Page 1

Welcome
Congratulations on your purchase of this Sony VAIO® computer, and welcome to the online VAIO® Computer User Guide.
This user guide provides detailed information on all aspects of using your new VAIO computer, from keyboard functions to
preinstalled software programs.
In the left navigation window, click the topics you want to learn more about, and that information will be displayed in this
main window.
View the Electronic Flyer, which provides updates and supplemental information about your computer.
Page 1
Page 2

Powering Your Computer
Your VAIO® computer comes with a battery and an AC adapter. This chapter explains how to install and use these supplied
accessories to power your computer. It also describes ways you can efficiently utilize the battery as a power source.
Using AC Power
Using the Battery
Conserving Battery Power
Page 2
Page 3

Using AC Power
The supplied battery is not charged when you receive your computer. To use your computer immediately, use the supplied
AC adapter as the power source. The computer charges the battery while you use AC power. See Using the Battery for
more information on installing and using your battery.
Connecting the AC adapter
Turning on the computer
Page 3
Page 4
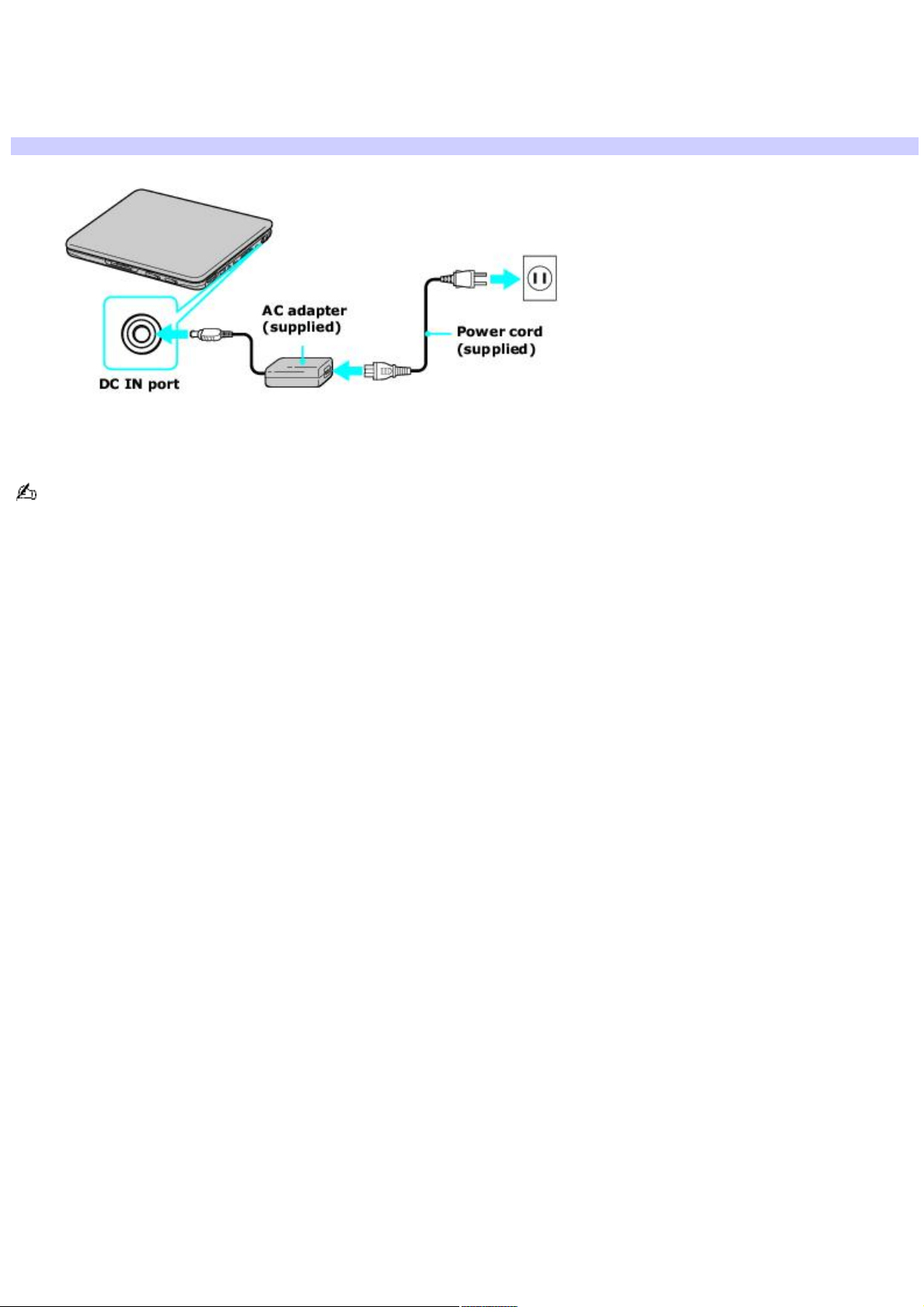
Connecting the AC adapter
To connect the AC adapter
1.
Plug the cable attached to the AC adapter into the DC IN port on your computer or docking station.
Connecting the AC Adapter to the Computer
2.
Plug one end of the power cord into the AC adapter, and plug the other end into an AC outlet.
Use only the supplied AC adapter with your computer.
Page 4
Page 5
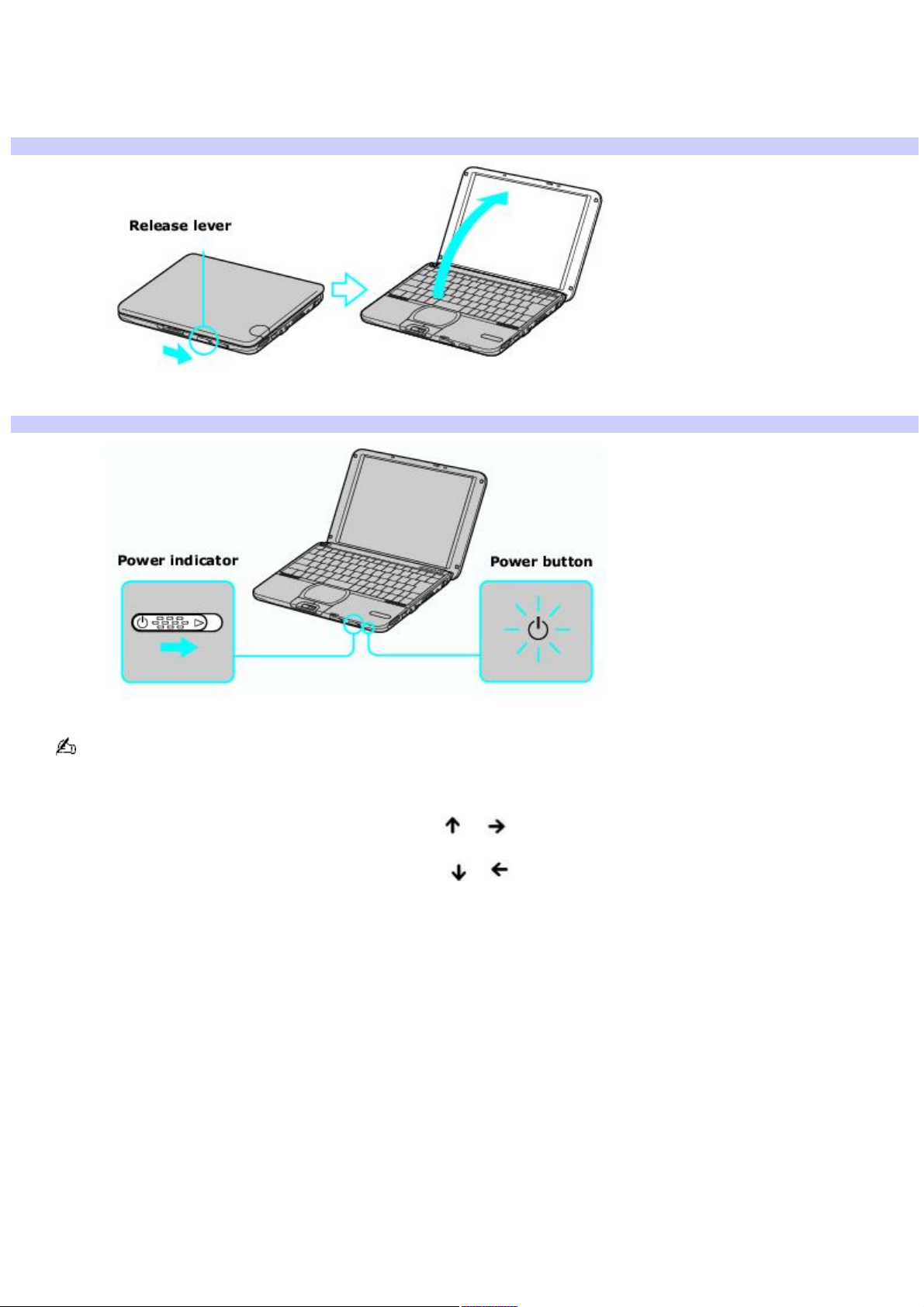
Turning on the computer
To turn on the computer
1.
Slide the release lever to the right, and lift the cover while holding the bottom of the computer firmly.
Opening the Computer
2.
Press the power button until the power indicator turns on.
Turning on the Computer
If you hold the power button down, the computer turns off.
3.
If necessary, adjust the brightness controls for the LCD display as follows:
To increase light intensity, press Fn+F5 and then or .
To decrease light intensity, press Fn+F5 and then or .
Page 5
Page 6

Using the Battery
A battery is an auxiliary power source you can use when your computer is not plugged into an AC outlet. Your computer
may come equipped with one or two battery bays, depending on the model you purchased. If your computer comes with
two battery bays, you can purchase a second rechargeable battery to extend your computing time. Regardless how many
batteries you use, you can always extend the life of the battery by conserving power. See Conserving Battery Power for
more information.
Inserting a battery
Removing a battery
Displaying battery information
Charging a battery
Notes on batteries
Frequently asked questions
The battery that comes with your computer is not fully charged at the time of purchase.
Page 6
Page 7
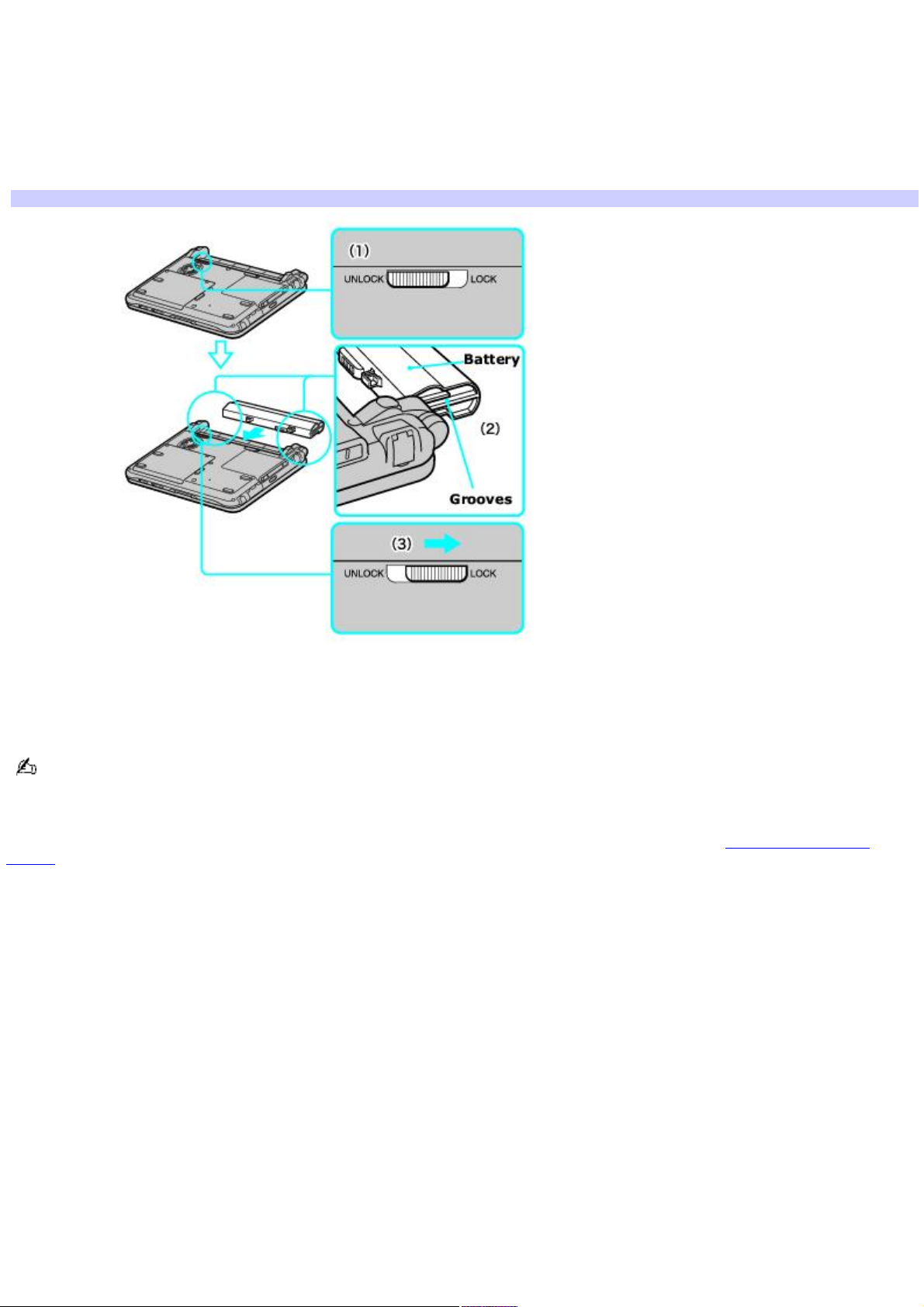
Inserting a battery
To insert a battery
1.
Turn the computer over, and slide the LOCK/UNLOCK switch on the bottom of the computer to the UNLOCK
position.
2.
Align the grooves and tabs on the battery with those on the back of the computer.
Inserting a Battery
3.
Slide the battery into the computer until it clicks into place.
4.
Slide the LOCK/UNLOCK switch into the LOCK position.
If the port replicator is attached to your computer, do not insert or remove the battery. Lifting and turning the
computer with the port replicator attached could cause a temporary loss of power.
Some software programs and peripheral devices prevent the system from entering Hibernate mode. If you are using a
program that prevents the system from entering Hibernate mode, save your data frequently. See Using power saving
modes for information on how you can manually activate a power saving mode.
Page 7
Page 8
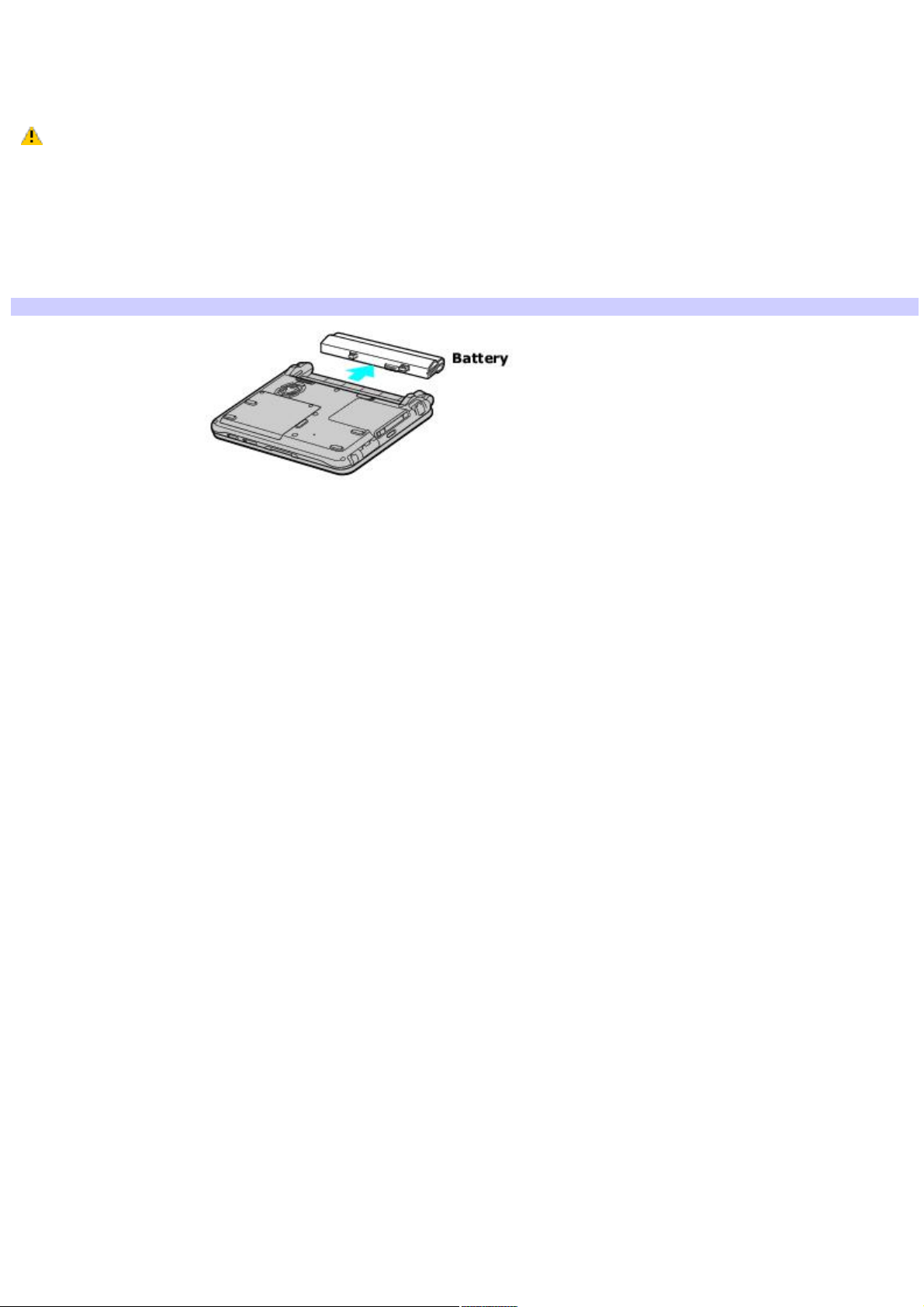
Removing a battery
If you are not using the computer for an extended period of time, remove the battery from the computer to avoid damaging
the battery. You can remove the battery when the computer is on or off.
If the computer is on, connect the AC adapter and exit a power saving mode before you remove the battery.
To remove a battery
1.
Turn the computer over, and slide the LOCK/UNLOCK switch on the bottom of the computer to the UNLOCK
position.
2.
Slide the battery away from the computer.
Remov ing a Battery
Page 8
Page 9
Displaying battery information
You can display the remaining battery charge on the Battery Information toolbar and/or the Battery Information window.
To display the Battery Information toolbar
1.
Right-click the center of the Windows® taskbar.
2.
Select Toolbars from the shortcut menu, and click Battery Information. The Battery Information toolbar
appears on the taskbar.
If the Battery Information toolbar is hidden behind the taskbar icons, click and drag the edge of the Battery
Information toolbar to the left until it is in clear view.
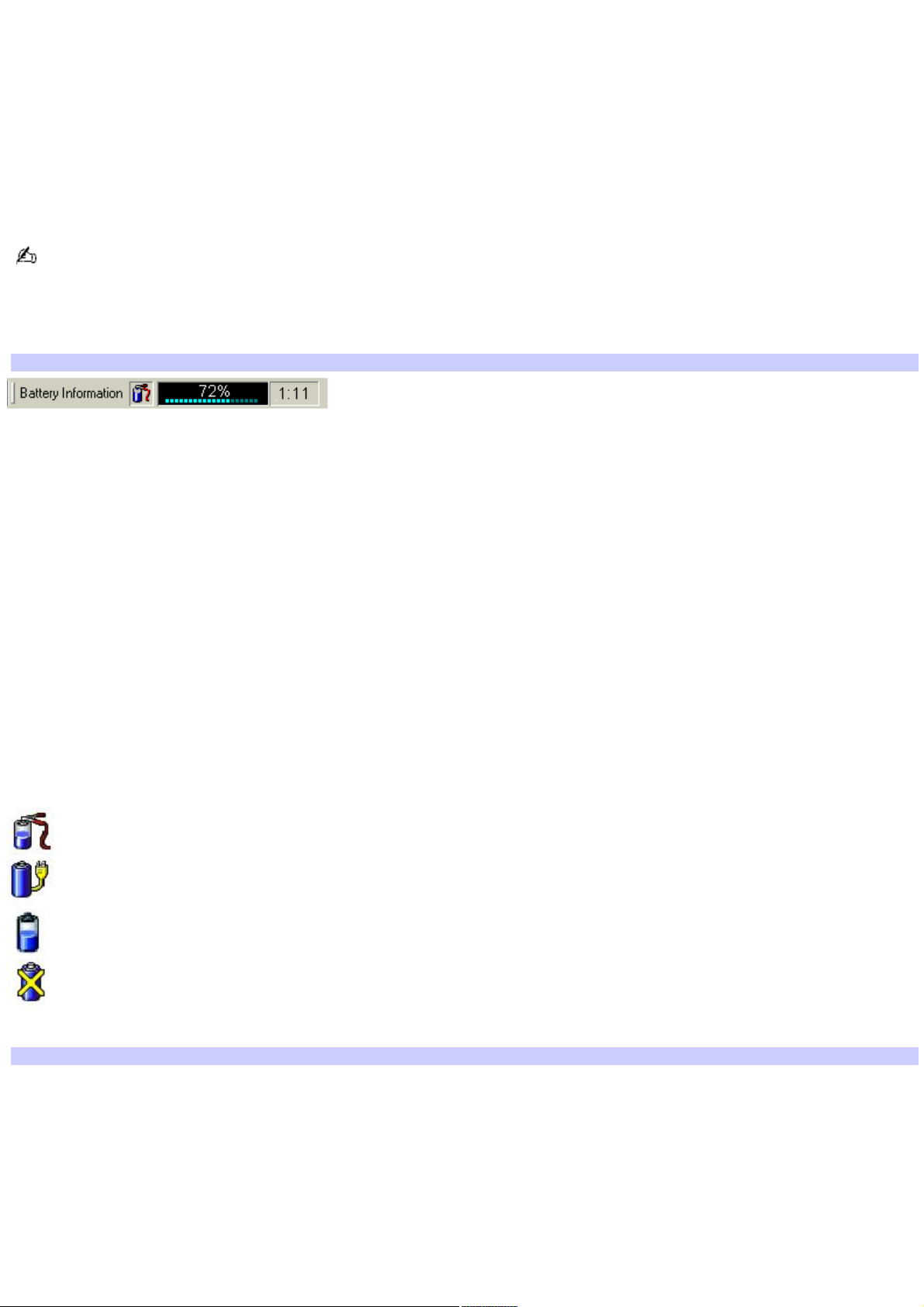
The total charge remaining in the battery is listed in percent and real-time values. The following toolbar indicates that there
is 72 percent or approximately 1 hour and 11 minutes of battery charge left.
Battery Information Toolbar
Percentage indicator — Displays the percentage of the remaining capacity.
Time indicator — Displays estimated time (hours : minutes) remaining before the battery fully discharges, also
known as the time-to-empty.
To close the Battery Information toolbar
1.
Right-click the Battery Information toolbar.
2.
Select Toolbars from the shortcut menu, and click to cancel Battery Information. The Battery Information
toolbar disappears from the toolbar.
To display the Battery Information window
The battery icons that appear on the Battery Information toolbar and the Battery Information window indicate the
current status of the installed battery.
Battery icon Battery status
Charging
Fully charged
Discharging
No battery
1.
Double-click the Battery icon on the Windows taskbar. The Battery Information window appears.
Battery Information Window
Page 9
Page 10
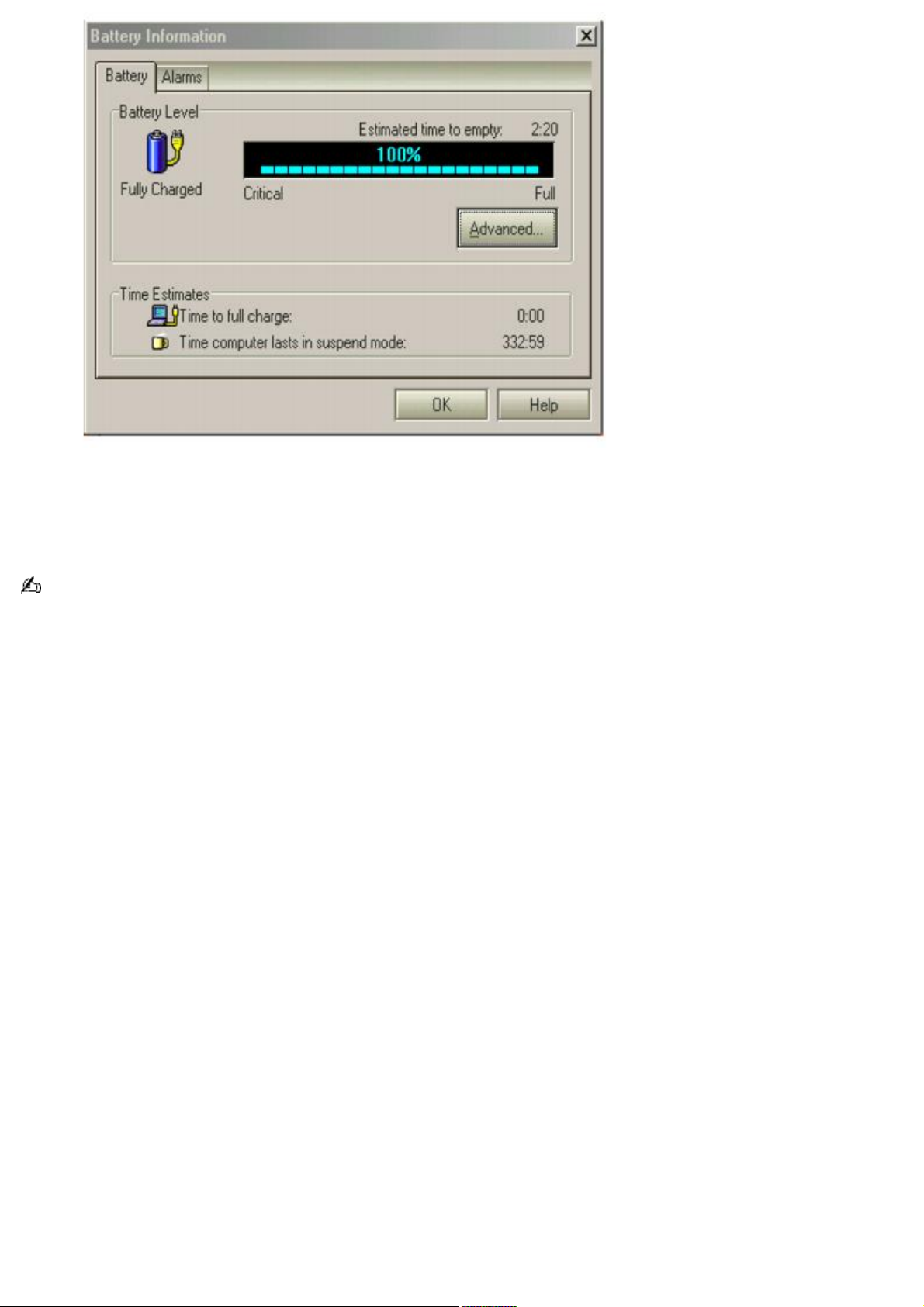
Battery tab — Displays the total charge remaining in the battery. You can click Advanced for specific
information on the battery.
Alarms tab — Displays the alarm settings, which notify you when the battery is fully charged and is too
low. You can change your computer's alarm settings on this window.
Click Help in the lower right corner of the window for more information.
Page 10
Page 11
Charging a battery
You will need to charge the battery if battery power drops below 10 percent or you have not used the battery for a
considerable amount of time. The lithium-ion battery supplied with your computer may be recharged at any time, whether
you wait until the battery is completely or partially discharged. Charging a partially discharged battery does not affect
battery life. If you charge the battery and find that battery power is still low, the battery may be reaching the end of its life,
and you may need to replace it.
The battery supplied with your computer is not charged at the time of purchase.
To charge a battery
You can charge the battery when the computer is on or off. However, the battery will charge faster when the computer is
off. Charging the battery takes several hours. See your VAIO® Computer Specifications on the Welcome page for the
approximate time needed to charge your battery.
Charge the battery at temperatures between 50°F and 80°F (10°C to 30°C). Lower temperatures require more time
to charge.
1.
Insert the battery into the battery bay.
2.
Connect the AC adapter to the computer. The computer automatically charges the battery as long as the
computer is using AC power.
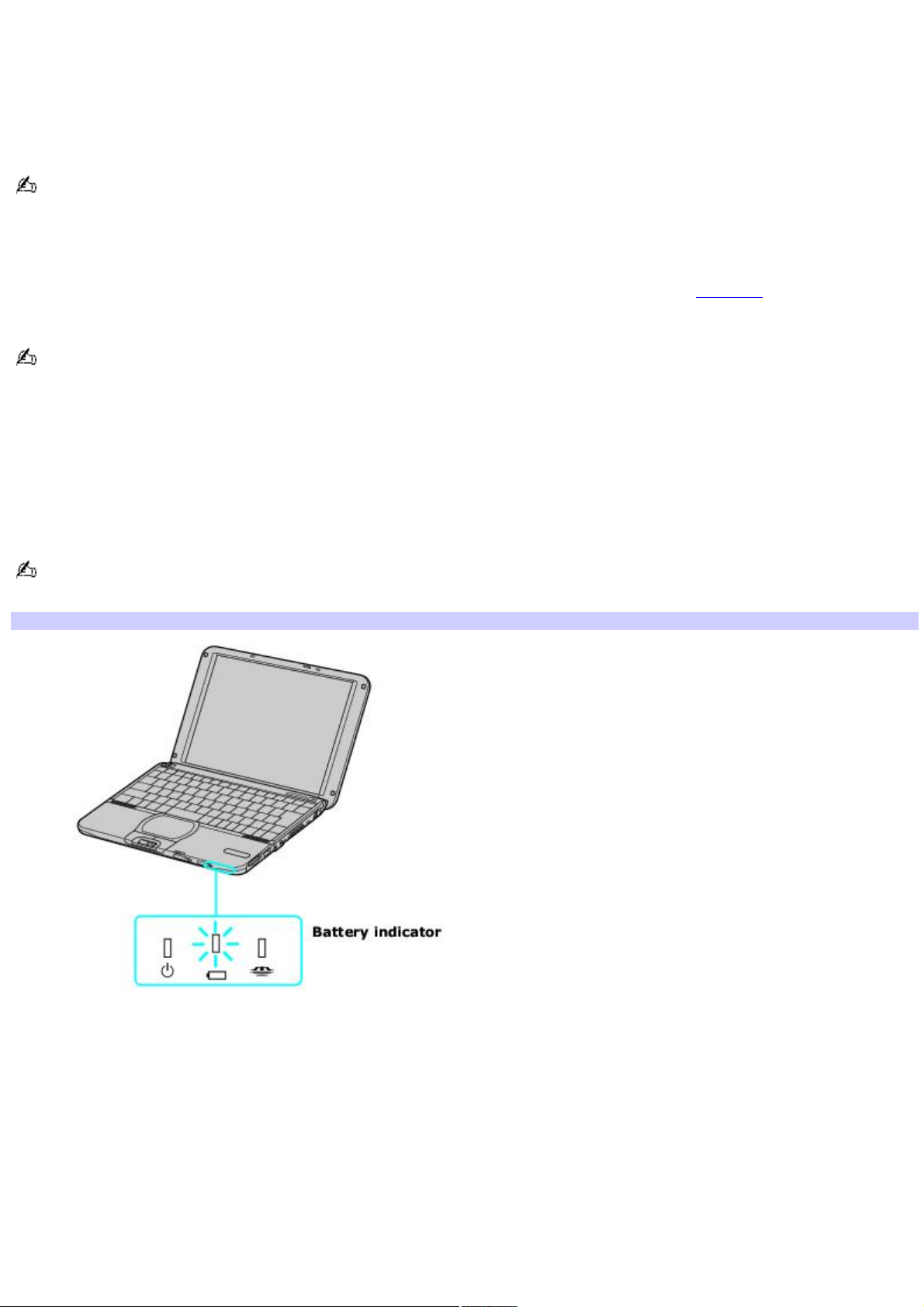
The battery indicator blinks while the battery charges. The battery indicator stops blinking when the battery is 100 percent
full.
When using two batteries, the battery you insert first charges first. The second battery you insert begins charging
when the first battery is 85 percent full.
Battery Indicator
Battery indicator status Description
On The computer is using battery power.
Single blink The battery is running out of power.
Double blink The battery is charging.
Off The computer is using AC power.
Page 11
Page 12

Notes on batteries
Never leave the battery in temperatures above 140° F (60° C), such as under direct sunlight or in a car parked in
the sun.
While the battery is in use or being discharged, the battery heats up. This is normal and is not cause for concern.
Keep the battery away from all sources of heat.
Keep the battery dry.
Do not open or disassemble the battery.
Do not expose the battery to any mechanical shock.
Battery life is shorter in a cold environment because of decreased battery efficiency at low temperatures.
Page 12
Page 13

Frequently asked questions
How do I know when the battery is charged?
To determine the remaining battery charge, see Displaying battery information.
When is the computer using AC power?
When the computer is directly connected to the AC adapter, it uses AC power, even if a battery is installed.
When should I recharge the battery?
When the battery level falls below 10 percent.
When both the battery and power indicators blink.
When you have not used the battery for a considerable amount of time.
Page 13
Page 14

Conserving Battery Power
You may use the power saving modes and PowerPanel or power schemes to conserve battery power. Conserving battery
power may significantly extend your computing time, depending on how you use your computer.
Using power saving modes
Using PowerPanel
Frequently asked questions
Page 14
Page 15

Using power saving modes
In addition to the normal operating mode, which allows you to turn off specific devices, your computer has two distinct
power saving modes: Standby and Hibernate. You can use the Standby and Hibernate power saving modes to override a
profile setting or initiate an immediate action.
Standby — Saves the state of the system and peripheral devices in memory (RAM). Power consumption is reduced
to a minimum. The system remains on, and the LCD is off.
Hibernate — Saves the state of the system and peripheral devices in the Save to Disk Partition on the hard disk.
Power consumption is reduced to the lowest possible setting without being completely off. Hibernate mode
consumes the lowest level of power. Your computer enters Hibernate mode with the remaining battery charge drops
below 5 percent, regardless of the setting you select.
Some software programs and peripheral devices prevent the system from entering Hibernate mode. If you are using a
program that prevents the system from entering Hibernate mode, save your data frequently to avoid data loss.
To activate Standby mode
1.
Press the key combination Fn+Esc or Fn+F12. The power indicator blinks in this mode.
2.
Press any key to return to Normal mode.
To activate Hibernate mode
1.
Press the power button and release it immediately. Do not move the computer until the power indicator turns
off.
2.
Press the power button to return to normal mode.
If the computer does not activate Hibernate mode, see Frequently asked questions for more information.
Page 15
Page 16

Using PowerPanel
The PowerPanel utility enables you to select and customize a predefined power management profile to conserve battery
life. The following table describes all the predefined power management profiles in PowerPanel. Your computer is set to
Automatic Profile Selection by default. You can customize the settings for all the following profiles, except the Disable Power
Management profile.
Profile
Icon Description
Maximum Performance
Provides the best system performance but conserves little power.
Maximum Battery Life
Provides power saving features to give you maximum battery life and good performance. It slows the computer and puts it
into Standby mode after a specified time period.
Ultimate Battery Life1
Extends the Maximum Battery Life by disabling the i.LINK port.
Power Management Off
Disables all power management settings, such as Standby and Hibernate modes. You cannot change the settings of this
profile.
AC Power
Indicates when AC power is in use. Similar to the Power Management Off setting. Power Management automatically loads
the AC profile unless you disable this feature.
Games
Disables the display and the Hard Disk Standby timer.
Presentation
Keeps the display on at all times while it conserves power. This option is ideal for slide show presentations. You can
establish settings for LCD (Video) Standby, Hard Disk Standby, and Standby mode to optimize power management for your
system.
Camera
Optimizes performance and power requirements for camera usage.
DVD
Optimizes performance and power requirements for DVD usage.
Word Processing
Optimizes power management with longer time-outs on the hard disk and display screen. You can also establish settings
for LCD (Video) Standby, Hard Disk Standby, and Standby mode to optimize power management for your system.
Spreadsheet
Optimizes performance and power requirements for spreadsheet programs.
Communications
Extends battery life by initiating a quick display time-out. The Internal modem remains powered. You can also establish
settings for LCD (Video) Standby, Hard Disk Standby, and Standby mode to optimize power management for your system.
Automatic Profile Selection
Switches automatically to a profile suitable for active software programs.
1
O n s elected models.
Page 16
Page 17

Do not choose the Automatic Profile Selection when connected to AC power.
To select a profile
1.
Right-click the Battery icon on the Windows taskbar. See To display the Battery Information window for a
description of the Battery icons.
2.
Select Profiles, and click the profile on the shortcut menu. The profile settings are implemented instantly. See
Using PowerPanel for descriptions of available profiles.
When you use the battery to power your computer, your system automatically selects the Maximum Battery Life
power management profile by default. If you select a different power management profile while using battery
power, that profile is selected automatically the next time you use the battery to power your computer.
See PowerPanel Help for information on customizing the power management profiles.
To customize your profile settings
You can customize your profile settings to sustain enough power for a particular computing function.
1.
Right-click the Battery icon on the Windows® taskbar. See To display the Battery Information window for a
description of the Battery icons.
2.
Select Edit/Create Profiles from the shortcut menu.
3.
In the left panel, click the profile that you want to change.
4.
Right-click the setting under System, LCD(Video), Hard Disk, or Other Devices that you want to change. See
the following table for a description of each power profile.
5.
Make your changes from the drop-down menu.
6.
Click File, and click Save.
Power profile Description
CPU Control1 Controls the processor speed. You can select either Performance, Adaptive, Battery Life, or More Battery
Life. These selections are listed in order from the greatest to least amount of power consumed.
System Standby Timer Controls the time it takes the system to activate the Standby mode when it is idle. The longer
you allow the computer to sit idle while it is not in a power saving mode the more power the computer will consume.
Hibernate Timer Controls the time it takes the system to activate the Hibernate mode when it is idle. The longer you
allow the computer to sit idle while it is not in a power saving mode the more power the computer consumes. Hibernate
mode conserves more power than Standby mode.
Thermal Control Strategy1 Controls the speed of the processor fan. You can adjust the fan speed to Quiet, which
conserves the most power, or Performance.
Lid Close Action Controls the state of your system when you close the computer's lid. You can select either Standby
or Hibernate mode, or you can select LCD Off. Hibernate or LCD Off conserves the most power.
Hibernate on Low Battery Controls the state of your system when the battery power is low. You can turn this setting
On or Off. Selecting On conserves the most power when the battery is low.
LCD Brightness Controls the brightness of the LCD screen. You can select a brightness level of one to nine, with one
being the darkest setting. The darker you set the LCD screen the more power you conserve.
LCD Standby Timer Controls the time it takes the system to switch the LCD to Standby mode when the system is idle.
This setting only turns off power to the LCD. The system itself still functions on full power.
Page 17
Page 18

HDD Standby Timer Controls the time it takes the system to switch the hard disk drive to Standby mode when the
system is idle. This setting only turns off power to the hard disk drive.
i.LINK Port Controls the power supply to the i.LINK port. You can disable power to the i.LINK port to conserve power.
Memory Stick Port Power-saving Controls the power supply to the Memory Stick slot. You can disable power to the
Memory Stick slot to conserve power.
1
Slows the process or s peed.
Page 18
Page 19

Frequently asked questions
Can my computer enter Hibernate mode while using battery power?
Your computer can enter Hibernate mode while using battery power, but some software programs and peripheral devices
prevent the system from entering Hibernate mode at all. If you are using a program that prevents the system from entering
Hibernate mode, save your data frequently. See Using power saving modes for information on how you can manually
activate Hibernate mode.
When should I replace the battery?
If, after fully charging the battery, the battery power is still low, the battery may be reaching the end of its life and should
be replaced.
Why is the battery warm?
While the battery is in use or being discharged, the battery heats up. This is normal and is not cause for concern.
Page 19
Page 20

Internet and Network Connections
Internet Connections
Network Connections
Connecting Another VAIO Computer
Page 20
Page 21

Internet Connections
This section describes the basic steps for setting up your dial-up or Ethernet connection to the Internet. The Internet
Connection Wizard guides you through the process of connecting to the Internet and choosing an Internet service provider
(ISP) or setting up an existing account. When you connect to the Internet, you can register your VAIO® computer, use online
services, and gain access to Sony Computing Support.
Setting up a dial-up Internet connection
Setting up an Ethernet Internet connection
Customizing your Internet connection
Frequently asked questions
Page 21
Page 22
Setting up a dial-up Internet connection
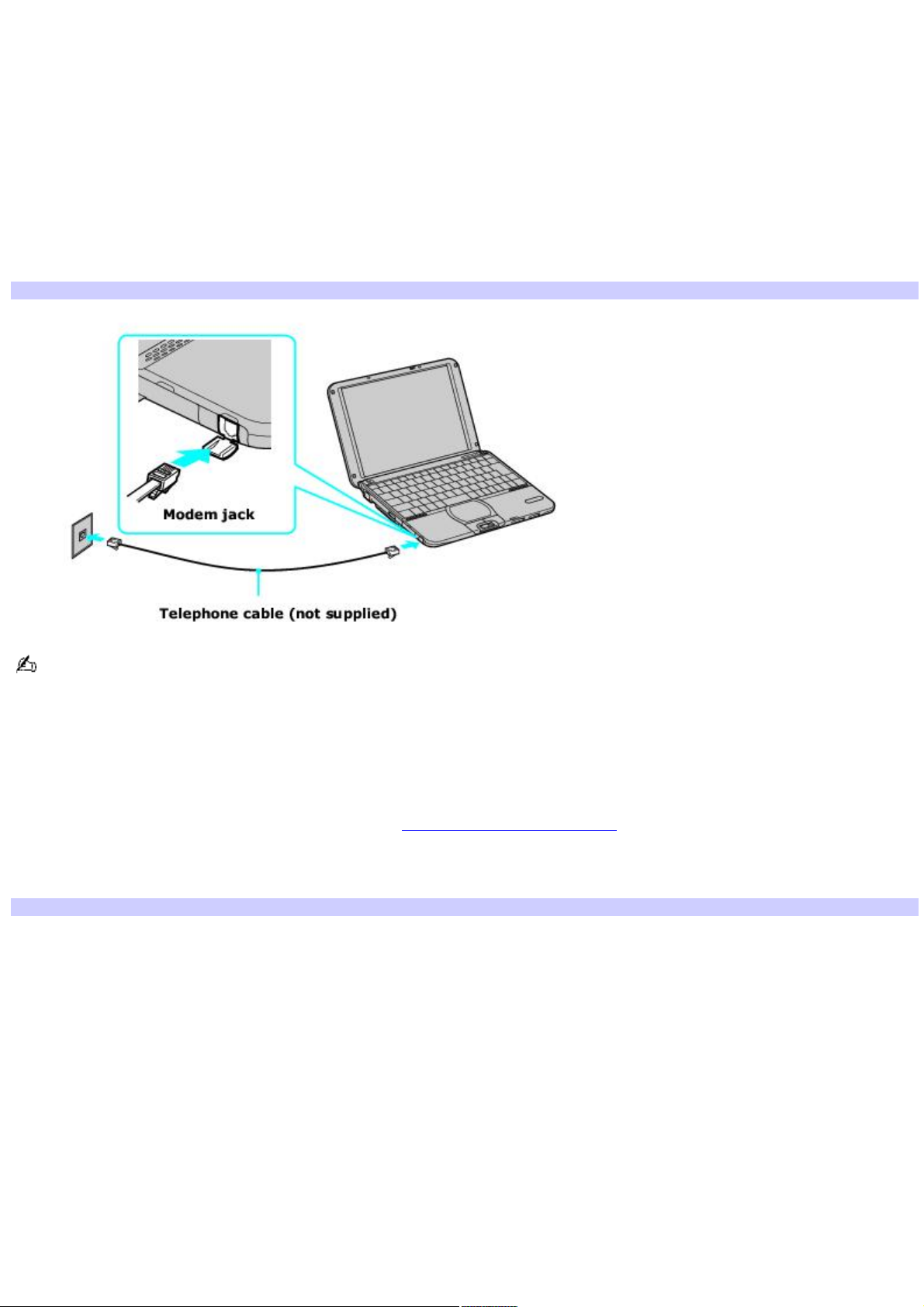
Before you can connect to the Internet, you need to connect your computer to a telephone line via a telephone cable (not
supplied). Once you have set up your telephone cable, you're ready to connect to the Internet.
To connect a telephone cable
1.
Locate the Modem jack on your computer. For location information, see Locating Ports and Controls in the Setting
Up chapter of your printed VAIO® Computer Quick Start.
2.
Plug one end of the telephone cable into the Modem jack. Make sure it clicks into place.
3.
Plug the other end into the wall jack.
Connecting a Telephone Cable
Your computer does not work with party lines, cannot be connected to a coin-operated telephone, and may not
work with multiple telephone lines or a private branch exchange (PBX). Some of these connections may result in excess
electrical current and could cause a malfunction in the internal modem.
If you connect a telephone cable coming through a splitter, the modem or connected device may not work properly.
To set up a dial-up connection to the Internet
1.
Connect your computer to a telephone line. See To connect a telephone cable for more information.
2.
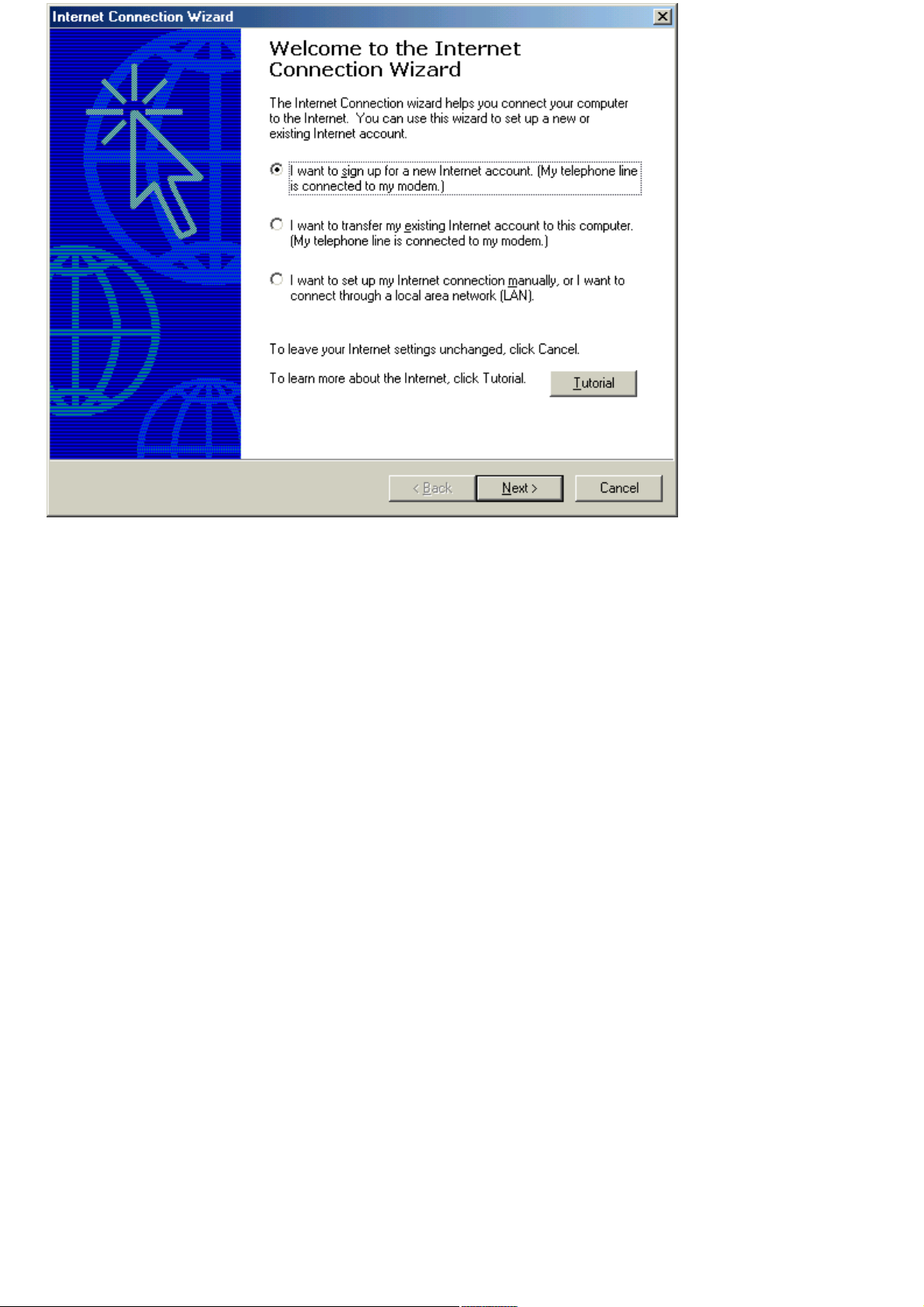
Click Start, point to Programs, Accessories, Communications, and click Internet Connection Wizard. The
Internet Connection Wizard appears.
Internet Connection Wizard
Page 22
Page 23
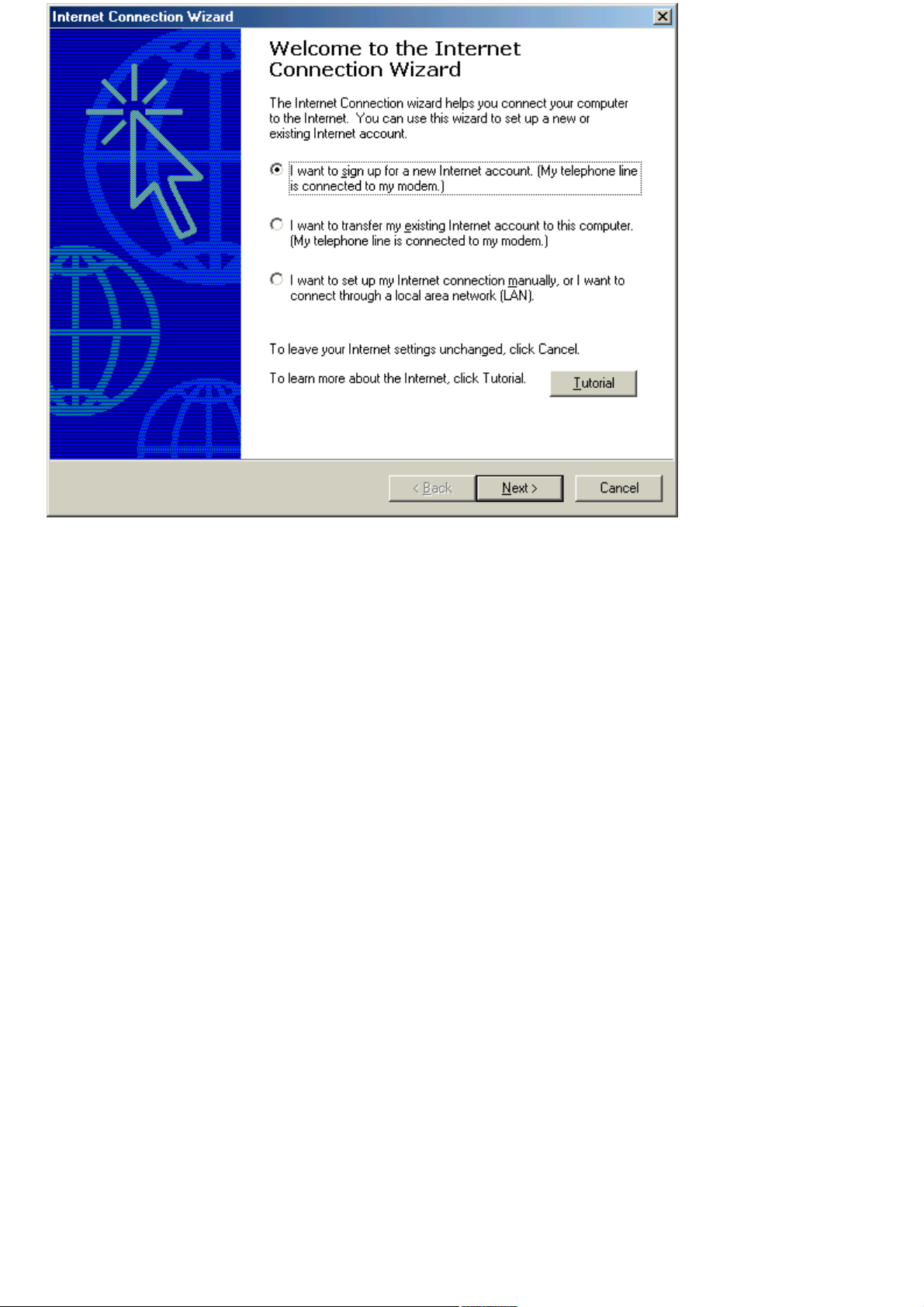
3.
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Page 23
Page 24
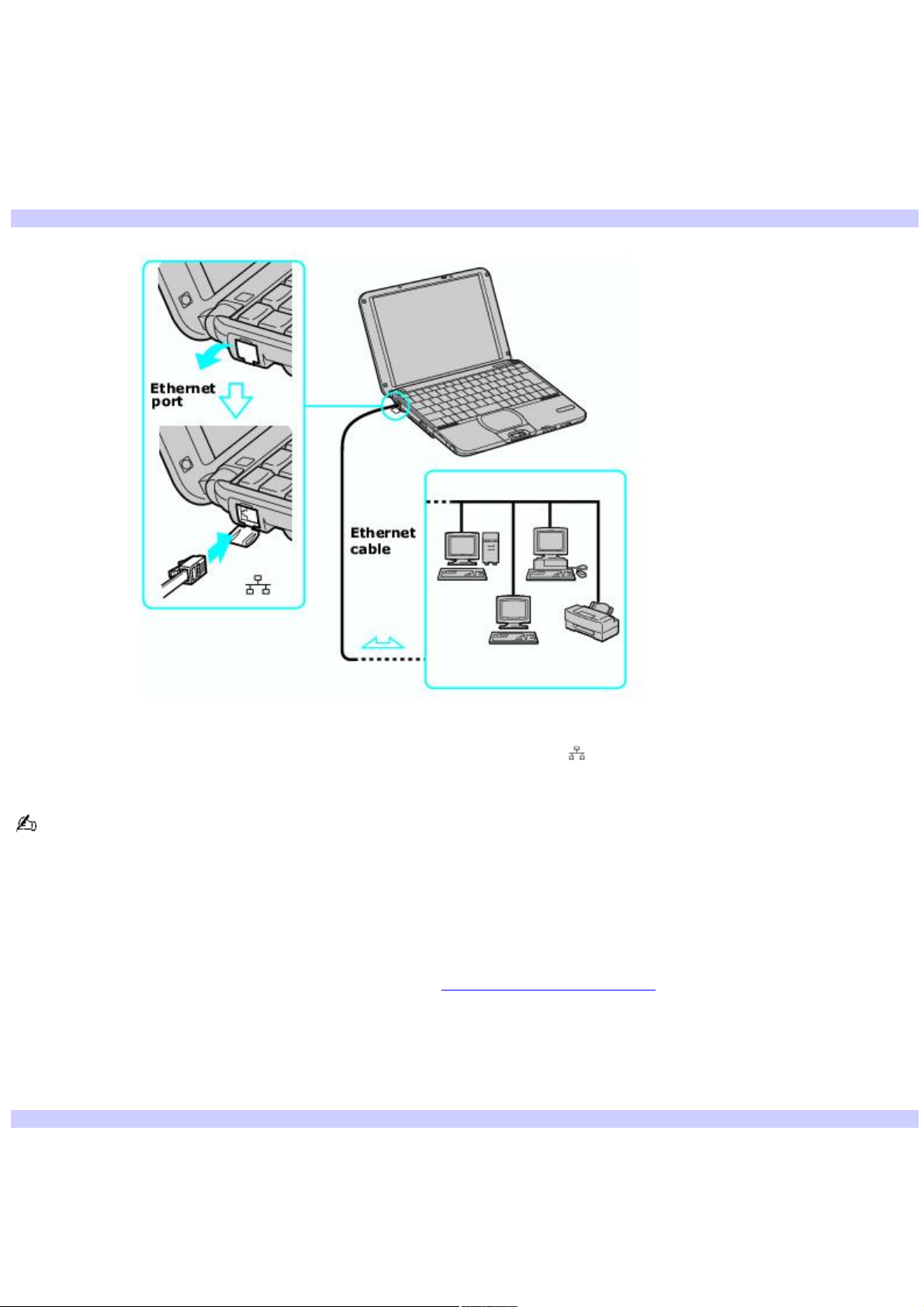
Setting up an Ethernet Internet connection
Your computer accommodates both 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet connections, with data transfer speeds of between
10 and 100 Mbps, depending on the line conditions and Ethernet cable.
To connect an Ethernet cable
1.
Locate the Ethernet port on your computer. For location information, see Locating Ports and Controls in the
Setting Up chapter of your printed VAIO® Computer Quick Start.
Connecting an Ethernet Cable
2.
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into your computer's Ethernet port and the other into the network
connection.
Your computer does not work with party lines, cannot be connected to a coin-operated telephone, and may not
work with multiple phone lines or a private branch exchange (PBX). Some of these connections may result in excess
electrical current and could cause a malfunction in the internal modem.
If you connect a telephone cable via a splitter, the modem or connected device may not work properly.
To set up an Ethernet connection to the Internet
1.
Connect your computer to a network connection. See To connect an Ethernet cable for more information.
2.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Internet Options. The Internet Properties dialog box
appears.
3.
Click to open the Connections tab, and click LAN Settings near the bottom of the page. The Local Area Network
(LAN) Settings dialog box appears.
Internet Connection Wizard
Page 24
Page 25
4.
Click to select the Automatically detect settings check box.
5.
Click to select the Use automatic configuration script, and type an address in the Address box.
6.
Click OK.
Page 25
Page 26

Customizing your Internet connection
The Internet Properties dialog box enables you to change the way you view the Internet. You can change your home page,
fonts, language, and colors. You can also regulate content and set your browsing preferences.
To open the Internet Properties dialog box
1.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Internet Options. The Internet Properties dialog box
appears.
2.
Click the tabs to view customizing options.
3.
Make changes, and click Apply to activate your changes.
4.
Click OK.
Page 26
Page 27

Frequently asked questions
Why doesn't my modem work?
Make sure the telephone cable is securely plugged into the Modem jack and the wall jack. See To connect a
telephone cable for more information.
Make sure the telephone cable is working by plugging the cable into an ordinary telephone and listening for a dial
tone.
Make sure the telephone number the program is dialing is correct.
Make sure the software you are using is compatible with the computer's modem. (All preinstalled Sony programs are
compatible.)
If you are still experiencing problems, use the supplied Application Recovery CD(s) to reinstall the modem driver
software. See Using the Application Recovery CD(s) for more information.
Why is my modem connection slow?
Your computer is equipped with a V.90 compatible modem. Many factors may influence modem connection speed, including
telephone line noise or compatibility with telephone equipment, such as fax machines or other modems. If you think your
modem is not connecting properly to other PC-based modems, fax machines, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP), follow
these steps:
Ask your telephone company to verify your telephone line is free of any line noise.
If your problem is fax-related, make sure there are no problems with the fax machine you are calling and that it is
compatible with fax modems.
If you are having a problem connecting with your ISP, make sure the ISP is not experiencing technical problems.
If you have a second telephone cable available, try connecting the modem to that cable.
Page 27
Page 28
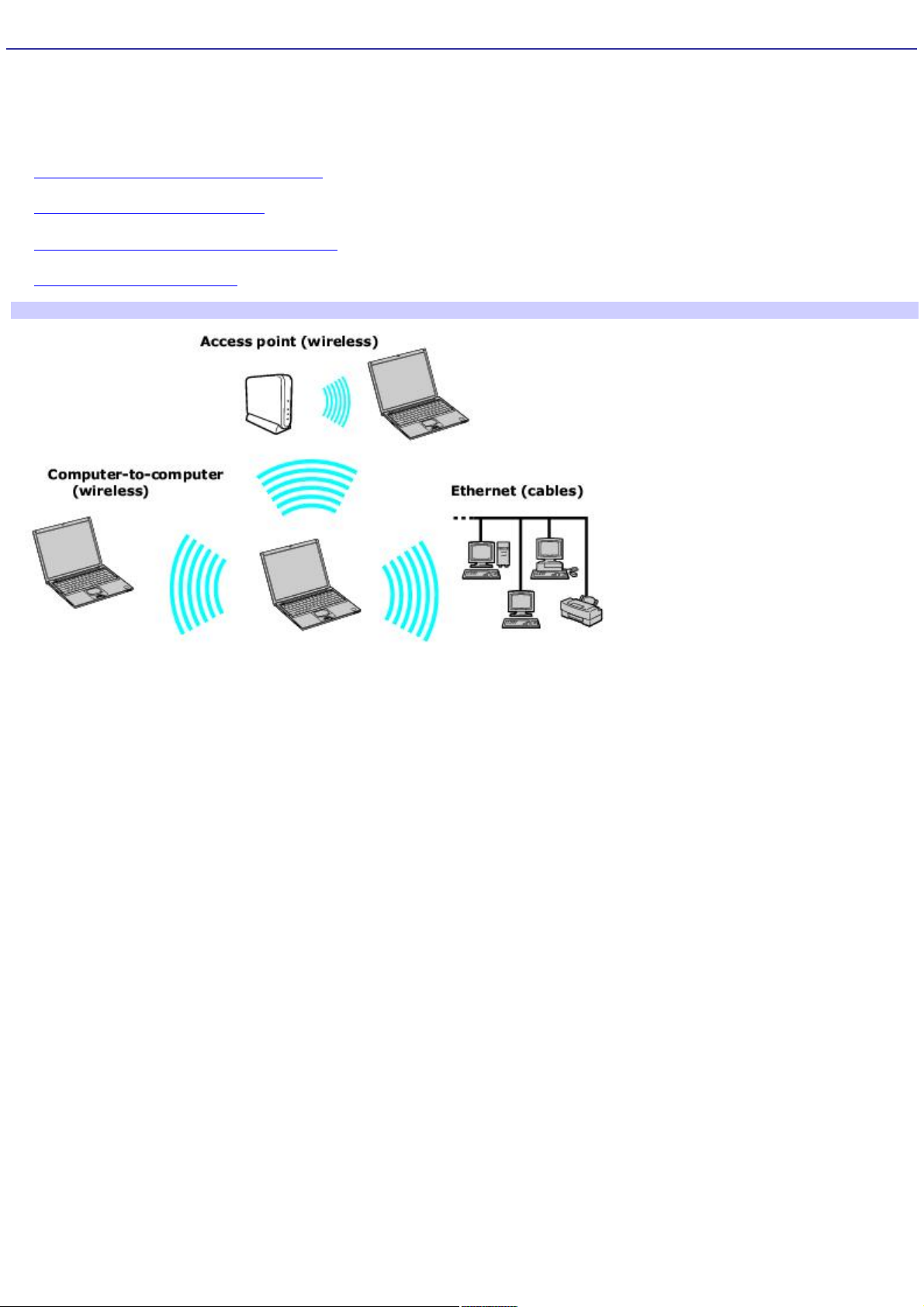
Network Connections
With a Sony computer, you can easily set up or connect to a variety of networks. The Network Connection Wizard makes it
easy to gain access to remote and local area networks (LANs) using wireless, Ethernet, or dial-up connections.
For more information about networking, click Start, Help, and then Networking.
Using Ethernet and dial-up connections
Using wireless LAN connections
Checking your network connection status
Frequently asked questions
Types of Networks
Page 28
Page 29
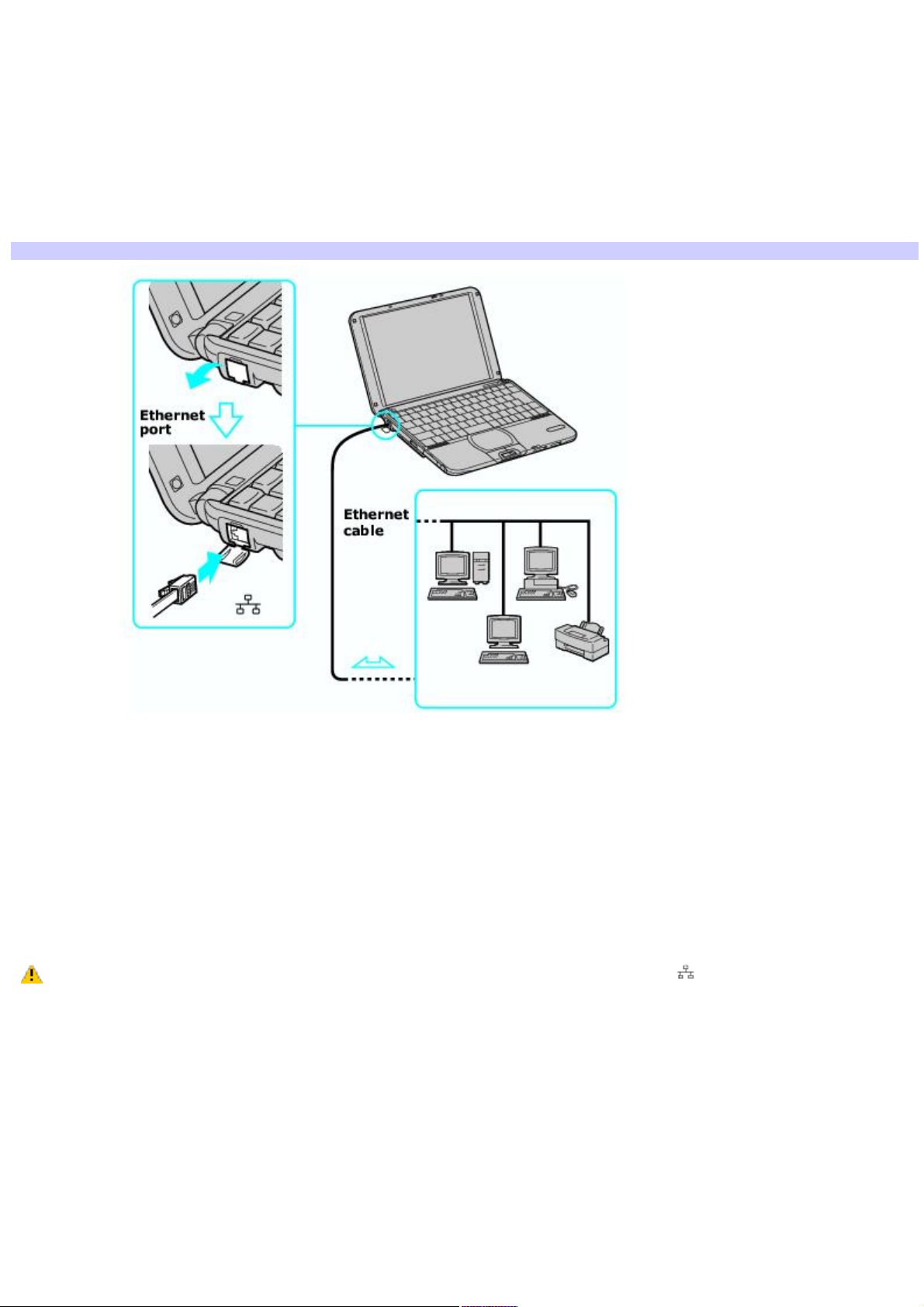
Using Ethernet and dial-up connections
Local area networks (LANs) comprise a group of computers and associated devices within a small geographic area, such as
a home or office building. For setting up LANs, Ethernet is a widely installed technology. Your computer accommodates both
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet connections, with data transfer speeds of between 10 and 100 Mbps, depending on
the Ethernet cable.
To set up an Ethernet LAN
1.
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into your computer's Ethernet port and the other into the network
connection.
Connecting an Ethernet Cable
2.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Internet Options. The Internet Properties dialog box
appears.
3.
Click to open the Connections tab, and click LAN Settings near the bottom of the page. The Local Area Network
(LAN) Settings dialog box appears.
4.
Click to select the Automatically detect settings check box.
5.
Click to select the Use automatic configuration script, and type an address in the Address box.
6.
Click OK.
Warning: Only connect 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX cables to the Ethernet port . Do not connect any other
type of network cable or any telephone cable. Connecting cables other than those listed above may result in an
electric current overload and could cause a malfunction, excessive heat, or fire in the port. To connect the unit to the
network, contact your network administrator.
You can connect to your company network from a remote location and use data, applications, and network resources. See
Microsoft® Windows® Help by clicking Help from the Start menu, and then clicking Networking in the left panel.
Page 29
Page 30
Using wireless LAN connections
A wireless local area network (LAN) is a network in which you can connect to a LAN through a wireless (radio) connection.
You can opt to purchase a Sony Wireless LAN Access Point to set up a LAN.
The Wireless LAN Access Point is designed for building a wireless LAN environment. Because a wireless LAN configuration
requires no wiring, you can operate multiple computers more freely than ever before.
You can also purchase an external Wireless LAN PC Card separately, but your computer (depending on the model you
purchased) may already come with a built-in mini PCI card that allows for wireless connections. For information about your
computer's wireless capabilities, see the Welcome page to view your VAIO® Computer Specifications. The Wireless LAN PC
Card is designed for a wireless LAN environment. You can use the Wireless LAN PC Card with or without the access point.
For more information on Sony Wireless LAN, go to http://www.sonystyle.com/vaio.
There are two types of wireless connections:
An infrastructure network is one that extends an existing wired local network to wireless devices by providing an
access point. The access point bridges the wireless and wired LAN and acts as a central controller for the Wireless
LAN. The access point coordinates transmission and reception from multiple wireless devices within a specific range.
A peer-to-peer group (ad-hoc) network is one in which a local network is created only by the wireless devices
themselves, with no other central controller or access point. Each device communicates directly with other devices in
the network. You can set up an ad-hoc network easily at home.
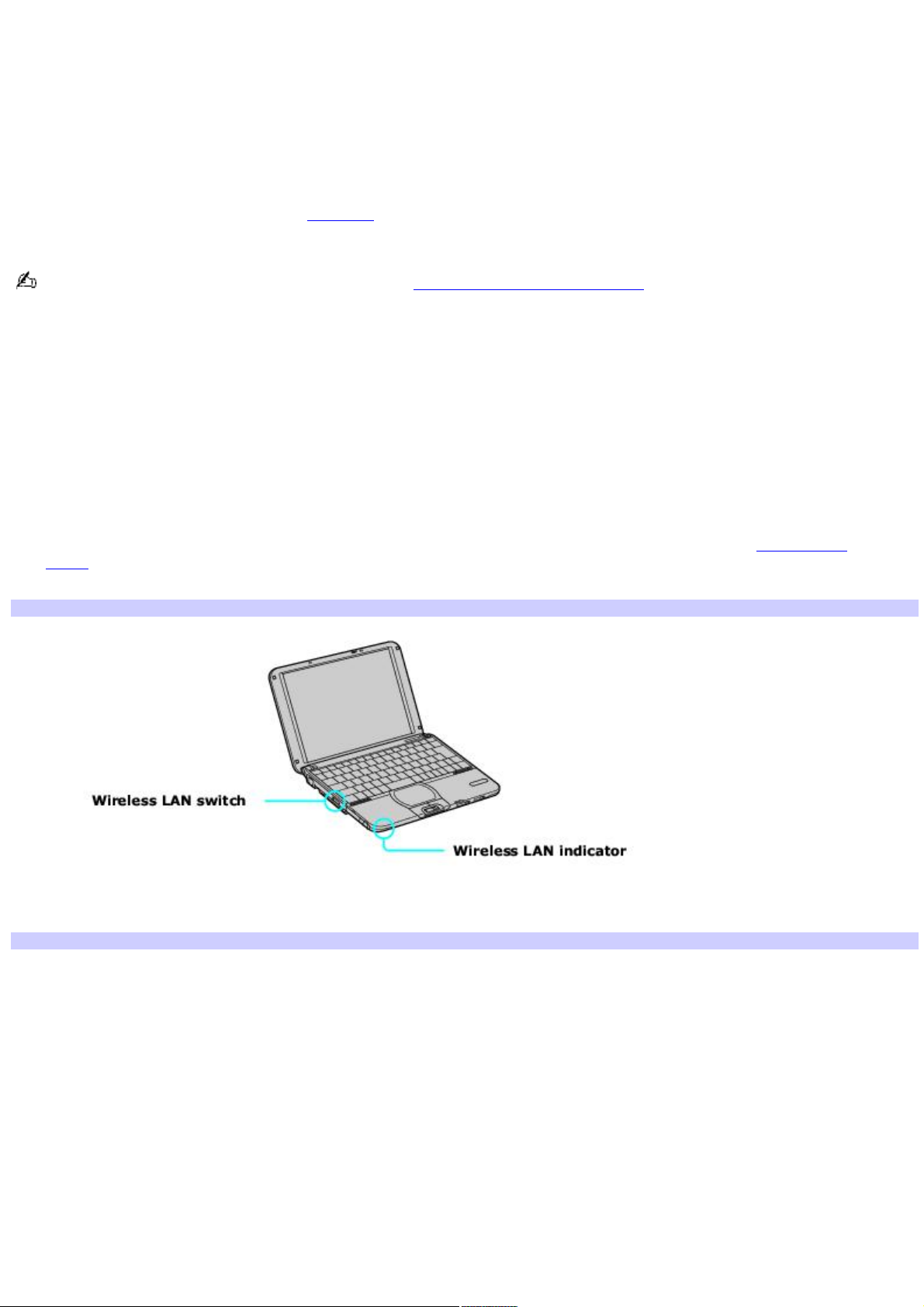
To connect to an existing wireless network
1.
Move the Wireless LAN switch to ON or insert a Wireless LAN PC Card into the PC Card slot. See Inserting PC
Cards for more information.
The Wireless LAN indicator turns on.
Connecting to a Wireless LAN
2.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Wireless Network. The Add/Edit Configuration Profile
window appears.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
Page 30
Page 31

3.
Click Add. The Edit Configuration dialog box appears.
4.
Type a profile name, and select Access Point from the Network Type drop-down list if it is not already selected.
5.
Click Next.
6.
Type a name in the Network Name box or click Scan to select a network.
7.
Click Next.
8.
If the network was set up with an encryption key:
1.
Click to select the Enable Data Security check box.
2.
Select either Use Alphanumeric Characters or Use Hexadecimal, depending on the encryption key.
3.
Type the five-character encryption key in the Key 1 box, and make sure Key 1 appears in the Encrypt
data with box. Ask the network administrator for the encryption key if you don't already have it.
4.
Click Next.
If the network was not set up with an encryption key, then click Next.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
9.
Select a power management option, and click Next.
Page 31
Page 32

10.
Click to select the Renew IP Address when selecting this profile check box, so you don't have to type the IP
Address everytime you want to connect to the network.
11.
Click Finish.
To set up a wireless network
1.
Move the Wireless LAN switch to ON or insert a Wireless LAN PC Card into the PC Card slot. See Inserting PC
Cards for more information.
The Wireless LAN indicator turns on.
Connecting to a Wireless LAN
2.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Wireless Network. The Add/Edit Configuration Profile
window appears.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
3.
Click Add. The Edit Configuration dialog box appears.
4.
Type a profile name, and select Access Point from the Network Type drop-down list if it is not already selected.
5.
Click Next.
6.
Type a name in the Network Name box.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Set up an encryption key, so only the individuals to whom you give the encryption key can gain access to the
network:
1.
Click to select the Enable Data Security check box.
2.
Select either Use Alphanumeric Characters or Use Hexadecimal.
Page 32
Page 33

3.
Type a five-character encryption key in the Key 1 box using either alphanumeric or hexadecimal
characters, depending on your selection in the previous step.
4.
Make sure Key 1 appears in the Encrypt data with box.
5.
Click Next.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
9.
Select a power management option, and click Next.
10.
Click to select the Renew IP Address when selecting this profile check box, so you don't have to type the IP
Address everytime you want to connect to the network.
11.
Click Finish.
To set up a peer-to-peer group (ad-hoc) network
1.
Move the Wireless LAN switch to ON or insert a Wireless LAN PC Card into the PC Card slot. See Inserting PC
Cards for more information.
The Wireless LAN indicator turns on.
Connecting to a Wireless LAN
2.
Click Start, point to Settings, Control Panel, and click Wireless Network. The Add/Edit Configuration Profile
window appears.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
Page 33
Page 34

3.
Click Add. The Edit Configuration dialog box appears.
4.
Type a profile name, and select Peer-to-Peer Group from the Network Type drop-down list.
5.
Click Next.
6.
Type a name in the Network Name box, and select a channel using the Channel Number drop-down list.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Set up an encryption key, so only the individuals to whom you give the encryption key can gain access to the
network:
1.
Click to select the Enable Data Security check box.
2.
Select either Use Alphanumeric Characters or Use Hexadecimal.
3.
Type a five-character encryption key in the Key box using either alphanumeric or hexadecimal
characters, depending on your selection in the previous step.
4.
Click Next.
Add/Edit Configuration Profile Window
9.
Select a power management option, and click Next.
10.
Click to select the Renew IP Address when selecting this profile check box, so you don't have to type the IP
Address everytime you want to connect to the network.
11.
Click Finish.
Page 34
Page 35

To disconnect from a wireless network
For computers with built-in wireless LAN functionality:
1.
Click Start, point to Settings, and click Network and Dial-up Connections.
2.
Right-click the appropriate Local Area Connection network icon, and select Disable.
3.
Move the Wireless LAN switch to OFF. The Wireless LAN indicator turns off.
For wireless LAN PC Card connections:
1.
Click Start, point to Settings, and click Network and Dial-up Connections.
2.
Right-click the appropriate Local Area Connection network icon, and select Disable.
3.
Correctly remove the PC Card. See Inserting PC Cards for more information.
Turning off the wireless LAN functionality while accessing remote documents, files, or resources may
result in data loss.
Page 35
Page 36

Checking your network connection status
To check the status of your network connection
Click Start on the Windows® taskbar, and point to Programs, ORiNOCO, and click Client Manager. The Status box
shows information about your network connection.
Page 36
Page 37

Frequently asked questions
Why can't my computer connect to a Wireless LAN Access Point?
Connection availability is affected by distance and obstructions. You may need to move your computer away from
obstructions or closer to any access point you may be using.
Make sure the Wireless LAN switch on the computer is in the ON position or the Wireless LAN PC Card is properly
inserted. See Inserting PC Cards for more information.
Make sure power to the access point is on.
Make sure the encryption key is correct.
Why can't I gain access to the Internet?
If you are using a Wireless LAN PC Card, make sure it is properly inserted into the PC Card slot. For more
information, see Inserting PC Cards.
Check the access point settings. Refer to the instructions supplied with the access point.
Make sure your computer and the access point are connected to one another.
Move your computer away from obstructions or closer to any access point you may be using.
Make sure your computer is properly configured for Internet access.
Why is the data transfer speed slow?
The Wireless LAN data transfer speed is affected by distance and obstructions between devices and access points.
Other factors include device configurations, radio conditions, and software compatibility. To maximize the data
transfer speed, move your computer away from obstructions or closer to any access point you may be using.
If you are using a Wireless LAN Access Point, the device may be temporarily overloaded depending on the number
of other devices communicating via the access point.
If your access point interferes with other access points, change the access point channel. See your access point
instructions for more information.
Why is the communication speed interrupted or slowed down when MPEG2 data is transferred?
The typical effective data transfer speed via an access point is 4-5 Mbps when adhering to the IEEE 802.11b standard.
High-rate stream transfers with MPEG2 data may lower this rate.
How do I avoid data transfer interruptions?
Data transfer interruptions may occur with large files or use of microwaves and cordless telephones when
connected to an access point.
Move the computer closer to the access point.
Make sure the access point connection is intact.
Change the access point channel. See your access point instructions for more information.
Can I connect to a IEEE 802.11a device?
Computers with built-in Wireless LAN support the IEEE 802.11b standard only. Devices connecting to a Wireless LAN using
the IEEE 802.11a standard cannot connect to devices using the IEEE 802.11b standard.
What are channels?
Wireless LAN communication occurs on divided frequency bands known as channels. Third-party Wireless LAN Access Point
channels may be preset to different channels from Sony devices.
If you are using a Wireless LAN Access Point, refer to connectivity information contained in your access point instructions.
Page 37
Page 38

Connecting Another VAIO Computer
You can use a compatible i.LINK®1 cable (not supplied) to connect two compatible mobile VAIO computers, and then use one
computer to edit, copy, or delete files on the other computer. You can also print from a printer that is attached to either
computer.
Only i.LINK cables may be used to connect two compatible mobile VAIO computers.
Frequently asked questions
To connect VAIO computers
1.
Plug one end of the i.LINK cable into the i.LINK port on each computer.
2.
Restart both computers and log on when prompted.
3.
ClickStart, point to Programs, Smart Connect, and click Smart Connect Monitor. The Smart Connect Monitor
window appears.
4.
Click Option, and select Run Smart Connect Switch.
5.
Click to select Enable Smart Connect.
6.
Click to select STD mode, if it is not already selected.
7.
Click OK. Your computers are connected.
8.
To view the folders on your network:
In the Smart Connect Monitor window, right-click a computer name, and select Open with Explorer.
Double-click My Network Places, and click Computers Near Me in the My Metwork Places window.
For more information, see Smart Connect Online Help.
Connecting Another Computer
To disconnect VAIO computers when the computers are on
1.
Close all open files that are shared with the connected computers.
2.
Unplug the i.LINK cable from the i.LINK port on each computer.
To disconnect VAIO computer when the computers are off
Unplug the i.LINK cable from the i.LINK port on each computer.
1
i.LINK is a trademark of Sony us ed to des ignate that a produc t c ontains an I E E E 1 3 9 4 c onnection. The i.LINK c onnec tion may vary, depending on the
software programs, operating system, and c ompatible i.LI N K devic es. A ll products with an i.LI N K c onnec tor may not c ommunic ate with eac h other. Refer to
the documentation that came with your compatible i.LIN K devic e for information on operating c onditions and proper c onnec tion. Before c onnecting
compatible i.LI N K P C peripherals to your system, s uch as a C D-RW or hard dis k drive, c onfirm their operating s ys tem c ompatibility and required operating
conditions.
Page 38
Page 39

Frequently asked questions
Why can't I establish a connection between two VAIO computers?
Your computer may not recognize an i.LINK1 connection if the i.LINK cable is not plugged securely into the i.LINK
ports. Disconnect the i.LINK cable and securely reconnect it to both computers. If neither computer responds after a
few moments, restart both computers.
If the computers do not recognize the i.LINK connection after resuming from a power saving mode (Standby or
Hibernate), restart both computers.
1
i.LINK is a trademark of Sony us ed only to des ignate that a produc t c ontains an I E E E 1 3 9 4 c onnection. The i.LINK c onnec tion may vary, depending on the
software applications, operating s ys tem, and c ompatible i.LI N K devices. A ll products with an i.LI N K c onnec tion may not c ommunic ate with eac h other. Refer
to the documentation that came with your compatible i.LIN K devic e for information on operating c onditions and proper c onnec tion. Before c onnec ting
compatible i.LI N K P C peripherals to your system, s uch as C D-RW or hard dis k drive, c onfirm their operating s ys tem c ompatibility and required operating
conditions.
Page 39
Page 40

CDs, DVDs, and Optical Drives
Connecting External Optical (Disc) Drives
Inserting and Ejecting CDs or DVDs
Copying and Playing CDs
Playing DVDs
Page 40
Page 41

Connecting External Optical (Disc) Drives
Depending on the model you purchased, your computer may come equipped with a built-in optical drive. If not, you can
purchase an external optical drive, such as PC Card or i.LINK1 drive, and connect it to your computer, so you can write to
and read CDs and DVDs. If you wish to purchase an external optical drive, shop Sony online at
http://www.sonystyle.com/vaio or contact your local retailer.
The Sony i.LINK optical drive is only compatible with certain Sony VAIO® PCG series computers that are preinstalled
with Microsoft® Windows® XP Home Edition or Professional software.
i.LINK optical (disc) drives
PC Card optical (disc) drives
Frequently asked questions
1
i.LINK is a trademark of Sony us ed only to des ignate that a produc t c ontains an I E E E 1 3 9 4 c onnection. The i.LINK c onnec tion may vary, depending on the
software applications, operating s ys tem, and c ompatible i.LI N K devices. A ll products with an i.LI N K c onnec tion may not c ommunic ate with eac h other. Refer
to the documentation that came with your compatible i.LIN K devic e for information on operating c onditions and proper c onnec tion. Before c onnec ting
compatible i.LI N K P C peripherals to your system, s uch as C D-RW or hard dis k drive, c onfirm their operating s ys tem c ompatibility and required operating
conditions.
Page 41
Page 42

i.LINK optical (disc) drives
The i.LINK drive enables you to read data stored on a DVD or CD. Your computer may come with an external i.LINK drive,
depending on the model you purchased. Once the i.LINK drive is connected, you can use the preinstalled software to create
CDs or play DVDs.
The i.LINK optical drive draws power from the computer through a peripheral cable. You must connect the peripheral cable
to both the i.LINK port and DC OUT jack on your computer.1
Do not use the i.LINK optical drive and the PC Card drive at the same time. Connecting both devices may cause the
computer to malfunction.
To connect an i.LINK optical drive
1.
Close any active programs to prevent data loss.
2.
Turn on power to the computer.
3.
Insert the L-shaped connector on the peripheral cable (supplied with the i.LINK optical drive) into the matching
port on the rear panel of the i.LINK optical drive.
Connecting the i.LINK Optical Drive
4.
Turn the LOCK device clockwise to secure the L-shaped connector.
5.
Insert the two-prong peripheral cable connector into both the i.LINK port and DC OUT jack on the computer.
The i.LINK drive power indicator turns on, and the computer automatically detects the connected drive.
6.
Restart your computer.
To use the i.LINK optical drive
1.
Double-click the My Computer icon on the desktop. The My Computer window appears.
2.
Double-click DVD/CD-RW Drive. The DVD/CD-RW Drive window appears.
To disconnect the i.LINK optical drive
1.
Close any active programs to prevent data loss.
Page 42
Page 43

2.
Double-click the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon on the taskbar. The Unplug or Eject Hardware window
appears.
3.
Select the i.LINK drive in the Hardware devices window, if it is not already selected.
4.
Click Stop. The Stop a Hardware device window appears.
5.
Make sure the i.LINK drive is selected, and click OK. A message appears stating it is now safe to remove the
hardware device.
6.
Unplug the i.LINK optical drive from the i.LINK port and DC OUT jack on the computer, port replicator, or docking
station.
1
I f you c onnec t and us e an i.LI N K optical drive when your c omputer is running on battery power, the battery life will be reduc ed.
Page 43
Page 44

PC Card optical (disc) drives
The PC Card drive enables you to read data stored on a DVD or CD. Your computer may come with an external PC Card
drive, depending on the model you purchased. Once the PC Card drive is connected, you can use the preinstalled software
to create CDs or play DVDs.
Do not use the i.LINK optical drive and the PC Card drive at the same time. Connecting both devices to may cause the
computer to malfunction.
If you connect a non-Sony DVD drive to your VAIO® computer, DVD playback may not function properly. The
supplied DVD software must be installed to play a DVD. For best performance, use a Sony compatible DVD drive.
To connect an optical drive
You can connect a PC Card drive while the computer is on. Connecting the drive when the computer is in a power saving
mode (Standby or Hibernate) may cause the computer to malfunction.
Instructions on connecting an optical drive may vary, depending on the specific drive you purchased.
1.
Remove the PC Card from the bottom of the optical drive.
Remov ing a PC Card
2.
Insert the PC Card into the PC Card slot with the logo facing up. See Inserting PC Cards for more information.
Inserting a PC Card
Remove the protective cover that is attached to the lens of the optical drive before you use the drive. See Inserting
and Ejecting CDs or DVDs for information on how to open the optical drive to access the lens.
See the manual that accompanied your optical drive for more information on its installation and use.
To disconnect the PC Card drive
1.
Close any active programs to help prevent data loss.
2.
Double-click the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon on the taskbar. The Unplug or Eject Hardware window
appears.
Page 44
Page 45

3.
Select the PC Card drive on the Hardware devices window, if it is not already selected, and click Stop. The
Stop a Hardware device window appears.
4.
Select the PC Card drive, and click OK. A message appears stating it is now safe to remove the hardware
device.
5.
Disconnect the PC Card drive from the computer.
Page 45
Page 46

Frequently asked questions
Why isn't my i.LINK drive playing a CD or DVD properly?
The i.LINK optical drive will not play a CD or DVD if the disc was inserted with the label facing down. Eject the CD or
DVD from the drive, and make sure the label is facing up.
The disc requires a particular software program that is not already installed on your computer. Install that program
according to the manufacturer's instructions.
The DVD is not compatible with the optical drive and a region code warning appears when you try to play it. Make
sure the region code listed on the DVD package is compatible with the drive.
Why won't my i.LINK drive play my computer programs?
If multiple i.LINK®1 devices are connected to the computer, the software supplied with your computer will not recognize
them. Turn off your computer and all connected devices. Disconnect the devices that are not in use. See i.LINK optical (disc)
drives for instructions on reconnecting the i.LINK device.
1
i.LINK is a trademark of Sony us ed only to des ignate that a produc t c ontains an I E E E 1 3 9 4 c onnection. The i.LINK c onnec tion may vary, depending on the
software applications, operating s ys tem, and c ompatible i.LI N K devices. A ll products with an i.LI N K c onnec tion may not c ommunic ate with eac h other. Refer
to the documentation that came with your compatible i.LIN K devic e for information on operating c onditions and proper c onnec tion. Before c onnec ting
compatible i.LI N K P C peripherals to your system, s uch as C D-RW or hard dis k drive, c onfirm their operating s ys tem c ompatibility and required operating
conditions.
Page 46
Page 47

Inserting and Ejecting CDs or DVDs
Avoid using adhesive labels to identify your CDs or DVDs. Adhesive labels may damage the optical drive if they come
off while the disc is in the drive.
To insert a CD or DVD
1.
Turn on the computer, and exit a power saving mode (Standby or Hibernate) if one is active. For more
information on power saving modes, see Using power saving modes.
2.
Press the Eject button on the optical drive cover to open the drive tray. The drive tray slides out.
Ejecting the Drive Tray
3.
Place a disc on the drive tray with the label facing up.
You can play some DVDs on both sides. Insert this type of DVD with the side you want to play facing up.
Inserting a Disc
4.
Press the disc onto the hub until the disc clicks securely into place.
If you do not seat the disc firmly over the hub, the disc may come loose while it is in the drive. A loose
disc may damage the optical drive and make opening the drive tray difficult.
5.
Push the drive tray gently to close it. The Busy indicator on the drive blinks while your computer is reading data
from the drive.
To ejecting a CD or DVD
1.
Turn on the computer, and exit a power saving mode (Standby or Hibernate) if one is active. For more
information on power saving modes, see Using power saving modes.
2.
Close all software programs that are open from the optical drive, and wait for the LED indicator to turn off.
3.
Press the Eject button on the optical drive cover to open the drive tray. The drive tray slides out.
If the Eject button does not work, turn off the computer and insert a thin, straight object (such as a paper clip)
into the manual eject hole next to the Eject button.
Page 47
Page 48

4.
Lift the disc from the drive.
5.
Push the drive tray gently to close it.
Page 48
Page 49

Copying and Playing CDs
Your optical drive can read CDs and DVDs. The type of optical drive installed in or connected to your computer may vary,
depending on the model you purchased. If you are using a CD-RW/DVD Combo Drive, you can write data to CD-Rs and
CD-RWs.
Playing CDs
Copying files to a CD-RW or CD-R
Do not remove the optical drive when the computer is in a power saving mode (Standby or Hibernate). Doing
so may cause the computer to malfunction.
Page 49
Page 50

Playing CDs
Before you play an audio CD, you may need to enable your computer's audio feature.
To enable the audio feature
1.
Click Start, and point to Settings and Control Panel, then click System. The System Properties window
appears.
2.
Select the Hardware tab, and click Device Manager in the Device Manager box. A window with a listing of the
computer's hardware devices appears.
3.
Double-click DVD/CD-ROM drives.
4.
Double-click the listed drive name, and select the Properties tab.
5.
Click to select the Enable digital CD audio for this CD-ROM device check box if it is not already selected.
6.
Click OK.
To adjust the volume for playing CDs and DVDs
Some software programs have built-in volume controls, which you can adjust. If there are no volume controls, then you can
adjust the volume of your computer's built-in speakers by doing one of the following:
Using the Function keys. An on-screen display may appear, notifying you when a change occurs.
To increase volume, press Fn+F4, then or .
To decrease volume, press Fn+F4, then or .
Using the Volume icon.
1.
Double click the Volume icon on the Windows® taskbar. The Volume Control dialog box appears.
2.
In the Volume Control and CD Audio columns, move the Volume sliders up to increase the volume and down to
decrease the volume.
To play an audio CD
1.
Insert the disc into the optical drive. See To insert a CD or DVD.
2.
Select an option in the Audio CD window.
3.
Click OK.
Page 50
Page 51

Copying files to a CD-RW or CD-R1
Before you write data to a CD-RW or CD-R, read the following notes to avoid a computer malfunction and ensure the best
writing results:
Deactivate the screen saver and exit anti-virus software.
Deactivate memory-resident disc utilities to avoid data loss.
Turn off the FindFast application if your computer has preinstalled Microsoft® Office applications, such as Excel, Word,
and Outlook.
Connect and use the AC adapter to power your computer.
Use CD-Rs that are compatible with 8x speed.
Your computer does not support 1x writing speed.
1.
Insert the disc into the optical drive, and open the preinstalled Sony SonicStage software by clicking Start, and
pointing to Programs and SonicStage, then clicking SonicStage from the submenu.
See SonicStage Help for more information on using the program. Click Start, and point to Programs and
SonicStage, then click SonicStage Help from the submenu.
2.
Once you finish copying files to a CD-R that is readable in a CD-ROM drive, click Finish to complete the writing
process before you eject the disc from the optical drive.
Do not strike or shake the computer while writing data to a disc.
1
For computer models equipped with a C D-RW/DV D C ombo Drive.
Page 51
Page 52

Playing DVDs
You can play DVDs in your computer's optical drive and view the video on a TV. The type of optical drive installed in or
connected to your computer may vary, depending on the model you purchased.
Watching DVDs on your computer
Frequently asked questions
Page 52
Page 53

Watching DVDs on your computer
Your computer is equipped with a CD-RW/DVD Combo (optical) drive, which enables you to watch most DVDs from your
computer.
To play a DVD while connected to the AC adapter
1.
Close all open programs.
2.
Insert the DVD into the CD-RW/DVD Combo drive.
3.
Select a preinstalled DVD program in which to play the DVD. The preinstalled DVD program launches the video
automatically. See Software Programs On Your Computer for a description of your preinstalled DVD software. For
detailed instructions on how to use the preinstalled DVD software, see the help guide included with the DVD
software.
To play a DVD while using battery power
1.
Set the power management profile to DVD.
1.
Close all open programs.
2.
Right-click the Battery icon on the Windows® taskbar. See To display the Battery Information window
for an illustration of the icon.
3.
Select Profiles from the shortcut menu, and then select DVD from the submenu. You can also select
Automatic Profile Selection, which sets the power management profile to DVD whenever a DVD is
inserted into the optical drive. See Conserving Battery Power for more information.
2.
Click Start and Shut Down, and select Restart, then click OK on the Shut Down Windows dialog box to restart
the computer.
3.
Insert the DVD into the CD-RW/DVD Combo drive.
4.
Select a preinstalled DVD program in which to play the DVD. The preinstalled DVD program launches the video
automatically. See Software Programs On Your Computer for a description of your preinstalled DVD software. For
detailed instructions on how to use the preinstalled DVD software, see the help guide included with the DVD
software.
Some discs recorded at 20 or 24 bits may produce noise while playing. If you have audio devices
connected, this may damage your hearing and the speakers. Reduce the volume before playing a DVD.
Do not switch the power saving modes while you are playing the DVD.
Do not use memory-resident utility software to speed up disc access. This may cause the computer to malfunction.
Page 53
Page 54

Frequently asked questions
How do I maintain CDs and DVDs?
Avoid touching the surface of the disc with your fingers. Fingerprints and dust on the surface of the disc may cause
reading errors.
To clean the disc, hold the edge of the disc, and use a soft cloth to wipe the surface from the center out. If the disc
is badly soiled, moisten a soft cloth with water, wring it out well, and use it to wipe the surface of the disc from the
center out. Wipe off any remaining moisture with a dry, soft cloth.
Do not clean the disc with solvents (such as benzine, thinner, commercially available cleaners, or anti-static spray),
which may damage the disc.
Do not drop or bend the disc.
Why does my computer freeze when I try to read a disc?
The disc your computer is trying to read may be dirty or damaged. Restart the computer, and eject the disc from the optical
drive. Examine the disc for dirt or damage. If the disc is dirty, see How do I maintain CDs and DVDs? for instructions on how
to clean it.
Why won't the drive tray open?
Make sure the computer is on.
Press the Eject button on the optical drive cover.
If the Eject button does not work, click Start on the Windows® taskbar, and click My Computer. Right click
DVD/CD-RW Drive, and select Eject from the shortcut menu.
If none of the above options work, insert a thin, straight object (such as a paper clip) in the manual eject hole to
the right of the Eject button.
Why isn't the optical drive playing my CD or DVD properly?
Make sure the CD or DVD was inserted into the drive with the label facing up.
Make sure the necessary software program(s) is installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
If the CD or DVD is dirty or damaged, the computer will stop responding. Follow these steps:
1.
Restart the computer by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete, and selecting Restart from the Shut Down menu of
the Windows Security dialog box.
2.
Remove the CD or DVD from the optical drive.
3.
Check the disc for dirt or damage. If you need to clean the disc, see How do I maintain CDs and DVDs?
for instructions.
If you are playing a CD or DVD and cannot hear sound, follow these steps:
1.
Double-click the Volume icon on the Windows taskbar, and click to cancel the Volume Control and CD
Audio Mute check boxes.
2.
Check the volume setting in the audio mixer.
3.
If you are using external speakers, check the volume settings on the speakers and the connections
between the speakers and the computer.
4.
Make sure the CD audio feature is enabled and the correct driver software is installed. Follow these steps:
1.
Click Start on the Windows® taskbar, and point to Setting and Control Panel, then click System.
The System Properties window appears.
2.
Select the Hardware tab, and then click Device Manager. The Device Manager window
appears.
Page 54
Page 55

3.
Double-click the listed DVD/CD-ROM drive. The Properties window appears.
4.
Click the Properties tab, and click to select the Enable digital CD audio for this CD-ROM device
check box, if it is not selected.
5.
Select the Driver tab, and click Driver Details to confirm the driver software.
Make sure an adhesive label was not attached to the CD or DVD. Adhesive labels can come off while the disc is in
the optical drive and damage the drive or cause it to malfunction.
If a region code warning appears, the disc may be incompatible with the optical drive. Check the DVD package to
make sure the region code is compatible with the optical drive.
If you notice condensation on the computer, do not use the computer for at least one hour. Condensation can
cause the computer to malfunction.
Why did the computer (LCD) screen go blank?
Your LCD screen may go blank if the computer has lost power or has entered a power saving mode (Standby or
Hibernate). If the computer is in LCD (Video) Standby mode, press any key to activate the LCD screen. See Using
power saving modes for more information.
Make sure the computer is plugged into a power source and is on. The power indicator on the computer will be on if
the computer is on.
If your computer is using battery power, make sure the battery is inserted properly and is charged. See Using the
Battery for more information.
If the display mode is set to external display, use the Fn+F7 key combination. See Selecting a Display Mode for
more information.
Why don't my changes appear on the computer (LCD) screen?
You may need to refresh the computer screen. Press the Windows key and press D twice.
Page 55
Page 56

Printer Connections
Printing With Your Computer
Page 56
Page 57

Printing With Your Computer
You can connect a universal serial bus (USB) printer or a parallel port printer to your computer. To print properly, the printer
you connect must be compatible with the Microsoft® Windows® operating system installed on your computer.
Connecting a printer
Disconnecting a printer
Frequently asked questions
Page 57
Page 58

Connecting a printer
Your computer is compatible with many popular printers. In many cases, you can simply connect the printer to the computer
and begin printing. Some printers require separate driver software installation. See the instructions that accompanied your
printer for more information. If you cannot print once you have connected your computer to your printer, see Frequently
asked questions in this section for more information.
To connect a USB printer
1.
Locate a USB port on the computer and the printer.
2.
Plug the USB cable into the USB port on your computer.
3.
Plug the other end of the USB cable into the USB port on the printer.
Connecting a USB Printer Cable
See the manual that came with the USB printer for more information on its installation and use.
Page 58
Page 59

Disconnecting a printer
If your computer is turned off, simply unplug the printer cable from your computer's USB port.
To disconnect a printer while the computer is on
1.
Double-click the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon on the taskbar. The Unplug or Eject Hardware window
appears.
2.
Select the printer in the Hardware devices window, if it is not already selected.
3.
Click Stop. The Stop a Hardware device window appears.
4.
Make sure the correct printer is selected, and click OK. A message appears stating it is now safe to remove the
hardware device.
5.
Unplug the printer cable from your computer's USB or Printer port.
Page 59
Page 60

Frequently asked questions
Why can't I print a document?
Make sure the printer is on, and the printer cable is securely connected to the ports on your printer and computer.
See Connecting a printer for more information.
Make sure the printer is compatible with the Microsoft® Windows® operating system installed on your computer.
You may need to install the printer driver software before you use the printer. See the instructions that came with
your printer for information about installing these drivers.
Change the default printer port setting, although this setting is generally correct for most printers.
1.
Click Start, and point to Settings, then click Printers. The Printers window appears.
2.
Right-click the printer, and select Properties from the shortcut menu.
3.
Select the Ports tab, and select a different LPT Port Number.
Page 60
Page 61

Computer Features
Using the Keyboard
Using the Touch Pad
Using Jog Dial Control
Using Memory Stick Media
Changing the Window Design of Sony Programs
Page 61
Page 62

Using the Keyboard
Your keyboard is very similar to a typewriter's, but your computer keyboard has additional keys that perform specific
computer-related tasks.
Key locations and descriptions
Combinations and functions with the Windows key
Indicators
Combinations and functions with the Fn key
Page 62
Page 63

Key locations and descriptions
Keyboard
Key Description
Numeric keypad Contains the keys found on a typical calculator. Use the numeric keypad area to type numbers or to
perform mathematical calculations such as addition and subtraction. Numbers appear on the front beveled edge of the
numeric keys. Press the Num Lock key to activate the numeric keypad. (When you do so, the Num Lock indicator lights up.)
Press the Num Lock key again to deactivate the numeric keypad.
Arrow keys The Left, Right, Up, and Down arrow keys move the pointer on the screen and also function as the Home,
End, Page Up, and Page Down keys, respectively.
Correction keys The Insert, Back Space, and Delete keys enable you to make corrections in your documents.
Function keys The 12 function keys along the top of the keyboard are used to perform designated tasks. For example, in
many programs, F1 is the Help key. The task associated with each function key may vary from one program to the next.
Escape key The Esc (Escape) key is used to cancel commands.
Print Screen key The Print Screen key takes an electronic snapshot of the screen and moves it to the Clipboard. You
can then paste the screen shot into a document and print it.
Operator keys
(Shift, Ctrl, Alt keys) Several keys are always used with at least one other key: Ctrl, Alt, and Shift. When held down with
another key, the Ctrl (Control) and Alt (Alternate) keys offer another way to give commands. For example, in many
programs, instead of choosing the Save command from a menu, you can hold down Ctrl and press S (referred to as Ctrl+S).
The Shift key operates the same way as on a typewriter; it is used to produce capital letters or special symbols such as @
and $.
Windows key
The key with the Windows® operating system logo displays the Start menu; it is the equivalent of clicking
Start on the taskbar. See Combinations and functions with the Windows key for more information.
Fn key The Fn key is used in combination with other keys to issue commands. See Combinations and functions with
the Fn key for more information.
Applications key
The Applications key displays a shortcut menu of context-sensitive choices. Pressing this key is the equivalent
of clicking the right mouse button.
Page 63
Page 64

Combinations and functions with the Windows key
Combination Function
+ F1 Displays the VAIO Help and Support Center window.
+ Tab Switches the selected button on the taskbar.
+ D Displays the desktop.
+ E Displays the My Computer window.
+ F Displays the Search Results window, where you can find a file or folder. This is the equivalent of selecting
Search from the Start menu.
+ Ctrl + F Displays the Search Results - Computers window, where you can locate other computers. This is the
equivalent of selecting Search, and then Computer from the Start menu.
+ M Minimizes all displayed windows.
Shift + + M Returns all minimized windows to their previous size.
+ R Displays the Run window. This is the equivalent of selecting Run from the Start menu.
Fn + + Insert Displays the System Properties window. This is the equivalent of selecting Control Panel, and then
System from the Start menu.
Page 64
Page 65

Indicators
Indicator Function
Power
Lights up when the power to the computer is on, flashes in Standby mode, and turns off when the computer
is in Hibernate mode or off.
Battery
Lights up when the computer is using battery power, blinks when the battery is running out of power,
double-blinks when the battery is charging.
Memory Stick®
Lights up when data is read from or written to the Memory Stick media. (Do not enter Standby mode or turn
off the computer when this indicator is on.) When the indicator is off, the Memory Stick media is not being accessed.
Hard disk
Lights up when data is read from or written to the hard disk. Do not enter Standby mode or shut down the
computer when this indicator is on.
Num Lock
Lights up when the number keys area in the numeric keypad are active. When the indicator is off, the
alphanumeric character keys in the keypad area are active.
Caps Lock
Lights up when the letters appear in uppercase as you type. The Shift key lowers the case of typed letters
when Caps Lock is on. When the indicator is off, the letters appear in lower case as you type (unless you hold down the
Shift key).
Scroll Lock
Lights up when the screen scrolls differently. (Exactly how it scrolls depends on the specific program. This
function does not work with all programs.) When the indicator is off, information moves across the display normally.
Wireless
LAN Lights up when the Wireless LAN function is running.
Page 65
Page 66

Combinations and functions with the Fn key
If you switch user identities during a computing session, the Fn+F7 key functionality (if available on your computer) will
be interrupted. To switch to an external display or monitor, see Selecting a Display Mode for more information.
Combinations/
Feature Function
Fn + (F3)
Mute On/Off Toggles the built-in speaker off and on.
Fn + (F4)
Speaker volume Adjusts the built-in speaker volume. An on-screen display appears notifying you when a change
occurs.
To increase volume, press Fn+F4, then or .
To decrease volume, press Fn+F4, then or .
Fn + (F5)
Brightness control Adjusts the brightness of the LCD.
To increase light intensity, press Fn+F5 and then or .
To decrease light intensity, press Fn+F5 and then or .
Fn + / (F7)
Switch to the external monitor/LCD Toggles between the LCD, a connected external display, and both the LCD and
external display.
Select one display at a time to playback DVDs. Connect the cable before you turn on the computer, otherwise Fn+F7 will not
work.
Fn + (F12)
Hibernate Provides for the lowest level of power consumption. When you run this command, the state of the
system and state of the peripheral devices are written to the hard disk and the system power is turned off. To return the
system to its original state, use the power button to turn on power.
Fn + Esc
Standby Puts the system into Standby mode, a power management state. To return the system to the active
state, press any key or press the power button.
Fn + E Ejects the CD.
Fn + B
Bass Boost Toggles the bass-boost function off and on. This feature is available only while using headphones.
You can also carry out these functions using the Jog Dial Control. Some functions are not available until the Windows
®
operating system launches.
Page 66
Page 67

Using the Touch Pad
The keyboard contains a pointing device called a touch pad. You can point to, select, drag, and scroll objects on the screen
using the built-in touch pad.
Describing the touch pad
Customizing the touch pad
Frequently asked questions
Page 67
Page 68

Describing the touch pad
Locating and describing the touch pad
Action Description
Point Slide one finger on the touch pad to place the pointer on an item or object.
Click Press the left button once.
Double-click Press the left button twice.
Right-click Press the right button once. In many programs, this action displays a shortcut menu of context-sensitive
choices.
Drag Slide one finger while pressing the left button.
Scroll Move your finger along the right edge of the touch pad to scroll vertically. Move your finger along the bottom to
scroll horizontally. (The scroll function is available only with programs that support a touch pad scroll feature.)
Page 68
Page 69

Customizing the touch pad
Sony Notebook Setup lets you customize your touch pad, such as enable or disable the touch pad. You can also open the
Mouse Properties dialog box, which enables you to set your touch pad and mouse preferences, such as changing pointers,
enabling or disabling the tapping feature, clicking both buttons simultaneously, and adjusting the touch pad speed.
To disable the touch pad
1.
Click Start on the Windows® taskbar, and point to Programs.
2.
Point to Sony Notebook Setup, and click Sony Notebook Setup in the submenu. The Sony Notebook Setup
dialog box appears.
3.
Click the Touchpad tab, and select Disable Touchpad.
4.
Click Apply.
5.
Click OK.
To enable the touch pad
1.
Press the Windows key . The Start menu appears.
2.
Press the Up Arrow key to select Programs, and press Enter.
3.
Press the Down Arrow key to select Sony Notebook Setup, and press Enter. A submenu appears.
4.
Press the Down Arrow key to select Sony Notebook Setup again, and press Enter. The Sony Notebook
Setup dialog box appears.
5.
Press the Right Arrow key to select the Touchpad tab.
6.
Press the Tab key to select the Default button, and press Enter. A pop-up window appears.
7.
Press the Left Arrow key to select OK, and press Enter. The Enable Touchpad option is automatically
selected.
8.
Press the Tab key to select the Apply button, and press Enter.
9.
Click OK.
To open the Mouse Properties dialog box
Right-click the Touchpad icon on the Windows® taskbar, and click Mouse Properties from the shortcut menu.
The Mouse Properties dialog box appears.
Page 69
Page 70

Frequently asked questions
Why doesn't the touch pad work?
You may have disabled the touch pad without connecting a mouse to the computer. See To enable the touch pad.
Restart the computer to activate the touch pad again.
If your touch pad is interpreting a single tap as a double-click, adjust the button assignments. Follow these steps:
1.
Press the Windows key . The Start menu appears.
2.
Press the Up Arrow key to select Programs, and press Enter.
3.
Press the Down Arrow key to select Sony Notebook Setup, and press Enter. A submenu appears.
4.
Press the Down Arrow key to select Sony Notebook Setup again, and press Enter. The Sony
Notebook Setup dialog box appears.
5.
Press the Right Arrow key to select the Touchpad tab, and press Alt+S simultaneously. The Mouse
Properties dialog box appears.
6.
Make sure the Buttons tab is open, and press the Up Arrow and Down Arrow keys to change the
button assignments. Press the Tab key to move between shortcut menus.
7.
Press Enter to save your changes and close the dialog box.
If you are still experiencing problems, make sure another mouse was not installed.
You may need to use your Application Recovery CD(s) to reinstall the mouse drivers. See Using the Application
Recovery CD(s) for more information.
Why doesn't the pointer move when I use the touch pad?
Try restarting your computer. Follow these steps:
1.
Press the Windows key .
2.
Press U. The Shut Down Windows dialog box appears.
3.
Press R to restart the computer.
4.
Press Enter.
If the computer does not restart,
1.
Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete simultaneously. The Windows Security dialog box appears.
2.
Press the Right Arrow key to select Shut Down.
3.
Press Enter.
4.
Press R.
5.
Press Enter.
If you still cannot restart your computer, press and hold the power button to shut down the computer.
If the pointer does not move while playing a disc, press Ctrl+Alt+Delete simultaneously to stop playback and
restart the computer.
You may need to use your supplied Application Recovery CD(s) to reinstall the touch pad or mouse drivers. See Using the
Application Recovery CD(s) for more information.
Page 70
Page 71

Using Jog Dial Control
Your computer is equipped with a Jog Dial Control below the keyboard. The Jog Dial Control enables you to open a
program, folder, or document from a predefined list by rotating and pressing the Jog Dial Control.
Using VAIO Action Setup
Locating the Jog Dial Control
Using Launcher mode
Using Guide mode
Using the Jog Dial Control with Sony programs
Using the Jog Dial Control with other programs
Setting the timer
Page 71
Page 72

Using VAIO Action Setup
VAIO Action Setup manages the settings for your computer's Jog Dial control interface and enables you to set a timer to
launch a program or document. For more information on customizing Jog Dial Control or setting the timer, right-click the Jog
Dial Control icon or in the taskbar and click Help Topics.
Page 72
Page 73

Locating the Jog Dial Control
The Jog Dial Control
Page 73
Page 74

Using Launcher mode
The Jog Dial Control window is either in the launcher mode or in the guide mode. The Jog Dial Control window is in launcher
mode until a software program is launched or the Jog Dial Control window becomes active. When an arrow is displayed
next to an item in the Jog Dial Control window, you can display a submenu of that item by selecting it and pressing the Jog
Dial Control. For more information, right-click the Jog Dial Control icon or , and click Help Topics.
To open the Jog Dial Launcher
Press the Jog Dial Control.
Double-click the Jog Dial Control icon on the taskbar.
Press the Jog Dial Control while pressing Ctrl on the keyboard to switch from guide mode to launcher mode.
To use the Jog Dial Control
1.
Turn the Jog Dial Control to select an item, and then press the Jog Dial Control. When you select an item, the
Launcher mode changes to Guide mode.
Jog Dial Launcher
2.
Turn or press the Jog Dial Control to use the desired function.To select another item, switch to Launcher mode by
pressing the Jog Dial Control and the Ctrl key.
Page 74
Page 75

Using Guide mode
The Jog Dial Control window is either in the launcher mode or in the guide mode. Launcher mode changes to Guide mode
when a program is active. Depending on the program, you can select items from the Jog Dial Guide window using the Jog
Dial Control. With some Sony programs, you can change the Jog Dial window to List View, Simple Menu, and Full Menu. For
more information, right-click the Jog Dial Control icon or , and click Help Topics.
Jog Dial Guide Dialog Box
Page 75
Page 76

Using the Jog Dial Control with Sony programs
If Sony programs that support the Jog Dial Control are active, you can use the Jog Dial's functions that are allocated to
that program. For more information, see the program's online Help.
Page 76
Page 77

Using the Jog Dial Control with other programs
If the program you are using does not support the Jog Dial Control, you can still select menu items to perform the following
functions:1
Maximize window
Minimize window
Close window
Scroll window
Scroll the File menu
1
Some programs do not support these func tions.
Page 77
Page 78

Setting the timer
You can use the internal timer to open a program at a specific time. When set, the timer can launch programs even when
the computer is off.
To set the timer
1.
Right-click the Jog Dial Control icon or on the taskbar, and select VAIO Action Setup. The VAIO Action
Setup dialog box appears.
2.
In the left panel, click Timer. The right panel is updated.
3.
Make sure the Timer Setting tab is open, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Page 78
Page 79

Using Memory Stick Media
This compact, portable, and versatile recording medium has a data capacity exceeding that of a floppy disk. The medium is
specially designed for exchanging and sharing digital data with compatible products. Because it is removable, the media can
be used for external data storage.
Selecting Memory Stick media
Inserting Memory Stick media
Viewing the contents
Write-protecting Memory Stick media
Formatting Memory Stick media
Removing Memory Stick media
Frequently asked questions
Page 79
Page 80

Selecting Memory Stick media
The following two types of Memory Stick media can be used with your computer:
MagicGate Memory Stick media (hereafter called MG Memory Stick media), which is provided with copyright
protection
Memory Stick media, which does not have the same copyright protection as MagicGate Memory Stick media
Some music files with secure copyright protection may be stored on MG Memory Stick media but not on regular Memory Stick
media.You can also use MagicGate media-compatible devices to record and playback music when they are connected to
your computer.
You can store mixed data on the Memory Stick media. For example, you can copy an ordinary file on a MG Memory Stick
media that already contains music.
What is MagicGate Memory Stick media?
MagicGate Memory Stick media provides copyright protection that consists of authentication and encryption technology.
Authentication technology ensures that protected content is only transferred between compliant devices and media.
Protected content is recorded and transferred in an encrypted format to prevent unauthorized duplication or playback.
MG Memory Stick media has the MG mark.
Page 80
Page 81

Inserting Memory Stick media
Before using Memory Stick media, back up important data. The media slot accommodates only one Memory Stick media at a
time.
To insert Memory Stick media
1.
Insert the Memory Stick media with the arrow facing up and toward the Memory Stick media slot.
Inserting the media in the wrong direction may damage the connector pins.
2.
Carefully slide the Memory Stick media into the slot until it clicks in place. The Memory Stick media indicator briefly
flashes.
Inserting Memory Stick Media
Page 81
Page 82

Viewing the contents
Depending on the model you purchased, the Sony Memory Stick window appears automatically when you insert a Memory
Stick media. From this window, you can choose to view, print, copy or organize your Memory Stick images or data. If the
Sony Memory Stick window does not appear when you insert your Memory Stick media, then follow these steps.
To view the contents
1.
Click My Computer on the desktop. The My Computer window appears.
2.
Double-click Removable Disk. The Removable Disk window appears, displaying the contents stored on the
Memory Stick media.
Page 82
Page 83

Write-protecting Memory Stick media
Memory Stick® media is designed with a write-protect tab to protect data from accidental erasure or overwriting. Move the
tab to the right or left to set or release write-protection. When the write-protect tab of the Memory Stick media is set to
LOCK, data cannot be recorded or erased.
Write-protect off Data can be saved on the Memory Stick media.
Write-protect on Data can be read from but not saved on the Memory Stick media.
Using the Write-Protect Tab
Page 83
Page 84

Formatting Memory Stick media
Memory Stick® media is formatted for immediate use when you purchase it. If you need to reformat Memory Stick media, use
the Memory Stick Formatter that is provided with the media. For more information about using Memory Stick Formatter, refer
to Formatter Help.
Formatting Memory Stick media erases all data, including music data, previously saved to it. Before you
reformat Memory Stick media, confirm that the media does not contain files you want to keep and back up important
data.
To format Memory Stick media
1.
Insert the Memory Stick media into the Memory Stick media slot. See Inserting Memory Stick media for more
information.
2.
From the Start menu, point to Programs, Memory Stick Utility, and then click Memory Stick Formatter. The
Memory Stick Formatter dialog box appears.
3.
Click to select the Memory Stick media drive, if it is not already selected.
4.
Click Start Format.
Page 84
Page 85

Removing Memory Stick media
If the media is removed prematurely, a blue screen with an error message appears prompting you to continue or exit.
Reinsert the media into the slot and press Enter to continue. This enables the media to finish reading or writing data.
To remove Memory Stick media
1.
Wait a minimum of 10 seconds after the Memory Stick media finishes reading or writing data before removing the
media.
2.
Make sure the access light is off.
3.
Push the Memory Stick media in toward the computer.
4.
When the Memory Stick media ejects, pull it out.
Be careful when removing the Memory Stick media, as it may eject completely from the slot.
Page 85
Page 86

Frequently asked questions
Why can't I open my image files?
You may need to reformat your Memory Stick media.
Formatting Memory Stick media erases all data, including music data, previously saved to it. Before you
reformat Memory Stick media, confirm that the media does not contain files you want to keep and back up important
data.
1.
Copy the data from the Memory Stick media onto your computer's hard disk to save data or images.
2.
Format the Memory Stick media using Memory Stick Formatter software preinstalled on your computer. For
instructions about formatting a Memory Stick media, see Formatting Memory Stick media.
Why can't I save music files onto my Memory Stick media?
Only MagicGate Memory Stick media can be used with copyright protected data, such as music.
Copyright protected music cannot be checked out to any Memory Stick media other than MG Memory Stick media.
Recorded music is limited to private use only. Using recorded music for any other purpose requires permission of the
copyright holders.
Sony is not responsible for music files that cannot be recorded from a CD or downloaded from other sources.
Can I copy images from a digital video camera using Memory Stick media?
Yes, and you can view video clips that you have recorded with Memory Stick media-compatible video camera recorders.
How do I prevent damage to the Memory Stick media?
Do not use the media in locations that are subject to static electricity or electrical noise.
Do not touch the media connector with your finger or metallic objects.
Do not attach labels other than the supplied label to a media.
Do not bend, drop, or apply strong shock to the media.
Do not disassemble or modify the media.
Do not allow the media to get wet.
How do I extend the life of the Memory Stick media?
Use the supplied storage case. See the instructions that came with your media for more information on its use.
Do not use or store the media in a location that is subject to:
Extremely high temperatures, such as in a car parked in the sun
Direct sunlight
High humidity or places with corrosive substances
Page 86
Page 87

Changing the Window Design of Sony Programs
This feature is available with UI Design Selector-compatible programs only.
To change the window design
1.
Click Start, and point to Settings, Control Panel, and click UI Design Selector.
2.
Click << or >> to view the designs.
3.
To select a design that appears in the center window, click Apply. The UI Design Selector window design
changes. The window design for your Sony software will match the UI Design Selector window.
4.
Click OK.
Page 87
Page 88

Connecting Mice and Keyboards
Using External Mice and Keyboards
Page 88
Page 89

Using External Mice and Keyboards
You can connect a universal serial bus (USB) mouse or keyboard to your computer. To function properly, the device you
connect must be compatible with the Microsoft® Windows® operating system installed on your computer. For information
about your computer's built-in keyboard and key functions, see Using the Keyboard in the Computer Features chapter.
Connecting a mouse or keyboard
Disconnecting a mouse or keyboard
Frequently asked questions
Page 89
Page 90

Connecting a mouse or keyboard
Your computer is compatible with many popular mice and keyboards. The New Hardware Wizard guides you through the
software installation process. Some devices require separate driver software installation. See the instructions that
accompanied your mouse or keyboard for more information. If the mouse or keyboard does not work once you have
connected it to your computer, see Frequently asked questions for more information.
Your computer can be on or off when connecting a mouse or keyboard.
To connect a USB mouse or keyboard to your computer
1.
Locate the USB port on your computer, port replicator, or docking station.
2.
Plug the USB cable into the USB port on the computer. (One USB port supports one USB device.) The New
Hardware Wizard appears.
3.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
Connecting a USB Mouse or Keyboard
See the manual that came with your mouse or keyboard for more information on its installation and use.
Page 90
Page 91

Disconnecting a mouse or keyboard
You can disconnect a USB mouse or keyboard when the computer is on or off. Disconnecting the USB mouse or keyboard
when the computer is in a power saving mode (Standby or Hibernate) may cause the computer to malfunction.
To disconnect the USB mouse or keyboard when the computer is off
Unplug the USB cable from the USB port on the computer.
Press and hold the power button. When the computer shuts down, press the power button again to restart the
computer.
To disconnect the USB mouse or keyboard when the computer is on
1.
Double-click the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon on the taskbar. The Unplug or Eject Hardware window
appears.
2.
Select the appropriate USB device in the Hardware devices window, if it is not already selected.
3.
Click Stop. The Stop a Hardware device window appears.
4.
Make sure the USB device is selected, and click OK. A message appears stating it is now safe to remove the
hardware device.
5.
Unplug the USB cable from the USB port on the computer.
Page 91
Page 92

Frequently asked questions
Why doesn't the computer recognize the USB mouse?
Make sure the mouse is securely plugged into the USB port. See Connecting a mouse or keyboard for more
information.
You may need to install or reinstall the mouse driver software. Use the supplied Application Recovery CD to install
the drivers. See Using the Application Recovery CD(s) for more information.
Why doesn't the pointer move when I use the USB mouse?
Make sure another mouse was not installed.
You may need to install or reinstall the mouse driver software. Use the supplied Application Recovery CD(s). See
Using the Application Recovery CD(s) for more information.
If you are playing a disc, press the Ctrl+Alt+Delete keys simultaneously to stop playback and restart the computer.
If you still cannot use the pointer, restart the computer. You can restart the computer three different ways:
Press the Windows key , and press U. When the Shut Down Windows window appears, press R to
select Restart, and press Enter.
Press the Ctrl+Alt+Delete keys simultaneously. When the Windows Security window appears, press the
Right Arrow key to select Shut Down, and then press Enter. Use the Down Arrow key to select
Restart, and press Enter.
Press and hold the power button. When the computer shuts down, press the power button again to restart
the computer.
Page 92
Page 93

Floppy Disk Drives and PC Cards
Using Floppy Disk Drives
Using PC Cards
Page 93
Page 94

Using Floppy Disk Drives
You can connect a floppy disk drive to your computer, port replicator, or docking station. The floppy disk drive enables you
to read data stored on a floppy disk.
Connecting a floppy disk drive
Inserting and removing floppy disks
Disconnecting a floppy disk drive
Carrying the floppy disk drive
Frequently asked questions
Page 94
Page 95

Connecting a floppy disk drive
You can connect a floppy disk drive when your computer is on or off. Connecting the drive when the computer is in a power
saving mode (Standby or Hibernate) may cause the computer to malfunction.
To connect a floppy disk drive
1.
Close any active programs to prevent data loss.
2.
Insert the USB connector (with the USB icon facing upward) into the USB port .
Connecting a Floppy Disk Drive
Page 95
Page 96

Inserting and removing floppy disks
Floppy disks are portable devices that store data. To protect your floppy disks, keep them away from magnets and direct
sunlight or other heat sources.
To insert a floppy disk
1.
Hold the floppy disk with the label facing up.
2.
Push the floppy disk into the drive until it clicks into place.
Inserting a Floppy Disk
Do not open the shutter manually and touch the surface of the floppy disk.
To remove a floppy disk
1.
Close all programs that were opened from the disk and wait for the LED indicator to turn off.
2.
Push the Eject button, and remove the disk.
To avoid losing data, do not push the Eject button when the LED indicator is on.
Remov ing a Floppy Disk
Page 96
Page 97

Disconnecting a floppy disk drive
You can disconnect a floppy disk drive when the computer is on or off. Disconnecting the drive when the computer is in a
power saving mode (Standby or Hibernate) may cause the computer to malfunction.
To disconnect a floppy disk drive
1.
Close any active programs to help prevent data loss.
2.
Double-click the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon on the taskbar. The Unplug or Eject Hardware window
appears.
3.
Select the floppy disk drive in the Hardware devices window, if it is not already selected.
4.
Click Stop. The Stop a Hardware device window appears.
5.
Make sure the appropriate device is selected, and click OK. A message appears stating it is safe to remove the
hardware device.
6.
Unplug the floppy disk drive from the USB port on the computer, port replicator, or docking station.
Page 97
Page 98

Carrying the floppy disk drive
Fold the floppy disk drive cable and connector into the side compartment on the floppy disk drive.
Carrying a Floppy Disk Drive
Page 98
Page 99

Frequently asked questions
Why doesn't the Unplug or Eject Hardware icon appear on the taskbar when the drive is connected?
The computer does not recognize that the floppy disk drive is connected to the computer. First, make sure the USB
connector is properly inserted into the USB port . If you need to secure the connection, wait a few moments for the
computer to recognize the drive. If the icon still does not appear, follow these steps:
1.
Close all programs that were opened from the disk and wait for the LED indicator to turn off.
2.
Push the Eject button, and remove the disk.
3.
Reconnect the floppy disk drive by inserting the USB connector (with the USB icon facing upward) into the USB
port .
4.
Restart the computer by clicking Start on the Windows® taskbar, and Turn Off Computer, then Restart.
Why is the drive unable to write data to a floppy disk?
The floppy disk drive cannot write data to a disk if it is inserted into the drive improperly. See Inserting and removing floppy
disks for instructions on how to insert the disk properly.
If the disk is inserted properly and you are still unable to write data to it, the disk may be write-protected. You can either
use a floppy disk that is not write-protected or disable the write-protect feature.
Page 99
Page 100

Using PC Cards
Your computer includes one or more PC Card slots. A PC Card enables you to connect portable external devices, such as
another hard disk drive or a PC Network Interface Card (NIC), to connect to a network.
See your VAIO® Computer Specifications for the type of PC Card that is compatible with your computer. These slots are
compatible with CardBus. If your computer has more than one PC Card slot, use the lower slot for Type III PC Cards. You do
not need to turn off your computer to insert or remove a PC Card.
Inserting PC Cards
Removing PC Cards
Connecting and disconnecting PC Card drives
Frequently asked questions
Page 100
 Loading...
Loading...