Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
This photo is CDP-338ESD
SPECIFICATIONS
Compact disc player
Frequency
response
Signal to noise ratio
Dynamic range
Harmonic distortion
Channel separation
2 Hz - 20 kHz ± 0.5 dB (CDP-338ESD)
2 Hz - 20 kHz ± 0.3 dB (CDP-608ESD)
More than 113 dB
More than 100 dB
Less than
0.0022%
More than 110 dB
Outputs
LINE OUT (FIXED)
(phono jacks)
LINE OUT (VARIABLE)
(phono jacks)
DIGITAL OUT
(COAXIAL)
(cable)
DIGITAL OUT (OPTICAL)
(optical output connector)
HEADPHONES
(stereo phone jack)
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK OR DOTTED
LINE WITH MARK ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS
AND IN THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE
OPERATION. REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH
SONY PARTS WHOSE PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS
SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR IN SUPPLEMENTS PUB
LISHED BY SONY.
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS PAR UNE MARQUE
SUR LES DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE
DES PIÈCES SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ
DE FONCTIONNEMENT. NE REMPLACER CES COM
POSANTS QUE PAR DES PIECES SONY DONT LES
NUMÉROS SONT DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL OU
DANS LES SUPPLÉMENTS PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.
Output level 2 V (at 50 kiloohms)
Load impedance over 10 kiloohms
Output level max. 2 V (at 50 kiloohms)
Load impedance over 50 kiloohms
Output level max. 0.5 Vp-p
Load impedance 75 ohms
Wave length 660 nm
Output level — 18 dBm
Output level max. 28 mW
Load impedance 32 ohms
À LA SÉCURITÉ!
CD Transport Mechanism Type
Optical Pick-Up Block Type
General
Power
requirements
Power
consumption
Dimensions
(approx., including
projections)
Weight (approx.)
Canadian Model
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism
AEP Model:
(CDP-338ESD)
220 V AC (or 240 V AC adjustable by
Sony personnel), 50/60 Hz
UK Model;
(CDP-338ESD)
240 V AC (or 220 V AC adjustable by
Sony personnel), 50/60 Hz
US, Canadian Model:
(CDP-608ESD)
120 VAC, 60Hz
E Model:
(CDP-338ESD)
110,120, 220 or 240 V AC adjustable,
50/60 Hz
27 W
470X125X375 mm
(w/h/d)
(18V bX5X 147 *
inches)
12.5 kg (27 lbs 11 oz)
COMPACT DISC PLAYER
US Model
CDP-608ESD
AEP Model
UK Model
E Model
CDP-338ESD
New
KSS-151A
BU-6B
continued on next page —
Page 2

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Remote commander
Remote control system
Power requirements
Dimensions
Weight
Supplied accessories
Connecting cord
Remote commander
Size AA batteries
Screws
Design and specifications subject to change without notice.
Infrared control
3 V DC with two batteries size AA
(lEC designation R6)
67X20X175 mm (w/h/d)
(2V.X’V,6X 7 inches)
135g(4.7oz)
Including batteries
1
(2 phono plugs
1
2
4
2 phono plugs)
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem,
perform the following safety check before releasing
the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized”
knobs, screws, and all other exposed metal parts for
AC leakage. Check leakage as described below.
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to
earth ground and from all exposed metal parts tp any
exposed metal part having a return to chassis, must
not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microampers). Leakage
current can be measured by any one of three
methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the
Simpson 229 or RCA WT-540A. Follow the
manufacturers’ instructions to use these instru
ments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data
Precision 245 digital multimeter is suitable for
this job.
Section Title
1. GENERAL
1-1. Location of Controls.....................................................3
2. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
.......................................
3. DIAGRAMS
3-1. Circuit Boards Location ..............................................7
3-2. Printed Wiring Boards.................................................9
3-3. Schematic Diagram.....................................................13
3- 4. Semiconductor Lead Layouts
.............
4. EXPLODED VIEWS
4- 1. Cover Section
4-2. Front Panel Section
.......................................
...................................................
4-3. Chassis Section............................................................23
4-4. Mechanism Section.....................................................24
4-5. Optical Pick-Up Block Section
5. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
.................................
..............................................
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by
means of a VOM or battery-operated AC volt
meter. The “limit” indication is 0.75 V, so
analog meters must have an accurate lowvoltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa
SH-63Trd are examples of a passive VOM that
is suitable. Nearly all battery operated digital
multimeters that have a 2V AC range are
suitable. (See Fig. A)
To Exposed Meta!
Parts on Set
0.15pF -p
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
•I.Skii
— Earth Ground
AC
voltmeter
(0.75 Vi
Page
4
18
21
22
25
26
SERVICING NOTE
NOTES ON HANDLING THE OPTICAL PICK
UP BLOCK OR BASE UNIT
The laser diode in the optical pick-up block may
suffer electrostatic breakdown because of the poten
tial difference generated by the charged electrostatic
load, etc. on clothing and the human body.
During repair, pay attention to electrostatic break
down and also use the procedure in the printed
matter which is included in the repair parts.
The flexible board is easily damaged and should be
handled with care.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance
of procedures other than those specified herein
may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
NOTES ON LASER DIODE EMISSION CHECK
The laser beam on this model is concentrated so as to be
focused on the disc reflective surface by the objective
lens in the optical pick-up block. Therefore, when check
ing the laser diode emission, observe from more than 30
cm away from the objective lens.
Page 3
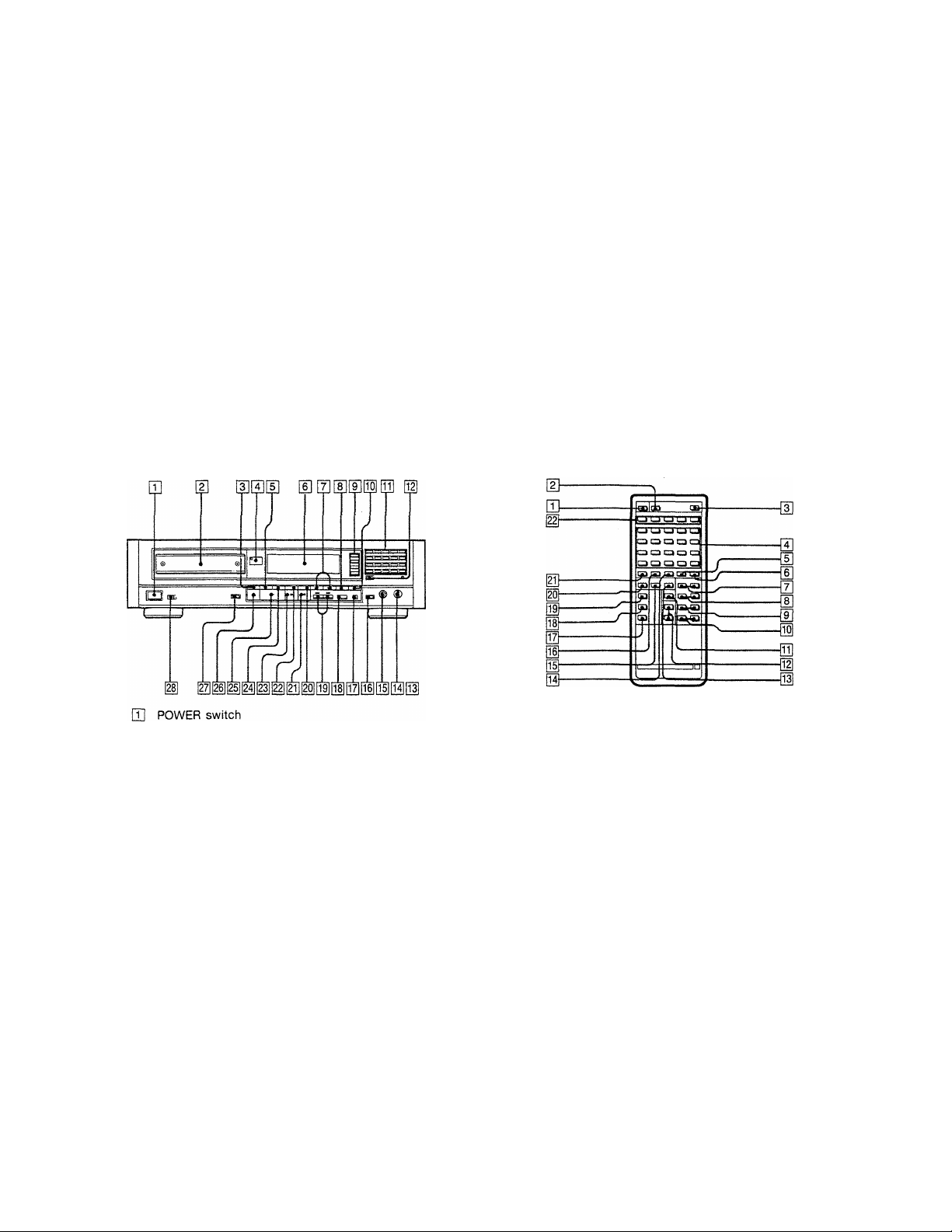
MODEL IDENTIFICATION — Label Model Number —
SONY®
COMPACT DISC PLAYER
□
1-1. LOCATION OF CONTROLS
CDP-338ESD only
MODEL No.
CDP-338ESD
CDP-608ESD
US model
Canadian model
AEP model
UK model
,E model
SECTION 1
GENERAL
AC :120V 60Hz 27W
AC :120V 60Hz 27W
AC:220V~50/60Hz 27W
AC:240V~50/60Hz 27W
AC:no, 120, 220, 240V~50/60Hz
27W
HJ Disc tray
[3] TIME/MEMO button
[3 Remote sensor
H] AUTO SPACE (auto space) button
[1] Display window
[7] (manual search) buttons
[U CHECK (program check) button
H] PLAY MODE buttons
PROGRAM button
SHUFFLE button
CONTINUE/SINGLE button
CUSTOM INDEX button
m CLEAR (program clear) button
[HI Numeric buttons
[12] >20 (over 20) button
m DISPLAY ON/OFF button
111 LINE OUT/PHONE LEVEL control
^ HEADPHONES jack
H EDIT/TIME FADE button
Hz) ERASE (memory erase) button
01 FILE (custom file) button
01 ►W (AMS*) buttons
[^ FILE RECALL button
■ (stop) button
^ FADER (fade in/fade out) button
^ II (pause) button
M REPEAT button
H ► (play) button
± (open/close) button
iZi DIGITAL OUTPUT ON/OFF button
^ Timer switch
*AMS is the abbreviation of Automatic Music Sensor.
A (open/close) button
m
FILE RECALL button
DISPLAY ON/OFF button
Numeric buttons
ERASE button
FILE (custom file) button
m
[g
◄◄ ►► (manual search) buttons
AMS buttons
INDEX buttons
^ ►► SLOW (low speed manual search)
buttons
FADER (fade in/fade out) button
LINE OUT VOLUME (line out/headphone
volume) buttons
TIME button
CLEAR (program clear) button
A«—repeat button
d
CHECK button
01
■ (stop) button
m
II (pause) button
► (play) button
CLEAR/REPEAT (A<-^B repeat clear/repeat)
button
>20 (over 20) button
PLAY MODE buttons
PGM (program button)
SHUFFLE button
CONTINUE button
SINGLE button
C. INDEX button
Page 4
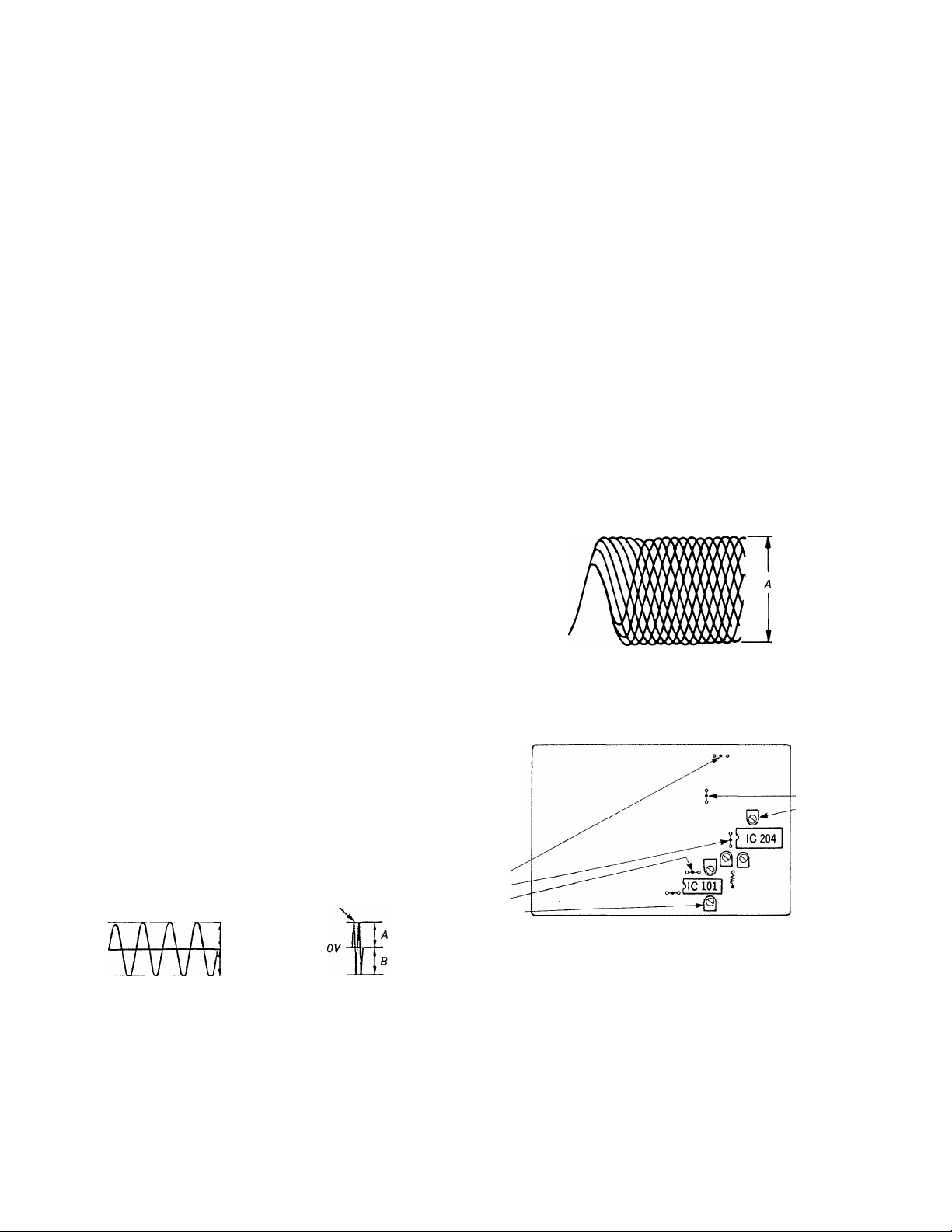
SECTION 2
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
1. Perform adjustments in the order given.
2. Use YEDS-18 (Part No: 3-702-101-01) disc unless otherwise
indicated.
3. Use the oscilloscope with more than 10 Mil impedance.
RF PLL Frequency Adjustment
Procedure:
frequency counter
main board
TP (PCK) O-
■O +
1. Connect the frequency counter to test point TP (PCK).
2. Turn POWER switch on.
3. Adjust RV201 so that the reading on the frequency counter is
4.3218MHz ±30kHz
4. Put disc (YEDS-18) in and press D> button.
5. Confirm that the reading on frequency counter is 4.3218MHz.
E-F Balance Adjustment
This adjustment should be made when replacing TOP (T-type
Optical Pick-up).
Procedure:
Focus Bias Adjustment
This adjustment should be made when replacing TOP (T-type
Optical Pick-up).
Procedure;
oscilloscope
(DC range)
main board
TP (RF) o-
О
-0
+
-o -
Connect oscilloscope to test point TP (RF).
Turn POWER switch on.
Put disc (YEDS-18) in and press > button.
Adjust RV104 for an optimum waveform eye pattern or so that
the peak is maximum. Optimum eye pattern means that shape
“O” can be clearly distinguished at the center of the waveform.
RF signal waveform
oscilloscope
(DC range)
main board
TP (TEO) o-
77Г
О
O-t-
1. Connect oscilloscope to test point TP (TEO).
2. Connect test point TP (ADJ) and test point TP (TES) to
ground with lead wire.
3. Turn POWER switch on.
4. Put disc (YEDS-18) in and press > button.
5. Adjust RVlOl so that the traverse waveform is symmetrical
above and below.
6. After adjustment, remove the lead wire connected in step 5.
Note: Prom inent that make a
long of sweep tim e.
OV-
A = B
(within 5%)
A = B (within5%)
VOLT/DIV: IV
TIME/DIV: 1ms
A = 1.3±0.3 (Vp-p)
Adjustment Location :main board
E-F
BALANCE
ADJ
(ADJ
I TES
1 TEO
[ RVlOl
RF PLL
FREQUENCY
ADJ
PCK \
RV201 I
Page 5
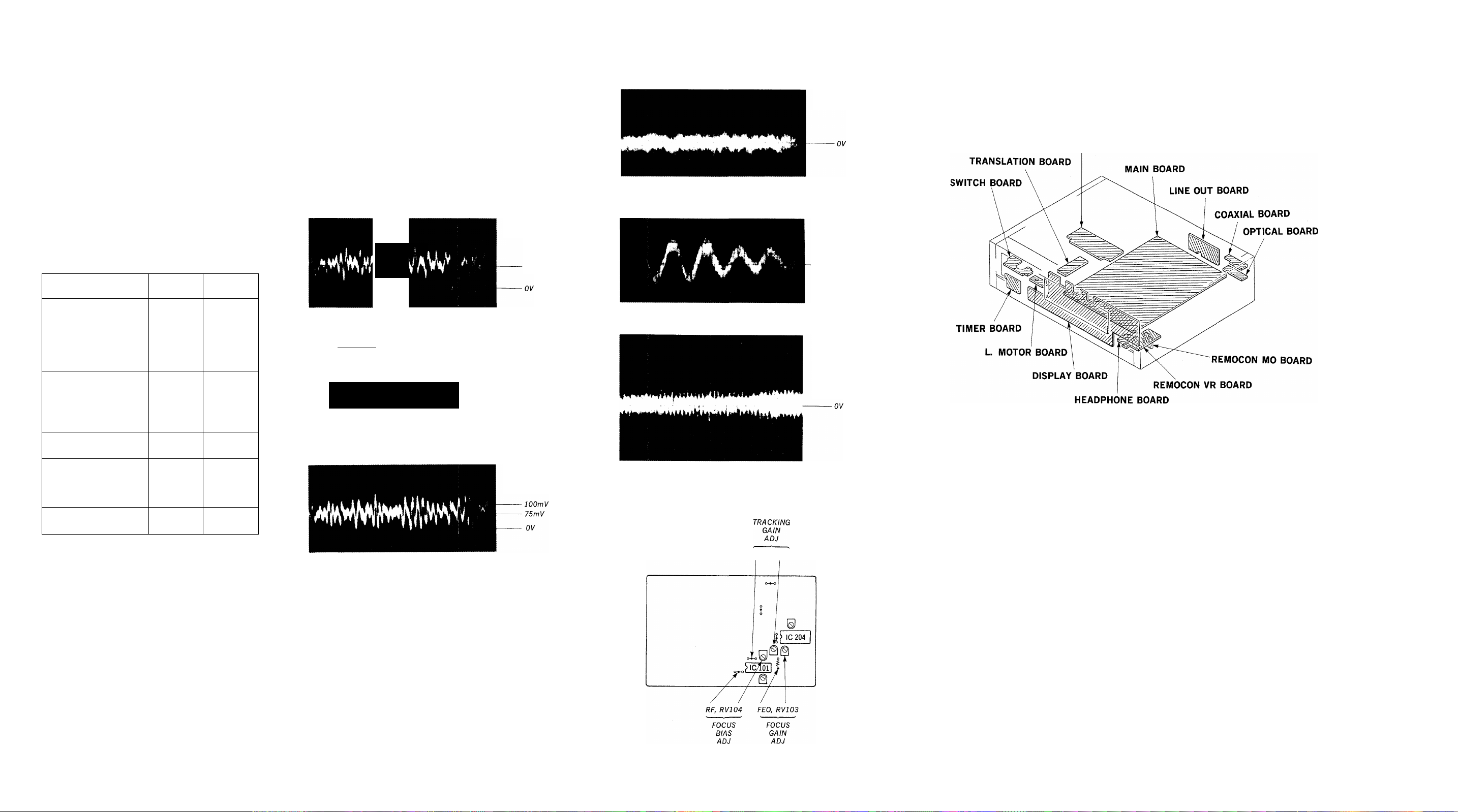
SECTION 3
DIAGRAMS
CDP-338ESD/608ESD
REFERENCE
Focus/Tracking Gain Adjustments
A frequency responce analyzer is necessary in order to perform
this adjustment exactly.
However, this gain has a margin, so even if it is slightly off,
there is no problem. Therefore, do not perform this adjustment.
Focus/tracking gain determines the pick-up follow up (vertical
and horizontal) relative to mechanical noise and shock when the
2-axis device operate.
However, as these reciprocate, the adjustment is at the point
where both are satisfied.
• When gain is raised, the noise when the 2-axis device operates
increases.
• When gain is lowered, mechanical shock and skipping occurs
more easily.
• When gain adjustment is off, the symptoms below appear.
Symptoms
Gain
Focus
Tracking
• The time until music
starts becomes longer
for ■ ^ O or automatic
selection. (Kl<l, [>t>l but
low
low or high
tons pressed.) (Normally
tapes about 1 seconds.)
• Music does not start and
disc continues to rotate
for ■ -> > or automatic
-
low
selection.
(KKl, OCH buttons pressed.)
• Disc table opens shortly
after ■->•[>.
low or high
-
• Sound is interrupted
during PLAY or time
counter display stops
— low
progressing.
• More noise during 2-axis
device operation.
high
high
1. Keep the set horizontal.
If the set is not horizontal, this adjustment \
(
cannot be performed due to the gravity against the
2-axis device. /
2. Insert disc (YEDS-18 : Fifth Selection) and press 0 button.
3. Connect oscilloscope to main board TP (FEO).
4. Adjust RV103 so that the waveform is as shown in the figure
below, (focus gain adjustment)
5. Connect oscilloscope to main board TP (TEO).
6. Adjust RV102 so that the waveform is as shown in the figure
below, (tracking gain adjustment)
VOLT/DIV: lOOmV
TIME/DIV: 2ms
WA
100 mV
' Incorrent Examples (DC level changes more than on adjusted
waveform)
_______
low focus gain
V *V '/
high focus gain
VOLT/DIV: lOOmV
TIME/DIV: 2mS
-250mV
OV
VOLT/DIV: lOOmV
TIME/DIV: 2mS
Incorrect Examples (fundamental wave appears)
low tracking g ain
high tracking gain
(higher fundamental wave than for low gain)
Adjustment Location : main board
VOLT/DIV: IV
TIME/DIV: 2mS
VOLT/DIV: IV
TIME/DIV: 2mS
-OV
VOLT/DIV: IV
TIME/DIV : 2m S
3-1. CIRCUIT BOARDS LOCATION
POWER BOARD
The following is a simple adjustment method.
—Primary Adjustment-
Note : Since exact adjustment cannot be performed, remember
the positions of the controls before performing the adjust
ment. If the position after the primary adjustment are only
a little different, return the controls to the original posi
tion.
Procedure :
oscilloscope
(DC range)
main board
TP (FEO) O
TP (TEO) o^- -
I ,
------------
O
0 +
L
o-
TEO , RV102
Page 6
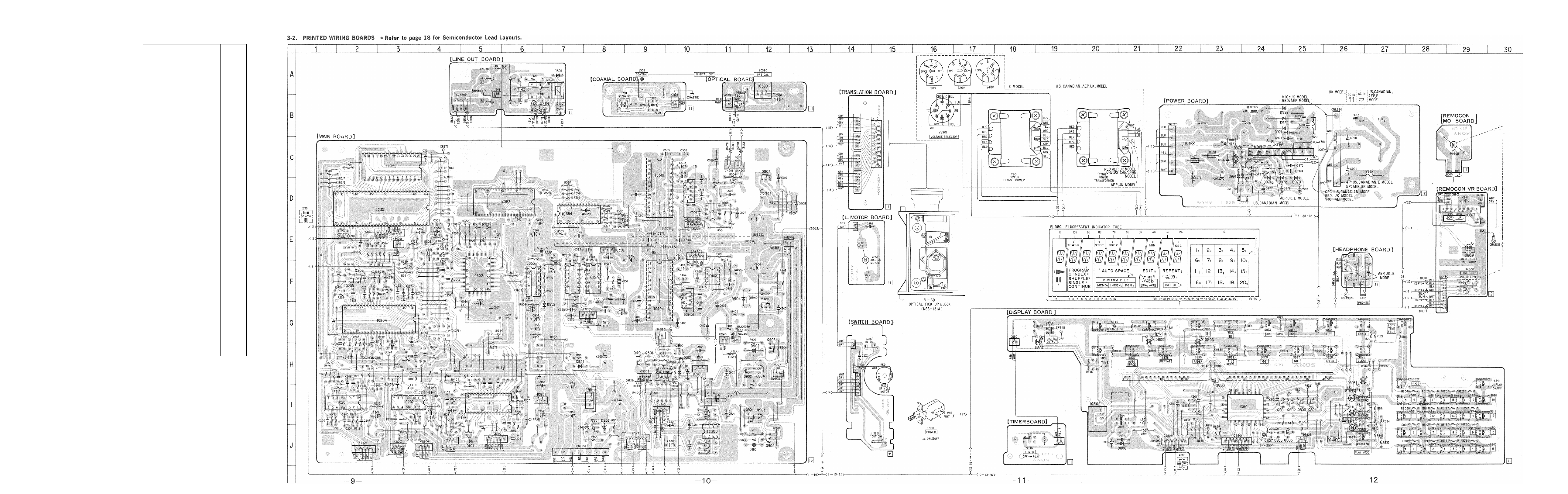
CDP-338ESD/608ESD
• Semiconductor Location
Ref.No. Location Ref. No.
DlOl J-5
D381 D-10
D391 F-26
D802 G-16
D901
D902 1-11
D903
D904
D950 1-10
D951 1-9
D952
D953 1-9
D955 1-8
D956
D957
D958
D961 1-9
D962 1-9
1-11
1-10
1-10
1-9
1-8
G-8
1-9
Q383 G-9
Q801
Q802 1-21
Q901
Q902 E-10
Q950
Q951
Q952
Q961
CDP-338ESD/608ESD CDP-338ESD/608ESD CDP-338ESD/608ESD CDP-338ESD/S08ESD
Location
H-20
E-10
G-9
H-9
1-8
H-8
ICIOI H-5
IC201
IC202 H-3
IC204
IC302 E-5
IC303 F-6
IC351 C-3
IC352
IC353
1C354
IC356
IC357
1C358
IC391
IC401
IC402
IC501
IC502 E-9
IC801 1-21
IC802 1-17
IC901 G-11
IC902
IC903 C-7
IC905 G-9
QlOl 1-5
Q205
Q206 E-2
Q381
Q382 F-7
H-2
F-3
B-3
D-7
C-6
C-11
C-11
F-9
E-24
C-8
C-9
E-8
G-10
E-2
G-10
Note on Printed Wiring Board;
: parts extracted from the component side,
indicates side identified with part number.
: Jumper wire connected to the ground pattern on
the component side.
: parts mounted on the conductor side.
-8-
Page 7

3-3. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM • Refer to page 17 for Waveforms.
1 I 2 I 3 I 4 I
8
10
11 12
13
14 15 16 17
18
19 20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[DISPLAY BOARD]
В
H
[L.MOTOR BOARD]
к
M
N
Note on Schematic Diagram:
• All capacitors are in juF unless otherwise noted. pF: ju^tF
50WV or less are not indicated except for electrolytics
and tantalums.
• All resistors are in SI and ‘/4W or less unless otherwise
specified.
• % : indicates tolerance.
• A : internal component.
• "^^3": fusible resistor.
Note:
The components identi
fied by mark Дог dot
ted line with mark Д
are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified.
0 : 8+ L
___
adjustment for repair.
Voltage and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
under no-signal conditions,
no mark : STOP
( ); PLAY
Voltages are taken with a VOM (Input impedance 1 OM Q )•
Voltage variations may be noted due to normal produc
tion tolerances.
Waveforms are taken with a oscilloscope.
Voltage variations may be noted due to normal produc
tion tolerances.
Circled numbers refer to waveforms.
Signal path.
^ : CD
ne
B- L
Note:
Lés composants identifiés par
une marque^sont critiques
pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spéci
fié.
13-
14 15-
-16
Page 8

• Waveforms
e
APPR0X.80mVp-p
IC204 (?) PIN
APPROX. 800mmVp-p
IC204 @PIN
—*|o.25psec j*—
IC80I @PIN
5.7VP-P
4.8Vp-p
“'AA/Vm
-*j l-h-
O.I2psec
IC302 C?)PIN
-H h-
0.06psec
IC302 @PIN
<0
[<— 0.46 psec —
IC302 @PIN
<D
2VP-P
0.7 Vp-p
7.6Vp-p
7.2 Vp-p
(D
Mm
2.8psec
IC353 (^PIN
vm
O.I2psec
IC353 (33)PIN
-H k-
O.I2psec
IC354 ©PIN
T
7.2VP-P
7VP-P
h-
3.8Vp-p
.3Vp-p
0
o
IC80I @PIN
O.I2psec
IC35I (^PIN
H k~
O.I2psec
IC35I @PIN
H k-
0.1 psec
IC302 Cd)PlN
4.4Vp-p
6.4 Vp-p
3.8VP-P
_L
22psec
IC302 @PIN
0
0.9VP-P
0
WWl/W
—A k—
OOBpsec
IC 353 r?)PIN
0
[<—0.46psec —*J
IC353 (i^PIN
0
[^-25jjsec —*j
IC353 @PIN
5.8VP-P
O.OGpsec
IC357 @PIN
—H k-
O.OGpsec
IC357 (4)PIN
PLAY
TP RF
3.6VP-P
_L
1,9V
■0.7V
- OV
17
Page 9

3-4. SEMICONDUCTOR LEAD LAYOUTS
BA6208
CXA1081S
UUDUUUUUUUUU’
(Top view)
CXA1182S
n II nilfl nil «1111111125
o
CXA1291P
nnnnnnnnn
UUUUUUUUU
(Top view)
15
finnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnn
jUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUir
9
M5F78M12
M5F7805
M5F7905
COMMON IN OUT
M50747-161SP
(Top view)
RC4556D
RC5532D-D
2SA985P
2SC2275A
2SA1138-F
2SB734
2SC2676
2SC3622A-K
I
HZ8.2E-B3
1SS202-1
10YD1.3-A
31DF2
5P-4M
AA5534S
BR3867S
CXD1165Q
CXP5058H-162Q
o o
CXD1244S
I 5 10 15 20
(Top view!
CXD8003S
LC9600R-183
PCM58P-J
12 3 4
(Top view}
TC74HCU04P
TC74HC02P
1413121110 9 8
n n n n n n n
u u u u u u u
1 2 3 4 b 0 ;
DTA114ES
DTC114ES
DTC114EF
2SC2673
RDF02M
i
_______
^
-----------
RD33ES-B2
RD4.7ES-B2
RD6.2JS-B2
11ES2
fit
7
BG5535S
/0/72 H^i/70/t
BR3371X
MAY3371X
MBG3371X
MPY3371X-117
18
Page 10

• 1C Block Diagrams
ICIOI CXA1081S
IC204 CXA1182S
IC302 CXD1165Q
IC355 TC74HC02P
IC401, 501 PCM58P-J
SERVO FIL
VDD
REF FIL
BPO FIL
BPO
I OUT
RF
V POT
BIT 1
(MSB ADJ)
BIT 2
BIT 3
BIT A
NC
NC
IC201, 202 CXA1291P
O- to S >- O 0 g
1 §
A GND
VSS
RF
D GND
MC
NC
NC
VSS
DATA
MC
LE
CLOCK
VTH FIL
-19
20-
Page 11

NOTE:
• The mechanical parts with no reference
number in the exploded views are not
supplied.
• The construction parts of an assembled
part are indicated with a collation num
ber in the remark column.
• Items marked are not stocked since
they are seldom required for routine
service. Some delay should be antici
pated when ordering these items.
SECTION 4
EXPLODED VIEWS
Due to standardization, parts with part
number suffix -XX and -X may be dif
ferent from the parts specified in the
components used on the set.
Color Indication of Appearance Parts
Example:
(RED) .. . KNOB, BALANCE (WHITE)
t t
Cabinet's Color Parts' Color
CND: Canadian model
CDP-338ESD/608ESD
The components identified by
rriark ^ or dotted line with mark
A are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ^ sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spécifé.
Ref.No Part No.
1
2
3
3
4
5
6
7
7
8
9 4-924-242-11 SCREW (M3X6), FLAT HEAD
10
11
12
7-621-996-05
4-884-635-00 BASE, ORNAMENTAL
X-4922-551-1 (CND, AEP, UK)... .PANEL ASSY, LOADING
X-4922-554-1 (US, E)... .PANEL ASSY, LOADING
4-929-073-01 SCREW (3X8)
3-703-685-21
4-885-979-11
X-4922-574-2 (AEP)... .BOARD (LEFT) ASSY, SIDE
X-4928-001-1 (US, CND. E)....PLATE (LEFT) ASSY, SIDE
*4-925-368-01 CASE (LEFT)
4-925-367-01
4-847-802-00
*4-923-563-01 CUSHION
Description Remarks Ref.No
BOLT, HEXAGON SOCKET 2.6X5
SCREW (+BV 3X8)
(US, CND. AEP, E)... .SCREW (4X25)
CASE (TOP PLATE)
(UK)....SCREW
Part No.
*4-925-369-01
13
X-4922-575-2
14
14 X-4928-002-1
X-4922-549-1 FOOT ASSY
15
7-682-664-09
16
*3-703-079-21
17
4-886-821-21 SCREW, M3 CASE STOPPER
18
19 *4-913-189-11 FELT (B), ACOUSTIC ABSORBENT
*4-923-557-01 DUMPER
20
21 4-928-025-11
*4-929-017-01 CUSHION
22
4-928-079-01 COVER, BATTERY
23
922 1-465-047-11
CASE (RIGHT)
(AEP)....BOARD (RIGHT) ASSY, SIDE
(US, CND. E)... .PLATE (RIGHT) ASSY. SIDE
SCREW +PSW 4X14
(UK)... .LABEL, CAUTION (BACK)
ESCUTCHEON (TOP PLATE)
REMOTE COMMANDER (RM-D670)
21
Description Rema
23
Page 12

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
4-2. FRONT PANEL SECTION
54
Ref.No
Part No. Description
4-908-848-01 EMBLEM, SONY
51
52
4-925-353-01
53
7-685-870-01
54
7-685-646-79
55 *4-925-374-01 ESCUTCHEON (POWER SWITCH)
56 4-925-375-01
57 4-925-373-01 PLATE, INDICATION
58 4-925-384-01 PLATE (BUTTON), GROUND
59 4-922-518-11
60
7-685-134-19 SCREW +BTP 2.6X8 TYPE2 N-S 903 *1-629-022-11
61
4-925-327-01 INDICATOR
62
*4-922-980-01 HOLDER (LED)
63 4-925-383-01
64
4-925-381-01
65 4-925-382-01 BUTTON (MODE HOLDER)
66 4-925-326-01
67 4-922-977-01 KNOB (HP)
68 4-922-978-01
69 4-922-979-01
70 *4-925-355-01 BASE (RIGHT), PANEL
PANEL. FRONT
SCREW +BVTT 3X5 (S) 73 *4-923-532-21 SPACER, LED
SCREW +BTP 3X8 TYPE2 N-S
PACKING (LOADING)
KNOB (TIMER)
BUTTON (DIAPLAY)
BUTTON (MODE)
BUTTON (D/A) FLD801 1-519-476-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT
HOLDER (FIBER) RV800 1-238-315-21 RES, VAR, CARBON lOK/lOK (LINE OUT)
INDICATOR (Including VOL MOTOR)
Remarks Ref.No
22
Part No.
71 4-927-604-01 BUTTON (MC)
72 *4-923-532-31
74
*4-922-524-01
75 *4-922-523-01 HOLDER (RIGHT)
4-925-366-01 PLATE (HP), GROUND
76
*4-929-021-01 CUSHION (20 KEY)
77
*1-629-023-11
901
902 *A-4655-076-A MOUNTED PCB, DISPLAY
*1-629-024-11 PC BOARD, REMOCON VR
904
*1-629-025-11 PC BOARD, REMOCON MO
905
D805 8-719-907-81
D806 8-719-907-75 DIODE AA5534S
D807 8-719-971-70
J303 1-507-796-61 JACK, LARGE TYPE (PHONES)
SPACER, LED
HOLDER (LEFT)
PC BOARD, TIMER
PC BOARD, HEADPHONE
DIODE 5P-4M
DIODE BR3867S
Description R
Remarks
Page 13

4-3. CHASSIS SECTION
CDP-338ESD/608ESD
UK model AEP model
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
no
111
112
112
113
113
113
113
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
-923-520-01
-682-547-09
-929-073-01
-575-524-00
-925-394-01
-831-441-XX
-682-560-04
-682-547-04
-685-873-09
-928-032-01
-888-798-00
-701-948-10
-701-947-08
-925-361-12
-925-361-22
-925-361-32
-925-361-42
-925-361-52
-231-019-00
-655-653-21
-922-525-01
-682-147-15
-363-146-00
-309-144-01
-885-838-00
KNOB, POWER
SCREW -EB 3X6
SCREW (3X8)
COVER, POWER SWITCH
SHEET, INSULATING
CUSHION (B), CABINET
SCREW -fBVTT 4X6 (S)
SCREW -fBVTT 3X6 (S)
SCREW -fBVTT 3X10 (S)
COLLAR (A)
BUSHING, RUBBER .
(AEP, UK)... .LABEL (T400MA), FUSE
(E)....LABEL (T500MA), FUSE
(US)....PANEL, BACK
(CND)....PANEL, BACK
(AEP)....PANEL, BACK
(UK)....PANEL, BACK
(E)....PANEL, BACK
CLAMPER, CORD
BAND (TAITON), BINDING
HEAT SINK
SCREW,TR
HEAT SINK, V.OUT
HEAT SINK
(AEP, UK, E)....LABEL, CLASS 1
23
*4 -
121
*4-
122
123
124
906
907
*1*1-
908
* A
909
*1-
910
*1-
911
*1-
912
Ll-
913
913
^.1-
913
4\.i -
913 A-1914 1-
F990 A-1
F990 A.l
F990 A.1S990 A-1T901 A.lT901 A.l
T901 A.1VS901A.1-
•929-013-01
•929-018-01
4-
•929-074-01
7-
•685-647-79
•533-183-11
1-
•535-688-11
■629-020-11
-4651-225-A
■629-017-11
•629-016-11
■629-019-11
•555-386-00
•555-795-00
556- 035-00
557- 577-11
526-565-00
•532-066-11
•532-279-00
•532-741-11
•570-156-11
■449-631-11
■449-632-11
■449-633-11
526-576-51
ABSORBENT, VIBRATION
ABSORBENT, VIBRATION
SCREW (3X8)
SCREW -f BVTP 3X10 TYPE2 N-S
HOLDER, FUSE
TERMINAL
PC BOARD, POWER
MOUNTED PCB, MAIN
PC BOARD, COAXIAL
PC BOARD, OPTICAL
PC BOARD, LINE OUT
(E)....CORD, POWER
(AEP)....COAD, POWER
(UK)....COAD, POWER
(US, CND)....COAD, POWER
(E)....AC PLUG ADAPTOR
(AEP, UK)... .FUSE, TIME-LAG T0.4A
(E)....FUSE, TIME-LAG T0.5A
(US, CND)... .FUSE, GLASS TUBE 1.25A 125V
SWITCH, PUSH (AC POWER)(l KEY)(POWER)
(E)....TRANSFORMER, POWER
(US,CND)....TRANSFORMER, POWER
(AEP, UK)... .TRANSFORMER, POWER
(E)....SELECTOR, POWER VOLTAGE
Page 14

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
4-4. MECHANISM SECTION
(CDM11A-6B)
Ref.No Part No. Description
151 7-685-647-79 SCREW +P 3X10 TYPE2 SLIT
152 *4-927-655-01 LIMITER
153 *4-927-642-01 TABLE (EXL), DISK
154 A-4665-024-A MAGNET ASSY
155 *4-927-638-03 HOLDER (A.P)
156 7-621-770-67
157
*4-918-679-04
158 *4-927-648-01
159
4-927-620-01 GEAR (P)
160
4-927-628-01 GEAR (C)
161
7-624-105-04
162
X-4927-608-1 ARM ASSY, SWING
163
4-929-724-01 PULLEY (B)
164
4-927-649-01
SCREW +BVTT 2.6X6 (S) 170 4-927-665-01
PULLEY, PRESS
SLIDER (GROUND) 172
STOP RING 2.3, TYPE -E
BELT
Remarks Ref.No Part No.
4-927-617-01
165
166 *4-927-641-04 CHASSIS (OUTSERT), MECHANICAL
167 7-621-775-08
■— 168
4-927-62?^01
4-927-624-01
169
4-927-635-01
171
3-659-338-00 SPRING, COMPRESSION
173 4-927-654-01
3-831-441-XX CUSHION
174
*4-917-583-21
175
*1-629-359-11
915
*1-629-360-11
916
A-4608-362-A
M251
24
Description
BAR, GUIDE
SCREW +P 2.6X3
ROLLER
CAM (L,A)
SHAFT (S)
CAM (L,B)
WASHER (LIMITER)
BRACKET, YOKE
PC BOARD, L.MOTOR
PC BOARD, SWITCH
MOTOR (L) ASSY (LOADING)
Remarks
Page 15

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
4-5. OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK SECTION
(BU-6B)
Note:
The components identi
fied by mark /^or dot
ted line with mark
are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified.
Note:
Les composants identifiés par
une marque ¿^sont critiques
pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spéci
fié.
Ref.No Part No.
201
3-318-203-61
202
*4-910-431-01
203
*4-917-582-01
204
7-685-646-79
205
206
207
7-685-134-19
208
4-927-634-01
209
4-917-562-01
210
7-621-255-25
211
X-4927-605-3
212
4-917-572-01
213
4-917-571-01
Description
SCREW (B1.7X4), TAPPING
SHAFT, SLIDE
CUSHION, SLIDE
SCREW, TAPPING
deletion
_______
deletion
------------
SCREW +BTP 2.6X8
HOLDER (SP)
INSULATOR
SCREW +P2X4
M. BASE ASSY(lncluding M252)
SPRING (B)
SPRING (A)
TYFKN-
Remarks
220
Ref.No Part No.
214
215 7-685-132-19
216
217
218
219 3-305-423-00 SPRING, COMPRESSION
220 7-621-773-86
f917
i
[918
919 *1-628-390-11
920
921
4-917-573-01
*4-927-637-01
4-927-6'|l-01
4-927-626-01
A-4638-084-A
A-4608-335-A
A-8-848-047-ni
---------
deletion ---------------
SPRING (E)
+ PTPWH (2.6X5)
HOLDER (BU-6)
ROLLER (L)
LEVER (L)
SCREW +BVTT 2.6X4 (S)
SENSOR ASSY, SPEED
MOTOR ASSY,LINEAR
PC BOARD, TRANSLATION
PICK UP, OPTICS (KSS-151A)
25
Description
219
Remarks
Page 16

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
SECTION 5
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
NOTE;
• Due to standardization, replacements in the parts
list may be different from the parts specified in
the diagrams or the components used on the set.
• Items marked are not stocked since they
are seldom required for routine service. Some
delay should be anticipated when ordering these
items.
• If there are two or more same circuits in a set
such as a stereophonic machine, only typical
circuit parts may be indicated and capacitors and
resistors in other same circuits may be omitted.
Ref.No Part No. Description
901
902
903 *1-629-022-11 PC BOARD, HEADPHONE
904
905
906 1-533-183-11
907
908 * 1-629-020-11
909
910 *1-629-017-11 PC BOARD, COAXIAL
911 *1-629-016-11
912
913 A. 1-555-386-00
913 A. 1-555-795-00
913 A. 1-556-035-00 (UK)....C0AD, POWER C223 1-124-927-11 ELECT
913 A. 1-557-577-11
914
915 *1-629-359-11
916
917 A-4638-084-A
918
919 *1-628-390-11 PC BOARD, TRANSLATION C230
920
921
922
BUS351 *1-560-242-21
BUS352 * 1-560-242-31
BUS353 * 1-560-242-31 BUS BAR 5P
BUS354 *1-566-959-11
BUS900 * 1-560-242-21
ClOl
C102 1-124-443-00
C105
C106 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC
C107
C108
C109 1-164-159-11
CllO 1-126-233-11 ELECT
cm 1-136-153-00
C112
C113 1-126-233-11 ELECT
C114 1-164-159-11
C115 1-161-375-00 CERAMIC
C116 1-130-480-00
C117
C200 1-161-379-00 CERAMIC
C201 1-123-333-00
C202
C203
C204
C205 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC
C206
C207
*1-629-023-11 PC BOARD, TIMER
*A-4655-076-A MOUNTED PCB, DISPLAY
*1-629-024-11
*1-629-025-11
*1-535-688-11
*A-4651-225-A
*1-629-019-11 PC BOARD, LINE OUT C220 1-136-165-00 FILM O.IMF
1-526-565-00 (E)....AC PLUG ADAPTOR C225
*1-629-360-11
A-4608-335-A
A8-848-047-01
1-465-047-11
1-164-088-11 CERAMIC
1-162-198-31
1-130-477-00
1-136-159-00
1-136-153-00
1-124-902-00
1-123-333-00
1-164-159-11 CERAMIC
1-164-159-11
1-162-294-31
1-164-159-11
PC BOARD, REMOCON VR
PC BOARD, REMOCON MO
HOLDER, FUSE
TERMINAL
PC BOARD, POWER
MOUNTED PCB, MAIN
PC BOARD, OPTICAL
(E)....CORD, POWER
(AEP)....COAD, POWER
(US, CND)....C0AD, POWER
PC BOARD, L.MOTOR
PC BOARD, SWITCH C227
SENSOR ASSY, SPEED
MOTOR ASSY .LINEAR
PICK UP. OPTICS (KSS-151A) C231
deletion —
----
REMOTE COMMANDER (RM-D670) C233
BUS BAR 4P C234 1-164-159-11
BUS BAR 5P
BAR, BUS C302
BUS BAR 4P
CAPACITOR
ELECT
CERAMIC
MYLAR
FILM
CERAMIC
FILM O.OIMF
FILM
CERAMIC
MYLAR 0.0056MF
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
---------
O.OOIMF
lOOMF
8.2PF
O.IMF 50V
0.0033MF
0.033MF
O.IMF 50V
22MF 20%
O.OIMF
22MF
O.IMF 50V C362 1-136-920-00
0.0022MF
0.47MF
O.OIMF
lOOMF
lOOMF
O.IMF
O.IMF 50V
O.OOIMF
0.001MF
O.IMF 50V
20%
10%
5%
5%
5%
5%
20%
30%
5%
20%
20%
20%
20%
10%
10%
CAPACITORS;
MF: mF, PF: цц Р.
RESISTORS
• All resistors are in ohms.
• F: nonflammable
COILS
e MMH: mH, UH: juH
SEMICONDUCTORS
In each case, U; д, for example;
UA...; juA..., UPA...; дРА...,
UPC...; дРС, UPD...; дРО...
• CND; Canadian model
Part No.
Ref.No
1-136-155-00
C208
1-136-161-00 FILM 0.047MF
C209
C210 1-164-159-11
C211 1-164-159-11
C212 1-123-333-00 ELECT lOOMF 20%
C213 1-123-333-00
1-126-233-11
C215
1-123-382-00 ELECT 3.3MF 20%
C216
C217 1-136-165-00
1-123-382-00 ELECT 3.3MF 20% 50V
C218
1-136-159-00
C219
1-106-359-00
C221
C222 1-124-499-11
1-126-233-11 ELECT
C224
1-162-294-31
1-162-282-31
C226
1-126-233-11 ELECT
1-130-472-00 MYLAR 0.0012MF
C228
1-164-159-11
C229
1-106-359-00 MYLAR
1-126-233-11 ELECT
C232 1-164-159-11
1-164-159-11 CERAMIC
1-136-157-00 FILM
C251
1-136-157-00 FILM
C252
1-126-233-11
1-161-379-00
C303
1-124-902-00
C304
1-136-159-00 FILM
C305
50V C306
6.3V C307 1-164-159-11
50V C308 1-164-159-11
50V
50V C350 1-164-159-11
25V
50V
50V
25V C361
16V
50V C364
50V
16V C366 1-123-382-00 ELECT
16V
16V
50V
50V
50V
1-136-173-00 FILM 0.47MF
1-164-159-11
C309
1-164-159-11 CERAMIC
C321
1-130-483-00 MYLAR
C358
1-130-483-00 MYLAR
C359
1-136-165-00 FILM
C360
T-124-119-00
1-136-920-00
C363
1-136-165-00
C365 1-164-159-11
C367 1-136-165-00
1-102-950-00
C368
1-102-950-00 CERAMIC 13PF
C369
1-124-517-11 ELECT 470MF 20%
C370
C371 1-106-359-00 MYLAR
C372 1-136-920-00
C373 1-136-920-00 FILM
The components identified by
rr^rk ^ or dotted line with mark
A are critical for safety,
f^place only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque A sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spécifié.
Description
FILM 0.015MF
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
ELECT lOOMF
ELECT
FILM O.IMF
FILM 0.033MF
MYLAR
ELECT IMF 20%
CERAMIC O.OOIMF
CERAMIC lOOPF
CERAMIC O.IMF
CERAMIC O.IMF
CERAMIC
ELECT
CERAMIC O.OIMF
ELECT
CERAMIC
CERAMIC O.IMF
CERAMIC O.IMF
(AEP, UK, E)....
CERAMIC
ELECT
FILM
FILM O.IMF
FILM
CERAMIC O.IMF
FILM
CERAMIC
FILM
O.IMF
O.IMF
22MF
0.0047MF
4.7MF 20% 50V
22MF 20%
22MF
0.0047MF
22MF 20%
O.IMF
O.IMF
0.022MF
0.022MF
22MF
0.47MF 20%
0.033MF
O.IMF 50V
O.IMF
O.IMF
O.OIMF
O.OIMF
O.IMF
330MF
O.IMF
O.IMF
33MF
O.IMF
13PF
0.0047MF
O.IMF
O.IMF
5%
5%
20%
20%
5%
5%
5%
5%
10%
10%
20%
5%
5%
5%
5%
20%
20% 16V
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
20% 16V
5%
5%
5%
20% 50V
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
50V
50V
50V
50V
16V
16V
25V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
25V
50V
50V
25V
50V
50V
50V
25V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
25V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
50V
26
Page 17

Note:
The components identi
fied by mark ^ or dot
ted line with mark ^
are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified.
Ref.No Part No.
C374
1-136-920-00
C375
1-136-920-00
1-124-130-00
C380
C381
1-124-130-00
C382
1-130-483-00
C390
1-123-380-00
C392
1-162-279-31
C401
1-123-380-00
C402
1-123-357-00
C403
1-126-059-11
C404
1-126-059-11
1-130-491-00
C405
1-136-854-00
C406
C407
1-136-870-00
C408
1-136-856-00
1-124-572-11
C409
C410
1-136-580-11
C413A
1-130-491-00
1-162-290-31
C413B
C414 1-130-477-00
1-130-477-00
C415
C430
1-124-130-00
1-123-380-00
C501
1-123-357-00
C502
C503
1-126-059-11
C504
1-126-059-11
1-130-491-00
C505
C506
1-136-854-00
1-136-870-00
C507
1-136-856-00
C508
1-124-572-11
C509
C510
1-136-580-11
C513A
1-130-491-00
C513B
1-162-290-31
C514 1-130-477-00
1-130-477-00
C515
1-124-130-00
C530
C800
1-164-159-11
C801
1-164-159-11
1-124-584-00
C802
C803
1-164-159-11
C804
1-164-159-11
1-164-159-11
C805
1-124-477-11
C806
C807
1-164-159-11
C809
1-126-233-11
1-124-611-00
C810
1-124-443-00
C811
1-102-950-00
C900
C901
1-124-713-11
1-124-713-11
C902
C903
1-124-130-00
C904
1-124-130-00
C905
1-126-170-11
C906
1-126-170-11
1-102-950-00
C909
C910
1-123-382-00
1-123-380-00
C911
C920
1-126-129-11
C921
1-126-129-11
C922
1-136-177-00
C923
1-130-483-00
C924
1-130-483-00
1-130-483-00
C925
Note:
Les composante identifiés par
une marquesont critiques
pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spéci
fié.
Description
FILM
FILM
ELECT
ELECT
MYLAR
ELECT
CERAMIC
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
MYLAR
FILM
FILM
FILM
ELECT
FILM
MYLAR
(AEP, UK, E)..
CERAMIC
MYLAR
MYLAR
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
MYLAR
FILM
FILM
FILM
ELECT
FILM
MYLAR
(AEP, UK, E)..
CERAMIC
MYLAR
MYLAR
ELECT
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
ELECT
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
ELECT
CERAMIC
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
CERAMIC
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
CERAMIC
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
FILM
MYLAR
MYLAR
MYLAR
O.IMF
O.IMF
lOOMF
lOOMF
0.01MF
IMF
75PF
IMF
22MF
lOMF
lOMF
0.047MF
O.OOIMF
0.0047MF 2%
0.0012MF 2%
lOOMF 20% 50V
0.47MF 10% 200V
0.047MF 5% 50V
470PF 10% 50V
0.0033MF 5% 50V
0.0033MF
lOOMF
IMF
22MF
lOMF
lOMF
0.047MF
O.OOIMF
0.0047MF
0.0012MF
lOOMF 20% 50V
0.47MF 10% 200V
0.047MF 5% 50V
470PF 10% 50V
0.0033MF 5% 50V
0.0033MF 5% 50V
lOOMF 20% 63V
O.IMF
O.IMF
lOOMF
O.IMF
O.IMF
O.IMF
47MF
O.IMF
22MF
IMF
lOOMF
13PF
470MF
470MF
lOOMF
lOOMF
lOOOMF
lOOOMF
13PF
33MF
IMF
6800MF
6800MF
IMF
O.OIMF
O.OIMF
O.OIMF
50V
5%
50V
5%
20% 63V
20% 63V
5% 50V
20% 50V
10% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
5% 50V
lOOV
2%
lOOV
lOOV
5% 50V
20% 63V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
5% 50V
lOOV
2%
lOOV
2%
lOOV
2%
50V
50V
20% lOV
50V
50V
50V
20% 25V
50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% lOV
5% 50V
20% 35V
20% 35V
20% 63V
20% 63V
20% 50V
20% 50V
5% 50V
20% 50V
20% 50V
20% 35V
20% 35V
50V
5%
50V
5%
50V
5%
50V
5%
Ref.No Part No.
C926
C951
C952
C953
C954
C955
C956
C957
C958
C960
C972
C973
C974
C975
C976
C977
C978
C980
C981
C989
C990
C991
CNIOI *1-564-338-71
CNllO *1-562-883-11
CN102 *1-564-340-00
CNllO *1-562-883-11
CN201 * 1-564-340-61
CN203 * 1-564-338-00
CN204 * 1-564-338-81
CN301 *1-564-342-11
CN302 * 1-564-336-00
CN305 *1-564-706-11
CN306 *1-564-506-11
CN381 *1-564-704-11
CN401 *1-564-704-11
CN403 *1-564-706-11
CN501 *1-564-704-11
CN802 * 1-564-337-00
CN951 *1-564-341-11
CNL301 * 1-508-829-12
CNL901 * 1-535-116-00
CNL920 *1-535-119-00
CNL921 *1-535-121-00
CNL951 * 1-535-120-00
CNL970 *1-535-115-00
CNL99Û *1-535-141-00
CNL990 *1-535-142-00
DlOl
D301
D801
D802
D803
D804
D805
D806
D807
D808
D809
D901
D902
D903
D904
D910
D921
1-130-483-00
1-124-360-00
1-124-360-00
1-124-556-11
1-126-103-11
1-126-244-51
1-124-902-00
1-124-927-11
1-136-177-00
1-124-910-11
1-126-017-11
1-124-898-11
1-130-483-00
1-130-483-00
1-136-177-00
1-124-130-00
1-124-484-11
1-130-483-00
1-130-483-00
1-124-484-11
Al-162-599-12
Ai-161-744-00
8-719-107-94
8-719-107-94
8-719-971-49
8-719-971-52
8-719-970-98
8-719-971-50
8-719-907-81
8-719-907-75
8-719-971-70
8-719-915-91
8-719-970-49
8-719-224-12
8-719-224-12
8-719-114-41
8-719-114-41
8-719-109-81
8-719-230-02
GDP-338ESD/608ESD
Description
MYLAR
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
FILM
ELECT
ELECT
ELECT
MYLAR
MYLAR
FILM
ELECT
ELECT
MYLAR
MYLAR
ELECT
CERAMIC
CERAMIC
PIN, CONNECTOR 4P
SOCKET, CONNECTOR 20P
PIN, CONNECTOR 6P
SOCKET, CONNECTOR 20P
PIN, CONNECTOR 6P
PIN, CONNECTOR 4P
PIN, CONNECTOR 4P
PIN, CONNECTOR 8P
PIN, CONNECTOR 2P
PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 4P
PLUG, CONNECTOR 3P
PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 2P
PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 2P
PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 4P
PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 2P
PIN, CONNECTOR 3P
PIN, CONNECTOR 7P
H TYPE BASE POST 2P
TERMINAL 3P
TERMINAL 6P
TERMINAL 8P
TERMINAL 7P
TERMINAL 2P
(US, CND, E)... .BASE POST 22MM (lOMM PITCH) 4P
(AEP, UK)... .BASE POST 22MM (lOMM PITCH) 5P
DIODE 1SS202-1
DIODE 1SS202-1
DIODE BR3371X
DIODE MAY3371X
DIODE MPY3371X-117
DIODE MBG3371X
DIODE 5P-4M
DIODE AA5534S
DIODE BR3867S
DIODE HZ8.2E-B3
DIODE BR4361F
DIODE 10YD1.3-A
DIODE 10YD1.3-A
DIODE RD6.2JS-B2
DIODE RD6.2JS-B2
DIODE RD4.7ES-B2
DIODE 31DF2
O.OIMF
lOOOMF
lOOOMF
2200MF
470MF
47000MF
0.47MF
4.7MF
IMF
47MF
6800MF
4700MF
O.OIMF
O.OIMF
IMF
lOOMF
220MF
O.OIMF
O.OIMF
220MF
0.0047MF
O.OIMF
5% 50V
20% 16V
20% 16V
20% 16V
20% 16V
5.5V
20% 50V
20% 50V
5% 50V
20% 50V
20% 16V
20% 16V
50V
5%
50V
5%
50V
5%
20% 63V
20% 35V
50V
5%
50V
5%
20% 35V
20% 400V
400V
27
Page 18

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
Ref.No Part No.
D922
8-719-230-02 DIODE 31DF2
D923
8-719-230-02 DIODE 31DF2
D924
8-719-230-02
D951 8-719-107-94 DIODE 1SS202-1
D952
8-719-107-94 DIODE 1SS202-1
D953
8-719-110-78
D970
8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D971
8-719-200-82
D972
8-719-200-82
D973
8-719-107-94 DIODE 1SS202-1
D974
8-719-107-94
D975 8-719-937-49 DIODE RDF02M
F990
A-1-532-066-11
F990
A.1-532-279-00 (E)....FUSE, TIME-LAG T0.5A
F990
A.1-532-741-11 (US, CND)... .FUSE, GLASS TUBE 1.25A 125V
FLD801 1-519-476-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT R102 1-249-512-11 CARBON
ICIOI
8-752-034-00
IC201
8-752-035-28
IC202
8-752-035-28
IC2Û4
8-752-032-33
IC302
8-752-325-59
8-759-631-47
IC351
IC352
8-759-820-64
IC353
8-752-328-61
IC354
8-759-978-53
IC355 8-759-202-12
IC356
8-759-202-13
IC357
8-759-202-13
IC358 8-759-604-29 1C M5F7805
IC380
8-759-981-85
IC390 8-759-977-71 1C GP1F31T
IC401
8-759-979-08
IC402
8-759-982-03
IC501
8-759-979-08
IC502
8-759-982-03
IC801 8-752-806-27 1C CXP5058H-162Q
IC802
8-749-920-03
IC803
8-759-962-08
IC901
8-759-604-39
IC951
8-759-604-29
IC952 8-759-604-47 1C M5F7905
J301
1-568-101-11
J302 1-566-922-21 JACK, PIN IP (DIGITAL OUT COAXIAL) R229
J303 1-507-796-61 JACK, LARGE TYPE (PHONES)
L350 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR lOUH
L351 *1-410-858-11 INDUCTOR OUH
1-421-946-11
L391
L801 1-408-080-00 INDUCTOR lOOUH
L802 1-408-080-00 INDUCTOR lOOUH
M251 A-4608-362-A MOTOR (L) ASSY (LOADING) R236
PS970
1-532-675-00
QlOl 8-729-140-97
Q205 8-729-900-80 TRANSISTOR DTC114ES R240 1-249-417-11
Q206 8-729-900-80 TRANSISTOR DTC114ES R241 1-249-417-11
Q301
8-729-900-61 TRANSISTOR DTA114ES R243
Q401
8-729-107-99
Q501
8-729-107-99 TRANSISTOR 2SC3622A-K
Q801
8-729-900-45
Q802
8-729-900-45 TRANSISTOR DTC114EF
Q803
8-729-900-45 TRANSISTOR DTC114EF R305 1-249-429-11
Q804
8-729-900-45
Q805
8-729-900-45 TRANSISTOR DTC114EF
Description
DIODE 31DF2
DIODE RD33ES-B2
DIODE 11ES2
DIODE 11ES2
DIODE 1SS202-1
(AEP, UK)....FUSE, TIME-LAG T0.4A
1C CXA1081S
1C CXA1291P
1C CXA1291P
1C CXA1182S
1C CXD1165Q R107
1C M50747-161SP
1C LC9600R-183
1C CXD1244S
1C CXD8003S Rill 1-249-432-11
1C TC74HC02P
1C TC74HCU04P R203
1C TC74HCU04P R205
1C RC4556D
1C PCM58P-J
1C RC5532DD
1C PCM58P-J
1C RC5532DD
1C GP1U52 R218
1C BA6208
1C M5F78M12
1C M5F7805
JACK, PIN 4P (LINE OUT) R228 1-247-896-11
TRANSFORMER, PULSE
(AEP, UK, E)....LINK, 1C R238 1-249-417-11
TRANSISTOR 2SB734
TRANSISTOR 2SC3622A-K
TRANSISTOR DTC114EF R303 1-215-469-00
TRANSISTOR DTC114EF
-28-
Ref.No
Part No. Description
Q806
8-729-900-45
Q807
8-729-900-45 TRANSISTOR DTC114EF
Q808
8-729-967-32
Q901
8-729-167-62
Q902
8-729-113-82 TRANSISTOR 2SA1138-F
Q903 8-729-107-53
Q904
8-729-190-53
Q905 8-729-113-82
Q906
8-729-167-62
Q907
8-729-167-62 TRANSISTOR 2SC2676
Q908 8-729-113-82
Q910 8-729-900-80
Q951 8-729-140-97 TRANSISTOR 2SB734
RlOl
1-247-806-11
R103 1-249-417-11
R104 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K
R105 1-249-421-11
R106
1-249-428-11
1-247-860-11
R108 1-249-425-11
R109 1-249-425-11
RllO 1-249-432-11
1-249-441-11 CARBON lOOK
R112
1-249-393-11
R201
1-249-393-11
1-249-441-11
1-247-881-00
R206
1-249-441-11
R208
1-247-881-00
R210
1-249-437-11
R211
R212 1-249-435-11
R214 1-247-846-11
1-249-393-11 CARBON 10
R216
R217 1-247-899-11
1-249-441-11
R219 1-249-424-11
1-247-882-11
R222
R223 1-249-393-11
R224 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10
1-249-431-11
R230 1-249-440-11
R231 1-249-440-11
R232 1-249-429-11
1-249-414-11
R233
1-249-441-11
R234
R235 1-215-434-00
1-249-433-11
1-249-441-11
R237
1-249-417-11
R239
1-247-854-11 CARBON
R244 1-247-854-11
R301
1-247-903-00
R304
1-215-469-00
R306 1-249-441-11
R307
1-249-429-11
Note:
The components identitied by mark /i\ or do.tted line with mark ^ pour la sécurité.
are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified. fié.
TRANSISTOR DTC114EF
TRANSISTOR 2SC2673
TRANSISTOR 2SC2676
TRANSISTOR 2SC2275-A
TRANSISTOR 2SA985-P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1138-F
TRANSISTOR 2SC2676
TRANSISTOR 2SA1138-F
TRANSISTOR DTC114ES
RESISTOR
CARBON
CARBON IK
CARBON
CARBON 8.2K
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 18K
CARBON 18K
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 120K
CARBON
CARBON 120K
CARBON 47K
CARBON
CARBON 4.3K
CARBON
CARBON lOOK
CARBON 3.9K
CARBON 130K
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON
METAL
CARBON
CARBON lOOK
CARBON IK
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON IK
CARBON 9.1K
CARBON
METAL
METAL
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON lOK
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
1%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
1%
1%
5%
5%
5%
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/6W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/6W
1/6W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
91
22
2.2K
16K
4.7K
4.7K
10
10
lOOK
lOOK
33K
680K
10
510K
15K
82K
82K
560
lOOK
3.6K
22K
IK
IK
9.1K
IM
lOOK
lOOK
lOOK
Note:
Les composants identifiés par
une marque ^
Ne les
pièce portant le
sont critiques
■emplacer que par une
numéro spéci-
Page 19

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
Ref.No Part No.
R308 1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
R309 1-249-433-11 CARBON
R310
1-247-903-00 CARBON
R311 1-249-429-11
R312
1-249-429-11 CARBON
R313 1-249-429-11
R314 1-249-429-11
R315 1-249-429-11
R316 1-249-429-11 CARBON lOK
R317 1-249-429-11
R318 1-249-429-11
1-249-429-11 CARBON
R319
R320
1-249-429-11
R321
1-249-429-11
R322
1-249-429-11 CARBON lOK
R323
1-249-429-11
1-249-417-11
R350
1-249-417-11
R351
R352 1-249-417-11
1-249-417-11
R353
R354 1-249-414-11 CARBON
1-249-417-11
R355
R356 1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
R357 1-249-417-11
1-249-414-11 CARBON
R359
R360 1-249-417-11
R361 1-249-417-11 CARBON
1-249-417-11
R362
1-249-411-11 CARBON
R363
R364 1-249-437-11
R365 1-247-891-00
R366 1-249-429-11 CARBON
1-249-417-11
R367
R368 1-249-417-11
R369 1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
R370
R371 1-249-417-11
R372 1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
R373 1-214-937-00
R374
1-249-409-11 CARBON 220
1-249-401-11
R375
R376 1-249-401-11
R377 1-249-411-11 CARBON
1-249-411-11 CARBON
R378
1-249-411-11
R379
1-249-411-11 CARBON
R380
R381 1-249-411-11
1-249-411-11
R382
1-249-526-11 CARBON
R385
R386 1-249-526-11
R387 1-249-441-11
R388 1-249-409-11
R390
1-249-405-11
1-247-804-11
R391
R392 1-249-410-11
R401
1-249-815-11
R402 1-249-556-11
1-249-556-11 CARBON 1.5K
R403
R404 1-247-700-11
l-247-891-(M
R405
R410 1-247-700-11
R411 1-249-466-11 CARBON 56K
1-249-460-11 CARBON
R412
1-249-460-11 CARBON 15K
R413
R414 1-249-421-11
Description
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON lOK
CARBON IK
CARBON IK
CARBON
CARBON IK
CARBON IK
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON IK
CARBON 47K
CARBON 330K
CARBON IK
CARBON IK
CARBON IK
CARBON IM
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 330
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 3.6K
CARBON 1.5K
CARBON
CARBON 330K
CARBON
CARBON 2.2K
47
47
330
330
330
330
330
82
82
220
75
270
22K
IM
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
IK
560
IK
560
IK
IK
330
lOK
lOOK
100
100
100
15K
Ref.No Part No. Description
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/2W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W R836
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W R841 1-249-429-11 CARBON lOK
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/2W
1%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
R420 1-247-700-11 CARBON
R501
1-249-815-11
1-249-556-11
R502
1-249-556-11 CARBON
R503
R504 1-247-700-11 CARBON
1-247-891-00
R505
R510 1-247-700-11 CARBON
1-249-466-11
R511
R512 1-249-460-11
1-249-460-11
R513
1-249-421-11 CARBON
R514
1-247-700-11
R520
1-249-422-11
R801
1-249-422-11 CARBON 2.7K
R802
1-249-422-11
R803
1-249-422-11
R804
1-249-422-11 CARBON 2.7K
R805
1-249-422-11 CARBON 2.7K
R806
1-249-422-11 CARBON 2.7K
R807
1-249-422-11 CARBON 2.7K
R808
1-249-424-11 CARBON 3.9K
R809
1-249-424-11 CARBON
R810
1-249-424-11
R811
1-249-424-11
R812
1-249-424-11 CARBON
R813
1-249-424-11 CARBON 3.9K
R814
1-249-424-11 CARBON 3.9K
R815
1-249-424-11 CARBON
R816
1-249-427-11
R817
1-249-427-11 CARBON 6.8K
R818
1-249-427-11
R819
1-249-427-11
R820
1-249-427-11 CARBON 6.8K
R821
1-249-427-11
R822
1-249-427-11 CARBON
R823
1-249-427-11
R824
1-249-432-11 CARBON 18K
R825
1-249-432-11 CARBON 18K
R826
1-249-432-11
R827
1-249-432-11
R828
1-249-432-11
R829
1-249-432-11
R830
1-249-432-11 CARBON
R831
1-249-432-11
R832
1-249-429-11
R833
1-249-429-11
R834
1-249-429-11
R835
1-249-429-11 CARBON
1-249-429-11
R837
1-249-429-11
R838
1-249-429-11
R839
R840 1-249-429-11
1-249-429-11
R842
1-249-429-11
R843
R844 1-249-429-11
1-249-429-11
R845
R846 1-249-429-11
1-249-429-11 CARBON lOK
R847
1-249-429-11 CARBON lOK
R848
1-249-411-11 CARBON
R849
1-249-418-11
R850
1-249-410-11 CARBON
R851
1-249-410-11
R852
1-249-407-11 CARBON
R853
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 56K
CARBON
CARBON 15K
CARBON 100
CARBON 2.7K
CARBON 2.7K
CARBON 2.7K
CARBON 3.9K
CARBON 3.9K
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 6.8K
CARBON 6.8K
CARBON
CARBON 18K
CARBON 18K
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON lOK
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON lOK
CARBON lOK
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
100
3.6K
1.5K
1.5K
100
330K
100
15K
2.2K
3.9K
3.9K
3.9K
6.8K
6.8K
6.8K
6.8K
18K
18K
18K
18K
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
lOK
330
1.2K
270
270
150
5%
1%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
5%
1/4W
1/2W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
1/4W
29
Page 20

CDP-338ESD/608ESD
Ref.No Part No. Description
R854 1-249-406-11
R855 1-249-409-11 CARBON
R856 1-249-412-11
R857
1-247-903-00 CARBON IM
R901 1-247-704-11
R902 1-247-704-11
R903
1-247-710-11
R904 1-247-710-11
R905
1-247-719-11 CARBON 3.3K
R906
1-247-719-11
R907
1-247-714-11 CARBON
R908 1-247-714-11 CARBON 1.2K
1-249-466-11
R909
R910
1-249-466-11 CARBON 56K
R911 1-249-556-11
R912 1-249-556-11
R913 1-249-417-11 CARBON IK
R914 1-247-713-11
R920 íL1-212-877-11 FUSIBLE
R951 1-249-405-11
R952 1-249-520-11 CARBON 47
R953 1-249-427-11 CARBON 6.8K
R954 1-247-883-00 CARBON 150K
1-249-556-11
R955
R956 1-249-429-11
4^.1-212-871-11
R970
1-228-995-00 RES, ADJ, CARBON 22K
RVlOl
RV102
1-228-995-00 RES, ADJ, CARBON 22K VS901A.1-526-576-51
1-228-995-00 RES, ADJ, CARBON 22K
RV103
RV104 1-228-993-00 RES, ADJ, CARBON 4.7K
1-228-990-00 RES, ADJ, METAL GLAZE IK
RV201
RV800 1-238-315-21
RY301 1-515-683-11 RELAY
1-571-736-11
5251
5252
1-571-736-11
5801
1-554-596-21
l-554-596r21
5802
5803
1-554-596-21
5804
1-554-596-21
1-554-596-21
5805
5806
1-554-596-21
5807
1-554-596-21
5808
1-554-596-21
5809
1-554-596-21
1-554-596-21
5810
1-554-596-21
5811
5812
1-554-596-21
5813
1-554-596-21
5814
1-554-596-21
1-554-596-21
5815
1-554-596-21
5816
5817
1-554-596-21
5818
1-554-596-21
5819
1-554-596-21
5820
1-554-596-21
5821
1-554-596-21
5822
1-554-596-21
5823
1-554-596-21
5824
1-554-596-21
5825
1-554-596-21
5826
1-554-596-21
5827
1-554-596-21
5828
1-554-596-21
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 220
CARBON
CARBON
CARBON 3.3K
CARBON 56K
CARBON 1.5K
CARBON 1.5K
CARBON IK
CARBON
CARBON 1.5K
CARBON lOK
FUSIBLE
RES, VAR, CARBON lOK/lOK (UNE OUT)
(Including VOL MOTOR)
SWITCH, LEAF. (OUT SW)
S'"'TCH, LEAF (IN SW)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (1)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (2)
SWITCH, KEY board (3)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (4)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (5)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (6)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (7)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (8)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (9)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (10)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (11)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (12)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (13)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (14)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (15)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (16)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (17)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (18)
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
SWITCH,
9-953-524-11
(Including 9-953-524-91
120
220
390
220
560
560
1.2K
68
100
39
KEY BOARD (19)
KEY BOARD (20)
KEY BOARD (PLAY MODE C INDEX)
KEY BOARD 020)
KEY BOARD (EDIT TIME FADE)
KEY BOARD (ERASE)
KEY BOARD (CLEAR)
KEY BOARD (CHECK)
KEY BOARD (►►)
KEY BOARD (◄◄)
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S832 1-554-596-21
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S834 1-554-596-21
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S836 1-554-595-21
5%
1/4W S837 1-554-596-21
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S841 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (CONTINUE/SINGLE)
5%
1/4W S842 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (SHUFFLE)
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S844 1-554-596-21
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W S990 A. 1-570-156-11 SWITCH, PUSH (AC POWER)(l KEY)
5%
1/4W F
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W T901 A.1-449-633-11 (AEP, UK)... .TRANSFORMER, POWER
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W
5%
1/4W F TH972 1-808-065-11
5%
Sony Corporation
-92)
Ref.No Part No.
S829 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (FILE RECALL)
S830
S831
S833
S835 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (FILE)
S838
S839 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (A)
S840 1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (AQPEN/CLOSE)
S843 1-554-596-21
S846 1-554-481-00
SW845
T901 A.1-449-631-11
T901 A. 1-449-632-11
TH970
TH971
TH973 1-808-065-11
X301
X350
X801
Audio Group
-30-
Description
1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (FADER)
1-554-595-21
1-554-595-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (KM)
1-554-596-21 SWITCH, KEY BOARD (REPEAT)
1-554-419-00
1-808-065-11
1-808-065-11
1-577-157-11 VIBRATOR, CERAMIC 8MHz
1-567-926-11 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL
1-577-082-11 VIBRATOR, CERAMIC 4MHz
Part No.
ACCESSORY & PACKING MATERIALS
•k-k'k'k'k'k'k'k'k-k-k-kic'k'k'k-k'k'k'k'k-kic
1-558-271-11 CORD, CONNECTION
3-786-738-11 (CND, AEP, UK, E)... .MANUAL, INSTRUCTION
3-786-738-21 (US).... MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH)
3-786-738-41 (AEP).... MANUAL, INSTRUCTION
3- 795-629-11 (AEP). ...INSTRUCTION
4- 847-802-00 (US, CND, AEP, E)... .SCREW
4-923-548-01 CUSHION (UPPER)
4-923-549-01 CUSHION (LOWER)
*4-929-016-01 STOPPER, DISK TABLE
*4-929-069-01 INDIVIDUAL CARTON
4-925-305-01 (UK).... CUSHION, SIDE
Note:
The components identi
fied by mark ^ or dot
ted line with mark ^
are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified.
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (II)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (■)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (I>l>l)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (TIME/MODE)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (AUTO SPACE)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (PROGRAM)
SWITCH, KEY BOARD (DISPLAY)
SWITCH, SLIDE (TIMER)
SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY) (DIGITAL OUTPUT)
(E)....TRANSFORMER, POWER
(US,CND)... .TRANSFORMER, POWER
THERMISTOR, POSITIVE
THERMISTOR, POSITIVE
THERMISTOR, POSITIVE
THERMISTOR, POSITIVE
(E)... .SELECTOR, POWER VOLTAGE
Description
(ENGLISH, FRENCH, SPANISH, PORTUGUESE)
(GERMAN, DUTCH, SWEDISH, ITALIAN)
Note:
Les composants identifiés pdr
une marque sont critiques
pour la sécurité.
Ne lés remplacer que par une
pièce portant le numéro spéci
fié.
Published by A/V Engineering Service Dept.
English
89D0482-1
Printed in Japan
©1989.4
 Loading...
Loading...