Page 1

IPv6 in SonicOS
Document Scope
This docume nt provide s an overview of So nicWAL L’s implementation of IPv6, how IPv6 operates, and how
to configure IPv6 for your network.
This document contains the following sections:
• “Feature Overview” section on page 1
–
“IPv6 Technology Overview” section on page 2
–
“IPv6 Benefits” section on page 3
–
“IPv6 Feature Support” section on page 4
• “Configuring IPv6” on page 4
–
“IPv6 Interface Configuration” section on page 5
–
“Configuring IPv6 Tunnel Interfaces” section on page 12
–
“Accessing the SonicWALL User Interface Using IPv6” section on page 16
–
“IPv6 Network Configuration” section on page 16
–
“IPv6 Access Rules Configuration” section on page 19
–
“IPv6 IPSec VPN Configuration” section on page 19
–
“SSL VPN Configuration for IPv6” section on page 20
• “IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring” section on page 21
–
“Packet Capture” on page 22
–
“IPv6 Ping” on page 23
–
“IPv6 DNS Lookup and Reverse Name Lookup” on page 24
–
“Connection Monitor” on page 24
Feature Overview
The following sections provide an overview of IPv6:
• “IPv6 Technology Overview” section on page 2
• “IPv6 Benefits” section on page 3
• “IPv6 Feature Support” section on page 4
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
1
Page 2

Feature Overview
IPv6 Technology Overview
Around 1992, the IETF became aware of a global shortage of IPv4 addresses, and technical obstacles in
deploying new protocols due to limitations imposed by IPv4. IPv6 base specification is specified in
RFC2460. IPv6 dramatically increases the number of available addresses.
IPv4’s 32-bit addresses = 4,294,967,296 possible devices
IPv6’s 128-bit addresses = 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 possible devices!
(or approximately 5 x 1028 addresses per person on the planet)
Address Allocations
• 2001::/16 is allocated for ipv6internet
• IANA has subdivided 2001::/16 address space to following RIRs
–
APNIC - 2001:02xx::/23, 2001:0cxx/23
–
ARIN - 2001:04xx::/23
–
RIPE NCC - 2001:06xx::/23
• ISPs allocates /48 to individual customers
• Customers allocate /64 to their multiple sites/subnets
ICMP Extension
ICMP packets in IPv6 are used in the IPv6 neighbor discovery process, path MTU discovery, and the
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) protocol for IPv6.
Transition Mechanisms
To coexist with an IPv4 infrastructure and to provide an eventual transition to an IPv6-only infrastructure,
the following mechanisms are used:
• IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling
• Translation
Sonicwall will provide IPv6 support to networks where no prior IPv6 connectivity exists via IPv6 Internet
gateway.
Note Networks must have IPv4 internet connectivity in order to get connected to IPv6 internet.
Note IPv6 stack must be enabled for PCs at SMB sites.
2
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 3
Here is a simplified picture showing connectivity model for a typical IPv6 deployment.
Feature Overview
IPv6 communication:
PC1 to PC2
PC2 to PC3
PC1 to S1,S2
PC2 to S1,S2
PC3 to S1, S2
SonicWALL
IPv6 Internet
Gateway
IPv6/IPv4
IPv4
PC1
SMB2
IPv4 Internet
IPv4
IPv4
SonicWALL FWSonicWALL FW
IPv6/IPv4
S1
IPv6 Internet
SonicWALL
IPv6 Internet
Gateway
PC2
IPv6 Public Servers
IPv6
S2
IPv6
SMB1
PC3
IPv6/IPv4
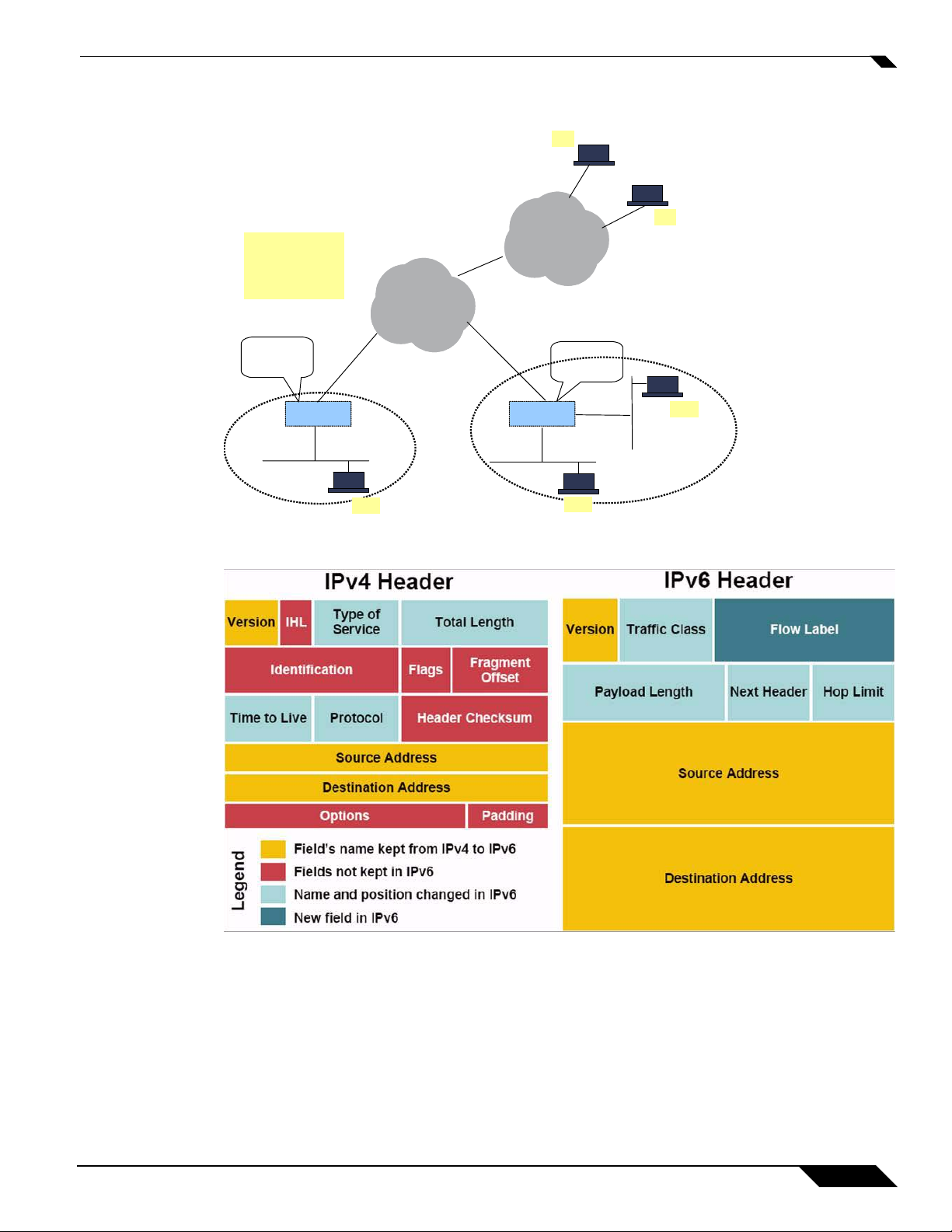
The following diagram shows a comparison of the header elements between IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv6 Benefits
IPv6 brings some key features to improve the limitations exposed by IPv4. The new IP standard extends
IPv4 in a number of important aspects:
• New header format
• Simplified IPv6 header - 40 Bytes with options removed from header
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
3
Page 4

Configuring IPv6
• Large address space - 128 bit IP address (6 x 1023 addresses per square meter of land on earth)
• Efficient and hierarchical addressing and routing infrastructure
• Auto address assignment to hosts/routers - NDP, DHCPv6
• Stateless and stateful address configuration
• Built-in security - AH and ESP strongly recommended
• Better support for QoS - Flow label in the header
• New protocol for neighboring node interaction
• Extensibility for new features using extension headers
IPv6 Feature Support
The following is a IPv6 services and features are supported:
• Site to site IPv6 connectivity
• Site to site IPv6 tunnel with IPSec for security.
• Access to hosted IPv4 services via IPv6 from outside
• Access to IPv4 website from inside via IPv6
• DNS Proxy.
• Security Services for IPv6 traffic with DPI
• Support for a stateful inspection of IPv6 traffic.
• Support for HTTP/HTTPS management and ping via IPv6.
• Support of logging IPv6 Events.
• Support for debugging tools for IPv6 like packet capture, connection monitor, etc.
Configuring IPv6
• “IPv6 Interface Configuration” on page 5
• “Configuring IPv6 Tunnel Interfaces” on page 12
• “Accessing the SonicWALL User Interface Using IPv6” on page 16
• “IPv6 Network Configuration” on page 16
• “IPv6 Access Rules Configuration” on page 19
• “IPv6 User Authentication Configuration” on page 21
• “IPv6 IPSec VPN Configuration” on page 19
• “SSL VPN Configuration for IPv6” on page 20
4
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 5
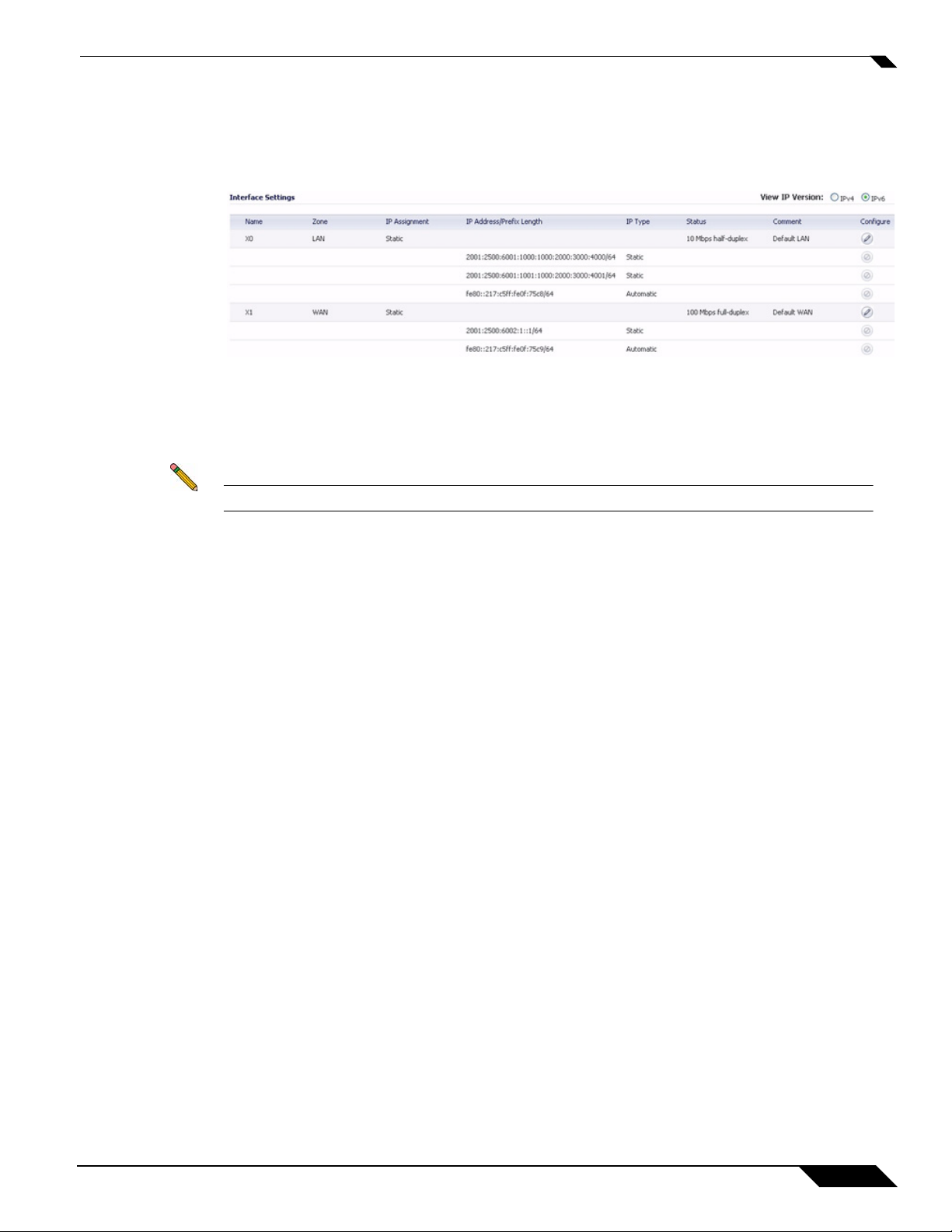
IPv6 Interface Configuration
IPv6 interfaces are configured on the Network > Interfaces page by clicking the IPv6 option for the View
IP Version radio button at the top right corner of the page.
By default, all IPv6 interfaces appear as routed with no IP address. Multiple IPv6 addresses can be added
on the same interface. Auto IP assignment can only be configured on WAN interface.
Each interface can be configured to receive router advertisement or not. IPv6 can be enabled or disabled
on each interface.
Note Zone must be configured prior to configuring IPv6 interfaces from IPv4 interface page.
Configuring IPv6
IPv6 Interface Configuration Constraints:
• The HA interface cannot be configured for IPv6.
• Only parent interface of a SwitchPort group can be configured as an IPv6 interface, hence all child of
a switch port group must be excluded from this list.
• IPv6 and IPv4 interface must remain in the same zone.
• Zone and L2Bridge are shared configuration both by IPv4 and IPv6. Once they are configured at IPv4
side, IPv6 will use the same configuration.
• Default Gateway and DNS Server 1/2/3 are only available for WAN zone interface.
• VLAN interfaces are not currently supported.
• An IPv6 assigned interface cannot be configured either as a switch port non-parent interface.
Configuring an Interface for IPv6 Static Mode
Static mode provides user a way to assign static IPv6 address besides auto-assigned address. Under this
mode, IPv6 interface could still listen to Router Advertisement and learn autonomous address from
appropriate prefix option. Static Mode doesn't disturb the running of Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
on IPv6 interface unless the user manually disables it.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
5
Page 6
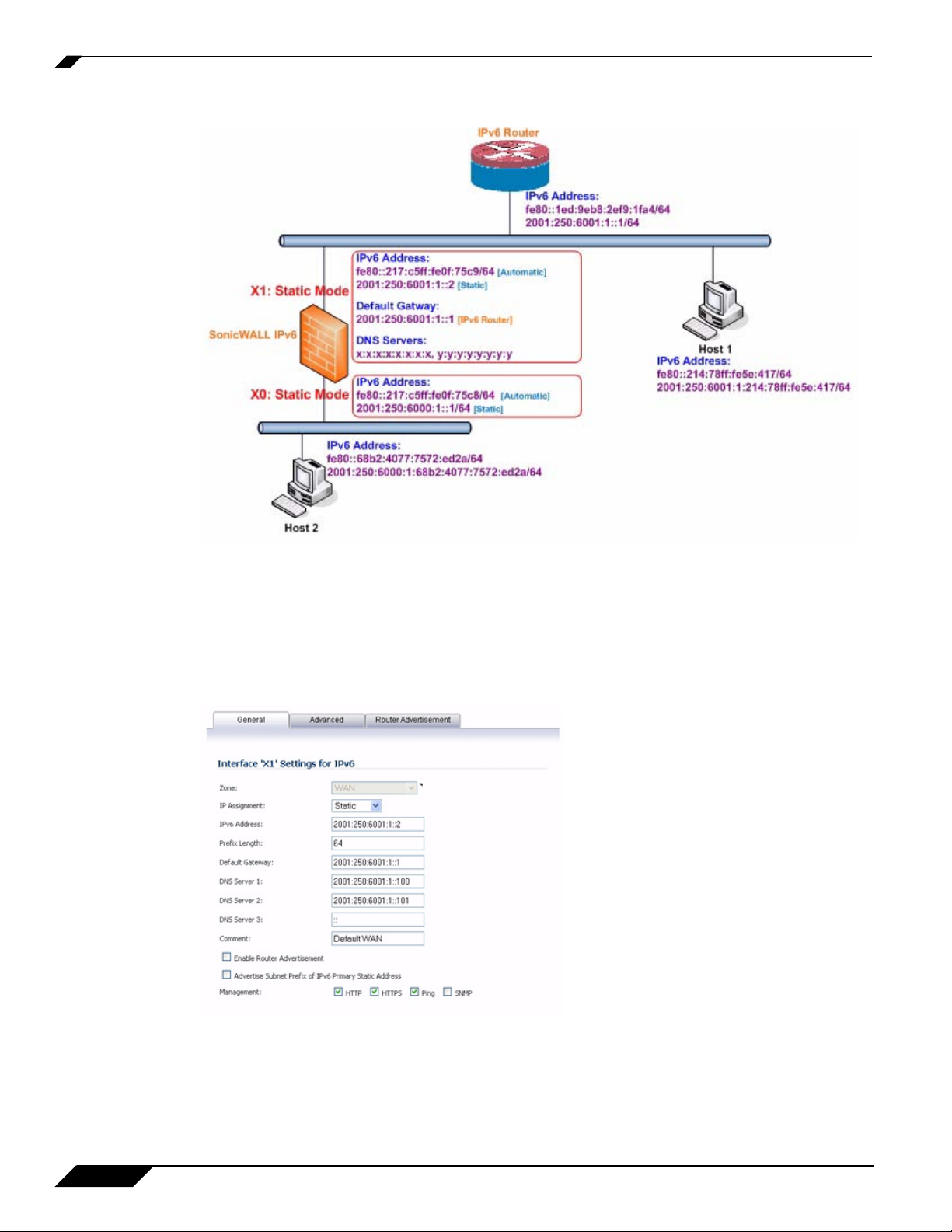
Configuring IPv6
The following diagram shows a sample topology with IPv6 configured in static mode.
3 types of IPv6 address are possible to assign under this mode:
• Automatic Address
• Autonomous Address
• Static Address
In Static Mode, the Primary Static Address is specified on the General tab. Default Gateway and DNS
Servers could also be set if it is a WAN zone interface.
Select Enable Router Advertisement to make this an advertising interface that distributes network and
prefix information.
Select Advertise Subnet Prefix of IPv6 Primary Static Address to add a default prefix into the interface
advertising prefix list. This prefix is the subnet prefix of interface IPv6 primary static address. This option
will help all hosts on the link stay in the same subnet.
6
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 7
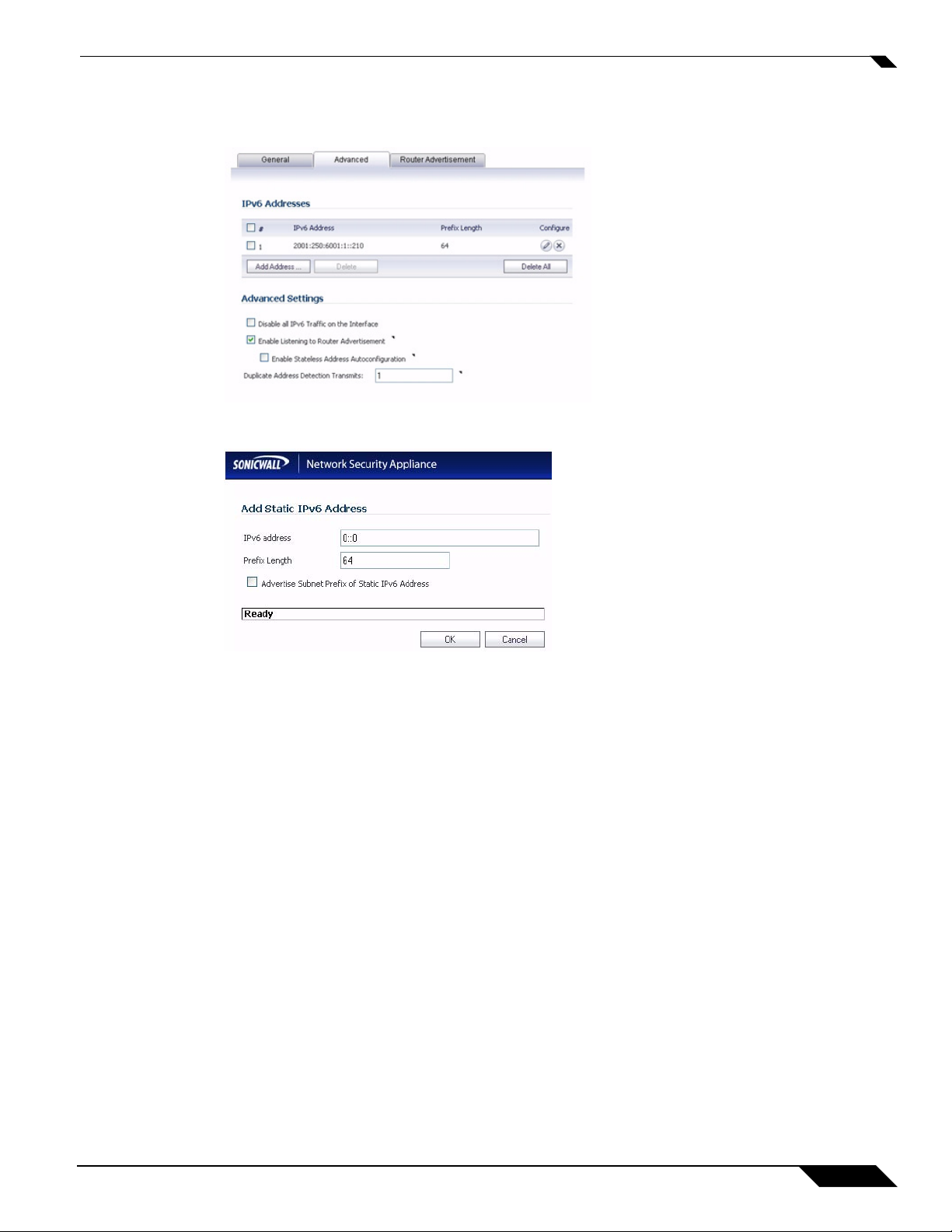
Configuring IPv6
If there is need to configure multiple static IPv6 addresses, Advanced tab provide a GUI to configure
additional static addresses.
Click the Add Address button to configure multiple static IPv6 addresses for the interface.
The following options can be configured on the Advanced tab:
• Select Disable all IPv6 Traffic on the Interface to stop the interface from handling all IPv6 traffic.
Disabling IPv6 traffic can improve firewall performance for non-IPv6 traffic. If t he firewall is deployed
in a pure IPv4 environment, SonicWALL recommends enabling this option.
• Select Enable Listening to Router Advertisement to have the firewall receive router advertisement.
If disabled, the interface filters all incoming Router Advertisement message, which can enhance security
by eliminating the possibility of receiving malicious network parameters (e.g. prefix information or
default gateway). This option is not visible for Auto mode. In Auto mode, it is always enabled.
• Select Enable Stateless Address Autoconfiguration to allow autonomous IPv6 addresses to be
assigned to this interface. If unchecked, all assigned autonomous IPv6 address will be removed from
this interface. This option is not visible for Auto mode. In Auto mode, it is always enabled.
• Enter a numeric value for Duplicate Address Detection Transmits to specify the number of
consecutive Neighbor Solicitation messages sent while performing Duplicate Address Detection
(DAD) before assigning a tentative address to interface. A value of 0 indicates that DAD is not
performed on the interface.
Similar with IPv4 gratuitous ARP, IPv6 node uses Neighbor Solicitation message to detect duplicate
IPv6 address on the same link. DAD must be performed on any Unicast address (except Anycast
address) before assigning a tentative to an IPv6 interface.
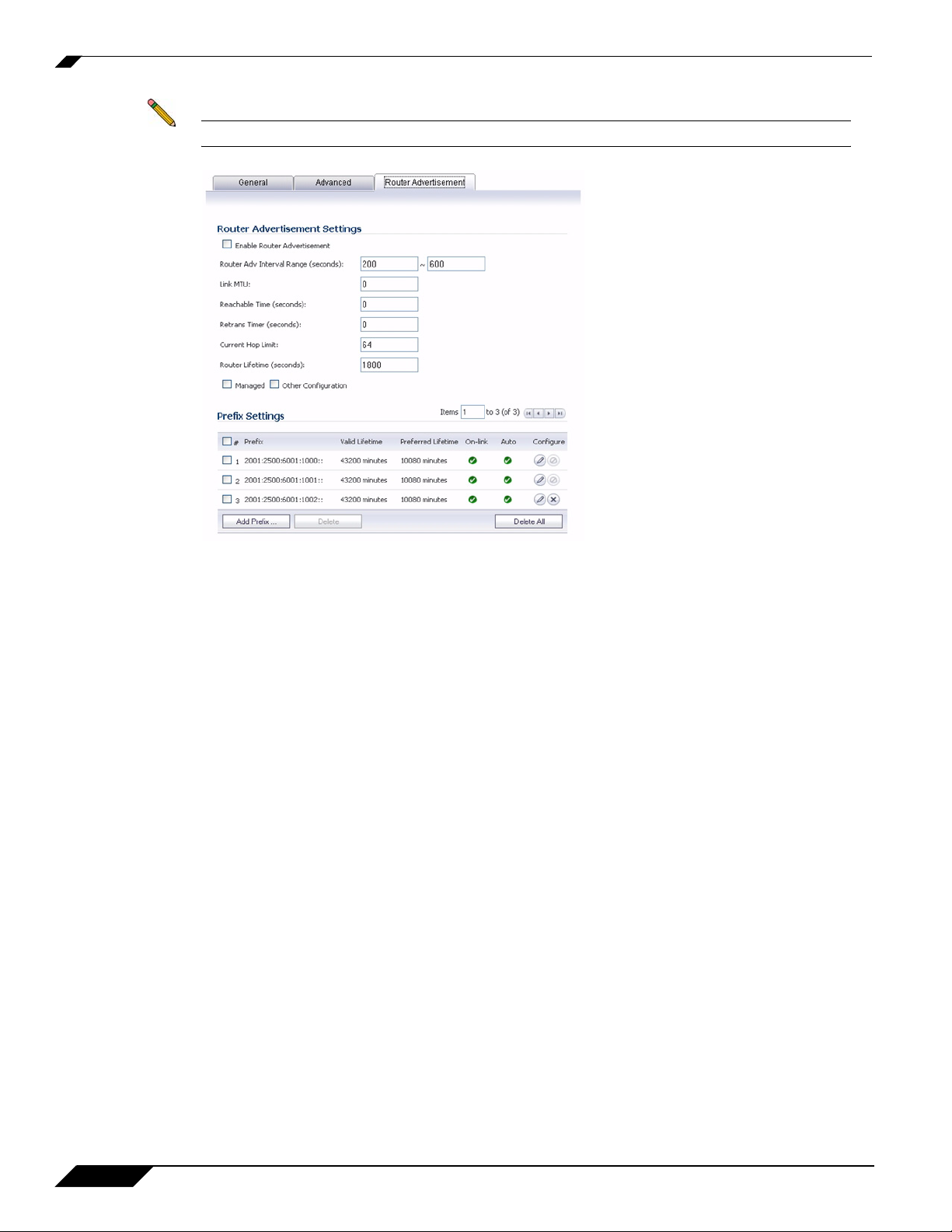
Configuring Router Advertisement Settings
SonicWALL IPv6 is full conformable with RFC 4861 in Router and Prefix Discovery.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
7
Page 8
Configuring IPv6
Note Router Advertisement can only be enabled when interface is under Static mode.
The following options can be configured on the Router Advertisement tab:
• Enable Router Advertisement - If enabled, this interface becomes an advertising interface and starts
to distribute network and prefix information.
• Router Adv Interval Range - The time interval allowed between sending unsolicited multicast Router
Advertisements from the interface, in seconds.
• Link MTU - The recommended MTU for the interface link. A value of 0 means firewall will not
advertise link MTU for the link.
• Reachable Time - The time that a node assumes a neighbor is reachable after having received a
reachability confirmation. A value of 0 means this parameter is unspecified by this firewall.
• Retrans Time - The time between retransmitted Neighbor Solicitation messages. A value of 0 means
this parameter is unspecified by this firewall.
• Current Hop Limit - The default value that should be placed in the Hop Count field of the IP header
for outgoing IP packets. A value of 0 means this parameter is unspecified by this firewall.
• Router Lifetime - The lifetime when firewall is accepted as a default router. A value of 0 means that
the router is not a default router.
• Managed - Sets the managed address configuration flag in the Router Advertisement message. If set,
it indicates that IPv6 addresses are available via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
• Other Configuration - Sets the Other configuration flag in Router Advertisement message. If set, it
indicates that other configuration information is available via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
• Add Prefix - Adds an advertising prefix.
8
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 9

Configuring IPv6
Click the Add Prefix button to configure a prefix.
Prefix - The prefix advertised with the Router Advertisement message which provides hosts with prefixes
for on-link determination and Address Autoconfiguration.
Valid Lifetime - The length of time that the prefix is valid for the purpose of on-link determination. A value
of "71582789" means the lifetime is infinite.
Preferred Lifetime - The length of time that addresses generated from the prefix via stateless address
autoconfiguration remain preferred. A value of "71582789 means the lifetime is infinite.
On-link - Enables the on-link flag in Prefix Information option, which indicates that this prefix can be used
for on-link determination.
Autonomous - Enables the autonomous address-configuration flag in Prefix Information option, which
indicates that this prefix can be used for stateless address configuration.
Configuring an Interface for DHCPv6 Mode
DHCPv6 (DHCP for IPv6) is a client/server protocol that provides stateful address configuration or
stateless configuration setting for IPv6 hosts. DHCPv6 client is enabled to learn IPv6 address and network
parameters when interface is configured to DHCPv6 mode.
DHCPv6 defines two different configuration modes:
• DHCPv6 stateful mode: DHCPv6 clients require IPv6 address together with other network parameters
(e.g. DNS Server, Domain Name, etc.).
• DHCPv6 stateless mode: DHCPv6 client only obtains network parameters other than IPv6 address.
Choosing which kind of those modes depends on Managed (M) Address Configuration and Other (O)
Configuration flag in the advertised Router Advertisement message:
–
M = 0, O = 0: No DHCPv6 infrastructure.
–
M = 1, O = 1: IPv6 host use DHCPv6 for both IPv6 address and other network parameter settings.
–
M = 1, O = 0: IPv6 host use DHCPv6 only for other network parameter settings, which known as
DHCPv6 stateless.
–
M = 0, O = 1: IPv6 host use DHCPv6 only for IPv6 address assignment.
As required by RFC, DHCPv6 client depends on Router Advertisement message to decide which mode
(stateful or stateless) it should choose. This definition will limit user's choice if they want to determine
DHCPv6 mode by itself. SonicWALL DHCPv6 client define two different modes to balance the
conformance and flexibility:
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
9
Page 10

Configuring IPv6
• Automatic - In this mode, IPv6 interface configures IPv6 addresses using stateless/stateful
autoconfiguration in accord with the M and O settings in the most recently received router
advertisement message.
• Manual - In Manual mode, DHCPv6 mode is manually configured regardless of any received Router
Advertisement. The Only Request Stateless Information option will determine which DHCPv6
mode is used. If this option is unchecked, DHCPv6 client is under stateful mode; if it is checked,
DHCPv6 client is under stateless mode and only obtains network parameters.
The following diagram shows a sample DHCPv6 topology.
10
There are three types of IPv6 addresses that can be assign under DHCPv6:
• Automatic Address
• Autonomous Address
• IPv6 Address assigned through DHCPv6 client
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 11

The following options can be configured for IPv6 interfaces configured for DHCPv6 mode:
• Use Rapid Commit Option - If enabled, DHCPv6 client use Rapid Commit Option to use the two
message exchange for address assignment.
• Send hints for renewing previous IP on startup - If enabled, DHCPv6 client will try to renew the
address assigned before when firewall startup.
• DHCPv6 Mode - Sets the DHCPv6 client mode.
–
Automatic: The interface configures IPv6 addresses using stateless/stateful autoconfiguration in
accord with the M and O settings in the most recently received router advertisement message.
–
Manual: The configuration of the IPv6 address is managed by the interface settings.
• Only Request Stateless Information - This option is only available for Manual mode. If enabled,
DHCPv6 client only requests network parameter setting from DHCPv6 server. IPv6 address is assigned
through stateless auto-configuration.
Configuring an Interface for Auto Mode
Auto mode is a new IP assignment for IPv6 interface. IPv6 interface is set to utilize IPv6 Stateless Address
Autoconfiguration to assign IPv6 address. In this mode, user doesn't need to do any other manual
configuration except setting IP Assignment type. Firewall listens to the network and prefix information
from neighboring routers. IPv6 build-in Stateless Address Autoconfiguration feature handles all
configuration details such as IPv6 address assignment, address deleting for address conflicting or lifetime
expiration, default gateway selection, etc., based on the information collected from on-link router.
Configuring IPv6
Note Auto mode can only be configured for the WAN zone. For security consider ation, Auto mode
is not available on LAN zone interface.
The following diagram shows a sample topology for IPv6 configured in Auto mode.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
11
Page 12

Configuring IPv6
In this mode, 2 types of IPv6 address are possible to assign:
• Automatic Address - The interface default link-local address. It is never timed out and is not able to be
edited or deleted.
• Autonomous Address - Assigned from Stateless Address Autoconfiguration. Users can manually delete
the address if they do not want to wait for its valid lifetime expires.
There are no new configuration options for Auto mode.
Configuring IPv6 Tunnel Interfaces
The features described here are used to tunnel IPv4 packets through IPv6 networks and IPv6 packets
through IPv4 networks. For instance, in order to pass IPv6 packets through the IPv4 network, the IPv6
packet will be encapsulated into an IPv4 packet at the ingress side of a tunnel. When the encapsulated packet
arrives at the egress of the tunnel, the IPv4 packet will be de-capsulated.
Tunnels can be either configured or automatic. A configured tunnel determines the endpoint addresses by
configuration information on the encapsulating node. An automatic tunnel determines the IPv4 endpoints
from the address of the embedded IPv6 datagram. IPv4 multicast tunneling determines the endpoints
through Neighbor Discovery.
The following diagram depicts an IPv6 to IPv4 tunnel.
Configuring the 6to4 Auto Tunnel
The 6to4 Auto Tunnel is an automatic tunnel: tunnel endpoints are extracted from the encapsulated IPv6
datagram, and so you do not need to configure them manually.
6to4 tunnels use a prefix of the form "2002:tunnel-IPv4-address::/48" (for instance,"2002:a01:203::1") to
tunnel IPv6 traffic over IPv4. Routers advertise a prefix of the form "2002:[IPv4]:xxxx/64" to IPv6 clients.
For complete information, see RFC 3056.
12
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 13

Configuring IPv6
The following diagram shows a sample 6to4 auto tunnel topology.
In the example, customers do not need to specify the tunnel endpoint, but only need to enable the 6to4 auto
tunnel. All packets with a 2002 prefix will be routed to the tunnel, and the tunnel's IPv4 destination will be
extract from the destination IPv6 address.
6to4 tunnels are easy to configure and use. Users must have a global IPv4 address and IPv6 address (must
have a 2002 prefix). Therefore, in general, user can only access network resource with a 2002 prefix.
Note Only one 6to4 auto tunnel can be configured on the firewall.
6to4 Relay Feature
To configure the 6to4 tunnel, set the Tunnel Type to 6to4 Auto Tunnel Interface and enable the Enable
IPv6 6to4 Tunnel checkbox.
By default, 6to4 auto tunnel can only access the destination with a 2002 prefix. The 6to4 relay feature can
be used to access non 2002 prefix destinations. To enable 6to4 relay, simply create a Route Policy to route
all traffic destined for 2003 prefixes over the 6to4 auto tunnel interface, as shown in the following example.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
13
Page 14

Configuring IPv6
This static route can be added on the 6to4 auto tunnel interface to enable the relay feature, which makes it
possible to access the IPv6 destination with non 2002: prefix through 6to4 tunnel. Note that, the gateway
must be the IPv6 address with the 2002: prefix.
Configuring a Manual Ipv6 Tunnel
To configure a manual IPv6 tunnel, select IPv6 Manual Tunnel Interface in the Tunnel Type pulldown
menu.
Enter the Remote IPv4 address for the tunnel endpoint.
For the Remote IPv6 network select an IPv6 Address object, which can be a group, range, network, or
Host.
14
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 15

Configuring a GRE IPv6 Tunnel
GRE can be used to tunnel IPv4 and IPv6 over IPv4 or IPv6. GRE tunnels are static tunnels where both
endpoints are specified manually. The following diagram shows a sample GRE IPv6 tunnel.
Configuring IPv6
The configuration of a GRE tunnel is similar to a manual tunnel, except GRE Tunnel Interface is selected
for the Tunnel Type.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
15
Page 16

Configuring IPv6
Accessing the SonicWALL User Interface Using IPv6
After IPv6 addressing has been configured on the firewall, the SonicWALL user interface can be accessed
by entering the IPv6 of the firewall in your browser’s URL field.
IPv6 Network Configuration
• “IPv6 DNS” section on page 16
• “Address Objects” section on page 17
• “Policy Based Routing” section on page 17
IPv6 DNS
• “IPv6 NAT Policies” section on page 17
• “DHCPv6 Configuration” section on page 18
DNS for IPv6 is configured in the same method as for IPv4. Simply click the IPv6 option in the View IP
Version radio button at the top left of the Network > DNS page.
16
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 17

Address Objects
IPv6 address objects or address groups can be added similar to IPv4. On the Network > Address Objects
page, the View IP Version radio button has three options: IPv4 only, IPv6 only, or IPv4 and IPv6.
Note Address Objects of type Host, Range and Network are supported. Dynamic address objects
for MAC and FQDN are not currently supported for IPv6 hosts.
Configuring IPv6
IPv4 interfaces define a pair of a default Address Object (DAO) and an Address Object Group for each
interface. The basic rule for IPv4 DAO is each IPv4 address corresponds to 2 address objects: Interface IP
and Interface Subnet. There are also couples of AO groups for Zone Interface IP, Zone Subnets, All
Interface IP, All Interface Management IP, etc.
IPv6 interface prepares the same DAO set for each interface. Because multiple IPv6 can be assigned to one
interface, all of those address can be added, edited, and deleted dynamically. Therefore, IPv6 DAOs need to
be created and deleted dynamically.
To address this, DAOs are not generated dynamically for IPv6 interfaces. Only limited interface DAO are
created, which results in limitation support for other module which needs to refer interface DAO.
Policy Based Routing
Policy Based Routing is fully supported for IPv6 by selecting IPv6 address objects and gateways for route
policies on the Network > Routing page. On the Network > Routing page, the View IP Version radio
button has three options: IPv4 only, IPv6 only, or IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv6 NAT Policies
NAT policies can be configured for IPv6 by selecting IPv6 address objects on the Network > NAT
Policies page. On the Network > NAT Policies page, the View IP Version radio button has three
options: IPv4 only, IPv6 only, or IPv4 and IPv6.
When configuring IPv6 NAT policies, the source and destination objects can only be IPv6 address objects.
Note IPv6 probing for NAT policies is not currently supported.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
17
Page 18

Configuring IPv6
Neighbor Discovery
The following table shows the IPv6 neighbor messages and functions that are analogous to the traditional
IPv4 neighbor messages.
IPv4 Neighbor message IPv6 Neighbor message
ARP request message Neighbor solicitation message
ARP relay message Neighbor advertisement message
ARP cache Neighbor cache
Gratuitous ARP Duplicate address detection
Router solicitation message (optional) Router solicitation (required)
Router advertisement message (optional) Router advertisement (required)
Redirect message Redirect Message
Just like ARP, static neighbor cache entry can be added, modified, or deleted. Dynamic neighbor cache entry
can be flushed.
The NDP Cache table displays all current IPv6 neighbors. The follow types of neighbors are displayed:
• REACHABLE - the neighbor is known to have been reachable within 30 seconds
• STALE - The neighbor is no longer known to be reachable, and traffic has been sent to the neighbor
within 1200s
• STATIC - The neighbor was manually configured as a static neighbor.
DHCPv6 Configuration
DHCPv6 server can be configured similar to IPv4 after selecting the IPv6 option in the View IP Version
radio button at the top left of the Network > DNS page.
18
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 19

IPv6 Access Rules Configuration
IPv6 firewall access rules can be configured in the same manner as IPv4 access rules by choosing IPv6
address objects instead of IPv4 address objects. On the Firewall > Access Rules page, the View IP
Version radio button has three options: IPv4 only, IPv6 only, or IPv4 and IPv6.
When adding an IPv6 access rule, the source and destination can only be IPv6 address objects.
Configuring IPv6
IPv6 IPSec VPN Configuration
IPSec VPNs can be configured for IPv6 in a similar manner to IPv4 VPNs after selecting the IPv6 option
in the View IP Version radio button at the top left of the VPN > Settings page.
There are certain VPN features that are currently not supported for IPv6, including:
• IKEv2 is supported, while IKE is currently not supported
• GroupVPN is not supported
• DHCP Over VPN is not supported.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
19
Page 20

Configuring IPv6
Note DHCP Over VPN and L2TP Server are not supported for IPv6.
When configuring an IPv6 VPN policy, on the General tab the gateways must be configured using IPv6
addresses. FQDN is not supported. When configuring IKE authentication, IPV6 addresses can be used for
the local and peer IKE IDs.
On the Network tab of the VPN policy, IPV6 address objects (or address groups that contain only IPv6
address objects) must be selected for the Local Network and Remote Network.
DHCP Over VPN is not supported, thus the DHCP options for protected network are not available
The Any address option for Local Networks and the Tunnel All option for Remote Networks are
removed. Select an all zero IPv6 Network address object could be selected for the same functionality and
behavior
On the Proposals tab, the configuration is identical for IPv6 and IPv4, except for the fact that IPv6 only
support IKEv2 mode.
On the Advanced tab, only Enable Keep Alive and the IKEv2 Settings can be configured for IPv6 VPN
policies.
Note Because an interface may have multiple IPv6 address, sometimes the local address of the
tunnel may vary periodically. If the user needs a consistent IP address, configure the VPN
policy to be bound to an interface instead of Zone, and specify the address manually. The
address must be one of IPv6 addresses for that interface.
SSL VPN Configuration for IPv6
SonicOS supports NetExtender connections for users with IPv6 addresses.
20
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 21

IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring
On the SSLVPN > Client Settings page, first configure the traditional IPv6 IP address pool, and then
configure an IPv6 IP Pool. Clients will be assigned two internal addresses: one IPv4 and one IPv6.
Note IPv6 DNS/Wins Server are not supported
On the SSLVPN > Client Routes page, user can select a client routes from the drop-down list of all address
objects including all the pre-defined IPv6 address objects.
Note IPv6 FQDN is supported.
IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring
SonicOS provides a full compliment of diagnostic tools for IPv6, including the following:
• “Packet Capture” on page 22
• “IPv6 Ping” on page 23
• “IPv6 DNS Lookup and Reverse Name Lookup” on page 24
• “Connection Monitor” on page 24
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
21
Page 22

IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring
Packet Capture
Packet Capture fully supports IPv6.
IPv6 keywords can be used to filter the packet capture.
22
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
Page 23

IPv6 Ping
IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring
The ping tool includes a new Ping IPv6 network preferred option.
When pinging a domain name, it uses the first IP address that is returned and shows the actual pinging
address. If both an IPv4 and IPv6 address are returned, by default, the firewall pings the IPv4 address.
If the Ping IPv6 network preferred option is enabled, the firewall will ping the IPv6 address.
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6
23
Page 24

IPv6 Diagnostics and Monitoring
IPv6 DNS Lookup and Reverse Name Lookup
When performing IPv6 DNS Lookup or IPv6 Reverse Name Lookup, you must enter the DNS server
address, either an IPv6 or IPv4 address can be used.
Connection Monitor
Connections Monitor does not currently accept IPv6 address as filters for the Source IP and Destination
IP fields.
24
SonicOS 5.5 - IPv6 PN 232-001999-00 Rev A
 Loading...
Loading...