Page 1

Low Power Wireless LAN Card
Type I CompactFlash card for adding Wireless LAN
connectivity to a Pocket PC 2002/2003 or
Windows 2000/XP notebook
User’s Guide
Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 4
Overview 4
About the Software 4
About the Link Indicator 5
Package Contents 5
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE 6
STEP 1: Register the Card 6
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information 6
STEP 3: Install the Software 7
STEP 4: Install Certificates (EAP-TLS or PEAP only) 8
STEP 5: Insert the Card 10
CHAPTER 3 INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000 12
STEP 1: Register the Card 12
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information 12
STEP 3: Install the Software 13
STEP 4: Insert the Card 14
STEP 5: Complete the New Hardware Wizard 15
CHAPTER 4 INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP 17
STEP 1: Register the Card 18
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information 18
STEP 3: Install Certificates (EAP-TLS or PEAP only) 18
STEP 4: Install the Software 19
STEP 5: Insert the Card 20
STEP 6: Complete the New Hardware Wizard 21
OPTIONAL: Enable Socket WLAN Tools 23
CHAPTER 5 CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN
PROFILE 24
Create a WLAN Profile 25
Connect to Your WLAN Profile 31
Open System, 40-bit or 128-bit WEP Key Network 31
802.1x Network 33
2
Page 3

CHAPTER 6 STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS 35
Accessing the Status and Options Screens 35
Signal Status Screen 36
Info Status Screen 37
IP Status Screen 37
Ping Status Screen 38
APs Status Screen 38
Peers Status Screen 40
Options Screen 41
CHAPTER 7 WLAN SEARCHES AND PROFILES 42
Initiate a WLAN Search 42
Create a WLAN Profile 43
Edit a WLAN Profile 43
Delete a WLAN Profile 44
Rearrange Profile List 44
CHAPTER 8 WIRELESS ZERO CONFIGURATION 45
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS 47
APPENDIX B SAFETY AND USAGE TIPS 51
APPENDIX C NETWORK INFORMATION 53
APPENDIX D TROUBLESHOOTING WEP
ENCRYPTION 55
APPENDIX E PASSKEYS FOR WEP ENCRYPTION 57
APPENDIX F GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING 58
APPENDIX G SUPPORT RESOURCES 59
Technical Support 59
Users’ Forum 59
Limited Warranty 60
Limited Software Warranty 61
Copyright Notice 62
Regulatory Compliance 63
3
Page 4

Chapter 1 Introduction
Overview
If you’re a mobile professional using a Pocket PC
2002/2003 or Windows 2000/XP notebook,
Socket’s Low Power Wireless LAN Card is the
perfect tool to connect to enterprise and public WiFi (IEEE 802.11b) Wireless LAN systems to access
the Internet, email, and corporate servers. Plus, you
can use Ad Hoc Mode to communicate directly with
other Wi-Fi users.
The Socket Low Power Wireless LAN Card uses Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum (DSSS) technology operating at 2.4 -2.5 GHz. The card conforms
to IEEE 802.11b specifications and is Wi-Fi compatible for interoperability
with Wi-Fi Certified products. Spread-spectrum communication provides a
high-capacity network within large or small environments. The card works
with an open system or WEP encryption with 40/64-bit WEP keys or 128bit WEP keys. The card is also compatible with 802.1x networks with EAPTLS or PEAP, so you can connect securely and avoid eavesdropping.
The Low Power Wireless LAN Card can be used in two operating modes.
In Infrastructure mode (default), the adapter transmits and receives data
with an associated access point (AP) or an infrastructure of networked APs.
Ad Hoc mode lets you create one-to-one or one-to-many peer-to-peer
networks without APs by connecting directly with other 802.11b cards.
About the Software
The Socket Low Power WLAN software includes the
Socket WLAN Tools, which make it easy to search
for WLAN networks and enter network settings. The
WLAN Tools let you create a unique profile for each
network, so you can connect to different networks
without changing settings every time.
Socket Cert Manage for Pocket PC 2002 and Cert Enroll for
Pocket PC 2003 make it easy to install a user certificate for
802.1x networks with EAP-TLS. See User’s Guide for details.
While connected, you can use the WLAN Tools status screens to quickly
check signal status, IP addresses, and other types of network information.
The WLAN Tools support 802.1x for Pocket PC 2002s only. For software
updates, go to: www.socketcom.com/support/support_wlan.asp
4 | CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Page 5

Pocket PC 2003 users
: Use your device’s Connection Manager, which
supports WLAN (including 802.1x). Socket’s software for Pocket PC 2003
includes card drivers and Cert Enroll, but no WLAN Tools at this time.
Windows XP users
: You have two software options.
• For a user interface similar to that of Socket’s WLAN Tools for
Windows CE, install Socket’s WLAN Tools for Windows 2000/XP.
However, Socket’s WLAN Tools for Windows 2000/XP do NOT support
802.1x. If you install Socket’s WLAN Tools on a Windows XP system,
you will disable Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service
and will have to uninstall and reinstall software to use it again.
• Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service is a utility built
into Windows XP that manages and automates WLAN connections. If
you want to use the WLAN card with WZC, install only Socket’s card
drivers. Windows XP with Service Pack 1 supports 802.1x.
To use the WLAN card with a Pocket PC 2000/HPC 2000, get version 124B
of Socket’s software: www.socketcom.com/support/support_wlan.asp
.
About the Link Indicator
The Low Power Wireless LAN Card Link Indicator is an LED that flashes a
green light to indicate connection with an access point.
Link Indicator
LED Status
Off The radio is disabled or incapable of transmission.
Function
Slow Flash The radio transmitter is on, and the card is trying to
connect to an access point.
Rapid Flash The card is connected to an access point. The LED
flashes faster to indicate greater network activity.
Package Contents
• A Socket Low Power Wireless LAN Card (CompactFlash card Type I)
• The Socket Low Power WLAN Installation CD
• The Quick Start Guide for Low Power Wireless LAN Card
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION | 5
Page 6

Chapter 2 Installation for
Windows CE
This chapter shows how to install the Low Power Wireless
LAN Card on a Pocket PC 2002. After installing the card,
refer to Chapter 4, “Socket WLAN Tools,” to learn how to
use Socket’s WLAN Tools software to create a profile and
connect to a WLAN.
Installation Steps Summary
STEP 1: Register the card.
STEP 2: Prepare network information.
STEP 3: Install the software.
STEP 4: Install certificates (EAP-TLS or PEAP only).
STEP 5: Insert the card.
STEP 1: Register the Card
Socket highly recommends that all users register their Socket products.
Registered users receive priority for technical support. Register your Socket
Low Power Wireless LAN Card online at www.socketcom.com/prodreg
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information
Before you can connect to a WLAN, you need to find out what settings it
uses. Complete the Network Information Form in Appendix C. If you are
trying to connect to a WLAN at your office, ask your network
administrator for help.
For a text-only version of the form that you can email to your network
administrator, go to the Docs folder on the installation CD or visit:
ftp://ftp.socketcom.com/wlan/WLAN_NetworkForm.txt
IMPORTANT! If you are using an 802.1x network, you must also
obtain a root (server) certificate
from your network administrator!!!
6 | CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE
Page 7

STEP 3: Install the Software
N
1. Make an active connection between your Pocket PC and a host PC.
Use ActiveSync and a serial/USB/Ethernet connection cable or cradle.
2. Insert the Socket Low Power WLAN Installation CD into your host PC.
ote: The host PC
can be a desktop
or notebook PC.
3. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to access your CD-ROM drive.
In the CD, click on SETUP.EXE.
4. Follow the instructions on your screen to install the software.
5. When software installation is complete, do the following:
• If you are not using an 802.1x network, disconnect the Pocket PC
from the host PC. Soft reset the Pocket PC by pressing the reset
button. Proceed to Step 5 to insert the card.
Pocket PC 2003: Do not soft reset the device when a Socket card
is inserted, or errors may occur in application(s) using the card. If
errors occur, remove the card and soft reset the device. Wait for
the device reset to finish before you re-insert the card.
• If you are using an 802.1x network, you must install certificate(s)
onto the Pocket PC (see Step 4).
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE | 7
Page 8

STEP 4: Install Certificates (EAP-TLS or PEAP only)
Note: This step is only needed if you want to connect to a WLAN network
that uses 802.1x security with EAP-TLS or PEAP authentication. Refer to
your Network Information Form to determine if your network supports this.
1. If you have not done so already, get a root (server) certificate from
your network administrator.
2. Make sure that you have an active connection between the Pocket PC
and host PC. Use ActiveSync and a serial/USB/Ethernet cable or cradle.
3. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to access your Mobile Device
and copy the root certificate into the Business folder of the Pocket PC.
Important! Remember the name of the certificate! You will need it
later.
4. Tap Start | Programs | Cert Manage.
5. The Manage Certificates screen will appear. Tap Root (server).
6. In the next screen, tap Browse and browse to the Business folder and
select the root (server) certificate that you copied to your Pocket PC.
7. In the Install Root Certificate screen, make sure that the Issued By and
Issued To fields have the same entry. Tap Install Certificate.
8 | CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE
Page 9

N
s
P
8. Tap ok. The Existing Certificates field should list the new certificate.
• If your network uses PEAP authentication, tap ok. Disconnect your
Pocket PC from the connection cable or cradle. Soft reset your
Pocket PC by pressing the reset button. Now you are ready to
proceed to Step 5 to insert the card.
• If your network uses EAP-TLS authentication, you also need to
install a user (client) certificate.
9. To install a user (client) certificate, in the Cert Manage screen, tap User
(client).
10. In the next screen, enter the User, Password, and Server information
from your completed Network Information Form. In the User field,
make sure you enter your domain and user name in the format shown.
Tap Retrieve.
ote: You must
till have an active
cabled connection
between your
ocket PC and a
host PC.
11. After your Pocket PC retrieves a user certificate, tap ok. The Existing
Certificates field should list your new certificate. Tap ok.
Note: The Enable server validation checkbox applies only to EAP-TLS.
This option should always be checked for maximum security. Only
network administrators should use this checkbox for troubleshooting.
12. After copying the certificate, disconnect the Pocket PC from the host
PC. Soft reset the Pocket PC by pressing the reset button. Now you are
ready to insert the card.
Pocket PC 2003
: Do not soft reset the device when a Socket card is
inserted, or errors may occur in application(s) using the card. If errors
occur, remove the card and soft reset the device. Wait for the device
reset to finish before you re-insert the card.
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE | 9
Page 10

STEP 5: Insert the Card
Important! Damage may occur!
Make sure the card is positioned correctly in the slot.
Do NOT insert the card upside down or shove the card in too hard.
Insert the card into your Pocket PC’s CompactFlash I/O or PC Card slot.
If using a PC Card slot, first plug the card into a PC Card adapter.
Make sure the card is right-side up, with the orange label on top.
OR
10 | CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE
Page 11

Whenever the card is inserted into your Pocket PC, the following icons will
N
d
appear:
• Signal strength icon: Visible from the top of every screen, shows signal
strength. Tap on the icon to view the WLAN card status bubble. The
bubble will not auto-update as the status changes. Close the bubble by
tapping elsewhere on the screen and reopen it to verify a status update.
• Socket status icon: Visible from only the Today screen. The card icon
varies to indicate network status; the column indicates signal strength.
ot
connecte
Connected,
Excellent
signal
strength
strength
icon.
Socket
status
Signal
icon.
Signal Strength Colors:
Green: good signal
Yellow: trying to connect
Red: critically low
White: no activity
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS CE | 11
Page 12

Chapter 3 Installation for
Windows 2000
This chapter shows how to install the Low Power
Wireless LAN Card on a Windows 2000 notebook. After
installing the card, refer to Chapter 5, “Create and
Connect to WLAN Profile,” to learn how to use Socket’s
WLAN Tools software to create a profile and connect to
a WLAN.
Note: The WLAN Tools software for Windows 2000/XP
does not support 802.1x.
Installation Steps Summary
STEP 1: Register the card.
STEP 2: Prepare network information.
STEP 3: Install the software.
STEP 4: Insert the card.
STEP 5: Complete the new hardware wizard
STEP 1: Register the Card
Socket highly recommends that all users register their Socket products.
Registered users receive priority for technical support. Register your Socket
Low Power Wireless LAN Card online at www.socketcom.com/prodreg
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information
Before you can connect to a WLAN, you need to find out what settings it
uses. Complete the Network Information Form in Appendix C. If you are
trying to connect to a WLAN at your office, ask your network
administrator for help.
For a text-only version of the form that you can email to your network
administrator, go to the Docs folder on the installation CD or visit:
ftp://ftp.socketcom.com/wlan/WLAN_NetworkForm.txt
12 | CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000
Page 13

STEP 3: Install the Software
1. Insert the Socket Low Power WLAN Installation CD.
2. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to access your CD-ROM drive.
In the CD, click on SETUP.EXE.
3. The Setup Center will start. Follow the instructions on your screen to
install the software for Windows 2000.
4. The Preinstaller will start. Follow the instructions on your screen.
5. After reading the new hardware wizard instructions in the last screen,
click OK. Leave the CD in your computer. Now you are ready to insert
the WLAN card.
CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000 | 13
Page 14

STEP 4: Insert the Card
Important! Damage may occur!
Make sure the card is positioned correctly in the slot.
Do NOT insert the card upside down or shove the card in too hard.
Insert the card into a CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter, then plug into your
computer’s PC Card slot.
Make sure the card is right-side up, with the orange label on top.
14 | CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000
Page 15

STEP 5: Complete the New Hardware Wizard
1. The first time you insert the card into your notebook computer, the
Found New Hardware Wizard will automatically appear to help you
install the card driver. Make sure that the installation CD is still inside
your computer.
2. Follow the wizard to install the card driver. When the wizard asks you
what you want it to do, select Search for a suitable driver for my device
(recommended).
3. In the next screen, check CD-ROM drives.
4. A Digital Signature Not Found screen will appear. Click Yes.
5. The wizard will search for and install the driver. In the last screen, click
Finish.
6. Wait for the Socket status icon to appear in the task tray. It may
take approximately 30 seconds. Do not click on any other icons
or messages that may appear.
WARNING!
A series of icon(s) and/or messages may appear in the task tray while you
wait for the Socket icon to appear. For example, icons/messages may report
new network connections and/or request that you run a network setup
wizard. DO NOT CLICK ON ANY OF THE ICONS OR MESSAGES. DO
NOT RUN ANY MORE WIZARDS.
CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000 | 15
Page 16

About the Socket Status Icon
R
N
d
After you install the card driver, whenever the card is inserted into your
computer, the Socket status icon will appear. The card icon varies to
indicate network status; the column indicates signal strength.
connecte
ot
Connected,
Excellent signal strength
Signal strength column —
Color designations:
Green: good signal
Yellow: trying to connect
ed: critically low
White: no activity
16 | CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000
Page 17

Chapter 4 Installation for
Windows XP
This chapter shows how to install the Low Power
Wireless LAN Card on a Windows XP notebook.
Note: You have two software options.
• For a user interface similar to that of Socket’s
WLAN Tools for Windows CE, install Socket’s
WLAN Tools for Windows 2000/XP. However,
Socket’s WLAN Tools for Windows 2000/XP do
NOT support 802.1x. If you install Socket’s
WLAN Tools on a Windows XP system, you will disable Microsoft’s
Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service and will have to uninstall
and reinstall software to use it again.
After you install Socket WLAN Tools, refer to Chapter 5, “Create and
Connect to a WLAN Profile.”
• Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service is a utility
built into Windows XP that manages and automates WLAN
connections. If you want to use the WLAN card with WZC, install only
Socket’s card drivers. Windows XP with Service Pack 1 supports
802.1x.
After you complete the Found New Hardware Wizard to install the card
driver, refer to Chapter 8, “Wireless Zero Configuration,” for
instructions on using WZC to enter network settings and connect to
your WLAN.
Installation Steps Summary
STEP 1: Register the card.
STEP 2: Prepare network information.
STEP 3: Install certificates (PEAP or EAP-TLS only).
STEP 4: Install the software.
STEP 5: Insert the card.
STEP 6: Complete the new hardware wizard
OPTIONAL: Enable Socket WLAN Tools
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP | 17
Page 18

STEP 1: Register the Card
Socket highly recommends that all users register their Socket products.
Registered users receive priority for technical support. Register your Socket
Low Power Wireless LAN Card online at www.socketcom.com/prodreg
STEP 2: Prepare Network Information
Before you can connect to a WLAN, you need to find out what settings it
uses. Complete the Network Information Form in Appendix C. If you want
to connect to your office WLAN, ask your network administrator for help.
For a text-only version of the form that you can email to your network
administrator, go to the Docs folder on the installation CD or visit:
ftp://ftp.socketcom.com/wlan/WLAN_NetworkForm.txt
STEP 3: Install Certificates (EAP-TLS or PEAP only)
Networks that use 802.1x security require that you install certificate(s) on
your computer that authenticate your identity and permission for network
access. You may need to install either one or two certificates onto your
computer, depending on what kind of authentication your 802.1x network
uses:
• EAP-TLS: Install both a user (client) and root (server) certificate.
This requires two separate installation processes.
• PEAP: Install only a root (server) certificate.
There are many methods for installing 802.1x certificates onto a Windows
XP system. Consult with your network administrator to choose the best
option and to obtain any necessary information (e.g., certification authority
name, domain credentials, etc.).
For more information on obtaining 802.1x certificates, please visit:
www.microsoft.com/technet/columns/cableguy/cg1202.asp?frame=true
18 | CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP
Page 19

STEP 4: Install the Software
1. Insert the Socket Low Power WLAN Installation CD.
2. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to access your CD-ROM drive.
In the CD, click on SETUP.EXE.
6. The Setup Center will start. Follow the instructions on your screen to
install the software for Windows XP.
7. The Preinstaller will start. Follow the instructions on your screen.
3. After reading the new hardware wizard instructions in the last screen,
click OK. Leave the CD in your computer. Now you are ready to insert
the WLAN card.
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP | 19
Page 20

STEP 5: Insert the Card
Important! Damage may occur!
Make sure the card is positioned correctly in the slot.
Do NOT insert the card upside down or shove the card in too hard.
Insert the card into a CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter, then plug into your
computer’s PC Card slot.
Make sure the card is right-side up, with the orange label on top.
20 | CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP
Page 21

STEP 6: Complete the New Hardware Wizard
1. The first time you insert the card into your notebook computer, the
Found New Hardware Wizard will automatically appear. Make sure that
the installation CD is still inside your computer.
2. In the welcome screen, select Install from a list or specific location
(Advanced). Click Next>.
3. In the next screen, make sure Search for the best driver in these locations
and Search removable media are selected. Click Next>. The wizard will
search for the driver.
4. A screen will warn that the software has not passed Windows Logo
testing. Click Continue Anyway.
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP | 21
Page 22

5. The wizard will install the driver.
6. After the drivers are installed, a series of icon(s) and bubble(s) may
appear in the task tray. Click Finish in the last wizard screen, then do the
following:
Warning! Do not click on the wrong icon or bubble!
• If you want to use Socket’s WLAN Tools, you must enable the
software. Do not click on any icons or bubbles that appear. Proceed to
OPTIONAL: Enable Socket WLAN Tools.
• If you want to use Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC)
service, do not click on anything yet. You are now ready to enter
network settings and connect to your WLAN. Refer to Chapter 8,
“Wireless Zero Configuration,” for instructions.
WARNING!
A series of Windows icon(s) and/or bubbles may appear in the task tray
after you install the driver. For example, icons/bubbles may report new
network connections and/or request that you run a network setup wizard.
DO NOT CLICK ON ANY OF THE WINDOWS ICONS OR BUBBLES.
DO NOT RUN ANY MORE WIZARDS.
22 | CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP
Page 23

OPTIONAL: Enable Socket WLAN Tools
R
N
d
1. Recommended: Insert the WLAN card into your computer before you
enable WLAN Tools.
2. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to navigate to the following:
C:\Program Files\Socket Communications\WLAN Tools
3. Click on XPWlanToolsEnabler.exe.
4. Follow the screens to enable the WLAN Tools software.
5. After WLAN Tools is enabled, if the WLAN card is inserted, the
WLAN Tools software will automatically launch. The Socket status icon
will appear in your task tray. WLAN Tools will search for WLANs
report any found networks in the Available WLAN Networks screen.
About the Socket Status Icon
After Socket’s WLAN Tools is installed, the Socket status icon will appear
whenever the card is inserted into your computer. The card icon varies to
indicate network status; the column indicates signal strength.
connecte
ot
Connected,
Excellent signal strength
Signal strength column —
Color designations:
Green: good signal
Yellow: trying to connect
ed: critically low
White: no activity
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP | 23
Page 24

Chapter 5 Create and Connect to
WLAN Profile
Note: Skip this chapter if you want to use Wireless Zero Configuration
(WZC) for Windows XP and did not enable Socket WLAN Tools.
This chapter explains how to use Socket’s WLAN Tools to create a WLAN
profile and connect to your network. The WLAN Tools software lets you
create a unique profile for each network, so you can connect to different
networks without entering new settings every time. Each profile consists of
the different mode, security, Internet Protocol (IP), and power settings for a
particular WLAN.
This chapter covers the following:
• Create a WLAN Profile
- Mode
- Security
- IP Config
- Power
• Connect to a WLAN Profile
- Open System, 40-bit or 128-bit WEP Key Network
This chapter shows Pocket PC 2002 screens. Windows 2000/XP screens
will be functionally equivalent except where otherwise noted. Wherever the
instructions say “tap,” please substitute with “click.”
Pocket PC 2002:
For help on any WLAN Tools page, tap
Start | Help.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help on any WLAN Tools page, click
on the Help icon in the upper right corner
of the WLAN Tools screen. The cursor
should now appear with a question mark.
Click on the WLAN Tools page you need
help on.
- 802.1x (Pocket PC only)
24 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 25

Create a WLAN Profile
1. Pocket PC 2002: The first time you insert the WLAN card into your
Pocket PC, the device will automatically search for WLAN networks.
Note: To start a search at any time, tap and hold
your stylus on the Socket Status icon in the task
tray of the Today screen. In the pop-up menu,
select Find WLANs.
Windows 2000/XP: After you insert the card and the Socket status icon
appears, you can initiate a WLAN search by right-clicking on the icon.
In the pop-up menu, select Find WLANs.
2. After several seconds, a list of Available WLAN Networks will appear.
The icon next to each network name indicates its security settings and
signal strength.
The blue key
indicates a secure
network.
The bars indicate
signal strength.
Socket
recommends
connecting only to
networks with at
least 3 yellow or
green bars.
3. Select the WLAN network that you wish to connect to, then tap
Connect. If the desired network is not listed, tap Search to search again.
4. After you tap Connect, the Mode screen will appear. Tap on the tabs to
enter any necessary settings for your network, as advised by your
network administrator. See the instructions for each screen in the
following pages.
Important! After you tap on all of the tabs to enter the settings, remember
to tap Ok to save the settings in a WLAN Profile!
CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE | 25
Page 26

Mode
Enter the appropriate settings for your WLAN:
Profile Name:
Enter a name for your
WLAN profile.
802.11 ESSID:
Enter the ESSID for
your network.
Operating Mode:
Select Infrastructure.
Country:
Select your country.
Note: Do not tap Ok until you have entered all of your network settings, or
you will exit the profile. To access the profile again, do the following:
• Pocket PC: Go to the Today screen and hold your stylus on the Socket
status icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles. In the profile list,
select your profile and tap Edit.
• Windows 2000/XP: Right-click on the Socket status icon. In the pop-up
menu, select WLAN Profiles. In the profile list, select your profile and
click Edit.
26 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 27
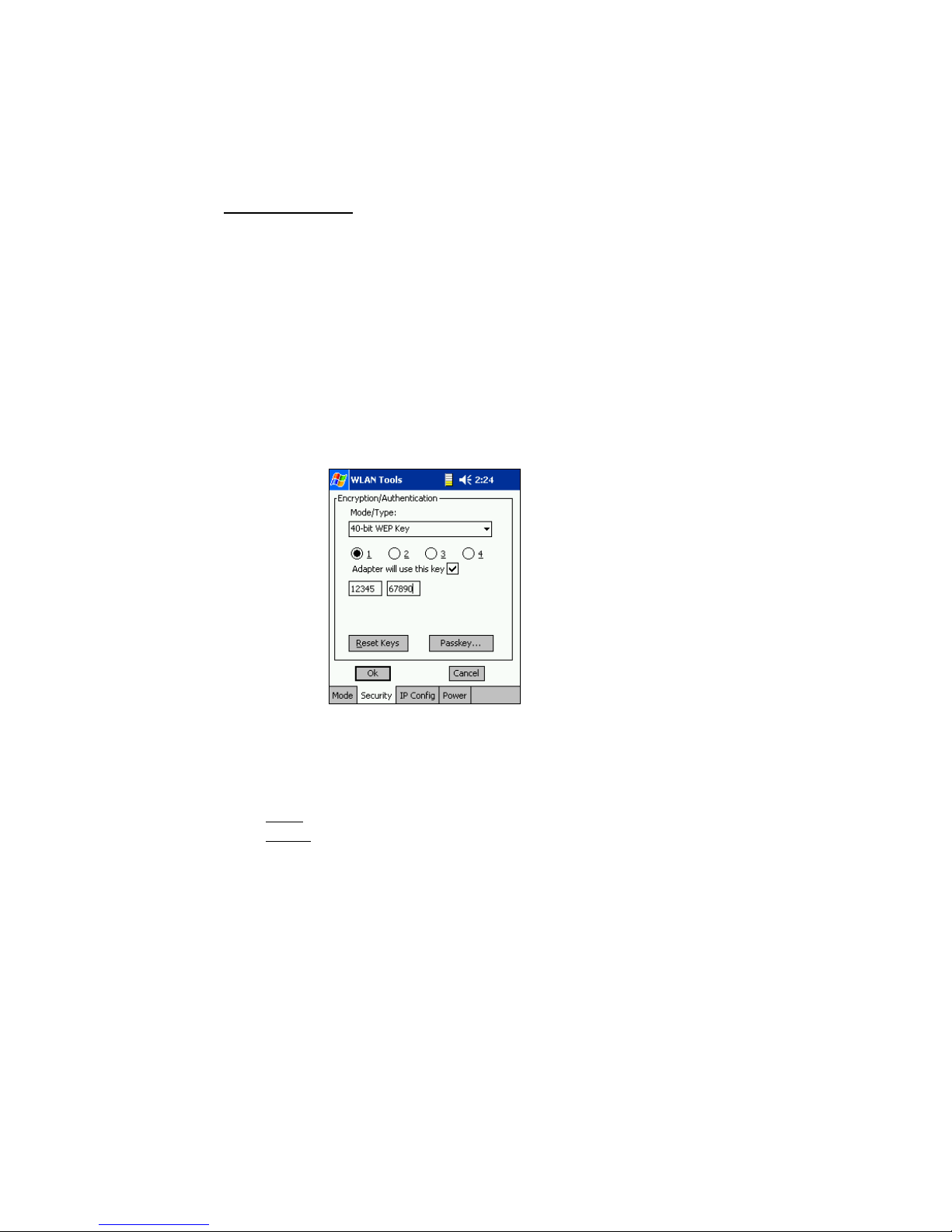
Security/Encryption
Note: WLAN Tools for Windows CE has a Security tab; WLAN Tools for
Windows 2000/XP has an Encryption tab.
Use the Mode/Type drop-down list and select the appropriate authentication
or encryption system.
Open System: This is the default setting. Select this setting if your
network needs no data packet encryption (i.e., needs no security for
transmitted data).
40-bit or 128-bit WEP Key: To use these encryption settings, you must
enter an encryption key in hexadecimal (hex) format. Enter the key by
spreading the 10 digits between the two fields provided.
Example:
If your 10-digit
encryption key is
“1234567890” enter
“12345” in the first
field and “67890” in
the second field.
If your network requires multiple keys, select the number of the
encryption key (1, 2, 3 or 4) and check Adapter will use this key before
entering the encryption key into the fields provided.
Encryption Keys: Enter the key by spreading the digits across the fields.
• 40-bit
• 128-bit
: Enter the 10-digit key by putting 5 digits in each field.
: Enter the 26-digit key by putting 5 digits each in the top row
of fields, then 4 digits each in the bottom row.
Important! Socket’s WLAN card only uses hexadecimal keys. Use
Appendix C to convert ASCII or decimal keys to hexadecimal.
Reset Keys: Tap to reset the keys to their original default values.
Passkey: If your network requires multiple sets of encryption keys, enter
the passkey for each set. For more information on using passkeys, please
refer to Appendix D, “Passkeys for WEP Encryption.”
CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE | 27
Page 28
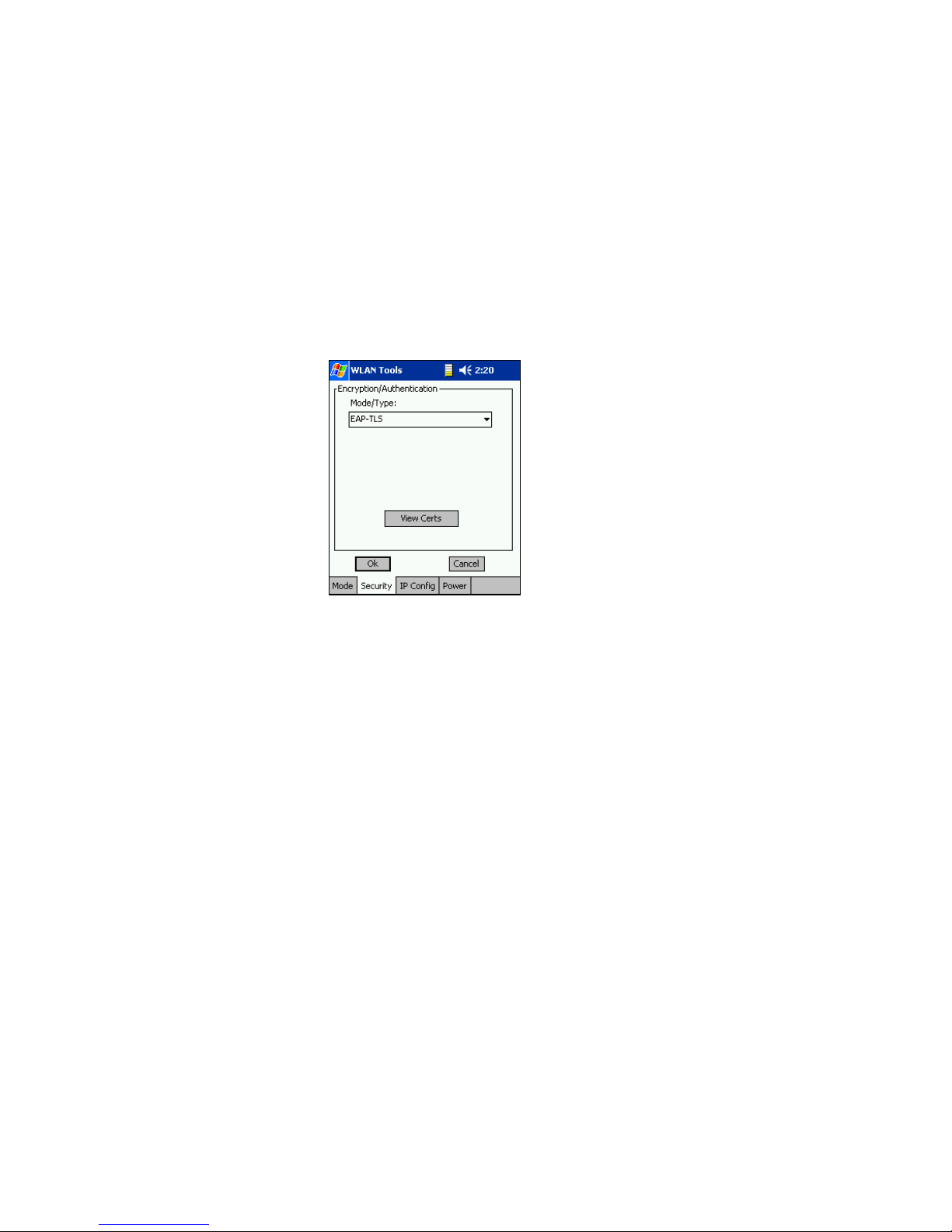
EAP-TLS: Select this if your 802.1x network uses EAP-TLS
authentication. The WEP keys are automatically generated by the
network. This option is only available for the Windows CE version of
Socket WLAN Tools.
PEAP: Select this if your 802.1x network uses PEAP authentication.
This option is only available for the Windows CE version of Socket
WLAN Tools.
You can tap View Certs to verify that the correct 802.1x certificates have
been installed on your Pocket PC. Without these certificates installed, you
will not be able to connect to your 802.1x network.
Note: The View Certs button does not appear for Windows 2000/XP.
28 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 29

IP Configuration
DHCP — This is the default setting. If your network supports DHCP,
the IP addresses and other information will be automatically assigned.
Static — Select this to manually enter the necessary IP addresses.
Note: Do not tap Ok until you have entered all of your network settings, or
you will exit the profile.
• Pocket PC
: Go to the Today screen and hold your stylus on the Socket
status icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles. In the profile list,
select your profile and tap Edit.
• Windows 2000/XP: Right-click on the Socket status icon. In the pop-up
menu, select WLAN Profiles. In the profile list, select your profile and
click Edit.
CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE | 29
Page 30

Power
The Power screen varies depending on operating mode.
Radio Transmission Power — Select Automatic to allow the Pocket PC
to dynamically change the power consumption based upon the amount
of radio activity.
Automatic Power Saving Mode — Recommended. Keep this box
checked so that the WLAN Card will automatically save power during
operation to maximize your Pocket PC’s battery life.
If you do not want to use automatic power saving, uncheck this box
and use the sliding scale to manually modify the power setting.
IMPORTANT!!!!
After entering all of your network settings, tap Ok
to save the
settings in a WLAN profile!!!
If you forget to tap Ok, your settings will not take effect!
30 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 31

Connect to Your WLAN Profile
The method for connecting to your profile varies depending on the type of
security features your network has.
Open System, 40-bit or 128-bit WEP Key Network
1. After you tap Ok to save your WLAN profile, a list of WLAN profiles
will appear, including the one you just created. Select your profile, and
tap Connect.
2. Your mobile computer will connect to the WLAN. For Pocket PCs, the
signal strength icon will show colored bars to indicate signal strength.
After connecting, tap Close.
Signal
strength
icon.
3. Tap and hold your stylus/right-click on the WLAN icon in the task tray
at the bottom of the screen (in the Today screen for Pocket PCs). In the
pop-up menu, select Status.
CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE | 31
Page 32

4. Tap on the IP Status tab. Make sure the IP address corresponds to a
legitimate local network address on your WLAN, as defined by your
network administrator.
Note: If your IP address is listed as 169.254.xxx.xxx, this is the default IP
address and not the correct IP address for your network. Tap Renew. It
may take up to 2 minutes to get the correct IP address.
If a valid IP address still does not appear, soft reset the Pocket PC by
pressing the reset button, or restart your Windows 2000/XP computer.
32 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 33

802.1x Network
Note: Only the Windows CE version of Socket’s WLAN Tools supports
802.1x.
1. After you tap Ok to save your WLAN profile, a list of WLAN profiles
will appear, including the new one you just created. Your Pocket PC
will automatically try to connect to the first profile on your list.
2. After a few seconds, the Network Log On screen will automatically
appear. Make sure the User Name and Domain are correct, and tap OK.
3. Tap on the signal strength icon at the top of the screen.
Signal
strength
icon.
CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE | 33
Page 34

4. The bubble that appears must report Authenticated before you can
complete the connection.
• You may need to repeatedly close and open the bubble every three or
four seconds until it reports Authenticating. Close the bubble by
tapping anywhere else on the screen. Reopen the bubble by tapping on
the icon.
• After it reports Authenticating, you may need to wait approximately
thirty seconds before it changes to Authenticated.
5. Your Pocket PC will connect to the WLAN. The signal strength icon
will show red, yellow or green bars to indicate the signal strength.
6. After connecting to your network, tap Close.
7. Tap Start | Today. Tap and hold your stylus on the WLAN icon in the
task tray at the bottom of the screen. In the pop-up menu, select Status.
8. Tap on the IP Status tab. Make sure the IP address corresponds to a
legitimate local network address on your WLAN. Refer to your
completed Network Information Form for a range of valid IP addresses.
Note: If your IP address is listed as 169.254.xxx.xxx, this is the default IP
address and not the correct IP address for your network. Tap Renew. It
may take up to 2 minutes to obtain the correct IP address. If a valid IP
address still does not appear, soft reset your Pocket PC by pressing the
reset button.
34 | CHAPTER 5: CREATE AND CONNECT TO WLAN PROFILE
Page 35

Chapter 6 Status and Options
Screens
Note: Skip this chapter if you want to use Wireless Zero Configuration
(WZC) for Windows XP and did not enable Socket WLAN Tools.
This chapter explains the Socket WLAN Tools status and options screens.
The Socket WLAN Tools includes several status screens that enable you to
monitor the activity of your WLAN Card. If you are in Infrastructure mode,
the Signal, Info, IP Status, Ping, and APs status screens will appear. If you
are in Ad-hoc mode, the Info, IP Status, and Peers status screens will
appear. The WLAN Tools Options screen enables you to modify special
options such as sounds and passwords.
Accessing the Status and Options Screens
Windows CE: From the Today screen, tap and hold your stylus on the
Socket status icon. In the pop-up menu, select Status or Options.
Windows 2000/XP: Right-click on the Socket status icon. In the pop-up
menu, select Status or Options.
Pocket PC 2002:
For help with WLAN Tools, tap Start | Help.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help with WLAN Tools, click on the Help icon in the upper right corner
of the WLAN Tools screen. The cursor should now appear with a question
mark. Click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on.
.
CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS | 35
Page 36

Signal Status Screen
Use the Signal screen to view radio signal transmission strength from the
WLAN Card to the associated access point.
The Signal screen displays a real-time graph of the signal quality received
by the adapter. It also reports the number of times the adapter has roamed
between APs, the AP MAC Address, the network in-range status, and the
current data rate.
The Missed Beacons graph shows the quantity of beacons missed by the
receiving adapter. The fewer the missed beacons, the better the signal.
The Txmit Retries graph shows the quantity of data packets retransmitted by
the adapter. The fewer the transmit replies, the stronger the signal.
The Signal graph shows the Relative Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) of the
signal transmitted between the access point and adapter.
If the LEDs to the right of the Missed Beacons, Txmit Retries, and Signal
graphs are green, the access point association is good. If the LEDs are red,
you may want to associate with a different access point for a better signal.
Note: This screen only appears in the Infrastructure operating mode.
Pocket PC 2002:
For help with WLAN Tools, tap Start | Help. To exit, tap Close.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help with WLAN Tools, click on the Help icon in the upper right
corner, then click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on. To exit, click
Close.
36 | CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS
Page 37

Info Status Screen
Use the Info screen to view the WLAN Card’s current version information
and status.
IP Status Screen
Use the IP Status screen to view the WLAN Card’s network address
information. Unlike the IP Config screen, the IP Status screen is view-only
with no user-configurable data fields.
Click Refresh to update the information.
Note: If the IP address is 169.254.xxx.xxx (the default), tap Renew. After 15
seconds to 2 minutes, the correct address should appear.
CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS | 37
Page 38

Ping Status Screen
Use the Ping screen to view the signal strength, data rate transmission, test
statistics and to perform data transmission test. This test sends ICMP ping
packets across the network to a selected address to test data transmissions
between wireless devices or between a wireless device and the associated
access point.
Use the IP field to enter the IP address of the target device. The IP address
of the associated Gateway will appear in this screen by default, but you can
enter the IP address of any device on the same wired or wireless network.
Select the size of packets sent from the Size pull-down menu.
Tap Start Test to begin the test. Each ping displays the round trip time it
took the ICMP ping to complete. The minimum, maximum and average
values are displayed as results. A real-time graph indicates the signal
strength and data rate transmission.
Note: This screen only appears in the Infrastructure operating mode.
Pocket PC 2002:
For help with WLAN Tools, tap Start | Help. To exit, tap Close.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help with WLAN Tools, click on the Help icon in the upper right
corner, then click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on. To exit, click
Close.
38 | CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS
Page 39

APs Status Screen
N
p
Use the APs page in Infrastructure mode to view access points with the
same ESSID as the adapter within the wireless network.
View the AP MAC address and signal of each located access point.
Radiation marks beside the antenna indicate the currently associated access
point. If the current WLAN Card signal strength is poor, one of the access
points displayed could provide a stronger signal.
ote: The APs
age is only
accessible in the
Infrastructure
operating mode.
Select and tap on an access point to display a pop-up menu used for setting
the adapter’s access point roaming capabilities.
• Selecting Set Mandatory prohibits the adapter from associating
with a different access point. The letter M displays on top of
the AP diagram when the Set Mandatory option is selected.
• Selecting Set Roaming enables the adapter to roam to another AP.
Tap Refresh to update the list of APs in range.
CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS | 39
Page 40

Peers Status Screen
When Ad-Hoc is selected as the operating mode, the Peers status screen
appears.
Use the Known Peers field to view the BSSID or MAC addresses of the
other WLAN Card users (peers) in the wireless network, their power mode,
their transmit rate, supported rate and the length of time an adapter has been
out of the Ad-Hoc network. These adapters are all available when forming a
peer-to-peer network in Ad Hoc mode.
The number of adapters in the network is displayed at the bottom or of the
screen. The Peers status screen is a view-only window with no configurable
data fields.
Tap Refresh to update the Peers status screen to the latest Ad Hoc network
performance and membership data.
Pocket PC 2002:
For help with WLAN Tools, tap Start | Help. To exit, tap Close.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help with WLAN Tools, click on the Help icon in the upper right
corner, then click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on. To exit, click
Close.
40 | CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS
Page 41

Options Screen
Access AP networks: Check if you want to include AP networks in WLAN
searches. Click Ok to enable this option.
Access Ad-Hoc networks: Check if you want to include peer (adapter)
networks in WLAN searches. Click Ok to enable this option.
Disable Profile Roaming: Check if you do not want the WLAN to switch
profiles during a connection if you move within range of another network.
Enable Sounds: Check to use sounds when performing a ping test or
associating with an access point.
Allow Pocket PC to suspend when wireless network is used: (Pocket PC only)
Check to let your Pocket PC automatically power-off to save power. This
option appears only for WLAN Tools for Windows CE.
Enable Connection Event Logging: (Pocket PC only) Check if you want to
enable connection event logging. This is most useful for 802.1x
troubleshooting by network administrators. The card must be removed and
reinserted after you change this setting. Use Pocket Word to view the
WiFiLog file.
Change Password: Tap on this button to use WLAN Tools’ password
protection feature. In the screen that appears, enter a case-sensitive
password (maximum 10 characters) and click OK. To change the password,
enter the current password in the Current Password field and enter a new
password in the New Password and Confirm New Password fields. Click OK.
CHAPTER 6: STATUS AND OPTIONS SCREENS | 41
Page 42

Chapter 7 WLAN Searches and
Profiles
This chapter explains how to initiate a WLAN search and manage WLAN
profiles.
Note: Skip this chapter if you want to use Wireless Zero Configuration
(WZC) for Windows XP and did not enable Socket WLAN Tools.
Initiate a WLAN Search
1. If you do not have any WLAN profiles saved, WLAN Tools will
automatically search for WLANs whenever the WLAN Card is inserted.
2. If you already have one or more WLAN profiles, you can initiate a WLAN
search by tapping and holding your stylus/righ-clicking on the Socket status
icon (in the Today screen for Pocket PCs). In the pop-up menu, select Find
WLANs.
3. After your mobile computer locates your network, you can create a
profile for it and attempt to connect to it, as described in Chapter 5,
“Create and Connect to a WLAN Profile”
42 | CHAPTER 7: WLAN SEARCHES AND PROFILES
Page 43
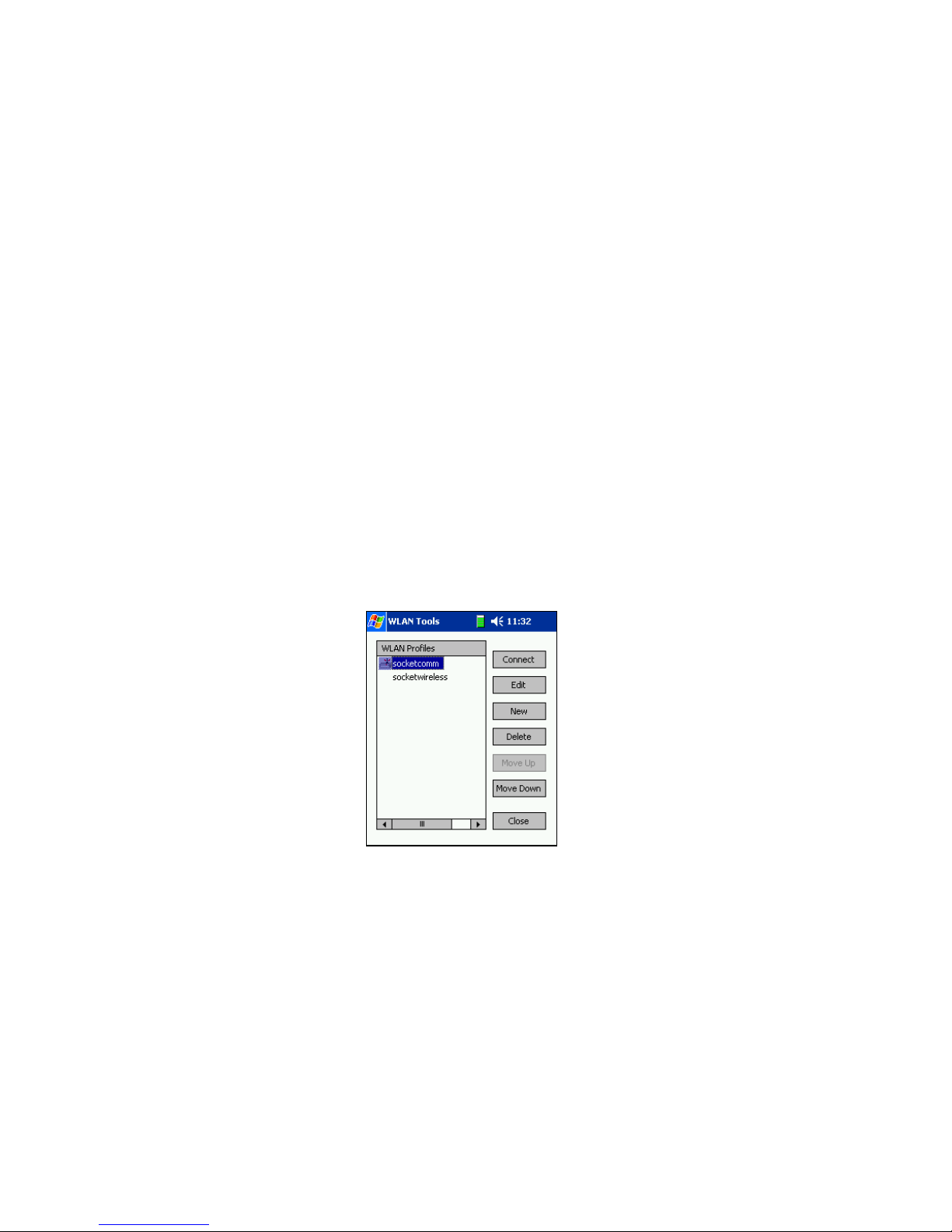
Create a WLAN Profile
After you find a new WLAN and try to connect with it, WLAN Tools will
automatically direct you to create a profile with it. See Chapter 5, “Create
and Connect to a WLAN Profile” for more information.
You can also create a new WLAN profile by doing the following:
1. From the Today screen, tap and hold your stylus on the Socket status
icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles.
2. In the next screen, tap New.
3. The Mode screen will appear. Tap on the tabs to enter any necessary
settings for your network. See Chapter 2, “Basic Setup,” for information
on each of the profile settings screens.
4. After entering all the network settings, tap Ok to save the settings in a
WLAN profile.
Edit a WLAN Profile
To change the settings of an already existing WLAN profile, do the
following:
1. From the Today screen, tap and hold your stylus on the Socket status
icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles.
2. Select the WLAN Profile that you wish to modify. Tap Edit.
3. The Mode screen will appear. Tap on the tabs and make any necessary
modifications. See Chapter 2, “Basic Setup,” for information on each of
the profile settings screens.
4. Tap Ok to save the changes.
CHAPTER 8: WINDOWS XP BUILT-IN WLAN UTILITY | 43
Page 44

Delete a WLAN Profile
1. From the Today screen, tap and hold your stylus on the Socket status
icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles.
2. Select the WLAN Profile that you wish to remove. Tap Delete.
Rearrange Profile List
If the current profile is lost, WLAN Tools will attempt to associate with the
first profile on the list and then the next until an association is achieved. To
rearrange the list to reflect your profile preferences, do the following:
1. From the Today screen, tap and hold your stylus on the Socket status
icon. In the pop-up menu, select WLAN Profiles.
2. Select the WLAN Profile that you wish to move. Tap Move Up or Move
Down.
Pocket PC 2002:
For help with WLAN Tools, tap Start | Help.
Windows 2000/XP:
For help with WLAN Tools, click on the Help icon in the upper right
corner, then click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on. To exit, click
Close.
44 | CHAPTER 7: WLAN SEARCHES AND PROFILES
Page 45
Chapter 8 Wireless Zero
Configuration
This chapter explains how to use Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration
(WZC) service to enter network settings and connect to your WLAN. WZC
is a utility built into Windows XP that manages and automates WLAN
connections. Windows XP with Service Pack 1 includes support for 802.1x.
Note: You cannot use WZC if you enabled Socket WLAN Tools on your
system. To use WZC again, you must uninstall Socket WLAN Tools (which
will also remove the card drivers), then run the Found New Hardware
Wizard again to reinstall the Socket card drivers.
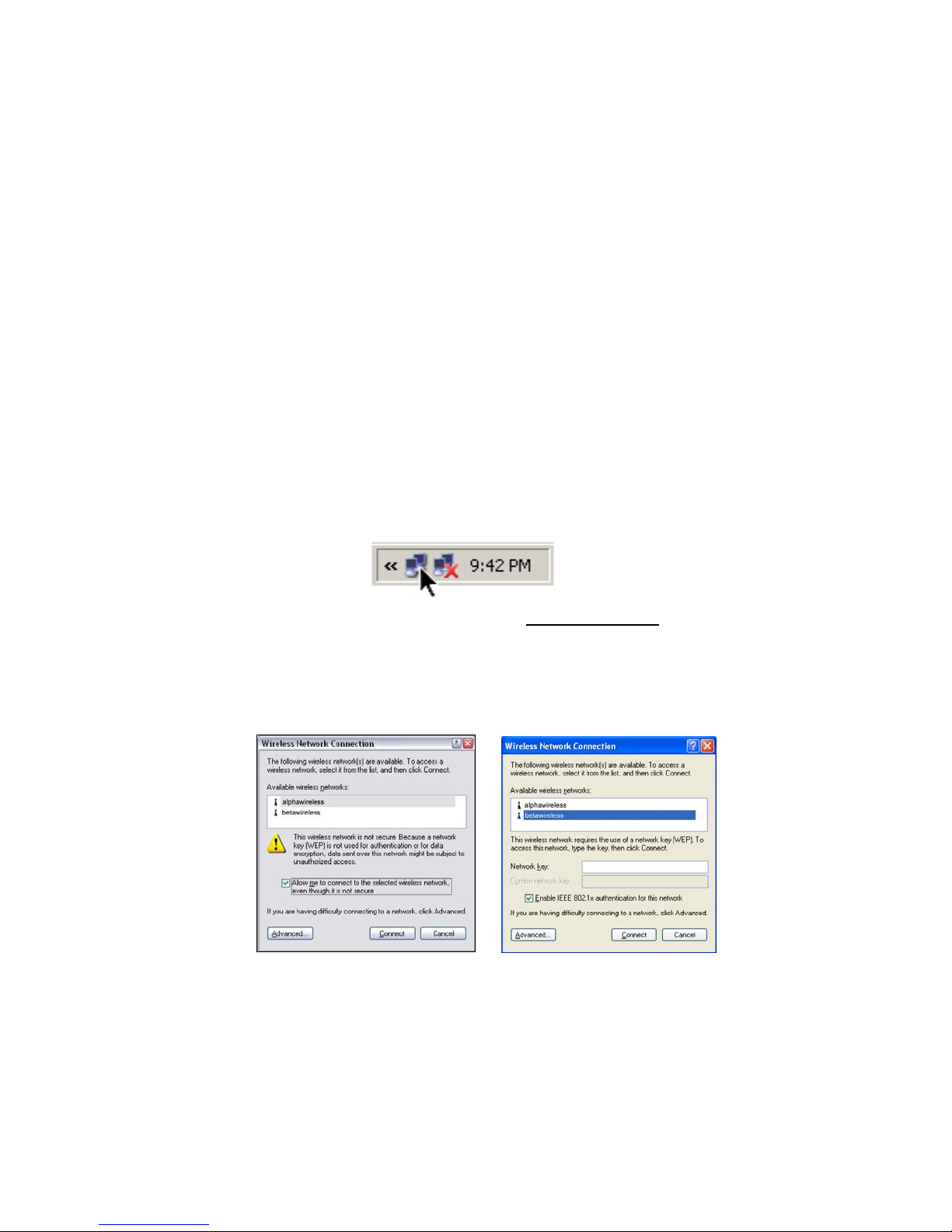
1. After you install the card driver via the Found New Hardware Wizard,
various icons and bubbles will appear in the task tray. Wait for an icon
with two computers to appear for a Wireless Connection, then click on
the icon.
WARNING! Be careful to click only on the Wireless Connection icon! Do
not click on any other icons or bubbles! Do not run any more wizards!
2. A list of networks will appear that are available for connection. Select
your network, and click Connect. The screen varies depending on which
security protocol your network uses.
Open System 802.1x
If the Connect button is disabled, you may need to enter network
settings or select certain options before you can click on it.
CHAPTER 8: WIRELESS ZERO CONFIGURATION | 45
Page 46

3. If you need to enter network settings before you can connect, do the
following:
• In the Wireless Network Connections screen, click Advanced.
• The connection properties screen will appear. Click on the Wireless
Networks tab.
• Select your network and click Configure. If the network you want is
not listed, click Refresh.
• Configure the network as needed, and click OK.
• In the connection properties screen, click OK.
• In the connection screen, select your WLAN and click Connect
46 | CHAPTER 8: WIRELESS ZERO CONFIGURATION
Page 47

Chapter 9 Pocket PC 2003
Connection Manager
The Connection Manager for Pocket PC 2003 support WLAN, including
802.1x. For more information on the Connection Manager, please refer to
your Pocket PC 2003 documentation.
For help with the Connection Manager, tap Start | Help.
1. After the card driver is installed, when you insert the card, your device
will automatically start searching for available WLANs. A bubble will
appear reporting any networks detected.
2. Select your network and what the network will connect to. Tap Connect.
The device will try to connect to the selected network.
If you are
In most
cases,
you
should
select
The
Internet.
3. If your device needs network settings to connect, the Configure Wireless
Networks screen will appear. Tap on your network in the list.
connecting to a
work network
that uses a
VPN/proxy
server, select
Work and refer
to your Pocket
PC 2003
documentation
for instructions.
APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS | 47
Page 48

4. In the next screen, tap on the Authentication tab. Enter the following:
N
o Data encryption (WEP Enabled): Check if your network uses
40/64/128-bit WEP encryption.
o Network Authentication (Shared mode): Uncheck!! Feature not
supported.
o Enter other settings as appropriate for your network.
Tap ok.
Uncheck.
ot supported
by Socket.
5. Tap and hold your stylus on your network in the list. In the pop-up
menu, tap Connect.
6. Your device will try to connect to the selected WLAN. When you have
connected, the Wireless networks list will report your WLAN as
Connected. Also, the connection icon on top of the screen will change.
Not Connected Connected
48 | APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS
Page 49

Appendix A Specifications
Physical Characteristics:
CF Type I Size: 2.18 x 1.69 x 0.13 in (55.4 x 42.8 x 3.3 mm)
Total Weight: 1.6 oz (45.4 g)
Operating Temperature: -4 to 158 °F (-20 to 70 °C)
Storage Temperature: -22 to 176 °F (-30 to 80 °C)
Power Consumption (3.3 V Supply):
Idle (listening): <20 mA
Transmission: 170 to 280 mA
Interface Standards:
CompactFlash Interface: CompactFlash I/O, Type I
With CompactFlash-to-PC Card Adapter: PCMCIA, Type II
Standards Conformance:
IEEE 802.11b High Rate, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Output Power:
100 mW maximum
Data Rate:
11 Mbps with Dynamic Rate Scaling to 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps to optimize
range and throughput
Frequency Range:
U.S., Europe, and Japan product covering 2.4-2.5 GHz, programmable
for different country regulations
Range:
Approx. 300 feet (open environment)
Access Protocol:
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance Protocol
(CSMA/CA)
Security Encryption/Authentication Hardware Support:
40-bit and 128-bit WEP data encryption
802.1x with EAP-TLS or PEAP
Operating System Support:
Windows CE for Pocket PC 2002/2003
Windows 2000 and XP
APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS | 49
Page 50

Software Compatibility:
Windows COM port
Software Included:
Socket Low Power WLAN Installation CD
Warranty:
CompactFlash Card: Three years
Certification/Compliance:
FCC: Part 15, Class B
C-TICK s.182
ETS 300 328
ETS 300 826
CompactFlash Spec. 2.0
TX Maximum Radiated EIRP:
FCC Part 15.247 in U.S.; ETS 300 328 in Europe; RCR STD-33 in Japan
TX Out-of-Band Emissions:
FCC Part 15.247, 15.205, 15.209 in U.S.; ETS 300 328 in Europe; RCR
STD-33 in Japan
50 | APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS
Page 51

Appendix B Safety and Usage Tips
Product Care
• Do not expose this product to liquid, moisture or extreme humidity.
• Do not expose this product to extreme high or low temperatures.
• Do not drop, throw or try to bend this product, as rough treatment could
damage it.
• Do not attempt to disassemble this product - a broken seal will void the
warranty. The product does not contain consumer serviceable
components. Should your Low Power Wireless LAN Card need service,
please contact Socket technical support at: support@socketcom.com
• Treat this product with care. Keep in a clean, dry and dust-free place.
• Changes or modifications of this product, not expressly approved by
Socket, may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Antenna Care
Do not place a metallic shield around your Low Power Wireless LAN Card
since it will reduce the radio transmission efficiency.
Efficient Use
For optimum performance, please make sure that there is no metallic
surrounding your Low Power Wireless LAN Card.
Driving
RF energy may affect some electronic systems in motor vehicles, such as
car stereo, safety equipment, etc. Check with your vehicle manufacturer’s
representative to be sure that your Low Power Wireless LAN Card will not
affect the electronic system in your vehicle.
Aircraft
• Turn off the Low Power Wireless LAN Card before boarding any
aircraft.
• To prevent interference with communications systems, you must not use
your Low Power Wireless LAN Card while the plane is in the air.
• Do not use it on the ground without permission from the crew.
.
APPENDIX B: SAFETY AND USAGE TIPS | 51
Page 52

Radio Frequency Exposure
Your Low Power Wireless LAN Card is a radio transmitter and receiver.
When in operation, it communicates with 802.11b-equipped devices by
receiving and transmitting radio frequency (RF) magnetic fields in the
frequency range 2.4 to 2.5 GHz. The maximum output power of the radio
transmitter is 100 mW.
The Low Power Wireless LAN Card unit is designed to be in compliance
with the RF exposure limits set by national authorities and international
health agencies when installed or used separately from other antennas or
radio transmitters.
Operation of this device excludes body-worn holsters, belt clips, or similar
operating configurations, as described in the FCC filing.
52 | APPENDIX B: SAFETY AND USAGE TIPS
Page 53
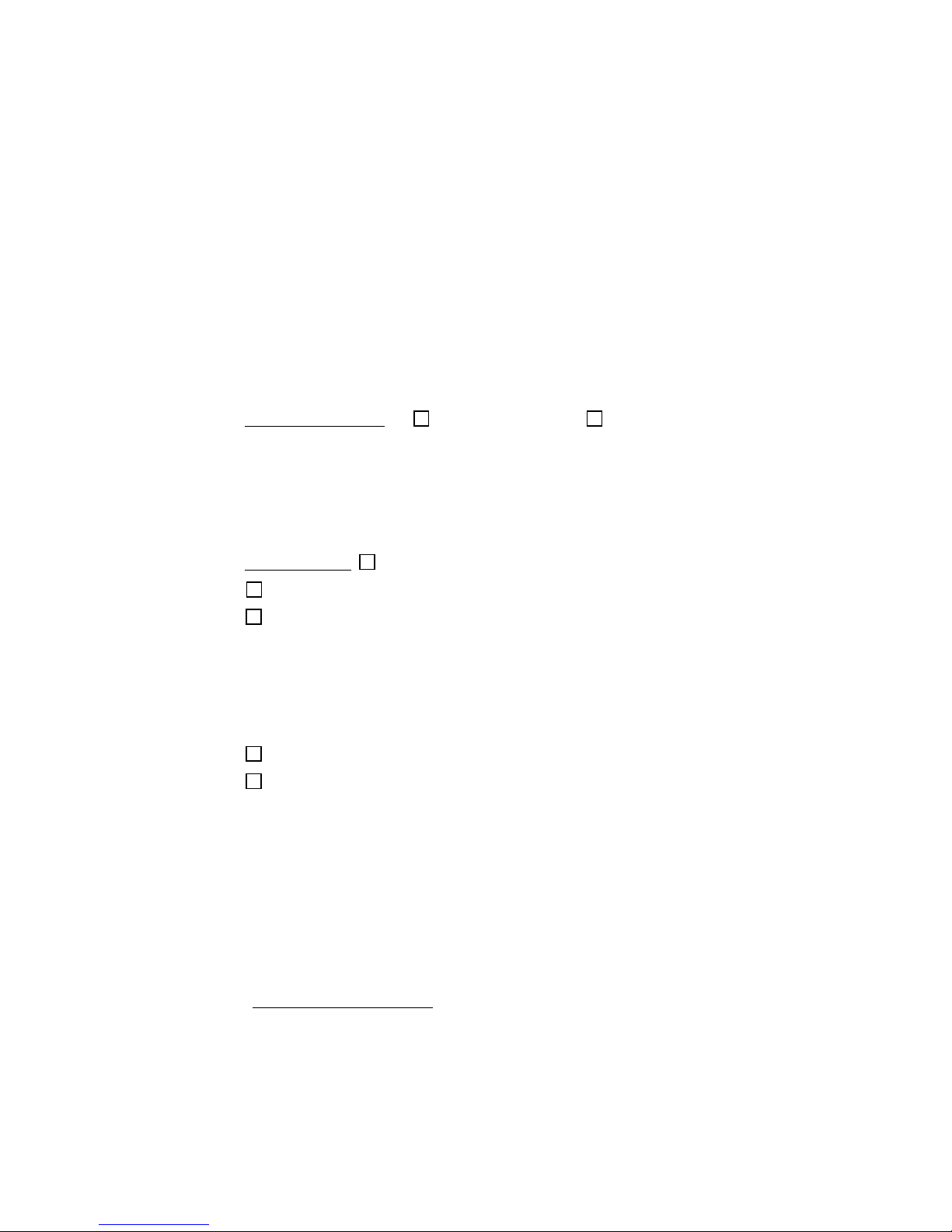
Appendix C Network Information
1. What is your wireless LAN’s ESSID (Extended Service Set Identifier)?
Note: ESSID is case-sensitive. BSSID is the ad-hoc version of ESSID.
_________________________________________________________
2. What type of security does your WLAN use? Check 1 of the 5 boxes
below, and provide any necessary settings.
802.1x Authentication EAP-TLS PEAP
User name: ____________________ Server:________________
(network login) (certificate server)
Password: _____________________ Domain: _________________
Important! If using 802.1x, get a root (server) certificate from your
network administrator!
WEP Encryption Open System (no keys needed)
__________; __________
NETWORK INFORMATION FORM
40-bit __________; __________ 40-bit is the same as 64-bit.
128-bit __________; __________; __________; __________;
40-bit or 128-bit only: What format are the WEP keys in? (Circle one)
Hexadecimal Decimal ASCII
3. Does the network support DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)?
YES. If Yes, then you do not need any of the IP address info below.
NO. If No, then please specify any applicable IP addresses:
(a) Mobile Computer IP address: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(b) Subnet Mask: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(c) Gateway: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(d) DNS: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(e) WINS*: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(f) MAC Address: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(g) Host Name: _________________________
*For Remote ActiveSync Only
: If your server does NOT have use WINS
services, use the IP address of the host PC instead of a WINS address.
APPENDIX C: NETWORK INFORMATION | 53
Page 54

4. What transmission power level is appropriate? More transmission power
is needed for devices spread far apart and/or for high interference.
Maximum 50% 25% 10% Minimum
5. Are access points at maximum throughput? YES NO
6. What is the range of legitimate IP addresses for your network?
_________________________________________________________
7. Is there any other important information from the site survey report?
You may want to ask your network administrator for a copy of this
report.
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
54 | APPENDIX C: NETWORK INFORMATION
Page 55

Appendix D Troubleshooting WEP
Encryption
If you have trouble connecting your WLAN with an AP that is using
encryption, try the steps below.
STEP 1: Start with Open System (If Possible)
See if your access point will allow an open system (i.e., encryption turned
off). Most do. Then set up a wireless connection with the WLAN card to
make sure that the card will communicate with the AP. After successfully
setting up a wireless connection using an open system, then go to Step 2.
STEP 2: Check the WEP Key Format
Socket’s WLAN software can only accept encryption keys in hexadecimal
(hex) format. If your AP uses ASCII or decimal keys, use the chart on the
next page to convert the keys to hexadecimal. Please note that all letters are
case-sensitive!
Example: The Lucent Orinoco RG-1000 access point uses the ASCII
encryption key “EE7Da.” You must convert it to hexidecimal:
ASCII Hexidecimal
E 45
E 45
7 37
D 44
a 61
APPENDIX D: TROUBLESHOOTING WEP ENCRYPTION | 55
In the Security
page, you would
enter the keys as:
45453 and 74461.
Page 56

Dec Hex ASCII ____ Dec Hex ASCII ____ Dec Hex ASCII ____ Dec Hex ASCII
0 00 NUL 32 20 SP 64 40 @ 96 60 '
1 01 SOH 33 21 ! 65 41 A 97 61 a
2 02 STX 34 22 " 66 42 B 98 62 b
3 03 ETX 35 23 # 67 43 C 99 63 c
4 04 EOT 36 24 $ 68 44 D 100 64 d
5 05 ENQ 37 25 % 69 45 E 101 65 e
6 06 ACK 38 26 & 70 46 F 102 66 f
7 07 BEL 39 27 ' 71 47 G 103 67 g
8 08 BS 40 28 ( 72 48 H 104 68 h
9 09 HT 41 29 ) 73 49 I 105 69 i
10 0A LF 42 2A * 74 4A J 106 6A j
11 0B VT 43 2B + 75 4B K 107 6B k
12 0C FF 44 2C , 76 4C L 108 6C l
13 0D CR 45 2D - 77 4D M 109 6D m
14 0E SO 46 2E . 78 4E N 110 6E n
15 0F SI 47 2F / 79 4F O 111 6F o
16 10 DLE 48 30 0 80 50 P 112 70 p
17 11 DC1 49 31 1 81 51 Q 113 71 q
18 12 DC2 50 32 2 82 52 R 114 72 r
19 13 DC3 51 33 3 83 53 S 115 73 s
20 14 DC4 52 34 4 84 54 T 116 74 t
21 15 NAK 53 35 5 85 55 U 117 75 u
22 16 SYN 54 36 6 86 56 V 118 76 v
23 17 ETB 55 37 7 87 57 W 119 77 w
24 18 CAN 56 38 8 88 58 X 120 78 x
25 19 EM 57 39 9 89 59 Y 121 79 y
26 1A SUB 58 3A : 90 5A Z 122 7A z
27 1B ESC 59 3B ; 91 5B [ 123 7B {
28 1C FS 60 3C < 92 5C \ 124 7C |
29 1D GS 61 3D = 93 5D ] 125 7D }
30 1E RS 62 3E > 94 5E ^ 126 7E ~
31 1F US 63 3F ? 95 5F _ 127 7F DEL
56 | APPENDIX D: TROUBLESHOOTING WEP ENCRYPTION
Page 57

Appendix E Passkeys for WEP
I
B
y
Encryption
WEP encryption keys are complex, and using them can be tedious and
error-prone. Each WEP key is 10 or 26 characters long, and Socket’s
WLAN Tools software only accepts them in hexadecimal format. As a
result, the passkey system was developed as a user-friendly, alternative
method of using WEP keys. Instead of requiring you to enter the 10 or 26character hexadecimal WEP key (this is known as the “string” method of
WEP key entry), the passkey system only requires you to enter a short word
or phrase, which the Socket software automatically translates into a proper
hexadecimal key of 10 or 26 characters. In this way, using a passkey is an
indirect method of using a WEP key.
Not all access points support the passkey system. Please check your access
point user documentation and/or consult with your network administrator to
verify what method you should use to enter WEP keys. Depending on the
manufacturer of your access point, the passkey may instead be called a
passphrase, magic word or password.
Follow these guidelines to use passkeys:
• Make sure your access point supports passkeys.
• While setting up the passkey on the access point, keep the passkey string
short and use only numbers and letters. Do not use spaces or other nonalphanumeric characters.
• After you set up the passkey on the access point, enter the same passkey
into the Socket WLAN software.
a) In the WLAN profile, tap on the Security tab and select 40-bit WEP
Key or 128-bit WEP Key, as appropriate for your network. Tap on the
Passkey button.
b) In the screen that appears, enter the same passkey that was set up on
the access point. Tap OK.
APPENDIX E: PASSKEYS FOR WEP ENCRYPTION | 57
mportant!
e careful to
enter the
correct passke
or you will not
be able to
connect to your
WLAN!
,
Page 58

Appendix F General Troubleshooting
SYMPTOM:
My mobile computer does not recognize the card.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The card driver was not installed
or installed incorrectly.
SYMPTOM:
The Socket status icon doesn’t appear on the task tray when I
insert the card.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your mobile computer may be
frozen.
The Low Power WLAN Card may
not be properly aligned in the CF
or PC Card slot.
There may be foreign material in
the CF card’s pinholes.
SYMPTOM:
My mobile computer does not recognize an IP address.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The IP address has not taken effect
yet.
The ESSID may be incorrect. Check and re-enter the ESSID.
In Infrastructure operating mode,
WEP encryption may not match
access point settings.
SYMPTOM:
My mobile computer does not associate with an access point
known to be within range.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The IP address may be incorrect. Correct IP address or use DHCP
The ESSID may be incorrect. Check and re-enter the ESSID.
In Infrastructure operating mode,
WEP encryption may not match
access point settings.
Install the software properly.
Remove the WLAN Card. If using a
Pocket PC, soft reset the device by
pressing the reset button. If using a
notebook, restart the computer.
Remove and carefully re-insert the card
in the slot.
Carefully remove any foreign material
from the pinholes using a small vacuum
or brush. Denatured alcohol may be
used sparingly.
Remove and reinsert the card or soft
reset the mobile computer.
Try using an ESSID of “any”.
Check with your company IT
department to confirm access point
security settings.
Try using an ESSID of “any”.
Check with your company IT
department to confirm access point
security settings.
58 | APPENDIX F: GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 59

Appendix G Support Resources
If you have trouble installing or using the Low Power Wireless LAN Card,
refer to Appendix C, “Troubleshooting WEP Encryption” or Appendix E,
“General Troubleshooting.” If you are using the card with a Pocket PC, you
can also tap Start | Help for help on the WLAN Tools page you have open.
For Windows 2000/XP, click on the help icon in the upper right corner,
then click on the WLAN Tools page you need help on.
Technical Support
If you have trouble installing or using the Low Power Wireless LAN Card,
contact Socket’s technical support department via the online support
system.
IMPORTANT! To obtain technical support for your product, you must
first register your product online at www.socketcom.com/prodreg
To submit an email inquiry through the online support system:
register your product, you will be presented with an option to 'submit a
problem'. Click on this option to follow the online process to submit an
email request for technical support.
This is the fastest way to obtain technical support and has the quickest
turnaround time. Registered customers who submit a question online will
receive priority service. If we are unable to resolve your support inquiry via
email, we can arrange for a technical support representative to call you at a
specific time.
Users’ Forum
If you would like to discuss the Socket Low Power Wireless LAN Card
with other users, visit Socket’s users’ forum at: www.socketforum.com
Important! Socket does NOT provide technical support via the users’ forum!
Note: Socket may, but is not obligated to, monitor or review any areas on
the Site where users transmit or post Communications or communicate
solely with each other, including but not limited to the user forum, and the
content of any such Communications. Socket, however, will have no
liability related to the content of any such Communications, whether or not
arising under the laws of copyright, libel, privacy, obscenity, or otherwise.
Socket retains the right to remove messages that include any material
Socket deems abusive, defamatory, obscene or otherwise unacceptable.
.
.
After you
APPENDIX G: SUPPORT RESOURCES | 59
Page 60

Limited Warranty
Socket Communications Incorporated (Socket) warrants this product against defects
in material and workmanship, under normal use and service, for the following
period from the date of purchase:
Plug-in card: Three years
Incompatibility is not a defect covered by Socket’s warranty. During the warranty
period, Socket will, at its option, repair or replace the defective product at no charge
when furnished with proof of retail purchase, provided that you deliver the product
to Socket or to an authorized Socket Service Center.
The returned product must be accompanied by a return material authorization
(RMA) number issued by Socket or by Socket's Authorized Service Center. If you
ship the product, you must use the original container or equivalent and you must pay
the shipping charges to Socket. Socket will pay shipping charges back to any
location in the contiguous United States. This warranty applies only to the original
retail purchaser and is not transferable.
Socket may, at its option, replace or repair the product with new or reconditioned
parts and the returned product becomes Socket's property. Socket warrants the
repaired or replaced products to be free from defects in material or workmanship for
ninety (90) days after the return shipping date, or for the duration of the original
warranty period, whichever is greater.
This warranty does not cover the replacement of products damaged by abuse,
accident, misuse or misapplication, nor as a result of service or modification other
than by Socket.
SOCKET IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES RESULTING FROM BREACH OF ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY, INCLUDING DAMAGE TO PROPERTY AND, TO THE EXTENT
PERMITTED BY LAW, DAMAGES FOR PERSONAL INJURY. THIS
WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES INCLUDING
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Some states do not allow limitation of implied warranties, or the exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so that the above limitations or
exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty gives you specific legal rights and
you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
This product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new.
For warranty information, email info@socketcom.com.
60
Page 61

Limited Software Warranty
LIMITED WARRANTY. SOCKET warrants that the original disk or CD ROM is
free from defects for 90 days from the date of delivery of the SOFTWARE.
CUSTOMER REMEDIES. SOCKET’S entire liability and your exclusive remedy
shall be, at SOCKET’S option, either (a) return of the price paid or (b) replacement
of the SOFTWARE which does not meet SOCKET’S Limited Warranty and which
is returned to SOCKET with a copy of your receipt. Any replacement SOFTWARE
will be warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period or 30 days,
whichever is longer. THESE REMEDIES ARE NOT AVAILABLE OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA.
NO OTHER WARRANTIES. SOCKET disclaims all other warranties, either
express or implied, including but not limited to implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to the
SOFTWARE and the accompanying written materials. This limited warranty gives
you specific legal rights. You may have others which vary from state to state.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. In no event shall SOCKET
or its suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation,
damages for loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of business
information, or other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use the
SOFTWARE, even if SOCKET has been advised of the possibility of such
damages. Because some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability
for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
EXPORT LAW ASSURANCES. You may not use or otherwise export or reexport
the SOFTWARE except as authorized by United States law and laws of the
jurisdiction in which the SOFTWARE was obtained. In particular, but without
limitation, none of the SOFTWARE may be used or otherwise exported or
reexported (a) into (or to a national or resident of) a United States embargoed
country or (b) to anyone on the U.S. Treasury Department’s list of Specially
Designated Nationals or the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Table of Denial
Orders. By using the SOFTWARE, you represent and warrant that you are not
located in, under control of, or a national or resident of any such country or on any
such list.
GOVERNMENT END USERS. If the SOFTWARE is supplied to the U. S.
Government, the SOFTWARE is classified as “restricted computer software” as
defined in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR. The U. S. Government ‘s rights to the
SOFTWARE are as provided in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR.
CONTROLLING LAW AND SEVERABILITY. This License shall be governed by
the laws of the United States and the State of California. If for any reason a court of
competent jurisdiction finds any provision, or portion thereof, to be unenforceable,
the remainder of this License shall continue in full force and effect.
61
Page 62

April 2003 Document # 6410-00170 E
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2003 Socket Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.
Socket, the Socket logo and Battery Friendly are registered trademarks of
Socket Communications, Inc. Low Power Wireless LAN Card is a
trademark of Socket Communications, Inc. All other brand and product
names are trademarks of their respective holders.
The Low Power Wireless LAN Card includes technology licensed under
United States Patent Nos. 4,543,450, 4,603,320, 4,686,506, and 4,972,470.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual without the permission of
Socket Communications is expressly prohibited. Please be aware that the
products described in this manual may change without notice.
Feel free to contact SOCKET COMMUNICATIONS at:
Socket Communications, Inc.
37400 Central Court
Newark, CA 94560
Other than the above, Socket Communications can assume no responsibility
for anything resulting from the application of information contained in this
manual.
Socket Communications requests that you refrain from any applications of
the Socket Low Power Wireless LAN Card that are not described in this
manual. Please refrain from disassembling the card. Disassembly of this
device will void the product warranty.
You can track new product releases, software updates and technical
bulletins by visiting Socket’s web page at: www.socketcom.com.
62
Page 63

Regulatory Compliance
The Socket Low Power Wireless LAN Card is designed to be compliant
with the rules and regulations in locations where they are sold and will be
labeled as required. This product is type approved users are not required to
obtain license or authorization before using.
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to
the following conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment is also ETS 300 328, ETS 300 826 and C-TICK compliant.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his or her
own expense.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user may try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna of the radio or television.
• Increase the distance separating the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a different branch circuit than
that of the receiver.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The user may find the following booklet helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
63
Page 64

Radio Frequency Interference Requirements – Canada
This Class B digital apparatus meets the requirements of the Canadian
Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations. Cet appareil numérique de la
Classe B respecte toutes les exigencies du Reglement sur le Matériel
Brouilleur du Canada.
NOTE: To comply with FCC and Industry Canada exposure requirements,
this device is approved for operations in a user’s hand when there is a
distance of 20 cm or more between the device antenna and the user’s body.
CE Marking & European Union Compliance
Products intended for sale within the European Union are marked with a
CEMark which indicates compliance to applicable Directives and European
Normes (EN), as follows. Amendments to these Directives or ENs are
included: Normes (EN), as follows:
Applicable Directives:
• Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 89/336/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
Applicable Standards:
• EN 55 022 – Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference
Characteristics of Information Technology Equipment.
• EN 50 082-1 – Electromagnetic Compatibility – General Immunity
Standard, Part 1: Residential, Commercial, Light Industry.
• IEC 801.2 – Electromagnetic Compatibility for Industrial Process
Measurement and Control Equipment, Part 2: Electrostatic Discharge
Requirements.
• IEC 801.3 – Electromagnetic Compatibility for Industrial Process
Measurement and Control Equipment, Part 3: Radiated Electromagnetc
Field Requirements.
• IEC 801.4 - Electromagnetic Compatibility for Industrial Process
Measurement and Control Equipment, Part 4: Electrical Fast Transients
Requirements.
• EN 60 950 + Amd 1 + Amd 2 – Safety of Information Technology
Equipment Including Business Equipment.
64
 Loading...
Loading...