Page 1

Network Camera
3-869-482-13 (1)
User’s Guide
Software Version 1.2
SNC-P1
© 2005 Sony Corporation
Page 2

Table of Contents
Overview
Features .................................................................. 4
Phenomena Specific CCD Image Sensors ........... 5
How to Use This User’s Guide .............................. 6
System Requirements ............................................ 6
Preparation
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera ............ 7
Assigning an IP address using the IP Setup
Program ............................................................ 7
When using Windows XP Service Pack 2 .......... 9
When using Windows Vista ............................. 11
Accessing the Camera Using the Web Browser 13
Basic Configuration by the Administrator ....... 15
Operating the Camera
Administrator and User ..................................... 16
Logging in to Homepage — Welcome Page ...... 17
Logging in as a User ........................................ 17
Displaying the setting window for the
administrator directly ..................................... 17
About Viewers .................................................. 18
Configuration of Main Viewer ........................... 19
Main menu ....................................................... 19
Camera Control Section ................................... 19
Monitor Image .................................................. 20
Controlling the Monitor Image .......................... 20
Monitoring the camera image .......................... 20
Zooming in the monitor image ......................... 21
Capturing a Monitor Image ............................... 21
Capturing a monitor image .............................. 21
Saving the captured image ............................... 22
Sending an Image File ......................................... 22
Sending a Monitor Image via e-Mail ............... 22
Sending a Monitor Image to an FTP Server ..... 22
Recording a Still Image in the Built-in Memory of
the Camera ........................................................... 23
Controlling Alarm output ................................... 23
Switching TCP/UDP Transmission Mode ......... 24
Administrating the Camera
Basic Operations of Easy mode ..........................25
How to set Easy mode ......................................25
Setting Options of Easy mode ..........................26
Easy mode (e-Mail) ..........................................27
Basic Operations of Advanced mode Menu ......28
How to set Advanced mode ..............................28
Configuration of Advanced mode Menu ..........29
Configuring the System — System setting menu
................................................................................31
System Tab ........................................................31
Date & time Tab ................................................31
Initialize Tab .....................................................32
System log Tab .................................................33
Access log tab ...................................................33
Setting the Camera Image and Audio
— Camera setting Menu .....................................34
Common Tab ....................................................34
Picture Tab ........................................................35
MPEG4 Tab ......................................................36
JPEG Tab ..........................................................37
Reset Tab ..........................................................37
Configuring the Network — Network setting
Menu .....................................................................38
Network Tab .....................................................38
PPPoE Tab - Setting of PPPoE Connection ......39
Dynamic IP address notification Tab — Notifying
the IP Address .................................................39
Setting the User — User setting Menu ...............41
Setting the Security
— Security setting Menu .....................................42
Sending an Image via mail — e-Mail (SMTP)
setting Menu .........................................................43
Common Tab — Setting the e-Mail (SMTP)
Function ..........................................................43
Alarm sending Tab — Setting the mail sending
mode when detecting the alarm ......................44
Periodical sending Tab — Setting the periodical
mail sending mode ..........................................45
Sending Images to FTP Server
— FTP client setting Menu .................................46
Common Tab — Setting the FTP Client Function
.........................................................................46
Alarm sending Tab — Setting the FTP client
action when detecting the alarm .....................47
Periodical sending Tab — Setting the Periodical
FTP Client Activity ........................................48
Recording Images in Memory
— Image memory setting Menu .........................49
Common Tab — Setting the Image memory
Function ..........................................................49
Alarm recording Tab — Setting the Image
Memory Function when Detecting the Alarm 50
Periodical recording Tab — Setting the Periodical
recording mode ...............................................51
2
Table of Contents
Page 3

Folder structure of image memory ...................51
Downloading Images from the Camera
— FTP server setting Menu ................................ 52
Setting the Alarm Output
— Alarm output setting Menu ........................... 53
Setting the Operations from the Viewer Page
— Trigger setting Menu ......................................54
Setting the Schedule
— Schedule setting Menu ................................... 55
Setting the Alarm Buffer — Alarm buffer setting
Menu ..................................................................... 56
Setting the Motion Detection Function
— Motion detection setting Menu ...................... 57
Setting the Motion Detection Area, Sensitivity and
Threshold level ............................................... 57
Using DDNS Service
— DDNS Setting Menu . 59
Others
Using the Supplied Setup Program .................... 63
Starting the Setup Program .............................. 63
Bandwidth Control Tab .................................... 63
Date time Tab ................................................... 64
PPPoE Tab ........................................................ 64
Rebooting the Camera ...................................... 65
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting
Audio to Camera .................................................. 65
Installing the SNC audio upload tool ............... 65
Connecting the Camera to the Computer ......... 66
Using the SNC audio upload tool .....................66
Using the SNC video player — Playing Video/
Audio File Recorded on Camera ........................ 71
Downloading the SNC video player ................. 71
Using the SNC video player ............................. 71
Using the Custom Homepage Installer .............. 72
Uploading the homepage to the camera using the
Custom Homepage Installer ........................... 72
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera Using
ARP Commands .................................................. 74
Using the SNMP ...................................................75
1. Inquiry Commands ...................................... 75
2. Setting Commands ...................................... 75
Glossary ................................................................ 77
Index ..................................................................... 79
Table of Contents
3
Page 4

Overview
Features
Overview
• You should keep in mind that the images or audio
you are monitoring may be protected by privacy and
other legal rights, and the responsibility for making
sure you are complying with applicable laws is yours
alone.
• Access to the images and audio is protected only by
a user name and the password you set up. No further
authentication is provided nor should you presume
that any other protective filtering is done by the
service. Since the service is Internet-based, there is a
risk that the image or audio you are monitoring can
be viewed or used by a third-party via the network.
• SONY IS NOT RESPONSIBLE, AND ASSUMES
ABSOLUTELY NO LIABILITY TO YOU OR
ANYONE ELSE, FOR SERVICE
INTERRUPTIONS OR DISCONTINUATIONS OR
EVEN SERVICE CANCELLATION. THE
SERVICE IS PROVIDED AS-IS, AND SONY
DISCLAIMS AND EXCLUDES ALL
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH
RESPECT TO THE SERVICE INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, ANY OR ALL IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR
THAT IT WILL OPERATE ERROR-FREE OR
CONTINUOUSLY.
• Always make a test recording, and verify that it was
recorded successfully. SONY WILL NOT BE
LIABLE FOR DAMAGES OF ANY KIND
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
COMPENSATION OR REIMBURSEMENT ON
ACCOUNT OF FAILURE OF THIS UNIT OR ITS
RECORDING MEDIA, EXTERNAL STORAGE
SYSTEMS OR ANY OTHER MEDIA OR
STORAGE SYSTEMS TO RECORD CONTENT
OF ANY TYPE.
• Always verify that the unit is operating properly
before use. SONY WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR
DAMAGES OF ANY KIND INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, COMPENSATION OR
REIMBURSEMENT ON ACCOUNT OF THE
LOSS OF PRESENT OR PROSPECTIVE
PROFITS DUE TO FAILURE OF THIS UNIT,
EITHER DURING THE WARRANTY PERIOD
OR AFTER EXPIRATION OF THE WARRANTY,
OR FOR ANY OTHER REASON WHATSOEVER.
• If you lose data by using this unit, SONY accepts no
responsibility for restoration of the data.
The SNC-P1 is a network camera equipped with a builtin Web server.
The camera has the following features:
Monitoring using the Web browser
Real-time monitoring of the image and sound from the
camera is possible using the Web browser on the
computer.
MPEG4 video compression
MPEG4 video compression allows a smooth streaming
of motion pictures with 30 fps (QVGA size). Motion
JPEG video streaming is also possible by selecting the
JPEG video compression format.
Offering video streaming in VGA size
The 1/4 type CCD supporting VGA offers high-quality
video streaming in VGA size. (The frame rate in VGA
size is less than 30 fps.)
Built-in microphone
A microphone (monaural) is built in the camera. Also,
the built-in microphone jack (minijack, monaural)
accepts a commercially available plug-in-power
microphone (rated voltage: 2.0V DC).
External speaker system can be
connected
The line output jack (minijack, monaural) allows
connection of a commercially available speaker system
with the built-in amplifier so that the sound transmitted
via the network can be output from the connected
speaker system.
Sending the image and controlling
peripheral devices by synchronizing with
the alarm
The camera is equipped with the motion detection
function (in MPEG4 mode), a sensor input terminal and
an alarm output terminal. You can send images from the
camera as an E-mail attachment or to an FTP server by
synchronizing with motion detection or external sensor
input, or control peripheral devices connected to the
alarm output terminal.
Image flip function
The image flip function allows rotation of images from
the camera by 180 degrees according to the installation
location of the camera.
4
Features
Page 5
Supplied IP Setup Program
The camera is supplied with the IP Setup Program for
easy performance of the network setting.
NOTICE TO USERS
© 2005 Sony Corporation. All rights reserved. This
manual or the software described herein, in whole or in
part, may not be reproduced, translated or reduced to
any machine readable form without prior written
approval from Sony Corporation.
SONY CORPORATION PROVIDES NO
WARRANTY WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL,
THE SOFTWARE OR OTHER INFORMATION
CONTAINED HEREIN AND HEREBY EXPRESSLY
DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY
PARTICULAR PURPOSE WITH REGARD TO THIS
MANUAL, THE SOFTWARE OR SUCH OTHER
INFORMATION. IN NO EVENT SHALL SONY
CORPORATION BE LIABLE FOR ANY
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL
DAMAGES, WHETHER BASED ON TORT,
CONTRACT, OR OTHERWISE, ARISING OUT OF
OR IN CONNECTION WITH THIS MANUAL, THE
SOFTWARE OR OTHER INFORMATION
CONTAINED HEREIN OR THE USE THEREOF.
Phenomena Specific CCD Image Sensors
The following phenomena that may appear in images are
specific to CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image
sensors. They do not indicate malfunctions.
White flecks
Although the CCD image sensors are produced with
high-precision technologies, fine white flecks may be
generated on the screen in rare cases, caused by cosmic
rays, etc.
This is related to the principle of CCD image sensors
and is not a malfunction.
The white flecks especially tend to be seen in the
following cases:
• when operating at a high environmental temperature
• when you have raised the gain (sensitivity)
• when using the slow shutter
Vertical smear
When an extremely bright object, such as a strong
spotlight or flashlight, is being shot, vertical tails may be
produced on the screen, or the image may be distorted.
Overview
Sony Corporation reserves the right to make any
modification to this manual or the information contained
herein at any time without notice.
The software described herein may also be governed by
the terms of a separate user license agreement.
• “IPELA” and are trademarks of Sony
Corporation.
• Microsoft, Windows, Internet Explorer and MS-DOS
are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in
the United States and/or other countries.
• Java is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the
United States and other countries.
• Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and
other countries.
• Adobe, Acrobat and Adobe Reader are trademarks of
Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/
or other countries.
All other company and product names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of the respective companies or
their respective makers.
Monitor screen
Vertical thin tails shown on
the image
Bright object (e.g. strong
spotlight, strong reflected
light, flashlight, the sun)
Aliasing
When fine patterns, stripes, or lines are shot, they may
appear jagged or flicker.
Phenomena Specific CCD Image Sensors
5
Page 6

How to Use This User’s
System Requirements
Overview
Guide
This User’s Guide explains how to operate the SNC-P1
Network Camera from a computer.
The User’s Guide is written to be read on the computer
display.
As this section gives tips on using the User’s Guide, read
it before you operate the camera.
Jumping to the related page
When you read the User’s Guide on the computer
display, click on the sentence to jump to the related page.
Software display examples
Note that the displays shown in the User’s Guide are
explanatory examples. Some displays may be different
from the ones which appear as you operate the
application software.
Printing the User’s Guide
Depending on your system, certain displays or
illustrations in the User’s Guide, when printed out, may
differ from those as portrayed on your screen.
These are the requirements for the computer that
displays the image or controls the camera.
Processor
Intel Pentium III 1 GHz or higher (Intel Pentium IV, 2
GHz or higher recommended)
RAM
256 MB or more
OS
Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista
Web browser
Microsoft Internet Explorer Ver. 6.0 or later
Installation Manual (printed matter)
The supplied Installation Manual describes the names
and functions of parts and controls of the Network
Camera, connecting examples and how to set up the
camera. Be sure to read the Installation Manual before
operating.
6
How to Use This User’s Guide / System Requirements
Page 7

Preparation
Assigning an IP address using the IP Setup Program
The Preparation section explains what the administrator
has to prepare for monitoring the images after
installation and connection of the camera.
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
To connect the camera to a network, you need to assign
a new IP address to the camera when installing the
camera for the first time.
You can assign an IP address in two ways:
• Using the setup program stored in the supplied CDROM (see page 7)
• Using the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
commands (see page 74)
This section explains how to assign an IP address to the
camera using the supplied setup program and how to
configure the network.
Before starting, connect the camera, referring to
“Connections” in the supplied Installation Manual.
Consult the administrator of the network about the
assigned IP address.
Note
1
Insert the CD-ROM in your CD-ROM drive.
A cover page appears automatically in your Web
browser.
If it does not appear automatically in the Web
browser, double-click on the index.htm file on the
CD-ROM.
When you are using Windows Vista, pop-up
“AutoPlay” may appear. For details, “Installing
software” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 11.
2
Click the Setup icon of IP Setup Program.
The “File Download” dialog opens.
When you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, a message regarding the active
contents may appear. For details, see “Installing
software” in “When using Windows XP Service
Pack 2” on page 9 or “Installing software” in
“When using Windows Vista” on page 11.
3
Click Open.
Note
If you click “Save this program to disk” on the “File
Download” dialog, you will not be able to perform
set up correctly. Delete the downloaded file, and
click the Setup icon again.
Preparation
• The IP Setup Program may not operate correctly if you
use a personal firewall or antivirus software in your
computer. In that case, disable the software or assign
an IP address to the camera using another method. For
example, see “Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
Using ARP Commands” on page 74.
• If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, disable the Windows Firewall
function. Otherwise the IP Setup Program will not
operate correctly. For the setting, see “Configuring
Windows Firewall” in “When using Windows XP
Service Pack 2” on page 10 or “Configuring Windows
Firewall” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 12.
4
Install the IP Setup Program on your computer
using the wizard.
If the Software License Agreement is displayed,
read it carefully and click Accept to continue with
the installation.
5
Start the IP Setup Program.
When you are using Windows Vista, message “User
Account Control – An unidentified program wants
access to your computer” may appear. In this case,
click Allow.
The program detects the network cameras
connected to the local network and lists them on the
Network tab window.
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
7
Page 8
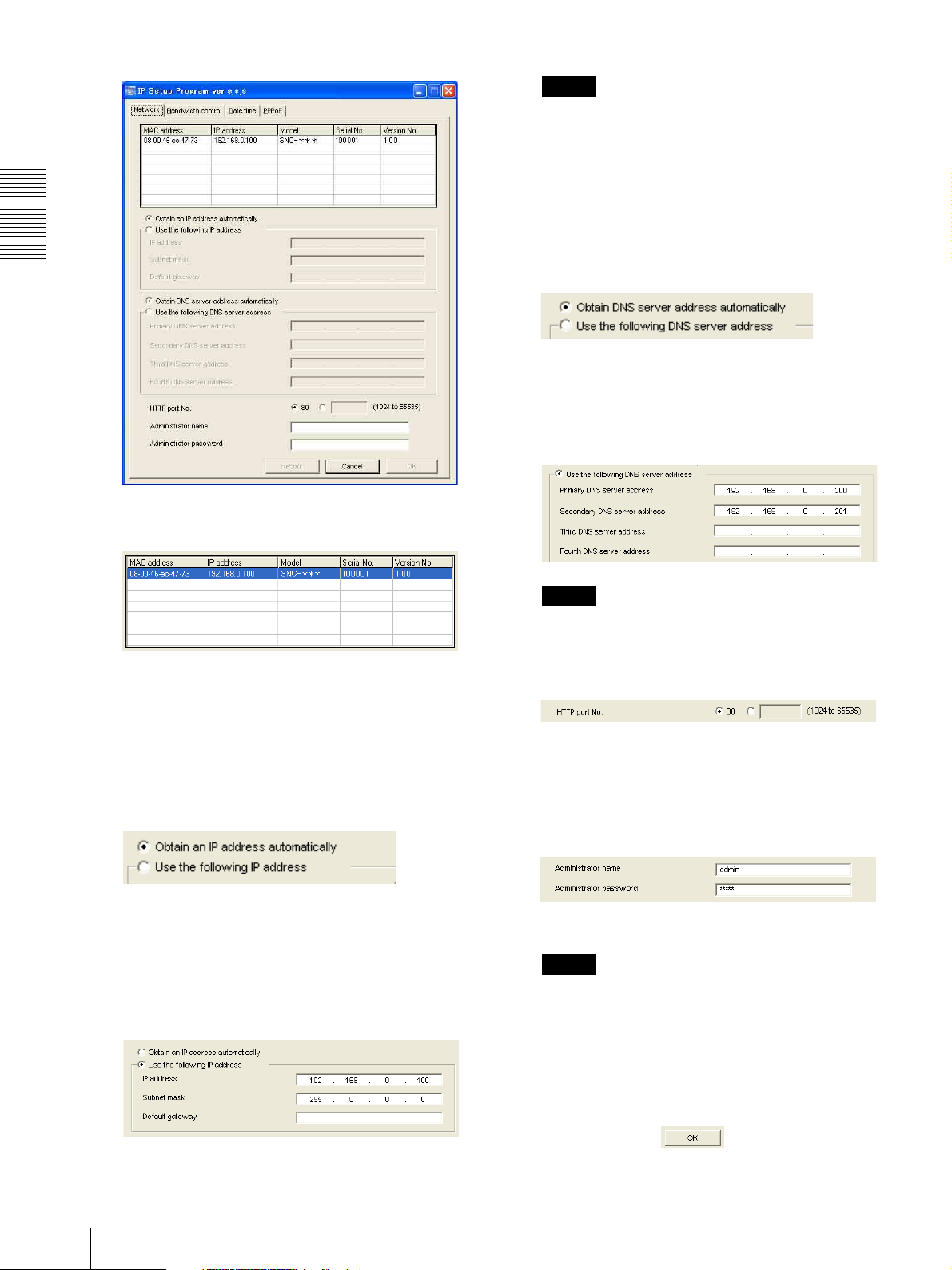
Preparation
6
Click on the camera in the list to which you want to
assign a new IP address.
Note
When you select Obtain an IP address
automatically, make sure that the DHCP server is
operating on the network.
8
Set the DNS server address.
To obtain the DNS server addresses
automatically:
Select Obtain DNS server address automatically.
To specify the DNS server addresses manually:
Select Use the following DNS server address, and
type the Primary DNS server address and
Secondary DNS server address in the relevant
boxes.
The network settings for the selected camera are
displayed.
7
Set the IP address.
To obtain the IP address automatically from a
DHCP server:
Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
The IP address, Subnet mask and Default gateway
are assigned automatically.
To specify the IP address manually:
Select Use the following IP address, and type the
IP address, Subnet mask and Default gateway in the
relevant boxes.
Note
The Third DNS server address and Fourth DNS
server address are invalid for this camera.
9
Set the HTTP port No.
Normally, select 80 for the HTTP port No. To use
another port number, type the port number between
1024 and 65535 in the text box.
10
Type the Administrator name and Administrator
password.
The factory settings of both items are “admin.”
Note
You cannot change the Administrator name and
Administrator password in this step. To change
these items, see “Setting the User — User setting
Menu” on page 41.
8
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
11
Confirm that all items are correctly set, then click
OK.
Page 9
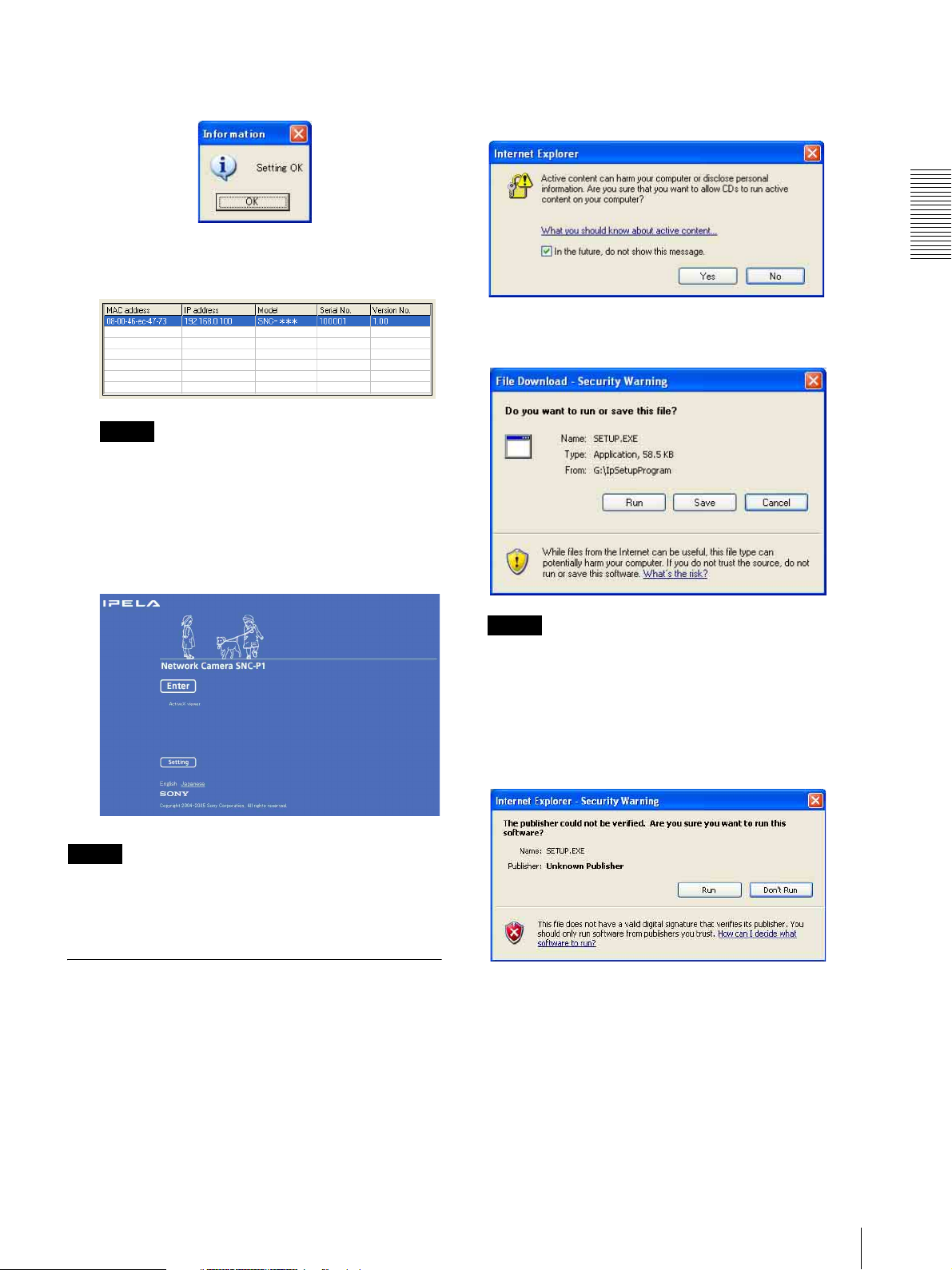
If “Setting OK” is displayed, the IP address is
correctly assigned.
12
To access the camera directly, double-click the
camera name in the list.
Tip
The factory setting of the camera network is as
follows.
IP address: 192.168.0.100
Subnet mask: 255.0.0.0
Example: In case of IP Setup Program
If message “Internet Explorer” appears, click Ye s.
Preparation
If message “File Download – Security Warning”
appears, click Run.
The welcome page of the network camera is displayed in
the Web browser.
Note
If the IP address is not set correctly, the welcome page
does not appear after step 12. In this case, try to set the
IP address again.
When using Windows XP Service Pack 2
Installing software
A warning message regarding the active contents may
appear when you install software such as IP Setup
Program from CD-ROM. In this case, operate as
follows:
Note
If you select Save in the “File Download – Security
Warning” dialog, you will not be able to perform
installation correctly. Delete the downloaded file, and
click the Setup icon again.
If message “Internet Explorer – Security Warning”
appears, click Run.
The software installation starts.
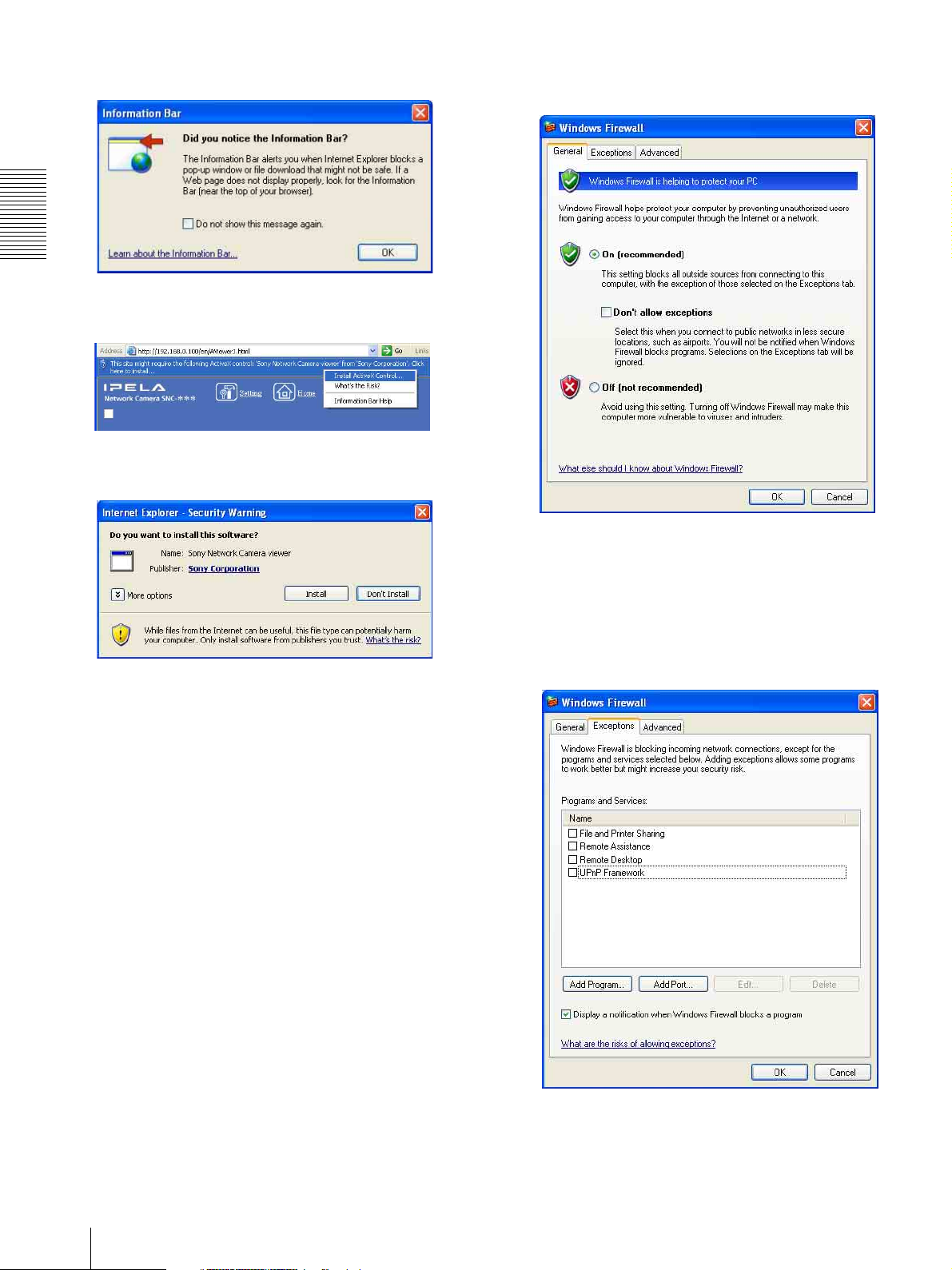
Installing ActiveX Control
During installation of ActiveX Control, the information
bar or “Security Warning” may appear. In this case,
operate as follows:
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
9
Page 10
Preparation
If message “Information Bar” appears, click OK.
If the information bar appears, click on the bar and select
Install ActiveX Control….
If “ Internet Explorer – Security Warning” appears, click
Install.
3
Select Windows Firewall and select Off in the
Windows Firewall dialog.
The cameras will be displayed in the list.
The installation of ActiveX Control starts. When
installation is completed, the main viewer or the Motion
detection setting menu appears.
Configuring Windows Firewall
The IP Setup Program or SNC audio upload tool may
not operate correctly depending on the configuration of
Windows Firewall. (No cameras are shown in the list
even if they are detected.) In this case, confirm the
Windows Firewall configuration as follows:
Example: In case of IP Setup Program
1
Select Control Panel from the Start menu of
Windows.
2
Select Security Center of the working field.
If you want to keep Windows Firewall On, continue
with the following steps.
4
Select the “Exceptions” tab.
5
Select Add Program….
10
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
Page 11
6
In the Add Program dialog, select IP Setup
Program and click OK.
Then the IP Setup Program is added to the
Programs and Services list.
7
Click OK.
If pop-up “AutoPlay” appears when a CD-ROM is
inserted into the CD-ROM drive, click Install or run
program.
Preparation
Note
If you click Open folder to view files, Web browser will
not open automatically. In this case, double-click the
“index.htm” file in the CD-ROM.
When the above procedure is completed, the
cameras connected in the local network are
displayed in the IP Setup Program.
When using Windows Vista
Installing software
A warning message regarding the active contents may
appear when you install software such as IP Setup
Program from CD-ROM. In this case, operate as
follows:
Example: In case of IP Setup Program
If message “Internet Explorer” appears, click Ye s.
If message “File Download – Security Warning”
appears, click Run.
Note
If you select Save in the “File Download – Security
Warning” dialog, you will not be able to perform
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
11
Page 12
Preparation
installation correctly. Delete the downloaded file, and
click the Setup icon again.
If message “Internet Explorer – Security Warning”
appears, click Run.
If “Internet Explorer – Security Warning” appears, click
Install.
The installation of ActiveX Control starts. When
installation is completed, the main viewer or the Motion
detection setting menu appears.
If message “User Account Control – An unidentified
program wants access to your computer” appear, click
Allow.
The software installation starts.
Starting the software
When you start software such as IP Setup Program,
message “User Account Control – An unidentified
program wants access to your computer” may appear. In
this case, click Allow.
Installing ActiveX Control
During installation of ActiveX Control, the information
bar or “Security Warning” may appear. In this case,
operate as follows:
If message “Information Bar” appears, click OK.
Configuring Windows Firewall
The IP Setup Program or SNC audio upload tool may
not operate correctly depending on the configuration of
Windows Firewall. (No cameras are shown in the list
even if they are detected.) In this case, confirm the
Windows Firewall configuration as follows:
Example: In case of IP Setup Program
1
Select Control Panel from the Start menu of
Windows.
2
Click Windows Firewall.
3
Select Turn Windows Firewall on or off.
“User Account Control – Windows needs your
permission to continue” may appear. In this case,
click Continue.
4
Select Off in the “General” tab.
If the information bar appears, click on the bar and select
Install ActiveX Control….
If message “User Account Control – Windows needs
your permission to continue” appear, click Continue.
12
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
Page 13
The cameras will be displayed in the list.
If you want to keep Windows Firewall On, continue
with the following steps.
5
Select the “Exceptions” tab.
6
Select Add Program….
7
If the Add Program dialog appears, select IP Setup
Program and click OK.
Accessing the Camera Using the Web Browser
When the IP address has been assigned to the camera,
check that you can actually access the camera using the
Web browser installed in your computer.
Use Internet Explorer as the Web browser.
1
Start the Web browser on the computer and type the
IP address of the camera in the URL box.
The welcome page of the network camera is
displayed in the Web browser.
Preparation
Then the IP Setup Program is added to the Program
or port list.
8
Click OK.
2
Click Enter.
The main viewer is displayed.
When the main viewer is correctly displayed, the IP
address assignment is completed.
When the above procedure is completed, the
cameras connected in the local network are
displayed in the IP Setup Program.
Accessing the Camera Using the Web Browser
13
Page 14
Preparation
When the main viewer of the camera is
displayed for the first time
When you click Enter, “Security Warning” is displayed.
When you click Ye s, ActiveX control is installed and the
main viewer is displayed.
Notes
• If Automatic configuration is enabled in the Local
Area Network (LAN) Settings of Internet Explorer,
the image may not be displayed. In that case, disable
Automatic configuration and set the Proxy server
manually. For the setting of the Proxy server, consult
your network administrator.
• When you install ActiveX Control, you should be
logged in to the computer as Administrator.
• When you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, the information bar or “Security
Warning” may appear as you click Enter. For details,
see “Installing ActiveX Control” in “When using
Windows XP Service Pack 2” on page 9 or “Installing
ActiveX Control” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 12.
3
Set the slider to Medium or lower. (If the slider is
not displayed, click Default Level.)
When using antivirus software, etc. on
the computer
• When you use antivirus software, security software,
personal firewall or pop-up blocker on your computer,
the camera performance may be reduced, for example,
the frame rate for displaying the image may be lower.
• The Web page displayed when you log in to the
camera uses JavaScript. The display of the Web page
may be affected if you use antivirus software or other
software described above on your computer.
Tip
Every page of this software is optimized as display
character size Medium for Internet Explorer.
To display the welcome page and the
main viewer correctly
To operate the welcome page and the main viewer
correctly, set the security level of the Internet Explorer
to Medium or lower, as follows:
1
Select Too ls from the menu bar for Internet
Explorer, then select Internet Options and click
the Security tab.
2
Click the Internet icon (when using the camera via
the Internet) or Local intranet icon (when using
the camera via a local network).
14
Accessing the Camera Using the Web Browser
Page 15
Basic Configuration by the Administrator
You can monitor the image of the camera by logging in
with the initial condition of this network camera. You
can also set various functions according to the install
position, network condition or purpose of the camera.
We recommend you configure the following items
before monitoring the image from the camera.
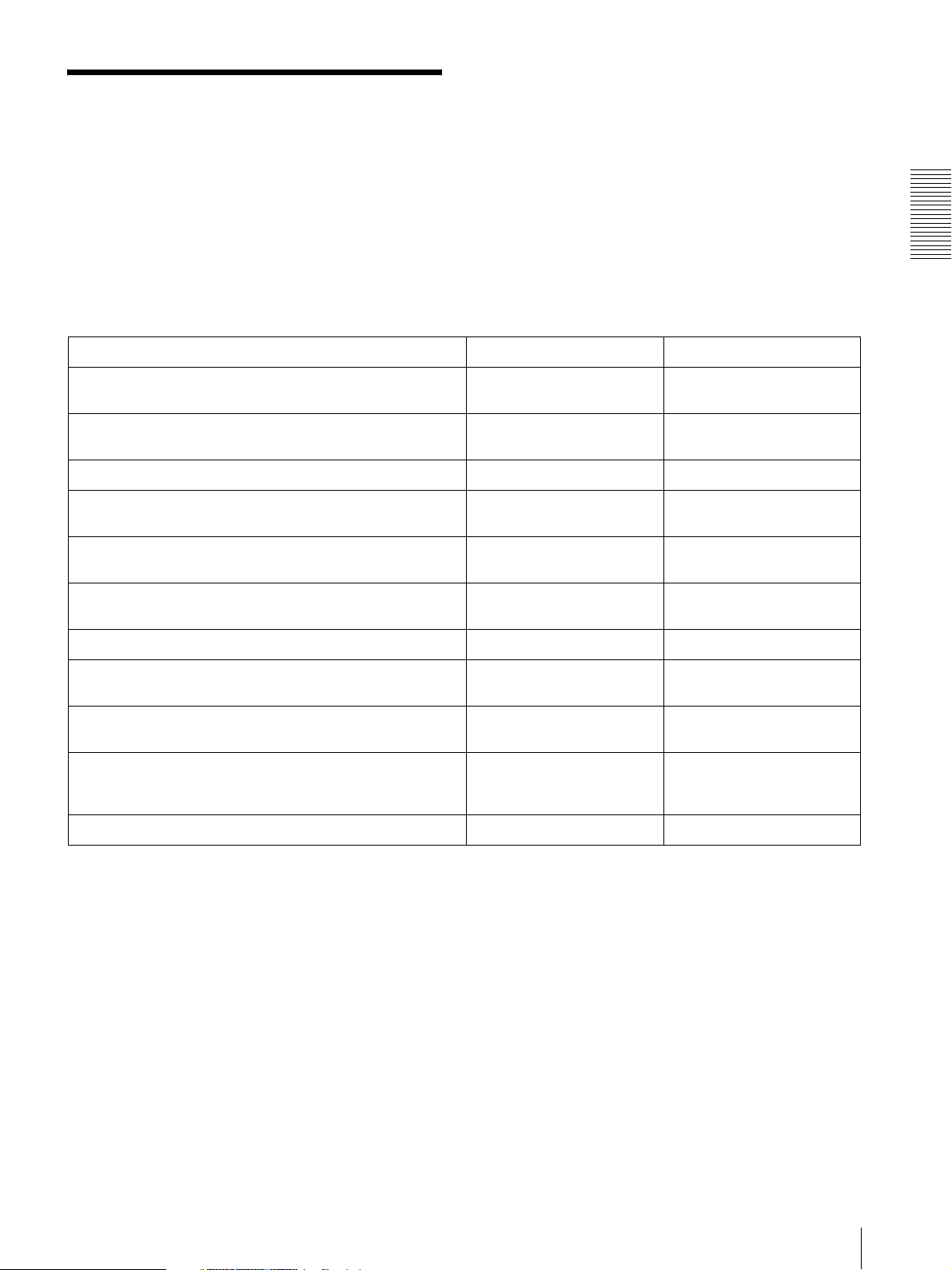
Setting contents Easy mode menu Advanced mode menu
Preparation
Select the white balance mode according to the installing
position (indoor or outdoor).
Flip the image according to the installation position (desk top or
ceiling).
Select the brightness of the blue LED on the top of the camera. Blue LED (page 26) Blue LED (page 31)
Set the format of the image sent from the camera (MPEG 4 or
JPEG).
Select the brightness of the image sent from the camera. Brightness (page 26) Exposure mode (page 36)
Select the quality of the image sent from the camera. Image quality (page 26) MPEG4 Tab (page 36)
Select the size of the image sent from the camera. Image size (page 26) Image size (page 34)
Select weather the audio from the camera microphone is sent or
not.
Accord date and time of the camera with those of the computer. Date & time setting
Make the setting for sending the monitor image attached to a
mail.
Set the access right of the user for the camera. – User setting Menu (page 41)
White balance (page 26) White balance (page 35)
Mount (page 26) Image flip (page 35)
– Video mode (page 34)
Brightness (page 36)
JPEG Tab (page 37)
Microphone (page 26) Microphone (page 35)
(page 26)
e-Mail (SMTP) (page 26)
Easy mode (e-Mail)
(page 27)
Date & time Tab (page 31)
e-Mail (SMTP) setting Menu
(page 43)
Basic Configuration by the Administrator
15
Page 16
Operating the Camera
The Operating the Camera section explains how to
monitor the image from the camera using the Web
browser. Use Internet Explorer as the Web browser.
The functions of the camera should be set by the
Administrator. For setting the camera, see
“Administrating the Camera” on page 25.
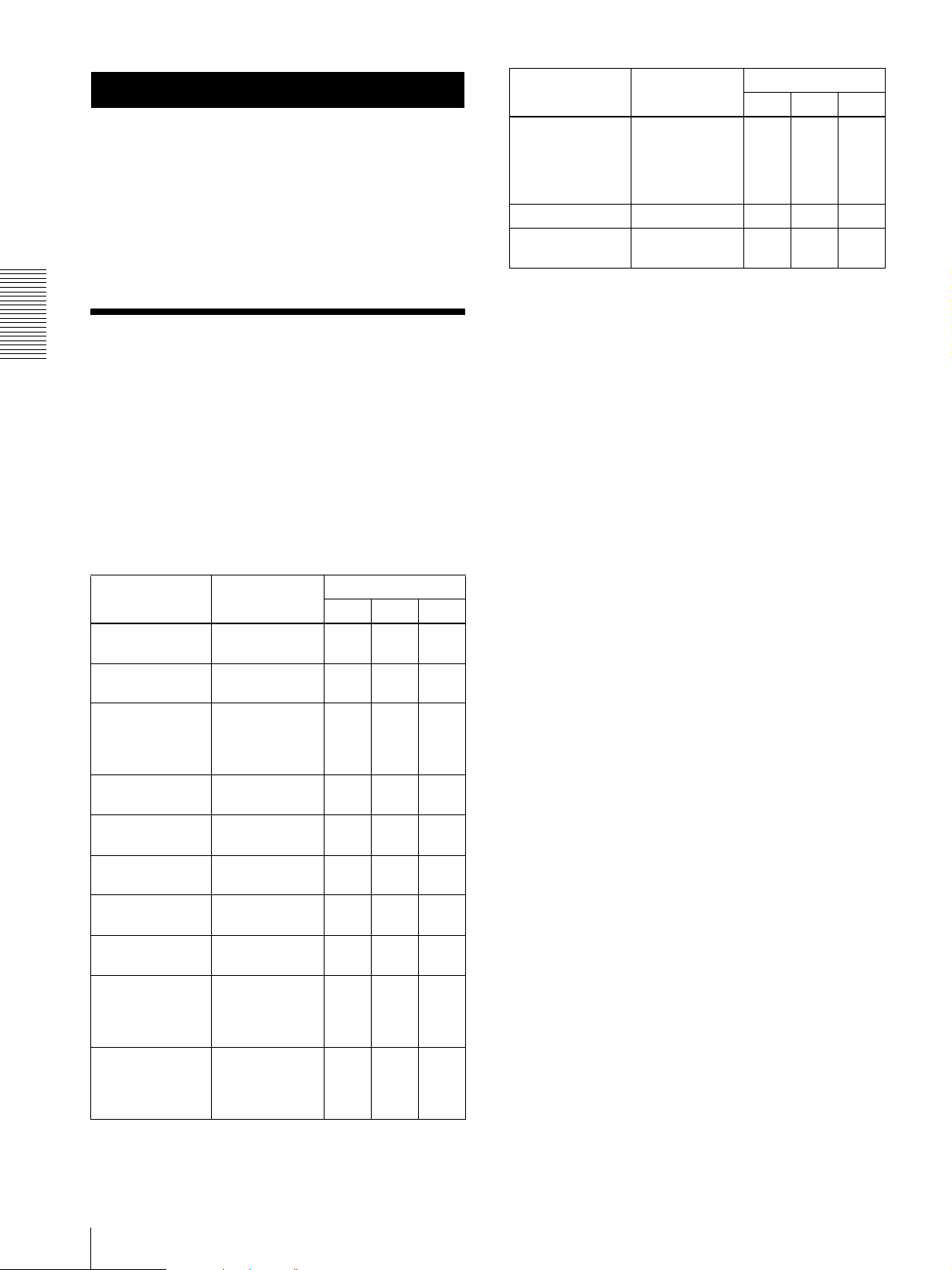
Function Administrator
Switch the TCP/
UDP transmission
mode (Available in
MPEG4 mode
only)
Control the audio z zzz
Control the setting
menu
z Usable function
2)
z
z –––
Full Light View
User
2)
z
––
– Not usable function
Administrator and User
Operating the Camera
This network camera classifies the people who log in as
the Administrator and the User.
The Administrator can use all functions of this network
camera including camera setting. The functions the
User can use are monitoring the image and audio from
the camera, and controlling the camera. The Viewer
1) This function is usable with the Java applet viewer.
2) This function is not usable with the Java applet
viewer.
The access rights of the administrator and the user can
be set in “Setting the User — User setting Menu” on the
Advanced mode menu for the administrator on page 41.
mode setting restricts the user's access right, and the
user is classified as the one of three types.
Each type of the user can use the following functions.
Function Administrator
Monitor a live
image
Watch date and
time
Control the frame
rate (Usable only
when JPEG mode
is selected)
Control the image
view size
Zoom a image by
the digital zoom
Save the still image
in the computer
Send an image file
to the FTP server
Send an image
attached to a mail
Record an image
on the inside
memory of the
camera
Control the Alarm
out of the I/O port
on the camera main
unit
z zzz
z zzz
zz––
zzz–
zzz–
zzz–
zz––
zz––
zz––
zz––
Full Light View
User
1)
16
Administrator and User
Page 17
Logging in to Homepage
— Welcome Page
Logging in as a User
1
Start the web browser on the computer and type the
IP address of the camera you want to monitor.
3
Select the viewer language.
Click English or Japanese at the bottom of the
welcome page.
4
Click Enter.
The main viewer appears.
With the ActiveX viewer (MPEG4)
The welcome page of the network camera is
displayed in the Web browser.
2
Select the viewer.
The usable viewers differ depending on the video
mode (page 34) of the camera.
When the video mode is set to MPEG4, you can
only select ActiveX viewer, and may not select
other viewers. (MPEG4 is default. See illustration
on Step 1 above.)
When the video mode is set to JPEG, you can
select ActiveX viewer or Java applet viewer.
For details, see “About Viewers” on page 18.
Welcome page when the video mode is
JPEG
Operating the Camera
With the Java applet viewer
Control the camera from the main viewer.
Note
If the Welcome page does not activate correctly, the
security level of the Internet Explorer may be set to
Medium or higher. See “To display the welcome page
and the main viewer correctly” on page 14 and check the
security level.
Displaying the setting window for the administrator directly
When the administrator sets the camera functions, the
setting window can be displayed directly from the
welcome page.
1
Select the viewer language on the welcome page.
Click English or Japanese at the bottom of the
welcome page.
Logging in to Homepage — Welcome Page
17
Page 18
2
Click Setting on the welcome page.
The following dialog appears.
and install ActiveX Control. You can use all the
functions of the viewer by using ActiveX Control.
Java applet viewer
You can select this viewer when the camera video mode
is set to JPEG. The frame rate is lower than the ActiveX
viewer.
The Java applet viewer operates only when Java is
installed and Java (Sun) is enabled. If it does not operate
correctly, check whether the effective Java version has
been installed successfully and Java (Sun) is enabled.
3
Enter the user name and password for
Administrator, then click OK.
Operating the Camera
The user name “admin” and the password “admin”
are set at the factory for the Administrator. You can
change them in the User setting menu of the
Advanced mode menu (see page 41).
The Advanced mode menu appears in another
window.
About Viewers
You can use the following viewer according to the Video
mode setting in the camera setting menu of the
Advanced mode menu (page 34).
ActiveX viewer
This viewer can monitor the image in both MPEG4 and
JPEG video modes.
You must install this viewer when you access to the main
viewer at the first time.
Effective versions: Java Plug-in Ver. 1.6.0_01
To check the Java version
Select Tools from the menu bar of Internet Explorer,
then select Internet Options and click the Advanced
mode tab. Check whether the version of Java displayed
for Java (Sun) is one of the versions specified above. If
Java (Sun) is not displayed, it means that Java is not
installed. You need to install Java.
To enable Java Plug-in
Check “Use JRE 1.6.0_01 for <applet> (requires
restart)” in “Java (Sun)”.
To install Java Plug-in
Download Java 2 Runtime Environment, Standard
Edition (JRE) from the homepage of Sun Microsystems,
Inc., and install it by following the instructions on the
installer.
Notes
• If Automatic configuration is enabled in the Local
Area Network (LAN) Settings of Internet Explorer,
the camera image may not be displayed. In that case,
disable Automatic configuration and set the Proxy
server manually. For the setting of the Proxy server,
consult your network administrator.
• When you install ActiveX Control, you should be
logged in to the computer as the Administrator.
Tip
Every page of this software is optimized for display
character size Medium for Internet Explorer.
When you display the main viewer of the
camera for the first time
When you log in the network camera using ActiveX
viewer for the first time (clicking Enter to enter the
main viewer), the Security Warning appears. Click Yes
18
Logging in to Homepage — Welcome Page
Page 19
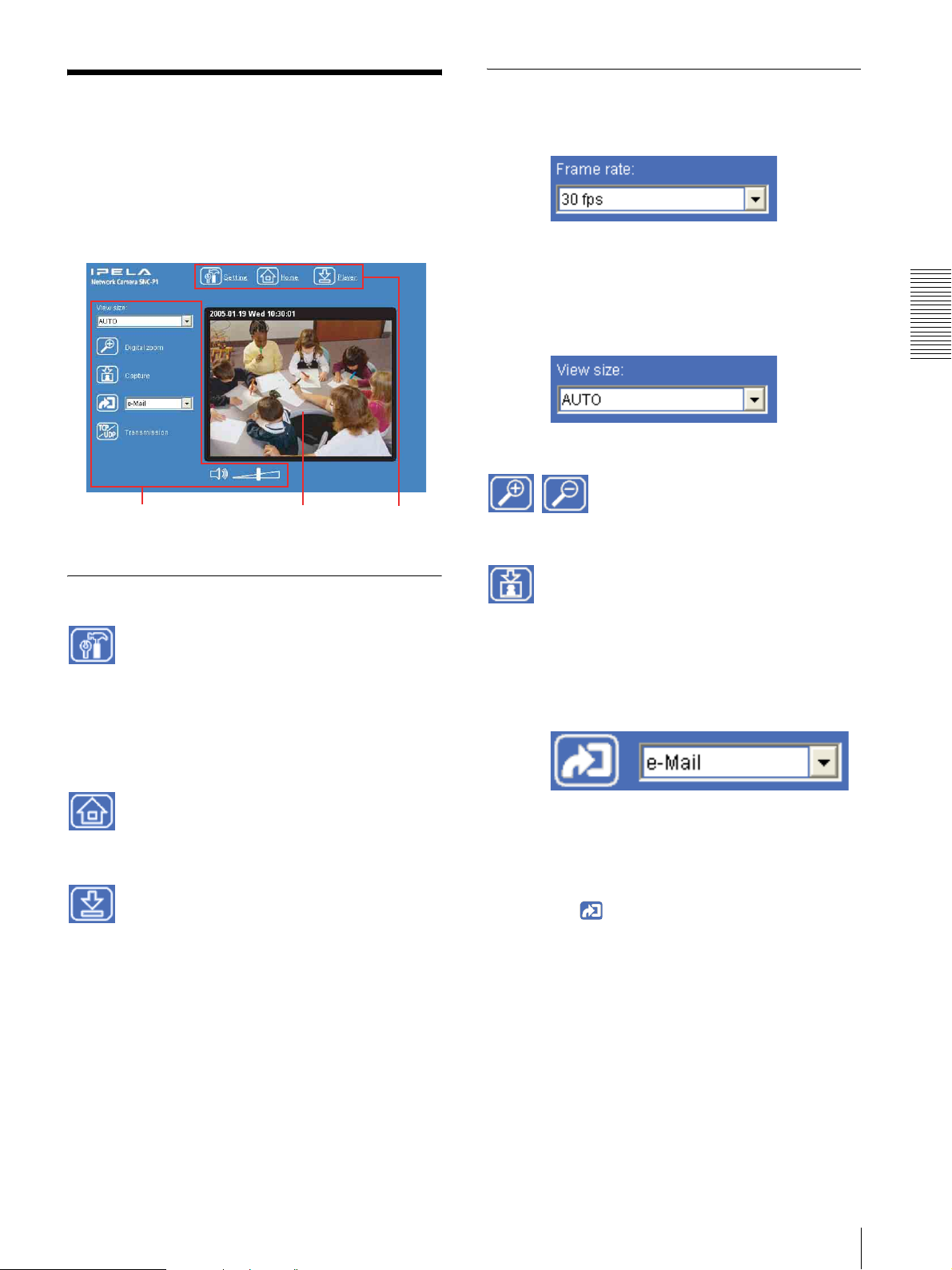
Configuration of Main
Camera Control Section
Viewer
This section explains the functions of the parts and
controls of the main viewer. For a detailed explanation
on each part or control, see the specified pages.
Main viewer
Camera control
section
Main menu
Setting
Click to display the Easy mode menu for Administrator
menu. (See “Basic Operations of Easy mode” on page
25.)
You can operate this function only when logging in as
the administrator.
Monitor image
section
Main menu
Frame rate
(Displayed only when the camera Video mode (page 34)
is set to JPEG.)
Selects the frame rate to transmit images.
View size
Operating the Camera
Selects the view size to be displayed. (page 21)
Digital zoom
Click to change the size of the digital zoom. (page 21)
Capture
Click to capture a still image shot by the camera and to
store it in the computer. (See “Capturing a Monitor
Image” on page 21.)
Trig ger
Home
Displays the Welcome page.
Player
Click to download the “SNC video player” application
program built in the camera. The SNC video player
allows you to play video/audio data recorded on the
camera with your computer. (See “Using the SNC video
player — Playing Video/Audio File Recorded on
Camera” on page 71.)
(Displayed only when the camera Viewer mode
(page 41) is set to Full and one or more triggers are
enabled in the Trigger menu (page 54).)
Select the function you want to use from the drop-down
list and click . The selected function is activated.
The selectable functions are as follows:
– send the still image files attached to an e-mail
(page 22)
– send the still image files to an FTP server (page 22)
– record the still image files in the built-in memory,
(page 23)
– switch the alarm output on/off (page 23)
Configuration of Main Viewer
19
Page 20
Transmission (Switching the TCP/
UDP transmission mode)
(Displayed only when the camera Video mode (page 34)
is set to MPEG4 and using the ActiveX viewer.)
Controlling the Monitor Image
Each click switches the transmission mode of the video/
audio data among TCP mode, UDP (Unicast) mode and
UDP (Multicast) mode. (page 24)
The last selected mode is saved in the computer, and will
stay selected for the next starting.
Vol ume
Operating the Camera
(Displayed when the Microphone (page 35) is set to
On.)
Drag the bar of icon to adjust the volume.
When you click icon, the icon changes to and
the audio output stops. To output the audio, click
again.
Note
If the volume icon is not displayed due to the use of
using Java applet viewer, Audio codec may not be set
G.711(64kbps) (page 35) or Java may not be installed
correctly.
To check if Java is installed correctly, refer to “Java
applet viewer” of “About Viewers” on page 18.
You can monitor the camera image on the monitor
window of the main viewer.
Monitoring the camera image
1
Log in to the home page to display the main viewer.
You can see how to log in on page 17, “Logging in
as a User”.
2
Select the frame rate (only when the camera Video
mode is set to JPEG).
Monitor Image
The image shot by the camera is shown here. Date and
time is displayed at the top of the window.
Click the Frame rate list box to select the frame
rate for transmitting the image. Selectable frame
rates are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 fps.
“fps” is a unit indicating the number of frames
transmitted per second.
If you select 30 fps, the image is sent at the
maximum speed of the connected line (30 fps
maximum).
Note
The frame rate options indicate the maximum
number of frames that can be transmitted.
The number of frames actually transmitted may
vary depending on network environments and
camera settings (image size and image quality
settings).
20
Controlling the Monitor Image
Page 21

3
Select the view size.
Click View size list box to select the view size from
among Auto, 640 × 480, 320 × 240 and 160 × 120.
Auto is determined by the image size specified in
the Camera setting page (page 34).
Zooming in the monitor image
1
Click Digital zoom icon.
2
Click the point you want to zoom in.
The image is expanded by about 1.5 times with the
clicked point at the center.
Capturing a Monitor Image
You can capture a monitoring image as a still image and
save it in the computer.
Capturing a monitor image
1
Monitor the camera image in the monitor window.
2
Click Capture icon.
The still image of the moment you click is captured,
and the still image is displayed in the monitor
window.
With the ActiveX viewer
Operating the Camera
The digital zoom icon changes to .
3
To cancel zooming in, click icon.
With the Java applet viewer
3
To cancel the still image, click Cancel or Close.
Capturing a Monitor Image
21
Page 22
Saving the captured image
Sending an Image File
With the ActiveX viewer
1
Capture the monitor image.
2
Click Save.
Save As dialog appears.
You can send a captured still image with an attached
mail or to the FTP server.
To use this function, you need to make the e-
Mail(SMTP) or FTP client active, and set the address
properly in the Trigger setting menu on the Advanced
mode menu (page 54).
Sending a Monitor Image via e-Mail
1
Monitor the image on the monitor window.
Operating the Camera
3
Select JPEG Files or Windows Bitmap Files as
Save as type.
4
Type the File name and specify Save in, then click
Save.
2
Select e-Mail from the Trigger list box.
3
Click .
The still image of the moment when you click is
captured, and the mail attached with the image file
is sent to the mail address you have set.
Sending a Monitor Image to an FTP
With the Java applet viewer
1
Capture the monitor image.
2
Right-click the mouse to display the menu and
select Save Picture As....
Save Picture dialog appears.
3
Select JPEG or Bit map as Save as type.
Server
1
Monitor the image on the monitor window.
2
Select FTP from the Trigger list box.
3
Click .
The still image of the moment when you click is
captured, and the image file is sent to the FTP
server.
4
22
Sending an Image File
Type in File name and specify Save in, then click
Save.
Page 23
Recording a Still Image
Controlling Alarm output
in the Built-in Memory of
the Camera
You can capture a camera image as a still image and
record it in the built-in memory of the camera.
To use this function, you need to make Image memory
active and to set details of the image memory in the
trigger setting menu on the Advanced mode menu
(page 54).
1
Monitor the image on the monitor window.
2
Select Image memory from the Trigger list box.
3
Click .
The still image of the moment when you click is
captured, and the image file is recorded in the builtin memory of the camera.
You can control the Alarm output On (short-circuit) and
Off (open).
To use this function, you need to make Alarm output
active in the Trigger setting menu on the Advanced
mode menu (page 55).
1
Monitor the image on the monitor window.
2
Select Alarm output from the Trigger list box.
3
Click .
Each click switches the Alarm output between On
(short-circuit) and Off (open) alternately.
Tip
For the connection of peripheral devices to the Alarm
output of the I/O port, see the supplied Installation
Manual.
Operating the Camera
Recording a Still Image in the Built-in Memory of the Camera / Controlling Alarm output
23
Page 24
fire-wall is installed between the camera and the
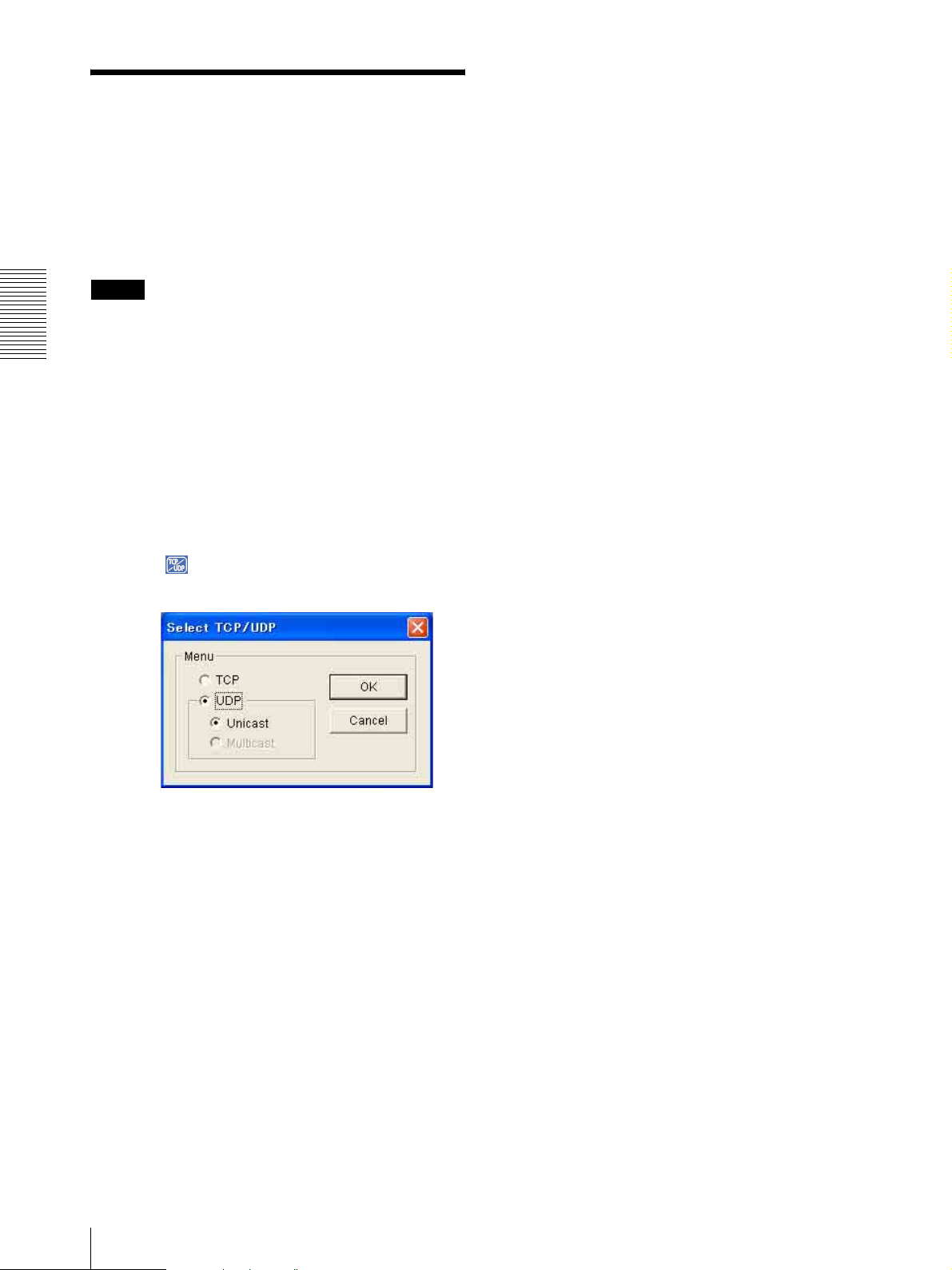
Switching TCP/UDP Transmission Mode
You can select the communication port of the video/
audio data as TCP or UDP.
This function can be used when the Video mode
(page 34) is set to MPEG4 and the ActiveX viewer is
used.
Notes
• The function may not operate correctly when you use
personal firewall software or antivirus software on
Operating the Camera
your computer. In that case, disable the software or
select the TCP mode.
• If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, disable “Windows Firewall.” For
details, see “Configuring Windows Firewall” in
“When using Windows XP Service Pack 2” on
page 10 or “Configuring Windows Firewall” in
“When using Windows Vista” on page 12.
1
Display the main viewer.
computer, or depending on the network
environment, the video/audio may not play
properly when UDP (Unicast) is selected. In this
case, select TCP.
UDP (Multicast): This is selectable when the
multicast streaming (page 34) is On. When UDP
(Multicast) is selected as the transmission port,
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) and UDP
multicast techniques are adopted for video/audio
transmission. By selecting it, the network
transmission load of the camera can be reduced. If
a router which does not correspond to the multicast
or the fire-wall is installed between the camera and
the computer, the video/audio may not play
properly. In this case, select TCP or UDP
(Unicast).
4
Click OK to close the dialog.
If you decide not change the transmission setting,
click Cancel.
2
Click TCP/UDP transmission selector icon.
Transmission mode selector dialog appears.
3
Click one of the buttons TCP, UDP (Unicast) or
UDP (Multicast).
TCP: This is normally selected.
When TCP is selected as the communication port,
HTTP communication is adopted for video/audio
communication.
HTTP is the protocol used for reading a usual Web
page.
In an environment capable of reading Web page,
you can watch or listen to the video/audio by
selecting TCP port.
UDP (Unicast): When UDP (Unicast) is selected
as the communication port, RTP (Real-time
Transport Protocol) is adopted for video/audio
communication. As RTP is the protocol for running
video/audio data, video/audio can be played
smoother than when TCP (HTTP) is selected. If the
24
Switching TCP/UDP Transmission Mode
Page 25

Administrating the Camera
The Administrating the Camera section explains how to
set the functions of the camera by the Administrator.
For monitoring the camera image, see “Operating the
Camera” on page 16.
Administrator setting menu includes the Easy mode
(basic setting) and the Advanced mode (detail settings
depending on the user's condition).
This section explains the basic operations of the Easy
mode and explains each option of the Easy mode, then
similarly for the Advanced mode.
Basic Operations of Easy mode
The Easy mode is used for basic settings for the network
camera.
Click Setting icon of the main viewer to display
Easy mode.
How to set Easy mode
1
Log in the home page to display the main viewer.
You can see how to log in on page 17 “Logging in
as a User”.
Easy mode appears.
Note
If you set “White balance”, “Image quality” and
“Image size” in Advanced mode to values not
shown in Easy mode, the radio button may be in the
statement that nothing is selected. In this case, you
can select it by clicking the radio button.
4
Click the radio button of the option you want to set
from among those in the Easy mode menu, or click
the setting item button to display the sub menu, and
decide details.
In the Easy mode menu, the new setting will
become active only by being selected.
For details on each setting option, see “Setting
Options of Easy mode” on page 26.
Administrating the Camera
2
Select the viewer language on the welcome page.
Click English or Japanese at the bottom of the
welcome page.
3
Click .
The authentication dialog appears. Enter the user
name and password for Administrator.
The user name “admin” and password “admin” are
set at the factory for the Administrator.
5
After setting, click .
The display returns to the main viewer.
Basic Operations of Easy mode
25
Page 26

Setting Options of Easy mode
Image size
You can select the image size sent from the network
camera.
640 × 480 (VGA), 320 × 240 (QVGA) or 160 × 120
(QQVGA) can be selected.
Microphone
Select whether you send the audio from the built-in
microphone or from the m microphone input
connector. Select On to send the audio from this
network camera microphone.
Note
When you change the Microphone setting, click
Refresh of the Web browser to reflect the change in the
opening main viewer page.
Date & time setting
Displays the Advanced mode menu (page 28).
Administrating the Camera
When you click Setting, date and time of the camera is
set to suit those of the computer.
White balance
Select the white balance mode.
Auto, Indoor or Outdoor can be selected.
Mount
The image can be displayed upside down.
Select Desk top when you use the network camera on
desktop, and select Ceiling when you use it fixed to the
ceiling. You can always watch the proper image
regardless of its position.
Note
The setting time may not accord with the exact time
according to the network environment.
e-Mail (SMTP)
This is the setting for sending an e-mail with an attached
image file of the monitor. Click e-Mail (SMTP) and the
“Easy mode (e-Mail)” setting mode menu appears.
(page 27)
Blue LED
You can select the brightness of the blue LED on the top
of the network camera.
Bright, Dark or Off can be selected.
Brightness
You can adjust the brightness of the image sent from the
network camera in eleven levels.
Click the button of the brightness you want to select. The
button on the left side is the darkest (Dark), and the
button on the right is the brightest (Bright).
Image quality
You can select the quality of the image sent from the
network camera.
Usually select Normal. To give priority to the
transmission speed and to watch a smooth image, select
Low. To give priority to the image quality, select High.
Note
According to the line condition, smooth image may not
be obtained even if you select Low.
26
Basic Operations of Easy mode
Page 27

Easy mode (e-Mail)
This is displayed when you click e-Mail (SMTP) of the
Easy mode menu.
Note
User name, Password
Type the user name and password of the user who has
the mail account. This setting is necessary when the
SMTP server which sends e-Mails performs
authentication.
While the camera video mode is set to MPEG4, the
image of the composite video signal output from the
video output connector of the camera may be distorted
during mail transmission.
e-Mail (SMTP)
Select On when you use e-Mail (SMTP) function. When
you select On, setting options are displayed. If you do
not use it, select Off and click OK below.
SMTP server name
Type the SMTP (sending mail) server name up to 64
characters, or type the IP address of the SMPT server.
Recipient e-Mail address
Type the address to which you send e-Mails to up to 64
characters. If you want to send to two or more addresses,
set them in the e-Mail (SMTP) setting menu (page 43) of
the Advanced mode menu.
Administrator e-Mail address
Type the e-Mail address of the administrator of the
camera up 64 characters.
This will be the address for return mail and system mail
from the mail server.
Subject
Type the subject up to 64 characters.
Message
Type the text up to 384 characters (Return corresponds
to two characters).
Mode
Set the e-Mail sending mode.
Motion detection: When the camera detects any action,
it sends the image file.
If you select Motion detection, the camera detects
activity in the shooting image due to the built-in motion
detection function. Then the camera sends the e-Mail
with the attached image file.
Administrating the Camera
Authentication
Select the authentication required when you send an eMail.
None: Select when no authentication is necessary when
an e-mail is sent.
SMTP Authentication: Select when authentication is
necessary when an e-mail is sent.
POP before SMTP: Select when POP before SMTP
authentication is necessary when an e-mail is sent.
POP server name
Type the POP (receiving mail) server name up to 64
characters, or type the IP address of the POP server. This
setting is necessary when the SMTP server which sends
e-mails performs authentication using the POP user
account.
Set the details of the motion detection of the camera in
the Motion detection setting menu (page 57) of the
Advanced mode menu.
Note
The picture attached to the e-Mail is of the moment the
motion detection function of the camera works. If the
next activity is detected during processing of the image
of the first detection, the process will be rejected.
The motion detection function may not work properly in
the following cases.
• During camera setting operation in the Camera setting
menu.
• When the object is dark.
• When the camera is shaken because the installation
location is unstable.
Basic Operations of Easy mode
27
Page 28

Periodical sending: The image file is sent regularly.
After checking it, select Every 1 hour or Every 6
hours.
Every 1 hour: The camera sends the e-Mail with
attached image file every 1 hour.
Every 6 hours: The camera sends the e-Mail with
attached image file every 6 hours.
OK
Click this after setting.
When you click it, the dialog "Send a test mail?"
appears. When you send a test mail to the address you
have set, select OK. If you do not wish to send it, select
Cancel.
Cancel
Click to return to the previous condition by canceling the
setting.
Basic Operations of Advanced mode Menu
You can set all functions to suit the user's condition in
the Advanced mode menu.
Click Setting in the welcome page or
button in the Easy mode menu to display the Advanced
mode menu.
Note on the display of menu options
In the setting menus of this unit, the options that you
cannot currently select will be grayed out.
The options that you can currently select will be
displayed automatically as you change the setting.
How to set Advanced mode
Administrating the Camera
1
Log in the home page to display the welcome page.
You can see how to log in on page 14 “Logging in
as a User”.
2
Select the viewer language on the welcome page.
Click English or Japanese at the bottom of the
welcome page.
3
Click Setting in the welcome page.
The authentication dialog appears. Enter the user
name and password for Administrator.
The user name “admin” and password “admin” are
set at the factory for the Administrator.
Advanced mode menu appears.
28
Basic Operations of Advanced mode Menu
The following steps also display the Advanced
mode menu.
1 Click Enter in the welcome page to display the
main viewer.
2 Click
3 Enter the user name and password for
Administrator.
Easy mode appears.
in the main viewer.
Page 29

4 Click .
4
Click the menu name (example: System) on the left
side of the Advanced mode menu.
The clicked setting menu appears.
Example: System setting menu
Click this button to invalidate the set values and return to
the previous settings.
General notes on setting menus
• After changing a setting on a setting menu, wait at
least 10 seconds before turning off immediately the
power of the camera.
If the power is turned off immediately, the changed
setting may not be stored correctly.
• When the camera settings are changed while watching
the main viewer, some settings cannot be restored. To
reflect the change on the opening main viewer, click
Refresh of the Web browser.
Configuration of Advanced mode Menu
5
Select the tab above the setting menu, and set each
setting option in the tab.
Example: “System” setting menu “Date & time”
tab
See page 29 to 58 for details of setting menu tabs
and setting options.
6
After setting, click OK.
The setting contents become active.
Click Cancel to invalidate the set values and return to
the previous settings.
Administrating the Camera
Displays the Easy mode menu (page 25).
System
Displays the System setting menu.
(“Configuring the System — System setting menu” on
page 31).
Camera
Displays Camera setting menu for setting the camera
image and audio. (“Setting the Camera Image and Audio
— Camera setting Menu” on page 34)
Buttons common to every setting menu
The following buttons are displayed on the setting
menus where they are necessary. The functions of the
buttons are the same on every setting page.
Click this button to validate the settings.
Network
Displays the network setting menu for setting the
network connection. (“Configuring the Network —
Network setting Menu” on page 38)
Basic Operations of Advanced mode Menu
29
Page 30

User
Displays the user setting menu for setting the user name
and the password to log in. (“Setting the User — User
setting Menu” on page 41)
Security
Displays the security setting menu for specifying the
computer allowed to connect to the camera. (“Setting the
Security — Security setting Menu” on page 42)
e-Mail (SMTP)
Displays the e-Mail (SMTP) setting menu for sending an
e-mail. (“Sending an Image via mail — e-Mail (SMTP)
setting Menu” on page 43)
FTP client
Displays the FTP client setting menu for sending an
image file to FTP server. (“Sending Images to FTP
Server — FTP client setting Menu” on page 46)
Motion detection
Displays the Motion detection setting menu for the
motion detection function built into the camera.
(“Setting the Motion Detection Function — Motion
detection setting Menu” on page 57)
DDNS
Displays the
*
DDNS setting menu for registration and
change in DDNS service. (“Using DDNS Service —
DDNS Setting Menu” on page 59)
* DDNS: Dynamic Domain Name Service
Administrating the Camera
Image memory
Displays the image memory setting menu for recording
a video/audio file in the built-in memory of the camera.
(“Recording Images in Memory — Image memory
setting Menu” on page 49)
FTP server
Displays the FTP Server menu for setting the FTP server
function of the camera.
(“Downloading Images from the Camera — FTP server
setting Menu” on page 52)
Alarm output
Displays the alarm out setting menu for the alarm out
terminal of the camera. (“Downloading Images from the
Camera — FTP server setting Menu” on page 52)
Trigger
Displays the trigger setting menu for the operations
when you click the trigger button in the main viewer.
(“Setting the Operations from the Viewer Page —
Trigger setting Menu” on page 54)
Schedule
Displays the schedule setting menu for FTP client
function, e-Mail (SMTP) function, Image memory
function and Alarm out function and so on. (“Setting the
Schedule — Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
Alarm buffer
Displays the alarm buffer setting menu for the buffer
which records the image and audio on the alarm
detection. (“Setting the Alarm Buffer — Alarm buffer
setting Menu” on page 56)
30
Basic Operations of Advanced mode Menu
Page 31

Configuring the System
— System setting menu
When you click System on the Advanced mode menu,
the System setting menu appears.
Use this menu to perform the principal settings of the
software.
The System setting menu is composed of five tabs which
are System, Date & time, Initialization, System Log
and Access Log.
System Tab
To display the homepage built in the camera
Select /index.html.
To display your individual homepage
You can display your favorite homepage. Store the
HTML file in the built-in flash memory using the
Custom Homepage Installer included in the supplied
CD-ROM.
For use of the Custom Homepage Installer, see page 72.
1
Select User Setting/ user/.
2
Type the path of the HTML file in the text box up to
64 characters.
Tip
Even when you select User Setting/ user/, the home
page inside the camera can be displayed by typing the
following URL in the address box of the Web browser.
Example: When the IP address of the camera is set to
192.168.0.100
http://192.168.0.100/en/index.html
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Administrating the Camera
Title bar name
Type a name to display on the title bar up to 32
characters. The characters typed here are displayed on
the title bar of the Web browser.
Welcome text
Type a text to show on the welcome page, with up to
1024 characters in HTML format. Use the <BR> tag for
a line break. (A line break is equivalent to 2 characters.)
Serial number
Displays the serial number of the camera.
Software version
The software version of this camera is displayed.
Blue LED
You can select the brightness of the blue LED on the top
of the network camera.
Bright, Dark or Off can be selected.
Date & time Tab
Current date & time
Displays the date and time set on the camera.
Note
After you have purchased the camera, be sure to check
the date and time of the camera and set them if
necessary.
Default URL
Select the homepage to be displayed when you enter the
IP address of the camera in the web address box of the
browser.
PC clock
Displays the date and time set on your computer.
Configuring the System — System setting menu
31
Page 32

Date & time format
Select the format of date and time to be displayed on the
main viewer from the drop-down list.
You can select from among yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
(year-month-day hour:minute:second), mm-dd-yyyy
hh:mm:ss (month-day-year hour:minute:second), and
dd-mm-yyyy hh:mm:ss (day-month-year
hour:minute:second).
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Initialize Tab
Adjust
Select to set the day and time.
Keep current setting: Select if you do not need to set
the date and time.
Synchronize with PC: Select if synchronizing the
camera's date and time with those of the computer.
Manual setting: Select if you want to set the camera's
date and time manually.
Select the lower 2-digits of year, month, date, hour,
minutes and seconds from each drop-down list.
Administrating the Camera
Synchronize with NTP: Select if synchronizing the
camera's date and time with those of the time sever
called NTP server (Network Time Protocol). Set the
NTP server name and the Interval.
NTP server name
Type the host name or IP address of the NTP server, up
to 64 characters.
Interval
Select the interval at which you want to adjust the
camera's time referring to the NTP server' time, between
1 and 24 hours. The set interval is a guide, and does not
indicate the exact time.
Note
The setting time may not accord with the exact time
according to the network environment.
Reboot
Reboots the camera.
Click Reboot, and the message “The SNC-P1 will be
rebooted. Are you sure?” appears. Click OK to reboot
the camera. It takes about two minutes to start again.
Factory default
Resets the camera to the factory settings.
Click Factory default, and the message “Set up data
will be initialized. Are you sure?” appears. When you
click OK, the network indicator and the Blue LED on
the camera start to blink. After adjustments of the
default settings have finished, the camera reboots
automatically. Do not turn off the camera until the
camera reboots.
Time zone
Set the time difference from Greenwich Mean Time in
the area where the camera is installed.
Select the time zone where the camera is installed from
the drop-down list.
Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving
time changes
When you select it, the clock is automatically adjusted
according to the daylight saving time of the selected
time zone.
Note
If the time zone selected on the Time zone menu is
different from that set on the computer, the time is
adjusted using the time zone difference and set on the
camera.
Tip
The camera can also be reset to the factory settings by
turning the power on of this unit while pressing the reset
switch on the camera. For details, see the supplied
Installation Manual.
Backup setting data
Saves the setting data of the camera in a file.
Click Save, and follow the instructions on the Web
browser to specify the folder and save the setting data of
the camera. The file name preset at the factory is “sncp1.cfg.”
Restore setting
Loads the stored setting data of the camera.
Click Browse and select the file in which the setting data
is stored. Then, click OK, and the camera is adjusted
according to the loaded data and restarted.
32
Configuring the System — System setting menu
Page 33

Notes
• With Restore setting, some items in the Network
setting menu (page 38) cannot be restored.
• The following item cannot be stored or restored with
Backup setting data or Restore setting.
– a homepage created using Custom Homepage
Installer
Delete user setting URL
By pressing Delete, you can delete the home page
recorded on the flash memory of the camera with
Custom Homepage Installer (page 72).
Firmware upgrade
Use this when upgrading the camera software. Click
Browse and specify the file for upgrading, then click
OK. The massage “Upgrade firmware? Are you sure?”
is displayed. Click OK and upgrading starts. After
completion, the camera starts again.
Notes
• Use only the upgrade file special to this camera. If
not, a problem may occur.
• Do not turn off the camera until the upgrading is
completed.
Access log tab
Access log
The access record of the camera is displayed.
Click Reload to reload to the latest data.
Administrating the Camera
System log Tab
System log
The data of the software activity of the camera are
recorded in this log. It includes data that are useful when
a problem occurs.
Click Reload to reload the latest data.
Configuring the System — System setting menu
33
Page 34

Setting the Camera
Image and Audio
— Camera setting Menu
When you click Camera on the Advanced mode menu,
the Camera setting menu appears.
Use this menu to set the functions of the camera.
The Camera setting menu consists of 5 tabs: Common,
Picture, MPEG4, JPEG and Reset.
Common Tab
When select On, set Multicast address, Multicast
video port number and Multicast audio port number
properly.
Multicast address: Type the multicast address used on
the Multicast streaming.
Multicast video port number: Specify the video
transmission port number used for the Multicast
streaming.
Multicast audio port number: Specify the audio
transmission port number used for the Multicast
streaming.
Image size
You can select the image size sent from the network
camera.
640 × 480 (VGA), 480 × 360, 384 × 288, 320 × 240
(QVGA), 256 × 192 or 160 × 120 (QQVGA) can be
selected.
Administrating the Camera
Video mode
Select the output format of the camera image.
MPEG4 or JPEG can be selected.
Unicast streaming
Specify the transmission port number of the video data
and audio data used when UDP (Unicast) is selected
with the TCP/UDP transmission switching icon in the
main viewer
Video port number: Specify the transmission port
number of the video data. It is initially set to 50000.
Specify an even number from 1024 to 65534.
Audio port number: Specify the transmission port
number of the audio data. It is initially set to 50002.
Specify an even number from 1024 to 65534.
When the image size is set to 640 × 480 (VGA), you can
crop a portion of the image and display the cropped
image on the computer. With the cropping, the
transmitting data size, and thus, the network load is
reduced and a higher frame rate is obtained.
Select On to crop the image, or Off.
• When Cropping is set to On, Motion detection
function does not work.
• While Cropping is set to On, the image of the
composite video signal output from the video output
connector of the camera may be distorted.
To crop an image
1
Set the Image size to 640 × 480(VGA).
The Cropping is displayed.
2
Set the Cropping to On and click the Area setting
button.
The “Area setting” display appears.
3
Specify the cropping area.
Cropping
Multicast streaming
Set whether the camera uses the Multicast streaming or
not. It reduces sending load on the camera by making the
computer of the same segment network (not above the
router) receive the same transmitting data.
Select On to allow the multicast sending and Off not to
allow.
34
Setting the Camera Image and Audio — Camera setting Menu
Page 35

Click the left button of the mouse on the still image
and drag it diagonally. The red frame that appears
as you drag indicates the cropping area.
Still image
Red trimming
frame
4
Click OK at the bottom of the window.
The cropped image is displayed on the main viewer.
5
To close the image, click in the upper-right
corner.
Click the left button of the mouse on
the still image and drag it.
Note
When the bit rate is set to other than G.711(64bps), the
audio is not output in case of using Java applet viewer.
Speaker output
Set whether you output the audio sent from the computer
connected with the audio input connector to the speaker
(active speaker for example) of the camer aconnected
via line output connectors using SNC audio upload tool
included in the supplied CD-ROM.
Select On to accept the audio data transmission from
SNC audio upload tool.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Picture Tab
You can set the color condition, exposure, etc. of the
camera.
Administrating the Camera
Color
Select Color or Monochrome for the image.
Image flip
The image can be displayed upside down. Select On
when you fix the camera to the ceiling.
Microphone
Select whether you send the audio from the built-in
microphone or from the m microphone input connector.
Select On to send the audio from this network camera.
Note
When you change the Microphone setting, click
Refresh on the Web browser to reflect the change when
opening main viewer page.
Mic volume
Set the volume level of the audio input from the built-in
microphone or the m microphone input connectors. It is
adjustable from –10 to +10.
Audio codec
Select the bit rate when you send the audio from the
built-in microphone or from the m microphone input
connectors. G.711 (64kbps), G.726 (40kbps), G.726
(32kbps), G.726 (24kbps) or G.726 (16kbps) can be
selected.
White balance
Select the white balance mode from among Auto,
Indoor, Outdoor, One push WB, and Manual.
Auto: to automatically adjust the white balance
Indoor: to adjust the white balance for shooting indoors
under an incandescent lamp (about 3200 K)
Outdoor: to adjust the white balance for shooting
outdoors (about 5800 K)
One push WB: The One push trigger button is
displayed. Click the button to adjust the white
balance instantly.
Manual: When you select this, R gain and B gain are
displayed and you can set them.
Selectable gain values are from 0 to 255.
Setting the Camera Image and Audio — Camera setting Menu
35
Page 36

Exposure mode
Select the exposure mode of the camera from among
Full auto, Shutter priority, and Manual.
The setting items required for each setting appear.
Full auto: The camera executes the gain adjustment and
the shutter speed adjustment automatically.
When you select this, Flickerless mode, Slow
shutter and Backlight compensation are displayed
and you can set them as you require.
Shutter priority: The camera executes the gain
adjustment automatically and you can select the
shutter speed. When you select it, Backlight
compensation and Shutter speed are displayed and
you can set them.
Manual: You can set the exposure manually. When you
select it, Shutter speed and Gain are displayed and
you can set them.
According to the Exposure mode, the following setting
Administrating the Camera
options are displayed.
Flickerless mode
If the image is flickering by the fluorescent light, select
On to reduce it.
Sharpness
Select the sharpness in 7 steps, from –3 to 3.
Selecting 3 gives the image with the highest sharpness.
Contrast
Select the contrast in 7 steps, from –3 to 3.
Selecting 3 gives the image with the highest contrast.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
User preset
You can save the present settings in the camera as the
custom, or you can load the settings saved in the camera.
Save: Click to save the present settings of the Picture
tab.
Load: Click to load the saved settings. To use them,
click OK.
MPEG4 Tab
Note
This mode is available only for CE model.
Slow shutter
Set the Slow shutter. When On is selected, auto
exposure setting including the long time exposure is set
to suit to the brightness of the scene.
Backlight compensation
You can set On or Off of the exposure compensation.
When you select On, the exposure compensation
function starts to work.
Shutter speed
Select the shutter speed of the camera from the list box.
Selectable values of the shutter speed are 1/10000,
1/4000, 1/2000, 1/1000, 1/500, 1/250, 1/100, 1/50, 1/30,
1/15, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2 and 1/1 second.
Gain
Select the gain from the list box.
Selectable values of the gain are 0, 6, 12 and 18 dB.
Brightness
Tweaks the exposure set in the exposure mode. It is
brighter when a large value is selected, and it is darker
when a small value is selected. The value among –5 to 5
can be set.
Frame rate
Set the frame rate of the MPEG image.
Selectable values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25 and
30 fps.
“fps” is a unit indicating the number of frames
transmitted per second.
Bit rate
Set the bit rate of MPEG image transmission for a line.
Selectable values are 64, 128, 256, 384, 512, 768, 1024,
1536 and 2048 kbps.
Saturation
Select the saturation in 7 steps, from –3 to 3.
Selecting 3 gives the image with the highest saturation.
36
Setting the Camera Image and Audio — Camera setting Menu
Page 37

Note
The selected frame rate and bit rate are a tentative value.
The actual frame rate and bit rate may be different
according to the image size, the shooting scene or the
network condition.
Image quality
Set the quality of JPEG image.
Selectable values are from Level 1 to Level 5.
Selecting Level 5 gives the image with the highest
quality.
I-picture interval
Set the I-picture inserting interval of MPEG4. I-picture
is the compression data serving the basic point when the
data compressed by MPEG4 is depressed. In the
condition that errors tends to occur, such as the network
environment variation, the distortion of the image is
reduced by selecting a small value. The selectable values
are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 seconds.
Auto rate control
This function adjusts the frame rate and the bit rate
automatically so that the camera plays a smooth image
to suit the connected computer environment. If On is
selected, the rate of MPEG4 image is automatically
adjusted.
Note
The maximum transmission rate will be the values set in
Frame rate and Bit rate.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Bandwidth control
When the video mode is set to JPEG, the network
bandwidth can be limited. Selectable bandwidths are
0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and Unlimited
Mbps. When you do not wish to limit the bandwidth,
select Unlimited.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Reset Tab
Administrating the Camera
JPEG Tab
Frame rate
Set the maximum frame rate of JPEG image that can be
monitored on the computer. Selectable frame rates are 5,
6, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 fps.
“fps” is a unit indicating the number of frames
transmitted per second.
Reset camera menu
Click Reset, and the message “Camera menu setting is
reset to default. Are you sure?” is displayed. To reset to
default, click OK.
Setting the Camera Image and Audio — Camera setting Menu
37
Page 38

Configuring the Network
Subnet mask
Type the subnet mask.
— Network setting Menu
When you click Network on the Advanced mode menu,
the Network setting menu appears.
Use this menu to configure the network to connect the
camera and the computer.
The Network setting menu consists of 3 tabs: Network,
PPPoE and Dynamic IP address notification.
Network Tab
This section provides the menus for connecting the
camera through the network cable.
Default gateway
Type the default gateway.
Obtain DNS server address automatically
Select this to obtain the address of DNS server
automatically. It can be set only when Obtain an IP
address automatically (DHCP) is selected.
Note
When you select “Obtain DNS server address
automatically”, make sure that DHCP server is active on
the network.
Use the following DNS server address
Select this when you set the fixed address as the IP
Administrating the Camera
address of DNS server.
Primary DNS server
Type the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS server
Type the IP address of the secondary DNS server, if
necessary.
MAC address
Displays the MAC address of the camera.
Obtain an IP address automatically
(DHCP)
DHCP server is installed on the network. Select it when
the IP address is assigned by DHCP server. IP address is
assigned automatically.
Note
When you set Obtain an IP address automatically
(DHCP), make sure that DHCP server is working on the
internet.
Use the following IP address
Select this when a fixed IP address is set.
IP address
Type the IP address of the camera.
Host name
Type the host name of the camera to be transmitted to the
DHCP server. This setting is valid only when Obtain an
IP address automatically (DHCP) is selected in the
Network tab.
Domain suffix
Type the domain suffix of the camera to be transmitted
to the DHCP server. This setting is valid only when
Obtain an IP address automatically (DHCP) is
selected in the Network tab.
Note
The domain suffix is sent to the DHCP server as FQDN
(Fully Qualified Domain Suffix) information when Host
name is set.
HTTP port number
Normally select 80. If you want to use a port number
other than 80, select the text box and type a port number
between 1024 and 65535.
Note
When you have set the HTTP port number to a number
other than 80 in the Network setting menu or in the IP
38
Configuring the Network — Network setting Menu
Page 39

Setup Program, access the camera again by typing the IP
address of the camera on your Web browser as follows:
Example: when HTTP port number is set to 8000
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Password
Type the password for the authentication necessary for
PPPoE connection. Type comfirm from 1 to 32
characters.
Re-type password
To comfirm the password, re-type the password typed in
the password box.
Obtain DNS server address automatically
Select to obtain the address of DNS server
automatically.
PPPoE Tab - Setting of PPPoE Connection
Use it when you connect the camera with PPPoE (Pointto-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE connection is
the protocol that is widely used in xDSL (digital affiliate
line such as ADSL, VDSL or SDSL) as the
authentication and connection system.
PPPoE
Set whether you connect the camera using PPPoE
function or not. When On is selected, PPPoE connection
is used.
Use the following DNS server address
Select to set the fixed address as the IP address of DNS
server.
Primary DNS server
Type the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS server
Type the IP address of the secondary DNS server, if
necessary.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Dynamic IP address notification
Tab — Notifying the IP Address
When the DHCP setting is set to On or PPPoE setting is
set to On on the Network tab, you can send notification
of the completion of the network settings using the
SMTP or HTTP protocol.
Administrating the Camera
IP address
When you connect to the network by PPPoE function, IP
address obtained at PPPoE connection is displayed.
User ID
Type the user ID for the authentication necessary for
PPPoE connection. Type up to 64 characters.
Configuring the Network — Network setting Menu
39
Page 40

e-Mail (SMTP) notification
Select On to send an e-Mail when the DHCP setting is
completed.
SMTP server name
Type the name or IP address of the SMTP server to use
for sending an e-Mail, up to 64 characters.
HTTP notification
Select On to output a command to the HTTP server
when the DHCP setting is completed. Using this
function, you can configure a useful system, for
example, to view the access log stored in the HTTP
server or start an external CGI program.
URL
Authentication
Select the authentication required when you send an eMail.
None: Select if no authentication is required when an e-
Mail is sent.
SMTP authentication: Select if authentication is
required if an e-Mail is sent.
POP before SMTP: Select if POP before SMTP is
required when an e-Mail is sent.
POP server name
Administrating the Camera
It is necessary when the POP before SMTP is selected
in Authentication.
Type the POP (receiving mail) server name up to 64
characters. Or type the IP address of the POP server.
This setting is necessary when the SMTP server which
sends e-Mails performs authentication using the POP
user account.
Specify the URL to send HTTP request, using up to 256
characters. The URL is normally written as follows:
http://ip_address[:port]/path?parameter
ip_address: Type the IP address or host name of the host
to which you want to connect.
[:port]: Specify the port number to which you want to
connect. If you want to use the well-known port
number 80, you do not need to input this value.
path: Type the command.
parameter: Type the command parameter if necessary.
You can use the special tags mentioned below for the
parameters.
Proxy server name
When you send HTTP request via a proxy server, type
the name or IP address of the proxy server, using up to
64 characters.
User name, Password
Type the user name and Password of the user who has
the mail account. This setting is necessary when the
SMTP server which sends e-Mails performs
authentication.
Recipient e-Mail address
Type the recipient e-Mail address up to 64 characters.
You can specify only one recipient e-Mail address.
Administrator e-Mail address
Type the e-Mail address of the camera administrator, up
to 64 characters. This is used as the reply address or the
address for a system mail from the mail server.
Subject
Type the subject/title of the e-Mail up to 64 characters.
Message
Type the text of the e-Mail up to 384 characters. (A line
break is equivalent to 2 characters.) You can describe
the information of the acquired IP address, etc. using the
special tags mentioned below.
Proxy port number
Specify the port number when you send HTTP request
via the proxy server. Set a port number between 1024
and 65535.
Method
Select the HTTP method GET or POST.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
About the special tags
You can use the following five special tags to allow the
notification of the settings acquired by the DHCP, such
as an IP address. Type the tags in the parameter section
of the URL that you described in the Message field of
the HTTP.
<IP>
Use this tag to embed the IP address acquired by the
DHCP in the text or parameter.
<HTTPPORT>
Use this tag to embed the specified HTTP server port
number in the text or parameters.
40
Configuring the Network — Network setting Menu
Page 41

<MACADDRESS>
Use this tag to embed the MAC address of the interface
whose IP address you have acquired by the DHCP, in the
text or parameter.
Setting the User
— User setting Menu
<MODELNAME>
Use this tag to embed the camera's model name (SNCP1) in the text or parameter.
<SERIAL>
Use this tag to embed the camera's serial number in the
text or parameter.
When you click User on the Advanced mode menu, the
User setting menu appears.
Use this menu to set the user names and passwords of
Administrator and up to 9 kinds of users (User 1 to User
9), and the access right of each user.
Administrating the Camera
Administrator, User 1 to 9
Specify User name, Password, Re-type password,
FTP user and Viewer mode for each user ID.
User name
Type a user name between 5 and 16 characters.
Password
Type a password between 5 and 16 characters.
Re-type password
To confirm the password, retype the password typed in
the Password box.
FTP user
Set whether allowed to log in to FTP server or not.
Check the box if allowed to log in to FTP server.
Viewer mode
If the user is authenticated when the main viewer is
displayed, you can select the viewer mode displayed
after authentication.
Full: You can operate all functions in this mode.
Light: You can operate the functions other than the
trigger button on the main viewer, TCP/UDP
switching button on the main viewer, and the frame
rate setting.
View: You can only monitor the camera image.
Setting the User — User setting Menu
41
Page 42

Viewer authentication
Set whether the user is authenticated or not when the
main viewer is displayed.
When you select On, the main viewer is displayed to suit
the authenticated user. When you select Off, select the
view mode of the main viewer page which is displayed
without authentication from Full, Light or View.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Administrating the Camera
Setting the Security
— Security setting Menu
When you click Security on the Advanced mode menu,
the Security setting menu appears.
Use this menu to limit the computers that can access the
camera.
Security function
To activate the security function, select On.
If you do not wish to use the security function, select
Off.
Default policy
Select the basic policy of the limit from Allow and Deny
for the computers specified on the Network address/
Subnet 1 to Network address/Subnet 10 menus below.
Network address/Subnet 1 to Network
address/Subnet 10
Type the IP addresses and subnet mask values you want
to allow or deny access to the camera.
You can specify up to 10 IP addresses and subnet mask
values. For a subnet mask, type 8 to 32.
Select Allow or Deny from the drop-down list on the
right for each IP address/subnet mask .
Tip
The subnet mask value represents the bit number from
the left of the network address.
For example, the subnet mask value for “255.255.255.0”
is 24.
If you set “192.168.0.0/24” and “Allow,” you can allow
access from the computers having an IP address between
“192.168.0.0” and “192.168.0.255”.
42
Setting the Security — Security setting Menu
Page 43

Note
You can access the camera even from a computer having
an IP address whose access right is set to Deny, if you
enter the user name and password set for the
Administrator boxes in the User setting menu.
Sending an Image via
mail
Menu
— e-Mail (SMTP) setting
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
When you click SMTP on the Advanced mode menu,
the SMTP setting menu appears.
By using e-Mail (SMTP) function, you can send a mail
with attached image file which has been shot linked with
the external sensor input or with the built-in motion
detection function. The image file can also be sent
periodically.
The e-Mail (SMTP) setting menu is composed of three
tabs: Common, Alarm sending and Periodical
sending.
Common Tab — Setting the e-Mail
(SMTP) Function
Administrating the Camera
e-Mail (SMTP)
Select On when you use the e-Mail (SMTP) function.
The common setting options are displayed below.
If you do not wish to use the e-Mail (SMTP) function,
select Off and click OK.
Notes
• During transmission of an image file via mail, the
frame rate and operation performance of the monitor
image of the main viewer decline.
• While the camera video mode is set to MPEG4, the
image of the composite video signal output from the
video output connector of the camera may be distorted
during mail transmission.
• You cannot send an audio file by using the mail
sending function.
Sending an Image via mail — e-Mail (SMTP) setting Menu
43
Page 44

SMTP server name
Type the SMTP server name up to 64 characters, or the
IP address of the SMTP server.
Alarm sending Tab — Setting the
mail sending mode when detecting
the alarm
Authentication
Select the authentication required when you send an eMail.
None: Select if no authentication is required when an e-
Mail is sent.
SMTP authentication: Select if authentication is
required when an e-Mail is sent.
POP before SMTP: Select if POP before SMTP
authentication is required when an e-Mail is sent.
POP server name
It is necessary when the POP before SMTP is selected
in Authentication.
Type the POP (receiving mail) server name up to 64
characters, or type the IP address of the POP server. This
Administrating the Camera
setting is necessary when the SMTP server which sends
e-mails performs authentication using the POP user
account.
Set to send the mail with connection to the alarm
detection by the external sensor input or by the built-in
motion detection function.
User name, Password
Type the user name and Password of the user who has
the mail account. This setting is necessary when the
SMTP server which sends e-mails performs
authentication.
Recipient e-Mail address
Type the recipient e-Mail address up to 64 characters.
You can specify up to three recipient e-Mail addresses.
Administrator e-Mail address
Type the Administrator e-Mail address up to 64
characters.
This address is used for reply mail and sending system
messages from the SMTP server.
Subject
Type the subject/title of the e-Mail up to 64 characters.
When Alarm sending of the alarm tab is set to ON, the
mail sent due to the alarm detection will indicate the
type of alarm in the subject. [SI] is added for sensor
input detection, and [MD] is added for motion detection.
Message
Type the text of the e-Mail up to 384 characters. (A line
break is equivalent to 2 characters.)
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Alarm sending
Select On to set to send mail with connection to the
alarm detection.
File attachment
Set whether an image file is to be attached to the mail or
not.
When On is selected, the image file made by the settings
below is attached. When Off is selected, only the
message is sent.
Image file name
Type the file name you want to assign to the image to
attach a mail. You can use up to 10 alphanumeric, (hyphen) and _ (underscore) for naming.
Suffix
Select a suffix to add to the file name.
None: No suffix is added. The Image file name is
assigned to the image to be sent via an e-Mail.
Date & time: The date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The date/time suffix consists of lower two-digits of
year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits), hour
(2 digits), minute (2 digits), second (2 digits), and
consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit number
is added to the file name.
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and two fixed
digits 00 is added to the Image file name.
44
Sending an Image via mail — e-Mail (SMTP) setting Menu
Page 45

Tip
A consecutive number added to Date & time and
Sequence number is used to identify each of multiple
files created with one alarm event.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear to reset the Sequence number suffix to 1.
Alarm
Select the connected alarm.
Sensor input: The external sensor which is connected to
the sensor input of the camera I/O port.
Motion detection: Click Motion detection button, and
the Motion detection setting menu is displayed. You
can set the motion detection function (page 57).
Note
Motion detection works only when the camera Video
mode is set to MPEG4 and the Cropping is set Off.
Effective period
Set the period when the alarm detection is effective.
Always: The alarm detection is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the alarm
detection is effective in the schedule setting in the
other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the
Effective period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule
— Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Periodical sending Tab — Setting
the periodical mail sending mode
You can set to send mails periodically.
Administrating the Camera
Periodical sending
Select On when you want to send mails periodically. If
you select Off, Periodical sending is not executed.
Image file name
Type the file name of the image attached to the mail up
to 10 alphanumeric, - (hyphen) and _ (under score).
Suffix
Select a suffix added to the file name used when the mail
is sent.
None: The name of the sent file will be the Image file
name.
Date & time: The date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The date & time suffix consists of lower two-digits of
year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits), hour
(2 digits), minute (2 digits) and second (2 digits), and
consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit number
is added to the file name.
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and two fixed
digits 00 is added to the Image file name.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear and the suffix of the sequence number
returns to 1.
Interval
Type the interval at which you want to send a mail
periodically. You can set the hour (H) and minutes (M)
between 30 minutes and 24 hours (one day).
Sending an Image via mail — e-Mail (SMTP) setting Menu
45
Page 46

Effective period
Set the period when the periodical sending is effective.
Always: The periodical sending is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the
periodical sending is effective in the schedule setting
in the other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule —
Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Sending Images to FTP
Server
— FTP client setting Menu
When you click FTP client on the Advanced mode
menu, the FTP client setting menu appears.
Use this menu to set up for capturing and sending still
images to an FTP server. By using FTP client function,
you can send the image and audio file which has been
shot and recorded linked with the external sensor input
or with the built-in motion detection function to FTP
server. The image file can also be sent periodically.
FTP client setting menu is composed of three tabs
Common, Alarm sending and Periodical sending.
Common Tab — Setting the FTP
Administrating the Camera
Client Function
46
Sending Images to FTP Server — FTP client setting Menu
FTP client function
To activate the FTP client function, select On. The FTP
client setting page appears.
When you do not wish to use the FTP client function,
select Off.
Note
The frame rate and operability on the main viewer may
decrease while a file is being transmitted by the FTP
client function.
FTP server name
Type the FTP server name to upload still images up to 64
characters, or the IP address of the FTP server.
User name
Type the user name for the FTP server.
Page 47

Password
Type the password for the FTP server.
Re-type password
To confirm the password, type the same characters as
you typed in the Password box.
Passive mode
Set whether you use the passive mode of FTP server or
not when connecting to FTP server. Select On to
connect to FTP server using the passive mode.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Alarm sending Tab — Setting the
FTP client action when detecting
the alarm
Suffix
Select a suffix to add to the file name.
Date & time: The date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The date/time suffix consists of lower two-digits of
year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits), hour
(2 digits), minute (2 digits) and second (2 digits), and
consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit number
is added to the file name.
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and an
consecutive 2 digits number is added to the Image
file name.
Tip
A consecutive number added to Date & time and
Sequence number is used to identify each of multiple
files created with one alarm event.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear to reset the Sequence number suffix to 1.
Administrating the Camera
Set to forward the image and audio file to the specified
FTP server linked with the alarm detection by the
external sensor input or by the built-in motion detection
function.
Alarm sending
Select On to send the image and audio file to FTP server
linked with the alarm detection.
Remote path
Type the path to the destination up to 64 characters.
Image file name
Type the file name you want to assign to the images
when sending to the FTP server. You can use up to 10
alphanumeric characters, - (hyphen) and _ (underscore)
for naming.
Alarm
Select the connected alarm.
Sensor input: The external sensor which is connected to
the sensor input of the camera I/O port.
Motion detection: Click Motion detection button, and
the Motion detection setting menu is displayed. You
can set the motion detection function (page 53).
Note
Motion detection works only when the Video mode is
set to MPEG4 and the Cropping is set to Off.
Effective period
Set the period when the alarm detection is effective.
Always: The alarm detection is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the alarm
detection is effective in the schedule setting in the
other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the
Effective period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule
— Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
Alarm buffer
Select Use alarm buffer when you forward the image/
audio of before and after the alarm detection (pre-alarm,
post-alarm).
If you do not select it, only the image of the moment of
the alarm detection is forwarded.
Click Alarm buffer to display the Alarm buffer setting
menu.
For details, see “Setting the Alarm Buffer — Alarm
buffer setting Menu” on page 56.
Sending Images to FTP Server — FTP client setting Menu
47
Page 48

OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Periodical sending Tab — Setting
the Periodical FTP Client Activity
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and two fixed
digits 00 is added to the Image file name.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear and the suffix of the sequence number
returns to 1.
You can set to send an image file to FTP server
periodically.
Administrating the Camera
Periodical sending
Select On when you want to use periodical sending. If
you select Off, Periodical sending is not executed.
Remote path
Type the remote path up to 64 characters.
Interval
Type the interval at which you want to send images to
the FTP server periodically. You can set the hour (H),
minutes (M) and seconds (S) between 1 second and 24
hours (one day).
Note
The actual interval may be longer than the set value,
depending on the image size, image quality setting, bit
rate and the network environments.
Effective period
Set the period when the periodical sending is effective.
Always: The periodical sending is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the
periodical sending is effective in the schedule setting
in the other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule —
Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Image file name
Type the file name of the image sent to FTP server up to
10 alphanumeric characters, - (hyphen) and _ (under
score).
Note
You cannot send the audio file by using the periodical
sending function of FTP.
Suffix
Select a suffix to be added to the file name sent to FTP
server.
None: The name of the sent file will be the Image file
name.
Date & time: The date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The date & time suffix consists of lower two-digits of
year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits), hour
(2 digits), minute (2 digits) and second (2 digits), and
consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit number
is added to the file name.
48
Sending Images to FTP Server — FTP client setting Menu
Page 49

Recording Images in
Free space
Shows the current free space of the builtin memory.
Memory
— Image memory setting Menu
When you click Image memory on the Advanced mode
menu, the Image memory setting menu appears.
By using the image memory function, you can record the
image and audio file, which has been shot being linked
with the external sensor input or with the built-in motion
detection function, to the built-in memory (about 8 MB)
of the camera. The image file can also be recorded
periodically.
The recorded image and audio files can be found or
downloaded to the computer using the FTP server
function. (See “Downloading Images from the Camera
— FTP server setting Menu” on page 52.)
Image memory setting menu is composed of three tabs
Common, Alarm recording and Periodical recording.
Notes
• The image and audio files recorded in the built-in
memory will be erased when the power of the camera
is turned off.
• The frame rate and operability on the main viewer
may decrease during image storage in the built-in
memory.
• When the Overwrite is set to On, a warning mail is not
sent to the Administrator.
Common Tab — Setting the Image
memory Function
Overwrite
Select to overwrite the file or not when there is
insufficient memory space to record the image.
Select On to allow overwriting. The oldest file or folder
is overwritten first.
Select Off to prohibit overwriting. In this case, a new
file cannot be stored.
Capacity warning
Select On to send a warning mail to the Administrator
when the built-in memory space is low or the memory is
full. Select Off if you do not want to send a warning
mail.
Note
When the Overwrite is set to On, a warning mail is not
sent to the Administrator.
SMTP server name
Type the name of the SMTP server to use for sending an
e-Mail, up to 64 characters.
Otherwise type the IP address of SMTP mail server.
Authentication
Select the authentication required if you send a mail.
None: Select if no authentication is required when an e-
mail is sent.
SMTP authentication: Select if authentication is
required when an e-Mail is sent.
POP before SMTP: Select if POP before SMTP
authentication is required when an e-Mail is sent.
Administrating the Camera
Image memory
Set whether you use the Image memory function or not.
When you select On, the Common setting options are
displayed in the below. If you do not use it, select Off
and click OK.
POP server name
This is necessary when POP before SMTP is selected
in Authentication.
Type POP (receiving mail) server name up to 64
characters. Otherwise type the IP address of POP server.
This setting is necessary when SMTP server that sends a
mail authenticates using the account of POP user.
User name, password
Type the user name and the password of the user who
has the mail account. This setting is necessary when
SMTP server that sends a mail authenticates.
Administrator e-Mail address
Type the e-Mail address of the recipient of the warning
mail (e-Mail address of the camera Administrator), up to
64 characters.
Recording Images in Memory — Image memory setting Menu
49
Page 50

OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Alarm recording Tab — Setting the
Image Memory Function when
Detecting the Alarm
Tip
A consecutive number added to Date & time and
Sequence number is used to identify each of multiple
files created with one alarm event.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear to reset the Sequence number suffix to 1.
You can set to record the image and audio file to the
built-in memory linked with the external sensor input or
with the built-in motion detection function.
Administrating the Camera
Alarm
Select the connected alarm.
Sensor input: The external sensor which is connected to
the sensor input of the camera I/O port.
Motion detection: Click Motion detection button, and
the Motion detection setting page is displayed. You
can set the motion detection function (page 53).
Note
Motion detection works only when the Video mode is
set to MPEG4 and the Cropping is set to Off.
Effective period
Set the period when the alarm detection is effective.
Always: The alarm detection is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the alarm
detection is effective in the schedule setting in the
other section.
Alarm recording
Select On to set to record the image and audio file to the
built-in memory linked with the external sensor input or
with the built-in motion detection function.
Image file name
Type the file name you want to assign to the images
when saving in the built-in memory. You can use up to
10 alphanumeric characters, - (hyphen) and _
(underscore) for naming.
Suffix
Select a suffix to add to the file name.
Date & time: The Date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The Date & time suffix consists of lower two-digits
of year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits),
hour (2 digits), minute (2 digits), second (2 digits)
and consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit
number is added to the file name.
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and an
consecutive 2 digits number is added to the Image
file name.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule —
Schedule setting Menu” on page 55)
Alarm buffer
Select Use alarm buffer when you forward the image/
audio of before and after the alarm detection (pre-alarm,
post-alarm).
If you do not select it, only the image of the moment of
the alarm detection is forwarded.
Click Alarm buffer to display the Alarm buffer setting
menu.
For details, see “Setting the Alarm Buffer — Alarm
buffer setting Menu” on page 56.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
50
Recording Images in Memory — Image memory setting Menu
Page 51

Periodical recording Tab — Setting
the Periodical recording mode
You can set to record the image file to the built-in
memory periodically.
Periodical recording
Select On when you want to use periodical recording. If
you select Off, the Periodical recording is not executed.
Image file name
Type the file name of the image recorded to the built-in
memory up to 10 alphanumeric, - (hyphen) and _ (under
score).
Note
Interval
Type the interval at which you want to record an image
in the built-in memory periodically. You can set the hour
(H), minutes (M) and seconds (S) between 1 second and
24 hours (one day).
Note
The actual interval may be longer than the set value,
depending on the image size or the network
environments.
Efective period
Set the period when the periodical recording is effective.
Always: The periodical recording is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the
periodical recording is effective in the schedule
setting in the other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule — Schedule
setting Menu” on page 55)
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Folder structure of image memory
When the image memory function is used, the images
are recorded with the following folder structure.
Administrating the Camera
You cannot send the audio file by using the periodical
recording function.
Suffix
Select a suffix to add to the file name.
None: The recording file name will be the Image file
name.
Date & time: The date & time suffix is added to the
Image file name.
The date/time suffix consists of lower two-digits of
year (2 digits), month (2 digits), date (2 digits), hour
(2 digits), minute (2 digits), second (2 digits), and
consecutive number (2 digits), thus 14-digit number
is added to the file name.
Sequence number: A consecutive number of 10 digits
between 0000000001 and 4294967295 and two fixed
digits 00 is added to the Image file name.
Sequence number clear
Click Clear and the suffix of the sequence number
returns to 1.
Root
Date_No.
Date_No.
xxxxxxx.m4f
yyyyyyy.m4f
aaaaaaa.jpg
bbbbbbb.jpf
ccccccc.m4f
zzzzzzz.m4f
qqqqqqq.m4f
A represents a folder created automatically.
The Date_No. folder has a 9-digit name consisting of the
last two digits of the year (2 digits), month (2 digits), day
(2 digits), underscore and sequence number (2 digits).
In the built-in memory, one folder automatically created
can store image files of about 1 MB. If the size of the
image files exceeds that value, a new folder is created
automatically to continue recording.
About the extension of a file
A file to be recorded/sent using the image memory
function or the FTP client function has one of the
Recording Images in Memory — Image memory setting Menu
51
Page 52

following three extensions depending on the video mode
setting and the recording/sending settings of the camera.
.m4f: Represents the MPEG4 video mode.
.jpf: Represents the JPEG video mode when Use alarm
buffer is checked in the alarm recording/alarm
sending menu. This file includes audio data.
.jpg: Represents the JPEG video mode when Use
alarm buffer is not checked in the alarm recording/
alarm sending menu. This file can be viewed with a
normal image viewer.
The SNC video player (page 71) allows playing of
“.m4f” and “.jpf” files.
Administrating the Camera
Downloading Images
from the Camera
server setting Menu
When you click FTP server on the Advance mode
menu, the FTP server setting menu appears. Use this
menu to set up for the FTP server function which finds a
specified image and audio file stored in the built-in
memory of the camera (about 8 MB) or download the
still image file from the camera.
— FTP
FTP server function
To activate the FTP server function, select On and click
OK.
When you do not use the FTP server function, select Off
and click OK.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Note
Note the followings when log in to FTP server of the
camera using the FTP client software on the computer.
• The frame rate and the operativity of the monitor
window in the main viewer will declime.
• While recording the image using the Image memory
function, you cannot delete the recording folder.
• When the recorded image or audio file is deleted, the
camera counts the free space of the built-in memory
again when logging off.
52
Downloading Images from the Camera — FTP server setting Menu
Page 53

Setting the Alarm Output
— Alarm output setting Menu
When you click Alarm output on the Advanced mode
menu, the Alarm output setting menu appears.
You can set in this menu to control the alarm out of I/O
port on the rear of the camera linked to the alarm
detection and the timer.
Alarm duration
Select the duration for which the alarm output is shortcircuited between 1 and 60 sec.
Effective period
This item is displayed when Mode is set to Alarm.
Set the period while the alarm detection is effective.
Always: The alarm detection is always effective.
Schedule: You can specify the period when the alarm
detection is effective in the schedule setting in the
other section.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule — Schedule
setting Menu” on page 55)
Schedule
This item is displayed when Mode is set to Timer.
Click Schedule and the setting menu for the effective
period is displayed. (“Setting the Schedule — Schedule
setting Menu” on page 55)
Administrating the Camera
Alarm output
To activate the Alarm output function, select On. The
basic setting options are displayed below.
When you do not use the Alarm output function, select
Off.
Mode
Select the mode of the Alarm output function.
Alarm: Controls alarm output by synchronizing with an
external sensor input or the built-in activity detection
function.
Timer: Controls alarm output by the timer.
Alarm
This item is displayed when Mode is set to Alarm.
Select the alarm to link the alarm output function. If the
selected alarm is detected, the alarm output status
changes.
Sensor input: External sensor connected to sensor input
of the camera I/O port
Motion detection: To set the motion detection function,
click Motion detection. The Motion detection
setting page appears (see page 57).
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Note
The motion detection function can activate or be set only
when the Video mode of the camera is set to MPEG4
and the Cropping is set Off.
Setting the Alarm Output — Alarm output setting Menu
53
Page 54

Note
Setting the Operations
from the Viewer Page
Trigger setting Menu
Click Trigge r on the Advanced Mode menu to display
the Trigger Setting menu.
In this menu, you will select the activities when
Trigger icon is clicked on the main viewer.
Administrating the Camera
—
While the Video mode is set to MPEG4, the image of
the composite video signal output from the video output
connector of the camera may be distorted during mail
transmission.
e-Mail (SMTP)
Checking this box allows you to select e-Mail from the
trigger drop-down list in the main viewer.
By selecting e-Mail and clicking , a still image of the
moment you click is captured, and your e-mail with the
image file attached is sent to the specified mail address.
When you click e-Mail (SMTP) button, the Trigger (e-
Mail) setting menu is displayed. You can set necessary
options here. The setting options and setting procedures
are the same as those of the e-Mail (SMTP) setting menu
(page 43).
FTP client
Checking this box allows you to select FTP from the
trigger drop-down list in the main viewer.
By selecting FTP and clicking , a still image of the
moment you click is captured, and the image file is sent
to the FTP server.
When you click FTP client button, the Trigger (setting)
FTP client menu is displayed. You can set necessary
options here. The setting options and setting procedures
are the same as those of the FTP client setting menu
(page 46).
54
Setting the Operations from the Viewer Page — Trigger setting Menu
Image memory
Checking this box allows you to select Image memory
from the trigger drop-down list in the main viewer.
Page 55

By selecting Image memory and clicking , a still
image of the moment you click is captured, and the
image file is recorded in the built-in memory.
When you click Image memory button, the Trigger
(setting) Image memory menu is displayed. You can
set necessary options here. The setting options and
setting procedures are the same as those of the Image
Memory setting menu (page 49).
Setting the Schedule
— Schedule setting Menu
When you click Schedule on the Advanced mode menu,
the Schedule setting menu appears.
This is the same menu as the setting menu which is
displayed when you click Schedule to set Effective
period and Schedule in FTP client setting menu, e-Mail
(SMTP) setting menu, Image memory setting menu,
Alarm out setting menu and so on.
Example: When setting e-Mail (SMTP) (the alarm
sending) in the Schedule setting menu
Administrating the Camera
Alarm output
Checking this box allows you to select Alarm output
from the trigger drop-down list in the main viewer.
You can control On (short circuit ) or Off (open) by
selecting Alarm output and clicking the .
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Schedule selection
Select the list box to specify the schedule you want to
set. e-Mail (SMTP) – Alarm, e-Mail (SMTP) –
Periodical, FTP – Alarm, FTP – Periodical, Image
memory – Alarm, Image memory – Periodical,
Alarm output – Alarm or Alarm output – Timer can
be selected.
The time period on the right of the checked day is the
effective period of the schedule.
Mon (Monday) to Sun (Sunday)
The time period on the right of the checked day is the
effective period of the schedule.
Start time, End time
Specify the Start time and the End time.
Use the same time schedule every day
When this is checked, the Start time and End time set
to Mon (Monday) are applied to all days. In this case,
the Start time and End time of the other days than Mon
(Monday) cannot be input.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Setting the Schedule — Schedule setting Menu
55
Page 56

Note
Setting the Alarm Buffer
— Alarm buffer setting Menu
When you click Alarm buffer on the Advanced mode
menu, the Alarm buffer Setting menu appears.
You can set the Pre-alarm image and audio (the image
and audio before the alarm detection) and the Post alarm image and audio. These can be set when Alarm
sending or Alarm recording of FTP client setting menu
or Image memory setting menu is set to On, and besides
when Use alarm buffer is selected.
Administrating the Camera
The value of Recording capacity differs depending on
Image size, Bit rate (for MPEG4) and Image quality (for
JPEG) in the camera setting menu.
OK/Cancel
See “Buttons common to every setting menu” on page
29.
Video mode
The Video mode setting in the Common tab of the
Camera setting menu is displayed.
MPEG4: Shows the present output format of the camera
is MPEG4.
JPEG: Shows the present output format of the camera is
JPEG.
Recording capacity
Displays the maximum recording capacity of alarm
buffer in the present camera setting of the video mode,
image size, bit rate and frame rate.
Pre-alarm period: Displays the maximum recording
capacity of image/audio before the alarm detection.
Post-alarm period: Displays the maximum recording
capacity of image/audio after the alarm detection.
Recording time
Set the recording time for the Pre-alarm image/audio
and Post alarm image/audio.
Pre alarm period: Type the recording time of the
image/audio before the alarm detection.
Post alarm period: Type the recording time of the
image/audio after the alarm detection.
56
Setting the Alarm Buffer — Alarm buffer setting Menu
Page 57

Setting the Motion
Detection Function
Motion detection setting Menu
—
Motion detection indicator
The moving level of the present shooting image inside
the specified Window is shown in the graph. The even
line shows the threshold level for Motion detection
which will be a guide to set the sensitivity properly.
When you click Motion detection on the Advanced
mode menu, the Motion detection setting menu appears.
You can set the conditions to activate the built-in motion
detection function in this menu.
This is the same menu with the setting menu which is
displayed when you click Motion detection in Alarm
sending of e-Mail (SMTP) setting menu, Alarm sending
or FTP client setting menu, Alarm recording of Image
memory setting menu and so on.
Notes
• The motion detection function can activate or be set
only when the Video mode of the camera is set to
MPEG4 and the Cropping is set Off.
• Before actual use, perform an operation test and
confirm that the Motion detection function works
correctly.
Sensitivity slider bar
Use it to set the detection sensitivity of the monitoring
image.
When the slider bar is moved to the left end, the
sensitivity will be 0 and any motion will not be detected.
The right end is the maximum sensitivity.
OK button
Click to send the set values to the camera and confirm
the settings.
Setting the Motion Detection Area, Sensitivity and Threshold level
Set the motion detection working area, the sensitivity
and the threshold level as follows:
1
Check Window 1 check box.
Window 1 is shown on the monitor display.
2
Settle Window 1 in the area you want to set Motion
detection.
Click and drag Window 1 to move it or change the
size of it.
Administrating the Camera
Monitor display
You can monitor the moving image and set the detection
Window.
Window 1 to 4 check box
When you check it, the specified Window is displayed
on the monitor display.
Threshold slider bar
Set the Threshold level so as to judge whether there has
been any motion in the camera image or not. You can
change the Threshold level displayed in the Motion
detection indicator.
3
Set the Sensitivity of Motion detection.
Adjust it referring to the level indicator of Motion
detection.
To increase the sensitivity, move the Sensitivity
slider bar to the right.
To decrease, move it to the left.
When you release the mouse, the new setting is
applied to the level of motion detection indicator.
4
Set the Threshold level of Motion detection.
Adjust the Threshold slider bar in the same way of
step 3 to set the level the camera executes motion
detection.
5
If necessary, set the Motion detection working
areas, the sensitivities and the Threshold level of
the other Windows 2, 3, 4 by following steps 1 to 4.
6
After all settings, click OK.
Setting the Motion Detection Function — Motion detection setting Menu
57
Page 58

Notes
• While motion detection setting menu is displayed,
motion detection of Mail (SMTP), FTP client, Image
memory and Alarm output notification will not work.
Make sure to close Motion detection setting menu
after setting.
• Before using the Motion detection, perform the
operation test to confirm correct operation.
• The Motion detection may not operate correctly in the
following cases:
– while changing a setting on the Camera setting
menu
– when the object is dark
– when the camera is installed in an unstable place
that causes vibration to the camera
– when a small bit rate (64 kbps, 128kbps) is selected
in Bit rate setting of MPEG4
Administrating the Camera
58
Setting the Motion Detection Function — Motion detection setting Menu
Page 59

URL: http://www.register-snccam.net/
Using DDNS Service —
DDNS Setting Menu
Click DDNS of Administrator Menu to display the
DDNS setting menu. In this menu you can use the
Network Camera DDNS Service and link the camera
host name to the domain name. If you use this service,
you can access the camera using an URL such as “http:/
/(your host name).snccam.net”. For details of DDNS
service, access the following URL.
LAN WAN (Internet)
Network Camera
Por t 80
Private IP address
192.168.1.110
Broadband router
Private IP address
192.168.1.1
Note
To use this function, the camera must be connected to
the Internet.
To use this function, you need knowledge of broadband
router and port forwarding. The following shows an
example of the most basic system configuration for
using the network camera in the Internet.
Computer B
Modem
Internet
DDNS server
Administrating the Camera
Global IP address
xyz.37.128.50
Port forwarding
Computer A
Private IP address
192.168.1.100
Por t 80
Private IP address
192.168.1.110
Set up the camera and broadband router (hereinafter
called router) as follows in the DDNS setting menu page
before registering for DDNS service.
1
Connect the camera to the router, and set up the
network.
Refer to “Assigning the IP Address to the Camera”
(page 7) of “Preparation” or “Configuring the
Network — Network setting Menu” (page 38).
Note
Be sure to perform DNS setting for the camera.
Type the IP address assigned by the Internet Service
Provider in the Primary/Secondary DNS server.
Global IP address
(xyz.37.128.50)
Domain name
(abc-123.snccam.net)
Linked
2
Open the setup window of the router, and set the
port forwarding to the IP address set in the camera.
(For example: For the settings in the diagram
above, set as follows.
Port 80 y Private IP address 192.168.1.110)
Notes
• Refer to the User’s Guide provided with the
router for details of port forwarding setup. Port
forwarding may not be supported on some
routers, or may be called by a different name. If
necessary, contact the router manufacturer for
details.
• If using a port other than 80, set the same port
number (in the range 1024 to 65535) in the
camera’s setting menu and for port forwarding on
the router.
Using DDNS Service — DDNS Setting Menu
59
Page 60

3
On the router’s setup menus, check the global IP
address (for example, xyz.37.128.50 in the above
diagram) on the WAN side currently assigned by
the provider. Type the global IP address in the PC
browser and check if you can access the camera.
[DDNS]
Select whether to use the dynamic DNS function or
not by on or off.
Even after you have registered for the dynamic
DNS service, set it to off when you are not using it.
Notes
• To specify a port number other than 80 for port
forwarding, type a colon (:) after the global IP
address and then type the port number. (For
example: http://xyz.37.128.50:1024)
• On some routers, you cannot access the WAN
side global IP address via a network on the LAN
side of the router. In this case, check it using
another Internet access.
• After the above setup, the camera can be accessed
from any computer connected to the Internet. If
you want to restrict access to the camera, perform
the user setting and security setting procedures in
the camera setting menus.
Administrating the Camera
• If you cannot access the camera after performing
the above setup, consider the following
possibilities.
A The IP address that the provider assigns may
not be a global IP address.
B The port number (for example, Port 80) set for
port forwarding may be blocked by the
Internet Service Provider.
t Check with the provider.
C The port number set for port forwarding may
be blocked by security software or a firewall
installed in the computer.
t Check the settings of the security software
or firewall.
4
Click DDNS of the Administrator setting menu to
display the DDNS setting menu.
[DDNS ID]
This is the ID special for the equipment which is
used for the dynamic DNS service. It is used when
you proceed with New registration, Modify/
Unregister, Forgot password and so on in the
registration site.
When you access the registration site through the
DDNS setting menu page, the DDNS ID will have
already been input.
[Password]
[Re-type password]
Type the password set for dynamic DNS access. It
must consist of 6 to 16 characters, including letters
of the alphabet and numerals.
[New registration]
It is used when you proceed with New registration
for the dynamic DNS service. For details, refer to
the instructions below.
[Modify registration/Unregister]
This is used to jump to the Modify/Unregister page
of the registration site. For details, refer to “Modify
Registration/Unregister Process” given in the
registration site (http://www.register-snccam.net).
[Forgot password]
This is used to jump to the Forgot password page of
the registration site.
[Refresh IP address]
This is used when you proceed with manual
updating of the IP address for the DDNS server.
The camera routinely proceeds with updating of the
IP address at about hourly intervals, so you do not
need to use this button.
When you have pressed the reset button or
proceeded with Factory default after registration for
dynamic DNS, you can restart the dynamic DNS
service by this button.
The followings are explanations for the setting
menu item.
60
Using DDNS Service — DDNS Setting Menu
Page 61

5
In the DDNS setting window of the camera, select
On of DDNS, type Password and Re-type
password, and then click OK.
The password for the DDNS service is saved in the
camera, and it prepares for DDNS service
registration.
Note
When using the DDNS function, the serial number
of camera, MAC address and IP address will be sent
to the server. You should agree it before you go to
the next step.
6
Click the Register button to proceed with new
registration for the DDNS service.
The camera proceeds with “Product information
registration” for the registration server to prepare
for your registration for DDNS service.
When “Product information registration” is done
properly, the new window of the browser is
displayed and a “New registration” display of the
registration site opens. Type the same DDNS ID
and password as in the DDNS setting menu of the
camera, then click Next.
7
Read the “Terms of Service”, and click I agree after
agreement.
8
Type all items in the registration form, then click
Next.
[Host name]
Type the host name you want to apply to. Usable
characters are alphabets, numbers and hyphens (-).
3 to 16 characters can be used. The last character
cannot be a hyphen.
Administrating the Camera
Note
A DDNS ID has been already input when the
window is displayed. You do not have to input it.
[E-Mail address]
[E-Mail address (for confirmation)]
Type the e-mail address of the person registered.
Take care to type it correctly because a
confirmation e-mail will be sent to it for actual
registration of the dynamic DNS service.
[Notify service availability by e-mail]
Set whether you wish to receive e-mails which give
information on the management condition of the
service (stopping of the service by interference, and
so on) or not.
[Your country of residence]
Select your country or region.
Using DDNS Service — DDNS Setting Menu
61
Page 62

9
Verify the entered registration information, then
click Request Registration.
A message appears, advising that your registration
request has been accepted and that a confirmation
e-Mail has been set.
10
The confirmation e-mail should arrive at the e-mail
Administrating the Camera
address you specified for your registration. Within
one hour of clicking the Request Registration
button, access the URL provided in the e-mail.
11
Registration is now complete.
It takes a few minutes until the host name is
reflected to the system. You can then access and
check.
62
Using DDNS Service — DDNS Setting Menu
Page 63

Others
This section explains how to use the application
software and commands, including the supplied CDROM.
Using the Supplied Setup Program
Explains the functions except the Network tab in the
Setup Program.
To install the Setup Program, to assign the IP address
and to set the network, see “Assigning the IP address to
the Camera” on page 7 in “Preparations”.
Notes
• The IP Setup Program may not operate correctly if you
use a personal firewall or antivirus software in your
computer. In that case, disable the software or assign
an IP address to the camera using another method. For
example, see “Assigning the IP Address to the Camera
Using ARP Commands” on page 74.
• If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, disable the Windows Firewall
function. Otherwise the IP Setup Program will not
operate correctly. For the setting, see “Configuring
Windows Firewall” in “When using Windows XP
Service Pack 2” on page 10 or “Configuring Windows
Firewall” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 12.
Starting the Setup Program
Bandwidth Control Tab
The communication bandwidth can be set when the
Video mode of the camera is set to JPEG.
Note
When the Video mode of the camera is set to MPEG4,
the bandwidth cannot be changed.
1
Click the Bandwidth control tab to display the
bandwidth setting window.
The current bandwidth is displayed in Current
bandwidth.
2
Click to select the camera to set the bandwidth from
the list box.
Others
Select Program from Start menu of Windows, then
select Program, IP Setup Program and IP Setup
Program in sequence.
The IP Setup Program starts.
Network tab appears. The IP Setup Program detects
cameras connected to the local network and lists them
on the Network tab window.
When you are using Windows Vista, message “User
Account Control – An unidentified program wants
access to your computer” may appear. In this case, click
Allow.
3
Click to select the desired bandwidth from the
Setting bandwidth list box.
4
Type the Administrator name and Administrator
password in each box.
The factory settings of both items are “admin.”
5
Click OK.
If “Setting OK” is displayed, the bandwidth setting
is completed.
Using the Supplied Setup Program
63
Page 64

Date time Tab
Note
You can set the date and time on the camera.
1
Click the Date time tab to display the date/time
setting window.
Due to network properties, there may be a slight
difference between the displayed computer's date and
time and those set on the camera.
PPPoE Tab
PPPoE is used to connect to an ISP (Internet Service
Provider) via the Internet. Using PPPoE, you can
automatically obtain an IP address to connect to the
Internet from the ISP.
The following PPPoE setting items are provided for the
SNC-P1.
• User ID assigned by your ISP
• Password for the user ID
• DNS setting (automatic/manual setting)
1
Click the PPPoE tab to display the PPPoE setting
window.
Others
2
Click to select the camera you want to set the date
and time for.
You can select multiple cameras and set the date
and time simultaneously.
3
Select the date/time format from the Date time
format drop-down list.
4
Select the area where the camera is installed from
the Time zone selecting drop-down list.
5
Set the date and time.
You can set the date and time in two ways.
Manual current date time setting
Set the current date and time on the Manual
current date time setting boxes, and click OK.
The setting boxes are for the year (last two digits),
month, date, hour, minutes and seconds from left to
right.
PC current date time setting
The date and time set on the computer is displayed
in the PC current date time setting box.
Click OK on the right to set the camera’s date and
time to the displayed computer's date and time.
2
Click to select the camera you want to make the
PPPoE settings for.
3
Select On below the list to enable the PPPoE
setting.
To disable the PPPoE setting, select Off.
4
Type the user ID assigned by the ISP in the User ID
box.
64
Using the Supplied Setup Program
5
Type the password for the user ID in the Password
box.
Page 65

6
Retype the password for the user ID in the Re-type
password box.
7
Set the DNS server address.
Using the SNC audio
upload tool
— Transmitting
To obtain the DNS server addresses
automatically:
Select Obtain DNS server address automatically.
To specify the DNS server addresses manually:
Select Use the following DNS server address, and
type the Primary DNS server address and
Secondary DNS server address in each box.
8
Type the Administrator name and Administrator
password in each box.
The factory settings of both items are “admin.”
9
Click OK.
If “Setting OK” is displayed, the PPPoE setting is
completed.
Rebooting the Camera
Click Reboot on the Network tab to reboot the camera.
It will take about two minutes to start again.
Audio to Camera
The supplied SNC audio upload tool allows you to
transmit sound from the computer to the camera.
This section explains the setup and operations of the
SNC audio upload tool.
The SNC audio upload tool supports the following audio
data to be transmitted.
Audio CODEC Transmission rate
G.711 (µ-LAW) 64 kbps
G.726 40 kbps
G.726 32 kbps
G.726 24 kbps
G.726 16 kbps
Note
Only one user can transmit sound to the camera.
Meanwhile, another user will not be able to transmit
sound to the camera.
Others
Installing the SNC audio upload tool
1
Insert the CD-ROM in your CD-ROM drive.
A cover page appears automatically in your Web
browser.
If it does not appear automatically in the Web
browser, double-click on the index.htm file on the
CD-ROM.
When you are using Windows Vista, pop-up
“AutoPlay” may appear. For details, “Installing
software” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 11.
2
Click the Setup icon of SNC audio upload tool.
The “File Download” dialog opens.
When you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, a message regarding the active
contents may appear. For details, see “Installing
software” in “When using Windows XP Service
Pack 2” on page 9 or “Installing software” in
“When using Windows Vista” on page 11.
3
Click Open.
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
65
Page 66

Note
If you click “Save this program to disk” on the “File
Download” dialog, you cannot install the tool
correctly. Delete the downloaded file, and click the
Setup icon again.
4
Install the SNC audio upload tool following the
wizard displayed.
If the Software License Agreement is displayed,
read it carefully and accept the agreement to
continue with the installation.
Connecting the Camera to the Computer
1
Connect a speaker to the 5 (line output) jack on the
camera.
2
Connect a microphone to the microphone input jack
on the computer.
Note
1
Select Sound from Control Panel.
2
Open the Recording tab and check that Windows
has recognized the hardware correctly.
Using the SNC audio upload tool
When you start the SNC audio upload tool, the Setting
tab is displayed.
Setting tab
Use this menu to set the camera to transmit audio from
a computer or upload an audio file.
Others
If the microphone input jack of the computer is not set
correctly, no sound is transmitted from the computer and
nothing is output from the speaker connected to the
camera.
Set the microphone input jack from the control panel of
Windows.
On Windows 2000
1 Select Sounds and Multimedia from Control Panel.
2 Click Vo lu m e in the Sound Recording section on
the Audio tab.
The Recording Control window opens
3 Check Select in the Microphone section.
On Windows XP
1 Select Sounds and Audio Device from Control
Panel.
2 Click Vo lu m e in the Sound Recording section on
the Audio tab.
The Recording Control window opens.
3 Check Select in the Microphone section.
On Windows Vista
There are no settings regarding the microphone jack.
If recording cannot be made, connect a microphone
device to the computer and check that the recording
device operates correctly, as follows.
User
Set the User ID and Password for the administrator.
The factory setting of the User ID for the Administrator
is “admin,” and the Password is “admin.”
Single sign-on: Select On to use the same user ID and
same password for all the cameras. Select Off to set
the user ID and password individually for each
camera.
For the setting with Off, see “User ID/Password” on
page 67.
User ID: This item can be set when Single sign-on is set
to On. The user ID specified here is applicable to all
cameras.
Password: This item can be set when Single sign-on is
set to On. The administrator password specified here
is applicable to all cameras.
Proxy
Check this box when you use a proxy server for
communications. When it is not checked, direct
communications with the camera is performed.
66
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
Page 67

Auto detect: Select On to obtain the proxy setting
automatically from Internet Explorer.
Proxy address: Type the IP address or host name of the
proxy server.
Proxy port: Type the port number used for
communications with the proxy server.
Note
address when the IP address is obtained with a
DHCP server.
Model: Displays the model name of the network
camera.
Serial: Displays the serial number of the network
camera.
User: Displays the specified user ID and password. The
password is shown with turned letters.
The Proxy setting is applicable to all cameras. You
cannot use individual proxy settings for each camera.
Codec
Select the audio mode (Codec) from the drop-down list.
Save camera setting
Check this box to store the current settings and camera
list in the Setting tab. The same settings will be recalled
when the camera is rebooted.
Click this button to hide the camera list. Click it again to
display the camera list.
Target camera(s) (Camera list)
When the SNC audio upload tool starts, it automatically
detects Sony network cameras connected to the local
network and displays them in the camera list. Up to 256
cameras can be displayed in the list.
Select the check box on the left of the row to enable
audio transmission and audio file uploading for that
camera. You can then enable these functions
simultaneously for multiple cameras.
Select all
Click to select all the cameras in the camera list. This is
usable when you delete all the cameras from the list or
specify the same user ID and password for all the
cameras,
User ID/Password
Use this item when you specify the user ID and
password to communicate with the selected camera(s)
only.
Select the camera(s) from the camera list and click this
button, and the following dialog opens.
Type the user ID and password for the administrator and
click OK.
Others
Notes
• If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, disable the Windows Firewall
function. Otherwise the camera list may not be
displayed automatically. For details, see “Configuring
Windows Firewall” in “When using Windows XP
Service Pack 2” on page 10 or “Configuring Windows
Firewall” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 12.
• The SNC audio upload tool cannot detect the cameras
that are connected to the local network after the
program has started.
• The SNC audio upload tool cannot detect the network
cameras that are not equipped with the audio feature.
Camera select checkbox: The check box is located on
the left end of the row. Select this check box to
enable audio transmission and audio file uploading
for that camera.
MAC address: Displays the MAC address of the
network camera.
IP address: Displays the IP address of the network
camera. “DHCP” is shown at the end of the IP
Note
If you select multiple cameras from the camera list, the
same user ID and password are set for all the selected
cameras. The factory settings of both items are “admin.”
Add
Use this item when you add a new network camera to the
camera list manually. Click this button, and the
following dialog opens.
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
67
Page 68

Type the IP address and port number for the camera to
be added and click OK.
Notes
• An error dialog appears if the specified IP address
already exists in the camera list, is assigned for a
device other than the network camera, or does not
exist in the network.
• You cannot add new cameras if the maximum of 256
cameras has been displayed in the camera list.
Delete
Click this button to delete the selected camera(s) from
the camera list.
Others
Note on switching the tab
If an error occurs when you switch from the Setting tab
N (start) / x (stop)
Click N (start) to start audio transmission. The
transmission speed is displayed in the Bitrate box during
transmission. You can adjust the microphone volume
and enable/disable the muting, if necessary.
To stop the audio transmission, click x (stop).
to the Audio upload tab or the Voice alert tab, the camera
is shown in red. In this case, check the camera settings
and the user ID and password settings.
Audio upload tab
Use this menu to transmit audio from the computer to
the camera. You can transmit audio to multiple cameras
displayed in the camera list simultaneously.
Before transmitting, set Speaker output to On on the
Common tab of the Camera menu.
Notes
• Audio transmission stops if you switch the tab during
the transmission.
• Audio may be interrupted when the IP address is
changed if Obtain an IP address automatically
(DHCP) is set on IP address in the Network setting
menu.
• Audio may be interrupted if you transmit it to many
cameras simultaneously.
Sound adjustment and indicators
Adjust the microphone input volume by moving the
slider bar. You can adjust the volume even
during transmission.
Click to enable/disable sound muting. The
microphone input volume is displayed at the Level.
The transmission rate is displayed in the Bitrate box.
68
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
Click this button to hide the camera list. Click it again to
display the camera list.
Target camera(s) (Camera list)
Displays the cameras selected with the camera select
checkbox of the camera list in the Setting tab.
The list shows the information and status of the selected
cameras.
Page 69

IP address: Displays the IP address of the network
camera. “DHCP” is shown at the end of the IP
address when the IP address is obtained with a
DHCP server.
Model: Displays the model name of the network
camera.
Serial: Displays the serial number of the network
camera.
Status: Displays the current status of the camera.
Ready: The camera is ready for connection.
Connected: The camera connection is successful.
Fault: The camera connection is unsuccessful.
Sending: Audio data being transmitted
Down: Transmission is interrupted due to a network
problem.
When you click it during playback, playback stops and
the progress bar display returns to the start position.
(recording)
Click to start recording of the sound input to the
computer microphone. The maximum recording time is
30 seconds.
The codec specified in the Setting tab is used for the
recording.
The recorded file is displayed as “RecordedFile.vof.”
Notes
• Recording or playback stops if you switch the tab
during recording or playback.
• The recorded file is not stored in the computer.
Voice alert tab
Use this menu to record the sound through the
microphone connected to the computer and upload the
recorded audio file to the camera. You can upload the
audio file to multiple cameras selected from the camera
list simultaneously.
Recording/playback progress bar
You can check recording or playback progress with this
bar.
During recording, the right end of the bar represents 30
seconds and the remaining recording time is displayed
below the bar.
During playback, the maximum time of the bar depends
on the recorded time.
(file open)
Click to select a previously saved audio file. You can
play the selected audio file or upload it to the camera.
(save)
Click to save the recorded audio file to the computer.
Voice alert number select
Others
(playback)
To start playback, open the recorded file or another
audio file and click this icon.
You can check the recorded sound or the contents of the
selected audio file. During playback, the progress bar
shows playback progress.
(stop)
Click to stop recording or playback.
When you click it during recording, recording stops, and
you can review the recorded sound or upload the
recording to the camera.
Specify the voice alert number to which you want to
upload the audio file. For example, select 1 when
uploading to voice alert 1.
The name of the uploaded audio file is displayed to the
right of the number.
“Not uploaded” is displayed if no audio file is uploaded
to the camera.
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
69
Page 70

The audio file name will be “RecordedFile” + “Voice
alert number” + “.vof” if you upload an audio file
recorded using and not stored in the computer.
Uploading the recorded audio file to the
camera
Notes
• The voice alert number select is disabled if the camera
specified in the Setting tab has old-version software.
• The audio file name for the camera selected in the
camera list is displayed here. To check the uploaded
file name, click on the camera in the camera list.
• The audio file is uploaded to the same voice alert
number on all the cameras in the camera list. If the
camera has old-version software, the audio file is
automatically uploaded to voice alert number 1.
(upload)
Click to upload the recorded or selected audio file to the
camera specified in the Setting tab. Only one audio file
can be uploaded to the camera at a time.
Note
Uploading a new audio file overwrites the audio file
previously uploaded to the camera.
Others
Click this button to hide the camera list. Click it again to
display the camera list.
Tip
Before operating, create an audio file and set the camera
for audio uploading. Set the camera using the Setting
tab.
1
Click (recording) in the Voice alert tab to
start recording.
2
Click (stop) to stop recording.
Recording will stop automatically in 30 seconds.
3
Select the voice alert number.
4
Click (upload) to transmit the audio file to the
camera.
Saving the recorded audio file to the
computer
1
Click (recording) in the Voice alert tab to
start recording.
2
Click (stop) to stop recording.
Recording will stop automatically in 30 seconds.
Target camera(s) (Camera list)
Displays the cameras selected with the camera select
checkbox of the camera list in the Setting tab.
The list shows the information and status of the selected
cameras.
IP address: Displays the IP address of the network
camera. “DHCP” is shown at the end of the IP
address when the IP address is obtained with a
DHCP server.
Model: Displays the model name of the network
camera.
Serial: Displays the serial number of the network
camera.
Progress: Displays the progress of audio file
transmission.
Status: Displays the current status of the camera.
Ready: The camera is ready for connection.
Inquiry: The camera information is being asked for.
No func: The camera does not support the Voice
alert function.
Uploading: The audio file is being uploaded.
Fault: The audio file uploading is unsuccessful.
Succeeded: The audio file uploading is successful.
3
Click (save).
The Save as dialog appears. Type the file name and
save it.
Uploading the saved audio file to the
camera
1
Click (file open) in the Voice alert tab and
select the audio file to be uploaded.
2
Select the voice alert number.
3
Click (upload) to transmit the audio file to the
camera.
70
Using the SNC audio upload tool — Transmitting Audio to Camera
Page 71

Using the SNC video player
Audio File Recorded on
— Playing Video/
3
Select the file you want to play.
Information boxes on the selected file are displayed
on the left side of the window as follows:
Each click on the (information) icon switches
between “display” and “Not to display” of the file
information.
Camera
The supplied SNC video player allows you to play
video/audio data recorded on the camera with your
computer.
This section explains the setup and operations of the
SNC video player.
Downloading the SNC video player
To download the SNC video player, click the Player
icon located on the upper part of the main viewer of the
camera.
Type the user name and password for the administrator
on the download dialog and click OK. (The factory
settings of both items are “admin”.)
On the “File Download” dialog, click Save. The SNC
video player is saved in the computer.
Note
To operate the SNC video player, a special DLL file is
necessary. This file is automatically installed in the
computer when you view camera images with the
ActiveX viewer.
Using the SNC video player
1
Double-click the SNC video player downloaded
from the camera to start this application.
File information
Model name: Model name of the camera with
which the file is recorded.
IP address: IP address of the camera with which
the file is recorded.
Serial number: Serial number of the camera with
which the file is recorded.
Record event: Type of event used for the
recording: Sensor input or Motion detection.
Date&time: Recording date and time
Movie: Video Codec
Audio: Audio Codec
Playing a video/audio file
Click (start) to start playing from the beginning of
the selected file.
To freeze the movie temporarily, click (pause).
Click again to restart playing.
To stop playing, click (stop).
To restart playing, click (start) again.
Play stops when the file is played to the end.
To play from a specified point
Move the slider bar below the image display, and the file
will play starts according to the position of the slider bar
position.
Adjusting the sound
Adjust the playing sound volume by moving the
slider bar. Move it to the left end for the
minimum volume, and to the right end for the maximum
volume.
Click the speaker icon to enable/disable the sound
muting.
When the sound muting is on, no sound is heard even if
you move the slider bar to the right.
Others
2
Click the icon.
The Select File dialog opens.
Saving an image
Click (capture) icon during playing or pause and the
captured image is displayed on a pop-up dialog. To save
the image, click Save on the dialog. You can specify the
destination to which the image is to be stored and select
the JPEG or Bitmap format.
Using the SNC video player — Playing Video/Audio File Recorded on Camera
71
Page 72

Using the Custom Homepage Installer
You can store the homepage that you have created in the
camera and watch it.
Notes on creating the homepage
When you are creating the homepage, note the following
points.
• The file name should be typed up to 24 characters
including the extension.
• The file size of the homepage should be 2.0 MB or
less.
• To see the created homepage, set the Default URL in
the System setting menu.
Uploading the homepage to the camera using the Custom Homepage Installer
1
Insert the CD-ROM in your CD-ROM drive.
Others
A cover page appears automatically in your Web
browser.
If it does not appear automatically in the Web
browser, double-click on the index.htm file on the
CD-ROM.
When you are using Windows Vista, pop-up
“AutoPlay” may appear. For details, “Installing
software” in “When using Windows Vista” on
page 11.
2
Click the Start icon of Custom Homepage
Installer.
The “File Download” dialog opens.
When you are using Windows XP Service Pack 2 or
Windows Vista, a message regarding the active
contents may appear. For details, see “Installing
software” in “When using Windows XP Service
Pack 2” on page 9 or “Installing software” in
“When using Windows Vista” on page 11.
Note
If you click “Save this program to disk” on the “File
Download” dialog, the
CustomHomepageInstaller.exe file will be saved on
the computer. Double-click the saved file to start it.
4
Read the notes carefully, and click Next.
The Software License Agreement is displayed.
3
Click Open.
The installer starts and notes are displayed.
When you are using Windows Vista, message “User
Account Control – An unidentified program wants
access to your computer” may appear. In this case,
click Allow.
72
Using the Custom Homepage Installer
Page 73

5
Read the agreement carefully, select Agree if you
accept it, then click Next.
6
Type the IP address of the camera to be uploaded in
the IP address box.
10
Confirm that all items are correct, then click Next.
11
Type the path for the folder in which your
homepage is stored in the Source folder box, then
click Next.
7
Specify the HTTP port No. of the camera.
Initial HTTP port No. is set to 80.
8
When you use a proxy server, set the following:
For the proxy server of your environments, consult
your network administrator.
When using an HTTP proxy server:
Select Use HTTP proxy server, and type your
settings in the Proxy server address and Proxy
server port No. boxes.
When using an FTP proxy server:
Select Use FTP proxy server, and type your
settings in the Proxy server address and Proxy
server port No. boxes.
Note
If you cannot establish communications with the
camera using the proxy server being used, connect
the camera to the local network and run the installer
without using the proxy server.
9
Type the Administrator name and Administrator
password of the camera to be uploaded.
The factory settings of both items are “admin.”
12
Click OK.
Uploading of the homepage file starts.
Note
Do not turn off the camera until the camera is
rebooted after uploading the homepage file.
Others
Using the Custom Homepage Installer
73
Page 74

The following page will appear after a while.
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera Using ARP Commands
This section explains how to assign an IP address to the
camera using ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
commands without using the supplied IP Setup
Program.
Note
When you turn on the camera, execute the ARP and
PING commands within 5 minutes. Also when you
restart the camera, execute the operation within 5
minutes.
1
Open the command prompt on the computer.
2
Enter the IP address and the MAC address of the
After displaying this page, the camera will be
adjusted and rebooted automatically in two
minutes.
13
Click Finish to exit the program.
Others
camera to assign a new IP address, using the
following ARP commands.
arp -s <Camera's IP address> <Camera's MAC address>
ping -t <Camera's IP address>
Example:
arp -s 192.168.0.100 08-00-46-21-00-00
ping -t 192.168.0.100
3
When the following line is displayed on the
command prompt, hold down Ctrl and press C.
The display stops.
Reply from 192.168.0.100:bytes=32 time...
You will normally receive a reply after about 5
repetitions of “Request time out.”
4
Wait until the execution of PING finishes, then
input the following code.
arp -d 192.168.0.100
Note
If you do not receive a reply, check the following:
– Did you enter the ARP commands within 5 minutes
after it was turned on?
If not, turn off the camera and restart the operation.
– Is the NETWORK indicator on the camera flashing?
If the indicator goes off, the network connection has a
problem. Connect the network correctly.
– Did you enter the IP address previously used for
another device?
Assign a new IP address to the camera.
– Do the computer and the camera have the same
network address?
If not, set the same network address on the computer
and the camera.
74
Assigning the IP Address to the Camera Using ARP Commands
Page 75

Using the SNMP
This unit supports SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol). You can read MIB-2 objects
and write some MIB-2 objects using software such as
SNMP manager software. This unit also supports the
coldStart trap which occurs when the power is turned on
or the unit restarts, and the Authentication failure trap
which informs of an illegal access using SNMP.
Using CGI commands, you can set community name
and access limitation, reading/writing right, host to send
traps, and some MIB-2 objects. To allow these settings,
you need authentication by the camera administrator.
4 describes the case of “mib-2.system. sysContact.0”.
This field is used to describe the information on
administrator of this camera. Nothing is set at the
factory.
5 describes the case of “mib-2.system. sysName.0”.
This field is used to describe administration node of
this camera. Nothing is set at the factory.
6 describes the case of “mib-2.snmpEnable
AuthenTraps.0”. This example shows when “1”
(enable) is set. With this setting, a trap occurs when
there is an Authentication failure. When “2”
(disable) is set, no Authentication failure trap
occurs.
1. Inquiry Commands
You can check the SNMP Agent settings using the
following CGI commands.
<Method>
GET, POST
<Command>
“http://ip_adr/snmpdconf/inquiry.cgi?inqjs=snmp
(JavaScript parameter format)
http://ip_adr/snmpdconf/inquiry.cgi?inq=snmp
(standard format)
With the above inquiry, you can obtain the following
setting information. The following explains the setting
information using the inqjs=snmp (JavaScript
parameter) format.
var sysDescr=“SONY Network Camera SNC-P1” ...1
var sysObjectID=“1.3.6.1.4.1.122.8501” ...2
var sysLocation=“” ...3
var sysContact=“” ...4
var sysName=“” ...5
var snmpEnableAuthenTraps=“1” ...6
var community=“public,0.0.0.0,read,1” ...7
var community=“private,192.168.0.101,write,2” ...8
var trap=“public,192.168.0.101.1” ...9
1 describes the case of “mib-2.system. sysDescr.0”.
You cannot change this parameter.
2 describes the case of “mib-2.system.
sysObjectID.0”. You cannot change this parameter.
3 describes the case of “mib-2.system.
sysLocation.0”. This field is used to describe
information on the location of this camera. Nothing
is set at the factory.
7 describes the community name and the reading/
writing attributes. This example shows the
identification number “ID=1”, the community
name public, and enables read from any IP address
(0.0.0.0).
8 describes the community name and the reading/
writing attributes, similarly to 7. This example
shows the identification number ID=2, the
community name “private”, and enables “read/
write” by the SNMP request packet from the host
“192.168.0.101”.
9 describes the host name to send a trap. This
example shows the identification number “ID=1”,
the community name “public”, and enables sending
of traps to the host having the IP address
“192.168.0.101”.
2. Setting Commands
The unit supports the following setting commands of
SNMP.
<Method>
GET, POST
<Command>
http://ip_adr/snmpdconf/snmpdconf.cgi?
<parameter>=<value>&<parameter>=...&...
First, perform the settings of the following parameters.
1) sysLocation=<string>
Set the case of “mib-2.system.sysLocation.0” in the
<string> position. The maximum length of
<string> is 255 characters.
2) sysContact=<string>
Set the case of “mib-2.system.sysContact.0” in the
<string> position. The maximum length of
<string> is 255 characters.
Others
Using the SNMP
75
Page 76

3) sysName=<string>
Set the case of “mib-2.system.sysName.0” in the
<string> position. The maximum length of
<string> is 255 characters.
4) enaAuthTraps=<value>
Set the case value of “mib-2.snmp.snmp
EnableAuthenTraps.0” in the <string> position.
Type “1” (enable) or “2” (disable) in the <value>
position.
5) community=<ID>,<rwAttr>,
<communityName>,<IpAddressString>
Set the community name and the reading/writing
attributes. <ID> describes the setting identification
number (1 to 8), <rwAttr> describes a character
representing the reading/writing attribute (“r”, “R”,
“w or “W”), <communityName> describes the
community name to be set, and <IpAddressString>
describes the IP address of the host you allow
access (0.0.0.0 for any host).
Example: To allow reading/writing by any host in the
“private” community and having the ID number “2”.
community=2,w,private,0.0.0.0
<Command>
http://ip_adr/snmpdconf/snmpdconf.cgi?
snmpd=restart
Others
6) trap=<ID>,<communityName>,
<IpAddressString>
Set the host you want to send traps to. <ID>
describes the setting identification number (1 to 8),
<communityName> describes the community
name to send traps to, and <IpAddressString>
describes the IP address of the host to send traps to.
Example: To specify the destination of traps as the
private community and the ID number “1”.
rap=1,public,192.168.0.101
7) delcommunity=<ID>
This parameter is used to delete the previous
community setting. <ID> describes the community
setting identification number (1 to 8).
8) deltrap=<ID>
This parameter is used to delete the previous setting
of the host to send traps to. <ID> describes the trap
setting identification number (1 to 8).
When you have finished changing the SNMP setting
information using the above parameters 1) to 8), check
the changed settings using an inquiry commands. If the
changed settings are OK, restart the SNMP using the
following CGI command.
SNMP restart command
<Method>
GET, POST
76
Using the SNMP
Page 77

Glossary
ActiveX control
A component program object that can be used with web
pages or other application programs. The technology for
creating ActiveX control is part of software developed
by Microsoft.
ARP commands
The commands for checking the entry of the IP address
and MAC address in a host computer, or for updating
them.
Bandwidth control
To limit the amount of transmitted data.
Bit rate
The rate at which data bits are transmitted.
Capture
To display the audio and video digital data from the
video equipment on a computer.
Codec
Software/hardware for coding/decoding video and audio
data.
Contrast
The difference in tone between the lightest and darkest
portions of the image.
Default gateway
Device that can be used to access the other network.
DNS server
Abbreviation for Domain Name System server. As an IP
address required for connecting to the device on an IP
network is numerical and difficult to remember, the
Domain Name System was established. A domain name
is alphabetic and is easier to remember. When a client
computer uses a domain name to connect to another
computer, it asks a DNS server to translate the name into
the corresponding IP address. Then the client computer
can obtain the IP address of the computer to be
connected.
Frame rate
The number of frames of a moving image that can be
transmitted per a second.
FTP client
Software to be used for accessing the FTP server.
FTP server
A server to be used to transfer files via a network.
HTTP port
A port used to communicate between the web server and
the web client such as a web browser.
IP address
Abbreviation for Internet Protocol Address. An
individual IP address is basically assigned to each piece
of equipment connected to the Internet.
I-picture interval
The interval between I-pictures in Moving Picture
Experts Group (MPEG). I-picture means the decoding
picture without using the other picture's information.
Others
DHCP server
Abbreviation for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
server. The IP address of a terminal without an
individual IP address can be automatically distributed by
the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). The
DHCP server assigns the IP addresses to the terminals.
Digital zoom
Zooming in/out function of an image without using an
optical zooming function.
Java applet
A program written in Java language that can be used in
the Web browser.
Java Virtual Machine
Software that transfers the Java applet's byte code to the
native code of your system to execute it.
JPEG
Abbreviation for Joint Photographic Expert Group. The
still image compression technology or standards of the
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
and ITU-T. Popularly used as image compression format
on the Internet, etc.
Glossary
77
Page 78

MAC address
A network address that uniquely identifies each LAN
card.
Secondary DNS Server
Subsidiary DNS server used when a primary DNS server
cannot be used.
MPEG4
Abbreviation for Moving Picture Experts Group4. One
of the MPEG standards for image compression format
aiming to transmit images at a high compression rate
with lower picture quality.
Multicast
The class D IP address assigned between 224.0.0.0 and
239.255.255.255. Using this IP address enables you to
transmit the same data to multiple equipment.
SMTP server
A server for sending or relaying e-mail messages
between servers.
SNMP
A protocol for monitoring and managing network
devices.
Subnet mask
32-bit stream used to distinguish the subnet address
from the IP address.
Network address
The portion that identifies the local network (subnet) in
an IP address.
Network bandwidth
Bit rate that can be used for networking.
TCP
Abbreviation for Transmission Control Protocol. A
standard protocol used for the Internet connection.
Compared with the other protocol, UDP, TCP provides
reliable communication but the communication speed is
slower.
NTP server
Others
Network time server that transmits and receives time
information over the networks.
Passive mode
The mode whereby a client FTP allows TCP connection
for data transmission to the FTP server.
UDP
Abbreviation for User Datagram Protocol. A standard
protocol used for the Internet connection. Compared
with the other protocol, TCP, UDP can transmit data
faster, but reliable communication is not guaranteed.
Unicast
POP server
A server for storing incoming e-mail until you have read
it.
Transmission of the data to the specified equipment on a
network by specifying a single address.
PPPoE
A protocol to enable use of the point-to-point protocol
(PPP) via the Ethernet.
Primary DNS server
One of the DNS servers that can first reply to a request
by connected devices or other DNS servers.
Proxy server
A server or software that acts as an intermediary
between a local network and the Internet so that it can
connect to the Internet in place of a computer on a local
network
Saturation
The degree to which the color is pure.
78
Glossary
Page 79

Index
A
Access log ...................................... 33
access right..................................... 42
ActiveX control.......................... 9
ActiveX viewer .............................. 18
activity detection function.............. 57
Administrator ........................... 16
administrator ............................ 16
Administrator e-mail address......... 27
administrator menu page................ 29
Advanced mode ............................. 28
Advanced mode Menu ...................28
Alarm ............................................. 47
alarm ........................................ 47
Alarm buffer........................30
alarm buffer.........................30
Alarm buffer setting Menu............. 56
Alarm output .......................23
alarm output ........................23
Alarm output setting Menu ............ 53
Alarm recording............................. 50
Alarm sending.......................... 44
ARP commands ............................. 74
Authentication................................ 27
authentication................................. 27
B
Backup setting data........................ 32
Bandwidth...................................... 63
Blue LED ................................. 26
blue LED.................................. 26
Brightness ...................................... 26
brightness ....................................... 26
C
, 12
, 41
, 41
, 53
, 47, 56
, 47, 56
, 30, 53
, 30, 53
, 47
, 31
, 31
cropping ......................................... 34
Custom Homepage Installer........... 31
D
Date & time.................................... 31
Date & time setting ........................26
date and time.......................26
Date_No. ........................................ 51
DDNS.............................................59
default gateway .............................. 38
Default policy.................................42
DHCP............................................. 38
Digital zoom............................. 19
digital zoom ............................. 19
DNS server..................................... 38
Domain suffix.................................38
Dynamic IP address notification.... 39
, 31, 64
, 21
, 21
E
Easy mode......................................25
e-Mail............................................. 30
e-Mail (SMTP)....................26
e-Mail (SMTP) setting Menu......... 43
e-Mail address................................40
, 27, 30
F
Factory default ...............................32
factory settings............................... 32
flash memory ................................. 31
Flickerless ......................................36
folder structure............................... 51
format of date and time.................. 32
Frame rate ................................ 19
frame rate ................................. 19
free space ....................................... 49
FTP client................................. 30
FTP client setting Menu................. 46
FTP server................................ 30
FTP server setting Menu................ 52
, 20
, 20
, 54
, 46
image memory.......................... 23
Image memory setting Menu ......... 49
Image quality.................................. 26
image quality.................................. 26
Image size ................................ 26
image size................................. 19
information bar...............................10
Information Bar message ............... 10
Internet Explorer ............................13
IP Address........................................7
IP address ............................. 7
IP address notification.................... 39
IP Setup Program .............................7
, 30
, 34
, 34
, 17, 38
J
Java.................................................18
Java applet viewer..........................18
JPEG......................................... 34
, 37
L
loading the setting data .................. 32
logging in .......................................17
M
MAC address..................................38
main viewer.............................. 13
main viewer page ...........................19
memory ..........................................49
menu section ..................................19
Message..........................................27
Microphone .................................... 26
Mode ..............................................27
monitor Image................................20
monitor image section.................... 20
Motion detection ...................... 30
motion detection....................... 30
Motion detection setting Menu ......57
Mount.............................................26
MPEG4..................................... 34
, 19
, 57
, 57
, 36
Others
Camera ........................................... 29
camera setting ................................ 34
Camera setting Menu ..................... 34
Cancel button ................................. 29
Capture..................................... 19
capture...................................... 19
CGI commands .............................. 75
communication bandwidth............. 63
contrast........................................... 36
Cropping ........................................ 34
, 21
, 21
H
Home.............................................. 19
Homepage Custom Tool................. 72
Host name ......................................38
HTTP.............................................. 40
HTTP commands ...........................40
I
Image memory ......................... 23, 30
N
Network.................................... 29, 38
network..................................... 29
network configuration.................... 38
Network setting Menu....................38
, 38
O
OK button.......................................29
overwrite ........................................49
Index
79
Page 80

P
Password .................................. 27, 41
password .................................. 27
Periodical recording....................... 51
periodical recording ....................... 51
Periodical sending.................... 45
periodical sending .................... 45
Picture ............................................ 35
Player ............................................. 19
POP server name............................ 27
port number.............................. 38
PPPoE ............................................ 64
Proxy port number ......................... 40
proxy server ................................... 40
Proxy server name.......................... 40
, 41
, 48
, 48
, 40
R
Reboot...................................... 32, 65
reboot ..................................32
Recipient e-mail address................ 27
recording images............................ 49
reset................................................ 37
, 34, 65
Software version ............................31
software version............................. 31
special tags..................................... 40
Subject............................................ 27
subject ............................................27
subnet mask.................................... 38
System...................................... 29
system configuring......................... 31
System log......................................33
, 31
T
TCP ................................................ 24
TCP/UDP ................................. 20
time difference ...............................32
Time zone....................................... 32
time zone........................................32
title .................................................40
title bar ...........................................31
Title bar name ................................31
Trigger.................................22
trigger............................19
Trigger setting Menu......................54
, 24
, 30, 54
, 22, 30, 54
White balance.................................26
white balance..................................26
Windows Firewall ..........................10
Windows Vista ...............................11
Windows XP Service Pack 2............ 9
S
saturation........................................ 36
saves the setting data...................... 32
Schedule................................... 30
schedule ................................... 30
Schedule setting Menu................... 55
Security ..........................................30
security........................................... 30
security setting ............................... 42
Security setting Menu .................... 42
Security Warning ..................9
sending images............................... 46
Serial number................................. 31
serial number.................................. 31
Setting ...................................... 19
Setup Program................................ 63
sharpness........................................ 36
SMTP server .................................. 40
SMTP server name......................... 27
SNC audio upload tool................... 65
SNC video player........................... 71
SNMP............................................. 75
, 55
, 55
, 10, 12
, 25
U
UDP (Multicast)............................. 24
UDP (Unicast)................................ 24
URL................................................ 31
User .....................................16
user......................................16
User name ................................ 27
user name ................................. 27
user setting ..................................... 41
User setting Menu .......................... 41
, 30, 41
, 30, 41
, 41
, 41
V
View size .................................. 19, 21
view size................................... 19
viewer.............................................18
Viewer mode .................................. 41
viewer mode................................... 41
voice alert number select................69
volume............................................ 20
, 21
W
welcome page......................13, 17, 31
Sony Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...