
Page 2
LED_KEYPAD
LED_BACKVOPTO30
LED_CAM1
OPTOTEMP
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSECHARGE_LED
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
STEPUP50
STEPUP50
Made for
Imaging Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page I1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
75 (124)
Page 76

MEASUREMENT POINTS Imaging - Display
VDDE18
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
CHARGE_LED
CHARGE_LED
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_DISPLAY_A_13_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_IMAGING
KAJSA_BOTTOM
DISPLAY_INTERFACE
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VBAT
A1
C4206
100nF
MP 118
V4206
1000-0407
SML-A12UT
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
BOOSTLED DRIVER
VDD_BOOST
AB3100
1202-0639 2
CA
PDI_RESn
MMI
SW_BOOST
BOOST_ISP
BOOST_ISN
VBOOST
PDI_D0
PDI_D1
PDI_D2
PDI_D3
PDI_D4
PDI_D5
PDI_D6
PDI_D7
PDI_C0
PDI_C1
PDI_C2
PDI_C3
PDI_C4
PDI_C5
R4216
100Kohms
LCD_D0
LCD_D1
LCD_D2
LCD_D3
LCD_D4
MMI
LED1_N
LED2_N
LED3_N
LED4_N
LED5_N
LED6_N
VDD_VIBR
LCD_D5
LCD_D6
LCD_D7
TV_TE
LCD_RS_1
TV_CS
LCD_RD
LCD_WR_1
TV_CSSEL
TV_RESn
B4
A4
D3
C3
A3
B3
B14C14
VBAT
SP4202
SP4203
N2010
APPLICATIONGPIO_14
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
APPLICATIONGPIO_19
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
SP4200
LCD_CS
LCD_VSYNC LCD_VSYNC_1
LCD_DAT7
LCD_DAT6
L17
K24
K22
J23
M18
H23
J24
M17
H24
L23
M22
L24
K23
N18
L22
VBAT
21
ST4202
0402 Size
R4200
10ohms
E3
C2
D2
B2
C4200
2.2uF
L4200
22uH
MP 117
V4200
NTJS4405N
1000-0293
6
5
2
1
G
3
S
4
R4202
150mohms
MP 119
R4201
0ohms
<NM>
C4201
33pF
<NM>
LCD_DAT5
LCD_DAT4
LCD_DAT3
LCD_DAT2
LCD_DAT1
LCD_DAT0
LCD_RS
LCD_WR
V4201
1000-0087
Leadfree
SP4201
R4219
R4220
X4201
X4202
0ohms
22ohms
C4202
330pF
25V
C4203
1uF
25V
1
1
Z4200
EMI-FILTER
1
2
I2-1
3
I3-1
4
I4-1
GND_1 GND_2
MP Z4200_Pins 1-8
MEA1608LC220T001
1000-7455
Z4201
EMI-FILTER
1
2
I2-1
3
I3-1
4
I4-1
GND_1 GND_2
MP Z4201_Pins 1-8
MEA1608LC220T001
1000-7455
Z4202
EMI-FILTER
1
2
I2-1
3
I3-1
4
I4-1
GND_1 GND_2
MP Z4202_Pins 1-8
MEA1608LC220T001
1000-7455
MP 51
ST4203
12
0402 Size
R4203
910Kohms
1%
R4204
62Kohms
1%
L4201
56nH
L4202
56nH
Radio components
K16
P23
TP4200
C4207
33pF
<NM>
C4204
33pF
<NM>
C4205
470pF
<NM>
R4215
100Kohms
<NM>
O1-2I1-1
O2-2
O3-2
O4-2
O1-2I1-1
O2-2
O3-2
O4-2
O1-2I1-1
O2-2
O3-2
O4-2
VBOOST
R4217
0ohms
5
R4218
0ohms
6
7
8
910
5
6
7
8
910
5
6
R4221
0ohms
7
R4222
22ohms
8
910
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
INDICATORLED CONTROL
Vibrator
K1/K2
A2
V4202
<NM>
1SS361
A1
C4208
2.2uF
VIBRATORCONTROL
VIBR_OUT
AB3100
1202-0639 2
C4209
100nF
N2700
S1D13771_HOSTIF
E5
MD0
F5
MD1
A6
MD2
D6
MD3
A7
MD4
B7
MD5
C7
MD6
C8
MD7
A3
TE
A5
D/C
CS
D5
RD
C5
WE
D4
CSSEL
C3
RESET
B3
GPIO_INT
NC
S1D13771
1200-0362
VBAT
R4205
10Kohms
C
B
5
E
LCDCS
3
V4203
BC847CDXV6T1G
1200-0320
4
4E4B
NC
NC
6
C
V4203
B
NC
2
BC847CDXV6T1G
1200-0320
E
1
NC
MP 52
TP4201
VDDE18
C4210
33pF
25V
<NM>
VDIG
VBOOST
C4215
33pF
<NM>
ST4201
12
0402 Size
ST4200
12
C4211
33pF
25V
<NM>
MP 89MP 92
CA
V4208
21
PESD15VS1UL
1201-0746
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
LED_BACK
C4213
100nF
C4218
1uF
C4214
100nF
LCD_RESn
LCD_CS_1
LCD_D7
LCD_D6
LCD_D5
LCD_D4
LCD_D3
LCD_D2
LCD_D1
LCD_D0
LCD_RS_1
LCD_WR_1
LCD_RD
LED_LCD
LED_CAM1
LED_CAM2
LED_CAM3
MP 86
C4216
33pF
<NM>
C4217
33pF
<NM>
X4200
1204-5252 2
100-pin
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
27
29
9
12
14
15
17
19
21
18
20
22
24
13
16
11
1
3
77
79
81
100
VOPTO30
80
78
76
2
5
7
10
23
25
26
28
30
31
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
49
51
53
55
56
57
59
62
74
75
82
83
91
95
99
(#1/6)
C4229
100nF
C4219
33pF
<NM>
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
C4220
33pF
<NM>
LED_KEYPAD
LED_CAM1
LED_BACK
OPTOTEMP
OPTOSENSE
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VDDE18
VOPTO30
VBAT
Made for
Imaging
VBAT
VDDE18
VDIG
VOPTO30
Display
Document Nr Revision
VDIG
1210-8302 Page I2 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
76 (124)
Page 77

MEASUREMENT POINTS Imaging - Camera
N2010
R18
APPLICATIONGPIO_02
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
XEFL_TRIG
CAMRESn
CAMSYSCLK
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
CAM_LDO_EN
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
CAM_LDO_EN
I2C switch
C4321
2.2uF
<NM>
VCAMIO18
C4320
100nF
B2
1C
D2
2A
C2
2B
A2
VCC
C4322
2.2uF
C4301
100nF
R4301
0ohms
I2CDAT_CAM
VCAMSA28 VCAMAF28
C4304
C4323
100nF
2.2uF
VDDE18
C4300
100nF
<NM>
C4324
2.2uF
C4303
100nF
VCAML12
C4325
2.2uF
CAMRESn
CAMSYSCLK
I2CDAT_CAM
I2CCLK_CAM
C4308
22pF
C4302
100nF
X4300
CAMERA FLEX
CONNECTOR
A1
B1
B14
B12
B10
B3
A10
A4
B13
A14
1200-1733
30-pin
GND springs
for Camera Shield
VCAMIO18
N2410
R4302
10Kohms
X4311
X4312
X4313
X4314
X4315
CAMIRQ
XEFL_TRI G
xSTL_EXP
33pF
<NM>
C4340
33pF
C4339
22ohmsR4321
22ohmsR4323
22ohmsR4324
33pF
33pF
33pF
<NM>
<NM>
C4336
C4338
33pF
33pF
C4335
C4337
<NM>
<NM>
33pF
33pF
<NM>
<NM>
<NM>
C4334
C4330
C4332
33pF
33pF
C4333
C4331
<NM>
<NM>
<NM>
B9
A9
A13
B2
A11
A12
A5
B5
A6
B6
A7
B7
A8
B8
A2
A3
A15
B4
B11
B15
Z1
Z2
Z3
Z4
1
1
1
1
1
MAX7327
1200-1951
GPIO_O11_OUTPUT
13
MP 87
XEFL_CHARGE_EN
R4303
100Kohms
VCAMIO18
N4300
A1
A
Y
B1
&
B
VCC GND
RYT326
1000-8704
CIPCLK
CIHSYNC
CIVSYNC
CID0
CID1
CID2
CID3
CID4
CID5
CID6
CID7
Video Companion Chip
N2500
MP202
1200-1414
MP 149
C2
C1A2
MP202_YUVIFMP202_YUVIF
R4304
100Kohms
YUV_DATA0
YUV_DATA1
YUV_DATA2
YUV_DATA3
YUV_DATA4
YUV_DATA5
YUV_DATA6
YUV_DATA7
YUV_CLK
YUV_VS
YUV_HS
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
N9
P9
M8
N8
P8
M7
N7
P7
P6
M6
N6
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_CAMERA_A_12_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_IMAGING
KAJSA_BOTTOM
CAMERA_INTERFACE
CI_PCLK
K18
CI_HSYNC
F23
CI_VSYNC
H22
CI_D0
G24
CI_D1
F24
CI_D2
G23
CI_D3
G22
CI_D4
J22
CI_D5
H25
CI_D6
E22
CI_D7
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
81L52F
CI_RESn
NC
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VCAMSD18
S4300
A1
1A
0ohmsR4300
B1
1B
C1
2C
D1
GND
SN74LVC2G66YZPR
1200-0333
VCAMSA28
VCAMIO18
VCAMAF28
VCAML12
VCAMSD18
VDDE18
VCAMIO18 VCAMAF28 81DSMACV21LMACV82ASMACV
VDDE18
Made for
Imaging
Camera
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page I3 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
77 (124)
Page 78

N2010
APPLICATIONGPIO_13
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
MEASUREMENT POINTS Imaging - LMU & Flash
MP 56
STEPUP50
L4401
ST4403
0402 size
21
MP 93
TP4401
MP 78
MP 77
MP 75
MP 79
TP4400
LED_NAV1
LED_NAV2
LED_NAV3
LED_NAV4
C4412
33pF
<NM>
C4413
33pF
<NM>
C4414
33pF
<NM>
STEPUP50
C4415
33pF
<NM>
C4410
100nF
X4200
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
33
48
50
52
54
1204-5252 2 (#3/6)
100-pin
VBAT
21
ST4401
0402 Strap
C4400
100nF
R24
AFLED_EN
C4401
10uF
L4400
4.7uH
MP 74MP 72
R4401
100ohms
<NM>
C4402
10pF
<NM>
R4400
100Kohms
C4406
22nF
VDDE18
C4407
100nF
R4402
0ohms
N4400
MAX8830
A3
LX
B4
IN
D2
AGND
A2
PGND
C4
COMP
MVON
C2
FLEN
D4
VDD
D3
SDA
C3
SCL
MAX8830
1200-1922
C4403
10uF
FLED
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
C4404
10uF
A4
OUT
A1
C1
B1
B2
1D3B
C4405
330pF
25V
BLM15EG121SN1
0ohmsR4403
0ohmsR4404
0ohmsR4405
0ohmsR4406
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
STEPUP50
STEPUP50
MEASUREMENT POINTS
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
XEFL_TRIG
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
XEFL_SPDA
LED_BACK
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
GPIO_O12_OUTPUT
GPIO_O13_OUTPUT
GPIO_O15_OUTPUT
GPIO_O14_OUTPUT
GPIO_O8_OUTPUT
XEFL_TRI G
XEFL_CHARGE_CTRL
14
XEFL_FC D
15
XEFL_SB
17
XEFL_SPD0
16
XEFL_SPD1
XEFL_SPDA
LED_BACK
10
LED_TALLY
I2CDAT1
I2CCLK1
SP4400
SP4401
SP4402
SP4403
MP 134
SP4404
STEPUP50
V4400
2SK2035
1000-8408
G
1
R4414
<NM>
ST4402
0ohms
VBAT
MP 148
ST4400
12
21
DS
3
2
C4416
10uF
1KohmsR4409
X4400
XE-FLASH MODULE
CONNECTOR
A1
A2
A3
A7
B5
B7
B4
A5
B3
B2
B6
A11
A10
Z1
Z2
Z3
Z4
1201-5197
24-pin
X4410
1
MP 133
A6
B8
A9
A4
A8
A12
B1
B9
(#1/2)
Extra ground
springconnector
for XE-Flash Module
C4411
33pF
<NM>
AF_LED
VDDE18
R4411
VDDE18
100Kohms
R4410
100nF
X_CHARGE_RDY
0ohmsR4413
COVER_OPEN
MP 41
N2010
K14
APPLICATIONGPIO_11
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
T18
APPLICATIONGPIO_03
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VBAT
VDDE18
VBAT VDDE18
Made for
Imaging
LMU & Flash
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page I4 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
78 (124)
Page 79

MEASUREMENT POINTS Access Top
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
MCLKREQ
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLK
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_ACCESS_A_14_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_ACCESS
RADIO_CTRL_IF
EGG_RADIO_IF
WCDMA/GSM_RADIO_IF
WCDMA_RADIO_IF
AB16
ADC_I1_NEG
AC16
ADC_I1_POS
AC15
ADC_Q1_NEG
AD15
ADC_Q1_POS
AD14
ADC_I2_NEG
AC14
ADC_I2_POS
AC13
ADC_Q2_NEG
AB13
ADC_Q2_POS
AB11
TX_POW
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
RF_CTRL_DATA
RF_CTRL_CLK
RF_CTRL_STRB0
RF_CTRL_STRB1
RF_CTRL_STRB2
ANT_SW0
ANT_SW1
ANT_SW2
ANT_SW3
TX_ADC_STRB
RF_DATA_A
RF_DATA_B
RF_DATA_C
RF_DATA_STRB
RF_WCDMA_EN0
RF_WCDMA_EN1
RF_WCDMA_EN2
RF_WCDMA_EN3
RF_WCDMA_EN4
RF_WCDMA_EN5
GSM_PA_ENABLE
DAC_I_NEG
DAC_I_POS
DAC_Q_NEG
DAC_Q_POS
VBATVDDE18
N2000
Ericsson AB 3100
OP AND SERVICES
DAC
C4
DAC_CLK
B5
DAC_STR
C5
DAC_DAT
AB3100
1202-0639
R1103
100Kohms
AE6
AC8
AC7
AD7
NC
AB5
NC
AB8
AC9
AD8
AE8
AC2
AD5
AC5
AD3
AC3
AE11
AD10
AB9
AD9
AB4
NC
AC4
NC
AA5
NC
AD12
AD13
AD11
AC10
R1101
100Kohms
A7
DACO_0
B6
DACO_1
A6
DACO_2
C6
DACO_3
2
R1102
100Kohms
DC_DC_REF1
BIAS_CTRL
NC
MCLKREQ
RADDAT
RADCLK
RADSTR
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
ANTSW2
ANTSW3
QDATA_AMP_MSB
IDATA_FREQ_MSB
AMP_LSB_FREQ_LSB
DCLK_DATSTR
WPA0_EN
WPA1_EN
WPA2_EN
WDETON
WTX_IB
WTX_IA
WTX_QB
WTX_QA
WTXPOWDET
WRX_QA
WRX_QB
WRX_IA
WRX_IB
TX_ADSTR
VBAT
VBAT
TX_ADSTR
AGPS_RSTnAGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLKAGPS_CLK
RTCCLK
TX_ADSTR
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_CLK
RTCCLK
AGPS
Page 2
VBAT
VDDE18
DC_DC_REF1
BIAS_CTRL
MCLKREQ
OPTO_EN
RADDAT TESTOUT
RADCLK MCLK
RADSTR MCLKSEC
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
ANTSW2
ANTSW3
QDATA_AMP_MSB
IDATA_FREQ_MSB
AMP_LSB_FREQ_LSB
DCLK_DATSTR
WPA0_EN
WPA1_EN
WPA2_EN
WDETON
WRX_QBWTX_IA
WRX_QAWTX_QB
WTXPOWDETWTX_QA
GSM & UMTS
Page 4
RF_ID
WRX_IB
WRX_IAWTX_IB
XEFL_SPDA
RF_ID
OPTO_EN
TESTOUT
MCLK
MCLKSEC
XEFL_SPDA
RF_ID
OPTO_EN
TESTOUT
MCLK
MCLKSEC
TX_ADSTR
MEASUREMENT POINTS
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
WLAN_CLK
VBAT
VDDE18
VBT27
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VDDE18VDIGVBT27
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
WLAN_CLK WLAN_CLK
VBAT VDDE18 VDIG VBT27 WLAN_VO33 WLAN_LDO18A W LAN_LDO30
VDIG
WLAN_VO18
VDDE18
VDIG
VBT27
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
BTRESn
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
WLAN_BT_STATE
ACC_SPI_DI
WLAN_CONFIRMn
Bluetooth
Page 3
Page 3
BT_CLKREQn
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
BT_ANT
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
BT_ANT
WLAN_BT_STATE
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
RTCCLK
WLAN_CONFIRMn
ACC_SPI_DI
VDIG
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO18A
WLAN_LDO30
VDIG
WLAN_CLK
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
BT_ANT
WLAN_BT_STATE
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
RTCCLK
WLAN
WLAN
BT_CLKREQn
Page 5
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
ACC_SPI_DI
WLAN_CONFIRMn
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
BT_CLKREQn
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
Made for
Access Top
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page R1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
79 (124)
Page 80

L1202
0.5pF
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
ANTSW2
ANTSW3
WTX_IA
WTX_IB
WTX_QA
WTX_QB
BIAS_CTRL
WDETON
RADCLK
RADDAT
RADSTR
QDATA_AMP_MSB
IDATA_FREQ_MSB
AMP_LSB_FREQ_LSB
DCLK_DATSTR
WPA1_EN
MCLKREQ
MP 167
MP 168
GSM/UMTS
ANTENNA
X1210
X1211
R1202
C1211
0.5pF
MEASUREMENT POINTS Access - GSM & UMTS
39nH
0ohms
R1201
MP 166
<NM>
Z1200
DEA101910DT
OUT
GND1
GND2
DEA101910DT-6005A2
1212-1502
IO
IN
G1
G2
X1200
GND
GND
CRS5001-4202E
1203-9688
C_TERMR_TERM
C1200
33pF
<NM>
MP 62MP 63
12
34
GND
56
GND
C1209
1pF
<NM>
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
ANTSW2
ANTSW3
WTX_IA
WTX_IB
WTX_QA
WTX_QB
BIAS_CTRL
WDETON
RADCLK
RADDAT
RADSTR
QDATA_AMP_MSB
IDATA_FREQ_MSB
AMP_LSB_FREQ_LSB
DCLK_DATSTR
WPA_A_EN
WPA1_EN
WPA_C_EN
MCLKREQ
VCC_WPA
C1219
2.2uF
<NM>
VBAT
C1220
68pF
<NM>
VRAD28
VDDE18
TIGER RF-Module
GSM / UMTS
N1200
A5
ANT
C2
ANTSW0
C1
ANTSW1
B2
ANTSW2
D2
ANTSW3
L4
WTX_IA
K4
WTX_IB
L5
WTX_QA
K5
WTX_QB
L7
BIAS_CTRL
A8
PASENSE_EN
J2
RADCLK
J1
RADDAT
H1
RADSTR
H2
EDATAA
G1
EDATAB
G2
EDATAC
F1
EDATASTR
K6
WPA_A_EN
G8
WPA_B_EN
K7
WPA_C_EN
K2
CLKREQ
L3
VDIGRAD_1V8
B8
VRADB_2V75
L6
VRADA_2V75
A3
VBAT1
B3
VBAT2
J8
VCC_PA1
H8
VCC_PA2
TIGER_I_VIII_MODULE
1210-9905
MCLK
MCLKSEC
TESTOUT
MODULE_SENSE
WRX_IA
WRX_IB
WRX_QA
WRX_QB
WTXPOWERSENSE
RFCTRL1
GND1
GND2
GND4
GND5
GND6
GND7
GND8
GND9
GND10
GND11
GND12
GND13
GND14
GND15
GND16
GND17
GND18
GND19
GND20
GND21
GND22
GND23
GND24
GND25
SLUG
D1
SLUG
L2
K3
K1
K9
E1
F2
E2
A7
L1
RF_CONT1
D8
E9
C9
D9
F9
G9
E8
A9
K8
B1
A4
B9
B5
L9
A2
L8
B4
B6
C8
A6
H9
J9
F8
B7
MCLK
MCLKSEC
TESTOUT
RF_ID
WRX_IA
WRX_IB
WRX_QA
WRX_QB
WTXPOWDET
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
MCLK
MCLKSEC
TESTOUT
RF_ID
WRX_IA
WRX_IB
WRX_QA
WRX_QB
WTXPOWDET
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VBAT
VDDE18
WPA0_EN
WPA2_EN
DC_DC_REF1
VBAT
VDDE18
PA Power Supply
MP 140
WPA0_EN
WPA2_EN
R1209
100Kohms
DC_DC_REF1
VBAT
ST1200
12
0402 Size
R1210
100Kohms
MP 144
C1204
100nF
R1203
100Kohms
C1216
1uF
<NM>
C1201
10uF
N1210
MAX8805
D2
EN1
B3
EN2
B2
PA_EN
A3
REFIN
C1
IN2
C3
IN1B
C4
IN1A
C2
HP
MAX8805WEWEEE+T
1203-5870
LDO1
LDO2
REFBP
AGND
PGND
RF_CONT1
VCC_WPA
L1200
2.2uH
B4
LX
D3
PAB
D4
PAA
D1
MP 143
B1
A1
A2
C1213
220nF
A4
C1214
100nF
MP 142
C1215
100nF
C1206
4.7uF
C1205
100nF
ST1201
MP 145
C1203
22pF
<NM>
21
Radio Power Supply
0ohms
VBAT
C1208
100nF
N2000
VBAT_A
AB3100
1202-0639 2
Ericsson AB 3100
POWER
RADIO
LDOA
2.8V
LDOA_OUT
EXT_LDO
VBAT
MP 163
31K21K
C12
C1218
C1217
2.2uF
2.2uF
N1211
5
VDD_1
6
VDD_2CEGND
RP102K281D-TR
1204-5903
R1211
<NM>
RP102K
2.8V
VOUT_1
VOUT_2
SLUG
OPTO_EN
VRAD28
14
2
MP 65
3
7
C1207
2.2uF
C1221
22pF
<NM>
OPTO_EN
Made for
Access
GSM & UMTS
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page R2 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
80 (124)
Page 81

ACC_SPI_DI
BTRESn
BT_CLK
RTCCLK
N2010
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
AD6
PCMULD/I2SULD
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
WLAN_CONFIRMn
WLAN_BT_STATE
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
ACCESS GPIO_21
ACCESS GPIO_22
KAJSA_BOTTOM
BLUETOOTH_A_11_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_BLUETOOTH
BLUETOOTH_PCM_I2S(ACCESS)
AA3
AB3
PCMCLK/I2SCLK
PCMSYN/I2SWS
PCMDLD/I2SDLD
SP1301 SP1302
Y5
AD4
U11
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
PCMCLK
PCMSYN
PCM_DLD_TO_KAJSA
PCM_ULD_FROM_KAJSA
WLAN_CONFIRMn
WLAN_BT_STATE
VDDE18
MEASUREMENT POINTS Access - Bluetooth
N1300
BLUETOOTH-FM_IO
BT_SYSCON
K7
BT_RSTn
F6
BT_REF_CLK_IN
K9
BT_RTCCLK
E7
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
BT_CLKREQ_IN1
F9
BT_CLKREQ_IN2
UART_RXD/SPI_DI
UART_CTS/SPI_CLK
M4
BT_PCM_CLK
N4
BT_PCM_SYNC
K5
BT_PCM_A
M5
BT_PCM_B
G9
BT_GPIO_0
L3
BT_GPIO_8
M3
BT_GPIO_9
K4
BT_GPIO_10
J3
BT_GPIO_16
L7
BT_CONFIG_1
M7
BT_CONFIG_2
N6
BT_CONFIG_3
G6
BT_AF_PRG
H2
BT_TEST1
G2
BT_TEST2
STLC2593
1200-9840
UART_&_SPI-INTERFACE
PCM_INTERFACE
BT_CLKREQ_OUT1
BT_CLKREQ_OUT2
HOST_WAKEUP/SPI_INTBT_WAKEUP
UART_TXD/SPI_DO
UART_RTS/SPI_CSn
GPIO
CONFIG-PINS
TESTPINS
RF
DO-NOT-USE
BT_REG_CTRL
BT_GPIO_11
BT_RFP
BT_RFN
BT_RSRV_D
BT_RSRV_RF
BT_RSRV_CL
BT_RSRV_DSM
BT_RSRV_N
BT_RSRV_CL
SP1300
J4
J7
NC
J8
E8L9
G7H9
J6K6
K3
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
K1
J1
M8
NC
M2
NC
B2
NC
C1
NC
C2
NC
C3
NC
MP 28
MP 27
NC
SP1303 SP1304 SP1305
W1300
BALUN
3
Unbal
Bal
4
GND
Bal
6
GND
NC
HHM1798
1200-5169
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
BT_CLKREQn
N2010
BT_SPI_INT
ACC_SPI_DI
BT_SPI_CSn
BT_ANT
ST1300
21
21
1
2
5
C1301
C1300
100nF
100nF
<NM>
ST1301
E10
ACCESS GPIO_27
Y4
ACCESS GPIO_20
C9
ACCESS GPIO_26
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VBT27VDDE18VDIG
12
MP 26
ST1302
C1302
100nF
N7
L2
D3
E1
E2
E4
M6
J9
N3
N5
G8
N1300
BT_HVD
BT_HVA1
BT_HVA2
BT_HVA2
BT_HVA2
BT_HVA2
BT_VIO_A
BT_VIO_B
BT_VIO_C
BT_VIO_D
BT_VIO_E
STLC2593
1200-9840
BLUETOOTH-FM_POWER
BTPOWER&GND
BT_CLKREQn
BT_ANT
BT_VDD_CLD
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_ANA
BT_VSS_DIG
BT_VSS_DIG
BT_VSS_DIG
BT_VSS_DIG
BT_VSS_DIG
BT_VSS_RF
BT_VSS_RF
BT_VSS_RF
BT_VSS_RF
MEASUREMENT POINTS
VDDE18
ST1303
21
E6
D1
D2
E3
F1
F2
F3
F4
G3
G4
H3
H4
G1
H6
H7
H8
K8
L8
H1
J2
K2
L1
C1303
100nF
VDDE18
VDIG
VBT27
VDDE18 VDIG
VBT27
Made for
Access
Bluetotth
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page R3 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
81 (124)
Page 82

MEASUREMENT POINTS Access AGPS
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
AGPS_CLK
RTCCLK
TX_ADSTR
AGPS_RSTn
N2410
GPIO_O1_OUTPUT
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2410
GPIO_O7_OUTPUT
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_17
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_10
ACCESS GPIO_11
ACCESS GPIO_12
ACCESS GPIO_13
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VBAT
MP 91
2
R1404
100Kohms
AGPS_CLK
ST1400
RTCCLK RTCCLK_AGPS
TX_ADSTR TX_ADSTR_AGPS
8
W5
V5
W3
V4
Y2
UART3_TX
UART3_CTS AGPS_RTS
UART3_RTS
21
ST1402
12
ST1407
12
ST1403
21
ST1404
21
ST1405
21
ST1406
12
MP 32
MP 2
MP 81
R1406
10Kohms
<NM>
R1401
100Kohms
0ohmsR1407 0ohmsR1408
C1400
120pF
<NM>
R1402
100Kohms
<NM>
L1400
220nH
<NM>
R1403
100Kohms
AGPS_LDO_EN
AGPS_PWRON
AGPS_RSTn
AGPS_SYNC
AGPS_TXUART3_RX
AGPS_RX
AGPS_CTS
X4200
100-pin
SLIDER FLEX
CONNECTOR
89
87
85
97
93
96
98
84
86
88
92
94
90
MEASUREMENT POINTS
(#4/6)21204-5252
VBAT
VBAT
Made for
Access AGPS
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page R4 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
82 (124)
Page 83

WLAN_CLK
RTCCLK
C1503
MEASUREMENT POINTS Access - WLAN
VDIG
R1506
51Kohms
WLAN_TX
L1502
2.7nH
<NM>
R1510
100Kohms
1KohmsR1511
R1515
3.3Kohms
1KohmsR1512
C1506
10pF
ST1520
C1507
10pF
68ohmsR1514
21
C1509
C1508
10pF
10pF
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_RX_P
WLAN_RX_N
NC
R1507
100Kohms
<NM>
R1505
100Kohms
R1508
100Kohms
L1500
L1501
C1505
10pF
3.3nH
3.3nH
R1509
100Kohms
C1504
TX2_OUT
TR_P
TR_N
TR3_N
10pF
J10P6
C10
01E9P
P5
M4
M5
P4
M3
K5
N1500
MARVELL_RF_IF
ANALOG
1nF
6.04KohmsR1502
1%
XPWDET2
A6
XTAL_I_XO
A7
XTAL_O
NC
REXT
A3
SLEEP_CLK/CLK_OUT PA_PE_G
RX2_IN_P
RX2_IN_N
DIG_IF
ANT_SEL_P
ANT_SEL_N
MP 47
88W8686
21200-0932
C1510
10uF
6
11
7
8
9
3
4
5
N1510
PD
WLAN_TX
WLAN_RXb
VREF_PA
VC1
VC2
VC3
VCC_PA
R041B
1200-6173
EPCOS_FEM_R041B
RF_IF
CONT_IF
PWR
BT_ANTWLAN_Rxa
GND_1
GND_2
GND_3
GND_4
GND_5
GND_6
GND_7
GND_8
ANT
GND
GND
MP 23MP 29
21
43
65
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
C1511
1.2pF
<NM>
C1530
4.7pF
C1512
0.75pF
X1500
C_TERM R_TERM
GND
GND
CRS5001-4202E
1203-9688
MP 48
0ohmsR1532
R1533
R1534
0ohms
0ohms
<NM>
<NM>
10pFC1502
L1503
4.7nH
17
2
1
10
12
13
14
15
18
9161
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
WLAN / BT
ANTENNA
X1530
1
2
3
4
ANTENNA
W_FL-R-SMT-1_48
1001-0637
CLIP
X1540
1
WLAN_SCLK
WLAN_CLKREQ
MP 21
MEASUREMENT POINTS
BT_ANT
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
WLAN_BT_PRIORITY
WLAN_BT_STATE
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_LDO18A
VDIG
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
GPIO_O9_OUTPUT
WLAN_VO18
WLAN_VO33
C1513
1uF
11
C1514
100nF
WLAN_LDO30
WLAN_LDO18A
C1515
1nF
WLAN_LDO18A
C1516
10pF
VDIG
C1517
10pF
BT_ANT
WLAN_RSTn_PDn
C1518
100nF
C1519
1nF
C1520
10pF
C1521
1nF
WLAN_LDO30
C1522
10pF
C1523
100nF
WLAN_VO18
C1524
1uF
C1525
100nF
C1526
100nF
C1527
1uF
C1528
100nF
NC
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_19
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
N1500
MARVELL POWER_SUPPLY
K3
VDD12
B9
L9
K7
P7
VDD18A
E6
D5
A8
K4
VDD18_LDO
K6
VDD30
A1
VIO_X1
P1
VIO_X2
M6
NC
88W8686
AA4
SP1507
VSS
N10
A10
E8
J8
C8
M7
H7
E7
C7
C6
H4
H3
0ohmsR1526
<NM>
ACC_SPI_DO
ACC_SPI_CLK
WLAN_SPI_CSn
WLAN_BT_STATE
WLAN_VO18
ST1518
12
12
ST1517
SP1503
R1525
100Kohms
SP1500
SP1501
R1517
100Kohms
2.7KohmsR1518
2.7KohmsR1519
N1500
MARVELL_HOST_IF
PWDWN_CTRL
A4
RESETn_PDn
CSP_HOST_IF
SPI_SDI/CMD
F1
SPI/SD_CLK
D1
SPI_SCSn/DAT0
A5
BT_PRIORITY
B4
BT_STATE
F4
GPIO0
H1
GPIO1
F3
GPIO2
D3
M2
P3
H6
M1
K1
F5
D4
G8
GPIO3
SRWB
SCLK
TRSTn
TCK
TDI
TMS1
TMS2
SCAN_EN
88W8686
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
SPI_SDO/DAT1
SPI_SINTn/DAT2
SD_DAT_3
BT_COEX
WL_ACTIVEn
GPIO
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
EEPROM_CTRL
SDA
ECSn
JTAG
TDO
21200-0932
2D2F
B1
B2
B5
H2
A2
B3
P2
K2
H5
ST1519
12
ACC_SPI_DI
WLAN_SPI_IRQ
SP1504
NC
WLAN_CONFIRMnWLAN_BT_PRIORITY
NC
R1521
100Kohms
NC
NC
SP1502
R1522
100Kohms
R10
R1527
100Kohms
ACC_SPI_DI
N2010
ACCESS GPIO_25
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
WLAN_CONFIRMn
Made for
Access
WLAN
21200-0932
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page R5 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
83 (124)
Page 84

N2010
ACCESS GPIO_24
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
VDDE18
Unused GPIO
N2410
D8
VDDE18
NC
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
N2410
MAX7327
1200-1951
GPIO_P4_BIDIR
GPIO_P5_BIDIR
GPIO_O0_OUTPUT
MEASUREMENT POINTS Test
5
NC
6
NC
1
NC
R5101
100Kohms
SP5105
R5100
10Kohms
<NM>
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_JTAG_A_16_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_TEST
JTAG_EMULATION_IF
TDI
R3
TMS
T3
TRSTn
U2
TCK
B24
TEMU0n
B3
TEMU1n
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
SP5101 SP5102 SP5103 SP5104
TDO
RTCK
VDDE18
SP5107SP5106
R5102
10Kohms
01T5P
T5
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
MEASUREMENT POINTS
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_ETM_A_17_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_ETM
KAJSA_BOTTOM
TEST_EMBEDDED_TRACE_IF
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
ETM_TCLK
ETM_TSYNC
ETM_TPKT0
ETM_TPKT1
ETM_TPKT2
ETM_TPKT3
ETM_TPKT4
ETM_TPKT5
ETM_TPKT6
ETM_TPKT7
ETM_PSTAT0
ETM_PSTAT1
ETM_PSTAT2
N2010
KAJSA_BOTTOM_UNUSED_A_5_24
KAJSA_BOTTOM_UNUSED
KAJSA_BOTTOM_NOT_USED
R5
NC
D6
NC
D5
NC
C8
NC
D9
NC
B6
NC
E9
NC
B9
NC
C6
NC
B8
NC
C7
NC
E8
NC
B5
NC
E7
NC
EFUSE_HV5
DB3210ADT/7POPHF
1208-3871
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
UNUSED
A1
A2
A3
B1
C1
AD1
AE1
AF1
AF2
AF3
AF24
AF25
AF26
AE26
AD26
A26
B26
C26
A25
A24
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
Made for
Test
Document Nr Revision
1210-8302 Page T1 5
1222-9526 rev. 1
84 (124)
Page 85

SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
COMCOMPPONONEENNT OT OVVEERRVIEVIEWW Front Side
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
12345
C905
W890
A
B
C
D
C3118
L3110
C3101 C3117
L3111
X2405
V2415
V2416
Z2400
SP5104
SP5103
SP5107
SP5102
SP5105
SP5106
SP2200
TP2204
TP2202
TP2201
C3105
C3107
C3104
C3108
N3100
R3128
C3106
ST3100
R3127
R3106
R3102
C3137
C3148
SP1302
R5102
ST1403
ST1407
C2348
R1102
R1101
SP2410
C2324
C2305
R1103
C2337
C2325
C2343
C2342
C2341
R2422
C2353
SP2104
C2354
C2104
C2340
R2115
C2339
R2122
C2338
C2336
C2326
C2320
ST2300
C2307
R2123
ST2110
C2103
R2102
C2327
C2349
SP2411
C2352
SP2103
C2345
C2404
C1217
ST2225
C2406
ST2402
ST4200
N2214
R1211
N1211
SP2401 SP2400
N2411
ST2401
C2405
C2251
IN
X1200
OUT
C2431
ST2422
R1527
SP2432
SP1304
SP1301
R5101
ST1404
ST1405
C2323
C2303
C2344
C2304
R4410
R2473
R2472
C2314
C2351
C2308
C2306
SP2105
C2268
ST2229
SP2504
C2263
C2267
C2265
C1221
C2254
R2210
C1207
R2445
C2437
SP5124
R2430
R2431
SP5116
C2436
C2433
SP2421
SP5123
R2442
C2434
C2435
R2470
R2475
R2471
C2322
C2301
N2010
N2020
E1001
R2228
C2329
C2328
C2309
C2350
SP2500
SP2501
C2261
C2269
C2255
C2264
N2500
R2503
C2259
C2270
C2253
SP2503
R2446
N2420
SP2435
SP2430
R2440
SP2422
C2302
R3202
R3201
R3204
R2223
R2501
C2271
R2215
ST2226
N2210
C2274
SP2429
ST2421
C2346
R2502
V2414
R2443
C2446
C2445
R2453
L2405
C2444
ST2233
R2441
SP2423 SP2424
C2282
SP2425
SP2426
SP2427
SP2428SP2420
R2451
C2432
R2452
SP5110
C2347
V2482
SP3208
SP3214
SP5101
C2469
SP3209
R3203
ST2228
C2278
C2252
N2212
C2266
C2262
C2277
C2256
L2213
C2468
V2481
C2258
C2257
C2260
ST4401
SP2505
C4401
L4400
ST2213
R2444
N2421
R2447
R2214
ST2230
R4216
R2213
C2279
R4215
N2700
C2281
C2280
ST2232
R2125
ST2108
ST2109
SP1303
R5100
R4205
C2321
C2313
R2113
R4220
C2331
R4219
R2101
R2112
R2407
R2108
C2312
ST2106
C2460
N2100
R2103
C2311
V2101
C2310
R2111
R2104
C2330
C2105
N2102
R2116
R2117
C2403
ST2107
R1404
ST2102
ST2103
ST2101
C2288
R3153
C2289
R2217
N2201
C4405
ST4403
C4403
C4402
C4404
R4401
R4405
ST2231
C4300
S4300
R4300
ST2105
N2410
N4400
L4401
L2407
V4203
C3139
C3140
ST2400
R1526
C4400
SP4203
SP4202
IN IN
IN
C4406
R4404
C2439
C2284
N2208
C2283
C2285
N2209
C2286
SP4201
R4301
Z4202
Z4201
Z4200
ST3105
ST3106
R2408
R2313
V2470
R1407
C1400
L1400
R4402
C4407
R4400
R4403
R2474
R4303
R1408
R4406
OUT
OUT
OUT
X1530
R3100
ST3103
C4210
C4211
R4222
R4221
SP4200
ST4201
C4213
C4214
C4410
R4218
R4217
C3159
C2472
C4215
V4208
C4218
C4216
C4217
C4229
R1402
R1403
ST1406
ST1402
R1406
ST1400
R1401
C1512
C1530
C3110
C1511
OUT
X1500
IN
0.8mm
B1
S2415
C3304
W1300
C1510
R1534
R1532
SP2102
SP1305
X4200
A1
L1503
ST3304
C3305
R3302
SP1300
ST1302
C1302
N1300
SP5125
R1533
N1510
ST1520
C1507
C1508
C1502
L3300
C2376
L2313
C3306
ST1303
C1303
E1003
C2371
C1513
L2310
ST2313
SP1502
ST2312
C1505
C1518
R1502
C1523
C1520
C1519
C1521
C1522
L1501
L1502
L1500
C1516
C1515
C1514
C1517
ST1301
C1301
ST1300
C1300
R1514
C1509
R1512
R1511
C1506
N1500
C1503
C2377
C4321
C4330
R4321
C4323
C4304
C4322
C4301
C4340
C4338
C4336
C4334
C4320
N2300
C2372
C2373
C2379
C1524
R1505
R1506
L2311
R1515
R1508
R1507
R1509
R1510
C1504
ST2311
ST2310
C1526
C2374
SP1500
C1528
SP1503
C1527
R1525
ST1517
ST1518
SP1507
SP1501
ST1519
C1525
SP1504
R1518
V2100
R1522
R1517
R1521
R1519
Cutout
Cutout
X4300
B1
C4324
C4303
R4324
C4332
R4323
C4331
ST4402
C4339
C4337
C4335
C4333
C4308
A1
C4302
C4325
E1000
TP4200
TP4201 TP2206
C4412
C4413
C4414
C4415
C4219
C4220
TP4400
TP2203
TP4401
LABEL
X4311
X4315
X4312
X4313
X4314
C2214
V2475 V2476
S2424
V2474
V2477
S2453S2454
A
B
C
D
COMPONENT OVERVIEW
COMPONENT OVERVIEW
C1207 1000-6901 D2
C1217 1000-6901 D2
C1300 1000-0048 B4
C1302 1000-0048 B3
C1303 1000-0048 B4
C1502 1000-0066 C3
C1503 1000-0053 C4
C1504 1000-0066 B4
C1505 1000-0066 B4
C1506 1000-0066 C3
C1507 1000-0066 C3
C1508 1000-0066 C3
C1509 1000-0066 B3
C1510 1000-0061 B3
C1512 1000-5938 B3
C1513 1000-0051 B4
C1514 1000-0048 C4
C1515 1000-0053 C4
C1516 1000-0066 C4
C1517 1000-0066 C4
C1518 1000-0048 B4
C1519 1000-0053 B4
C1520 1000-0066 B4
C1521 1000-0053 B4
C1522 1000-0066 B4
C1523 1000-0048 B4
C1524 1000-0051 B4
C1525 1000-0048 B4
C1526 1000-0048 B4
C1527 1000-0051 B4
C1528 1000-0048 B4
C1530 1000-5956 B3
C2105 1000-0039 C3
C2214 1000-0335 D4
C2251 1000-6901 D2
C2252 1000-0048 D2
C2253 1000-0048 D2
C2254 1000-0048 D2
C2255 1000-0048 D2
C2256 1000-0048 D2
C2257 1000-0051 D2
C2258 1000-0048 D2
C2259 1000-0048 D2
C2260 1000-0048 D2
C2261 1000-0048 D2
C2262 1000-0048 D2
C2263 1000-0048 D2
C2264 1000-0048 D2
C2265 1000-0048 D2
C2266 1000-0048 D2
C2267 1000-0048 D2
C2268 1000-0048 D2
C2269 1000-0048 D2
C2270 1000-0048 D2
12345
C2271 1000-6901 D2
C2274 1000-0051 D2
C2277 1000-6901 D2
C2278 1000-6901 D2
C2279 1000-0048 B3
C2280 1000-0048 B3
C2281 1000-0048 B3
C2282 1000-0048 B2
C2283 1000-6901 B3
C2284 1000-6901 B3
C2285 1000-6901 B3
C2286 1000-6901 B3
C2288 1000-6901 D3
C2289 1000-6901 D3
C2301 1000-0051 B2
C2302 1000-0048 B2
C2303 1000-0048 B2
C2304 1000-0048 B2
C2305 1000-0048 C2
C2306 1000-0048 C2
C2307 1000-0048 C2
C2308 1000-0048 C2
C2309 1000-0048 C2
C2310 1000-0048 C3
C2311 1000-0048 C3
C2312 1000-0048 C3
C2313 1000-0048 C3
C2314 1000-0048 C2
C2320 1000-0051 C2
C2321 1000-0048 C3
C2322 1000-0048 B2
C2323 1000-0048 B2
C2324 1000-0048 C2
C2325 1000-0048 C2
C2326 1000-0048 C2
C2327 1000-0048 C2
C2328 1000-0048 C2
C2329 1000-0048 C2
C2330 1000-0048 C3
C2331 1000-0048 C3
C2336 1000-0051 C2
C2337 1000-0048 C2
C2338 1000-0048 C2
C2339 1000- 00 48 C2
C2340 1000-0048 C2
C2341 1000-0048 C2
C2342 1000-0048 C2
C2343 1000-0048 C2
C2344 1000-0048 B2
C2345 1000-6901 C2
C2346 1000-0048 B2
C2347 1000-0048 C2
C2348 1000-0048 B2
C2349 1000-0048 C2
C2350 1000-0048 C2
C2351 1000-0048 C2
C2352 1000-0048 C2
C2353 1000-0068 C2
C2354 1000-0068 C2
C2371 1000-0061 B4
C2372 1000-0061 B4
C2373 1000-0048 B4
C2374 1000-0061 B4
C2376 1000-0061 B4
C2377 1000-0061 B4
C2379 1000-0061 B4
C2403 1000-0048 C3
C2404 1000-0061 D2
C2405 1000-0048 D2
C2406 1000-0048 D2
C2431 1000-0061 B2
C2432 1000-0048 B2
C2433 1000-0051 B2
C2434 1000-0048 B2
C2435 1000-0039 B2
C2436 1000-0048 B2
C2437 1000-0039 B2
C2439 1000-0076 B3
C2444 1000-0338 B2
C2445 1000-6884 B2
C2446 1000-0056 B2
C3101 1000-0056 D1
C3104 1000-0340 B2
C3106 1000-0061 B2
C3107 1000-6080 B2
C3108 1000-6080 B2
C3137 1000-0340 B2
C3304 1000-0075 B3
C3305 1000-0048 B3
C3306 1000-0161 B4
C4213 1000-0048 C3
C4214 1000-0048 C3
C4218 1000-0051 D3
C4229 1000-0048 D3
C4301 1000-0048 B5
C4302 1000-0048 B5
C4303 1000-0048 B5
C4304 1000-0048 B5
C4308 1000-0049 B5
C4320 1000-0048 B5
C4321 1000-6901 B5
C4322 1000-6901 B5
C4323 1000-6901 B5
C4324 1000-6901 B5
C4325 1000-6901 B5
C4400 1000-0048 D3
C4401 1000-0061 D2
C4403 1000-0061 D3
C4404 1000-0061 D3
C4405 1200-0286 D3
C4406 1000-0075 D3
C4407 1000-0048 D3
C4410 1000-0048 C3
L1500 1203-5872 B4
L1501 1203-5872 B4
L1503 1000-0113 C3
L2213 1200-0317 D2
L2310 1000-0118 B4
L2311 1200-0119 B4
L2313 1200-2028 B4
L2405 1000-1156 B2
L2407 1000-2617 B3
L3110 1203-8594 D1
L3111 1203-8594 D1
L3300 1000-1899 B4
L4400 1201-6416 D2
L4401 1000-2617 D3
N1211 1204-5903 D2
N1300 1200-9840 B3
N1500 1200-0932 B4
N1510 1200-6173 B3
N2010 1208-3871 C2
N2020 1205- 5912 C2
N2100 1200-0425 C3
N2102 1204- 8 667 C3
N2201 1000 -8623 D3
N2208 1000 -8623 B3
N2209 1001-0062 B3
N2210 1201-9681 D2
N2212 1200-1974 D2
N2214 1212-7867 D2
N2300 1203-2790 B4
N2410 1200-1951 D3
N2411 1202-1676 D2
N2420 1200-1694 B2
N2421 1200- 63 09 B3
N2500 1200-1414 D2
N2700 1200- 03 62 B3
N3100 1200-9 978 B2
N4400 1200-1922 D3
R1101 1000-0231 C2
R1102 1000-0231 B2
R1103 1000-0231 C2
R1401 1000-0231 D3
R1403 1000-0231 D3
R1404 1000-0231 C3
R1407 1000-0181 D3
R1408 1000-0181 D3
R1502 1201-1031 B4
R1505 1000-0376 B4
R1506 1000-4158 B4
R1508 1000-0376 B4
R1509 1000-0376 B4
R1510 1000-0376 B4
R1511 1000-0230 C3
R1512 1000-0230 C3
R1514 1000-0241 B3
R1515 1000-4134 B4
R1517 1000-0376 C4
R1518 1000-4133 C4
R1519 1000-4133 C4
R1521 1000-0376 C4
R1522 1000-0376 C4
R1525 1000-0376 B4
R1527 1000-0376 B2
R1532 1000-0181 B3
R2101 1000-0231 C3
R2104 1000-0231 C3
R2108 1000-0231 C3
R2111 1000-0378 C3
R2113 1000-0388 C3
R2115 1000-0230 C2
R2116 1000-0231 C3
R2117 1000-0231 C3
R2122 1000-4034 C2
R2123 1000-4034 C2
R2125 1000-0231 C3
R2210 1000-0231 D2
R2213 1000-0231 B3
R2214 1000-0231 B3
R2215 1000-0231 D2
R2217 1000-0231 D3
R2223 1000-0231 D2
R2228 1000-0231 C2
R2313 1000-0231 D3
R2407 1000-0243 C3
R2408 1000-0243 C3
R2422 1000-4063 C2
R2431 1000-0231 B2
R2441 1000-4147 B2
R2442 1000-0240 B2
R2443 1000-0179 B2
R2444 1000-0231 B3
R2445 1000-0234 B2
R2446 1203-6621 B2
R2447 1000-0231 B3
R2451 1000-0380 B2
R2452 1000-4128 B2
R2453 1000-4099 B2
R2470 1000-0175 B2
R2471 1000-0175 B2
R2472 1000-0175 C2
R2473 1000-0175 C2
R2474 1000-0175 C3
R2475 1000-0175 B2
R2501 1000-0231 D2
R2502 1000-4063 D2
R3100 1000-0181 C3
R3102 1000-0388 B2
R3106 1000-0249 B2
R3128 1000-0181 B2
R3153 1000-0231 D3
R3204 1000 -0231 D2
R3302 1000-0243 B3
R4205 1000-0175 C3
R4216 1000-0231 B3
R4217 1000-0181 C3
R4218 1000-0181 C3
R4219 1000-0181 C3
R4220 1000-4034 C3
R4221 1000-0181 C3
R4222 1000-4034 C3
R4300 1000-0181 C3
R4301 1000-0181 B3
R4303 1000-0231 D3
R4321 1000-4034 B5
R4323 1000-4034 B5
R4324 1000-4034 B5
R4400 1000-0231 D3
R4402 1000-0181 D3
R4403 1000-0179 D3
R4404 1000-0179 D3
R4405 1000-0179 D3
R4406 1000-0179 D3
R4410 1000-0048 C2
R5101 1000-0231 B2
R5102 1000-0175 B2
S2415 1204-1127 D3
S2424 1204-1127 D4
S2453 1204-1127 D5
S2454 1204-1127 D5
W1300 1200-5169 B3
V2100 1000-8463 B4
V2101 1000-0391 C3
V2414 1201-8440 B3
V2415 1201-8440 B2
V2416 1201-8440 B2
V2470 1000-0391 D3
V2474 1207-3081 D5
V2475 1207-3081 D3
V2476 1207-3081 D3
V2477 1207-3081 D5
V2481 1000-0087 D3
V2482 1000-0087 C2
V4203 1200-0320 C3
V4208 1201-0746 D3
X1200 1203-9688 D2
X1500 1203-9688 B3
X1530 1001-0637 B3
X2405 1202-1195 A2
X4200 1204- 5252 C3
X4300 1200-1733 B5
X4311 1204- 9 353 C 4
X4312 1204- 9 353 C5
X4313 1204- 9 353 D5
X4314 1204- 9 353 D5
X4315 1204- 9 353 D4
Z2400 1201-6833 B2
Z4200 1000-7455 C3
Z4201 1000-7455 C3
Z4202 1000-7455 C3
R - Replaceable
See Appendix for
more information.
1222-9526 rev. 1
85 (124)
Page 86

COMPONENT OVERVIEW Back Side
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
12345
C905
A
B
C
D
X4202
L4202
R2448
C2448
N2422
C2414
C2473
L2404
SP3213
SP3205
C2207
C2447
V2202
ST2201
L2449
C2438
R2434
C2440
R2478
C2441
V2417
C2215
L2201
C2217
SP3204
C2221
C2223
SP3206
C2224
N2000
C2225
C3154
C1208
R3154
C3138
C1218
C2204
N1200
C2470
C2466
C2471
ST2214
C2229
C2201
C2200
R2200
ST2211
ST2212
L1200
C1220
V4206
R2231
C2233
C2202
C2203
C1203
C1205
C1219
L3108
C2400
R2400
C1209
R1201
V3101
L3109
Z1200
X2201
C1211
X1211
X1210
R1202
L1202
X3103
X3102
V2412
C2231
ST2210
C2218
L2200
C2219
C4200
C2230
R1203
C1214
C1215
R1210
V4201
C4203
ST4203
L2202
C2232
R2207
R2208
ST4202
N2200
C2228
V2200
C4202
ST1200
R1209
C1213
C1201
C1204
N1210
C1206
ST1201
C1200
C2220
C4206
R4203
C4204
C4205
E1002
R4204
R2402
R2403
R2404
C2402
ST2104
C2227
ST2240
C2226
R2203
C4209
C2205
C2213
R2204
V2484
ST2209
V2201
L4200
C4201
R4201
R4200
R4202
V4200
C2100
B2100
ST2100
C2101
C1216
R2406
R2405
ST2207
X2411
C2216
C2209
C2208
ST2203
ST2202
SP2106
SP2107
R2476
C2474
V2471
V2472
V2486
V2473
V2487
V2413
L2403
L2402
L2401
C3115 C3116
N3101
L3125
C3149
R3149
N3103
C3145
R3151
C2465
C2467
R3147
C3167
C3114
R3156
C3150
C3112
C3156
ST3101
C3131
C3121
R3155
C3165
R3160
C2461 C2463
L2408
C2443
L2406
C2449
SP2434
C3158
C3157
C3153
R2416
ST2411
V2400
R2415
ST2410
C2412
C2413
C3136
C3151
C3152
ST3102
C3102
C3100
C3124
C3126
C3127
R3112
C3125
C3133
C3155
C3146
C2212
C3135
ST2206
R3150
C3166
ST2205
ST2204
B1
X2410
A1
C2462
SP2433
C2442
R2450
C2430
R2201
C2222
SP3207
C2211
ST2200
C2206
C2464
C2210
X1540
R2417
R2419
R2418
X4201
X2401
R2420
C2411
R2421
SP2412
C2421
C2410
C2422
L3126
R3148
Cutout
V4202
L4201
C4208
C4207
TP2209
TP2208
TP2210
TP2207
ST3104 C3144
R3118
R4409 R4413
X4400
R4411
X4410
R4414
V4400
R2211
C2287
R2212
C2245 ST2222
C2292
C2290
R2226
E1004
R4302
R2220
V2212
ST2224
SP4401
C4411
SP4404
R4304
C2243
N2206
ST2220
R2221
L2212
C2249
A1
B1
SP4400
C2241
N2205
N4300
N2213
C2248
SP4402
ST2221
C2242 C2244
C2240
C2250
C2272
ST2223
C2417
X2402
ST4400
C4416
C2416
C2419
SP4403
C2418
C2420
C2415
V2480
V2479
V2478
A
B
C
COMPONENT OVERVIEW
D
B2100 1000-0036 C4
C1201 1000-0061 C5
C1204 1000-0048 C5
C1205 1000-0048 C5
C1206 1000-0039 C5
C1208 1000-0048 C4
C1211 1200-42 95 D5
C1213 1000-6900 C4
C1214 1000-0048 C4
C1215 1000-0048 C4
C1218 1000-6901 C4
C2100 1000-6078 C4
C2101 1000-6078 C4
C2202 1000-0049 C5
C2203 1000-0064 C5
C2204 1000-0061 C4
C2205 1000-0061 C4
C2206 1000-0039 C4
C2207 1000-6901 C4
C2208 1000-0051 C4
C2209 1000-6901 C4
12345
C2210 1000-6901 C4
C2211 1000-6901 C4
C2212 1000-6901 C4
C2213 1000-0051 C4
C2215 1000-0048 B4
C2216 1000-0048 B4
C2217 1000-0061 B4
C2218 1000-0061 B4
C2219 1000-0061 B4
C2220 1000-0048 B4
C2222 1000-0076 B4
C2223 1000-0048 B4
C2224 1000-0051 B4
C2225 1000-0067 C4
C2226 1000-0051 C4
C2227 1000-0048 C4
C2228 1000-0061 B5
C2231 1000-0061 B5
C2232 1000-0049 B5
C2240 1000-6901 C3
C2241 1000-6901 C3
C2242 1000-6901 C3
C2243 1000-6901 C3
C2244 1000-6901 C3
C2248 1000-6901 D3
C2249 1000-6901 D2
C2250 1000-6901 C3
C2272 1000-0068 C3
C2287 1000-0068 C2
C2290 1000-6900 C2
C2292 1000-0048 C2
C2402 1000-0048 B4
C2410 1000-6901 B3
C2412 1000-0048 B4
C2413 1000-0338 B4
C2414 1000-0051 B4
C2419 1000-0045 D3
C2420 1000-0051 D3
C2421 1000-0048 B3
C2422 1000-6901 B3
C2430 1000-0048 B4
C2440 1000-0076 B4
C2441 1000-0057 B4
C2442 1000-0045 B4
C2443 1000-0045 B4
C2447 1000-6838 B4
C2448 1000-6838 B4
C2449 1000-0048 B4
C3100 1000-6900 B4
C3112 1000-6900 B4
C3121 1000-6900 C4
C3124 1000-0048 B4
C3125 1000-0048 B4
C3131 1000-6900 C4
C3133 1000-6900 B4
C3135 1000-0048 C4
C3136 1000-0056 B4
C3138 1000-0069 C4
C3145 1000-6900 C4
C3146 1000-6900 C4
C3149 1200-4608 B4
C3150 1200-4608 B4
C3151 1000-0051 B4
C3152 1000-0048 B4
C3154 1000-6840 C4
C3155 1000-0340 C4
C3156 1000-0340 B4
C3157 1000-0056 B4
C3158 1000-0061 B4
C3165 1000-0056 C4
C3166 1000-0061 C4
C3167 1000-0048 B4
C4200 1000-0059 B4
C4202 1200- 028 6 B5
C4203 1000-0076 B4
C4206 1000-0048 B4
C4208 1000-6901 C1
C4209 1000-0048 C4
C4416 1000-0061 D2
L1200 1200-2028 C5
L1202 1200-4295 D5
L2200 1201-2245 B4
L2201 1000-0118 B4
L2202 1204-4910 B5
L2212 1201-5637 D2
L2401 1200-0317 A4
L2402 1200-0317 A4
L2403 1200-0317 A4
L2404 1200-0317 A4
L2406 1209-2182 B4
L2408 1203-0723 A4
L2449 1000-0257 A4
L3108 1201-0706 C5
L3109 1201-0706 C5
L3125 1000-3366 B4
L3126 1000-3366 B4
L4200 1200-6306 B4
L4201 1000-0360 C1
L4202 1000-0360 C1
N1200 1210-9905 D4
N1210 1203-5870 C5
N2000 1202-0639 B4
N2200 1204- 465 5 B5
N2205 1001-5573 C3
N2206 1201-6517 C2
N2213 1208-4678 D3
N2422 1201-4120 B4
N3101 1000-0198 B4
N3103 1213-5382 B4
N4300 1000-8704 C3
R1202 1215-5115 D5
R1203 1000 -0231 C4
R1209 1000 -0231 C4
R1210 1000-0231 C4
R2200 1214-4223 C5
R2201 1000-0252 B4
R2203 1000-0376 C4
R2204 1000-0249 C4
R2207 1212-1178 B5
R2208 1000-4169 B5
R2211 1000-0249 C2
R2212 1000-0231 C2
R2220 1000-0388 C2
R2221 1000-0231 C2
R2226 1000-0245 C2
R2400 1000-5865 C5
R2402 1000-0226 B4
R2403 1000-0226 B4
R2404 1000-0226 B4
R2405 1000-0243 C4
R2406 1000-0243 C4
R2415 1000-0175 B4
R2416 1000-0175 B4
R2417 1000-0231 B3
R2418 1000-0231 B3
R2419 1000-0231 B3
R2420 1000-0231 B3
R2421 1000-0231 B3
R2434 1000-0230 B4
R2448 1000-0179 A4
R2450 1000-0231 B4
R2476 1000-4034 D4
R2478 1000-0254 B4
R3118 1000-0181 D2
R3147 1000-0388 B4
R3148 1000-0388 B4
R3149 1000-0231 B4
R3150 1000-0254 C4
R3154 1000-4152 C4
R3155 1000-0388 C4
R3156 1000-0254 B4
R3160 1000-0179 C4
R4200 1000-0378 B4
R4202 1000-0264 B4
R4203 1200-1061 B4
R4204 1000-4160 B4
R4302 1000-0175 C2
R4304 1000-0231 D2
R4409 1000-0172 D2
R4411 1000-0231 D2
R4413 1000-0181 D2
V2200 1000-0282 B5
V2201 1000-0087 B4
V2202 1200-0145 B4
V2212 1204-1592 C2
V2412 1000-0272 B4
V2413 1201-2253 A4
V2417 1000-0272 B4
V2471 1207-3081 D4
V2472 1207-3081 D4
V2473 1207-3081 D4
V2478 1207-3081 D3
V2479 1207-3081 D3
V2480 1207-3081 D3
V2484 1207-3081 D4
V2486 1207-3081 D4
V2487 1207-3081 D4
V3101 1001-0730 C5
V4200 1000-0293 B4
V4201 1000-0087 B4
V4206 1000-0407 B5
V4400 1000-8408 D2
X1210 1200-2144 D5
X1211 1200-2144 D5
X1540 1211-1063 B3
X2201 1201-0774 B5
X2401 1200-9764 B3
X2402 1202-0528 D3
X2410 1208-3264 D4
X2411 1208-2932 D4
X3102 1200-2144 D5
X3103 1200-2144 D5
X4400 1201-5197 D2
X4410 1208- 0 925 D2
Z1200 1212-1502 D5
R - Replaceable
See Appendix for
more information.
1222-9526 rev. 1
86 (124)
Page 87

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
C905 Function Overview
Features
Camera
8.1 megapixel camera
Up to 16x digital zoom
Auto focus, Face detection
Smart contrast
BestPic™, Photo fix
Photo feeds, x-Pict Story™
Xenon flash
Video light
Red-eye reduction
PictBridge printing
Image stabilizer
Video stabilizer
Picture blogging
Video blogging
Video recording
Music
Media player, Bluetooth™ stereo (A2DP), Album art,
Music tones (MP3/AAC), PlayNow™, TrackID™
Internet
Access NetFront™, Web browser, Web feeds
General Information
Size
104 X 49 X 18 mm
Weight
136 grams
Colors
Ice Silver
Copper Gold
Night Black
Screen
262,144 color TFT, Resolution 240 x 320 pixels, Size: 2.4 inches
Phone memory
Up to 160 MB
Memory Stick Micro™ (M2™) support
Talk time
GSM/GPRS: Up to 9 hrs
UMTS: Up to 4 hrs
Communication
Video calling, Speaker phone, Polyphonic ringtones, Vibrating alert
Messaging
Email, Exchange ActiveSync®, Text messaging (SMS), Picture messaging (MMS),
Instant messaging, Predictive text input, Sound recorder
Design
Navigation key, Auto rotate, Picture wallpaper, Wallpaper animation
Entertainment
3D games, FM radio, Java, Video streaming, Video viewing
Organiser
Calendar, Phone book, Tasks, Notes, Alarm clock, Timer, Calculator, Stopwatch, Flight
mode
Location-based services
aGPS, Pre-installed maps, Geo tagging of photos
Connectivity
DLNA Certified™, Bluetooth™ technology, Modem, Synchronization, USB mass storage,
USB, support, Wi-Fi™
Note! Wi-Fi (WLAN) is only supported by C905 and C905a.
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
Standby time
GSM/GPRS: Up to 380 hrs
UMTS: Up to 360 hrs
Networks
C905: GSM/GPRS/EDGE 850/900/1800/1900, UMTS/HSDPA 2100
C905a: GSM/GPRS/EDGE 850/900/1800/1900, UMTS/HSDPA 850/1900/2100
C905c: GSM/GPRS/EDGE 850/900/1800/1900
1222-9526 rev. 1
87 (124)
Page 88

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Hardware Overview
Platform Information
The C905 is using the U365 platform provided by Ericsson Mobile Platform (EMP)
U365 Platform Block Diagram:
Hardware Overview
Baseband Part
Analog Baseband Controller N2000 (Vera)
This component is not replaceable on SL 4 because Baseband calibration is required. The
analog baseband controller is the main power management circuit. It has converters and
regulators that generate a number of supply voltages, each optimized for its load.
The analog baseband controller is a mixed digital and analog device that supports the
following circuitry:
• Power management circuitry
• Voltage regulation circuitry
• Eight Low Dropout (LDO) regulators and low power regulator
• 600 mA integrated Buck regulator
• Boost step-up DC/DC converter for White Light Emitting Diode (WLED) driving
• Battery charging and communication circuitry
• Battery fuel gauging circuitry
• Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
• Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
• SIM interface
• Six programmable LED drivers
• Accurate band gap reference
• Vibrator driver
• Real Time Clock (RTC)
• 8-byte One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory
• Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) voice coder/decoder
• PCM audio coder/decoder
• Microphone interface
• Stereo line input
• Earphone driver
• Earpiece driver
• 8-Ω speaker driver / Stereo line output
The analog baseband controller is controlled by an I2C™ interface. It also comprises the
main power management circuits, equipped with a number of converters and regulators
for generating the required supply voltages.
The analog baseband controller supports the following features:
• Lithium battery
• Full audio CODEC functionality
• Supports stereo audio sampling rates of 8/16 kHz voice coding/decoding and 44.1/48
kHz for high quality audio recording/playback (for example MIDI and MP3 applications)
• Double CODEC I2S/PCM interfaces
• Flexible microphone interface
• Integrated headphone amplifiers
• Integrated earpiece amplifiers
• Integrated speaker amplifier
• Integrated flexible audio mixing functionality
• Boost driver capable of driving up to four WLEDs in series, supplying 50 mA
• Designed to meet power management demands of GSM and WCDMA
• Automated power management ADC to relieve CPU
• Battery identification and communication
• Single-terminal charger and accessory power interface for compact connector design
• Integrated USB charging
• OTP memory
• Integrated hardware fuel gauge to accurately monitor battery capacity
• Reduced number of external components as a result of integrated programmable LED
and vibrator drivers
• 32 kHz real time clock with alarm wake up capability
• Designed to support two host controllers.
1222-9526 rev. 1
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
88 (124)
Page 89

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Functional Blocks of the Analog Baseband Controller:
Connection Diagram:
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
89 (124)
Page 90

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Charger Control
A programmable charger is used for battery charging. Limits can be set for the output
voltage at CHSENSE- and the output current from DCIO through the sense resistor to
CHSENSE-. The programmable charger is enabled or disabled by the assertion/negation
of the external signal DCIO. Parts of the programmable charger are activated and
deactivated depending on the level of VBAT. The rest of the programmable charger is
activated and deactivated through I2C.
The programmable charger supports the following functions:
• Constant current charging
• Constant voltage charging
• Trickle charging
• PWM controlled charging
• Over-voltage and over current detection
• Watchdog termination
• DCIO assertion/removal detection
• Voltage and current measure functions
• Low resistive path (reverse mode)
The programmable charger is able to control the voltage and limit the current to a load
seen at CHSENSE-. The programmable charger can also be run in PWM mode to turn the
charging on and off in accordance with the particular period and duty cycle. When the
charging is on, it is set to the current and voltage selected by I2C.
A low resistive path from VBAT to DCIO can be formed when DCIO is not detected.
When this setting is done in the appropriate registers, a lowering of CHREG to 0 V turns
on the external pass device. The pass device is automatically turned off when an
external source is detected on DCIO, or when the watchdog termination block times out.
The watchdog termination block must be active when the external switch is enabled,
both in normal
charging mode and in the low resistive path mode. The watchdog is set through the
serial interface, and if it has not been set again before timeout, the watchdog turns off
the external switch. The watchdog is disregarded during trickle charging. When no
battery is present, the system can be booted and supplied from DCIO by
applying the correct voltage on DCIO.
Resistance Identification and Temperature Measurement
The resistance identification mode utilizes the constant current source to feed the
battery data output while monitoring the voltage at the battery data node with general
purpose ADC the conversion is started through I2C.
Resistance Identification (A) and Temperature Measurement (B):
SIM Interface
The SIM interface supplies level is shifting between the digital baseband controller and
the SIM/USIM card. Moreover, hard-wired SIM deactivation functionality manages
removal of a SIM card that has not been powered down.
Block Diagram of the SIM Interface:
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
USB Charger
The analog baseband controller contains a standalone USB charger.
The USB charger has a separate input and incorporates full functionality during low VBAT.
The programmable charger supports the following functions:
• Trickle charging
• Constant current charging
• Watchdog termination
• Trickle LED indication
• VBUS assertion/removal detection
1222-9526 rev. 1
90 (124)
Page 91

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
CODEC Overview
The CODEC is encoding analog audio signals and analog voice signals into digital signals
using Analog to Digital converters (ADCs). This is done in the coder section of the
CODEC, also named the TX path (transfer section). The CODEC is also decoding digital
audio signals and digital voice signals into analog signals using DACs. This is done in the
decoder section of the CODEC, also named the RX path (receiver section).
CODEC Block Schematic:
CODEC CCO Voltage Source
There is an internal voltage source CCO that provides the necessary drive current for
electret microphones. The voltage source is I²C programmable to 2.2 V or 2.4 V. The
source can be disabled during standby. A typical use case with a microphone connected
to MIC1 and the CCO is shown in picture below.
Earphone Amplifier
The earphone amplifiers (BEARP and BEARN) are mainly intended to be differentially
configured and drive a low impedance dynamic transducer (earpiece) but they can also
be single ended configured. The BEARP and BEARN amplifiers can be powered down by
the I2C. The amplifiers can exhibit high impedance to 1.4V or low impedance to ground
when powered-down. Fifty-one gains are available for BEARP and BEARN: from +15dB
down to –60dB in 1.5dB steps. When the BEARP and BEARN outputs are operating in
differential mode, an I²C selectable bit must invert one of the inputs.
Speaker Amplifier
The speaker amplifiers, SPKRP and SPKRN, are intended to drive a low impedance (8Ω)
speaker in a differential mode or to be used as a stereo configured line output amplifier
supporting external high power amplifiers. The output buffer shall exhibit low impedance
to ground when powered-down and the current consumption shall be minimal. When the
SPKRP and SPKRN outputs are operating in differential mode, an I²C selectable bit must
invert one of the inputs.
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
91 (124)
Page 92

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Digital Baseband Controller (CPU)
N2010 (Kajsa)
This component is not replaceable on SL 4 because Baseband calibration is required.
The Digital Baseband Controller is divided in two subsystems: Access and Application
Access Subsystem
All modem functionality in the digital baseband controller resides in the Access
subsystem. This includes EDGE/GPRS/GSM interface, WCDMA interface, USB, IrDA, and
other peripheral modules. The control CPU is an ARM926 and a DSP is used for signal
processing and layer one control code.
The main communication between the blocks in the Access subsystem is done through
the Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB) matrix, which is a set of control buses
connecting the different parts together. A block called Syscon is responsible for
distributing clocks and resets to all parts of the Access subsystem. This block is under
SW control. The Access subsystem is connected to the Shared EMIF, an interface for
communication with an external SDRAM. The Shared EMIF is shared between the Access
subsystem and the Application subsystem.
Access Subsystem:
Application Subsystem
The Application subsystem contains functionality related to functions such as MMI,
graphics, audio and memory media. The control CPU is an ARM926 with three external
memory interfaces, one shared with the Access subsystem and two dedicated for the
Application subsystem. The Application subsystem contains several blocks. The main
communication between the blocks is done through the Advanced High performance bus
(AHB) matrix, which is a set of control buses connecting the different parts. A block
called Syscon is responsible for distributing clocks and resets to all parts of the
Application subsystem. This block is under SW control. The Application subsystem is
connected to the Shared EMIF that is used for code execution or data storage. In
addition, a dedicated EMIF that support SDRAM or static memory like NOR, PsRAM or
NAND are also available. The Application EMIF is a general interface for communication
with, for example external SDRAM, PSRAM, NOR flash, NAND flash and companion chips
Application Subsystem:
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
92 (124)
Page 93

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
The functional blocks of the digital baseband controller:
Radio Part
Antenna
The mobile system antenna interface connects the Wideband Code Division Multiple
Access (WCDMA) and Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) input/output to
the antenna of the Mobile Phone. It is a bi-directional RF interface containing signals in
the range 800 MHz to 2.2 GHz. The mobile system antenna interface is the interface
between the Mobile Phone Radio Frequency (RF) input/output and the mobile system
antenna. The interface handles the GSM 850, EGSM 900, GSM 1800, GSM 1900 and
WCDMA Band I, II and V, RF inputs/outputs.
Mobile System Antenna Interface:
Radio Module N1200 (Tiger)
Keypad
The keypad interface block supports up to 30 keys with 65 columns and 6 rows and
operates in both scan and idle mode. The keypad scan is performed by software. Any
transition in the state of the column inputs is written directly to the register. The keypad
interface differentiates between single key presses, simultaneous presses of any keys
with a function key, and any key releases. The period between successive scans is
programmable over the range 5 ms to 80 ms, in 5 ms steps. During scan mode, the
keypad generates an interrupt whenever a valid keypad state change occurs (including a
release of any pressed keys). The scan function is disabled during system power-up. The
keypad is able to detect at least four simultaneous key presses. Not all combinations are
supported.
Front End
The Front End block connects the proper block in the radio system to the antenna. The
Front End has two inputs for EDGE/GSM/GPRS, one for low band (850/900 MHz) and
one for high band (1800/1900 MHz). The EDGE/GSM/GPRS power amplifier output is
filtered by the low pass filter in the Front End and then connected to the antenna
through a switch. In receive mode, the EDGE/GSM/GPRS signal from the antenna passes
through the switch to one of the four receive SAW filters. The SAW filter provides receive
band selectivity. In GSM/GRPS/EDGE systems, transmit and receive operations are
divided in time and the switch connects the proper block in accordance with the mode of
operation (that is, transmit or receive; one at a time).
In WCDMA the transmit outputs from the WCDMA transceiver are filtered by an external
SAW filter that cleans up the spectrum. The SAW filter output is connected to the power
amplifier, one for each band. For power control, a sample of the transmit output is taken
by a directional coupler and converted to a DC level by the power detection circuit. This
signal is used to control the transmitter output power. The transmit signal passes
through an isolator and then a duplexer. The duplexer output is selected by the switch in
the Front End for connection to the antenna. In WCDMA receive mode the signal from
the antenna is switched by the Front End to the correct duplexer. The output from the
duplexer is connected to the LNA input in the WCDMA receiver.
Transceiver
The transceiver is a multi-mode transceiver for WCDMA/EGDE/GPRS/GSM. The
EDGE/GPRS/GSM part of the transceiver use a digital baseband interface that is shared
between received and transmitted data. The receive interface is based on I and Q data
and the transmitter interface is based on envelope and frequency data. The WCDMA part
of the transceiver use differential analog in-phase and quadrature-phase interfaces,
which is an IQ-interface, in the receiver and the transmitter data paths.
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
93 (124)
Page 94

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Frequency Generation
The 26 MHz reference signal is used as the reference for the on-chip synthesizers. To
cover the required frequency range, the integrated Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
operates at twice the frequency for band 1800/1900/2100, and at four times the desired
frequency for band 800/900. The two synthesizers are controlled through the serial bus
from the access side of the digital baseband controller.
EDGE/GPRS/GSM Transmitter Part
Polar modulation transmitter architecture based on the direct phase/frequency
modulation/synthesizer architecture is implemented for GSM, GPRS and EDGE. This
architecture has the capability of generating both the GSM/GPRS constant envelope
GMSK modulation and the linear EDGE 8-PSK modulation in a very cost efficient way.
The motivation for a polar modulation transmitter architecture compared to traditionally
linear architectures is to reduce the output noise (thus eliminating the need for off-chip
filters) reduce the power consumption by utilizing non-linear switching analog signal
processing blocks, and to eliminate the need for an RF isolator.
In brief, the phase/frequency modulator in this polar modulation architecture is a sigmadelta controlled fractional-N frequency synthesizer with an additional frequency insertion
point after the loop filter at the input of the VCO. The Phase-locked Loop (PLL) has two
information inputs: the divider ratio in the feedback path and a direct path to the VCO.
The phase locked loop generates the radio frequency carrier including the phase
modulation information at the desired channel frequency.
Ericsson RF 3300 Block Diagram:
WCDMA Transmitter Part
The WCDMA transmitter architecture is an on frequency linear direct up-conversion IQmodulator. The in-phase and quadrature-phase reconstruction filters are fully integrated
and a programmable gain amplifier implements the gain control. An external SAW filter
between the WCDMA circuit and the power amplifier is used to improve noise
performance. After the power amplifier, the signal is sent through an isolator and
through the duplex filter, which directs the transmit signal to the antenna connector
through the antenna switch. The supply voltage and bias of the power amplifier are
adapted depending on the output power to achieve high efficiency at every transmitter
power level. A high efficiency DC/DC converter regulates the supply voltage and the bias
operation point is controlled by a D/A-converter in the WCDMA radio circuit.
Receiver Part
The receiver architecture is a direct down-conversion zero-IF receiver with integrated
low-pass filters. The complete receiver with seven Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs), one for
each supported band, is integrated on chip. After the down-conversion, the in-phase and
quadrature-phase components are low pass filtered and if the receiver is in
EDGE/GPRS/GSM mode the signals are fed to the integrated high dynamic range sigmadelta A/D-converters.
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
94 (124)
Page 95

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical Description
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
RF System Control
The access side of the digital baseband controller controls the overall radio system.
In both EDGE/GSM/GPRS and WCDMA air interface mode, the digital baseband controller
controls the radio system through a three-wire serial bus. The digital baseband
controller also manages PA band control and the antenna switch mechanism in the front
end module. The 26 MHz VCXO clock residing in the transceiver is turned on only when
required and initiated by the digital baseband controller.
The control flow for the RF system:
EDGE/GPRS/GSM
TX Frequency, Channel and Power Level Range:
EGSM 900:
RX Frequency Range: 925,2 MHZ – 934,8 MHZ
Channel Range RX: 975 – 1023
DCS 1800:
RX Frequency Range: 1805,2 MHZ – 1879,8 MHZ
Channel Range RX: 512 – 885
PCS 1900:
RX Frequency Range: 1930,2 MHZ – 1989,8 MHZ
Channel Range RX: 512 - 810
WCDMA
TX and RX Frequency and Channel Range
Band I:
Channel Range TX: 9612 - 9888
TX Frequency Range: 1920 – 1980 MHz
Channel Range RX: 10562 - 10838
RX Frequency Range: 2110 – 2170 MHz
Band II:
Channel Range TX: 9262 - 9538
TX Frequency Range: 1850 – 1910 MHz
Channel Range RX: 9662 - 9938
RX Frequency Range: 1930 – 1990 MHz
GSM 850:
TX Frequency Range: 824,2 MHZ – 848,8 MHZ
Channel Range TX: 128 – 251
Power Level: Min 19 – Max 5
GSM 900:
TX Frequency Range: 890,2 MHZ – 914,8 MHZ
Channel Range TX: 1 - 124
Power Level: Min 19 – Max 5
EGSM 900:
TX Frequency Range: 880,2 MHZ – 889,8 MHZ
Channel Range TX: 975 - 1023
Power Level: Min 19 – Max 5
DCS 1800:
TX Frequency Range: 1710,2 MHZ – 1784,8 MHZ
Channel Range TX: 512 – 885
Power Level: Min 15 – Max 0
PCS 1900:
TX Frequency Range: 1850,2 MHZ – 1909,8 MHZ
Channel Range TX: 512 - 810
Power Level: Min 15 – Max 0
Band V:
Channel Range TX: 4132 – 4233
TX Frequency Range: 824 –849 MHz
Channel Range RX: 4357 – 4458
RX Frequency Range: 869 –894 MHz
Band VIII:
Channel Range TX: 2712 – 2863
TX Frequency Range: 880 –915 MHz
Channel Range RX: 2937 – 3088
RX Frequency Range: 925 – 960 MHz
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
RX Frequency and Channel Range:
GSM 850:
RX Frequency Range: 869,2 MHZ – 893,8 MHZ
Channel Range RX: 128 – 251
GSM 900:
Frequency Range: 935,2 MHZ – 959,8 MHZ
Channel Range RX: 1 - 124
1222-9526 rev. 1
95 (124)
Page 96

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Technical DescriptionFUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Bluetooth and FM Radio
The Bluetooth/FM Radio circuit combines Bluetooth and FM tuner functionality into one.
Bluetooth
The Bluetooth implementation is compliant with Bluetooth specification 2.1 + EDR.
The Bluetooth
2480 MHz. The same band is used for both transmission and reception. This gives 79
frequency channels.
TM
transceiver has frequency channels with 1 MHz separation from 2402 to
Receiver
The Bluetooth section implements a low-IF receiver for Bluetooth modulated input
signals. The radio signal is taken from a balanced RF input and amplified by an LNA. The
mixers are driven by two quadrature LO signals, which are locally generated from a VCO
signal running at twice the frequency. The I and Q mixer output signals are band pass
filtered by a poly-phase filter for channel filtering and image rejection. The output of the
band pass filter is amplified by a VGA to the optimal input range for the A/D converter.
Further channel filtering is done in the digital part. The digital part demodulates the
GFSK, π/4-DQPSK or 8-DPSK coded bit stream by evaluating the phase information.
RSSI data is extracted. Overall automatic gain amplification in the receive path is
controlled digitally. The RC time constants for the analog filters are automatically
calibrated on chip.
Transmitter
The transmitter uses the serial transmit data from the Bluetooth Controller. The
transmitter modulator converts this data into GFSK, π/4-DQPSK or 8-DPSK modulated I
and Q digital signals for respectively 1, 2 and 3 Mbps transmission speed. These signals
are then converted to analog signals that are low pass filtered before up-conversion. The
carrier frequency drift is limited by a closed loop PLL.
FM Radio
FM Receiver
The receiver uses a digital low-IF architecture. The receive (RX) section integrates a low
noise amplifier (LNA) supporting the worldwide FM broadcast band (76 to 108 MHz). An
automatic gain control (AGC) circuit controls the gain of the LNA to optimize sensitivity
and rejection of strong interferers. An image-reject mixer down converts the RF signal to
low-IF. The quadrature mixer output is amplified, filtered and digitized with high
resolution analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). This advanced architecture allows the
use of digital signal processing (DSP) to perform channel selection, FM demodulation
and stereo audio processing.
Tuning
The receiver uses frequency synthesizer technology including a completely integrated
VCO. The frequency synthesizer generates the quadrature local oscillator signal used to
downconvert the RF input to a low intermediate frequency. The VCO frequency is locked
to the reference clock and adjusted with an automatic frequency control (AFC) servo
loop during reception. The tuning frequency is defined as: Freq (MHz) = Spacing (kHz) ×
Channel + Bottom of Band (MHz)
External Connectors
External units are connected to the transceiver by means of a 12-pin connector on the
bottom of the phone.
System connector pin input/output overview:
Clocks
Clock Distribution
The clocking for the access and application subsystems is separated. This means that
the subsystems can wake up or go to sleep mode independently. The access subsystem
is clocked by the 26 MHz Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillator (VCXO) located in the
GSM/EDGE circuit. When the access subsystem has a job to do, the Master Clock (MCLK)
signal is requested from the RF part. Most other clocks needed within the access
subsystem are generated from the MCLK. Some minor parts like sleep timer and cable
detect use the 32 kHz real-time clock. The 32 kHz real-time clock clocks the application
subsystem, and all other internal clocks needed within the application subsystem are
generated from this clock. However, when audio is transferred between the application
and the access subsystems, the MCLK is used.
Master Clock
(26 MHz)
The 26.00 MHz VCXO-based MCLK is distributed as a square wave signal from the
GSM/EDGE circuit. In order to have full control over the load on the MCLK, only the
access side of the digital baseband controller is allowed to request the MCLK. However,
by indirect means also the application side CPU can issue the request. A VCXO-based
square wave is also distributed to the WCDMA circuit, but is turned on only upon a
command from the digital baseband controller.
Real-time Clock
(32. 768 KHz)
A 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator provides a low frequency clock whenever the platform
has power. This clock is used to keep the Real-Time Clock (RTC) block functioning, so
that the platform can keep track of the time and date. The low frequency clock is
generated in the analog baseband controller and distributed to the digital baseband
controller, and if necessary to external devices like Bluetooth, FM radio and A-GPS.
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
96 (124)
Page 97

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
A-GPS
The Assisted GPS functionality in the phone is realized with the Global Locate
Hammerhead GPS module. The Global Locate Hammerhead belongs to the Type 2 GPS
solutions. The PMB 2525 Hammerhead II GPS IC is a GPS single chip device containing a
complete radio frequency front-end as well as the signal processing functionality in a
single die. The device allows the usage of assistance data by supporting A-GPS (assisted
GPS) standards (RRLP, RRC, OMA SUPL). One of three serial interfaces, UART, I²C or SPI,
is used for communication with the host system.
Clock Reference Frequency
The platform provides two reference frequencies, a 32.768 kHz clock (RTCCLK) from the
Analog Baseband Controller, and a 26 MHz reference clock (SYSCLK) from the Digital
Baseband Controller. The RTCCLK is used by the phone real time clock function. The
RTCCLK is distributed to the A-GPS module as a logical square wave. SYSCLK is derived
from the reference modulation clock MCLK to the platform access system and is
distributed from the Digital Baseband Controller to the A-GPS module. This 26 MHz clock
is synchronized with the cellular network to an accuracy of ±0.1 ppm. Automatic
frequency updates can also cause large frequency corrections, with associated phase
discontinuities. In order to isolate the A-GPS module for the unstable effects of SYSCLK,
an external reference clock is required. This external reference frequency provided by a
TCXO is required to provide a clock with very high short term stability. The frequency of
the TCXO is calibrated against the cellular reference clock by the A-GPS module enabling
the use of a more economical less accurate TCXO.
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
A-GPS Block Diagram:
Interface and Control
The Interface and control consists of system timing and control. The control interface
includes a communication link where both data and control information are transferred
between platform and the A-GPS module. Data and command information is transferred
using a full-duplex Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) interface.
Other control signals include the following:
• A GPIO or platform reset used as a reset signal (nRESET) to the GPS module.
• A Transmission On signal (TXON/ RX_HOLD), is used to indicate to the A-GPS module
when the ME is transmitting. The A-GPS modules receiver is disabled whilst the ME is
transmitting.
• A hardware timing pulse (GPSSTART/SYNC) providing the A-GPS module with a
highly accurate timing reference. The A-GPS is able to accurately synchronize its
GPS time to this reference pulse.
• A GPIO used as an enable (POWERON) signal to the GPS module.
• A GPIO used for power control for the GPS module.
WLAN (Wi-Fi)
This WLAN module is based on the new Marvell 88W8686 chipset. WLAN module is
designed to support IEEE 802.11a or 802.11g payload data rates of 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48 and 54 Mbps, as well as 802.11b data rates of 1, 2, 5.5 and 11 Mbps. For security
the WLAN module supports the IEEE 802.11i security standard through implementation
of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)/Counter Mode CBC-MAC Protocol (CCMP),
and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) with Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) security
mechanism. For video, voice and multimedia applications the WLAN module supports
802.11e Quality of Service (QoS). The 3-wire Bluetooth / WiFi co-existence interface is
also supported. The WLAN module has a fully integrated RF to baseband transceiver that
operates in both the 2.4 GHz ISM radio band for 802.11g/b WLAN applications and 5
GHz UNII radio band for 802.11a WLAN applications. It contains all the circuitry to
support both transmit and receive operations. The integrated LNA and AGC on the
receive path is seamlessly controlled by baseband functions. Integrated transmitters upconvert the quadrature baseband signal and the deliver the RF signals to external power
amplifiers for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio band transmission. Local oscillator frequencies
are generated by a fully integrated programmable frequency synthesizer. The loop
bandwith is optimized for phase noise and dynamic performance and quadrature signals
are generated on-chip.
BT/WLAN Co-existence
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
Standards bodies did not fully anticipate the range of scenarios in which WLAN and
Bluetooth would compete for the same spectrum therefore IEEE 802.11 (WLAN) and
Bluetooth use the same 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band (although they use different access
mechanisms). They also did not include comprehensive, robust, and cooperative
mechanisms in their respective standards to mitigate interference. Since no mechanism
for exchanging signal status information has been built into the two standards, the task
of minimizing interference must be accomplished by other means. Co-location refers to
the situation where both Bluetooth and WLAN are in functional mode, that is, they are
both fully radio operational, performing either transmission or reception activities (or
ready to do so immediately). They also either share an antenna or each module has its
1222-9526 rev. 1
97 (124)
Page 98

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
own antenna, on the same device. Because both Bluetooth and WLAN operate in the
same unlicensed ISM band (2.4GHz), steps are required to avoid disturbances and allow
coexistence. The HW solution is a single antenna controlled by an Antenna Switch with
3-wired lines between WLAN Device and BT Device. The used algorithm to decision
whether WLAN device or BT device gets the antenna is Packet Traffic Arbitration (PTA).
WLAN LD configures the PTA during startup of the WLAN device. All PTA parameters are
stored in GDFS. The PTA is configured to prioritize BT traffic if it is a BT high request. All
WLAN traffic should have priority before any BT traffic that is categorized as BT low
requests.
WLAN Driver sends status events to BT Driver to inform about:
• WLAN startup and shutdown
• WLAN association and disassociation
• The current WLAN channel in use
In the cases of WLAN startup and shutdown the BT Logical Driver configures the BT
Device to request the antenna from PTA or not. BT LD also monitors if WLAN have any
connection running. In that case, BT avoids the BT frequencies mapping to the WLAN
channel. WLAN monitors if BT has started any BT Inquiry or page. If this happens any
link loss mechanisms should be temporary turned off for the BT Inquiry or page period.
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Bluetooth and WLAN PTA Mechanism:
Bluetooth and WLAN Chip 3-wire Interface:
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
1222-9526 rev. 1
98 (124)
Page 99

BATTERY
uP SAFETY
DCIO
VBAT
BDATA
GND
RX Diversity for WCDMA
GSM/EDGE
PA + AntSw.
ESD
VBAT
100
mohm
25
mohm
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW Platform Block Diagram
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
D(0-15)
DMA
AHB IF
Video
Enc
RAM0
Video
Encoder
AHB
Master
CEVAX1622
DRAM
128 kB
IRAM
64 kB
B
26MHz
EX1030 Filters
Hook
CCO
CCO
VDD
VDDQ
VSS
VSSQ
NAND Flash IF
ECCAHB Slave
ARM926
AHB
Master
Vide
Enc
RAM1
AHB
Slave
ARB
SPI
UART 0
o
Control
IMem
1.8 V
VIO
Cache
32 kB
DI/DO/CLK
CS0-2
CTS/
RX/TX
I
RTS
ARM9EJ-S
AHB BUS IF
AHB
Master
GRAM
64k byte
GAMEACC
(3D)
MCiDCT
(Video)
AHB
Slave
WDOG
TIMER0
TIMER1
RTC
32kHz
BUSTR
Event H
MMC/SD
ATMS
Microphone
EMIF2_SDCAS_RE_OE
MMU
TLB
AHB
Slave
AHB2APB
32
32
32
16
APLL
13M
32
32
I2C2
CAM 1 STBY
RESETOUT0
EMIF2_CLE_A17
EMIF2_ALE_A18
EMIF2_WE
EMIF2 CS0
EMIF2 NFIF READY
ARM9 Sub system
DMem
Control
D
Cache
32 kB
AHB
Master
GAMCON
13 MHz
16
32
PPM
16
SYSCON
DPLL
208M
16
GPIO
32
UART 0
MS PRO
PHF
Jack
DB 3210 POP
NAND Flash1Gbit
WP
CLE
ALE
RE
WE
CE
1.8 V
VIO
Digital Baseband
Controller DB 3210
XGAM
PAR/ SSI
PDI
PDICON
CDICON
CDI
KEYPAD
CAM POW
VIO
1.8V
26
27
25
24
KEYOUT(0-4)
23
22
21
20
All 48 GPIOs here
have switchable
pullups.
GPIOif
VDD
VSS
D(0-7)
R/B
28-35
MC_DATADIR
MC_CMDDIR
MC_CMD/BS
MMCCLK
CAM 2 STBY
I2CSCL2
I2CSDA2
MC_CLK
1.8 V
VIO
1.2/1.05 V
VCORE
1.8 V
VIO
IO
CIVSYN
CIHSYN
CIPCLK
CIRES
1.2/1.05 V
VCORE
Core
IO
1.8 V
VIO
I2CSCL2
I2CSDA2
AHBS lave
AAIF
AHB2AP
AHB IF
ARB
26MHz
1.8V
VIO
VDD
VDDQ
VSS
VSSQ
1.8V
VIO
EMIF
MSL
AHB2AHB
APEX
DSP
Sub System
JTAG
CRU
8
GPIO
B
WCDMA
Cipher0 ,1
WCDMA
Integrity
SDA
GPRS
CRYPTO
I2C0
I2S/PCM
(BT)
H
VDD_SPKR
VSS_SPKR
VDDBEAR
VMID
VSSBEAR
CCO1
CCO
CCO2
MIC1P
MIC2N
MIC3N
MIC4N
LINE1
LINE2
DB 3210 POP
SDRAM 512 Mbit
CKE
Shared EMIF
58 Channels
50 Requests
B
AH
IF
52MHz
WTIM-
GEN
32+
5
32+3
32+3
32+3
32+
3
32+5
AHB2APB
26MHz
CTS/RTS
ADC2REF ADC3REF
SDCKE
SDCLK
SDCS
WE
SDCAS
SDRAS
A14
A15
BE0
BE1
EMIF1
EMIF Control
AHBSlav
DMA
AHBIFAHB
IF
WINT-
WSYS-
COM
CON
IO
AHB IF
32
IRAM
7k x 32
32
bit
52 MHz
EGG
Sub System
Random noise
generator
Boot ROM
8k x 32 bit
INTCON
FS_USB/
HS_USB
UART0
UART2
UART3
I2SBUS
DAC
4
DAC
3
DAC
2
DAC
1
ADC
1
ADC
2
ADC
3
CLK
CS
WE
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
LDQM D(0-15)
UDQM
EMIF Arbiter
e
IM
Bridge
AHB
Slave +
Sequ.
Bridge
26MHz
RS232
BT
IRDA
SPI
TXRX
PGA
PGA
PGA
PGA
RF 3300 WCDMA RX (other functions unused)
GSM/EDGE
HB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
HB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
LB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
LB
BandI
BandII
BandV
VBAT
2.8 V
VRAD
LDO
2.8 V
VRAD2
2.8 V
GSM/
EDGELB
GSM/
EDGEHB
VBAT
1930 – 1990 MHz
1805 – 1880 MHz
925 – 960 MHz
869 – 894 MHz
VAPC
UL:1920–1980MHz
DL:2110–2170MHz
Band 1
GSM850/
900 Input
PA
DCS/PCS
Input
PA
824–915MHz
1710–1910 MHz
VccWPA
VBAT
PWM/PFM
WDCDCREF
Switch
ont
EnC
rol
RFCtrl1
Logic
GSM/
EDGELB
GSM/
EDGEHB
VccWPA
Power
FUEL
GAUGE
ADDER
coupler
Power
coupler
Power
coupler
2.75 V
VRAD
RF Pow det
Det
En
WR
FCTRL
2.75 V
AUTO
CTL
M
I2C
U
ADC
X
10bit
LED Control
2.65 V
VANA
UL: 1850 – 1910 MHz
DL:1930 –1990MHz
Band 2
UL: 824 – 849 MHz
DL: 869 – 894MHz
Band 5
TEMP_BIAS
V_TEMP
Plac
ed
close toRF
TEMP_BIAS
LCDTEMP
Placed
closeto
LCD
DAC0
DACO0
11 bits
DAC1
WDAC1
DACO1
11 bits
SERCON
DAC2
WDAC2
DACO2
11 bits
DAC3
DACO3
11 bits
CHREG
CHSENSE+
CHSENSE-
USB
DET
USBCHRG
CONTROL
I2C
DCIO CHRG
CONTROL
DCIO
DET
IMEAS
VMEAS
S-D
ADC
VIBRATOR
I2C
CONTROL
UART
TRICKLE
VBAT
VBUS
VBAT_C
DCIO
DCIO_INT
FGSENSE+
FGSENSE-
VDD_REF
1uF
BDATA
LED interfaceVibrator if WLED interface SIM interface
Bias
En
VccWPA
Bias
En
26MHzX-tal
VccWPA
Bias
En
WTXPOW_DET
3
1.2/1.05 V
VBAT
BAND
GAP
VCORE
Internal BUCK
1.8to0.9V
600 mA
BOOST
(Soft start)
6-22 V, 30 mA
5%
VBAT
LED Control
Analog
LDOf
30 mA
2.5~1.05V
2.5 V
VANA
VBAT
VBAT
2.65V
VAUDIO
2.75 V
VIR
VBAT
LNA
WCDMA HB
LNA
WCDMA HB
LNA
WCDMALB
LNA
DAC
GSM/EDGE
AM
+
RFCtrl1
RFCtrl1
RFCtrl2
RFCtrl2
WCDMA HB3
WCDMA HB2
WCDMA HB1
WCDMALB
XOp
XO
RF 3300 WCDMA/GSM/GPRS/EDGE TRX
GSM/EDGE
HB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
HB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
LB
LNA
GSM/EDGE
LB
LNA
WCDMA HB
LNA
WCDMA HB
LNA
WCDMALB
LNA
DAC
GSM/EDGE
AM
+
RFCtrl1
RFCtrl1
RFCtrl2
RFCtrl2
WCDMA HB3
CDMA HB2
W
WCDMA HB1
WCDMALB
XOp
XO
2.8V
VRAD
VBAT
RF LDOa
EGG/WBTX
150mA;
2.8 V
CONTROL
MemCard
LDOc
LDOg
200 mA
100 mA ;
2.65 V
2.85 V
Camera
IR LDOk
LDOh
200 mA
100 mA ;
2.75 V
2.75 V
VBAT
2.85 V
VCARD
2.75V
VCAM+Display
SLEEP
DAC
DAC
LDO d
200 mA ;
2.65 V
2.65 V
VANA
0
90
VCO
VCO
LPF+ChP PhD
LPF ChP PhD
VCO
+
0
90
VCO
VCO
LPF+ChP PhD
LPF ChP PhD
VCO
+
VIO
2
C
I
I/O/Core
LDOe
200mA
1.8~0.9V
1.8V
VIO
÷
N.M
DAC
÷
N.M
0
90
÷
N.M
DAC
÷
N.M
0
90
VANA
PLL
44/48
Level
shift
SIM
LDO
WRxIA
WRxIB
WRxQA
WRxQB
EDataStr
A
EDataB
D
EDataC
A
EDataA
D
XO
DAC
CLK
Serial
DATA
STROBE
Control
TestOut
WTxIA
WTxIB
WTxQA
WTxQB
MCLKsec
CLKREQ
MCLK
WRxIA
WRxIB
WRxQA
WRxQB
EDataStr
A
EDataB
D
EDataC
A
EDataA
D
XO
DAC
CLK
Serial
DATA
STROBE
Control
TestOut
WTxIA
WTxIB
WTxQA
WTxQB
MCLKsec
CLKREQ
MCLK
I2C BUS Internal Acc and App
Backup
Cap
32 kHz
osc
1MHz
OSC
G
LDOLP
2.2 V
VDDLP
VBAT
Backup
capacitor
2.8 V
VRAD2
1.8 V
VIO
RF_CTRL_CLK
RF_CTRL_DATA
RF_CTRL_STRB1
GPA4
MClkSec
BT+ WL AN
RF_DATA_STRB
RF_DATA_B
RF_DATA_C
RF_DATA_A
2.8 V
VRAD
1.8V
VIO
RF_CTRL_CLK
RF_CTRL_DATA
RF_CTRL_STRB0
GPA4
MClkSec
CLKREQ
MCLK
SYSCLK1
VBAT
100k
0k
10
100k
VRTC
SYSTEM
POR
PWRRST
XTAL_OUT
OTP
64 bits
Power Management
AB 3100
VBACKUP
C1
GND
VCC
C2
RST
NC
C3
DAT
CLK
SIM card
External to Platform
Internal to Platform
ToMux
Digital
Baseband
Controller
Decaps
1.2/1.05 V
VCORE
1.2/1.05 V
VCORE
WRX1_In
WRX1_Ip
WRX1_Qn
WRX1_Qp
WRX0_In
W
RX0_Ip
WRX0_Qn
WTX_In
WTX_Ip
WTX_Qn
WTX_Qp
SCLK
SRST
To NAND WP
WRX0_Qp
PWRRST
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
ANTSW2
ANTSW3
TXADC
RF_DATA_STRB
RF_DATA_A
RF_DATA_B
RF_DATA_C
WTXPOW_DET
WRFCTRL0
WRFCTRL1
WRFCTRL2
WRFCTRL3
RF_CTRL_CLK
RF_CTRL_DATA
RF_CTRL_STRB0
RF_CTRL_STRB1
CLKREQ
To Camera
IRQAcc
IRQApp
2.5 V
VANA
IRQa
IRQb
EICE
JTAG DEBUG TCM IF
ARM926
I Mem
Control
AHB
Master
ADC2_I_NEG
ADC2_I_POS
ADC2_Q_NEG
ADC2_Q_POS
ADC1_I_NEG
_POS
ADC1_I
ADC1_Q_NEG
ADC1_Q_POS
TX_POW
DAC_I_NEG
DAC_I_POS
DAC_Q_NEG
DAC_Q_POS
RFWBENABLE 0
RFWBENABLE 1
RFWB ENABLE 3
RFWB ENABLE4
RFWB ENABLE5
ANT_SW0
ANT_SW1
ANT_SW2
ANT_SW3
TX ADCSTRB
GSMPA ENABLE
RFCTRL CLK
A
RFCT RLDAT
RFCTRL STRB0
RFCTRL STRB1
RFCTRL STRB2
RF_DATA_STRB
RF_DATAA0
RF_DATAB1
RF_DATAC2
SIM_CLK
SIM_RSTn
PWRRSTn
RESOUT0n
RESOUT1n
RESOUT
2n
DCON
ACCSLEEP
APPSLEEP
MCLKREQ
MCLK
MCLK
SYSCLK0REQ
SYSCLK0
SYSCLK2
SYSCLK1
SYSCLK1
32KHz
RTCCLKIN
SERVICEn
MSACCIRQn
MSAPPIRQn
APLL
IO
1.8V
VIO
I
Cache
32 kB
ADC
O
R
15
32KHZ
I2S_CLK1
I2S_WS1
I2S_TX1
1
I2S_RX
I2S_CL
K0
I2S_WS0
I2S_TX0
I2S_RX0
C5
On/Off
C6
Switch
C7
Debug Inte rface
ACB/
Debug
ARM9Subsystem
ITCM
ETM9
26 kB
ETM IF
ARM9EJ-S
MMU
TLB
AHB BUS IF
Master
WCDMA SUB System
CLK
16
CON
TIM
16
GEN
16
SER
CON
16
TXIF
16
RFIF
16
RXIF
Bus
SIMIF
Tracer
cce
A
ss
Timer
SYS
GPIO
CON
DPLL
APLL
Audio Part AB3100
PCMCLK
PCM/
PCMSYN
I2S
PCMI
Inter-
PCMO
face 1
PCM
DECODER
ENCODER
VDDDIG
PCMCLK
PCM/
PCMSYN
I2S
PCMI
Inter-
PCMO
face2
DTCM
8kB
DMem
Control
D
Cache
32 kB
AHB
AHB
Default
slave
ARB ARB
16
GSM
CRYPTO
16
VA
16
DFSE
26MHz
32+3
32+3
32+5
32+5
26MHz
Watch
Event
Dog
Hist
ETX
Cable
Detect
EDC
RX
Vol
PGA2
RX
Vol
PGA2
RX
Vol
PGA2
RX
Vol
PGA1
SIDE
TONE
TX
PGA1
TX
PGA2
TX
PGA3
Memory interface
AHBSlave
AAIF
MSL
AHB IF
52MHz
MS
32
PRO
32
INTCON
Boot
32
ROM
APEX+
APEX
RAM
ROM
APEX
DMA
40 Channels
40 Requests
AHB
Slave
SRAM
332 kB
AHB Slave
Timer0
ICU PMU
SCL
1.8 V
VIO
VBAT
SDCKE
CS(0-2)
OE/CAS
ADV/RAS
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
XpertCEVA
CLK
WE
A13
A14
BE0
BE1
ARB
AHB
Master
PCM0
PCM1
2.65 V
VAUDIO
2
PDROM
Timer1
I2C1
I2S/
I2S/
Mobile SDRAM
xxx Mbit
CKE
CLK
CS
WE
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
LDQM
UDQM
EMIF2
464kB
AHB Master
AH
Slave
AHB2APB
GPA4
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
1.8V
VIO
I2CSDA2
SUB-LCD
I2CSCL2
I2CSDA2
L C D
I2CSCL2
CAM 1 STBY
I2CSDA2
I2CSCL2
CAM 2 STBY
Camera 1
Camera 2
Image
proc
SYSCLK0
CIVSYN
CIHSYN
CIPCLK
CIRES
1.8 V
2.85 V
VCARD
1.8 V
VIO
S
L
VIO
1.8V
I/O&
Vcc
IRDA
Supply
RXD
IRDA_RX
COM
AMP
P
TXD
IRDA_TX
RC
IRDA_SD
Log&
Contr
MODE
Debug
equipm.
USB if
HS_CLOCK
HS_DAT0-7
HS_DIR
HS_STP
HS_NXT
ULPI_CS
VIO 1.8V
BTSPI CS
BTSPI DI
BTSPI DO
BTSPI CLK
RESOUT2
SYSCLKREQ1
MCLKSEC
PCMCLK
PCMSYN
PCMULD
PCMDLD
BTSPI IRQ
HS-USB Transceiver with ULPI, ISP 1508
XI
SYSCLK2n
XO
CLOCK
D0-D7
DIR
iflogic
STP
NXT
CSn
VDD3V3
VDD1V8
VBAT
VBAT
Voltage
regulators
VIO
REF
Voltage
SPI
MCLKSEC
32kHz
SYSCLKREQ1
Bluetooth
32KHz
Baseband
OSC
PLL
1
Serializer
Deserializer
Internal
power
USB 2.0 ATX
Termination
Resistors
IDde t
VBUS
Comp
Chrg/
dischrg
resistors
ULPI
Reg
map
POR
Int Ref
1222-9526 rev. 1
Control
VIO
Resistors
VIR
2.75V
VIO
1.8V
PowerDown
INT
Bluetooth
Radio
A
D
C
WLAN
PSW_N
1.8 V
VIO
Sensor
DP
DM
ID
VBUS
2.75 V
VCAM
2.75 V
VCAM
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
C0 C1 C2 C3 C4
Data Card
MS Pro
MMC/SD
VBAT
VBAT
REG
2.75V
99 (124)
CAM POW
Y N
1
*
D+
D-
VBUS
C
87
09#
GND
C905
VBAT
VBAT
32
654
VBAT
VIO
1.8V
C
O
N
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
Page 100

FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW Block D i agr a m Power Distr i b ut i on
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
C905
Charge
resistor
VBAT
100 mOhm
DCIO
CHREG
VBAT_A
VBAT_B
VDD_ADC
VBAT_C
VBAT_D
VBAT_E
VDD_IO
VBAT_F
Fuel
gauge
Block
VBAT_G
VDD_AUDIO
VDD_BEAR
VDD_AUXO
VDD_SPKR
VBUS
VBAT_K
VBAT_L
VBAT_M
LED1n
LED2n
LED3n
2.8V/150mA
2.85V/100mA
2.65V/200mA
GPADC
2.2V/7mA
2.50V/30mA
1.80V/200mA
I/O
2.75V/100mA
2.75V/200mA
2.65V/200mA
CODEC
VBUS
Charger
SIM LDO
1.8/2.85V
Vibrator
driver
BOOST
W-LED driver
DAC1
DAC2
LDOa
LDOg
LDOd
Back-up
capacitor
LDO LP
4.7k
Buck
1.2V (1.05)/600mA
Control
LDOf
LDOe
LDOh
LDOk
LDOc
VBAT_H
LED5n
LED4n
TRICKLE TRICKLE
VccB
VccA
Vcc
VCC1
VLED
VCC_IO
VANA
VACT
VDIG
VBOOST
KEY_LED_C
ATHODE
VDD2V7
ANODE
CATHODE
VDD1V8
20
12
2
2
AVDD
DVDD
VBAT_ACT
VDDCO
VDDANA
VDDIO
VDDIO
VDDIO_PLL
VDDCO_PLL
VCCAD
VCCDA
VCCGPAD
VDDAD
VDDA_AF
PoP
Bluetooth
Subsystem
1.8 V
6
10
2
ON/OFF
IN
OUT
ECO/Low Pow
1.2 V
2.5 V
D-VDDQ
F-VDD
VCC_N
VCC OEn
VDD_IO_A
VDD_IO_B
VDD_CLD
VDD_HV_A
VDD_HV_D
CLK_REQ_OUT2
CLK_REQ_OUT1
VBAT
VBAT
EN
RF Subsystem
VDD
PVIN
REF
SW
FB
VccA1
VccA2
VccD
VccA1
VccA2
VccD
WLAN Subsystem
Switching Reg 3
3.3V/250mA
PVIN
LDO3
3V/300mA
LDO2
1.8V/300mA
LDO1
1.8V/300mA
V33A
V3A
V18A
V18D
VCC
VCONTROL
VCC
VCONTROL
VCC
VCONTROL
VCCPA
VDD30
VDD18A
VDD18_LDO
VIO_X1
VIO_X2
FUNCTIONAL OVE R VIEW
VCC I/O
VBAT
VBUS
1222-9526 rev. 1
100 (124)
 Loading...
Loading...